Mars Sample Return The Apollo Perspective
|
|
|
- Thomasina Melton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mars Sample Return The Apollo Perspective D. A. Papanastassiou Science Division, Jet Propulsion Laboratory Ground Truth from Mars, Albuquerque, NM, April 21-23, 2008
2 Purpose Share some of the excitement of the Apollo returned samples Share the excitement of addressing lunar evolution from hard data and lifting the veil of estimates, guesses and theories That many facts prior to Apollo were wrong does not diminish the importance of earlier orbital and in situ data Wish the same excitement in your lifetime
3 Overview of Conclusions Prior to sample return, we interpret wonderful orbital and in situ observations of other planets in terms of our very detailed terrestrial experience For the Moon, Apollo samples demonstrated that our interpretations and theories were inaccurate This will be reasonably true about Mars too Hence, applying our terrestrial interpretations to Mars and requiring earth-centric, detailed sample collection processes may over-constrain MSR It is important to identify which scientific questions and which part of Mars evolution, should actually be addressed by the first MSR and get on with it
4 Between 1969 and 1972, six Apollo missions returned 382 Kg of rocks, soils, and core samples from the lunar surface First samples allocated in Sept. 1969, after quarantine, biohazard assessment and Prelim. Examin.; 1st Lun. Sci. Conf. January 5-8, 1970 Houston, TX These samples are treated as a national treasure and allocated conservatively, for state-of-the-art, original scientific investigations
5 MARS We will have to work with much, much less returned material from a far more complex planet But after many orbital and detailed, in situ missions, it is time to bite the bullet, and seek the ground truth provided by returned samples Need to choose with care a landing site and processes to be addressed The time scale of processes on Mars is key If some of my statements are like bringing owls to Athens, it is deliberate, in the interest of keeping it simple, lower risk, and affordable
6 Ground Truth for the Moon From the Apollo 11 contigency soil Anorthositic fragments => anorthositic crust Luny Rock 1 => granitic component (=> KREEP) Magic (Rb/Sr) component in soils vs. high-k basalts Glass shells, spheres, dumb-bells, zap pits, agglutinates Breccias Pristine, coarse grained rocks On Mars it is harder and we can not count on serendipity Sample rocks (igneous, metamorphic, sedimentary; in that order) Sample soils Sample evaporites, modern or ancient brines? Do not sample the detailed stratigraphy of soil-like outcrops of siliciclastic matter plus chemical sediments, especially if dealing with an incomplete or not in equilibrium evaporite sequence Meridiani Outcrops; B. C. Clark et al. (2005) EPSL 240, 73.
7 If this was Apollo again Prior to Apollo Photography of lunar surface Crater counting chronology: erroneous, based on assumption of constant cratering flux Expectations for very young Moon or very old Moon Surveyor landings on the Moon, essentially every two months, for Surveyors 3-7; chemical compositions from Tony Turkevich s alpha back scattering instrument Implications of high Ca addressed (crust and planet density) Implications of low K not adequately recognized Extensive VIS-IR spectroscopy from orbit needed to be recalibrated and reinterpreted based on the presence of glass, agglutinates and space weathering Apollo returned a grab (contingency) sample, rocks, breccias, soil, for the ground truth
8 Prior Knowledge or Lack of It: Moon A plethora of scientific expectations and predictions prior to sample return, including the possibility of sinking through the lunar soil Scientific expectations not confirmed by returned samples Completely unanticipated processes Glass and agglutinate formation on airless surfaces, exposed to micrometeorites Amorphous soil grain surfaces, due to irradiation Reduction of Fe by solar wind hydrogen; darkening of Fe-bearing minerals Overall modification of spectroscopic properties (VIS-NIR) Completely unanticipated impact crater-age relationships Completely unexpected regolith gardening processes, e. g., depositing 2-4 m layers and leaving them undisturbed for Ga, as established by neutron capture effects
9 Tools at the Start of Apollo Age dating by 87 Rb -87 Sr and 40 Ar- 39 Ar, only Dating by U-Pb only of soils, during the missions No U-Th-Pb ages on rocks for several years due to high U/Pb and Th/Pb, very low 204 Pb, and high Pb analytical blanks No 147,146 Sm- 143,142 Nd, 187 Re- 187 Os, 182 Hf- 182 W Platinum Group Elements by INAA and RNAA, with very low sensitivity (no Re, almost no Os measurements) -- no NTIMS, MC-ICP-MS, MC- TIMS Apollo funding resulted in key developments of instruments and analytical techniques and science
10 Apollo Chronology 87 Rb- 87 Sr: at the starting gate, only one laboratory with sufficiently precise and sensitive mass spectrometry (and chemistry) to measure internal isochrons on Apollo 11 low-k and high-k basalts Rb-Sr internal isochrons depended on unpredicted minor phases with low Rb, Sr (Rb/Sr~0/0, higher than in major phases, e. g., in ilmenite, cristobalite, quintessence) 40 Ar- 39 Ar: stepwise heating technique developed to perfection (G. Turner, CIT, Phys. Inst., Berne); Most reliable ages on plagioclase mineral separates Less reliable results on highland samples (due to redistribution of 39 Ar from recoil from fine grained interstitial phases); reverting to judicious K-Ar ages Learning how to date Mars rocks will not be trivial
11 Neutron Capture Effects Taking advantage of high thermal and epithermal neutron capture cross sections for Gd and Sm Funded by Apollo, early development of REE chemical separations (Tera) and Gd mass spectrometry (Wasserburg, Burnett, Eugster), with high efficiency of ionization for Gd as GdO +, followed closely by development of Sm (SmO + ) (Burnett, Russ, Wasserburg) Production rates, as a function of depth, confirmed in situ by the Lunar Neutron Probe, flown on Apollo 17 (Burnett, Woolum, Weiss, Bauman) Regolith gardening rates determined Effects can also help address irradiation effects for humans Extension of techniques to NdO + led directly to the development of Sm-Nd dating (Lugmair) N. B. Ionization efficiencies: NdO + >> SmO + > GdO +!
12 Post Apollo Missions Development of U-Th-Pb Measurement of highland breccias Recognition of volatile, parentless radiogenic Pb, produced between Ga and mobilized on a grand scale at 4.0 Ga Recognition and proposal for a Terminal Lunar Cataclysm (Tera, Wasserburg, Papanastassiou, 1974) Development of Sm-Nd First on meteorites (Juvinas, G. Lugmair, 1975) Used on lunar samples (first, DePaolo, Papanastassiou, Wasserburg, 1978) Recognition of long-standing crustal and mantle reservoirs on the Moon Extensive Sm-Nd dating of lunar samples since then
13 The Apollo Effect Apollo funding permitted the shift of physicists, chemists, and geologists to interdisciplinary planetary sciences and the development of advanced analytical techniques and instrumentation (which was later applied to and revolutionized terrestrial work) The Ares Effect? When will Mars Sample Return funding permit the equivalent flourishing of planetary sample science and life-detection?
14 What Makes MSR Different? Extensive prior orbital and in situ work Small expected sample size and, hence, small number of samples and limited diversity Extensive planetary evolution to present Water and other volatiles as prerequisites for biologic activity The probability for biological activity, extinct or extant Extent of sample alteration
15 Moon 6 landing sites 58 to 741 samples per site (2196 samples, total) 22 to 111 kg per site (382 kg total) Rocks, soil, cores Mars Sample Size and Diversity 1 or 2 landing sites Tens of samples per site ~ 500 g per site (but needs to be updated) Rocks, soils, (cores), atmosphere
16 Life on Mars? Moon No evidence of present or past life in any sample Mars Conceivable that some locations may be capable of supporting life (both past and present), having capabilities of terrestrial extremophiles Are extremophiles considered hardy organisms? Characteristics and hazard of Mars life (if it exists) are unknown Abundance of Mars life (if it exists) is probably extremely low in samples (organic molecules in the soil < 1 ppb) This level of uncertainty will persist until the first sample return mission and probably after it
17 Terrestrial-Type Assumptions Follow The water The brines The acid or oxidizing brines The hydrated components Timescale of water evolution? For Earth: climate change chronologies based on U-Th disequilibrium dating of corals not applicable on Mars if timescale for evaporites is greater than 0.5 Ma and if U/Th fractionation is not mediated by organisms
18 Conclusions Prior to sample return, we interpret wonderful orbital and in situ observations of other planets in terms of our very detailed terrestrial experience For the Moon, Apollo samples demonstrated that our interpretations and theories were inaccurate The same will be reasonably true about Mars Hence, applying our terrestrial interpretations to Mars and requiring earth-centric, detailed sample collection processes may over-constrain MSR It is important to identify which scientific questions and which part of Mars evolution, should actually be addressed by the first MSR and get on with it
19 SAMPLE HANDLING Since This is a CAPTEM-Sponsored Meeting
20 Key Concepts Sample handling and preservation and hazard assessment are important functions Preliminary examination of samples is necessary for sample hazard assessment and for sample allocations Clean facilities and clean sample handling are required Conflicts, cross contamination issues will be present and need to be resolved, to maximize science return Extensive experience is available for extraterrestrial samples and must be sought and applied Extensive experience is available in studies of pathogens and life detection and must be sought and applied as required by law and as scientifically necessary An Advisory and Oversight Committee must be in place, combining the extensive experience in diverse sciences Apollo experience and committee structure (LSAPT, CAPTEM) offer a key perspective to emulate
21 Sample Handling Starts with flight mission design, material choices and documentation, contamination removal and characterization, sample collection, sample storage, container sealing, prior to return Design Mars Sample Receiving and Sample Curation facilities Devise a unified advisory committee to oversee activities from the mission design start and into the distant future, as indicated by LSAPT/CAPTEM experience Invest in technology, in R&A, and in people, and take advantage of multidisciplinary experience. The Apollo generation is on its way out. Any advice we provide is based on experience and is not for our personal scientific gain
22 Back-up slides
23 Sample Temperatures Moon Surface at the equator (mean) -19 ± 140 o C 100 cm depth ~ -19 o C (isothermal) Mars Surface average -57 o C ± 80 o C 100 cm depth ~ -53 o C (isothermal) A first sample return need not be maintained cold, any more than lunar samples should have been maintained under vacuum The decision will be a combination of science, technology, and cost, for MSR to remain a reality
24 Moon No evidence of water in any Apollo sample Solar wind implanted H, He, C <200 ppm No atmosphere Mars Water and Other Volatiles Water ice Hydrated minerals Adsorbed atmospheric gas Atmosphere (95% CO 2 ; 6 mb)
Importance of Sample Return to Understanding Mars. Meenakshi Wadhwa, ASU Curation and Analysis Planning Team for Extraterrestrial Materials (CAPTEM)
 Importance of Sample Return to Understanding Mars Meenakshi Wadhwa, ASU Curation and Analysis Planning Team for Extraterrestrial Materials (CAPTEM) Outline General Principles for Planetary Missions Importance
Importance of Sample Return to Understanding Mars Meenakshi Wadhwa, ASU Curation and Analysis Planning Team for Extraterrestrial Materials (CAPTEM) Outline General Principles for Planetary Missions Importance
Background Image: SPA Basin Interior; LRO WAC, NASA/GSFC/ASU
 B. L. Jolliff1, C. K. Shearer2, N. E. Petro3, D. A. Papanastassiou,4 Y. Liu,4 and L. Alkalai4 1Dept. of Earth & Planetary Sciences, Washington University, St. Louis, MO 2Institute of Meteoritics, University
B. L. Jolliff1, C. K. Shearer2, N. E. Petro3, D. A. Papanastassiou,4 Y. Liu,4 and L. Alkalai4 1Dept. of Earth & Planetary Sciences, Washington University, St. Louis, MO 2Institute of Meteoritics, University
Volatiles (H, C, N, F, S, Cl) in the lunar mantle, crust, and regolith: What questions remain and where to go next?
 Volatiles (H, C, N, F, S, Cl) in the lunar mantle, crust, and regolith: What questions remain and where to go next? Francis M. McCubbin & Charles K. Shearer Motivation behind this work 100, In Revision,
Volatiles (H, C, N, F, S, Cl) in the lunar mantle, crust, and regolith: What questions remain and where to go next? Francis M. McCubbin & Charles K. Shearer Motivation behind this work 100, In Revision,
Trace Elements - Definitions
 Trace Elements - Definitions Elements that are not stoichiometric constituents in phases in the system of interest For example, IG/MET systems would have different trace elements than aqueous systems Do
Trace Elements - Definitions Elements that are not stoichiometric constituents in phases in the system of interest For example, IG/MET systems would have different trace elements than aqueous systems Do
DRAFT Coarse-fines 569 grams
 10085 Coarse-fines 569 grams DRAFT Figure 1: Selected coarse fines from 10085. Scale is in mm. Photo from Wood et al. 1969. Introduction!0085 and 10084 were created during the Apollo 11 preliminary examination
10085 Coarse-fines 569 grams DRAFT Figure 1: Selected coarse fines from 10085. Scale is in mm. Photo from Wood et al. 1969. Introduction!0085 and 10084 were created during the Apollo 11 preliminary examination
Radiogenic Isotopes. W. F. McDonough 1 1 Department of Earth Sciences and Research Center for
 Radiogenic Isotopes W. F. McDonough 1 1 Department of Earth Sciences and Research Center for Neutrino Science, Tohoku University, Sendai 980-8578, Japan (Dated: May 17, 2018) I. SUMMRY Isotope systems
Radiogenic Isotopes W. F. McDonough 1 1 Department of Earth Sciences and Research Center for Neutrino Science, Tohoku University, Sendai 980-8578, Japan (Dated: May 17, 2018) I. SUMMRY Isotope systems
Lunar Discovery and Exploration program
 Lunar Discovery and Exploration program Space Policy Directive-1 (December 11, 2017) amends the National Space Policy to include the following paragraph: Lead an innovative and sustainable program of exploration
Lunar Discovery and Exploration program Space Policy Directive-1 (December 11, 2017) amends the National Space Policy to include the following paragraph: Lead an innovative and sustainable program of exploration
The Moon. Tidal Coupling Surface Features Impact Cratering Moon Rocks History and Origin of the Moon
 The Moon Tidal Coupling Surface Features Impact Cratering Moon Rocks History and Origin of the Moon Earth Moon Semi-major Axis 1 A.U. 384 x 10 3 km Inclination 0 Orbital period 1.000 tropical year 27.32
The Moon Tidal Coupling Surface Features Impact Cratering Moon Rocks History and Origin of the Moon Earth Moon Semi-major Axis 1 A.U. 384 x 10 3 km Inclination 0 Orbital period 1.000 tropical year 27.32
UV-V-NIR Reflectance Spectroscopy
 UV-V-NIR Reflectance Spectroscopy Methods and Results A. Nathues Naturally-occurring inorganic substances with a definite and predictable chemical composition and physical properties Major groups: Silicates
UV-V-NIR Reflectance Spectroscopy Methods and Results A. Nathues Naturally-occurring inorganic substances with a definite and predictable chemical composition and physical properties Major groups: Silicates
The Moon. Part II: Solar System. The Moon. A. Orbital Motion. The Moon s Orbit. Earth-Moon is a Binary Planet
 Part II: Solar System The Moon Audio update: 2014Feb23 The Moon A. Orbital Stuff B. The Surface C. Composition and Interior D. Formation E. Notes 2 A. Orbital Motion 3 Earth-Moon is a Binary Planet 4 1.
Part II: Solar System The Moon Audio update: 2014Feb23 The Moon A. Orbital Stuff B. The Surface C. Composition and Interior D. Formation E. Notes 2 A. Orbital Motion 3 Earth-Moon is a Binary Planet 4 1.
Our Barren Moon. Chapter Ten. Guiding Questions
 Our Barren Moon Chapter Ten Guiding Questions 1. Is the Moon completely covered with craters? 2. Has there been any exploration of the Moon since the Apollo program in the 1970s? 3. Does the Moon s interior
Our Barren Moon Chapter Ten Guiding Questions 1. Is the Moon completely covered with craters? 2. Has there been any exploration of the Moon since the Apollo program in the 1970s? 3. Does the Moon s interior
Italian Lunar Science Studies and Possible Missions a.k.a. The Moon: an Italian Approach. Angioletta Coradini Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica
 Italian Lunar Science Studies and Possible Missions a.k.a. The Moon: an Italian Approach Angioletta Coradini Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica Goals of the Study The primary goal of the present study is
Italian Lunar Science Studies and Possible Missions a.k.a. The Moon: an Italian Approach Angioletta Coradini Istituto Nazionale di Astrofisica Goals of the Study The primary goal of the present study is
In Situ Noble Gas-based Dating On Terrestrial Planet Surfaces
 In Situ Noble Gas-based Dating On Terrestrial Planet Surfaces Tim Swindle Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, University of Arizona Decadal Survey Terrestrial Planets Panel Irvine, California October 26, 2009
In Situ Noble Gas-based Dating On Terrestrial Planet Surfaces Tim Swindle Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, University of Arizona Decadal Survey Terrestrial Planets Panel Irvine, California October 26, 2009
9/15/16. Guiding Questions. Our Barren Moon. The Moon s Orbit
 Our Barren Moon Guiding Questions 1. Is the Moon completely covered with craters? 2. Has there been any exploration of the Moon since the Apollo program in the 1970s? 3. Does the Moon s interior have a
Our Barren Moon Guiding Questions 1. Is the Moon completely covered with craters? 2. Has there been any exploration of the Moon since the Apollo program in the 1970s? 3. Does the Moon s interior have a
Science and Exploration: Moon to Mars. Dr. Jim Garvin NASA Chief Scientist Exploration Conference Orlando, Florida Feb. 1, 2005
 Science and Exploration: Moon to Mars Dr. Jim Garvin NASA Chief Scientist Exploration Conference Orlando, Florida Feb. 1, 2005 Enabling Exploration! Science supports Exploration Basic inventorying 0 th
Science and Exploration: Moon to Mars Dr. Jim Garvin NASA Chief Scientist Exploration Conference Orlando, Florida Feb. 1, 2005 Enabling Exploration! Science supports Exploration Basic inventorying 0 th
Extralunar Materials in Lunar Regolith
 ExtralunarMaterialsinLunarRegolith AWhitePaperSubmittedfortheNRCDecadalSurvey Authors: MarcFries,JetPropulsionLaboratory,PasadenaCA JohnArmstrong,WeberStateUniversity,OgdenUT JamesAshley,ArizonaStateUniversity,TempeAZ
ExtralunarMaterialsinLunarRegolith AWhitePaperSubmittedfortheNRCDecadalSurvey Authors: MarcFries,JetPropulsionLaboratory,PasadenaCA JohnArmstrong,WeberStateUniversity,OgdenUT JamesAshley,ArizonaStateUniversity,TempeAZ
,1,2,3,4,9, Impact Melt Breccia 65.4 grams
 63335 Impact Melt Breccia 65.4 grams,1,2,3,4,9,10,8 Figure 2: 63335,6. Cube is 1 cm. S75-33389.,7 Introduction 63335 is a sample chipped off of Shadow Rock (Ulrich 1973). It was collected as several fragments
63335 Impact Melt Breccia 65.4 grams,1,2,3,4,9,10,8 Figure 2: 63335,6. Cube is 1 cm. S75-33389.,7 Introduction 63335 is a sample chipped off of Shadow Rock (Ulrich 1973). It was collected as several fragments
page - Lab 13 - Introduction to the Geology of the Terrestrial Planets
 page - Lab 13 - Introduction to the Geology of the Terrestrial Planets Introduction There are two main families of planets in our solar system: the inner Terrestrial planets (Earth, Mercury, Venus, and
page - Lab 13 - Introduction to the Geology of the Terrestrial Planets Introduction There are two main families of planets in our solar system: the inner Terrestrial planets (Earth, Mercury, Venus, and
Insights into the Evolution of the Solar System from Isotopic Investigations of Samples. Lars Borg
 Insights into the Evolution of the Solar System from Isotopic Investigations of Samples Lars Borg Harold Masursky Harold Masursky was a stalwart of the U.S. planetary exploration program for nearly three
Insights into the Evolution of the Solar System from Isotopic Investigations of Samples Lars Borg Harold Masursky Harold Masursky was a stalwart of the U.S. planetary exploration program for nearly three
Presentation to the NAC Planetary Science Subcommittee June 7, 2007
 Presentation to the NAC Planetary Science Subcommittee June 7, 2007 Dedicated to Maximizing Planetary Sample Science While Protecting the Integrity of NASA Collected Extraterrestrial Materials June 11,
Presentation to the NAC Planetary Science Subcommittee June 7, 2007 Dedicated to Maximizing Planetary Sample Science While Protecting the Integrity of NASA Collected Extraterrestrial Materials June 11,
Where we are now. The Moon Chapters 8.2, 9. Topography. Outline
 Where we are now Introduction Little things - comets, asteroids, KBOs Slightly larger things - Moon Larger still - Terrestrial planets Really large - Jovian planets Jovian moons + Pluto Extrasolar Planets
Where we are now Introduction Little things - comets, asteroids, KBOs Slightly larger things - Moon Larger still - Terrestrial planets Really large - Jovian planets Jovian moons + Pluto Extrasolar Planets
Astronomy 101 The Solar System Tuesday, Thursday 2:30-3:45 pm Hasbrouck 20. Tom Burbine
 Astronomy 101 The Solar System Tuesday, Thursday 2:30-3:45 pm Hasbrouck 20 Tom Burbine tomburbine@astro.umass.edu Course Course Website: http://blogs.umass.edu/astron101-tburbine/ Textbook: Pathways to
Astronomy 101 The Solar System Tuesday, Thursday 2:30-3:45 pm Hasbrouck 20 Tom Burbine tomburbine@astro.umass.edu Course Course Website: http://blogs.umass.edu/astron101-tburbine/ Textbook: Pathways to
grams grams Double Drive tube 61 cm
 68002 583.5 grams 68001 840.7 grams Double Drive tube 61 cm Figure 1a: Surface photo for double drive tube 68001-2. AS16-108-17684. Introduction Station 8 was the closest to South Ray Crater so premission
68002 583.5 grams 68001 840.7 grams Double Drive tube 61 cm Figure 1a: Surface photo for double drive tube 68001-2. AS16-108-17684. Introduction Station 8 was the closest to South Ray Crater so premission
Iron and Titanium: Important Elements. posted October 20, References:
 1 of 6 posted October 20, 1997 Moonbeams and Elements Written by G. Jeffrey Taylor Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology To determine how a planetary body formed and evolved, we must determine
1 of 6 posted October 20, 1997 Moonbeams and Elements Written by G. Jeffrey Taylor Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology To determine how a planetary body formed and evolved, we must determine
Wed. Oct. 04, Makeup lecture time? Will Friday noon work for everyone? No class Oct. 16, 18, 20?
 Wed. Oct. 04, 2017 Reading: For Friday: Bugiolacchi et al. 2008 Laurence et al. 1998" Makeup lecture time? Will Friday noon work for everyone? No class Oct. 16, 18, 20? Today: Finish Lunar overview (from
Wed. Oct. 04, 2017 Reading: For Friday: Bugiolacchi et al. 2008 Laurence et al. 1998" Makeup lecture time? Will Friday noon work for everyone? No class Oct. 16, 18, 20? Today: Finish Lunar overview (from
Lead Isotope Dates and the Age of the Earth Kevin R. Henke, Ph.D.
 Lead Isotope Dates and the Age of the Earth Kevin R. Henke, Ph.D. The following material may be freely copied and distributed as long as the author is properly acknowledged and the material is not altered,
Lead Isotope Dates and the Age of the Earth Kevin R. Henke, Ph.D. The following material may be freely copied and distributed as long as the author is properly acknowledged and the material is not altered,
InSight Spacecraft Launch for Mission to Interior of Mars
 InSight Spacecraft Launch for Mission to Interior of Mars InSight is a robotic scientific explorer to investigate the deep interior of Mars set to launch May 5, 2018. It is scheduled to land on Mars November
InSight Spacecraft Launch for Mission to Interior of Mars InSight is a robotic scientific explorer to investigate the deep interior of Mars set to launch May 5, 2018. It is scheduled to land on Mars November
CAPTEM. Curation and Analysis Planning Team for Extraterrestrial Materials. Kevin D. McKeegan Dept. of Earth, Planetary, and Space Sciences UCLA
 CAPTEM Curation and Analysis Planning Team for Extraterrestrial Materials Kevin D. McKeegan Dept. of Earth, Planetary, and Space Sciences UCLA Planetary Science Advisory Committee NASA HQ, Feb. 23, 2018
CAPTEM Curation and Analysis Planning Team for Extraterrestrial Materials Kevin D. McKeegan Dept. of Earth, Planetary, and Space Sciences UCLA Planetary Science Advisory Committee NASA HQ, Feb. 23, 2018
10. Our Barren Moon. Moon Data (Table 10-1) Moon Data: Numbers. Moon Data: Special Features 1. The Moon As Seen From Earth
 10. Our Barren Moon Lunar plains & craters Manned lunar exploration The lunar interior The Moon s geologic history The formation of the Moon Moon Data (Table 10-1) Moon Data: Numbers Diameter: 3,476.km
10. Our Barren Moon Lunar plains & craters Manned lunar exploration The lunar interior The Moon s geologic history The formation of the Moon Moon Data (Table 10-1) Moon Data: Numbers Diameter: 3,476.km
Halogen and argon evidence of Martian hydrous fluids in nakhlite meteorites Ray Burgess
 Halogen and argon evidence of Martian hydrous fluids in nakhlite meteorites Ray Burgess School of Earth, Atmospheric and Environmental Sciences University of Manchester, UK Topics Halogens and noble gases
Halogen and argon evidence of Martian hydrous fluids in nakhlite meteorites Ray Burgess School of Earth, Atmospheric and Environmental Sciences University of Manchester, UK Topics Halogens and noble gases
Moon and Mercury 3/8/07
 The Reading Assignment Chapter 12 Announcements 4 th homework due March 20 (first class after spring break) Reminder about term paper due April 17. Next study-group session is Monday, March 19, from 10:30AM-12:00Noon
The Reading Assignment Chapter 12 Announcements 4 th homework due March 20 (first class after spring break) Reminder about term paper due April 17. Next study-group session is Monday, March 19, from 10:30AM-12:00Noon
Latitudinal Enrichment of Hydrogen in the Lunar Polar Regions: Constraints on Hydrogen Mobility
 Latitudinal Enrichment of Hydrogen in the Lunar Polar Regions: Constraints on Hydrogen Mobility W. V. Boynton, G. F. Droege, K. Harshman, M. A. Schaffner, I. G. Mitrofanov, T. P. McClanahan, and the LEND
Latitudinal Enrichment of Hydrogen in the Lunar Polar Regions: Constraints on Hydrogen Mobility W. V. Boynton, G. F. Droege, K. Harshman, M. A. Schaffner, I. G. Mitrofanov, T. P. McClanahan, and the LEND
Chapter 21. The Moon and Mercury: Comparing Airless Worlds
 Chapter 21 The Moon and Mercury: Comparing Airless Worlds Outline I. The Moon A. The View From Earth B. The Apollo Missions C. Moon Rocks D. The History of the Moon E. The Origin of Earth's Moon II. Mercury
Chapter 21 The Moon and Mercury: Comparing Airless Worlds Outline I. The Moon A. The View From Earth B. The Apollo Missions C. Moon Rocks D. The History of the Moon E. The Origin of Earth's Moon II. Mercury
GEOLOGIC TIME. Smith and Pun, Chapter 7 DETERMINING THE ORDER OF EVENTS
 GEOLOGIC TIME Smith and Pun, Chapter 7 DETERMINING THE ORDER OF EVENTS Examination of ancient rocks reveals the history of our planet. Sedimentary and volcanic rocks record processes that occur on the
GEOLOGIC TIME Smith and Pun, Chapter 7 DETERMINING THE ORDER OF EVENTS Examination of ancient rocks reveals the history of our planet. Sedimentary and volcanic rocks record processes that occur on the
Lab 5: An Investigation of Meteorites Geology 202: Earth s Interior
 Lab 5: An Investigation of Meteorites Geology 202: Earth s Interior Asteroids and Meteorites: What is the difference between asteroids and meteorites? Asteroids are rocky and metallic objects that orbit
Lab 5: An Investigation of Meteorites Geology 202: Earth s Interior Asteroids and Meteorites: What is the difference between asteroids and meteorites? Asteroids are rocky and metallic objects that orbit
In-situ geochronology General overview
 In-situ geochronology General overview Timothy D. Swindle, University of Arizona, Tucson AZ F. Scott Anderson, Southwest Research Institute, Boulder CO October 26, 2009 Decadal Survey Inner Planets Panel
In-situ geochronology General overview Timothy D. Swindle, University of Arizona, Tucson AZ F. Scott Anderson, Southwest Research Institute, Boulder CO October 26, 2009 Decadal Survey Inner Planets Panel
Moon 101. Bellaire High School Team: Rachel Fisher, Clint Wu, Omkar Joshi
 Moon 101 Bellaire High School Team: Rachel Fisher, Clint Wu, Omkar Joshi Part I Formation of the Moon Planetary Formation In the solar nebula, dust particles coalesced to form smaller planetesimals and
Moon 101 Bellaire High School Team: Rachel Fisher, Clint Wu, Omkar Joshi Part I Formation of the Moon Planetary Formation In the solar nebula, dust particles coalesced to form smaller planetesimals and
Report to the Planetary Science Subcommittee September, 2016 Hap McSween, Chair
 Dedicated to maximizing planetary sample science while protecting the integrity of NASA-collected extraterrestrial materials Report to the Planetary Science Subcommittee September, 2016 Hap McSween, Chair
Dedicated to maximizing planetary sample science while protecting the integrity of NASA-collected extraterrestrial materials Report to the Planetary Science Subcommittee September, 2016 Hap McSween, Chair
2016 PLED 576 Earth and Space Science Correlation to Next Generation Science Standards (NGSS) High School Earth and Space Science
 2016 PLED 576 Earth and Space Science Correlation to Next Generation Science Standards () High School Earth and Space Science Course Objectives 1. Evaluate the differing theories that explain the structure,
2016 PLED 576 Earth and Space Science Correlation to Next Generation Science Standards () High School Earth and Space Science Course Objectives 1. Evaluate the differing theories that explain the structure,
Table of Isotopic Masses and Natural Abudances
 Table of Isotopic Masses and Natural Abudances in amu, where 1amu = 1/12 mass 12 C Atomic weight element = M i (abun i )+M j (abun j ) + Four types of radioactive decay 1) alpha (α) decay - 4 He nucleus
Table of Isotopic Masses and Natural Abudances in amu, where 1amu = 1/12 mass 12 C Atomic weight element = M i (abun i )+M j (abun j ) + Four types of radioactive decay 1) alpha (α) decay - 4 He nucleus
12013 Breccia with granite 82.3 grams
 12013 Breccia with granite 82.3 grams Figure 1: Close-up photo of 12013,11. Field of view is 4.5 cm. NASA# S70-43636 Introduction 12013 is a unique lunar sample, but it did not appear to be remarkable
12013 Breccia with granite 82.3 grams Figure 1: Close-up photo of 12013,11. Field of view is 4.5 cm. NASA# S70-43636 Introduction 12013 is a unique lunar sample, but it did not appear to be remarkable
Phys 214. Planets and Life
 Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 10. Geology and life. Part 1 (Page 99-123)
Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 10. Geology and life. Part 1 (Page 99-123)
Dept., Univ. of ela as are, 'i?ewark, DE Approximately 130 low specific gravity ((2.601, high silica
 HIGH (760%) SiO LUNAR GLASS%. ir.f. Glass, Geoloey Dept., Univ. of ela as are, 'i?ewark, DE. 1971 1 Approximately 130 low specific gravity ((2.601, high silica p602) glass particles recovered from a 4.88
HIGH (760%) SiO LUNAR GLASS%. ir.f. Glass, Geoloey Dept., Univ. of ela as are, 'i?ewark, DE. 1971 1 Approximately 130 low specific gravity ((2.601, high silica p602) glass particles recovered from a 4.88
Strand 1: Inquiry Process
 Strand 1: Inquiry Process Concept 1: Observations, Questions, and Hypotheses Formulate predictions, questions, or hypotheses based on observations. Locate appropriate resources. PO 1. Formulate questions
Strand 1: Inquiry Process Concept 1: Observations, Questions, and Hypotheses Formulate predictions, questions, or hypotheses based on observations. Locate appropriate resources. PO 1. Formulate questions
Question 1 (1 point) Question 2 (1 point) Question 3 (1 point)
 Question 1 (1 point) If the Earth accreted relatively slowly, the heat obtained from the gravitational potential energy would have had time to escape during its accretion. We know that the Earth was already
Question 1 (1 point) If the Earth accreted relatively slowly, the heat obtained from the gravitational potential energy would have had time to escape during its accretion. We know that the Earth was already
72335 Impact melt Breccia grams
 Impact melt Breccia 108.9 grams Figure 1: Location of on boulder #2 on landslide off of South Massif. Boulder is ~ 2-3 meters high. AS17-137-20918. Transcript Hey, that s a different rock, Gene (station
Impact melt Breccia 108.9 grams Figure 1: Location of on boulder #2 on landslide off of South Massif. Boulder is ~ 2-3 meters high. AS17-137-20918. Transcript Hey, that s a different rock, Gene (station
Identify and explain monthly patterns in the phases of the Moon.
 (NGSS in Parentheses) Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards The phases of the Moon are caused by the orbit of the moon around the Earth. (ESS1.A) The phases
(NGSS in Parentheses) Grade Big Idea Essential Questions Concepts Competencies Vocabulary 2002 Standards The phases of the Moon are caused by the orbit of the moon around the Earth. (ESS1.A) The phases
Volatiles on Venus: A missing link in understanding terrestrial planet evolution
 Volatiles on Venus: A missing link in understanding terrestrial planet evolution Melissa G. Trainer Planetary Environments Laboratory NASA Goddard Space Flight Center 12 July 2017 Trainer - DS Mid-Term
Volatiles on Venus: A missing link in understanding terrestrial planet evolution Melissa G. Trainer Planetary Environments Laboratory NASA Goddard Space Flight Center 12 July 2017 Trainer - DS Mid-Term
Lunar Exploration Requirements and Data Acquisition Architectures
 Lunar Exploration Requirements and Data Acquisition Architectures J. Plescia P. Spudis B. Bussey Johns Hopkins University / Applied Physics Laboratory 2005 International Lunar Conference The Vision and
Lunar Exploration Requirements and Data Acquisition Architectures J. Plescia P. Spudis B. Bussey Johns Hopkins University / Applied Physics Laboratory 2005 International Lunar Conference The Vision and
Classroom Space Regolith Formation Teacher s Guide
 Regolith Formation on the Earth and the Moon. Background The loose fragments of material on the Moon s surface are called regolith. This regolith, a product of bombardment by meteorites, is the debris
Regolith Formation on the Earth and the Moon. Background The loose fragments of material on the Moon s surface are called regolith. This regolith, a product of bombardment by meteorites, is the debris
Bishop Ussher (1650) Absolute Age Dating. Early attempts at the age of the Earth
 Absolute Age Dating Relative age dating just says that one rock unit or geologic event is younger or older than another Dave is older than Steve Absolute age dating gives a number to the age Dave is 89
Absolute Age Dating Relative age dating just says that one rock unit or geologic event is younger or older than another Dave is older than Steve Absolute age dating gives a number to the age Dave is 89
Teachers Guide. Making Regolith. Down to Earth KS3
 Teachers Guide Making Regolith Making Regolith - Teachers Guide - 2 Making Regolith on the Earth and the Moon Background All Moon rocks originated through hightemperature processes with little or no involvement
Teachers Guide Making Regolith Making Regolith - Teachers Guide - 2 Making Regolith on the Earth and the Moon Background All Moon rocks originated through hightemperature processes with little or no involvement
The Main Point. Basic Properties of Mars. Observations. Lecture #19: Mars
 Mars: Overview General properties Telescopic observations Space missions Atmospheric Characteristics Reading: Chapters 7.1 (Mars), 9.4, 10.4 Lecture #19: Mars The Main Point Changes in the Martian surface
Mars: Overview General properties Telescopic observations Space missions Atmospheric Characteristics Reading: Chapters 7.1 (Mars), 9.4, 10.4 Lecture #19: Mars The Main Point Changes in the Martian surface
65055 Basaltic Impact Melt grams
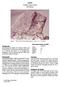 65055 Basaltic Impact Melt 500.8 grams Figure 1: Photo of 65055 showing large zap pit. Cube is 1 cm. S72-43869. Introduction According to the Apollo 16 Catalog by Ryder and Norman, 65055 is an aluminous,
65055 Basaltic Impact Melt 500.8 grams Figure 1: Photo of 65055 showing large zap pit. Cube is 1 cm. S72-43869. Introduction According to the Apollo 16 Catalog by Ryder and Norman, 65055 is an aluminous,
grams g g g g Regolith Breccia
 15306 134.2 grams 15315 35.6 g 15324 32.3 g 15325 57.8 g 15330 57.8 g Regolith Breccia Figure 1a,b: Photo of dust-covered 15306. Sample is 7 cm across. S71-43064 and 067. Introduction 15306 is a regolith
15306 134.2 grams 15315 35.6 g 15324 32.3 g 15325 57.8 g 15330 57.8 g Regolith Breccia Figure 1a,b: Photo of dust-covered 15306. Sample is 7 cm across. S71-43064 and 067. Introduction 15306 is a regolith
Teachersʼ Guide. Creating Craters. Down to Earth KS3
 Teachersʼ Guide Creating Craters Creating Craters! Creating Craters - Teachersʼ Guide - 2 Overview This lesson allows pupils to create impact craters in layered dry materials. Pupils can perform controlled
Teachersʼ Guide Creating Craters Creating Craters! Creating Craters - Teachersʼ Guide - 2 Overview This lesson allows pupils to create impact craters in layered dry materials. Pupils can perform controlled
The Moon: Internal Structure & Magma Ocean
 The Moon: Internal Structure & Magma Ocean 1 Lunar Magma Ocean & Lunar Interior 2 Two possible views of the Moon s interior: The Moon: Internal Structure 3 Like Earth, the Moon is a differentiated body.
The Moon: Internal Structure & Magma Ocean 1 Lunar Magma Ocean & Lunar Interior 2 Two possible views of the Moon s interior: The Moon: Internal Structure 3 Like Earth, the Moon is a differentiated body.
Thermal, Thermophysical, and Compositional Properties of the Moon Revealed by the Diviner Lunar Radiometer
 Thermal, Thermophysical, and Compositional Properties of the Moon Revealed by the Diviner Lunar Radiometer Benjamin T. Greenhagen Jet Propulsion Laboratory David A. Paige and the Diviner Science Team LEAG
Thermal, Thermophysical, and Compositional Properties of the Moon Revealed by the Diviner Lunar Radiometer Benjamin T. Greenhagen Jet Propulsion Laboratory David A. Paige and the Diviner Science Team LEAG
Signature: GEOLOGICAL SCIENCES 0050
 GEOLOGICAL SCIENCES 0050 I am aware of the Brown University Honor Code [see the Student Handbook, which can be accessed through the Geo0050 web site], understand that this exercise falls under that code,
GEOLOGICAL SCIENCES 0050 I am aware of the Brown University Honor Code [see the Student Handbook, which can be accessed through the Geo0050 web site], understand that this exercise falls under that code,
Earth History 8/21/2016. Introduction to Environmental Geology GEO-106 Instructor: Calvin K. Prothro; PG. Inception: 4.
 Introduction to Environmental Geology GEO-106 Instructor: Calvin K. Prothro; PG Earth History Inception: 4.6 billion yrs Figure 1.A The planetary densities are consistent with a higher metal and rock content
Introduction to Environmental Geology GEO-106 Instructor: Calvin K. Prothro; PG Earth History Inception: 4.6 billion yrs Figure 1.A The planetary densities are consistent with a higher metal and rock content
The Surprising Lunar Maria
 1 of 5 posted June 23, 2000 The Surprising Lunar Maria Written by G. Jeffrey Taylor Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology The lunar maria, the dark, smooth areas on the Moon, formed when lava
1 of 5 posted June 23, 2000 The Surprising Lunar Maria Written by G. Jeffrey Taylor Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology The lunar maria, the dark, smooth areas on the Moon, formed when lava
The Age of the Earth and the Planets. Sara Russell
 The Age of the Earth and the Planets Sara Russell Sarr@nhm.ac.uk The Natural History Museum, London Talk structure Historical ideas about the age of the Earth The use of radioactive isotopes as geological
The Age of the Earth and the Planets Sara Russell Sarr@nhm.ac.uk The Natural History Museum, London Talk structure Historical ideas about the age of the Earth The use of radioactive isotopes as geological
GEOCHRONOLOGY Lecture 07 Common Lead Dating
 GEOCHRONOLOGY 2008 Lecture 07 Common Lead Dating Common Lead vs Radiogenic Lead Pb derived from decay of U and Th is described as radiogenic lead. In a system containing U and Th, the isotopic composition
GEOCHRONOLOGY 2008 Lecture 07 Common Lead Dating Common Lead vs Radiogenic Lead Pb derived from decay of U and Th is described as radiogenic lead. In a system containing U and Th, the isotopic composition
The origin of geochemical diversity of lunar mantle sources inferred from the combined U Pb, Rb Sr, and Sm Nd isotope systematics of mare basalt 10017
 Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 71 (2007) 3656 3671 www.elsevier.com/locate/gca The origin of geochemical diversity of lunar mantle sources inferred from the combined U Pb, Rb Sr, and Sm Nd isotope systematics
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 71 (2007) 3656 3671 www.elsevier.com/locate/gca The origin of geochemical diversity of lunar mantle sources inferred from the combined U Pb, Rb Sr, and Sm Nd isotope systematics
Stas Barabash 1 Yoshifumi Futaana 1 and the SELMA Team. Swedish Institute of Space Physics Kiruna, Sweden. DAP, Boulder, January, 2017
 Stas Barabash 1 Yoshifumi Futaana 1 and the SELMA Team 1 Swedish Institute of Space Physics Kiruna, Sweden DAP, Boulder, January, 2017 1 SELMA core team 2 SELMA main scientific questions SELMA (Surface,
Stas Barabash 1 Yoshifumi Futaana 1 and the SELMA Team 1 Swedish Institute of Space Physics Kiruna, Sweden DAP, Boulder, January, 2017 1 SELMA core team 2 SELMA main scientific questions SELMA (Surface,
GLY August, Ms. Nelda Breedt. Fragment of extra-terrestrial material that strikes the surface of the Earth.
 Meteorite Impacts Ms. Nelda Breedt GLY 162 Environmental Geology 2 Meteorite Impacts Meteorite Fragment of extra-terrestrial material that strikes the surface of the Earth. Meteoroid Before hitting the
Meteorite Impacts Ms. Nelda Breedt GLY 162 Environmental Geology 2 Meteorite Impacts Meteorite Fragment of extra-terrestrial material that strikes the surface of the Earth. Meteoroid Before hitting the
AN INTRODUCTION TO COSMOCHEMISTRY
 AN INTRODUCTION TO COSMOCHEMISTRY CHARLES R. COWLEY Professor of Astronomy, University of Michigan CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Foreword V a % e x i 1 Overview 1 1.1 The Scope of Cosmochemistry 1 1.2 Cosmochemistry
AN INTRODUCTION TO COSMOCHEMISTRY CHARLES R. COWLEY Professor of Astronomy, University of Michigan CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Foreword V a % e x i 1 Overview 1 1.1 The Scope of Cosmochemistry 1 1.2 Cosmochemistry
Comets and the Origin and Evolution of Life
 Paul J. Thomas Christopher F. Chyba Christopher P. McKay Editors Comets and the Origin and Evolution of Life With 47 Illustrations Springer Contents Contributors xi Introduction: Comets and the Origin
Paul J. Thomas Christopher F. Chyba Christopher P. McKay Editors Comets and the Origin and Evolution of Life With 47 Illustrations Springer Contents Contributors xi Introduction: Comets and the Origin
NASA: BACK TO THE MOON
 NASA: BACK TO THE MOON Don Campbell Cornell University "I believe that this nation should commit itself to achieving the goal, before this decade is out, of landing a man on the moon and returning him
NASA: BACK TO THE MOON Don Campbell Cornell University "I believe that this nation should commit itself to achieving the goal, before this decade is out, of landing a man on the moon and returning him
LUNAR STRATIGRAPHY AND SEDIMENTOLOGY.
 LUNAR STRATIGRAPHY AND SEDIMENTOLOGY. Developments in Solar System- and Space Science, 3 Editors: Z. KOPAL and A.G.W. CAMERON Developments in Solar System- and Space Science, 3 LUNAR STRATIGRAPHY AND SEDIMENTOLOGY
LUNAR STRATIGRAPHY AND SEDIMENTOLOGY. Developments in Solar System- and Space Science, 3 Editors: Z. KOPAL and A.G.W. CAMERON Developments in Solar System- and Space Science, 3 LUNAR STRATIGRAPHY AND SEDIMENTOLOGY
Neutron activation analysis. Contents. Introduction
 Neutron activation analysis Contents Neutron activation analysis... 1 Introduction... 1 Principle of method... 2 Detection of radionuclides... 3 Kinetics of activation... 4 Choosing the appropriate procedure...
Neutron activation analysis Contents Neutron activation analysis... 1 Introduction... 1 Principle of method... 2 Detection of radionuclides... 3 Kinetics of activation... 4 Choosing the appropriate procedure...
The Moon. A look at our nearest neighbor in Space! Free powerpoints at
 The Moon A look at our nearest neighbor in Space! Free powerpoints at http://www.worldofteaching.com What is the Moon? A natural satellite One of more than 96 moons in our Solar System The only moon of
The Moon A look at our nearest neighbor in Space! Free powerpoints at http://www.worldofteaching.com What is the Moon? A natural satellite One of more than 96 moons in our Solar System The only moon of
Surface analysis techniques
 Experimental methods in physics Surface analysis techniques 3. Ion probes Elemental and molecular analysis Jean-Marc Bonard Academic year 10-11 3. Elemental and molecular analysis 3.1.!Secondary ion mass
Experimental methods in physics Surface analysis techniques 3. Ion probes Elemental and molecular analysis Jean-Marc Bonard Academic year 10-11 3. Elemental and molecular analysis 3.1.!Secondary ion mass
Cosmic Building Blocks: From What is Earth Made?
 Cosmic Building Blocks: From What is Earth Made? The Sun constitutes 99.87% of the mass of the Solar system. Earth is big and important, so its composition should be similar to that of the average Solar
Cosmic Building Blocks: From What is Earth Made? The Sun constitutes 99.87% of the mass of the Solar system. Earth is big and important, so its composition should be similar to that of the average Solar
of Copernicus and the source of nonmare materials
 Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 70 (2006) 6016 6031 www.elsevier.com/locate/gca 40 Ar/ 39 Ar dating of Apollo 12 regolith: Implications for the age of Copernicus and the source of nonmare materials Fernando
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 70 (2006) 6016 6031 www.elsevier.com/locate/gca 40 Ar/ 39 Ar dating of Apollo 12 regolith: Implications for the age of Copernicus and the source of nonmare materials Fernando
2 Igneous Rock. How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture of igneous rock? BEFORE YOU READ. Rocks: Mineral Mixtures
 CHAPTER 2 2 Igneous Rock SECTION Rocks: Mineral Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture
CHAPTER 2 2 Igneous Rock SECTION Rocks: Mineral Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture
Mercury = Hermes Mythology. Planet Mercury, Element, Mercredi God of Commerce, Messenger God, guide to Hades Winged sandals and staff
 Mercury = Hermes Mythology Planet Mercury, Element, Mercredi God of Commerce, Messenger God, guide to Hades Winged sandals and staff Mercury s Orbit Mercury never seen more than 28 from the sun Revolves/orbits
Mercury = Hermes Mythology Planet Mercury, Element, Mercredi God of Commerce, Messenger God, guide to Hades Winged sandals and staff Mercury s Orbit Mercury never seen more than 28 from the sun Revolves/orbits
Complete the crossword puzzle. The Moon. (Key # )
 Name Complete the crossword puzzle. The Moon Date (Key # 1-168014) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Across 1 : The moon appears bigger on the horizon than it does high in the sky, but in reality it is the same
Name Complete the crossword puzzle. The Moon Date (Key # 1-168014) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Across 1 : The moon appears bigger on the horizon than it does high in the sky, but in reality it is the same
Earth History 870:035
 Earth History 870:035 Course goal: To describe the history of Earth and its inhabitants Most of Earth s history predates humanity, so it has not been observed Therefore, we will emphasize how scientists
Earth History 870:035 Course goal: To describe the history of Earth and its inhabitants Most of Earth s history predates humanity, so it has not been observed Therefore, we will emphasize how scientists
GEOLOGIC EVENTS SEDIMENTARY ROCKS FAULTING FOLDING TILTING
 RELATIVE TIME (DATING) ABSOLUTE TIME (DATING) GEOLOGIC TIME List the order in which events occurred, without regard to the amount of time separating them. Refers to the age of a rock in relation to other
RELATIVE TIME (DATING) ABSOLUTE TIME (DATING) GEOLOGIC TIME List the order in which events occurred, without regard to the amount of time separating them. Refers to the age of a rock in relation to other
Teacher Background. Impact! Down to Earth KS 3&4
 Teacher Background Impact! Impact! - Teacher Background- 2 Meteorites What Are They, and Where Do They Come From? Meteorites are rocks from space that have passed through the atmosphere and landed on the
Teacher Background Impact! Impact! - Teacher Background- 2 Meteorites What Are They, and Where Do They Come From? Meteorites are rocks from space that have passed through the atmosphere and landed on the
Constraints on the U-Pb isotopic systematics of Mars inferred from a combined U-Pb, Rb-Sr, and Sm-Nd isotopic study of the Martian meteorite Zagami
 doi:10.1016/j.gca.2005.08.007 Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, Vol. 69, No. 24, pp. 5819 5830, 2005 Copyright 2005 Elsevier Ltd Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0016-7037/05 $30.00.00 Constraints
doi:10.1016/j.gca.2005.08.007 Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, Vol. 69, No. 24, pp. 5819 5830, 2005 Copyright 2005 Elsevier Ltd Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0016-7037/05 $30.00.00 Constraints
Vital Statistics. The Moon. The Tides The gravitational pull between the Earth, the Moon and the Sun causes three inter-related effects: Lunar Phases
 Vital Statistics Orbit & tides Apollo & beyond Surface Interior Origin The Moon Vital Statistics Mean distance from Earth 384400 km Orbital period (sidereal) Rotational period 27.322 days Eccentricity
Vital Statistics Orbit & tides Apollo & beyond Surface Interior Origin The Moon Vital Statistics Mean distance from Earth 384400 km Orbital period (sidereal) Rotational period 27.322 days Eccentricity
Martian Meteorites 1
 Martian Meteorites 1 The SNCs How do we know the SNCs are from Mars? [Taylor & McLennan, 2009] 2 The SNCs Abundances and isotopic compositions of gases trapped in impact melt glasses match those measured
Martian Meteorites 1 The SNCs How do we know the SNCs are from Mars? [Taylor & McLennan, 2009] 2 The SNCs Abundances and isotopic compositions of gases trapped in impact melt glasses match those measured
Detection of Adsorbed Water and Hydroxyl on the Moon
 Detection of Adsorbed Water and Hydroxyl on the Moon Roger N. Clark U. S. Geological Survey, MS 964, Box 25046 Federal Center, Denver CO 80227, USA. E-mail: rclark@usgs.gov Data from the Visual and Infrared
Detection of Adsorbed Water and Hydroxyl on the Moon Roger N. Clark U. S. Geological Survey, MS 964, Box 25046 Federal Center, Denver CO 80227, USA. E-mail: rclark@usgs.gov Data from the Visual and Infrared
Part 1: The Search for Evidence of Life on Mars. Chair: Dan McCleese
 Part 1: The Search for Evidence of Life on Mars by the Mars Expeditions Strategy Group Chair: Dan McCleese Focus Did life ever exist on Mars? A multi-disciplinary group of scientists brought together by
Part 1: The Search for Evidence of Life on Mars by the Mars Expeditions Strategy Group Chair: Dan McCleese Focus Did life ever exist on Mars? A multi-disciplinary group of scientists brought together by
Geologic Time: Concepts and Principles
 Geologic Time: Concepts and Principles Introduction - An appreciation for the immensity of geologic time is essential for understanding the history of our planet - Geologists use two references for time
Geologic Time: Concepts and Principles Introduction - An appreciation for the immensity of geologic time is essential for understanding the history of our planet - Geologists use two references for time
General Introduction. The Earth as an evolving geologic body
 General Introduction The Earth as an evolving geologic body Unique/important attributes of Planet Earth 1. Rocky planet w/ strong magnetic field Mercury has a weak field, Mars has a dead field 1 Unique/important
General Introduction The Earth as an evolving geologic body Unique/important attributes of Planet Earth 1. Rocky planet w/ strong magnetic field Mercury has a weak field, Mars has a dead field 1 Unique/important
Composition of the Moon's Crust
 1 of 7 posted December 10, 2004 Composition of the Moon's Crust --- New empirical calibrations of Lunar Prospector and Clementine data yield improved global maps of Th, K, and FeO. The movie of the Moon,
1 of 7 posted December 10, 2004 Composition of the Moon's Crust --- New empirical calibrations of Lunar Prospector and Clementine data yield improved global maps of Th, K, and FeO. The movie of the Moon,
GCSE ready intervention tasks
 7. Earth 1 LEARNING CONTEXT AQA Big idea: 3.7 Earth AQA Strand: 3.7.1 Earth structure 3.7.2 Universe AQA Enquiry processes: 2.3 Draw conclusions 2.7 Critique claims How this provides GCSE readiness: The
7. Earth 1 LEARNING CONTEXT AQA Big idea: 3.7 Earth AQA Strand: 3.7.1 Earth structure 3.7.2 Universe AQA Enquiry processes: 2.3 Draw conclusions 2.7 Critique claims How this provides GCSE readiness: The
The Moon. Tides. Tides. Mass = 7.4 x 1025 g = MEarth. = 0.27 REarth. (Earth 5.5 g/cm3) Gravity = 1/6 that of Earth
 The Moon Mass = 7.4 x 1025 g = 0.012 MEarth Radius = 1738 km = 0.27 REarth Density = 3.3 g/cm3 (Earth 5.5 g/cm3) Gravity = 1/6 that of Earth Dark side of the moon We always see the same face of the Moon.
The Moon Mass = 7.4 x 1025 g = 0.012 MEarth Radius = 1738 km = 0.27 REarth Density = 3.3 g/cm3 (Earth 5.5 g/cm3) Gravity = 1/6 that of Earth Dark side of the moon We always see the same face of the Moon.
Analyzing Next to Nothing
 1 of 5 posted April 26, 2000 Analyzing Next to Nothing Written by G. Jeffrey Taylor Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology Analytical techniques have advanced so far that it is possible to slice
1 of 5 posted April 26, 2000 Analyzing Next to Nothing Written by G. Jeffrey Taylor Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology Analytical techniques have advanced so far that it is possible to slice
A geologic process An erosional force A chronological tool An influence on biology
 Impact Cratering: Physics and Chronology A geologic process An erosional force A chronological tool An influence on biology Impact features are common All solar system bodies with solid surfaces show evidence
Impact Cratering: Physics and Chronology A geologic process An erosional force A chronological tool An influence on biology Impact features are common All solar system bodies with solid surfaces show evidence
DARPA Lunar Study: Reducing the technical risk associated with lunar resource utilization and lunar surface presence
 Space Missions DARPA Lunar Study: Reducing the technical risk associated with lunar resource utilization and lunar surface presence International Lunar Conference 2005 Toronto, Canada Paul Fulford 1, Karen
Space Missions DARPA Lunar Study: Reducing the technical risk associated with lunar resource utilization and lunar surface presence International Lunar Conference 2005 Toronto, Canada Paul Fulford 1, Karen
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 ASTRO 102/104 Prelim 2 Name Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) This is version E of the exam. Please fill in (E). A) This
ASTRO 102/104 Prelim 2 Name Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) This is version E of the exam. Please fill in (E). A) This
How old is Earth? Bishop of Ireland James Ussher
 Geologic Time How old is Earth? Bishop of Ireland James Ussher Not so long ago, the Bible was regarded as the ultimate source of truth. Through the 18th and 19th centuries it was believed that the world
Geologic Time How old is Earth? Bishop of Ireland James Ussher Not so long ago, the Bible was regarded as the ultimate source of truth. Through the 18th and 19th centuries it was believed that the world
Habitable Environments of Ancient Mars: Deciphering the Rock Record. John Grotzinger
 Habitable Environments of Ancient Mars: Deciphering the Rock Record John Grotzinger Modern Mars: Recurring Slope Lineae McEwan et al., 2014 Mars Timeline: Water-related environments Ehlmann et al., 2011,
Habitable Environments of Ancient Mars: Deciphering the Rock Record John Grotzinger Modern Mars: Recurring Slope Lineae McEwan et al., 2014 Mars Timeline: Water-related environments Ehlmann et al., 2011,
Overview of Lunar Science Objectives. Opportunities and guidelines for future missions.
 Overview of Lunar Science Objectives. Opportunities and guidelines for future missions. Chip Shearer Institute of Meteoritics University of New Mexico Albuquerque, New Mexico 87131 A rich scientific target
Overview of Lunar Science Objectives. Opportunities and guidelines for future missions. Chip Shearer Institute of Meteoritics University of New Mexico Albuquerque, New Mexico 87131 A rich scientific target
Stardust and Hayabusa Missions. Mike Zolensky NASA JSC
 Stardust and Hayabusa Missions Mike Zolensky NASA JSC 150 km from nucleus ΔV= 6.1 km/s January 2, 2004 Wild 2 (81P) A Jupiter family comet captured into present orbit in 1973 after a 0.006 AU Jupiter encounter
Stardust and Hayabusa Missions Mike Zolensky NASA JSC 150 km from nucleus ΔV= 6.1 km/s January 2, 2004 Wild 2 (81P) A Jupiter family comet captured into present orbit in 1973 after a 0.006 AU Jupiter encounter
Origin of Earth's moon Short Course Notes
 Origin of Earth's moon Short Course Notes I gave this short course several times to groups of high school earth science teachers, 1994-1998. The information herein was derived from many sources, some of
Origin of Earth's moon Short Course Notes I gave this short course several times to groups of high school earth science teachers, 1994-1998. The information herein was derived from many sources, some of
