Science & Literacy Activity GRADES 6-8
|
|
|
- Lambert Jones
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Science & Literacy Activity GRADES 6-8 OVERVIEW This activity, which is aligned to the Common Core State Standards (CCSS) for English Language Arts, introduces students to scientific knowledge and language related to natural hazards. Students will read content-rich texts, visit the Nature s Fury: The Science of Natural Disasters exhibition, and use what they have learned to complete a CCSS-aligned writing task by creating an illustrated text about natural hazards. Materials in this activity include: Teacher instructions for: o Pre-visit student reading o Visit to Nature s Fury and Student Worksheet o Post-visit writing task Text for student reading: Avoiding Earthquake Surprises in the Pacific Northwest Student Worksheet for the Nature s Fury visit Student Writing Guidelines Teacher rubric for writing assessment Common Core State Standards: WHST.6-8.2, WHST.6-8.8, WHST.6-8.9, RST.6-8.1, RST.6-8.2, RST.6-8.4, RST New York State Science Standards: PS2.2a Next Generation Science Standards: Disciplinary Core Idea ESS3.B: Natural Hazards. Mapping the history of natural hazards in a region, combined with an understanding of related geologic forces can help forecast the locations and likelihoods of future events. Science and Engineering Practice 8: Obtaining, Evaluating, and Communicating Information SUPPORTS FOR DIVERSE LEARNERS: An Overview This resource has been designed to engage all learners with the principles of Universal Design for Learning in mind. It represents information in multiple ways and offers multiple ways for your students to engage with content as they read about, discuss, view, and write about scientific concepts. Different parts of the experience (e.g. reading texts, locating information in the exhibition) may challenge individual students. However, the arc of learning is designed to offer varied opportunities to learn. We suggest that all learners experience each activity, even if challenging. We have provided ways to adapt each step of the activities for students with different skill-levels. If any students have an Individualized Education Program (IEP), consult it for additional accommodations or modifications. 1. BEFORE YOUR VISIT This part of the activity engages students in reading a non-fiction text about natural hazards. The reading will prepare students for their visit by introducing them to the topic and framing their investigation. Student Reading Have students read Avoiding Earthquake Surprises in the Pacific Northwest. Ask them to write notes in the large righthand margin. For example, they could underline key passages, paraphrase important information, or write down any questions. Discussion Questions: What causes earthquakes? (Earthquakes are powerful waves that pass through the ground. They are caused by the sudden release of stored up strain in rocks. When the rocks break, this stored energy surges through Earth.) How do scientists compare the power of different earthquakes? How does the magnitude scale work? (Scientists compare earthquakes based on the amount of energy they put out. They use the magnitude scale to measure this energy. Each step up the magnitude scale represents a thirty-fold increase in power.) What evidence did scientists find that great quakes were possible in the Cascadia region? (Scientists have found evidence that past earthquakes flooded and killed forests, filled cracks in rock with quicksand, and even caused massive waves called tsunamis.) 1
2 GRADES 6-8 How does this research help scientists forecast the locations and likelihood of future earthquakes? What measures are being taken to protect humans from future earthquakes? (Scientists have been able to determine that very large earthquakes have occurred in the Cascadia region in the past. They may be rare, but these great quakes are very powerful. In order to withstand them, structures like dams, bridges, schools, and hospitals in regions that are at risk are strengthened.) Students can work in pairs, small groups, or as a class. During discussion, remind them to use evidence from the text to explain their thinking, and to use specific examples. SUPPORTS FOR DIVERSE LEARNERS: Student Reading Chunking the reading can help keep them from becoming overwhelmed by the length of the text. Present them with only a few sentences or a single paragraph to read and discuss before moving on to the next chunk. Provide wait-time for students after you ask a question. This will allow time for students to search for textual evidence or to more clearly formulate their thinking before they speak. After the reading, show students the following: o Tsunami Science: Reducing the Risk: amnh.org/explore/science-bulletins/(watch)/earth/documentaries/tsunami-science-reducing-the-risk o Plates on the Move: amnh.org/ology/features/plates 2. DURING YOUR VISIT This part of the activity engages students in exploring the Nature s Fury exhibition. Museum Visit & Student Worksheet Explain to students that they will learn about earthquakes, volcanoes, tornadoes, and hurricanes, and use worksheets to gather information about these natural hazards. Tell students that back in the classroom they will refer to these notes when completing the writing assignment. SUPPORTS FOR DIVERSE LEARNERS: Museum Visit Review the Student Worksheet with students, clarifying what information they should collect during the visit. Have students explore the exhibition in pairs, with each student completing their own Student Worksheet. Encourage student pairs to ask you or their peers for help locating information. Tell students they may not share answers with other pairs, but they may point each other to places in the exhibition where answers are located. 3. BACK IN THE CLASSROOM This part of the activity engages students in an informational writing task that draws on the pre-visit reading and on observations made at the Museum. Writing Task Distribute the Student Writing Guidelines handout, which includes the following prompt for the writing task: Based on your reading, your visit to the Nature s Fury exhibition, and your discussions, write an essay in which you describe the cause of earthquakes and one other type of natural hazard, and explain how scientists can help forecast future events. Go over the handout with students. Tell them that they will use it while writing, and use it afterwards to evaluate and revise their essays. Before they begin to write, have students use the prompt and guidelines to discuss the information that they gathered in Nature s Fury, and compare their findings. They can work in pairs, small groups, or as a class. Referring to the writing prompt, have students underline or highlight all relevant passages and information from the reading and from their notes from the exhibition. As they compare findings, students may take notes on information gathered by their peers. Students should write their essays individually. SUPPORTS FOR DIVERSE LEARNERS: Writing Task Re-read the Before Your Visit assignment with students. Ask what they saw in the exhibition that helps them understand natural hazards. Allow time for students to read their essay drafts to a peer and receive feedback based on the Student Writing Guidelines. 2
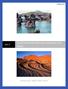
3 Student Reading Avoiding Earthquake Surprises in the Pacific Northwest How Vulnerable Is the Pacific Northwest? Cascadia is a region in the Pacific Northwest. It includes southern British Columbia, Washington, Oregon, and northern California. This region is at risk of being hit by earthquakes. Until the mid-1980s, Earth scientists thought that the threat was limited to quakes of magnitude 7 1 or below. But more recently, Earth scientists discovered evidence that more intense earthquakes repeatedly struck the region over the past several thousand years. And they are likely to occur again. Earthquakes of magnitude 8 and 9 are considered great quakes. An earthquake of magnitude 8 releases about thirty times as much energy as a quake of magnitude 7. A quake of magnitude 9 is another thirty times larger. Why the Pacific Northwest Is at Risk Earth s rigid outer shell is made up of vast rocky pieces called tectonic plates. These plates move as slowly as fingernails grow. They separate, collide, or grind against each other at plate boundaries. Where the plates grind together, pressure builds up and the rocks eventually break. This sends stored-up energy surging through Earth. This energy is what causes earthquakes. AMNH Earth s surface is broken into massive rocky plates called tectonic plates. 1 Over the years, seismologists devised various magnitude scales as measures of earthquake size. The moment magnitude scale is used today. 3
4 Most earthquakes occur along certain plate boundaries called subduction zones. A subduction zone is where a more dense oceanic plate subducts, or sinks below, a continental plate. Decades ago, scientists recognized that a subduction zone runs along the Pacific coast. It lies between southern British Columbia and northern California. It s called the Cascadia subduction zone. The two largest earthquakes since 1900 occurred along subduction zones. They were a Chilean earthquake of magnitude 9.5 in 1960, and an Alaskan earthquake of magnitude 9.2 in During each of these earthquakes, the continental plate lurched 20 meters toward the sea. This movement thinned the plate by stretching its rocks. The thinning lowered the coast enough for tides to drown coastal forests. Today, ghostly tree trunks provide natural clues that the huge earthquakes occurred. Clues of Ancient Quakes Earth scientists have found similar, much older, remains of flooded forests in Cascadia. They were discovered along bays and river mouths on the coasts of British Columbia, Washington, Oregon, and northern California. Scientists also found other evidence of strong earthquakes in the same locations. These include sheets of sand that were deposited by floods from the sea and ground cracks that were filled with quicksand. Scientists concluded that earthquakes of magnitude 8 or larger have struck Cascadia repeatedly in the past several thousand years. Teams of scientists worked together to determine the exact date and an approximate size for the most recent of these Cascadia earthquakes. First, American scientists discovered clues in some dead trees. The trees recorded sudden lowering of coastal land during this earthquake. Radiocarbon dating showed that they died between 1680 and Scientists study dead trees in a tidal marsh along the Pacific coast of Washington. They provide evidence that a great earthquake occurred in January Courtesty of Brian F. Atwater 4
5 Japanese researchers were paying attention to these discoveries in North America. They knew that if the Cascadia earthquake was big enough, it would have started a tsunami in the Pacific Ocean. And they had been looking for the mysterious source of a tsunami that caused flooding and damage in Japan in January They proposed that a great Cascadia earthquake occurred in the evening of January 26, They estimated its size as magnitude 9. To test this proposed date and size, American scientists returned to some of the earthquake-killed trees in Washington. By measuring thin and thick rings, they assigned dates to individual tree rings. They were able to narrow the time of the earthquake to the months between August 1699 and May This evidence supported the date proposed by Japanese researchers. The findings combined to give the 1700 Cascadia earthquake a place in history. Northwesterners Respond to the Risk Earthquakes can t be prevented. However, people can take measures to minimize the damage they cause. In some cases, communities can strengthen structures that already exist. These include dams, bridges, water systems, schools, hospitals, and lifelines (electrical, gas, and water lines). They can also design and build earthquake-resistant structures in the future. Until 1994, the Uniform Building Code placed an area of Washington in a zone with the second highest hazard level (out of six). Most of the rest of Oregon and Washington was placed in a zone with a lower hazard level. The 1994 edition of the Uniform Building Code redrew the map for the Pacific Northwest. All parts of Oregon and Washington that are at risk of great earthquakes were upgraded to the higher-level hazard zone. This revision of the code was an important first step toward meeting the great-earthquake threat in the Pacific Northwest. In the areas upgraded to the second highest level, new buildings are designed to withstand earthquakes fifty percent stronger than under the old code. How Safe Are Other Parts of the United States? People in other earthquake-prone states started asking questions about whether they were adequately prepared for future earthquakes. These states include Massachusetts, New York, South Carolina, Missouri, Indiana, Utah, California, and Alaska. Many of the questions cannot be answered satisfactorily until we know more about past earthquakes. Deciphering the geologic past is one of the ways that Earth scientists help to protect people from loss of life and property. This reading was adapted from a 1995 USGS Fact Sheet, Averting Surprises in the Pacific Northwest, by Brian F. Atwater, Thomas S. Yelin, Craig S. Weaver, James W. Hendley, II. 2 The Uniform Building Code was replaced in 2000 by the International Building Code. 5
6 Student Worksheet This exhibition contains four sections about four natural hazards: Earthquakes, volcanoes, tornadoes, and hurricanes. In each section, record information about the type of hazard discussed there. 1. Earthquakes What causes earthquakes? Draw and label a diagram of this earthquake. Pick one specific earthquake and record the location and year of What tools do scientists use to research earthquakes? How do scientists forecast future earthquakes? 2. Volcanoes What causes volcanoes? Draw and label a diagram of this eruption. Pick one specific volcano and record the location and year of What tools do scientists use to study volcanoes? How do scientists forecast future volcanic eruptions? 6
7 3. Tornadoes What causes tornadoes? Draw and label a diagram of this tornado. Pick one specific tornado and record the location and year of What tools do scientists use to study tornadoes? What is tornado alley? What states are most likely to have a tornado in the future? 4. Hurricanes What causes hurricanes? Draw and label a diagram of this hurricane. Pick one specific hurricane and record the location and year of What tools do scientists use to study hurricanes? How do scientists forecast future hurricanes? 7
8 Student Worksheet ANSWER KEY This exhibition contains four sections about four natural hazards: Earthquakes, volcanoes, tornadoes, and hurricanes. In each section, record information about the type of hazard discussed there. 1. Earthquakes What causes earthquakes? (Earthquakes are powerful waves that pass through the ground. They are caused by the sudden release of stored up strain in rocks. When the rocks break, this stored energy surges through Earth.) Draw and label a diagram of this earthquake. Pick one specific earthquake and record the location and year of (Sample answer: Haiti Earthquake, 2010) What tools do scientists use to research earthquakes? (seismograph) How do scientists forecast future earthquakes? (Scientists can determine where earthquakes happen most often, such as near faults, and determine how frequently earthquakes happen in these locations.) 2. Volcanoes What causes volcanoes? (A volcano is an opening in Earth s crust that releases molten rock and gas. Magma and gas deep within Earth are under tremendous pressure. In an eruption, they are forced to the surface to the surface.) Draw and label a diagram of this eruption. Pick one specific volcano and record the location and year of (Sample answer: Mt. Vesuvius, 79 AD) What tools do scientists use to study volcanoes? (Scientists can use GPS to measure the change in elevation of a volcano.) How do scientists forecast future volcanic eruptions? (Scientists can monitor volcanoes for sudden changes or an increase in activity that can indicate that an eruption is likely.) 8
9 3. Tornadoes What causes tornadoes? (A tornado is a rapidly rotating column of air. They form from the movement of air in powerful thunderstorms.) Draw and label a diagram of this tornado. ANSWER KEY Pick one specific tornado and record the location and year of (Sample answer: Greensburg, Kansas, 2007) What tools do scientists use to study tornadoes? (Scientists can use armored cameras to see inside of a tornado.) What is tornado alley? What states are most likely to have a tornado in the future? (Tornado alley is a region in the central United States where most tornadoes occur. Iowa, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Texas are the states with the most tornadoes.) 4. Hurricanes What causes hurricanes? (A hurricane, or tropical cyclone, is an extremely large and powerful storm. They normally form over warm water in the tropics; they gain energy when this water evaporates.) Draw and label a diagram of this hurricane. Pick one specific hurricane and record the location and year of (Sample answer: Galveston hurricane, 1900) What tools do scientists use to study hurricanes? (Scientists can use land stations, ships, balloons, aircraft buoys at sea, and satellites to make millions of measurements every day.) How do scientists forecast future hurricanes? (Scientists can track the formation and movement of hurricanes and compare them to previous storms. This allows them to forecast the path and strength of each new hurricane.) 9
10 Student Writing Guidelines Based on your reading, your visit to the Nature s Fury exhibition, and your discussions, write an illustrated essay in which you describe the cause of earthquakes and one other type of natural hazard, and explain how scientists can forecast future events. Be sure to include: one example of a natural hazard an explanation of this natural hazard an illustration of this natural hazard with at least three labels an explanation of how scientists study this type of natural hazard an explanation of how scientific research forecasts where such an event might occur in the future, what the likelihood is, and how to prepare for it Support your essay with evidence from the reading and your visit to Nature s Fury. Use this checklist to ensure that you have included all of the required elements in your essay. I introduced one natural hazard. I clearly named one type of natural hazard and described how it occurs. I included a labeled illustration of one natural hazard with at least three labels. I only included relevant information about natural hazards. I used information from the reading, Avoiding Earthquake Surprises in the Pacific Northwest, to explain one kind of natural hazard in detail. I used information from the Nature s Fury exhibition to explain one kind of natural hazard in detail. I used academic, non-conversational tone and language. I included a conclusion at the end. I proofread my essay for grammar and spelling errors. 10
11 Assessment Rubric Scoring Elements Below Expectations Approaches Expectations Meets Expectations Exceeds Expectations RESEARCH Reading AMNH Exhibition Attempts to present information in response to the prompt, but lacks connections to the texts or relevance to the purpose of the prompt. Attempts to present information in response to the prompt, but lacks connections to the Museum exhibit content or relevance to the purpose of the prompt. Presents information from the text relevant to the purpose of the prompt with minor lapses in accuracy or completeness. Presents information from the Museum exhibit relevant to the purpose of the prompt with minor lapses in accuracy or completeness. Presents information from the text relevant to the prompt with accuracy and sufficient detail. Presents information from the Museum exhibit relevant to the prompt with accuracy and sufficient detail. Accurately presents information relevant to all parts of the prompt with effective paraphrased details from the text. Accurately presents information relevant to all parts of the prompt with effective paraphrased details from the Museum exhibit. Focus Attempts to address the prompt, but lacks focus or is off-task. Addresses the prompt appropriately, but with a weak or uneven focus. Addresses the prompt appropriately and maintains a clear, steady focus. Addresses all aspects of the prompt appropriately and maintains a strongly developed focus. WRITING Development Conventions Attempts to provide details in response to the prompt, including retelling, but lacks sufficient development or relevancy. Attempts to demonstrate standard English conventions, but lacks cohesion and control of grammar, usage, and mechanics. Presents appropriate details to support the focus and controlling idea. Demonstrates an uneven command of standard English conventions and cohesion. Uses language and tone with some inaccurate, inappropriate, or uneven features. Presents appropriate and sufficient details to support the focus and controlling idea. Demonstrates a command of standard English conventions and cohesion, with few errors. Response includes language and tone appropriate to the purpose and specific requirements of the prompt. Presents thorough and detailed information to strongly support the focus and controlling idea. Demonstrates and maintains a welldeveloped command of standard English conventions and cohesion, with few errors. Response includes language and tone consistently appropriate to the purpose and specific requirements of the prompt. SCIENCE Content Understanding Attempts to include science content in explanations, but understanding of the topic is weak; content is irrelevant, inappropriate, or inaccurate. Briefly notes science content relevant to the prompt; shows basic or uneven understanding of the topic; minor errors in explanation. Accurately presents science content relevant to the prompt with sufficient explanations that demonstrate understanding of the topic. Integrates relevant and accurate science content with thorough explanations that demonstrate in-depth understanding of the topic. 11
This article is provided courtesy of the American Museum of Natural History.
 Avoiding Earthquake Surprises in the Pacific Northwest This article is provided courtesy of the American Museum of Natural History. How Vulnerable Is the Pacific Northwest? Cascadia is a region in the
Avoiding Earthquake Surprises in the Pacific Northwest This article is provided courtesy of the American Museum of Natural History. How Vulnerable Is the Pacific Northwest? Cascadia is a region in the
Science & Literacy Activity GRADES 3-5
 Science & Literacy Activity GRADES 3-5 OVERVIEW This activity, which is aligned to the Common Core State Standards (CCSS) for English Language Arts, introduces students to scientific knowledge and language
Science & Literacy Activity GRADES 3-5 OVERVIEW This activity, which is aligned to the Common Core State Standards (CCSS) for English Language Arts, introduces students to scientific knowledge and language
Science & Literacy Activity GRADES 6-8
 Science & Literacy Activity GRADES 6-8 OVERVIEW This activity, which is aligned to the Common Core State Standards (CCSS) for English Language Arts, introduces students to scientific knowledge and language
Science & Literacy Activity GRADES 6-8 OVERVIEW This activity, which is aligned to the Common Core State Standards (CCSS) for English Language Arts, introduces students to scientific knowledge and language
Science & Literacy Activity GRADES 9-12
 Science & Literacy Activity GRADES 9-12 OVERVIEW This activity, which is aligned to the Common Core State Standards (CCSS) for English Language Arts, introduces students to scientific knowledge and language
Science & Literacy Activity GRADES 9-12 OVERVIEW This activity, which is aligned to the Common Core State Standards (CCSS) for English Language Arts, introduces students to scientific knowledge and language
Mondo Quake in Pacific Northwest? By Leander Kahney
 Introduction to College Reading D Natural Disasters: Earthquake NAME I. Pre-reading. Discuss the following topics with other students at your table. What countries or regions of the world have earthquakes?
Introduction to College Reading D Natural Disasters: Earthquake NAME I. Pre-reading. Discuss the following topics with other students at your table. What countries or regions of the world have earthquakes?
Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model
 Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model The Cascadia tectonic margin is caught between several tectonic forces, during the relentless motions of the giant Pacific Plate, the smaller subducting
Activity Pacific Northwest Tectonic Block Model The Cascadia tectonic margin is caught between several tectonic forces, during the relentless motions of the giant Pacific Plate, the smaller subducting
Science & Literacy Activity GRADES 3-5
 Science & Literacy Activity GRADES 3-5 OVERVIEW This activity, which is aligned to the Common Core State Standards (CCSS) for English Language Arts, introduces students to scientific knowledge and language
Science & Literacy Activity GRADES 3-5 OVERVIEW This activity, which is aligned to the Common Core State Standards (CCSS) for English Language Arts, introduces students to scientific knowledge and language
Los Angeles Unified School District. Administration and Scoring Guide
 Los Angeles Unified School District Office of Curriculum, Instruction, and School Support INTERIM ASSESSMENT Grade 6 Science Instructional Component 1 2014-2015 Administration and Scoring Guide ASSESSMENT
Los Angeles Unified School District Office of Curriculum, Instruction, and School Support INTERIM ASSESSMENT Grade 6 Science Instructional Component 1 2014-2015 Administration and Scoring Guide ASSESSMENT
SCIENCE IN THE NEWS Plate Tectonics
 SCIENCE IN THE NEWS Plate Tectonics From VOA Learning English, this is Science in the News. I m Anna Matteo. And I m Christopher Cruise. Scientists who study the Earth tell us the continents and ocean
SCIENCE IN THE NEWS Plate Tectonics From VOA Learning English, this is Science in the News. I m Anna Matteo. And I m Christopher Cruise. Scientists who study the Earth tell us the continents and ocean
Plates & Boundaries The earth's continents are constantly moving due to the motions of the tectonic plates.
 Plates & Boundaries The earth's continents are constantly moving due to the motions of the tectonic plates. As you can see, some of the plates contain continents and others are mostly under the ocean.
Plates & Boundaries The earth's continents are constantly moving due to the motions of the tectonic plates. As you can see, some of the plates contain continents and others are mostly under the ocean.
Science & Literacy Activity GRADES 9-12
 Science & Literacy Activity GRADES 9-12 OVERVIEW This activity, which is aligned to the Common Core State Standards (CCSS) for English Language Arts, introduces students to scientific knowledge and language
Science & Literacy Activity GRADES 9-12 OVERVIEW This activity, which is aligned to the Common Core State Standards (CCSS) for English Language Arts, introduces students to scientific knowledge and language
Directed Reading. Section: The Theory of Plate Tectonics. to the development of plate tectonics, developed? HOW CONTINENTS MOVE
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: The Theory of Plate Tectonics 1. The theory that explains why and how continents move is called. 2. By what time period was evidence supporting continental drift,
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: The Theory of Plate Tectonics 1. The theory that explains why and how continents move is called. 2. By what time period was evidence supporting continental drift,
Hazards in the Seattle Area. Disaster Questions. Where Were You? Where Were You? Volcanoes St. Helens Adams, Rainier, Glacier, Baker
 Hazards in the Seattle Area Volcanoes St. Helens Adams, Rainier, Glacier, Baker Earthquakes Outer coast Puget Sound (Seattle Fault & others) Tsunami Outer coast Puget Sound (Seattle Fault & others) Disaster
Hazards in the Seattle Area Volcanoes St. Helens Adams, Rainier, Glacier, Baker Earthquakes Outer coast Puget Sound (Seattle Fault & others) Tsunami Outer coast Puget Sound (Seattle Fault & others) Disaster
4 Deforming the Earth s Crust
 CHAPTER 7 4 Deforming the Earth s Crust SECTION Plate Tectonics BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What happens when rock is placed under stress?
CHAPTER 7 4 Deforming the Earth s Crust SECTION Plate Tectonics BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What happens when rock is placed under stress?
Chapter 1 The Nature Of Science. Scientists are much like detectives trying to solve a mystery. Problem: What caused the huge ocean waves?
 Chapter 1 The Nature Of Science Section 1 Science All Around Mysteries and Problems Scientists are much like detectives trying to solve a mystery. 1996- While looking through historical data, scientists
Chapter 1 The Nature Of Science Section 1 Science All Around Mysteries and Problems Scientists are much like detectives trying to solve a mystery. 1996- While looking through historical data, scientists
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
TO GO TO ANY OF THE PAGES LISTED BELOW, CLICK ON ITS TITLE
 TO GO TO ANY OF THE PAGES LISTED BELOW, CLICK ON ITS TITLE CHAPTER 6 Plate Tectonics 1 6-1 What is continental drift? 2 6-2 Why is the seafloor spreading? 3 6-3 What evidence supports seafloor spreading?
TO GO TO ANY OF THE PAGES LISTED BELOW, CLICK ON ITS TITLE CHAPTER 6 Plate Tectonics 1 6-1 What is continental drift? 2 6-2 Why is the seafloor spreading? 3 6-3 What evidence supports seafloor spreading?
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Review: What is an earthquake? Earthquake is the vibration (shaking) and/or displacement of the ground produced by the sudden release of energy. The point inside the Earth where
Read the Article. Plate Tectonics, Tectonic Plates Information, Facts, News, Photos science.nationalgeographic.com
 Name: Period: Plate Tectonics Performance Task Due: plate tec ton ics noun a theory explaining the structure of the earth's crust and many associated phenomena as resulting from the interaction of rigid
Name: Period: Plate Tectonics Performance Task Due: plate tec ton ics noun a theory explaining the structure of the earth's crust and many associated phenomena as resulting from the interaction of rigid
General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 8 Plate Boundaries Beneath the Sea Complete by Thursday at 11:00 PM
 General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 8 Plate Boundaries Beneath the Sea Complete by Thursday at 11:00 PM Name Expedition Objectives Learn about the types of plate boundaries and their key characteristics
General Oceanography Geology 105 Expedition 8 Plate Boundaries Beneath the Sea Complete by Thursday at 11:00 PM Name Expedition Objectives Learn about the types of plate boundaries and their key characteristics
TASC Transition Curriculum Project
 TASC Transition Curriculum Project MODULE 3: WORKSHOP 9 REVIEWING THE CROSS-CUTTING CONCEPTS INVOLVED IN SOLVING PROBLEMS PLACED ON STUDENTS IN TASC ABOUT DISCIPLINARY CORE IDEAS POSED IN THE PHYSICAL
TASC Transition Curriculum Project MODULE 3: WORKSHOP 9 REVIEWING THE CROSS-CUTTING CONCEPTS INVOLVED IN SOLVING PROBLEMS PLACED ON STUDENTS IN TASC ABOUT DISCIPLINARY CORE IDEAS POSED IN THE PHYSICAL
Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics: From Hypothesis to Theory
 Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics: From Hypothesis to Theory 1 Key Understandings Internal structure of the earth/structure of the crust. Difference between continental drift & plate tectonics. Evidence
Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics: From Hypothesis to Theory 1 Key Understandings Internal structure of the earth/structure of the crust. Difference between continental drift & plate tectonics. Evidence
Earthquake Hazards. Tsunami
 Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Measuring Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the power or strength of an earthquake are: Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale based
Earthquake Hazards Tsunami Measuring Earthquakes Two measurements that describe the power or strength of an earthquake are: Intensity a measure of the degree of earthquake shaking at a given locale based
Natural Disasters. Why Are There Earthquakes? 197 words. The Power of the Earth 221 words. Big Waves! 188 words
 ARTICLE-A-DAY Natural Disasters 6 Articles Check articles you have read: Why Are There Earthquakes? 197 words The Power of the Earth 221 words Big Waves! 188 words The Volcano That Keeps Erupting 228 words
ARTICLE-A-DAY Natural Disasters 6 Articles Check articles you have read: Why Are There Earthquakes? 197 words The Power of the Earth 221 words Big Waves! 188 words The Volcano That Keeps Erupting 228 words
4 Deforming the Earth s Crust
 CHAPTER 7 4 Deforming the Earth s Crust SECTION Plate Tectonics BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What happens when rock is placed under stress?
CHAPTER 7 4 Deforming the Earth s Crust SECTION Plate Tectonics BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What happens when rock is placed under stress?
Earth s Plates, Part 1: What Are They, Where Are They and What Do They Do?
 Earth s Plates, Part 1: What Are They, Where Are They and What Do They Do? A scientist named Alfred Wegener believed that, at one time, all of the continents were one landmass. Although he had no real
Earth s Plates, Part 1: What Are They, Where Are They and What Do They Do? A scientist named Alfred Wegener believed that, at one time, all of the continents were one landmass. Although he had no real
4 th Grade PSI. Slide 1 / 107 Slide 2 / 107. Slide 3 / 107. Slide 4 / 107. Slide 5 / 107. Slide 6 / 107. The History of Planet Earth
 Slide 1 / 107 Slide 2 / 107 4 th Grade PSI The History of Planet Earth 2015-11-10 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 107 Slide 4 / 107 The History of Planet Earth The Structure of Earth Rock Layers Fossils and Relative
Slide 1 / 107 Slide 2 / 107 4 th Grade PSI The History of Planet Earth 2015-11-10 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 107 Slide 4 / 107 The History of Planet Earth The Structure of Earth Rock Layers Fossils and Relative
CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY
 CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY Proof or crazy idea? CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY What is Continental Drift Theory? Continental drift theory (CDT): Alfred Wegener found all the continents were once together called
CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY Proof or crazy idea? CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY What is Continental Drift Theory? Continental drift theory (CDT): Alfred Wegener found all the continents were once together called
Earth Science Lesson 3 Dynamic Earth Processes (Grades 8-12 ) Instruction 3-3 Plate Boundaries
 As we told you in a recent Instruction, much of the Earth's lithosphere (its Crust and the top layer of its Outer Mantle) is made up of moving masses of rock called tectonic plates (tectonic means moving).
As we told you in a recent Instruction, much of the Earth's lithosphere (its Crust and the top layer of its Outer Mantle) is made up of moving masses of rock called tectonic plates (tectonic means moving).
What is the theory of plate tectonics? Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Lesson 3
 Name Plate Tectonics What is the theory of plate tectonics? Date Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about plate tectonics Record your thoughts in the first column Pair
Name Plate Tectonics What is the theory of plate tectonics? Date Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about plate tectonics Record your thoughts in the first column Pair
Collision and transform Boundaries
 Collision and transform Boundaries I. The collision boundary Sometimes when two plates move together they are both continental rather than one being continental and one being oceanic as at the destructive
Collision and transform Boundaries I. The collision boundary Sometimes when two plates move together they are both continental rather than one being continental and one being oceanic as at the destructive
1.4 Notes: Plates Converge or Scrape Past Each Other Think About Tectonic Plates Push Together at Convergent Boundaries
 1.4 Notes: Plates Converge or Scrape Past Each Other Think About If new crust is created at divergent boundaries, why does the total amount of crust on Earth stay the same? Tectonic Plates Push Together
1.4 Notes: Plates Converge or Scrape Past Each Other Think About If new crust is created at divergent boundaries, why does the total amount of crust on Earth stay the same? Tectonic Plates Push Together
Read & Learn Earthquakes & Faults
 Read Earthquakes & Faults Read the provided article. Use the information in the reading to answer the questions on the task cards on your answer sheet. Make sure your answers are in the correct spot on
Read Earthquakes & Faults Read the provided article. Use the information in the reading to answer the questions on the task cards on your answer sheet. Make sure your answers are in the correct spot on
Science 2015 Earth Science. Study Guide
 Adult Basic Education Level II Science Science 2015 Earth Science Study Guide Resources: Discovering Science 7 Level II Science Courses Science 2011 Life Science Science 2012 Physical Science Science 2013
Adult Basic Education Level II Science Science 2015 Earth Science Study Guide Resources: Discovering Science 7 Level II Science Courses Science 2011 Life Science Science 2012 Physical Science Science 2013
Grade 7 Science Unit 4: The Earth s Crust PLATE TECTONIC THEORY
 Grade 7 Science Unit 4: The Earth s Crust PLATE TECTONIC THEORY Alfred Wegener 1880 1930 German meteorologist He noticed that the continents fit together like a puzzle. He said that at one time all continents
Grade 7 Science Unit 4: The Earth s Crust PLATE TECTONIC THEORY Alfred Wegener 1880 1930 German meteorologist He noticed that the continents fit together like a puzzle. He said that at one time all continents
Stratford School Academy Schemes of Work GEOG: RESTLESS EARTH
 Case studies Drawing maps, graphs and diagrams. Stratford School Academy Year 10 Restless Earth Geography: YEAR 10 Restless Earth Number of weeks Content of the unit Assumed prior learning (tested at the
Case studies Drawing maps, graphs and diagrams. Stratford School Academy Year 10 Restless Earth Geography: YEAR 10 Restless Earth Number of weeks Content of the unit Assumed prior learning (tested at the
Lesson Plan Summary Magic Tree House #28: High Tide in Hawaii Standing on Solid Ground??
 Lesson Plan Summary Magic Tree House #28: High Tide in Hawaii Standing on Solid Ground?? DURING THIS BOOK STUDY, EACH STUDENT WILL: COMMON CORE STANDARDS ADDRESSED: Discover facts about the layers of the
Lesson Plan Summary Magic Tree House #28: High Tide in Hawaii Standing on Solid Ground?? DURING THIS BOOK STUDY, EACH STUDENT WILL: COMMON CORE STANDARDS ADDRESSED: Discover facts about the layers of the
MCAS QUESTIONS: THE EARTH S INTERIOR, CONTINENTAL DRIFT, PLATE TECTONICS
 NAME: PER: MCAS QUESTIONS: THE EARTH S INTERIOR, CONTINENTAL DRIFT, PLATE TECTONICS 1. Which of the following statements best explains why the lower mantle of Earth is much more rigid and dense than the
NAME: PER: MCAS QUESTIONS: THE EARTH S INTERIOR, CONTINENTAL DRIFT, PLATE TECTONICS 1. Which of the following statements best explains why the lower mantle of Earth is much more rigid and dense than the
Tectonic Forces Simulation: Earthquakes Activity One
 Tectonic Forces Simulation: Earthquakes Activity One Introduction If you marked all the earthquakes from the past century on a world map, you'd notice that most tend to occur along certain lines around
Tectonic Forces Simulation: Earthquakes Activity One Introduction If you marked all the earthquakes from the past century on a world map, you'd notice that most tend to occur along certain lines around
Geology 101 Study Guide #4
 Geology 101 Study Guide #4 Our last unit is the study of the earthquakes, the Earth s interior and plate tectonics. We live in a region which has been added on to North America through plate tectonics.
Geology 101 Study Guide #4 Our last unit is the study of the earthquakes, the Earth s interior and plate tectonics. We live in a region which has been added on to North America through plate tectonics.
1. In the block diagram shown here, which is the oldest rock unit?
 Pre/Post GCI Name (print) 1. In the block diagram shown here, which is the oldest rock unit? 2. Referring to the same diagram as the previous question, which of the labeled rock units is the youngest?
Pre/Post GCI Name (print) 1. In the block diagram shown here, which is the oldest rock unit? 2. Referring to the same diagram as the previous question, which of the labeled rock units is the youngest?
Earth s Changing Surface
 Earth s Changing Surface Tectonics What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or
Earth s Changing Surface Tectonics What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement or
Earthquake Investigation
 Exploration A Earthquake Investigation 1. Obtain a piece of plastic putty and knead it into a rectangular shape. 2. Push the ends of the putty toward the middle. Draw and describe what it looks like below.
Exploration A Earthquake Investigation 1. Obtain a piece of plastic putty and knead it into a rectangular shape. 2. Push the ends of the putty toward the middle. Draw and describe what it looks like below.
Tectonic Plates Lexile 840L
 6.10: Tectonic Plates Tectonic Plates Lexile 840L 1 On March 11, 2011, an earthquake measuring 8.9 on the Richter scale rocked the sea floor. It made a giant wave, which grew as tall as 30 feet (9.14 meters)
6.10: Tectonic Plates Tectonic Plates Lexile 840L 1 On March 11, 2011, an earthquake measuring 8.9 on the Richter scale rocked the sea floor. It made a giant wave, which grew as tall as 30 feet (9.14 meters)
What is a natural hazard?
 What is a natural hazard? Give me a definition not examples These words might help you A natural hazard is a naturally occurring event that might have a negative effect on people or the environment. Location
What is a natural hazard? Give me a definition not examples These words might help you A natural hazard is a naturally occurring event that might have a negative effect on people or the environment. Location
Earthquakes & Volcanoes
 Earthquakes & Volcanoes Geology - the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change geo = Earth; ology = study of Earth s Layers Plate Tectonics - the
Earthquakes & Volcanoes Geology - the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change geo = Earth; ology = study of Earth s Layers Plate Tectonics - the
Earth s Dynamic Surface
 Earth s Dynamic Surface Shaping Earth s Surface What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the
Earth s Dynamic Surface Shaping Earth s Surface What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the
Benchmark #: State Language: Student Friendly Language: The student models earth s cycles, constructive and
 Science, Grade: 7 Mastery Check Benchmark #: 7.4.1.2 4 State Language: Student Friendly Language: The student models earth s cycles, constructive and I will be able to describe weathering, erosion, and
Science, Grade: 7 Mastery Check Benchmark #: 7.4.1.2 4 State Language: Student Friendly Language: The student models earth s cycles, constructive and I will be able to describe weathering, erosion, and
EARTH S SYSTEMS: PROCESSES THAT SHAPE THE EARTH
 9 Week Unit UNIT 2 EARTH S SYSTEMS: PROCESSES THAT SHAPE THE EARTH Fourth Grade Rogers Public Schools : Earth s Systems: Processes that Shape the Earth 9 weeks In this unit, students develop understandings
9 Week Unit UNIT 2 EARTH S SYSTEMS: PROCESSES THAT SHAPE THE EARTH Fourth Grade Rogers Public Schools : Earth s Systems: Processes that Shape the Earth 9 weeks In this unit, students develop understandings
The Rock Cycle R U Ap An E Cr. Atmospheric Pressure and Condensation R U Ap An E Cr. Earthquake Warning System R U Ap An E Cr
 Taxonomy Exercise Review the examples of exercises used in a general education Earth Science course at UA and rank them according to the Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching, and Assessing. Place each exercise
Taxonomy Exercise Review the examples of exercises used in a general education Earth Science course at UA and rank them according to the Taxonomy for Learning, Teaching, and Assessing. Place each exercise
Inside Earth Review Packet
 1. The slow movement of the continents across the Earth s surface is defined as - A Newton s 1 st Law of Motion B Continental Drift C Law of Transformation of Energy D Earth s movement 2. The scientist
1. The slow movement of the continents across the Earth s surface is defined as - A Newton s 1 st Law of Motion B Continental Drift C Law of Transformation of Energy D Earth s movement 2. The scientist
Tsunami! Beyond the Book. FOCUS Book
 FOCUS Book Use the engineering design process to design a structure that will protect a coastal town from possible tsunami damage. Brainstorm design ideas for your structure with a group of classmates.
FOCUS Book Use the engineering design process to design a structure that will protect a coastal town from possible tsunami damage. Brainstorm design ideas for your structure with a group of classmates.
Do Now: Vocabulary: Objectives. Vocabulary: 1/5/2016. Wegener? (Can they move?) the idea that continents have moved over time?
 Do Now: 1. Who was Alfred Wegener? 2. What was Pangaea? 3. Are continents fixed? (Can they move?) 4. What evidence supports the idea that continents have moved over time? Objectives What evidence suggests
Do Now: 1. Who was Alfred Wegener? 2. What was Pangaea? 3. Are continents fixed? (Can they move?) 4. What evidence supports the idea that continents have moved over time? Objectives What evidence suggests
Topics. Nuclear waste storage, risk analysis, evidence and tradeoffs, Groundwater, aquifer, aquitard. literacy
 UNIT OVERVIEW GEOLOGICAL PROCESSES Listed below is a summary of the activities in this unit. Note that the total teaching time is listed as 26 32 periods of approximately 45 50 minutes (approximately 6
UNIT OVERVIEW GEOLOGICAL PROCESSES Listed below is a summary of the activities in this unit. Note that the total teaching time is listed as 26 32 periods of approximately 45 50 minutes (approximately 6
TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology
 Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
NAME: DATE: Geography: The Earth. Geography The Earth
 Geography The Earth It is not necessary to carry out all the activities contained in this unit. Please see Teachers Notes for explanations, additional activities, and tips and suggestions. Theme The Earth
Geography The Earth It is not necessary to carry out all the activities contained in this unit. Please see Teachers Notes for explanations, additional activities, and tips and suggestions. Theme The Earth
A Model of Three Faults
 A Model of Three Faults Grades 7-12 Adapted from the USGS Learning Web Lesson Plans Background One of the most frightening and destructive phenomena of nature is a severe earthquake and its terrible aftereffects.
A Model of Three Faults Grades 7-12 Adapted from the USGS Learning Web Lesson Plans Background One of the most frightening and destructive phenomena of nature is a severe earthquake and its terrible aftereffects.
From VOA Learning English, this is SCIENCE IN THE NEWS, in Special English. I m Kelly Jean Kelly.
 From VOA Learning English, this is SCIENCE IN THE NEWS, in Special English. I m Kelly Jean Kelly. And I m Christopher Cruise. Scientists who study the Earth tell us the continents and ocean floors are
From VOA Learning English, this is SCIENCE IN THE NEWS, in Special English. I m Kelly Jean Kelly. And I m Christopher Cruise. Scientists who study the Earth tell us the continents and ocean floors are
Local Weather History
 Local Weather History 52 40- to 2+ 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW P RO J E C T Students design and conduct a survey to learn about the history of weather disasters in the local area, and then compare
Local Weather History 52 40- to 2+ 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW P RO J E C T Students design and conduct a survey to learn about the history of weather disasters in the local area, and then compare
water erosion lithosphere Describe the process of erosion and deposition. chemical weathering Dissolving limestone is an example of.
 At one time, there was one large island off the coast of Mississippi and now it is two separate islands. What caused the island to be split into two? water erosion The crust and the top part of the upper
At one time, there was one large island off the coast of Mississippi and now it is two separate islands. What caused the island to be split into two? water erosion The crust and the top part of the upper
Not all eruptions are the same. Sometimes, there is a huge explosion. The hot magma shoots
 Natural Disasters A natural disaster is an event that happens in nature. It is an event that can cause a lot of damage. Volcanoes, earthquakes, and tsunamis are all natural disasters. Volcanoes A volcano
Natural Disasters A natural disaster is an event that happens in nature. It is an event that can cause a lot of damage. Volcanoes, earthquakes, and tsunamis are all natural disasters. Volcanoes A volcano
What Do Scientists Know About Earth s Surface and Interior?
 What Do Scientists Know About Earth s Surface and Interior? Earth s crust is very thick, and scientists may never be able to observe Earth s interior directly by going through the crust. But when a volcano
What Do Scientists Know About Earth s Surface and Interior? Earth s crust is very thick, and scientists may never be able to observe Earth s interior directly by going through the crust. But when a volcano
Changes to Land 5.7B. landforms: features on the surface of Earth such as mountains, hills, dunes, oceans and rivers
 All the landforms on Earth have changed over time and continue to change. Many of the changes were caused by wind, moving water, and moving ice. Mountains have grown and shrunk. Rivers have cut away land
All the landforms on Earth have changed over time and continue to change. Many of the changes were caused by wind, moving water, and moving ice. Mountains have grown and shrunk. Rivers have cut away land
Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics. Plate tectonics accounts for important features of Earth s surface and major geologic events.
 Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics accounts for important features of Earth s surface and major geologic events. 7-2 Alfred Wegener s Hypothesis of Continental Drift (1915) He noticed that the continents
Chapter 7 Plate Tectonics Plate tectonics accounts for important features of Earth s surface and major geologic events. 7-2 Alfred Wegener s Hypothesis of Continental Drift (1915) He noticed that the continents
Discusssion / Activity 1 Suggested Answers. INSPECTION COPY for schools only
 Earth Structure Discusssion / Activity 1 Suggested Answers 1. Clearly label the diagram to show the main layers of the Earth. 2. What is the lithosphere? The lithosphere is the crust, plus a thin part
Earth Structure Discusssion / Activity 1 Suggested Answers 1. Clearly label the diagram to show the main layers of the Earth. 2. What is the lithosphere? The lithosphere is the crust, plus a thin part
Plate Tectonics CHAPTER 17
 Plate Tectonics CHAPTER 17 Layers of the Earth A. Crust- solid, 5-70 km thick Moho Two Types of Crust: Oceanic- ocean floor, more dense then because of more iron Continental-dry land (mostly silicates
Plate Tectonics CHAPTER 17 Layers of the Earth A. Crust- solid, 5-70 km thick Moho Two Types of Crust: Oceanic- ocean floor, more dense then because of more iron Continental-dry land (mostly silicates
Plate Tectonics. These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page.
 Plate Tectonics These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates the slide contains activities created in Flash. These activities are
Plate Tectonics These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates the slide contains activities created in Flash. These activities are
Conceptual narrative Science: The Earth s surface
 Year 9 Conceptual narrative Science: The Earth s surface In the Earth and space sciences sub-strand, there are two main conceptual threads being developed from Foundation through to Year 10, Earth in space
Year 9 Conceptual narrative Science: The Earth s surface In the Earth and space sciences sub-strand, there are two main conceptual threads being developed from Foundation through to Year 10, Earth in space
Think about the landforms where you live. How do you think they have changed over time? How do you think they will change in the future?
 reflect All the landforms on Earth have changed over time and continue to change. Many of the changes were caused by wind, moving water, and moving ice. Mountains have grown and shrunk. Rivers have cut
reflect All the landforms on Earth have changed over time and continue to change. Many of the changes were caused by wind, moving water, and moving ice. Mountains have grown and shrunk. Rivers have cut
"The Big One" by sea and not by land
 "The Big One" by sea and not by land By Los Angeles Times, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.24.14 Word Count 629 Surfer Lee Johnson emerges from the water at San Onofre State Beach, Calif., with the twin
"The Big One" by sea and not by land By Los Angeles Times, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.24.14 Word Count 629 Surfer Lee Johnson emerges from the water at San Onofre State Beach, Calif., with the twin
Slow and Steady By ReadWorks
 By ReadWorks How did all the amazing things on our planet form? How did magnificent mountain ranges rise up in one place and beautiful beaches form elsewhere? Why do some places experience earthquakes
By ReadWorks How did all the amazing things on our planet form? How did magnificent mountain ranges rise up in one place and beautiful beaches form elsewhere? Why do some places experience earthquakes
The Cascading Hazards from Cascadia s Earthquakes
 Tsunamis The Cascading Hazards from Cascadia s Earthquakes Earthquakes (Nisqually earthquake, Seattle, WA) Volcanoes (Mt St Helens eruption, WA) Joan Gomberg gomberg@usgs.gov Landslides (Oso landslide,
Tsunamis The Cascading Hazards from Cascadia s Earthquakes Earthquakes (Nisqually earthquake, Seattle, WA) Volcanoes (Mt St Helens eruption, WA) Joan Gomberg gomberg@usgs.gov Landslides (Oso landslide,
Name Test Date Hour. the interior of the Earth to the surface. younger less dense plate.
 Name Test Date Hour Earth Processes#2 - Notebook Plate Tectonics LEARNING TARGETS I can identify and describe the three main layers of Earth. I can explain the difference between an oceanic and a continental
Name Test Date Hour Earth Processes#2 - Notebook Plate Tectonics LEARNING TARGETS I can identify and describe the three main layers of Earth. I can explain the difference between an oceanic and a continental
12.2 Plate Tectonics
 12.2 Plate Tectonics LAYERS OF THE EARTH Earth is over 1200 km thick and has four distinct layers. These layers are the crust, mantle (upper and lower), outer core, and inner core. Crust outer solid rock
12.2 Plate Tectonics LAYERS OF THE EARTH Earth is over 1200 km thick and has four distinct layers. These layers are the crust, mantle (upper and lower), outer core, and inner core. Crust outer solid rock
The Dynamic Earth Section 1. Chapter 3 The Dynamic Earth Section 1: The Geosphere DAY 1
 Chapter 3 The Dynamic Earth Section 1: The Geosphere DAY 1 The Earth as a System The Earth is an integrated system that consists of rock, air, water, and living things that all interact with each other.
Chapter 3 The Dynamic Earth Section 1: The Geosphere DAY 1 The Earth as a System The Earth is an integrated system that consists of rock, air, water, and living things that all interact with each other.
Earth Systems Curriculum
 Earth Systems Curriculum Course Description This course provides the opportunity to develop knowledge and understanding about the relationships between the structure, processes, and resources on Earth
Earth Systems Curriculum Course Description This course provides the opportunity to develop knowledge and understanding about the relationships between the structure, processes, and resources on Earth
discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms and bodies of
 Chapter 7 Natural Environments of North America Chapter 7 focuses on the natural environments of North America. The chapter opens with a discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms
Chapter 7 Natural Environments of North America Chapter 7 focuses on the natural environments of North America. The chapter opens with a discussion of North America s physical features, including its landforms
Full file at
 Chapter 2 PLATE TECTONICS AND PHYSICAL HAZARDS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. What direction is the Pacific Plate currently moving, based on the chain of Hawaiian Islands with only the easternmost island
Chapter 2 PLATE TECTONICS AND PHYSICAL HAZARDS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. What direction is the Pacific Plate currently moving, based on the chain of Hawaiian Islands with only the easternmost island
Earth s History. The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
 Earth s History Date: Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
Earth s History Date: Been There, Done That What is the principle of uniformitarianism? The principle of states that geologic processes that happened in the past can be explained by current geologic processes.
TECTONIC PLATES. reflect
 reflect Has anyone ever told you to sit still? You may do as you re told, but in truth, you can never really sit still. You have probably already learned that Earth is constantly moving through space,
reflect Has anyone ever told you to sit still? You may do as you re told, but in truth, you can never really sit still. You have probably already learned that Earth is constantly moving through space,
FLOODING. Flood any relatively high stream flow overtopping the natural or artificial banks in a water system.
 CATASTROPHIC EVENTS FLOODING Flood any relatively high stream flow overtopping the natural or artificial banks in a water system. Common Causes: Long-lasting rainfall over a broad area Locally intense
CATASTROPHIC EVENTS FLOODING Flood any relatively high stream flow overtopping the natural or artificial banks in a water system. Common Causes: Long-lasting rainfall over a broad area Locally intense
Earthquakes in Ohio? Teacher Directions and Lesson
 Earthquakes in Ohio? Teacher Directions and Lesson If I say, earthquake what state do you think of? Answers will vary, but California is a likely answer. What if I asked you, Where could you live in the
Earthquakes in Ohio? Teacher Directions and Lesson If I say, earthquake what state do you think of? Answers will vary, but California is a likely answer. What if I asked you, Where could you live in the
Earthquakes. Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics. Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics. Chapter 6 Modern Earth Science. Modern Earth Science. Section 6.
 Earthquakes Chapter 6 Modern Earth Science Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics Section 6.1 Modern Earth Science Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics Earthquakes are the result of stresses in Earth s s lithosphere.
Earthquakes Chapter 6 Modern Earth Science Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics Section 6.1 Modern Earth Science Earthquakes and Plate Tectonics Earthquakes are the result of stresses in Earth s s lithosphere.
A Living Planet. The Earth Inside and Out
 A Living Planet The Earth Inside and Out Planet Earth Earth s Rotation, Revolution, and Tilt Most of Earth s energy comes from the Sun, which we call solar energy. Imagine that the Earth has an imaginary
A Living Planet The Earth Inside and Out Planet Earth Earth s Rotation, Revolution, and Tilt Most of Earth s energy comes from the Sun, which we call solar energy. Imagine that the Earth has an imaginary
SCIENCE TEST1 (VWILLIAMSSCIENCETEST1)
 Name: Date: 1. In which of the following areas would soil erosion MOST LIKELY occur if they received the same amount of rainfall? A. a forest B. flat agricultural lands C. agricultural lands on steep slopes
Name: Date: 1. In which of the following areas would soil erosion MOST LIKELY occur if they received the same amount of rainfall? A. a forest B. flat agricultural lands C. agricultural lands on steep slopes
Science in the News - Plate Tectonics 1. Story
 Science in the News - Plate Tectonics 1. Story Scientists who study the Earth tell us the continents and ocean floors are always moving. This movement sometimes can be violent, causing death and destruction.
Science in the News - Plate Tectonics 1. Story Scientists who study the Earth tell us the continents and ocean floors are always moving. This movement sometimes can be violent, causing death and destruction.
Directed Reading. Section: How Mountains Form MOUNTAIN RANGES AND SYSTEMS. Skills Worksheet
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: How Mountains Form 1. How high is Mount Everest? a. about 1980 km above sea level b. more than 8 km below sea level c. more than 8 km above sea level d. more
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: How Mountains Form 1. How high is Mount Everest? a. about 1980 km above sea level b. more than 8 km below sea level c. more than 8 km above sea level d. more
All instruction should be three-dimensional. NGSS Example Bundles. Page 1 of 14
 Middle School Topic Model Course II Bundle 3 Geologic Changes to the Earth This is the third bundle of the Middle School Topics Model Course II. Each bundle has connections to the other bundles in the
Middle School Topic Model Course II Bundle 3 Geologic Changes to the Earth This is the third bundle of the Middle School Topics Model Course II. Each bundle has connections to the other bundles in the
Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway
 Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway The Earth is more than a giant ball made up of dirt, rocks, and minerals. The Earth may look like a giant ball from when looking at it from
Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway The Earth is more than a giant ball made up of dirt, rocks, and minerals. The Earth may look like a giant ball from when looking at it from
HURRICANES AND TORNADOES
 HURRICANES AND TORNADOES The most severe weather systems are hurricanes and tornadoes. They occur in extremely low pressure systems, or cyclones, when the air spirals rapidly into the center of a low.
HURRICANES AND TORNADOES The most severe weather systems are hurricanes and tornadoes. They occur in extremely low pressure systems, or cyclones, when the air spirals rapidly into the center of a low.
Surviving Tsunamis on the Oregon Coast
 Slide 1 Surviving Tsunamis on the Oregon Coast Coastal Engineers Think Inside the Box This talk generally covers civil engineering, coastal engineering, and how engineers work within limitations to create
Slide 1 Surviving Tsunamis on the Oregon Coast Coastal Engineers Think Inside the Box This talk generally covers civil engineering, coastal engineering, and how engineers work within limitations to create
The map below shows the locations of earthquakes and volcanoes
 45 Understanding Plate Boundaries R E A D I N G The map below shows the locations of earthquakes and volcanoes on the earth s surface. Today, many of the world s most active volcanoes are located around
45 Understanding Plate Boundaries R E A D I N G The map below shows the locations of earthquakes and volcanoes on the earth s surface. Today, many of the world s most active volcanoes are located around
PSc 201 Chapter 3 Homework. Critical Thinking Questions
 PSc 201 Chapter 3 Homework Critical Thinking Questions 1. (adapted from text) Seawater is denser than fresh water. A ship moving from the Atlantic Ocean into the Great Lakes goes from seawater to fresh
PSc 201 Chapter 3 Homework Critical Thinking Questions 1. (adapted from text) Seawater is denser than fresh water. A ship moving from the Atlantic Ocean into the Great Lakes goes from seawater to fresh
UNIT 6 PLATE TECTONICS
 UNIT 6 PLATE TECTONICS CONTINENTAL DRIFT Alfred Wegner proposed the theory that the crustal plates are moving over the mantle. He argued that today s continents once formed a single landmass, called Pangaea
UNIT 6 PLATE TECTONICS CONTINENTAL DRIFT Alfred Wegner proposed the theory that the crustal plates are moving over the mantle. He argued that today s continents once formed a single landmass, called Pangaea
Location Option Details. 1. Florida
 1. Florida Florida has the smallest number of earthquaes in the United States. Florida is the U.S. location where hurricanes are most frequent. Of the six deadliest hurricanes to hit the continental U.S.,
1. Florida Florida has the smallest number of earthquaes in the United States. Florida is the U.S. location where hurricanes are most frequent. Of the six deadliest hurricanes to hit the continental U.S.,
Section 1: The Geosphere
 Section 1: The Geosphere Preview Classroom Catalyst Objectives The Earth as a System Discovering Earth s Interior The Composition of the Earth The Structure of the Earth Plate Tectonics Section 1: The
Section 1: The Geosphere Preview Classroom Catalyst Objectives The Earth as a System Discovering Earth s Interior The Composition of the Earth The Structure of the Earth Plate Tectonics Section 1: The
9.3. Earthquakes. Earthquakes at Divergent Boundaries
 9.3 Earthquakes Preview the headings on these two pages. What can you say about where earthquakes occur? As the plates that make up Earth s crust move, the rough edges lock together. Over time, pressure
9.3 Earthquakes Preview the headings on these two pages. What can you say about where earthquakes occur? As the plates that make up Earth s crust move, the rough edges lock together. Over time, pressure
Finding Fault with Food or Modeling Plate Movement
 Finding Fault with Food or Modeling Plate Movement Objective: Use models to describe how tectonic plates cause major geological events such as; ocean basins, earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain building.
Finding Fault with Food or Modeling Plate Movement Objective: Use models to describe how tectonic plates cause major geological events such as; ocean basins, earthquakes, volcanoes, and mountain building.
LAB 7. Lab 7. Formation of Geologic Features: How Can We Explain the Growth of the Hawaiian Archipelago Over the Past 100 Million Years?
 LAB 7 Lab Handout Lab 7. Formation of Geologic Features: How Can We Explain the Growth of the Hawaiian Archipelago Over the Past 100 Million Years? Introduction Scientists use the theory of plate tectonics
LAB 7 Lab Handout Lab 7. Formation of Geologic Features: How Can We Explain the Growth of the Hawaiian Archipelago Over the Past 100 Million Years? Introduction Scientists use the theory of plate tectonics
Exploring Geography. Chapter 1
 Exploring Geography Chapter 1 The Study of Geography Geography is the study of where people, places, and things are located and how they relate to each other. Greek meaning writing about or describing
Exploring Geography Chapter 1 The Study of Geography Geography is the study of where people, places, and things are located and how they relate to each other. Greek meaning writing about or describing
