Although fractured basement rocks can sometimes form hydrocarbon reservoirs, such as. Intra-Basement Intrusions in the STACK Area of Oklahoma
|
|
|
- Rodney Thornton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Intra-Basement Intrusions in the STACK Area of Oklahoma May 2018 Satinder Chopra, Lennon Infante Paez, Kurt Marfurt Although fractured basement rocks can sometimes form hydrocarbon reservoirs, such as found in Vietnam and Venezuela, in general they are considered to have insufficient porosity to contain significant amounts of hydrocarbons. The top of basement also often represents a major unconformity. While a given seismic acquisition and processing program might accurately image the overlying moderately dipping sedimentary section, more steeply dipping features in the basement might be poorly imaged, resulting in a low frequency, wormy character. For these two reasons, relatively little has been published on the appearance of basement features in 3-D seismic data volumes. In many parts of the world, basement faults control shallower faulting in the overlying sedimentary cover. Such faults can enable fluid migration up and down.
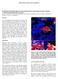
2 Hot fluids from below can diagenetically alter fault zones in the shallow section. Wastewater injection from above can find its way into the basement, potentially lubricating previously locked faults. In addition to fluids, magma can also flow within the basement and depending on the age of magmatism, into the sedimentary column. These magmatic flows may follow previous zones of weakness. The revitalization of old basins by technological advances in producing unconventional reservoirs has justified the acquisition of modern, high-density 3-D seismic surveys of areas that were thought to be well understood. In Oklahoma, these surveys provide new images of the basement that was previously thought to be relatively homogeneous granite and rhyolite. While extrusive and intrusive igneous rocks sometimes form good hydrocarbon reservoirs, more often they pose an interpretation hazard. In the absence of well control and a clear understanding of the seismic polarity, volcanic mounds can be misinterpreted as carbonate buildups, lava-filled incised valleys as turbidites and sills as bright spots. Although mafic dikes and sills are well-documented in the sedimentary column of the North Sea, Australia and offshore Brazil, and andesitic features in the sedimentary section of Mexico and Argentina, their appearance internal to the basement is less well documented. Fortuitously, a suite of papers in the August 2017 issue of Interpretation on volcanics provided new insights into the seismic geomorphology of intrusive and extrusive igneous features. Using concepts of seismic geomorphology, coupled with an understanding of the Midcontinent Rift from gravity and magnetic surveys, these analogues provide insight into the character of these previously unseen features in recently acquired 3-D seismic data. Figure 1: (a) The residual Bouguer anomaly map showing the extent of the Midcontinent Rift extending from Lake Superior, through Kansas, and thought to continue into north central Oklahoma. (b) An image from a legacy survey acquired over the Osage High showing a hypothesized intrusion dipping up the east. The black horizon indicates top of basement, while the red horizon indicates the top Mississippi Limestone. (After Elebiju et al., 2011.) Figure 2: A vertical slice through a modern, high density, wide-azimuth survey acquired to image the Stack play of northern Oklahoma. This survey also images the deeper basement and the hypothesized southern extension of the Midcontinent Rift (indicated by the symbol MCR? in figure 1. We interpret the steeply dipping strong reflectors indicated by the cyan
3 The Midcontinent Rift and the Osage High From gravity and magnetic surveys, the North American Midcontinent Rift appears to continue southward into Oklahoma (indicated by the? in figure 1a). Shallow basement (about 3,000 feet) also occurs over the Osage High, where legacy surveys suggest the presence of igneous sills stepping up to the east. The Wah-Zha-Zhi well reported on in the December 2012 AAPG Explorer drilled 7,000 feet into basement in this area encountered rhyolite, granite and gabbro. A recent August 2017 special section on the subsurface expression of igneous features published in the AAPG- SEG journal Interpretation provides additional insight on seismic geomorphology, reflection strength compared with that of the host rocks, cross-cutting relationships and stepping of the reflectors. In 2016, TGS acquired and processed a 3-D wideazimuth seismic survey over Kingfisher, Canadian and Blaine counties of Oklahoma in order to image the Meramec, Woodford, Osage and other targets that form the Sooner Trend Anadarko Canadian and Kingfisher, or STACK play. The quality of these images is vastly superior to older seismic images in the same area, where the suite of stepping-up-to-thewest sills seen in figure 2 are significantly better focused than similar features seen on legacy surveys such as in figure 1a. The overlying sedimentary structure in figure 2 is gently dipping to the left of this image, such that we can discount these steeply dipping events as being multiples. Yellow arrows indicate the stepping up features seen in sedimentary column of the North Sea, Brazil and New Zealand. These steps are sometimes misinterpreted to be faults, although some of these offsets are due to faults observed as lineaments in the curvature attribute extracted on the basement map. Flatter arrows to be sills that potentially follow earlier zones of weakness. Yellow arrows indicate vertical steps in these sills where we can image the sill. Other offsets might be faults that offset them, some of which continue into the sedimentary section (blue curves). While events that gently dip to the west (paralleling the top basement) may be multiples, flatter events are reflectors in the basement that either existed before the sill emplacement or are additional flatlying sills. Red arrows indicate the sill mapped in figure 3. Data courtesy of TGS in Houston. Figure 3: (a) Time-structure map of the picked intrusive event indicated by the red arrow in figure 2 with representative vertical slices section through the seismic amplitude volume. Abrupt changes in this timestructure map correlate to step-up features. (b) The corresponding horizon slice through the instantaneous envelope (also called reflection strength) along the same horizon, which we interpret to
4 events indicated by the green arrows are either flatlying, potentially volcanoclastic sediments, or flat-lying intrusive sills. Some of the discontinuities correspond to faults (in green) that continue into the sedimentary cover (black curves). represent the heterogeneity of the sill thickness. Data courtesy of TGS in Houston. Figure 3a shows a time-structure map of the sill indicated by the red arrows in figure 2. Discontinuities in this map correspond to step-up features in the sill. If we assume that the host rock is relatively homogeneous granite or rhyolite, the lateral changes in reflection strength shown in figure 3b correlate to lateral changes in sill thickness. Figure 4 is a photograph of an outcrop analogue, intruding through a sedimentary section. Note how the sill climbs using a series of step-ups through the relatively flat-lying strata. Smaller sills extend from the main intrusion, sub parallel to the relatively flat-lying sedimentary layers. Our Interpretation Magma typically forms during break up of continents as a result of decompression and partial melting of the asthenosphere. It can intrude laterally or vertically through the rock layers above depending on the rock types, the localized structures prevalent there, and more importantly the state of stress in the areas. Our current hypothesis is that these intrusions were fed by the magmatism that created the Mid-Continent Rift System when the North American craton began to split during the Precambrian about 1.1 billion years ago by thinning of the lithosphere due to convection of the hot but solid asthenosphere. None of these intrusions cut through the overlying Cambrian sediments that lie above the top basement. This igneous bodies appear to be inclined sheets flowing from a deep source point (maybe from a series of sub vertical dikes that cannot be imaged in the seismic data) that also extents outwards like many of the studies we have seen before from the European side of the North Atlantic margin. In this part of Oklahoma, the few wells that tag basement find it to be felsic in composition (granite or rhyolite) although there is a lack of information about its nature and extension. Using this assumption, the high reflectivity between the felsic basement and the igneous intrusions indicate a change in magma composition. Therefore, we interpret the composition of these inclined sheets to be mafic (having more magnesium and iron rich minerals such as pyroxene and olivine) which have higher impedance (ρ 3.0 g/cm3, vp 7 km/s) compared to their felsic counterpart (ρ 2.7 g/ cm3, vp 6 km/s). This difference in magma composition is consistent with a continental rift setting in which continental crust that is melted by conduction of the hot Asthenosphere would create felsic magma, whereas magma that intruded near the upper crust through discontinuities such zones of weakness have retained their original mafic composition.
5 Summary Surface seismic studies have dramatically changed our perception of igneous systems due to the possibility of studying igneous bodies in 3-D. Such high-quality data promise to provide a much deeper understanding of the Midcontinent Rift. Such studies help understand the occurrence of sills or intrusive bodies in sedimentary rocks. The transport or flow pathway mechanisms include the intrusion of magma along faults or compliant lithologies. Three-dimensional surface seismic data help us understand the shapes of such intrusive bodies, interpret or understand rock deformation mechanisms and map flow pathways that magma might have followed. As these bodies offer high acoustic impedance contrast than the different sedimentary rock layer interfaces, they are conspicuous by their higher amplitudes. Explorer Geophysical Corner (Click to View Column Archives ) The Geophysical Corner is a regular column in the EXPLORER that features geophysical case studies, techniques and application to the petroleum industry. R. Randy Ray, consulting geophysicist/geologist in Lakewood, Colo., served as editor of Geophysical Corner from January 2001 until January Bob A. Hardage, senior research scientist at the Bureau of Economic Geology, the University of Texas at Austin was editor of Geophysical Corner from January 2006 until Satinder Chopra, award-winning chief geophysicist (reservoir) at Arcis Seismic Solutions, Calgary, Canada, and a past AAPG-SEG Joint Distinguished Lecturer began serving as the editor of the Geophysical Corner column in Satinder Chopra Satinder Chopra, award-winning chief geophysicist (reservoir), at Arcis Seismic Solutions, Calgary, Canada, and a past AAPG-SEG Joint Distinguished Lecturer began serving as the editor of the Geophysical Corner column in 2012.
6 Lennon Infante Paez Student Member of AAPG and Doctoral Student at University of Oklahoma Kurt Marfurt Kurt currently serves as the Frank and Henrietta Schultz Professor of Geophysics within the ConocoPhillips School of Geology and Geophysics. Marfurt also served as the EAGE/SEG Distinguished Short Course Instructor for 2006 (on seismic attributes). Share this article: Figure 4: A photo showing igneous sills rising through a sedimentary section in Greenland, showing a morphology similar to the hypothesized sills seen in the basement features shown in figures 2 and 3. Note how the sills "step up" into the shallower section. Photo courtesy of John Howell (pesgb.org.uk/events/event-240). Extended reading
Nemaha Strike-Slip Fault Expression on 3-D Seismic Data in SCOOP Trend
 Nemaha Strike-Slip Fault Expression on 3-D Seismic Data in SCOOP Trend June 2018 Satinder Chopra, Kurt Marfurt, Folarin Kolawole, Brett M. Carpenter Fthe meaningful recognition of the faults within the
Nemaha Strike-Slip Fault Expression on 3-D Seismic Data in SCOOP Trend June 2018 Satinder Chopra, Kurt Marfurt, Folarin Kolawole, Brett M. Carpenter Fthe meaningful recognition of the faults within the
Using Curvature to Map Faults, Fractures
 Using Curvature to Map Faults, Fractures by SATINDER CHOPRA and KURT J. MARFURT Editor s note: Chopra is with Arcis Corp., Calgary, Canada; Marfurt is with the University of Oklahoma. Both are AAPG members.
Using Curvature to Map Faults, Fractures by SATINDER CHOPRA and KURT J. MARFURT Editor s note: Chopra is with Arcis Corp., Calgary, Canada; Marfurt is with the University of Oklahoma. Both are AAPG members.
Some Machine Learning Applications in Seismic Interpretation
 Some Machine Learning Applications in Seismic Interpretation August 2018 Satinder Chopra, David Lubo-Robles, Kurt Marfurt data and data analytics are the buzzwords these days. The oil and gas industry
Some Machine Learning Applications in Seismic Interpretation August 2018 Satinder Chopra, David Lubo-Robles, Kurt Marfurt data and data analytics are the buzzwords these days. The oil and gas industry
Seismic modeling evaluation of fault illumination in the Woodford Shale Sumit Verma*, Onur Mutlu, Kurt J. Marfurt, The University of Oklahoma
 Seismic modeling evaluation of fault illumination in the Woodford Shale Sumit Verma*, Onur Mutlu, Kurt J. Marfurt, The University of Oklahoma Summary The Woodford Shale is one of the more important resource
Seismic modeling evaluation of fault illumination in the Woodford Shale Sumit Verma*, Onur Mutlu, Kurt J. Marfurt, The University of Oklahoma Summary The Woodford Shale is one of the more important resource
Questions and Topics
 Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Questions and Topics 1. What are the theories of Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift? 2. What is the evidence that Continents move? 3. What are the forces that
Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift Questions and Topics 1. What are the theories of Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift? 2. What is the evidence that Continents move? 3. What are the forces that
Igneous Rocks. Igneous Rocks. Genetic Classification of
 Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
Igneous Rocks Fig. 5.1 Genetic Classification of Igneous Rocks Intrusive: crystallized from slowly cooling magma intruded within the Earth s crust; e.g. granite, gabbro 1 Fig. 5.2 Genetic Classification
Downloaded 01/29/13 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 An integrated study of a Mississippian tripolitic chert reservoir Osage County, Oklahoma, USA Benjamin L. Dowdell*, Atish Roy, and Kurt J. Marfurt, The University of Oklahoma Summary With the advent of
An integrated study of a Mississippian tripolitic chert reservoir Osage County, Oklahoma, USA Benjamin L. Dowdell*, Atish Roy, and Kurt J. Marfurt, The University of Oklahoma Summary With the advent of
Seismic Attributes and Their Applications in Seismic Geomorphology
 Academic article Seismic Attributes and Their Applications in Seismic Geomorphology Sanhasuk Koson, Piyaphong Chenrai* and Montri Choowong Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University,
Academic article Seismic Attributes and Their Applications in Seismic Geomorphology Sanhasuk Koson, Piyaphong Chenrai* and Montri Choowong Department of Geology, Faculty of Science, Chulalongkorn University,
Geometric attributes such as coherence and curvature are
 SATINDER CHOPRA, Arcis Seismic Solutions, Calgary, Canada KURT J. MARFURT, University of Oklahoma, Norman, USA Geometric attributes such as coherence and curvature are commonly used for mapping structural
SATINDER CHOPRA, Arcis Seismic Solutions, Calgary, Canada KURT J. MARFURT, University of Oklahoma, Norman, USA Geometric attributes such as coherence and curvature are commonly used for mapping structural
In a marine environment, topographic features on the sea
 Coordinated by ALAN JACKSON Seismic attribute expression of differential compaction SATINDER CHOPRA, Arcis Seismic Solutions, Calgary, Canada KURT J. MARFURT, University of Oklahoma, Norman, USA In a marine
Coordinated by ALAN JACKSON Seismic attribute expression of differential compaction SATINDER CHOPRA, Arcis Seismic Solutions, Calgary, Canada KURT J. MARFURT, University of Oklahoma, Norman, USA In a marine
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Grotzinger Jordan. Understanding Earth. Sixth Edition
 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Solids from Melts 1 About Igneous Rocks Igneous
Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011 by W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 4: Igneous Rocks: Solids from Melts 1 About Igneous Rocks Igneous
Downloaded 03/27/18 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Calibrating seismic fracture prediction using borehole image logs, application to the Mississippian Limestone Stephanie Cook*, Abdulmohsen Alali, Kurt J. Marfurt, Matthew J. Pranter The University of Oklahoma
Calibrating seismic fracture prediction using borehole image logs, application to the Mississippian Limestone Stephanie Cook*, Abdulmohsen Alali, Kurt J. Marfurt, Matthew J. Pranter The University of Oklahoma
1. are most likely to study the images sent back from Mars. A. Astronomers B. Geologists C. Doctors D. Engineers
 1. are most likely to study the images sent back from Mars. A. Astronomers B. Geologists C. Doctors D. Engineers 2. When did the Earth form? A. About 540 million years ago B. About 2.5 billion years ago
1. are most likely to study the images sent back from Mars. A. Astronomers B. Geologists C. Doctors D. Engineers 2. When did the Earth form? A. About 540 million years ago B. About 2.5 billion years ago
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks
 Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
Chapter 4 Rocks & Igneous Rocks Rock Definition A naturally occurring consolidated mixture of one or more minerals e.g, marble, granite, sandstone, limestone Rock Definition Must naturally occur in nature,
A) B) C) D) 4. Which diagram below best represents the pattern of magnetic orientation in the seafloor on the west (left) side of the ocean ridge?
 1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
Earthquakes. Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy
 Earthquakes Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy The amount of energy released determines the magnitude of the earthquake Seismic waves carry the energy away from its origin Fig. 18.1 Origin
Earthquakes Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy The amount of energy released determines the magnitude of the earthquake Seismic waves carry the energy away from its origin Fig. 18.1 Origin
technical article Satinder Chopra 1*, Kurt J. Marfurt 2 and Ha T. Mai 2
 first break volume 27, October 2009 technical article Using automatically generated 3D rose diagrams for correlation of seismic fracture lineaments with similar lineaments from attributes and well log
first break volume 27, October 2009 technical article Using automatically generated 3D rose diagrams for correlation of seismic fracture lineaments with similar lineaments from attributes and well log
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy)
 Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Answers: Internal Processes and Structures (Isostasy) 1. Analyse the adjustment of the crust to changes in loads associated with volcanism, mountain building, erosion, and glaciation by using the concept
Standard 2, Objective 1: Evaluate the source of Earth s internal heat and the evidence of Earth s internal structure.
 Standard 2: Students will understand Earth s internal structure and the dynamic nature of the tectonic plates that form its surface. Standard 2, Objective 1: Evaluate the source of Earth s internal heat
Standard 2: Students will understand Earth s internal structure and the dynamic nature of the tectonic plates that form its surface. Standard 2, Objective 1: Evaluate the source of Earth s internal heat
Interaction between Faults and Igneous Intrusions in Sedimentary Basins: Insights from 3D Seismic Reflection Data*
 Interaction between Faults and Igneous Intrusions in Sedimentary Basins: Insights from 3D Seismic Reflection Data* Craig Magee¹, Christopher A. Jackson¹, and Nick Schofield² Search and Discovery Article
Interaction between Faults and Igneous Intrusions in Sedimentary Basins: Insights from 3D Seismic Reflection Data* Craig Magee¹, Christopher A. Jackson¹, and Nick Schofield² Search and Discovery Article
Downloaded 10/10/13 to Redistribution subject to SEG license or copyright; see Terms of Use at
 Characterizing a fault-zone and associated fractures using lab experiments and attribute-based seismic analysis: an example from Woodford Shale, Anadarko basin, Oklahoma Zonghu Liao*, Ze ev Reches, and
Characterizing a fault-zone and associated fractures using lab experiments and attribute-based seismic analysis: an example from Woodford Shale, Anadarko basin, Oklahoma Zonghu Liao*, Ze ev Reches, and
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals. Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane SGM 210_2013
 Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Igneous and Metamorphic Rock Forming Minerals Department of Geology Mr. Victor Tibane 1 SGM 210_2013 Grotzinger Jordan Understanding Earth Sixth Edition Chapter 4: IGNEOUS ROCKS Solids from Melts 2011
Most mafic magmas come from the upper mantle and lower crust. This handout will address five questions:
 Geology 101 Origin of Magma From our discussions of the structure of the interior of the Earth, it is clear that the upper parts of the Earth (crust and mantle) are mostly solid because s-waves penetrate
Geology 101 Origin of Magma From our discussions of the structure of the interior of the Earth, it is clear that the upper parts of the Earth (crust and mantle) are mostly solid because s-waves penetrate
Seismic attributes for fault/fracture characterization
 Satinder Chopra* and Kurt J. Marfurt + *Arcis Corporation, Calgary; + University of Houston, Houston Summary Seismic attributes have proliferated in the last three decades at a rapid rate and have helped
Satinder Chopra* and Kurt J. Marfurt + *Arcis Corporation, Calgary; + University of Houston, Houston Summary Seismic attributes have proliferated in the last three decades at a rapid rate and have helped
Igneous Rock. Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere
 Igneous Rock Magma Molten rock under the surface Temperature = 600 o 1400 o C Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere Magma chamber - most all magma consists of silicon and oxygen (silicate)
Igneous Rock Magma Molten rock under the surface Temperature = 600 o 1400 o C Magma Chamber Large pool of magma in the lithosphere Magma chamber - most all magma consists of silicon and oxygen (silicate)
INTRODUCTION to AMPLITUDES
 INTRODUCTION to AMPLITUDES Since 2008 SoleGeo is focused on exploration in NORWAY providing geo-science consultancy services in the APA2008, APA2009 and the 20th round. The objective is adding value in
INTRODUCTION to AMPLITUDES Since 2008 SoleGeo is focused on exploration in NORWAY providing geo-science consultancy services in the APA2008, APA2009 and the 20th round. The objective is adding value in
Chapter 8: The Dynamic Planet
 Chapter 8: The Dynamic Planet I. The Pace of Change A. The Geologic Time Scale II. Earth s Structure and Internal Energy A. The Earth s Core B. The Earth s Mantle C. The Earth s Crust III. The Geologic
Chapter 8: The Dynamic Planet I. The Pace of Change A. The Geologic Time Scale II. Earth s Structure and Internal Energy A. The Earth s Core B. The Earth s Mantle C. The Earth s Crust III. The Geologic
Amplitude variation with offset AVO. and. Direct Hydrocarbon Indicators DHI. Reflection at vertical incidence. Reflection at oblique incidence
 Amplitude variation with offset AVO and Direct Hydrocarbon Indicators DHI Reflection at vertical incidence Reflection coefficient R(p) c α 1 S wavespeed β 1 density ρ 1 α 2 S wavespeed β 2 density ρ 2
Amplitude variation with offset AVO and Direct Hydrocarbon Indicators DHI Reflection at vertical incidence Reflection coefficient R(p) c α 1 S wavespeed β 1 density ρ 1 α 2 S wavespeed β 2 density ρ 2
SEG/San Antonio 2007 Annual Meeting
 ; Application to Forth Worth Basin Suat Aktepe, Kurt J. Marfurt, Center for Applied Geosciences and Energy, Dept. of Geosciences, University of Houston Summary By definition, the focus of seismic exploration
; Application to Forth Worth Basin Suat Aktepe, Kurt J. Marfurt, Center for Applied Geosciences and Energy, Dept. of Geosciences, University of Houston Summary By definition, the focus of seismic exploration
Applications of texture attribute analysis to 3D seismic data
 INTERPRETER S CORNER Coordinated by Rebecca B. Latimer Applications of texture attribute analysis to 3D seismic data SATINDER CHOPRA and VLADIMIR ALEXEEV, Arcis Corporation, Calgary, Alberta, Canada In
INTERPRETER S CORNER Coordinated by Rebecca B. Latimer Applications of texture attribute analysis to 3D seismic data SATINDER CHOPRA and VLADIMIR ALEXEEV, Arcis Corporation, Calgary, Alberta, Canada In
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics
 Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Wegener s continental drift hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined to form a single supercontinent. Wegener proposed that the
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Wegener s continental drift hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined to form a single supercontinent. Wegener proposed that the
Topic 12: Dynamic Earth Pracatice
 Name: Topic 12: Dynamic Earth Pracatice 1. Earth s outer core is best inferred to be A) liquid, with an average density of approximately 4 g/cm 3 B) liquid, with an average density of approximately 11
Name: Topic 12: Dynamic Earth Pracatice 1. Earth s outer core is best inferred to be A) liquid, with an average density of approximately 4 g/cm 3 B) liquid, with an average density of approximately 11
Late 20 th Century Tests of the Continental Drift Hypothesis
 Late 20 th Century Tests of the Continental Drift Hypothesis 5 Characteristics of the Ocean Trenches Unless otherwise noted the artwork and photographs in this slide show are original and by Burt Carter.
Late 20 th Century Tests of the Continental Drift Hypothesis 5 Characteristics of the Ocean Trenches Unless otherwise noted the artwork and photographs in this slide show are original and by Burt Carter.
1. In the diagram below, letters A and B represent locations near the edge of a continent.
 1. In the diagram below, letters A and B represent locations near the edge of a continent. A geologist who compares nonsedimentary rock samples from locations A and B would probably find that the samples
1. In the diagram below, letters A and B represent locations near the edge of a continent. A geologist who compares nonsedimentary rock samples from locations A and B would probably find that the samples
6. In the diagram below, letters A and B represent locations near the edge of a continent.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
PHYSICAL GEOLOGY AND THE ENVIRONMENT (2 ND CANADIAN EDITION)
 Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Chapter Summary: Plate tectonics is a theory that suggests Earth's surface is divided into several large plates that change position and size. Intense geologic activity occurs
Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Chapter Summary: Plate tectonics is a theory that suggests Earth's surface is divided into several large plates that change position and size. Intense geologic activity occurs
L.O: THE CRUST USE REFERENCE TABLE PAGE 10
 USE REFERENCE TABLE PAGE 10 1. The oceanic crust is thought to be composed mainly of A) granite B) sandstone C) basalt D) rhyolite 2. To get sample material from the mantle, drilling will be done through
USE REFERENCE TABLE PAGE 10 1. The oceanic crust is thought to be composed mainly of A) granite B) sandstone C) basalt D) rhyolite 2. To get sample material from the mantle, drilling will be done through
Composition of the earth, Geologic Time, and Plate Tectonics
 Composition of the earth, Geologic Time, and Plate Tectonics Layers of the earth Chemical vs. Mechanical Chemical : Mechanical: 1) Core: Ni and Fe 2) Mantle: Mostly Peridotite 3) Crust: Many different
Composition of the earth, Geologic Time, and Plate Tectonics Layers of the earth Chemical vs. Mechanical Chemical : Mechanical: 1) Core: Ni and Fe 2) Mantle: Mostly Peridotite 3) Crust: Many different
Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift
 Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift Predecessor to modern plate tectonics Shape and fit of the continents was the initial evidence Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Taylor (1908) Wegner (1915) Fig.
Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift Predecessor to modern plate tectonics Shape and fit of the continents was the initial evidence Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Taylor (1908) Wegner (1915) Fig.
Plate Tectonics. entirely rock both and rock
 Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Structural Geology of the Mountains
 Structural Geology of the Mountains Clinton R. Tippett Shell Canada Limited, Calgary, Alberta clinton.tippett@shell.ca INTRODUCTION The Southern Rocky Mountains of Canada (Figure 1) are made up of several
Structural Geology of the Mountains Clinton R. Tippett Shell Canada Limited, Calgary, Alberta clinton.tippett@shell.ca INTRODUCTION The Southern Rocky Mountains of Canada (Figure 1) are made up of several
We A Multi-Measurement Integration Case Study from West Loppa Area in the Barents Sea
 We-16-12 A Multi-Measurement ntegration Case Study from West Loppa Area in the Barents Sea. Guerra* (WesternGeco), F. Ceci (WesternGeco), A. Lovatini (WesternGeco), F. Miotti (WesternGeco), G. Milne (WesternGeco),
We-16-12 A Multi-Measurement ntegration Case Study from West Loppa Area in the Barents Sea. Guerra* (WesternGeco), F. Ceci (WesternGeco), A. Lovatini (WesternGeco), F. Miotti (WesternGeco), G. Milne (WesternGeco),
As compaction and cementation of these sediments eventually occur, which area will become siltstone? A) A B) B C) C D) D
 1. A student obtains a cup of quartz sand from a beach. A saltwater solution is poured into the sand and allowed to evaporate. The mineral residue from the saltwater solution cements the sand grains together,
1. A student obtains a cup of quartz sand from a beach. A saltwater solution is poured into the sand and allowed to evaporate. The mineral residue from the saltwater solution cements the sand grains together,
Lecture 3 Rocks and the Rock Cycle Dr. Shwan Omar
 Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Rocks A naturally occurring aggregate of one or more minerals (e.g., granite), or a body of non-crystalline material (e.g., obsidian glass), or of solid organic material (e.g., coal). Rock Cycle A sequence
Plate tectonics, rock cycle
 Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
Dikes, Antarctica Rock Cycle Plate tectonics, rock cycle The Rock Cycle A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one
Theory of Plate Tectonics
 Plate Tectonics Theory of Plate Tectonics Lithosphere is made of sections called plates that move around called continental drift Plates move because they float on the asthenosphere Most plates consist
Plate Tectonics Theory of Plate Tectonics Lithosphere is made of sections called plates that move around called continental drift Plates move because they float on the asthenosphere Most plates consist
Volumetric curvature attributes for fault/fracture characterization
 first break volume 25, July 2007 technical article Volumetric curvature attributes for fault/fracture characterization Satinder Chopra 1 and Kurt J. Marfurt 2 Introduction Seismic attributes have proliferated
first break volume 25, July 2007 technical article Volumetric curvature attributes for fault/fracture characterization Satinder Chopra 1 and Kurt J. Marfurt 2 Introduction Seismic attributes have proliferated
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 9 Plate Tectonics 9.1 Continental Drift An Idea Before Its Time Wegener s continental drift hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 9 Plate Tectonics 9.1 Continental Drift An Idea Before Its Time Wegener s continental drift hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 9 Plate Tectonics 9.1 Continental Drift An Idea Before Its Time Wegener s continental drift hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 9 Plate Tectonics 9.1 Continental Drift An Idea Before Its Time Wegener s continental drift hypothesis stated that the continents had once been joined
Prologue. Summary. Introduction
 Prologue The following paper will form a major part of Yanxia Guo s M.S. thesis. A shorter version of this paper has been submitted to the SEG as an expanded abstract for 2010 Annual Meeting. I provide
Prologue The following paper will form a major part of Yanxia Guo s M.S. thesis. A shorter version of this paper has been submitted to the SEG as an expanded abstract for 2010 Annual Meeting. I provide
INTEGRATED GEOPHYSICAL INTERPRETATION METHODS FOR HYDROCARBON EXPLORATION
 INTEGRATED GEOPHYSICAL INTERPRETATION METHODS FOR HYDROCARBON EXPLORATION Instructor : Kumar Ramachandran 31 July 4 August 2017 Jakarta COURSE OUTLINE The course is aimed at imparting working knowledge
INTEGRATED GEOPHYSICAL INTERPRETATION METHODS FOR HYDROCARBON EXPLORATION Instructor : Kumar Ramachandran 31 July 4 August 2017 Jakarta COURSE OUTLINE The course is aimed at imparting working knowledge
DE-FG26-06NT Line 120. Line ft ft
 A B 1240 ms ms PreSTM-RMOTC 1212 1212 ms ms PreSTM-UH PreSTM-UH Figure 13. Coherence time slices near top granite basement extracted from UH processed and commercially processed (RMOTC data) prestack time
A B 1240 ms ms PreSTM-RMOTC 1212 1212 ms ms PreSTM-UH PreSTM-UH Figure 13. Coherence time slices near top granite basement extracted from UH processed and commercially processed (RMOTC data) prestack time
12. The diagram below shows the collision of an oceanic plate and a continental plate.
 Review 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below, which shows the boundary between two lithospheric plates. Point X is a location in the continental lithosphere. The depth
Review 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below, which shows the boundary between two lithospheric plates. Point X is a location in the continental lithosphere. The depth
MUHAMMAD S TAMANNAI, DOUGLAS WINSTONE, IAN DEIGHTON & PETER CONN, TGS Nopec Geological Products and Services, London, United Kingdom
 Geological and Geophysical Evaluation of Offshore Morondava Frontier Basin based on Satellite Gravity, Well and regional 2D Seismic Data Interpretation MUHAMMAD S TAMANNAI, DOUGLAS WINSTONE, IAN DEIGHTON
Geological and Geophysical Evaluation of Offshore Morondava Frontier Basin based on Satellite Gravity, Well and regional 2D Seismic Data Interpretation MUHAMMAD S TAMANNAI, DOUGLAS WINSTONE, IAN DEIGHTON
10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves.
 Map of ocean floor Evidence in Support of the Theory of Plate Tectonics 10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves. The Earth's magnetic field behaves as if there were a bar magnet in the center of
Map of ocean floor Evidence in Support of the Theory of Plate Tectonics 10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves. The Earth's magnetic field behaves as if there were a bar magnet in the center of
GeoNeurale. announces THE ADVANCED SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES ANALYSIS. 3D Seismic Attributes for Prospect Identification and Reservoir Characterization
 GeoNeurale announces THE ADVANCED SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES ANALYSIS 3D Seismic Attributes for Prospect Identification and Reservoir Characterization Munich - Germany 0.50 0.40 0.30 0.20 0.10 0.00-0.40-0.30-0.20-0.10
GeoNeurale announces THE ADVANCED SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES ANALYSIS 3D Seismic Attributes for Prospect Identification and Reservoir Characterization Munich - Germany 0.50 0.40 0.30 0.20 0.10 0.00-0.40-0.30-0.20-0.10
Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway
 Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway The Earth is more than a giant ball made up of dirt, rocks, and minerals. The Earth may look like a giant ball from when looking at it from
Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway The Earth is more than a giant ball made up of dirt, rocks, and minerals. The Earth may look like a giant ball from when looking at it from
Essentials of Geology, 11e
 Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Welcome to GEO 101 Introduction to Geology
 Welcome to GEO 101 Introduction to Geology so what is Geology? not just rocks! Geology is... study of Earth and planetary bodies processes responsible for formation processes that modify all areas of geology
Welcome to GEO 101 Introduction to Geology so what is Geology? not just rocks! Geology is... study of Earth and planetary bodies processes responsible for formation processes that modify all areas of geology
ENVI.2030L Geologic Time
 Name ENVI.2030L Geologic Time I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in their order of occurrence. No attempt
Name ENVI.2030L Geologic Time I. Introduction There are two types of geologic time, relative and absolute. In the case of relative time geologic events are arranged in their order of occurrence. No attempt
Structure of the Earth
 Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High in Magnesium (Mg) and Iron (Fe) Core: High in Nickel
Structure of the Earth Compositional (Chemical) Layers Crust: Low density Moho: Density boundary between crust and mantle Mantle: Higher density High in Magnesium (Mg) and Iron (Fe) Core: High in Nickel
Dynamic Crust Practice
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
2 Igneous Rock. How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture of igneous rock? BEFORE YOU READ. Rocks: Mineral Mixtures
 CHAPTER 2 2 Igneous Rock SECTION Rocks: Mineral Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture
CHAPTER 2 2 Igneous Rock SECTION Rocks: Mineral Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture
THE ADVANCED SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES ANALYSIS
 Society of Exploration Geophysicists announce Kurt Marfurt GeoNeurale THE ADVANCED SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES ANALYSIS 3D Seismic Attributes for Prospect Identification and Reservoir Characterization 29-31 May
Society of Exploration Geophysicists announce Kurt Marfurt GeoNeurale THE ADVANCED SEISMIC ATTRIBUTES ANALYSIS 3D Seismic Attributes for Prospect Identification and Reservoir Characterization 29-31 May
Plate Tectonics Lab II: Background Information
 Plate Tectonics Lab II: Background Information This lab is based on a UW ESS101 Lab. Note: Hand in only the Answer Sheet at the back of this guide to your Instructor Introduction One of the more fundamental
Plate Tectonics Lab II: Background Information This lab is based on a UW ESS101 Lab. Note: Hand in only the Answer Sheet at the back of this guide to your Instructor Introduction One of the more fundamental
Plate Tectonics: A Scientific Revolution Unfolds
 Chapter 2 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Eleventh Edition Plate Tectonics: A Scientific Revolution Unfolds Tarbuck and Lutgens From Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics Prior to the
Chapter 2 Lecture Earth: An Introduction to Physical Geology Eleventh Edition Plate Tectonics: A Scientific Revolution Unfolds Tarbuck and Lutgens From Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics Prior to the
Rocks: Stony Stalwarts: Adapted from:
 Rocks: Stony Stalwarts: Adapted from: http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/earth/inside-the-earth/rocks-article/ Rocks are so common that most of us take them for granted cursing when we hit them
Rocks: Stony Stalwarts: Adapted from: http://science.nationalgeographic.com/science/earth/inside-the-earth/rocks-article/ Rocks are so common that most of us take them for granted cursing when we hit them
Chapter Two. Figure 02_02. Geography of the Ocean Basins. The Sea Floor
 Chapter Two The Sea Floor Geography of the Ocean Basins Figure 02_02 The world ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area. In the Northern Hemisphere, 61% of the total area is ocean. In
Chapter Two The Sea Floor Geography of the Ocean Basins Figure 02_02 The world ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area. In the Northern Hemisphere, 61% of the total area is ocean. In
Plate Tectonics 22/12/2017
 Map of the tectonic plates. Plate Tectonics In 1912 the meteorologist Alfred Wegener independently developed what he called continental drift, (expanded in his 1915 book The Origin of Continents and Oceans).
Map of the tectonic plates. Plate Tectonics In 1912 the meteorologist Alfred Wegener independently developed what he called continental drift, (expanded in his 1915 book The Origin of Continents and Oceans).
FUNDAMENTALS OF SEISMIC EXPLORATION FOR HYDROCARBON
 FUNDAMENTALS OF SEISMIC EXPLORATION FOR HYDROCARBON Instructor : Kumar Ramachandran 10 14 July 2017 Jakarta The course is aimed at teaching the physical concepts involved in the application of seismic
FUNDAMENTALS OF SEISMIC EXPLORATION FOR HYDROCARBON Instructor : Kumar Ramachandran 10 14 July 2017 Jakarta The course is aimed at teaching the physical concepts involved in the application of seismic
Earth s Continents and Seafloors. GEOL100 Physical Geology Ray Rector - Instructor
 Earth s Continents and Seafloors GEOL100 Physical Geology Ray Rector - Instructor OCEAN BASINS and CONTINENTAL PLATFORMS Key Concepts I. Earth s rocky surface covered by of two types of crust Dense, thin,
Earth s Continents and Seafloors GEOL100 Physical Geology Ray Rector - Instructor OCEAN BASINS and CONTINENTAL PLATFORMS Key Concepts I. Earth s rocky surface covered by of two types of crust Dense, thin,
Earth s s Topographic Regions
 Earth s s Topographic Regions Continental Shields GEOLOGY OF THE USA Atlantic Ocean Crustal Ages Clues to Earth s s Surface Mountains only in certain areas Rock types differ regionally Shields in interior
Earth s s Topographic Regions Continental Shields GEOLOGY OF THE USA Atlantic Ocean Crustal Ages Clues to Earth s s Surface Mountains only in certain areas Rock types differ regionally Shields in interior
Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory
 Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory Chapter Outline 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Early Ideas About Continental Drift 2.3 What Is the Evidence for Continental Drift? 2.4 Features of the Seafloor 2.5 Earth
Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory Chapter Outline 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Early Ideas About Continental Drift 2.3 What Is the Evidence for Continental Drift? 2.4 Features of the Seafloor 2.5 Earth
Most mafic magmas come from the upper mantle and lower crust. This handout will address five questions:
 IDS 102 Origin of Magma From our discussions of the structure of the interior of the Earth, it is clear that the upper parts of the Earth (crust and mantle) are mostly solid because s-waves penetrate those
IDS 102 Origin of Magma From our discussions of the structure of the interior of the Earth, it is clear that the upper parts of the Earth (crust and mantle) are mostly solid because s-waves penetrate those
Seismic Reflection Imaging across the Johnson Ranch, Valley County, Idaho
 Seismic Reflection Imaging across the Johnson Ranch, Valley County, Idaho Report Prepared for the Skyline Corporation Lee M. Liberty Center for Geophysical Investigation of the Shallow Subsurface (CGISS)
Seismic Reflection Imaging across the Johnson Ranch, Valley County, Idaho Report Prepared for the Skyline Corporation Lee M. Liberty Center for Geophysical Investigation of the Shallow Subsurface (CGISS)
EDIMENTARY BASINS. What is a Sedimentary Basin? by Prof. Dr. Abbas Mansour
 EDIMENTARY BASINS What is a Sedimentary Basin? by Prof. Dr. Abbas Mansour WHAT IS A SEDIMENTARY BASIN? A low area on the Earth s surface relative to surroundings e.g. deep ocean basin (5-10 km deep) e.g.
EDIMENTARY BASINS What is a Sedimentary Basin? by Prof. Dr. Abbas Mansour WHAT IS A SEDIMENTARY BASIN? A low area on the Earth s surface relative to surroundings e.g. deep ocean basin (5-10 km deep) e.g.
Induced microseismic fracture prediction
 Predicting hydraulically-induced microseismic fractures from seismic inversion volumes: A North Texas Barnett Shale case study Xavier E. Refunjol*, University of Oklahoma, Joël Le Calvez, Schlumberger,
Predicting hydraulically-induced microseismic fractures from seismic inversion volumes: A North Texas Barnett Shale case study Xavier E. Refunjol*, University of Oklahoma, Joël Le Calvez, Schlumberger,
GLY 155 Introduction to Physical Geology, W. Altermann. Press & Siever, compressive forces. Compressive forces cause folding and faulting.
 Press & Siever, 1995 compressive forces Compressive forces cause folding and faulting. faults 1 Uplift is followed by erosion, which creates new horizontal surface. lava flows Volcanic eruptions cover
Press & Siever, 1995 compressive forces Compressive forces cause folding and faulting. faults 1 Uplift is followed by erosion, which creates new horizontal surface. lava flows Volcanic eruptions cover
TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology
 Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Structural Styles and Geotectonic Elements in Northwestern Mississippi: Interpreted from Gravity, Magnetic, and Proprietary 2D Seismic Data
 Structural Styles and Geotectonic Elements in Northwestern Mississippi: Interpreted from Gravity, Magnetic, and Proprietary 2D Seismic Data Nick Loundagin 1 and Gary L. Kinsland 2 1 6573 W. Euclid Pl.,
Structural Styles and Geotectonic Elements in Northwestern Mississippi: Interpreted from Gravity, Magnetic, and Proprietary 2D Seismic Data Nick Loundagin 1 and Gary L. Kinsland 2 1 6573 W. Euclid Pl.,
Chapter 4 8/27/2013. Igneous Rocks. and Intrusive Igneous Activity. Introduction. The Properties and Behavior of Magma and Lava
 Introduction Chapter 4 Igneous rocks form by the cooling of magma (or lava). Large parts of the continents and all the oceanic crust are composed of. and Intrusive Igneous Activity The Properties and Behavior
Introduction Chapter 4 Igneous rocks form by the cooling of magma (or lava). Large parts of the continents and all the oceanic crust are composed of. and Intrusive Igneous Activity The Properties and Behavior
Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
 1 Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Presentation modified from: Instructor Resource Center on CD-ROM, Foundations of Earth Science,, 4 th Edition, Lutgens/Tarbuck, Rock Cycle Igneous Rocks Today 2 Rock
1 Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Presentation modified from: Instructor Resource Center on CD-ROM, Foundations of Earth Science,, 4 th Edition, Lutgens/Tarbuck, Rock Cycle Igneous Rocks Today 2 Rock
EARTH SCIENCE. Geology, the Environment and the Universe. Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks
 EARTH SCIENCE Geology, the Environment and the Universe Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks Section 5.1 What are igneous rocks? Section 5.2 Classification of Igneous Rocks Click a hyperlink
EARTH SCIENCE Geology, the Environment and the Universe Chapter 5: Igneous Rocks CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks Section 5.1 What are igneous rocks? Section 5.2 Classification of Igneous Rocks Click a hyperlink
Churning seismic attributes with principal component analysis
 Satinder Chopra + * and Kurt J. Marfurt + Arcis Seismic Solutions, Calgary; The University of Oklahoma, Norman Summary Seismic attributes are an invaluable aid in the interpretation of seismic data. Different
Satinder Chopra + * and Kurt J. Marfurt + Arcis Seismic Solutions, Calgary; The University of Oklahoma, Norman Summary Seismic attributes are an invaluable aid in the interpretation of seismic data. Different
Section 7. Reading the Geologic History of Your Community. What Do You See? Think About It. Investigate. Learning Outcomes
 Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 7 Reading the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section,
Chapter 3 Minerals, Rocks, and Structures Section 7 Reading the Geologic History of Your Community What Do You See? Learning Outcomes In this section, you will Goals Text Learning Outcomes In this section,
3. GEOLOGY. 3.1 Introduction. 3.2 Results and Discussion Regional Geology Surficial Geology Mine Study Area
 3. GEOLOGY 3.1 Introduction This chapter discusses the baseline study of the geology and mineralization characteristics of the mine study area. The study consolidates existing geological data and exploration
3. GEOLOGY 3.1 Introduction This chapter discusses the baseline study of the geology and mineralization characteristics of the mine study area. The study consolidates existing geological data and exploration
Continental Landscapes
 Continental Landscapes Landscape influenced by tectonics, climate & differential weathering Most landforms developed within the last 2 million years System moves toward an equilibrium Continental Landscapes
Continental Landscapes Landscape influenced by tectonics, climate & differential weathering Most landforms developed within the last 2 million years System moves toward an equilibrium Continental Landscapes
APPENDIX C GEOLOGICAL CHANCE OF SUCCESS RYDER SCOTT COMPANY PETROLEUM CONSULTANTS
 APPENDIX C GEOLOGICAL CHANCE OF SUCCESS Page 2 The Geological Chance of Success is intended to evaluate the probability that a functioning petroleum system is in place for each prospective reservoir. The
APPENDIX C GEOLOGICAL CHANCE OF SUCCESS Page 2 The Geological Chance of Success is intended to evaluate the probability that a functioning petroleum system is in place for each prospective reservoir. The
ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017
 ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017 Why is there no oceanic crust older than 200 million years? SUBDUCTION If new oceanic crust is being continuously created along the earth
ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017 Why is there no oceanic crust older than 200 million years? SUBDUCTION If new oceanic crust is being continuously created along the earth
Practice Questions: Plate Tectonics
 Practice Questions: Plate Tectonics 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which type of plate boundary is shown? A) divergent
Practice Questions: Plate Tectonics 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which type of plate boundary is shown? A) divergent
EASC100: EXAM1 (07) Lithosphere and Hydrosphere
 EASC100: EXAM1 (07) Lithosphere and Hydrosphere Name: 1. Why do Mercury and the Moon lack an atmosphere? A) They formed after all the gas had been used up. B) They are so cold that all their gases have
EASC100: EXAM1 (07) Lithosphere and Hydrosphere Name: 1. Why do Mercury and the Moon lack an atmosphere? A) They formed after all the gas had been used up. B) They are so cold that all their gases have
Introduction. Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth
 Introduction Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth Example: Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii Hot (~1,200 o C) lava pools around the volcanic vent. Hot, syrupy lava runs downhill as a lava flow. The
Introduction Volcano a vent where molten rock comes out of Earth Example: Kilauea Volcano, Hawaii Hot (~1,200 o C) lava pools around the volcanic vent. Hot, syrupy lava runs downhill as a lava flow. The
The McCully gas field in southern New Brunswick was discovered in the year 2000 on a joint drilling exploration venture by Corridor Resources Inc.
 1 The McCully gas field in southern New Brunswick was discovered in the year 2000 on a joint drilling exploration venture by Corridor Resources Inc. and Potash Corporation of Saskatchewan. Located about
1 The McCully gas field in southern New Brunswick was discovered in the year 2000 on a joint drilling exploration venture by Corridor Resources Inc. and Potash Corporation of Saskatchewan. Located about
Why does the Earth have volcanoes? Why is there Earthquakes?
 Why does the Earth have volcanoes? Why is there Earthquakes? Turn to your neighbor and review: How and when did the Earth form? How old are the first traces of life on Earth? Logical? * 1.5Ga (1 st multicellular
Why does the Earth have volcanoes? Why is there Earthquakes? Turn to your neighbor and review: How and when did the Earth form? How old are the first traces of life on Earth? Logical? * 1.5Ga (1 st multicellular
Chicontepec Basin is one of the most productive in
 SPECIAL Latin SECTION: America L a tin America Impact of shallow volcanics on seismic data quality in Chicontepec Basin, Mexico VICTOR PENA, University of Oklahoma SERGIO CHÁVEZ-PÉREZ, Instituto Mexicano
SPECIAL Latin SECTION: America L a tin America Impact of shallow volcanics on seismic data quality in Chicontepec Basin, Mexico VICTOR PENA, University of Oklahoma SERGIO CHÁVEZ-PÉREZ, Instituto Mexicano
Shale gas reservoir characterization workflows
 Shale gas reservoir characterization workflows Satinder Chopra + *, Ritesh K. Sharma +, James Keay + and Kurt J. Marfurt + Arcis Seismic Solutions, Calgary; The University of Oklahoma, Norman Downloaded
Shale gas reservoir characterization workflows Satinder Chopra + *, Ritesh K. Sharma +, James Keay + and Kurt J. Marfurt + Arcis Seismic Solutions, Calgary; The University of Oklahoma, Norman Downloaded
Multifocusing 3D diffraction imaging for dectection of fractured zones in mudstone reservoirs
 Multifocusing 3D diffraction imaging for dectection of fractured zones in mudstone reservoirs Alana Schoepp, Evgeny Landa, Stephane Labonte Shell Canada Ltd., Geomage, Shell CanadaLtd Summary Unconventional
Multifocusing 3D diffraction imaging for dectection of fractured zones in mudstone reservoirs Alana Schoepp, Evgeny Landa, Stephane Labonte Shell Canada Ltd., Geomage, Shell CanadaLtd Summary Unconventional
Name Class Date. In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements.
 CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
CHAPTER 5 Igneous Rocks SECTION 5.1 What are igneous rocks? In your textbook, read about the nature of igneous rocks. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the following statements. basaltic
Crustal Boundaries. As they move across the asthenosphere and form plate boundaries they interact in various ways. Convergent Transform Divergent
 Name: Date: Period: Plate Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonic plates are constantly moving and interacting As they move across the asthenosphere and form plate boundaries
Name: Date: Period: Plate Tectonics The Physical Setting: Earth Science CLASS NOTES Tectonic plates are constantly moving and interacting As they move across the asthenosphere and form plate boundaries
Search and Discovery Article #40507 (2010) Posted February 12, Abstract
 Click to view slides prepared for presentation. Application of From Seismic Interpretation to Tectonic Reconstruction Methodology to Study Pre-Tertiary Fractured Granite Basement Reservoir in Cuu Long
Click to view slides prepared for presentation. Application of From Seismic Interpretation to Tectonic Reconstruction Methodology to Study Pre-Tertiary Fractured Granite Basement Reservoir in Cuu Long
