The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Linear Systems
|
|
|
- Clifford Terry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Swiss Federal Institute of Technolog Page The Finite Element Method for the Analsis of Linear Sstems Prof. Dr. Michael Havbro Faber Swiss Federal Institute of Technolog ETH Zurich, Switzerland
2 Swiss Federal Institute of Technolog Page Contents t of Toda's Lecture - Bi-linear four node element - Singularit of Jacobian matrix Element matrices in global coordinate sstem
3 Swiss Federal Institute of Technolog Page 3 Bi-linear four node element: In the following we will for matters of convenience consider the iso-parametric representation: Displacement fields as well as the geometrical representation of the finite elements are approximated using the same approximating functions shape functions uˆ, vˆ -, s, u ˆ, v ˆ 3 uˆ, vˆ 3 3 r uˆ, vˆ x -, -, -
4 Swiss Federal Institute of Technolog Page Bi-linear four node element: For the bi-linear four node element the shape functions in this coordinate sstem stem become: h s = ( r) ( s) -, h = 3 ( + r) ( s) h3 = ( + r) ( + s) -, - h = ( r) ( + s),, - r
5 Swiss Federal Institute of Technolog Page 5 Bi-linear four node element: s Numerical integration: Gauss rule (x) (, ) 3 (, ) r Stiffness matrix: K = V T B CB dv dv = det J dr ds dt (, ) (, ) T K = B CBdet J V dr ds dt 5-Apr-08
6 Swiss Federal Institute of Technolog Page 6 Singularit it of Jacobian matrix: Considering the general three-dimensional case there is: φ x z φ r r r r x φ x z φ = s s s s φ x z φ t t t t z The inverse of Jacobian matrix is = J = J r x x r required! 5-Apr-08
7 Swiss Federal Institute of Technolog Page 7 Singularit it of Jacobian matrix: The existence of the inverse of Jacobian matrix provides the unique correspondence between een natural and local coordinates. Let us consider a quadrilateral element -, s, 3 x xrs (, ) = ( r)( sx ) + ( + r)( sx ) + ( + r)( + sx ) + ( r)( + sx ) rs (, ) = ( r )( s ) + ( + r )( s ) + ( + r )( + s ) + ( r)( + s ) 5-Apr-08 ( ) ( ) -, -, r
8 Swiss Federal Institute of Technolog Page 8 Singularit it of Jacobian matrix: Let us consider a quadrilateral element xrs (, ) = ( r)( sx ) + ( + r)( sx ) + ( + r)( + sx ) + ( r)( + sx ) ( rs, ) = ( r)( s ) + ( + r)( s) + ( + r)( + s) + ( r)( + s) ( ) 3 ( ) 3 x -, -, - s, 3, - r det J x r r = x s s x+ x + x3 x + s( x x + x3 x) s( + 3 ) = x x + x + x + r ( x x + x x ) r ( + ) Apr-08
9 Swiss Federal Institute of Technolog Page 9 Singularit it of Jacobian matrix: Let us consider a quadrilateral element -, -, - s, 3 det J is a linear function of the coordinates r and s. Therefore, det J 0 in the element onl if its values in all nodes are positive or negative. x, - r We have to inspect the values at the nodes. node : ( )( ) ( )( ) det J = x x x x 5-Apr-08
10 Swiss Federal Institute of Technolog Page 0 Singularit it of Jacobian matrix: Let us consider a quadrilateral element ( )( ) ( )( ) det J = x x x x x -, -, - s, 3, - r It is connected with the value of the product of the vectors: b α 3 a b = a b sinα a a b is positive if α < π x 5-Apr-08
11 Swiss Federal Institute of Technolog Page Singularit it of Jacobian matrix: Let us consider a quadrilateral element If all angles of the quadrilateral element are smaller than 80 degrees, det J will not be 0. If this is not the case, there will be singularit somewhere in the element and it will not be possible to establish unique relation between natural and local coordinates. α 3 5-Apr-08 x
12 Swiss Federal Institute of Technolog Page Following the same principle one ma define isoparametric shape functions for three-dimensional quadrilateral elements (see Bathe pp ) 35 z t r s x
13 Swiss Federal Institute of Technolog Page 3 We can also construct the triangular element directl from the quadrilateral element b so-called collapsing: 3 3
14 Swiss Federal Institute of Technolog Page We can also construct the triangular element directl from the quadrilateral element b so-called collapsing: x = hxˆ + hxˆ + hxˆ + hxˆ = h ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ + h + h33 + h 3 = xˆ = xˆ x = hxˆ + ( h + h) xˆ + hxˆ 3 = h ˆ + ( h + h ) ˆ + h ˆ 3 3
15 Swiss Federal Institute of Technolog Page 5 Element matrices in global l coordinate sstem Local to global coordinate transformations: It is often more convenient to define the element stiffness relations and to calculate their contributions to the load vector in a local coordinate sstem (e.g. displacements ũ) this is often specific for each individual element. In this case we need to transform the element matrixes into global coordinates (e.g. displacements û) before we can assemble the global stiffness relation. Transformation relationship can be written as: u = Tuˆ T being a transformation matrix.
16 Swiss Federal Institute of Technolog Page 6 Element matrices in global l coordinate sstem Y v u v u α X u = Tuˆ u cosα sinα 0 0 u v sinα cosα 0 0 v = u 0 0 cosα sinαu v 0 0 sinα cosα v
17 Swiss Federal Institute of Technolog Page 7 Element matrices in global l coordinate sstem Let us tr to establish the stiffness matrix of the truss element using directl global nodal point displacements. (see example 5., Bathe pp ) 388) K = V T B CB dv For the truss element considered we have [ α ] u=cos ( ru ) + ( + ru ) sinα ( r ) V + ( + r) V
18 Swiss Federal Institute of Technolog Page 8 Element matrices in global l coordinate sstem Let us tr to establish the stiffness matrix of the truss element using directl global nodal point displacements. (see example 5., Bathe pp ) 388) u u Using ε =, ε = in the natural coordinate sstem, x L r B= [ cosα sinα cosα sinα] L
19 Swiss Federal Institute of Technolog Page 9 Element matrices in global l coordinate sstem Let us tr to establish the stiffness matrix of the truss element using directl global nodal point displacements. (see example 5., Bathe pp ) 388) we have AL dv = dr, and C = E Finall, we obtain cos α cosαsinα cos α cosαsinα AE sin α cosαsinα sin α K= L cos α cos α sin α sm sin α
Lecture 21: Isoparametric Formulation of Plane Elements.
 6.6. Rectangular Plane Stress/Strain Element. he CS element uses a triangular shape. he 3 nodes of the CS element allow us to employ linear multivariate approximations to the u and v displacements. he
6.6. Rectangular Plane Stress/Strain Element. he CS element uses a triangular shape. he 3 nodes of the CS element allow us to employ linear multivariate approximations to the u and v displacements. he
 Code No: RT41033 R13 Set No. 1 IV B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November - 2016 FINITE ELEMENT METHODS (Common to Mechanical Engineering, Aeronautical Engineering and Automobile Engineering)
Code No: RT41033 R13 Set No. 1 IV B.Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, November - 2016 FINITE ELEMENT METHODS (Common to Mechanical Engineering, Aeronautical Engineering and Automobile Engineering)
MMJ1153 COMPUTATIONAL METHOD IN SOLID MECHANICS PRELIMINARIES TO FEM
 B Course Content: A INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW Numerical method and Computer-Aided Engineering; Phsical problems; Mathematical models; Finite element method;. B Elements and nodes, natural coordinates,
B Course Content: A INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW Numerical method and Computer-Aided Engineering; Phsical problems; Mathematical models; Finite element method;. B Elements and nodes, natural coordinates,
Chapter 6 2D Elements Plate Elements
 Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 6 2D Elements Plate Elements Method of Finite Elements I Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Continuum Elements Plane Stress Plane Strain Toda
Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 6 2D Elements Plate Elements Method of Finite Elements I Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Continuum Elements Plane Stress Plane Strain Toda
JEPPIAAR ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 JEPPIAAR ENGINEERING COLLEGE Jeppiaar Nagar, Rajiv Gandhi Salai 600 119 DEPARTMENT OFMECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK VI SEMESTER ME6603 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS Regulation 013 SUBJECT YEAR /SEM: III
JEPPIAAR ENGINEERING COLLEGE Jeppiaar Nagar, Rajiv Gandhi Salai 600 119 DEPARTMENT OFMECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK VI SEMESTER ME6603 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS Regulation 013 SUBJECT YEAR /SEM: III
Stress analysis of a stepped bar
 Stress analysis of a stepped bar Problem Find the stresses induced in the axially loaded stepped bar shown in Figure. The bar has cross-sectional areas of A ) and A ) over the lengths l ) and l ), respectively.
Stress analysis of a stepped bar Problem Find the stresses induced in the axially loaded stepped bar shown in Figure. The bar has cross-sectional areas of A ) and A ) over the lengths l ) and l ), respectively.
Chapter 14 Truss Analysis Using the Stiffness Method
 Chapter 14 Truss Analsis Using the Stiffness Method Structural Mechanics 2 ept of Arch Eng, Ajou Univ Outline undamentals of the stiffness method Member stiffness matri isplacement and force transformation
Chapter 14 Truss Analsis Using the Stiffness Method Structural Mechanics 2 ept of Arch Eng, Ajou Univ Outline undamentals of the stiffness method Member stiffness matri isplacement and force transformation
Discretization Methods Exercise # 5
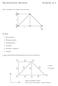 Discretization Methods Exercise # 5 Static calculation of a planar truss structure: a a F Six steps: 1. Discretization 2. Element matrices 3. Transformation 4. Assembly 5. Boundary conditions 6. Solution
Discretization Methods Exercise # 5 Static calculation of a planar truss structure: a a F Six steps: 1. Discretization 2. Element matrices 3. Transformation 4. Assembly 5. Boundary conditions 6. Solution
Post Graduate Diploma in Mechanical Engineering Computational mechanics using finite element method
 9210-220 Post Graduate Diploma in Mechanical Engineering Computational mechanics using finite element method You should have the following for this examination one answer book scientific calculator No
9210-220 Post Graduate Diploma in Mechanical Engineering Computational mechanics using finite element method You should have the following for this examination one answer book scientific calculator No
ME FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS FORMULAS
 ME 2353 - FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS FORMULAS UNIT I FINITE ELEMENT FORMULATION OF BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS 01. Global Equation for Force Vector, {F} = [K] {u} {F} = Global Force Vector [K] = Global Stiffness
ME 2353 - FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS FORMULAS UNIT I FINITE ELEMENT FORMULATION OF BOUNDARY VALUE PROBLEMS 01. Global Equation for Force Vector, {F} = [K] {u} {F} = Global Force Vector [K] = Global Stiffness
The Finite Element Method
 Page he Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and Dynamic Systems Prof. o. Dr. Michael Havbro bo Faber Dr. Nebojsa Mojsilovic Swiss Federal Institute of EH Zurich, Switzerland Contents of
Page he Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and Dynamic Systems Prof. o. Dr. Michael Havbro bo Faber Dr. Nebojsa Mojsilovic Swiss Federal Institute of EH Zurich, Switzerland Contents of
ME 1401 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS UNIT I PART -A. 2. Why polynomial type of interpolation functions is mostly used in FEM?
 SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR, TIRUCHIRAPPALLI 621 105 Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 1401 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS 1.
SHRI ANGALAMMAN COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution) SIRUGANOOR, TIRUCHIRAPPALLI 621 105 Department of Mechanical Engineering ME 1401 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS 1.
Lecture 20: Isoparametric Formulations.
 Chapter #0 Isoparametric Formulation. Isoparametric formulations help us solve two problems. Help simplify the definition of the approimate displacement field for more comple planar elements (4-sided elements,
Chapter #0 Isoparametric Formulation. Isoparametric formulations help us solve two problems. Help simplify the definition of the approimate displacement field for more comple planar elements (4-sided elements,
Geometry review, part I
 Geometr reie, part I Geometr reie I Vectors and points points and ectors Geometric s. coordinate-based (algebraic) approach operations on ectors and points Lines implicit and parametric equations intersections,
Geometr reie, part I Geometr reie I Vectors and points points and ectors Geometric s. coordinate-based (algebraic) approach operations on ectors and points Lines implicit and parametric equations intersections,
Finite Element Method-Part II Isoparametric FE Formulation and some numerical examples Lecture 29 Smart and Micro Systems
 Finite Element Method-Part II Isoparametric FE Formulation and some numerical examples Lecture 29 Smart and Micro Systems Introduction Till now we dealt only with finite elements having straight edges.
Finite Element Method-Part II Isoparametric FE Formulation and some numerical examples Lecture 29 Smart and Micro Systems Introduction Till now we dealt only with finite elements having straight edges.
Chapter 11 Three-Dimensional Stress Analysis. Chapter 11 Three-Dimensional Stress Analysis
 CIVL 7/87 Chapter - /39 Chapter Learning Objectives To introduce concepts of three-dimensional stress and strain. To develop the tetrahedral solid-element stiffness matri. To describe how bod and surface
CIVL 7/87 Chapter - /39 Chapter Learning Objectives To introduce concepts of three-dimensional stress and strain. To develop the tetrahedral solid-element stiffness matri. To describe how bod and surface
IV B.Tech. I Semester Supplementary Examinations, February/March FINITE ELEMENT METHODS (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80
 www..com www..com Code No: M0322/R07 Set No. 1 IV B.Tech. I Semester Supplementary Examinations, February/March - 2011 FINITE ELEMENT METHODS (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
www..com www..com Code No: M0322/R07 Set No. 1 IV B.Tech. I Semester Supplementary Examinations, February/March - 2011 FINITE ELEMENT METHODS (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80 Answer
3. Numerical integration
 3. Numerical integration... 3. One-dimensional quadratures... 3. Two- and three-dimensional quadratures... 3.3 Exact Integrals for Straight Sided Triangles... 5 3.4 Reduced and Selected Integration...
3. Numerical integration... 3. One-dimensional quadratures... 3. Two- and three-dimensional quadratures... 3.3 Exact Integrals for Straight Sided Triangles... 5 3.4 Reduced and Selected Integration...
Lecture 5: 3-D Rotation Matrices.
 3.7 Transformation Matri and Stiffness Matri in Three- Dimensional Space. The displacement vector d is a real vector entit. It is independent of the frame used to define it. d = d i + d j + d k = dˆ iˆ+
3.7 Transformation Matri and Stiffness Matri in Three- Dimensional Space. The displacement vector d is a real vector entit. It is independent of the frame used to define it. d = d i + d j + d k = dˆ iˆ+
BHAR AT HID AS AN ENGIN E ERI N G C O L L E G E NATTR A MPA LL I
 BHAR AT HID AS AN ENGIN E ERI N G C O L L E G E NATTR A MPA LL I 635 8 54. Third Year M E C H A NICAL VI S E M ES TER QUE S T I ON B ANK Subject: ME 6 603 FIN I T E E LE ME N T A N A L YSIS UNI T - I INTRODUCTION
BHAR AT HID AS AN ENGIN E ERI N G C O L L E G E NATTR A MPA LL I 635 8 54. Third Year M E C H A NICAL VI S E M ES TER QUE S T I ON B ANK Subject: ME 6 603 FIN I T E E LE ME N T A N A L YSIS UNI T - I INTRODUCTION
THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD 2017 Dept. of Solid Mechanics
 THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD 07 Dept. of Solid Mechanics EXAMINATION: 07-05-9 A maximum of 60 points can be achieved in this examination. To pass at least 0 points are required. Permitted aid: Pocket calculator.
THE FINITE ELEMENT METHOD 07 Dept. of Solid Mechanics EXAMINATION: 07-05-9 A maximum of 60 points can be achieved in this examination. To pass at least 0 points are required. Permitted aid: Pocket calculator.
Level 7 Postgraduate Diploma in Engineering Computational mechanics using finite element method
 9210-203 Level 7 Postgraduate Diploma in Engineering Computational mechanics using finite element method You should have the following for this examination one answer book No additional data is attached
9210-203 Level 7 Postgraduate Diploma in Engineering Computational mechanics using finite element method You should have the following for this examination one answer book No additional data is attached
Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering
 Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering Short Course on + Dynamics Boulder, Colorado January 5-8, 2004 Stein Sture Professor of Civil Engineering University of Colorado at Boulder Contents Steps
Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering Short Course on + Dynamics Boulder, Colorado January 5-8, 2004 Stein Sture Professor of Civil Engineering University of Colorado at Boulder Contents Steps
Structural Analysis of Truss Structures using Stiffness Matrix. Dr. Nasrellah Hassan Ahmed
 Structural Analysis of Truss Structures using Stiffness Matrix Dr. Nasrellah Hassan Ahmed FUNDAMENTAL RELATIONSHIPS FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS In general, there are three types of relationships: Equilibrium
Structural Analysis of Truss Structures using Stiffness Matrix Dr. Nasrellah Hassan Ahmed FUNDAMENTAL RELATIONSHIPS FOR STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS In general, there are three types of relationships: Equilibrium
Applications in Solid Mechanics
 Companies, 4 CHAPTER 9 Applications in Solid 9. INTRODUCTION The bar and beam elements discussed in Chapters 4 are line elements, as only a single coordinate axis is required to define the element reference
Companies, 4 CHAPTER 9 Applications in Solid 9. INTRODUCTION The bar and beam elements discussed in Chapters 4 are line elements, as only a single coordinate axis is required to define the element reference
Chapter 5 Structural Elements: The truss & beam elements
 Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 5 Structural Elements: The truss & beam elements Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Chapter Goals Learn how to formulate the Finite Element Equations
Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 5 Structural Elements: The truss & beam elements Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Chapter Goals Learn how to formulate the Finite Element Equations
Lecture 15: Revisiting bars and beams.
 3.10 Potential Energy Approach to Derive Bar Element Equations. We place assumptions on the stresses developed inside the bar. The spatial stress and strain matrices become very sparse. We add (ad-hoc)
3.10 Potential Energy Approach to Derive Bar Element Equations. We place assumptions on the stresses developed inside the bar. The spatial stress and strain matrices become very sparse. We add (ad-hoc)
Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1. Method of Finite Elements I. Chapter 2. The Direct Stiffness Method. Method of Finite Elements I
 Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 2 The Direct Stiffness Method Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Direct Stiffness Method (DSM) Computational method for structural analysis Matrix
Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 2 The Direct Stiffness Method Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Direct Stiffness Method (DSM) Computational method for structural analysis Matrix
Lecture 8: Assembly of beam elements.
 ecture 8: Assembly of beam elements. 4. Example of Assemblage of Beam Stiffness Matrices. Place nodes at the load application points. Assembling the two sets of element equations (note the common elemental
ecture 8: Assembly of beam elements. 4. Example of Assemblage of Beam Stiffness Matrices. Place nodes at the load application points. Assembling the two sets of element equations (note the common elemental
Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1. Method of Finite Elements I. Chapter 2. The Direct Stiffness Method. Method of Finite Elements I
 Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 2 The Direct Stiffness Method Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Direct Stiffness Method (DSM) Computational method for structural analysis Matrix
Institute of Structural Engineering Page 1 Chapter 2 The Direct Stiffness Method Institute of Structural Engineering Page 2 Direct Stiffness Method (DSM) Computational method for structural analysis Matrix
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME 6603 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS PART A (2 MARKS)
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME 6603 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS UNIT I : FINITE ELEMENT FORMULATION OF BOUNDARY VALUE PART A (2 MARKS) 1. Write the types
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, CHENNAI DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME 6603 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS UNIT I : FINITE ELEMENT FORMULATION OF BOUNDARY VALUE PART A (2 MARKS) 1. Write the types
Large deflection analysis of planar solids based on the Finite Particle Method
 yuying@uiuc.edu 10 th US National Congress on Computational Mechanics Large deflection analysis of planar solids based on the Finite Particle Method 1, 2 Presenter: Ying Yu Advisors: Prof. Glaucio H. Paulino
yuying@uiuc.edu 10 th US National Congress on Computational Mechanics Large deflection analysis of planar solids based on the Finite Particle Method 1, 2 Presenter: Ying Yu Advisors: Prof. Glaucio H. Paulino
Geometric Stiffness Effects in 2D and 3D Frames
 Geometric Stiffness Effects in D and 3D Frames CEE 41. Matrix Structural Analsis Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Duke Universit Henri Gavin Fall, 1 In situations in which deformations
Geometric Stiffness Effects in D and 3D Frames CEE 41. Matrix Structural Analsis Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Duke Universit Henri Gavin Fall, 1 In situations in which deformations
NEW QUADRANGULAR SHELL ELEMENT IN SAFIR
 NEW QUADRANGULAR SHELL ELEMENT IN SAFIR Didier TALAMONA Jean-Marc FRANSSEN Univ. of Liège, SPEC, Chemin des Chevreuils, 4000 Liège, Belgium d.talamona@ulg.ac.be jm.franssen@ulg.ac.be Abstract SAFIR is
NEW QUADRANGULAR SHELL ELEMENT IN SAFIR Didier TALAMONA Jean-Marc FRANSSEN Univ. of Liège, SPEC, Chemin des Chevreuils, 4000 Liège, Belgium d.talamona@ulg.ac.be jm.franssen@ulg.ac.be Abstract SAFIR is
Math 181/281. Rumbos Spring 2011 Page 1. Solutions to Assignment #5. Hence, the dynamical system, θ(t, p, q), for (t, p, q) R 3 corresponding = F.
 Math 181/281. Rumbos Spring 2011 Page 1 Solutions to Assignment #5 1. For real numbers a and b with a 2 + b 2 = 0, let F : R 2 R 2 be given b ( ) ( ) ( ) x ax b x F =, for all R 2. (1) bx + a (a) Explain
Math 181/281. Rumbos Spring 2011 Page 1 Solutions to Assignment #5 1. For real numbers a and b with a 2 + b 2 = 0, let F : R 2 R 2 be given b ( ) ( ) ( ) x ax b x F =, for all R 2. (1) bx + a (a) Explain
ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 3 Solutions [Multiple Integration; Lines of Force]
![ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 3 Solutions [Multiple Integration; Lines of Force] ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 3 Solutions [Multiple Integration; Lines of Force]](/thumbs/84/89723886.jpg) ENGI 44 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Facult of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set Solutions [Multiple Integration; Lines of Force]. Evaluate D da over the triangular region D that is bounded
ENGI 44 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Facult of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set Solutions [Multiple Integration; Lines of Force]. Evaluate D da over the triangular region D that is bounded
Using MATLAB and. Abaqus. Finite Element Analysis. Introduction to. Amar Khennane. Taylor & Francis Croup. Taylor & Francis Croup,
 Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Using MATLAB and Abaqus Amar Khennane Taylor & Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Croup, an informa business
Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Using MATLAB and Abaqus Amar Khennane Taylor & Francis Croup Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Croup, an informa business
WRT in 2D: Poisson Example
 WRT in 2D: Poisson Example Consider 2 u f on [, L x [, L y with u. WRT: For all v X N, find u X N a(v, u) such that v u dv v f dv. Follows from strong form plus integration by parts: ( ) 2 u v + 2 u dx
WRT in 2D: Poisson Example Consider 2 u f on [, L x [, L y with u. WRT: For all v X N, find u X N a(v, u) such that v u dv v f dv. Follows from strong form plus integration by parts: ( ) 2 u v + 2 u dx
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Module - 01 Lecture - 13
 Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras (Refer Slide Time: 00:25) Module - 01 Lecture - 13 In the last class, we have seen how
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras (Refer Slide Time: 00:25) Module - 01 Lecture - 13 In the last class, we have seen how
Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Using Pro/MECHANICA Wildfire 5.0
 Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Using Pro/MECHANICA Wildfire 5.0 Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com Better Textbooks.
Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Using Pro/MECHANICA Wildfire 5.0 Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com Better Textbooks.
Prepared by M. GUNASHANKAR AP/MECH DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY-KARUR FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS 2 MARKS QUESTIONS WITH ANSWER Prepared by M. GUNASHANKAR AP/MECH DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY-KARUR FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS 2 MARKS QUESTIONS WITH ANSWER Prepared by M. GUNASHANKAR AP/MECH DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
Contents as of 12/8/2017. Preface. 1. Overview...1
 Contents as of 12/8/2017 Preface 1. Overview...1 1.1 Introduction...1 1.2 Finite element data...1 1.3 Matrix notation...3 1.4 Matrix partitions...8 1.5 Special finite element matrix notations...9 1.6 Finite
Contents as of 12/8/2017 Preface 1. Overview...1 1.1 Introduction...1 1.2 Finite element data...1 1.3 Matrix notation...3 1.4 Matrix partitions...8 1.5 Special finite element matrix notations...9 1.6 Finite
MEI solutions to exercise 4 1
 MEI-55 solutions to exercise Problem Solve the stationary two-dimensional heat transfer problem shown in the figure below by using linear elements Use symmetry to reduce the problem size The material is
MEI-55 solutions to exercise Problem Solve the stationary two-dimensional heat transfer problem shown in the figure below by using linear elements Use symmetry to reduce the problem size The material is
Effects Of Temperature, Pre-strain & Support Displacement
 Lecture 14: TEMPERTURE, PRESTRIN & SUPPORT Effects Of Temperature, Pre-strain & Support Displacement In the previous sections we have only considered loads acting on the structure. We would also like to
Lecture 14: TEMPERTURE, PRESTRIN & SUPPORT Effects Of Temperature, Pre-strain & Support Displacement In the previous sections we have only considered loads acting on the structure. We would also like to
Math 425 Lecture 1: Vectors in R 3, R n
 Math 425 Lecture 1: Vectors in R 3, R n Motiating Questions, Problems 1. Find the coordinates of a regular tetrahedron with center at the origin and sides of length 1. 2. What is the angle between the
Math 425 Lecture 1: Vectors in R 3, R n Motiating Questions, Problems 1. Find the coordinates of a regular tetrahedron with center at the origin and sides of length 1. 2. What is the angle between the
The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and Dynamic Systems: Thermomechanics
 The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and Dynamic Systems: Thermomechanics Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi Dr. Giuseppe Abbiati, Dr. Konstantinos Agathos Lecture 13-14 December, 2017 1 / 30 Forewords
The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and Dynamic Systems: Thermomechanics Prof. Dr. Eleni Chatzi Dr. Giuseppe Abbiati, Dr. Konstantinos Agathos Lecture 13-14 December, 2017 1 / 30 Forewords
4 Finite Element Method for Trusses
 4 Finite Element Method for Trusses To solve the system of linear equations that arises in IPM, it is necessary to assemble the geometric matrix B a. For the sake of simplicity, the applied force vector
4 Finite Element Method for Trusses To solve the system of linear equations that arises in IPM, it is necessary to assemble the geometric matrix B a. For the sake of simplicity, the applied force vector
CIVL4332 L1 Introduction to Finite Element Method
 CIVL L Introduction to Finite Element Method CIVL L Introduction to Finite Element Method by Joe Gattas, Faris Albermani Introduction The FEM is a numerical technique for solving physical problems such
CIVL L Introduction to Finite Element Method CIVL L Introduction to Finite Element Method by Joe Gattas, Faris Albermani Introduction The FEM is a numerical technique for solving physical problems such
Chapter 3. Formulation of FEM for Two-Dimensional Problems
 Chapter Formulation of FEM for Two-Dimensional Problems.1 Two-Dimensional FEM Formulation Many details of 1D and 2D formulations are the same. To demonstrate how a 2D formulation works we ll use the following
Chapter Formulation of FEM for Two-Dimensional Problems.1 Two-Dimensional FEM Formulation Many details of 1D and 2D formulations are the same. To demonstrate how a 2D formulation works we ll use the following
Truss Structures: The Direct Stiffness Method
 . Truss Structures: The Companies, CHAPTER Truss Structures: The Direct Stiffness Method. INTRODUCTION The simple line elements discussed in Chapter introduced the concepts of nodes, nodal displacements,
. Truss Structures: The Companies, CHAPTER Truss Structures: The Direct Stiffness Method. INTRODUCTION The simple line elements discussed in Chapter introduced the concepts of nodes, nodal displacements,
Structural Dynamics. Spring mass system. The spring force is given by and F(t) is the driving force. Start by applying Newton s second law (F=ma).
 Structural Dynamics Spring mass system. The spring force is given by and F(t) is the driving force. Start by applying Newton s second law (F=ma). We will now look at free vibrations. Considering the free
Structural Dynamics Spring mass system. The spring force is given by and F(t) is the driving force. Start by applying Newton s second law (F=ma). We will now look at free vibrations. Considering the free
Topic 5: Finite Element Method
 Topic 5: Finite Element Method 1 Finite Element Method (1) Main problem of classical variational methods (Ritz method etc.) difficult (op impossible) definition of approximation function ϕ for non-trivial
Topic 5: Finite Element Method 1 Finite Element Method (1) Main problem of classical variational methods (Ritz method etc.) difficult (op impossible) definition of approximation function ϕ for non-trivial
Applications of Gauss-Radau and Gauss-Lobatto Numerical Integrations Over a Four Node Quadrilateral Finite Element
 Avaiable online at www.banglaol.info angladesh J. Sci. Ind. Res. (), 77-86, 008 ANGLADESH JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC AND INDUSTRIAL RESEARCH CSIR E-mail: bsir07gmail.com Abstract Applications of Gauss-Radau
Avaiable online at www.banglaol.info angladesh J. Sci. Ind. Res. (), 77-86, 008 ANGLADESH JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC AND INDUSTRIAL RESEARCH CSIR E-mail: bsir07gmail.com Abstract Applications of Gauss-Radau
Ph.D. Preliminary Examination Analysis
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY Spring Semester 2017 Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering Structural Engineering, Mechanics and Materials Name:......................................... Ph.D.
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY Spring Semester 2017 Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering Structural Engineering, Mechanics and Materials Name:......................................... Ph.D.
CHAPTER 7 EARTHQUAKE RESPONSE OF INELASTIC SYSTEMS. Base shear force in a linearly elastic system due to ground excitation is Vb
 CHAPTER 7 EARTHQUAKE RESPONSE OF INELASTIC SYSTEMS Base shear force in a linearl elastic sstem due to ground excitation is Vb = ( A/ g) w where A is the pseudo-acceleration corresponding to natural period
CHAPTER 7 EARTHQUAKE RESPONSE OF INELASTIC SYSTEMS Base shear force in a linearl elastic sstem due to ground excitation is Vb = ( A/ g) w where A is the pseudo-acceleration corresponding to natural period
IMPLEMENTATION or METHODS IN COMPUTER PROGRAMS; EXAMPLES SAP, ADINA
 IMPLEMENTATION or METHODS IN COMPUTER PROGRAMS; EXAMPLES SAP, ADINA LECTURE 5 56 MINUTES 5 1 "pi_entation of metllods in computer progradls; examples SIP, ADlRA LECTURE 5 Implementation of the finite element
IMPLEMENTATION or METHODS IN COMPUTER PROGRAMS; EXAMPLES SAP, ADINA LECTURE 5 56 MINUTES 5 1 "pi_entation of metllods in computer progradls; examples SIP, ADlRA LECTURE 5 Implementation of the finite element
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF A PILE SUBJECTED TO LATERAL LOADS
 IGC 009, Guntur, INDIA NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF A PILE SUBJECTED TO LATERAL LOADS Mohammed Younus Ahmed Graduate Student, Earthquake Engineering Research Center, IIIT Hyderabad, Gachibowli, Hyderabad 3, India.
IGC 009, Guntur, INDIA NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF A PILE SUBJECTED TO LATERAL LOADS Mohammed Younus Ahmed Graduate Student, Earthquake Engineering Research Center, IIIT Hyderabad, Gachibowli, Hyderabad 3, India.
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras. Lecture - 06
 Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 06 In the last lecture, we have seen a boundary value problem, using the formal
Finite Element Analysis Prof. Dr. B. N. Rao Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 06 In the last lecture, we have seen a boundary value problem, using the formal
MEEN 673 ********************************* NONLINEAR FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS ********************************* J. N. Reddy
 MEEN 673 ********************************* NONLINEAR FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS ********************************* J. N. Reddy e-mail: jnreddy@tamu.edu Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-3123 USA
MEEN 673 ********************************* NONLINEAR FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS ********************************* J. N. Reddy e-mail: jnreddy@tamu.edu Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843-3123 USA
Modelling and Finite Element Analysis of Double Wishbone Suspension
 Modelling and Finite Element Analysis of Double Wishbone Suspension Amol Patil, Varsha Patil, Prashant Uhle P.G. Student, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, S S B T S College of Engineering, Jalgaon, Maharastra,
Modelling and Finite Element Analysis of Double Wishbone Suspension Amol Patil, Varsha Patil, Prashant Uhle P.G. Student, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, S S B T S College of Engineering, Jalgaon, Maharastra,
Schur decomposition in the scaled boundary finite element method in elastostatics
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering Schur decomposition in the scaled boundary finite element method in elastostatics o cite this article: M Li et al 010 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering Schur decomposition in the scaled boundary finite element method in elastostatics o cite this article: M Li et al 010 IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci.
Meshfree Inelastic Frame Analysis
 Theory & Results Louie L. Yaw, Sashi Kunnath and N. Sukumar University of California, Davis Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Minisymposium 47 Recent Advances in Modeling of Engineering
Theory & Results Louie L. Yaw, Sashi Kunnath and N. Sukumar University of California, Davis Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Minisymposium 47 Recent Advances in Modeling of Engineering
Two Dimensional Linear Systems of ODEs
 34 CHAPTER 3 Two Dimensional Linear Sstems of ODEs A first-der, autonomous, homogeneous linear sstem of two ODEs has the fm x t ax + b, t cx + d where a, b, c, d are real constants The matrix fm is 31
34 CHAPTER 3 Two Dimensional Linear Sstems of ODEs A first-der, autonomous, homogeneous linear sstem of two ODEs has the fm x t ax + b, t cx + d where a, b, c, d are real constants The matrix fm is 31
Introduction to Finite Element computations
 Non Linear Computational Mechanics Athens MP06/2012 Introduction to Finite Element computations Vincent Chiaruttini, Georges Cailletaud vincent.chiaruttini@onera.fr Outline Continuous to discrete problem
Non Linear Computational Mechanics Athens MP06/2012 Introduction to Finite Element computations Vincent Chiaruttini, Georges Cailletaud vincent.chiaruttini@onera.fr Outline Continuous to discrete problem
Numerical integration in the axisymmetric finite element formulation
 Advances in Engineering Software 31 (2000) 137 141 Short Communication Numerical integration in the axisymmetric finite element formulation J.D. Clayton a, J.J. Rencis b, * a The George W. Woodruff School
Advances in Engineering Software 31 (2000) 137 141 Short Communication Numerical integration in the axisymmetric finite element formulation J.D. Clayton a, J.J. Rencis b, * a The George W. Woodruff School
Shape Function Generation and Requirements
 Shape Function Generation and Requirements Requirements Requirements (A) Interpolation condition. Takes a unit value at node i, and is zero at all other nodes. Requirements (B) Local support condition.
Shape Function Generation and Requirements Requirements Requirements (A) Interpolation condition. Takes a unit value at node i, and is zero at all other nodes. Requirements (B) Local support condition.
Methods of Analysis. Force or Flexibility Method
 INTRODUCTION: The structural analysis is a mathematical process by which the response of a structure to specified loads is determined. This response is measured by determining the internal forces or stresses
INTRODUCTION: The structural analysis is a mathematical process by which the response of a structure to specified loads is determined. This response is measured by determining the internal forces or stresses
A Simple Problem Which Students Can Solve and Check Using an Inexpensive Calculator
 Session 3649 A Simple Problem Which Students Can Solve and Check Using an Inexpensive Calculator Patrick J. Cronin The Pennsylvania State University New Kensington Campus Abstract This paper proposes a
Session 3649 A Simple Problem Which Students Can Solve and Check Using an Inexpensive Calculator Patrick J. Cronin The Pennsylvania State University New Kensington Campus Abstract This paper proposes a
New Formula for Geometric Stiffness Matrix Calculation
 Journal of Applied Mathematics and Phsics, 016, 4, 733-748 Published Online April 016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jamp http://d.doi.org/10.436//jamp.016.44084 ew Formula for Geometric Stiffness
Journal of Applied Mathematics and Phsics, 016, 4, 733-748 Published Online April 016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jamp http://d.doi.org/10.436//jamp.016.44084 ew Formula for Geometric Stiffness
The Finite Element Method
 The Finite Element Method Contents. Introduction 2. A Simple Example 3. Trusses 4. Linear Systems of Equations 5. Basic Equations of Elasticity Theory 6. Finite Elements for Plane Stress Problems 7. Finite
The Finite Element Method Contents. Introduction 2. A Simple Example 3. Trusses 4. Linear Systems of Equations 5. Basic Equations of Elasticity Theory 6. Finite Elements for Plane Stress Problems 7. Finite
Linear Strain Triangle and other types of 2D elements. By S. Ziaei Rad
 Linear Strain Triangle and other tpes o D elements B S. Ziaei Rad Linear Strain Triangle (LST or T6 This element is also called qadratic trianglar element. Qadratic Trianglar Element Linear Strain Triangle
Linear Strain Triangle and other tpes o D elements B S. Ziaei Rad Linear Strain Triangle (LST or T6 This element is also called qadratic trianglar element. Qadratic Trianglar Element Linear Strain Triangle
Finite element-based elasto-plastic optimum reinforcement dimensioning of spatial concrete panel structures
 Research Collection Report Finite element-based elasto-plastic optimum reinforcement dimensioning of spatial concrete panel structures Author(s): Tabatabai, Seyed Mohammad Reza Publication Date: 1996 Permanent
Research Collection Report Finite element-based elasto-plastic optimum reinforcement dimensioning of spatial concrete panel structures Author(s): Tabatabai, Seyed Mohammad Reza Publication Date: 1996 Permanent
Steps in the Finite Element Method. Chung Hua University Department of Mechanical Engineering Dr. Ching I Chen
 Steps in the Finite Element Method Chung Hua University Department of Mechanical Engineering Dr. Ching I Chen General Idea Engineers are interested in evaluating effects such as deformations, stresses,
Steps in the Finite Element Method Chung Hua University Department of Mechanical Engineering Dr. Ching I Chen General Idea Engineers are interested in evaluating effects such as deformations, stresses,
A two-dimensional FE truss program
 A two-dimensional FE truss program 4M020: Design Tools Eindhoven University of Technology Introduction The Matlab program fem2d allows to model and analyze two-dimensional truss structures, where trusses
A two-dimensional FE truss program 4M020: Design Tools Eindhoven University of Technology Introduction The Matlab program fem2d allows to model and analyze two-dimensional truss structures, where trusses
Department of Architecture & Civil Engineering
 MODE ANSWER age: 1 4. The students are given approximately 4 hours of lectures devoted to this topic. Thus the emphasis in the answer must be in demonstrating an understanding of the physical principals
MODE ANSWER age: 1 4. The students are given approximately 4 hours of lectures devoted to this topic. Thus the emphasis in the answer must be in demonstrating an understanding of the physical principals
Lecture 3. Motion in more than one dimension
 4/9/19 Phsics 2 Olga Dudko UCSD Phsics Lecture 3 Toda: The vector description of motion. Relative Motion. The principle of Galilean relativit. Motion in more than one dimension 1D: position is specified
4/9/19 Phsics 2 Olga Dudko UCSD Phsics Lecture 3 Toda: The vector description of motion. Relative Motion. The principle of Galilean relativit. Motion in more than one dimension 1D: position is specified
Back Matter Index The McGraw Hill Companies, 2004
 INDEX A Absolute viscosity, 294 Active zone, 468 Adjoint, 452 Admissible functions, 132 Air, 294 ALGOR, 12 Amplitude, 389, 391 Amplitude ratio, 396 ANSYS, 12 Applications fluid mechanics, 293 326. See
INDEX A Absolute viscosity, 294 Active zone, 468 Adjoint, 452 Admissible functions, 132 Air, 294 ALGOR, 12 Amplitude, 389, 391 Amplitude ratio, 396 ANSYS, 12 Applications fluid mechanics, 293 326. See
Structural Matrices in MDOF Systems
 in MDOF Systems http://intranet.dica.polimi.it/people/boffi-giacomo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile Ambientale e Territoriale Politecnico di Milano April 9, 2016 Outline Additional Static Condensation
in MDOF Systems http://intranet.dica.polimi.it/people/boffi-giacomo Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile Ambientale e Territoriale Politecnico di Milano April 9, 2016 Outline Additional Static Condensation
2. Polynomial interpolation
 2. Polynomial interpolation Contents 2. POLYNOMIAL INTERPOLATION... 1 2.1 TYPES OF INTERPOLATION... 1 2.2 LAGRANGE ONE-DIMENSIONAL INTERPOLATION... 2 2.3 NATURAL COORDINATES*... 15 2.4 HERMITE ONE-DIMENSIONAL
2. Polynomial interpolation Contents 2. POLYNOMIAL INTERPOLATION... 1 2.1 TYPES OF INTERPOLATION... 1 2.2 LAGRANGE ONE-DIMENSIONAL INTERPOLATION... 2 2.3 NATURAL COORDINATES*... 15 2.4 HERMITE ONE-DIMENSIONAL
As an example, the two-bar truss structure, shown in the figure below will be modelled, loaded and analyzed.
 Program tr2d 1 FE program tr2d The Matlab program tr2d allows to model and analyze two-dimensional truss structures, where trusses are homogeneous and can behave nonlinear. Deformation and rotations can
Program tr2d 1 FE program tr2d The Matlab program tr2d allows to model and analyze two-dimensional truss structures, where trusses are homogeneous and can behave nonlinear. Deformation and rotations can
CIVL 8/7117 Chapter 12 - Structural Dynamics 1/75. To discuss the dynamics of a single-degree-of freedom springmass
 CIV 8/77 Chapter - /75 Introduction To discuss the dynamics of a single-degree-of freedom springmass system. To derive the finite element equations for the time-dependent stress analysis of the one-dimensional
CIV 8/77 Chapter - /75 Introduction To discuss the dynamics of a single-degree-of freedom springmass system. To derive the finite element equations for the time-dependent stress analysis of the one-dimensional
Lecture 12: Finite Elements
 Materials Science & Metallurgy Part III Course M6 Computation of Phase Diagrams H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia Lecture 2: Finite Elements In finite element analysis, functions of continuous quantities such as temperature
Materials Science & Metallurgy Part III Course M6 Computation of Phase Diagrams H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia Lecture 2: Finite Elements In finite element analysis, functions of continuous quantities such as temperature
Lecture 27: Structural Dynamics - Beams.
 Chapter #16: Structural Dynamics and Time Dependent Heat Transfer. Lectures #1-6 have discussed only steady systems. There has been no time dependence in any problems. We will investigate beam dynamics
Chapter #16: Structural Dynamics and Time Dependent Heat Transfer. Lectures #1-6 have discussed only steady systems. There has been no time dependence in any problems. We will investigate beam dynamics
ENGI 3424 Mid Term Test Solutions Page 1 of 9
 ENGI 344 Mid Term Test 07 0 Solutions Page of 9. The displacement st of the free end of a mass spring sstem beond the equilibrium position is governed b the ordinar differential equation d s ds 3t 6 5s
ENGI 344 Mid Term Test 07 0 Solutions Page of 9. The displacement st of the free end of a mass spring sstem beond the equilibrium position is governed b the ordinar differential equation d s ds 3t 6 5s
Modeling and Analysis of Dynamic Systems
 Modeling and Analysis of Dynamic Systems Dr. Guillaume Ducard Fall 2017 Institute for Dynamic Systems and Control ETH Zurich, Switzerland G. Ducard c 1 / 21 Outline 1 Lecture 4: Modeling Tools for Mechanical
Modeling and Analysis of Dynamic Systems Dr. Guillaume Ducard Fall 2017 Institute for Dynamic Systems and Control ETH Zurich, Switzerland G. Ducard c 1 / 21 Outline 1 Lecture 4: Modeling Tools for Mechanical
Review of Strain Energy Methods and Introduction to Stiffness Matrix Methods of Structural Analysis
 uke University epartment of Civil and Environmental Engineering CEE 42L. Matrix Structural Analysis Henri P. Gavin Fall, 22 Review of Strain Energy Methods and Introduction to Stiffness Matrix Methods
uke University epartment of Civil and Environmental Engineering CEE 42L. Matrix Structural Analysis Henri P. Gavin Fall, 22 Review of Strain Energy Methods and Introduction to Stiffness Matrix Methods
Topic 2-2: Derivatives of Vector Functions. Textbook: Section 13.2, 13.4
 Topic 2-2: Derivatives of Vector Functions Textbook: Section 13.2, 13.4 Warm-Up: Parametrization of Circles Each of the following vector functions describe the position of an object traveling around the
Topic 2-2: Derivatives of Vector Functions Textbook: Section 13.2, 13.4 Warm-Up: Parametrization of Circles Each of the following vector functions describe the position of an object traveling around the
Outline. Structural Matrices. Giacomo Boffi. Introductory Remarks. Structural Matrices. Evaluation of Structural Matrices
 Outline in MDOF Systems Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile e Ambientale, Politecnico di Milano May 8, 014 Additional Today we will study the properties of structural matrices, that is the operators that
Outline in MDOF Systems Dipartimento di Ingegneria Civile e Ambientale, Politecnico di Milano May 8, 014 Additional Today we will study the properties of structural matrices, that is the operators that
* τσ σκ. Supporting Text. A. Stability Analysis of System 2
 Supporting Tet A. Stabilit Analsis of Sstem In this Appendi, we stud the stabilit of the equilibria of sstem. If we redefine the sstem as, T when -, then there are at most three equilibria: E,, E κ -,,
Supporting Tet A. Stabilit Analsis of Sstem In this Appendi, we stud the stabilit of the equilibria of sstem. If we redefine the sstem as, T when -, then there are at most three equilibria: E,, E κ -,,
TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK
 St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad-500 014 Subject: FINITE ELEMENT METHODS Class : MECH III TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK UNIT - I 1 Using variational approach (potential energy), describe
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad-500 014 Subject: FINITE ELEMENT METHODS Class : MECH III TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK UNIT - I 1 Using variational approach (potential energy), describe
Chapter Two: Numerical Methods for Elliptic PDEs. 1 Finite Difference Methods for Elliptic PDEs
 Chapter Two: Numerical Methods for Elliptic PDEs Finite Difference Methods for Elliptic PDEs.. Finite difference scheme. We consider a simple example u := subject to Dirichlet boundary conditions ( ) u
Chapter Two: Numerical Methods for Elliptic PDEs Finite Difference Methods for Elliptic PDEs.. Finite difference scheme. We consider a simple example u := subject to Dirichlet boundary conditions ( ) u
Lecture #6: 3D Rate-independent Plasticity (cont.) Pressure-dependent plasticity
 Lecture #6: 3D Rate-independent Plasticity (cont.) Pressure-dependent plasticity by Borja Erice and Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, Chair of Computational Modeling
Lecture #6: 3D Rate-independent Plasticity (cont.) Pressure-dependent plasticity by Borja Erice and Dirk Mohr ETH Zurich, Department of Mechanical and Process Engineering, Chair of Computational Modeling
ENT 151 STATICS. Contents. Introduction. Definition of a Truss
 CHAPTER 6 Analysis ENT 151 STATICS Lecture Notes: Mohd Shukry Abdul Majid KUKUM of Structures Contents Introduction Definition of a Truss Simple Trusses Analysis of Trusses by the Method of Joints Joints
CHAPTER 6 Analysis ENT 151 STATICS Lecture Notes: Mohd Shukry Abdul Majid KUKUM of Structures Contents Introduction Definition of a Truss Simple Trusses Analysis of Trusses by the Method of Joints Joints
4 NON-LINEAR ANALYSIS
 4 NON-INEAR ANAYSIS arge displacement elasticity theory, principle of virtual work arge displacement FEA with solid, thin slab, and bar models Virtual work density of internal forces revisited 4-1 SOURCES
4 NON-INEAR ANAYSIS arge displacement elasticity theory, principle of virtual work arge displacement FEA with solid, thin slab, and bar models Virtual work density of internal forces revisited 4-1 SOURCES
Analytical Mechanics: Elastic Deformation
 Analytical Mechanics: Elastic Deformation Shinichi Hirai Dept. Robotics, Ritsumeikan Univ. Shinichi Hirai (Dept. Robotics, Ritsumeikan Univ.) Analytical Mechanics: Elastic Deformation 1 / 60 Agenda Agenda
Analytical Mechanics: Elastic Deformation Shinichi Hirai Dept. Robotics, Ritsumeikan Univ. Shinichi Hirai (Dept. Robotics, Ritsumeikan Univ.) Analytical Mechanics: Elastic Deformation 1 / 60 Agenda Agenda
Theoretical Manual Theoretical background to the Strand7 finite element analysis system
 Theoretical Manual Theoretical background to the Strand7 finite element analysis system Edition 1 January 2005 Strand7 Release 2.3 2004-2005 Strand7 Pty Limited All rights reserved Contents Preface Chapter
Theoretical Manual Theoretical background to the Strand7 finite element analysis system Edition 1 January 2005 Strand7 Release 2.3 2004-2005 Strand7 Pty Limited All rights reserved Contents Preface Chapter
Axial force-moment interaction in the LARSA hysteretic beam element
 Axial force-moment interaction in the LARSA hsteretic beam element This document briefl discusses the modeling of tri-axial interaction (i.e. between axial force and bending moments) in the LARSA beam
Axial force-moment interaction in the LARSA hsteretic beam element This document briefl discusses the modeling of tri-axial interaction (i.e. between axial force and bending moments) in the LARSA beam
Formulation of Finite Element Matrices
 Topic 6 Formulation of Finite Element Matrices Contents: Summary of principle of virtual work equations in total and updated Lagrangian formulations Deformation-independent and deformation-dependent loading
Topic 6 Formulation of Finite Element Matrices Contents: Summary of principle of virtual work equations in total and updated Lagrangian formulations Deformation-independent and deformation-dependent loading
EML4507 Finite Element Analysis and Design EXAM 1
 2-17-15 Name (underline last name): EML4507 Finite Element Analysis and Design EXAM 1 In this exam you may not use any materials except a pencil or a pen, an 8.5x11 formula sheet, and a calculator. Whenever
2-17-15 Name (underline last name): EML4507 Finite Element Analysis and Design EXAM 1 In this exam you may not use any materials except a pencil or a pen, an 8.5x11 formula sheet, and a calculator. Whenever
Lecture 1: Course Introduction.
 Lecture : Course Introduction. What is the Finite Element Method (FEM)? a numerical method for solving problems of engineering and mathematical physics. (Logan Pg. #). In MECH 40 we are concerned with
Lecture : Course Introduction. What is the Finite Element Method (FEM)? a numerical method for solving problems of engineering and mathematical physics. (Logan Pg. #). In MECH 40 we are concerned with
