EARTH STRUCTURE & DYNAMICS EARTHQUAKE SEISMOLOGY PRACTICALS. G.R. Foulger
|
|
|
- Rosamond McKenzie
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 EARTH STRUCTURE & DYNAMICS EARTHQUAKE SEISMOLOGY PRACTICALS G.R. Foulger 1. A large earthquake is recorded well at a three-component seismic station in Hawaii (coordinates 205 E, 20 N). The epicentral distance was measured, by examining the arrival times of the P, PP, S, Rayleigh and Love phases, and found to be The direction of arrival of the waves was measured, using the amplitudes of S waves on the horizontal components and the phases of the Rayleigh waves, and the azimuth of the earthquake from the station was found to be Using spherical trigonometry, calculate the longitude and latitude of the earthquake and plot it on Figure 1. The formulae you require are: a = cos!1 (cos bcosc + sin bsinc cos A) C = cos!1 " cosc! cos acosb$ # sina sinb % Spherical geometry for great-circle paths 2. Sketch a cross section of the Earth showing the major seismic boundaries and sketch the following waves: PKIKP, PKiKP, PKJKP, ss, Sg, Pn, PS. 3. Your are provided with three-component teleseismic seismograms, with clock marks at minute intervals, for two earthquakes, Earthquake 1 and Earthquake 2. Determine their epicentral distances.
2 2 To do this, take a long strip of paper and lay it on the seismograms one-by-one, marking the positions of the phases you can see. The following phases are clear: Phase EQ 1 EQ 2 P (very faint!) PP SKS S PS SS G (Love) R (Rayleigh) Note that P arrivals and R are expected to be clearest on the vertical component. For the vertical record of Earthquake 1, R is the strongest arrival, P is second strongest, PP third strongest and S fourth strongest. S arrivals and G are expected to be clearest on the horizontal components. You are provided with a Gutenberg-Richter travel time chart for earthquakes at 25 km depth. This is a chart of time in minutes (vertical axis) : epicentral distance in degrees (horizontal axis). The vertical axis is at the same scale as your seismograms. Lay your marked paper strip on the chart and estimate the epicentral distance of each earthquake. 4. Measure the magnitudes of Earthquakes 1 and 2 using the surface waves. The equation is: M S = log A! log A 0 (" ) M S = surface-wave magnitude A = amplitude in mm of surface waves with period ~ 20 s! = epicentral distance of the earthquake, log A 0 (! ) = logarithm of the amplitude of a magnitude zero earthquake at distance! Use the zero-earthquake amplitude table given below to compute log A 0 (! ).
3 3 Zero-earthquake amplitude table, from Richter (1958). 5. You are provided with three-component seismograms for surface waves from a large, distant earthquake recorded at station CMB (Earthquake 3). This station is located in the Sierra Nevada of California (Figure 1). Label the Love and Rayleigh waves. Remember that Love waves travel faster than Rayleigh waves. On rotated seismograms, Love waves are only recorded on the transverse component and Rayleigh waves are only recorded on the vertical and radial components. Determine the approximate direction of approach by looking at the particle motion of the earliest part of the Rayleigh wave train. Remember that particle motion in Rayleigh waves traces a retrograde ellipse in a direction parallel to the direction of travel of the ray. The NS component seismogram shows clear Love waves but very poor Rayleigh waves. Is this observation consistent with your conclusion from the particle motion? Construct a surface-wave dispersion curve for Earthquake 3. For the first 5 cycles of the Rayleigh wave, and every 5th cycle thereafter, measure the arrival time from the first arrival and the period of one cycle. The time marks on the seismograms are spaced at intervals of 1 minute. Calculate the group velocity of each cycle, assuming the epicentral distance to be 10,000 km and the travel time of the earliest Rayleigh wave arrival to be 50 min. Plot a graph of group velocity (km/s) : period (s). You are provided with surface-wave dispersion curves for typical oceanic and continental structures. Which does your curve most resemble? Is your conclusion in agreement with the direction of approach you calculated for this earthquake?
4 4 6. The table below gives the numbers of earthquakes Ms > 7.1 for the world. In the right most two columns write down the cumulative numbers of earthquakes > each magnitude range. Plot a graph of cumulative number : magnitude on semi-log graph paper. (Assign the average magnitude to the earthquakes in each magnitude band, and plot magnitude on the linear scale). < Ms < # eqs (M S ) #eqs (Mw used for 10 largest eqs) Cum. # eqs (M S ) Cum. # eqs (M w used for 10 largest eqs) If the events are distributed fractally they will follow the formula: log 10!N = a " bm where ΣN is the cumulative number > magnitude M and a and b are constants. The value of b for the world is almost exactly = 1. Draw a best-fit line with slope -1 passing through the points for the smallest magnitudes. These points are dependent on larger numbers of earthquakes than the points for the largest magnitudes, and thus they are more reliable. Your write-up should include the following: 1. A table showing your data; 2. Your b-value plot; 3. A 300-word write-up describing your results. This should include: a. a description of how the data are distributed, whether they fit both the lowand high-magnitude ends of the plot well, a) for M S and b) for M W ; b. suggested reasons for your observations.
5 5 Marks will be given for evidence of clear understanding of the goodness-of-fit of the data in the low- and high-magnitude ranges, and for critical comment that illustrates understanding of the relevant interpretive issues. 7. A system where a series is generated by inputting the output from a previous step has the potential to behave chaotically. Thus, natural systems have this potential, as their evolution following any point in time is dependent upon their state at that point. Chaotic systems are very sensitive to starting conditions and, although their state may vary within certain bounds and have structure, can only be predicted exactly a short time into the future. The weather is a well-known example of a chaotic system. However, the weather is a very complicated system. What is less well known is that even extremely simple systems can behave chaotically. This is an exercise designed to increase your understanding of chaos and provoke thoughts about what implications it has for earthquake occurrence and prediction. Work in pairs for this exercise. You are provided with four graphs of the parabolic function y = 4λx(1-x), for λ = 0.7, 0.785, 0.87 and 0.9. Also drawn on the graphs is the line x = y. 1. Starting with the graph for λ = 0.7, draw a line vertically upwards from the x-axis at x = 0.04 until it reaches the parabola. 2. Note the value of y. Your partner will simultaneously plot a graph of step # : y-value. (Adjust the axes on the paper to give room to go up to 30 steps.) 3. Your value of y at this point (the "output") will become your next value of x (the "input"). In order to make it easy to continue, draw a line horizontally from the point of intersection with the parabola until it intersects the line y = x. Then draw a second vertical line to the parabola from that intersection point. 4. Go to 2 Continue repeating steps 2-4 until the resultant pattern is clear. Repeat this exercise for the other three graphs. How do the four graphs of step # : y- value differ? When the whole class has finished all four graphs, compare all the graphs of step # : y-value. How similar are they for each of the four values of λ? This exercise illustrates the different types of behaviour that can occur when what happens next is dependent on what the situation is now. What implications does it have for earthquake occurrence? Stress in the Earth is governed by many factors (e.g., rain, nearby earthquakes, Earth tides, plate motions, heat flow) and thus how it varies is complicated. Is this the reason why earthquakes are difficult to predict? For more information on this fascinating subject, look at: Hofstadter, D. R., Mathematical Chaos and Strange Attractors, Chapter 16, pp , in Metamagical Themas, Basic Books Inc., New York, pp 852, You are provided with an equal-area transparent plot of seismogram polarities for the M ~ 6 earthquake of 1633:44 UTC 25 May 1980 at Mammoth Lakes, California. Use the stereo net provided to plot nodal lines of the best-fitting double couple solution. These
6 6 nodal lines are great circles and should intersect at 90. What is the minimum number of violations you can achieve? You are also provided with a plot of the nodal lines of a CLVD source with its plane of symmetry with a hade of 8. Also shown are the nodal lines for a CLVD+20% explosion and a CLVD+20% implosion. Plot on the polarity plot the best fitting nodal lines for an interpretation involving a CLVD+implosion. These lines will form members of the "family" of CLVD+implosion lines shown. What is the minimum number of violations you can achieve? What can you say about the area of the focal sphere violated by each interpretation? Do you think that these data are convincing evidence for non-double couple earthquakes? 9. For the case of an expanding cavity, the equivalent seismic moment is given by the equation: M o = 4! 3 a 3 (" µ)#$ where a = the radius of a spherical volume,!" = the fractional change in volume, and! " µ " 3 N m -2. In the period 1975 to 1984 the magma chamber beneath the Krafla volcano, Iceland, which is thought to be roughly spherical and about 50 km 3 in volume, was inflated by the continuous inflow of 5 m 3 s -1 of magma. Calculate the equivalent seismic moment of this inflation. If all this energy was released seismically, what would be the moment magnitude of the resulting earthquake? The moment magnitude relationship is: M = 2 log Mo! 6.0 w You are provided with seismograms for events A, B, C and D (Figure 2). The events occurred in southern Xinjiang, China, and the seismograms were recorded at station ARU (Figure 3). The objective of this exercise is to discriminate which is/are earthquake(s) and which is/are nuclear explosion(s). Comment on the quasi-sinusoidal signal on the seismogram for event D. Below is a table of co-ordinates. Calculate the epicentral distances in degrees between ARU and the events. Event/station Longitude Latitude ARU A B C D
7 7 Assuming all the events to have occurred at or close to the surface, use the Gutenberg- Richter travel time chart to predict the time of arrival of the S waves and the first Rayleigh waves. Figure 4 shows the seismograms high-pass filtered at 12.5 s. Mark the first P-wave arrivals and the predicted first S- and Rayleigh-wave arrivals. How clear are the S waves compared to the P waves for each event? How strong is the surface wave train compared with the P-wave train for each event? Using the blow-ups of the seismograms (Figures 5-8), measure the amplitudes of the highest-amplitude body and surface wave for each event and tabulate the results. Tabulate also the ratio of the logarithm of the surface-wave amplitude to the logarithm of the body-wave amplitude. This is analogous to (but not the same as) the ratio of M S :m b. Comment on your results. You are provided with spectra for the P and S waves for each event (Figures 9-12). For frequencies of 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 Hz, measure the amplitudes of the P and S waves. Smooth the spectra by eye as you make the measurements. Plot graphs of amp P amp S : frequency for each of the four events, on the same piece of paper. Use all your results to decide which events are nuclear explosions and which are earthquakes. State clearly the evidence you have for your conclusions.
8 Figure 1 2
9 3
10 4
11 5
12 6
13 7
14 8
15 9
16 10
17 Figure 2 11
18 Figure 3 12
19 Figure 4 13
20 Figure 5 14
21 Figure 6 15
22 Figure 7 16
23 Figure 8 17
24 Figure 9 18
25 Figure 10 19
26 Figure 11 20
27 Figure 12 21
Decoding seismograms, theoretical travel times. Simple velocity models of the Earth
 Decoding seismograms, theoretical travel times Once you think you have located an earthquake on your record you can find out what the details of the seismogram are showing you by finding out the predicted
Decoding seismograms, theoretical travel times Once you think you have located an earthquake on your record you can find out what the details of the seismogram are showing you by finding out the predicted
Earthquake Lab Introduction: Purpose: Method: Equipment needed: Fundamental Concepts and Key Terms:
 Earthquake Lab Introduction: Seismology is that branch of the geological sciences which is concerned with the study of earthquakes. Purpose: The purpose of this exercise is to introduce some fundamental
Earthquake Lab Introduction: Seismology is that branch of the geological sciences which is concerned with the study of earthquakes. Purpose: The purpose of this exercise is to introduce some fundamental
OCEAN/ESS 410. Lab 12. Earthquake Focal Mechanisms. You can write your answers to all be (e) on this paper.
 Lab 1. Earthquake Focal Mechanisms You can write your answers to all be (e) on this paper. In this class we are going to use P-wave first motions to obtain a double-couple focal mechanism for a subduction
Lab 1. Earthquake Focal Mechanisms You can write your answers to all be (e) on this paper. In this class we are going to use P-wave first motions to obtain a double-couple focal mechanism for a subduction
5. EARTHQUAKES AND EARTH S INTERIOR
 LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 5. EARTHQUAKES AND EARTH S INTERIOR EARTHQUAKE An earthquake is ground shaking caused by sudden and rapid movement of one block of rock slipping past another along
LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: 5. EARTHQUAKES AND EARTH S INTERIOR EARTHQUAKE An earthquake is ground shaking caused by sudden and rapid movement of one block of rock slipping past another along
LAB 3: GLOBAL SEISMOLOGY
 NAME: LAB TIME: LAB 3: GLOBAL SEISMOLOGY This lab will introduce you to the basic concepts of global seismology and the Earth s interior structure. This is a hybrid assignment: some aspects can be done
NAME: LAB TIME: LAB 3: GLOBAL SEISMOLOGY This lab will introduce you to the basic concepts of global seismology and the Earth s interior structure. This is a hybrid assignment: some aspects can be done
Lab Activity Locating Epicenters
 Lab Activity Locating Epicenters Key Features: Analyzing Seismograms P-waves & S-waves Using ESRT page 11 Drawing Epicenter Circles By Kaitlin Coder https://www.teacherspayteachers.com/store/nys-earth-science-and-living-environment-regents
Lab Activity Locating Epicenters Key Features: Analyzing Seismograms P-waves & S-waves Using ESRT page 11 Drawing Epicenter Circles By Kaitlin Coder https://www.teacherspayteachers.com/store/nys-earth-science-and-living-environment-regents
Objective: You will learn to interpret a seismogram and, using differences in seismic waves, locate the epicenter of an earthquake.
 Earth Science Dynamic Crust Name Period Finding Epicenters Lab# Introduction: Earthquakes occur when there is movement along a fault. The friction between rock masses rubbing against one another generates
Earth Science Dynamic Crust Name Period Finding Epicenters Lab# Introduction: Earthquakes occur when there is movement along a fault. The friction between rock masses rubbing against one another generates
HOW ARE EARTHQUAKES LOCATED?
 HOW ARE EARTHQUAKES LOCATED? 175 Practice Problem 1 Add 4 hours:15 minutes:35 seconds to 10 hours:50 minutes:35 seconds. Practice Problem 2 Subtract 5 hours:30 minutes:45 seconds from 10 hours:25 minutes:40
HOW ARE EARTHQUAKES LOCATED? 175 Practice Problem 1 Add 4 hours:15 minutes:35 seconds to 10 hours:50 minutes:35 seconds. Practice Problem 2 Subtract 5 hours:30 minutes:45 seconds from 10 hours:25 minutes:40
Surface Waves and Free Oscillations. Surface Waves and Free Oscillations
 Surface waves in in an an elastic half spaces: Rayleigh waves -Potentials - Free surface boundary conditions - Solutions propagating along the surface, decaying with depth - Lamb s problem Surface waves
Surface waves in in an an elastic half spaces: Rayleigh waves -Potentials - Free surface boundary conditions - Solutions propagating along the surface, decaying with depth - Lamb s problem Surface waves
SURFACE WAVE DISPERSION PRACTICAL (Keith Priestley)
 SURFACE WAVE DISPERSION PRACTICAL (Keith Priestley) This practical deals with surface waves, which are usually the largest amplitude arrivals on the seismogram. The velocity at which surface waves propagate
SURFACE WAVE DISPERSION PRACTICAL (Keith Priestley) This practical deals with surface waves, which are usually the largest amplitude arrivals on the seismogram. The velocity at which surface waves propagate
Earthquake Focal Mechanisms and Waveform Modeling
 Earthquake Focal Mechanisms and Waveform Modeling Rengin Gök Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory USA RELEMR Workshop İstanbul 2008 Gudmundar E. Sigvaldason The Dynamic Earth, USGS The size of the event
Earthquake Focal Mechanisms and Waveform Modeling Rengin Gök Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory USA RELEMR Workshop İstanbul 2008 Gudmundar E. Sigvaldason The Dynamic Earth, USGS The size of the event
7.2.1 Seismic waves. Waves in a mass- spring system
 7..1 Seismic waves Waves in a mass- spring system Acoustic waves in a liquid or gas Seismic waves in a solid Surface waves Wavefronts, rays and geometrical attenuation Amplitude and energy Waves in a mass-
7..1 Seismic waves Waves in a mass- spring system Acoustic waves in a liquid or gas Seismic waves in a solid Surface waves Wavefronts, rays and geometrical attenuation Amplitude and energy Waves in a mass-
they help tell Earth s story! Regents Earth Science With Ms. Connery
 they help tell Earth s story! Regents Earth Science With Ms. Connery EARTHQUAKE VOCABULARY earthquake fault convergent divergent transform (or transverse) seismic energy epicenter focus Richter scale magnitude
they help tell Earth s story! Regents Earth Science With Ms. Connery EARTHQUAKE VOCABULARY earthquake fault convergent divergent transform (or transverse) seismic energy epicenter focus Richter scale magnitude
Seismogram Interpretation. Seismogram Interpretation
 Travel times in the Earth Ray paths, phases and their name Wavefields in the Earth: SH waves, P-SV waves Seismic Tomography Receiver Functions Seismogram Example Long-period transverse displacement for
Travel times in the Earth Ray paths, phases and their name Wavefields in the Earth: SH waves, P-SV waves Seismic Tomography Receiver Functions Seismogram Example Long-period transverse displacement for
Earthquakes How and Where Earthquakes Occur
 Earthquakes How and Where Earthquakes Occur PPT Modified from Troy HS Is there such thing as earthquake weather? Absolutely NOT!!! Geologists believe that there is no connection between weather and earthquakes.
Earthquakes How and Where Earthquakes Occur PPT Modified from Troy HS Is there such thing as earthquake weather? Absolutely NOT!!! Geologists believe that there is no connection between weather and earthquakes.
Anatomy of an Earthquake Focus (or hypocentre): the center of energy release.
 Anatomy of an Earthquake Focus (or hypocentre): the center of energy release. Epicentre: the point on the ground surface immediately above the focus (closest point on the surface to the focus). Types of
Anatomy of an Earthquake Focus (or hypocentre): the center of energy release. Epicentre: the point on the ground surface immediately above the focus (closest point on the surface to the focus). Types of
Earthquakes and Seismotectonics Chapter 5
 Earthquakes and Seismotectonics Chapter 5 What Creates Earthquakes? The term Earthquake is ambiguous: Applies to general shaking of the ground and to the source of the shaking We will talk about both,
Earthquakes and Seismotectonics Chapter 5 What Creates Earthquakes? The term Earthquake is ambiguous: Applies to general shaking of the ground and to the source of the shaking We will talk about both,
Earthquake location at teleseismic distances from 3-component records (Tutorial with exercise by hand)
 Topic Author Version Earthquake location at teleseismic distances from 3-component records (Tutorial with exercise by hand) Peter Bormann (formerly GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences, D-14473 Potsdam,
Topic Author Version Earthquake location at teleseismic distances from 3-component records (Tutorial with exercise by hand) Peter Bormann (formerly GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences, D-14473 Potsdam,
Earthquakes and Seismic Waves Lesson 4 2
 Earthquakes and Seismic Waves Lesson 4 2 Apr 15 8:52 PM What are seismic waves? How are earthquakes measured? How is an earthquake located? Apr 15 8:54 PM 1 What are seismic waves An earthquake is the
Earthquakes and Seismic Waves Lesson 4 2 Apr 15 8:52 PM What are seismic waves? How are earthquakes measured? How is an earthquake located? Apr 15 8:54 PM 1 What are seismic waves An earthquake is the
How Do Scientists Find the Epicenter of an Earthquake?
 3.4 Explore How Do Scientists Find the Epicenter of an Earthquake? Seismograph data says that the earthquake is 100 km (62 mi) away, but at which point on the circle is the earthquake located? EE 116 3.4
3.4 Explore How Do Scientists Find the Epicenter of an Earthquake? Seismograph data says that the earthquake is 100 km (62 mi) away, but at which point on the circle is the earthquake located? EE 116 3.4
PEAT SEISMOLOGY Lecture 12: Earthquake source mechanisms and radiation patterns II
 PEAT8002 - SEISMOLOGY Lecture 12: Earthquake source mechanisms and radiation patterns II Nick Rawlinson Research School of Earth Sciences Australian National University Waveform modelling P-wave first-motions
PEAT8002 - SEISMOLOGY Lecture 12: Earthquake source mechanisms and radiation patterns II Nick Rawlinson Research School of Earth Sciences Australian National University Waveform modelling P-wave first-motions
Dangerous tsunami threat off U.S. West Coast
 Earthquakes Ch. 12 Dangerous tsunami threat off U.S. West Coast Earthquakes What is an Earthquake? It s the shaking and trembling of the Earth s crust due to plate movement. The plates move, rocks along
Earthquakes Ch. 12 Dangerous tsunami threat off U.S. West Coast Earthquakes What is an Earthquake? It s the shaking and trembling of the Earth s crust due to plate movement. The plates move, rocks along
The Solid Earth Chapter 4 Answers to selected questions. (1) Love waves involve transverse motion, generally arrive before Rayleigh waves.
 The Solid Earth Chapter 4 Answers to selected questions (1) Love waves involve transverse motion, generally arrive before Rayleigh waves. () (a) T = 10 s, v ~4 kms -1, so wavelength is ~40 km. (b) T =
The Solid Earth Chapter 4 Answers to selected questions (1) Love waves involve transverse motion, generally arrive before Rayleigh waves. () (a) T = 10 s, v ~4 kms -1, so wavelength is ~40 km. (b) T =
Introduction to Earthquake Seismology Assignment 18
 Introduction to Earthquake Seismology Assignment 18 Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Instructor: Robert B. Herrmann Office: O Neil Hall 203 Tel: 314 977 3120 EASA-462 Office Hours: By appointment
Introduction to Earthquake Seismology Assignment 18 Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences Instructor: Robert B. Herrmann Office: O Neil Hall 203 Tel: 314 977 3120 EASA-462 Office Hours: By appointment
ERTH2020 Introduction to Geophysics The Seismic Method. 1. Basic Concepts in Seismology. 1.1 Seismic Wave Types
 ERTH2020 Introduction to Geophysics The Seismic Method 1. Basic Concepts in Seismology 1.1 Seismic Wave Types Existence of different wave types The existence of different seismic wave types can be understood
ERTH2020 Introduction to Geophysics The Seismic Method 1. Basic Concepts in Seismology 1.1 Seismic Wave Types Existence of different wave types The existence of different seismic wave types can be understood
Seismic Source Mechanism
 Seismic Source Mechanism Yuji Yagi (University of Tsukuba) Earthquake Earthquake is a term used to describe both failure process along a fault zone, and the resulting ground shaking and radiated seismic
Seismic Source Mechanism Yuji Yagi (University of Tsukuba) Earthquake Earthquake is a term used to describe both failure process along a fault zone, and the resulting ground shaking and radiated seismic
Lab 9: Satellite Geodesy (35 points)
 Lab 9: Satellite Geodesy (35 points) Here you will work with GPS Time Series data to explore plate motion and deformation in California. This lab modifies an exercise found here: http://www.unavco.org:8080/cws/pbonucleus/draftresources/sanandreas/
Lab 9: Satellite Geodesy (35 points) Here you will work with GPS Time Series data to explore plate motion and deformation in California. This lab modifies an exercise found here: http://www.unavco.org:8080/cws/pbonucleus/draftresources/sanandreas/
LAB. Balboa Heights, Panama. Boulder, Colorado. Mexico City, Mexico. Data Table. Difference Between P-wave and S-wave. S-wave Arrival Time
 Name: Date: Lab Period: Locating the Epicenter of an Earthquake Introduction: The epicenter is the point on Earth's surface directly above an earthquake. Seismic stations detect earthquakes by the tracings
Name: Date: Lab Period: Locating the Epicenter of an Earthquake Introduction: The epicenter is the point on Earth's surface directly above an earthquake. Seismic stations detect earthquakes by the tracings
Please be sure to save a copy of this activity to your computer!
 Thank you for your purchase Please be sure to save a copy of this activity to your computer! This activity is copyrighted by AIMS Education Foundation. All rights reserved. No part of this work may be
Thank you for your purchase Please be sure to save a copy of this activity to your computer! This activity is copyrighted by AIMS Education Foundation. All rights reserved. No part of this work may be
Section Forces Within Earth. 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes
 Section 19.1 - Forces Within Earth 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes Stress and Strain Stress - is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area (cause) Strain deformation of materials
Section 19.1 - Forces Within Earth 8 th Grade Earth & Space Science - Class Notes Stress and Strain Stress - is the total force acting on crustal rocks per unit of area (cause) Strain deformation of materials
Moho (Mohorovicic discontinuity) - boundary between crust and mantle
 Earth Layers Dynamic Crust Unit Notes Continental crust is thicker than oceanic crust Continental Crust Thicker Less Dense Made of Granite Oceanic Crust Thinner More Dense Made of Basalt Moho (Mohorovicic
Earth Layers Dynamic Crust Unit Notes Continental crust is thicker than oceanic crust Continental Crust Thicker Less Dense Made of Granite Oceanic Crust Thinner More Dense Made of Basalt Moho (Mohorovicic
THE SEISMICITY OF THE EARTH
 OUTLINE THE SEISMICITY OF THE EARTH The earthquake source Types of earthquake: - from impacts and minor tremors to tectonic earthquakes, elastic rebound theory, deep earthquakes. Location of earthquakes:
OUTLINE THE SEISMICITY OF THE EARTH The earthquake source Types of earthquake: - from impacts and minor tremors to tectonic earthquakes, elastic rebound theory, deep earthquakes. Location of earthquakes:
Earthquake information
 Name: Date: Block Earthquake information The graph below shows travel time in minutes and distance traveled for primary and secondary waves. Primary and secondary waves start at the same time but do not
Name: Date: Block Earthquake information The graph below shows travel time in minutes and distance traveled for primary and secondary waves. Primary and secondary waves start at the same time but do not
How Do We Know Where an Earthquake Originated? Teacher's Guide
 How Do We Know Where an Earthquake Originated? Teacher's Guide Standard Addressed: Grades 6-8: Scientific Inquiry 1 B/1, 2 Mathematical Inquiry 2 C/2 Technology and Science 3 A/2 Processes that shape the
How Do We Know Where an Earthquake Originated? Teacher's Guide Standard Addressed: Grades 6-8: Scientific Inquiry 1 B/1, 2 Mathematical Inquiry 2 C/2 Technology and Science 3 A/2 Processes that shape the
Slinky Lab- Simulating the Motion of Earthquake Waves.
 Name Date Period Slinky Lab- Simulating the Motion of Earthquake Waves. Background: You will utilize a slinky to model earthquake waves, learn the speed, direction and behavior of different waves which
Name Date Period Slinky Lab- Simulating the Motion of Earthquake Waves. Background: You will utilize a slinky to model earthquake waves, learn the speed, direction and behavior of different waves which
An Earthquake is a rapid vibration or shaking of the Earth s crust created by a release in energy from sudden movement of a part of a plate along a
 An Earthquake is a rapid vibration or shaking of the Earth s crust created by a release in energy from sudden movement of a part of a plate along a fault. Energy released radiates in all directions from
An Earthquake is a rapid vibration or shaking of the Earth s crust created by a release in energy from sudden movement of a part of a plate along a fault. Energy released radiates in all directions from
INTERPRETATION OF SEISMOGRAMS
 INTERPRETATION OF SEISMOGRAMS INTRODUCTION 2 SEISMIC ONSETS 3 PROPERTIES 3 NOMENCLATURE 4 BODY WAVES 4 CRUSTAL PHASES 4 DEPTH PHASES 4 CORE PHASES 4 SURFACE WAVES 5 SURFACE WAVE RECURRENCE 6 TRAVEL TIME
INTERPRETATION OF SEISMOGRAMS INTRODUCTION 2 SEISMIC ONSETS 3 PROPERTIES 3 NOMENCLATURE 4 BODY WAVES 4 CRUSTAL PHASES 4 DEPTH PHASES 4 CORE PHASES 4 SURFACE WAVES 5 SURFACE WAVE RECURRENCE 6 TRAVEL TIME
REVIEW OF KEY CONCEPTS
 REVIEW OF KEY CONCEPTS 8.1 8. Equations of Loci Refer to the Key Concepts on page 598. 1. Sketch the locus of points in the plane that are cm from a circle of radius 5 cm.. a) How are the lines y = x 3
REVIEW OF KEY CONCEPTS 8.1 8. Equations of Loci Refer to the Key Concepts on page 598. 1. Sketch the locus of points in the plane that are cm from a circle of radius 5 cm.. a) How are the lines y = x 3
ENV-5004B/ENVK5005B. Figure 6. Student Registration No. ENV-5004B/ENVK5005B Version 2
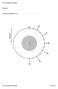 ENV-5004B/ENVK5005B Figure 6 Student Registration No UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Environmental Sciences Main Series UG Examination 014-15 SOLID EARTH GEOPHYSICS SOLID EARTH GEOPHYSICS WITH FIELDCOURSE
ENV-5004B/ENVK5005B Figure 6 Student Registration No UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Environmental Sciences Main Series UG Examination 014-15 SOLID EARTH GEOPHYSICS SOLID EARTH GEOPHYSICS WITH FIELDCOURSE
Earthquakes.
 Earthquakes http://quake.usgs.gov/recenteqs/latestfault.htm An earthquake is a sudden motion or shaking of the Earth's crust, caused by the abrupt release of stored energy in the rocks beneath the surface.
Earthquakes http://quake.usgs.gov/recenteqs/latestfault.htm An earthquake is a sudden motion or shaking of the Earth's crust, caused by the abrupt release of stored energy in the rocks beneath the surface.
Pitch Circle. Problem 8.17
 Follower Travel, mm Displacement, cm 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Cam Rotation Angle 90 Pitch Circle 0 1 3 4 5 10 9 8 7 6 Problem 8.17 Construct the profile of a disk cam that follows the displacement
Follower Travel, mm Displacement, cm 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Cam Rotation Angle 90 Pitch Circle 0 1 3 4 5 10 9 8 7 6 Problem 8.17 Construct the profile of a disk cam that follows the displacement
A Violent Pulse: Earthquakes. Lecture #2
 A Violent Pulse: Earthquakes Lecture #2 Earthquakes Are Always Happening ~ 1,000,000 / yr Most are small o Detected only by instruments Large EQ ~ 20 / yr cause extensive damage ~ 1 catastrophic EQ / year
A Violent Pulse: Earthquakes Lecture #2 Earthquakes Are Always Happening ~ 1,000,000 / yr Most are small o Detected only by instruments Large EQ ~ 20 / yr cause extensive damage ~ 1 catastrophic EQ / year
Spacetime Diagrams Lab Exercise
 Spacetime Diagrams Lab Exercise The spacetime diagram (also known as a Minkowski diagram) is a tool that can used to graphically describe complex problems in special relativity. In many cases, with a properly
Spacetime Diagrams Lab Exercise The spacetime diagram (also known as a Minkowski diagram) is a tool that can used to graphically describe complex problems in special relativity. In many cases, with a properly
Earthquake Engineering GE / CE - 479/679
 Earthquake Engineering GE / CE - 479/679 Topic 4. Seismometry John G. Anderson Director February 4-6, 2003 1 Wood-Anderson Seismograph Important because: Principles of operation are widely used. Basis
Earthquake Engineering GE / CE - 479/679 Topic 4. Seismometry John G. Anderson Director February 4-6, 2003 1 Wood-Anderson Seismograph Important because: Principles of operation are widely used. Basis
Dynamic Triggering Semi-Volcanic Tremor in Japanese Volcanic Region by The 2016 Mw 7.0 Kumamoto Earthquake
 Dynamic Triggering Semi-Volcanic Tremor in Japanese Volcanic Region by The 016 Mw 7.0 Kumamoto Earthquake Heng-Yi Su 1 *, Aitaro Kato 1 Department of Earth Sciences, National Central University, Taoyuan
Dynamic Triggering Semi-Volcanic Tremor in Japanese Volcanic Region by The 016 Mw 7.0 Kumamoto Earthquake Heng-Yi Su 1 *, Aitaro Kato 1 Department of Earth Sciences, National Central University, Taoyuan
Topic 5: The Dynamic Crust (workbook p ) Evidence that Earth s crust has shifted and changed in both the past and the present is shown by:
 Topic 5: The Dynamic Crust (workbook p. 65-85) Evidence that Earth s crust has shifted and changed in both the past and the present is shown by: --sedimentary horizontal rock layers (strata) are found
Topic 5: The Dynamic Crust (workbook p. 65-85) Evidence that Earth s crust has shifted and changed in both the past and the present is shown by: --sedimentary horizontal rock layers (strata) are found
Topic 12 Review Book Earth s Dynamic Crust and Interior
 Topic 12 Review Book Earth s Dynamic Crust and Interior Define the Vocabulary 1. asthenosphere 2. continental crust 3. Convection current 4. Convergent plate boundary 5. Divergent plate boundary 6. earthquake
Topic 12 Review Book Earth s Dynamic Crust and Interior Define the Vocabulary 1. asthenosphere 2. continental crust 3. Convection current 4. Convergent plate boundary 5. Divergent plate boundary 6. earthquake
A. Locate the Epicenter
 Name: Block: Earthquake Lab The goal of this portion of the lab is to learn how recording of earthquakes seismograms are used to locate earthquakes, determine their magnitudes, and to understand the sense
Name: Block: Earthquake Lab The goal of this portion of the lab is to learn how recording of earthquakes seismograms are used to locate earthquakes, determine their magnitudes, and to understand the sense
The Unique Source Mechanism of an Explosively Induced Mine Collapse
 The Unique Source Mechanism of an Explosively Induced Mine Collapse Xiaoning Yang, Brian W. Stump, W. Scott Phillips Geophysics Group - EES-3, Los Alamos National Laboratory Contract No. W-7405-ENG-36
The Unique Source Mechanism of an Explosively Induced Mine Collapse Xiaoning Yang, Brian W. Stump, W. Scott Phillips Geophysics Group - EES-3, Los Alamos National Laboratory Contract No. W-7405-ENG-36
An earthquake is the result of a sudden displacement across a fault that releases stresses that have accumulated in the crust of the earth.
 An earthquake is the result of a sudden displacement across a fault that releases stresses that have accumulated in the crust of the earth. Measuring an Earthquake s Size Magnitude and Moment Each can
An earthquake is the result of a sudden displacement across a fault that releases stresses that have accumulated in the crust of the earth. Measuring an Earthquake s Size Magnitude and Moment Each can
Circles. Example 2: Write an equation for a circle if the enpoints of a diameter are at ( 4,5) and (6, 3).
 Conics Unit Ch. 8 Circles Equations of Circles The equation of a circle with center ( hk, ) and radius r units is ( x h) ( y k) r. Example 1: Write an equation of circle with center (8, 3) and radius 6.
Conics Unit Ch. 8 Circles Equations of Circles The equation of a circle with center ( hk, ) and radius r units is ( x h) ( y k) r. Example 1: Write an equation of circle with center (8, 3) and radius 6.
Distance and Midpoint Formula 7.1
 Distance and Midpoint Formula 7.1 Distance Formula d ( x - x ) ( y - y ) 1 1 Example 1 Find the distance between the points (4, 4) and (-6, -). Example Find the value of a to make the distance = 10 units
Distance and Midpoint Formula 7.1 Distance Formula d ( x - x ) ( y - y ) 1 1 Example 1 Find the distance between the points (4, 4) and (-6, -). Example Find the value of a to make the distance = 10 units
Seismic Recording Station TA_109C Summary Report
 Seismic Recording Station TA_109C Summary Report Thank you for hosting station TA_109C on your property. We hope that you find the enclosed report interesting. Your station is one of the 2000 USArray seismic
Seismic Recording Station TA_109C Summary Report Thank you for hosting station TA_109C on your property. We hope that you find the enclosed report interesting. Your station is one of the 2000 USArray seismic
Lab 6: Earthquake Focal Mechanisms (35 points)
 Lab 6: Earthquake Focal Mechanisms (35 points) Group Exercise 1. Drawing Nodal Planes (8 pts) The outline map below labeled Figure 4.60a shows the positions of two earthquakes recorded on the Mid-Atlantic
Lab 6: Earthquake Focal Mechanisms (35 points) Group Exercise 1. Drawing Nodal Planes (8 pts) The outline map below labeled Figure 4.60a shows the positions of two earthquakes recorded on the Mid-Atlantic
Automatic Magnitude Determination
 Automatic Magnitude Determination by Wolfgang A. Lenhardt & Nikolaus Horn AUG Trieste, 2004 Content: Moment Magnitude Other Magnitudes Moment Magnitude - Steps 1. The location of the earthquake must be
Automatic Magnitude Determination by Wolfgang A. Lenhardt & Nikolaus Horn AUG Trieste, 2004 Content: Moment Magnitude Other Magnitudes Moment Magnitude - Steps 1. The location of the earthquake must be
SURFACE WAVE MODELLING USING SEISMIC GROUND RESPONSE ANALYSIS
 43 SURFACE WAVE MODELLING USING SEISMIC GROUND RESPONSE ANALYSIS E John MARSH And Tam J LARKIN SUMMARY This paper presents a study of surface wave characteristics using a two dimensional nonlinear seismic
43 SURFACE WAVE MODELLING USING SEISMIC GROUND RESPONSE ANALYSIS E John MARSH And Tam J LARKIN SUMMARY This paper presents a study of surface wave characteristics using a two dimensional nonlinear seismic
Seismic Recording Station AZ_PFO Summary Report
 Seismic Recording Station AZ_PFO Summary Report Thank you for hosting station AZ_PFO on your property. We hope that you find the enclosed report interesting. Your station is one of the 2000 USArray seismic
Seismic Recording Station AZ_PFO Summary Report Thank you for hosting station AZ_PFO on your property. We hope that you find the enclosed report interesting. Your station is one of the 2000 USArray seismic
Module 7: Plate Tectonics and Earth's Structure Topic 4 Content : Earthquakes Presentation Notes. Earthquakes
 Earthquakes 1 Topic 4 Content: Earthquakes Presentation Notes Earthquakes are vibrations within the Earth produced by the rapid release of energy from rocks that break under extreme stress. Earthquakes
Earthquakes 1 Topic 4 Content: Earthquakes Presentation Notes Earthquakes are vibrations within the Earth produced by the rapid release of energy from rocks that break under extreme stress. Earthquakes
C) 10:20:40 A) the difference between the arrival times of the P -wave and the S -wave
 1. The arrival time of the first earthquake P-wave at a seismograph station was 10:11:20 (hours:minutes:seconds). If the epicenter of the earthquake is 8000 km away, what was the approximate arrival time
1. The arrival time of the first earthquake P-wave at a seismograph station was 10:11:20 (hours:minutes:seconds). If the epicenter of the earthquake is 8000 km away, what was the approximate arrival time
Multi-station Seismograph Network
 Multi-station Seismograph Network Background page to accompany the animations on the website: IRIS Animations Introduction One seismic station can give information about how far away the earthquake occurred,
Multi-station Seismograph Network Background page to accompany the animations on the website: IRIS Animations Introduction One seismic station can give information about how far away the earthquake occurred,
Science Starter. Describe in your own words what an Earthquake is and what causes it. Answer The MSL
 Science Starter Describe in your own words what an Earthquake is and what causes it. Answer The MSL WHAT IS AN EARTHQUAKE AND HOW DO WE MEASURE THEM? Chapter 8, Section 8.1 & 8.2 Looking Back Deserts Wind-shaped
Science Starter Describe in your own words what an Earthquake is and what causes it. Answer The MSL WHAT IS AN EARTHQUAKE AND HOW DO WE MEASURE THEM? Chapter 8, Section 8.1 & 8.2 Looking Back Deserts Wind-shaped
Earthquake Investigation
 Exploration A Earthquake Investigation 1. Obtain a piece of plastic putty and knead it into a rectangular shape. 2. Push the ends of the putty toward the middle. Draw and describe what it looks like below.
Exploration A Earthquake Investigation 1. Obtain a piece of plastic putty and knead it into a rectangular shape. 2. Push the ends of the putty toward the middle. Draw and describe what it looks like below.
Homework II Seismological Topics
 Revised September 6, 2012 EENS 6340/4340 Homework II Seismological Topics The Earth 1. The relationship between energy released, E, and earthquake magnitude, M, is given by the empirical relationship:
Revised September 6, 2012 EENS 6340/4340 Homework II Seismological Topics The Earth 1. The relationship between energy released, E, and earthquake magnitude, M, is given by the empirical relationship:
Global Seismology Chapter 4
 Global Seismology Chapter 4 Earthquake: an event of ground shaking usually caused by the rupturing of a fault within the Earth. Who studies Earthquakes? Seismologists waves Geophysicists Mechanics Geodesy
Global Seismology Chapter 4 Earthquake: an event of ground shaking usually caused by the rupturing of a fault within the Earth. Who studies Earthquakes? Seismologists waves Geophysicists Mechanics Geodesy
Tracing rays through the Earth
 Tracing rays through the Earth Ray parameter p: source receiv er i 1 V 1 sin i 1 = sin i 2 = = sin i n = const. = p V 1 V 2 V n p is constant for a given ray i 2 i 3 i 4 V 2 V 3 V 4 i critical If V increases
Tracing rays through the Earth Ray parameter p: source receiv er i 1 V 1 sin i 1 = sin i 2 = = sin i n = const. = p V 1 V 2 V n p is constant for a given ray i 2 i 3 i 4 V 2 V 3 V 4 i critical If V increases
Determining the Earthquake Epicenter: Japan
 Practice Name: Hour: Determining the Earthquake Epicenter: Japan Measuring the S-P interval There are hundreds of seismic data recording stations throughout the United States and the rest of the world.
Practice Name: Hour: Determining the Earthquake Epicenter: Japan Measuring the S-P interval There are hundreds of seismic data recording stations throughout the United States and the rest of the world.
MAT100 OVERVIEW OF CONTENTS AND SAMPLE PROBLEMS
 MAT100 OVERVIEW OF CONTENTS AND SAMPLE PROBLEMS MAT100 is a fast-paced and thorough tour of precalculus mathematics, where the choice of topics is primarily motivated by the conceptual and technical knowledge
MAT100 OVERVIEW OF CONTENTS AND SAMPLE PROBLEMS MAT100 is a fast-paced and thorough tour of precalculus mathematics, where the choice of topics is primarily motivated by the conceptual and technical knowledge
Determining the relationship between the summit and Pu u Ō ō on Kilauea
 Name: Determining the relationship between the summit and Pu u Ō ō on Kilauea After completing this activity, you will be able to: 1. summarize the physical events that produce the data volcanologists
Name: Determining the relationship between the summit and Pu u Ō ō on Kilauea After completing this activity, you will be able to: 1. summarize the physical events that produce the data volcanologists
MIGRATING SWARMS OF BRITTLE-FAILURE EARTHQUAKES IN THE LOWER CRUST BENEATH MAMMOTH MOUNTAIN, CALIFORNIA
 MIGRATING SWARMS OF BRITTLE-FAILURE EARTHQUAKES IN THE LOWER CRUST BENEATH MAMMOTH MOUNTAIN, CALIFORNIA David Shelly and David Hill GRL, October 2011 Contents Tectonic Setting Long Valley Caldera Mammoth
MIGRATING SWARMS OF BRITTLE-FAILURE EARTHQUAKES IN THE LOWER CRUST BENEATH MAMMOTH MOUNTAIN, CALIFORNIA David Shelly and David Hill GRL, October 2011 Contents Tectonic Setting Long Valley Caldera Mammoth
Epicenter - a point, directly above the true center of disturbance, from which the shock waves of an earthquake apparently radiate.
 Name: Date: Period: Earthquakes Epicenter - a point, directly above the true center of disturbance, from which the shock waves of an earthquake apparently radiate. Define each of the following terms in
Name: Date: Period: Earthquakes Epicenter - a point, directly above the true center of disturbance, from which the shock waves of an earthquake apparently radiate. Define each of the following terms in
Module 7 : Applications of Integration - I. Lecture 21 : Relative rate of growth of functions [Section 21.1] Objectives
![Module 7 : Applications of Integration - I. Lecture 21 : Relative rate of growth of functions [Section 21.1] Objectives Module 7 : Applications of Integration - I. Lecture 21 : Relative rate of growth of functions [Section 21.1] Objectives](/thumbs/89/99619893.jpg) Module 7 : Applications of Integration - I Lecture 21 : Relative rate of growth of functions [Section 211] Objectives In this section you will learn the following : How to compare the rate of growth of
Module 7 : Applications of Integration - I Lecture 21 : Relative rate of growth of functions [Section 211] Objectives In this section you will learn the following : How to compare the rate of growth of
8.6 Translate and Classify Conic Sections
 8.6 Translate and Classify Conic Sections Where are the symmetric lines of conic sections? What is the general 2 nd degree equation for any conic? What information can the discriminant tell you about a
8.6 Translate and Classify Conic Sections Where are the symmetric lines of conic sections? What is the general 2 nd degree equation for any conic? What information can the discriminant tell you about a
LAB 6 SUPPLEMENT. G141 Earthquakes & Volcanoes
 G141 Earthquakes & Volcanoes Name LAB 6 SUPPLEMENT Using Earthquake Arrival Times to Locate Earthquakes In last week's lab, you used arrival times of P- and S-waves to locate earthquakes from a local seismograph
G141 Earthquakes & Volcanoes Name LAB 6 SUPPLEMENT Using Earthquake Arrival Times to Locate Earthquakes In last week's lab, you used arrival times of P- and S-waves to locate earthquakes from a local seismograph
Imaging sharp lateral velocity gradients using scattered waves on dense arrays: faults and basin edges
 2017 SCEC Proposal Report #17133 Imaging sharp lateral velocity gradients using scattered waves on dense arrays: faults and basin edges Principal Investigator Zhongwen Zhan Seismological Laboratory, California
2017 SCEC Proposal Report #17133 Imaging sharp lateral velocity gradients using scattered waves on dense arrays: faults and basin edges Principal Investigator Zhongwen Zhan Seismological Laboratory, California
Elastic rebound theory
 Elastic rebound theory Focus epicenter - wave propagation Dip-Slip Fault - Normal Normal Fault vertical motion due to tensional stress Hanging wall moves down, relative to the footwall Opal Mountain, Mojave
Elastic rebound theory Focus epicenter - wave propagation Dip-Slip Fault - Normal Normal Fault vertical motion due to tensional stress Hanging wall moves down, relative to the footwall Opal Mountain, Mojave
Once you have opened the website with the link provided choose a force: Earthquakes
 Name: Once you have opened the website with the link provided choose a force: Earthquakes When do earthquakes happen? On the upper left menu, choose number 1. Read What is an Earthquake? Earthquakes happen
Name: Once you have opened the website with the link provided choose a force: Earthquakes When do earthquakes happen? On the upper left menu, choose number 1. Read What is an Earthquake? Earthquakes happen
Gutenberg-Richter Relationship: Magnitude vs. frequency of occurrence
 Quakes per year. Major = 7-7.9; Great = 8 or larger. Year Major quakes Great quakes 1969 15 1 1970 20 0 1971 19 1 1972 15 0 1973 13 0 1974 14 0 1975 14 1 1976 15 2 1977 11 2 1978 16 1 1979 13 0 1980 13
Quakes per year. Major = 7-7.9; Great = 8 or larger. Year Major quakes Great quakes 1969 15 1 1970 20 0 1971 19 1 1972 15 0 1973 13 0 1974 14 0 1975 14 1 1976 15 2 1977 11 2 1978 16 1 1979 13 0 1980 13
) in the box next to your answer. (1) (b) Explain why it is difficult to predict when an earthquake will happen. (2)
 Earthquakes 1 (a) Seismic (earthquake) waves can be either P-waves or S-waves. Which row of the table is correct for P-waves? Put a cross ( ) in the box next to your answer. (1) type of wave can they be
Earthquakes 1 (a) Seismic (earthquake) waves can be either P-waves or S-waves. Which row of the table is correct for P-waves? Put a cross ( ) in the box next to your answer. (1) type of wave can they be
High-precision location of North Korea s 2009 nuclear test
 Copyright, Seismological Research Letters, Seismological Society of America 1 High-precision location of North Korea s 2009 nuclear test Lianxing Wen & Hui Long Department of Geosciences State University
Copyright, Seismological Research Letters, Seismological Society of America 1 High-precision location of North Korea s 2009 nuclear test Lianxing Wen & Hui Long Department of Geosciences State University
Worksheet for Exploration 24.1: Flux and Gauss's Law
 Worksheet for Exploration 24.1: Flux and Gauss's Law In this Exploration, we will calculate the flux, Φ, through three Gaussian surfaces: green, red and blue (position is given in meters and electric field
Worksheet for Exploration 24.1: Flux and Gauss's Law In this Exploration, we will calculate the flux, Φ, through three Gaussian surfaces: green, red and blue (position is given in meters and electric field
Some aspects of seismic tomography
 Some aspects of seismic tomography Peter Shearer IGPP/SIO/U.C. San Diego September 7, 2009 Earthquake Research Institute Part 1: Global Tomography P velocity perturbations 200 km 1000 km 2700 km MIT 2006
Some aspects of seismic tomography Peter Shearer IGPP/SIO/U.C. San Diego September 7, 2009 Earthquake Research Institute Part 1: Global Tomography P velocity perturbations 200 km 1000 km 2700 km MIT 2006
Introduction to Computer Graphics (Lecture No 07) Ellipse and Other Curves
 Introduction to Computer Graphics (Lecture No 07) Ellipse and Other Curves 7.1 Ellipse An ellipse is a curve that is the locus of all points in the plane the sum of whose distances r1 and r from two fixed
Introduction to Computer Graphics (Lecture No 07) Ellipse and Other Curves 7.1 Ellipse An ellipse is a curve that is the locus of all points in the plane the sum of whose distances r1 and r from two fixed
Improvements to Seismic Monitoring of the European Arctic Using Three-Component Array Processing at SPITS
 Improvements to Seismic Monitoring of the European Arctic Using Three-Component Array Processing at SPITS Steven J. Gibbons Johannes Schweitzer Frode Ringdal Tormod Kværna Svein Mykkeltveit Seismicity
Improvements to Seismic Monitoring of the European Arctic Using Three-Component Array Processing at SPITS Steven J. Gibbons Johannes Schweitzer Frode Ringdal Tormod Kværna Svein Mykkeltveit Seismicity
Energy Efficiency, Acoustics & Daylighting in building Prof. B. Bhattacharjee Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Energy Efficiency, Acoustics & Daylighting in building Prof. B. Bhattacharjee Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 05 Introduction & Environmental Factors (contd.)
Energy Efficiency, Acoustics & Daylighting in building Prof. B. Bhattacharjee Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 05 Introduction & Environmental Factors (contd.)
5. What is an earthquake 6. Indicate the approximate radius of the earth, inner core, and outer core.
 Tutorial Problems 1. Where Do Earthquakes Happen? 2. Where do over 90% of earthquakes occur? 3. Why Do Earthquakes Happen? 4. What are the formulae for P and S velocity 5. What is an earthquake 6. Indicate
Tutorial Problems 1. Where Do Earthquakes Happen? 2. Where do over 90% of earthquakes occur? 3. Why Do Earthquakes Happen? 4. What are the formulae for P and S velocity 5. What is an earthquake 6. Indicate
OVERVIEW INTRODUCTION 3 WHAT'S MISSING? 4 OBJECTIVES 5
 OVERVIEW INTRODUCTION 3 WHAT'S MISSING? 4 OBJECTIVES 5 DISTORTION OF SEISMIC SOURCE SPECTRUM 6 PRINCIPLE 7 SEISMIC SOURCE SPECTRUM 8 EFFECT OF RECORDING INSTRUMENTS 9 SEISMOMETERS 9 CORRECTION FOR FREQUENCY
OVERVIEW INTRODUCTION 3 WHAT'S MISSING? 4 OBJECTIVES 5 DISTORTION OF SEISMIC SOURCE SPECTRUM 6 PRINCIPLE 7 SEISMIC SOURCE SPECTRUM 8 EFFECT OF RECORDING INSTRUMENTS 9 SEISMOMETERS 9 CORRECTION FOR FREQUENCY
Earthquakes. Earthquakes and Earth s Interior Earth Science, 13e Chapter 8. Elastic rebound. Earthquakes. Earthquakes 11/19/2014.
 and Earth s Interior Earth Science, 13e Chapter 8 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College General features Vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Associated with movements
and Earth s Interior Earth Science, 13e Chapter 8 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College General features Vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Associated with movements
(c) Find the gradient of the graph of f(x) at the point where x = 1. (2) The graph of f(x) has a local maximum point, M, and a local minimum point, N.
 Calculus Review Packet 1. Consider the function f() = 3 3 2 24 + 30. Write down f(0). Find f (). Find the gradient of the graph of f() at the point where = 1. The graph of f() has a local maimum point,
Calculus Review Packet 1. Consider the function f() = 3 3 2 24 + 30. Write down f(0). Find f (). Find the gradient of the graph of f() at the point where = 1. The graph of f() has a local maimum point,
RELATION BETWEEN RAYLEIGH WAVES AND UPLIFT OF THE SEABED DUE TO SEISMIC FAULTING
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 1359 RELATION BETWEEN RAYLEIGH WAVES AND UPLIFT OF THE SEABED DUE TO SEISMIC FAULTING Shusaku INOUE 1,
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 1359 RELATION BETWEEN RAYLEIGH WAVES AND UPLIFT OF THE SEABED DUE TO SEISMIC FAULTING Shusaku INOUE 1,
Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating.
 CH Earthquakes Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating Earthquakes Section 19.4: Earthquakes and Society Section 19.1 Forces
CH Earthquakes Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating Earthquakes Section 19.4: Earthquakes and Society Section 19.1 Forces
(Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank Physics 1
 1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
1. A transverse wave travels from left to right. The diagram below shows how, at a particular instant of time, the displacement of particles in the medium varies with position. Which arrow represents the
STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE. Functions & Graphs
 STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Functions & Graphs Contents Functions and Relations... 1 Interval Notation... 3 Graphs: Linear Functions... 5 Lines and Gradients... 7 Graphs: Quadratic
STUDY KNOWHOW PROGRAM STUDY AND LEARNING CENTRE Functions & Graphs Contents Functions and Relations... 1 Interval Notation... 3 Graphs: Linear Functions... 5 Lines and Gradients... 7 Graphs: Quadratic
SIMULATED SEISMOGRAMS
 SIMULATED SEISMOGRAMS Great Falls, Montana I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I 8:03 8:04 8:05 8:06 8:07 P-wave arrival S-wave arrival Little Rock, Arkansas I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I
SIMULATED SEISMOGRAMS Great Falls, Montana I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I 8:03 8:04 8:05 8:06 8:07 P-wave arrival S-wave arrival Little Rock, Arkansas I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I
Name Hour. Environmental Science Semester 2 Study Guide. Plate Tectonics. 1. Explain sea floor spreading.
 Name Hour Environmental Science Semester 2 Study Guide Plate Tectonics 1. Explain sea floor spreading. 2. Describe Wegener s idea of continental drift. 3. List 5 pieces of evidence to support the idea
Name Hour Environmental Science Semester 2 Study Guide Plate Tectonics 1. Explain sea floor spreading. 2. Describe Wegener s idea of continental drift. 3. List 5 pieces of evidence to support the idea
SKILL BUILDER TEN. Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables. If x = 2 then y = = = 7 and (2, 7) is a solution.
 SKILL BUILDER TEN Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables A first degree equation is called a linear equation, since its graph is a straight line. In a linear equation, each term is a constant or
SKILL BUILDER TEN Graphs of Linear Equations with Two Variables A first degree equation is called a linear equation, since its graph is a straight line. In a linear equation, each term is a constant or
IGPP. Departmental Examination
 IGPP Departmental Examination 1994 Departmental Examination, 1994 This is a 4 hour exam with 12 questions. Write on the pages provided, and continue if necessary onto further sheets. Please identify yourself
IGPP Departmental Examination 1994 Departmental Examination, 1994 This is a 4 hour exam with 12 questions. Write on the pages provided, and continue if necessary onto further sheets. Please identify yourself
Earth s Interior Structure - Seismic Travel Times in a Constant Velocity Sphere
 Earth s Interior Structure Seismic Travel Page 1 of 14 Earth s Interior Structure - Seismic Travel Times in a Constant Velocity Sphere Raypath (chord of length S) Receiver S/2 R = 6371 km Earth s Surface
Earth s Interior Structure Seismic Travel Page 1 of 14 Earth s Interior Structure - Seismic Travel Times in a Constant Velocity Sphere Raypath (chord of length S) Receiver S/2 R = 6371 km Earth s Surface
INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKES
 INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKES Seismology = Study of earthquakes Seismologists = Scientists who study earthquakes Earthquake = Trembling or shaking of the earth s surface, usually as a result of the movement
INTRODUCTION TO EARTHQUAKES Seismology = Study of earthquakes Seismologists = Scientists who study earthquakes Earthquake = Trembling or shaking of the earth s surface, usually as a result of the movement
PEAT SEISMOLOGY Lecture 9: Anisotropy, attenuation and anelasticity
 PEAT8002 - SEISMOLOGY Lecture 9: Anisotropy, attenuation and anelasticity Nick Rawlinson Research School of Earth Sciences Australian National University Anisotropy Introduction Most of the theoretical
PEAT8002 - SEISMOLOGY Lecture 9: Anisotropy, attenuation and anelasticity Nick Rawlinson Research School of Earth Sciences Australian National University Anisotropy Introduction Most of the theoretical
Geophysics Physics of the Earth
 Geophysics 210 - Physics of the Earth Final exam Section GEOPH 210 Lecture A01 Instructor Dr. Martyn Unsworth Date Friday December 12 th 2008 Time allowed 9:00 a.m. noon Total = 104 points Please attempt
Geophysics 210 - Physics of the Earth Final exam Section GEOPH 210 Lecture A01 Instructor Dr. Martyn Unsworth Date Friday December 12 th 2008 Time allowed 9:00 a.m. noon Total = 104 points Please attempt
