Cyber Enabled Earth Exploration (CE )
|
|
|
- Shanon Tyler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cyber Enabled Earth Exploration 3 (CE ) Field Notebook Module 2: Introduction to Earthquakes
2 Investigation 1: Earthquake Hazards Table of Contents Folder 1: Describing Earthquakes... 3 Folder 2: Shaanxi, China... 4 Folder 3: San Francisco, California... 6 Folder 4: East Indian Ocean... 8 Investigation Summary Folder 5: Going Further Going Further 1: Tsunami Preparedness Going Further 2: Mapping Damage CE3 Field Notebook - Module 2 Page 2
3 Folder 1: Describing Earthquakes Instructions Step 1. Click on the radio buttons next to Inv 2: Earthquake Hazards and Introduction. 2. Double click on Introduction to open the balloon. Read the information. Then click on the X in the upper right hand corner of the balloon to close it. 3. Expand Folder 1: Describing Earthquakes by clicking on the triangle on the right. Open and read the Earthquake Anatomy placemark balloon. Record any information you can in the Observations section. 4. Open and read the Earthquake Size placemark balloon. Hint: See your notes on Mount Rainier in the Introduction to Volcanoes module if you can't remember what a seismograph is. Record any information you can in the Observations section. You can refer to these answers later. Complete Observations What is a hypocenter? What is an epicenter? What is magnitude? What is the Moment Magnitude Scale? What is intensity? What is the Mercalli Intensity Scale? What is the difference between earthquake intensity and magnitude? CE3 Field Notebook - Module 2 Page 3
4 Notes and Questions Folder 2: Shaanxi, China Earthquakes happen suddenly. Where should people build new homes, schools, and businesses to be safe in earthquake- prone areas? Geologists can help city planners decide. Instructions Step 1. Expand Folder 2: Shaanxi, China and click on the radio button. Open the Shaanxi Earthquake placemark balloon. Read the information and watch the video on landslides. 2. Record any information you can. Then close the balloon. 3. Open the Damage folder. Look at the geographic extent of the reported earthquake damage. Use your ruler tool to measure the distance from Weinan to Huayin in km. Record these observations. 4. Fly to your town in Google Earth. Using your ruler tool, click on your town and drag the ruler out to 900 km. Move your cursor in a circle around your town to see all of the area that is about 900 km away. Any town in this area could be damaged if a similar earthquake happened in your town. Note the biggest towns in your circle in your observations. 5. Use your observations to answer the Investigation question. Be sure to use complete sentences. Complete Observations Year of earthquake: Estimated magnitude: Estimated death toll: Type of damage occurred in Huaxian, Weinan, and Huayin: CE3 Field Notebook - Module 2 Page 4
5 Approximate location of epicenter: How far is Weinan from Huayin (km): Largest towns within 900 km of my town: What is a landslide? What is our source of information about the Shaanxi earthquake? Notes and Questions Interpretation If you were living in Shaanxi and were caught in an earthquake, would you want to be on a hillside? Claim: Evidence: Reasoning: CE3 Field Notebook - Module 2 Page 5
6 Folder 3: San Francisco, California Geologists compare earthquake intensity in different areas to find out which areas shake the most and why. Instructions Step 1. Expand Folder 3: San Francisco, California and click on the radio button. Open the San Francisco Earthquake placemark balloon. Read the information and explore the GigaPan of the city right after the earthquake. Record any information you can. Then close the balloon. 2. Double- click on the Fault Rupture folder and measure the length of the rupture (from San Juan Bautista to Cape Mendocino). Record this observation. 3. Double- click on the Geology folder to see the distribution of the bedrock, soft ( unconsolidated ) sediments, and artificial fill. Tilt your view to see how the geologic units relate to the landscape. Record these observations. 4. Use your observations to answer the Investigation question. Be sure to use complete sentences. Complete Observations Year of earthquake: Earthquake magnitude: Estimated death toll: Causes of deaths and damage: Where did displaced people live after the 1906 earthquake? Was the earthquake intensity higher or lower farther away from san Francisco? What is a fault rupture? Approximate length of rupture (km): CE3 Field Notebook - Module 2 Page 6
7 Approximate side to side shift along the rupture as shown by the fence in the photo (m): Which types of soils shook the most? Which areas shook the least? Which geologic unit is found mostly on the hills? Which geologic unit is found mostly along the shore? Notes and Questions Interpretation Is it safer to build a home in the South Basin area or on the hills of San Francisco? (You can look at the Geology folder to decide.) Claim: Evidence: Reasoning: CE3 Field Notebook - Module 2 Page 7
8 Folder 4: East Indian Ocean Earthquakes in the sea floor present special hazards for coastal communities. In some cases, people can be warned of these hazards ahead of time. Instructions Step 1. Expand Folder 4: East Indian Ocean and click on the radio button. Open the East Indian Ocean Earthquake placemark balloon. Read the information and view the tsunami animation. Record any information you can. Then close the balloon. 2. Double- click on the Earthquake and Tsunami Records folder to see what areas were affected by the earthquake and tsunami. Locate the farthest place from the epicenter that the earthquake was felt. Locate the farthest place from the epicenter that the tsunami was observed. Measure the distance from the epicenter to these points and record your findings. 3. Use your observations to answer the Investigation question. Be sure to use complete sentences. 4. Open and read the Summary placemark balloon. Then answer the questions in the Investigation Summary. Be sure to use complete sentences. Complete Observations Year of earthquake: Earthquake magnitude: Estimated death toll: Causes of deaths and damage: What is a tsunami? Distance from epicenter earthquake was felt: Distance from epicenter tsunami was observed: CE3 Field Notebook - Module 2 Page 8
9 Notes and Questions Interpretation Imagine that you could dive down to the epicenter of the East Indian Ocean earthquake. Would you expect to see a sideways shift in the sea floor like in San Francisco? Or would you expect to see a vertical shift with one side of the rupture much higher than the other side? Claim: Evidence: Reasoning: CE3 Field Notebook - Module 2 Page 9
10 Investigation Summary What causes earthquakes? What types of effects can occur? What factors affect earthquake magnitude and does it vary from place to place? How far from the epicenter can an earthquake be felt by people? What factors affect earthquake intensity at any given place? How can we compare the intensity of earthquakes observed by different people in different places at different times? CE3 Field Notebook - Module 2 Page 10
11 Folder 5: Going Further Going Further 1: Tsunami Preparedness Instructions Step Complete 1. Open Folder 5: Going Further. Open and read the Going Further 1: Tsunami Preparedness placemark balloon. Watch the video on tsunami preparedness. 2. Fly to Maputo, Mozambique by typing it into the search box at the top left of your screen and clicking the Search button. 3. Then answer the following questions. Be sure to use complete sentences. Describe your tsunami preparedness plan. What difficulties might you encounter if you were living in a small coastal village in India when the tsunami warning was issued? What additional problems might you encounter if you were living on the island of Mauritius? CE3 Field Notebook - Module 2 Page 11
12 Going Further 2: Mapping Damage Instructions Step 1. Open the Going Further 2: Mapping damage folder and click on the radio button. Turn off all folders except Port- au- Prince, Haiti. Open and read this placemark balloon. Record any information you can. Then close the balloon. 2. Look closely at the blue and white objects in the parks next to the palace. These are tents. Click on the Historical Imagery Timeline feature from the toolbar at the top of your screen (the clock icon). Move the pointer on the time line back to before the earthquake happened. Compare what you see before and after the earthquake in the Observations section. Close the Historical Imagery Timeline box. 3. Open the MMI Values folder to see the network of seismograph stations in Haiti and the Dominican Republic. Be sure to double- click on the folder to zoom out to a useful view. The numbers on the dots are the MMI values. Look at the legend at the bottom of the screen to see how the shades of pink and red correspond to intensity. Do not close the MMI Values folder. 4. Open the USGS ShakeMap folder to see how the MMI values are combined into a ShakeMap for easier viewing. Look at the legend at the top of the screen to see how the colors correspond to intensity. Turn off the MMI Values folder but leave the USGS ShakeMap folder on. 5. Open the Population Density folder. Again, be sure to double- click on the folder to zoom out to a useful view. Record any observations you can. 6. Use your observations to answer the Investigation question. Be sure to use complete sentences. Complete Observations Year of earthquake: Estimated death toll: Changes seen before and after earthquake: Are people still living in tent cities today? What is a ShakeMap? CE3 Field Notebook - Module 2 Page 12
13 Where do most people in Haiti live? Where do most people in the Dominican Republic live? What intensity did each city experience during the earthquake? Notes and Questions Interpretation Imagine that you are helping with emergency response after the Haiti earthquake. Which would be more helpful, a map showing the MMI values at various seismograph stations or a ShakeMap? Explain. What would have happened if the epicenter had been located in Santo Domingo? What other information would help you predict? CE3 Field Notebook - Module 2 Page 13
Module 2, Investigation 1: Earthquake Hazards
 Module 2, Investigation 1: Earthquake Hazards Introduction Welcome! In the last module, you assumed the role of a volcanologist and learned how volcanoes are described and monitored. You will now assume
Module 2, Investigation 1: Earthquake Hazards Introduction Welcome! In the last module, you assumed the role of a volcanologist and learned how volcanoes are described and monitored. You will now assume
Cyber Enabled Earth Exploration (CE )
 Cyber Enabled Earth Exploration 3 (CE ) Field Notebook Module 1: Introduction to Volcanoes Investigation 1: Volcanic Hazards and Benefits Table of Contents Folder 1: Mount Vesuvius, Italy... 3 Folder 2:
Cyber Enabled Earth Exploration 3 (CE ) Field Notebook Module 1: Introduction to Volcanoes Investigation 1: Volcanic Hazards and Benefits Table of Contents Folder 1: Mount Vesuvius, Italy... 3 Folder 2:
Cyber Enabled Earth Exploration (CE 3 )
 Cyber Enabled Earth Exploration (CE 3 ) Field Notebook Module 3: Introduction to Plate Tectonics Investigation 1: Continental Drift Table of Contents Folder 1: Geographic Evidence... 3 Folder 2: Fossil
Cyber Enabled Earth Exploration (CE 3 ) Field Notebook Module 3: Introduction to Plate Tectonics Investigation 1: Continental Drift Table of Contents Folder 1: Geographic Evidence... 3 Folder 2: Fossil
Investigation 3: Plate Tectonics
 Investigation 3: Plate Tectonics Table of Contents Folder 1: Plate Geography and Structure... 18 Folder 2: Rates of Plate Movement... 19 Folder 3: Driving Forces... 20 Folder 4: Plate Interactions... 22
Investigation 3: Plate Tectonics Table of Contents Folder 1: Plate Geography and Structure... 18 Folder 2: Rates of Plate Movement... 19 Folder 3: Driving Forces... 20 Folder 4: Plate Interactions... 22
SHAKE, RATTLE, AND ROLL INVESTIGATING EARTHQUAKES
 NAME DATE PARTNER(S) SHAKE, RATTLE, AND ROLL INVESTIGATING EARTHQUAKES The city of San Francisco was destroyed by a 7.8 magnitude earthquake that ruptured gas lines and set the city ablaze. March 28, 1964
NAME DATE PARTNER(S) SHAKE, RATTLE, AND ROLL INVESTIGATING EARTHQUAKES The city of San Francisco was destroyed by a 7.8 magnitude earthquake that ruptured gas lines and set the city ablaze. March 28, 1964
Investigation 3: Predicting Eruptions
 Investigation 3: Predicting Eruptions Table of Contents Folder 1: Seismic Activity... 23 Folder 2: Ground Deformation (Mount St. Helens, Washington)... 25 Folder 3: Hot Spots... 26 Folder 4: Gas Emissions...
Investigation 3: Predicting Eruptions Table of Contents Folder 1: Seismic Activity... 23 Folder 2: Ground Deformation (Mount St. Helens, Washington)... 25 Folder 3: Hot Spots... 26 Folder 4: Gas Emissions...
Earthquakes and Earth s Interior
 - What are Earthquakes? Earthquakes and Earth s Interior - The shaking or trembling caused by the sudden release of energy - Usually associated with faulting or breaking of rocks - Continuing adjustment
- What are Earthquakes? Earthquakes and Earth s Interior - The shaking or trembling caused by the sudden release of energy - Usually associated with faulting or breaking of rocks - Continuing adjustment
Magnitude 6.3 SOUTH ISLAND OF NEW ZEALAND
 A magnitude 6.3 earthquake shook the southern New Zealand city of Christchurch. At least 100 people are reported dead, and there are reports of collapsed buildings, cracked streets and flooding due to
A magnitude 6.3 earthquake shook the southern New Zealand city of Christchurch. At least 100 people are reported dead, and there are reports of collapsed buildings, cracked streets and flooding due to
Magnitude 7.0 N of ANCHORAGE, ALASKA
 A magnitude 7.0 earthquake occurred just before 8:30 am local time 8 miles north of Anchorage at a depth of 40.9 km (25.4 miles). There are reports of major infrastructure damage and damage to many homes
A magnitude 7.0 earthquake occurred just before 8:30 am local time 8 miles north of Anchorage at a depth of 40.9 km (25.4 miles). There are reports of major infrastructure damage and damage to many homes
Seismic vulnerability in Latinamerica Speaker: Rafael Osiris de León Sciences Academy of Dominican Republic.
 Seismic vulnerability in Latinamerica Speaker: Rafael Osiris de León Sciences Academy of Dominican Republic. IANAS GENERAL ASSEMBLY Punta Cana, 16-20 July, 2013 TECTONIC PLATES AND EARTHQUAKES Pacific
Seismic vulnerability in Latinamerica Speaker: Rafael Osiris de León Sciences Academy of Dominican Republic. IANAS GENERAL ASSEMBLY Punta Cana, 16-20 July, 2013 TECTONIC PLATES AND EARTHQUAKES Pacific
Investigation 5: What happens when plates move sideways past each other?
 Tectonics Investigation 5: Teacher Guide Investigation 5: What happens when plates move sideways past each other? Plates move sideways past each other at transform boundaries. At these boundaries, the
Tectonics Investigation 5: Teacher Guide Investigation 5: What happens when plates move sideways past each other? Plates move sideways past each other at transform boundaries. At these boundaries, the
Earthquakes!! Be sure to fill in your notes sheet as you go through the power point!
 Earthquakes!! Be sure to fill in your notes sheet as you go through the power point! Plate Boundary Review Click on the link below to try some plate boundary movement simulations. The link will take you
Earthquakes!! Be sure to fill in your notes sheet as you go through the power point! Plate Boundary Review Click on the link below to try some plate boundary movement simulations. The link will take you
LAB 9: Earthquakes & Seismic Activity
 LAB 9: Earthquakes & Seismic Activity Objectives Identify P, S, and surface waves on a simple seismogram Locate the epicenter of an earthquake using seismograms and travel times curves Describe how the
LAB 9: Earthquakes & Seismic Activity Objectives Identify P, S, and surface waves on a simple seismogram Locate the epicenter of an earthquake using seismograms and travel times curves Describe how the
EXERCISE 1 (15 POINTS): EARTH S DYNAMIC NATURE, VISIBLE AT ITS SURFACE
 GEOLOGICAL SCIENCES 0050 I am aware of the Brown University Honor Code [see the Student Handbook, which can be accessed through the Geo0050 web site], understand that this exercise falls under that code,
GEOLOGICAL SCIENCES 0050 I am aware of the Brown University Honor Code [see the Student Handbook, which can be accessed through the Geo0050 web site], understand that this exercise falls under that code,
Once you have opened the website with the link provided choose a force: Earthquakes
 Name: Once you have opened the website with the link provided choose a force: Earthquakes When do earthquakes happen? On the upper left menu, choose number 1. Read What is an Earthquake? Earthquakes happen
Name: Once you have opened the website with the link provided choose a force: Earthquakes When do earthquakes happen? On the upper left menu, choose number 1. Read What is an Earthquake? Earthquakes happen
22.5 Earthquakes. The tsunami triggered by the 2004 Sumatra earthquake caused extensive damage to coastal areas in Southeast Asia.
 The tsunami triggered by the 2004 Sumatra earthquake caused extensive damage to coastal areas in Southeast Asia. An earthquake is a movement of Earth s lithosphere that occurs when rocks in the lithosphere
The tsunami triggered by the 2004 Sumatra earthquake caused extensive damage to coastal areas in Southeast Asia. An earthquake is a movement of Earth s lithosphere that occurs when rocks in the lithosphere
Module 1, Investigation 3: Predicting Eruptions
 Module 1, Investigation 3: Predicting Eruptions Introduction Welcome! Volcanoes are either "active" or "extinct". Active means that the volcano has erupted during the past 10,000 years. It can also mean
Module 1, Investigation 3: Predicting Eruptions Introduction Welcome! Volcanoes are either "active" or "extinct". Active means that the volcano has erupted during the past 10,000 years. It can also mean
Magnitude 7.7 QUEEN CHARLOTTE ISLANDS REGION
 A major 7.7 magnitude earthquake struck at 8:04 PM local time in western British Columbia, Canada. The epicenter is located on Moresby Island, the southern large island in the Queen Charlotte Islands region.
A major 7.7 magnitude earthquake struck at 8:04 PM local time in western British Columbia, Canada. The epicenter is located on Moresby Island, the southern large island in the Queen Charlotte Islands region.
b. Why is the area affected by each earthquake circular or nearly circular? Where is the epicenter of each quake located?
 Name: Skill Sheet 29-A Interpreting Geologic Hazard Maps Plate tectonics and the weather are often the cause of geologic hazards such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and flooding. Geologic hazard events
Name: Skill Sheet 29-A Interpreting Geologic Hazard Maps Plate tectonics and the weather are often the cause of geologic hazards such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and flooding. Geologic hazard events
Magnitude 7.9 SE of KODIAK, ALASKA
 A magnitude 7.9 earthquake occurred at 12:31 am local time 181 miles southeast of Kodiak at a depth of 25 km (15.5 miles). There are no immediate reports of damage or fatalities. Light shaking from this
A magnitude 7.9 earthquake occurred at 12:31 am local time 181 miles southeast of Kodiak at a depth of 25 km (15.5 miles). There are no immediate reports of damage or fatalities. Light shaking from this
Rapid Changes on Earth: Earthquakes, Volcanoes, Landslides. Chapter 6 Study Guide
 Rapid Changes on Earth: Earthquakes, Volcanoes, Landslides Chapter 6 Study Guide Magma is 1. The point underground where an earthquake starts. 2. Molten rock beneath the Earth s surface. 3. Molten rock
Rapid Changes on Earth: Earthquakes, Volcanoes, Landslides Chapter 6 Study Guide Magma is 1. The point underground where an earthquake starts. 2. Molten rock beneath the Earth s surface. 3. Molten rock
Forces in Earth s Crust
 Name Date Class Earthquakes Section Summary Forces in Earth s Crust Guide for Reading How does stress in the crust change Earth s surface? Where are faults usually found, and why do they form? What land
Name Date Class Earthquakes Section Summary Forces in Earth s Crust Guide for Reading How does stress in the crust change Earth s surface? Where are faults usually found, and why do they form? What land
ESCI 121 Physical Geology
 Observing Streams & Rivers in Google Earth Dr. Jennifer L. Piatek Dept. of Physics and Earth Sciences Central Connecticut State University 506 Copernicus Hall 1615 Stanley Street New Britain, CT 06050
Observing Streams & Rivers in Google Earth Dr. Jennifer L. Piatek Dept. of Physics and Earth Sciences Central Connecticut State University 506 Copernicus Hall 1615 Stanley Street New Britain, CT 06050
Magnitude 7.0 SOUTH ISLAND OF NEW ZEALAND
 A powerful 7.0-magnitude earthquake shook much of New Zealand's South Island early Saturday morning local time. USGS A damaged building near Manchester St. New Zealand Herald Photo / Colin Cross A car
A powerful 7.0-magnitude earthquake shook much of New Zealand's South Island early Saturday morning local time. USGS A damaged building near Manchester St. New Zealand Herald Photo / Colin Cross A car
Homework Assignment II. Seismological Exercises Spring 2018
 Page 1 of 8 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Homework Assignment II. Seismological Exercises Spring 2018 This page last updated on 30-Jan-2018 Answer the following
Page 1 of 8 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Homework Assignment II. Seismological Exercises Spring 2018 This page last updated on 30-Jan-2018 Answer the following
Earthquakes Modified
 Plate Tectonics Earthquakes Modified Recall that the earth s crust is broken into large pieces called. These slowly moving plates each other, each other, or from each other. This causes much on the rocks.
Plate Tectonics Earthquakes Modified Recall that the earth s crust is broken into large pieces called. These slowly moving plates each other, each other, or from each other. This causes much on the rocks.
Three Fs of earthquakes: forces, faults, and friction. Slow accumulation and rapid release of elastic energy.
 Earthquake Machine Stick-slip: Elastic Rebound Theory Jerky motions on faults produce EQs Three Fs of earthquakes: forces, faults, and friction. Slow accumulation and rapid release of elastic energy. Three
Earthquake Machine Stick-slip: Elastic Rebound Theory Jerky motions on faults produce EQs Three Fs of earthquakes: forces, faults, and friction. Slow accumulation and rapid release of elastic energy. Three
Natural Disasters Spring, LECTURE #8: Earthquake Disasters: Monitoring & Mitigation. Date: 1 Feb 2018 (lecturer: Dr.
 GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #8: Earthquake Disasters: Monitoring & Mitigation Date: 1 Feb 2018 (lecturer: Dr. Shawn Wright) I. Exam I - Reminder Feb 6 th next class details:
GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #8: Earthquake Disasters: Monitoring & Mitigation Date: 1 Feb 2018 (lecturer: Dr. Shawn Wright) I. Exam I - Reminder Feb 6 th next class details:
I. Locations of Earthquakes. Announcements. Earthquakes Ch. 5. video Northridge, California earthquake, lecture on Chapter 5 Earthquakes!
 51-100-21 Environmental Geology Summer 2006 Tuesday & Thursday 6-9:20 p.m. Dr. Beyer Earthquakes Ch. 5 I. Locations of Earthquakes II. Earthquake Processes III. Effects of Earthquakes IV. Earthquake Risk
51-100-21 Environmental Geology Summer 2006 Tuesday & Thursday 6-9:20 p.m. Dr. Beyer Earthquakes Ch. 5 I. Locations of Earthquakes II. Earthquake Processes III. Effects of Earthquakes IV. Earthquake Risk
Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating.
 CH Earthquakes Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating Earthquakes Section 19.4: Earthquakes and Society Section 19.1 Forces
CH Earthquakes Section 19.1: Forces Within Earth Section 19.2: Seismic Waves and Earth s Interior Section 19.3: Measuring and Locating Earthquakes Section 19.4: Earthquakes and Society Section 19.1 Forces
Lecture notes Bill Engstrom: Instructor Earthquakes GLG 101 Physical Geology
 Lecture notes Bill Engstrom: Instructor Earthquakes GLG 101 Physical Geology Now that we ve seen what faults are and how mountains are built, we can look at what happens when there is movement along those
Lecture notes Bill Engstrom: Instructor Earthquakes GLG 101 Physical Geology Now that we ve seen what faults are and how mountains are built, we can look at what happens when there is movement along those
Introducing IMS. v) Select the Zoom to Full Extent tool. Did you return to the original view?
 Ocean/ENVIR 260, Winter 2006 Lab 1, Get to Know the Puget Sound Watershed Name Introducing IMS 1) Open your web browser and navigate to http://128.208.23.127/website/lab1. (This link can be found on the
Ocean/ENVIR 260, Winter 2006 Lab 1, Get to Know the Puget Sound Watershed Name Introducing IMS 1) Open your web browser and navigate to http://128.208.23.127/website/lab1. (This link can be found on the
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Geology 101 Study Guide #4
 Geology 101 Study Guide #4 Our last unit is the study of the earthquakes, the Earth s interior and plate tectonics. We live in a region which has been added on to North America through plate tectonics.
Geology 101 Study Guide #4 Our last unit is the study of the earthquakes, the Earth s interior and plate tectonics. We live in a region which has been added on to North America through plate tectonics.
Earthquakes. Earthquake Magnitudes 10/1/2013. Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena
 Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena Fall 2013 Northridge 1994 Kobe 1995 Mexico City 1985 China 2008 Earthquakes Earthquake Magnitudes Earthquake Magnitudes Richter Magnitude
Environmental Geology Chapter 8 Earthquakes and Related Phenomena Fall 2013 Northridge 1994 Kobe 1995 Mexico City 1985 China 2008 Earthquakes Earthquake Magnitudes Earthquake Magnitudes Richter Magnitude
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Measuring Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the power or strength of an earthquake are: Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale based
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Measuring Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the power or strength of an earthquake are: Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale based
Earthquakes & Volcanoes
 Earthquakes & Volcanoes Geology - the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change geo = Earth; ology = study of Earth s Layers Plate Tectonics - the
Earthquakes & Volcanoes Geology - the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change geo = Earth; ology = study of Earth s Layers Plate Tectonics - the
Disclaimer. This report was compiled by an ADRC visiting researcher (VR) from ADRC member countries.
 Disclaimer This report was compiled by an ADRC visiting researcher (VR) from ADRC member countries. The views expressed in the report do not necessarily reflect the views of the ADRC. The boundaries and
Disclaimer This report was compiled by an ADRC visiting researcher (VR) from ADRC member countries. The views expressed in the report do not necessarily reflect the views of the ADRC. The boundaries and
Figure Diagram of earth movements produced by (a) P-waves and (b) S-waves.
 Geology 101 Name(s): Lab 10: Earthquakes When the stresses in a rock (which may or may not already be faulted) exceed the tensile strength of the rock, the rock ruptures at a point called the focus or
Geology 101 Name(s): Lab 10: Earthquakes When the stresses in a rock (which may or may not already be faulted) exceed the tensile strength of the rock, the rock ruptures at a point called the focus or
 three days. After an earthquake, fires can be caused by ruptured gas lines, damage to fuel storage tanks, and downed power lines. Pages 107 109: Class Activity (Reinforcement) To reinforce earthquake safety
three days. After an earthquake, fires can be caused by ruptured gas lines, damage to fuel storage tanks, and downed power lines. Pages 107 109: Class Activity (Reinforcement) To reinforce earthquake safety
Before exploring the effects of the 1906 earthquake, watch the video on ground shaking and liquefaction at:
 Seismic Risk: Pre- Work Paper Maps Version Early on the morning of April 16, 1906, a magnitude 7.8 earthquake struck on the San Andreas Fault. The 1906 San Francisco earthquake revolutionized our understanding
Seismic Risk: Pre- Work Paper Maps Version Early on the morning of April 16, 1906, a magnitude 7.8 earthquake struck on the San Andreas Fault. The 1906 San Francisco earthquake revolutionized our understanding
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
UNIT - 7 EARTHQUAKES
 UNIT - 7 EARTHQUAKES WHAT IS AN EARTHQUAKE An earthquake is a sudden motion or trembling of the Earth caused by the abrupt release of energy that is stored in rocks. Modern geologists know that most earthquakes
UNIT - 7 EARTHQUAKES WHAT IS AN EARTHQUAKE An earthquake is a sudden motion or trembling of the Earth caused by the abrupt release of energy that is stored in rocks. Modern geologists know that most earthquakes
Magnitude 6.5 OFFSHORE NORTHERN CALIFORNIA
 A powerful offshore earthquake that struck near the Northern California coast left a hodgepodge of debris for communities to sort through Sunday but spared residents any serious injury. After 25,000 people
A powerful offshore earthquake that struck near the Northern California coast left a hodgepodge of debris for communities to sort through Sunday but spared residents any serious injury. After 25,000 people
Magnitude 7.6 SOUTH OF IQUIQUE, CHILE
 A powerful aftershock struck off northern Chile prompting an evacuation of the coastal area and raising fears of a tsunami. This magnitude 7.6 earthquake is the largest of a series of aftershocks following
A powerful aftershock struck off northern Chile prompting an evacuation of the coastal area and raising fears of a tsunami. This magnitude 7.6 earthquake is the largest of a series of aftershocks following
Identifying Landslides Using Google Earth
 Identifying Landslides (This draft updated on 1 Dec 2014) Page 1 of 15 1. Introduction Identifying Landslides Using Google Earth 1.1. Workshop Aims 1. Identify landslides from Google Earth images 2. Approximate
Identifying Landslides (This draft updated on 1 Dec 2014) Page 1 of 15 1. Introduction Identifying Landslides Using Google Earth 1.1. Workshop Aims 1. Identify landslides from Google Earth images 2. Approximate
Read & Learn Earthquakes & Faults
 Read Earthquakes & Faults Read the provided article. Use the information in the reading to answer the questions on the task cards on your answer sheet. Make sure your answers are in the correct spot on
Read Earthquakes & Faults Read the provided article. Use the information in the reading to answer the questions on the task cards on your answer sheet. Make sure your answers are in the correct spot on
Not all eruptions are the same. Sometimes, there is a huge explosion. The hot magma shoots
 Natural Disasters A natural disaster is an event that happens in nature. It is an event that can cause a lot of damage. Volcanoes, earthquakes, and tsunamis are all natural disasters. Volcanoes A volcano
Natural Disasters A natural disaster is an event that happens in nature. It is an event that can cause a lot of damage. Volcanoes, earthquakes, and tsunamis are all natural disasters. Volcanoes A volcano
The L.A. Earthquake Sourcebook
 The L.A. Earthquake Sourcebook If searched for the ebook The L.A. Earthquake Sourcebook in pdf format, then you have come on to the faithful website. We furnish complete option of this ebook in doc, DjVu,
The L.A. Earthquake Sourcebook If searched for the ebook The L.A. Earthquake Sourcebook in pdf format, then you have come on to the faithful website. We furnish complete option of this ebook in doc, DjVu,
Japan Disaster: 9.0 Earthquake
 Well thank you all for coming. So I'm here to talk about the earthquake itself, and then we have other speakers who will talk about the tsunami and nuclear power, and radioactive fallout. So what happened
Well thank you all for coming. So I'm here to talk about the earthquake itself, and then we have other speakers who will talk about the tsunami and nuclear power, and radioactive fallout. So what happened
An entire branch of Earth science, called, is devoted to the study of earthquakes.
 Lesson One Essential Question Where do earthquakes take place? What causes earthquakes? What are three different types of faults that occur at plate boundaries? How does energy from earthquakes travels
Lesson One Essential Question Where do earthquakes take place? What causes earthquakes? What are three different types of faults that occur at plate boundaries? How does energy from earthquakes travels
Identifying the causes and effects of earthquakes
 Science 3 Physical Earth and Space Life LESSON 57 Identifying the causes and effects of earthquakes Lesson Preparation Program Materials Child s Booklet E Exploring the Earth s Structure (pp. 12 13) Optional:
Science 3 Physical Earth and Space Life LESSON 57 Identifying the causes and effects of earthquakes Lesson Preparation Program Materials Child s Booklet E Exploring the Earth s Structure (pp. 12 13) Optional:
San Andreas Movie Can It Happen?
 San Andreas Movie Can It Happen? Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 14: Faults and Quakes Read: Chapter 10 and 11 Homework #12 due Thursday 12pm What we ll learn today:! 1. Compare strike-slip to dip-slip
San Andreas Movie Can It Happen? Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 14: Faults and Quakes Read: Chapter 10 and 11 Homework #12 due Thursday 12pm What we ll learn today:! 1. Compare strike-slip to dip-slip
Homework Assignment II. Seismological Exercises Fall 2014
 Page 1 of 8 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Homework Assignment II. Seismological Exercises Fall 2014 This page last updated on 03-Sep-2014 Answer the following questions.
Page 1 of 8 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Homework Assignment II. Seismological Exercises Fall 2014 This page last updated on 03-Sep-2014 Answer the following questions.
Earthquakes Physical Geology 2017 Part 1: Exploring Earthquake distributions. Home butto California Earthquakes: 1) 2) 3) above
 Earthquakes Physical Geology 2017 Adapted from a lab by Jennifer Wenner This lab is designed to give you experience exploring seismicity associated with different plate boundaries. You will examine seismograms
Earthquakes Physical Geology 2017 Adapted from a lab by Jennifer Wenner This lab is designed to give you experience exploring seismicity associated with different plate boundaries. You will examine seismograms
Magnitude 7.1 NEAR THE EAST COAST OF HONSHU, JAPAN
 Japan was rattled by a strong aftershock and tsunami warning Thursday night nearly a month after a devastating earthquake and tsunami flattened the northeastern coast. This earthquake can be considered
Japan was rattled by a strong aftershock and tsunami warning Thursday night nearly a month after a devastating earthquake and tsunami flattened the northeastern coast. This earthquake can be considered
Important Concepts. Earthquake hazards can be categorized as:
 Lecture 1 Page 1 Important Concepts Monday, August 17, 2009 1:05 PM Earthquake Engineering is a branch of Civil Engineering that requires expertise in geology, seismology, civil engineering and risk assessment.
Lecture 1 Page 1 Important Concepts Monday, August 17, 2009 1:05 PM Earthquake Engineering is a branch of Civil Engineering that requires expertise in geology, seismology, civil engineering and risk assessment.
Earthquake Investigation
 Exploration A Earthquake Investigation 1. Obtain a piece of plastic putty and knead it into a rectangular shape. 2. Push the ends of the putty toward the middle. Draw and describe what it looks like below.
Exploration A Earthquake Investigation 1. Obtain a piece of plastic putty and knead it into a rectangular shape. 2. Push the ends of the putty toward the middle. Draw and describe what it looks like below.
Magnitude 7.0 VANUATU
 A major earthquake struck in the southwest Pacific Ocean at a depth of 27 km beneath the island of Melampa in the Vanuatu island chain. There are no reports of damage. The Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI)
A major earthquake struck in the southwest Pacific Ocean at a depth of 27 km beneath the island of Melampa in the Vanuatu island chain. There are no reports of damage. The Modified Mercalli Intensity (MMI)
Studying Topography, Orographic Rainfall, and Ecosystems (STORE)
 Introduction Studying Topography, Orographic Rainfall, and Ecosystems (STORE) Lesson: Using ArcGIS Explorer to Analyze the Connection between Topography, Tectonics, and Rainfall GIS-intensive Lesson This
Introduction Studying Topography, Orographic Rainfall, and Ecosystems (STORE) Lesson: Using ArcGIS Explorer to Analyze the Connection between Topography, Tectonics, and Rainfall GIS-intensive Lesson This
Magnitude 7.1 PHILIPPINES
 A magnitude 7.1 earthquake struck in the southeastern Philippines just after 8 am local time Tuesday morning killing 82 people and reducing a 17 th century church to rubble. Offices and schools were closed
A magnitude 7.1 earthquake struck in the southeastern Philippines just after 8 am local time Tuesday morning killing 82 people and reducing a 17 th century church to rubble. Offices and schools were closed
6. The lithosphere is
 Name: APES: Geology and Nonrenewable Mineral Resources Earth Composition and Structure Webquest Date: I. Earth Structure http://scign.jpl.nasa.gov/learn/plate1.htm Click on the button press here to see
Name: APES: Geology and Nonrenewable Mineral Resources Earth Composition and Structure Webquest Date: I. Earth Structure http://scign.jpl.nasa.gov/learn/plate1.htm Click on the button press here to see
Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model
 Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model The Cascadia tectonic margin is caught between several tectonic forces, during the relentless motions of the giant Pacific Plate, the smaller subducting
Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model The Cascadia tectonic margin is caught between several tectonic forces, during the relentless motions of the giant Pacific Plate, the smaller subducting
Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College
 Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth, produced by the rapid release of energy.
Earthquakes and Earthquake Hazards Earth - Chapter 11 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College What Is an Earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth, produced by the rapid release of energy.
Earthquakes.
 Earthquakes http://thismodernworld.com/comic-archive Elastic rebound http://projects.crustal.ucsb.edu/understanding/elastic/rebound.html Elastic rebound Rocks store energy elastically When stored stress
Earthquakes http://thismodernworld.com/comic-archive Elastic rebound http://projects.crustal.ucsb.edu/understanding/elastic/rebound.html Elastic rebound Rocks store energy elastically When stored stress
Magnitude 7.0 NEW CALEDONIA
 A magnitude 7.0 earthquake has occurred 82km ENE of Maré Island, the secondlargest of the Loyalty Islands in the archipelago of New Caledonia. The initial report of the magnitude and shallow 10km depth
A magnitude 7.0 earthquake has occurred 82km ENE of Maré Island, the secondlargest of the Loyalty Islands in the archipelago of New Caledonia. The initial report of the magnitude and shallow 10km depth
Earthquakes and Seismic Waves Lesson 4 2
 Earthquakes and Seismic Waves Lesson 4 2 Apr 15 8:52 PM What are seismic waves? How are earthquakes measured? How is an earthquake located? Apr 15 8:54 PM 1 What are seismic waves An earthquake is the
Earthquakes and Seismic Waves Lesson 4 2 Apr 15 8:52 PM What are seismic waves? How are earthquakes measured? How is an earthquake located? Apr 15 8:54 PM 1 What are seismic waves An earthquake is the
9.3. Earthquakes. Earthquakes at Divergent Boundaries
 9.3 Earthquakes Preview the headings on these two pages. What can you say about where earthquakes occur? As the plates that make up Earth s crust move, the rough edges lock together. Over time, pressure
9.3 Earthquakes Preview the headings on these two pages. What can you say about where earthquakes occur? As the plates that make up Earth s crust move, the rough edges lock together. Over time, pressure
Earthquakes. Building Earth s Surface, Part 2. Science 330 Summer What is an earthquake?
 Earthquakes Building Earth s Surface, Part 2 Science 330 Summer 2005 What is an earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all
Earthquakes Building Earth s Surface, Part 2 Science 330 Summer 2005 What is an earthquake? An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all
EQ Monitoring and Hazards NOTES.notebook. January 07, P-wave. S-wave. surface waves. distance
 Earthquake Monitoring and Hazards Reading a Seismogram General guidelines: P-wave First disruption of trace = Second disruption of trace = surface waves Largest disruption of trace = Not the distance to
Earthquake Monitoring and Hazards Reading a Seismogram General guidelines: P-wave First disruption of trace = Second disruption of trace = surface waves Largest disruption of trace = Not the distance to
Earthquakes Earth, 9th edition, Chapter 11 Key Concepts What is an earthquake? Earthquake focus and epicenter What is an earthquake?
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Earthquakes Earth, 9 th edition, Chapter 11 Key Concepts Earthquake basics. "" and locating earthquakes.. Destruction resulting from earthquakes. Predicting earthquakes. Earthquakes
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Earthquakes Earth, 9 th edition, Chapter 11 Key Concepts Earthquake basics. "" and locating earthquakes.. Destruction resulting from earthquakes. Predicting earthquakes. Earthquakes
What causes an earthquake? Giant snakes, turtles, catfish, and spiders?
 What causes an earthquake? Giant snakes, turtles, catfish, and spiders? What causes an earthquake? The movement of Earth s plates creates enormous forces that squeeze or pull the rock in the crust as if
What causes an earthquake? Giant snakes, turtles, catfish, and spiders? What causes an earthquake? The movement of Earth s plates creates enormous forces that squeeze or pull the rock in the crust as if
Name Date Class. radiate in all directions, carrying some of the. of plate boundaries have different usual patterns of.
 Chapter Outline Earthquakes CHAPTER 6 Lesson 1: Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries A. What is an earthquake? 1. A(n) is the rupture and sudden movement of rocks along a fault. A fault is a fracture surface
Chapter Outline Earthquakes CHAPTER 6 Lesson 1: Earthquakes and Plate Boundaries A. What is an earthquake? 1. A(n) is the rupture and sudden movement of rocks along a fault. A fault is a fracture surface
Trouble-Shooting Coordinate System Problems
 Trouble-Shooting Coordinate System Problems Written by Barbara M. Parmenter, revised 2/25/2014 OVERVIEW OF THE EXERCISE... 1 COPYING THE MAP PROJECTION EXERCISE FOLDER TO YOUR H: DRIVE OR DESKTOP... 2
Trouble-Shooting Coordinate System Problems Written by Barbara M. Parmenter, revised 2/25/2014 OVERVIEW OF THE EXERCISE... 1 COPYING THE MAP PROJECTION EXERCISE FOLDER TO YOUR H: DRIVE OR DESKTOP... 2
Global Earthquake Distribution
 GeoPatterns Activity Global Earthquake Distribution Background One of the things scientists do is look for patterns in nature. Geologists look for patterns so they can answer questions about how Earth
GeoPatterns Activity Global Earthquake Distribution Background One of the things scientists do is look for patterns in nature. Geologists look for patterns so they can answer questions about how Earth
Lab 11: Earthquakes. Figure 7-1. Diagram of earth movements produced by (a) P-waves and (b) S-waves.
 Geology 101 Name(s): Lab 11: Earthquakes When the stresses in a rock (which may or may not already be faulted) exceed the tensile strength of the rock, the rock ruptures at a point called the focus or
Geology 101 Name(s): Lab 11: Earthquakes When the stresses in a rock (which may or may not already be faulted) exceed the tensile strength of the rock, the rock ruptures at a point called the focus or
Magnitude 8.2 NORTHWEST OF IQUIQUE, CHILE
 An 8.2-magnitude earthquake struck off the coast of northern Chile, generating a local tsunami. The USGS reported the earthquake was centered 95 km (59 miles) northwest of Iquique at a depth of 20.1km
An 8.2-magnitude earthquake struck off the coast of northern Chile, generating a local tsunami. The USGS reported the earthquake was centered 95 km (59 miles) northwest of Iquique at a depth of 20.1km
Geophysics 189 Natural Hazards Homework 2 Earthquake Locations and Hazards Due February 15, 2005
 Geophysics 189 Natural Hazards Homework 2 Earthquake Locations and Hazards Due February 15, 2005 Objective: The objective of this homework is to give you experience using real seismograms to locate an
Geophysics 189 Natural Hazards Homework 2 Earthquake Locations and Hazards Due February 15, 2005 Objective: The objective of this homework is to give you experience using real seismograms to locate an
Figure Diagram of earth movements produced by (a) P-waves and (b) S-waves.
 Geology 101 Name(s): Lab 11: Earthquakes When the stresses in a rock (which may or may not already be faulted) exceed the tensile strength of the rock, the rock ruptures at a point called the focus or
Geology 101 Name(s): Lab 11: Earthquakes When the stresses in a rock (which may or may not already be faulted) exceed the tensile strength of the rock, the rock ruptures at a point called the focus or
Earthquakes Chapter 19
 Earthquakes Chapter 19 Does not contain complete lecture notes. What is an earthquake An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all directions
Earthquakes Chapter 19 Does not contain complete lecture notes. What is an earthquake An earthquake is the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy Energy released radiates in all directions
Figure 2-1. Diagram of earth movements produced by (a) P-waves and (b) S-waves.
 Geology 102, Winter 2006 Name(s): Lab 2: Earthquakes When the stresses in a rock (which may or may not already be faulted) exceed the tensile strength of the rock, the rock ruptures at a point called the
Geology 102, Winter 2006 Name(s): Lab 2: Earthquakes When the stresses in a rock (which may or may not already be faulted) exceed the tensile strength of the rock, the rock ruptures at a point called the
Finding an Earthquake Epicenter Pearson Education, Inc.
 Finding an Earthquake Epicenter Measuring the Size of Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the size of an earthquake are: 1. Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale
Finding an Earthquake Epicenter Measuring the Size of Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the size of an earthquake are: 1. Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale
Earthquake Epicenters
 TEACHER RESOURCES Inquiry Lab Earthquake Epicenters DATASHEET Teacher Notes This lab has students use three seismograms to locate the epicenter of an earthquake (covers standard 6.1.g). TIME REQUIRED One
TEACHER RESOURCES Inquiry Lab Earthquake Epicenters DATASHEET Teacher Notes This lab has students use three seismograms to locate the epicenter of an earthquake (covers standard 6.1.g). TIME REQUIRED One
Magnitude 6.9 GULF OF CALIFORNIA
 A pair of strong earthquakes struck off the coast of Mexico early Thursday only minutes apart. The magnitude 6.9 and 6.2 were centered about 85 miles northeast of Guerrero Negro in the Mexican state of
A pair of strong earthquakes struck off the coast of Mexico early Thursday only minutes apart. The magnitude 6.9 and 6.2 were centered about 85 miles northeast of Guerrero Negro in the Mexican state of
Students will be able, using GIS, to locate the largest and most destructive earthquakes;
 Exploring Earthquake Hazards with GIS Laboratory for Introduction to Geophysics, Spring 2007 Prof. Constantin Cranganu Brooklyn College of the City University of New York Learning Objectives: Students
Exploring Earthquake Hazards with GIS Laboratory for Introduction to Geophysics, Spring 2007 Prof. Constantin Cranganu Brooklyn College of the City University of New York Learning Objectives: Students
Tsunami! Beyond the Book. FOCUS Book
 FOCUS Book Use the engineering design process to design a structure that will protect a coastal town from possible tsunami damage. Brainstorm design ideas for your structure with a group of classmates.
FOCUS Book Use the engineering design process to design a structure that will protect a coastal town from possible tsunami damage. Brainstorm design ideas for your structure with a group of classmates.
11/30/16 EARTHQUAKES ELASTIC LIMIT FAULT FORCE AND PLATES WHAT DO YOU NOTICE?
 ELASTIC LIMIT EARTHQUAKES Bend sitck but do not break it. What do you notice? No bend until it breaks. Describe the energy and forces at work. (Kinetic, potential etc) 8 TH GRADE FAULT FORCE AND PLATES
ELASTIC LIMIT EARTHQUAKES Bend sitck but do not break it. What do you notice? No bend until it breaks. Describe the energy and forces at work. (Kinetic, potential etc) 8 TH GRADE FAULT FORCE AND PLATES
Earthquakes down under: a rare but real hazard
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2015 Earthquakes down under: a rare but real hazard Solomon Buckman University
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health - Papers Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2015 Earthquakes down under: a rare but real hazard Solomon Buckman University
Magnitude 7.5 NEW BRITAIN REGION, PAPUA NEW GUINEA
 A magnitude 7.5 earthquake struck off the eastern coast of Papua New Guinea on Tuesday, approximately 130 km (81 mi) southsouthwest of Kokopo at a depth of 42 km (26.1 mi). There are reports of some structural
A magnitude 7.5 earthquake struck off the eastern coast of Papua New Guinea on Tuesday, approximately 130 km (81 mi) southsouthwest of Kokopo at a depth of 42 km (26.1 mi). There are reports of some structural
Life on the edge. Module 2, Lesson 2. Task 1: Open the map and identify cities
 Module 2, Lesson 2 Life on the edge In this activity, you will investigate the Pacific Ocean s Ring of Fire, with particular focus on earthquake and volcanic activity in East Asia, where millions of people
Module 2, Lesson 2 Life on the edge In this activity, you will investigate the Pacific Ocean s Ring of Fire, with particular focus on earthquake and volcanic activity in East Asia, where millions of people
Magnitude 7.2 OAXACA, MEXICO
 A magnitude 7.2 earthquake has occurred in Oaxaca, Mexico at a depth of 24.6 km (15 miles). It was felt as far away as Guatemala. There have been no reported deaths directly linked to the earthquake. Emergency
A magnitude 7.2 earthquake has occurred in Oaxaca, Mexico at a depth of 24.6 km (15 miles). It was felt as far away as Guatemala. There have been no reported deaths directly linked to the earthquake. Emergency
Name: KEY California Geology. Unit IX Earthquakes
 Unit IX Earthquakes Name: KEY California Geology The following assignment is based on information presented in Unit IX. Be sure to read the paragraphs (Note 1) provided before you attempt to answer the
Unit IX Earthquakes Name: KEY California Geology The following assignment is based on information presented in Unit IX. Be sure to read the paragraphs (Note 1) provided before you attempt to answer the
Magnitude 7.1 PERU. There are early reports of homes and roads collapsed leaving one dead and several dozen injured.
 A magnitude 7.1 earthquake has occurred offshore Peru. The earthquake struck just after 4 a.m. local time and was centered near the coast of Peru, 40 km (25 miles) south-southwest of Acari, Peru at a depth
A magnitude 7.1 earthquake has occurred offshore Peru. The earthquake struck just after 4 a.m. local time and was centered near the coast of Peru, 40 km (25 miles) south-southwest of Acari, Peru at a depth
Contour Line Overlays in Google Earth
 Overview: Students download a section of a topographic map of their community from the ATEP website. This file will overlay the Google Earth satellite imagery. Students use the path tool to trace a contour
Overview: Students download a section of a topographic map of their community from the ATEP website. This file will overlay the Google Earth satellite imagery. Students use the path tool to trace a contour
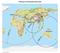
Mw 7.8, Southwest of Sumatra, Indonesia Wed, 2 March 2016 at 12:49:48 UTC M /03/03
 Earthquake overview AFGHANISTA N PAKISTA N INDIA A moment magnitude (Mw) 7.8 earthquake struck in South West, Indonesia. The epicentre was centered about 800 km West South West of Padang, Sumatra province,
Earthquake overview AFGHANISTA N PAKISTA N INDIA A moment magnitude (Mw) 7.8 earthquake struck in South West, Indonesia. The epicentre was centered about 800 km West South West of Padang, Sumatra province,
NPTEL Video Course on Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering
 NPTEL Video Course on Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering by Prof. Deepankar Choudhury Professor, Dept. of Civil Engg., Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Bombay Powai, Mumbai 400076, India. Email: dc@civil.iitb.ac.in
NPTEL Video Course on Geotechnical Earthquake Engineering by Prof. Deepankar Choudhury Professor, Dept. of Civil Engg., Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Bombay Powai, Mumbai 400076, India. Email: dc@civil.iitb.ac.in
Slide 1. Earth Science. Chapter 5 Earthquakes
 Slide 1 Earth Science Chapter 5 Earthquakes Slide 2 Forces in Earth's Crust A force that acts on rock to change its shape or volume is stress 3 types of stress acting on rock layers Tension pulls on the
Slide 1 Earth Science Chapter 5 Earthquakes Slide 2 Forces in Earth's Crust A force that acts on rock to change its shape or volume is stress 3 types of stress acting on rock layers Tension pulls on the
2.3 Notes: Earthquake Damage Can Be Reduced
 2.3 Notes: Earthquake Damage Can Be Reduced Earthquakes can cause severe damage and loss of life Each year, there is about one earthquake with a magnitude of or higher-this is an extremely earthquake.
2.3 Notes: Earthquake Damage Can Be Reduced Earthquakes can cause severe damage and loss of life Each year, there is about one earthquake with a magnitude of or higher-this is an extremely earthquake.
Chapter 13 Earthquakes and Earth s Interior
 Chapter 13 Earthquakes and Earth s Interior The crust of the Earth is made up of floating tectonic plates- huge continent-sized chunks of solid rock floating on molten rock. Rock masses along the boundaries
Chapter 13 Earthquakes and Earth s Interior The crust of the Earth is made up of floating tectonic plates- huge continent-sized chunks of solid rock floating on molten rock. Rock masses along the boundaries
Hazards in the Seattle Area. Disaster Questions. Where Were You? Where Were You? Volcanoes St. Helens Adams, Rainier, Glacier, Baker
 Hazards in the Seattle Area Volcanoes St. Helens Adams, Rainier, Glacier, Baker Earthquakes Outer coast Puget Sound (Seattle Fault & others) Tsunami Outer coast Puget Sound (Seattle Fault & others) Disaster
Hazards in the Seattle Area Volcanoes St. Helens Adams, Rainier, Glacier, Baker Earthquakes Outer coast Puget Sound (Seattle Fault & others) Tsunami Outer coast Puget Sound (Seattle Fault & others) Disaster
