October 30 November 3. Daily Log
|
|
|
- Timothy Evelyn King
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 October 30 November 3 Daily Log
2 October 30 th Bellwork In general there is a decrease in atomic radii as you move from left to right across a period. This trend, is caused by the increasing positive charge in the nucleus and the fact that the principal energy level within a period remains the same. Each successive element has 1 addition proton and electron. What is the trend in atomic radii across a period?
3 October 30, 2017 Today s focus: 1. Ionization Energy- Look at Graphs and look at first few questions for the graphing activity, finish and turn in, then: 2. Complete the following using your book: On page 167, #85 write out e.config and orbital diagram for each.(e.c. is the 1s 2 2s 2 and the orbital is the arrows. 3. On page 168, #90 write the electron dot structure. E. dot is dots representing valence electrons N,S,E,W then pair the electrons.
4 October 31 Bellwork Atoms can gain or lose electrons to form ions. Because electrons are negatively charged, atoms that gain or lose electrons acquire a net charge. An ion is an atom or bonded group of atoms that has a positive or negative charge. When atoms lose electrons they always become smaller. Why do atoms that become ions become smaller in size?
5 Homework/Book Assignment p 167, Write the elements orbital notation(arrows with boxes) and the complete electron configuration for: a. beryllium c. nitrogen b. aluminum d. sodium
6 Electron Dot for page Draw the ELECTRON dot structure(lewis dots) for: a. carbon b. arsenic c. polonium d. potassium e. barium
7 Review: Electron Configuration Which element has the electron configuration 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 4s 2 3d 8?
8 What is the long hand of Germanium Write out the entire electron configuration for Germanium
9 1. How do you write the shorthand configuration for an element?
10 For Example: Germanium is on the row below Argon so put the symbol for Argon in brackets then finish the electron configuration for the row Ge is on.
11 3 RULES you MUST be able to identify Aufbau Principle electrons will fill LOWEST ENERGY level first Pauli Exclusion Principle electrons will have opposite spins if they are in the same orbital Hunds Rule electrons must fill one at a time first at equal orbital levels then they can pair
12 Orbital diagrams- Examples You make a box or line or circle to represent the (ORBEDTAL) arrows = electrons Remember only 2 total electrons per orbital Hunds rule says only one electron per orbital Until all the orbitals with the same energy have At least one and then you pair them up. Look at Carbon below for example. Arrows go Up first in all the same type of orbital and then Pair up with arrow down. (opposite spin) Only 1 s orbital in an energy level 3 p orbitals possible in energy level 5 d orbitals possible in energy level 7 f orbitals possible in energy level
13 Orbital Diagram of Iron
14 POP Quiz : Atoms and Electrons 6. CHOICES are: Aufbau, Pauli, Hunds?
15 Lewis Dot Review Only draw the VALENCE ELECTRONS What is a proper dot structure for Fluorine? Is this one the ONLY proper way?
16 October 31 Today s focus: Review Chapter 6 Periodic Table- 1. Practice Electron Configuration, Orbital Diagrams and Lewis Dot Structures 2. Review Aufbau, Hunds, Pauli 3. Receive a review sheet for the test(for a grade) NO food or drink, No phones, No talking please unless it is about the review information
17 November 1 Bellwork Atoms gain or lose electrons to attain the Noble gas configuration because noble gases have full outside energy levels. The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose or share electrons in order to acquire a full set of 8 valence electrons. If there is a full set of 8 electrons then both the s and p block are full. Helium is the exception, it is full at the s block. What is the goal of the octet rule?
18 November 1 Today s Focus: Play Kahoot then complete the Test Review using FIB notes and all other handouts and notes.
19 November 2 Bellwork NONE Teacher Absent
20 November 2 CHAPTER 6 TEST Periodic TABLE
21 November 3 Bellwork When an writing the electron configuration for an element the number in front of the letter represents the energy level or ring around the nucleus of an atom. The letter, (s,p,d or f) represents the orbital. The exponent represents the number of electrons in the orbital. S sublevel can only have one orbital, p can only have 3 orbitals, d can have 5 orbitals and f can have 7 orbitals. If each orbital (orbedital) can only hold 2 electrons, How many electrons maximum can s hold, p hold, d hold, f hold?
22 November 3 Today s Focus Introduction to Ionic Bonding- Read Sections 7.1 and 7.2 and fill in your notes
Unit 4B- Electron Configuration- Guided Notes
 Unit 4B- Electron Configuration- Guided Notes Atomic Structure Electrons are arranged in or around the nucleus of an atom o First shell can hold a maximum of electrons o Second shell can hold a maximum
Unit 4B- Electron Configuration- Guided Notes Atomic Structure Electrons are arranged in or around the nucleus of an atom o First shell can hold a maximum of electrons o Second shell can hold a maximum
Orbital Diagram Rules: 1. The Aufbau Principle: Under normal condition, each electron occupies the
 Honors Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Orbital Diagram Rules: 1. The Aufbau Principle: Under normal condition, each electron occupies the 2. The Pauli Exclusion Principle: a maximum of can occupy an orbital
Honors Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block Orbital Diagram Rules: 1. The Aufbau Principle: Under normal condition, each electron occupies the 2. The Pauli Exclusion Principle: a maximum of can occupy an orbital
DUE DATE: JUNE 25 TH. SUMMER REV: Electron Configurations
 NAME: DUE DATE: JUNE 25 TH AP Chemistry SUMMER REV: Electron s Why? The electron structure of an atom is very important. Scientists use the electronic structure of atoms to predict bonding in molecules,
NAME: DUE DATE: JUNE 25 TH AP Chemistry SUMMER REV: Electron s Why? The electron structure of an atom is very important. Scientists use the electronic structure of atoms to predict bonding in molecules,
Unit Five Practice Test (Part I) PT C U5 P1
 Unit Five Practice Test (Part I) PT C U5 P1 Name Period LPS Standard(s): --- State Standard(s): 12.3.1 Short Answers. Answer the following questions. (5 points each) 1. Write the electron configuration
Unit Five Practice Test (Part I) PT C U5 P1 Name Period LPS Standard(s): --- State Standard(s): 12.3.1 Short Answers. Answer the following questions. (5 points each) 1. Write the electron configuration
UNIT 2 PART 1: ELECTRONS
 UNIT 2 PART 1: ELECTRONS Electrons in an Atom Bohr s Model: Electrons resided in an allowed orbit. Quantum Mechanics Model: Probability of finding an electron in an area around the nucleus. This area around
UNIT 2 PART 1: ELECTRONS Electrons in an Atom Bohr s Model: Electrons resided in an allowed orbit. Quantum Mechanics Model: Probability of finding an electron in an area around the nucleus. This area around
Electron Configurations
 Electron Configurations Parts of the atom Protons identify the element. Neutrons add mass and help glue the nucleus together ( all those protons are NOT happy being stuck next to each other). Parts of
Electron Configurations Parts of the atom Protons identify the element. Neutrons add mass and help glue the nucleus together ( all those protons are NOT happy being stuck next to each other). Parts of
Wave-Mechanical Model of the Atom. Aim: To write orbital notation and electron configurations representing the wave mechanical model of the atom.
 Wave-Mechanical Model of the Atom Aim: To write orbital notation and electron configurations representing the wave mechanical model of the atom. Wave-Mechanical Model of the Atom Atoms contain protons,
Wave-Mechanical Model of the Atom Aim: To write orbital notation and electron configurations representing the wave mechanical model of the atom. Wave-Mechanical Model of the Atom Atoms contain protons,
POGIL: Electron Configurations
 Name DUE DATE Period Chemistry POGIL: Electron Configurations Why? The electron structure of an atom is very important. Scientists use the electronic structure of atoms to predict bonding in molecules,
Name DUE DATE Period Chemistry POGIL: Electron Configurations Why? The electron structure of an atom is very important. Scientists use the electronic structure of atoms to predict bonding in molecules,
Atoimic Structure and the Periodic Table: Unit Objective Study Guide Part 2
 Name Date Due Atoimic Structure and the Periodic Table: Unit Objective Study Guide Part 2 Directions: Write your answers to the following questions in the space provided. For problem solving, all of the
Name Date Due Atoimic Structure and the Periodic Table: Unit Objective Study Guide Part 2 Directions: Write your answers to the following questions in the space provided. For problem solving, all of the
Electrons! Chapter 5, Part 2
 Electrons! Chapter 5, Part 2 3. Contained within sublevels are orbitals: pairs of electrons each having a different space or region they occupy a. Each sublevel contains certain orbitals: i. s sublevel
Electrons! Chapter 5, Part 2 3. Contained within sublevels are orbitals: pairs of electrons each having a different space or region they occupy a. Each sublevel contains certain orbitals: i. s sublevel
Student Exploration: Electron Configuration
 Name: Date: Student Exploration: Electron Configuration Vocabulary: atomic number, atomic radius, Aufbau principle, chemical family, diagonal rule, electron configuration, Hund s rule, orbital, Pauli exclusion
Name: Date: Student Exploration: Electron Configuration Vocabulary: atomic number, atomic radius, Aufbau principle, chemical family, diagonal rule, electron configuration, Hund s rule, orbital, Pauli exclusion
LIMITATIONS OF RUTHERFORD S ATOMIC MODEL
 ELECTRONS IN ATOMS LIMITATIONS OF RUTHERFORD S ATOMIC MODEL Did not explain the chemical properties of atoms For example, it could not explain why metals or compounds of metals give off characteristic
ELECTRONS IN ATOMS LIMITATIONS OF RUTHERFORD S ATOMIC MODEL Did not explain the chemical properties of atoms For example, it could not explain why metals or compounds of metals give off characteristic
Unit Two: Elements & Matter. February 1, 2016
 Unit Two: Elements & Matter February 1, 2016 Warm-Up: 2/1/2016 1. Fill in the following information: Atomic Symbol Ca 2+ Atomic Number Proton Neutron Electron 34 36 Mass Num. 2. Identify which family the
Unit Two: Elements & Matter February 1, 2016 Warm-Up: 2/1/2016 1. Fill in the following information: Atomic Symbol Ca 2+ Atomic Number Proton Neutron Electron 34 36 Mass Num. 2. Identify which family the
Notes: Electrons and Periodic Table (text Ch. 4 & 5)
 Name Per. Notes: Electrons and Periodic Table (text Ch. 4 & 5) NOTE: This set of class notes is not complete. We will be filling in information in class. If you are absent, it is your responsibility to
Name Per. Notes: Electrons and Periodic Table (text Ch. 4 & 5) NOTE: This set of class notes is not complete. We will be filling in information in class. If you are absent, it is your responsibility to
Valence electron- Energy sublevel- Transition element- Period 10. Electronegativity- Alkaline earth metal- 11. Ion- Halogen- 12.
 Mrs. Hilliard 1. Valence electron 2. Period 3. Alkaline earth metal 4. Halogen 5. Metalloid 6. Hund s Rule 7. Representative element 8. Energy sublevel 9. Transition element 10. Electronegativity 11. Ion
Mrs. Hilliard 1. Valence electron 2. Period 3. Alkaline earth metal 4. Halogen 5. Metalloid 6. Hund s Rule 7. Representative element 8. Energy sublevel 9. Transition element 10. Electronegativity 11. Ion
Electronic Structure of Atoms and the Periodic table. Electron Spin Quantum # m s
 Electronic Structure of Atoms and the Periodic table Chapter 6 & 7, Part 3 October 26 th, 2004 Homework session Wednesday 3:00 5:00 Electron Spin Quantum # m s Each electron is assigned a spinning motion
Electronic Structure of Atoms and the Periodic table Chapter 6 & 7, Part 3 October 26 th, 2004 Homework session Wednesday 3:00 5:00 Electron Spin Quantum # m s Each electron is assigned a spinning motion
Unit 3: The Periodic Table and Atomic Theory
 Name: Period: Unit 3: The Periodic Table and Atomic Theory Day Page # Description IC/HW 1 2-3 Periodic Table and Quantum Model Notes IC 1 4-5 Orbital Diagrams Notes IC 1 14 3-A: Orbital Diagrams Worksheet
Name: Period: Unit 3: The Periodic Table and Atomic Theory Day Page # Description IC/HW 1 2-3 Periodic Table and Quantum Model Notes IC 1 4-5 Orbital Diagrams Notes IC 1 14 3-A: Orbital Diagrams Worksheet
General Rules. Pauli Exclusion Principle. Each orbital can hold TWO electrons with opposite spins. Wolfgang Pauli
 General Rules Pauli Exclusion Principle Each orbital can hold TWO electrons with opposite spins. Wolfgang Pauli General Rules Aufbau Principle Electrons fill the lowest energy orbitals first. Lazy Tenant
General Rules Pauli Exclusion Principle Each orbital can hold TWO electrons with opposite spins. Wolfgang Pauli General Rules Aufbau Principle Electrons fill the lowest energy orbitals first. Lazy Tenant
2 e. 14 e. # e # orbitals. 10 e 5. sublevel. shape of orbital. Orbital Shapes. Notes Orbital Notation; e Config; NGN.
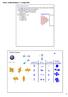 How to build an atom: The bigger (more massive) the atom, the more protons (and neutrons) The bigger the atom, the more electrons Electrons fill lower energy levels first "Aufbau" Principle ("To build
How to build an atom: The bigger (more massive) the atom, the more protons (and neutrons) The bigger the atom, the more electrons Electrons fill lower energy levels first "Aufbau" Principle ("To build
The Periodic Table & Formation of Ions
 The Periodic Table & Formation of Ions Development of the Periodic Table Mendeleev: Considered to be the father of the periodic table Arranged elements by increasing atomic mass Placed elements with similar
The Periodic Table & Formation of Ions Development of the Periodic Table Mendeleev: Considered to be the father of the periodic table Arranged elements by increasing atomic mass Placed elements with similar
= proton (positive charge) = electron (negative charge) = neutron (no charge) A Z. ,, and are notations that represent isotopes of carbon.
 ChemQuest 8 Name: Date: Hour: Information: Structure of the Atom Note the following symbols: (they are not to scale) = proton (positive charge) = electron (negative charge) = neutron (no charge) The following
ChemQuest 8 Name: Date: Hour: Information: Structure of the Atom Note the following symbols: (they are not to scale) = proton (positive charge) = electron (negative charge) = neutron (no charge) The following
Objectives: Learn how to show Electron configuration using:
 4 WAYS to SHOW the Electron Configuration(Electron arrangement) Objectives: Learn how to show Electron configuration using: 1. Using Aufbau Energy Diagrams 2. Orbital Diagrams 3. Long hand Electron configuration
4 WAYS to SHOW the Electron Configuration(Electron arrangement) Objectives: Learn how to show Electron configuration using: 1. Using Aufbau Energy Diagrams 2. Orbital Diagrams 3. Long hand Electron configuration
Use the Venn Diagram to compare and contrast the Bohr Model of the atom with the Quantum Mechanical Model of atom
 Use the Venn Diagram to compare and contrast the Bohr Model of the atom with the Quantum Mechanical Model of atom Bohr Model Quantum Model Energy level Atomic orbital Quantum Atomic number Quantum mechanical
Use the Venn Diagram to compare and contrast the Bohr Model of the atom with the Quantum Mechanical Model of atom Bohr Model Quantum Model Energy level Atomic orbital Quantum Atomic number Quantum mechanical
Electron Configurations
 Electron Configurations Electron Arrangement in an Atom The arrangement of electrons in an atom is its electron configuration. It is impossible to know where an electron is or how fast it is traveling
Electron Configurations Electron Arrangement in an Atom The arrangement of electrons in an atom is its electron configuration. It is impossible to know where an electron is or how fast it is traveling
Electron Configurations
 Section 3 Electron Configurations Key Terms electron configuration Pauli exclusion principle noble gas Aufbau principle Hund s rule noble-gas configuration Main Ideas Electrons fill in the lowest-energy
Section 3 Electron Configurations Key Terms electron configuration Pauli exclusion principle noble gas Aufbau principle Hund s rule noble-gas configuration Main Ideas Electrons fill in the lowest-energy
Atomic Emission Spectra, & Electron Configuration. Unit 1 Coral Gables Senior High Ms. Kiely Pre-IB Chemistry I
 Atomic Emission Spectra, & Electron Configuration Unit 1 Coral Gables Senior High Ms. Kiely Pre-IB Chemistry I Bell-Ringer What does Heisenberg s Uncertainty Principle state? Answer Heisenberg s Uncertainty
Atomic Emission Spectra, & Electron Configuration Unit 1 Coral Gables Senior High Ms. Kiely Pre-IB Chemistry I Bell-Ringer What does Heisenberg s Uncertainty Principle state? Answer Heisenberg s Uncertainty
Electrons in the outermost s and p orbitals. These are the electrons most often involved in bonding.
 Electrons in the outermost s and p orbitals. These are the electrons most often involved in bonding. The organization of electrons in an atom or ion, from the lowest energy orbital ( s ) to the highest
Electrons in the outermost s and p orbitals. These are the electrons most often involved in bonding. The organization of electrons in an atom or ion, from the lowest energy orbital ( s ) to the highest
Section 3 Electron Configurations. Chapter 4. Preview
 Preview Lesson Starter Objectives Electron Configurations Rules Governing Electron Configurations Representing Electron Configurations Elements of the Second Period Elements of the Third Period Elements
Preview Lesson Starter Objectives Electron Configurations Rules Governing Electron Configurations Representing Electron Configurations Elements of the Second Period Elements of the Third Period Elements
Chapter 3: Electron Structure and the Periodic Law
 Chapter 3: Electron Structure and the Periodic Law PERIODIC LAW This is a statement about the behavior of the elements when they are arranged in a specific order. In its present form the statement is:
Chapter 3: Electron Structure and the Periodic Law PERIODIC LAW This is a statement about the behavior of the elements when they are arranged in a specific order. In its present form the statement is:
Honors Unit 6 Atomic Structure
 Honors Unit 6 Atomic Structure Miss Adams Honors Chemistry 1 Name: 1 Homework #1: Frequency, Wavelength and the Speed of Light Show all of your work for the problems, including the initial formula, substitution
Honors Unit 6 Atomic Structure Miss Adams Honors Chemistry 1 Name: 1 Homework #1: Frequency, Wavelength and the Speed of Light Show all of your work for the problems, including the initial formula, substitution
An Electron s Address: Orbital Diagrams and Electron Configuration
 AP Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block An Electron s Address: Orbital Diagrams and Electron Configuration Information: Energy Levels and Sublevels As you know, in his solar system model Bohr proposed that
AP Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block An Electron s Address: Orbital Diagrams and Electron Configuration Information: Energy Levels and Sublevels As you know, in his solar system model Bohr proposed that
Electron Arrangement - Part 2
 Brad Collins Electron Arrangement - Part 2 Chapter 9 Some images Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Review Energy Levels Multi-electron 4d 4d 4d 4d 4d n = 4 4s 4p 4p 4p 3d 3d 3d 3d 3d n=3, l = 2
Brad Collins Electron Arrangement - Part 2 Chapter 9 Some images Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Review Energy Levels Multi-electron 4d 4d 4d 4d 4d n = 4 4s 4p 4p 4p 3d 3d 3d 3d 3d n=3, l = 2
Name: Unit 3 Guide-Electrons In Atoms
 Name: Unit 3 Guide-Electrons In Atoms Importance of Electrons Draw a complete Bohr model of the atom. Write an element s electron configuration. Know how the symbols used in ECs relate to electron properties
Name: Unit 3 Guide-Electrons In Atoms Importance of Electrons Draw a complete Bohr model of the atom. Write an element s electron configuration. Know how the symbols used in ECs relate to electron properties
2.3 Periodic Table and Atomic Theory
 2.3 Periodic Table and Atomic Theory https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/chemistry-- of-life/electron-shells-and-orbitals/v/orbitals https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ghan8xzq-d8 2.3 Periodic Table
2.3 Periodic Table and Atomic Theory https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/chemistry-- of-life/electron-shells-and-orbitals/v/orbitals https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ghan8xzq-d8 2.3 Periodic Table
The orbitals in an atom are arranged in shells and subshells. orbital 3s 3p 3d. Shell: all orbitals with the same value of n.
 Shells and Subshells The orbitals in an atom are arranged in shells and subshells. n=3 orbital 3s 3p 3d Shell: all orbitals with the same value of n n=3 3s 3p 3d Subshell: all orbitals with the same value
Shells and Subshells The orbitals in an atom are arranged in shells and subshells. n=3 orbital 3s 3p 3d Shell: all orbitals with the same value of n n=3 3s 3p 3d Subshell: all orbitals with the same value
Model 1: Orbitals. 1. What is an atomic orbital? What are the four different orbitals?
 Name: Date: Period: POGIL: Electron Configuration and Orbitals Model 1: Orbitals The quantum mechanical model determines the allowed energies an electron can have and how likely it is to find the electron
Name: Date: Period: POGIL: Electron Configuration and Orbitals Model 1: Orbitals The quantum mechanical model determines the allowed energies an electron can have and how likely it is to find the electron
Ionic Bonding Ionic bonding occurs when metals and nonmetals trade one or more electrons and the resulting opposite charges attract each other. Metals
 Chemical Bonding Now that we know what atoms look like A very small (less than 0.001% of the volume) and massive (more than 99.99% of the mass) nucleus with protons (+) and neutrons (neutral) and electrons
Chemical Bonding Now that we know what atoms look like A very small (less than 0.001% of the volume) and massive (more than 99.99% of the mass) nucleus with protons (+) and neutrons (neutral) and electrons
Atomic Structure Chapter 4 Mr. Hines
 Atomic Structure Chapter 4 Mr. Hines Part A Standard model of the atom Learning Targets and I can statements 1 List, label, and describe the parts of an atom. 2 Identify the atomic number and the atomic
Atomic Structure Chapter 4 Mr. Hines Part A Standard model of the atom Learning Targets and I can statements 1 List, label, and describe the parts of an atom. 2 Identify the atomic number and the atomic
5. The outermost principal energy level electron configuration of the element bromine is: a. 4s 2 c. 4s 2 4p 5 b. 4p 5 d.
 1 c E = h 1. Sodium and potassium have similar properties because they have the same a. atomic radii. c. number of valence electrons. b. ionization energy. d. electronegativity. 2. Electrons must be added
1 c E = h 1. Sodium and potassium have similar properties because they have the same a. atomic radii. c. number of valence electrons. b. ionization energy. d. electronegativity. 2. Electrons must be added
Komperda. Electron Configuration and Orbital Notation
 Electron Configuration and Orbital Notation Dmitri Mendeleyev Father of the Modern P.T. Periods and Group Period horizontal row on P.T. Each period represents an energy level (think back to models of the
Electron Configuration and Orbital Notation Dmitri Mendeleyev Father of the Modern P.T. Periods and Group Period horizontal row on P.T. Each period represents an energy level (think back to models of the
Chemistry Day 20. Monday, October 15 th Tuesday, October 16 th, 2018
 Chemistry Day 20 Monday, October 15 th Tuesday, October 16 th, 2018 Do-Now: Quantum Number WS 1. Take out your Ch. 11 B Notes (WS) 2. Make sure you picked up the worksheet from the front 3. Complete at
Chemistry Day 20 Monday, October 15 th Tuesday, October 16 th, 2018 Do-Now: Quantum Number WS 1. Take out your Ch. 11 B Notes (WS) 2. Make sure you picked up the worksheet from the front 3. Complete at
Honors Chemistry Unit 3 ( )
 Honors Chemistry Unit 3 (2017-2018) Quantum numbers Electron orbital shapes Rules: o Aufbau principle o Hund s Rule o Pauli Exclusion principle Orbital notations Electron configuration Noble gas notation
Honors Chemistry Unit 3 (2017-2018) Quantum numbers Electron orbital shapes Rules: o Aufbau principle o Hund s Rule o Pauli Exclusion principle Orbital notations Electron configuration Noble gas notation
Honors Unit 6 Notes - Atomic Structure
 Name: Honors Unit 6 Notes - Atomic Structure Objectives: 1. Students will have a general understanding of the wave nature of light and the interrelationship between frequency, wavelength, and speed of
Name: Honors Unit 6 Notes - Atomic Structure Objectives: 1. Students will have a general understanding of the wave nature of light and the interrelationship between frequency, wavelength, and speed of
Bohr Model of Atom: electrons move around nucleus in orbits similar to how planets orbit the sun energy levels for electrons are quantized
 Chemistry I: Quantum Mechanics Notes Bohr Model of Atom: electrons move around nucleus in orbits similar to how planets orbit the sun energy levels for electrons are quantized Major developments that put
Chemistry I: Quantum Mechanics Notes Bohr Model of Atom: electrons move around nucleus in orbits similar to how planets orbit the sun energy levels for electrons are quantized Major developments that put
Test Review # 4. Chemistry: Form TR4-9A
 Chemistry: Form TR4-9A REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 4 Location of electrons. Electrons are in regions of the atom known as orbitals, which are found in subdivisions of the principal energy levels
Chemistry: Form TR4-9A REVIEW Name Date Period Test Review # 4 Location of electrons. Electrons are in regions of the atom known as orbitals, which are found in subdivisions of the principal energy levels
Electron Configurations: Assigning each electron in an atom to the energy level and sublevel it occupies in the atom. Number of Electrons
 First some terms and more information about the structure of the atom: 1) Energy level is no longer an orbit but more like a boundary or maximum distance from the nucleus that electrons occupy. 1, 2, 3
First some terms and more information about the structure of the atom: 1) Energy level is no longer an orbit but more like a boundary or maximum distance from the nucleus that electrons occupy. 1, 2, 3
Chemistry- Unit 3. Section II - Chapter 7 ( , 7.11) Quantum Mechanics
 Chemistry- Unit 3 Section II - Chapter 7 (7.6-7.8, 7.11) Quantum Mechanics Atomic Review What subatomic particles do you get to play with? Protons Neutrons Electrons NO! It would change the element Don
Chemistry- Unit 3 Section II - Chapter 7 (7.6-7.8, 7.11) Quantum Mechanics Atomic Review What subatomic particles do you get to play with? Protons Neutrons Electrons NO! It would change the element Don
Lab Overview: In this lab, you will be building atoms and illustrating ionic bonds. You will be using M&M s and paper plates to build your atom.
 Name: Date: Period: Discovering Ionic Bonds Activity Lab Overview: In this lab, you will be building atoms and illustrating ionic bonds. You will be using M&M s and paper plates to build your atom. Materials:
Name: Date: Period: Discovering Ionic Bonds Activity Lab Overview: In this lab, you will be building atoms and illustrating ionic bonds. You will be using M&M s and paper plates to build your atom. Materials:
Today is Monday, October 9 th, 2017
 In This Lesson: Valence Electrons and Lewis Dot Structures (Lesson 4 of 4) Today is Monday, October 9 th, 2017 Stuff You Need: Periodic Table Pre-Class: You ve probably heard of the special name we give
In This Lesson: Valence Electrons and Lewis Dot Structures (Lesson 4 of 4) Today is Monday, October 9 th, 2017 Stuff You Need: Periodic Table Pre-Class: You ve probably heard of the special name we give
The Quantum Mechanical Model
 Recall The Quantum Mechanical Model Quantum Numbers Four numbers, called quantum numbers, describe the characteristics of electrons and their orbitals Quantum Numbers Quantum Numbers The Case of Hydrogen
Recall The Quantum Mechanical Model Quantum Numbers Four numbers, called quantum numbers, describe the characteristics of electrons and their orbitals Quantum Numbers Quantum Numbers The Case of Hydrogen
Chapter 3: Electron Structure and the Periodic Law
 PERIODIC LAW This is a statement about the behavior of the elements when they are arranged in a specific order. In its present form the statement is: Elements with similar chemical properties occur at
PERIODIC LAW This is a statement about the behavior of the elements when they are arranged in a specific order. In its present form the statement is: Elements with similar chemical properties occur at
Warm Up 2: Energy Levels
 Warm Up 2: Energy Levels 2-21-17 LT I can explain how the periodic table is organized around electron energy levels and sub levels. Q1. What is an electron cloud? Q2. What does "n" mean in reference to
Warm Up 2: Energy Levels 2-21-17 LT I can explain how the periodic table is organized around electron energy levels and sub levels. Q1. What is an electron cloud? Q2. What does "n" mean in reference to
Electron Configuration! Chapter 5
 Electron Configuration! Chapter 5 Helpful Videos https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j-djeilynje Quantum Mechanics Better than any previous model, quantum mechanics does explain how the atom behaves. Quantum
Electron Configuration! Chapter 5 Helpful Videos https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j-djeilynje Quantum Mechanics Better than any previous model, quantum mechanics does explain how the atom behaves. Quantum
Topic 2 Atomic Structure. IB Chemistry SL Coral Gables Senior High School Ms. Kiely
 Topic 2 Atomic Structure IB Chemistry SL Coral Gables Senior High School Ms. Kiely Bell Ringer (i) Calculate the number of neutrons and electrons in one atom of ⁶⁵Cu. (ii) State one difference in the physical
Topic 2 Atomic Structure IB Chemistry SL Coral Gables Senior High School Ms. Kiely Bell Ringer (i) Calculate the number of neutrons and electrons in one atom of ⁶⁵Cu. (ii) State one difference in the physical
Orbital Diagrams & Electron Configurations for Atoms and Ions
 Orbital Diagrams & Electron Configurations for Atoms and Ions Section 3.5 The Periodic Table is like a MAP that describes the arrangement of electrons within their orbitals. Orbital diagrams represent
Orbital Diagrams & Electron Configurations for Atoms and Ions Section 3.5 The Periodic Table is like a MAP that describes the arrangement of electrons within their orbitals. Orbital diagrams represent
The element having chemical properties most similar to As is. The properties of the elements are determined by the arrangement of in their atoms.
 Group 17 (7A) Halogens - Colorful and corrosive nonmetals - Found in nature only in with other elements, such as with sodium in table salt (sodium chloride, NaCl) - All except At are as pure elements.
Group 17 (7A) Halogens - Colorful and corrosive nonmetals - Found in nature only in with other elements, such as with sodium in table salt (sodium chloride, NaCl) - All except At are as pure elements.
Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
 CHAPTER 4 REVIEW Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms SECTION 1 SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. In what way does the photoelectric effect support the particle theory
CHAPTER 4 REVIEW Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms SECTION 1 SHORT ANSWER Answer the following questions in the space provided. 1. In what way does the photoelectric effect support the particle theory
1. The total number of protons AND neutrons in Aluminum 27 is:
 The ATOM test VERSION B Name 1. The total number of protons AND neutrons in Aluminum 27 is: 2. The number of protons in Aluminum 27 is: 3. The number of electrons in Aluminum 27 is: 4. The number of neutrons
The ATOM test VERSION B Name 1. The total number of protons AND neutrons in Aluminum 27 is: 2. The number of protons in Aluminum 27 is: 3. The number of electrons in Aluminum 27 is: 4. The number of neutrons
Unit 2 - Electrons and Periodic Behavior
 Unit 2 - Electrons and Periodic Behavior I. The Bohr Model of the Atom A. Electron Orbits, or Energy Levels 1. Electrons can circle the nucleus only in allowed paths or orbits 2. The energy of the electron
Unit 2 - Electrons and Periodic Behavior I. The Bohr Model of the Atom A. Electron Orbits, or Energy Levels 1. Electrons can circle the nucleus only in allowed paths or orbits 2. The energy of the electron
#9 Modern Atomic Theory Quantitative Chemistry
 Name #9 Modern Atomic Theory Quantitative Chemistry Student Learning Map Unit EQ: What is the current model of the atom? Key Learning: The current model of the atom is based on the quantum mechanical model.
Name #9 Modern Atomic Theory Quantitative Chemistry Student Learning Map Unit EQ: What is the current model of the atom? Key Learning: The current model of the atom is based on the quantum mechanical model.
Electronic Structure and the Periodic Table. Unit 6 Honors Chemistry
 Electronic Structure and the Periodic Table Unit 6 Honors Chemistry Wave Theory of Light James Clerk Maxwell Electromagnetic waves a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels through
Electronic Structure and the Periodic Table Unit 6 Honors Chemistry Wave Theory of Light James Clerk Maxwell Electromagnetic waves a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels through
CHAPTER 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms
 CHAPTER 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms SECTION 1 The Development of a New Atomic Model OBJECTIVES 1. Explain the mathematical relationship among the speed, wavelength, and frequency of electromagnetic
CHAPTER 4 Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms SECTION 1 The Development of a New Atomic Model OBJECTIVES 1. Explain the mathematical relationship among the speed, wavelength, and frequency of electromagnetic
Model 1 The Boarding House
 NS D4 Electron Configurations Name What is the electron structure in an atom? The electron structure of an atom is very important. Scientists use the electronic structure of atoms to predict bonding in
NS D4 Electron Configurations Name What is the electron structure in an atom? The electron structure of an atom is very important. Scientists use the electronic structure of atoms to predict bonding in
Name: Electrons in Atoms Chemical Periodicity Chapters 13 and 14
 Name: Electrons in Atoms Chemical Periodicity Chapters 13 and 14 1 Chapter 13 Electrons in Atoms We need to further develop our understanding of atomic structure to help us understand how atoms bond to
Name: Electrons in Atoms Chemical Periodicity Chapters 13 and 14 1 Chapter 13 Electrons in Atoms We need to further develop our understanding of atomic structure to help us understand how atoms bond to
Agenda. Warm Up. Objective. Electron Configurations. Where are the e- s in an atom? Quantum numbers can tell us. Principle Quantum Number (n) 10/14/14
 Warm Up Agenda Worksheet: Orbital shapes Review: Quantum numbers (PAP) (Quiz next class) Lots of handouts Whiteboards: Quantum numbers practice (PAP) Turn in Flame test Lab Coloring: periodic table s,
Warm Up Agenda Worksheet: Orbital shapes Review: Quantum numbers (PAP) (Quiz next class) Lots of handouts Whiteboards: Quantum numbers practice (PAP) Turn in Flame test Lab Coloring: periodic table s,
Electron Configuration & Periodicity Unit 3
 Name: Electron Configuration & Periodicity Unit 3 (seven class periods) Unit 3.1: First Ionization Energy & Photoelectron Spectroscopy 1) Coulombs Law a) The force of attraction between two charged objects
Name: Electron Configuration & Periodicity Unit 3 (seven class periods) Unit 3.1: First Ionization Energy & Photoelectron Spectroscopy 1) Coulombs Law a) The force of attraction between two charged objects
Unit 2: Chemical Reactions
 Unit 2: Chemical Reactions Title Oct 13 10:33 AM Chemistry Review Activity: 29 Brains are better than 1... 1. At your first station, brainstorm with your group and try to write down as much information
Unit 2: Chemical Reactions Title Oct 13 10:33 AM Chemistry Review Activity: 29 Brains are better than 1... 1. At your first station, brainstorm with your group and try to write down as much information
Work hard. Be nice. Name: Period: Date: UNIT 3: Electrons Lesson 4: The Octet Rule. Nitrogen Neon Carbon He
 Name: Period: Date: UNIT 3: Electrons Lesson 4: The Octet Rule Do Now: By the end of today, you will have an answer to: What role do valence electrons play in chemical changes? Draw the following lewis
Name: Period: Date: UNIT 3: Electrons Lesson 4: The Octet Rule Do Now: By the end of today, you will have an answer to: What role do valence electrons play in chemical changes? Draw the following lewis
WARM-UP. Draw each of the three models of the atom that we learned about last unit. Who came up with each? What was wrong with each?
 WARM-UP Draw each of the three models of the atom that we learned about last unit. Who came up with each? What was wrong with each? 1:59 1:58 1:57 1:56 1:55 1:54 1:53 1:52 1:51 1:50 1:49 1:48 1:47 1:46
WARM-UP Draw each of the three models of the atom that we learned about last unit. Who came up with each? What was wrong with each? 1:59 1:58 1:57 1:56 1:55 1:54 1:53 1:52 1:51 1:50 1:49 1:48 1:47 1:46
Part I: It s Just a Trend
 Part I: It s Just a Trend 1. What is the trend with the atomic numbers of the elements as you move from left to right across a period on the Periodic Table? How does this sequence continue to the next
Part I: It s Just a Trend 1. What is the trend with the atomic numbers of the elements as you move from left to right across a period on the Periodic Table? How does this sequence continue to the next
Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT.
 ELECTRONS IN ATOMS Chapter Quiz Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 1. The orbitals of a principal energy level are lower in energy than the orbitals
ELECTRONS IN ATOMS Chapter Quiz Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 1. The orbitals of a principal energy level are lower in energy than the orbitals
INTRODUCTION TO IONS
 Name: INTRODUCTION TO IONS Block: Vocabulary: chemical family, electron affinity, ion, ionic bond, metal, nonmetal, octet rule, shell, valence electron Review 1. What are the 3 subatomic particles of an
Name: INTRODUCTION TO IONS Block: Vocabulary: chemical family, electron affinity, ion, ionic bond, metal, nonmetal, octet rule, shell, valence electron Review 1. What are the 3 subatomic particles of an
THE PERIODIC TABLE & PERIODIC LAW! Development of the Modern Periodic Table!
 THE PERIODIC TABLE & PERIODIC LAW! Development of the Modern Periodic Table! Development of the Periodic Table! Main Idea: The periodic table evolved over time as scientists discovered more useful ways
THE PERIODIC TABLE & PERIODIC LAW! Development of the Modern Periodic Table! Development of the Periodic Table! Main Idea: The periodic table evolved over time as scientists discovered more useful ways
Chemistry. Friday, October 13 th Monday, October 16 th, 2017
 Chemistry Friday, October 13 th Monday, October 16 th, 2017 Do-Now: Atomic Orbital WS 1. Write down today s FLT 2. What was wrong with Rutherford s atomic model? 3. Sketch a diagram of Bohr s model. Label
Chemistry Friday, October 13 th Monday, October 16 th, 2017 Do-Now: Atomic Orbital WS 1. Write down today s FLT 2. What was wrong with Rutherford s atomic model? 3. Sketch a diagram of Bohr s model. Label
Atomic Electron Configurations and Periodicity
 Atomic Electron Configurations and Periodicity Electron Spin The 4 th quantum number is known as the spin quantum number and is designated by m s. It can have the value of either + ½ or ½ It roughly translates
Atomic Electron Configurations and Periodicity Electron Spin The 4 th quantum number is known as the spin quantum number and is designated by m s. It can have the value of either + ½ or ½ It roughly translates
Electronic configuration
 Electronic configuration The energy of electrons The electrons of an atom all have the same charge and the same mass, but each electron has a different amount of energy. Electrons that have the lowest
Electronic configuration The energy of electrons The electrons of an atom all have the same charge and the same mass, but each electron has a different amount of energy. Electrons that have the lowest
An Electron s Address
 Honors Chemistry Name Date Block An Electron s Address Information: Energy Levels and Sublevels As you know, in his solar system model Bohr proposed that electrons are located in energy levels. The current
Honors Chemistry Name Date Block An Electron s Address Information: Energy Levels and Sublevels As you know, in his solar system model Bohr proposed that electrons are located in energy levels. The current
Chem I - Wed, 9/16/15
 Chem I - Wed, 9/16/15 Do Now Complete the back of worksheet 4.5 Homework Pennium Lab if not Finished E- Config POGIL Agenda Return Papers Wks 4.5 Pennium Lab Electron Config Chapter 5 Quantum Theory and
Chem I - Wed, 9/16/15 Do Now Complete the back of worksheet 4.5 Homework Pennium Lab if not Finished E- Config POGIL Agenda Return Papers Wks 4.5 Pennium Lab Electron Config Chapter 5 Quantum Theory and
Electrons in Atoms. Section 5.1 Light and Quantized Energy
 Name Date Class 5 Electrons in Atoms Section 5.1 Light and Quantized Energy In your textbook, read about the wave nature of light. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage. amplitude
Name Date Class 5 Electrons in Atoms Section 5.1 Light and Quantized Energy In your textbook, read about the wave nature of light. Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage. amplitude
Questions: Use the information above to answer the following questions 1. How many sublevels exist in the 1 st energy level?
 Honors Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block An Electron s Address Information: Energy Levels and Sublevels As you know, in his solar system model Bohr proposed that electrons are located in energy levels.
Honors Chemistry Ms. Ye Name Date Block An Electron s Address Information: Energy Levels and Sublevels As you know, in his solar system model Bohr proposed that electrons are located in energy levels.
4.2 WHERE are the electrons in the { atom???? QUANTUM NUMBERS
 4.2 WHERE are the electrons in the { atom???? QUANTUM NUMBERS Bohr s Model Contradicts Common Sense If only certain orbits with definite energies are allowed and the electrons constantly gives off radiation,
4.2 WHERE are the electrons in the { atom???? QUANTUM NUMBERS Bohr s Model Contradicts Common Sense If only certain orbits with definite energies are allowed and the electrons constantly gives off radiation,
Chemistry: Hood River Valley High School Unit 3 Note Packet and Goals. Description A1. Marble Lab. Nailon Isotope Lab A2.
 Chemistry: Hood River Valley High School Unit 3 Note Packet and Goals Name: Period: Unit 3 Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Unit Goals- As you work through this unit, you should be able to: 1. describe
Chemistry: Hood River Valley High School Unit 3 Note Packet and Goals Name: Period: Unit 3 Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Unit Goals- As you work through this unit, you should be able to: 1. describe
Periodic Table and Trends Structure and Properties of Matter. Background
 Background Periodic trends are the patterns observed in elemental properties across a row or down a column on the Periodic Table. Some of these trends were observed when the Periodic Table was first being
Background Periodic trends are the patterns observed in elemental properties across a row or down a column on the Periodic Table. Some of these trends were observed when the Periodic Table was first being
Terms to Know. 10.Angular quantum number 11.Magnetic quantum number 12.Spin quantum number
 Terms to Know 1. Photon 2. Atomic emission spectrum 3. Ground state 4. Atomic orbital 5. Aufbau principle 6. Pauli exclusion principle 7. Hunds rule 8. Electron configuration 9. Principle quantum number
Terms to Know 1. Photon 2. Atomic emission spectrum 3. Ground state 4. Atomic orbital 5. Aufbau principle 6. Pauli exclusion principle 7. Hunds rule 8. Electron configuration 9. Principle quantum number
Chapter 5. Periodicity and the Electronic Structure of Atoms
 Chapter 5 Periodicity and the Electronic Structure of Atoms Electron Spin experiments by Stern and Gerlach showed a beam of silver atoms is split in two by a magnetic field the experiment reveals that
Chapter 5 Periodicity and the Electronic Structure of Atoms Electron Spin experiments by Stern and Gerlach showed a beam of silver atoms is split in two by a magnetic field the experiment reveals that
Starter # (1) Why was Rutherford s model not good enough and need to be modified by scientists?
 1. (1) Why was Rutherford s model not good enough and need to be modified by scientists? It could not explain or predict any chemical behavior of any elements 2. (1) What is one of the only things that
1. (1) Why was Rutherford s model not good enough and need to be modified by scientists? It could not explain or predict any chemical behavior of any elements 2. (1) What is one of the only things that
Warm Up 2: Energy Levels
 Warm Up 2: Energy Levels 10-25-17 LT I can explain how the periodic table is organized around electron energy levels and sub levels. Q1. What is an electron cloud? Q2. What does "n" mean in reference to
Warm Up 2: Energy Levels 10-25-17 LT I can explain how the periodic table is organized around electron energy levels and sub levels. Q1. What is an electron cloud? Q2. What does "n" mean in reference to
Notes: Unit 6 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table
 Name KEY Block Notes: Unit 6 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table In the 1790's Antoine Lavoisier compiled a list of the known elements at that time. There were only 23 elements. By the 1870's
Name KEY Block Notes: Unit 6 Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table In the 1790's Antoine Lavoisier compiled a list of the known elements at that time. There were only 23 elements. By the 1870's
WP Unit 2 Practice: The Atom
 WP Unit 2 Practice: The Atom Name 1. Name, and identify them clearly in your answer, one halogen, one noble gas, one alkali metal, one alkali earth metal, one metalloid, one transition metal and finally
WP Unit 2 Practice: The Atom Name 1. Name, and identify them clearly in your answer, one halogen, one noble gas, one alkali metal, one alkali earth metal, one metalloid, one transition metal and finally
Electron Orbitals. Cartoon courtesy of lab-initio.com
 Electron Orbitals Cartoon courtesy of lab-initio.com Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom The model says that the nucleus is surrounded by a space in which electrons orbit- the electron cloud. The model
Electron Orbitals Cartoon courtesy of lab-initio.com Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom The model says that the nucleus is surrounded by a space in which electrons orbit- the electron cloud. The model
Practice Periodic Table Review
 Practice Periodic Table Review Name 1. An electron will emit energy in quanta when its energy state changes from 4p to A) 5s B) 5p C) 3s D) 6p 2. Which electron configuration represents an atom in the
Practice Periodic Table Review Name 1. An electron will emit energy in quanta when its energy state changes from 4p to A) 5s B) 5p C) 3s D) 6p 2. Which electron configuration represents an atom in the
Chapter 9 Bonding - 1. Dr. Sapna Gupta
 Chapter 9 Bonding - 1 Dr. Sapna Gupta Lewis Dot Symbol Lewis dot symbols is a notation where valence electrons are shown as dots. Draw the electrons symmetrically around the sides (top, bottom, left and
Chapter 9 Bonding - 1 Dr. Sapna Gupta Lewis Dot Symbol Lewis dot symbols is a notation where valence electrons are shown as dots. Draw the electrons symmetrically around the sides (top, bottom, left and
ELEMENTS & MATTER. September 7, 2016
 ELEMENTS & MATTER September 7, 2016 Review Problems: 9/7/2016 1. Fill in the following information: Atomic Symbol Atomic Number Proton Neutron Electron Mass Num. Atomic Mass 34 36 Ca 2+ 2. Identify which
ELEMENTS & MATTER September 7, 2016 Review Problems: 9/7/2016 1. Fill in the following information: Atomic Symbol Atomic Number Proton Neutron Electron Mass Num. Atomic Mass 34 36 Ca 2+ 2. Identify which
Name Chemistry-PAP Period. Notes: Electrons. Light travels through space as a wave. Waves have three primary characteristics:
 Name Chemistry-PAP Period The Wave Nature of Light Notes: Electrons Light travels through space as a wave. Waves have three primary characteristics: Wavelength (λ): the distance between 2 consecutive crests
Name Chemistry-PAP Period The Wave Nature of Light Notes: Electrons Light travels through space as a wave. Waves have three primary characteristics: Wavelength (λ): the distance between 2 consecutive crests
: the smallest particle that has the properties of an element. In, this Greek philosopher suggested that the universe was made of.
 Notes: ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE Atomic Structure: : the smallest particle that has the properties of an element. From the early concept of the atom to the modern atomic theory, scientists have built
Notes: ATOMS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE Atomic Structure: : the smallest particle that has the properties of an element. From the early concept of the atom to the modern atomic theory, scientists have built
Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of an element s atoms.
 7.1 Periodic Trends > Valence Electrons Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of an element s atoms. 1 of 31 Periodic Trends > 2 of 31 Periodic Trends > 3 of 31 7.1 Periodic
7.1 Periodic Trends > Valence Electrons Valence electrons are the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of an element s atoms. 1 of 31 Periodic Trends > 2 of 31 Periodic Trends > 3 of 31 7.1 Periodic
Light, Waves, and Electrons
 Light, Waves, and Electrons Light: Travels 1. 2. Light Waves Wavelength Frequency Electromagnetic Spectrum Speed of light The product of frequency of a wave and wavelength = the speed of light Calculate
Light, Waves, and Electrons Light: Travels 1. 2. Light Waves Wavelength Frequency Electromagnetic Spectrum Speed of light The product of frequency of a wave and wavelength = the speed of light Calculate
Unit 1: INTRO TO CHEM
 CHEMISTRY MIDTERM EXAM REVIEW: FALL SEMESTER MIDTERM WILL INCLUDE: 1. DISTRICT MIDTERM 50 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (50 POINTS) 2. DISTRICT CONSTRUCTED RESPONSES (2O POINTS) 3. TEACHER PORTION: 15 MULTIPLE
CHEMISTRY MIDTERM EXAM REVIEW: FALL SEMESTER MIDTERM WILL INCLUDE: 1. DISTRICT MIDTERM 50 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (50 POINTS) 2. DISTRICT CONSTRUCTED RESPONSES (2O POINTS) 3. TEACHER PORTION: 15 MULTIPLE
HL Chemistry. Wednesday August 19th Wednesday, August 19, 15
 HL Chemistry Wednesday August 19th 2015 Agenda Warm Up: Atomic Orbital Energies Research with ipads for Atom Project Review Topic 2.2 (?) Exit Ticket: 3-2-1 Warm Up You have 5 minutes ONLY! GO! What is
HL Chemistry Wednesday August 19th 2015 Agenda Warm Up: Atomic Orbital Energies Research with ipads for Atom Project Review Topic 2.2 (?) Exit Ticket: 3-2-1 Warm Up You have 5 minutes ONLY! GO! What is
6.4 Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations)
 Chapter 6 Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties of Elements 317 Orbital n l m l degeneracy Radial nodes (no.) 4f 4 3 7 0 4p 4 1 3 2 7f 7 3 7 3 5d 5 2 5 2 Check Your Learning How many orbitals have
Chapter 6 Electronic Structure and Periodic Properties of Elements 317 Orbital n l m l degeneracy Radial nodes (no.) 4f 4 3 7 0 4p 4 1 3 2 7f 7 3 7 3 5d 5 2 5 2 Check Your Learning How many orbitals have
