Impact Events in Earth History: The Cretaceous-Paleogene Boundary Ejecta Layer and its Source Crater at Chicxulub
|
|
|
- Sheryl Fisher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Impact Events in Earth History: The Cretaceous-Paleogene Boundary Ejecta Layer and its Source Crater at Chicxulub Christian Koeberl Dept. of Lithospheric Research, Univ. Vienna, 1090 Vienna, Austria & Natural History Museum, Burgring 7, A-1010 Vienna, Austria
2 Earth is constantly accreting extraterrestrial material. Total mass of extraterrestrial objects that strike the Earth is called meteorite flux. This flux is at present around 10 7 to 10 9 kg/year. Much of this material comprises dustsized objects called micrometeorites. On occasion, there are catastrophic accretion events cratering.
3
4
5
6 Orbits of known asteroids >1 km in diameter (yellow are earth-orbit crossing)
7
8
9 Early Earth dominated by impacts
10 Later (Early Archean) Impacts: Early record of impact on the Earth is limited and circumstantial First real rock record of impact events about 400 to 500 million years after end of the LHB Distal(?) ejecta layers - spherule layers in the ~3.4 Ga Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa Interpreted as the result of large asteroid or comet impacts onto the early Earth
11
12 Earliest Impact Craters Preserved on Earth Vredefort structure The oldest 2023±4 Ma we (close have to Johannesburg) The Vredefort Dome is an ~80 km wide relict of the central uplift of a complex crater (D= km); high-graded late Archean-Paleoproterozoic gneisses; variety of impact-related features (shatter cones, coesite, stishovite, PDFs, impact melt breccias) Absence of a crater and fallback breccias suggest that intensive erosion has taken place (5-10m of post-impact deposits were removed); no ejecta have been found yet Sudbury structure 1850±3 Ma (close to Ontario) Only very recently (2005) impact ejecta layers km from the impact site have been found A spherule layer in Greenland which has an age similar to of both of these craters ( Ga) was found in 2001 and could represent distal ejecta from either of two impacts (new Cr isotope data indicate a meteoritic component & thus a link to Vredefort. Also at Karelia (Russia)
13 Impact Craters on Earth
14 Today: The importance of impact cratering on terrestrial planets is obvious from the abundance of craters on their surfaces In the 1970s: Only about 50 impact craters recognized on Earth; studies of impact craters and shock metamorphism mostly restricted to few mineralogists, petrologists and cosmochemists who worked on lunar rocks; impact cratering not part of any geology curriculum
15 Torricella KT section, 1979 Luis and Walter Alvarez at Gubbio
16
17 There s nothing like discovering the smoking gun.
18 Impact evidence interelement ratios of the PGEs in K-T boundary clay samples very similar to values observed in chondritic meteorites osmium- and Cr-isotopic studies of the K-T boundary provide further evidence of an extraterrestrial component later Os and Cr-isotope data indicated a carbonaceous chondritic composition of the impactor K-T boundary locations around the world show evidence for global wildfires in the form of a charcoal and soot layer that coincides with the Ir-rich layer
19 Distinct Os and Cr isotopic composition: Evidence for extraterrestrial components
20 Shocked feldspar Shocked quartz
21 Impact evidence (continued): shocked minerals (including shocked quatz and shocked zircon) impact glass (some fresh, some devitrified) impact-derived diamonds spinel (spinel at the K-T boundary can be used as an event marker, as it shows an abundance peak similar to that observed for the PGEs)
22
23
24 At terrestrial sections (e.g., Western Interior of North America) the K-T boundary consists of two layers: lower kaolinitic (melt ejecta) layer (altered distal impact ejecta deposit) upper smectitic (fireball) layer (with shocked minerals, high-nickel magnesioferrite crystals, and high amount of iridium) --- originated from a cloud of vaporized bolide and entrained target material at some sites, the lower and upper boundary layers were deposited in a coal swamp, interbedded with or overlain by coal or impure coal
25
26 Chicxulub Impact Structure, Mexico ca. 200 km diameter, 65 Ma is the K-T boundary impact crater: Distribution of ejecta led to Chicxulub location Geochemistry (isotopic composition) of ejecta identical to melt rock composition; ejecta mineralogy fits with source region Zircon isotopics in ejecta and in melt rocks the same Largest crater during past several 100 Ma (similar crater statistics on Venus); two craters implausible; need two ejecta layers High-resolution and quantitative planktic foraminiferal biostratigraphy of ejecta
27
28 Evidence Correlating Chicxulub with K/Pg Boundary Schulte et al., Science, 2010 K/Pg boundary sites show a distinct ejecta distribution pattern related to distance from the Chicxulub crater. 1 to >80-m-thick ejecta-rich deposits are present in the surrounding Central American region. In the NW Gulf of Mexico region the boundary is indicative of tsunamis and gravity flows km distances the layer is 2 to 10-cm-thick with spherules and shocked minerals. Distal sections 2 to 5-mm-thick clay rich in impact ejecta material and iridium.
29 IODP EXPEDITION 364 Chicxulub K-Pg Impact Crater
30 IODP EXPEDITION 364 Chicxulub K-Pg Impact Crater Drill site is located at ~30 km off the coast of the Yucatan peninsula (Mexico). (Hand, Science, 2016)
31 IODP EXPEDITION 364 Chicxulub K-Pg Impact Crater Coring completed! Coring was completed on May 26 th to a depth of meters below sea floor. Downhole logging at the borehole (with tools used to collect data on resistivity, gamma ray, sonic velocity, magnetic susceptibility and temperature, as well as acoustic and optical images, VSP logging, etc.) was achieved on May 28 th.
32 IODP EXPEDITION 364 Chicxulub K-Pg Impact Crater IODP EXPEDITION 364 Chicxulub K-Pg Impact Crater
33 IODP EXPEDITION 364 Chicxulub K-Pg Impact Crater The offshore phase of Expedition 364 Chicxulub K-Pg Impact Crater is complete! Summary of IODP Expedition 364 Offshore phase: o Number of holes: 1 o Number of expedition days: 55 o Total depth drilled: m o Open hole drilled: m o Length cored: m o Length recovered: m o Recovery: 100%! o Number of core bits used: 8 o Number of cores: 303 o Number of sections: 830 o Number of samples: 1075 o Total length of open hole downhole logs: 5.8 km o Number of visitors and media: 46
34 IODP EXPEDITION 364 Chicxulub K-Pg Impact Crater A success (so far)!
35 IODP 364 PR (2016)
36 Soot effects after the impact (Bardeen et al., PNAS, 2017): after the impact: ca. 1 Mio tons soot in the atmosphere little or no sunlight reaches the surface for over a year photosynthesis is impossible and continents and oceans cool by as much as 28 C and 11 C, respectively. absorption of light by the soot heats the upper atmosphere by hundreds of degrees these high temperatures, together with a massive injection of water, which is a source of odd-hydrogen radicals, destroy the stratospheric ozone layer thus Earth s surface receives high doses of UV radiation for about a year once the soot clears, five years after the impact temperatures remain above freezing in the oceans, coastal areas, and parts of the Tropics photosynthesis is severely inhibited for the first 1 y to 2 y Freezing temperatures persist at middle latitudes for 3 y to 4 y Refugia from these effects would have been very limited
37 Soot effects after the impact (Bardeen et al., PNAS, 2017)
38 Summary The debate that followed the suggestion by Alvarez et al. (1980) finally led over the 1990s and the 2000s to a more general realization that impact cratering is an important process on the Earth as well, and not only on other planetary bodies. For the last few decades, planetary scientists, astronomers, and meteoriticists, who work with the products of impact cratering, have grown to accept impact cratering as a normal geological phenomenon, whereas another group, the paleontologists, is confounded by what appears to be an ad hoc theory about a non-existent phenomenon (Raup, in Glen, 1994, p. 147). The evidence for a large-scale impact event exactly coinciding with the K-Pg boundary/mass extinction is overwhelming Effects of the impact event were rather nasty for quite some time...
39 Thank you for your attention!
Impact Craters on Earth and in the Solar System
 Impact Craters on Earth and in the Solar System Christian KOEBERL Natural History Museum & University of Vienna, Austria The importance of impact cratering on terrestrial planets is obvious from the abundance
Impact Craters on Earth and in the Solar System Christian KOEBERL Natural History Museum & University of Vienna, Austria The importance of impact cratering on terrestrial planets is obvious from the abundance
Biodiversity Through Earth History
 Chapter 13 Biodiversity Through Earth History Underlying assumption is that the process of evolution is occurring evolution: creation of new species random mutation: genetic changes natural selection:
Chapter 13 Biodiversity Through Earth History Underlying assumption is that the process of evolution is occurring evolution: creation of new species random mutation: genetic changes natural selection:
Mass Extinctions of the Phanerozoic: The Big Five Total number of families end Ord.
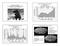 Cretaceous Calamity: The Cretaceous-Tertiary Mass Extinction (and other mass extinctions) Mass Extinctions of the Phanerozoic: The Big Five Total number of families Ord. late Dev. Perm. Tri. Cret. Mass
Cretaceous Calamity: The Cretaceous-Tertiary Mass Extinction (and other mass extinctions) Mass Extinctions of the Phanerozoic: The Big Five Total number of families Ord. late Dev. Perm. Tri. Cret. Mass
Ch. 17 Review. Life in the Cretaceous
 Ch. 17 Review Life in the Cretaceous Diversification of diatoms, planktonic forams, calcareous nannoplankton Diversification of mobile predators (especially mollusks and teleost fishes) Origin of the angiosperms
Ch. 17 Review Life in the Cretaceous Diversification of diatoms, planktonic forams, calcareous nannoplankton Diversification of mobile predators (especially mollusks and teleost fishes) Origin of the angiosperms
Philippe Claeys Earth System Sciences. Meteorite in - Dino s out
 Philippe Claeys Earth System Sciences Meteorite in - Dino s out KT Clay Lower Paleocene KT clay KT Clay KT Clay Upper Maastrichtian Contessa, Italy El Guayal, Tabasco, Mexico Raton Basin, Stevns Caravaca,
Philippe Claeys Earth System Sciences Meteorite in - Dino s out KT Clay Lower Paleocene KT clay KT Clay KT Clay Upper Maastrichtian Contessa, Italy El Guayal, Tabasco, Mexico Raton Basin, Stevns Caravaca,
Where do they come from?
 Exploring Meteorite Mysteries Lesson 7 Crater Hunters Objectives Students will: observe impact craters on Earth and other solar system bodies. discuss geologic forces that have removed most of the evidence
Exploring Meteorite Mysteries Lesson 7 Crater Hunters Objectives Students will: observe impact craters on Earth and other solar system bodies. discuss geologic forces that have removed most of the evidence
GLY August, Ms. Nelda Breedt. Fragment of extra-terrestrial material that strikes the surface of the Earth.
 Meteorite Impacts Ms. Nelda Breedt GLY 162 Environmental Geology 2 Meteorite Impacts Meteorite Fragment of extra-terrestrial material that strikes the surface of the Earth. Meteoroid Before hitting the
Meteorite Impacts Ms. Nelda Breedt GLY 162 Environmental Geology 2 Meteorite Impacts Meteorite Fragment of extra-terrestrial material that strikes the surface of the Earth. Meteoroid Before hitting the
PTYS 214 Fall Announcements. Materials from last week moved to web page. Midterm #4 next Tuesday!
 PTYS 214 Fall 2017 Announcements Materials from last week moved to web page Midterm #4 next Tuesday! 1 Previously Radiometric Dating Compare parent / daughter to determine # of half lives 14C, 40K, 238U,
PTYS 214 Fall 2017 Announcements Materials from last week moved to web page Midterm #4 next Tuesday! 1 Previously Radiometric Dating Compare parent / daughter to determine # of half lives 14C, 40K, 238U,
Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard. Earth and Space Science Level 2
 Exemplar for internal assessment resource Earth and Space Science for Achievement Standard 91188 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Earth and Space Science Level 2 This exemplar supports assessment
Exemplar for internal assessment resource Earth and Space Science for Achievement Standard 91188 Exemplar for Internal Achievement Standard Earth and Space Science Level 2 This exemplar supports assessment
PTYS 214 Spring Announcements. Midterm #4 one week from Tuesday!
 PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4 one week from Tuesday! 1 Previously Atmospheric O Respiration UV protection; O2, O3 O sources / sinks Evidence for early O history BIFs Sulfur MIF Forest fires
PTYS 214 Spring 2018 Announcements Midterm #4 one week from Tuesday! 1 Previously Atmospheric O Respiration UV protection; O2, O3 O sources / sinks Evidence for early O history BIFs Sulfur MIF Forest fires
5/3/17. Extinction of the Dinosaurs. Extinction of Dinosaurs - Causes. #40 Meteorite Impacts III - Dinosaur Extinction, Future Risk, Mitigation
 Paper Scores are posted Please check grades Web Exercise #6 LATE; was Due by 1 pm, Monday 5/1 There is a 2-point penalty for every 24-hour period the assignment is late. No Web Exercise #6 will be accepted
Paper Scores are posted Please check grades Web Exercise #6 LATE; was Due by 1 pm, Monday 5/1 There is a 2-point penalty for every 24-hour period the assignment is late. No Web Exercise #6 will be accepted
Where did all the dinosaurs go?
 Where did all the dinosaurs go? Mass extinctions Why are we asking about the dinosaurs in this book? The reason is that (as we examine in Ch. 17, due to global warming, and in Ch. 26), humanity is causing
Where did all the dinosaurs go? Mass extinctions Why are we asking about the dinosaurs in this book? The reason is that (as we examine in Ch. 17, due to global warming, and in Ch. 26), humanity is causing
What is the K/T boundary?
 What is the K/T boundary? Subject: Geology Grade Level: 9 th 11 th Rational or Purpose: This lesson is designed to let students take a more in depth look at the K/T boundary, and see if there are any clues
What is the K/T boundary? Subject: Geology Grade Level: 9 th 11 th Rational or Purpose: This lesson is designed to let students take a more in depth look at the K/T boundary, and see if there are any clues
Lunar Crater Activity - Teacher Pages
 Adapted from: http://www.nasa.gov/pdf/180572main_etm.impact.craters.pdf I took the activity and simplified it so that there was just one independent variable: the drop height, and one dependent variable:
Adapted from: http://www.nasa.gov/pdf/180572main_etm.impact.craters.pdf I took the activity and simplified it so that there was just one independent variable: the drop height, and one dependent variable:
The impact flux (hazard?) on Earth
 The impact flux (hazard?) on Earth The young Earth and Moon suffered the same heavy bombardment early in the Solar System Only the Moon preserves the record of this The lunar record indicates roughly constant
The impact flux (hazard?) on Earth The young Earth and Moon suffered the same heavy bombardment early in the Solar System Only the Moon preserves the record of this The lunar record indicates roughly constant
The Good Earth: Introduction to Earth Science 3rd Edition Test Bank Chapter 03 - Near-Earth Objects
 Test Bank The Good Earth: Introduction to Earth Science 3rd Edition McConnell Steer Completed download: https://testbankreal.com/download/good-earth-introduction-earth-science- 3rd-edition-test-bank-mcconnell-steer/
Test Bank The Good Earth: Introduction to Earth Science 3rd Edition McConnell Steer Completed download: https://testbankreal.com/download/good-earth-introduction-earth-science- 3rd-edition-test-bank-mcconnell-steer/
What we ll learn today:!
 Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 17: Age Dating and Earth History Read: Chapter 12-13 Homework #14 What we ll learn today:! 1. 1. Define the concept of half-life and absolute age dating! 2. 2. List the
Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 17: Age Dating and Earth History Read: Chapter 12-13 Homework #14 What we ll learn today:! 1. 1. Define the concept of half-life and absolute age dating! 2. 2. List the
Origin of terrestrial life: in situ hypothesis. The terrestrial and astronomical context for the emergence of life
 Origin of terrestrial life: in situ hypothesis The terrestrial and astronomical context for the emergence of life Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo To contrain the chronology and physical/chemical
Origin of terrestrial life: in situ hypothesis The terrestrial and astronomical context for the emergence of life Planets and Astrobiology (2016-2017) G. Vladilo To contrain the chronology and physical/chemical
Biodiversity Through Earth History. What does the fossil record tell us about past climates and past events?
 Biodiversity Through Earth History What does the fossil record tell us about past climates and past events? Useful terminology: Evolution Natural Selection Adaptation Extinction Taxonomy Logistic Growth
Biodiversity Through Earth History What does the fossil record tell us about past climates and past events? Useful terminology: Evolution Natural Selection Adaptation Extinction Taxonomy Logistic Growth
Teacher Background. Impact! Down to Earth KS 3&4
 Teacher Background Impact! Impact! - Teacher Background- 2 Meteorites What Are They, and Where Do They Come From? Meteorites are rocks from space that have passed through the atmosphere and landed on the
Teacher Background Impact! Impact! - Teacher Background- 2 Meteorites What Are They, and Where Do They Come From? Meteorites are rocks from space that have passed through the atmosphere and landed on the
Terrestrial Planets: The Earth as a Planet
 Terrestrial Planets: The Earth as a Planet In today s class, we want to look at those characteristics of the Earth that are also important in our understanding of the other terrestrial planets. This is
Terrestrial Planets: The Earth as a Planet In today s class, we want to look at those characteristics of the Earth that are also important in our understanding of the other terrestrial planets. This is
Finding Impact Craters with Landsat
 Name Finding Impact Craters with Landsat Known Effects of Impact Events When an object from space hits the Earth, here is what can happen. There's a huge explosion. The impact makes a big hole or crater
Name Finding Impact Craters with Landsat Known Effects of Impact Events When an object from space hits the Earth, here is what can happen. There's a huge explosion. The impact makes a big hole or crater
What Next? Current Problems and Future Investigations
 What Next? Current Problems and Future Investigations 101 What Next? Current Problems and Future Investigations > 8.1. IDENTIFICATION OF NEW IMPACT STRUCTURES Despite the apparent abundance of impact structures
What Next? Current Problems and Future Investigations 101 What Next? Current Problems and Future Investigations > 8.1. IDENTIFICATION OF NEW IMPACT STRUCTURES Despite the apparent abundance of impact structures
The Rock that Changed the World
 # 54 The Rock that Changed the World Dr. Sean Gulick May 2, 2008 Produced by and for Hot Science - Cool Talks by the Environmental Science Institute. We request that the use of these materials include
# 54 The Rock that Changed the World Dr. Sean Gulick May 2, 2008 Produced by and for Hot Science - Cool Talks by the Environmental Science Institute. We request that the use of these materials include
Terrestrial Planetary Atmospheres
 Terrestrial For the first time in my life, I saw the horizon as a curved line. It was accentuated by a thin seam of dark blue light our atmosphere. Obviously this was not the ocean of air I had been told
Terrestrial For the first time in my life, I saw the horizon as a curved line. It was accentuated by a thin seam of dark blue light our atmosphere. Obviously this was not the ocean of air I had been told
Death From the Skies
 Death From the Skies Learning Objectives! Use the Titius-Bode Rule to list the planet s distances. What connects the Titius-Bode Rule to the asteroids?! How big is Ceres? How big are typical asteroids?
Death From the Skies Learning Objectives! Use the Titius-Bode Rule to list the planet s distances. What connects the Titius-Bode Rule to the asteroids?! How big is Ceres? How big are typical asteroids?
12.3 Pluto: Lone Dog No More
 12.3 Pluto: Lone Dog No More Our goals for learning: How big can a comet be? What are the large objects of the Kuiper belt like? Are Pluto and Eris planets? How big can a comet be? Pluto s Orbit Pluto
12.3 Pluto: Lone Dog No More Our goals for learning: How big can a comet be? What are the large objects of the Kuiper belt like? Are Pluto and Eris planets? How big can a comet be? Pluto s Orbit Pluto
Meteorites, Impacts, and Mass Extinction
 Page 1 of 13 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Meteorites, Impacts, and Mass Extinction This document last updated on 27-Apr-2018 Meteorites On February 15, 2013 a meteor
Page 1 of 13 EENS 3050 Tulane University Natural Disasters Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Meteorites, Impacts, and Mass Extinction This document last updated on 27-Apr-2018 Meteorites On February 15, 2013 a meteor
Impact Craters Teacher Page Purpose
 1 of 5 2008-05-01 12:15 PM Hawai'i Space Grant College, Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology, University of Hawai'i, 1996 Background Impact Craters Teacher Page Purpose To determine the factors
1 of 5 2008-05-01 12:15 PM Hawai'i Space Grant College, Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology, University of Hawai'i, 1996 Background Impact Craters Teacher Page Purpose To determine the factors
Section 7. Reading the Geologic History of Your Community. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 7 Reading the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section,
Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 7 Reading the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section,
Arctic Impacts. Details. Materials. Learning Resources
 Details Learning Resources Completion Time: About one period Permission: Download, Share, and Remix Arctic Impacts Overview Lake El gygytgyn (67. o N, 17 o E) is one of the best preserved large asteroid
Details Learning Resources Completion Time: About one period Permission: Download, Share, and Remix Arctic Impacts Overview Lake El gygytgyn (67. o N, 17 o E) is one of the best preserved large asteroid
Terrestrial World Surfaces
 1 Terrestrial World Surfaces Solid rocky surfaces shaped (to varying degrees) by: Impact cratering Volcanism Tectonics (gross movement of surface by interior forces) Erosion (by impacts or by weather)
1 Terrestrial World Surfaces Solid rocky surfaces shaped (to varying degrees) by: Impact cratering Volcanism Tectonics (gross movement of surface by interior forces) Erosion (by impacts or by weather)
The Official CA State Science Education Standards for Earth Science K 8
 The Official CA State Science Education Standards for Earth Science K 8 Kindergarten The Earth is composed of land, air and water. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. characteristics
The Official CA State Science Education Standards for Earth Science K 8 Kindergarten The Earth is composed of land, air and water. As a basis for understanding this concept, students know: a. characteristics
Lab 5: An Investigation of Meteorites Geology 202: Earth s Interior
 Lab 5: An Investigation of Meteorites Geology 202: Earth s Interior Asteroids and Meteorites: What is the difference between asteroids and meteorites? Asteroids are rocky and metallic objects that orbit
Lab 5: An Investigation of Meteorites Geology 202: Earth s Interior Asteroids and Meteorites: What is the difference between asteroids and meteorites? Asteroids are rocky and metallic objects that orbit
At the beginning of the solar system, impacts and collisions were
 Impact Processes on the Early Earth Christian Koeberl 1 At the beginning of the solar system, impacts and collisions were dominant processes. After an early collision that may have led to the formation
Impact Processes on the Early Earth Christian Koeberl 1 At the beginning of the solar system, impacts and collisions were dominant processes. After an early collision that may have led to the formation
Comet Science Goals II
 Comet Science Goals II {questions for goals} Don Brownlee Did the events postulated by the Nice Hypothesis really happen? Were there wide-spread solar system wide impact events that were coeval with the
Comet Science Goals II {questions for goals} Don Brownlee Did the events postulated by the Nice Hypothesis really happen? Were there wide-spread solar system wide impact events that were coeval with the
Hypervelocity Impacts of Macroscopic Bodies
 154 Chapter 5 Hypervelocity Impacts of Macroscopic Bodies 5.1 Asteroid impacts on the Earth Although the Earth is constantly bombarded with small meteorites and micrometeorites, large impacts are (thankfully)
154 Chapter 5 Hypervelocity Impacts of Macroscopic Bodies 5.1 Asteroid impacts on the Earth Although the Earth is constantly bombarded with small meteorites and micrometeorites, large impacts are (thankfully)
Phys 214. Planets and Life
 Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 10. Geology and life. Part 1 (Page 99-123)
Phys 214. Planets and Life Dr. Cristina Buzea Department of Physics Room 259 E-mail: cristi@physics.queensu.ca (Please use PHYS214 in e-mail subject) Lecture 10. Geology and life. Part 1 (Page 99-123)
K-T Extinction - Reading
 The End of the Dinosaurs: The K-T extinction (This essay, written in 1999, is a chapter from the book History of Life, published by Blackwell Science, Boston, Massachusetts, 2000. Richard Cowen. You may
The End of the Dinosaurs: The K-T extinction (This essay, written in 1999, is a chapter from the book History of Life, published by Blackwell Science, Boston, Massachusetts, 2000. Richard Cowen. You may
THE PLANETARY SCIENTIST'S COMPANION
 THE PLANETARY SCIENTIST'S COMPANION Katharina Lodders Bruce Fegley, Jr. New York Oxford Oxford University Press 1998 Contents 1 Technical data Table 1.1 The Greek alphabet 1 Table 1.2 Prefixes used with
THE PLANETARY SCIENTIST'S COMPANION Katharina Lodders Bruce Fegley, Jr. New York Oxford Oxford University Press 1998 Contents 1 Technical data Table 1.1 The Greek alphabet 1 Table 1.2 Prefixes used with
Origin of Earth s Water When Earth first formed it was so hot that the original water would be lost to space Water added later by comets and/or
 Origin of Earth s Water When Earth first formed it was so hot that the original water would be lost to space Water added later by comets and/or asteroids?? Some water (H 2 +O) formed in Protoplanetary
Origin of Earth s Water When Earth first formed it was so hot that the original water would be lost to space Water added later by comets and/or asteroids?? Some water (H 2 +O) formed in Protoplanetary
page - Lab 13 - Introduction to the Geology of the Terrestrial Planets
 page - Lab 13 - Introduction to the Geology of the Terrestrial Planets Introduction There are two main families of planets in our solar system: the inner Terrestrial planets (Earth, Mercury, Venus, and
page - Lab 13 - Introduction to the Geology of the Terrestrial Planets Introduction There are two main families of planets in our solar system: the inner Terrestrial planets (Earth, Mercury, Venus, and
Questions. 1. How likely is in your estimate the chances for a major nuclear war within the next decade? Please justify your opinion!
 Questions 1. How likely is in your estimate the chances for a major nuclear war within the next decade? Please justify your opinion! 2. What is the dose the average South Bend citizen would receive from
Questions 1. How likely is in your estimate the chances for a major nuclear war within the next decade? Please justify your opinion! 2. What is the dose the average South Bend citizen would receive from
Today. Events. The Little Things. Impacts & extinctions. Dwarf Planets. Homework 5 DUE
 Today The Little Things Impacts & extinctions Dwarf Planets Events Homework 5 DUE Facts About Impacts on Earth Asteroids and comets have hit the Earth. A major impact is only a matter of time: not IF but
Today The Little Things Impacts & extinctions Dwarf Planets Events Homework 5 DUE Facts About Impacts on Earth Asteroids and comets have hit the Earth. A major impact is only a matter of time: not IF but
Homework #3 is due Friday at 11:50am! Nighttime observing has 10 more nights. Check the webpage. 1 st exam is October 10 th 2 weeks from Friday.
 Homework #3 is due Friday at 11:50am! Nighttime observing has 10 more nights. Check the webpage. 1 st exam is October 10 th 2 weeks from Friday. Outline Back to Atoms for fun The Earth as a Planet. magnetic
Homework #3 is due Friday at 11:50am! Nighttime observing has 10 more nights. Check the webpage. 1 st exam is October 10 th 2 weeks from Friday. Outline Back to Atoms for fun The Earth as a Planet. magnetic
Outline. Atoms in the Solar System. Atoms in the Earth. Back to Atoms for fun The Earth as a Planet. Homework #3 is due Friday at 11:50am!
 Homework #3 is due Friday at 11:50am! Nighttime observing has more nights. Check the webpage. 1 st exam is October th 2 weeks from Friday. Outline Back to Atoms for fun The Earth as a Planet. magnetic
Homework #3 is due Friday at 11:50am! Nighttime observing has more nights. Check the webpage. 1 st exam is October th 2 weeks from Friday. Outline Back to Atoms for fun The Earth as a Planet. magnetic
Where we are now. The Moon Chapters 8.2, 9. Topography. Outline
 Where we are now Introduction Little things - comets, asteroids, KBOs Slightly larger things - Moon Larger still - Terrestrial planets Really large - Jovian planets Jovian moons + Pluto Extrasolar Planets
Where we are now Introduction Little things - comets, asteroids, KBOs Slightly larger things - Moon Larger still - Terrestrial planets Really large - Jovian planets Jovian moons + Pluto Extrasolar Planets
Planet Earth. Our Home APOD
 Planet Earth Our Home APOD 1 Earth a highly evolved planet = altered dramatically since formation, due to flow of energy from interior to surface 2 Planet Earth Facts diameter (equator) 12,756 km radius
Planet Earth Our Home APOD 1 Earth a highly evolved planet = altered dramatically since formation, due to flow of energy from interior to surface 2 Planet Earth Facts diameter (equator) 12,756 km radius
Importance of Solar System Objects discussed thus far. Interiors of Terrestrial Planets. The Terrestrial Planets
 Importance of Solar System Objects discussed thus far Interiors of Terrestrial Planets Chapter 9 Sun: Major source of heat for the surfaces of planets Asteroids: Provide possible insight to the composition
Importance of Solar System Objects discussed thus far Interiors of Terrestrial Planets Chapter 9 Sun: Major source of heat for the surfaces of planets Asteroids: Provide possible insight to the composition
Chapter 20 Earth: The Standard of Comparative Planetology
 Chapter 20 Earth: The Standard of Comparative Planetology Guidepost In the preceding chapter, you learned how our solar system formed as a by-product of the formation of the sun. You also saw how distance
Chapter 20 Earth: The Standard of Comparative Planetology Guidepost In the preceding chapter, you learned how our solar system formed as a by-product of the formation of the sun. You also saw how distance
Creation Answers. In this issue...! Craters and Noah s Flood! Climate Change and. Who does this newsletter? Extinctions! ICR Opens Dallas Office
 Creation Answers Creation Education Materials, P.O. Box 153402, Irving, TX 75015-3402 Who does this newsletter? This newsletter is produced by Wayne Spencer on a Quarterly basis. Its purpose is to bring
Creation Answers Creation Education Materials, P.O. Box 153402, Irving, TX 75015-3402 Who does this newsletter? This newsletter is produced by Wayne Spencer on a Quarterly basis. Its purpose is to bring
Earth. Physical Properties of Earth kg. Average Density g/cm 2. Surface Gravity 9.8 m/s o C to 50 o C. Surface Temperature
 Earth Physical Properties of Earth Equatorial Diameter Mass 12,756 km 5.976 10 24 kg Average Density 5.497 g/cm 2 Surface Gravity 9.8 m/s 2 Escape Velocity Surface Temperature 11.2 km/s -50 o C to 50 o
Earth Physical Properties of Earth Equatorial Diameter Mass 12,756 km 5.976 10 24 kg Average Density 5.497 g/cm 2 Surface Gravity 9.8 m/s 2 Escape Velocity Surface Temperature 11.2 km/s -50 o C to 50 o
ERSC 1P92 Extreme Earth. Example questions for the midterm test.
 ERSC 1P92 Extreme Earth Example questions for the midterm test. The following provides example questions from each of the 4 sections that have been covered in the course prior to the midterm test. These
ERSC 1P92 Extreme Earth Example questions for the midterm test. The following provides example questions from each of the 4 sections that have been covered in the course prior to the midterm test. These
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 ASTRO 102/104 Prelim 2 Name Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) This is version E of the exam. Please fill in (E). A) This
ASTRO 102/104 Prelim 2 Name Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) This is version E of the exam. Please fill in (E). A) This
In class, Wednesday Oct 25. Please wait outside AT BACK until told to enter the room. Must write IN PEN. Non programming calculators allowed (and
 Midterm material In class, Wednesday Oct 25. Please wait outside AT BACK until told to enter the room. Must write IN PEN. Non programming calculators allowed (and required) No notes or hats. Formulae provided
Midterm material In class, Wednesday Oct 25. Please wait outside AT BACK until told to enter the room. Must write IN PEN. Non programming calculators allowed (and required) No notes or hats. Formulae provided
The Curious Tale of Asteroid Hermes
 Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the passage and diagram below. The diagram shows the orbits of the four inner planets and the asteroid Hermes around the Sun. Point A represents a position
Base your answers to questions 1 through 4 on the passage and diagram below. The diagram shows the orbits of the four inner planets and the asteroid Hermes around the Sun. Point A represents a position
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 ASTRO 102/104 Prelim 2 Name Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) This is version B of the exam. Please fill in (B). A) This
ASTRO 102/104 Prelim 2 Name Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) This is version B of the exam. Please fill in (B). A) This
The Solar System. Earth as a Planet
 The Solar System Earth as a Planet Earth s Interior Core: Highest density; nickel and iron Mantle: Moderate density; silicon, oxygen, etc. Crust: Lowest density; granite, basalt, etc. Differentiation Gravity
The Solar System Earth as a Planet Earth s Interior Core: Highest density; nickel and iron Mantle: Moderate density; silicon, oxygen, etc. Crust: Lowest density; granite, basalt, etc. Differentiation Gravity
Climate Change. But first... Throughout the Solar System. Lecture 11: Earth as a Planet. Earth as a Planet. PDFs for Lectures 7, 8, and 11 are posted
 Climate Change Throughout the Solar System Lecture 11: Earth as a Planet Astro 202 Prof. Jim Bell (jfb8@cornell.edu) Spring 2008 But first... PDFs for Lectures 7, 8, and 11 are posted Paper 3 is due at
Climate Change Throughout the Solar System Lecture 11: Earth as a Planet Astro 202 Prof. Jim Bell (jfb8@cornell.edu) Spring 2008 But first... PDFs for Lectures 7, 8, and 11 are posted Paper 3 is due at
Scholarship 2015 Earth and Space Science
 S 93104R Scholarship 2015 Earth and Space Science 2.00 p.m. Tuesday 1 December 2015 RESOURCE BOOKLET Refer to this booklet to answer the questions for Scholarship Earth and Space Science 93104. Check that
S 93104R Scholarship 2015 Earth and Space Science 2.00 p.m. Tuesday 1 December 2015 RESOURCE BOOKLET Refer to this booklet to answer the questions for Scholarship Earth and Space Science 93104. Check that
Chapter 25: The Origin and Evolutionary History of Life on Earth
 Chapter 25: The Origin and Evolutionary History of Life on Earth Chemical conditions of the early Earth A model for the first cells First life Life changes the planet: oxygenating Earth s oceans and atmosphere
Chapter 25: The Origin and Evolutionary History of Life on Earth Chemical conditions of the early Earth A model for the first cells First life Life changes the planet: oxygenating Earth s oceans and atmosphere
Laboratory 15: Meteor Impact
 Laboratory 15: Meteor Impact Figure 1: Meteor Crater Meteor Crater was formed about 50,000 years ago by a massive meteorite striking the Earth. There were no humans living in North America at that time:
Laboratory 15: Meteor Impact Figure 1: Meteor Crater Meteor Crater was formed about 50,000 years ago by a massive meteorite striking the Earth. There were no humans living in North America at that time:
The End of the World...
 The End of the World... as we know it. Impacts in the Inner Solar System Collisions have played a key role in the past formation of planets by accretion fragmentation (formation of the Moon) sustained
The End of the World... as we know it. Impacts in the Inner Solar System Collisions have played a key role in the past formation of planets by accretion fragmentation (formation of the Moon) sustained
SEIS on School :
 SEIS on Mars @ School : EGU GIFT 2016 : An example of hands-on activity focused on martian meteorite craters: for teachers and for their pupils Diane Carrer Science teacher : Biology & geology teacher
SEIS on Mars @ School : EGU GIFT 2016 : An example of hands-on activity focused on martian meteorite craters: for teachers and for their pupils Diane Carrer Science teacher : Biology & geology teacher
GEOL 02: Historical Geology Lab 12: The Mesozoic Dies
 Name: Date: This assignment accompanies the video The Day the Mesozoic Died. This was adopted from BioInteractive. INTRODUCTION Dinosaurs roamed Earth for over 150 million years before they went extinct.
Name: Date: This assignment accompanies the video The Day the Mesozoic Died. This was adopted from BioInteractive. INTRODUCTION Dinosaurs roamed Earth for over 150 million years before they went extinct.
Be Approximately 4.6 Billions Years Based On The Data From
 The Age Of The Solar System Is Believed To Be Approximately 4.6 Billions Years Based On The Data From 1. The iron in our solar system was created from smaller mass atomic nuclei in. The age of the solar
The Age Of The Solar System Is Believed To Be Approximately 4.6 Billions Years Based On The Data From 1. The iron in our solar system was created from smaller mass atomic nuclei in. The age of the solar
FOLLOWING THE TRAIL OF EVIDENCE
 INTRODUCTION FOLLOWING THE TRAIL OF EVIDENCE Dinosaurs roamed Earth for over 150 million years before they went extinct. Scientists have proposed a number of hypotheses to explain the mass extinction,
INTRODUCTION FOLLOWING THE TRAIL OF EVIDENCE Dinosaurs roamed Earth for over 150 million years before they went extinct. Scientists have proposed a number of hypotheses to explain the mass extinction,
Credit: Adapted from NASA/JPL Caltech
 Credit: Adapted from NASA/JPL Caltech Three Puzzling Ice Age Mysteries 1. Sudden return of Ice Age temperatures 12,800 years ago After about 1400 years of warming, temperatures plunged 10 C (50 F) That
Credit: Adapted from NASA/JPL Caltech Three Puzzling Ice Age Mysteries 1. Sudden return of Ice Age temperatures 12,800 years ago After about 1400 years of warming, temperatures plunged 10 C (50 F) That
The History of the Earth
 The History of the Earth We have talked about how the universe and sun formed, but what about the planets and moons? Review: Origin of the Universe The universe began about 13.7 billion years ago The Big
The History of the Earth We have talked about how the universe and sun formed, but what about the planets and moons? Review: Origin of the Universe The universe began about 13.7 billion years ago The Big
Lecture 18 Paleoceanography 2
 Lecture 18 Paleoceanography 2 May 26, 2010 Trend and Events Climatic evolution in Tertiary Overall drop of sea level General cooling (Figure 9-11) High latitude (deep-water) feature Two major step Middle
Lecture 18 Paleoceanography 2 May 26, 2010 Trend and Events Climatic evolution in Tertiary Overall drop of sea level General cooling (Figure 9-11) High latitude (deep-water) feature Two major step Middle
Vagabonds of the Solar System
 Vagabonds of the Solar System Guiding Questions 1. How and why were the asteroids first discovered? 2. Why didn t the asteroids coalesce to form a single planet? 3. What do asteroids look like? 4. How
Vagabonds of the Solar System Guiding Questions 1. How and why were the asteroids first discovered? 2. Why didn t the asteroids coalesce to form a single planet? 3. What do asteroids look like? 4. How
12/3/14. Guiding Questions. Vagabonds of the Solar System. A search for a planet between Mars and Jupiter led to the discovery of asteroids
 Guiding Questions Vagabonds of the Solar System 1. How and why were the asteroids first discovered? 2. Why didn t the asteroids coalesce to form a single planet? 3. What do asteroids look like? 4. How
Guiding Questions Vagabonds of the Solar System 1. How and why were the asteroids first discovered? 2. Why didn t the asteroids coalesce to form a single planet? 3. What do asteroids look like? 4. How
Hydrogen on Venus, μdiamonds on Earth and Valhalla on Callisto: signposts of ******s in the Solar System
 Hydrogen on Venus, μdiamonds on Earth and Valhalla on Callisto: signposts of ******s in the Solar System José Antonio Caballero Centro de Astrobiología (CSIC-INTA) CAB-ESAC μseminars Atmospheric mass ratio
Hydrogen on Venus, μdiamonds on Earth and Valhalla on Callisto: signposts of ******s in the Solar System José Antonio Caballero Centro de Astrobiología (CSIC-INTA) CAB-ESAC μseminars Atmospheric mass ratio
Differentiation of planetary interiors. Rocky Planets Interiors and surface geophysics
 Differentiation of planetary interiors Rocky Planets Interiors and surface geophysics Process of separation of internal planetary layers that takes place as a result of the physical and chemical properties
Differentiation of planetary interiors Rocky Planets Interiors and surface geophysics Process of separation of internal planetary layers that takes place as a result of the physical and chemical properties
The performance expectation above was developed using the following elements from the NRC document A Framework for K-12 Science Education:
 MS-ESS2-1 Earth's Systems Students who demonstrate understanding can: MS-ESS2-1. Develop a model to describe the cycling of Earth's materials and the flow of energy that drives this process. [Clarification
MS-ESS2-1 Earth's Systems Students who demonstrate understanding can: MS-ESS2-1. Develop a model to describe the cycling of Earth's materials and the flow of energy that drives this process. [Clarification
IX Life on Earth.
 IX Life on Earth http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 9.0 Introduction Life exists on the surface layers of the Earth. We cannot consider life and the planet separately: they interact with one
IX Life on Earth http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 9.0 Introduction Life exists on the surface layers of the Earth. We cannot consider life and the planet separately: they interact with one
Class Exercise. Today s Class. Overview of Mercury. Terrestrial Planet Interiors. Today s Class: Mercury & Venus
 Today s Class: Mercury & Venus Homework: Further reading on Venus for next class Sections 10.1 and 10.5 in Cosmic Perspective. Space in the News: 'Frankenstein' Galaxy Surprises Astronomers Presenter:
Today s Class: Mercury & Venus Homework: Further reading on Venus for next class Sections 10.1 and 10.5 in Cosmic Perspective. Space in the News: 'Frankenstein' Galaxy Surprises Astronomers Presenter:
Use models to describe the sun s place in space in relation to the Milky Way Galaxy and the distribution of galaxy clusters in the universe.
 The Milky Way Galaxy consists of more than two hundred billion stars, the sun being one of them, and is one of hundreds of billions of galaxies in the known universe. s of the formation and structure of
The Milky Way Galaxy consists of more than two hundred billion stars, the sun being one of them, and is one of hundreds of billions of galaxies in the known universe. s of the formation and structure of
PHYSICS OF ASTROPHSYICS - Energy.
 PHYSICS OF ASTROPHSYICS - Energy http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ ENERGY Result of a force acting through a distance. units = erg = dyne cm i.e., force x distance = gm cm 2 /sec 2 Two types: kinetic - energy
PHYSICS OF ASTROPHSYICS - Energy http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ ENERGY Result of a force acting through a distance. units = erg = dyne cm i.e., force x distance = gm cm 2 /sec 2 Two types: kinetic - energy
What is Nuclear Winter?
 Nuclear Winter What is Nuclear Winter? Prediction by some scientists that smoke and debris rising from massive fires of a nuclear war could block sunlight for weeks or months, cooling the earth's surface
Nuclear Winter What is Nuclear Winter? Prediction by some scientists that smoke and debris rising from massive fires of a nuclear war could block sunlight for weeks or months, cooling the earth's surface
Differentiation 2: mantle, crust OUTLINE
 Differentiation 2: mantle, crust OUTLINE Reading this week: Should have been White Ch 10 and 11!! 7- Nov Differentiation of the Earth, Core formation W 10.6.6, 11.4 9- Nov Moon, crust, mantle, atmosphere
Differentiation 2: mantle, crust OUTLINE Reading this week: Should have been White Ch 10 and 11!! 7- Nov Differentiation of the Earth, Core formation W 10.6.6, 11.4 9- Nov Moon, crust, mantle, atmosphere
The end-cretaceous mass extinction and the Chicxulub impact
 The end-cretaceous mass extinction and the Chicxulub impact by Rebecca Teed, Wright State University, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- Noncommercial-Share Alike 4.0 License. What Do We Know
The end-cretaceous mass extinction and the Chicxulub impact by Rebecca Teed, Wright State University, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution- Noncommercial-Share Alike 4.0 License. What Do We Know
Meteorite impact structures: the good and the bad
 Feature Meteorite impact structures: the good and the bad Meteorite impact structures are found on all planetary bodies in the Solar System with a solid surface. On many planets, impact craters are the
Feature Meteorite impact structures: the good and the bad Meteorite impact structures are found on all planetary bodies in the Solar System with a solid surface. On many planets, impact craters are the
PHYSICS OF ASTROPHSYICS - Energy.
 PHYSICS OF ASTROPHSYICS - Energy http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ ENERGY Result of a force acting through a distance. units = erg = dyne cm i.e., force x distance = gm cm 2 /sec 2 Two types: kinetic - energy
PHYSICS OF ASTROPHSYICS - Energy http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ ENERGY Result of a force acting through a distance. units = erg = dyne cm i.e., force x distance = gm cm 2 /sec 2 Two types: kinetic - energy
Chapter 11. The Archean Era of Precambrian Time
 Chapter 11 The Archean Era of Precambrian Time 1 Guiding Questions When and how did Earth and its moon come into being? How did the core, mantle, crust form? Where did Archean rocks form, and what is their
Chapter 11 The Archean Era of Precambrian Time 1 Guiding Questions When and how did Earth and its moon come into being? How did the core, mantle, crust form? Where did Archean rocks form, and what is their
Pluto s orbit is tilted and significantly elliptical. Neptune orbits three times during the time Pluto orbits twice resonance prevents a collision.
 Chapter 9 Part 2 Dwarf Planets and Impacts Pluto s Orbit Pluto s orbit is tilted and significantly elliptical. Neptune orbits three times during the time Pluto orbits twice resonance prevents a collision.
Chapter 9 Part 2 Dwarf Planets and Impacts Pluto s Orbit Pluto s orbit is tilted and significantly elliptical. Neptune orbits three times during the time Pluto orbits twice resonance prevents a collision.
Asteroids, Comets and NEOs. (Answers) Solar System Impacts. Author: Sarah Roberts
 Asteroids, Comets and NEOs (Answers) Author: Sarah Roberts Asteroids, Comets and NEOs - Impact craters on the Earth 1. Using the data given below for real impact craters on the Earth, investigate the effect
Asteroids, Comets and NEOs (Answers) Author: Sarah Roberts Asteroids, Comets and NEOs - Impact craters on the Earth 1. Using the data given below for real impact craters on the Earth, investigate the effect
Page One. GEOL 1030 Pre test S15. Please enter your rst and last name.
 GEOL 1030 Pre test S15 Page One Please enter your rst and last name. First Name: Last Name: 1. The most common elements in the Earth's crust, in order of decreasing abundance, are: a. feldspar, quartz,
GEOL 1030 Pre test S15 Page One Please enter your rst and last name. First Name: Last Name: 1. The most common elements in the Earth's crust, in order of decreasing abundance, are: a. feldspar, quartz,
Impact Cratering. David A. Hardy MARS EDUCATION PROGRAM
 Impact Cratering David A. Hardy MARS EDUCATION PROGRAM Impact cratering overview: What we will learn about impact craters today: Causes of impacts - meteorites! Impact craters in our solar system Formation
Impact Cratering David A. Hardy MARS EDUCATION PROGRAM Impact cratering overview: What we will learn about impact craters today: Causes of impacts - meteorites! Impact craters in our solar system Formation
Solar System. Sun, 8 planets, hundred moons, thousand.dwarf.planets million asteroids, billion comets etc.
 Solar System Sun, 8 planets, hundred moons, thousand.dwarf.planets million asteroids, billion comets etc. Comparative Planetology Compares planets and other solar system bodies to help understand how they
Solar System Sun, 8 planets, hundred moons, thousand.dwarf.planets million asteroids, billion comets etc. Comparative Planetology Compares planets and other solar system bodies to help understand how they
Asteroids: Introduction
 Asteroids: Introduction Name Read through the information below. Then complete the Fill-Ins at the bottom of page. Asteroids are rocky objects that orbit the Sun in our solar system. Also known as minor
Asteroids: Introduction Name Read through the information below. Then complete the Fill-Ins at the bottom of page. Asteroids are rocky objects that orbit the Sun in our solar system. Also known as minor
GY 112 Lecture Notes Archean Geology
 GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 GY 112 Lecture Notes Archean Geology Lecture Goals: A) Time frame (the Archean and earlier) B) Rocks and tectonic elements (shield/platform/craton) C) Tectonics
GY 112 Lecture Notes D. Haywick (2006) 1 GY 112 Lecture Notes Archean Geology Lecture Goals: A) Time frame (the Archean and earlier) B) Rocks and tectonic elements (shield/platform/craton) C) Tectonics
Formation of the Solar System
 Formation of the Solar System What theory best explains the features of our solar system? The nebular theory states that our solar system formed from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar
Formation of the Solar System What theory best explains the features of our solar system? The nebular theory states that our solar system formed from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar
Relative Dating. How do we determine a rocks age by the surrounding rocks?
 Relative Dating How do we determine a rocks age by the surrounding rocks? 1 Geologic History 2 Relative Dating Uniformitarianism - the idea that forces working on our planet today worked on our planet
Relative Dating How do we determine a rocks age by the surrounding rocks? 1 Geologic History 2 Relative Dating Uniformitarianism - the idea that forces working on our planet today worked on our planet
TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology
 Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Chapter 12. ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration. Class 34: Asteroids and Comets [4/13/07] Announcements. Near-Earth Objects
![Chapter 12. ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration. Class 34: Asteroids and Comets [4/13/07] Announcements. Near-Earth Objects Chapter 12. ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration. Class 34: Asteroids and Comets [4/13/07] Announcements. Near-Earth Objects](/thumbs/89/98264569.jpg) ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site: www.ruf.rice.edu/~dalex/astr202_s07 Class 34: Asteroids and Comets [4/13/07] Announcements Near-Earth Objects
ASTRONOMY 202 Spring 2007: Solar System Exploration Instructor: Dr. David Alexander Web-site: www.ruf.rice.edu/~dalex/astr202_s07 Class 34: Asteroids and Comets [4/13/07] Announcements Near-Earth Objects
Vagabonds of the Solar System. Chapter 15
 Vagabonds of the Solar System Chapter 15 ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 13 Nov. 26, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-15)
Vagabonds of the Solar System Chapter 15 ASTR 111 003 Fall 2007 Lecture 13 Nov. 26, 2007 Introduction To Modern Astronomy I: Solar System Introducing Astronomy (chap. 1-6) Planets and Moons (chap. 7-15)
heating and cooling of a containerair pressure with balloon on flask: crumpled napkin in glass in container of water: clouds or clouds sweating.
 Content Categories Standards MIDDLE GRADES EARTH SCIENCE CONTENT CATEGORIES AND CHOSEN CELLS FOR TESTS KNOWLEDGE TYPES S T A Declarative Science Inquiry Schematic Pedagogical STS 1. Atmosphere/ Hydrosphere
Content Categories Standards MIDDLE GRADES EARTH SCIENCE CONTENT CATEGORIES AND CHOSEN CELLS FOR TESTS KNOWLEDGE TYPES S T A Declarative Science Inquiry Schematic Pedagogical STS 1. Atmosphere/ Hydrosphere
What are they? Where do they come from?
 Comets What are they? Where do they come from? Lesson Objectives To distinguish between the orbits of planets and those of comets. To describe the likely origins of short-period and long-period comets.
Comets What are they? Where do they come from? Lesson Objectives To distinguish between the orbits of planets and those of comets. To describe the likely origins of short-period and long-period comets.
Astronomy 103: First Exam
 Name: Astronomy 103: First Exam Stephen Lepp October 27, 2010 Each question is worth 2 points. Write your name on this exam and on the scantron. 1 Short Answer A. What is the largest of the terrestrial
Name: Astronomy 103: First Exam Stephen Lepp October 27, 2010 Each question is worth 2 points. Write your name on this exam and on the scantron. 1 Short Answer A. What is the largest of the terrestrial
