Quantum Monte Carlo Simulations of Exciton Condensates
|
|
|
- Russell Phillips
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Quantum Monte Carlo Simulations of Exciton Condensates J. Shumway a and D. M. Ceperley b a Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ 8583 b Dept. of Physics, University of Illinois, 1110 W. Green St., Urbana, IL Abstract We have studied scattering states and thermodynamic properties of electron-hole systems. Starting from the constituent electrons and holes and Coulomb interactions, we have used quantum Monte Carlo simulation techniques to sample properties of wavefunctions and thermal density matrices. We have studied three types of systems: (1) the scattering of two excitons, with full-quantum treatment of the four constituent particles, () the thermodynamic equilibrium of 14 electron-hole pairs having two spin states for each particle, which form excitons and biexcitons at low temperatures, and (3) the thermodynamic equilibrium of 7 spin-polarized electron-hole pairs, which form a dilute exciton gas that undergoes Bose condensation at low temperatures. We compare our results with predictions of the Saha equation for exciton and biexciton formation, and Bogoliubov theory for the energy of the dilute Bose gas of excitons. We also discuss the outlook for future quantum Monte Carlo simulations on these systems. Key words: A. Semiconductors, D. Excitons, D. Bose-Einstein Condensation, E: Computer Simulations PACS: Cc, Dr 1 Introduction Electron-hole systems in semiconductors have been a source of interesting new physics for forty years. The bound state of an electron and a hole, an exciton, is a neutral bosonic excitation of a semiconductor. Formation of a Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC) of excitons has been a target of many experiments [1,], though none have produced clear proof of Bose condensation. Some issues that arise concern the exciton-exciton scattering length, the rate of Auger decay [3], the formation of biexcitons or electron-hole liquids, and the nature of the BEC transition at high densities [4]. Preprint submitted to Elsevier Science June 004
2 Theoretically, an electron-hole system is an interacting quantum system. Interactions typically make exact solutions impossible, leading theorists to consider perturbative solutions or numerical simulations. Quantum Monte Carlo (QMC) techniques use random sampling to estimate properties of interacting quantum systems. The accuracy of QMC is often limited only by computer time and by small errors from fermion fixed-node approximations. Good scaling of computer time with the number of particles (usually low-order polynomial or even linear scaling) and the ability to treat detailed models has made QMC appealing for nanometer scale systems, such as semiconductor heterostructures. In this work we summarize our QMC calculations on bulk electron-hole systems. Numerical results have appeared previously in Refs [5 7], but some of the analysis presented here is new. We have taken as a starting model for interacting electrons and holes the effective-mass Hamiltonian H = N i=1 p i + q i q j, (1) m i i<j r ij with m e = m h = 1, q e = q h = e = 1, and = 1. In these units the exciton has an energy E X = 0.5 and radius a X =. We describe the density by a radius r s that satisfies 4 3 πr3 S = V/N eh, where V is the simulation volume and N eh is the number of electron-hole pairs. This simple Hamiltonian omits many effects, such as radiative recombination, multiple-band coupling, anisotropic effective masses, band non-parabolicity, and frequency and momentum dependence of the dielectric function. Even with these approximations, this interacting Hamiltonian still dictates a rich variety of states, including excitons, biexcitons, ionized plasmas, and excitonic Bose condensation. It is sensible to first study this simplified model; we anticipate that future QMC will utilize more realistic Hamiltonians. To study the properties of the electron-hole system, Eq. (1), we have constructed QMC simulations that use random walks to sample quantum and thermal expectation values of wavefunctions or density matrices. We have conducted three series of simulations: Exciton-exciton scattering. As described in detail in Ref. [7], we have calculated phase shifts and scattering lengths for elastic collisions of two excitons. The formalism starts from four-particle variational wavefunctions describing low-energy scattering states and any bound states. We fix a node (Ψ = 0) in the relative wavefunciton at a series of relative separation distance in order to discretize the scattering spectrum and then probe a series of relative momenta. The essentially exact energies of these scattering states were sampled using an excited state diffusion Monte Carlo algorithm [8,9]. The phase shifts and scattering lengths were inferred from the calculated relationship between energy and the node position.
3 Formation of excitons and biexcitons. To study the equilibrium phases of the e-h system, we developed QMC simulations based on Feynman path integrals [10,11]. To handle the fermion sign problem we used a free-particle fixed node approximation [1]. From these path integral simulations, we computed spin-dependent pair correlation functions for electrons and holes. These correlation functions indicate exciton formation as short-range attraction of electrons and holes, and biexciton formation as short-range attraction between two electrons (or holes) with opposite spin. A more accurate identification of excitons and biexcitons could be obtained by sampling the two-body density matrix and identifying natural orbitals. We conducted a simulation of 14 unpolarized electron-hole pairs and studied their pair correlation functions at different temperatures. Bose-condensation of excitons. Path integrals are a natural language for discussing BEC of interacting particles [10,11]. The phase transition appears as permuting paths that extend many times the interparticle spacing, and the phase transition itself resembles classical percolation [10,11]. Superfluidity can be calculated from path winding, condensate fraction can be calculated from the off-diagonal electron-hole density matrix, and other thermodynamic quantities such as energy and specific heat can indirectly indicate the BEC transition. We studied the energetics and superfluid order parameter for 19 spin-polarized electron hole pairs at different densities. Results of Computer Simulations Our computer simulation data were previously published in [5 7]. Here we report on new analysis of the data. Exciton-exciton scattering. Since publication of Ref. [7] we have learned of a better analysis technique based on an effective range expansion [13,14], k cot δ 0 (k) = 1 a + 1 r ek. () We have refit our data from Ref. [7] using effective range theory and present the values in Table. 1. Formation of excitons and biexcitons. Path integral QMC calculations of 14 unpolarized electron-hole (eh) pairs at a density r s /a X = 5 showed evidence of exciton and biexciton formation in pair correlation functions [5]. To extend this analysis, we now estimate the fraction of e-h pairs in excitons and biexcitons by integrating the pair correlation function out to a radius of.5 a X and 3.0 a X. We take an enhancement of electron-electron pairing as a clear evidence of a biexciton, and any additional enhancement of electron-hole pairing (beyond 3
4 Table 1 Scattering length for various elastic scattering processes, in units of excitonic radius. Here para and ortho refer to the exciton singlet and triplet state, repectively. From Ref. [7], with new analysis using effective range theory [14]. process a s (excitonic radii) para-para.18(7) ortho-orth (S=0) 3.759() ortho-orth (S=).18(7) ortho-para 0.706(14) ortho-ortho para-para (17) that expected in the biexciton) as evidence of isolated excitons. Figure 1 shows our estimated exciton and biexciton fractions. We compare these results to the Saha equation. Assuming three phases: an ionized e-h plasma (P), an exciton gas (X), and a biexciton gas (XX), classical gas equations give the following chemical potentials for eh pairs, [ ] N µ p eh = k n p BT log V λ3 e µ X eh = k B T log N V = k BT log N V µ XX eh ( λe ) 3 n X E X 4 ( ) 3 λe n XX E XX where n p, n X, and n XX are the percentage of e-h pairs in each phase, and E X and E XX are exciton and biexciton binding energies (E XX =.064E X ). Equating chemical potentials gives n X = 3 n p ( N V λ3 e n XX = n4 p ) exp E X k B T ( ) N 3 V λ3 e exp E XX k B T, which, along with the normalization condition n p + n X + n XX = 1, can be solved for n p, n X, and n XX as a function of temperature and density. We show the Saha equation predictions for excitons and biexcitons in Fig. 1, where we see good agreement with path integral QMC results. Bose condensation of excitons. In Ref. [6] we reported superfluid densities and energetics of the BEC transition. To see BEC in our QMC simulations we found it was necessary to add pairing the the fixed-node restriction. In Fig. we show one of our most convincing results, the energy of an eh system as the (3) (4) 4
5 Fig. 1. Fraction of electron-hole pairs bound in excitons (solid line and circles) and biexcitons (dashed line and s) as a function of temperature at a density r s /a x = 5. Data points are estimated by integrating PIMC pair correlation functions previously published in Ref. [6]. Lines are predictions of the Saha equation. Fig.. Energy as a function of density at constant temperature, k B T = 1 8 E x. Inset shows the free particle transition temperature T C (solid line) and the k B T = 1 8 E x isotherm, which crosses T C at r s = 4.04 a X. Adapted from Ref. [6]. density is varied across the BEC transition. The theoretical curves show the energies of a dilute classical gas and a Bose gas with Bogoliubov theory [15], using the a s =.18a X value from our scattering calculations. The energetics are strongly suggestive of a BEC transition at r s 4a X. 5
6 3 Conclusions and Outlook These simulations illustrate the ability of QMC to identify and quantify features in the phase diagram of an electron-hole system. The most crucial technical issue to be addressed is a study of the fixed-node approximation in the context of the BEC transition. A natural extension of these calculations would be to consider more detailed models, especially coupled quantum well structures. Anisotropic mass and three-dimensional confining potentials are straightforward to add to QMC and would allow direct contact with current experiments. Acknowledgments: We thank Jim Mitroy for his comments to us about scattering calculations and the use of effective range theory. Work supported by NSF grants DMR , DGE , DMR and computer resources at NCSA. References [1] D. W. Snoke, J. P. Wolfe, A. Mysyrowicz, Phys. Rev. B 41 (1990), [] E. Fortin, S. Fafard, A. Mysyrowicz, Phys. Rev. Lett. 70 (1993), [3] K. E. O Hara, J. R. Gullingsrud, J. P. Wolfe, Phys. Rev. B 60 (1999), [4] A. J. Leggett, in: Modern Trends in Condensed Matter Physics, edited by A. Pekalski, J. Przystawa, pp (Springer, Berlin, 1980). [5] J. Shumway, Quantum Monte Carlo Simulations of Electrons and Holes, Ph.D. thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL (1999). [6] J. Shumway, D. M. Ceperley, J. Phys. IV France 10 (000), Pr5. [7] J. Shumway, D. M. Ceperley, Phys. Rev. B 63 (001), [8] D. M. Ceperley, B. Bernu, J. Chem. Phys. 89 (1988), [9] B. Bernu, D. M. Ceperley, W. A. Lester, Jr., J. Chem. Phys. 93 (1990), 55. [10] R. P. Feynman, Statistical Mechanics (Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA, 197). [11] D. M. Ceperley, Rev. Mod. Phys. 67 (1995), 79. [1] D. M. Ceperley, Phys. Rev. Lett. 69 (199), 331. [13] G. F. Chew, M. L. Goldberger, Phys. Rev 75 (1949), [14] I. A. Ivanov, Phys. Rev. A 67 (003), [15] A. A. Abrikosov, L. P. Gorkov, I. E. Dzyaloshinski, Methods of Quantum Field Theory in Statistical Physics (Dover, New York, 1963). 6
Quantum Monte Carlo treatment of elastic exciton-exciton scattering
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 6, 6509 Quantum Monte Carlo treatment of elastic exciton-exciton scattering J. Shumway* and D. M. Ceperley Department of Physics and the National Center for Supercomputing Applications,
PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 6, 6509 Quantum Monte Carlo treatment of elastic exciton-exciton scattering J. Shumway* and D. M. Ceperley Department of Physics and the National Center for Supercomputing Applications,
Condensate fraction for a polarized three-dimensional Fermi gas
 Condensate fraction for a polarized three-dimensional Fermi gas Luca Salasnich Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Galileo Galilei, Università di Padova, Italy Camerino, June 26, 2014 Collaboration with:
Condensate fraction for a polarized three-dimensional Fermi gas Luca Salasnich Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Galileo Galilei, Università di Padova, Italy Camerino, June 26, 2014 Collaboration with:
Many-body wavefunctions for normal liquid 3 He
 Many-body wavefunctions for normal liquid 3 He Markus Holzmann, 1 Bernard Bernu, 1 and D. M. Ceperley 2 1 LPTMC, UMR 7600 of CNRS, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris, France 2 Department of Physics
Many-body wavefunctions for normal liquid 3 He Markus Holzmann, 1 Bernard Bernu, 1 and D. M. Ceperley 2 1 LPTMC, UMR 7600 of CNRS, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris, France 2 Department of Physics
Physics 127c: Statistical Mechanics. Application of Path Integrals to Superfluidity in He 4
 Physics 17c: Statistical Mechanics Application of Path Integrals to Superfluidity in He 4 The path integral method, and its recent implementation using quantum Monte Carlo methods, provides both an intuitive
Physics 17c: Statistical Mechanics Application of Path Integrals to Superfluidity in He 4 The path integral method, and its recent implementation using quantum Monte Carlo methods, provides both an intuitive
Fermionic condensation in ultracold atoms, nuclear matter and neutron stars
 Fermionic condensation in ultracold atoms, nuclear matter and neutron stars Luca Salasnich Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Galileo Galilei, Università di Padova, Italy Prague, July 16, 2013 Collaboration
Fermionic condensation in ultracold atoms, nuclear matter and neutron stars Luca Salasnich Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia Galileo Galilei, Università di Padova, Italy Prague, July 16, 2013 Collaboration
Path Integral Calculations of exchange in solid 4 He
 Path Integral Calculations of exchange in solid 4 He B. Bernu LPTL, UMR 7600 of CNRS, Université P. et M. Curie, Paris, France D. M. Ceperley Dept. of Physics and NCSA, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign,
Path Integral Calculations of exchange in solid 4 He B. Bernu LPTL, UMR 7600 of CNRS, Université P. et M. Curie, Paris, France D. M. Ceperley Dept. of Physics and NCSA, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign,
Polariton Condensation
 Polariton Condensation Marzena Szymanska University of Warwick Windsor 2010 Collaborators Theory J. Keeling P. B. Littlewood F. M. Marchetti Funding from Macroscopic Quantum Coherence Macroscopic Quantum
Polariton Condensation Marzena Szymanska University of Warwick Windsor 2010 Collaborators Theory J. Keeling P. B. Littlewood F. M. Marchetti Funding from Macroscopic Quantum Coherence Macroscopic Quantum
INTERACTING BOSE GAS AND QUANTUM DEPLETION
 922 INTERACTING BOSE GAS AND QUANTUM DEPLETION Chelagat, I., *Tanui, P.K., Khanna, K.M.,Tonui, J.K., Murunga G.S.W., Chelimo L.S.,Sirma K. K., Cheruiyot W.K. &Masinde F. W. Department of Physics, University
922 INTERACTING BOSE GAS AND QUANTUM DEPLETION Chelagat, I., *Tanui, P.K., Khanna, K.M.,Tonui, J.K., Murunga G.S.W., Chelimo L.S.,Sirma K. K., Cheruiyot W.K. &Masinde F. W. Department of Physics, University
The 4th Windsor Summer School on Condensed Matter Theory Quantum Transport and Dynamics in Nanostructures Great Park, Windsor, UK, August 6-18, 2007
 The 4th Windsor Summer School on Condensed Matter Theory Quantum Transport and Dynamics in Nanostructures Great Park, Windsor, UK, August 6-18, 2007 Kondo Effect in Metals and Quantum Dots Jan von Delft
The 4th Windsor Summer School on Condensed Matter Theory Quantum Transport and Dynamics in Nanostructures Great Park, Windsor, UK, August 6-18, 2007 Kondo Effect in Metals and Quantum Dots Jan von Delft
Many-Body Problems and Quantum Field Theory
 Philippe A. Martin Francois Rothen Many-Body Problems and Quantum Field Theory An Introduction Translated by Steven Goldfarb, Andrew Jordan and Samuel Leach Second Edition With 102 Figures, 7 Tables and
Philippe A. Martin Francois Rothen Many-Body Problems and Quantum Field Theory An Introduction Translated by Steven Goldfarb, Andrew Jordan and Samuel Leach Second Edition With 102 Figures, 7 Tables and
Small Trapped s-wave Interacting Fermi Gases: How to Quantify Correlations?
 Image: Peter Engels group at WSU Small Trapped s-wave Interacting Fermi Gases: How to Quantify Correlations? Doerte Blume and Kevin M. Daily Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, Washington State University,
Image: Peter Engels group at WSU Small Trapped s-wave Interacting Fermi Gases: How to Quantify Correlations? Doerte Blume and Kevin M. Daily Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, Washington State University,
Physics 598 ESM Term Paper Giant vortices in rapidly rotating Bose-Einstein condensates
 Physics 598 ESM Term Paper Giant vortices in rapidly rotating Bose-Einstein condensates Kuei Sun May 4, 2006 kueisun2@uiuc.edu Department of Physics, University of Illinois at Urbana- Champaign, 1110 W.
Physics 598 ESM Term Paper Giant vortices in rapidly rotating Bose-Einstein condensates Kuei Sun May 4, 2006 kueisun2@uiuc.edu Department of Physics, University of Illinois at Urbana- Champaign, 1110 W.
Strongly correlated systems in atomic and condensed matter physics. Lecture notes for Physics 284 by Eugene Demler Harvard University
 Strongly correlated systems in atomic and condensed matter physics Lecture notes for Physics 284 by Eugene Demler Harvard University January 25, 2011 2 Chapter 12 Collective modes in interacting Fermi
Strongly correlated systems in atomic and condensed matter physics Lecture notes for Physics 284 by Eugene Demler Harvard University January 25, 2011 2 Chapter 12 Collective modes in interacting Fermi
Intensity / a.u. 2 theta / deg. MAPbI 3. 1:1 MaPbI 3-x. Cl x 3:1. Supplementary figures
 Intensity / a.u. Supplementary figures 110 MAPbI 3 1:1 MaPbI 3-x Cl x 3:1 220 330 0 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 2 theta / deg Supplementary Fig. 1 X-ray Diffraction (XRD) patterns of MAPbI3 and MAPbI 3-x Cl
Intensity / a.u. Supplementary figures 110 MAPbI 3 1:1 MaPbI 3-x Cl x 3:1 220 330 0 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 2 theta / deg Supplementary Fig. 1 X-ray Diffraction (XRD) patterns of MAPbI3 and MAPbI 3-x Cl
Superfluidity in Hydrogen-Deuterium Mixed Clusters
 Journal of Low Temperature Physics - QFS2009 manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Superfluidity in Hydrogen-Deuterium Mixed Clusters Soomin Shim Yongkyung Kwon Received: date / Accepted: date
Journal of Low Temperature Physics - QFS2009 manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Superfluidity in Hydrogen-Deuterium Mixed Clusters Soomin Shim Yongkyung Kwon Received: date / Accepted: date
Stress dependence of exciton relaxation processes in Cu 2 O
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 65, 085211 Stress dependence of exciton relaxation processes in Cu 2 O S. Denev and D. W. Snoke Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Pittsburgh, 3941 O Hara Street,
PHYSICAL REVIEW B, VOLUME 65, 085211 Stress dependence of exciton relaxation processes in Cu 2 O S. Denev and D. W. Snoke Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Pittsburgh, 3941 O Hara Street,
in-medium pair wave functions the Cooper pair wave function the superconducting order parameter anomalous averages of the field operators
 (by A. A. Shanenko) in-medium wave functions in-medium pair-wave functions and spatial pair particle correlations momentum condensation and ODLRO (off-diagonal long range order) U(1) symmetry breaking
(by A. A. Shanenko) in-medium wave functions in-medium pair-wave functions and spatial pair particle correlations momentum condensation and ODLRO (off-diagonal long range order) U(1) symmetry breaking
CONTENTS. vii. CHAPTER 2 Operators 15
 CHAPTER 1 Why Quantum Mechanics? 1 1.1 Newtonian Mechanics and Classical Electromagnetism 1 (a) Newtonian Mechanics 1 (b) Electromagnetism 2 1.2 Black Body Radiation 3 1.3 The Heat Capacity of Solids and
CHAPTER 1 Why Quantum Mechanics? 1 1.1 Newtonian Mechanics and Classical Electromagnetism 1 (a) Newtonian Mechanics 1 (b) Electromagnetism 2 1.2 Black Body Radiation 3 1.3 The Heat Capacity of Solids and
An Overview of Quantum Monte Carlo Methods. David M. Ceperley
 An Overview of Quantum Monte Carlo Methods David M. Ceperley Department of Physics and National Center for Supercomputing Applications University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign Urbana, Illinois 61801 In
An Overview of Quantum Monte Carlo Methods David M. Ceperley Department of Physics and National Center for Supercomputing Applications University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign Urbana, Illinois 61801 In
Hexatic and microemulsion phases in a 2D quantum Coulomb gas
 Hexatic and microemulsion phases in a 2D quantum Coulomb gas Bryan K Clark (University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign) Michele Casula (Ecole Polytechnique, Paris) David M Ceperley (University of Illinois
Hexatic and microemulsion phases in a 2D quantum Coulomb gas Bryan K Clark (University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign) Michele Casula (Ecole Polytechnique, Paris) David M Ceperley (University of Illinois
Pushing the Auger limit: Kinetics of excitons in traps in Cu 2 O
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 61, NUMBER 4 15 JANUARY 2000-II Pushing the Auger limit: Kinetics of excitons in traps in Cu 2 O D. W. Snoke and V. Negoita Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Pittsburgh,
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 61, NUMBER 4 15 JANUARY 2000-II Pushing the Auger limit: Kinetics of excitons in traps in Cu 2 O D. W. Snoke and V. Negoita Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Pittsburgh,
2D Bose and Non-Fermi Liquid Metals
 2D Bose and Non-Fermi Liquid Metals MPA Fisher, with O. Motrunich, D. Sheng, E. Gull, S. Trebst, A. Feiguin KITP Cold Atoms Workshop 10/5/2010 Interest: A class of exotic gapless 2D Many-Body States a)
2D Bose and Non-Fermi Liquid Metals MPA Fisher, with O. Motrunich, D. Sheng, E. Gull, S. Trebst, A. Feiguin KITP Cold Atoms Workshop 10/5/2010 Interest: A class of exotic gapless 2D Many-Body States a)
Landau Theory of Fermi Liquids : Equilibrium Properties
 Quantum Liquids LECTURE I-II Landau Theory of Fermi Liquids : Phenomenology and Microscopic Foundations LECTURE III Superfluidity. Bogoliubov theory. Bose-Einstein condensation. LECTURE IV Luttinger Liquids.
Quantum Liquids LECTURE I-II Landau Theory of Fermi Liquids : Phenomenology and Microscopic Foundations LECTURE III Superfluidity. Bogoliubov theory. Bose-Einstein condensation. LECTURE IV Luttinger Liquids.
Effects of spin-orbit coupling on the BKT transition and the vortexantivortex structure in 2D Fermi Gases
 Effects of spin-orbit coupling on the BKT transition and the vortexantivortex structure in D Fermi Gases Carlos A. R. Sa de Melo Georgia Institute of Technology QMath13 Mathematical Results in Quantum
Effects of spin-orbit coupling on the BKT transition and the vortexantivortex structure in D Fermi Gases Carlos A. R. Sa de Melo Georgia Institute of Technology QMath13 Mathematical Results in Quantum
Superfluid 3 He. Miguel A. Morales
 Superfluid 3 He Miguel A. Morales Abstract In this report I will discuss the main properties of the superfluid phases of Helium 3. First, a brief description of the experimental observations and the phase
Superfluid 3 He Miguel A. Morales Abstract In this report I will discuss the main properties of the superfluid phases of Helium 3. First, a brief description of the experimental observations and the phase
Two-Dimensional Spin-Polarized Hydrogen at Zero
 J Low Temp Phys (2013) 171:685 692 DOI 10.1007/s10909-012-0756-7 Two-Dimensional Spin-Polarized Hydrogen at Zero Temperature L. Vranješ Markić J. Boronat Received: 13 July 2012 / Accepted: 16 September
J Low Temp Phys (2013) 171:685 692 DOI 10.1007/s10909-012-0756-7 Two-Dimensional Spin-Polarized Hydrogen at Zero Temperature L. Vranješ Markić J. Boronat Received: 13 July 2012 / Accepted: 16 September
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supporting online material SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 0.038/nPHYS8 A: Derivation of the measured initial degree of circular polarization. Under steady state conditions, prior to the emission of the
Supporting online material SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 0.038/nPHYS8 A: Derivation of the measured initial degree of circular polarization. Under steady state conditions, prior to the emission of the
BCS-BEC Crossover. Hauptseminar: Physik der kalten Gase Robin Wanke
 BCS-BEC Crossover Hauptseminar: Physik der kalten Gase Robin Wanke Outline Motivation Cold fermions BCS-Theory Gap equation Feshbach resonance Pairing BEC of molecules BCS-BEC-crossover Conclusion 2 Motivation
BCS-BEC Crossover Hauptseminar: Physik der kalten Gase Robin Wanke Outline Motivation Cold fermions BCS-Theory Gap equation Feshbach resonance Pairing BEC of molecules BCS-BEC-crossover Conclusion 2 Motivation
ELECTRIC FIELD EFFECTS ON THE EXCITON BOUND TO AN IONIZED DONOR IN PARABOLIC QUANTUM WELLS
 Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials Vol. 7, No. 5, October 005, p. 775-78 ELECTRIC FIELD EFFECTS ON THE EXCITON BOUND TO AN IONIZED DONOR IN PARABOLIC QUANTUM WELLS E. C. Niculescu *, L.
Journal of Optoelectronics and Advanced Materials Vol. 7, No. 5, October 005, p. 775-78 ELECTRIC FIELD EFFECTS ON THE EXCITON BOUND TO AN IONIZED DONOR IN PARABOLIC QUANTUM WELLS E. C. Niculescu *, L.
Circumventing the pathological behavior of path-integral Monte Carlo for systems with Coulomb potentials
 Circumventing the pathological behavior of path-integral Monte Carlo for systems with Coulomb potentials M. H. Müser and B. J. Berne Department of Chemistry, Columbia University, New York, New York 10027
Circumventing the pathological behavior of path-integral Monte Carlo for systems with Coulomb potentials M. H. Müser and B. J. Berne Department of Chemistry, Columbia University, New York, New York 10027
Introduction to Bose-Einstein condensation 4. STRONGLY INTERACTING ATOMIC FERMI GASES
 1 INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL OF PHYSICS "ENRICO FERMI" Varenna, July 1st - July 11 th 2008 " QUANTUM COHERENCE IN SOLID STATE SYSTEMS " Introduction to Bose-Einstein condensation 4. STRONGLY INTERACTING ATOMIC
1 INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL OF PHYSICS "ENRICO FERMI" Varenna, July 1st - July 11 th 2008 " QUANTUM COHERENCE IN SOLID STATE SYSTEMS " Introduction to Bose-Einstein condensation 4. STRONGLY INTERACTING ATOMIC
Density Functional Theory for Electrons in Materials
 Density Functional Theory for Electrons in Materials Richard M. Martin Department of Physics and Materials Research Laboratory University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 1 Density Functional Theory for
Density Functional Theory for Electrons in Materials Richard M. Martin Department of Physics and Materials Research Laboratory University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign 1 Density Functional Theory for
Supplementary Information for Observation of dynamic atom-atom correlation in liquid helium in real space
 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Supplementary Information for Observation of dynamic atom-atom correlation in liquid helium in real space Supplementary Note : Total PDF The total (snap-shot) PDF is obtained
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Supplementary Information for Observation of dynamic atom-atom correlation in liquid helium in real space Supplementary Note : Total PDF The total (snap-shot) PDF is obtained
Bosonic Path Integrals
 Bosonic Path Integrals 1. Overview of effect of bose statistics 2. Permutation sampling considerations 3. Calculation of superfluid density and momentum distribution. 4. Applications of PIMC to liquid
Bosonic Path Integrals 1. Overview of effect of bose statistics 2. Permutation sampling considerations 3. Calculation of superfluid density and momentum distribution. 4. Applications of PIMC to liquid
Monte Carlo Simulation of Bose Einstein Condensation in Traps
 Monte Carlo Simulation of Bose Einstein Condensation in Traps J. L. DuBois, H. R. Glyde Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware Newark, Delaware 19716, USA 1. INTRODUCTION In this paper
Monte Carlo Simulation of Bose Einstein Condensation in Traps J. L. DuBois, H. R. Glyde Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Delaware Newark, Delaware 19716, USA 1. INTRODUCTION In this paper
Physics 127a: Class Notes
 Physics 127a: Class Notes Lecture 15: Statistical Mechanics of Superfluidity Elementary excitations/quasiparticles In general, it is hard to list the energy eigenstates, needed to calculate the statistical
Physics 127a: Class Notes Lecture 15: Statistical Mechanics of Superfluidity Elementary excitations/quasiparticles In general, it is hard to list the energy eigenstates, needed to calculate the statistical
Path-integral calculation of the two-dimensional 4 He phase diagram
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 58, NUMBER 10 1 SEPTEMBER 1998-II Path-integral calculation of the two-dimensional 4 He phase diagram M. C. Gordillo and D. M. Ceperley National Center for Supercomputing Applications
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 58, NUMBER 10 1 SEPTEMBER 1998-II Path-integral calculation of the two-dimensional 4 He phase diagram M. C. Gordillo and D. M. Ceperley National Center for Supercomputing Applications
Variational wave function for a two-electron quantum dot
 Physica B 255 (1998) 145 149 Variational wave function for a two-electron quantum dot A. Harju *, V.A. Sverdlov, B. Barbiellini, R.M. Nieminen Laboratory of Physics, Helsinki University of Technology,
Physica B 255 (1998) 145 149 Variational wave function for a two-electron quantum dot A. Harju *, V.A. Sverdlov, B. Barbiellini, R.M. Nieminen Laboratory of Physics, Helsinki University of Technology,
Strongly paired fermions
 Strongly paired fermions Alexandros Gezerlis TALENT/INT Course on Nuclear forces and their impact on structure, reactions and astrophysics July 4, 2013 Strongly paired fermions Neutron matter & cold atoms
Strongly paired fermions Alexandros Gezerlis TALENT/INT Course on Nuclear forces and their impact on structure, reactions and astrophysics July 4, 2013 Strongly paired fermions Neutron matter & cold atoms
Is a system of fermions in the crossover BCS-BEC. BEC regime a new type of superfluid?
 Is a system of fermions in the crossover BCS-BEC BEC regime a new type of superfluid? Finite temperature properties of a Fermi gas in the unitary regime Aurel Bulgac,, Joaquin E. Drut, Piotr Magierski
Is a system of fermions in the crossover BCS-BEC BEC regime a new type of superfluid? Finite temperature properties of a Fermi gas in the unitary regime Aurel Bulgac,, Joaquin E. Drut, Piotr Magierski
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 17 Mar 1993
 dvi file made on February 1, 2008 Angular Momentum Distribution Function of the Laughlin Droplet arxiv:cond-mat/9303030v1 17 Mar 1993 Sami Mitra and A. H. MacDonald Department of Physics, Indiana University,
dvi file made on February 1, 2008 Angular Momentum Distribution Function of the Laughlin Droplet arxiv:cond-mat/9303030v1 17 Mar 1993 Sami Mitra and A. H. MacDonald Department of Physics, Indiana University,
Potential energy, from Coulomb's law. Potential is spherically symmetric. Therefore, solutions must have form
 Lecture 6 Page 1 Atoms L6.P1 Review of hydrogen atom Heavy proton (put at the origin), charge e and much lighter electron, charge -e. Potential energy, from Coulomb's law Potential is spherically symmetric.
Lecture 6 Page 1 Atoms L6.P1 Review of hydrogen atom Heavy proton (put at the origin), charge e and much lighter electron, charge -e. Potential energy, from Coulomb's law Potential is spherically symmetric.
Correlation in correlated materials (mostly transition metal oxides) Lucas K. Wagner University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
 Correlation in correlated materials (mostly transition metal oxides) Lucas K. Wagner University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Understanding of correlated materials is mostly phenomenological FN- DMC
Correlation in correlated materials (mostly transition metal oxides) Lucas K. Wagner University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Understanding of correlated materials is mostly phenomenological FN- DMC
Computation of the High Temperature Coulomb Density Matrix in Periodic Boundary Conditions
 Computation of the High Temperature Coulomb Density Matrix in Periodic Boundary Conditions B. Militzer Department of Earth and Planetary Science and Department of Astronomy, University of California, Berkeley,
Computation of the High Temperature Coulomb Density Matrix in Periodic Boundary Conditions B. Militzer Department of Earth and Planetary Science and Department of Astronomy, University of California, Berkeley,
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 5 Aug 2002
 Superfluidity in a Doped Helium Droplet E. W. Draeger and D. M. Ceperley Department of Physics and National Center for Supercomputing Applications, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, 68 Path Integral
Superfluidity in a Doped Helium Droplet E. W. Draeger and D. M. Ceperley Department of Physics and National Center for Supercomputing Applications, University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, 68 Path Integral
Magneto-Excitons in Semiconductor Quantum Rings
 phys. stat. sol. (a) 190, No. 3, 781 785 (2002) Magneto-Excitons in Semiconductor Quantum Rings I. Galbraith 1 ), F. J. Braid, and R. J. Warburton Department of Physics, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh,
phys. stat. sol. (a) 190, No. 3, 781 785 (2002) Magneto-Excitons in Semiconductor Quantum Rings I. Galbraith 1 ), F. J. Braid, and R. J. Warburton Department of Physics, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh,
Condensed matter theory Lecture notes and problem sets 2012/2013
 Condensed matter theory Lecture notes and problem sets 2012/2013 Dmitri Ivanov Recommended books and lecture notes: [AM] N. W. Ashcroft and N. D. Mermin, Solid State Physics. [Mar] M. P. Marder, Condensed
Condensed matter theory Lecture notes and problem sets 2012/2013 Dmitri Ivanov Recommended books and lecture notes: [AM] N. W. Ashcroft and N. D. Mermin, Solid State Physics. [Mar] M. P. Marder, Condensed
Superfluidity in bosonic systems
 Superfluidity in bosonic systems Rico Pires PI Uni Heidelberg Outline Strongly coupled quantum fluids 2.1 Dilute Bose gases 2.2 Liquid Helium Wieman/Cornell A. Leitner, from wikimedia When are quantum
Superfluidity in bosonic systems Rico Pires PI Uni Heidelberg Outline Strongly coupled quantum fluids 2.1 Dilute Bose gases 2.2 Liquid Helium Wieman/Cornell A. Leitner, from wikimedia When are quantum
Preface Introduction to the electron liquid
 Table of Preface page xvii 1 Introduction to the electron liquid 1 1.1 A tale of many electrons 1 1.2 Where the electrons roam: physical realizations of the electron liquid 5 1.2.1 Three dimensions 5 1.2.2
Table of Preface page xvii 1 Introduction to the electron liquid 1 1.1 A tale of many electrons 1 1.2 Where the electrons roam: physical realizations of the electron liquid 5 1.2.1 Three dimensions 5 1.2.2
MAJORANAFERMIONS IN CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS
 MAJORANAFERMIONS IN CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS A. J. Leggett University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign based in part on joint work with Yiruo Lin Memorial meeting for Nobel Laureate Professor Abdus Salam
MAJORANAFERMIONS IN CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS A. J. Leggett University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign based in part on joint work with Yiruo Lin Memorial meeting for Nobel Laureate Professor Abdus Salam
Path-integral Monte Carlo simulation of helium at negative pressures
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 61, NUMBER 13 1 APRIL 2000-I Path-integral Monte Carlo simulation of helium at negative pressures Gregory H. Bauer, David M. Ceperley, and Nigel Goldenfeld Department of Physics,
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 61, NUMBER 13 1 APRIL 2000-I Path-integral Monte Carlo simulation of helium at negative pressures Gregory H. Bauer, David M. Ceperley, and Nigel Goldenfeld Department of Physics,
1 Interaction of Quantum Fields with Classical Sources
 1 Interaction of Quantum Fields with Classical Sources A source is a given external function on spacetime t, x that can couple to a dynamical variable like a quantum field. Sources are fundamental in the
1 Interaction of Quantum Fields with Classical Sources A source is a given external function on spacetime t, x that can couple to a dynamical variable like a quantum field. Sources are fundamental in the
Supplementary Figure S1 Definition of the wave vector components: Parallel and perpendicular wave vector of the exciton and of the emitted photons.
 Supplementary Figure S1 Definition of the wave vector components: Parallel and perpendicular wave vector of the exciton and of the emitted photons. Supplementary Figure S2 The calculated temperature dependence
Supplementary Figure S1 Definition of the wave vector components: Parallel and perpendicular wave vector of the exciton and of the emitted photons. Supplementary Figure S2 The calculated temperature dependence
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 10 Sep 2014
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 10 Sep 2014 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 10 Sep 2014](/thumbs/80/81458966.jpg) Overcoming the fermion sign problem in homogeneous systems Jonathan L DuBois and Berni J. Alder Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA 94550, USA Ethan W. Brown Department of Physics, University
Overcoming the fermion sign problem in homogeneous systems Jonathan L DuBois and Berni J. Alder Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA 94550, USA Ethan W. Brown Department of Physics, University
Ground-state properties, excitations, and response of the 2D Fermi gas
 Ground-state properties, excitations, and response of the 2D Fermi gas Introduction: 2D FG and a condensed matter perspective Auxiliary-field quantum Monte Carlo calculations - exact* here Results on spin-balanced
Ground-state properties, excitations, and response of the 2D Fermi gas Introduction: 2D FG and a condensed matter perspective Auxiliary-field quantum Monte Carlo calculations - exact* here Results on spin-balanced
Thermodynamics of the polarized unitary Fermi gas from complex Langevin. Joaquín E. Drut University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
 Thermodynamics of the polarized unitary Fermi gas from complex Langevin Joaquín E. Drut University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill INT, July 2018 Acknowledgements Organizers Group at UNC-CH (esp. Andrew
Thermodynamics of the polarized unitary Fermi gas from complex Langevin Joaquín E. Drut University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill INT, July 2018 Acknowledgements Organizers Group at UNC-CH (esp. Andrew
Quantum Phase Transition
 Quantum Phase Transition Guojun Zhu Department of Physics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana IL 61801, U.S.A. (Dated: May 5, 2002) A quantum system can undergo a continuous phase transition
Quantum Phase Transition Guojun Zhu Department of Physics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana IL 61801, U.S.A. (Dated: May 5, 2002) A quantum system can undergo a continuous phase transition
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 16 Jun 1993
 Comment on Theory of Impure Superconductors: Anderson versus Abrikosov and Gor kov R. J. Radtke Department of Physics and the James Franck Institute, arxiv:cond-mat/9306037v1 16 Jun 1993 The University
Comment on Theory of Impure Superconductors: Anderson versus Abrikosov and Gor kov R. J. Radtke Department of Physics and the James Franck Institute, arxiv:cond-mat/9306037v1 16 Jun 1993 The University
Clas s ical and path integral Monte Carlo s imulation of charged particles in traps
 Clas s ical and path integral Monte Carlo s imulation of charged particles in traps Alexei Filinov, Michael B onitz, in c o lla b o r a tio n w ith Vladimir Filinov, Patrick Ludwig, Jens B öning, Henning
Clas s ical and path integral Monte Carlo s imulation of charged particles in traps Alexei Filinov, Michael B onitz, in c o lla b o r a tio n w ith Vladimir Filinov, Patrick Ludwig, Jens B öning, Henning
Ab Initio Calculations for Large Dielectric Matrices of Confined Systems Serdar Ö güt Department of Physics, University of Illinois at Chicago, 845 We
 Ab Initio Calculations for Large Dielectric Matrices of Confined Systems Serdar Ö güt Department of Physics, University of Illinois at Chicago, 845 West Taylor Street (M/C 273), Chicago, IL 60607 Russ
Ab Initio Calculations for Large Dielectric Matrices of Confined Systems Serdar Ö güt Department of Physics, University of Illinois at Chicago, 845 West Taylor Street (M/C 273), Chicago, IL 60607 Russ
Bound states of two particles confined to parallel two-dimensional layers and interacting via dipole-dipole or dipole-charge laws
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 55, NUMBER 8 15 FEBRUARY 1997-II Bound states of two particles confined to parallel two-dimensional layers and interacting via dipole-dipole or dipole-charge laws V. I. Yudson
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 55, NUMBER 8 15 FEBRUARY 1997-II Bound states of two particles confined to parallel two-dimensional layers and interacting via dipole-dipole or dipole-charge laws V. I. Yudson
Challenges in Path Integral Monte Carlo. David Ceperley Physics UIUC
 Challenges in Path Integral Monte Carlo David Ceperley Physics UIUC Imaginary time path integrals Exchange in quantum crystals The fermion sign problem Restricted paths The Penalty method Quantum dynamics?
Challenges in Path Integral Monte Carlo David Ceperley Physics UIUC Imaginary time path integrals Exchange in quantum crystals The fermion sign problem Restricted paths The Penalty method Quantum dynamics?
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 19 Dec 2005
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 19 Dec 2005 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 19 Dec 2005](/thumbs/74/70382724.jpg) Released momentum distribution of a Fermi gas in the BCS-BEC crossover arxiv:cond-mat/5246v [cond-mat.other] 9 Dec 25 M.L. Chiofalo, S. Giorgini 2,3 and M. Holland 2 INFM and Classe di Scienze, Scuola
Released momentum distribution of a Fermi gas in the BCS-BEC crossover arxiv:cond-mat/5246v [cond-mat.other] 9 Dec 25 M.L. Chiofalo, S. Giorgini 2,3 and M. Holland 2 INFM and Classe di Scienze, Scuola
EXCHANGE IN QUANTUM CRYSTALS: MAGNETISM AND MELTING OF THE LOW DENSITY 2D WIGNER CRYSTAL. David M. CEPERLEY
 united nations educational, scientific and cultural organization the abdus salam international centre for theoretical physics international atomic energy agency SMR 1595-28 Joint DEMOCRITOS - ICTP School
united nations educational, scientific and cultural organization the abdus salam international centre for theoretical physics international atomic energy agency SMR 1595-28 Joint DEMOCRITOS - ICTP School
Workshop on Coherent Phenomena in Disordered Optical Systems May 2014
 2583-12 Workshop on Coherent Phenomena in Disordered Optical Systems 26-30 May 2014 Nonlinear Excitations of Bose-Einstein Condensates with Higherorder Interaction Etienne WAMBA University of Yaounde and
2583-12 Workshop on Coherent Phenomena in Disordered Optical Systems 26-30 May 2014 Nonlinear Excitations of Bose-Einstein Condensates with Higherorder Interaction Etienne WAMBA University of Yaounde and
The Nuclear Many-Body Problem. Lecture 2
 The Nuclear Many-Body Problem Lecture 2 How do we describe nuclei? Shell structure in nuclei and the phenomenological shell model approach to nuclear structure. Ab-initio approach to nuclear structure.
The Nuclear Many-Body Problem Lecture 2 How do we describe nuclei? Shell structure in nuclei and the phenomenological shell model approach to nuclear structure. Ab-initio approach to nuclear structure.
From BEC to BCS. Molecular BECs and Fermionic Condensates of Cooper Pairs. Preseminar Extreme Matter Institute EMMI. and
 From BEC to BCS Molecular BECs and Fermionic Condensates of Cooper Pairs Preseminar Extreme Matter Institute EMMI Andre Wenz Max-Planck-Institute for Nuclear Physics and Matthias Kronenwett Institute for
From BEC to BCS Molecular BECs and Fermionic Condensates of Cooper Pairs Preseminar Extreme Matter Institute EMMI Andre Wenz Max-Planck-Institute for Nuclear Physics and Matthias Kronenwett Institute for
Landau Bogolubov Energy Spectrum of Superconductors
 Landau Bogolubov Energy Spectrum of Superconductors L.N. Tsintsadze 1 and N.L. Tsintsadze 1,2 1. Department of Plasma Physics, E. Andronikashvili Institute of Physics, Tbilisi 0128, Georgia 2. Faculty
Landau Bogolubov Energy Spectrum of Superconductors L.N. Tsintsadze 1 and N.L. Tsintsadze 1,2 1. Department of Plasma Physics, E. Andronikashvili Institute of Physics, Tbilisi 0128, Georgia 2. Faculty
Fermions in the unitary regime at finite temperatures from path integral auxiliary field Monte Carlo simulations
 Fermions in the unitary regime at finite temperatures from path integral auxiliary field Monte Carlo simulations Aurel Bulgac,, Joaquin E. Drut and Piotr Magierski University of Washington, Seattle, WA
Fermions in the unitary regime at finite temperatures from path integral auxiliary field Monte Carlo simulations Aurel Bulgac,, Joaquin E. Drut and Piotr Magierski University of Washington, Seattle, WA
Pairing properties, pseudogap phase and dynamics of vortices in a unitary Fermi gas
 Pairing properties, pseudogap phase and dynamics of vortices in a unitary Fermi gas Piotr Magierski (Warsaw University of Technology/ University of Washington, Seattle) Collaborators: Aurel Bulgac (Seattle)
Pairing properties, pseudogap phase and dynamics of vortices in a unitary Fermi gas Piotr Magierski (Warsaw University of Technology/ University of Washington, Seattle) Collaborators: Aurel Bulgac (Seattle)
We can then linearize the Heisenberg equation for in the small quantity obtaining a set of linear coupled equations for and :
 Wednesday, April 23, 2014 9:37 PM Excitations in a Bose condensate So far: basic understanding of the ground state wavefunction for a Bose-Einstein condensate; We need to know: elementary excitations in
Wednesday, April 23, 2014 9:37 PM Excitations in a Bose condensate So far: basic understanding of the ground state wavefunction for a Bose-Einstein condensate; We need to know: elementary excitations in
The remarkable properties of superfluids, in particular the
 Simulation of dynamical properties of normal and superfluid helium Akira Nakayama* and Nancy Makri* *Department of Chemistry, University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign, 601 South Goodwin Avenue, Urbana,
Simulation of dynamical properties of normal and superfluid helium Akira Nakayama* and Nancy Makri* *Department of Chemistry, University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign, 601 South Goodwin Avenue, Urbana,
Microcavity Exciton-Polariton
 Microcavity Exciton-Polariton Neil Na ( 那允中 ) Institute of Photonics Technologies National Tsing-Hua University 5/3/2012 Outline Microcavity Exciton-polariton QW excitons Microcavity photons Strong coupling
Microcavity Exciton-Polariton Neil Na ( 那允中 ) Institute of Photonics Technologies National Tsing-Hua University 5/3/2012 Outline Microcavity Exciton-polariton QW excitons Microcavity photons Strong coupling
arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.supr-con] 6 Jun 2005
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.supr-con] 6 Jun 2005 arxiv:cond-mat/ v2 [cond-mat.supr-con] 6 Jun 2005](/thumbs/72/67149936.jpg) BCS-to-BEC crossover from the exact BCS solution G. Ortiz and J. Duelsy Theoretical Division, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico 87, USA Instituto de Estructura de la Materia, CSIC,
BCS-to-BEC crossover from the exact BCS solution G. Ortiz and J. Duelsy Theoretical Division, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico 87, USA Instituto de Estructura de la Materia, CSIC,
Quantum Monte Carlo calculations of medium mass nuclei
 Quantum Monte Carlo calculations of medium mass nuclei Diego Lonardoni FRIB Theory Fellow In collaboration with: J. Carlson, LANL S. Gandolfi, LANL X. Wang, Huzhou University, China A. Lovato, ANL & UniTN
Quantum Monte Carlo calculations of medium mass nuclei Diego Lonardoni FRIB Theory Fellow In collaboration with: J. Carlson, LANL S. Gandolfi, LANL X. Wang, Huzhou University, China A. Lovato, ANL & UniTN
Lecture 4: Superfluidity
 Lecture 4: Superfluidity Kicking Bogoliubov quasiparticles FIG. 1. The Bragg and condensate clouds. (a) Average of two absorption images after 38 msec time of flight, following a resonant Bragg pulse with
Lecture 4: Superfluidity Kicking Bogoliubov quasiparticles FIG. 1. The Bragg and condensate clouds. (a) Average of two absorption images after 38 msec time of flight, following a resonant Bragg pulse with
Publications. Articles:
 Publications Articles: 1. R. Combescot Coupling between Planes and Chains in Y Ba 2 Cu 3 O 7 : A Possible Solution for the Order Parameter Controversy, Phys. Rev. Lett. 75 (1995) 3732-3735 2. X. Leyronas
Publications Articles: 1. R. Combescot Coupling between Planes and Chains in Y Ba 2 Cu 3 O 7 : A Possible Solution for the Order Parameter Controversy, Phys. Rev. Lett. 75 (1995) 3732-3735 2. X. Leyronas
Summary lecture VI. with the reduced mass and the dielectric background constant
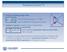 Summary lecture VI Excitonic binding energy reads with the reduced mass and the dielectric background constant Δ Statistical operator (density matrix) characterizes quantum systems in a mixed state and
Summary lecture VI Excitonic binding energy reads with the reduced mass and the dielectric background constant Δ Statistical operator (density matrix) characterizes quantum systems in a mixed state and
Swinburne Research Bank
 Swinburne Research Bank http://researchbank.swinburne.edu.au Deuar, P., & Drummond, P. D. (001). Stochastic gauges in quantum dynamics for many-body simulations. Originally published in Computer Physics
Swinburne Research Bank http://researchbank.swinburne.edu.au Deuar, P., & Drummond, P. D. (001). Stochastic gauges in quantum dynamics for many-body simulations. Originally published in Computer Physics
Soft Carrier Multiplication by Hot Electrons in Graphene
 Soft Carrier Multiplication by Hot Electrons in Graphene Anuj Girdhar 1,3 and J.P. Leburton 1,2,3 1) Department of Physics 2) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, and 3) Beckman Institute
Soft Carrier Multiplication by Hot Electrons in Graphene Anuj Girdhar 1,3 and J.P. Leburton 1,2,3 1) Department of Physics 2) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, and 3) Beckman Institute
Supplementary Figure 3: Interaction effects in the proposed state preparation with Bloch oscillations. The numerical results are obtained by
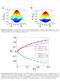 Supplementary Figure : Bandstructure of the spin-dependent hexagonal lattice. The lattice depth used here is V 0 = E rec, E rec the single photon recoil energy. In a and b, we choose the spin dependence
Supplementary Figure : Bandstructure of the spin-dependent hexagonal lattice. The lattice depth used here is V 0 = E rec, E rec the single photon recoil energy. In a and b, we choose the spin dependence
UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND Department of Physics College Park, Maryland. PHYSICS Ph.D. QUALIFYING EXAMINATION PART II
 UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND Department of Physics College Park, Maryland PHYSICS Ph.D. QUALIFYING EXAMINATION PART II January 20, 2017 9:00 a.m. 1:00 p.m. Do any four problems. Each problem is worth 25 points.
UNIVERSITY OF MARYLAND Department of Physics College Park, Maryland PHYSICS Ph.D. QUALIFYING EXAMINATION PART II January 20, 2017 9:00 a.m. 1:00 p.m. Do any four problems. Each problem is worth 25 points.
COOPER PAIRING IN EXOTIC FERMI SUPERFLUIDS: AN ALTERNATIVE APPROACH
 Lecture 4 COOPER PAIRING IN EXOTIC FERMI SUPERFLUIDS: AN ALTERNATIVE APPROACH Anthony J. Leggett Department of Physics University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign based largely on joint work with Yiruo
Lecture 4 COOPER PAIRING IN EXOTIC FERMI SUPERFLUIDS: AN ALTERNATIVE APPROACH Anthony J. Leggett Department of Physics University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign based largely on joint work with Yiruo
The phases of matter familiar for us from everyday life are: solid, liquid, gas and plasma (e.f. flames of fire). There are, however, many other
 1 The phases of matter familiar for us from everyday life are: solid, liquid, gas and plasma (e.f. flames of fire). There are, however, many other phases of matter that have been experimentally observed,
1 The phases of matter familiar for us from everyday life are: solid, liquid, gas and plasma (e.f. flames of fire). There are, however, many other phases of matter that have been experimentally observed,
16.55 Ionized Gases Problem Set #5
 16.55 Ionized Gases Problem Set #5 Problem 1: A probe in a non-maxellian plasma The theory of cold probes, as explained in class, applies to plasmas with Maxwellian electron and ion distributions. However,
16.55 Ionized Gases Problem Set #5 Problem 1: A probe in a non-maxellian plasma The theory of cold probes, as explained in class, applies to plasmas with Maxwellian electron and ion distributions. However,
The Gross-Pitaevskii Equation and the Hydrodynamic Expansion of BECs
 The Gross-Pitaevskii Equation and the Hydrodynamic Expansion of BECs i ( ) t Φ (r, t) = 2 2 2m + V ext(r) + g Φ (r, t) 2 Φ (r, t) (Mewes et al., 1996) 26/11/2009 Stefano Carignano 1 Contents 1 Introduction
The Gross-Pitaevskii Equation and the Hydrodynamic Expansion of BECs i ( ) t Φ (r, t) = 2 2 2m + V ext(r) + g Φ (r, t) 2 Φ (r, t) (Mewes et al., 1996) 26/11/2009 Stefano Carignano 1 Contents 1 Introduction
Journal of Atoms and Molecules
 Research article Journal of Atoms and Molecules An International Online Journal ISSN 77 147 Hot Electron Transport in Polar Semiconductor at Low Lattice Temperature A. K. Ghorai Physics Department, Kalimpong
Research article Journal of Atoms and Molecules An International Online Journal ISSN 77 147 Hot Electron Transport in Polar Semiconductor at Low Lattice Temperature A. K. Ghorai Physics Department, Kalimpong
T-matrix calculations for the electron-impact ionization of hydrogen in the Temkin-Poet model
 T-matrix calculations for the electron-impact ionization of hydrogen in the Temkin-Poet model M. S. Pindzola, D. Mitnik, and F. Robicheaux Department of Physics, Auburn University, Auburn, Alabama 36849
T-matrix calculations for the electron-impact ionization of hydrogen in the Temkin-Poet model M. S. Pindzola, D. Mitnik, and F. Robicheaux Department of Physics, Auburn University, Auburn, Alabama 36849
Electronic and Optoelectronic Properties of Semiconductor Structures
 Electronic and Optoelectronic Properties of Semiconductor Structures Jasprit Singh University of Michigan, Ann Arbor CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS PREFACE INTRODUCTION xiii xiv 1.1 SURVEY OF ADVANCES
Electronic and Optoelectronic Properties of Semiconductor Structures Jasprit Singh University of Michigan, Ann Arbor CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS PREFACE INTRODUCTION xiii xiv 1.1 SURVEY OF ADVANCES
Interaction between atoms
 Interaction between atoms MICHA SCHILLING HAUPTSEMINAR: PHYSIK DER KALTEN GASE INSTITUT FÜR THEORETISCHE PHYSIK III UNIVERSITÄT STUTTGART 23.04.2013 Outline 2 Scattering theory slow particles / s-wave
Interaction between atoms MICHA SCHILLING HAUPTSEMINAR: PHYSIK DER KALTEN GASE INSTITUT FÜR THEORETISCHE PHYSIK III UNIVERSITÄT STUTTGART 23.04.2013 Outline 2 Scattering theory slow particles / s-wave
Exchange Frequencies in 2D Solids: Example of Helium 3 Adsorbed on Graphite and the Wigner Crystal
 John von Neumann Institute for Computing Exchange Frequencies in 2D Solids: Example of Helium 3 Adsorbed on Graphite and the Wigner Crystal Bernard Bernu, Ladir Cândido, David M. Ceperley published in
John von Neumann Institute for Computing Exchange Frequencies in 2D Solids: Example of Helium 3 Adsorbed on Graphite and the Wigner Crystal Bernard Bernu, Ladir Cândido, David M. Ceperley published in
arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 5 Jun 2004
![arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 5 Jun 2004 arxiv:cond-mat/ v1 [cond-mat.other] 5 Jun 2004](/thumbs/74/70280953.jpg) arxiv:cond-mat/0406141v1 [cond-mat.other] 5 Jun 2004 Moving Beyond a Simple Model of Luminescence Rings in Quantum Well Structures D. Snoke 1, S. Denev 1, Y. Liu 1, S. Simon 2, R. Rapaport 2, G. Chen 2,
arxiv:cond-mat/0406141v1 [cond-mat.other] 5 Jun 2004 Moving Beyond a Simple Model of Luminescence Rings in Quantum Well Structures D. Snoke 1, S. Denev 1, Y. Liu 1, S. Simon 2, R. Rapaport 2, G. Chen 2,
Efficiency of genetic algorithm and determination of ground state energy of impurity in a spherical quantum dot
 Efficiency of genetic algorithm and determination of ground state energy of impurity in a spherical quantum dot +DOXNùDIDN 1* 0HKPHWùDKLQ 1, Berna Gülveren 1, Mehmet Tomak 1 Selcuk University, Faculty
Efficiency of genetic algorithm and determination of ground state energy of impurity in a spherical quantum dot +DOXNùDIDN 1* 0HKPHWùDKLQ 1, Berna Gülveren 1, Mehmet Tomak 1 Selcuk University, Faculty
Quantum Momentum Distributions
 Journal of Low Temperature Physics, Vol. 147, Nos. 5/6, June 2007 ( 2007) DOI: 10.1007/s10909-007-9344-7 Quantum Momentum Distributions Benjamin Withers and Henry R. Glyde Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Journal of Low Temperature Physics, Vol. 147, Nos. 5/6, June 2007 ( 2007) DOI: 10.1007/s10909-007-9344-7 Quantum Momentum Distributions Benjamin Withers and Henry R. Glyde Department of Physics and Astronomy,
Improved Kelbg potential for correlated Coulomb systems
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICSPUBLISHING JOURNAL OFPHYSICSA: MATHEMATICAL AND GENERAL J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 36 (2003) 5957 5962 PII: S0305-4470(03)55108-3 Improved Kelbg potential for correlated Coulomb systems
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICSPUBLISHING JOURNAL OFPHYSICSA: MATHEMATICAL AND GENERAL J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 36 (2003) 5957 5962 PII: S0305-4470(03)55108-3 Improved Kelbg potential for correlated Coulomb systems
Quantum Monte Carlo methods
 Quantum Monte Carlo methods Lubos Mitas North Carolina State University Urbana, August 2006 Lubos_Mitas@ncsu.edu H= 1 2 i i 2 i, I Z I r ii i j 1 r ij E ion ion H r 1, r 2,... =E r 1, r 2,... - ground
Quantum Monte Carlo methods Lubos Mitas North Carolina State University Urbana, August 2006 Lubos_Mitas@ncsu.edu H= 1 2 i i 2 i, I Z I r ii i j 1 r ij E ion ion H r 1, r 2,... =E r 1, r 2,... - ground
Department of Physics and NCSA University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign, IL, 61801, USA
 UNDERSTANDING ELECTRONIC WAVE FUNCTIONS D. M. Ceperley Department of Physics and NCSA University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign, IL, 61801, USA INTRODUCTION In this article I discuss some aspects of what
UNDERSTANDING ELECTRONIC WAVE FUNCTIONS D. M. Ceperley Department of Physics and NCSA University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign, IL, 61801, USA INTRODUCTION In this article I discuss some aspects of what
Squeezing and superposing many-body states of Bose gases in confining potentials
 Squeezing and superposing many-body states of Bose gases in confining potentials K. B. Whaley Department of Chemistry, Kenneth S. Pitzer Center for Theoretical Chemistry, Berkeley Quantum Information and
Squeezing and superposing many-body states of Bose gases in confining potentials K. B. Whaley Department of Chemistry, Kenneth S. Pitzer Center for Theoretical Chemistry, Berkeley Quantum Information and
Pseudopotential Theory of Semiconductor Quantum Dots
 phys. stat. sol. (b) 224, No. 3, 727 734 (2001) Pseudopotential Theory of Semiconductor Quantum Dots Alex Zunger National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, CO 80401, USA (Received July 31, 2000; accepted
phys. stat. sol. (b) 224, No. 3, 727 734 (2001) Pseudopotential Theory of Semiconductor Quantum Dots Alex Zunger National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, CO 80401, USA (Received July 31, 2000; accepted
Fractional charge in the fractional quantum hall system
 Fractional charge in the fractional quantum hall system Ting-Pong Choy 1, 1 Department of Physics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 1110 W. Green St., Urbana, IL 61801-3080, USA (Dated: May
Fractional charge in the fractional quantum hall system Ting-Pong Choy 1, 1 Department of Physics, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 1110 W. Green St., Urbana, IL 61801-3080, USA (Dated: May
