Exercise(#2" Estimating(Strain(in(Naturally(Deformed(Rocks(with(the(Rf===Phi(Method"
|
|
|
- Jerome Cross
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exercise(#2" Estimating(Strain(in(Naturally(Deformed(Rocks(with(the(Rf===Phi(Method" Paul"Karabinos" Department"of"Geosciences,"Williams"College,"Williamstown,"MA"01267" This"exercise"is"suitable"for"an"undergraduate"structural"geology"course."It"assumes" that"students"have"read"session'5)))'practical'strain'measurement:'initially'circular' and'elliptical'markers,'from"ramsay"and"huber"(1987,"p."73ooo87)"questions"to"be" answered"are"in"blue"to"make"it"easier"to"find"them." Estimating"strain"in"naturally"deformed"rocks"in"the"field"typically"involves" using"a"ruler"and"protractor"to"measure"the"long"and"short"axes"of"deformed"pebbles" and"the"orientation"of"the"long"axis."even"though"it s"lots"of"fun,"this"approach"does" not"allow"the"geologist"to"make"a"visual"record"of"the"pebbles"measured."after"field" measurements"are"complete,"the"results"are"plotted"in"graphs"of"rf"vs."phi"to" estimate"strain"as"described"by"ramsay"and"huber"(1987)." In"this"exercise,"you"will"estimate"strain"using"a"photograph"of"a"deformed" conglomerate."you"will"use"the"photograph"as"a"background"image"to"create"ellipses" that"approximate"the"shape,"size,"and"orientation"of"naturally"deformed"pebbles."the" photograph"shows"the"basal"conglomerate"member"of"the"dalton"formation,"an" Ediacaran"to"Cambrian"unit"in"western"New"England."The"outcrop"is"along"the" Appalachian"Trail"on"Day"Mountain"in"Dalton,"Massachusetts."The"outcrop"also" features"a"famous"unconformity"between"mesoproterozoic"rocks"at"least"1179"ma" and"the"conglomerate,"which"is"approximately"550"ma."thus,"the"time"gap"is"about" 600"million"years!" As"you"digitize"pebbles,"the"points"are"automatically"added"to"the"Cartesian" or"polar"rfooophi"plots."the"best"part"is"that"you"end"up"with"a"visual"record"of"the" deformed"pebbles"used"to"estimate"strain."geoshear"can"be"used"to" undeform "the" pebbles"using"your"estimate"of"strain."this"allows"you"to"assess"how"reasonable" your"strain"calculations"are." Part(1.(Loading(the(Background(Image(and(Digitizing(Pebbles." 1) Open"GeoShear."You"will"see"the"following"resizable"window"with"a"Main"Menu, Control"Panel,"and"User"Interface: 1"
2 2) In"the"Control"Panel,"click"on"the"Edit"Mode"button,"and"then"click"the" Background"Image"button." 3) Navigate"to"the"Geoshear_2.1/Background"Images"folder,"and"select" Deformed_Conglomerate."Use"the"mouse"scroll"wheel,"the"Zoom"Slider,"and" Center"in"view"button"" at"the"top"of"the"control"panel"to"get"the" full"photo"in"view." 4) This"is"a"picture"of"a"deformed"pebble"conglomerate"from"Day"Mountain"in" Dalton,"Massachusetts." 5) Create(new(pebbles:"Because"you"needed"the"Edit"Mode"to"load"the"background" image,"you"are"ready"to"start"digitizing"pebbles"from"the"photograph."note:(you( must(be(in(edit(mode(to(add(new(pebbles."you(must(exit(edit(mode(to(use" GeoShear(to(deform(the(pebbles." a) Zoom"in"to"magnify"individual"pebbles"in"the"photo." b) Hold"down"the"SHIFT"key"or"enable"the"CAP"LOCKS"key,"leftOOOclick"on"one" end"of"a"pebble"longoooaxis,"drag"the"cursor"to"the"other"end"of"the"long"axis," hit"the"space"bar"to"accept"the"first"line,"drag"the"cursor"away"from"the"long" axis"to"define"the"short"axis,"and"hit"the"space"bar"to"accept"the"ellipse."you" must"hold"down"the"leftoooclick"button"throughout"the"process." c) It"is"easier"to"see"how"good"your"work"is"by"not"invoking"the"Fill"Pebbles" option"from"the"display"menu." d) Open"the"RfOOOPhi"Cartesian"plot"to"observe"that"points"are"added"as"pebbles" are"digitized."from"the"control"button"on"the"rfooophi"plot,"select"adaptive" Rf"Scale"so"all"pebbles"will"be"shown"as"they"are"digitized." e) Continue"digitizing"pebbles"until"you"are"confident"that"you"have"all"of"the" wellooodefined"pebbles"visible"in"the"photo." f) During"the"process"of"digitizing"pebbles,"you"might"notice"that"some"pebbles" indent"other"pebbles."this"is"evidence"for"pressure"solution." g) You"might"also"observe"that"the"average"orientation"of"the"long"axes"of" pebbles"varies"from"one"part"of"the"photo"to"another."if"you"do,"you"should" ask"whether"this"variation"reflects"differences"in"strain,"i.e."nonooo" homogeneous"strain"or"perhaps"bedoootoooobed"differences"in"preferred" orientation"of"pebble"long"axes."! 2"
3 6) To"save"your"work"go"to"Main"Menu/File/Save"Current"State"and"give"the".tab"file an"eastoootooooremember"name. Part(2.(Estimating(Strain(with(the(Cartesian(Rf===Phi(plot." 1. Using"the"RfOOOPhi"plot"as"described"by"Ramsay"and"Huber"(1987)"to estimate"strain"requires"identification"of"the"maximum"and"minimum pebble"axial"ratios,"rfmax"and"rfmin,"respectively. 2. The"axial"ratios"of"specific"pebbles"can"be"found"quite"easily"in"the"plot"by clicking"on"the"corresponding"points"and"reading"the"values"that"appear"on the"screen."the"difficulty"in"finding"rfmax"and"rfmin"in"a"real"data"set"is identifying"outliers. A"few"anomalously"elliptical"pebbles"in"the"original"conglomerate"can"lead"to an"overestimate"of"strain."in"exercise"1,"you"learned"that"the"rfooophi method 1) assumes"a"nonooopreferred"initial"orientation"of"pebble"long"axes,"and"2) that"the(reliability(of(the(method(depends(critically(on(a(non= ==preferred(and(wide(initial(distribution(of(the(most(elliptical(pebbles." GeoShear"does"not"have"a"builtOOOin"algorithm"for"finding"outliers"in"the" population." 3. The"RfOOOPhi"plot"shows"a"closed"envelope"of"points;"this"indicates"that"the strain"ellipse"ratio"(rs)"is"greater"than"the"maximum"initial'ellipse"axial"ratio (Rimax). 4. Use" all( points( in" the" Cartesian" RfOOOPhi" plot," and" the" equations" for" a closed" envelope" (Ramsay" and" Huber," 1987)," shown" below" to" calculate the" strain" ellipse" axial" ratio," Rs," and" the" maximum" initial" pebble" ratio, Rimax. a. Rs"="(Rfmax*Rfmin) 1/2" = b. Rimax"="(Rfmax/Rfmin)" 1/2" = 5. Eliminate(obvious(outliers(in"the"Cartesian"RfOOOPhi"plot,"and"the"equations for"a"closed"envelope"(ramsay"and"huber,"1987),"shown"below"to"calculate the"strain"ellipse"axial"ratio,"rs,"and"the"maximum"initial"pebble"ratio,"rimax. a. Rs"="(Rfmax*Rfmin) 1/2" = b. Rimax"="(Rfmax/Rfmin)" 1/2" = Part(3.(Using(GeoShear(to( Undeform (the(pebbles." 1) Using"the"Cartesian"RfOOOPhi"plot"to"find"Rfmax"and"Rfmin,"as"described above,"does"not"allow"us"to"assess"visually"how"reasonable"the"strain estimate"is."here"is"a"simple"way"to"estimate"strain"that" undeforms "the pebbles,"yields"the"reciprocal"strain"ellipse,"and"gives"us"a"visual representation"of"the"pebbles"before"deformation. 2) If"necessary,"disable"Edit"Mode"by"clicking"on"the"button. 3) Click"in"the"deg."box"under"rotation."Use"the"upOOOarrow"or"downOOOarrow"on 3"
4 the"keyboard"to"rotate"the"pebbles"until"the"yellow"horizontal"line"coincides" with" 4"
5 Phi"="0."The"arrow"keys"give"one"degree"increments;"you"can"click"in"the"box" and"type"in"more"precise"degree"values"to"help"center"the"yellow"line"at"phi"=" 0. This"yellow"line"is"the"vector"mean"of"the"pebble"long"axes."Click"Apply"in the"control"panel." 4) Now"that"the"vector"mean"coincides"with"Phi"="0,"we"can"use"pure"shear"to undeform "the"pebbles"in"the"xooodirection."click"in"the"x"box"under"pure shear"and"use"the"upoooarrow"on"the"keyboard"to"shorten"the"pebbles"in"the xooo"direction."continue"shortening"in"the"xooodirection"until"the"points"cover the"full"range"of"phi"values"(ooo90"to"90);"there(shouldn t(be(any(large concentrations(of(points(or(gaps(over(the(range(of(phi,"and"collectively the"range(of(rf(values(should(be(minimized."this"approach"attempts"to recreate"an"idealized"initially"random"distribution"of"pebble"long"axes. 5) Note"that"outliers"now"stick"out"like"sore"thumbs"that"you"just"hit"with"a"rock hammer. 6) Click"Apply"to"lock"this"increment"of"deformation"in."Then"go"to"the"Main Menu/File/Save"All"History"to"save"the"original"pebble"data"and"the"two transformations"you"used"to"undeform"the"pebbles."give"the"file"an"easyoootoo OO"remember"name."If"you"want"to"export"information"for"transformed"pebble data,"use"the"save"current"state"option"in"the"file"menu."this"will"give"the"x,"y coordinates,"long"and"short"axis"lengths,"and"long"axis"orientations"of"pebbles after"they"have"been"transformed"to"analyze"in"a"spreadsheet"or"in"another program. 7) To"review"the"transformations"you"just"applied,"use"the"forward"and backward"arrows"on"the"control"panel"" to"cycle"through the"steps."you"can"also"review"the"transformation"matrices"by"opening"the Deformation"Matrix"window. 8) The"strain"ellipse"shape"estimated"using"this"approach"is"given"by"the"ratio"of the"reciprocal(strain(ellipse."this"is"simply"the"rs"value"below"the"black matrix"in"the"control"panel. 9) The"Phi"value"of"the"strain"ellipse"is"given"by"the"rotation"you"applied"in"step 3"above"to"get"the"vector"mean"to"coincide"with"Phi"="0. 10) What"is"the"axial"ratio"of"the"strain"ellipse"determined"by" undeforming "the pebbles? 11) How"does"this"estimate"compare"with"the"one"determined"in"Part"2? 12) As"a"bonus,"this"flexible"approach"to"estimating"strain"by" undeforming "the pebbles"makes"it"possible"to"evaluate"visually"the"results."the"deformed background"image"produced"above"is"really"a"picture"of"what"the"pebbles should"have"looked"like"before"strain"if"this"estimate"is"valid. 13) Does"the" undeformed "pebble"population"look"like"a"naturally"deposited conglomerate"to"you? 14) Explain"your"answer"above: 5"
6 15) This"visual"approach"of" undeforming "pebbles"can"be"accomplished"with polar"rfooophi"plots;"in"fact"it"is"arguably"easier."follow"the"same"procedure you"used"with"the"cartesian"rfooophi"plot:"click"in"the"deg."box"under"rotation and"rotate"the"pebbles"until"the"yellow"line"coincides"with"phi"="0,"then"click in"the"x"box"under"pure"shear"and"shorten"the"pebbles"in"the"xooodirection until"the"pebbles"are"clustered"in"the"center"of"the"polar"plot. 16) What"is"the"axial"ratio"of"the"strain"ellipse"determined"by" undeforming "the pebbles"using"the"polar"rfooophi"plot? 17) Which"plot"do"you"think"does"a"better"job"of"handling"outliers"during"the undeforming "simulation? 18) Explain"your"answer"to"17"above. 6"
Elements of Continuum Elasticity. David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II February 25, 2004
 Elements of Continuum Elasticity David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II 2.002 February 25, 2004 Solid Mechanics in 3 Dimensions: stress/equilibrium, strain/displacement, and intro to linear elastic
Elements of Continuum Elasticity David M. Parks Mechanics and Materials II 2.002 February 25, 2004 Solid Mechanics in 3 Dimensions: stress/equilibrium, strain/displacement, and intro to linear elastic
Strain page 1. Strain. Paul Bons Mineralogie & Geodynamik, Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen
 page 1 Paul Bons Mineralogie & Geodynamik, Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen Figure 1. Population of Asaphus trilobites before and after a homogeneous deformation event. The amount of strain is visualised
page 1 Paul Bons Mineralogie & Geodynamik, Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen Figure 1. Population of Asaphus trilobites before and after a homogeneous deformation event. The amount of strain is visualised
I t s h o u l d n o t b e u s e d a s t h e b a s i s f o r a n y i n v e s t m e n t d e c i s i o n.
 1 T h e f o l l o w i n g p r e s e n t a t i o n i n c l u d e s i n f o r m a t i o n t h a t r e p r e s e n t s s o m e o f t h e c u r r e n t d e v e l o p m e n t s c e n a r i o s w e a r e i n
1 T h e f o l l o w i n g p r e s e n t a t i o n i n c l u d e s i n f o r m a t i o n t h a t r e p r e s e n t s s o m e o f t h e c u r r e n t d e v e l o p m e n t s c e n a r i o s w e a r e i n
lecture 6 Methods of Structural Geology W k = W R " F ij = $ W k and type of strain This lecture The Mohr circle for strain Vorticity
 Methods of Structural Geology lecture 6 Last lectures Mohr circle for strain This lecture This lecture Look at deformation history of individual lines/planes Different deformation histories: same result?
Methods of Structural Geology lecture 6 Last lectures Mohr circle for strain This lecture This lecture Look at deformation history of individual lines/planes Different deformation histories: same result?
Find two positive factors of 24 whose sum is 10. Make an organized list.
 9.5 Study Guide For use with pages 582 589 GOAL Factor trinomials of the form x 2 1 bx 1 c. EXAMPLE 1 Factor when b and c are positive Factor x 2 1 10x 1 24. Find two positive factors of 24 whose sum is
9.5 Study Guide For use with pages 582 589 GOAL Factor trinomials of the form x 2 1 bx 1 c. EXAMPLE 1 Factor when b and c are positive Factor x 2 1 10x 1 24. Find two positive factors of 24 whose sum is
Concept Question Comment on the general features of the stress-strain response under this loading condition for both types of materials
 Module 5 Material failure Learning Objectives review the basic characteristics of the uni-axial stress-strain curves of ductile and brittle materials understand the need to develop failure criteria for
Module 5 Material failure Learning Objectives review the basic characteristics of the uni-axial stress-strain curves of ductile and brittle materials understand the need to develop failure criteria for
Pre Algebra Section 4.2
 Unit 4 - Equations Section 2 Solving One-Step Equations In this section we will be looking for solutions to equations. A solution is a number that can be plugged into an equation that keeps the equation
Unit 4 - Equations Section 2 Solving One-Step Equations In this section we will be looking for solutions to equations. A solution is a number that can be plugged into an equation that keeps the equation
Exam in : GEO-3104 Advanced Structural. Geology. Date : Time : Approved remedies : Ruler (linjal), Compasses (passer),
 Page 1 of 5 pages FINAL EXAM IN GEO-3104 Exam in : GEO-3104 Advanced Structural Geology Date : 28-02-2013 Time : 9.00 12.00 Place : Aud.Max. Approved remedies : Ruler (linjal), Compasses (passer), Protractor
Page 1 of 5 pages FINAL EXAM IN GEO-3104 Exam in : GEO-3104 Advanced Structural Geology Date : 28-02-2013 Time : 9.00 12.00 Place : Aud.Max. Approved remedies : Ruler (linjal), Compasses (passer), Protractor
FOLD CLASSIFICATIONS
 GG303 Lecture 28 9/4/01 1 FOLD CLASSIFICATIONS I Main Topics A Fold nomenclature B Ramsay's classification schemes C Interference of folds D Superposition of folds II Fold nomenclature and classification
GG303 Lecture 28 9/4/01 1 FOLD CLASSIFICATIONS I Main Topics A Fold nomenclature B Ramsay's classification schemes C Interference of folds D Superposition of folds II Fold nomenclature and classification
Pressure Vessels Stresses Under Combined Loads Yield Criteria for Ductile Materials and Fracture Criteria for Brittle Materials
 Pressure Vessels Stresses Under Combined Loads Yield Criteria for Ductile Materials and Fracture Criteria for Brittle Materials Pressure Vessels: In the previous lectures we have discussed elements subjected
Pressure Vessels Stresses Under Combined Loads Yield Criteria for Ductile Materials and Fracture Criteria for Brittle Materials Pressure Vessels: In the previous lectures we have discussed elements subjected
Module 7 : Applications of Integration - I. Lecture 21 : Relative rate of growth of functions [Section 21.1] Objectives
![Module 7 : Applications of Integration - I. Lecture 21 : Relative rate of growth of functions [Section 21.1] Objectives Module 7 : Applications of Integration - I. Lecture 21 : Relative rate of growth of functions [Section 21.1] Objectives](/thumbs/89/99619893.jpg) Module 7 : Applications of Integration - I Lecture 21 : Relative rate of growth of functions [Section 211] Objectives In this section you will learn the following : How to compare the rate of growth of
Module 7 : Applications of Integration - I Lecture 21 : Relative rate of growth of functions [Section 211] Objectives In this section you will learn the following : How to compare the rate of growth of
Lecture 9: Measuring Strain and Mohr s Circle for Strain
 Lecture 9: Measuring Strain and Mohr s Circle for Strain The last lecture explained the basic ideas about strain and introduced the strain tensor. This lecture explores a few different ways to measure
Lecture 9: Measuring Strain and Mohr s Circle for Strain The last lecture explained the basic ideas about strain and introduced the strain tensor. This lecture explores a few different ways to measure
WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE
 WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT STRESS ANALYSIS ES-2502, C 2012 Lecture 07: Stress and Strain 24 January 2012 General information Instructor: Cosme Furlong HL-151 (508)
WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT STRESS ANALYSIS ES-2502, C 2012 Lecture 07: Stress and Strain 24 January 2012 General information Instructor: Cosme Furlong HL-151 (508)
GY403 Structural Geology. Tectonite Fabrics
 GY403 Structural Geology Tectonite Fabrics Tectonite Fabric A tectonite is a rock that possess a penetrative fabric consisting of cleavage, foliation and/or lineation Tectonite fabrics are associated with
GY403 Structural Geology Tectonite Fabrics Tectonite Fabric A tectonite is a rock that possess a penetrative fabric consisting of cleavage, foliation and/or lineation Tectonite fabrics are associated with
Lecture 9 Laminar Diffusion Flame Configurations
 Lecture 9 Laminar Diffusion Flame Configurations 9.-1 Different Flame Geometries and Single Droplet Burning Solutions for the velocities and the mixture fraction fields for some typical laminar flame configurations.
Lecture 9 Laminar Diffusion Flame Configurations 9.-1 Different Flame Geometries and Single Droplet Burning Solutions for the velocities and the mixture fraction fields for some typical laminar flame configurations.
STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY. Deformation
 eformation STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY Styles of deformation These items can be used to demonstrate different styles of deformation to the class. To show elastic deformation: elastic band, sponge or plastic ruler,
eformation STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY Styles of deformation These items can be used to demonstrate different styles of deformation to the class. To show elastic deformation: elastic band, sponge or plastic ruler,
CHAPTER 5 : THE STRAIGHT LINE
 EXERCISE 1 CHAPTER 5 : THE STRAIGHT LINE 1. In the diagram, PQ is a straight line. P 4 2 4 3 2 1 0 1 2 2 2. Find (a) the -intercept, (b) the gradient, of the straight line. Q (5,18) Q Answer :a).. b) 3
EXERCISE 1 CHAPTER 5 : THE STRAIGHT LINE 1. In the diagram, PQ is a straight line. P 4 2 4 3 2 1 0 1 2 2 2. Find (a) the -intercept, (b) the gradient, of the straight line. Q (5,18) Q Answer :a).. b) 3
Plane Curves and Parametric Equations
 Plane Curves and Parametric Equations MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction We typically think of a graph as a curve in the xy-plane generated by the
Plane Curves and Parametric Equations MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2018 Introduction We typically think of a graph as a curve in the xy-plane generated by the
Mechanical Properties of Materials
 Mechanical Properties of Materials Strains Material Model Stresses Learning objectives Understand the qualitative and quantitative description of mechanical properties of materials. Learn the logic of
Mechanical Properties of Materials Strains Material Model Stresses Learning objectives Understand the qualitative and quantitative description of mechanical properties of materials. Learn the logic of
CURVATURE AND RADIUS OF CURVATURE
 CHAPTER 5 CURVATURE AND RADIUS OF CURVATURE 5.1 Introduction: Curvature is a numerical measure of bending of the curve. At a particular point on the curve, a tangent can be drawn. Let this line makes an
CHAPTER 5 CURVATURE AND RADIUS OF CURVATURE 5.1 Introduction: Curvature is a numerical measure of bending of the curve. At a particular point on the curve, a tangent can be drawn. Let this line makes an
GG303 Lab 12 11/7/18 1
 GG303 Lab 12 11/7/18 1 DEFORMATION AROUND A HOLE This lab has two main objectives. The first is to develop insight into the displacement, stress, and strain fields around a hole in a sheet under an approximately
GG303 Lab 12 11/7/18 1 DEFORMATION AROUND A HOLE This lab has two main objectives. The first is to develop insight into the displacement, stress, and strain fields around a hole in a sheet under an approximately
Exercise: concepts from chapter 5
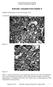 Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch 5 1) Study the oöids depicted in Figure 1a and 1b. Figure 1a Figure 1b Figure 1. Nearly undeformed (1a) and significantly deformed (1b) oöids with spherulitic
Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch 5 1) Study the oöids depicted in Figure 1a and 1b. Figure 1a Figure 1b Figure 1. Nearly undeformed (1a) and significantly deformed (1b) oöids with spherulitic
Fluid Dynamics Exercises and questions for the course
 Fluid Dynamics Exercises and questions for the course January 15, 2014 A two dimensional flow field characterised by the following velocity components in polar coordinates is called a free vortex: u r
Fluid Dynamics Exercises and questions for the course January 15, 2014 A two dimensional flow field characterised by the following velocity components in polar coordinates is called a free vortex: u r
STRAIN. Normal Strain: The elongation or contractions of a line segment per unit length is referred to as normal strain denoted by Greek symbol.
 STRAIN In engineering the deformation of a body is specified using the concept of normal strain and shear strain whenever a force is applied to a body, it will tend to change the body s shape and size.
STRAIN In engineering the deformation of a body is specified using the concept of normal strain and shear strain whenever a force is applied to a body, it will tend to change the body s shape and size.
The Change-of-Variables Formula for Double Integrals
 The Change-of-Variables Formula for Double Integrals Minh-Tam Trinh In this document, I suggest ideas about how to solve some of the exercises in ection 15.9 of tewart, Multivariable Calculus, 8th Ed.
The Change-of-Variables Formula for Double Integrals Minh-Tam Trinh In this document, I suggest ideas about how to solve some of the exercises in ection 15.9 of tewart, Multivariable Calculus, 8th Ed.
Concept: Solving Absolute Value Equations
 Concept: Solving Absolute Value Equations Warm Up Name: 1. Determine what values of x make each inequality true. Graph each answer. (a) 9 x - 2 7 x + 8 9 x - 2 7 x + 8-7x) 2 x - 2 8 +2) 2 x 10 2) x 5 Remember:
Concept: Solving Absolute Value Equations Warm Up Name: 1. Determine what values of x make each inequality true. Graph each answer. (a) 9 x - 2 7 x + 8 9 x - 2 7 x + 8-7x) 2 x - 2 8 +2) 2 x 10 2) x 5 Remember:
1. To analyze the deformation of a conical membrane, it is proposed to use a two-dimensional conical-polar coordinate system ( s,
 EN2210: Continuum Mechanics Homework 2: Kinematics Due Wed September 26, 2012 School of Engineering Brown University 1. To analyze the deformation of a conical membrane, it is proposed to use a two-dimensional
EN2210: Continuum Mechanics Homework 2: Kinematics Due Wed September 26, 2012 School of Engineering Brown University 1. To analyze the deformation of a conical membrane, it is proposed to use a two-dimensional
Lecture 7: The Beam Element Equations.
 4.1 Beam Stiffness. A Beam: A long slender structural component generally subjected to transverse loading that produces significant bending effects as opposed to twisting or axial effects. MECH 40: Finite
4.1 Beam Stiffness. A Beam: A long slender structural component generally subjected to transverse loading that produces significant bending effects as opposed to twisting or axial effects. MECH 40: Finite
(Relatively) Painless Stress Tensors
 (Relatively) Painless Stress Tensors Colin A. Shaw, University of Wisconsin, Eau Claire shawca@uwec.edu A graphical approach to introducing tensors Adapted from Means (1976) Context Presentation: The activity
(Relatively) Painless Stress Tensors Colin A. Shaw, University of Wisconsin, Eau Claire shawca@uwec.edu A graphical approach to introducing tensors Adapted from Means (1976) Context Presentation: The activity
Vectors. Section 3: Using the vector product
 Vectors Section 3: Using the vector product Notes and Examples These notes contain subsections on Using the vector product in finding the equation of a plane The intersection of two planes The distance
Vectors Section 3: Using the vector product Notes and Examples These notes contain subsections on Using the vector product in finding the equation of a plane The intersection of two planes The distance
Table : Specific rates of Breakage and Breakage Distribution Function for the Hammer Mill
 SOLUTIONS TO CHAPTER 12: SIZE REDUCTION EXERCISE 12.1 a) Rittinger's energy law postulated that the energy expended in crushing is proportional to the area of new surface created. Derive an expression
SOLUTIONS TO CHAPTER 12: SIZE REDUCTION EXERCISE 12.1 a) Rittinger's energy law postulated that the energy expended in crushing is proportional to the area of new surface created. Derive an expression
A two-dimensional FE truss program
 A two-dimensional FE truss program 4M020: Design Tools Eindhoven University of Technology Introduction The Matlab program fem2d allows to model and analyze two-dimensional truss structures, where trusses
A two-dimensional FE truss program 4M020: Design Tools Eindhoven University of Technology Introduction The Matlab program fem2d allows to model and analyze two-dimensional truss structures, where trusses
Lecture 8. Stress Strain in Multi-dimension
 Lecture 8. Stress Strain in Multi-dimension Module. General Field Equations General Field Equations [] Equilibrium Equations in Elastic bodies xx x y z yx zx f x 0, etc [2] Kinematics xx u x x,etc. [3]
Lecture 8. Stress Strain in Multi-dimension Module. General Field Equations General Field Equations [] Equilibrium Equations in Elastic bodies xx x y z yx zx f x 0, etc [2] Kinematics xx u x x,etc. [3]
Structural Geology. Part 1: Continuum mechanics and rheology
 12.113 Structural Geology Part 1: Continuum mechanics and rheology Fall 2005 2 Contents 1 Stress and strain 5 1.1 Stress (T&M pp.128 164)........................... 5 1.1.1 Introduction...............................
12.113 Structural Geology Part 1: Continuum mechanics and rheology Fall 2005 2 Contents 1 Stress and strain 5 1.1 Stress (T&M pp.128 164)........................... 5 1.1.1 Introduction...............................
21 Symmetric and skew-symmetric matrices
 21 Symmetric and skew-symmetric matrices 21.1 Decomposition of a square matrix into symmetric and skewsymmetric matrices Let C n n be a square matrix. We can write C = (1/2)(C + C t ) + (1/2)(C C t ) =
21 Symmetric and skew-symmetric matrices 21.1 Decomposition of a square matrix into symmetric and skewsymmetric matrices Let C n n be a square matrix. We can write C = (1/2)(C + C t ) + (1/2)(C C t ) =
SEQUENCES AND SERIES
 A sequence is an ordered list of numbers. SEQUENCES AND SERIES Note, in this context, ordered does not mean that the numbers in the list are increasing or decreasing. Instead it means that there is a first
A sequence is an ordered list of numbers. SEQUENCES AND SERIES Note, in this context, ordered does not mean that the numbers in the list are increasing or decreasing. Instead it means that there is a first
= 1, where a is semi-major axis, and b is semi-minor axis, a b. This ellipse
 Solutions of Homework 6 1 Let C be an ellipse in the plane E such that its foci are at points F 1 = 1, 0) and F = 1, 0) and it passes through the point K = 0, ). Write down the analytical formula which
Solutions of Homework 6 1 Let C be an ellipse in the plane E such that its foci are at points F 1 = 1, 0) and F = 1, 0) and it passes through the point K = 0, ). Write down the analytical formula which
Provided by Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. for An Introduction to Structural Methods DVD-ROM
 Provided by Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. for An Introduction to Structural Methods DVD-ROM http://www.tasagraphicarts.com/progstruct.html AN INTRODUCTION TO STRUCTURAL METHODS - DETAILED CONTENTS: (Navigate
Provided by Tasa Graphic Arts, Inc. for An Introduction to Structural Methods DVD-ROM http://www.tasagraphicarts.com/progstruct.html AN INTRODUCTION TO STRUCTURAL METHODS - DETAILED CONTENTS: (Navigate
Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering
 Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering Short Course on + Dynamics Boulder, Colorado January 5-8, 2004 Stein Sture Professor of Civil Engineering University of Colorado at Boulder Contents Steps
Finite Element Method in Geotechnical Engineering Short Course on + Dynamics Boulder, Colorado January 5-8, 2004 Stein Sture Professor of Civil Engineering University of Colorado at Boulder Contents Steps
GEL 3300 Lab #2: Measuring Strain
 GEL 3300 Lab #2: Measuring Strain The objective of this lab exercise is to use strain markers to determine the orientation of the finite strain ellipse for a deformed rock that contains deformed fossil
GEL 3300 Lab #2: Measuring Strain The objective of this lab exercise is to use strain markers to determine the orientation of the finite strain ellipse for a deformed rock that contains deformed fossil
Artin-Schelter regular algebras and the Steenrod algebra
 Artin-Schelter regular algebras and the Steenrod algebra J. H. Palmieri and J. J. Zhang University of Washington Los Angeles, 10 October 2010 Exercise Let A(1) be the sub-hopf algebra of the mod 2 Steenrod
Artin-Schelter regular algebras and the Steenrod algebra J. H. Palmieri and J. J. Zhang University of Washington Los Angeles, 10 October 2010 Exercise Let A(1) be the sub-hopf algebra of the mod 2 Steenrod
Chapter 2: Rigid Bar Supported by Two Buckled Struts under Axial, Harmonic, Displacement Excitation..14
 Table of Contents Chapter 1: Research Objectives and Literature Review..1 1.1 Introduction...1 1.2 Literature Review......3 1.2.1 Describing Vibration......3 1.2.2 Vibration Isolation.....6 1.2.2.1 Overview.
Table of Contents Chapter 1: Research Objectives and Literature Review..1 1.1 Introduction...1 1.2 Literature Review......3 1.2.1 Describing Vibration......3 1.2.2 Vibration Isolation.....6 1.2.2.1 Overview.
Postulates of Quantum Mechanics
 EXERCISES OF QUANTUM MECHANICS LECTURE Departamento de Física Teórica y del Cosmos 018/019 Exercise 1: Stern-Gerlach experiment Postulates of Quantum Mechanics AStern-Gerlach(SG)deviceisabletoseparateparticlesaccordingtotheirspinalonga
EXERCISES OF QUANTUM MECHANICS LECTURE Departamento de Física Teórica y del Cosmos 018/019 Exercise 1: Stern-Gerlach experiment Postulates of Quantum Mechanics AStern-Gerlach(SG)deviceisabletoseparateparticlesaccordingtotheirspinalonga
Introducing Stress Transformation and Mohr s Circle
 Paper ID #14948 Introducing Stress Transformation and Mohr s Circle Mr. Philip A Jones P.E., Pennsylvania State University, Erie Mr. Philip Jones is a lecturer in engineering in the School of Engineering
Paper ID #14948 Introducing Stress Transformation and Mohr s Circle Mr. Philip A Jones P.E., Pennsylvania State University, Erie Mr. Philip Jones is a lecturer in engineering in the School of Engineering
Senior Math Circles February 18, 2009 Conics III
 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Senior Math Circles February 18, 2009 Conics III Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Eccentricity of Conics Fix a point F called the focus, a
University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Senior Math Circles February 18, 2009 Conics III Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Eccentricity of Conics Fix a point F called the focus, a
Rotation of Axes. By: OpenStaxCollege
 Rotation of Axes By: OpenStaxCollege As we have seen, conic sections are formed when a plane intersects two right circular cones aligned tip to tip and extending infinitely far in opposite directions,
Rotation of Axes By: OpenStaxCollege As we have seen, conic sections are formed when a plane intersects two right circular cones aligned tip to tip and extending infinitely far in opposite directions,
Exercise: concepts from chapter 8
 Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch 8 1) The following exercises explore elementary concepts associated with a linear elastic material that is isotropic and homogeneous with respect to elastic
Reading: Fundamentals of Structural Geology, Ch 8 1) The following exercises explore elementary concepts associated with a linear elastic material that is isotropic and homogeneous with respect to elastic
Conic Sections Session 3: Hyperbola
 Conic Sections Session 3: Hyperbola Toh Pee Choon NIE Oct 2017 Toh Pee Choon (NIE) Session 3: Hyperbola Oct 2017 1 / 16 Problem 3.1 1 Recall that an ellipse is defined as the locus of points P such that
Conic Sections Session 3: Hyperbola Toh Pee Choon NIE Oct 2017 Toh Pee Choon (NIE) Session 3: Hyperbola Oct 2017 1 / 16 Problem 3.1 1 Recall that an ellipse is defined as the locus of points P such that
lecture 7 Foliations & lineations
 Kristallingeologie lecture 7 Foliations & lineations 28 participants Results test A, 2008 Maximum 70 points Pass!35 points (!50%) Best result 67 points Average result 54 points ("2.3) Worst result 30 points
Kristallingeologie lecture 7 Foliations & lineations 28 participants Results test A, 2008 Maximum 70 points Pass!35 points (!50%) Best result 67 points Average result 54 points ("2.3) Worst result 30 points
Mechanical Modeling and Analysis of Braided Wire Rope
 5th International Conference on Measurement, Instrumentation and Automation (ICMIA 016) Mechanical Modeling and Analysis of Braided Wire Rope ZHAO Xia1, a WANG Hui1, b ZHAO Ping1, c KE ShengJun1, d SONG
5th International Conference on Measurement, Instrumentation and Automation (ICMIA 016) Mechanical Modeling and Analysis of Braided Wire Rope ZHAO Xia1, a WANG Hui1, b ZHAO Ping1, c KE ShengJun1, d SONG
Ductile deformation - Finite strain
 327 Ductile deformation - Finite strain Deformation includes any process that results in a change in shape, size or location of a body. A solid body subjected to external forces tends to move or change
327 Ductile deformation - Finite strain Deformation includes any process that results in a change in shape, size or location of a body. A solid body subjected to external forces tends to move or change
Table of Contents. Preface... xiii
 Preface... xiii PART I. ELEMENTS IN FLUID MECHANICS... 1 Chapter 1. Local Equations of Fluid Mechanics... 3 1.1. Forces, stress tensor, and pressure... 4 1.2. Navier Stokes equations in Cartesian coordinates...
Preface... xiii PART I. ELEMENTS IN FLUID MECHANICS... 1 Chapter 1. Local Equations of Fluid Mechanics... 3 1.1. Forces, stress tensor, and pressure... 4 1.2. Navier Stokes equations in Cartesian coordinates...
EXPERIMENTAL DEFORMATION AND FOLDING IN PHYLLITE AND PALEOSTRESS ANALYSIS FROM TRIANGULAR PLOT. Speaker : Yu-Sheng Liang
 1 EXPERIMENTAL DEFORMATION AND FOLDING IN PHYLLITE AND PALEOSTRESS ANALYSIS FROM TRIANGULAR PLOT Speaker : Yu-Sheng Liang References 2 Paterson, M.S. and Weiss, L.E. (1966) Experimental deformation and
1 EXPERIMENTAL DEFORMATION AND FOLDING IN PHYLLITE AND PALEOSTRESS ANALYSIS FROM TRIANGULAR PLOT Speaker : Yu-Sheng Liang References 2 Paterson, M.S. and Weiss, L.E. (1966) Experimental deformation and
The CR Formulation: BE Plane Beam
 6 The CR Formulation: BE Plane Beam 6 Chapter 6: THE CR FORMUATION: BE PANE BEAM TABE OF CONTENTS Page 6. Introduction..................... 6 4 6.2 CR Beam Kinematics................. 6 4 6.2. Coordinate
6 The CR Formulation: BE Plane Beam 6 Chapter 6: THE CR FORMUATION: BE PANE BEAM TABE OF CONTENTS Page 6. Introduction..................... 6 4 6.2 CR Beam Kinematics................. 6 4 6.2. Coordinate
Numerical Sound Synthesis
 Numerical Sound Synthesis Finite Difference Schemes and Simulation in Musical Acoustics Stefan Bilbao Acoustics and Fluid Dynamics Group/Music, University 01 Edinburgh, UK @WILEY A John Wiley and Sons,
Numerical Sound Synthesis Finite Difference Schemes and Simulation in Musical Acoustics Stefan Bilbao Acoustics and Fluid Dynamics Group/Music, University 01 Edinburgh, UK @WILEY A John Wiley and Sons,
Vectors. 1 Basic Definitions. Liming Pang
 Vectors Liming Pang 1 Basic Definitions Definition 1. A vector in a line/plane/space is a quantity which has both magnitude and direction. The magnitude is a nonnegative real number and the direction is
Vectors Liming Pang 1 Basic Definitions Definition 1. A vector in a line/plane/space is a quantity which has both magnitude and direction. The magnitude is a nonnegative real number and the direction is
A FAILURE CRITERION FOR POLYMERS AND SOFT BIOLOGICAL MATERIALS
 Material Technology A FALURE CRTERON FOR POLYMERS AND SOFT BOLOGCAL MATERALS Authors: William W. Feng John O. Hallquist Livermore Software Technology Corp. 7374 Las Positas Road Livermore, CA 94550 USA
Material Technology A FALURE CRTERON FOR POLYMERS AND SOFT BOLOGCAL MATERALS Authors: William W. Feng John O. Hallquist Livermore Software Technology Corp. 7374 Las Positas Road Livermore, CA 94550 USA
Section 5.5. Complex Eigenvalues
 Section 5.5 Complex Eigenvalues Motivation: Describe rotations Among transformations, rotations are very simple to describe geometrically. Where are the eigenvectors? A no nonzero vector x is collinear
Section 5.5 Complex Eigenvalues Motivation: Describe rotations Among transformations, rotations are very simple to describe geometrically. Where are the eigenvectors? A no nonzero vector x is collinear
Parametric Equations
 Parametric Equations By: OpenStaxCollege Consider the path a moon follows as it orbits a planet, which simultaneously rotates around the sun, as seen in [link]. At any moment, the moon is located at a
Parametric Equations By: OpenStaxCollege Consider the path a moon follows as it orbits a planet, which simultaneously rotates around the sun, as seen in [link]. At any moment, the moon is located at a
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Tables and Supplementary References
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Tables and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Movie 1 Description: The movie shows compression behaviour
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Tables and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Movie 1 Description: The movie shows compression behaviour
Section 7: Discriminant Analysis.
 Section 7: Discriminant Analysis. Ensure you have completed all previous worksheets before advancing. 1 Linear Discriminant Analysis To perform Linear Discriminant Analysis in R we will make use of the
Section 7: Discriminant Analysis. Ensure you have completed all previous worksheets before advancing. 1 Linear Discriminant Analysis To perform Linear Discriminant Analysis in R we will make use of the
QMUL, School of Physics and Astronomy Date: 18/01/2019
 QMUL, School of Physics and stronomy Date: 8//9 PHY Mathematical Techniques Solutions for Exercise Class Script : Coordinate Systems and Double Integrals. Calculate the integral: where the region is defined
QMUL, School of Physics and stronomy Date: 8//9 PHY Mathematical Techniques Solutions for Exercise Class Script : Coordinate Systems and Double Integrals. Calculate the integral: where the region is defined
= L 1 # L o = " L o. = L 1! L o
 GG303 Lab 9 10/20/09 1 STRAIN I Main Topics A General deformation B Homogeneous 2-D strain and the strain ellipse C Homogeneous 3-D strain and the strain ellipsoid (Flinn Diagrams) D Comments on measuring
GG303 Lab 9 10/20/09 1 STRAIN I Main Topics A General deformation B Homogeneous 2-D strain and the strain ellipse C Homogeneous 3-D strain and the strain ellipsoid (Flinn Diagrams) D Comments on measuring
EAS MIDTERM EXAM
 Ave = 98/150, s.d. = 21 EAS 326-03 MIDTERM EXAM This exam is closed book and closed notes. It is worth 150 points; the value of each question is shown at the end of each question. At the end of the exam,
Ave = 98/150, s.d. = 21 EAS 326-03 MIDTERM EXAM This exam is closed book and closed notes. It is worth 150 points; the value of each question is shown at the end of each question. At the end of the exam,
7.2. Exercises on lines in space
 .. Exercises on lines in space Exercise : Change of support and direction vectors. Check whether P or Q are on g.. Use the point found in. to find both a new support vector and a new direction vector for
.. Exercises on lines in space Exercise : Change of support and direction vectors. Check whether P or Q are on g.. Use the point found in. to find both a new support vector and a new direction vector for
Module 7: Micromechanics Lecture 25: Strength of Materials Approach. Introduction. The Lecture Contains. Effective Transverse Modulus
 Introduction In the previous lecture we have introduced the concept of Representative Volume Element or Unit Cell. This is the basic building block in a micromechanical study. Further, we explained the
Introduction In the previous lecture we have introduced the concept of Representative Volume Element or Unit Cell. This is the basic building block in a micromechanical study. Further, we explained the
This exercise is to be completed during your lab period during the week of October 24-30, 2018.
 MOLECULAR MODELLING EXERCISE II This exercise is to be completed during your lab period during the week of October 24-30, 2018. You will need to continue to know and understand, and be able to apply, the
MOLECULAR MODELLING EXERCISE II This exercise is to be completed during your lab period during the week of October 24-30, 2018. You will need to continue to know and understand, and be able to apply, the
Sets and Functions. MATH 464/506, Real Analysis. J. Robert Buchanan. Summer Department of Mathematics. J. Robert Buchanan Sets and Functions
 Sets and Functions MATH 464/506, Real Analysis J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2007 Notation x A means that element x is a member of set A. x / A means that x is not a member of A.
Sets and Functions MATH 464/506, Real Analysis J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Summer 2007 Notation x A means that element x is a member of set A. x / A means that x is not a member of A.
MAE 3130: Fluid Mechanics Lecture 7: Differential Analysis/Part 1 Spring Dr. Jason Roney Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering
 MAE 3130: Fluid Mechanics Lecture 7: Differential Analysis/Part 1 Spring 2003 Dr. Jason Roney Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Outline Introduction Kinematics Review Conservation of Mass Stream Function
MAE 3130: Fluid Mechanics Lecture 7: Differential Analysis/Part 1 Spring 2003 Dr. Jason Roney Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Outline Introduction Kinematics Review Conservation of Mass Stream Function
9. Stereochemistry: Introduction to Using Molecular Models
 9. Stereochemistry: Introduction to Using Molecular Models The first part of this document reviews some of the most important stereochemistry topics covered in lecture. Following the introduction, a number
9. Stereochemistry: Introduction to Using Molecular Models The first part of this document reviews some of the most important stereochemistry topics covered in lecture. Following the introduction, a number
DETAILED SYLLABUS FOR DISTANCE EDUCATION. Diploma. (Three Years Semester Scheme) Diploma in Architecture (DARC)
 DETAILED SYLLABUS FOR DISTANCE EDUCATION Diploma (Three Years Semester Scheme) Diploma in Architecture (DARC) COURSE TITLE DURATION : Diploma in ARCHITECTURE (DARC) : 03 Years (Semester System) FOURTH
DETAILED SYLLABUS FOR DISTANCE EDUCATION Diploma (Three Years Semester Scheme) Diploma in Architecture (DARC) COURSE TITLE DURATION : Diploma in ARCHITECTURE (DARC) : 03 Years (Semester System) FOURTH
Folds and Folding. Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics. Ben van der Pluijm. WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 3/4/ :15
 Folds and Folding Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 3/4/2017 17:15 We Discuss Folds and Folding Fold Description Fold Classification
Folds and Folding Processes in Structural Geology & Tectonics Ben van der Pluijm WW Norton+Authors, unless noted otherwise 3/4/2017 17:15 We Discuss Folds and Folding Fold Description Fold Classification
Paper Reference. Further Pure Mathematics FP3 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary. Monday 24 June 2013 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 6669/01 Edexcel GCE Further Pure Mathematics FP3 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Monday 24 June 2013 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes This is
Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 6669/01 Edexcel GCE Further Pure Mathematics FP3 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Monday 24 June 2013 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes This is
Comparative Study of Variation of Mooney- Rivlin Hyperelastic Material Models under Uniaxial Tensile Loading
 Comparative Study of Variation of Mooney- Rivlin Hyperelastic Material Models under Uniaxial Tensile Loading A. N. Jadhav 1, Dr. S.R. Bahulikar, N.H. Sapate 3 1 M Tech Design Engg, Mechanical Engineering,
Comparative Study of Variation of Mooney- Rivlin Hyperelastic Material Models under Uniaxial Tensile Loading A. N. Jadhav 1, Dr. S.R. Bahulikar, N.H. Sapate 3 1 M Tech Design Engg, Mechanical Engineering,
Vibrations of Structures
 Vibrations of Structures Module III: Vibrations of Beams Lesson 26: Special Topics in Beam Vibrations - II Contents: 1. Introduction 2. Influence of Axial Force on Dynamic Stability Keywords: Stability,
Vibrations of Structures Module III: Vibrations of Beams Lesson 26: Special Topics in Beam Vibrations - II Contents: 1. Introduction 2. Influence of Axial Force on Dynamic Stability Keywords: Stability,
Lecture 15 Strain and stress in beams
 Spring, 2019 ME 323 Mechanics of Materials Lecture 15 Strain and stress in beams Reading assignment: 6.1 6.2 News: Instructor: Prof. Marcial Gonzalez Last modified: 1/6/19 9:42:38 PM Beam theory (@ ME
Spring, 2019 ME 323 Mechanics of Materials Lecture 15 Strain and stress in beams Reading assignment: 6.1 6.2 News: Instructor: Prof. Marcial Gonzalez Last modified: 1/6/19 9:42:38 PM Beam theory (@ ME
Parametric Equations *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49409 1 Parametric Equations * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 In this section, you will: Abstract Parameterize
OpenStax-CNX module: m49409 1 Parametric Equations * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 In this section, you will: Abstract Parameterize
BLUE PRINT - III MATHEMATICS - XII. (b) Applications of Derivatives (1) 44 (11) (b) 3 - dimensional geometry - 4 (1) 6 (1) 17 (6)
 BLUE PRINT - III MATHEMATICS - XII S.No. Topic VSA SA LA TOTAL 1. (a) Relations and Functions 1 (1) 4 (1) - 10 (4) (b) Inverse trigonometric 1 (1) 4 (1) - Functions. (a) Matrices () - 6 (1) - (b) Determinants
BLUE PRINT - III MATHEMATICS - XII S.No. Topic VSA SA LA TOTAL 1. (a) Relations and Functions 1 (1) 4 (1) - 10 (4) (b) Inverse trigonometric 1 (1) 4 (1) - Functions. (a) Matrices () - 6 (1) - (b) Determinants
circular voids On the interaction between two in a nonlinear elastic solid ACTA MECHANICA J. P. Zhang and R. C. Batra, Rolla, Missouri
 Acta Mechanica 105, 161-171 (1994) ACTA MECHANICA 9 Springer-Verlag 1994 On the interaction between two in a nonlinear elastic solid circular voids J. P. Zhang and R. C. Batra, Rolla, Missouri (Received
Acta Mechanica 105, 161-171 (1994) ACTA MECHANICA 9 Springer-Verlag 1994 On the interaction between two in a nonlinear elastic solid circular voids J. P. Zhang and R. C. Batra, Rolla, Missouri (Received
CHAPTER 2 Failure/Fracture Criterion
 (11) CHAPTER 2 Failure/Fracture Criterion (12) Failure (Yield) Criteria for Ductile Materials under Plane Stress Designer engineer: 1- Analysis of loading (for simple geometry using what you learn here
(11) CHAPTER 2 Failure/Fracture Criterion (12) Failure (Yield) Criteria for Ductile Materials under Plane Stress Designer engineer: 1- Analysis of loading (for simple geometry using what you learn here
MODELING OF CONCRETE MATERIALS AND STRUCTURES. Kaspar Willam
 MODELING OF CONCRETE MATERIALS AND STRUCTURES Class Meeting #1: Fundamentals Kaspar Willam University of Colorado at Boulder Notation: Direct and indicial tensor formulations Fundamentals: Stress and Strain
MODELING OF CONCRETE MATERIALS AND STRUCTURES Class Meeting #1: Fundamentals Kaspar Willam University of Colorado at Boulder Notation: Direct and indicial tensor formulations Fundamentals: Stress and Strain
Kevin James. MTHSC 3110 Section 2.2 Inverses of Matrices
 MTHSC 3110 Section 2.2 Inverses of Matrices Definition Suppose that T : R n R m is linear. We will say that T is invertible if for every b R m there is exactly one x R n so that T ( x) = b. Note If T is
MTHSC 3110 Section 2.2 Inverses of Matrices Definition Suppose that T : R n R m is linear. We will say that T is invertible if for every b R m there is exactly one x R n so that T ( x) = b. Note If T is
VERSION 4.0. Nanostructure semiconductor quantum simulation software for scientists and engineers.
 VERSION 4.0 Heterostructure Design Studio Nanostructure semiconductor quantum simulation software for scientists and engineers sales@optronicsdesign.com www.optronicsdesign.com Product description Heterostructure
VERSION 4.0 Heterostructure Design Studio Nanostructure semiconductor quantum simulation software for scientists and engineers sales@optronicsdesign.com www.optronicsdesign.com Product description Heterostructure
Non-linear and time-dependent material models in Mentat & MARC. Tutorial with Background and Exercises
 Non-linear and time-dependent material models in Mentat & MARC Tutorial with Background and Exercises Eindhoven University of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering Piet Schreurs July 7, 2009
Non-linear and time-dependent material models in Mentat & MARC Tutorial with Background and Exercises Eindhoven University of Technology Department of Mechanical Engineering Piet Schreurs July 7, 2009
1.5 STRESS-PATH METHOD OF SETTLEMENT CALCULATION 1.5 STRESS-PATH METHOD OF SETTLEMENT CALCULATION
 Module 6 Lecture 40 Evaluation of Soil Settlement - 6 Topics 1.5 STRESS-PATH METHOD OF SETTLEMENT CALCULATION 1.5.1 Definition of Stress Path 1.5. Stress and Strain Path for Consolidated Undrained Undrained
Module 6 Lecture 40 Evaluation of Soil Settlement - 6 Topics 1.5 STRESS-PATH METHOD OF SETTLEMENT CALCULATION 1.5.1 Definition of Stress Path 1.5. Stress and Strain Path for Consolidated Undrained Undrained
Lecture 10: Multiple Integrals
 Lecture 10: Multiple Integrals 1. Key points Multiple integrals as Iterated Integrals Change of variables: Jacobian Maple int(f(x,y),[xa..b,yc..d]) VectorCalculus[Jacobian] LinearAlgebra[Determinant] 2.
Lecture 10: Multiple Integrals 1. Key points Multiple integrals as Iterated Integrals Change of variables: Jacobian Maple int(f(x,y),[xa..b,yc..d]) VectorCalculus[Jacobian] LinearAlgebra[Determinant] 2.
Basic Surveying Week 3, Lesson 2 Semester 2017/18/2 Vectors, equation of line, circle, ellipse
 Basic Surveying Week 3, Lesson Semester 017/18/ Vectors, equation of line, circle, ellipse 1. Introduction In surveying calculations, we use the two or three dimensional coordinates of points or objects
Basic Surveying Week 3, Lesson Semester 017/18/ Vectors, equation of line, circle, ellipse 1. Introduction In surveying calculations, we use the two or three dimensional coordinates of points or objects
Final EXAM Preparation Sheet
 Final EXAM Preparation Sheet M369 Fall 217 1 Key concepts The following list contains the main concepts and ideas that we have explored this semester. For each concept, make sure that you remember about
Final EXAM Preparation Sheet M369 Fall 217 1 Key concepts The following list contains the main concepts and ideas that we have explored this semester. For each concept, make sure that you remember about
ELASTICITY AND FRACTURE MECHANICS. Vijay G. Ukadgaonker
 THEORY OF ELASTICITY AND FRACTURE MECHANICS y x Vijay G. Ukadgaonker Theory of Elasticity and Fracture Mechanics VIJAY G. UKADGAONKER Former Professor Indian Institute of Technology Bombay Delhi-110092
THEORY OF ELASTICITY AND FRACTURE MECHANICS y x Vijay G. Ukadgaonker Theory of Elasticity and Fracture Mechanics VIJAY G. UKADGAONKER Former Professor Indian Institute of Technology Bombay Delhi-110092
GG303 Lecture 29 9/4/01 1 FABRICS
 GG303 Lecture 29 9/4/01 1 FABRICS I Main Topics A What are fabrics? B Planar fabrics C Linear fabrics D Penetrative vs. non-penetrative fabrics E Cleavage and folds F Comments on use of grain-scale observations
GG303 Lecture 29 9/4/01 1 FABRICS I Main Topics A What are fabrics? B Planar fabrics C Linear fabrics D Penetrative vs. non-penetrative fabrics E Cleavage and folds F Comments on use of grain-scale observations
Module 4 Lecture 20 Pore water pressure and shear strength - 4 Topics
 Module 4 Lecture 20 Pore water pressure and shear strength - 4 Topics 1.2.6 Curvature of the Failure Envelope Effect of angularity of soil particles Effect of rate of loading during the test 1.2.7 Shear
Module 4 Lecture 20 Pore water pressure and shear strength - 4 Topics 1.2.6 Curvature of the Failure Envelope Effect of angularity of soil particles Effect of rate of loading during the test 1.2.7 Shear
Constant acceleration, Mixed Exercise 9
 Constant acceleration, Mixed Exercise 9 a 45 000 45 km h = m s 3600 =.5 m s 3 min = 80 s b s= ( a+ bh ) = (60 + 80).5 = 5 a The distance from A to B is 5 m. b s= ( a+ bh ) 5 570 = (3 + 3 + T ) 5 ( T +
Constant acceleration, Mixed Exercise 9 a 45 000 45 km h = m s 3600 =.5 m s 3 min = 80 s b s= ( a+ bh ) = (60 + 80).5 = 5 a The distance from A to B is 5 m. b s= ( a+ bh ) 5 570 = (3 + 3 + T ) 5 ( T +
SERIES AND SEQUENCE. solution. 3r + 2r 2. r=1. r=1 = = = 155. solution. r 3. 2r +
 Series 1 + + 3 + 4 +... SERIES AND SEQUENCE Sequence 1,, 3, 4,... example The series 1 + + 3 + 4 +... + n = n r=1 r n r=1 r = 1 + + 3 +... + n = n(n + 1) Eg.1 The sum of the first 100 natural numbers is
Series 1 + + 3 + 4 +... SERIES AND SEQUENCE Sequence 1,, 3, 4,... example The series 1 + + 3 + 4 +... + n = n r=1 r n r=1 r = 1 + + 3 +... + n = n(n + 1) Eg.1 The sum of the first 100 natural numbers is
Properties of surfaces II: Second moment of area
 Properties of surfaces II: Second moment of area Just as we have discussing first moment of an area and its relation with problems in mechanics, we will now describe second moment and product of area of
Properties of surfaces II: Second moment of area Just as we have discussing first moment of an area and its relation with problems in mechanics, we will now describe second moment and product of area of
Unit 13 Review of Simple Beam Theory
 MIT - 16.0 Fall, 00 Unit 13 Review of Simple Beam Theory Readings: Review Unified Engineering notes on Beam Theory BMP 3.8, 3.9, 3.10 T & G 10-15 Paul A. Lagace, Ph.D. Professor of Aeronautics & Astronautics
MIT - 16.0 Fall, 00 Unit 13 Review of Simple Beam Theory Readings: Review Unified Engineering notes on Beam Theory BMP 3.8, 3.9, 3.10 T & G 10-15 Paul A. Lagace, Ph.D. Professor of Aeronautics & Astronautics
Characterization of Thermo-mechanical Performances related to Breeder Pebble Beds by Discrete Element Method
 Characterization of Thermo-mechanical Performances related to Breeder Pebble Beds by Discrete Element Method Presented by Zhiyong (John) An With contributions from: A. Ying and M. Abdou Mechanical & Aerospace
Characterization of Thermo-mechanical Performances related to Breeder Pebble Beds by Discrete Element Method Presented by Zhiyong (John) An With contributions from: A. Ying and M. Abdou Mechanical & Aerospace
Stress analysis of a stepped bar
 Stress analysis of a stepped bar Problem Find the stresses induced in the axially loaded stepped bar shown in Figure. The bar has cross-sectional areas of A ) and A ) over the lengths l ) and l ), respectively.
Stress analysis of a stepped bar Problem Find the stresses induced in the axially loaded stepped bar shown in Figure. The bar has cross-sectional areas of A ) and A ) over the lengths l ) and l ), respectively.
MAE 322 Machine Design. Dr. Hodge Jenkins Mercer University
 MAE 322 Machine Design Dr. Hodge Jenkins Mercer University What is this Machine Design course really about? What you will learn: How to design machine elements 1) Design so they won t break under varying
MAE 322 Machine Design Dr. Hodge Jenkins Mercer University What is this Machine Design course really about? What you will learn: How to design machine elements 1) Design so they won t break under varying
Chapter 0. Preliminaries. 0.1 Things you should already know
 Chapter 0 Preliminaries These notes cover the course MATH45061 (Continuum Mechanics) and are intended to supplement the lectures. The course does not follow any particular text, so you do not need to buy
Chapter 0 Preliminaries These notes cover the course MATH45061 (Continuum Mechanics) and are intended to supplement the lectures. The course does not follow any particular text, so you do not need to buy
= n. 1 n. Next apply Snell s law at the cylindrical boundary between the core and cladding for the marginal ray. = n 2. sin π 2.
 EXERCISE.-9 First, re-derive equation.-5 considering the possibility that the index at the entrance to the fiber bay be different than one. Snell s law at the entrance to the fiber is where all symbols
EXERCISE.-9 First, re-derive equation.-5 considering the possibility that the index at the entrance to the fiber bay be different than one. Snell s law at the entrance to the fiber is where all symbols
