2 This different functional groups on hydroxyapatite formation. Therefore in this study, SAMs were modified with four functional groups, -COOH, -NH 2,
|
|
|
- Cornelia Benson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 This 2010; 29(4): Chemical analyses of hydroxyapatite formation on SAM surfaces modified with COOH, NH 2, CH 3, and OH functions Isao HIRATA 1, Mai AKAMATSU 1, Eri FUJII 1, Suchit POOLTHONG 2 and Masayuki OKAZAKI 1 1 Department of Biomaterials Science, Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, Hiroshima University, Kasumi, Minami-ku, Hiroshima , Japan 2 Department of Operative Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, Chulalongkorn University, Henri Dunant Rd, Bangkok 10330, Thailand Corresponding author, Masayuki OKAZAKI; okazakix@hiroshima-u.ac.jp Hydroxyapatite formation was examined at the surface of self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) modified with four functional groups, -COOH, -NH 2, -CH 3, and -OH. For COOH-SAM and NH 2-SAM, scanning electron spectroscopic observation showed that flake-like sheet crystals covered the whole wafer and small broccoli-like crystals were observed occasionally on the flake-like crystal base layer. For CH 3-SAM and OH-SAM, no flake-like sheet crystals were observed; broccoli-like crystals were observed in a dispersed manner for CH 3-SAM, but in localized spots for OH-SAM. X-ray diffraction patterns showed a strong apatite pattern oriented toward the c-axis direction for COOH-SAM. ESCA analysis revealed distinct Ca, P, O peaks for COOH-, NH 2-, CH 3-, and OH-SAM. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis indicated that during the supply of supersaturated calcium phosphate solution, the deposition of precipitates increased monotonically with time for COOH-SAM, increased slightly for NH 2-SAM, but little increase in deposition was detected for CH 3-SAM and OH-SAM. Keywords: Hydroxyapatite formation, SAM surfaces, Surface plasmon resonance INTRODUCTION It is speculated that organic substances such as proteins play an important role at the initial stage of in vivo apatite formation. For example, collagen behaves as an extracellular matrix during bone formation 1) and non-collagenous proteins such as gene proteins are present during enamel formation. The main functional groups of amino acids that construct proteins are -COOH, -NH 2, -CH 3, and -OH. It is interesting to note that these functional groups may be involved in initial apatite formation. A self-assembled monolayer (SAM) is an organized layer of adjacent multiple linear organic molecules with a coupling agent at one end and a functionalized end group at the other, separated by an organic spacer. For research into the interfacial phenomena of bioadhesion and biocompatibility, SAMs have attracted significant attention because they provide a systematic way to modify the surface properties of materials such as gold wafers. To date, it has been reported that SAM surfaces on gold wafers could be modified with four typical functional groups, -COOH, -NH 2, -CH 3, and -OH, for apatite formation 2-4). Apart from the use of SAMs to produce biocompatible hydroxyapatite (HA) coatings on implant substrates, attention is also turned to biomaterials such as titanium and its alloys or sintered ceramics which possess the dual properties of good biocompatibility and strength. To expedite patient recovery, the need for implants to be rapidly osseointegrated led to the need for biomaterials with functionalized surfaces. Various techniques have been developed for producing HA coatings on implant surfaces, such as plasma spraying 5), hot isostatic pressing (HIP) 6), sol-gel technique and biomimetic precipitation 7). Unfortunately, subsequent heat treatment at high temperature results in cracking and poor bond strength between the hydroxyapatite coating and metal substrate. Further, an HA coating of high crystallinity, which is desirable for optimal biocompatibility, could not be achieved through these methods. To improve the biological properties of HA coatings on biomaterials, several studies have explored and examined the approach of SAM-assisted HA coating of Ti implant surfaces. Liu et al. 8) reported that HA formation was successfully achieved with -PO 4H 2 and -COOH, but not with -OH and -CH=CH 2. Notably, the -COOH end group appeared to provide the optimal SAM surface for nucleation and growth of biomimetic crystalline HA 8). This finding reinforced the notion that human bone sialoprotein is a potent nucleator of HA and is linked to the protein s glutamic acid-rich sequences. Therefore, the affinity for interaction between polar side groups on the protein and positive (calcium) or negative (phosphate) sites in the crystal is of significant interest. However, no detailed crystallographic and morphological studies of apatite formation on SAM surfaces have been reported. Many researchers have used simulated body fluid (SBF) solutions in their investigations of apatite formation on functionalized surfaces 4,7-11), but the reproducibility of data posed a problem. Moreover, in most investigations, SBF solutions were adapted to simulate clinical use, such as hydroxyapatite coating on titanium surface. In contrast, our focus was to obtain reproducible and stable results on the effects of Received Feb 5, 2010: Accepted Apr 1, 2010 doi: /dmj JOI JST.JSTAGE/dmj/
2 2 This different functional groups on hydroxyapatite formation. Therefore in this study, SAMs were modified with four functional groups, -COOH, -NH 2, -CH 3, and -OH 12-14), on gold wafer surfaces. Our next focus was to conduct a basic research on chemical analysis, where surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis in addition to SEM, XRD, ESCA was used for real-time observation of the early initial deposition of calcium phosphate. In view of this focus on chemical analysis, a simple CaP supersaturated solution was used in this study as opposed to an SBF containing Ca 2+ 3, PO 4, and OH ions with other trace elements, which was frequently used in experiments on biomimetic hydroxyapatite formation 4,7-11). MATERIALS AND METHODS Preparation of gold wafers Glass plates (diameter: 15 mm, thickness: 1 mm) were supplied from Matsunami Glass Industries (Osaka, Japan). Gold wafers were prepared in Osaka Vacuum Industrial Co. Ltd. (Osaka, Japan) by first depositing Cr (1 nm) and then Au (49 nm) onto the glass plates under Pa with electron beam heating. Preparation of self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) 1-dodecanethiol (CH 3-SH) was purchased from Wako Pure Chemical Industries (Osaka, Japan). 11- mercapto-1-undecanol (OH-SH), 11-mercapto-1- undecanoic acid (COOH-SH), and 11-amino-1- undecanthiol (NH 2-SH) reagents were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Japan (Tokyo, Japan). The gold wafers were cleaned by immersion in a piranha solution (7:3 volume ratio of sulfuric acid and 30% H 2O 2) for 15 minutes and then washed three times with ultrapure water to remove contaminants. Following which, the gold wafers were immersed in ultrapure water until SAM deposition. 1 mmol/l COOH-SH, NH 2-SH, CH 3-SH and OH-SH solutions were prepared with nitrogen gas bubbled through deoxidized ethanol for 1 hour. The gold wafers were immersed in these alkanethiol solutions for 24 hours, and different kinds of SAMs (COOH-SAM, NH 2 SAM, CH 3-SAM and OH-SAM) were formed independently on gold wafer surfaces (Fig. 1). These SAM wafers were immersed in 2-propanol until experiment was carried out. Characterization of SAM surfaces Surface chemical compositions of SAMs were determined using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS or ESCA, AXIS-HS, Kratos, Manchester, UK) under 10 7 Pa. Monochromatic Al-Kα X-rays were used with a 15 kv acceleration voltage and 10 ma filament electric current. High-resolution spectra for carbon and oxygen elements were obtained at a takeoff angle of 35. Wettability of SAMs was measured beforehand using a lab-made static water contact angle measurement apparatus. For each water contact angle Fig. 1 Schema of a self-assembled monolayer (SAM). measurement, 0.5 µl of ultrapure water was dropped on each SAM a measurement process which was repeated five times for each SAM. The mean contact angles of COOH-SAM, NH 2-SAM, CH 3-SAM, and OH- SAM were 14.1±4.1, 55.5±4.3, 104.4±2.8, and 4.6±1.6 degrees respectively (n=5). SEM observation, XRD and ESCA analyses of precipitates on SAM surfaces 50 mmol/l Ca(CH 3COOH) 2.H 2O, 30 mmol/l NH 4H 2PO 4, and 1.3 mol/l CH 3COONH 4 were mixed at 1:1:2 to prepare a buffer solution of ph 7.4±0.2. Final calcium and phosphate concentrations in the mixed solution were 12.5 mmol/l and 7.5 mmol/l respectively. In a preliminary experiment, the solution of 12.5 mmol/l calcium and 7.5 mmol/l phosphate did not show observable precipitation for several hours after mixing, but slight precipitation after one-day incubation at 37 C. With a solution of 10.0 mmol/l calcium and 6.0 mmol/l phosphate, no precipitation was observed even after one-month incubation at 37 C. Therefore, in this study, the solution of Ca=12.5 mmol/l and P=7.5 mmol/ L was adopted for the supersaturated calcium phosphate solution. 10 ml of the calcium phosphate solution was gently flowed into a plastic vessel, in which gold wafers coated with each SAM were set and incubated at 37ºC (n=6). After 3 days and 1 week, SAM wafers were
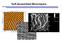
3 This 3 which showed the intensity of the reflected light angle against the incidence angle, was recorded. Next, the same acetate buffer solution containing calcium phosphate described above was injected and allowed to flow into the cell for 15 minutes. Finally, the calcium phosphate solution was washed out of the flow cell with ultrapure water and the SPR reflectivity curve was recorded again. Amount of calcium phosphate deposited on each SAM was determined based on the SPR angle shift, which was defined as the angle difference between the minima of two SPR reflectivity curves. Medium flow was 2.5 ml/min and temperature was kept at 25ºC. RESULTS SEM observations of precipitates on SAM surfaces After 3-day incubation, each wafer was washed three times and dried in a desiccator. COOH-SAM and NH 2 SAM surfaces were completely covered with a white precipitate, while CH 3-SAM was partially covered with a white precipitate. With OH-SAM, only a small amount of precipitate was observed on the wafer (Fig. 3: upper center). For COOH-SAM and NH 2-SAM, SEM observation showed that flake-like sheet crystals covered the whole wafer and small broccoli-like crystals were observed occasionally on the flake-like crystal base layer (Figs. 3a and 3b). For CH 3-SAM and OH-SAM, no flake-like sheet crystals were observed and broccoli-like crystals were observed in a dispersed manner for CH 3-SAM (Fig. 3c). For OH-SAM, broccoli-like crystals were observed in localized spots (Fig. 3d). After 1-week incubation, there were no fundamental differences in the precipitate crystals formed on COOH-SAM (Fig. 4a). At high magnification, large plate-like crystals in the flake-like base layer were observed (Fig. 4b). Fig. 2 Principle of surface plasmon resonance (SPR) detection. rinsed with ultrapure water three times and then dried in a desiccator. After which, the SAM wafer surfaces were observed with a scanning electron microscope (SEM) and analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis (ESCA). SPR analysis of calcium phosphate deposition In this study, amount of calcium phosphate deposition on each SAM was measured using a lab-made surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensor. SPR is an optical technique for determining refractive index changes at a surface, which is typically an interface between a solid support phase and a liquid phase (Fig. 2). A SAM wafer was set on the SPR flow stage. First, ultrapure water was injected and allowed to flow into the flow cell. At this juncture, a SPR reflectivity curve, XRD analysis of precipitates on SAM surfaces X-ray diffraction patterns showed a strong apatite pattern orientated toward the c-axis direction for COOH-SAM (Fig. 5a) and NH 2-SAM. For CH 3-SAM, no clear orientation of apatite was observed and peak intensity was weak (Fig. 5b). For OH-SAM, X-ray diffraction analysis was difficult because too few crystals were formed on the wafer surface. ESCA analysis of precipitates on SAM surfaces ESCA analysis revealed a strong O peak and distinct Ca and P peaks for COOH-, NH 2-, CH 3- and OH-SAM (Fig. 6). For NH 2-SAM, an Au peak was observed probably because only a thin layer of hydroxyapatite was formed. For OH-SAM with only a small amount of precipitate formed on the wafer and a detected Au peak, ESCA analysis was still possible because ESCA analysis required only a limited micrometer area. SPR analysis of calcium phosphate deposition on SAM surfaces The SPR analysis shown in Fig. 7 indicated that the
4 4 This deposition of precipitates increased with time monotonically for COOH-SAM during the supply of supersaturated calcium phosphate solution, increased slightly for NH 2-SAM, but increase in deposition was scarcely detected for CH 3-SAM and OH-SAM, probably because of lower affinity and short (15 minutes) supply of calcium phosphate solution. DISCUSSION SAM is a monolayer formed on the gold surface by inter-molecular attraction (Van der Waals forces) Fig. 3 Photo (upper center) and scanning electron micrographs (SEM) of the precipitates deposited on the surfaces of COOH-SAM (a), NH 2-SAM (b), CH 3-SAM (c), and OH-SAM (d) wafers after 3-day incubation at 37ºC.
5 This 5 Fig. 4 Scanning electron micrographs (SEM) of the precipitates deposited on the surface of COOH-SAM after 1-week incubation at 37ºC (a) and the magnified photo of its flake-like base layer (b). Fig. 5 X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of the precipitates deposited on the surface of COOH SAM (a) and CH 3-SAM (b) wafer after 3-day incubation at 37ºC. between a gold thiol head group and an alkyl chain group. Therefore, the physical adsorption of each functional group -COOH, -NH 2, -CH 3, and -OH on the gold wafer surfaces is caused by and controlled by Van der Waals force (Fig. 1). Results of this study then showed that the surface properties of SAM significantly affected the formation of calcium phosphate precipitates. Whereas adsorption was traditionally and typically explained using the concept of hydrophilic and hydrophobic phenomena, which are represented by -OH (water contact angle: 4.6 degree) and -CH 3 (water contact angle: degree) functions respectively, this study revealed that there was low adsorption of calcium phosphate crystals on OH-SAM despite its very low water contact angle. On the other hand, COOH-SAM (water contact angle: 14.1 degree) and NH 2-SAM (water contact angle: 55.5 degree), which had an electrical charge, were favorable for apatite formation. When discussing the wettability of a material s surface, chemical composition and especially electrical charge in addition to surface roughness and morphology must also be considered because interface affinity is very important. Since hydroxyapatite is an ionic crystal, the attraction and adsorption of positively charged calcium ions would promote apatite formation. As illustrated in Fig. 8, calcium ions are apt to be trapped by the double scissors of COO function to form a columnar Ca framework in hydroxyapatite (HAp) crystal. Subsequently, the hydroxyapatite crystals gradually oriented along the c- axis as shown in Fig. 5a. In this study, the morphology of hydroxyapatite crystals dramatically changed according to the different functional groups, -COOH, -NH 2, -CH 3, and -OH, modified onto the SAM. For -COOH and -NH 2, large flake-like crystals were formed on the SAM surfaces. For -CH 3 and -OH, only small round crystals precipitated on the SAM surfaces. The morphological
6 6 This Fig. 6 Electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis (ESCA) spectra of the precipitates deposited on the surfaces of COOH- SAM, NH 2-SAM, CH 3-SAM, and OH-SAM wafers after 3-day incubation at 37ºC. Fig. 7 SPR angle shifts as a function of real-time deposition on the surfaces of COOH-SAM, NH 2 SAM, CH 3-SAM, and OH-SAM wafers. differences probably arose from the differences in electrical force attracting the calcium and phosphate ions, whereby the latter ions then initiated the formation of hydroxyapatite on SAM surfaces. In addition, it must be highlighted that the crystallinity and orientation reflected on the X-ray diffraction patterns (Fig. 6) are affected by crystal morphology, hence careful attention was paid to the experimental conditions in this study. By using a simple calcium phosphate solution of a relatively higher concentration than SBF, stable and reproducible results were obtained in this study. On the quantitative assessment of apatite formation, SPR analysis was used in this study as opposed to the quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) which was used in previous studies 9-11). The QCM detects weight gain on the charged surfaces, but is strongly affected by small changes in temperature, viscosity, and/or hydrodynamic conditions. On the contrary, SPR uses laser light to detect angle changes on a material surface until a stable SPR angle signal is attained and is less affected by the aforementioned conditions. Therefore, compared to QCM, SPR is capable of analyzing molecular-level surfaces and is hence more suitable for detecting the initial stage of apatite formation.
7 This 7 unit dimension of hydroxyapatite was formed. Another important factor that influences calcium phosphate formation is the ph condition. Hydroxyapatite (HAp) forms in alkaline conditions; in strongly acidic conditions, it is mainly dicalcium phosphate dehydrate (DCPD) 17) ; and in weakly acidic conditions near ph 7.0, it could be tricalcium phosphate (TCP) 18) and octacalcium phosphate (OCP) 19). In the present study, an acetate buffer solution of ph 7.4 was used. Therefore, the deposited calcium phosphate would transform to hydroxyapatite if the experiment were to continue for a longer period. Nonetheless, it must be put into perspective that the deposition obtained during this short 15-minute SPR experiment was estimated as a single unit layer, and coupled with a very low experimental temperature at 25ºC, it was difficult to clearly identify the deposited crystal as hydroxyapatite. This is because apart from the ph condition, the morphology of calcium phosphate crystals is also significantly affected by the temperature and coexisting trace elements in the solution. Fig. 8 Schematic model of initial hydroxyapatite (HAp) crystal formation on COOH-SAM surface. SPR is commonly used for nanometer-scale detection of protein-protein interactions, molecular adsorption, and surface structure changes, using an He-Ne laser light, Knoll s method 15), and a Kretschmann configuration 16). General SPR sensor chips are produced by depositing gold on a glass surface with an ultrathin layer of chromium or titanium as a binding material. With the use of SPR in this study, calcium phosphate formation was successfully observed in realtime. Precipitate deposition results seemed to suggest that the calcium phosphate formed might be hydroxyapatite, although a direct identification was difficult because of real-time deposition during SPR analysis and an extremely small amount of deposition. At the same time, however, the SPR angle (mda) for COOH-SAM shown in Fig. 7 enabled the thickness of the precipitate layer to be estimated to be 0.71 nm. This was because the SPR angle shift was 352 mda/ nm, and the net value of angle shift for COOH-SAM was read as 250 mda from the data in Fig. 7. This value was close to the c-axis unit dimension of hydroxyapatite, which was nm. In other words, it was suggested that during the 15-minute supply of calcium phosphate solution, a monolayer of amorphous calcium phosphate approximately equal to the c-axis CONCLUSION The -COOH, -NH 2, -CH 3, and -OH functional groups of proteins exhibited different behaviors in terms of hydroxyapatite formation. -COOH and -NH 2 functions were favorable for hydroxyapatite formation when compared with -OH and -CH 3. These results would be useful toward the design and development of novel functionalized biomaterials. SPR analysis was also found to be very useful for real-time observation of nanoscale calcium phosphate deposition, and the results obtained positively complemented with those of SEM, XRD, and ESCA. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This study was supported in part by a Grant-in-aid for Scientific Research, No , from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan. REFERENCES 1) Alberts B, Bray D, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Watson JD. Molecular biology of the cell, 3 rd ed. New York: Garland Publishing; p ) Campbell AA, Fryxell GE, Linehan JC, Graff GL. Surfaceinduced mineralization: a new method for producing calcium phosphate coatings. J Biomed Mater Res 1996; 32: ) Liu Q, Ding J, Mante FK, Wunder SL, Baran GR. The role of surface functional groups in calcium phosphate nucleation on titanium foil: a self-assembled monolayer technique. Biomaterials 2002; 23: ) Tanahashi M, Matsuda T. Surface functional group dependence on apatite formation on self-assembled monolayers in a simulated body fluid. J Biomed Mater Res 1997; 34: ) Yan L, Leng Y, Weng LT. Characterization of chemical inhomogeneity in plasma-sprayed hydroxyapatite coatings. Biomaterials 2003; 24: ) Hero H, Wie H, Jorgensen RB. Hydroxyapatite coatings on
8 8 This Ti produced by hot isostatic pressing. J Biomed Mater Res 1994; 28: ) Kokubo T, Kusitani H, Sakka S, Kitsugi T, Yamamuro T. Solutions able to reproduce in vivo surface structure changes in bioactive glass-ceramic. Biomaterials 1990; 24: ) Liu DP, Majewski P, O Neill BK, Ngothai Y, Colby CB. The optimal SAM surface functional group for producing a biomimetic HA coating on Ti. J Biomed Mater Res A 2006; 77: ) Zhu PX, Masuda Y, Koumoto K. Site-selective adhesion of hydroxyapatite microparticles on charged surfaces in a supersaturated solution. J Colloid and Interface Sci 2001; 243: ) Zhu PX, Masuda Y, Yonezawa T, Koumoto K. Investigation of apatite deposition onto charged surfaces in aqueous solutions using a quartz-crystal microbalance. J Am Ceram Soc 2003; 86: ) Zhu PX, Masuda Y, Koumoto K. The effect of surface charge on hydroxyapatite nucleation. Biomaterials 2004; 25: ) Hirata I, Hioki Y, Toda M, Kitazawa T, Murakami Y, Kitano E, Kitamura H, Ikada Y, Iwata H. Deposition of complement protein, C3b, on mixed self-assembled monolayers carrying surface hydroxyl and methyl groups studied by surface plasmon resonance. J Biomed Mater Res A 2003; 66: ) Hirata I, Morimoto Y, Murakami Y, Iwata H, Kitano E, Kitamura H, Ikada Y. Study of complement activation on well-defined surfaces using surface plasmon resonance. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2000; 18: ) Fuse Y, Hirata I, Kurihara H, Okazaki M. Cell adhesion and proliferation patterns on mixed self-assembled monolayers carrying various ratios of hydroxyl and methyl groups. Dent Mater J 2007; 26: ) Knoll W. Polymer thin films and interfaces characterized with evanescent light. Makromol Chem 1991; 192: ) Kretschmann E. Determination of the optical constants of metals by excitation of surface plasma. Z Phys 1971; 241: ) Brown WE, Patel PR, Chow LC. Formation of CaHPO 4.2H 2O from enamel mineral and its relationship to caries mechanism. J Dent Res 1975; 54: ) Termine JD, Posner AS. Amorphous crystalline interrelationship in bone mineral. Calcif Tiss Res 1967; 1: ) Brown WE. Crystal growth of bone mineral. Clin Orthop 1966; 44:
Effect of Non-Ionic Surfactants on Dispersion and. Polar Interactions in the Adsorption of Cellulases. onto Lignin
 Supporting Information Effect of Non-Ionic Surfactants on Dispersion and Polar Interactions in the Adsorption of Cellulases onto Lignin Feng Jiang, Chen Qian, Alan R. Esker and Maren Roman, * Macromolecules
Supporting Information Effect of Non-Ionic Surfactants on Dispersion and Polar Interactions in the Adsorption of Cellulases onto Lignin Feng Jiang, Chen Qian, Alan R. Esker and Maren Roman, * Macromolecules
Mechanism of apatite formation on pure titanium treated with alkaline solution
 Bio-Medical Materials and Engineering 14 (2004) 5 11 5 IOS Press Mechanism of apatite formation on pure titanium treated with alkaline solution C.X. Wang a,,x.zhou b and M. Wang a a School of Mechanical
Bio-Medical Materials and Engineering 14 (2004) 5 11 5 IOS Press Mechanism of apatite formation on pure titanium treated with alkaline solution C.X. Wang a,,x.zhou b and M. Wang a a School of Mechanical
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study of the nucleation and growth of apatite on chemically treated pure titanium
 May 2002 Materials Letters 54 (2002) 30 36 www.elsevier.com/locate/matlet Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study of the nucleation and growth of apatite on chemically treated pure titanium C.X. Wang
May 2002 Materials Letters 54 (2002) 30 36 www.elsevier.com/locate/matlet Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study of the nucleation and growth of apatite on chemically treated pure titanium C.X. Wang
Supporting Information s for
 Supporting Information s for # Self-assembling of DNA-templated Au Nanoparticles into Nanowires and their enhanced SERS and Catalytic Applications Subrata Kundu* and M. Jayachandran Electrochemical Materials
Supporting Information s for # Self-assembling of DNA-templated Au Nanoparticles into Nanowires and their enhanced SERS and Catalytic Applications Subrata Kundu* and M. Jayachandran Electrochemical Materials
Controlled Electroless Deposition of Nanostructured Precious Metal Films on Germanium Surfaces
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION. Controlled Electroless Deposition of Nanostructured Precious Metal Films on Germanium Surfaces Lon A. Porter, Jr., Hee Cheul Choi, Alexander E. Ribbe, and Jillian M. Buriak Department
SUPPORTING INFORMATION. Controlled Electroless Deposition of Nanostructured Precious Metal Films on Germanium Surfaces Lon A. Porter, Jr., Hee Cheul Choi, Alexander E. Ribbe, and Jillian M. Buriak Department
Study of Apatite Deposition in a Simulated Body Fluid Immersion Experiment
 J Oral Tissue Engin 2016;14(1):9-14 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Study of Apatite Deposition in a Simulated Body Fluid Immersion Experiment Hajime SUZUKI 1,2, Ryo YAGI 3, Takuya WAKI 3, Takeshi WADA 1,4, Chikahiro
J Oral Tissue Engin 2016;14(1):9-14 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Study of Apatite Deposition in a Simulated Body Fluid Immersion Experiment Hajime SUZUKI 1,2, Ryo YAGI 3, Takuya WAKI 3, Takeshi WADA 1,4, Chikahiro
Visualizing the bi-directional electron transfer in a Schottky junction consisted of single CdS nanoparticles and a planar gold film
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Visualizing the bi-directional electron transfer in
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Visualizing the bi-directional electron transfer in
Localized and Propagating Surface Plasmon Co-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Based on Evanescent Field Excitation
 Supplementary Information Localized and Propagating Surface Plasmon Co-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Based on Evanescent Field Excitation Yu Liu, Shuping Xu, Haibo Li, Xiaoguang Jian, Weiqing Xu* State Key
Supplementary Information Localized and Propagating Surface Plasmon Co-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Based on Evanescent Field Excitation Yu Liu, Shuping Xu, Haibo Li, Xiaoguang Jian, Weiqing Xu* State Key
Supporting information for
 Supporting information for Metallic Few-layered VS 2 Ultrathin Nanosheets: High Two-Dimensional Conductivity for In-Plane Supercapacitors Jun Feng, Xu Sun, Changzheng Wu*, Lele Peng, Chenwen Lin, Shuanglin
Supporting information for Metallic Few-layered VS 2 Ultrathin Nanosheets: High Two-Dimensional Conductivity for In-Plane Supercapacitors Jun Feng, Xu Sun, Changzheng Wu*, Lele Peng, Chenwen Lin, Shuanglin
CHAPTER 10. Characteristics of the Surfaces of Biomaterials
 CHAPTER 10 Characteristics of the Surfaces of Biomaterials 10.1 Surface Characteristics Related to Chemical Bonding 10.2 Surface Chemistry Related to Bonding of Biological Molecules 10.3 Porosity 10.4
CHAPTER 10 Characteristics of the Surfaces of Biomaterials 10.1 Surface Characteristics Related to Chemical Bonding 10.2 Surface Chemistry Related to Bonding of Biological Molecules 10.3 Porosity 10.4
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 29 69451 Weinheim, Germany Voltage-Induced Payload Release and Wettability Control on O 2 and O 2 Nanotubes** Yan-Yan Song, Poulomi Roy, Indhumati Paramasivam, and Patrik
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 29 69451 Weinheim, Germany Voltage-Induced Payload Release and Wettability Control on O 2 and O 2 Nanotubes** Yan-Yan Song, Poulomi Roy, Indhumati Paramasivam, and Patrik
Supplementary Material for. Zinc Oxide-Black Phosphorus Composites for Ultrasensitive Nitrogen
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale Horizons. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Material for Zinc Oxide-Black Phosphorus Composites for Ultrasensitive
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale Horizons. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary Material for Zinc Oxide-Black Phosphorus Composites for Ultrasensitive
Synthesis of 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted Nucleation for Plasmon-Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of Au@UiO-66(NH 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information Synthesis of Au@UiO-66(NH 2 ) Structures by Small Molecule-Assisted
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Visible Light-Driven BiOI-Based Janus Micromotors in Pure Water Renfeng Dong, a Yan Hu, b Yefei Wu, b Wei Gao, c Biye Ren, b* Qinglong Wang, a Yuepeng Cai a* a School of Chemistry
Supporting Information Visible Light-Driven BiOI-Based Janus Micromotors in Pure Water Renfeng Dong, a Yan Hu, b Yefei Wu, b Wei Gao, c Biye Ren, b* Qinglong Wang, a Yuepeng Cai a* a School of Chemistry
CHAPTER 10. Characteristics of the Surfaces of Biomaterials
 CHAPTER 10 Characteristics of the Surfaces of Biomaterials 10.1 Surface Characteristics Related to Chemical Bonding 10.2 Surface Chemistry Related to Bonding of Biological Molecules 10.3 Porosity 10.4
CHAPTER 10 Characteristics of the Surfaces of Biomaterials 10.1 Surface Characteristics Related to Chemical Bonding 10.2 Surface Chemistry Related to Bonding of Biological Molecules 10.3 Porosity 10.4
Synthesis and Characterization of Porous Silica Gels for Biomedical Applications
 Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs, Vol 18 (2), January 2005 http://www.sbaoi.org Synthesis and Characterization of Porous Silica Gels for Biomedical Applications U. Vijayalakshmi, A. Balamurugan and S. Rajeswari
Trends Biomater. Artif. Organs, Vol 18 (2), January 2005 http://www.sbaoi.org Synthesis and Characterization of Porous Silica Gels for Biomedical Applications U. Vijayalakshmi, A. Balamurugan and S. Rajeswari
Supplementary Information. ZIF-8 Immobilized Ni(0) Nanoparticles: Highly Effective Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane
 Supplementary Information ZIF-8 Immobilized Ni() Nanoparticles: Highly Effective Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane Pei-Zhou Li, a,b Kengo Aranishi, a and Qiang Xu* a,b
Supplementary Information ZIF-8 Immobilized Ni() Nanoparticles: Highly Effective Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane Pei-Zhou Li, a,b Kengo Aranishi, a and Qiang Xu* a,b
ph-depending Enhancement of Electron Transfer by {001} Facet-Dominating TiO 2 Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution under Visible Irradiation
 S1 ph-depending Enhancement of Electron Transfer by {001} Facet-Dominating TiO 2 Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution under Visible Irradiation Masato M. Maitani a *, Zhan Conghong a,b, Dai Mochizuki
S1 ph-depending Enhancement of Electron Transfer by {001} Facet-Dominating TiO 2 Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic H 2 Evolution under Visible Irradiation Masato M. Maitani a *, Zhan Conghong a,b, Dai Mochizuki
A Novel Electroless Method for the Deposition of Single-Crystalline Platinum Nanoparticle Films On
 Supplementary Information A Novel Electroless Method for the Deposition of Single-Crystalline Platinum Nanoparticle Films On an Organic Solid Matrix in the Presence of Gold Single Crystals Khaleda Banu,,,*
Supplementary Information A Novel Electroless Method for the Deposition of Single-Crystalline Platinum Nanoparticle Films On an Organic Solid Matrix in the Presence of Gold Single Crystals Khaleda Banu,,,*
Supplementary Figure 1. Temperature profile of self-seeding method for polymer single crystal preparation in dilute solution.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Temperature profile of self-seeding method for polymer single crystal preparation in dilute solution. Supplementary Figure 2. 1 H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra (a) and
Supplementary Figure 1. Temperature profile of self-seeding method for polymer single crystal preparation in dilute solution. Supplementary Figure 2. 1 H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectra (a) and
Self-Assembled Monolayers
 Self-Assembled Monolayers Literature and Further Information Surface Chemistry: www.chem.qmul.ac.uk/surfaces/scc/ www.nottingham.ac.uk/~ppzpjm/amshome.htm venables.asu.edu/grad/lectures.html SAM s: www.ifm.liu.se/applphys/ftir/sams.html
Self-Assembled Monolayers Literature and Further Information Surface Chemistry: www.chem.qmul.ac.uk/surfaces/scc/ www.nottingham.ac.uk/~ppzpjm/amshome.htm venables.asu.edu/grad/lectures.html SAM s: www.ifm.liu.se/applphys/ftir/sams.html
An Optimal Substrate Design for SERS: Dual-Scale Diamond-Shaped Gold Nano-Structures Fabricated via Interference Lithography
 Supporting Information An Optimal Substrate Design for SERS: Dual-Scale Diamond-Shaped Gold Nano-Structures Fabricated via Interference Lithography Hyo-Jin Ahn a, Pradheep Thiyagarajan a, Lin Jia b, Sun-I
Supporting Information An Optimal Substrate Design for SERS: Dual-Scale Diamond-Shaped Gold Nano-Structures Fabricated via Interference Lithography Hyo-Jin Ahn a, Pradheep Thiyagarajan a, Lin Jia b, Sun-I
-organic Thin Film From an Aqueous Solution
 Fabrication and Characterization of -organic Thin Film From an Aqueous Solution Fabrication and Characterization of TiO 2 -organic Thin Film From an Aqueous Solution W.N. Mu 1 and S.Z. Shi 2 1 2 School
Fabrication and Characterization of -organic Thin Film From an Aqueous Solution Fabrication and Characterization of TiO 2 -organic Thin Film From an Aqueous Solution W.N. Mu 1 and S.Z. Shi 2 1 2 School
Electronic Supplementary Information. Molecular Antenna Tailored Organic Thin-film Transistor for. Sensing Application
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Materials Horizons. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Molecular Antenna Tailored Organic Thin-film Transistor
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Materials Horizons. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Electronic Supplementary Information Molecular Antenna Tailored Organic Thin-film Transistor
Model Solutions Spring 2003
 Exam 2 BE.462J/3.962J Model Solutions Spring 2003 (80 points total possible) 1. (10 points) Explain the phenomenon of phsensitive swelling in polyelectrolyte hydrogels. Why does the swelling depend on
Exam 2 BE.462J/3.962J Model Solutions Spring 2003 (80 points total possible) 1. (10 points) Explain the phenomenon of phsensitive swelling in polyelectrolyte hydrogels. Why does the swelling depend on
Supporting Information. Plasmon Ruler for Measuring Dielectric Thin Films
 Supporting Information Single Nanoparticle Based Hetero-Nanojunction as a Plasmon Ruler for Measuring Dielectric Thin Films Li Li, *a,b Tanya Hutter, c Wenwu Li d and Sumeet Mahajan *b a School of Chemistry
Supporting Information Single Nanoparticle Based Hetero-Nanojunction as a Plasmon Ruler for Measuring Dielectric Thin Films Li Li, *a,b Tanya Hutter, c Wenwu Li d and Sumeet Mahajan *b a School of Chemistry
Fabrication of ordered array at a nanoscopic level: context
 Fabrication of ordered array at a nanoscopic level: context Top-down method Bottom-up method Classical lithography techniques Fast processes Size limitations it ti E-beam techniques Small sizes Slow processes
Fabrication of ordered array at a nanoscopic level: context Top-down method Bottom-up method Classical lithography techniques Fast processes Size limitations it ti E-beam techniques Small sizes Slow processes
Antibody- and Label-Free Phosphoprotein Sensor Device Based on an Organic Transistor
 Supporting Information Antibody- and Label-Free Phosphoprotein Sensor Device Based on an Organic Transistor Tsukuru Minamiki, Tsuyoshi Minami,*, Petr Koutnik, Pavel Anzenbacher, Jr., and Shizuo Tokito
Supporting Information Antibody- and Label-Free Phosphoprotein Sensor Device Based on an Organic Transistor Tsukuru Minamiki, Tsuyoshi Minami,*, Petr Koutnik, Pavel Anzenbacher, Jr., and Shizuo Tokito
X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Prof. Paul K. Chu
 X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Prof. Paul K. Chu X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Introduction Qualitative analysis Quantitative analysis Charging compensation Small area analysis and XPS imaging
X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Prof. Paul K. Chu X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Introduction Qualitative analysis Quantitative analysis Charging compensation Small area analysis and XPS imaging
and their Maneuverable Application in Water Treatment
 Hierarchical Films of Layered Double Hydroxides by Using a Sol-Gel Process and their Maneuverable Application in Water Treatment Yufei Zhao, Shan He, Min Wei,* David G. Evans, Xue Duan State Key Laboratory
Hierarchical Films of Layered Double Hydroxides by Using a Sol-Gel Process and their Maneuverable Application in Water Treatment Yufei Zhao, Shan He, Min Wei,* David G. Evans, Xue Duan State Key Laboratory
Visible-light Driven Plasmonic Photocatalyst Helical Chiral TiO 2 Nanofibers
 Visible-light Driven Plasmonic Photocatalyst Ag/AgCl @ Helical Chiral TiO 2 Nanofibers Dawei Wang, Yi Li*, Gianluca Li Puma, Chao Wang, Peifang Wang, Wenlong Zhang, and Qing Wang Fig. S1. The reactor of
Visible-light Driven Plasmonic Photocatalyst Ag/AgCl @ Helical Chiral TiO 2 Nanofibers Dawei Wang, Yi Li*, Gianluca Li Puma, Chao Wang, Peifang Wang, Wenlong Zhang, and Qing Wang Fig. S1. The reactor of
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Precisely Controllable Core-Shell Ag@Carbon Dots Nanoparticles: Application to in Situ Super-Sensitive Monitoring of Catalytic Reactions Jing Jin, Shoujun Zhu, Yubin Song, Hongyue
Supporting Information Precisely Controllable Core-Shell Ag@Carbon Dots Nanoparticles: Application to in Situ Super-Sensitive Monitoring of Catalytic Reactions Jing Jin, Shoujun Zhu, Yubin Song, Hongyue
Two-Dimensional (C 4 H 9 NH 3 ) 2 PbBr 4 Perovskite Crystals for. High-Performance Photodetector. Supporting Information for
 Supporting Information for Two-Dimensional (C 4 H 9 NH 3 ) 2 PbBr 4 Perovskite Crystals for High-Performance Photodetector Zhenjun Tan,,ǁ, Yue Wu,ǁ, Hao Hong, Jianbo Yin, Jincan Zhang,, Li Lin, Mingzhan
Supporting Information for Two-Dimensional (C 4 H 9 NH 3 ) 2 PbBr 4 Perovskite Crystals for High-Performance Photodetector Zhenjun Tan,,ǁ, Yue Wu,ǁ, Hao Hong, Jianbo Yin, Jincan Zhang,, Li Lin, Mingzhan
Case Study of Electronic Materials Packaging with Poor Metal Adhesion and the Process for Performing Root Cause Failure Analysis
 Case Study of Electronic Materials Packaging with Poor Metal Adhesion and the Process for Performing Root Cause Failure Analysis Dr. E. A. Leone BACKGRUND ne trend in the electronic packaging industry
Case Study of Electronic Materials Packaging with Poor Metal Adhesion and the Process for Performing Root Cause Failure Analysis Dr. E. A. Leone BACKGRUND ne trend in the electronic packaging industry
Surface potential change in bioactive polymer during the process of biomimetic apatite formation in a simulated body fluid{
 PAPER www.rsc.org/materials Journal of Materials Chemistry Surface potential change in bioactive polymer during the process of biomimetic apatite formation in a simulated body fluid{ Isabel B. Leonor,*
PAPER www.rsc.org/materials Journal of Materials Chemistry Surface potential change in bioactive polymer during the process of biomimetic apatite formation in a simulated body fluid{ Isabel B. Leonor,*
Thin film techniques: the layer-by-layer self assembly technique
 Thin film techniques: the layer-by-layer self assembly technique Carmelina Ruggiero University of Genoa Overview Thin films Thin film techniques Langmuir-Blodgett technique Chemical self-assembling Layer-by-Layer
Thin film techniques: the layer-by-layer self assembly technique Carmelina Ruggiero University of Genoa Overview Thin films Thin film techniques Langmuir-Blodgett technique Chemical self-assembling Layer-by-Layer
Electronic Supplementary Information. Precursor Salt Assisted Syntheses of High-Index Faceted Concave Hexagon and Nanorod like Polyoxometalates
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Precursor Salt Assisted Syntheses of High-Index Faceted Concave
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Precursor Salt Assisted Syntheses of High-Index Faceted Concave
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Plasmonics-enhanced metal-organic frameworks nanofilms
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Plasmonics-enhanced metal-organic frameworks nanofilms
Scanned Chemical Enhancement of Surface-Enhanced Raman. Scattering Using a Charge-Transfer Complex
 Supporting Information Scanned Chemical Enhancement of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Using a Charge-Transfer Complex Wei Ji, a Xiangxin Xue, a Weidong Ruan, a Chunxu Wang, a Nan Ji, a Lei Chen, a Zhishi
Supporting Information Scanned Chemical Enhancement of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Using a Charge-Transfer Complex Wei Ji, a Xiangxin Xue, a Weidong Ruan, a Chunxu Wang, a Nan Ji, a Lei Chen, a Zhishi
Interaction of Gold Nanoparticle with Proteins
 Chapter 7 Interaction of Gold Nanoparticle with Proteins 7.1. Introduction The interfacing of nanoparticle with biomolecules such as protein is useful for applications ranging from nano-biotechnology (molecular
Chapter 7 Interaction of Gold Nanoparticle with Proteins 7.1. Introduction The interfacing of nanoparticle with biomolecules such as protein is useful for applications ranging from nano-biotechnology (molecular
Synthesis of Biphasic Calcium Phosphate and its Behaviour in Simulated Body Fluid
 ASEAN J. Sci. Technol. Dev., 33(2): 63 68 Synthesis of Biphasic Calcium Phosphate and its Behaviour in Simulated Body Fluid X. V. BÙI 1,2 AND T. D. THẮNG 1 The main goal of this study is to elaborate and
ASEAN J. Sci. Technol. Dev., 33(2): 63 68 Synthesis of Biphasic Calcium Phosphate and its Behaviour in Simulated Body Fluid X. V. BÙI 1,2 AND T. D. THẮNG 1 The main goal of this study is to elaborate and
The Effect of Additives on Characteristics of Hydroxyapatite Particles Produced in Flame Reactor
 The Effect of Additives on Characteristics of Hydroxyapatite Particles Produced in Flame Reactor Widiyastuti a*, Kusdianto a, Agung Nugroho a, Hakun Wira a, Sugeng Winardi a, and Kikuo Okuyama b a Department
The Effect of Additives on Characteristics of Hydroxyapatite Particles Produced in Flame Reactor Widiyastuti a*, Kusdianto a, Agung Nugroho a, Hakun Wira a, Sugeng Winardi a, and Kikuo Okuyama b a Department
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Visualization of equilibrium position of colloidal particles at fluid-water
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supplementary Information Visualization of equilibrium position of colloidal particles at fluid-water
dissolved into methanol (20 ml) to form a solution. 2-methylimidazole (263 mg) was dissolved in
 Experimental section Synthesis of small-sized ZIF-8 particles (with average diameter of 50 nm): Zn(NO 3 ) 2 (258 mg) was dissolved into methanol (20 ml) to form a solution. 2-methylimidazole (263 mg) was
Experimental section Synthesis of small-sized ZIF-8 particles (with average diameter of 50 nm): Zn(NO 3 ) 2 (258 mg) was dissolved into methanol (20 ml) to form a solution. 2-methylimidazole (263 mg) was
PLASMA-POLYMER MODIFICATION OF BASAL PLANE GRAPHITE SURFACES FOR IMPROVED BIOCOMPATIBILITY
 PLASMA-POLYMER MODIFICATION OF BASAL PLANE GRAPHITE SURFACES FOR IMPROVED BIOCOMPATIBILITY Anca Orăşanu, Marcus R. Davidson, Robert H. Bradley Advanced Materials & Biomaterials Research Centre, School
PLASMA-POLYMER MODIFICATION OF BASAL PLANE GRAPHITE SURFACES FOR IMPROVED BIOCOMPATIBILITY Anca Orăşanu, Marcus R. Davidson, Robert H. Bradley Advanced Materials & Biomaterials Research Centre, School
PHI 5000 Versaprobe-II Focus X-ray Photo-electron Spectroscopy
 PHI 5000 Versaprobe-II Focus X-ray Photo-electron Spectroscopy The very basic theory of XPS XPS theroy Surface Analysis Ultra High Vacuum (UHV) XPS Theory XPS = X-ray Photo-electron Spectroscopy X-ray
PHI 5000 Versaprobe-II Focus X-ray Photo-electron Spectroscopy The very basic theory of XPS XPS theroy Surface Analysis Ultra High Vacuum (UHV) XPS Theory XPS = X-ray Photo-electron Spectroscopy X-ray
Manufacturing of Anisotropic Particles by Site Specific Oxidation of Thiols
 Manufacturing of Anisotropic Particles by Site Specific Oxidation of Thiols Kristofer Eriksson, LarsErik Johansson, Emmanuelle Göthelid, Leif Nyholm and Sven Oscarsson Supporting Information Experimental.
Manufacturing of Anisotropic Particles by Site Specific Oxidation of Thiols Kristofer Eriksson, LarsErik Johansson, Emmanuelle Göthelid, Leif Nyholm and Sven Oscarsson Supporting Information Experimental.
Mechanism of apatite formation on wollastonite coatings in simulated bodyfluids
 Biomaterials 25 (2004) 1755 1761 Mechanism of apatite formation on wollastonite coatings in simulated bodyfluids Xuanyong Liu a,b, *,1, Chuanxian Ding a, Paul K. Chu b a Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai
Biomaterials 25 (2004) 1755 1761 Mechanism of apatite formation on wollastonite coatings in simulated bodyfluids Xuanyong Liu a,b, *,1, Chuanxian Ding a, Paul K. Chu b a Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai
International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology
 Int. J. Pure Appl. Sci. Technol., 9(1) (2012), pp. 1-8 International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology ISSN 2229-6107 Available online at www.ijopaasat.in Research Paper Preparation,
Int. J. Pure Appl. Sci. Technol., 9(1) (2012), pp. 1-8 International Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences and Technology ISSN 2229-6107 Available online at www.ijopaasat.in Research Paper Preparation,
PREPARATION OF SILICON DOPED HYDROXYAPATITE
 PREPARATION OF SILICON DOPED HYDROXYAPATITE Klaudia Paljar, Sebastijan Orlić, Emilija Tkalčec, Hrvoje Ivanković Faculty of Chemical Engineering and Technology, University of Zagreb HR-10001 Zagreb, Marulićev
PREPARATION OF SILICON DOPED HYDROXYAPATITE Klaudia Paljar, Sebastijan Orlić, Emilija Tkalčec, Hrvoje Ivanković Faculty of Chemical Engineering and Technology, University of Zagreb HR-10001 Zagreb, Marulićev
2.1 Composition and Structure of Natural Bones
 1 Introduction Most bone diseases pose serious health problems and directly impact on a patient s lifelong mobility, activity and quality of life. Normally, a bone graft or implant is required There are
1 Introduction Most bone diseases pose serious health problems and directly impact on a patient s lifelong mobility, activity and quality of life. Normally, a bone graft or implant is required There are
Supporting Information. Temperature dependence on charge transport behavior of threedimensional
 Supporting Information Temperature dependence on charge transport behavior of threedimensional superlattice crystals A. Sreekumaran Nair and K. Kimura* University of Hyogo, Graduate School of Material
Supporting Information Temperature dependence on charge transport behavior of threedimensional superlattice crystals A. Sreekumaran Nair and K. Kimura* University of Hyogo, Graduate School of Material
Supporting Information:
 Supporting Information: Columnar Self-assembly of Cu 2 S Hexagonal Nanoplates Induced by Tin (IV)-X Complex Inorganic Surface Ligand Xiaomin Li, Huaibin Shen, Jinzhong Niu, Sen Li, Yongguang Zhang, Hongzhe
Supporting Information: Columnar Self-assembly of Cu 2 S Hexagonal Nanoplates Induced by Tin (IV)-X Complex Inorganic Surface Ligand Xiaomin Li, Huaibin Shen, Jinzhong Niu, Sen Li, Yongguang Zhang, Hongzhe
CHIMICA DELLE SUPERFICI ED INTERFASI
 CHIMICA DELLE SUPERFICI ED INTERFASI DOTT. GIULIA FIORAVANTI UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DELL AQUILA LAUREA MAGISTRALE IN INGEGNERIA CHIMICA A.A. 2013-2014 OUTLINE SURFACE CHEMICAL GRADIENTS DROPLET MOVEMENT
CHIMICA DELLE SUPERFICI ED INTERFASI DOTT. GIULIA FIORAVANTI UNIVERSITÀ DEGLI STUDI DELL AQUILA LAUREA MAGISTRALE IN INGEGNERIA CHIMICA A.A. 2013-2014 OUTLINE SURFACE CHEMICAL GRADIENTS DROPLET MOVEMENT
Supporting Information. for. Gold Nanoparticles Supported on Alumina as a Catalyst for Surface Plasmon-Enhanced Selective Reductions of Nitrobenzene
 Supporting Information for Gold Nanoparticles Supported on Alumina as a Catalyst for Surface Plasmon-Enhanced Selective Reductions of Nitrobenzene Kittichai Chaiseeda, Shun Nishimura, and Kohki Ebitani
Supporting Information for Gold Nanoparticles Supported on Alumina as a Catalyst for Surface Plasmon-Enhanced Selective Reductions of Nitrobenzene Kittichai Chaiseeda, Shun Nishimura, and Kohki Ebitani
Supporting information
 Supporting information A Facile Photo-induced Synthesis of COOH Functionalized Mesomacroporous Carbon Film and its Excellent Sensing Capability for Aromatic Amines Lichao Jia, Gurudas P. Mane, Chokkalingam
Supporting information A Facile Photo-induced Synthesis of COOH Functionalized Mesomacroporous Carbon Film and its Excellent Sensing Capability for Aromatic Amines Lichao Jia, Gurudas P. Mane, Chokkalingam
Sol gel preparation of bioactive apatite films
 Surface and Coatings Technology 167 (2003) 292 296 Sol gel preparation of bioactive apatite films a, b a a a a a Wenjian Weng *, Sam Zhang, Kui Cheng, Haibo Qu, Piyi Du, Ge Shen, Jun Yuan, Gaorong Han
Surface and Coatings Technology 167 (2003) 292 296 Sol gel preparation of bioactive apatite films a, b a a a a a Wenjian Weng *, Sam Zhang, Kui Cheng, Haibo Qu, Piyi Du, Ge Shen, Jun Yuan, Gaorong Han
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 1.138/nnano.21.29 Gammadion fabrication The gammadions were designed using CAD software with a line width of 8 nm and a periodicity of 8 nm, figure S1. They were arrayed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 1.138/nnano.21.29 Gammadion fabrication The gammadions were designed using CAD software with a line width of 8 nm and a periodicity of 8 nm, figure S1. They were arrayed
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Photonic sensing via SRS method. Reflection spectra of a) a dried SiO 2 opal and b-d) the SiO 2 opal infiltrated with different organic solvents, whose refractive
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Photonic sensing via SRS method. Reflection spectra of a) a dried SiO 2 opal and b-d) the SiO 2 opal infiltrated with different organic solvents, whose refractive
Supplementary Figure 1 Detailed illustration on the fabrication process of templatestripped
 Supplementary Figure 1 Detailed illustration on the fabrication process of templatestripped gold substrate. (a) Spin coating of hydrogen silsesquioxane (HSQ) resist onto the silicon substrate with a thickness
Supplementary Figure 1 Detailed illustration on the fabrication process of templatestripped gold substrate. (a) Spin coating of hydrogen silsesquioxane (HSQ) resist onto the silicon substrate with a thickness
Surface Characteristics of a Polyimide Film Treated with a Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 54, No. 3, March 2009, pp. 11561160 Surface Characteristics of a Polyimide Film Treated with a Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma S. M. Kang, W. J. Park and
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 54, No. 3, March 2009, pp. 11561160 Surface Characteristics of a Polyimide Film Treated with a Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma S. M. Kang, W. J. Park and
Supporting information
 Supporting information Polymer-Single-Crystal@Nanoparticle Nanosandwich for Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Bin Dong, Wenda Wang, David L. Miller, Christopher Y. Li* Department of Material Science
Supporting information Polymer-Single-Crystal@Nanoparticle Nanosandwich for Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Bin Dong, Wenda Wang, David L. Miller, Christopher Y. Li* Department of Material Science
Effect of Spiral Microwave Antenna Configuration on the Production of Nano-crystalline Film by Chemical Sputtering in ECR Plasma
 THE HARRIS SCIENCE REVIEW OF DOSHISHA UNIVERSITY, VOL. 56, No. 1 April 2015 Effect of Spiral Microwave Antenna Configuration on the Production of Nano-crystalline Film by Chemical Sputtering in ECR Plasma
THE HARRIS SCIENCE REVIEW OF DOSHISHA UNIVERSITY, VOL. 56, No. 1 April 2015 Effect of Spiral Microwave Antenna Configuration on the Production of Nano-crystalline Film by Chemical Sputtering in ECR Plasma
Abstract. The principles and applicability of surface structure and hydrophobicity of polymers (PS, PDMS),
 Contact Angle Goniometer: Hydrophobicity of Biomaterial Surfaces and Protein Coatings Eman Mousa Alhajji North Carolina State University Department of Materials Science and Engineering MSE 255 Lab Report
Contact Angle Goniometer: Hydrophobicity of Biomaterial Surfaces and Protein Coatings Eman Mousa Alhajji North Carolina State University Department of Materials Science and Engineering MSE 255 Lab Report
Formation mechanism and Coulomb blockade effect in self-assembled gold quantum dots
 Formation mechanism and Coulomb blockade effect in self-assembled gold quantum dots S. F. Hu a) National Nano Device Laboratories, Hsinchu 300, Taiwan R. L. Yeh and R. S. Liu Department of Chemistry, National
Formation mechanism and Coulomb blockade effect in self-assembled gold quantum dots S. F. Hu a) National Nano Device Laboratories, Hsinchu 300, Taiwan R. L. Yeh and R. S. Liu Department of Chemistry, National
Light-Induced Atom Desorption in Alkali Vapor Cells
 Fundamental Physics Using Atoms, 2010/08/09, Osaka Light-Induced Atom Desorption in Alkali Vapor Cells A. Hatakeyama (Tokyo Univ. Agr. Tech.) K. Hosumi K. Kitagami Alkali vapor cells UHV cell for laser
Fundamental Physics Using Atoms, 2010/08/09, Osaka Light-Induced Atom Desorption in Alkali Vapor Cells A. Hatakeyama (Tokyo Univ. Agr. Tech.) K. Hosumi K. Kitagami Alkali vapor cells UHV cell for laser
The sacrificial role of graphene oxide in stabilising Fenton-like catalyst GO Fe 3 O 4
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 The sacrificial role of graphene oxide in stabilising Fenton-like catalyst GO Fe 3 O 4 Nor Aida
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 The sacrificial role of graphene oxide in stabilising Fenton-like catalyst GO Fe 3 O 4 Nor Aida
Control of Optical Properties by the Stepwise Chemical and Plasma Spray Treatment of Polycarbonate
 Appl. Sci. Converg. Technol. 27(6): 135-139 (2018) https://doi.org/10.5757/asct.2018.27.6.135 Research Paper Control of Optical Properties by the Stepwise Chemical and Plasma Spray Treatment of Polycarbonate
Appl. Sci. Converg. Technol. 27(6): 135-139 (2018) https://doi.org/10.5757/asct.2018.27.6.135 Research Paper Control of Optical Properties by the Stepwise Chemical and Plasma Spray Treatment of Polycarbonate
Thin and Ultrathin Plasma Polymer Films and Their Characterization
 WDS'13 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 134 138, 2013. ISBN 978-80-7378-252-8 MATFYZPRESS Thin and Ultrathin Plasma Polymer Films and Their Characterization M. Petr, O. Kylián, J. Hanuš, A.
WDS'13 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 134 138, 2013. ISBN 978-80-7378-252-8 MATFYZPRESS Thin and Ultrathin Plasma Polymer Films and Their Characterization M. Petr, O. Kylián, J. Hanuš, A.
Formation of organically modified octacalcium phosphate in solutions containing various amounts of benzenedicarboxylic acids
 Paper Formation of organically modified octacalcium phosphate in solutions containing various amounts of benzenedicarboxylic acids Taishi YOKOI, ³ Masanobu KAMITAKAHARA, * Masakazu KAWASHITA ** and Chikara
Paper Formation of organically modified octacalcium phosphate in solutions containing various amounts of benzenedicarboxylic acids Taishi YOKOI, ³ Masanobu KAMITAKAHARA, * Masakazu KAWASHITA ** and Chikara
Supporting Information
 Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2018. Supporting Information for Small, DOI: 10.1002/smll.201801523 Ultrasensitive Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Detection Based
Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 2018. Supporting Information for Small, DOI: 10.1002/smll.201801523 Ultrasensitive Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Detection Based
Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO
 Supporing Information Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO Chun-Jiang Jia, Yong Liu, Hans Bongard, Ferdi Schüth* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung,
Supporing Information Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO Chun-Jiang Jia, Yong Liu, Hans Bongard, Ferdi Schüth* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung,
Shape-selective Synthesis and Facet-dependent Enhanced Electrocatalytic Activity and Durability of Monodisperse Sub-10 nm Pt-Pd Tetrahedrons and Cubes
 Supporting Information Shape-selective Synthesis and Facet-dependent Enhanced Electrocatalytic Activity and Durability of Monodisperse Sub-10 nm Pt-Pd Tetrahedrons and Cubes An-Xiang Yin, Xiao-Quan Min,
Supporting Information Shape-selective Synthesis and Facet-dependent Enhanced Electrocatalytic Activity and Durability of Monodisperse Sub-10 nm Pt-Pd Tetrahedrons and Cubes An-Xiang Yin, Xiao-Quan Min,
Special Properties of Au Nanoparticles
 Special Properties of Au Nanoparticles Maryam Ebrahimi Chem 7500/750 March 28 th, 2007 1 Outline Introduction The importance of unexpected electronic, geometric, and chemical properties of nanoparticles
Special Properties of Au Nanoparticles Maryam Ebrahimi Chem 7500/750 March 28 th, 2007 1 Outline Introduction The importance of unexpected electronic, geometric, and chemical properties of nanoparticles
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Assembly and Densification of Nanowire Arrays via Shrinkage Jaehoon Bang, Jonghyun Choi, Fan Xia, Sun Sang Kwon, Ali Ashraf, Won Il Park, and SungWoo Nam*,, Department of Mechanical
Supporting Information Assembly and Densification of Nanowire Arrays via Shrinkage Jaehoon Bang, Jonghyun Choi, Fan Xia, Sun Sang Kwon, Ali Ashraf, Won Il Park, and SungWoo Nam*,, Department of Mechanical
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Titanium Dioxide: Modification with Graphene Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide Xuandong Li,* Meirong Kang, Xijiang Han, Jingyu Wang, and Ping Xu
Supporting Information Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Titanium Dioxide: Modification with Graphene Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide Xuandong Li,* Meirong Kang, Xijiang Han, Jingyu Wang, and Ping Xu
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Direct Synthesis of a Macroscopic Array of Naked Ag Nanoparticles Omar Ayyad,* a,b,c David Muñoz-Rojas, a Pedro Gómez-Romero* a,c Experimental details Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP40T-500G,
Supplementary Information Direct Synthesis of a Macroscopic Array of Naked Ag Nanoparticles Omar Ayyad,* a,b,c David Muñoz-Rojas, a Pedro Gómez-Romero* a,c Experimental details Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP40T-500G,
UV-vis Analysis of the Effect of Sodium Citrate on the Size and the Surface Plasmon Resonance of Au NPs. Eman Mousa Alhajji
 UV-vis Analysis of the Effect of Sodium Citrate on the Size and the Surface Plasmon Resonance of Au NPs Eman Mousa Alhajji North Carolina State University Department of Materials Science and Engineering
UV-vis Analysis of the Effect of Sodium Citrate on the Size and the Surface Plasmon Resonance of Au NPs Eman Mousa Alhajji North Carolina State University Department of Materials Science and Engineering
CHAPTER 3. FABRICATION TECHNOLOGIES OF CdSe/ZnS / Au NANOPARTICLES AND NANODEVICES. 3.1 THE SYNTHESIS OF Citrate-Capped Au NANOPARTICLES
 CHAPTER 3 FABRICATION TECHNOLOGIES OF CdSe/ZnS / Au NANOPARTICLES AND NANODEVICES 3.1 THE SYNTHESIS OF Citrate-Capped Au NANOPARTICLES Au NPs with ~ 15 nm were prepared by citrate reduction of HAuCl 4
CHAPTER 3 FABRICATION TECHNOLOGIES OF CdSe/ZnS / Au NANOPARTICLES AND NANODEVICES 3.1 THE SYNTHESIS OF Citrate-Capped Au NANOPARTICLES Au NPs with ~ 15 nm were prepared by citrate reduction of HAuCl 4
Supporting Information. Controlled mineralization by extracellular matrix: monodisperse, colloidal stable calcium phosphate-hyaluronan
 Supporting Information Controlled mineralization by extracellular matrix: monodisperse, colloidal stable calcium phosphate-hyaluronan hybrid nanospheres Zhenhua Chen, a Huihui Zhou, b Xiaoliang Wang, a
Supporting Information Controlled mineralization by extracellular matrix: monodisperse, colloidal stable calcium phosphate-hyaluronan hybrid nanospheres Zhenhua Chen, a Huihui Zhou, b Xiaoliang Wang, a
Surface Plasmon Wave
 Surface Plasmon Wave In this experiment you will learn about a surface plasmon wave. Certain metals (Au, Ag, Co, etc) exhibit a negative dielectric constant at certain regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Surface Plasmon Wave In this experiment you will learn about a surface plasmon wave. Certain metals (Au, Ag, Co, etc) exhibit a negative dielectric constant at certain regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Interaction of charged hydroxyapatite and living cells. I. Hydroxyapatite polarization properties
 Mathematical biology and bioinformatics, 2009. V. 4. 2. P. 7-11. URL: http://www.matbio.org/downloads_en/bystrov_en2009(4_7).pdf ====================== MATHEMATICAL MODELING ======================= UDK
Mathematical biology and bioinformatics, 2009. V. 4. 2. P. 7-11. URL: http://www.matbio.org/downloads_en/bystrov_en2009(4_7).pdf ====================== MATHEMATICAL MODELING ======================= UDK
applied as UV protective films
 Nanocomposite gels via in-situ photoinitiation and disassembly of TiO 2 -Clay composites with polymers applied as UV protective films Chuanan Liao, Qing Wu, Teng Su, Da Zhang, Qingsheng Wu and Qigang Wang*
Nanocomposite gels via in-situ photoinitiation and disassembly of TiO 2 -Clay composites with polymers applied as UV protective films Chuanan Liao, Qing Wu, Teng Su, Da Zhang, Qingsheng Wu and Qigang Wang*
Review. Surfaces of Biomaterials. Characterization. Surface sensitivity
 Surfaces of Biomaterials Three lectures: 1.23.05 Surface Properties of Biomaterials 1.25.05 Surface Characterization 1.27.05 Surface and Protein Interactions Review Bulk Materials are described by: Chemical
Surfaces of Biomaterials Three lectures: 1.23.05 Surface Properties of Biomaterials 1.25.05 Surface Characterization 1.27.05 Surface and Protein Interactions Review Bulk Materials are described by: Chemical
Controlled self-assembly of graphene oxide on a remote aluminum foil
 Supplementary Information Controlled self-assembly of graphene oxide on a remote aluminum foil Kai Feng, Yewen Cao and Peiyi Wu* State key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of
Supplementary Information Controlled self-assembly of graphene oxide on a remote aluminum foil Kai Feng, Yewen Cao and Peiyi Wu* State key Laboratory of Molecular Engineering of Polymers, Department of
Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties. and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions Yonghong Ni *a, Kai Mi a, Chao Cheng a, Jun Xia a, Xiang
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Urchin-like Ni-P microstructures: A facile synthesis, properties and application in the fast removal of heavy-metal ions Yonghong Ni *a, Kai Mi a, Chao Cheng a, Jun Xia a, Xiang
Digitized single scattering nanoparticles for probing molecular binding
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Digitized single scattering nanoparticles for probing molecular binding Yue Liu a, Cheng Zhi Huang a,b* a Education Ministry Key Laboratory on Luminescence and
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Digitized single scattering nanoparticles for probing molecular binding Yue Liu a, Cheng Zhi Huang a,b* a Education Ministry Key Laboratory on Luminescence and
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Ultrathin Spinel-Structured Nanosheets Rich in Oxygen Deficiencies for Enhanced Electrocatalytic Water Oxidation** Jian Bao, Xiaodong Zhang,* Bo Fan, Jiajia Zhang, Min Zhou, Wenlong
Supporting Information Ultrathin Spinel-Structured Nanosheets Rich in Oxygen Deficiencies for Enhanced Electrocatalytic Water Oxidation** Jian Bao, Xiaodong Zhang,* Bo Fan, Jiajia Zhang, Min Zhou, Wenlong
Synthesis of Highly Concentrated Ag Nanoparticles in a Heterogeneous Solid-Liquid System under Ultrasonic Irradiation
 Materials Transactions, Vol. 51, No. 10 (2010) pp. 1764 to 1768 Special Issue on Lead-Free and Advanced Interconnection Materials for Electronics #2010 The Japan Institute of Metals Synthesis of Highly
Materials Transactions, Vol. 51, No. 10 (2010) pp. 1764 to 1768 Special Issue on Lead-Free and Advanced Interconnection Materials for Electronics #2010 The Japan Institute of Metals Synthesis of Highly
Facile Synthesis of Gold Wavy Nanowires and Investigation of
 Supporting Information for Facile Synthesis of Gold Wavy Nanowires and Investigation of Their Growth Mechanism Cun Zhu,, Hsin-Chieh Peng, Jie Zeng, Jingyue Liu, Zhongze Gu and Younan Xia,,* The Wallace
Supporting Information for Facile Synthesis of Gold Wavy Nanowires and Investigation of Their Growth Mechanism Cun Zhu,, Hsin-Chieh Peng, Jie Zeng, Jingyue Liu, Zhongze Gu and Younan Xia,,* The Wallace
Influence of Hot Spot Heating on Stability of. Conversion Efficiency of ~14%
 Influence of Hot Spot Heating on Stability of Large Size Perovskite Solar Module with a Power Conversion Efficiency of ~14% Kunpeng Li, Junyan Xiao, Xinxin Yu, Tongle Bu, Tianhui Li, Xi Deng, Sanwan Liu,
Influence of Hot Spot Heating on Stability of Large Size Perovskite Solar Module with a Power Conversion Efficiency of ~14% Kunpeng Li, Junyan Xiao, Xinxin Yu, Tongle Bu, Tianhui Li, Xi Deng, Sanwan Liu,
Biomaterial Scaffolds
 Biomaterial Scaffolds Biomaterial Properties Surface properties Bulk properties Biological properties Types of Biomaterials Biological materials Synthetic materials Surface Properties The body reads the
Biomaterial Scaffolds Biomaterial Properties Surface properties Bulk properties Biological properties Types of Biomaterials Biological materials Synthetic materials Surface Properties The body reads the
Supporting Information. For. Preparation and Characterization of Highly Planar Flexible Silver
 Supporting Information For Preparation and Characterization of Highly Planar Flexible Silver Crystal Belts Dharmesh Varade and Kazutoshi Haraguchi* [*] Dr. K. Haraguchi (Corresponding-Author), Dr. D. Varade
Supporting Information For Preparation and Characterization of Highly Planar Flexible Silver Crystal Belts Dharmesh Varade and Kazutoshi Haraguchi* [*] Dr. K. Haraguchi (Corresponding-Author), Dr. D. Varade
6. Plasmon coupling between a flat gold interface and gold nanoparticles.
 6. Plasmon coupling between a flat gold interface and gold nanoparticles. 6.1. Introduction In this outlook oriented chapter the applicability of the multilayered system used in chapter 4.1., for the study
6. Plasmon coupling between a flat gold interface and gold nanoparticles. 6.1. Introduction In this outlook oriented chapter the applicability of the multilayered system used in chapter 4.1., for the study
Enhanced photocurrent of ZnO nanorods array sensitized with graphene. quantum dots
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Enhanced photocurrent of ZnO nanorods array sensitized with graphene quantum dots Bingjun Yang,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Enhanced photocurrent of ZnO nanorods array sensitized with graphene quantum dots Bingjun Yang,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Under-Oil Switchable Superhydrophobicity to Superhydrophilicity Transition on TiO 2 Nanotube Arrays Hongjun Kang, Yuyan Liu, Hua Lai, Xiaoyan Yu, Zhongjun Cheng, and Lei Jiang MIIT
Supporting Information Under-Oil Switchable Superhydrophobicity to Superhydrophilicity Transition on TiO 2 Nanotube Arrays Hongjun Kang, Yuyan Liu, Hua Lai, Xiaoyan Yu, Zhongjun Cheng, and Lei Jiang MIIT
New Developments in Raman Spectroscopic Analysis
 New Developments in Raman Spectroscopic Analysis Mike Kayat B&W Tek, Inc 19 Shea Way Newark, DE 19713 United States of America +1 302 368 7824 mikek@bwtek.com 1 Overview Raman spectroscopy is now an established
New Developments in Raman Spectroscopic Analysis Mike Kayat B&W Tek, Inc 19 Shea Way Newark, DE 19713 United States of America +1 302 368 7824 mikek@bwtek.com 1 Overview Raman spectroscopy is now an established
Applications of XPS, AES, and TOF-SIMS
 Applications of XPS, AES, and TOF-SIMS Scott R. Bryan Physical Electronics 1 Materials Characterization Techniques Microscopy Optical Microscope SEM TEM STM SPM AFM Spectroscopy Energy Dispersive X-ray
Applications of XPS, AES, and TOF-SIMS Scott R. Bryan Physical Electronics 1 Materials Characterization Techniques Microscopy Optical Microscope SEM TEM STM SPM AFM Spectroscopy Energy Dispersive X-ray
Hierarchically Structured Nanoporous Poly(Ionic Liquid) Membranes: Facile Preparation and Application in Fiber-optic ph Sensing
 Supporting Information Hierarchically Structured Nanoporous Poly(Ionic Liquid) Membranes: Facile Preparation and Application in Fiber-optic ph Sensing Qiang Zhao, a Mingjie Yin, b A. Ping Zhang, b Simon
Supporting Information Hierarchically Structured Nanoporous Poly(Ionic Liquid) Membranes: Facile Preparation and Application in Fiber-optic ph Sensing Qiang Zhao, a Mingjie Yin, b A. Ping Zhang, b Simon
Shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
 Shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy Jian Feng Li, Yi Fan Huang, Yong Ding, Zhi Lin Yang, Song Bo Li, Xiao Shun Zhou, Feng Ru Fan, Wei Zhang, Zhi You Zhou, De Yin Wu, Bin Ren, Zhong
Shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy Jian Feng Li, Yi Fan Huang, Yong Ding, Zhi Lin Yang, Song Bo Li, Xiao Shun Zhou, Feng Ru Fan, Wei Zhang, Zhi You Zhou, De Yin Wu, Bin Ren, Zhong
