a b + c b = a+c a b c d = ac a b c d = a b d a does not exist
|
|
|
- Barbara Fitzgerald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pre-precalculus Boot Camp: Arithmetic with fractions page Aug, 0 Arithmetic with fractions To add fractions with the same denominator, add the numerators: () a b + c b = a+c b To multiply fractions, multiply the numerators and denominators: () a b c d = ac bd To divide fractions, invert and multiply: () a b c d = a b d c Division by zero is not allowed: () a 0 does not eist (because a 0 =? would mean a = 0?, which has no solution if a 0 and infinitely many solutions if a = 0.) As a consequence of (), () ac bc = a b (because ac bc = a b c c = a b.) We use this either to simplify a fraction by canceling common factors,, = = or to obtain common denominators for adding fractions,, + = + = 0 + =. There s nothing inherently wrong with an improper fraction, but to write an improper fraction as a mied number, we use long divisio For eample, = with remainder means that = +.. Find the sum or differenc
2 Pre-precalculus Boot Camp: Arithmetic with fractions page Aug, 0. Find the sum or differenc t. + + w... Find the sum or differenc Hint: always use the least common demonimato t w Find the sum or differenc Hint: n = n Find the product. Hint: cancel common factors before multiplyin t. w... Find the quotient. Remember that division by zero is not allowe t. w.. y. z Answers t. 0 w t. 0 0 w DNE 0 DNE 0 t. w DNE DNE 0 DNE DNE t. w.. y. z
3 Pre-precalculus Boot Camp: Rationalizing the denominator page Sept, 0 Rationalizing the denominator It s sometimes handy to rewrite a fraction so that no radicals appear in the denominato To do this, we multiply the fraction by in an appropriate form, thus changing the appearance of the fraction but not its actual valu a Case : Rationalizing b c. In this case we can rationalize the denominator by multiplying by = c c. For eample, = = ( ) = = =. a Case : Rationalizing b±c d. When the last operation in the denominator is addition or subtraction, we rationalize the denominator by multiplying by = b c d b c and using d ( y)(+y) = y. (b c d is called the conjugate of b±c ) For instance, = + + = (+ ) ( ) = (+ ) = (+ ) = (+ ) Tip: look for common factors in the numerator and denominator and for perfect squares under the radical,, = =.. Rationalize the denominato 0 t. 0 w. 0.. Rationalize the denominato t w. +. Answers 0 0 t. w ( ) (+ ) ( ) (+ ) (+ ) ( 0) (+ ) ( ) 0 (+ ) (+ ) ( 0) (+ ) (+ ) 0 (+ ) t. (+ ) (+ 0) w. (+ ). (+ )
4 Pre-precalculus Boot Camp: Laws of eponents page Jan 0, 0 Laws of eponents We use eponents to denote repeated multiplication,, It s easiest to remember the laws a = a a a m a n = a m+n (a m ) n = a mn (ab) n = a n b n () ( a b) n = a n b n a m a n = am n = a n by thinking of simple eample For instance, and and a a = (a a a) (a a) = a, (a ) = (a a a) = (a a a) (a a a) = a, (ab) = (ab)(ab)(ab) = a a a b b b = a b, are eamples of the first three laws in (). The laws () are also true for eponents that are zero, negative or rational numbers after we define () a 0 = a n = a n a m/n = n (a m ) = ( n a) m, with some restriction For instance, we can t raise 0 to a negative eponent, since 0 is undefined, and the last two equations are true only if the corresponding roots are define (Remember that we can t take an even root of a negative numbe) The most common mistake students make with the laws of eponents is to confuse (ab) n with (a+b) n. In general, (a+b) n is not equal a n +b n. Radicals n a refers to a solution to the equation n = a, if one eist If n is odd, then every real number has eactly one nth root. For instance =, since is the unique solution to the equation =. If n is even, then negative numbers don t posses real nth roots, and every positive number has two real nth roots, one positive and one negativ In that case, the symbol n a stands for the positive nth root of The radical symbol with no inde is always assumed to mean the square root. Eample : Both and are solutions to = ; both and are square roots of, but stands for the positive square root, or. end Eample Eample : The equation = has no real solutions, so does not eist. One of the reasons that we can think of n a as a power of a is the fact that end Eample n ab = n a n b
5 Pre-precalculus Boot Camp: Laws of eponents page Jan 0, 0 provided all three roots eist. That is, (ab) /n = a /n b /n, as in (). This is useful when we have to simplify epressions of the form n a where n is a positive integer and a is an intege We look for the perfect nth powers that are factors of a, which we could always find by factoring a down to prime number Eample : = = =. end Eample Eample : = = =. If we hadn t noticed that is the largest square factor of, we still could have simplified this radical completely by finding that the prime factorization of is. Then = ( ) / = / / = + = / =. end Eample Eample : = = =. Since = / = /, the answer can be simplified further to. end Eample There s one important hitch in using the laws of eponents with fractional eponent If a 0, then both (a /n ) n and (a n ) /n correctly simplify to However, if a < 0 and n is an even integer, (a /n ) n doesn t eist, and, because n refers to the positive nth root, (a n ) /n = a, as in this eample: Eample : (( ) ) / = ( ) = =. In particular, the result is not. The rule to remember in general is end Eample If n is an even integer, then (a n ) /n = a.. Simplify the radical or state that it does not eist Simplify the radical or state that it does not eist , ,000 0,000 t w. 0. y. z...
6 Pre-precalculus Boot Camp: Laws of eponents page Jan 0, 0. Rewrite the epression in simplest radical form or state that it does not eist. / ( ) / ( ) / () / ( ) / ( ) / / / / / / / / / / / / / / t. 0 / () / () / w. 0 /. 0 / y. / z. ( 0) /. ( ) /. /. / 0. 0 /. ( 00) /. 00 /. Rewrite without parenthese Epress your answer without negative eponents, and again without fractions (other than eponents themselves). Assume all variables are positiv ( y ) (u / v / ) y ( y ) (a bc b a ) / (uv u v ) / (( y ) y ) / a (ab ) / b a b c (b) (cb ) (a c ) u (v ) wu 0 y( y) (y z) ( y) / ( / y ) / y ( / y / ) y ((+y)) (u v) (uv) ab (+ab) ( ab) (y y) ( y ) y ( y) ( y) y t. ( y ) (y ) v ( uv u v ) ( u v / ) / ( u v )(v u ) v v a(b a ) a ((b ) / ) / Answers DNE DNE DNE DNE t w. 0. 0y. 0z. 0. DNE 0. DNE w. t DNE.. y 0 = y 0 y. z. u v = u v y = y a / c v u = u v y/ = y / b / a / = a / b / a c b = a b c u v w / z = / y / z y / / y / y / + y + y uv v + u u v = u v v + u v u ab a b + a b = a b a b + a b y 0 = y 0 y = y v u = u v y y = y y t. u / v / b /
7 Pre-precalculus Boot Camp: Factoring polynomials page Jan 0, 0 Factoring polynomials To factor an algebraic epression is to rewrite it in an equivalent form in which the last operation performed is multiplicatio When factoring a polynomial,. Factor out any common factor. Then try to factor the polynomial with one of these method If the polynomial has two terms, try using one of the special product If the polynomial has three terms, try factoring it with backwards-foil. It also pays to be able to recognize the perfect square a +ab+b = (a+b). If the polynomial has four terms, try factoring it by groupin. Test whether you can factor the factor Eample : +0 Since the polynomial has four terms, we factor the first two terms and the last two and hope to find a common facto ( )+(0 ) = ( )+( ) = ( +)( ). end Eample Eample : y + y + y This polynomial has a common factor of y: y + y + y = y( ++). To factor the three-term polynomial, look for a factorization (a ± b)(c ± d) that, when multiplied using FOIL, gives First =, Last =, and Outside+Inside = : y( ++) = y(+)(+). The familiar difference of squares formula is just one of large number of special products: y = ( y)(+y) y = ( y)( +y +y ) y = ( y)( + y +y +y ) y = ( y)( + y + y +y +y ) y = ( y)( + y + y + y +y +y ). end Eample You can verify any of these yourself by carefully multiplying out the right sid When we replace y with y in the odd-lines, we also obtain +y = (+y)( y +y ) +y = (+y)( y + y y +y ).. Eample : u +v = (u) +v = (u+v)(u uv +v ) The three-term polynomial can t be factored further using integer end Eample Eample 0: = ( )( + ++)
8 Pre-precalculus Boot Camp: Factoring polynomials page Jan 0, 0 This polynomial hasn t been factored completely because the cubic polynomial factors further by grouping: ( + )+(+) = (+)+(+) = (+)( +), so = ( )(+)( +). We also could have arrived at this factorization by using square-minus-square: = ( ) = ( )( +) = ( )(+)( +). end Eample 0 The quadratic + is said to be irreducible, meaning that it has no real zeros and, consequently cannot be factored further without comple number The quadratic + is also irreducible, since b ac = ( ) = < 0, so u uv+v can t be factored without using comple numbers for coefficient In fact, the quadratic factor that appears in the difference-of-cubes formula is always irreducibl Every polynomial with real coefficients can be factored as a product of linear and irreducible quadratic factors with real coefficients (although there is no method that produces the eact factorization of all polynomials). If we allow ourselves to use comple coefficients, then every polynomials can be factored as a product of linear factors only. When we use only real coefficients in our factors, we re said to be factoring the polynomial over the real number When we allow comple coefficients in our factors, we re said to be factoring the polynomial over the comple number. Factor the polynomial over the real number u y y y + y y y u v +uv 0 +y +y y y t. u u v y w. y y. y y. +. Factor the polynomial over the real number y +y + +y+y y y 0 y +0 y +0y t. +y y y +y y +0y w. +y y. 0y+0y y. y +y z. + y +y. 0 y +y. + y +y
9 Pre-precalculus Boot Camp: Factoring polynomials page Jan 0, 0. Factor the polynomial over the real number y +y y 0u u v +uv v u u v uv +v u u v uv +v y+y y u v u u v + Answers (+)( ) ( )(+) ( )(+) ( )(+) ( u)(+u) ( )(+)) ( y)(+y) y( y)(+y) ( )(+ ) does not factor further ( y)( +y +y ) y ( y)( +y+y ) vu(u+v)(u uv+v ) (+y)( 0y+y ) ( +y)( y+y ) (y )( y +y+) ( )(+)( +) ( y)(+y)( +y ) ( )(+ )( +) t. ( u )(+u )(+u ) (u v)(u+v)(u +v ) ( y)(+y+ y ) w. y( y )(+y ). ( y)(+y)( y+y )( +y+y ) y. Has no real zeros; hence, does not factor without using comple coefficient (+)( ) ( )( ) (+)( ) ( )( ) (+) ( y) ( ) (+y) (+)( ) (+)( ) (+)( ) ( )(+) (+)( ) ( + )( ) ( + y)( y) 0y( + y) ( ) ( + ) ( ) ( + ) t. ( y)( + y) ( y)( y) ( y)( 0y) w. ( + y)( y). ( y)( y) y. ( y )( y ) z. ( +y )( +y ). ( y)( y). ( +y )( +y ) ( +)( ) ( + )( + ) ( + )( ), or, ( + )( ) ( + )( ) ( + y )( y) (u +v )(u v) ( )(+)( ) (+)( )(+) ( )(+)( ) (u v)(u+v)(u v) (u v)(u+v)(u v) (+ )( )( ) ( )(+ )(+), or ( )( +)(+) (+)( )( ++) ( y)(+y)( y+y ) ( )( )(+)( ++) (+)( +)( +) (uv )(uv +)(u )
10 Pre-precalculus Boot Camp: Solving polynomial equations page 0 Sept, 0 Solving polynomial equations One reason we factor polynomials is to find their zeros,, the -values that cause the polynomial to equal zer We rely heavily on a special property of the number zer For the product of two numbers to be zero, it is both necessary and sufficient that one of the two must be zer That is, ab = 0 if and only if a = 0 or b = 0. It is important to remember that no number other than zero has this property. For instance, ab = does not mean that a or b has to equal. To solve a polynomial equation, try to Get zero on one side and factor the othe Eample : Solve for in the equation 0 = + Factor the right sid + = (+)( ). So, for this product to equal zero, one factor or the other must be zero: + = 0 = 0 = = / = = / That is, 0 = + has two solutions: = / and = /. Eample : Solve for in the equation + =. Get a zero on one side by subtracting to both sides: + = 0. end Eample Now factor the left sid First factor out the common factor of, and then factor the three term polynomial using backwards FOIL: ( + ) = ( )(+) = 0. For the product of, ( ), and (+) to equal zero, one of these factors has to be zero: = 0 = 0 = 0 = / + = 0 = That is, the solutions to + = 0. are = 0, /, and. end Eample The problem of find y-intercepts usually boils down to solving an equation, as the net eample show Eample : Find the - and y-intercepts along the curve y =. To find the y-intercepts, we set = 0 and calculate y = 0 0 =. That it, (0, ) is the y-intercept. To find the -intercepts, set y = 0 and solve for by factoring: The solutions are 0 = = ( )(+). = 0 = = / so this curve has two -intercepts: (/,0) and ( /,0) + = 0 = = / end Eample
11 Pre-precalculus Boot Camp: Solving polynomial equations page Sept, 0. Find the zeros of the polynomia u. Solve for. = 0 + = 0 0 = 0 + = 0 + = = = + = + = 0 = + = + = 0 Answers = ± = ± = ± = ± u = ± = ±/ = ±/ = 0 or ± / = ± / =, / = /, =, = /,/ = / = / = 0,/ = / = /, / =, / =, / =,
12 Pre-precalculus Boot Camp: Rational functions page Jan, 0 Rational functions A rational function is a fraction whose numerator and denominator are both polynomial We perform arithmetic on rational functions just as with any fraction Simplification isn t something you do in your last step to satisfy your math professor; it s something you do at every step to make your work easie Be on the lookout for common factors of the numerator and denominator and cancel thes Eample : + = + ( )(+) = Notice that is considerably simpler than +. Canceling the + was a good mov end Eample Eample : Can I cancel the in +? + has no common factors, at least as it is written at present. You can cancel the from top and bottom if you factor it out first, but the result might not be very useful: + = ( ) + = +. end Eample. Simplify the rational functio t
13 Pre-precalculus Boot Camp: Rational functions page Jan, 0. Perform the operation indicated and simplify the resulting rational functio y t. w. z ( )(+) Perform the operation indicated and simplify the resulting rational functio Answers does not simplify further + + t ( )(+) ( )( ) ( )( ) + ( +)(+) ++ (+)(+)( ) 0 ( )(+) ( )(+) ( )( ) + ( )(+)( ) (+)(+) ( +)(+) + ( )( +) ++ ( )(+)( ++) ( )(+) + ( )( +)( +) + ( +)( ) + ( ) (+) t. y. (+)( ) z.. (+)( ) 0 + ( ) ( ) ( ) (+)(+) ( )( ) 0 w. + ( +)(+) ( )(+) (+)( +) 0 (+)( ) ( ) (+)( ) 0 ( )(+)
EXPONENT REVIEW!!! Concept Byte (Review): Properties of Exponents. Property of Exponents: Product of Powers. x m x n = x m + n
 Algebra B: Chapter 6 Notes 1 EXPONENT REVIEW!!! Concept Byte (Review): Properties of Eponents Recall from Algebra 1, the Properties (Rules) of Eponents. Property of Eponents: Product of Powers m n = m
Algebra B: Chapter 6 Notes 1 EXPONENT REVIEW!!! Concept Byte (Review): Properties of Eponents Recall from Algebra 1, the Properties (Rules) of Eponents. Property of Eponents: Product of Powers m n = m
ACCUPLACER MATH 0310
 The University of Teas at El Paso Tutoring and Learning Center ACCUPLACER MATH 00 http://www.academics.utep.edu/tlc MATH 00 Page Linear Equations Linear Equations Eercises 5 Linear Equations Answer to
The University of Teas at El Paso Tutoring and Learning Center ACCUPLACER MATH 00 http://www.academics.utep.edu/tlc MATH 00 Page Linear Equations Linear Equations Eercises 5 Linear Equations Answer to
Radical Expressions and Functions What is a square root of 25? How many square roots does 25 have? Do the following square roots exist?
 Topic 4 1 Radical Epressions and Functions What is a square root of 25? How many square roots does 25 have? Do the following square roots eist? 4 4 Definition: X is a square root of a if X² = a. 0 Symbolically,
Topic 4 1 Radical Epressions and Functions What is a square root of 25? How many square roots does 25 have? Do the following square roots eist? 4 4 Definition: X is a square root of a if X² = a. 0 Symbolically,
1 Rational Exponents and Radicals
 Introductory Algebra Page 1 of 11 1 Rational Eponents and Radicals 1.1 Rules of Eponents The rules for eponents are the same as what you saw earlier. Memorize these rules if you haven t already done so.
Introductory Algebra Page 1 of 11 1 Rational Eponents and Radicals 1.1 Rules of Eponents The rules for eponents are the same as what you saw earlier. Memorize these rules if you haven t already done so.
Dr. Relja Vulanovic Professor of Mathematics Kent State University at Stark c 2008
 MATH-LITERACY MANUAL Dr. Relja Vulanovic Professor of Mathematics Kent State University at Stark c 2008 2 Algebraic Epressions 2.1 Terms and Factors 29 2.2 Types of Algebraic Epressions 32 2.3 Transforming
MATH-LITERACY MANUAL Dr. Relja Vulanovic Professor of Mathematics Kent State University at Stark c 2008 2 Algebraic Epressions 2.1 Terms and Factors 29 2.2 Types of Algebraic Epressions 32 2.3 Transforming
ACCUPLACER MATH 0311 OR MATH 0120
 The University of Teas at El Paso Tutoring and Learning Center ACCUPLACER MATH 0 OR MATH 00 http://www.academics.utep.edu/tlc MATH 0 OR MATH 00 Page Factoring Factoring Eercises 8 Factoring Answer to Eercises
The University of Teas at El Paso Tutoring and Learning Center ACCUPLACER MATH 0 OR MATH 00 http://www.academics.utep.edu/tlc MATH 0 OR MATH 00 Page Factoring Factoring Eercises 8 Factoring Answer to Eercises
Algebra Review C H A P T E R. To solve an algebraic equation with one variable, find the value of the unknown variable.
 C H A P T E R 6 Algebra Review This chapter reviews key skills and concepts of algebra that you need to know for the SAT. Throughout the chapter are sample questions in the style of SAT questions. Each
C H A P T E R 6 Algebra Review This chapter reviews key skills and concepts of algebra that you need to know for the SAT. Throughout the chapter are sample questions in the style of SAT questions. Each
Basic ALGEBRA 2 SUMMER PACKET
 Name Basic ALGEBRA SUMMER PACKET This packet contains Algebra I topics that you have learned before and should be familiar with coming into Algebra II. We will use these concepts on a regular basis throughout
Name Basic ALGEBRA SUMMER PACKET This packet contains Algebra I topics that you have learned before and should be familiar with coming into Algebra II. We will use these concepts on a regular basis throughout
A Quick Algebra Review
 1. Simplifying Epressions. Solving Equations 3. Problem Solving 4. Inequalities 5. Absolute Values 6. Linear Equations 7. Systems of Equations 8. Laws of Eponents 9. Quadratics 10. Rationals 11. Radicals
1. Simplifying Epressions. Solving Equations 3. Problem Solving 4. Inequalities 5. Absolute Values 6. Linear Equations 7. Systems of Equations 8. Laws of Eponents 9. Quadratics 10. Rationals 11. Radicals
Multi-Step Equations and Inequalities
 Multi-Step Equations and Inequalities Syllabus Objective (1.13): The student will combine like terms in an epression when simplifying variable epressions. Term: the parts of an epression that are either
Multi-Step Equations and Inequalities Syllabus Objective (1.13): The student will combine like terms in an epression when simplifying variable epressions. Term: the parts of an epression that are either
Introduction. So, why did I even bother to write this?
 Introduction This review was originally written for my Calculus I class, but it should be accessible to anyone needing a review in some basic algebra and trig topics. The review contains the occasional
Introduction This review was originally written for my Calculus I class, but it should be accessible to anyone needing a review in some basic algebra and trig topics. The review contains the occasional
Pre-Algebra 8 Notes Unit 02B: Linear Equations in One Variable Multi-Step Equations
 Pre-Algebra 8 Notes Unit 02B: Linear Equations in One Variable Multi-Step Equations Solving Two-Step Equations The general strategy for solving a multi-step equation in one variable is to rewrite the equation
Pre-Algebra 8 Notes Unit 02B: Linear Equations in One Variable Multi-Step Equations Solving Two-Step Equations The general strategy for solving a multi-step equation in one variable is to rewrite the equation
Complex fraction: - a fraction which has rational expressions in the numerator and/or denominator
 Comple fraction: - a fraction which has rational epressions in the numerator and/or denominator o 2 2 4 y 2 + y 2 y 2 2 Steps for Simplifying Comple Fractions. simplify the numerator and/or the denominator
Comple fraction: - a fraction which has rational epressions in the numerator and/or denominator o 2 2 4 y 2 + y 2 y 2 2 Steps for Simplifying Comple Fractions. simplify the numerator and/or the denominator
Polynomials and Factoring
 7.6 Polynomials and Factoring Basic Terminology A term, or monomial, is defined to be a number, a variable, or a product of numbers and variables. A polynomial is a term or a finite sum or difference of
7.6 Polynomials and Factoring Basic Terminology A term, or monomial, is defined to be a number, a variable, or a product of numbers and variables. A polynomial is a term or a finite sum or difference of
Section 4.3: Quadratic Formula
 Objective: Solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula. In this section we will develop a formula to solve any quadratic equation ab c 0 where a b and c are real numbers and a 0. Solve for this
Objective: Solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula. In this section we will develop a formula to solve any quadratic equation ab c 0 where a b and c are real numbers and a 0. Solve for this
Algebra. Robert Taggart
 Algebra Robert Taggart Table of Contents To the Student.............................................. v Unit 1: Algebra Basics Lesson 1: Negative and Positive Numbers....................... Lesson 2: Operations
Algebra Robert Taggart Table of Contents To the Student.............................................. v Unit 1: Algebra Basics Lesson 1: Negative and Positive Numbers....................... Lesson 2: Operations
Algebra Concepts Equation Solving Flow Chart Page 1 of 6. How Do I Solve This Equation?
 Algebra Concepts Equation Solving Flow Chart Page of 6 How Do I Solve This Equation? First, simplify both sides of the equation as much as possible by: combining like terms, removing parentheses using
Algebra Concepts Equation Solving Flow Chart Page of 6 How Do I Solve This Equation? First, simplify both sides of the equation as much as possible by: combining like terms, removing parentheses using
Define a rational expression: a quotient of two polynomials. ..( 3 10) (3 2) Rational expressions have the same properties as rational numbers:
 1 UNIT 7 RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS & EQUATIONS Simplifying Rational Epressions Define a rational epression: a quotient of two polynomials. A rational epression always indicates division EX: 10 means..( 10)
1 UNIT 7 RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS & EQUATIONS Simplifying Rational Epressions Define a rational epression: a quotient of two polynomials. A rational epression always indicates division EX: 10 means..( 10)
Conceptual Explanations: Radicals
 Conceptual Eplanations: Radicals The concept of a radical (or root) is a familiar one, and was reviewed in the conceptual eplanation of logarithms in the previous chapter. In this chapter, we are going
Conceptual Eplanations: Radicals The concept of a radical (or root) is a familiar one, and was reviewed in the conceptual eplanation of logarithms in the previous chapter. In this chapter, we are going
COUNCIL ROCK HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS. A Note Guideline of Algebraic Concepts. Designed to assist students in A Summer Review of Algebra
 COUNCIL ROCK HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS A Note Guideline of Algebraic Concepts Designed to assist students in A Summer Review of Algebra [A teacher prepared compilation of the 7 Algebraic concepts deemed
COUNCIL ROCK HIGH SCHOOL MATHEMATICS A Note Guideline of Algebraic Concepts Designed to assist students in A Summer Review of Algebra [A teacher prepared compilation of the 7 Algebraic concepts deemed
Lesson #33 Solving Incomplete Quadratics
 Lesson # Solving Incomplete Quadratics A.A.4 Know and apply the technique of completing the square ~ 1 ~ We can also set up any quadratic to solve it in this way by completing the square, the technique
Lesson # Solving Incomplete Quadratics A.A.4 Know and apply the technique of completing the square ~ 1 ~ We can also set up any quadratic to solve it in this way by completing the square, the technique
QUADRATIC EQUATIONS. + 6 = 0 This is a quadratic equation written in standard form. x x = 0 (standard form with c=0). 2 = 9
 QUADRATIC EQUATIONS A quadratic equation is always written in the form of: a + b + c = where a The form a + b + c = is called the standard form of a quadratic equation. Eamples: 5 + 6 = This is a quadratic
QUADRATIC EQUATIONS A quadratic equation is always written in the form of: a + b + c = where a The form a + b + c = is called the standard form of a quadratic equation. Eamples: 5 + 6 = This is a quadratic
LESSON 9.1 ROOTS AND RADICALS
 LESSON 9.1 ROOTS AND RADICALS LESSON 9.1 ROOTS AND RADICALS 67 OVERVIEW Here s what you ll learn in this lesson: Square Roots and Cube Roots a. Definition of square root and cube root b. Radicand, radical
LESSON 9.1 ROOTS AND RADICALS LESSON 9.1 ROOTS AND RADICALS 67 OVERVIEW Here s what you ll learn in this lesson: Square Roots and Cube Roots a. Definition of square root and cube root b. Radicand, radical
Study Guide for Math 095
 Study Guide for Math 095 David G. Radcliffe November 7, 1994 1 The Real Number System Writing a fraction in lowest terms. 1. Find the largest number that will divide into both the numerator and the denominator.
Study Guide for Math 095 David G. Radcliffe November 7, 1994 1 The Real Number System Writing a fraction in lowest terms. 1. Find the largest number that will divide into both the numerator and the denominator.
Fundamental Theorem of Algebra (NEW): A polynomial function of degree n > 0 has n complex zeros. Some of these zeros may be repeated.
 .5 and.6 Comple Numbers, Comple Zeros and the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Pre Calculus.5 COMPLEX NUMBERS 1. Understand that - 1 is an imaginary number denoted by the letter i.. Evaluate the square root
.5 and.6 Comple Numbers, Comple Zeros and the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra Pre Calculus.5 COMPLEX NUMBERS 1. Understand that - 1 is an imaginary number denoted by the letter i.. Evaluate the square root
A2T. Rational Expressions/Equations. Name: Teacher: Pd:
 AT Packet #1: Rational Epressions/Equations Name: Teacher: Pd: Table of Contents o Day 1: SWBAT: Review Operations with Polynomials Pgs: 1-3 HW: Pages -3 in Packet o Day : SWBAT: Factor using the Greatest
AT Packet #1: Rational Epressions/Equations Name: Teacher: Pd: Table of Contents o Day 1: SWBAT: Review Operations with Polynomials Pgs: 1-3 HW: Pages -3 in Packet o Day : SWBAT: Factor using the Greatest
A. Incorrect! Apply the rational root test to determine if any rational roots exist.
 College Algebra - Problem Drill 13: Zeros of Polynomial Functions No. 1 of 10 1. Determine which statement is true given f() = 3 + 4. A. f() is irreducible. B. f() has no real roots. C. There is a root
College Algebra - Problem Drill 13: Zeros of Polynomial Functions No. 1 of 10 1. Determine which statement is true given f() = 3 + 4. A. f() is irreducible. B. f() has no real roots. C. There is a root
Math Analysis/Honors Math Analysis Summer Assignment
 Math Analysis/Honors Math Analysis Summer Assignment To be successful in Math Analysis or Honors Math Analysis, a full understanding of the topics listed below is required prior to the school year. To
Math Analysis/Honors Math Analysis Summer Assignment To be successful in Math Analysis or Honors Math Analysis, a full understanding of the topics listed below is required prior to the school year. To
Topic: Expressions & Operations AII.1
 Topic: Epressions & Operations AII.1 AII.1 The student will identify field properties, aioms of equality and inequality, and properties of order that are valid for the set of real numbers and its subsets,
Topic: Epressions & Operations AII.1 AII.1 The student will identify field properties, aioms of equality and inequality, and properties of order that are valid for the set of real numbers and its subsets,
Math-2 Lesson 2-4. Radicals
 Math- Lesson - Radicals = What number is equivalent to the square root of? Square both sides of the equation ( ) ( ) = = = is an equivalent statement to = 1.7 1.71 1.70 1.701 1.7008... There is no equivalent
Math- Lesson - Radicals = What number is equivalent to the square root of? Square both sides of the equation ( ) ( ) = = = is an equivalent statement to = 1.7 1.71 1.70 1.701 1.7008... There is no equivalent
Which Mathematics Course Should You Take? August 22, 2018 Which mathematics course you should take depends on your current mathematics skill level
 Which Mathematics Course Should You Take? August, 018 Which mathematics course you should take depends on your current mathematics skill level and your intended major. This is a conversation you should
Which Mathematics Course Should You Take? August, 018 Which mathematics course you should take depends on your current mathematics skill level and your intended major. This is a conversation you should
Algebra II Notes Polynomial Functions Unit Introduction to Polynomials. Math Background
 Introduction to Polynomials Math Background Previously, you Identified the components in an algebraic epression Factored quadratic epressions using special patterns, grouping method and the ac method Worked
Introduction to Polynomials Math Background Previously, you Identified the components in an algebraic epression Factored quadratic epressions using special patterns, grouping method and the ac method Worked
Algebra 1 Skills Needed for Success in Math
 Algebra 1 Skills Needed for Success in Math A. Simplifing Polnomial Epressions Objectives: The student will be able to: Appl the appropriate arithmetic operations and algebraic properties needed to simplif
Algebra 1 Skills Needed for Success in Math A. Simplifing Polnomial Epressions Objectives: The student will be able to: Appl the appropriate arithmetic operations and algebraic properties needed to simplif
University of Colorado at Colorado Springs Math 090 Fundamentals of College Algebra
 University of Colorado at Colorado Springs Math 090 Fundamentals of College Algebra Table of Contents Chapter The Algebra of Polynomials Chapter Factoring 7 Chapter 3 Fractions Chapter 4 Eponents and Radicals
University of Colorado at Colorado Springs Math 090 Fundamentals of College Algebra Table of Contents Chapter The Algebra of Polynomials Chapter Factoring 7 Chapter 3 Fractions Chapter 4 Eponents and Radicals
Mini Lecture 9.1 Finding Roots
 Mini Lecture 9. Finding Roots. Find square roots.. Evaluate models containing square roots.. Use a calculator to find decimal approimations for irrational square roots. 4. Find higher roots. Evaluat. a.
Mini Lecture 9. Finding Roots. Find square roots.. Evaluate models containing square roots.. Use a calculator to find decimal approimations for irrational square roots. 4. Find higher roots. Evaluat. a.
Concept Category 5. Limits. Limits: graphically & algebraically Rate of Change
 Concept Category 5 Limits Limits: graphically & algebraically Rate of Change Skills Factoring and Rational Epressions (Alg, CC1) Behavior of a graph (Alg, CC1) Sketch a graph:,,, Log, (Alg, CC1 & ) 1 Factoring
Concept Category 5 Limits Limits: graphically & algebraically Rate of Change Skills Factoring and Rational Epressions (Alg, CC1) Behavior of a graph (Alg, CC1) Sketch a graph:,,, Log, (Alg, CC1 & ) 1 Factoring
8.3 Zero, Negative, and Fractional Exponents
 www.ck2.org Chapter 8. Eponents and Polynomials 8.3 Zero, Negative, and Fractional Eponents Learning Objectives Simplify epressions with zero eponents. Simplify epressions with negative eponents. Simplify
www.ck2.org Chapter 8. Eponents and Polynomials 8.3 Zero, Negative, and Fractional Eponents Learning Objectives Simplify epressions with zero eponents. Simplify epressions with negative eponents. Simplify
Review: Properties of Exponents (Allow students to come up with these on their own.) m n m n. a a a. n n n m. a a a. a b a
 Algebra II Notes Unit Si: Polynomials Syllabus Objectives: 6. The student will simplify polynomial epressions. Review: Properties of Eponents (Allow students to come up with these on their own.) Let a
Algebra II Notes Unit Si: Polynomials Syllabus Objectives: 6. The student will simplify polynomial epressions. Review: Properties of Eponents (Allow students to come up with these on their own.) Let a
Polynomials and Polynomial Functions
 Unit 5: Polynomials and Polynomial Functions Evaluating Polynomial Functions Objectives: SWBAT identify polynomial functions SWBAT evaluate polynomial functions. SWBAT find the end behaviors of polynomial
Unit 5: Polynomials and Polynomial Functions Evaluating Polynomial Functions Objectives: SWBAT identify polynomial functions SWBAT evaluate polynomial functions. SWBAT find the end behaviors of polynomial
Equations. Rational Equations. Example. 2 x. a b c 2a. Examine each denominator to find values that would cause the denominator to equal zero
 Solving Other Types of Equations Rational Equations Examine each denominator to find values that would cause the denominator to equal zero Multiply each term by the LCD or If two terms cross-multiply Solve,
Solving Other Types of Equations Rational Equations Examine each denominator to find values that would cause the denominator to equal zero Multiply each term by the LCD or If two terms cross-multiply Solve,
Intermediate Algebra. Gregg Waterman Oregon Institute of Technology
 Intermediate Algebra Gregg Waterman Oregon Institute of Technology c August 2013 Gregg Waterman This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
Intermediate Algebra Gregg Waterman Oregon Institute of Technology c August 2013 Gregg Waterman This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
Math ~ Exam #1 Review Guide* *This is only a guide, for your benefit, and it in no way replaces class notes, homework, or studying
 Math 1050 2 ~ Exam #1 Review Guide* *This is only a guide, for your benefit, and it in no way replaces class notes, homework, or studying General Tips for Studying: 1. Review this guide, class notes, the
Math 1050 2 ~ Exam #1 Review Guide* *This is only a guide, for your benefit, and it in no way replaces class notes, homework, or studying General Tips for Studying: 1. Review this guide, class notes, the
Polynomial Division. You may also see this kind of problem written like this: Perform the division x2 +2x 3
 Polynomial Division 5015 You do polynomial division the way you do long division of numbers It s difficult to describe the general procedure in words, so I ll work through some eamples stepbystep Eample
Polynomial Division 5015 You do polynomial division the way you do long division of numbers It s difficult to describe the general procedure in words, so I ll work through some eamples stepbystep Eample
a = B. Examples: 1. Simplify the following expressions using the multiplication rule
 Section. Monomials Objectives:. Multiply and divide monomials.. Simplify epressions involving powers of monomials.. Use epressions in scientific notation. I. Negative Eponents and Eponents of Zero A. Rules.
Section. Monomials Objectives:. Multiply and divide monomials.. Simplify epressions involving powers of monomials.. Use epressions in scientific notation. I. Negative Eponents and Eponents of Zero A. Rules.
In this unit we will study exponents, mathematical operations on polynomials, and factoring.
 GRADE 0 MATH CLASS NOTES UNIT E ALGEBRA In this unit we will study eponents, mathematical operations on polynomials, and factoring. Much of this will be an etension of your studies from Math 0F. This unit
GRADE 0 MATH CLASS NOTES UNIT E ALGEBRA In this unit we will study eponents, mathematical operations on polynomials, and factoring. Much of this will be an etension of your studies from Math 0F. This unit
Eby, MATH 0310 Spring 2017 Page 53. Parentheses are IMPORTANT!! Exponents only change what they! So if a is not inside parentheses, then it
 Eby, MATH 010 Spring 017 Page 5 5.1 Eponents Parentheses are IMPORTANT!! Eponents only change what they! So if a is not inside parentheses, then it get raised to the power! Eample 1 4 b) 4 c) 4 ( ) d)
Eby, MATH 010 Spring 017 Page 5 5.1 Eponents Parentheses are IMPORTANT!! Eponents only change what they! So if a is not inside parentheses, then it get raised to the power! Eample 1 4 b) 4 c) 4 ( ) d)
4.2 Reducing Rational Functions
 Section. Reducing Rational Functions 1. Reducing Rational Functions The goal of this section is to review how to reduce a rational epression to lowest terms. Let s begin with a most important piece of
Section. Reducing Rational Functions 1. Reducing Rational Functions The goal of this section is to review how to reduce a rational epression to lowest terms. Let s begin with a most important piece of
Math 154 :: Elementary Algebra
 Math :: Elementar Algebra Section. Section. Section. Section. Section. Section. Math :: Elementar Algebra Section. Eponents. When multipling like-bases, ou can add the eponents to simplif the epression..
Math :: Elementar Algebra Section. Section. Section. Section. Section. Section. Math :: Elementar Algebra Section. Eponents. When multipling like-bases, ou can add the eponents to simplif the epression..
Intermediate Algebra 100A Final Exam Review Fall 2007
 1 Basic Concepts 1. Sets and Other Basic Concepts Words/Concepts to Know: roster form, set builder notation, union, intersection, real numbers, natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers,
1 Basic Concepts 1. Sets and Other Basic Concepts Words/Concepts to Know: roster form, set builder notation, union, intersection, real numbers, natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers,
Algebra Summer Review Packet
 Name: Algebra Summer Review Packet About Algebra 1: Algebra 1 teaches students to think, reason, and communicate mathematically. Students use variables to determine solutions to real world problems. Skills
Name: Algebra Summer Review Packet About Algebra 1: Algebra 1 teaches students to think, reason, and communicate mathematically. Students use variables to determine solutions to real world problems. Skills
Working with Square Roots. Return to Table of Contents
 Working with Square Roots Return to Table of Contents 36 Square Roots Recall... * Teacher Notes 37 Square Roots All of these numbers can be written with a square. Since the square is the inverse of the
Working with Square Roots Return to Table of Contents 36 Square Roots Recall... * Teacher Notes 37 Square Roots All of these numbers can be written with a square. Since the square is the inverse of the
A summary of factoring methods
 Roberto s Notes on Prerequisites for Calculus Chapter 1: Algebra Section 1 A summary of factoring methods What you need to know already: Basic algebra notation and facts. What you can learn here: What
Roberto s Notes on Prerequisites for Calculus Chapter 1: Algebra Section 1 A summary of factoring methods What you need to know already: Basic algebra notation and facts. What you can learn here: What
Day 3: Section P-6 Rational Expressions; Section P-7 Equations. Rational Expressions
 1 Day : Section P-6 Rational Epressions; Section P-7 Equations Rational Epressions A rational epression (Fractions) is the quotient of two polynomials. The set of real numbers for which an algebraic epression
1 Day : Section P-6 Rational Epressions; Section P-7 Equations Rational Epressions A rational epression (Fractions) is the quotient of two polynomials. The set of real numbers for which an algebraic epression
Unit 7: Factoring Quadratic Polynomials
 Unit 7: Factoring Quadratic Polynomials A polynomial is represented by: where the coefficients are real numbers and the exponents are nonnegative integers. Side Note: Examples of real numbers: Examples
Unit 7: Factoring Quadratic Polynomials A polynomial is represented by: where the coefficients are real numbers and the exponents are nonnegative integers. Side Note: Examples of real numbers: Examples
Algebra I Part B. Help Pages & Who Knows
 Algebra I Part B & Who Knows 83 Vocabulary General Absolute Value the distance between a number,, and zero on a number line; written as. Eample: 5 = 5 reads The absolute value of 5 is 5. -7 = 7 reads The
Algebra I Part B & Who Knows 83 Vocabulary General Absolute Value the distance between a number,, and zero on a number line; written as. Eample: 5 = 5 reads The absolute value of 5 is 5. -7 = 7 reads The
Algebra/Trigonometry Review Notes
 Algebra/Trigonometry Review Notes MAC 41 Calculus for Life Sciences Instructor: Brooke Quinlan Hillsborough Community College ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR CALCULUS 1 TOPIC 1: POLYNOMIAL BASICS, POLYNOMIAL END BEHAVIOR,
Algebra/Trigonometry Review Notes MAC 41 Calculus for Life Sciences Instructor: Brooke Quinlan Hillsborough Community College ALGEBRA REVIEW FOR CALCULUS 1 TOPIC 1: POLYNOMIAL BASICS, POLYNOMIAL END BEHAVIOR,
3.4. ZEROS OF POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS
 3.4. ZEROS OF POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS What You Should Learn Use the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra to determine the number of zeros of polynomial functions. Find rational zeros of polynomial functions. Find
3.4. ZEROS OF POLYNOMIAL FUNCTIONS What You Should Learn Use the Fundamental Theorem of Algebra to determine the number of zeros of polynomial functions. Find rational zeros of polynomial functions. Find
Further factorising, simplifying, completing the square and algebraic proof
 Further factorising, simplifying, completing the square and algebraic proof 8 CHAPTER 8. Further factorising Quadratic epressions of the form b c were factorised in Section 8. by finding two numbers whose
Further factorising, simplifying, completing the square and algebraic proof 8 CHAPTER 8. Further factorising Quadratic epressions of the form b c were factorised in Section 8. by finding two numbers whose
Analysis. The student was expected to know and use the Pythagorean theorem to find the missing side. a 2 + b 2 = c 2
 Analysis. Correct Answer : meters (m) The student was epected to know and use the Pythagorean theorem to find the missing side. a + b c 8 + 7 64 + 89 89 64 SKILL: Use the Pythagorean theorem to find the
Analysis. Correct Answer : meters (m) The student was epected to know and use the Pythagorean theorem to find the missing side. a + b c 8 + 7 64 + 89 89 64 SKILL: Use the Pythagorean theorem to find the
Math Lecture 3 Notes
 Math 1010 - Lecture 3 Notes Dylan Zwick Fall 2009 1 Operations with Real Numbers In our last lecture we covered some basic operations with real numbers like addition, subtraction and multiplication. This
Math 1010 - Lecture 3 Notes Dylan Zwick Fall 2009 1 Operations with Real Numbers In our last lecture we covered some basic operations with real numbers like addition, subtraction and multiplication. This
Bishop Kelley High School Summer Math Program Course: Algebra 2 A
 06 07 Bishop Kelley High School Summer Math Program Course: Algebra A NAME: DIRECTIONS: Show all work in packet!!! The first 6 pages of this packet provide eamples as to how to work some of the problems
06 07 Bishop Kelley High School Summer Math Program Course: Algebra A NAME: DIRECTIONS: Show all work in packet!!! The first 6 pages of this packet provide eamples as to how to work some of the problems
Chapter 1A -- Real Numbers. iff. Math Symbols: Sets of Numbers
 Fry Texas A&M University! Fall 2016! Math 150 Notes! Section 1A! Page 1 Chapter 1A -- Real Numbers Math Symbols: iff or Example: Let A = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16,...} and let B = {3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18,
Fry Texas A&M University! Fall 2016! Math 150 Notes! Section 1A! Page 1 Chapter 1A -- Real Numbers Math Symbols: iff or Example: Let A = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16,...} and let B = {3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18,
x 2e e 3x 1. Find the equation of the line that passes through the two points 3,7 and 5, 2 slope-intercept form. . Write your final answer in
 Algebra / Trigonometry Review (Notes for MAT0) NOTE: For more review on any of these topics just navigate to my MAT187 Precalculus page and check in the Help section for the topic(s) you wish to review!
Algebra / Trigonometry Review (Notes for MAT0) NOTE: For more review on any of these topics just navigate to my MAT187 Precalculus page and check in the Help section for the topic(s) you wish to review!
M098 Carson Elementary and Intermediate Algebra 3e Section 11.3
 Objectives. Solve equations by writing them in quadratic form.. Solve equations that are quadratic in form by using substitution. Vocabulary Prior Knowledge Solve rational equations: Clear the fraction.
Objectives. Solve equations by writing them in quadratic form.. Solve equations that are quadratic in form by using substitution. Vocabulary Prior Knowledge Solve rational equations: Clear the fraction.
Math Lecture 23 Notes
 Math 1010 - Lecture 23 Notes Dylan Zwick Fall 2009 In today s lecture we ll expand upon the concept of radicals and radical expressions, and discuss how we can deal with equations involving these radical
Math 1010 - Lecture 23 Notes Dylan Zwick Fall 2009 In today s lecture we ll expand upon the concept of radicals and radical expressions, and discuss how we can deal with equations involving these radical
Rational and Radical Expressions and Equations
 Rational and Radical Epressions and Equations Secondary Mathematics Page 44 Jordan School District Unit Cluster 7 (AAPR6 and AAPR7): Rational Epressions Cluster 7: Rewrite rational epressions 7 Rewrite
Rational and Radical Epressions and Equations Secondary Mathematics Page 44 Jordan School District Unit Cluster 7 (AAPR6 and AAPR7): Rational Epressions Cluster 7: Rewrite rational epressions 7 Rewrite
A-2. Polynomials and Factoring. Section A-2 1
 A- Polynomials and Factoring Section A- 1 What you ll learn about Adding, Subtracting, and Multiplying Polynomials Special Products Factoring Polynomials Using Special Products Factoring Trinomials Factoring
A- Polynomials and Factoring Section A- 1 What you ll learn about Adding, Subtracting, and Multiplying Polynomials Special Products Factoring Polynomials Using Special Products Factoring Trinomials Factoring
4.3 Division of Polynomials
 4.3 Division of Polynomials Learning Objectives Divide a polynomials by a monomial. Divide a polynomial by a binomial. Rewrite and graph rational functions. Introduction A rational epression is formed
4.3 Division of Polynomials Learning Objectives Divide a polynomials by a monomial. Divide a polynomial by a binomial. Rewrite and graph rational functions. Introduction A rational epression is formed
Example 1: What do you know about the graph of the function
 Section 1.5 Analyzing of Functions In this section, we ll look briefly at four types of functions: polynomial functions, rational functions, eponential functions and logarithmic functions. Eample 1: What
Section 1.5 Analyzing of Functions In this section, we ll look briefly at four types of functions: polynomial functions, rational functions, eponential functions and logarithmic functions. Eample 1: What
Table of Contents. Unit 3: Rational and Radical Relationships. Answer Key...AK-1. Introduction... v
 These materials may not be reproduced for any purpose. The reproduction of any part for an entire school or school system is strictly prohibited. No part of this publication may be transmitted, stored,
These materials may not be reproduced for any purpose. The reproduction of any part for an entire school or school system is strictly prohibited. No part of this publication may be transmitted, stored,
SOLVING QUADRATIC EQUATIONS USING GRAPHING TOOLS
 GRADE PRE-CALCULUS UNIT A: QUADRATIC EQUATIONS (ALGEBRA) CLASS NOTES. A definition of Algebra: A branch of mathematics which describes basic arithmetic relations using variables.. Algebra is just a language.
GRADE PRE-CALCULUS UNIT A: QUADRATIC EQUATIONS (ALGEBRA) CLASS NOTES. A definition of Algebra: A branch of mathematics which describes basic arithmetic relations using variables.. Algebra is just a language.
A. Simplifying Polynomial Expressions
 A. Simplifing Polnomial Epressions I. Combining Like Terms - You can add or subtract terms that are considered "like", or terms that have the same variable(s) with the same eponent(s). E. 1: 5-7 + 10 +
A. Simplifing Polnomial Epressions I. Combining Like Terms - You can add or subtract terms that are considered "like", or terms that have the same variable(s) with the same eponent(s). E. 1: 5-7 + 10 +
Pre-Algebra 8 Notes Exponents and Scientific Notation
 Pre-Algebra 8 Notes Eponents and Scientific Notation Rules of Eponents CCSS 8.EE.A.: Know and apply the properties of integer eponents to generate equivalent numerical epressions. Review with students
Pre-Algebra 8 Notes Eponents and Scientific Notation Rules of Eponents CCSS 8.EE.A.: Know and apply the properties of integer eponents to generate equivalent numerical epressions. Review with students
Variables and Expressions
 Variables and Expressions A variable is a letter that represents a value that can change. A constant is a value that does not change. A numerical expression contains only constants and operations. An algebraic
Variables and Expressions A variable is a letter that represents a value that can change. A constant is a value that does not change. A numerical expression contains only constants and operations. An algebraic
Bishop Kelley High School Summer Math Program Course: Algebra 2 A
 015 016 Bishop Kelley High School Summer Math Program Course: Algebra A NAME: DIRECTIONS: Show all work in packet!!! The first 16 pages of this packet provide eamples as to how to work some of the problems
015 016 Bishop Kelley High School Summer Math Program Course: Algebra A NAME: DIRECTIONS: Show all work in packet!!! The first 16 pages of this packet provide eamples as to how to work some of the problems
Lesson 7.1 Polynomial Degree and Finite Differences
 Lesson 7.1 Polynomial Degree and Finite Differences 1. Identify the degree of each polynomial. a. 1 b. 0.2 1. 2 3.2 3 c. 20 16 2 20 2. Determine which of the epressions are polynomials. For each polynomial,
Lesson 7.1 Polynomial Degree and Finite Differences 1. Identify the degree of each polynomial. a. 1 b. 0.2 1. 2 3.2 3 c. 20 16 2 20 2. Determine which of the epressions are polynomials. For each polynomial,
Finding Slope. Find the slopes of the lines passing through the following points. rise run
 Finding Slope Find the slopes of the lines passing through the following points. y y1 Formula for slope: m 1 m rise run Find the slopes of the lines passing through the following points. E #1: (7,0) and
Finding Slope Find the slopes of the lines passing through the following points. y y1 Formula for slope: m 1 m rise run Find the slopes of the lines passing through the following points. E #1: (7,0) and
Appendix A A318. Appendix A.1 (page A8) Vocabulary Check (page A8) Answers to All Exercises and Tests. x (c) Bounded
 A Answers to All Eercises and Tests Appendi A Appendi A. (page A) Vocabulary Check (page A). rational. irrational. absolute value. composite. prime. variables; constants. terms. coefficient 9. Zero-Factor
A Answers to All Eercises and Tests Appendi A Appendi A. (page A) Vocabulary Check (page A). rational. irrational. absolute value. composite. prime. variables; constants. terms. coefficient 9. Zero-Factor
Secondary Math 2H Unit 3 Notes: Factoring and Solving Quadratics
 Secondary Math H Unit 3 Notes: Factoring and Solving Quadratics 3.1 Factoring out the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) Factoring: The reverse of multiplying. It means figuring out what you would multiply together
Secondary Math H Unit 3 Notes: Factoring and Solving Quadratics 3.1 Factoring out the Greatest Common Factor (GCF) Factoring: The reverse of multiplying. It means figuring out what you would multiply together
Math-1010 Lesson 4-2. Add and Subtract Rational Expressions
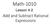 Math-00 Lesson - Add and Subtract Rational Epressions What are like terms? Like variables: Like powers: y y Multiples of the same variable same base and same eponent. Like radicals: same radicand and same
Math-00 Lesson - Add and Subtract Rational Epressions What are like terms? Like variables: Like powers: y y Multiples of the same variable same base and same eponent. Like radicals: same radicand and same
CHAPTER 3: Quadratic Functions and Equations; Inequalities
 MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 3: Quadratic Functions and Equations; Inequalities 3.1 The Complex Numbers 3.2 Quadratic Equations, Functions, Zeros, and
MAT 171 Precalculus Algebra Dr. Claude Moore Cape Fear Community College CHAPTER 3: Quadratic Functions and Equations; Inequalities 3.1 The Complex Numbers 3.2 Quadratic Equations, Functions, Zeros, and
Math Review. for the Quantitative Reasoning measure of the GRE General Test
 Math Review for the Quantitative Reasoning measure of the GRE General Test www.ets.org Overview This Math Review will familiarize you with the mathematical skills and concepts that are important for solving
Math Review for the Quantitative Reasoning measure of the GRE General Test www.ets.org Overview This Math Review will familiarize you with the mathematical skills and concepts that are important for solving
ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS AND POLYNOMIALS
 MODULE - ic Epressions and Polynomials ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS AND POLYNOMIALS So far, you had been using arithmetical numbers, which included natural numbers, whole numbers, fractional numbers, etc. and
MODULE - ic Epressions and Polynomials ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONS AND POLYNOMIALS So far, you had been using arithmetical numbers, which included natural numbers, whole numbers, fractional numbers, etc. and
Core Connections Algebra 2 Checkpoint Materials
 Core Connections Algebra 2 Note to Students (and their Teachers) Students master different skills at different speeds. No two students learn eactly the same way at the same time. At some point you will
Core Connections Algebra 2 Note to Students (and their Teachers) Students master different skills at different speeds. No two students learn eactly the same way at the same time. At some point you will
Algebra & Trig Review
 Algebra & Trig Review 1 Algebra & Trig Review This review was originally written for my Calculus I class, but it should be accessible to anyone needing a review in some basic algebra and trig topics. The
Algebra & Trig Review 1 Algebra & Trig Review This review was originally written for my Calculus I class, but it should be accessible to anyone needing a review in some basic algebra and trig topics. The
Geometry 21 Summer Work Packet Review and Study Guide
 Geometry Summer Work Packet Review and Study Guide This study guide is designed to accompany the Geometry Summer Work Packet. Its purpose is to offer a review of the ten specific concepts covered in the
Geometry Summer Work Packet Review and Study Guide This study guide is designed to accompany the Geometry Summer Work Packet. Its purpose is to offer a review of the ten specific concepts covered in the
Practical Algebra. A Step-by-step Approach. Brought to you by Softmath, producers of Algebrator Software
 Practical Algebra A Step-by-step Approach Brought to you by Softmath, producers of Algebrator Software 2 Algebra e-book Table of Contents Chapter 1 Algebraic expressions 5 1 Collecting... like terms 5
Practical Algebra A Step-by-step Approach Brought to you by Softmath, producers of Algebrator Software 2 Algebra e-book Table of Contents Chapter 1 Algebraic expressions 5 1 Collecting... like terms 5
Lesson #9 Simplifying Rational Expressions
 Lesson #9 Simplifying Rational Epressions A.A.6 Perform arithmetic operations with rational epressions and rename to lowest terms Factor the following epressions: A. 7 4 B. y C. y 49y Simplify: 5 5 = 4
Lesson #9 Simplifying Rational Epressions A.A.6 Perform arithmetic operations with rational epressions and rename to lowest terms Factor the following epressions: A. 7 4 B. y C. y 49y Simplify: 5 5 = 4
Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions
 Adding and Subtracting Rational Epressions As a review, adding and subtracting fractions requires the fractions to have the same denominator. If they already have the same denominator, combine the numerators
Adding and Subtracting Rational Epressions As a review, adding and subtracting fractions requires the fractions to have the same denominator. If they already have the same denominator, combine the numerators
Algebra, Part I. x m x = n xm i x n = x m n = 1
 Lesson 7 Algebra, Part I Rules and Definitions Rules Additive property of equality: If a, b, and c represent real numbers, and if a=b, then a + c = b + c. Also, c + a = c + b Multiplicative property of
Lesson 7 Algebra, Part I Rules and Definitions Rules Additive property of equality: If a, b, and c represent real numbers, and if a=b, then a + c = b + c. Also, c + a = c + b Multiplicative property of
Math 101 Study Session Spring 2016 Test 4 Chapter 10, Chapter 11 Chapter 12 Section 1, and Chapter 12 Section 2
 Math 101 Study Session Spring 2016 Test 4 Chapter 10, Chapter 11 Chapter 12 Section 1, and Chapter 12 Section 2 April 11, 2016 Chapter 10 Section 1: Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials A monomial is
Math 101 Study Session Spring 2016 Test 4 Chapter 10, Chapter 11 Chapter 12 Section 1, and Chapter 12 Section 2 April 11, 2016 Chapter 10 Section 1: Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials A monomial is
A.5. Solving Equations. Equations and Solutions of Equations. Linear Equations in One Variable. What you should learn. Why you should learn it
 A46 Appendi A Review of Fundamental Concepts of Algebra A.5 Solving Equations What you should learn Identify different types of equations. Solve linear equations in one variable and equations that lead
A46 Appendi A Review of Fundamental Concepts of Algebra A.5 Solving Equations What you should learn Identify different types of equations. Solve linear equations in one variable and equations that lead
Math 90 Lecture Notes Chapter 1
 Math 90 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Section 1.1: Introduction to Algebra This textbook stresses Problem Solving! Solving problems is one of the main goals of mathematics. Think of mathematics as a language,
Math 90 Lecture Notes Chapter 1 Section 1.1: Introduction to Algebra This textbook stresses Problem Solving! Solving problems is one of the main goals of mathematics. Think of mathematics as a language,
22. RADICALS. x add 5. multiply by 7
 22. RADICALS doing something, then undoing it The concept of doing something and then undoing it is very important in mathematics. Here are some eamples: Take a number. Add 5 to it. How can you get back
22. RADICALS doing something, then undoing it The concept of doing something and then undoing it is very important in mathematics. Here are some eamples: Take a number. Add 5 to it. How can you get back
Algebra 31 Summer Work Packet Review and Study Guide
 Algebra Summer Work Packet Review and Study Guide This study guide is designed to accompany the Algebra Summer Work Packet. Its purpose is to offer a review of the ten specific concepts covered in the
Algebra Summer Work Packet Review and Study Guide This study guide is designed to accompany the Algebra Summer Work Packet. Its purpose is to offer a review of the ten specific concepts covered in the
Algebra Final Exam Review Packet
 Algebra 1 00 Final Eam Review Packet UNIT 1 EXPONENTS / RADICALS Eponents Degree of a monomial: Add the degrees of all the in the monomial together. o Eample - Find the degree of 5 7 yz Degree of a polynomial:
Algebra 1 00 Final Eam Review Packet UNIT 1 EXPONENTS / RADICALS Eponents Degree of a monomial: Add the degrees of all the in the monomial together. o Eample - Find the degree of 5 7 yz Degree of a polynomial:
Section 1.3 Review of Complex Numbers
 1 Section 1. Review of Complex Numbers Objective 1: Imaginary and Complex Numbers In Science and Engineering, such quantities like the 5 occur all the time. So, we need to develop a number system that
1 Section 1. Review of Complex Numbers Objective 1: Imaginary and Complex Numbers In Science and Engineering, such quantities like the 5 occur all the time. So, we need to develop a number system that
Core Connections Algebra 2 Checkpoint Materials
 Core Connections Algebra 2 Note to Students (and their Teachers) Students master different skills at different speeds. No two students learn eactly the same way at the same time. At some point you will
Core Connections Algebra 2 Note to Students (and their Teachers) Students master different skills at different speeds. No two students learn eactly the same way at the same time. At some point you will
Math Analysis Chapter 2 Notes: Polynomial and Rational Functions
 Math Analysis Chapter Notes: Polynomial and Rational Functions Day 13: Section -1 Comple Numbers; Sections - Quadratic Functions -1: Comple Numbers After completing section -1 you should be able to do
Math Analysis Chapter Notes: Polynomial and Rational Functions Day 13: Section -1 Comple Numbers; Sections - Quadratic Functions -1: Comple Numbers After completing section -1 you should be able to do
