Measuring freeze-out parameters on the Bielefeld GPU cluster
|
|
|
- Tamsin Higgins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Measuring freeze-out parameters on the Bielefeld GPU cluster
2 Outline Fluctuations and the QCD phase diagram Fluctuations from Lattice QCD The Bielefeld hybrid GPU cluster Freeze-out conditions from QCD BNL-Bielefeld Collaboration: A. Bazavov, H.-T. Ding, P. Hegde, O. Kaczmarek, F. Karsch, E. Laermann, S. Mukherjee, P. Petreczky, C. Schmidt, D. Smith, W. Soeldner, M. Wagner
3 Fluctuations and the QCD phase diagram different QCD phases characterized by chiral symmetry confinement aspects possible critical end-point T [GeV] 0.16 critical end-point QCD Figure from C. Schmidt quark-gluon-plasma 2nd order phase transition hadron gas divergent correlation length divergent susceptibility 0 vacuum nuclear matter neutron stars chemical potential µ B
4 Fluctuations from Lattice QCD expansion of the pressure in p 1 T 4 = X i,j,k 1 i!j!k! BQS ijk µb T i µq T j µs T k B,Q,S conserved charges (baryon number, electric charge, strangeness) generalized susceptibilities BQS ijk = 1 B /T Q /T S /T ) Z(T,µ) µ=0 related to cumulants of net charge fluctuations, e.g. VT 3 B 2 = h( N B ) 2 i = N 2 B 2N B hn B i + hn B i 2
5 Calculation of susceptibilities from Lattice QCD µ-dependence is contained in the fermion determinant Z Z = DU(det M(µ)) N f /4 exp( S g ), calculation of susceptibilities requires µ-derivatives of fermion 2 * nf ln Z (ln det det 2 = 2 + formulate all operator in terms of traces over space-time, color (and spin) evaluate using noisy estimators ensemble average large number of configurations (~3000 for each beta)
6 Noisy estimators traces required for 2 (ln det 2 =Tr =Tr. M 2 noisy estimators large number of random vectors η (~1500 / n 1 M n M M n...m 1 1 NX = n 1 M 2 N!1 k n M M n...m 1 2 k dominant operation: fermion matrix inversion (~ 99%) Tr k=1
7 Configuration generation sequential process use RHMC algorithm to evaluate the system in simulation time = P two dominant parts of the calculation (90% of the runtime) fermion force ~50% for improved actions (HISQ) fermion matrix inversion ~90% for standard action
8 staggered Fermion Matrix (Dslash) Krylov space inversion of fermion matrix dominates runtime sparse Matrix w x = D x,x 0v x 0 = 3X µ=0 n o U x,µ v x+ˆµ U x ˆµ,µ v x ˆµ memory: 8 SU(3) matrices input, 8 color vectors input, 1 color vector output 8 x ( ) + 24 bytes = 792 bytes ( 1584 for double precision) Flops: (CM = complex mult, CA = complex add) 4 x ( 2 x 3 x (3 CM + 2 CA) + 3 CA) + 3 x 3 CA = 570 flops flops / byte ratios: 0.72
9 History of QCD machines in Bielefeld special purpose APE machines optimized low-latency network fast complex a x b + c GFlops (single precision) APE100 APEmille APEnext
10 GPUs as Accelerators typical CPU data performance ~ 150 GFlops bandwidth ~ 30 GB/s power consumption ~ 125W price ~ Euro typical GPU data performance ~ 1 TFlops bandwidth ~ 200 GB/s power consumption ~ 250W price ~ 2000 Euro (Tesla 6 GB) ~ 500 Euro (GTX 3 GB)
11 GPUs are throughput processors Low Latency or High Throughput? Figure from Nvidia CPU Optimized for low-latency access to cached data sets Control logic for out-of-order and speculative execution GPU Optimized for data-parallel, throughput computation Architecture tolerant of memory latency More transistors dedicated to computation
12 The Bielefeld GPU cluster hybrid GPU / CPU cluster inauguration 2/ compute nodes in 14x19 racks 400 GPUs with 1824 GB memory 304 CPUs (1216 cores) with 7296 GB memory 7 storage nodes / 2 head nodes 1.1 million founded with federal and state government funds (~50% for GPUs)
13 Installation
14 Tesla nodes 104 Tesla Nodes (1U) Dual Intel Xeon X GB memory 2 x Nvidia Tesla M2075 (6GB - ECC) 515 Gflops double precision 1030 Gflops single precision 150 GB/s memory bandwidth
15 GTX nodes 48 GTX Nodes (4U) 7ST' Dual Intel Xeon X GB memory 4 x Nvidia GTX 580 (3GB - no ECC) 198 Gflops double precision 1581 Gflops single precision 192 GB/s memory bandwidth
16 Cooling and power consumption power consumption: ~125kW (CPU+GPU) compute nodes in 14 racks: < 10kW / rack cold aisle containment (~ 24 ) GPUs running at ~ 90 / ~ 60 (GTX/Tesla) hot aisle containment (~ 39 ) to prevent heat pollution in data center
17 Stability artificial stress tests tests based on QCD production code Tesla cards with ECC after 1/2 year (total 208 cards) 4 cards with single bit errors (corrected) 2 cards with double bit errors (program aborted) GTX cards (gamer cards) after 1/2 year (total 192 cards) 12 cards with wrong results in tests, 2 died replace faulty cards (also Tesla w/ single bit errors)
18 Bandwidth bound low flops/byte ratio GTX cards are always faster even for double precision calculations linear algebra has an even worse flop / byte ratio flops are free - but registers are limited (more later) Dslash efficiency Tesla: 0.72 flop/byte * 144 Gbytes/s = 103 Gflops (10% peak) memory bandwidth is the relevant performance indicator general issue for supercomputing Card GFlops (32 bit) GFlops (32 bit) GBytes/s Flops / byte Flops/ byte GTX Tesla M
19 optimizing memory access use coalesced memory layout: structure of arrays (SoA) instead of AoS one can reconstruct a SU(3) matrix also from 8 or 12 floats improved actions result in matrices that are no longer SU(3): must load 18 floats exploit possibility of texture access allows to get near 100% of the bandwidth ECC hurts (naive 12.5%, real world ~ %) do more work with less bytes: mixed precision inverters
20 optimizing memory access use coalesced memory layout: structure of arrays (SoA) instead of AoS one can reconstruct a SU(3) matrix also from 8 or 12 floats improved actions result in matrices that are no longer SU(3): single precision must load 18 floats 100 exploit possibility of texture access allows to get near 100% of the bandwidth 20 ECC hurts (naive 12.5%, real world ~ %) Gflop/s HISQ inverter on single GPU GTX580 (3GB) M2075 (6GB) double precision lattice size do more work with less bytes: mixed precision inverters
21 Registers... improved fermion action require sum over products of up to 7 SU(3) matrices SU(3) Matrix: 18 / 36 registers Fermi architecture: 63 registers (4 byte) / thread optimize SU(3) *= SU(3) operation for register usage spilling causes significant performance drop for bandwidth bound kernels however: spilling is often better than shared memory 48kB L1 cache precomputed products can help but must be stored somewhere
22 Impact of the cluster on our results 4 B Evolution from 2/2012 to 9/2012, Nt=8 4 Q T [MeV] T [MeV]
23 Impact of the cluster on our results 4 B Evolution from 2/2012 to 9/2012, Nt=8 4 Q T [MeV] T [MeV]
24 Status of HISQ lattice data B 2 B 4 T c =154(9) MeV N =6 8 BNL-Bielefeld preliminary B T [MeV] Q N = T c =154(9) MeV Q BNL-Bielefeld 0.25 preliminary Q T [MeV]
25 Freeze-out curve from heavy-ion collision cf. Talks by Gelis, Rischke, Klein-Bösing initial conditions T [GeV] RHIC@BNL Figure from C. Schmidt quark-gluon-plasma cf. Talk by Petreczky Lattice EoS 0.16 FAIR@GSI NICA@JINR evolution freeze-out hadron gas Ratio Hadron abundances from HRG model s NN =130 GeV freeze-out 0 vacuum nuclear matter chemical potential neutron stars µ B 10-2 Data Model 10-3 π - π + T=165.5, µ b =38 MeV - K K + p p Λ Λ Ξ Ξ Ω Ω K + π + - K π - p π - Λ π - Ξ π - Ω π - φ K - * K K - T f ( p s),µ f ( p s)
26 Freeze-out curve from heavy-ion collision cf. Talks by Gelis, Rischke, Klein-Bösing initial conditions T [GeV] RHIC@BNL Figure from C. Schmidt quark-gluon-plasma cf. Talk by Petreczky Lattice EoS 0.16 FAIR@GSI NICA@JINR evolution freeze-out hadron gas Fluctuations from Lattice QCD B 2 B 4 T c =154(9) MeV N =6 8 BNL-Bielefeld preliminary B T [MeV] Q N = T c =154(9) MeV Q BNL-Bielefeld 0.25 preliminary Q T [MeV] freeze-out 0 vacuum nuclear matter T f ( p s),µ f ( p s) chemical potential neutron stars µ B
27 Constraining isospin and strangeness Assume: homogenous model in thermal equilibrium Exploit: initial conditions strangeness neutrality: hn S i =0 isospin assymetry: hn Q i = r hn B i expand in powers of solve for µ Q,µ S µ B,µ Q,µ S µ Q (T,µ B )=q 1 (T )µ B + q 3 (T )µ 3 B µ S (T,µ B )=s 1 (T )µ B + s 3 (T )µ 3 B LO NLO µ f Q µ Q(T f,µ f B ) µ f S µ S(T f,µ f B ) two independent parameter remain: T f,µ f B
28 Constraining isospin and strangeness µ Q (T,µ B )=q 1 (T )µ B + q 3 (T )µ 3 B µ S (T,µ B )=s 1 (T )µ B + s 3 (T )µ 3 B q 1 HRG LO N =6 N =8 N =12 free s 1 HRG LO N =6 N =8 N =12 free q 3 /q 1 NLO HRG T [MeV] free s 3 /s NLO free T [MeV] LO: continuum extrapolated based on Nt=6,8,12 BNL-BI, arxiv: NLO: small cut-off dependence, continuum estimate based on Nt=6,8 HRG NLO corrections <10% for µ B /T. 1.3
29 Isospin and strangeness constrained BNL-BI, arxiv: µ Q /µ B T = 160 MeV T = 150 MeV T = 170 MeV HRG µq(t,µb)/µb bands for 3 temperatures comparison with HRG (lines) µ S /µ B T = 170 MeV T = 160 MeV T = 150 MeV HRG µ B [MeV] µs(t,µb)/µb deviations from HRG < 5-15 %
30 Pinning down the freeze-out parameters need two experimental ratios to determine (T f,µ f B ) baryon number fluctuations are not directly accessible in experiments we consider ratios of electric charge fluctuations M Q ( p s) 2 Q (p s) = hn Q Qi h( N Q ) 2 i = 1 (T,µ B) Q 2 (T,µ B) = RQ,1 12 µ B + R Q,3 12 µ3 B + = RQ 12 (T,µ B) LO linear in, fixes µ B µ f B M : mean : variance S : skewness S Q ( p s) 3 Q (p s) M Q ( p s) = ( NQ ) 3 = hn Q i Q 3 (T,µ B) Q 1 (T,µ B) = RQ, RQ,2 31 µ2 B + = RQ 31 (T,µ B) LO independent of µ B, fixes T f
31 Determination of freeze-out temperature 3.0 R Q 31 (T,µ B)=R Q, RQ,2 31 µ2 B Q R 31 small cutoff effects small NLO corrections (<10%) for μ/t < HRG µ B /T=1 µ B /T=0 N =6 N =8 S Q 3 Q /M Q T f [MeV ] 1.0 & free T [MeV] & 165 Bands: Continuum estimate
32 Determination of freeze-out chemical potential R Q 12 (T,µ B)=R Q,1 12 µ B + R Q,3 12 µ3 B Q,1 R 12 HRG LO N =6 N =8 N =12 free small cutoff effects at NLO small NLO corrections (<10%) for μ/t < Q,3 Q,1 R 12 /R12 NLO 0.04 HRG T [MeV] free Bands: LO Continuum extrapolation NLO Continuum estimate
33 Determination of freeze-out chemical potential R Q 12 (T,µ B)=R Q,1 12 µ B + R Q,3 12 µ3 B Q R µ B /T HRG Bands: LO Continuum extrapolation NLO Continuum estimate T = 160 MeV T = 170 MeV T = 150 MeV small cutoff effects at NLO small NLO corrections (<10%) for μ/t < 1.3 M Q / 2 Q µ f B /T f (for T f 160 MeV )
34 Summary Fluctuations of conserved charges with HISQ action Determination of freeze-out parameters from Lattice QCD eliminate the need of thermal model experimentally measured ratios of fluctuations can be translated to freeze-out parameters Bielefeld Hybrid-GPU Cluster 400 GPUs, combination of professional Tesla and GTX gamer cards challenges for simulating lattice QCDs
The strange degrees of freedom in QCD at high temperature. Christian Schmidt
 The strange degrees of freedom in QCD at high temperature Christian Schmidt Christian Schmidt LAT 213 1 Abstract We use up to fourth order cumulants of net strangeness fluctuations and their correlations
The strange degrees of freedom in QCD at high temperature Christian Schmidt Christian Schmidt LAT 213 1 Abstract We use up to fourth order cumulants of net strangeness fluctuations and their correlations
Conserved Charge Fluctuations and Correlations from Lattice QCD and the Beam Energy Scan
 Conserved Charge Fluctuations and Correlations from Lattice QCD and the Beam Energy Scan Frithjof Karsch Brookhaven National Laboratory & Bielefeld University Bielefeld-BNL-CCNU Collaboration A. Bazavov,
Conserved Charge Fluctuations and Correlations from Lattice QCD and the Beam Energy Scan Frithjof Karsch Brookhaven National Laboratory & Bielefeld University Bielefeld-BNL-CCNU Collaboration A. Bazavov,
arxiv: v1 [cs.dc] 4 Sep 2014
![arxiv: v1 [cs.dc] 4 Sep 2014 arxiv: v1 [cs.dc] 4 Sep 2014](/thumbs/93/114366338.jpg) and NVIDIA R GPUs arxiv:1409.1510v1 [cs.dc] 4 Sep 2014 O. Kaczmarek, C. Schmidt and P. Steinbrecher Fakultät für Physik, Universität Bielefeld, D-33615 Bielefeld, Germany E-mail: okacz, schmidt, p.steinbrecher@physik.uni-bielefeld.de
and NVIDIA R GPUs arxiv:1409.1510v1 [cs.dc] 4 Sep 2014 O. Kaczmarek, C. Schmidt and P. Steinbrecher Fakultät für Physik, Universität Bielefeld, D-33615 Bielefeld, Germany E-mail: okacz, schmidt, p.steinbrecher@physik.uni-bielefeld.de
Fluctuations of conserved charges and freeze-out conditions in heavy ion collisions
 Probing the Extremes of Matter with Heavy Ions - Erice, 34th Course Fluctuations of conserved charges and freeze-out conditions in heavy ion collisions Frithjof Karsch Brookhaven National Laboratory &
Probing the Extremes of Matter with Heavy Ions - Erice, 34th Course Fluctuations of conserved charges and freeze-out conditions in heavy ion collisions Frithjof Karsch Brookhaven National Laboratory &
QCD thermodynamics OUTLINE:
 QCD thermodynamics Frithjof Karsch, BNL OUTLINE: Equation of state and transition temperature QCD phase diagram close to the chiral limit Charge fluctuations and the RHIC search for the critical point
QCD thermodynamics Frithjof Karsch, BNL OUTLINE: Equation of state and transition temperature QCD phase diagram close to the chiral limit Charge fluctuations and the RHIC search for the critical point
QCD thermodynamics. Frithjof Karsch, BNL/Bielefeld
 QCD thermodynamics Frithjof Karsch, BNL/Bielefeld Key Questions NSAC Long Range Plan 2007 What are the phases of strongly interacting matter, and what role do they play in the cosmos? What does QCD predict
QCD thermodynamics Frithjof Karsch, BNL/Bielefeld Key Questions NSAC Long Range Plan 2007 What are the phases of strongly interacting matter, and what role do they play in the cosmos? What does QCD predict
Deconfinement at high temperatures and moderately high baryon densities Péter Petreczky
 Deconfinement at high temperatures and moderately high baryon densities Péter Petreczky What is the limiting temperature on hadronic matter? What is the nature of the deconfined matter? In this talk: Chiral
Deconfinement at high temperatures and moderately high baryon densities Péter Petreczky What is the limiting temperature on hadronic matter? What is the nature of the deconfined matter? In this talk: Chiral
Lattice QCD at non-zero temperature and density
 Lattice QCD at non-zero temperature and density Frithjof Karsch Bielefeld University & Brookhaven National Laboratory QCD in a nutshell, non-perturbative physics, lattice-regularized QCD, Monte Carlo simulations
Lattice QCD at non-zero temperature and density Frithjof Karsch Bielefeld University & Brookhaven National Laboratory QCD in a nutshell, non-perturbative physics, lattice-regularized QCD, Monte Carlo simulations
Efficient implementation of the overlap operator on multi-gpus
 Efficient implementation of the overlap operator on multi-gpus Andrei Alexandru Mike Lujan, Craig Pelissier, Ben Gamari, Frank Lee SAAHPC 2011 - University of Tennessee Outline Motivation Overlap operator
Efficient implementation of the overlap operator on multi-gpus Andrei Alexandru Mike Lujan, Craig Pelissier, Ben Gamari, Frank Lee SAAHPC 2011 - University of Tennessee Outline Motivation Overlap operator
arxiv: v1 [hep-lat] 19 Feb 2012
![arxiv: v1 [hep-lat] 19 Feb 2012 arxiv: v1 [hep-lat] 19 Feb 2012](/thumbs/92/108755397.jpg) Cent. Eur. J. Phys. -5 Author version Central European Journal of Physics Determination of Freeze-out Conditions from Lattice QCD Calculations Review Article arxiv:.473v [hep-lat] 9 Feb Frithjof Karsch,
Cent. Eur. J. Phys. -5 Author version Central European Journal of Physics Determination of Freeze-out Conditions from Lattice QCD Calculations Review Article arxiv:.473v [hep-lat] 9 Feb Frithjof Karsch,
The QCD Equation of State at μ B > 0 from Lattice QCD
 The QCD Equation of State at μ B > 0 from Lattice QCD Hiroshi Ohno (BNL-Bielefeld-CCNU Collaboration) CCS, University of Tsukuba Brookhaven National Laboratory arxiv:1701.04325 [hep-lat] 7 th Workshop
The QCD Equation of State at μ B > 0 from Lattice QCD Hiroshi Ohno (BNL-Bielefeld-CCNU Collaboration) CCS, University of Tsukuba Brookhaven National Laboratory arxiv:1701.04325 [hep-lat] 7 th Workshop
Accelerating Quantum Chromodynamics Calculations with GPUs
 Accelerating Quantum Chromodynamics Calculations with GPUs Guochun Shi, Steven Gottlieb, Aaron Torok, Volodymyr Kindratenko NCSA & Indiana University National Center for Supercomputing Applications University
Accelerating Quantum Chromodynamics Calculations with GPUs Guochun Shi, Steven Gottlieb, Aaron Torok, Volodymyr Kindratenko NCSA & Indiana University National Center for Supercomputing Applications University
Insights (?) from lattice QCD at finite baryo-chemical potential (title given to me)
 Exploring the QCD Phase Diagram through Energy Scans Insights (?) from lattice QCD at finite baryo-chemical potential (title given to me) Frithjof Karsch Bielefeld University & Brookhaven National Laboratory
Exploring the QCD Phase Diagram through Energy Scans Insights (?) from lattice QCD at finite baryo-chemical potential (title given to me) Frithjof Karsch Bielefeld University & Brookhaven National Laboratory
Exploring the QCD phase diagram with conserved charge fluctuations
 New Frontiers in QCD 2013 Exploring the QCD phase diagram with conserved charge fluctuations Frithjof Karsch Brookhaven National Laboratory & Bielefeld University OUTLINE conserved charge fluctuations
New Frontiers in QCD 2013 Exploring the QCD phase diagram with conserved charge fluctuations Frithjof Karsch Brookhaven National Laboratory & Bielefeld University OUTLINE conserved charge fluctuations
Phase diagram and EoS from a Taylor expansion of the pressure
 he XXVI International Symposium on Lattice Field heory (Lattice 28), Williamsburg, Virginia, USA, 28 July 14 19. Phase diagram and EoS from a aylor expansion of the pressure Christian Schmidt Universität
he XXVI International Symposium on Lattice Field heory (Lattice 28), Williamsburg, Virginia, USA, 28 July 14 19. Phase diagram and EoS from a aylor expansion of the pressure Christian Schmidt Universität
Lattice based Equation(s) of State and its (their) effect(s) on the hydrodynamical evolution
 Lattice based Equation(s) of State and its (their) effect(s) on the hydrodynamical evolution Pasi Huovinen J. W. Goethe Universität, Frankfurt Quantifying the properties of Hot QCD matter June 11, 1, Institute
Lattice based Equation(s) of State and its (their) effect(s) on the hydrodynamical evolution Pasi Huovinen J. W. Goethe Universität, Frankfurt Quantifying the properties of Hot QCD matter June 11, 1, Institute
Fluctuations and QCD phase structure
 Fluctuations and QCD phase structure Guo-yun Shao ( 邵国运 ) Xi an Jiaotong University Outline: Motivation Methods to describe fluctuations of conserved charges in heavy-ion collisions Numerical results and
Fluctuations and QCD phase structure Guo-yun Shao ( 邵国运 ) Xi an Jiaotong University Outline: Motivation Methods to describe fluctuations of conserved charges in heavy-ion collisions Numerical results and
QCD Thermodynamics Péter Petreczky
 QCD Thermodynamics Péter Petreczky What is deconfinement in QCD? What is the nature of the deconfined matter? Tools: screening of color charges, EoS, fluctuation of conserved quantum numbers QGP: state
QCD Thermodynamics Péter Petreczky What is deconfinement in QCD? What is the nature of the deconfined matter? Tools: screening of color charges, EoS, fluctuation of conserved quantum numbers QGP: state
Fluctuations of conserved charges and freeze-out conditions in heavy ion collisions
 Freeze-out parameters Fluctuations of conserved charges and freeze-out conditions in heavy ion collisions Claudia Ratti University of Houston, Texas (USA) S. Borsanyi, Z. Fodor, S. Katz, S. Krieg, C. R.,
Freeze-out parameters Fluctuations of conserved charges and freeze-out conditions in heavy ion collisions Claudia Ratti University of Houston, Texas (USA) S. Borsanyi, Z. Fodor, S. Katz, S. Krieg, C. R.,
Lattice QCD Thermodynamics at zero and nonzero baryon density
 IN Program 10-2a: Quantifying the Poperties of Hot QCD Matter Institute for Nuclear heory, July 16, 2010, Seattle, WA, USA Lattice QCD hermodynamics at zero and nonzero baryon density Christian Schmidt
IN Program 10-2a: Quantifying the Poperties of Hot QCD Matter Institute for Nuclear heory, July 16, 2010, Seattle, WA, USA Lattice QCD hermodynamics at zero and nonzero baryon density Christian Schmidt
STRANGENESS NEUTRALITY AND THE QCD PHASE STRUCTURE
 STRANGENESS NEUTRALITY AND THE QCD PHASE STRUCTURE Fabian Rennecke Brookhaven National Laboratory [Fu, Pawlowski, FR, hep-ph/1808.00410] [Fu, Pawlowski, FR, hep-ph/1809.01594] NUCLEAR PHYSICS COLLOQUIUM
STRANGENESS NEUTRALITY AND THE QCD PHASE STRUCTURE Fabian Rennecke Brookhaven National Laboratory [Fu, Pawlowski, FR, hep-ph/1808.00410] [Fu, Pawlowski, FR, hep-ph/1809.01594] NUCLEAR PHYSICS COLLOQUIUM
Equation of state. Pasi Huovinen Uniwersytet Wroc lawski. Collective Flows and Hydrodynamics in High Energy Nuclear Collisions
 Equation of state Pasi Huovinen Uniwersytet Wroc lawski Collective Flows and Hydrodynamics in High Energy Nuclear Collisions Dec 14, 2016, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China The
Equation of state Pasi Huovinen Uniwersytet Wroc lawski Collective Flows and Hydrodynamics in High Energy Nuclear Collisions Dec 14, 2016, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China The
Probing QCD Phase Diagram in Heavy Ion Collisions
 LQCD LHC Probing QCD Phase Diagram in Heavy Ion Collisions QCD Phase Diagram from LQCD Fluctuations of conserved charges as probe of thermalization and QCD phase boundary Linking LQCD results to HIC data
LQCD LHC Probing QCD Phase Diagram in Heavy Ion Collisions QCD Phase Diagram from LQCD Fluctuations of conserved charges as probe of thermalization and QCD phase boundary Linking LQCD results to HIC data
Bulk Thermodynamics: What do we (want to) know?
 Bulk Thermodynamics: What do we (want to) know? µ = : properties of transition in, ( + 1)-flavor QCD: crossover or phase transition, deconfinement vs. chiral symmetry restoration, universality,... T c,
Bulk Thermodynamics: What do we (want to) know? µ = : properties of transition in, ( + 1)-flavor QCD: crossover or phase transition, deconfinement vs. chiral symmetry restoration, universality,... T c,
QCD matter with isospin-asymmetry. Gergely Endrődi. Goethe University of Frankfurt in collaboration with Bastian Brandt, Sebastian Schmalzbauer
 QCD matter with isospin-asymmetry Gergely Endrődi Goethe University of Frankfurt in collaboration with Bastian Brandt, Sebastian Schmalzbauer SIGN 2017 22. March 2017 Outline introduction: QCD with isospin
QCD matter with isospin-asymmetry Gergely Endrődi Goethe University of Frankfurt in collaboration with Bastian Brandt, Sebastian Schmalzbauer SIGN 2017 22. March 2017 Outline introduction: QCD with isospin
Thermodynamics of (2+1)-flavor QCD from the lattice
 INT Seattle, December 7, 2006 Thermodynamics of (2+1)-flavor QCD from the lattice Christian Schmidt for the RBC-Bielefeld Collaboration --- results from QCDOC --RIKEN BNL Saumen Datta Frithjof Karsch Chulwoo
INT Seattle, December 7, 2006 Thermodynamics of (2+1)-flavor QCD from the lattice Christian Schmidt for the RBC-Bielefeld Collaboration --- results from QCDOC --RIKEN BNL Saumen Datta Frithjof Karsch Chulwoo
Fluctuations of conserved charges and freeze-out conditions in heavy ion collisions
 Fluctuations of conserved charges and freeze-out conditions in heavy ion collisions Claudia Ratti Università degli Studi di Torino, INFN, Sezione di Torino and University of Houston, Texas S. Borsanyi,
Fluctuations of conserved charges and freeze-out conditions in heavy ion collisions Claudia Ratti Università degli Studi di Torino, INFN, Sezione di Torino and University of Houston, Texas S. Borsanyi,
Claude Tadonki. MINES ParisTech PSL Research University Centre de Recherche Informatique
 Claude Tadonki MINES ParisTech PSL Research University Centre de Recherche Informatique claude.tadonki@mines-paristech.fr Monthly CRI Seminar MINES ParisTech - CRI June 06, 2016, Fontainebleau (France)
Claude Tadonki MINES ParisTech PSL Research University Centre de Recherche Informatique claude.tadonki@mines-paristech.fr Monthly CRI Seminar MINES ParisTech - CRI June 06, 2016, Fontainebleau (France)
Role of van der Waals interactions in hadron systems: from nuclear matter to lattice QCD
 Role of van der Waals interactions in hadron systems: from nuclear matter to lattice QCD Volodymyr Vovchenko a,b,c a Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies b Institute for Theoretical Physics, University
Role of van der Waals interactions in hadron systems: from nuclear matter to lattice QCD Volodymyr Vovchenko a,b,c a Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies b Institute for Theoretical Physics, University
Case Study: Quantum Chromodynamics
 Case Study: Quantum Chromodynamics Michael Clark Harvard University with R. Babich, K. Barros, R. Brower, J. Chen and C. Rebbi Outline Primer to QCD QCD on a GPU Mixed Precision Solvers Multigrid solver
Case Study: Quantum Chromodynamics Michael Clark Harvard University with R. Babich, K. Barros, R. Brower, J. Chen and C. Rebbi Outline Primer to QCD QCD on a GPU Mixed Precision Solvers Multigrid solver
High Temperature/Density QCD
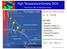 High Temperature/Density QCD Frithjof Karsch, BNL and Bielefeld University Temperature ~17 MeV Early Universe Future LHC Experiments Crossover Current RHIC Experiments RHIC Energy Scan Critical Point 1
High Temperature/Density QCD Frithjof Karsch, BNL and Bielefeld University Temperature ~17 MeV Early Universe Future LHC Experiments Crossover Current RHIC Experiments RHIC Energy Scan Critical Point 1
Lattice QCD at non-zero temperature and density
 Lattice QCD at non-zero temperature and density Frithjof Karsch Bielefeld University & Brookhaven National Laboratory QCD in a nutshell, non-perturbative physics, lattice-regularized QCD, Monte Carlo simulations
Lattice QCD at non-zero temperature and density Frithjof Karsch Bielefeld University & Brookhaven National Laboratory QCD in a nutshell, non-perturbative physics, lattice-regularized QCD, Monte Carlo simulations
Fluctuations of Conserved Charges
 Fluctuations of Conserved Charges Theory, Experiment, and Lattice Masakiyo Kitazawa (Osaka U.) KEK, 2014/Jan./20 QCD @ nonzero T Theory (Motivation) QCD @ nonzero T Lattice Heavy Ion Collisions QCD @ nonzero
Fluctuations of Conserved Charges Theory, Experiment, and Lattice Masakiyo Kitazawa (Osaka U.) KEK, 2014/Jan./20 QCD @ nonzero T Theory (Motivation) QCD @ nonzero T Lattice Heavy Ion Collisions QCD @ nonzero
arxiv: v1 [hep-lat] 7 Oct 2010
![arxiv: v1 [hep-lat] 7 Oct 2010 arxiv: v1 [hep-lat] 7 Oct 2010](/thumbs/79/80346009.jpg) arxiv:.486v [hep-lat] 7 Oct 2 Nuno Cardoso CFTP, Instituto Superior Técnico E-mail: nunocardoso@cftp.ist.utl.pt Pedro Bicudo CFTP, Instituto Superior Técnico E-mail: bicudo@ist.utl.pt We discuss the CUDA
arxiv:.486v [hep-lat] 7 Oct 2 Nuno Cardoso CFTP, Instituto Superior Técnico E-mail: nunocardoso@cftp.ist.utl.pt Pedro Bicudo CFTP, Instituto Superior Técnico E-mail: bicudo@ist.utl.pt We discuss the CUDA
Deconfinement and Polyakov loop in 2+1 flavor QCD
 Deconfinement and Polyakov loop in 2+ flavor QCD J. H. Weber in collaboration with A. Bazavov 2, N. Brambilla, H.T. Ding 3, P. Petreczky 4, A. Vairo and H.P. Schadler 5 Physik Department, Technische Universität
Deconfinement and Polyakov loop in 2+ flavor QCD J. H. Weber in collaboration with A. Bazavov 2, N. Brambilla, H.T. Ding 3, P. Petreczky 4, A. Vairo and H.P. Schadler 5 Physik Department, Technische Universität
Lattice QCD based equation of state at finite baryon density
 Lattice QCD based equation of state at finite baryon density Pasi Huovinen J. W. Goethe Universität & Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies Hydrodynamics for Strongly Coupled Fluids May 12, 214, ECT*,
Lattice QCD based equation of state at finite baryon density Pasi Huovinen J. W. Goethe Universität & Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies Hydrodynamics for Strongly Coupled Fluids May 12, 214, ECT*,
The Beam Energy Scan at RHIC
 2013 ICNT Program @ FRIB, MSU July 31, 2013 The Beam Energy Scan at RHIC Jinfeng Liao Indiana University, Physics Dept. & CEEM RIKEN BNL Research Center 1 Outline Brief Intro: High Energy Heavy Ion Collisions
2013 ICNT Program @ FRIB, MSU July 31, 2013 The Beam Energy Scan at RHIC Jinfeng Liao Indiana University, Physics Dept. & CEEM RIKEN BNL Research Center 1 Outline Brief Intro: High Energy Heavy Ion Collisions
LQCD at non-zero temperature : strongly interacting matter at high temperatures and densities Péter Petreczky
 LQCD at non-zero temperature : strongly interacting matter at high temperatures and densities Péter Petreczky QCD and hot and dense matter Lattice formulation of QCD Deconfinement transition in QCD : EoS
LQCD at non-zero temperature : strongly interacting matter at high temperatures and densities Péter Petreczky QCD and hot and dense matter Lattice formulation of QCD Deconfinement transition in QCD : EoS
Lattice QCD. QCD 2002, I. I. T. Kanpur, November 19, 2002 R. V. Gavai Top 1
 Lattice QCD QCD 2002, I. I. T. Kanpur, November 19, 2002 R. V. Gavai Top 1 Lattice QCD : Some Topics QCD 2002, I. I. T. Kanpur, November 19, 2002 R. V. Gavai Top 1 Lattice QCD : Some Topics Basic Lattice
Lattice QCD QCD 2002, I. I. T. Kanpur, November 19, 2002 R. V. Gavai Top 1 Lattice QCD : Some Topics QCD 2002, I. I. T. Kanpur, November 19, 2002 R. V. Gavai Top 1 Lattice QCD : Some Topics Basic Lattice
F. Karsch for USQCD, LQCD II p. 1/27. Lattice QCD at High Temperature and Density. Frithjof Karsch for USQCD Brookhaven National Laboratory
 F. Karsch for USQCD, LQCD II p. 1/27 Lattice QCD at High Temperature and Density Frithjof Karsch for USQCD Brookhaven National Laboratory F. Karsch for USQCD, LQCD II p. 2/27 Towards A New State of Matter
F. Karsch for USQCD, LQCD II p. 1/27 Lattice QCD at High Temperature and Density Frithjof Karsch for USQCD Brookhaven National Laboratory F. Karsch for USQCD, LQCD II p. 2/27 Towards A New State of Matter
Influence of Van der Waals interactions between hadrons on observables from heavy-ion collisions and lattice QCD
 Influence of Van der Waals interactions between hadrons on observables from heavy-ion collisions and lattice QCD Volodymyr Vovchenko In collaboration with P. Alba, M. Gorenstein, H. Stoecker based on arxiv:69.975
Influence of Van der Waals interactions between hadrons on observables from heavy-ion collisions and lattice QCD Volodymyr Vovchenko In collaboration with P. Alba, M. Gorenstein, H. Stoecker based on arxiv:69.975
from Taylor expansion at non-zero density From Lattices to Stars INT, University of Washington, Seattle, 28. April 2004
 The chiral critical point in 3 flavor QCD from Taylor expansion at non-zero density From Lattices to Stars INT, University of Washington, Seattle, 28. April 2004 Christian Schmidt Universität Wuppertal
The chiral critical point in 3 flavor QCD from Taylor expansion at non-zero density From Lattices to Stars INT, University of Washington, Seattle, 28. April 2004 Christian Schmidt Universität Wuppertal
Weakly coupled QGP? Péter Petreczky
 Weakly coupled QGP? Péter Petreczky QGP is expected to be strongly coupled around T c : how does this features manifest itself in terms of different quantities, how do we observe it on lattice? QGP: state
Weakly coupled QGP? Péter Petreczky QGP is expected to be strongly coupled around T c : how does this features manifest itself in terms of different quantities, how do we observe it on lattice? QGP: state
Lattice Quantum Chromodynamics on the MIC architectures
 Lattice Quantum Chromodynamics on the MIC architectures Piotr Korcyl Universität Regensburg Intel MIC Programming Workshop @ LRZ 28 June 2017 Piotr Korcyl Lattice Quantum Chromodynamics on the MIC 1/ 25
Lattice Quantum Chromodynamics on the MIC architectures Piotr Korcyl Universität Regensburg Intel MIC Programming Workshop @ LRZ 28 June 2017 Piotr Korcyl Lattice Quantum Chromodynamics on the MIC 1/ 25
Phase diagram of QCD: the critical point
 Phase diagram of QCD: the critical point p. 1/1 Phase diagram of QCD: the critical point M. Stephanov U. of Illinois at Chicago Phase diagram of QCD: the critical point p. 2/1 Phase Diagram of QCD Basic
Phase diagram of QCD: the critical point p. 1/1 Phase diagram of QCD: the critical point M. Stephanov U. of Illinois at Chicago Phase diagram of QCD: the critical point p. 2/1 Phase Diagram of QCD Basic
Tuning And Understanding MILC Performance In Cray XK6 GPU Clusters. Mike Showerman, Guochun Shi Steven Gottlieb
 Tuning And Understanding MILC Performance In Cray XK6 GPU Clusters Mike Showerman, Guochun Shi Steven Gottlieb Outline Background Lattice QCD and MILC GPU and Cray XK6 node architecture Implementation
Tuning And Understanding MILC Performance In Cray XK6 GPU Clusters Mike Showerman, Guochun Shi Steven Gottlieb Outline Background Lattice QCD and MILC GPU and Cray XK6 node architecture Implementation
Baryon Number Fluctuations in Energy Scan Program at RHIC
 Baryon Number Fluctuations in Energy Scan Program at RHIC Masakiyo Kitazawa (Osaka U.) MK, Asakawa, arxiv:1107.2755 (to appear in PRC) HIRSCHEGG2012, 18, Jan, 2012, Hirschegg Energy Scan Program @ RHIC
Baryon Number Fluctuations in Energy Scan Program at RHIC Masakiyo Kitazawa (Osaka U.) MK, Asakawa, arxiv:1107.2755 (to appear in PRC) HIRSCHEGG2012, 18, Jan, 2012, Hirschegg Energy Scan Program @ RHIC
The QCD phase diagram from the lattice
 The QCD phase diagram from the lattice Sourendu Gupta ILGTI: TIFR ICPAGQP Student Day Doan Paula, Goa December 5, 2010 Zero baryon density Background Exact SU(2) flavour symmetry Exact SU(3) flavour symmetry
The QCD phase diagram from the lattice Sourendu Gupta ILGTI: TIFR ICPAGQP Student Day Doan Paula, Goa December 5, 2010 Zero baryon density Background Exact SU(2) flavour symmetry Exact SU(3) flavour symmetry
The QCD phase diagram from the lattice
 The QCD phase diagram from the lattice Sourendu Gupta ILGTI: TIFR CBM Meeting VECC Kolkata July 31, 2010 Zero baryon density Background Exact SU(2) flavour symmetry Exact SU(3) flavour symmetry Broken
The QCD phase diagram from the lattice Sourendu Gupta ILGTI: TIFR CBM Meeting VECC Kolkata July 31, 2010 Zero baryon density Background Exact SU(2) flavour symmetry Exact SU(3) flavour symmetry Broken
The critical end point of QCD: lattice and experiment
 The critical end point of QCD: lattice and experiment Sourendu Gupta ILGTI: TIFR Patnitop 2009 January 2, 2010 SG (ILGTI: TIFR) CEP: lattice and experiment Patnitop 09 1 / 28 Outline 1 On lattice 2 In
The critical end point of QCD: lattice and experiment Sourendu Gupta ILGTI: TIFR Patnitop 2009 January 2, 2010 SG (ILGTI: TIFR) CEP: lattice and experiment Patnitop 09 1 / 28 Outline 1 On lattice 2 In
Lattice Boltzmann simulations on heterogeneous CPU-GPU clusters
 Lattice Boltzmann simulations on heterogeneous CPU-GPU clusters H. Köstler 2nd International Symposium Computer Simulations on GPU Freudenstadt, 29.05.2013 1 Contents Motivation walberla software concepts
Lattice Boltzmann simulations on heterogeneous CPU-GPU clusters H. Köstler 2nd International Symposium Computer Simulations on GPU Freudenstadt, 29.05.2013 1 Contents Motivation walberla software concepts
Thermodynamic Signatures of Additional Strange and Charm Baryons
 Thermodynamic Signatures of Additional Strange and Charm Baryons Swagato Mukherjee April 2015, GHP, Baltimore, MD Heavy-ion collisions: a sketch Time initial state QGP, hydro. expansion Tc, μ c freeze-out
Thermodynamic Signatures of Additional Strange and Charm Baryons Swagato Mukherjee April 2015, GHP, Baltimore, MD Heavy-ion collisions: a sketch Time initial state QGP, hydro. expansion Tc, μ c freeze-out
The melting and abundance of open charm hadrons
 The melting and abundance of open charm hadrons A. Bazavov a, H.-T. Ding b, P. Hegde b, O. Kaczmarek c, F. Karsch c,d, E. Laermann c, Y. Maezawa c, Swagato Mukherjee d, H. Ohno d,e, P. Petreczky d, C.
The melting and abundance of open charm hadrons A. Bazavov a, H.-T. Ding b, P. Hegde b, O. Kaczmarek c, F. Karsch c,d, E. Laermann c, Y. Maezawa c, Swagato Mukherjee d, H. Ohno d,e, P. Petreczky d, C.
Complex Saddle Points in Finite Density QCD
 Complex Saddle Points in Finite Density QCD Michael C. Ogilvie Washington University in St. Louis in collaboration with Hiromichi Nishimura (Bielefeld) and Kamal Pangeni (WUSTL) XQCD4 June 9th, 24 Outline
Complex Saddle Points in Finite Density QCD Michael C. Ogilvie Washington University in St. Louis in collaboration with Hiromichi Nishimura (Bielefeld) and Kamal Pangeni (WUSTL) XQCD4 June 9th, 24 Outline
arxiv: v1 [hep-lat] 31 Oct 2015
![arxiv: v1 [hep-lat] 31 Oct 2015 arxiv: v1 [hep-lat] 31 Oct 2015](/thumbs/74/71106348.jpg) and Code Optimization arxiv:1511.00088v1 [hep-lat] 31 Oct 2015 Hwancheol Jeong, Sangbaek Lee, Weonjong Lee, Lattice Gauge Theory Research Center, CTP, and FPRD, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Seoul
and Code Optimization arxiv:1511.00088v1 [hep-lat] 31 Oct 2015 Hwancheol Jeong, Sangbaek Lee, Weonjong Lee, Lattice Gauge Theory Research Center, CTP, and FPRD, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Seoul
2.14 Constraining the Hadronic Spectrum from Lattice QCD Thermodynamics
 2.14 Constraining the Hadronic Spectrum from QCD Thermodynamics Paolo Alba Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies Goethe Universität Frankfurt D-60438 Frankfurt am Main, Germany Rene Bellwied Physics
2.14 Constraining the Hadronic Spectrum from QCD Thermodynamics Paolo Alba Frankfurt Institute for Advanced Studies Goethe Universität Frankfurt D-60438 Frankfurt am Main, Germany Rene Bellwied Physics
QCD at T > 0 and B > 0. Kalman Szabo Bergische Universitat, Wuppertal
 QCD at T > 0 and B > 0 Kalman Szabo Bergische Universitat, Wuppertal Fairly well established (continuum, physical mass, staggered): Crossover T c EoS Crossover [Wuppertal-Budapest,WB, 06] volume dependence
QCD at T > 0 and B > 0 Kalman Szabo Bergische Universitat, Wuppertal Fairly well established (continuum, physical mass, staggered): Crossover T c EoS Crossover [Wuppertal-Budapest,WB, 06] volume dependence
arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 18 Feb 2016
![arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 18 Feb 2016 arxiv: v1 [hep-ph] 18 Feb 2016](/thumbs/72/67559516.jpg) Nuclear Physics A Nuclear Physics A 00 (2016) 1 5 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia arxiv:1602.05811v1 [hep-ph] 18 Feb 2016 Abstract Confronting fluctuations of conserved charges in central nuclear collisions
Nuclear Physics A Nuclear Physics A 00 (2016) 1 5 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia arxiv:1602.05811v1 [hep-ph] 18 Feb 2016 Abstract Confronting fluctuations of conserved charges in central nuclear collisions
arxiv: v1 [hep-lat] 8 Nov 2014
![arxiv: v1 [hep-lat] 8 Nov 2014 arxiv: v1 [hep-lat] 8 Nov 2014](/thumbs/78/77830057.jpg) Staggered Dslash Performance on Intel Xeon Phi Architecture arxiv:1411.2087v1 [hep-lat] 8 Nov 2014 Department of Physics, Indiana University, Bloomington IN 47405, USA E-mail: ruizli AT umail.iu.edu Steven
Staggered Dslash Performance on Intel Xeon Phi Architecture arxiv:1411.2087v1 [hep-lat] 8 Nov 2014 Department of Physics, Indiana University, Bloomington IN 47405, USA E-mail: ruizli AT umail.iu.edu Steven
Freeze-out parameters: lattice meets experiment
 Freeze-out parameters: lattice meets experiment Claudia Ratti Università degli Studi di Torino and INFN, Sezione di Torino In collaboration with R. Bellwied, S. Borsanyi, Z. Fodor, S. Katz, S. Krieg, K.
Freeze-out parameters: lattice meets experiment Claudia Ratti Università degli Studi di Torino and INFN, Sezione di Torino In collaboration with R. Bellwied, S. Borsanyi, Z. Fodor, S. Katz, S. Krieg, K.
Lattice QCD + Hydro/Cascade Model of Heavy Ion Collisions
 Lattice QCD + Hydro/Cascade Model of Heavy Ion Collisions Michael Cheng Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory 2010 Winter Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics Ocho Rios, Jamaica, January 2-9, 2010 Outline Calculation
Lattice QCD + Hydro/Cascade Model of Heavy Ion Collisions Michael Cheng Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory 2010 Winter Workshop on Nuclear Dynamics Ocho Rios, Jamaica, January 2-9, 2010 Outline Calculation
van der Waals Interactions in Hadron Resonance Gas:
 van der Waals Interactions in Hadron Resonance Gas: From Nuclear Matter to Lattice QCD Volodymyr Vovchenko Collaborators: P. Alba, D. Anchishkin, M. Gorenstein, and H. Stoecker Based on Phys. Rev. Lett.
van der Waals Interactions in Hadron Resonance Gas: From Nuclear Matter to Lattice QCD Volodymyr Vovchenko Collaborators: P. Alba, D. Anchishkin, M. Gorenstein, and H. Stoecker Based on Phys. Rev. Lett.
Hadron Resonance Gas Model
 Hadron Resonance Gas Model Valentina Mantovani Sarti QGP lectures-torino 2017 12 April 2017 V.Mantovani Sarti Hadron Resonance Gas Model 12 April 2017 1 / 6 References Particle production in heavy ion
Hadron Resonance Gas Model Valentina Mantovani Sarti QGP lectures-torino 2017 12 April 2017 V.Mantovani Sarti Hadron Resonance Gas Model 12 April 2017 1 / 6 References Particle production in heavy ion
Effective theories for QCD at finite temperature and density from strong coupling
 XQCD 2011 San Carlos, July 2011 Effective theories for QCD at finite temperature and density from strong coupling Owe Philipsen Introduction to strong coupling expansions SCE for finite temperature: free
XQCD 2011 San Carlos, July 2011 Effective theories for QCD at finite temperature and density from strong coupling Owe Philipsen Introduction to strong coupling expansions SCE for finite temperature: free
Accelerating Linear Algebra on Heterogeneous Architectures of Multicore and GPUs using MAGMA and DPLASMA and StarPU Schedulers
 UT College of Engineering Tutorial Accelerating Linear Algebra on Heterogeneous Architectures of Multicore and GPUs using MAGMA and DPLASMA and StarPU Schedulers Stan Tomov 1, George Bosilca 1, and Cédric
UT College of Engineering Tutorial Accelerating Linear Algebra on Heterogeneous Architectures of Multicore and GPUs using MAGMA and DPLASMA and StarPU Schedulers Stan Tomov 1, George Bosilca 1, and Cédric
The QCD equation of state at high temperatures
 The QCD equation of state at high temperatures Alexei Bazavov (in collaboration with P. Petreczky, J. Weber et al.) Michigan State University Feb 1, 2017 A. Bazavov (MSU) GHP2017 Feb 1, 2017 1 / 16 Introduction
The QCD equation of state at high temperatures Alexei Bazavov (in collaboration with P. Petreczky, J. Weber et al.) Michigan State University Feb 1, 2017 A. Bazavov (MSU) GHP2017 Feb 1, 2017 1 / 16 Introduction
Accelerating linear algebra computations with hybrid GPU-multicore systems.
 Accelerating linear algebra computations with hybrid GPU-multicore systems. Marc Baboulin INRIA/Université Paris-Sud joint work with Jack Dongarra (University of Tennessee and Oak Ridge National Laboratory)
Accelerating linear algebra computations with hybrid GPU-multicore systems. Marc Baboulin INRIA/Université Paris-Sud joint work with Jack Dongarra (University of Tennessee and Oak Ridge National Laboratory)
Probing the QCD phase diagram with higher moments
 Probing the QCD phase diagram with higher moments in collaboration with: F. Karsch B.-J. Schaefer A. Walther J. Wambach Outline Why higher moments? Algorithmic differentiation Lattice Taylor expansion
Probing the QCD phase diagram with higher moments in collaboration with: F. Karsch B.-J. Schaefer A. Walther J. Wambach Outline Why higher moments? Algorithmic differentiation Lattice Taylor expansion
arxiv: v1 [hep-lat] 26 Dec 2009
![arxiv: v1 [hep-lat] 26 Dec 2009 arxiv: v1 [hep-lat] 26 Dec 2009](/thumbs/78/77523973.jpg) arxiv:091.5037v1 [hep-lat] 6 Dec 009 On Equation of State at physical quark masses Physics Department, Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton NY 11973 E-mail: petreczk@bnl.gov QCD equation of state is calculated
arxiv:091.5037v1 [hep-lat] 6 Dec 009 On Equation of State at physical quark masses Physics Department, Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton NY 11973 E-mail: petreczk@bnl.gov QCD equation of state is calculated
The QCD phase diagram at low baryon density from lattice simulations
 ICHEP 2010 Paris, July 2010 The QCD phase diagram at low baryon density from lattice simulations Owe Philipsen Introduction Lattice techniques for finite temperature and density The phase diagram: the
ICHEP 2010 Paris, July 2010 The QCD phase diagram at low baryon density from lattice simulations Owe Philipsen Introduction Lattice techniques for finite temperature and density The phase diagram: the
Fluctuations of conserved charges and freeze-out conditions in heavy ion collisions
 Fluctuations of conserved charges and freeze-out conditions in heavy ion collisions Claudia Ratti University of Houston, Texas (USA) S. Borsanyi, Z. Fodor, S. Katz, S. Krieg, C. R., K. Szabo, PRL 2014
Fluctuations of conserved charges and freeze-out conditions in heavy ion collisions Claudia Ratti University of Houston, Texas (USA) S. Borsanyi, Z. Fodor, S. Katz, S. Krieg, C. R., K. Szabo, PRL 2014
Rapidity Dependence of Chemical Freeze out in Au Au Collisions
 Rapidity Dependence of Chemical Freeze out in Au Au Collisions Kristen Parzuchowski Research Experience for Undergraduates Wayne State University August 7, 2015 Abstract The study of nuclear matter is
Rapidity Dependence of Chemical Freeze out in Au Au Collisions Kristen Parzuchowski Research Experience for Undergraduates Wayne State University August 7, 2015 Abstract The study of nuclear matter is
Heavy quark free energies and screening from lattice QCD
 Heavy quark free energies and screening from lattice QCD Olaf Kaczmarek Universität Bielefeld February 9, 29 RBC-Bielefeld collaboration O. Kaczmarek, PoS CPOD7 (27) 43 RBC-Bielefeld, Phys.Rev.D77 (28)
Heavy quark free energies and screening from lattice QCD Olaf Kaczmarek Universität Bielefeld February 9, 29 RBC-Bielefeld collaboration O. Kaczmarek, PoS CPOD7 (27) 43 RBC-Bielefeld, Phys.Rev.D77 (28)
Understanding hadronization on the basis of fluctuations of conserved charges
 Understanding hadronization on the basis of fluctuations of conserved charges R. Bellwied (University of Houston) in collaboration with S. Jena, D. McDonald (University of Houston) C. Ratti, P. Alba, V.
Understanding hadronization on the basis of fluctuations of conserved charges R. Bellwied (University of Houston) in collaboration with S. Jena, D. McDonald (University of Houston) C. Ratti, P. Alba, V.
Hybrid CPU/GPU Acceleration of Detection of 2-SNP Epistatic Interactions in GWAS
 Hybrid CPU/GPU Acceleration of Detection of 2-SNP Epistatic Interactions in GWAS Jorge González-Domínguez*, Bertil Schmidt*, Jan C. Kässens**, Lars Wienbrandt** *Parallel and Distributed Architectures
Hybrid CPU/GPU Acceleration of Detection of 2-SNP Epistatic Interactions in GWAS Jorge González-Domínguez*, Bertil Schmidt*, Jan C. Kässens**, Lars Wienbrandt** *Parallel and Distributed Architectures
Introduction to numerical computations on the GPU
 Introduction to numerical computations on the GPU Lucian Covaci http://lucian.covaci.org/cuda.pdf Tuesday 1 November 11 1 2 Outline: NVIDIA Tesla and Geforce video cards: architecture CUDA - C: programming
Introduction to numerical computations on the GPU Lucian Covaci http://lucian.covaci.org/cuda.pdf Tuesday 1 November 11 1 2 Outline: NVIDIA Tesla and Geforce video cards: architecture CUDA - C: programming
Unraveling the mysteries of quarks with hundreds of GPUs. Ron Babich NVIDIA
 Unraveling the mysteries of quarks with hundreds of GPUs Ron Babich NVIDIA Collaborators and QUDA developers Kip Barros (LANL) Rich Brower (Boston University) Mike Clark (NVIDIA) Justin Foley (University
Unraveling the mysteries of quarks with hundreds of GPUs Ron Babich NVIDIA Collaborators and QUDA developers Kip Barros (LANL) Rich Brower (Boston University) Mike Clark (NVIDIA) Justin Foley (University
The phase diagram of strongly interacting matter
 The phase diagram of strongly interacting matter TIFR Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore November 25, 2011 Introduction 1 Introduction 2 Bulk Strongly Interacting Matter 3 Relativistic Heavy-ion Collisions
The phase diagram of strongly interacting matter TIFR Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore November 25, 2011 Introduction 1 Introduction 2 Bulk Strongly Interacting Matter 3 Relativistic Heavy-ion Collisions
Thermodynamics. Quark-Gluon Plasma
 Thermodynamics of the Quark-Gluon Plasma Claudia Ratti Torino University and INFN, Italy Claudia Ratti 1 Quick review of thermodynamics In lectures I and II we saw... QCD and its symmetries Polyakov loop
Thermodynamics of the Quark-Gluon Plasma Claudia Ratti Torino University and INFN, Italy Claudia Ratti 1 Quick review of thermodynamics In lectures I and II we saw... QCD and its symmetries Polyakov loop
Baryon number fluctuations within the functional renormalization group approach
 Baryon number fluctuations within the functional renormalization group approach Wei-jie Fu Dalian University of Technology wjfu@dlut.edu.cn The Third Symposium on Chiral Effective Field Theory, Oct. 28-Nov.
Baryon number fluctuations within the functional renormalization group approach Wei-jie Fu Dalian University of Technology wjfu@dlut.edu.cn The Third Symposium on Chiral Effective Field Theory, Oct. 28-Nov.
Role of fluctuations in detecting the QCD phase transition
 Role of fluctuations in detecting the QCD phase transition Fluctuations of the Polyakov loop and deconfinement in a pure SU(N) gauge theory and in QCD Fluctuations of conserved charges as probe for the
Role of fluctuations in detecting the QCD phase transition Fluctuations of the Polyakov loop and deconfinement in a pure SU(N) gauge theory and in QCD Fluctuations of conserved charges as probe for the
Dimensional reduction near the deconfinement transition
 Dimensional reduction near the deconfinement transition Aleksi Kurkela ETH Zürich Wien 27.11.2009 Outline Introduction Dimensional reduction Center symmetry The deconfinement transition: QCD has two remarkable
Dimensional reduction near the deconfinement transition Aleksi Kurkela ETH Zürich Wien 27.11.2009 Outline Introduction Dimensional reduction Center symmetry The deconfinement transition: QCD has two remarkable
Critical end point of Nf=3 QCD at finite temperature and density
 Critical end point of Nf=3 QCD at finite temperature and density a,b, Xiao-Yong Jin b, Yoshinobu Kuramashi b,c,d, Yoshifumi Nakamura b, and Akira Ukawa b a Institute of Physics, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa
Critical end point of Nf=3 QCD at finite temperature and density a,b, Xiao-Yong Jin b, Yoshinobu Kuramashi b,c,d, Yoshifumi Nakamura b, and Akira Ukawa b a Institute of Physics, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa
Noise reduction for charge fluctuations: an investigation on many-core architecture
 Noise reduction for charge fluctuations: an investigation on many-core architecture Master s Thesis submitted by Patrick Steinbrecher Fakultät für Physik Universität Bielefeld February 2015 Supervisor
Noise reduction for charge fluctuations: an investigation on many-core architecture Master s Thesis submitted by Patrick Steinbrecher Fakultät für Physik Universität Bielefeld February 2015 Supervisor
Higher order net baryon number cumulants in the strong coupling lattice QCD
 Higher order net baryon number cumulants in the strong coupling lattice QCD Terukazu Ichihara in collaborate with Akira Ohnishi and Kenji Morita Department of Physics and YITP, Kyoto U. News! We got an
Higher order net baryon number cumulants in the strong coupling lattice QCD Terukazu Ichihara in collaborate with Akira Ohnishi and Kenji Morita Department of Physics and YITP, Kyoto U. News! We got an
HOT HADRONIC MATTER. Hampton University and Jefferson Lab
 200 Cr oss sect ion (m b) 0 K ptotal 20 5 K pelastic 2 1 K N 1 1.6 2 3 4 2 5 6 7 8 9 20 30 3 40 THE ROLE OF BARYON RESONANCES IN Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) HOT HADRONIC MATTER Au+Au K d 2.5
200 Cr oss sect ion (m b) 0 K ptotal 20 5 K pelastic 2 1 K N 1 1.6 2 3 4 2 5 6 7 8 9 20 30 3 40 THE ROLE OF BARYON RESONANCES IN Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) HOT HADRONIC MATTER Au+Au K d 2.5
The Chiral and Deconfinement Phase Transitions in Strongly-Interacting Matter
 The Chiral and Deconfinement Phase Transitions in Strongly-Interacting Matter in collaboration with: B-J. Schaefer & J. Wambach Schaefer, MW: PRD 79 (1418) arxiv: 812.2855 [hep-ph] 9.3.29 Mathias Wagner
The Chiral and Deconfinement Phase Transitions in Strongly-Interacting Matter in collaboration with: B-J. Schaefer & J. Wambach Schaefer, MW: PRD 79 (1418) arxiv: 812.2855 [hep-ph] 9.3.29 Mathias Wagner
The phase diagram of strongly interacting matter
 The phase diagram of strongly interacting matter IOP Bhubaneshwar August 8, 2011 Introduction Introduction Bulk Strongly Interacting Matter Relativistic Heavy-ion Collisions Fluctuations of Conserved Quantities
The phase diagram of strongly interacting matter IOP Bhubaneshwar August 8, 2011 Introduction Introduction Bulk Strongly Interacting Matter Relativistic Heavy-ion Collisions Fluctuations of Conserved Quantities
The QCD phase diagram at real and imaginary chemical potential
 Strongnet Meeting Trento, October 211 The QCD phase diagram at real and imaginary chemical potential Owe Philipsen Is there a critical end point in the QCD phase diagram? Is it connected to a chiral phase
Strongnet Meeting Trento, October 211 The QCD phase diagram at real and imaginary chemical potential Owe Philipsen Is there a critical end point in the QCD phase diagram? Is it connected to a chiral phase
Critical lines and points. in the. QCD phase diagram
 Critical lines and points in the QCD phase diagram Understanding the phase diagram Phase diagram for m s > m u,d quark-gluon plasma deconfinement quark matter : superfluid B spontaneously broken nuclear
Critical lines and points in the QCD phase diagram Understanding the phase diagram Phase diagram for m s > m u,d quark-gluon plasma deconfinement quark matter : superfluid B spontaneously broken nuclear
Lecture 2: The First Second origin of neutrons and protons
 Lecture 2: The First Second origin of neutrons and protons Hot Big Bang Expanding and cooling Soup of free particles + anti-particles Symmetry breaking Soup of free quarks Quarks confined into neutrons
Lecture 2: The First Second origin of neutrons and protons Hot Big Bang Expanding and cooling Soup of free particles + anti-particles Symmetry breaking Soup of free quarks Quarks confined into neutrons
van der Waals Interactions in Hadron Resonance Gas:
 van der Waals Interactions in Hadron Resonance Gas: From Nuclear Matter to Lattice QCD Volodymyr Vovchenko Based on: V.V, Anchishkin, Gorenstein, Phys. Rev. C 9, 6434 (25) V.V, Anchishkin, Gorenstein,
van der Waals Interactions in Hadron Resonance Gas: From Nuclear Matter to Lattice QCD Volodymyr Vovchenko Based on: V.V, Anchishkin, Gorenstein, Phys. Rev. C 9, 6434 (25) V.V, Anchishkin, Gorenstein,
Results from the beam energy scan at RHIC: Exploring the QCD phase structure in A+A collisions
 Results from the beam energy scan at RHIC: Exploring the QCD phase structure in A+A collisions Bedanga Mohanty NaConal InsCtute of Science EducaCon and Research (NISER) Outline: ² Phase diagram of QCD
Results from the beam energy scan at RHIC: Exploring the QCD phase structure in A+A collisions Bedanga Mohanty NaConal InsCtute of Science EducaCon and Research (NISER) Outline: ² Phase diagram of QCD
A Quantum Chemistry Domain-Specific Language for Heterogeneous Clusters
 A Quantum Chemistry Domain-Specific Language for Heterogeneous Clusters ANTONINO TUMEO, ORESTE VILLA Collaborators: Karol Kowalski, Sriram Krishnamoorthy, Wenjing Ma, Simone Secchi May 15, 2012 1 Outline!
A Quantum Chemistry Domain-Specific Language for Heterogeneous Clusters ANTONINO TUMEO, ORESTE VILLA Collaborators: Karol Kowalski, Sriram Krishnamoorthy, Wenjing Ma, Simone Secchi May 15, 2012 1 Outline!
arxiv: v2 [hep-lat] 13 Aug 2014
![arxiv: v2 [hep-lat] 13 Aug 2014 arxiv: v2 [hep-lat] 13 Aug 2014](/thumbs/71/66020417.jpg) Additional trange Hadrons from QCD Thermodynamics and trangeness Freeze-out in Heavy Ion Collisions arxiv:1404.6511v2 [hep-lat] 13 Aug 2014 A. azavov, 1 H.-T. Ding, 2 P. Hegde, 2 O. Kaczmarek, 3 F. Karsch,
Additional trange Hadrons from QCD Thermodynamics and trangeness Freeze-out in Heavy Ion Collisions arxiv:1404.6511v2 [hep-lat] 13 Aug 2014 A. azavov, 1 H.-T. Ding, 2 P. Hegde, 2 O. Kaczmarek, 3 F. Karsch,
Cold QCD. Meeting on Computational Nuclear Physics. Washington, DC July Thomas Luu Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
 Cold QCD Meeting on Computational Nuclear Physics Washington, DC July 2012 Thomas Luu Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy
Cold QCD Meeting on Computational Nuclear Physics Washington, DC July 2012 Thomas Luu Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department of Energy
EQUATION OF STATE AND FLUCTUATIONS FROM THE LATTICE Claudia Ratti University of Houston (USA)
 EQUATION OF STATE AND FLUCTUATIONS FROM THE LATTICE Claudia Ratti University of Houston (USA) Collaborators: Paolo Alba, Rene Bellwied, Szabolcs Borsanyi, Zoltan Fodor, Jana Guenther, Sandor Katz, Stefan
EQUATION OF STATE AND FLUCTUATIONS FROM THE LATTICE Claudia Ratti University of Houston (USA) Collaborators: Paolo Alba, Rene Bellwied, Szabolcs Borsanyi, Zoltan Fodor, Jana Guenther, Sandor Katz, Stefan
Can we locate the QCD critical endpoint with a Taylor expansion?
 Can we locate the QCD critical endpoint with a Taylor expansion? Bernd-Jochen Schaefer Karl-Franzens-Universität Graz, Austria 7 th February - 6 th March, 1 48. Internationale Universitätswochen für Theoretische
Can we locate the QCD critical endpoint with a Taylor expansion? Bernd-Jochen Schaefer Karl-Franzens-Universität Graz, Austria 7 th February - 6 th March, 1 48. Internationale Universitätswochen für Theoretische
Flavoured aspects of the QCD thermodynamics
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Flavoured aspects of the QCD thermodynamics To cite this article: O. Kaczmarek 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 668 012003 View the article online for updates
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Flavoured aspects of the QCD thermodynamics To cite this article: O. Kaczmarek 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 668 012003 View the article online for updates
Shortest Lattice Vector Enumeration on Graphics Cards
 Shortest Lattice Vector Enumeration on Graphics Cards Jens Hermans 1 Michael Schneider 2 Fréderik Vercauteren 1 Johannes Buchmann 2 Bart Preneel 1 1 K.U.Leuven 2 TU Darmstadt SHARCS - 10 September 2009
Shortest Lattice Vector Enumeration on Graphics Cards Jens Hermans 1 Michael Schneider 2 Fréderik Vercauteren 1 Johannes Buchmann 2 Bart Preneel 1 1 K.U.Leuven 2 TU Darmstadt SHARCS - 10 September 2009
