ON POINT-PICKING GAMES
|
|
|
- Duane Simpson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Volue 10, 1985 Pges ON POINT-PICKING GAMES by I. Juhász Topology Proceedigs Web: Mil: Topology Proceedigs Deprtet of Mthetics & Sttistics Aubur Uiversity, Alb 36849, USA E-il: ISSN: COPYRIGHT c by Topology Proceedigs. All rights reserved.
2 TOPOLOGY PROCEEDINGS Volue ON POINT-PICKING GAMES I. Juhsz 1. Itroductio Let X be topologicl spce, P property of subsets of X d ordil the the poit-pickig ge GP(X) is defied s follos: To plyers, I d II, tke turs plyig. A roud cosists of Plyer I choosig (o-epty) ope set U c X d the Plyer II choosig poit x E U. A roud is plyed for ech ordil less th. Plyer I is the ge if the set of poits picked by Plyer II hs property 'P, otherise Plyer II is. This ge s itroduced d ivestigted for the cses P = D (= dese) d P = SD (= soehere dese) i [BJ], here, og other thigs, resoble criteri ere forulted d prove for Plyer I to hve iig strtegy. The i here is to try to do the se for Plyer II. As e shll see, the situtio is ore coplex i this cse. Let us put for y spce X o(x) = sup{d(y): Y c X dese i X}. It is strightforrd to sho tht if is y ordil d o(x) > the II t GD(X). I fct, s A. Berer hs sho i [B], this is exctly he Plyer II hs so-clled sttiory iig strtegy for GD(X). Our i is to ivestigte uder ht circustces is this obvious d turl sufficiet coditio for II to i lso ecessry. I fct, e shll oly do this for the cse i hich the legth of the ge is.
3 104 Juhsz Before e forulte our i result let us recll tht, for T 3 spce X, I t G~(X) if d oly if (X) =, see [BJ]. It ill lso be helpful to keep i id tht, gi for T spce X, oe lys hs o(x) < (X) < 2 o (X). 3 Our i result reds s follos: Theore 1. for y give crdil K ~ 2 : The folloig to stteets re equivlet (1) There exists (T ) spce X ith o(x) d 3 (X) = K such tht II t GD(X). (2) The rel lie R c be ritte s the uio of < K ohere dese subsets. Before e give the proof of this result let us dd fe coets. If K = the this is trivil sice both (1) d (2) re flse. If K = 2 (the xiu possible vlue of K) the (2) of course is vlid, hece so is (1), hece e get ZFC exple of T spce X ot stisfyig 3 O(X) > d such tht II t GD(X). Filly, if < K < 2 the theore 1 shos tht, t lest for (T 3 ) spces of -eight K, it is idepedet of ZFC hether the coditio o(x) > is lso ecessry for Plyer II to i the ge GD(X). 2. ProofofTheore 1 As is ell ko, see e.g. [K], the egtio of stteet (2) of theore 1, i.e. tht R is ot the uio of < K ohere dese sets, is equivlet to MACK' hich deotes Mrti's xio for coutble posets d ~ K dese sets. Hece the folloig result yields "oe hlf" of theore 1.
4 TOPOLOGY PROCEEDINGS Volue Theore 2. Assue MACK d let X be y spce ith 6(X) = d (X) < K. The Plyep II does ot hve iig strtegy for G D (X). Proof. Let s: l(x}< x lex) ~ X be strtegy for Plyer II, e shll sho tht s is o't iig. I order to do this e first defie, by iductio o E, for every sequece E coutble dese subset S s follos. of X To defie S e first cosider the set X = {s(u}: U E l(x)} hich is dese i X sice s is strtegy for Plyer II, hece e y, by 6(X) =, tke S to be coutble dese subset of X. No, let E d ssue k tht S hs bee defied for ll E u{ : k < }, ore over, for every such 0, So ope sets U O such tht x {x o : ill E } d e hve soe here = (0) is the legth (i.e. doi) of o. ~i ht follos, e shll rite U(o,i) isted of Uo~i).} l No, if E + X o the e cosider the set (I {s(u(o,o),u(o,l),,u(o,)"u): U E T(X)} hich is gi dese i X hece hs cout:ble dese subset S {xo: E}, d, of course, e y choose for ech ill E ope set UO such tht x O s(u(o,o},u(o,l},,u(o,),u ). This copletes the iductio. The (obviously coutble) prtil order tht e t to pply MACK to is < ith the extesio of sequeces s the prtil order. To get the dese sets e first recll tht X hs -bse B ith IBI ~ K d for every B E B e put
5 106 Juhsz < o ~i (3i < (0)) (xo(i) = x(o,i) E B)}. Sice every So is dese i X it is obvious tht DB is dese i < for ech B E 8, cosequetly by MAC geeric brch T E WW over the fily {DB: B E B}. K there is Hoever, it is iedite fro our iductive costructio tht «U(T,i),x(T,i»: i E ) is ply of the ge GD(X) i hich Plyer II hs folloed the strtegy sd still the set {x(t,i): i E } is dese i X (becuse it itersects every B E B), hece s is ot iig. I vie of our bove rerk, it ieditely follos tht (1) iplies (2) i theore 1. To see the coverse, e first prove the folloig result. Theore 3. Let S ith lsi = K be T 2 spce ith coutble bse B hich dits fuctio ~: B + R+ = (0,00) stisfyig the folloig to properties: (i) for every pes d every s > 0 there is BE B such tht p E B d ~(B) < s; (ii) there is sequece {s : E} c R+ such tht for every {B : E } c B if ~ (B ) < s holds for ech E the S t- U{B : E}. The 2 K hs coutble dese subspce X for hich SD D II t G (X) (hece II t G (X) s e ll). Note tht (X) = K d o(x) = IXI. Proof. Let us strt by otig tht, possibly by pssig to pproprite subsequece of {E: E}, e y ssue tht i (ii) for every {B : E} c B ith
6 TOPOLOGY PROCEEDINGS Volue (B ) < E e ctully hve tht S\U{B : E} is ifiite (or, i fct, ucoutble). The costructio of the spce X, for coveiece e S K shll defie it s subspce of 2 rther th 2, is stdrd, see e.g. [H] or [J]. Let D deote the set of ll fuctios d such tht do(d) is fiite d disjoit subset of Bd rge(d) c 2, d for every d E De defie f d E 2 S by puttig: fd(p) = {d(b), if P E B E do(d); 0, if p E S\U do(d). We the put X {f d : d ED}, it is ell-ko tht X is S (coutble) dese subset of 2. We o describe, iforlly, iig strtegy for Plyer II i the ge G~D(X). First, it clerly suffices to do this oly for oves of Plyer I hich re trces of eleetry ope sets i 2 8, i.e. hve the for [3] = {f E X: s c f}, here s is y 0-1 fuctio defied o soe fiite subset of S. Suppose tht Plyer lis first ~ove is [so] here do(so) = O = {p~: i < O}. I respose to this Plyer II 1 first picks disjoit collectio B O = {~i: i < O} c B such tht Pi E B d (B ) < E hold for ll i < O. i i i This is possible by (i). The II y pick the eleet f of [so], here do ED is give: by do(do) = B O d d do(b.) so(p.) for ech i < O. If i the ext roud the 1 1 l ope set [sl] is plyed by I, here do(sl) = 1 1 {Pi: i < }, the II first chooses disjoit collectio Bl = {B : < j < l } such tht p. E: B d j O+i
7 108 Juhsz (B 0.) < 0. 1 for i < d the picks the poit l fdl E [sl], here do(d ) = B l d dl(b 0.) = Sl(p~) l i <. +1 for Cotiuig i this y, he the ply is fiished sequece {B i : i E } is geerted ith the property tht (Bi) < f for ll i E, hece S\U{B : i E } is ifiite. i i But clerly every choice fdi of Plyer II i this ply is such tht fdi(p) = 0 for every p E S\ {B : i E }, hece i {fdi: i E } is ohere dese i 2 S d cosequetly i X s ell. This shos tht the strtegy e described is ideed iig. A iedite corollry of theore 3 is tht if there is set S E [R]K hich does ot hve strog esure 0 the there is coutble dese X c 2 K such tht II t GSD(X). Hoever, i order to fiish the proof of theore 1 e shll hve to look t soe other exples. Let us cosider the Bire spce WW ith its stdrd coutble bse B = {[s]: s E <}, the "Bire itervls." For y subset S c W e let B S = {S [s]: s E <} d defie s: B s ~ 1 21s/ R+ by It is obvious tht (s,bs' s > lys stisfies (i) of theore 3. No, the fil lik i the proof of Theore 1 is give by the folloig (so fr upublished) result of A. Miller d D. Freli [MF]: Propositio (Miller-Freli). The folloig to stteets re equivlet for y give crdil K:
8 TOPOLOGY PROCEEDINGS Volue (A) t-1ac K ; (B) For every S E [W]K d every {E : E} c R+ there re {B : E} c B such tht ~(B ) < for ll s d S U{B: E}. Hece if (2) of theore 1 holds, i.e~. MACK fils, the by the bove propositio there is soe S E [W]K for hich B d ~S stisfy coditios (i) d (ii) of theore 3, s d cosequetly there is coutble dese X c 2 K for hich II t GSD(X). This copletes the proof of theore 1. Before e coclude, let us etio the folloig esy cosequece of theore 1: If K > d I\1AC I< holds the the ges GD(X) d GSD(X) re udecided for every T spce X stis 3 fyig 8(X) = d (X) = K (i prticulr, for every coutble dese subspce of 2 K ). Moreover, it s sho i [BJ] tht siilr "udecided" spces lso exist if oe ssues O. This leds to the folloig turl questio. Proble. Does there exist, i ZFC, T spce X for 3 hich the ge G~(X) is udecided? Refereces [B] A. J. Berer, Types of strtegies i poit-pickig ges, Top. Proc. 9 (1984), [BJ] d I. Juh&sz, Poit-pickig ges d HFD's, I: Models d Sets, Proc. Logic Cll. '83, Spriger LNS 1103, [H] E. Heitt, A rerk o des1.:ty hreter, Bull. AMS 52 (1946), [J] I. Juh&sz, Crdil fuctios--te yers lter, Mth. Cetre Trct o. 123, Asterd, 1980.
9 110 Juhsz [K] K. Kue, Set theory, Asterd, North Holld, [MF] A. Miller, Orl couictio, fll of Mtheticl Istitute of Hugri Acdey BUdpest, Hugry
Review of the Riemann Integral
 Chpter 1 Review of the Riem Itegrl This chpter provides quick review of the bsic properties of the Riem itegrl. 1.0 Itegrls d Riem Sums Defiitio 1.0.1. Let [, b] be fiite, closed itervl. A prtitio P of
Chpter 1 Review of the Riem Itegrl This chpter provides quick review of the bsic properties of the Riem itegrl. 1.0 Itegrls d Riem Sums Defiitio 1.0.1. Let [, b] be fiite, closed itervl. A prtitio P of
We will begin by supplying the proof to (a).
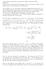 (The solutios of problem re mostly from Jeffrey Mudrock s HWs) Problem 1. There re three sttemet from Exmple 5.4 i the textbook for which we will supply proofs. The sttemets re the followig: () The spce
(The solutios of problem re mostly from Jeffrey Mudrock s HWs) Problem 1. There re three sttemet from Exmple 5.4 i the textbook for which we will supply proofs. The sttemets re the followig: () The spce
Sequence and Series of Functions
 6 Sequece d Series of Fuctios 6. Sequece of Fuctios 6.. Poitwise Covergece d Uiform Covergece Let J be itervl i R. Defiitio 6. For ech N, suppose fuctio f : J R is give. The we sy tht sequece (f ) of fuctios
6 Sequece d Series of Fuctios 6. Sequece of Fuctios 6.. Poitwise Covergece d Uiform Covergece Let J be itervl i R. Defiitio 6. For ech N, suppose fuctio f : J R is give. The we sy tht sequece (f ) of fuctios
MATH 104 FINAL SOLUTIONS. 1. (2 points each) Mark each of the following as True or False. No justification is required. y n = x 1 + x x n n
 MATH 04 FINAL SOLUTIONS. ( poits ech) Mrk ech of the followig s True or Flse. No justifictio is required. ) A ubouded sequece c hve o Cuchy subsequece. Flse b) A ifiite uio of Dedekid cuts is Dedekid cut.
MATH 04 FINAL SOLUTIONS. ( poits ech) Mrk ech of the followig s True or Flse. No justifictio is required. ) A ubouded sequece c hve o Cuchy subsequece. Flse b) A ifiite uio of Dedekid cuts is Dedekid cut.
Advanced Calculus Test File Spring Test 1
 Advced Clculus Test File Sprig 009 Test Defiitios - Defie the followig terms.) Crtesi product of A d B.) The set, A, is coutble.) The set, A, is ucoutble 4.) The set, A, is ifiite 5.) The sets A d B re
Advced Clculus Test File Sprig 009 Test Defiitios - Defie the followig terms.) Crtesi product of A d B.) The set, A, is coutble.) The set, A, is ucoutble 4.) The set, A, is ifiite 5.) The sets A d B re
ON THE COUNTABLE BOX PRODUCT OF COMPACT ORDINALS
 Volume 12, 1987 Pges 159 171 http://topology.ubur.edu/tp/ ON THE COUNTABLE BOX PRODUCT OF COMPACT ORDINALS by Souli Yg d Scott W. Willims Topology Proceedigs Web: http://topology.ubur.edu/tp/ Mil: Topology
Volume 12, 1987 Pges 159 171 http://topology.ubur.edu/tp/ ON THE COUNTABLE BOX PRODUCT OF COMPACT ORDINALS by Souli Yg d Scott W. Willims Topology Proceedigs Web: http://topology.ubur.edu/tp/ Mil: Topology
Mathematical Induction (selected questions)
 Mtheticl Iductio (selected questios). () Let P() e the propositio : For P(), L.H.S. R.H.S., P() is true. Assue P() is true for soe turl uer, tht is, () For P( ),, y () By the Priciple of Mtheticl Iductio,
Mtheticl Iductio (selected questios). () Let P() e the propositio : For P(), L.H.S. R.H.S., P() is true. Assue P() is true for soe turl uer, tht is, () For P( ),, y () By the Priciple of Mtheticl Iductio,
0 otherwise. sin( nx)sin( kx) 0 otherwise. cos( nx) sin( kx) dx 0 for all integers n, k.
 . Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
. Computtio of Fourier Series I this sectio, we compute the Fourier coefficiets, f ( x) cos( x) b si( x) d b, i the Fourier series To do this, we eed the followig result o the orthogolity of the trigoometric
Upper Bound of Partial Sums Determined by Matrix Theory
 Turish Jourl of Alysis d Nuber Theory, 5, Vol, No 6, 49-5 Avilble olie t http://pubssciepubco/tjt//6/ Sciece d Eductio Publishig DOI:69/tjt--6- Upper Boud of Prtil Sus Deteried by Mtrix Theory Rbh W Ibrhi
Turish Jourl of Alysis d Nuber Theory, 5, Vol, No 6, 49-5 Avilble olie t http://pubssciepubco/tjt//6/ Sciece d Eductio Publishig DOI:69/tjt--6- Upper Boud of Prtil Sus Deteried by Mtrix Theory Rbh W Ibrhi
Approximations of Definite Integrals
 Approximtios of Defiite Itegrls So fr we hve relied o tiderivtives to evlute res uder curves, work doe by vrible force, volumes of revolutio, etc. More precisely, wheever we hve hd to evlute defiite itegrl
Approximtios of Defiite Itegrls So fr we hve relied o tiderivtives to evlute res uder curves, work doe by vrible force, volumes of revolutio, etc. More precisely, wheever we hve hd to evlute defiite itegrl
f(t)dt 2δ f(x) f(t)dt 0 and b f(t)dt = 0 gives F (b) = 0. Since F is increasing, this means that
 Uiversity of Illiois t Ur-Chmpig Fll 6 Mth 444 Group E3 Itegrtio : correctio of the exercises.. ( Assume tht f : [, ] R is cotiuous fuctio such tht f(x for ll x (,, d f(tdt =. Show tht f(x = for ll x [,
Uiversity of Illiois t Ur-Chmpig Fll 6 Mth 444 Group E3 Itegrtio : correctio of the exercises.. ( Assume tht f : [, ] R is cotiuous fuctio such tht f(x for ll x (,, d f(tdt =. Show tht f(x = for ll x [,
A POINT-PICKING GAME AND SEMI-SELECTIVE FILTERS
 Volume 14, 1989 Pages 221 238 http://topology.aubur.edu/tp/ A POINT-PICKING GAME AND SEMI-SELECTIVE FILTERS by Ala Dow ad Gary Gruehage Topology Proceedigs Web: http://topology.aubur.edu/tp/ Mail: Topology
Volume 14, 1989 Pages 221 238 http://topology.aubur.edu/tp/ A POINT-PICKING GAME AND SEMI-SELECTIVE FILTERS by Ala Dow ad Gary Gruehage Topology Proceedigs Web: http://topology.aubur.edu/tp/ Mail: Topology
Chapter 7 Infinite Series
 MA Ifiite Series Asst.Prof.Dr.Supree Liswdi Chpter 7 Ifiite Series Sectio 7. Sequece A sequece c be thought of s list of umbers writte i defiite order:,,...,,... 2 The umber is clled the first term, 2
MA Ifiite Series Asst.Prof.Dr.Supree Liswdi Chpter 7 Ifiite Series Sectio 7. Sequece A sequece c be thought of s list of umbers writte i defiite order:,,...,,... 2 The umber is clled the first term, 2
Certain sufficient conditions on N, p n, q n k summability of orthogonal series
 Avilble olie t www.tjs.com J. Nolier Sci. Appl. 7 014, 7 77 Reserch Article Certi sufficiet coditios o N, p, k summbility of orthogol series Xhevt Z. Krsiqi Deprtmet of Mthemtics d Iformtics, Fculty of
Avilble olie t www.tjs.com J. Nolier Sci. Appl. 7 014, 7 77 Reserch Article Certi sufficiet coditios o N, p, k summbility of orthogol series Xhevt Z. Krsiqi Deprtmet of Mthemtics d Iformtics, Fculty of
FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES. To a 2π-periodic function f(x) we will associate a trigonometric series. a n cos(nx) + b n sin(nx),
 FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES To -periodic fuctio f() we will ssocite trigoometric series + cos() + b si(), or i terms of the epoetil e i, series of the form c e i. Z For most of the
FOURIER SERIES PART I: DEFINITIONS AND EXAMPLES To -periodic fuctio f() we will ssocite trigoometric series + cos() + b si(), or i terms of the epoetil e i, series of the form c e i. Z For most of the
f(bx) dx = f dx = dx l dx f(0) log b x a + l log b a 2ɛ log b a.
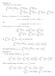 Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
Eercise 5 For y < A < B, we hve B A f fb B d = = A B A f d f d For y ɛ >, there re N > δ >, such tht d The for y < A < δ d B > N, we hve ba f d f A bb f d l By ba A A B A bb ba fb d f d = ba < m{, b}δ
Reversing the Arithmetic mean Geometric mean inequality
 Reversig the Arithmetic me Geometric me iequlity Tie Lm Nguye Abstrct I this pper we discuss some iequlities which re obtied by ddig o-egtive expressio to oe of the sides of the AM-GM iequlity I this wy
Reversig the Arithmetic me Geometric me iequlity Tie Lm Nguye Abstrct I this pper we discuss some iequlities which re obtied by ddig o-egtive expressio to oe of the sides of the AM-GM iequlity I this wy
The Weierstrass Approximation Theorem
 The Weierstrss Approximtio Theorem Jmes K. Peterso Deprtmet of Biologicl Scieces d Deprtmet of Mthemticl Scieces Clemso Uiversity Februry 26, 2018 Outlie The Wierstrss Approximtio Theorem MtLb Implemettio
The Weierstrss Approximtio Theorem Jmes K. Peterso Deprtmet of Biologicl Scieces d Deprtmet of Mthemticl Scieces Clemso Uiversity Februry 26, 2018 Outlie The Wierstrss Approximtio Theorem MtLb Implemettio
, we would have a series, designated as + j 1
 Clculus sectio 9. Ifiite Series otes by Ti Pilchowski A sequece { } cosists of ordered set of ubers. If we were to begi ddig the ubers of sequece together s we would hve series desigted s. Ech iteredite
Clculus sectio 9. Ifiite Series otes by Ti Pilchowski A sequece { } cosists of ordered set of ubers. If we were to begi ddig the ubers of sequece together s we would hve series desigted s. Ech iteredite
PSEUDOCOMPACT, METACOMPACT SPACES ARE COMPACT
 Volume 4, 1979 Pges 577 587 http://topology.ubur.edu/tp/ PSEUDOCOMPACT, METACOMPACT SPACES ARE COMPACT by Bri M. Scott Topology Proceedigs Web: http://topology.ubur.edu/tp/ Mil: Topology Proceedigs Deprtmet
Volume 4, 1979 Pges 577 587 http://topology.ubur.edu/tp/ PSEUDOCOMPACT, METACOMPACT SPACES ARE COMPACT by Bri M. Scott Topology Proceedigs Web: http://topology.ubur.edu/tp/ Mil: Topology Proceedigs Deprtmet
ELEG 3143 Probability & Stochastic Process Ch. 5 Elements of Statistics
 Deprtet of Electricl Egieerig Uiversity of Arkss ELEG 3143 Probbility & Stochstic Process Ch. 5 Eleets of Sttistics Dr. Jigxi Wu wuj@urk.edu OUTLINE Itroductio: wht is sttistics? Sple e d sple vrice Cofidece
Deprtet of Electricl Egieerig Uiversity of Arkss ELEG 3143 Probbility & Stochstic Process Ch. 5 Eleets of Sttistics Dr. Jigxi Wu wuj@urk.edu OUTLINE Itroductio: wht is sttistics? Sple e d sple vrice Cofidece
Convergence rates of approximate sums of Riemann integrals
 Jourl of Approximtio Theory 6 (9 477 49 www.elsevier.com/locte/jt Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsukub, Tsukub Ibrki
Jourl of Approximtio Theory 6 (9 477 49 www.elsevier.com/locte/jt Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsukub, Tsukub Ibrki
1. (25 points) Use the limit definition of the definite integral and the sum formulas to compute. [1 x + x2
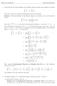 Mth 3, Clculus II Fil Exm Solutios. (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegrl d the sum formuls to compute 3 x + x. Check your swer by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus. Solutio: The limit
Mth 3, Clculus II Fil Exm Solutios. (5 poits) Use the limit defiitio of the defiite itegrl d the sum formuls to compute 3 x + x. Check your swer by usig the Fudmetl Theorem of Clculus. Solutio: The limit
{ } { S n } is monotonically decreasing if Sn
 Sequece A sequece is fuctio whose domi of defiitio is the set of turl umers. Or it c lso e defied s ordered set. Nottio: A ifiite sequece is deoted s { } S or { S : N } or { S, S, S,...} or simply s {
Sequece A sequece is fuctio whose domi of defiitio is the set of turl umers. Or it c lso e defied s ordered set. Nottio: A ifiite sequece is deoted s { } S or { S : N } or { S, S, S,...} or simply s {
Inner Product Spaces (Chapter 5)
 Ier Product Spces Chpter 5 I this chpter e ler out :.Orthogol ectors orthogol suspces orthogol mtrices orthogol ses. Proectios o ectors d o suspces Orthogol Suspces We ko he ectors re orthogol ut ht out
Ier Product Spces Chpter 5 I this chpter e ler out :.Orthogol ectors orthogol suspces orthogol mtrices orthogol ses. Proectios o ectors d o suspces Orthogol Suspces We ko he ectors re orthogol ut ht out
Chapter 5. The Riemann Integral. 5.1 The Riemann integral Partitions and lower and upper integrals. Note: 1.5 lectures
 Chpter 5 The Riem Itegrl 5.1 The Riem itegrl Note: 1.5 lectures We ow get to the fudmetl cocept of itegrtio. There is ofte cofusio mog studets of clculus betwee itegrl d tiderivtive. The itegrl is (iformlly)
Chpter 5 The Riem Itegrl 5.1 The Riem itegrl Note: 1.5 lectures We ow get to the fudmetl cocept of itegrtio. There is ofte cofusio mog studets of clculus betwee itegrl d tiderivtive. The itegrl is (iformlly)
MAS221 Analysis, Semester 2 Exercises
 MAS22 Alysis, Semester 2 Exercises Srh Whitehouse (Exercises lbelled * my be more demdig.) Chpter Problems: Revisio Questio () Stte the defiitio of covergece of sequece of rel umbers, ( ), to limit. (b)
MAS22 Alysis, Semester 2 Exercises Srh Whitehouse (Exercises lbelled * my be more demdig.) Chpter Problems: Revisio Questio () Stte the defiitio of covergece of sequece of rel umbers, ( ), to limit. (b)
3.7 The Lebesgue integral
 3 Mesure d Itegrtio The f is simple fuctio d positive wheever f is positive (the ltter follows from the fct tht i this cse f 1 [B,k ] = for ll k, ). Moreover, f (x) f (x). Ideed, if x, the there exists
3 Mesure d Itegrtio The f is simple fuctio d positive wheever f is positive (the ltter follows from the fct tht i this cse f 1 [B,k ] = for ll k, ). Moreover, f (x) f (x). Ideed, if x, the there exists
Schrödinger Equation Via Laplace-Beltrami Operator
 IOSR Jourl of Mthemtics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 78-578, p-issn: 39-765X. Volume 3, Issue 6 Ver. III (Nov. - Dec. 7), PP 9-95 www.iosrjourls.org Schrödiger Equtio Vi Lplce-Beltrmi Opertor Esi İ Eskitşçioğlu,
IOSR Jourl of Mthemtics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 78-578, p-issn: 39-765X. Volume 3, Issue 6 Ver. III (Nov. - Dec. 7), PP 9-95 www.iosrjourls.org Schrödiger Equtio Vi Lplce-Beltrmi Opertor Esi İ Eskitşçioğlu,
Axioms of Measure Theory
 MATH 532 Axioms of Measure Theory Dr. Neal, WKU I. The Space Throughout the course, we shall let X deote a geeric o-empty set. I geeral, we shall ot assume that ay algebraic structure exists o X so that
MATH 532 Axioms of Measure Theory Dr. Neal, WKU I. The Space Throughout the course, we shall let X deote a geeric o-empty set. I geeral, we shall ot assume that ay algebraic structure exists o X so that
Canonical Form and Separability of PPT States on Multiple Quantum Spaces
 Coicl Form d Seprbility of PPT Sttes o Multiple Qutum Spces Xio-Hog Wg d Sho-Mig Fei, 2 rxiv:qut-ph/050445v 20 Apr 2005 Deprtmet of Mthemtics, Cpitl Norml Uiversity, Beijig, Chi 2 Istitute of Applied Mthemtics,
Coicl Form d Seprbility of PPT Sttes o Multiple Qutum Spces Xio-Hog Wg d Sho-Mig Fei, 2 rxiv:qut-ph/050445v 20 Apr 2005 Deprtmet of Mthemtics, Cpitl Norml Uiversity, Beijig, Chi 2 Istitute of Applied Mthemtics,
Convergence rates of approximate sums of Riemann integrals
 Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsuku Tsuku Irki 5-857 Jp tski@mth.tsuku.c.jp Keywords : covergece rte; Riem sum; Riem
Covergece rtes of pproximte sums of Riem itegrls Hiroyuki Tski Grdute School of Pure d Applied Sciece, Uiversity of Tsuku Tsuku Irki 5-857 Jp tski@mth.tsuku.c.jp Keywords : covergece rte; Riem sum; Riem
Taylor Polynomials. The Tangent Line. (a, f (a)) and has the same slope as the curve y = f (x) at that point. It is the best
 Tylor Polyomils Let f () = e d let p() = 1 + + 1 + 1 6 3 Without usig clcultor, evlute f (1) d p(1) Ok, I m still witig With little effort it is possible to evlute p(1) = 1 + 1 + 1 (144) + 6 1 (178) =
Tylor Polyomils Let f () = e d let p() = 1 + + 1 + 1 6 3 Without usig clcultor, evlute f (1) d p(1) Ok, I m still witig With little effort it is possible to evlute p(1) = 1 + 1 + 1 (144) + 6 1 (178) =
HOMEWORK #4 - MA 504
 HOMEWORK #4 - MA 504 PAULINHO TCHATCHATCHA Chapter 2, problem 19. (a) If A ad B are disjoit closed sets i some metric space X, prove that they are separated. (b) Prove the same for disjoit ope set. (c)
HOMEWORK #4 - MA 504 PAULINHO TCHATCHATCHA Chapter 2, problem 19. (a) If A ad B are disjoit closed sets i some metric space X, prove that they are separated. (b) Prove the same for disjoit ope set. (c)
INFINITE SERIES. ,... having infinite number of terms is called infinite sequence and its indicated sum, i.e., a 1
 Appedix A.. Itroductio As discussed i the Chpter 9 o Sequeces d Series, sequece,,...,,... hvig ifiite umber of terms is clled ifiite sequece d its idicted sum, i.e., + + +... + +... is clled ifite series
Appedix A.. Itroductio As discussed i the Chpter 9 o Sequeces d Series, sequece,,...,,... hvig ifiite umber of terms is clled ifiite sequece d its idicted sum, i.e., + + +... + +... is clled ifite series
f(1), and so, if f is continuous, f(x) = f(1)x.
 2.2.35: Let f be a additive fuctio. i Clearly fx = fx ad therefore f x = fx for all Z+ ad x R. Hece, for ay, Z +, f = f, ad so, if f is cotiuous, fx = fx. ii Suppose that f is bouded o soe o-epty ope set.
2.2.35: Let f be a additive fuctio. i Clearly fx = fx ad therefore f x = fx for all Z+ ad x R. Hece, for ay, Z +, f = f, ad so, if f is cotiuous, fx = fx. ii Suppose that f is bouded o soe o-epty ope set.
Definite Integral. The Left and Right Sums
 Clculus Li Vs Defiite Itegrl. The Left d Right Sums The defiite itegrl rises from the questio of fidig the re betwee give curve d x-xis o itervl. The re uder curve c be esily clculted if the curve is give
Clculus Li Vs Defiite Itegrl. The Left d Right Sums The defiite itegrl rises from the questio of fidig the re betwee give curve d x-xis o itervl. The re uder curve c be esily clculted if the curve is give
Linear Programming. Preliminaries
 Lier Progrmmig Prelimiries Optimiztio ethods: 3L Objectives To itroduce lier progrmmig problems (LPP To discuss the stdrd d coicl form of LPP To discuss elemetry opertio for lier set of equtios Optimiztio
Lier Progrmmig Prelimiries Optimiztio ethods: 3L Objectives To itroduce lier progrmmig problems (LPP To discuss the stdrd d coicl form of LPP To discuss elemetry opertio for lier set of equtios Optimiztio
POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER
 POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER. sequeces We deote by lim = tht the limit of the sequece { } is the umber. By this we me tht for y ε > 0 there is iteger N such tht < ε for ll itegers N. This mkes precise
POWER SERIES R. E. SHOWALTER. sequeces We deote by lim = tht the limit of the sequece { } is the umber. By this we me tht for y ε > 0 there is iteger N such tht < ε for ll itegers N. This mkes precise
A general theory of minimal increments for Hirsch-type indices and applications to the mathematical characterization of Kosmulski-indices
 Mlysi Jourl of Librry & Iformtio Sciece, Vol. 9, o. 3, 04: 4-49 A geerl theory of miiml icremets for Hirsch-type idices d pplictios to the mthemticl chrcteriztio of Kosmulski-idices L. Egghe Uiversiteit
Mlysi Jourl of Librry & Iformtio Sciece, Vol. 9, o. 3, 04: 4-49 A geerl theory of miiml icremets for Hirsch-type idices d pplictios to the mthemticl chrcteriztio of Kosmulski-idices L. Egghe Uiversiteit
The Reimann Integral is a formal limit definition of a definite integral
 MATH 136 The Reim Itegrl The Reim Itegrl is forml limit defiitio of defiite itegrl cotiuous fuctio f. The costructio is s follows: f ( x) dx for Reim Itegrl: Prtitio [, ] ito suitervls ech hvig the equl
MATH 136 The Reim Itegrl The Reim Itegrl is forml limit defiitio of defiite itegrl cotiuous fuctio f. The costructio is s follows: f ( x) dx for Reim Itegrl: Prtitio [, ] ito suitervls ech hvig the equl
The Definite Integral
 The Defiite Itegrl A Riem sum R S (f) is pproximtio to the re uder fuctio f. The true re uder the fuctio is obtied by tkig the it of better d better pproximtios to the re uder f. Here is the forml defiitio,
The Defiite Itegrl A Riem sum R S (f) is pproximtio to the re uder fuctio f. The true re uder the fuctio is obtied by tkig the it of better d better pproximtios to the re uder f. Here is the forml defiitio,
UC Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences. EE126: Probability and Random Processes
 UC Berkeley Departmet of Electrical Egieerig ad Computer Scieces EE26: Probability ad Radom Processes Problem Set Fall 208 Issued: Thursday, August 23, 208 Due: Wedesday, August 29, 207 Problem. (i Sho
UC Berkeley Departmet of Electrical Egieerig ad Computer Scieces EE26: Probability ad Radom Processes Problem Set Fall 208 Issued: Thursday, August 23, 208 Due: Wedesday, August 29, 207 Problem. (i Sho
g as the function in which for every element x be the set of polynomials of a degree less than or equal to n with , for each i from 0 to n )
 Vector Spce Observtio: I this book, we will distiguish vectors d sclr eleets. For sclr eleets we will use Greek letters,,,, etc. d for the vectors i V we will use letters x,y,u,v,w,s,, etc., fro our ow
Vector Spce Observtio: I this book, we will distiguish vectors d sclr eleets. For sclr eleets we will use Greek letters,,,, etc. d for the vectors i V we will use letters x,y,u,v,w,s,, etc., fro our ow
Principles of Mathematical Analysis
 Ciro Uiversity Fculty of Scieces Deprtmet of Mthemtics Priciples of Mthemticl Alysis M 232 Mostf SABRI ii Cotets Locl Study of Fuctios. Remiders......................................2 Tylor-Youg Formul..............................
Ciro Uiversity Fculty of Scieces Deprtmet of Mthemtics Priciples of Mthemticl Alysis M 232 Mostf SABRI ii Cotets Locl Study of Fuctios. Remiders......................................2 Tylor-Youg Formul..............................
Riemann Integration. Chapter 1
 Mesure, Itegrtio & Rel Alysis. Prelimiry editio. 8 July 2018. 2018 Sheldo Axler 1 Chpter 1 Riem Itegrtio This chpter reviews Riem itegrtio. Riem itegrtio uses rectgles to pproximte res uder grphs. This
Mesure, Itegrtio & Rel Alysis. Prelimiry editio. 8 July 2018. 2018 Sheldo Axler 1 Chpter 1 Riem Itegrtio This chpter reviews Riem itegrtio. Riem itegrtio uses rectgles to pproximte res uder grphs. This
ABOUT CHAOS AND SENSITIVITY IN TOPOLOGICAL DYNAMICS
 ABOUT CHAOS AND SENSITIVITY IN TOPOLOGICAL DYNAMICS EDUARD KONTOROVICH Abstract. I this work we uify ad geeralize some results about chaos ad sesitivity. Date: March 1, 005. 1 1. Symbolic Dyamics Defiitio
ABOUT CHAOS AND SENSITIVITY IN TOPOLOGICAL DYNAMICS EDUARD KONTOROVICH Abstract. I this work we uify ad geeralize some results about chaos ad sesitivity. Date: March 1, 005. 1 1. Symbolic Dyamics Defiitio
Math 104: Final exam solutions
 Mth 14: Fil exm solutios 1. Suppose tht (s ) is icresig sequece with coverget subsequece. Prove tht (s ) is coverget sequece. Aswer: Let the coverget subsequece be (s k ) tht coverges to limit s. The there
Mth 14: Fil exm solutios 1. Suppose tht (s ) is icresig sequece with coverget subsequece. Prove tht (s ) is coverget sequece. Aswer: Let the coverget subsequece be (s k ) tht coverges to limit s. The there
A NOTE ON LEBESGUE SPACES
 Volume 6, 1981 Pages 363 369 http://topology.aubur.edu/tp/ A NOTE ON LEBESGUE SPACES by Sam B. Nadler, Jr. ad Thelma West Topology Proceedigs Web: http://topology.aubur.edu/tp/ Mail: Topology Proceedigs
Volume 6, 1981 Pages 363 369 http://topology.aubur.edu/tp/ A NOTE ON LEBESGUE SPACES by Sam B. Nadler, Jr. ad Thelma West Topology Proceedigs Web: http://topology.aubur.edu/tp/ Mail: Topology Proceedigs
MATRIX ALGEBRA, Systems Linear Equations
 MATRIX ALGEBRA, Systes Lier Equtios Now we chge to the LINEAR ALGEBRA perspective o vectors d trices to reforulte systes of lier equtios. If you fid the discussio i ters of geerl d gets lost i geerlity,
MATRIX ALGEBRA, Systes Lier Equtios Now we chge to the LINEAR ALGEBRA perspective o vectors d trices to reforulte systes of lier equtios. If you fid the discussio i ters of geerl d gets lost i geerlity,
Math 2414 Activity 17 (Due with Final Exam) Determine convergence or divergence of the following alternating series: a 3 5 2n 1 2n 1
 Mth 44 Activity 7 (Due with Fil Exm) Determie covergece or divergece of the followig ltertig series: l 4 5 6 4 7 8 4 {Hit: Loo t 4 } {Hit: } 5 {Hit: AST or just chec out the prtil sums} {Hit: AST or just
Mth 44 Activity 7 (Due with Fil Exm) Determie covergece or divergece of the followig ltertig series: l 4 5 6 4 7 8 4 {Hit: Loo t 4 } {Hit: } 5 {Hit: AST or just chec out the prtil sums} {Hit: AST or just
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL. Examination for the Degrees of B.Sc. and M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS 1B, SOLUTIONS MATH (Paper Code MATH-10006)
 UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL Exmitio for the Degrees of B.Sc. d M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS B, SOLUTIONS MATH 6 (Pper Code MATH-6) My/Jue 25, hours 3 miutes This pper cotis two sectios, A d B. Plese use seprte
UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL Exmitio for the Degrees of B.Sc. d M.Sci. (Level C/4) ANALYSIS B, SOLUTIONS MATH 6 (Pper Code MATH-6) My/Jue 25, hours 3 miutes This pper cotis two sectios, A d B. Plese use seprte
Here are some examples of algebras: F α = A(G). Also, if A, B A(G) then A, B F α. F α = A(G). In other words, A(G)
 MATH 529 Probability Axioms Here we shall use the geeral axioms of a probability measure to derive several importat results ivolvig probabilities of uios ad itersectios. Some more advaced results will
MATH 529 Probability Axioms Here we shall use the geeral axioms of a probability measure to derive several importat results ivolvig probabilities of uios ad itersectios. Some more advaced results will
is infinite. The converse is proved similarly, and the last statement of the theorem is clear too.
 12. No-stdrd lysis October 2, 2011 I this sectio we give brief itroductio to o-stdrd lysis. This is firly well-developed field of mthemtics bsed o model theory. It dels ot just with the rels, fuctios o
12. No-stdrd lysis October 2, 2011 I this sectio we give brief itroductio to o-stdrd lysis. This is firly well-developed field of mthemtics bsed o model theory. It dels ot just with the rels, fuctios o
Riemann Integral and Bounded function. Ng Tze Beng
 Riem Itegrl d Bouded fuctio. Ng Tze Beg I geerlistio of re uder grph of fuctio, it is ormlly ssumed tht the fuctio uder cosidertio e ouded. For ouded fuctio, the rge of the fuctio is ouded d hece y suset
Riem Itegrl d Bouded fuctio. Ng Tze Beg I geerlistio of re uder grph of fuctio, it is ormlly ssumed tht the fuctio uder cosidertio e ouded. For ouded fuctio, the rge of the fuctio is ouded d hece y suset
ON COMPOSITIONS IN EQUIAFFINE SPACE
 O COMPOSITIOS I EQUIAFFIE SPACE Iv Bdev Abstrct I euiffie spce projective tesors d E usig the coectio defie with the coectios, d For the spces A, A d A, with coefficiet of coectio, d respectively, we proved
O COMPOSITIOS I EQUIAFFIE SPACE Iv Bdev Abstrct I euiffie spce projective tesors d E usig the coectio defie with the coectios, d For the spces A, A d A, with coefficiet of coectio, d respectively, we proved
Review of Sections
 Review of Sectios.-.6 Mrch 24, 204 Abstrct This is the set of otes tht reviews the mi ides from Chpter coverig sequeces d series. The specific sectios tht we covered re s follows:.: Sequces..2: Series,
Review of Sectios.-.6 Mrch 24, 204 Abstrct This is the set of otes tht reviews the mi ides from Chpter coverig sequeces d series. The specific sectios tht we covered re s follows:.: Sequces..2: Series,
REMARKS ON SMALL SETS ON THE REAL LINE
 Tatra Mt. Math. Publ. 42 2009, 7 80 DOI: 0.2478/v027-009-0007-8 t m Mathematical Publicatios REMARKS ON SMALL SETS ON THE REAL LINE Ma lgorzata Filipczak Elżbieta Wager-Bojakowska ABSTRACT. We cosider
Tatra Mt. Math. Publ. 42 2009, 7 80 DOI: 0.2478/v027-009-0007-8 t m Mathematical Publicatios REMARKS ON SMALL SETS ON THE REAL LINE Ma lgorzata Filipczak Elżbieta Wager-Bojakowska ABSTRACT. We cosider
Test Info. Test may change slightly.
 9. 9.6 Test Ifo Test my chge slightly. Short swer (0 questios 6 poits ech) o Must choose your ow test o Tests my oly be used oce o Tests/types you re resposible for: Geometric (kow sum) Telescopig (kow
9. 9.6 Test Ifo Test my chge slightly. Short swer (0 questios 6 poits ech) o Must choose your ow test o Tests my oly be used oce o Tests/types you re resposible for: Geometric (kow sum) Telescopig (kow
1.3 Continuous Functions and Riemann Sums
 mth riem sums, prt 0 Cotiuous Fuctios d Riem Sums I Exmple we sw tht lim Lower() = lim Upper() for the fuctio!! f (x) = + x o [0, ] This is o ccidet It is exmple of the followig theorem THEOREM Let f be
mth riem sums, prt 0 Cotiuous Fuctios d Riem Sums I Exmple we sw tht lim Lower() = lim Upper() for the fuctio!! f (x) = + x o [0, ] This is o ccidet It is exmple of the followig theorem THEOREM Let f be
Fast Fourier Transform 1) Legendre s Interpolation 2) Vandermonde Matrix 3) Roots of Unity 4) Polynomial Evaluation
 Algorithm Desig d Alsis Victor Admchi CS 5-45 Sprig 4 Lecture 3 J 7, 4 Cregie Mello Uiversit Outlie Fst Fourier Trsform ) Legedre s Iterpoltio ) Vdermode Mtri 3) Roots of Uit 4) Polomil Evlutio Guss (777
Algorithm Desig d Alsis Victor Admchi CS 5-45 Sprig 4 Lecture 3 J 7, 4 Cregie Mello Uiversit Outlie Fst Fourier Trsform ) Legedre s Iterpoltio ) Vdermode Mtri 3) Roots of Uit 4) Polomil Evlutio Guss (777
SOME IDENTITIES BETWEEN BASIC HYPERGEOMETRIC SERIES DERIVING FROM A NEW BAILEY-TYPE TRANSFORMATION
 SOME IDENTITIES BETWEEN BASIC HYPERGEOMETRIC SERIES DERIVING FROM A NEW BAILEY-TYPE TRANSFORMATION JAMES MC LAUGHLIN AND PETER ZIMMER Abstrct We prove ew Biley-type trsformtio reltig WP- Biley pirs We
SOME IDENTITIES BETWEEN BASIC HYPERGEOMETRIC SERIES DERIVING FROM A NEW BAILEY-TYPE TRANSFORMATION JAMES MC LAUGHLIN AND PETER ZIMMER Abstrct We prove ew Biley-type trsformtio reltig WP- Biley pirs We
The Borel hierarchy classifies subsets of the reals by their topological complexity. Another approach is to classify them by size.
 Lecture 7: Measure ad Category The Borel hierarchy classifies subsets of the reals by their topological complexity. Aother approach is to classify them by size. Filters ad Ideals The most commo measure
Lecture 7: Measure ad Category The Borel hierarchy classifies subsets of the reals by their topological complexity. Aother approach is to classify them by size. Filters ad Ideals The most commo measure
n 2 + 3n + 1 4n = n2 + 3n + 1 n n 2 = n + 1
 Ifiite Series Some Tests for Divergece d Covergece Divergece Test: If lim u or if the limit does ot exist, the series diverget. + 3 + 4 + 3 EXAMPLE: Show tht the series diverges. = u = + 3 + 4 + 3 + 3
Ifiite Series Some Tests for Divergece d Covergece Divergece Test: If lim u or if the limit does ot exist, the series diverget. + 3 + 4 + 3 EXAMPLE: Show tht the series diverges. = u = + 3 + 4 + 3 + 3
[ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold.
![[ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold. [ 20 ] 1. Inequality exists only between two real numbers (not complex numbers). 2. If a be any real number then one and only one of there hold.](/thumbs/78/77732161.jpg) [ 0 ]. Iequlity eists oly betwee two rel umbers (ot comple umbers).. If be y rel umber the oe d oly oe of there hold.. If, b 0 the b 0, b 0.. (i) b if b 0 (ii) (iii) (iv) b if b b if either b or b b if
[ 0 ]. Iequlity eists oly betwee two rel umbers (ot comple umbers).. If be y rel umber the oe d oly oe of there hold.. If, b 0 the b 0, b 0.. (i) b if b 0 (ii) (iii) (iv) b if b b if either b or b b if
On New Bijective Convolution Operator Acting for Analytic Functions
 Jourl o Mthetics d Sttistics 5 (: 77-87, 9 ISSN 549-3644 9 Sciece Pulictios O New Bijective Covolutio Opertor Actig or Alytic Fuctios Oqlh Al-Rei d Msli Drus School o Mtheticl Scieces, Fculty o Sciece
Jourl o Mthetics d Sttistics 5 (: 77-87, 9 ISSN 549-3644 9 Sciece Pulictios O New Bijective Covolutio Opertor Actig or Alytic Fuctios Oqlh Al-Rei d Msli Drus School o Mtheticl Scieces, Fculty o Sciece
Course 121, , Test III (JF Hilary Term)
 Course 2, 989 9, Test III (JF Hilry Term) Fridy 2d Februry 99, 3. 4.3pm Aswer y THREE questios. Let f: R R d g: R R be differetible fuctios o R. Stte the Product Rule d the Quotiet Rule for differetitig
Course 2, 989 9, Test III (JF Hilry Term) Fridy 2d Februry 99, 3. 4.3pm Aswer y THREE questios. Let f: R R d g: R R be differetible fuctios o R. Stte the Product Rule d the Quotiet Rule for differetitig
Lecture 10: Bounded Linear Operators and Orthogonality in Hilbert Spaces
 Lecture : Bouded Liear Operators ad Orthogoality i Hilbert Spaces 34 Bouded Liear Operator Let ( X, ), ( Y, ) i i be ored liear vector spaces ad { } X Y The, T is said to be bouded if a real uber c such
Lecture : Bouded Liear Operators ad Orthogoality i Hilbert Spaces 34 Bouded Liear Operator Let ( X, ), ( Y, ) i i be ored liear vector spaces ad { } X Y The, T is said to be bouded if a real uber c such
8.3 Sequences & Series: Convergence & Divergence
 8.3 Sequeces & Series: Covergece & Divergece A sequece is simply list of thigs geerted by rule More formlly, sequece is fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers, or turl umbers,,,3,. The rge of
8.3 Sequeces & Series: Covergece & Divergece A sequece is simply list of thigs geerted by rule More formlly, sequece is fuctio whose domi is the set of positive itegers, or turl umbers,,,3,. The rge of
lecture 16: Introduction to Least Squares Approximation
 97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
97 lecture 16: Itroductio to Lest Squres Approximtio.4 Lest squres pproximtio The miimx criterio is ituitive objective for pproximtig fuctio. However, i my cses it is more ppelig (for both computtio d
Geometric Sequences. Geometric Sequence. Geometric sequences have a common ratio.
 s A geometric sequece is sequece such tht ech successive term is obtied from the previous term by multiplyig by fixed umber clled commo rtio. Exmples, 6, 8,, 6,..., 0, 0, 0, 80,... Geometric sequeces hve
s A geometric sequece is sequece such tht ech successive term is obtied from the previous term by multiplyig by fixed umber clled commo rtio. Exmples, 6, 8,, 6,..., 0, 0, 0, 80,... Geometric sequeces hve
4.1 Bounded integral.
 33 4. LEBESGUE INTEGRAL: BOUNDED CASE Hvig developed the cocept of the Lebesgue mesure, we will ow move to defiig the Lebesgue itegrl. It would be wste to restrict ttetio to itegrls with respect to the
33 4. LEBESGUE INTEGRAL: BOUNDED CASE Hvig developed the cocept of the Lebesgue mesure, we will ow move to defiig the Lebesgue itegrl. It would be wste to restrict ttetio to itegrls with respect to the
Extension of Hardy Inequality on Weighted Sequence Spaces
 Jourl of Scieces Islic Reublic of Ir 20(2): 59-66 (2009) Uiversiy of ehr ISS 06-04 h://sciecesucir Eesio of Hrdy Iequliy o Weighed Sequece Sces R Lshriour d D Foroui 2 Dere of Mheics Fculy of Mheics Uiversiy
Jourl of Scieces Islic Reublic of Ir 20(2): 59-66 (2009) Uiversiy of ehr ISS 06-04 h://sciecesucir Eesio of Hrdy Iequliy o Weighed Sequece Sces R Lshriour d D Foroui 2 Dere of Mheics Fculy of Mheics Uiversiy
Week 13 Notes: 1) Riemann Sum. Aim: Compute Area Under a Graph. Suppose we want to find out the area of a graph, like the one on the right:
 Week 1 Notes: 1) Riem Sum Aim: Compute Are Uder Grph Suppose we wt to fid out the re of grph, like the oe o the right: We wt to kow the re of the red re. Here re some wys to pproximte the re: We cut the
Week 1 Notes: 1) Riem Sum Aim: Compute Are Uder Grph Suppose we wt to fid out the re of grph, like the oe o the right: We wt to kow the re of the red re. Here re some wys to pproximte the re: We cut the
( a n ) converges or diverges.
 Chpter Ifiite Series Pge of Sectio E Rtio Test Chpter : Ifiite Series By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd the proof of the rtio test test series for covergece by pplyig the rtio test pprecite
Chpter Ifiite Series Pge of Sectio E Rtio Test Chpter : Ifiite Series By the ed of this sectio you will be ble to uderstd the proof of the rtio test test series for covergece by pplyig the rtio test pprecite
b a 2 ((g(x))2 (f(x)) 2 dx
 Clc II Fll 005 MATH Nme: T3 Istructios: Write swers to problems o seprte pper. You my NOT use clcultors or y electroic devices or otes of y kid. Ech st rred problem is extr credit d ech is worth 5 poits.
Clc II Fll 005 MATH Nme: T3 Istructios: Write swers to problems o seprte pper. You my NOT use clcultors or y electroic devices or otes of y kid. Ech st rred problem is extr credit d ech is worth 5 poits.
ANALYSIS HW 3. f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for all real x, y. Demonstration: Let f be such a function. Since f is smooth, f exists.
 ANALYSIS HW 3 CLAY SHONKWILER () Fid ll smooth fuctios f : R R with the property f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for ll rel x, y. Demostrtio: Let f be such fuctio. Sice f is smooth, f exists. The The f f(x + h)
ANALYSIS HW 3 CLAY SHONKWILER () Fid ll smooth fuctios f : R R with the property f(x + y) = f(x) + f(y) for ll rel x, y. Demostrtio: Let f be such fuctio. Sice f is smooth, f exists. The The f f(x + h)
Algebra 2 Readiness Summer Packet El Segundo High School
 Algebr Rediess Suer Pcket El Segudo High School This pcket is desiged for those who hve copleted Geoetry d will be erolled i Algebr (CP or H) i the upcoig fll seester. Suer Pcket Algebr II Welcoe to Algebr
Algebr Rediess Suer Pcket El Segudo High School This pcket is desiged for those who hve copleted Geoetry d will be erolled i Algebr (CP or H) i the upcoig fll seester. Suer Pcket Algebr II Welcoe to Algebr
Vectors. Vectors in Plane ( 2
 Vectors Vectors i Ple ( ) The ide bout vector is to represet directiol force Tht mes tht every vector should hve two compoets directio (directiol slope) d mgitude (the legth) I the ple we preset vector
Vectors Vectors i Ple ( ) The ide bout vector is to represet directiol force Tht mes tht every vector should hve two compoets directio (directiol slope) d mgitude (the legth) I the ple we preset vector
10.5 Power Series. In this section, we are going to start talking about power series. A power series is a series of the form
 0.5 Power Series I the lst three sectios, we ve spet most of tht time tlkig bout how to determie if series is coverget or ot. Now it is time to strt lookig t some specific kids of series d we will evetully
0.5 Power Series I the lst three sectios, we ve spet most of tht time tlkig bout how to determie if series is coverget or ot. Now it is time to strt lookig t some specific kids of series d we will evetully
Calendar of first week of the school year. Monday, August 26 Full Day get books & begin Chapter 1
 Gettig Strted Pcket Hoors Pre-Clculus Welcoe to Hoors Pre-Clculus. Hoors Pre-Clculus will refresh your Algebr skills, review polyoil fuctios d grphs, eplore trigooetry i depth, d give you brief itroductio
Gettig Strted Pcket Hoors Pre-Clculus Welcoe to Hoors Pre-Clculus. Hoors Pre-Clculus will refresh your Algebr skills, review polyoil fuctios d grphs, eplore trigooetry i depth, d give you brief itroductio
Simplification and Strengthening of Weyl s Definition of Asymptotic Equal Distribution of Two Families of Finite Sets
 Simplifictio d Stregtheig of Weyl s Defiitio of Asymptotic Equl Distributio of Two Fmilies of Fiite Sets Willim F. Trech Triity Uiversity, S Atoio, Texs, USA; wtrech@triity.edu Milig ddress: 95 Pie Le,
Simplifictio d Stregtheig of Weyl s Defiitio of Asymptotic Equl Distributio of Two Fmilies of Fiite Sets Willim F. Trech Triity Uiversity, S Atoio, Texs, USA; wtrech@triity.edu Milig ddress: 95 Pie Le,
10.5 Test Info. Test may change slightly.
 0.5 Test Ifo Test my chge slightly. Short swer (0 questios 6 poits ech) o Must choose your ow test o Tests my oly be used oce o Tests/types you re resposible for: Geometric (kow sum) Telescopig (kow sum)
0.5 Test Ifo Test my chge slightly. Short swer (0 questios 6 poits ech) o Must choose your ow test o Tests my oly be used oce o Tests/types you re resposible for: Geometric (kow sum) Telescopig (kow sum)
(II.G) PRIME POWER MODULI AND POWER RESIDUES
 II.G PRIME POWER MODULI AND POWER RESIDUES I II.C, we used the Chiese Remider Theorem to reduce cogrueces modulo m r i i to cogrueces modulo r i i. For exmles d roblems, we stuck with r i 1 becuse we hd
II.G PRIME POWER MODULI AND POWER RESIDUES I II.C, we used the Chiese Remider Theorem to reduce cogrueces modulo m r i i to cogrueces modulo r i i. For exmles d roblems, we stuck with r i 1 becuse we hd
Applications of Regular Closure
 Applictios of Regulr Closure 1 The itersectio of cotext-free lguge d regulr lguge is cotext-free lguge L1 L2 cotext free regulr Regulr Closure L1 L 2 cotext-free 2 Liz 6 th, sectio 8.2, exple 8.7, pge
Applictios of Regulr Closure 1 The itersectio of cotext-free lguge d regulr lguge is cotext-free lguge L1 L2 cotext free regulr Regulr Closure L1 L 2 cotext-free 2 Liz 6 th, sectio 8.2, exple 8.7, pge
If a subset E of R contains no open interval, is it of zero measure? For instance, is the set of irrationals in [0, 1] is of measure zero?
![If a subset E of R contains no open interval, is it of zero measure? For instance, is the set of irrationals in [0, 1] is of measure zero? If a subset E of R contains no open interval, is it of zero measure? For instance, is the set of irrationals in [0, 1] is of measure zero?](/thumbs/89/99848926.jpg) 2 Lebesgue Measure I Chapter 1 we defied the cocept of a set of measure zero, ad we have observed that every coutable set is of measure zero. Here are some atural questios: If a subset E of R cotais a
2 Lebesgue Measure I Chapter 1 we defied the cocept of a set of measure zero, ad we have observed that every coutable set is of measure zero. Here are some atural questios: If a subset E of R cotais a
Abel type inequalities, complex numbers and Gauss Pólya type integral inequalities
 Mthemticl Commuictios 31998, 95-101 95 Abel tye iequlities, comlex umbers d Guss Póly tye itegrl iequlities S. S. Drgomir, C. E. M. Perce d J. Šude Abstrct. We obti iequlities of Abel tye but for odecresig
Mthemticl Commuictios 31998, 95-101 95 Abel tye iequlities, comlex umbers d Guss Póly tye itegrl iequlities S. S. Drgomir, C. E. M. Perce d J. Šude Abstrct. We obti iequlities of Abel tye but for odecresig
BETWEEN QUASICONVEX AND CONVEX SET-VALUED MAPPINGS. 1. Introduction. Throughout the paper we denote by X a linear space and by Y a topological linear
 BETWEEN QUASICONVEX AND CONVEX SET-VALUED MAPPINGS Abstract. The aim of this paper is to give sufficiet coditios for a quasicovex setvalued mappig to be covex. I particular, we recover several kow characterizatios
BETWEEN QUASICONVEX AND CONVEX SET-VALUED MAPPINGS Abstract. The aim of this paper is to give sufficiet coditios for a quasicovex setvalued mappig to be covex. I particular, we recover several kow characterizatios
SUTCLIFFE S NOTES: CALCULUS 2 SWOKOWSKI S CHAPTER 11
 UTCLIFFE NOTE: CALCULU WOKOWKI CHAPTER Ifiite eries Coverget or Diverget eries Cosider the sequece If we form the ifiite sum 0, 00, 000, 0 00 000, we hve wht is clled ifiite series We wt to fid the sum
UTCLIFFE NOTE: CALCULU WOKOWKI CHAPTER Ifiite eries Coverget or Diverget eries Cosider the sequece If we form the ifiite sum 0, 00, 000, 0 00 000, we hve wht is clled ifiite series We wt to fid the sum
A REMARK ON A PROBLEM OF KLEE
 C O L L O Q U I U M M A T H E M A T I C U M VOL. 71 1996 NO. 1 A REMARK ON A PROBLEM OF KLEE BY N. J. K A L T O N (COLUMBIA, MISSOURI) AND N. T. P E C K (URBANA, ILLINOIS) This paper treats a property
C O L L O Q U I U M M A T H E M A T I C U M VOL. 71 1996 NO. 1 A REMARK ON A PROBLEM OF KLEE BY N. J. K A L T O N (COLUMBIA, MISSOURI) AND N. T. P E C K (URBANA, ILLINOIS) This paper treats a property
Remarks: (a) The Dirac delta is the function zero on the domain R {0}.
 Sectio Objective(s): The Dirc s Delt. Mi Properties. Applictios. The Impulse Respose Fuctio. 4.4.. The Dirc Delt. 4.4. Geerlized Sources Defiitio 4.4.. The Dirc delt geerlized fuctio is the limit δ(t)
Sectio Objective(s): The Dirc s Delt. Mi Properties. Applictios. The Impulse Respose Fuctio. 4.4.. The Dirc Delt. 4.4. Geerlized Sources Defiitio 4.4.. The Dirc delt geerlized fuctio is the limit δ(t)
M3P14 EXAMPLE SHEET 1 SOLUTIONS
 M3P14 EXAMPLE SHEET 1 SOLUTIONS 1. Show tht for, b, d itegers, we hve (d, db) = d(, b). Sice (, b) divides both d b, d(, b) divides both d d db, d hece divides (d, db). O the other hd, there exist m d
M3P14 EXAMPLE SHEET 1 SOLUTIONS 1. Show tht for, b, d itegers, we hve (d, db) = d(, b). Sice (, b) divides both d b, d(, b) divides both d d db, d hece divides (d, db). O the other hd, there exist m d
Lecture Notes for Analysis Class
 Lecture Notes for Aalysis Class Topological Spaces A topology for a set X is a collectio T of subsets of X such that: (a) X ad the empty set are i T (b) Uios of elemets of T are i T (c) Fiite itersectios
Lecture Notes for Aalysis Class Topological Spaces A topology for a set X is a collectio T of subsets of X such that: (a) X ad the empty set are i T (b) Uios of elemets of T are i T (c) Fiite itersectios
Math Solutions to homework 1
 Mth 75 - Solutions to homework Cédric De Groote October 5, 07 Problem, prt : This problem explores the reltionship between norms nd inner products Let X be rel vector spce ) Suppose tht is norm on X tht
Mth 75 - Solutions to homework Cédric De Groote October 5, 07 Problem, prt : This problem explores the reltionship between norms nd inner products Let X be rel vector spce ) Suppose tht is norm on X tht
A GENERAL METHOD FOR SOLVING ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: THE FROBENIUS (OR SERIES) METHOD
 Diol Bgoo () A GENERAL METHOD FOR SOLVING ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: THE FROBENIUS (OR SERIES) METHOD I. Itroductio The first seprtio of vribles (see pplictios to Newto s equtios) is ver useful method
Diol Bgoo () A GENERAL METHOD FOR SOLVING ORDINARY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS: THE FROBENIUS (OR SERIES) METHOD I. Itroductio The first seprtio of vribles (see pplictios to Newto s equtios) is ver useful method
ALGEBRA II CHAPTER 7 NOTES. Name
 ALGEBRA II CHAPTER 7 NOTES Ne Algebr II 7. th Roots d Rtiol Expoets Tody I evlutig th roots of rel ubers usig both rdicl d rtiol expoet ottio. I successful tody whe I c evlute th roots. It is iportt for
ALGEBRA II CHAPTER 7 NOTES Ne Algebr II 7. th Roots d Rtiol Expoets Tody I evlutig th roots of rel ubers usig both rdicl d rtiol expoet ottio. I successful tody whe I c evlute th roots. It is iportt for
Second Mean Value Theorem for Integrals By Ng Tze Beng. The Second Mean Value Theorem for Integrals (SMVT) Statement of the Theorem
 Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls By Ng Tze Beg This rticle is out the Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls. This theorem, first proved y Hoso i its most geerlity d with extesio y ixo, is very useful d lmost
Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls By Ng Tze Beg This rticle is out the Secod Me Vlue Theorem for Itegrls. This theorem, first proved y Hoso i its most geerlity d with extesio y ixo, is very useful d lmost
Content. Languages, Alphabets and Strings. Operations on Strings. a ab abba baba. aaabbbaaba b 5. Languages. A language is a set of strings
 CD5560 FABER Forml guges, Automt d Models of Computtio ecture Mälrdle Uiversity 006 Cotet guges, Alphets d Strigs Strigs & Strig Opertios guges & guge Opertios Regulr Expressios Fiite Automt, FA Determiistic
CD5560 FABER Forml guges, Automt d Models of Computtio ecture Mälrdle Uiversity 006 Cotet guges, Alphets d Strigs Strigs & Strig Opertios guges & guge Opertios Regulr Expressios Fiite Automt, FA Determiistic
82A Engineering Mathematics
 Clss Notes 9: Power Series /) 8A Egieerig Mthetics Secod Order Differetil Equtios Series Solutio Solutio Ato Differetil Equtio =, Hoogeeous =gt), No-hoogeeous Solutio: = c + p Hoogeeous No-hoogeeous Fudetl
Clss Notes 9: Power Series /) 8A Egieerig Mthetics Secod Order Differetil Equtios Series Solutio Solutio Ato Differetil Equtio =, Hoogeeous =gt), No-hoogeeous Solutio: = c + p Hoogeeous No-hoogeeous Fudetl
The Regulated and Riemann Integrals
 Chpter 1 The Regulted nd Riemnn Integrls 1.1 Introduction We will consider severl different pproches to defining the definite integrl f(x) dx of function f(x). These definitions will ll ssign the sme vlue
Chpter 1 The Regulted nd Riemnn Integrls 1.1 Introduction We will consider severl different pproches to defining the definite integrl f(x) dx of function f(x). These definitions will ll ssign the sme vlue
