Alternative Mechanisms for Volcanic Activity in Hotspot-Ridge Systems: The Northern Galapagos Province
|
|
|
- Aleesha Paul
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
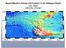
1 ABSTRACT for the Plume IV Penrose Conference Alternative Mechanisms for Volcanic Activity in Hotspot-Ridge Systems: The Northern Galapagos Province Karen S. Harpp, Colgate University, Department of Geology, Hamilton, NY Dennis J. Geist, University of Idaho, Department of Geological Sciences, Moscow, ID Many geologic features of the Galápagos Archipelago conform to the Hawaiianstyle hotspot model (Morgan, 1971). Most importantly, the islands near the central axis of the chain get older to the east as predicted from Nazca plate motion, and recent volcanic activity is focused in the western archipelago. Upon closer inspection, however, the Galápagos deviate from the simple hotspot model: (1) the islands are broadly distributed instead of forming a linear chain in the direction of plate motion; (2) most of the volcanoes are active (e.g., White et al., 1993); (3) geochemical variations define complex spatial patterns, reflecting contributions from multiple mantle reservoirs (Geist et al., 1988; White et al., 1993; Kurz and Geist, 1999; Harpp and White, 2001); and (4) the hotspot may be interacting extensively with the adjacent Galápagos spreading center (e.g., Schilling et al., 1982). Many of the deviations from the conventional hotspot model are most prominently expressed by the enigmatic volcanic features that grace the northern perimeter of the archipelago, including Genovesa, Marchena, and Pinta Islands, the northeast platform seamounts, and a bathymetric lineament including Wolf and Darwin islands and several elongate seamounts (Figure 1). In general, the northern volcanoes have been challenging to incorporate into regional models for the plume (e.g., Harpp and White, 2001). The present-day hotspot is thought to be centered near Fernandina Island (Kurz and Geist, 1999), and absolute motion of the Nazca plate is essentially eastward (Gripp and Gordon, 1990). Therefore, the northern volcanoes do not lie downstream from the plume and cannot be explained by the traditional mantle plume hypothesis. Lavas erupted on the northern islands exhibit a wide range of chemical compositions, from enriched (Pinta) to depleted (northeast platform seamounts), spanning nearly the entire range observed in the archipelago (White et al., 1993). The northern islands are some of the smallest volcanic centers in the Galápagos, exhibiting little resemblance to the large western shields. Many are morphologically unusual, and possess elongate, composite structures rather than symmetrical, conical shapes (Christie et al., 1992). Perhaps most importantly, the northern volcanoes are located between the main archipelago and the Galápagos spreading center, one of the few places in the world where two fundamental mantle processes operate in such proximity. We present results from a series of detailed field studies of Northern Galápagos volcanic centers, including Genovesa Island, a submarine ridge that extends from Genovesa, and the Wolf-Darwin Lineament.
2 A. Genovesa Island and Genovesa Ridge Genovesa Island, which lies between the central Galápagos Platform and the Galápagos Spreading Center, is unusual in several respects. Exposed Genovesa lavas are the most isotopically depleted intraplate ocean island basalts on the planet (Georoc database). Despite its circular coastline and calderas, it is crosscut by both eruptive and non-eruptive fissures trending NE-SW. The 075 bearing of the fissures parallels that of Genovesa Ridge, a 55 km-long volcanic rift zone that is the most prominent submarine rift in the Galápagos and constitutes the majority of the volume of the Genovesa magmatic complex (Figure 1). Genovesa Ridge was the focus of detailed multibeam and side-scan sonar surveys during the Revelle/Drift04 cruise in The ridge consists of three left-stepping en echelon segments; the abundances of lava flows, volcanic terraces, and eruptive cones are all consistent with constructive volcanic processes. The non-linear arrangement of eruptive vents and the ridge s en echelon structure indicate that it did not form over a single dike. Major and trace element compositions of Genovesa Ridge glasses are modeled by fractional crystallization along the same liquid line of descent as the island lavas, but some of the glasses are more primitive than any lavas sampled from the island. Most lavas on both the ridge and island have accumulated plagioclase. Incompatible trace element abundances of dredged Genovesa Ridge rocks are lower than the island s lavas, but ratios of the elements are similar in the two settings. The geochemical similarities indicate that the island and ridge lavas have nearly identical mantle sources. Glass inclusions in plagioclase phenocrysts from the ridge are compositionally diverse, with both higher and lower MgO than the matrix glass, suggesting homogenization at shallow levels. The structural and geochemical observations are best reconciled if Genovesa Ridge did not form in response to injection of magma laterally from a hotspot-supplied central volcano, which is how Kilauea s Puna Ridge is thought to operate. Instead, Genovesa Ridge and its western extension appear to be the result of passive upwelling directed by far-field tectonic stresses that are generated by tension across the 91 W transform. The proximity of the hotspot system causes magmatism in the extensional zones where it would not ordinarily occur. B. The Wolf-Darwin Lineament The Wolf-Darwin Lineament (WDL) lies between the focus of the Galápagos hotspot and the Galápagos Spreading Center, extending to the SE from its intersection with the ridge (Figure 1). Consequently, most researchers have attributed its origin to interaction between the plume and the adjacent ridge. We propose that the WDL is caused only partially by plume-ridge interaction, and instead that it is primarily the result of tensional stresses emanating from the inside corner of the transform fault at 91 W. An additional factor that amplifies the tension in this region is the oblique orientation of the major transform fault with respect to the Nazca plate s spreading direction. This setting creates a transtensional zone whereby strain is partitioned into strike-slip motion along the transform and extension throughout the inside corner of the ridge-transform system (Figure 2). The area under tension is magmatic owing to the overlapping effects of the ridge and the Galápagos plume.
3 The extensional model predicts no age progressive volcanism, which is supported by observed age relationships. The WDL volcanoes define two distinct chemical groups; lavas erupted south of Wolf Island have compositions similar to those produced along the GSC west of 93 W, while those from the northern WDL resemble GSC lavas from the segment directly north of the lineament. This geographic distribution implies that the WDL is supplied by the same type of hotspot-affected mantle as the segment of the GSC that produced the lithosphere underlying the volcanoes. The observed WDL geochemical gradients are consistent with the extension model; the region under tension simply taps hybrid products of mixing at the margins of the sub-ridge convection system and the periphery of the hotspot. The results of our Genovesa Ridge and WDL studies, in essence, are pointing toward a single, coherent explanation for the distribution, orientation, eruptive behavior, and compositional variations of all the Northern Galápagos volcanoes. These volcanic centers may be explained not as the direct result of hotspot activity, but instead as the serendipitous product of the proximity of a plume hotspot to the major transform that offsets the GSC at 91 W. The adjacent plume and mid-ocean ridge magmatic systems serve to generate widespread melting throughout the northern Galápagos region by causing upwelling in the mantle where it might not otherwise occur. The melts then migrate to the surface along tectonically controlled zones of tension imposed by an extensional transform (Figure 2). In effect, then, the adjacent plume illuminates the regional stress field with magma; at mid-ocean ridge systems without a proximate plume, such zones are not rendered observable. The range of lava compositions erupted throughout the Northern Galápagos, then, reflects the heterogeneous nature of the underlying mantle and provides a rare opportunity to assess the extent and distribution of the Galápagos plume as well as its interaction with the nearby ridge.
4 Figure 1. Bathymetric map of the northern Galápagos region, as compiled by Dr. William Chadwick of NOAA and Oregon State University and available at Solid and dashed black line is the Galapagos Spreading Center (GSC).
5 Figure 2. Conceptual model of the tectonic origin of the WDL. Orange tones indicate zone of influence of the Galápagos plume. Long arrows at the bottom of the figure oriented 186º show spreading direction of the Nazca plate. Short arrows represent extension necessary to accommodate plate spreading after strike-slip component of transform fault is removed. Bold red lines are observed volcanic lineaments (interpreted from bathymetric map, Figure 1). Ellipses are from the model of Gudmundsson [1995] for stresses around a transform fault-ridge intersection. Inset shows vector representation in velocity space of a model for strain partitioning through a combination of transform and extensional motions.
Roca Redonda as a result of an extensional transform zone
 Roca Redonda as a result of an extensional transform zone Heidi Berkenbosch 1 November 22, 2005 1 School of Oceanography, Box 357940, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington, 98195-7940. (206) 819-6978
Roca Redonda as a result of an extensional transform zone Heidi Berkenbosch 1 November 22, 2005 1 School of Oceanography, Box 357940, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington, 98195-7940. (206) 819-6978
Magma Migration, Storage and Evolution in the Galápagos Region John Sinton University of Hawai i
 Magma Migration, Storage and Evolution in the Galápagos Region John Sinton University of Hawai i The Importance of Magma Supply and its relationship to mantle melting Magma Chamber Processes as deduced
Magma Migration, Storage and Evolution in the Galápagos Region John Sinton University of Hawai i The Importance of Magma Supply and its relationship to mantle melting Magma Chamber Processes as deduced
G 3. AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society
 Geosystems G 3 AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society Article Volume 3, Number 11 29 November 2002 8504, doi: ISSN: 1525-2027 Wolf Darwin lineament and
Geosystems G 3 AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society Article Volume 3, Number 11 29 November 2002 8504, doi: ISSN: 1525-2027 Wolf Darwin lineament and
Roca Redonda Island formation due to development of an extensional transform zone, northern Galápagos Archipelago. Heidi Berkenbosch 1 4 March 2006
 Roca Redonda Island formation due to development of an extensional transform zone, northern Galápagos Archipelago Heidi Berkenbosch 1 4 March 2006 1 School of Oceanography, Box 357940, University of Washington,
Roca Redonda Island formation due to development of an extensional transform zone, northern Galápagos Archipelago Heidi Berkenbosch 1 4 March 2006 1 School of Oceanography, Box 357940, University of Washington,
Regional and local variations in geochemistry and tectonics along and across Central America
 Regional and local variations in geochemistry and tectonics along and across Central America Michael J. Carr, Department of Geological Sciences, Wright Lab Rutgers University, 610 Taylor Rd., Piscataway
Regional and local variations in geochemistry and tectonics along and across Central America Michael J. Carr, Department of Geological Sciences, Wright Lab Rutgers University, 610 Taylor Rd., Piscataway
SEA-FLOOR SPREADING. In the 1950 s and early 1960 s detailed study of the oceans revealed the following surprising information:-
 SEA-FLOOR SPREADING In the 1950 s and early 1960 s detailed study of the oceans revealed the following surprising information:- Detailed bathymetric (depth) studies showed that there was an extensive submarine
SEA-FLOOR SPREADING In the 1950 s and early 1960 s detailed study of the oceans revealed the following surprising information:- Detailed bathymetric (depth) studies showed that there was an extensive submarine
ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017
 ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017 Why is there no oceanic crust older than 200 million years? SUBDUCTION If new oceanic crust is being continuously created along the earth
ANOTHER MEXICAN EARTHQUAKE! Magnitude 7.1, Tuesday Sept. 19, 2017 Why is there no oceanic crust older than 200 million years? SUBDUCTION If new oceanic crust is being continuously created along the earth
Stop the Presses! New discovery about the origin of tetrapods!
 Mantle Plumes and Intraplate Volcanism Origin of Oceanic Island Volcanoes Lecture 20 Stop the Presses! New discovery about the origin of tetrapods! Tiktaalik rosaea Volcanism on the Earth Mid-ocean ridges
Mantle Plumes and Intraplate Volcanism Origin of Oceanic Island Volcanoes Lecture 20 Stop the Presses! New discovery about the origin of tetrapods! Tiktaalik rosaea Volcanism on the Earth Mid-ocean ridges
Lab 1: Plate Tectonics April 2, 2009
 Name: Lab 1: Plate Tectonics April 2, 2009 Objective: Students will be introduced to the theory of plate tectonics and different styles of plate margins and interactions. Introduction The planet can be
Name: Lab 1: Plate Tectonics April 2, 2009 Objective: Students will be introduced to the theory of plate tectonics and different styles of plate margins and interactions. Introduction The planet can be
Plate Tectonics. entirely rock both and rock
 Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Plate Tectonics I. Tectonics A. Tectonic Forces are forces generated from within Earth causing rock to become. B. 1. The study of the origin and arrangement of Earth surface including mountain belts, continents,
Volcanology and Petrology of the Taney Seamounts, Northeast Pacific Ocean
 MSc Research Proposal Volcanology and Petrology of the Taney Seamounts, Northeast Pacific Ocean Jason Coumans Introduction: Short chains of seamounts are observed near mid-ocean ridges and have been previously
MSc Research Proposal Volcanology and Petrology of the Taney Seamounts, Northeast Pacific Ocean Jason Coumans Introduction: Short chains of seamounts are observed near mid-ocean ridges and have been previously
Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms.
 Chapter 10 Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms. Reading Strategy Previewing Before you read the section,
Chapter 10 Section 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions This section discusses volcanic eruptions, types of volcanoes, and other volcanic landforms. Reading Strategy Previewing Before you read the section,
G 3. AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society
 Geosystems G 3 AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society Article Volume 7, Number 12 19 December 2006 Q12007, doi:10.1029/2006gc001290 ISSN: 1525-2027 Click
Geosystems G 3 AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society Article Volume 7, Number 12 19 December 2006 Q12007, doi:10.1029/2006gc001290 ISSN: 1525-2027 Click
Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # Main Idea:
 Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # A. Viscosity Group # B. Dissolved Gases Group # II. Volcanic Material
Chapter 10: Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Section 1: The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions I. Factors Affecting Eruptions Group # A. Viscosity Group # B. Dissolved Gases Group # II. Volcanic Material
Geologic Evolution of Latin America. Plate Tectonics: General Concepts & Applications to Latin America
 Geologic Evolution of Latin America Plate Tectonics: General Concepts & Applications to Latin America Structure of Earth: 3 major divisions of Core, Mantle, and Crust Upper mantle differs in the way that
Geologic Evolution of Latin America Plate Tectonics: General Concepts & Applications to Latin America Structure of Earth: 3 major divisions of Core, Mantle, and Crust Upper mantle differs in the way that
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
Plate Tectonics Lab II: Background Information
 Plate Tectonics Lab II: Background Information This lab is based on a UW ESS101 Lab. Note: Hand in only the Answer Sheet at the back of this guide to your Instructor Introduction One of the more fundamental
Plate Tectonics Lab II: Background Information This lab is based on a UW ESS101 Lab. Note: Hand in only the Answer Sheet at the back of this guide to your Instructor Introduction One of the more fundamental
OCN 201 Mantle plumes and hot spots
 OCN 201 Mantle plumes and hot spots Question Long-term (>50 million years) changes in sea level are caused by: A. Changes in the volume of water in the ocean B. Changes in the volume of the ocean basins
OCN 201 Mantle plumes and hot spots Question Long-term (>50 million years) changes in sea level are caused by: A. Changes in the volume of water in the ocean B. Changes in the volume of the ocean basins
Plate Tectonics. Essentials of Geology, 11 th edition Chapter 15
 1 Plate Tectonics Essentials of Geology, 11 th edition Chapter 15 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Plate Tectonics: summary in haiku form Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later...
1 Plate Tectonics Essentials of Geology, 11 th edition Chapter 15 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Plate Tectonics: summary in haiku form Alfred Wegener gave us Continental Drift. Fifty years later...
Multiple expressions of plume-ridge interaction in the Galápagos: Volcanic lineaments and ridge jumps
 Article Volume 13, Number 5 31 May 2012 Q05018, doi:10.1029/2012gc004093 ISSN: 1525-2027 Multiple expressions of plume-ridge interaction in the Galápagos: Volcanic lineaments and ridge jumps E. Mittelstaedt
Article Volume 13, Number 5 31 May 2012 Q05018, doi:10.1029/2012gc004093 ISSN: 1525-2027 Multiple expressions of plume-ridge interaction in the Galápagos: Volcanic lineaments and ridge jumps E. Mittelstaedt
Lecture 24 Hawaii. Hawaii
 Lecture 24 Hawaii Friday, April 22 nd 2005 Hawaii The Hawaiian Islands, in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, are volcanic islands at the end of a long chain of submerged volcanoes. These volcanoes get progressively
Lecture 24 Hawaii Friday, April 22 nd 2005 Hawaii The Hawaiian Islands, in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, are volcanic islands at the end of a long chain of submerged volcanoes. These volcanoes get progressively
MAR110 LECTURE #6 West Coast Earthquakes & Hot Spots
 17 September 2007 Lecture 6 West Coast Earthquakes & Hot Spots 1 MAR110 LECTURE #6 West Coast Earthquakes & Hot Spots Figure 6.1 Plate Formation & Subduction Destruction The formation of the ocean crust
17 September 2007 Lecture 6 West Coast Earthquakes & Hot Spots 1 MAR110 LECTURE #6 West Coast Earthquakes & Hot Spots Figure 6.1 Plate Formation & Subduction Destruction The formation of the ocean crust
24. Ocean Basins p
 24. Ocean Basins p. 350-372 Background The majority of the planet is covered by ocean- about %. So the majority of the Earth s crust is. This crust is hidden from view beneath the water so it is not as
24. Ocean Basins p. 350-372 Background The majority of the planet is covered by ocean- about %. So the majority of the Earth s crust is. This crust is hidden from view beneath the water so it is not as
REVIEW: The Setting - Climatology of the Hawaiian Archipelago
 REVIEW: The Setting - Climatology of the Hawaiian Archipelago Atmosphere and Ocean 5 facts: NE trade-winds tropical water subtropical gyre Seasonality N S gradients Four dominant swell regimes: north Pacific
REVIEW: The Setting - Climatology of the Hawaiian Archipelago Atmosphere and Ocean 5 facts: NE trade-winds tropical water subtropical gyre Seasonality N S gradients Four dominant swell regimes: north Pacific
Wolf Volcano, Galápagos Archipelago: Melting and Magmatic Evolution at the Margins of a Mantle Plume
 JOURNAL OF PETROLOGY PAGE 1 of 28 doi:10.1093/petrology/egi052 Journal of Petrology Advance Access published June 13, 2005 Wolf Volcano, Galápagos Archipelago: Melting and Magmatic Evolution at the Margins
JOURNAL OF PETROLOGY PAGE 1 of 28 doi:10.1093/petrology/egi052 Journal of Petrology Advance Access published June 13, 2005 Wolf Volcano, Galápagos Archipelago: Melting and Magmatic Evolution at the Margins
Imagine the first rock and the cycles that it has been through.
 A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
Geology 300, Physical Geology Spring 2019 Quiz Ch 19, Plate Tectonics Name
 Geology 300, Physical Geology Spring 2019 Quiz Ch 19, Plate Tectonics Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The portion of a fracture
Geology 300, Physical Geology Spring 2019 Quiz Ch 19, Plate Tectonics Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The portion of a fracture
Earthquakes. Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy
 Earthquakes Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy The amount of energy released determines the magnitude of the earthquake Seismic waves carry the energy away from its origin Fig. 18.1 Origin
Earthquakes Earthquakes are caused by a sudden release of energy The amount of energy released determines the magnitude of the earthquake Seismic waves carry the energy away from its origin Fig. 18.1 Origin
Study guide chapter 9
 Study guide chapter 9 1. What are the three ways solid mantle material can change phase to a liquid? Associate a boundary/hot spot to each way mantle material changes phase. 1. A decrease in pressure which
Study guide chapter 9 1. What are the three ways solid mantle material can change phase to a liquid? Associate a boundary/hot spot to each way mantle material changes phase. 1. A decrease in pressure which
Practice Questions: Plate Tectonics
 Practice Questions: Plate Tectonics 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which type of plate boundary is shown? A) divergent
Practice Questions: Plate Tectonics 1. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. Which type of plate boundary is shown? A) divergent
TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology
 Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Name Period Date TAKE HOME EXAM 8R - Geology PART 1 - Multiple Choice 1. A volcanic cone made up of alternating layers of lava and rock particles is a cone. a. cinder b. lava c. shield d. composite 2.
Map shows 3 main features of ocean floor
 Map shows 3 main features of ocean floor 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 3 Marine Provinces 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Chapter 3 Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean
Map shows 3 main features of ocean floor 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. Chapter 3 Marine Provinces 2017 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Chapter 3 Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean
A) B) C) D) 4. Which diagram below best represents the pattern of magnetic orientation in the seafloor on the west (left) side of the ocean ridge?
 1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
1. Crustal formation, which may cause the widening of an ocean, is most likely occurring at the boundary between the A) African Plate and the Eurasian Plate B) Pacific Plate and the Philippine Plate C)
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE
 Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Factors that determine the violence of an eruption
Prentice Hall EARTH SCIENCE Tarbuck Lutgens Chapter 10 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity 10.1 The Nature of Volcanic Eruptions Factors Affecting Eruptions Factors that determine the violence of an eruption
Lithospheric Stress State Responsible for Hotspots at Ridge-Transform- Intersections? Erin K Beutel College of Charleston Contrary to our current
 Lithospheric Stress State Responsible for Hotspots at Ridge-Transform- Intersections? Erin K Beutel College of Charleston Contrary to our current understanding of ridge-hotspot interactions, several papers
Lithospheric Stress State Responsible for Hotspots at Ridge-Transform- Intersections? Erin K Beutel College of Charleston Contrary to our current understanding of ridge-hotspot interactions, several papers
PHYSICAL GEOLOGY AND THE ENVIRONMENT (2 ND CANADIAN EDITION)
 Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Chapter Summary: Plate tectonics is a theory that suggests Earth's surface is divided into several large plates that change position and size. Intense geologic activity occurs
Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics Chapter Summary: Plate tectonics is a theory that suggests Earth's surface is divided into several large plates that change position and size. Intense geologic activity occurs
Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory
 Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory Chapter Outline 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Early Ideas About Continental Drift 2.3 What Is the Evidence for Continental Drift? 2.4 Features of the Seafloor 2.5 Earth
Chapter 2: Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory Chapter Outline 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Early Ideas About Continental Drift 2.3 What Is the Evidence for Continental Drift? 2.4 Features of the Seafloor 2.5 Earth
CHAPTER 2 THE WAY THE EARTH WORKS: EXAMINING PLATE TECTONICS
 CHAPTER 2 THE WAY THE EARTH WORKS: EXAMINING PLATE TECTONICS Coverage of plate tectonics is required early in introductory Geology as context for the mineralogy, petrology, structure, internal processes,
CHAPTER 2 THE WAY THE EARTH WORKS: EXAMINING PLATE TECTONICS Coverage of plate tectonics is required early in introductory Geology as context for the mineralogy, petrology, structure, internal processes,
Chapter 16. Mountain Building. Mountain Building. Mountains and Plate Tectonics. what s the connection?
 Chapter 16 Mountains and Plate Tectonics what s the connection? Mountain Building Most crustal deformation occurs along plate margins. S.2 Active Margin Passive Margin Mountain Building Factors Affecting
Chapter 16 Mountains and Plate Tectonics what s the connection? Mountain Building Most crustal deformation occurs along plate margins. S.2 Active Margin Passive Margin Mountain Building Factors Affecting
UNIT SIX: Earth s Structure. Chapter 18 Earth s History and Rocks Chapter 19 Changing Earth Chapter 20 Earthquakes and Volcanoes
 UNIT SIX: Earth s Structure Chapter 18 Earth s History and Rocks Chapter 19 Changing Earth Chapter 20 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Chapter Twenty: Earthquakes and Volcanoes 20.1 Earthquakes 20.2 Volcanoes
UNIT SIX: Earth s Structure Chapter 18 Earth s History and Rocks Chapter 19 Changing Earth Chapter 20 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Chapter Twenty: Earthquakes and Volcanoes 20.1 Earthquakes 20.2 Volcanoes
Galápagos and Easter: A Tale of Two Hotspots
 3 Galápagos and Easter: A Tale of Two Hotspots Karen S. Harpp 1, Paul S. Hall 2, and Matthew G. Jackson 3 ABSTRACT Spatial asymmetry in the isotopic composition of volcanic rocks has been identified at
3 Galápagos and Easter: A Tale of Two Hotspots Karen S. Harpp 1, Paul S. Hall 2, and Matthew G. Jackson 3 ABSTRACT Spatial asymmetry in the isotopic composition of volcanic rocks has been identified at
Plate Tectonics and the cycling of Earth materials
 Plate Tectonics and the cycling of Earth materials Plate tectonics drives the rock cycle: the movement of rocks (and the minerals that comprise them, and the chemical elements that comprise them) from
Plate Tectonics and the cycling of Earth materials Plate tectonics drives the rock cycle: the movement of rocks (and the minerals that comprise them, and the chemical elements that comprise them) from
Bathymetry Measures the vertical distance from the ocean surface to mountains, valleys, plains, and other sea floor features
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces Chapter Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces Chapter Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools.
Part A GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES. Name
 GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES Name Part A 1. The rough, jumbled blocky or jagged surface of a lava flow is called a. pahoehoe b. lahar c. aa d. phreatic 2. The Cascade volcanoes like Mt. St.
GEOLOGY 12 CHAPTER 4 WORKSHEET VOLCANOES Name Part A 1. The rough, jumbled blocky or jagged surface of a lava flow is called a. pahoehoe b. lahar c. aa d. phreatic 2. The Cascade volcanoes like Mt. St.
VOLCANIC STRATIGRAPHY AND PETROLOGY OF THE NORTHERN SNAEFELLSNES RIFT, SOUTHERN LAXÁRDALSFJÖLL, ICELAND
 VOLCANIC STRATIGRAPHY AND PETROLOGY OF THE NORTHERN SNAEFELLSNES RIFT, SOUTHERN LAXÁRDALSFJÖLL, ICELAND LEBN SCHUYLER Whitman College Sponsor: John Winter INTRODUCTION Iceland is exposed above sea level
VOLCANIC STRATIGRAPHY AND PETROLOGY OF THE NORTHERN SNAEFELLSNES RIFT, SOUTHERN LAXÁRDALSFJÖLL, ICELAND LEBN SCHUYLER Whitman College Sponsor: John Winter INTRODUCTION Iceland is exposed above sea level
The Nature of Igneous Rocks
 The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
Answer ALL questions in Section A, and TWO questions from Section B.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Environmental Sciences Main Series Undergraduate Examination 2012-2013 Candidate s no.: GEODYNAMICS: EARTH S ENGINE ENV-2A43 Time allowed: 2 hours. Answer ALL questions
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Environmental Sciences Main Series Undergraduate Examination 2012-2013 Candidate s no.: GEODYNAMICS: EARTH S ENGINE ENV-2A43 Time allowed: 2 hours. Answer ALL questions
Origin and Evolution of the Ocean Floor
 Origin and Evolution of the Ocean Floor Outline Mapping the Ocean Floor Continental Margins Origin of Oceanic Lithosphere Structure of Ocean Crust Mapping the ocean floor Depth originally measured by lowering
Origin and Evolution of the Ocean Floor Outline Mapping the Ocean Floor Continental Margins Origin of Oceanic Lithosphere Structure of Ocean Crust Mapping the ocean floor Depth originally measured by lowering
Full file at
 Chapter 2 PLATE TECTONICS AND PHYSICAL HAZARDS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. What direction is the Pacific Plate currently moving, based on the chain of Hawaiian Islands with only the easternmost island
Chapter 2 PLATE TECTONICS AND PHYSICAL HAZARDS MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. What direction is the Pacific Plate currently moving, based on the chain of Hawaiian Islands with only the easternmost island
Dynamic Earth A B1. Which type of plate boundary is located at the Jordan Fault? (1) divergent (3) convergent (2) subduction (4) transform
 Dynamic Earth A B1 1. The edges of most lithospheric plates are characterized by (1) reversed magnetic orientation (2) unusually rapid radioactive decay (3) frequent volcanic activity (4) low P-wave and
Dynamic Earth A B1 1. The edges of most lithospheric plates are characterized by (1) reversed magnetic orientation (2) unusually rapid radioactive decay (3) frequent volcanic activity (4) low P-wave and
Magma. Objectives. Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary.
 Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
Magma Objectives Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Vocabulary viscosity Magma Magma The ash that spews from some volcanoes can form
What can isotopes tell us about mantle dynamics? Sujoy Mukhopadhyay. Harvard University
 What can isotopes tell us about mantle dynamics? Sujoy Mukhopadhyay Harvard University The mantle zoo Hofmann, 1997 187 Os/ 188 Os 0.168 0.156 0.144 0.132 EM1 Hawaii Pitcairn DMM peridotites Shield Basalts
What can isotopes tell us about mantle dynamics? Sujoy Mukhopadhyay Harvard University The mantle zoo Hofmann, 1997 187 Os/ 188 Os 0.168 0.156 0.144 0.132 EM1 Hawaii Pitcairn DMM peridotites Shield Basalts
The High Lava Plains Project: Understanding the Causes of Continental Intraplate Tectonomagmatism
 The High Lava Plains Project: Understanding the Causes of Continental Intraplate Tectonomagmatism The High Lava Plains (HLP) of the northwestern USA is one of the most accessible yet least understood examples
The High Lava Plains Project: Understanding the Causes of Continental Intraplate Tectonomagmatism The High Lava Plains (HLP) of the northwestern USA is one of the most accessible yet least understood examples
Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway
 Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway The Earth is more than a giant ball made up of dirt, rocks, and minerals. The Earth may look like a giant ball from when looking at it from
Beneath our Feet: The 4 Layers of the Earty by Kelly Hashway The Earth is more than a giant ball made up of dirt, rocks, and minerals. The Earth may look like a giant ball from when looking at it from
6. In the diagram below, letters A and B represent locations near the edge of a continent.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below and on your knowledge of Earth science. The cross section represents the distance and age of ocean-floor bedrock found on both sides
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earthquakes Lesson 2 Volcanoes Chapter Wrap-Up
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earthquakes Lesson 2 Volcanoes Chapter Wrap-Up What causes earthquakes and volcanic eruptions? What do you think? Before you begin, decide if you agree or disagree with each
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Earthquakes Lesson 2 Volcanoes Chapter Wrap-Up What causes earthquakes and volcanic eruptions? What do you think? Before you begin, decide if you agree or disagree with each
Chapter Overview. Bathymetry. Measuring Bathymetry. Measuring Bathymetry
 CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces Chapter Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
CHAPTER 3 Marine Provinces Chapter Overview The study of bathymetry determines ocean depths and ocean floor topography. Echo sounding and satellites are efficient bathymetric tools. Most ocean floor features
LAST NAME: FIRST NAME: LAS POSITAS COLLEGE OCEANOGRAPHY LAB LAB 6 PLATE TECTONICS
 LAST NAME: FIRST NAME: LAS POSITAS COLLEGE OCEANOGRAPHY LAB LAB 6 PLATE TECTONICS (Modified from Exercise 4, Sea Floor Spreading and Plate Tectonics, Laboratory Exercises in Oceanography, Bernard W. Pipkin
LAST NAME: FIRST NAME: LAS POSITAS COLLEGE OCEANOGRAPHY LAB LAB 6 PLATE TECTONICS (Modified from Exercise 4, Sea Floor Spreading and Plate Tectonics, Laboratory Exercises in Oceanography, Bernard W. Pipkin
Full file at
 Essentials of Oceanography, 10e (Trujillo/Keller) Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all. A)
Essentials of Oceanography, 10e (Trujillo/Keller) Chapter 2 Plate Tectonics and the Ocean Floor Match the term with the appropriate phrase. You may use each answer once, more than once or not at all. A)
3. PLATE TECTONICS LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: PLATES
 LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: PLATES 3. PLATE TECTONICS The outer layers of the Earth are divided into the lithosphere and asthenosphere. The division is based on differences in mechanical properties
LAST NAME (ALL IN CAPS): FIRST NAME: PLATES 3. PLATE TECTONICS The outer layers of the Earth are divided into the lithosphere and asthenosphere. The division is based on differences in mechanical properties
Shape of the seafloor. Shape of the seafloor. Shape of the seafloor. Shape of the seafloor. Shape of the seafloor. Shape of the seafloor
 Multibeam echo sounders - Research vessel Scripps Institution of Oceanography R/V Roger Revelle depth Source: Scripps Institution of Oceanography http://woodshole.er.usgs.gov/project-pages/caribbean/movie1.html
Multibeam echo sounders - Research vessel Scripps Institution of Oceanography R/V Roger Revelle depth Source: Scripps Institution of Oceanography http://woodshole.er.usgs.gov/project-pages/caribbean/movie1.html
Divergent Boundaries: Origin and Evolution of the Ocean Floor Earth - Chapter 13 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College
 Divergent Boundaries: Origin and Evolution of the Ocean Floor Earth - Chapter 13 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Mapping the Ocean Floor Depth was originally measured by lowering weighted lines
Divergent Boundaries: Origin and Evolution of the Ocean Floor Earth - Chapter 13 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Mapping the Ocean Floor Depth was originally measured by lowering weighted lines
Chapter 02 The Sea Floor
 Chapter 02 The Sea Floor Multiple Choice Questions 1. One of the following is not one of the world's major ocean basins: A. Atlantic Ocean B. Arctic Ocean C. Indian Ocean D. Antarctic Ocean E. Pacific
Chapter 02 The Sea Floor Multiple Choice Questions 1. One of the following is not one of the world's major ocean basins: A. Atlantic Ocean B. Arctic Ocean C. Indian Ocean D. Antarctic Ocean E. Pacific
Laboratory #7: Plate Tectonics
 Materials Needed: 1. Pencil 2. Colored Pencils 3. Metric/Standard Ruler 4. Calculator 5. Tracing Paper Laboratory #7: Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics The Earth is composed of layers. At the center is a
Materials Needed: 1. Pencil 2. Colored Pencils 3. Metric/Standard Ruler 4. Calculator 5. Tracing Paper Laboratory #7: Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics The Earth is composed of layers. At the center is a
Ch. 9 Review. Pgs #1-31 Write Questions and Answers
 Ch. 9 Review Pgs. 356-357 #1-31 Write Questions and Answers 356-357 #1-5 Answers 1. The layer of the upper mantle that can flow is the: A - Asthenosphere 2. Most scientists rejected Wegener s theory of
Ch. 9 Review Pgs. 356-357 #1-31 Write Questions and Answers 356-357 #1-5 Answers 1. The layer of the upper mantle that can flow is the: A - Asthenosphere 2. Most scientists rejected Wegener s theory of
Earth s Continents and Seafloors. GEOL100 Physical Geology Ray Rector - Instructor
 Earth s Continents and Seafloors GEOL100 Physical Geology Ray Rector - Instructor OCEAN BASINS and CONTINENTAL PLATFORMS Key Concepts I. Earth s rocky surface covered by of two types of crust Dense, thin,
Earth s Continents and Seafloors GEOL100 Physical Geology Ray Rector - Instructor OCEAN BASINS and CONTINENTAL PLATFORMS Key Concepts I. Earth s rocky surface covered by of two types of crust Dense, thin,
Name Class Date. 1. What is the outermost layer of the Earth called?. a. core b. lithosphere c. asthenosphere d. mesosphere
 Name Class Date Assessment Geology Plate Tectonics MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. What is the outermost layer of the Earth called?. a. core b. lithosphere
Name Class Date Assessment Geology Plate Tectonics MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the letter of the correct answer in the space provided. 1. What is the outermost layer of the Earth called?. a. core b. lithosphere
Overview of Ch. 4. I. The nature of volcanic eruptions 9/19/2011. Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5
 Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
Overview of Ch. 4 Volcanoes and Other Igneous Activity Chapter 4 or 5 I. Nature of Volcanic Eruptions II. Materials Extruded from a Volcano III.Types of Volcanoes IV.Volcanic Landforms V. Plutonic (intrusive)
G 3. AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society
 Geosystems G 3 AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society Article Volume 3, Number 10 10 October 2002 8501, doi:10.1029/2002gc000350 ISSN: 1525-2027 Correlated
Geosystems G 3 AN ELECTRONIC JOURNAL OF THE EARTH SCIENCES Published by AGU and the Geochemical Society Article Volume 3, Number 10 10 October 2002 8501, doi:10.1029/2002gc000350 ISSN: 1525-2027 Correlated
Structure of the Earth and the Origin of Magmas
 Page 1 of 12 EENS 2120 Petrology Tulane University Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Structure of the Earth and the Origin of Magmas This document last updated on 23-Jan-2015 Magmas do not form everywhere beneath
Page 1 of 12 EENS 2120 Petrology Tulane University Prof. Stephen A. Nelson Structure of the Earth and the Origin of Magmas This document last updated on 23-Jan-2015 Magmas do not form everywhere beneath
Module 7: Plate Tectonics and Earth's Structure Topic 3 Content: Volcanoes - The Basics Notes. Volcanoes The Basics
 Volcanoes The Basics 1 Hello, my name is Dr. Simpson, and I am a volcanologist. I am here to explain some basic information about volcanoes to you. 3 I think we should get started by taking a look at the
Volcanoes The Basics 1 Hello, my name is Dr. Simpson, and I am a volcanologist. I am here to explain some basic information about volcanoes to you. 3 I think we should get started by taking a look at the
12. The diagram below shows the collision of an oceanic plate and a continental plate.
 Review 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below, which shows the boundary between two lithospheric plates. Point X is a location in the continental lithosphere. The depth
Review 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below, which shows the boundary between two lithospheric plates. Point X is a location in the continental lithosphere. The depth
Earth and Space Science Semester 2 Exam Review. Part 1. - Convection currents circulate in the Asthenosphere located in the Upper Mantle.
 Earth and Space Science 2015 Semester 2 Exam Review Part 1 Convection -A form of heat transfer. - Convection currents circulate in the Asthenosphere located in the Upper Mantle. - Source of heat is from
Earth and Space Science 2015 Semester 2 Exam Review Part 1 Convection -A form of heat transfer. - Convection currents circulate in the Asthenosphere located in the Upper Mantle. - Source of heat is from
Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory
 Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory What is Plate Tectonics? - 7 large tectonic plates and many smaller ones that break up the lithosphere - Plates are brittle and float on asthenosphere and glide past
Plate Tectonics: A Unifying Theory What is Plate Tectonics? - 7 large tectonic plates and many smaller ones that break up the lithosphere - Plates are brittle and float on asthenosphere and glide past
Lecture 38. Igneous geochemistry. Read White Chapter 7 if you haven t already
 Lecture 38 Igneous geochemistry Read White Chapter 7 if you haven t already Today. Magma mixing/afc 2. Spot light on using the Rare Earth Elements (REE) to constrain mantle sources and conditions of petrogenesis
Lecture 38 Igneous geochemistry Read White Chapter 7 if you haven t already Today. Magma mixing/afc 2. Spot light on using the Rare Earth Elements (REE) to constrain mantle sources and conditions of petrogenesis
Unit 6: The Sea Floor
 Unit 6: The Sea Floor Turn to Page 62 in Introduction to the World s Oceans Study the bathymetric chart What features do you see? How do the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans differ? What do you think accounts
Unit 6: The Sea Floor Turn to Page 62 in Introduction to the World s Oceans Study the bathymetric chart What features do you see? How do the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans differ? What do you think accounts
Plate Tectonics. Earth has distinctive layers - Like an onion
 Plate Tectonics Earth has distinctive layers - Like an onion Earth s Interior Core: Metallic (Iron, Nickel) Inner (hot, solid, dense, Iron, Nickel) Outer (cooler, liquid, less dense) Crust (outermost layer):
Plate Tectonics Earth has distinctive layers - Like an onion Earth s Interior Core: Metallic (Iron, Nickel) Inner (hot, solid, dense, Iron, Nickel) Outer (cooler, liquid, less dense) Crust (outermost layer):
Unit 4 Lesson 4 Volcanoes. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 Magma Magic What is a volcano? A volcano is any place where gas, ash, or melted rock come out of the ground. Many volcanoes are dormant, meaning an eruption has not occurred in a long period of time. What
Magma Magic What is a volcano? A volcano is any place where gas, ash, or melted rock come out of the ground. Many volcanoes are dormant, meaning an eruption has not occurred in a long period of time. What
MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY
 MARINE GEOLOGY MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY Marine Geology 4 LAYERS OF THE EARTH CRUST THICKNESS: VARIES BETWEEN OCEAN & CONTINENTS 5-40 KM STATE: SOLID ELEMENTS: SILICON, ALUMINUM, CALCIUM, SODIUM, POTASSIUM
MARINE GEOLOGY MARINE GEOLOGY & GEOGRAPHY Marine Geology 4 LAYERS OF THE EARTH CRUST THICKNESS: VARIES BETWEEN OCEAN & CONTINENTS 5-40 KM STATE: SOLID ELEMENTS: SILICON, ALUMINUM, CALCIUM, SODIUM, POTASSIUM
Lecture Marine Provinces
 Lecture Marine Provinces Measuring bathymetry Ocean depths and topography of ocean floor Sounding Rope/wire with heavy weight Known as lead lining Echo sounding Reflection of sound signals 1925 German
Lecture Marine Provinces Measuring bathymetry Ocean depths and topography of ocean floor Sounding Rope/wire with heavy weight Known as lead lining Echo sounding Reflection of sound signals 1925 German
USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES
 USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES Observe the world map and each enlargement Pacific Northwest Tibet South America Japan 03.00.a1 South Atlantic Arabian Peninsula Observe features near the Pacific Northwest
USU 1360 TECTONICS / PROCESSES Observe the world map and each enlargement Pacific Northwest Tibet South America Japan 03.00.a1 South Atlantic Arabian Peninsula Observe features near the Pacific Northwest
Why Does Oceanic Crust Sink Beneath Continental Crust At Convergent Boundaries
 Why Does Oceanic Crust Sink Beneath Continental Crust At Convergent Boundaries What is the process by which oceanic crust sinks beneath a deep-ocean Why does oceanic crust sink beneath continental crust
Why Does Oceanic Crust Sink Beneath Continental Crust At Convergent Boundaries What is the process by which oceanic crust sinks beneath a deep-ocean Why does oceanic crust sink beneath continental crust
Tectonic-Igneous Associations
 Tectonic-Igneous Associations Associations on a larger scale than the petrogenetic provinces An attempt to address global patterns of igneous activity by grouping provinces based upon similarities in occurrence
Tectonic-Igneous Associations Associations on a larger scale than the petrogenetic provinces An attempt to address global patterns of igneous activity by grouping provinces based upon similarities in occurrence
1. I can describe evidence for continental drift theory (e.g., fossil evidence, mountain belts, paleoglaciation)
 Science 10 Review Earth Science Vocabulary asthenosphere continental drift theory converging plates diverging plates earthquakes epicentre fault hot spot inner core lithosphere mantle mantle convection
Science 10 Review Earth Science Vocabulary asthenosphere continental drift theory converging plates diverging plates earthquakes epicentre fault hot spot inner core lithosphere mantle mantle convection
Plate Tectonics: The New Paradigm
 Earth s major plates Plate Tectonics: The New Paradigm Associated with Earth's strong, rigid outer layer: Known as the lithosphere Consists of uppermost mantle and overlying crust Overlies a weaker region
Earth s major plates Plate Tectonics: The New Paradigm Associated with Earth's strong, rigid outer layer: Known as the lithosphere Consists of uppermost mantle and overlying crust Overlies a weaker region
Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift
 Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift Predecessor to modern plate tectonics Shape and fit of the continents was the initial evidence Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Taylor (1908) Wegner (1915) Fig.
Before Plate Tectonics: Theory of Continental Drift Predecessor to modern plate tectonics Shape and fit of the continents was the initial evidence Snider-Pelligrini (1858) Taylor (1908) Wegner (1915) Fig.
The Sea Floor. Chapter 2
 The Sea Floor Chapter 2 Geography of the Ocean Basins World ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area Northern Hemisphere = 61% of the total area is ocean. Southern Hemisphere = about
The Sea Floor Chapter 2 Geography of the Ocean Basins World ocean is the predominant feature on the Earth in total area Northern Hemisphere = 61% of the total area is ocean. Southern Hemisphere = about
The role of lithospheric gabbros on the composition of Galapagos lavas
 Earth and Planetary Science Letters 257 (2007) 391 406 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl The role of lithospheric gabbros on the composition of Galapagos lavas A.E. Saal a,, M.D. Kurz b, S.R. Hart c, J.S. Blusztajn
Earth and Planetary Science Letters 257 (2007) 391 406 www.elsevier.com/locate/epsl The role of lithospheric gabbros on the composition of Galapagos lavas A.E. Saal a,, M.D. Kurz b, S.R. Hart c, J.S. Blusztajn
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. What can cause some of the most dramatic changes to Earth s surface? a. solar activity b. tides c. geysers d. volcanic eruptions
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. What can cause some of the most dramatic changes to Earth s surface? a. solar activity b. tides c. geysers d. volcanic eruptions
Visualizing Earth Science. Chapter Overview. Volcanoes and Eruption Types. By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner. Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other
 Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 9 Volcanism and Other Igneous Processes Volcanoes types and effects of eruption Chapter Overview Melting and cooling of rocks Geological
Plate Tectonics. Continental Drift Sea Floor Spreading Plate Boundaries
 Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Sea Floor Spreading Plate Boundaries Continental Drift 1915, Alfred Wegener - Pangea hypothesis: suggested Earth s continents were part of a large super-continent 200
Plate Tectonics Continental Drift Sea Floor Spreading Plate Boundaries Continental Drift 1915, Alfred Wegener - Pangea hypothesis: suggested Earth s continents were part of a large super-continent 200
When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere.
 When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere. A volcano is a mountain that forms when magma reaches the
When Mount St. Helens erupted, trapped gases caused the north side of the mountain to explode. Volcanic ash was ejected high into the atmosphere. A volcano is a mountain that forms when magma reaches the
! Profile of Mauna Loa in Hawaii. Mauna Loa is one of five huge shield volcanoes that make up the island of Hawaii.
 - Shield Volcanoes - Low, rounded profiles; slope angles 2-10 ; composed of numerous flows of mafic composition and little explosive activity - Largest of all volcanoes! Shield volcanoes consist of numerous
- Shield Volcanoes - Low, rounded profiles; slope angles 2-10 ; composed of numerous flows of mafic composition and little explosive activity - Largest of all volcanoes! Shield volcanoes consist of numerous
10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves.
 Map of ocean floor Evidence in Support of the Theory of Plate Tectonics 10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves. The Earth's magnetic field behaves as if there were a bar magnet in the center of
Map of ocean floor Evidence in Support of the Theory of Plate Tectonics 10. Paleomagnetism and Polar Wandering Curves. The Earth's magnetic field behaves as if there were a bar magnet in the center of
WHAT IS A MAGMA. Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth.
 UNIT - 8 VOLCANOES WHAT IS A MAGMA Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth. In some instances, it solidifies within the crust to form plutonic
UNIT - 8 VOLCANOES WHAT IS A MAGMA Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth. In some instances, it solidifies within the crust to form plutonic
60% water. Big Bang: 14,000 millions years ago The Earth originated about 4,500 millions years ago its orbit allows water to exist in a liquid state!
 Ch2. The Sea Floor #1 Why geology of the oceans? Marine habitats are directly shaped by geological processes The form of the coastlines The depth of the water Type of bottom (muddy, sandy, rocky) #2 Geological
Ch2. The Sea Floor #1 Why geology of the oceans? Marine habitats are directly shaped by geological processes The form of the coastlines The depth of the water Type of bottom (muddy, sandy, rocky) #2 Geological
Plate Tectonics Notes
 Plate Tectonics Notes Last 30 Days Earthquakes Physical Features Last 30 Days Earthquakes with Plate Boundaries Earth s Structure Earth s Layers Core: Inner Core: Center of the earth, solid ball of metal
Plate Tectonics Notes Last 30 Days Earthquakes Physical Features Last 30 Days Earthquakes with Plate Boundaries Earth s Structure Earth s Layers Core: Inner Core: Center of the earth, solid ball of metal
Tectonics. Planets, Moons & Rings 9/11/13 movements of the planet s crust
 Tectonics Planets, Moons & Rings 9/11/13 movements of the planet s crust Planetary History Planets formed HOT Denser materials fall to center Planet cools by conduction, convection, radiation to space
Tectonics Planets, Moons & Rings 9/11/13 movements of the planet s crust Planetary History Planets formed HOT Denser materials fall to center Planet cools by conduction, convection, radiation to space
GEOLOGY 101 LABORATORY LAB
 Student Name: College: Grade: GEOLOGY 101 LABORATORY LAB Isostasy and Plate Tectonics Understanding and Analyzing Vertical and Horizontal Plate Motion Part I. Density and Isostatic Equilibrium Introduction:
Student Name: College: Grade: GEOLOGY 101 LABORATORY LAB Isostasy and Plate Tectonics Understanding and Analyzing Vertical and Horizontal Plate Motion Part I. Density and Isostatic Equilibrium Introduction:
Directed Reading. Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. Some volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than a(n) a. hand grenade. b. earthquake. c. geyser. d. atomic bomb. 2. The cause
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading Section: Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics 1. Some volcanic eruptions can be more powerful than a(n) a. hand grenade. b. earthquake. c. geyser. d. atomic bomb. 2. The cause
