Proceedings of the 1966 Linear Accelerator Conference, Los Alamos, New Mexico, USA
|
|
|
- Shon Allen
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 OPTIMIZATION CRITERIA FOR STANDING WAVE TRANSVERSE MAGNETIC DEFLECTION CAVITIES Jacb Haimsn Massachustts Institut f Tchnlgy* Cambridg, Massachustts 1. Intrductin An imprtant linar acclratr rquirmnt, in rdr t dmnstrat narrw nrgy spctra, is th injctin f lctrn bunchs f narrw phas sprad and ngligibl intr-bunch currnt. This can b achivd by r-f transvrs mdulatin and clipping f th bam by an aprtur prir t injctin int th acclratr wavguid, i.., chppr pratin. By magntically biasing th bam t n sid f th cntrlin, it is pssibl t arrang fr transmissin int th acclratr at a tim during ach r-f cycl whn th radial mmntum impartd t th bam by th chppr cavity is passing thrugh zr. Th lw fficincy f bam utilizatin nrmally assciatd with this typ f pratin, bcaus f th high rati f cllctd t transmittd currnt, can b cnsidrably imprvd by cmbining th transvrs chpping actin with a suitably phasd lngitudinal vlcity mdulating fild I as btaind frm a simpl prbunching cavity. Transvrs r-f dflctin tchniqus als nabl sub-harmnic bunch slctin and injctin int linar acclratrs which ar usd as injctrs fr lctrn synchrtrns. This is achivd by driving th chppr cavity at th sam frquncy as th synchrtrn r-f systm (which is maintaind at a prcis sub-multipl f th linar acclratr fundamntal frquncy) and thn prbunching th chppd bam at th fundamntal frquncy prir t injctin int th linar acclratr.. Micrwav Charactristics A natural chic fr th r-f dflctr in a linar acclratr injctin systm is a rsnant cavity f small dimnsins which can b lcatd in a narrw rgin adjacnt t th gun and. Prfrably, th Q shuld b high nugh t prvid adquat dflctin snsitivity at a rlativly lw driv lvl but nt as high as t caus significant bam dflctin variatins du t small thrmal r input pwr fluctuatins. An lctrn bam travrsing a cavity at right angls t th r-f lctric fild will tnd t undrg a nt zr dflctin bcaus f th cmpnsating ffct f th assciatd r-f magntic fild. 3 On th thr hand, cavitis which prsnt purly transvrs magntic filds t th bam ffr a simpl mans f achiving particl dflctin. Althugh th magntic dflcting frc is a functin f th lctrn nrgy, th nt transvrs mmntum impartd by th magntic fild (nglcting transit tim) will b indpndnt f axial vlcity (rfr t Equatin (3.3 )). Thus th bam dflctin, and thrfr th rsulting currnt transmittd thrugh a clipping aprtur, will b lss affctd by gun vltag rippl than in a cmparabl systm using pur transvrs lctric dflctin. Fr bam dflctin applicatins, w ar primarily intrstd in dtrmining (a) th lcatin f maximum H fild in th cavity, (b) th gradint f th fild at this lcatin and vr a shrt distanc rthrgnul t th fild lins (i.., in th transvrs dflctin path f th bam), (c) th wall lsss rquird t stablish a givn magntic fild strngth, and, (d) th cavity quality factr Q s that th rspns f th systm t thrmal and r-f variatins can b assssd. Th lcatin and gradint f th magntic filds can b dtrmind frm th fild quatins, and a cls apprximatin t th pwr lss - magntic fild strngth rlatinship can b btaind by cnsidring th idal cnductr pak currnt surfac dnsitis J A (as dtrmind frm th tangntial magntic filds) and applying ths t walls f knwn surfac rsistivity (Rs) and ara (A), i.., = 1: R \J \ A P L s A whr PL is th pwr lss avragd vr th r-f cycl. Th lin intgral f magntic fild, takn arund a path which brdrs n th cnducting walls and thn xtnds t infinity, can b quatd t th nclsd cnductin currnt; and sinc J and if ar rthgnal, w can writ in vctr frm, (.1) J=nxH (.) whr n is a unit vctr pinting prpndicularly utward frm th cnducting surfac and II is th magntic fild at th surfac. Thus, frm Equatin (.1) w btain th basic rlatinship btwn th pwr lss in th walls and th tim scillating magntic fild, * Frmrly at Varian Assciats, Pal Alt, Califrnia (.3) 33
2 Th fild quatins als nabl th cavity strd nrgy (U) t b valuatd frm th vlum intgrals (U E ) JffIEIdV max V r (.4) (U) = IfJi 1111 dv H max sinc th ttal nrgy is strd within bth th E and H filds, and whn n is a maximum, th thr is zr. Finally, frm a knwldg f PL and U, th quality factr Q can b dtrmind frm th wll knwn rlatinship btwn strd nrgy and avrag pwr lss pr cycl, V It has bn shwn 4,5 that rsnant frquncis f th nrmal-md filds fr a right circular cylindr ar xprssd in trms f Bssl functin rts such that th fr spac wavlngth f th rsnant frquncy is.) ;\. (.6) (:!m)- + (J Fr TM mds, th mn intgrs ar dfind by th H fild cmpnnts; and X m is th m th rt f J ( kca) =, whr kc is th prpagatin cnstant at th cut-ff wavlngth. Als, th fild quatins ar dfind in Bssl and trignmtric functins such that fr th T1\1 cmpnnts that will b f intrst in th fllwing discussin (n = ) w hav Q (.5) E z (.7). 1 Gnral Exprssins fr th Elctric and Magntic Filds Tw simpl cavitis which ffr th dsird typ f fild distributin ar th pill bx and sctinalizd rctangular wavguid prating in th dminant md as shwn in Figur 1. Th cavitis hav bn rintd such that th magntic filds will b transvrs and th lctric fild paralll t a lngitudinally dirctd bam. Bth cavitis hav magntic filds surrunding th displacmnt currnt rprsntd by th tim varying lctric fild which is a maximum (E) n axis and falls t zr at th cnducting walls. In th cas f th pill bx cavity, th fild cmpnnts rmain cnstant in bth th azimuthal and axial dirctins; whras in th rctangular cavity th fild cmpnnts ar cnstant nly in th axial dirctin. In kping with cnvntin th rctangular cavity can b cnsidrd as a prtin f wavguid which nrmally has a transvrs lctric fild prpagating in th p dirctin but with rflcting plans intrducd with Ag/ sparatin t satisfy th cavity cnditin f zr lctric fild at th walls. Thus fr this cas and with th md dfind as th numbr f half wav variatins in th x, y, 7, dirctins, w btain TE mnp TE xyz E { } n7tz H cp T) J. (k c r) Asirucp + BcsJ7(jJ cs h (.8) E J/kc r ) } n7tz H j {Acsfcp - BSinJ7cp cs -h (.9) r 7) k r c whr A and B ar cnstants dtrmind by th md rintatin and r J7 = Fr J7 =, I, II z A A E C) 1 E r and and B B 1.). Fr th TEmnp mds f a rctangular rsnatr th prpagatin cnstants ar givn by and k ;\. (.1) (.11) Th circular cavity md is dscribd in th azimuthal, radial and axial dirctins, rspctivly, as TM = TM = TM nm cprz 1 Ths cnvntins will b rfrrd t again whn daling with highr md filds latr in this sctin. Th assciatd fild cmpnnts ar xprssd in trignmtric trms such that fr th TE mds f intrst (n = ) w hav. u;c 111 ::x E (m::) sin J -;- sin cs (.1) Y a h cl k c 34
3 II z = C cs Ill7TX cs sin a h (.13) d H x _ C!! sin 7TX cs 7TZ dad (.) Ii x and C k c (m)() - sm--cs. m7tx a d a h cs d (.14) and ad J a + d (.1) H Y E x E z. Cmparisn f TM1 and TE11 Dflctin Fild Charactristics Th fild distributins fr ths simpl dminant mds (s Figur 1) may b drivd by cnsidring th standing wav pattrn prducd (a) in th cylindrical cavity by inward and utward radially prpagatd wavs and (b) in th rctangular cavity by th rflctins btwn nd walls sparatd by d = Ag/...1 Fild Distributins. Fr th TMOlO md, substituting Q =, m = 1, and n = int Equatins (. 7), (.8) and (.9) givs E E/(\l') (.15) /. II<!J E I) J 1 (k c l') (.16) as th nly fild cmpnnts. YJ is th intrinsic impdanc f th mdium (YJ =,J Il/ E = 17T hm in fr spac). In rdr t satisfy th bundary cnditin in this dminant md, zr lctric fild tangntial t th wall at r = a, th first rt f th J Bssl functin dtrmins th rlatinship btwn th prpagatin cnstant (kcl and cavity radius (a), i.., kca =.45 which lads t th wll knwn rsnanc rquirmnt A =. 61a (.17) Th radial variatin f H</> is shwn plttd in Figur. It incrass in magnitud frm zr n axis t a maximum valu (H</>M) at rm = O. 766a and thn falls t O. 89H</>M at th cavity wall. This suggsts that, fr maximum dflctin snsitivity, a bam travrsal hl r radial slt shuld b lcatd at radius rm as shwn by Hr in Figur l(a). Th TE11 md fild cmpnnts (E y ' Hz, and Hx) ar btaind by substituting m = 1, n = and p = 1 in Equatins (.1) - (.14) giving,!! 7TX 7Tz E - jwilc sin sin d (.18) Y 7T a II C cs 7Tx sin 7TZ z a d (.19) Ths quatins shw that th pak magntic filds Hz and Hx ccur immdiatly adjacnt t th walls such that, at x = and a, and z = d/, and at z = and d, and x = a/, (.) (.3) Equatin (.3) rvals an intrsting fatur f th TE lol cavity in that with th xcptin f a squar gmtry (a = d) th magntic fild strngth alngsid th cntr f th lng walls will always b mr intns than at th cntr f th shrt walls. Th bam cntrlin lcatins, fr maximum dflctin, crrspnding t Haz and Bx ar shwn as Hz and Hx, rspctivly, in Figur l(b). In practic, in rdr t tak full advantag f th fild maxima adjacnt t th wall surfac, a small prtubranc in th wall, paralll t th surfac currnts, can b prvidd t avid bam cllisin during that prtin f ach r-f cycl in which th bam is bing dflctd tward th wall. Th Figur graphs shw magntic fild strngth distributins in th dirctins f bam dflctin H</>(r), Hz(x), and Hx(z), plttd against th rspctiv smicavity dimnsins a, x/, and z/ and nrmalizd fr qual maxima. A cmparisn f mr practical valu can b btaind by valuating th cavity wall lsss and intrprting thm in trms f th maximum magntic fild strngth prducd by a givn lvl f r-f pwr cupld in frm an xtrnal gnratr. Th TElOl wall lss calculatins can b simplifid if w mdify th magntic fild quatins as fllws: Frm Equatins (.18) and (.) th maximum lctric fild (E) at x = a/ and z = d/ is givn by E (.4) Substituting fr Hz in Equatins (.19) and (.) w btain H z YJ E a cs 7TX 7TZ a sin d (.5) 35
4 H x 1) E sin 7rX cs HZ d a d (.6).. Evaluatin f Wall Lsss. Fr th O 1 md using Equatins (.3) and (.16) th lsss in th flat nd caps can b writtn as Similarly, fr th lsss in th circumfrntial wall, P LW 1 - R III (a)1 1fah s cp E) = 1fR J (k a)ah s ( 1) 1 c (.31) E) a 7TR s ( 1) 1 c f J (k r)rdr (.7) T valuat this intgral, rfrring t R. V. Churchill "Furir Sris and Bundary Valu Prblms," 1941, pag 16, (.8) Th ttal lsss in th cavity can nw b btaind frm Equatins (.3) and (.31) t giv P l' + P L LE LW 1f1{ (E ) J (k a) (a + ah) s 1) 1 c (.3) Th PLC and PLW quatins als nabl th distributin f lsss btwn th wall and th nd caps t b dtrmind. Infrmatin f this natur assists in cling dsign and in th slctin f matrials fr th cntrl f cavity Q. Frm th abv quatins w btain th simpl and usful rlatinship, h a (.33) Als, sinc J (k a) + J (k a), n-1 c n+1 c Finally, an xprssin rlating th maximum magntic fild and r-f pwr fr th TMOlO md can b btaind frm Equatins (.16) and (.3) such that -- J (k a) = J (k a) + J (k a) (k a) 1 c c c c (.9) + all) But t satisfy th bundary cnditins fr rsnanc (s Equatins (.16) and (.17» J(kca) must qual zr, giving and fr J (k a) -k-j (k a) c (ca) 1 c O.7EiEi, O.JO ar (a + 11) s (.34) Substituting this in Equatin (.8) givs J (k a) a 1 c which whn substitutd int Equatin (.7) givs th lss in th nd caps as ( E ) P = 1fIt a J. (k a) LE s 1) 1 c (.3) A similar prcdur can b usd fr th TE11 cavity t valuat th lsss in th six intrnal surfacs. Thr ar qual and ppsit chargs n th "bam inlt" and "bam utlt" nd walls, and th rsulting circulating cnductin currnts hav radial flw pattrns frm th cntr f ths walls (initially) which bcm paralll in th sid walls. Frm Equatin (.3) and Figur l(b), 36
5 It shuld b ntd that th surfac rsistivity Rs is a functin f AO and is dfind by th matrial cnductivity (') and skin dpth () as, Fr cppr ' = 5.8 x 1 7 mhs pr mtr and J.l = 4 IT x 1-7 hnrys pr mtr, and substituting fr Hz and Hx frm Equatins (.5) and (.6) x 1..R s A hms (.39) (.35) Fr a givn ''h'' dimnsin in th TElOl md, hwvr, th "a" and "d" dimnsins can b varid vr a wid rang whil still satisfying th Equatin (.1) cnditin fr rsnanc, i.., Th pak magntic fild can b rlatd t th r-f pwr by using Equatins (.4) and (.3) t giv (.4) H,) z 4d P L Rs [ h(a 3 + d ) + ad(a 3 + i)] (.36) Thus, bcaus th H x 4a P L Rs[h(a d ) + ad(a + d (.37)..3 Cmparisn f Optimizd Magntic Fild Maxima. Th TM1 and TE1l magntic fild strngths can nw b cmpard n th practical basis f (a) th sam ''h'' dimnsin alng th bam cntrlin, (b) th sam r-f pwr and frquncy, (c) th sam cavity matrial. Bcaus th "a" dimnsin in th TM1 md is dtrmind by AO nly, th chic f an "h" dimnsin allws th maximum valu f th dflctin factr dflctin factrs will vary accrdingly, a maningful cmparisn with th uniquly dfind TMOlO maximum fild rquirs that th TE11 ptimum aid rati cndi tins b invstigatd. Equatins (.35) and (.36) suggst th xistnc f an ptimum cnditin bcaus an initial rductin f "a" with rspct t "d" will caus Hz t incras. T larg a rductin, hwvr, will rsult in rducd filds du t th rapid third rdr grwth f "d". Ltting F qual th right hand sid f Equatin (.36) w hav which lads t af -+ ad ijf (da) ija dd t b uniquly dfind. This can b xprssd in AO nrmalizd dimnsins, using Equatin (.34), as R A s.4 (.38) [ h(a + d ) + ad(a + d 37
6 Thus, fr a maximum r minimum, stting th numratr f this xprssin t zr, nrmalizing t A O ' and substituting frm Equatin (.39) givs (.41) Th TE 11 md ptimum a/d rati, btaind frm th slutin f Equatin (.41), has bn plttd against h/a as shwn by curv A Figur 3. This curv indicats that th ptimum rati is a slw functin f th "h" dimnsin having a/ d ratis f.69,.66 and. 63 fr h/a valus f O. 15,.39 and.49, rspctivly. Infrmatin f this natur substitutd int Equatin (.36) nabls th maximum valu f t b dtrmind. Th advantag f th ptimally dimnsind TE11 cavity vr th thr cnfiguratins is clarly indicatd by cmparisn f th TM1 and TE11 magntic fild maxima ptimizd as discussd abv and listd in Tabl I fr a rang f h/a valus. Crrspnding magntic fild maxima fr TE11 "squar" cavitis (a = d) ar als listd in Tabl I. A scald cmparisn f th magntic fild gradints in th dirctin f bam dflctin, Hz(x), Hx(z) and Hp (r), is shwn in Figur 4 fr h/a =.39. Ths curvs shw that, fr th sam pwr and frquncy, th maximum dflcting magntic filds fr th TM1 and "squar" TE 1 1 cavitis ar 75 and pr cnt, rspctivly, f th ptimizd TElOl magntic fild maximum. Applicatin f th abv thry t an actual dsign prblm will clarify th trms and assist th radr in dfining th units. Fr xampl, lt us assum a matchd TE11 cppr cavity prating at 856 MHz with a pak r-f input pwr f 1 kw. Fr th ptimum a/d rati and a valu f h/a =.15 (h = 1. 6 cm) what is th maximum thrtical valu f HzM? Frm Tabl I and Equatin (.39) w hav, (1 6 \ 1/)1/ HzM = \ 4.5 = 48 amp pr mtr. B = 48 x.il wbr pr mtr. 7 1 = 6 gauss (A. =.15 m) It shuld b ntd that this valu f fild is basd upn a thrtical lss calculatin which, as xplaind in an arlir sctin, is rlatd t svral assumptins cncrning a prfct cnductr. In practic th cavity lsss ar invariably highr, smtims up t pr cnt, dpnding n th matching and fabricatin tchniqu; and this causs a rductin f th thrtical fild valu (1/). Furthrmr, th indicatd valus f "a", lid" and "h" fr a givn AO ar slightly mdifid in practic t allw fr th dtuning ffcts f bam aprtur gmtry, multipactr supprssin tratmnt, mnitring dvics, tc. Rfrring again t Tabl I, rductin f th magntic fild factrs with incrasing h/a. fr th sam md shuld nt b rgardd as a disadvantag frm th vrall pint f viw f bam dflctin. As will b shwn in a latr sctin, fr a givn bam nrgy, th dflctin angl is a functin f th intgratd magntic fild strngth xprincd by th particl during travrsal thrugh th cavity, i.., a prduct f th cavity "h" dimnsin, and th transit tim and phas crrctd valu f magntic fild. Thus a cavity with a larg "h" valu can b a vry fficint dflctr vn thugh its factr is lw. An imprtant practical aspct which may influnc th abv ptimizatin prcdur and which shuld b givn carful cnsidratin is th cavity quality factr Q...4 Evaluatin and Discussin f Q. A knwldg f th cavity strd nrgy and lss nabls th Q t b dtrmind frm Equatin (.5). Fr th TMOlO md, using Equatins (.4) and (.15) th strd nrgy maxima can b xprssd as and substituting Equatins (.4) and (.3) int (.5) givs =() Q H a + h :i Equatin (.17) nabls this t b simplifid such that QH MKS (.43) '" which fr cppr cavitis rducs t 38
7 MKS (.44) Th vlum intgral f th lctric fild Equatin (. 18) givs th TE1l md maximum strd nrgy as (.45) and by cmbining this with th lss Equatin (.35) 3 _ I1 h (a + d ) / J QRs (.46) [ h(a + d ) + ad(a + d ) Th variatin f QRs with cavity lngth (h/;\) fr th TM OlO md is shwn as curv A in Figur 5 and th TE lol md QRs has bn plttd against (a/a) in Figur 6 fr thr spcific valus f (h/a)' Ths curvs indicat that th TM OlO Q valus rmain smwhat highr (5 t 1 pr cnt) than th valus fr th crrspnding ptimally dimnsind TElOl cavitis vr a rang f h/a' Sm typical valus hav bn listd in Tabl II. Fr th cavity xampls shwn in Figur 4, with h/a =.39, th QRs curvs indicat Q's f 15, fr cppr surfacs and a frquncy f 856 MHz. Q valus f this magnitud ar usually undsirabl in practic bcaus highly stabl frquncy and tmpratur cntrl systms ar ssntial if trublsm variatins f th bam dflctin ar t b avidd. Evn if ths bjctins wr vrcm, a mr srius disadvantag bcms apparnt whn, fr pulsd systms, th xcitatin tim f th cavity is cnsidrd. Fr xampl, th rat f build-up f magntic (r lctric) fild strngth can b xprssd as -u:t/ql) H =H 1- t (.47) whr H is th stady-stat fild, H t is th fild strngth at tim "t" aftr th start f cxcitatin and Q L is th ladd Q f th cavity which quals, Q/ fr matchd cnditins. If w disrgard th mismatch rflctin ffcts, du t th rtardd impdanc grwth during build-up, thn with a Q f 15, at 856 MHz th magntic fild will rquir.5 Ilsc fr build-up t th 95 pr cnt lvl. At 13 MHz a cavity f 15, Q will tak 5.5 Ilsc t build-up t th 95 pr cnt lvl. Figur 7 shws a typical buildup charactristic fr th magntic fild strngth in a matchd cavity f 1, Q prating at 856 MHz. Th build-up tim (t) at any thr frquncy and/r Q can b btaind by mdifying th tim (tc) givn by th Figur 7 curv as fllws: Q 856 t = t x - x f(mhz) c 14 (.48) In gnral, a build-up tim f svral micrscnds, as fr th abv Q = 15, xampl, is unaccptabl fr acclratr injctr cavitis (chpprs and prbunchrs) which rciv pulsd driv pwr frm th sam r-f surc as th wavguid sctins. Optimum acclratr pratin ftn rquirs th injctin f a stady-stat bam shrtly aftr cmmncing applicatin f th r-f puls pwr t th wavguid sctins. Undr ths circumstancs th chppr and/r prbunchr cavity build-up tims must b lss than th wavguid fill-tim,.g., f th rdr f.3 Ilsc at S-band. Th magntic fild build-up prblm bcms vn mr acut fr systms that rquir bunch slctin using chppr cavitis which prat at a submultipl f th acclratr frquncy; say 476 MHz t prvid 1 bunch in 6 at 856 MHz. Clarly in this cas, with build-up tims f th rdr f Ilsc, prxcitatin with a lng r-f puls width is rquird. A tchniqu cmmnly usd t nsur shrt transint tims f a fw tnths f a micrscnd at S-band is th aggrandizmnt f cavity lsss such that Q <. This is achivd by cnstructing th cavity (fully r partially) with stainlss stl surfacs r by using lssy cating matrials. 6 In additin t lwring Q, th tim t rach a givn fild strngth can b rducd by arranging fr a cavity cupling factr f3 > 1. Fr a givn fild strngth, hwvr, bth tchniqus rquir incrasd lvls f driv pwr t supply th additinal wall, rflctin, and (in sm cass) islatin lsss. If th build-up tim rstrictin t Q wr rmvd, th highr mr naturally availabl Q's and magntic filds culd b xplitd up t th practical limits f frquncy stability. This argus strngly in favr f transvrs dflctin cavitis fr CW pratin f linar acclratrs, narrw band-pass r-f gnratrs, tc., using bam scanning, chpping and/r rtating tchniqus. Tw imprtant advantags (prbably vital, with high Q cavitis) f this typ f pratin ar (a) th highr dgr f systm stability inhrnt with CW pratin and (b) th as f prviding a highly snsitiv fdback cntrl systm. Th mannr in which th TE11 cavity dflcting magntic fild varis with a/a fr a givn r-f pwr lvl and frquncy is shwn plttd in Figur 6 fr h/a =.15,.39 and.49. Ths curvs indicat that slctin f th ptimum (a/d) rati, rathr than th "squar" cnditin (a = d), nt nly prvids th highst magntic fild but als rsults in a lwring f th Q valu. Bcaus th particl dflctin is prprtinal t th prduct f magntic fild and a functin f th cavity "h" dimnsin (s Equatin (3. 1) in a latr sctin), fr sm applicatins it will b advantagus t tradff maximum magntic fild and minimum transit tim fr largr ''h'' and Q valus. In brif summary thn, ptimizatin f th micrwav paramtrs fr a dflctin cavity rquirs 39
8 (a) stablishing th largst prmissibl "h" dimnsin and Q, (th frmr is usually dpndnt upn bam prvanc, transit tim and systm layut rstrictins) and (b) slcting th mst fficint md and cavity dimnsins t prvid th bst cmbinatin f minimum bam abrratin and a maximum H /PL factr..3 Cmparisn f TMllO and TE1 Dflctin Fild Charactristics Th TMOlO and TE 11 magntic fild gradints in th dirctin f bam dflctin ar asymmtrical n ithr sid f th undflctd bam psitin (H maxima). Fr th TM1 md this is a small ffct and if ncssary can b asily crrctd by a slight radial inward mvmnt f th bam cntr-lin frm th H psitin shwn in Figur l(a). With th TE11 distributin, hwvr, (s Figur ) larg bam crss-sctins r dflctin angls culd rsult in abrratins that may b unaccptabl. Tw xampls f bam dflcting highr rdr mds, which ffr symmtric H fild gradints, ar th TMn and TE1 shwn in Figur S. It will b f intrst t study th dflctin charactristics f ths highr rdr mds and cmpar thm with ths f th dminant mds..3.1 Fild Distributins. Using th sam crdinats as in Figur 1, th TI\111 filds f intrst can b btaind by substituting = 1, m = 1, and n = in Equatins (.7), (.8) and (.9) t giv E E J 1 (k c r)sin<;:> (.49) z E II - j- 7] J '(k r)sin cp 1 c (.5) H r = j E J 1 (kc r ) 7] k r c cs (.51) Als frm Equatin (.6) by substituting X m = 3. S3 as th first rt f J1(k c a) w btain th rsnant cnditin 1.64a (.5) Th fild quatins prvid an intrsting dscriptin f th azimuthal and radial variatin f magntic fild which is nt immdiatly apparnt frm inspctin f Figur S(a). Fr xampl, (a) Whn = rr / r 3rr /, H has a maximum valu (H M1 at r = and an accmpanying but lwr scndary pak, f ppsit plarity, at r =.91Sa. Als, H falls t zr at r =.4S1a and is SO. 5 pr cnt f H M at I' = a. (b) Whn = r rr, H is zr fr all valus f r, including r =. (c) HI' is zr fr all valus f r whn = rr/, 3rr/. (d) Hr is always zr at r = a. Ths fild cnditins suggst that, fr maximum dflctin snsitivity, th bam travrsal hl (r slt) shuld b lcatd at th axis f th cavity as shwn in Figur 8(a) by H r' Th transvrs magntic fild distributins Hr(r) in th = plan and H (r) in th = rr/ plan hav bn plttd in Figur 9. Aftr passing thrugh zr, th H (r) rvrs plarity distributin fllws a pattrn similar t th dminant md with a pak intnsity just prir t raching th cavity wall. Th magntic fild rvrsal pints dfind by th plar c-rdinats r =.481a, = 7':/, and 3rr/, rprsnt rgins f maximum lctric fild strngth with qual and ppsit "z" dirctd vctrs f magnitud givn by Equatins (.49) and (.5) E = E J T(.481) =.58 E zm Th Figur 9 curvs indicat that th TM 11 md has xcllnt abrratin - fr charactristics vr a larg cntral rgin f th cavity. Th maximum variatin f transvrs magntic fild is lss than 5 pr cnt fr bam diamtrs up t O. 1 A' Th cntur sktchs f Figur 9 shw plar plts f Hcp and HI" and th minr distrtin f th rsultant magntic fild IHI abut I' = rvals th abrratin - fr qualitis f th md. At r = th rsultant fild can b xprssd as E ] 1/ E _. =D [(. <JS!ilO) + (O.')cs<l:» =. D Th TE1 fild cmpnnts ar btaind by substituting m = 1, n =, and p = int Equatins (.1) - (.14) and using Equatin (.4), giving E - y l! 1I z II x A ac.l :a 7) j II sin ;:x sin A z :1 z c" itx a sin 7TZ :!a :rx II sin - L'OS d ()Z a d ;-:-z d rrz d (.53) (.54) (.55) (.56) Unlik th singl cntrally lcatd TE 1 1 lctric fild maxima (Equatin (.1S)), Equatin (.54) indicats tw qual and ppsitly dirctd lctric fild vctrs 31
9 fr th TE1 md with maxima ccurring at x = a/. z = d/4, and x = a/, z = :ld/4. (S Figur 8(b).) Th displacmnt currnts, assciatd with ths tim varying E filds, ar surrundd by H filds which prduc a pattrn in th cntr f th cavity such that (a) Hx is th nly cmpnnt f magntic fild, and its maximum ccurs at x = a/, z = d/, (b) th Hx fild distributin is symmtric abut this maximum psitin having a sinusidal dpndnc in th "x" dirctin, a c sinusidal distributin in th "z" dirctin, and a cnstant intnsity in th "y" dirctin. Thus, fr dflctin applicatins, a lgical lcatin fr bam cntr-lin is as shwn by Hx in Figur 8(b). Th rsnanc Equatin (.53) indicats that fr qual frquncis, and th sam "a" dimnsin as th TE 1 1 md, th TE1 cavity must hav twic th "d" dimnsin. Als, Equatins (.55) and (.56) shw that th pak valus f magntic fild ar rlatd by (.57) Bcaus th TE11 analysis indicatd a strng prfrnc fr Hz rathr than Hx filds, and bcaus f th absnc f wall lsss whr th E fild gs t zr at z = d/, thr is caus t bliv that this highr rdr TE 1 md may pssss diffrnt ptimizatin charactristics than that f th dminant md. It is cncivabl, fr xampl, that if th symmtry charactristics f th Rx(z) distributin ar ssntial fr a particular applicatin, ptimizing th cavity t prduc a maximum factr may rsult in a lwr bam dflcting magntic fild than th ptimizd maximum Hz fild at th walls f th cavity. Qustins f this natur can b rslvd, as in th prvius sctin, first by analyzing th highr rdr md wall lsss and thn btaining rlatinships btwn pwr lss and magntic fild strngth..3. Evaluatin f Wall Lsss. Fr th TM11 md, using Equatins (.3) and th circumfrntial fild cmpnnt Equatin (.5), th lsss in th cylindrical wall can b writtn Similarly, fr th lsss in th nd caps w hav Sinc :, l i ((,,) (,) n :: 'T,.J d,d. (diffrntiatin with rspct t kcr) R 1f(E ) = _s_ -. a J (k a) 7J C (.59) J (k r)j (k r) c 1 c k r c (.6) Equatins (.58) and (.6) rval that th rati f wall t nd cap lsss is th sam as fr th TMOlO md, namly, P LW P LE h a (.61) Thrfr, fr th sam frquncy and ''h'' dimnsin, th nd cap lsss fr th TM11 md will b 59 pr cnt highr (.61/1.64) than th TM1 cavity. Th TM 11 md ttal dissipatin is btaind frm Equatins (.58) and (.6) such that P LW dzdcp R1f(E) _6_ -. ahj (k a) 7J c (.58) (This can b cmpard against th dminant md, s Equatin (.3)). Fr th TE 1 cavity, bcaus f th symmtric pattrn, th surfac intgrals vr th yz and xz walls can b btaind vr th half-dimnsin limits and thn 311
10 multiplid by fur. Using Equatin (.3) and Figur 8 w hav giving a minimum at ria =.481, and f hfa (a 7fx) + \ct H z s in ---;- z= dxdy (.63) d/ a +4f f f!t 7fX 7fz) L\H z cs --;- sin d a 7fX 7fz\1 1 + ( d Hzsin -;:;:- cs -d) J dxdzj. s dh 4ah 1 d 4a R(EA)[.. L 8 1) a i a d/. p = ( :.\ ( 64) Thus, fr th cas f a = d, th lsss f th yz, xy and zx walls ar prprtinal t h/a, h/a and, rspctivly. Th magntic filds can b rlatd t th pwr lss by using Equatins (.54)-(.57) and (.64) t giv [? ] J (k c r) J (k r) (k r) 1 c \r c giving a maximum at r = and a rlativ maximum at ria =.918. Thus, at r =, th maximum fild can b dfind in A nrmalizd dimnsins as H A s.).981 a ( A ) ah + A (.68) Fr th TE 1 md, Equatin (.57) indicats that H H if a d x z Als, sinc Ac = a and Equatin (.53) can b rwrittn as (.65) (.69) 16a '= (.66) :3 1 + d ) + ad(4a + d.3.3 Optimizatin and Cmparisn f th Transvrs Magntic Filds fr th TM11 and TEI Mds. Fr th TM11 md, Equatins (.5) and (.6) prvid a rlatinship btwn Rf> and pwr lss such that it is clar that aid < and aid > ratis can b chsn t satisfy th rsnant cnditin. Thrfr, ithr th Hx r th Hz cmpnnt f magntic fild can b mad t prdminat. Th ptimum dimnsins t maximiz ithr f ths cmpnnts can b dtrmind by diffrntiating Equatins (.65) and (.66) in a mannr similar t th TE11 xampl. T maximiz Hx w hav + uf (da) ua dd R 7fJ (k a) ra + ah1 sc L J Th maximum and minimum cnditins btaind fr sinf> = 1 frm ar u(=o ur (.67) whr F = right hand sid f Equatin (.66), and da/dd = - 4(a/d)3 frm Equatin (.53). Analgus t Equatin (.41), th abv prvids a maximum valu f magntic fild (H x l\l) fr a givn input pwr whn 31
11 r : [ + 8() - 1G() J 41-8() + 1G() J (.7) Th TE 1 md ptimum (a/d) ratis t prvid Hx fild maxima fr givn h/l valus, as btaind frm th slutin f Equatin (.7), hav bn plttd as curv B in Figur 3. As bfr, this prvs t hav a slwly changing charactristic with (a/d) ratis f.875,.881ando.883frh/l valusfo.15,.39 and.49, rspctivly. Th cnditin t maximiz Hz can b btaind by diffrntiating Equatin (.65) which givs 1 [ 41 4() () - 48() J (.71) Th slutin f this quatin is plttd as curv C in Figur 3; and ptimum (a/d) ratis f.315,.337 and. 344 ar btaind fr h/l valus f.15,.39 and.49, rspctivly. Th maximum dflctin filds, HzM and HxM' as btaind by substituting th ptimum (a/d) ratis int Equatis (.65) and (.66) ar shwn listd in Tabl III. Th crrspnding magntic fild maxima fr th TM11 md and fr th a = d, TE1 md ar als listd fr cmparisn purpss. An intrsting fatur f th Tabl III data is that, unlik th dminant md xampls, th circular cavity is suprir t th rctangular cavity in attaining a maximum magntic fild fr a givn pwr lss. Als, fr th TE 1 md it can b ntd that th Hx fild cmbins th advantags f bth th highr rdr and dminant mds; namly, a symmtric distributin abut th bam cntr-lin and th capability f bing ptimizd t prvid th highr f th tw transvrs fild maxima. Th intrchang f prdminanc btwn th TE1 magntic fild cmpnnts Hx and Hz with incrasing (a/d) ratis is shwn plttd against a/l in Figur 1 fr h/l =.15. Ths curvs shw that th magntic fild strngths at th crss-vr pint a/l =.77 (a = d) ar 35 pr cnt lwr than th cmparabl "squar" (a = d) TE11 cas. (Rfr t Tabl 1.) Th maximum magntic fild, HzM, which is lcatd at th zy walls (s inst sktch Figur 1), is critically dpndnt n th "a" dimnsin bcaus f its cls prximity t cut-ff fr th ptimum (a/d) rati. In cntrast, th Hx cmpnnt has a rlativly brad ptimum and a 5 t 1 pr cnt highr maximum valu than HzM fr th rang f h/l indicatd in Tabl III. It can b shwn that th TE1 charactristics ar rprducd xactly by th rthgnal md, TE1' Rpating th ptimizatin prcdurs with th substitutins m =, n =, and p = 1 in th fild quatins mrly rsults in an intrchang f rls btwn th Hx and Hz fild cmpnnts. Th mst favrabl magntic fild still ccurs at th cavity cntr and is dirctd paralll t th shrt sid walls, i.., th dirctin f bam dflctin rmains paralll t th lng walls. A scald cmparisn f th TM11 and TE1 ptimum magntic fild gradints in th dirctin f bam dflctins, H<j>(r), Hx(z) and Hz(x) is shwn in Figur 11 fr h/l =.39. It shuld b ntd that nly half f th H<j>(r) and Hx(z) distributins ar shwn and ths filds ar symmtric abut th maximum intnsity pints lcatd at thir rspctiv rigins, r = and z = d/. On th thr hand, th Hz(x) distributin is shwn plttd frm th maximum intnsity pint at n wall (x = ), thrugh th minimum, t HzM at th thr wall (x = a). Th distributins ar plttd with rspct t l s that fild gradints acrss th bam, fr th varius mds, can b cmpard with cnvninc. This subjct is discussd in sctin.4. As bfr, th chic f md and cavity dimnsin, fr a particular applicatin, can b strngly influncd by th Q valu which fr ths highr rdrs (cmparing qual frquncis) is usually gratr than th rlatd dminant md Evaluatin f Strd Enrgy and Q fr th TM11 and TE1 Mds. Fr th TMn md, using Equatins (.4) and (.49), th strd nrgy can b xprssd as.'.u a 7r h Elf f U = - E J (k r)sin rdzd.pdr l Eh H f HE 4 a rj (kc r)dr 1 E a hj (k a) C (.7) (.73) A cmparisn with Equatin (.4) indicats that th dminant md has 11 pr cnt lss strd nrgy at th sam frquncy and fr th sam "h" dimnsin. Substituting Equatins (.73) and (.6) int (.5) givs 313
12 Q and using Equatin (.5) ') itfe"halt Hs(a +h) QR s itt) 7 (.74) Fr th TE1 md, bcaus th.lctric fild Equatin (.54) is th sam as fr th dminant md, th strd nrgy xprssin rmains th sam as Equatin (.45) i.., u E"ahd E 8 (Th actual numrical valus will, f curs, b diffrnt.) Cmbining this with th pwr lss Equatin (.64) and substituting in Equatin (.5), w btain 4iTahdlJ Q= "-----"'-"-' R A. 3 [JL (a + h) + 4 (d + h s a d J Substituting fr 1.. frm Equatin (.53) givs QR s (.75) Th dpndnc f QRs n cavity lngth (h/a) fr th TM 11 md is plttd as curv B in Figur 5. Cmparisn with curv A shws an incras in gain f Q vr th dminant md fr incrasing valus f "h". A graph f QRs vrsus a/a fr th TE1 md and h/a =.15 is shwn in Figur 1 and indicats a 1 t pr cnt incras vr th TE 11 md. (S Figur 6.) Thrtical Q valus fr th TM 11 and ptimizd TE1 cavitis ar listd in Tabl IV and, fr th sam h/a. can b cmpard dirctly with Tabl II valus fr th TMOlO and TE11 mds..4 Cmparisn f Bam Abrratin Effcts Bcaus f th finit siz f th bam, it can b xpctd that svral factrs will cntribut t bam abrratins. Majr amng ths ar (a) th magntic fild gradint acrss th bam in th dirctin f dflctin, (This will b bth tim and' spac dpndnt and as a cnsqunc will vary with ntry phas angl, dgr f dflctin and transit tim.) (b) th magntic fild gradint acrss th bam at right angls t th dirctin f dflctin, (In vry cas this gradint is lss than that f th ptimizd maximum dflcting magntic fild,.g., rfr Figur 4, Hz(x), Hx(z), Figur 9, H<p(r), IIr(r), tc.) (c) nn-cancllatin f th vlcity mdulatin ffcts f th lngitudinal lctric filds, spcially fr th priphral particls, and (d) fring and lakag filds du t larg r incrrctly shapd bam aprturs. Fr a givn bam diamtr, all f ths factrs ar strngly rlatd t th chic f md and, mr particularly, t whthr r nt th dflcting fild is symmtric abut th bam cntr-lin. Tabl V cmpars th dflcting magntic fild gradints acrss incrasing bam diamtrs fr th ptimizd cnditins f th prviusly discussd mds and h/a =.39. Th rsults ar listd as prcntag bins f th apprpriat maxima t cvr th asymmtric distributin cass, and thy disrgard th small transvrs displacmnt f th bam during transit. In gnral th data bars ut an intuitiv bsrvatin that, fr qual pwr and frquncy and a givn rati f bam diamtr t fr spac wavlngth, th highr th ptimum valu f dflcting magntic fild, th wrs th gradint acrss th bam. Avidanc f an ff-st bam cntr-lin, with rspct t th pak fild psitin, nabls th thr symmtric distributins f Tabl V t xhibit lw abrratin charactristics. Fr bam diamtrs up t th maximum H gradints ar lss than 9 pr cnt and as th gradints at right angls t th bam dflctin ar vn lwr, it is sn that th Tl\I 1 ' Tl\I llo and Hx ptimizd TE 1 mds ar mr favrably suitd fr th dflctin f larg bams than th TE 11 md. On th thr hand, th high dflctin factr f th Hz ptimizd TE 11 md maks this a natural chic fr small bam applicatins and whn 1'-f pwr is at a prmium. Slctin f 1 bunch in 6 fr linar acclratr injctin int synchrtrns is an xcllnt xampl in this catgry bcaus th chppr cavity prats at 1/6 f th fundamntal frquncy, i.., th rati f bam diamtr t th chppr fr spac wavlngth is rducd by a factr f 6. As discussd in th intrductin, dflctin cmpnsatin, du t crssd E and H filds, is avidd by arranging fr th bam t travrs th cavity paralll t th lctric fild. Fr this cnditin, hwvr, a scnd rdr dflctin ffct is intrducd by th vlcity mdulating actin f th lngitudinal lctric fild. Fr xampl, cnsidr th highr rdr mds 314
13 which prvid mtric fild distributins abut th bam cntr-lin. Whn th particl rachs th cntr f th cavity, tl] dflcting magntic fild is a maximum, and th qual and ppsitly dirctd E filds n ithr sid f th bam fall t zr. On ntring th cavity, hwvr, th vlcity f priphral particls n n sid f th cntr-lin will b rducd and n th thr sid incrasd. Whn th slwr particls rach th cntr f th cavity, thy will hav bn dflctd away frm th cntr-lin mr than th fastr particls will hav bn bnt twards it. At this pint th E filds will rvrs; and bcaus th slwr particls ar cldsr t th rgin f E fild maximum, thy will xprinc mr vltag gain than that rquird t cmpnsat fr thir initial lss in vlcity. Als, ths particls will b ntring rgins f lwr magntic fild than th fastr particls, which will b cntinuing t dflct tward rgins f highr R fild and lwr (undr-cmpnsating) E filds. This prcss will rsult in a crss-sctinal fcusing frc in th plan f dflctin. Th abv dscriptin applis fr particls, in azimuthal psitins alng th cntral plan f dflctin, which pass thrugh th cavity cntr whn th dflcting magntic fild is at a maximum. Th prcss will chang (a) fr particls in thr azimuthal psitins, wing t additinal crss-prduct trms giving ris t diffrnt vlcity mdulatin and transvrs frcs, and (b) with tim during th r-f cycl. (This is discussd furthr in Sctin ) Bam abrratins during dflctin can als b prducd by fring and lakag filds assciatd with th bam aprturs in th cavity. With sm highr rdr mds, fr xampl, th us f bam aprturs which hav larg dimnsins at right angls t th paths f th nd-cap currnts can caus transvrs lctric fild pattrns t b stablishd acrss th aprtur tnding t cuntract bam dflctin. Bad prturbatin tchniqus ar cmmnly usd t valuat th dflctin and abrratin charactristics f a givn cavity dsign. Althugh utsid th scp f this rprt, sm bad prturbatin data rlating t a TE 1 md ar shwn in Figur 1. Th vltag transmissin charactristics as btaind whn a cramic bad is drawn dwn th lng axis is shwn in Figur 1(a). Th rsult f a mtal bad drawn thrugh th cavity paralll t th bam axis at diffrnt lcatins within th aprtur is shwn in Figur 1(b). Th rducd prturbatin ffct du t cmpnsatin f th Rand E filds can b clarly ntd fr th A and C psitins. An analysis f th ffcts f abrratin at th pint f applicatin f th dflctd bam must f curs tak int accunt spac charg frcs and intrvning paramtrs such as typ f fcusing, lngth f drift spac, amunt f bam biasing (if any), tc., and will dpnd, thrfr, n th particular systm layut..5 Cmparisn f Elctric Fild Maxima Apart frm dflctin applicatins, th transvrs magntic fild cavitis can als b usd fr r-f signal xtractin,.g., lctrn bam psitin mnitring, r-f pwr gnratin, tc. A cmparisn f th ptimizd E fild maxima fr varius mds is givn in Tabl VI. If w assum th factr is a cnstant, thn fr h/a =.15 th EzM rati f TM llo t th TMOlO is qual t.75. Als, bcaus th TMllO md EzM =.58 E (frm Sctin.3.1. ) and th TMOIO md EzM = E, th E rati f TMllO t TM O I is qual t A scald cmparisn f th radial variatin f E z fr ths tw mds is shwn plttd in Figur 13. Lcatin f bam aprturs in th nd walls f ths cavitis, at th pak fild psitins, will f curs mdify ths idal distributins and shuld b takn in accunt in bam intractin analysis. 3. Bam Dflctin and Abrratin Calculatins Fr th purps f cnsistncy, th fllwing analysis will us th sam c-rdinats as in Sctin. Cnsidring th TMllO cavity, fr xampl, th initial bam path lis alng th "z" axis and th Rp fild will caus dflctin in th "r" dirctin as shwn in Figur 14. On this basis, w wish t dtrmin th transvrs displacmnt and mmntum f a particl at z = h, i.., th plan f dpartur. A knwldg f th axial vlcity ((3c) and drift lngth (S) thn nabls th ttal dflctin (X) t b cmputd Bam Dflctin Drivd frm Simplifid Equatin f Mtin Frm Figur 14, th transvrs mmntum (P.L) gaind during a small intrval f tim may b writtn whr Rp is th ffctiv transvrs magntic fild xprincd by an axial particl whil travrsing a distanc, whr (3.1) t.z (3 ct.t (3.) '" j.. mr rrz) II 'in +""(3i: dz pm (3.3) 315
14 T = transit tim crrctin factr...l rcos - cst +, (3.4) T T 1J is th phas f th magntic fild crrspnding t th particl arrival tim at th ntry plan z = (fr a cnvntin f pak magntic fild at = 7r / whn th particl is at th cntr f th cavity), and IJ T is th transit angl givn by = 7r ẖ - T j3 A (3.5) Th rductin factr applid t H M du t th transit tim crrctin will b minimizd by ptimum slctin f th ntry phas angl such that 7r T (3.6) tano'. X x (3.11) (S + ) -4 \.35 x 1 - (h) 7rh \S + Y " H Msin j3"a (3.1) Fr a givn systm gmtry and a knwldg f H l\i' as btaind frm Sctin, Equatin (3.1) prvids a cnvnint and rasnably accurat mthd f dtrmining th bam dflctin Gnralizd Bam Dflctin Equatins in Trms f Driv Pwr and Cavity Dimnsins. Equatin (3.1) may b xprssd in th mr gnral trms f r-f pwr and cavity dimnsins by making th apprpriat substitutin fr th magntic fild strngth. Fr th TM 11 md, substituting frm Equatins (.68) and (.5) givs Substituting this int Equatin (3.4) and using Equatin (3.5) IJ. T IJ sm T j3 A. 7rh 7rh sm {3'i:" (3.7) Th transvrs vlcity can nw b xprssd in trms f th mst favrabl magntic fild cnditin by using Equatins (3.3) and (3.7) giving x.98 x Fr a cppr cavity, and Equatin (3.13) may b writtn 7rh j3 A (3.13) Dfining th dflctin angl (') as tano' = r j3 c (3.8) (;3. 9) x 44.;1 x 7rh (3.14) Fr a frquncy f 856 ;'.]Hz and assuming a practical Q 1 pr cnt lwr than th thrtical valu, Equatin (3.14) bcms, J..I.A 7rh ( ) tano' = y 7r c H M sin {3T x (S + \ P 7.75 x 1-\-:!-; [O.6 + which in th MKS systm may b rducd t (3.15) -4 tano' =.35 x 1 y (3.1) sin 9.9h i3 mtr Als, frm Figur 14, th dflctin angl can b xprssd as Fr th ptimizd IIZl\1 TI 1 1 md, substituting frm Tabl I fr h/a O. 15 nabls Equatin (3. 1) t b writtn 316
15 x (s + \ P )1/ x 1-4\) 1.881(R which fr a cppr cavity bcms..479 sm -{3-- (3.16) -4 ( s + l! X = GS. 7 x 1 -y-- (PL A OI/)1/..479 \' sm -(3- (3.17) At 856 MHz, assuming a 1 pr cnt rductin in th thrtical valu f Q, fr h =. 16m Equatin (3. 17) bcms, X = ;,5.5 sm -(3- mtr X 1-4 (s +. 8) P L1/..479 (3.18) Fr th ptimizd HxlVI TEI md and a valu f h/a =.15, substituting frm Tabl III nabls Equatin (3.1) fr a cppr cavity t b writtn..479 sm -{3- (3.19) Fr 856 lvihz and a 1 pr cnt rductin f thrtical Q, Equatin (3.19) bcms Fr thr valus f h/a ' th HzM r HxlVI substitutins can b intrplatd frm th Tabl I r Tabl III data. Graphs f bam dflctin vrsus drift distanc fr a 856 MHz, TM llo cppr cavity (Equatin (3.15)) having h/a valus f O. 15 and.39 ar shwn plttd in Figur 15 fr lctrn nrgis f 7 and 15 kv and a pak input r-f pwr lvl f 4 kw. It can b ntd that th 7 and 15 kv bams hav qual transvrs displacmnts, at S = 14 cm, fr cavitis with h/a f.15 and.39, rspctivly. Furthrmr, unlik th 15 kv bam, th dflctin f th 7 kv bam will actually b rducd whn a cavity having th largr h/a valu is mplyd. Ths ffcts ar du t an intr-rlatin btwn th particl transit tim and transvrs mmntum at mrgnc frm th cavity. Th data indicats that th Figur 15, h/a valus will nt prduc maximum dflctin fr a givn r-f input pwr and that an ptimizatin prcdur shuld b applid t th vrall trajctry in rdr t btain th idal valu f h/a fr a givn bam nrgy and drift lngth. 3. l. Optimizatin f th "h" Dimnsin t Prduc Maximum Dflctin fr a Givn Drift Lngth and Bam Enrgy. Fr th TMllO md, substituting fr HcpM frm Equatin (. 68) int Equatin (3. 1), diffrntiating with rspct t "h", and quating t zr, w btain giving!() + ah]sin + (S + l!) [_ sin A {3 A, {3 A A ", S = h ] ] ) A. a ah 7f 7fh + (\ + ' 73'T cs 73'T = (a + h) 7fh ( a + h) ctan (3.1) Th ptimum ''h'' dimnsin t prvid maximum dflctin fr a givn input r-f pwr may b dtrmind frm th slutin f Equatin (3.1) fr a givn drift lngth, bam nrgy and prating frquncy. As AO = 1. 64a, fr th TlVI llo md, at a frquncy f 856 MHz Equatin (3.1) mayb rducd t h.64 + h S = - ' C:..:..=:.::...:...:" h (3. ) f3 (.64 + h) ctan (3 Fr th TE1 md, th dflctin Equatin (3.1) may b writtn X (s + ) sin 7fh (3 A (3.3) Unlik th TlVI 11 md, hwvr, this rlatinship invlvs tw dpndnt variabls, "d" and "h", and X will b a maximum if But,.QX = h and X _ ad - H xm 8d= (3.4) 317
16 As bfr, Equatin (3.4) is satisfid by Equatin (.7) which may b r-writtn as h (3.5) and 1 [zh(a: l + d'!) + :lj(a:': + ia sm,.3:: s= :1:1 :Th - [ 3;1 ).::,1 1l'h - (a + d ) Sin --;it + -;;-;:- :.!h(a... d ) + ad(a- + d )J L"OS t'o (3.3) whr "a" is a functin f "d" givn by Equatin (.53). Als, fr 3X/3h =, frm Equatin (3.3) w btain - 1 HxM sin {37l' + _7l'_ (S +.!!\ H cs 1\ fi A \' } xm fi A t h) 7l'h ahxm + \S + ' sin'j3t' ---ah = (3.6) and diffrntiating Equatin (.66) with rspct t ''h'' givs --=-- ahxm 1 (PL) - 3a (4a d) ah H R xm s [ h ( 4a \ I )J + d J + ad\4a + d Substituting fr ahxm/ah frm Equatin (3.7) int Equatin (3.6) and r-arranging w btain 1 [ ;J:I ] rrh " h(4a + d ) + ad(4a... J ) Sin C \() s rr [ 3:s J 1fh :1;1 rrh "'if): h(4a + d ) + ad(4a... d J cs - (4a + d ) Sin -:;>:: (' c (3.7) (3.8) Th slutin f Equatin (3.8), aftr substituting fr "h" frm Equatin (3.5), prvids th ptimum rlatinship btwn th drift lngth and th TE1 cavity ''h'' dimnsin t prduc maximum dflctin fr a givn bam nrgy and systm frquncy. Fr th TE11 md, a similar prcdur as that usd fr th TE1 cas yilds h (3.9) th cmbind slutin f which prvids th ptimum rlatinship btwn drift lngth and TE11 cavity "h" dimnsin. Slutins f th TE11 Equatins (3.9) and (3. 3), th TMn Equatin (3.) and th TE1 Equatins (3.5) and (3.8) ar shwn in Figur 16 fr an pratinal frquncy f 856 MHz. Optimum ''h'' valus hav bn plttd against drift distanc fr fi valus f.4759,.5584, and.6343, crrspnding t bam nrgis f 7, 15 and 15 kv, rspctivly. As an xampl, fr th TMn md and a givn input r-f pwr, maximum dflctin f 7, 15 and 15 ky bams will b prducd at th nd f a cm drift lngth with cavity ''h'' valus f.4,.8, and 3. cm, rspctivly. Th Figur 16 graphs rval that th ptimum "h" valus xtnd vr a brad rang, dpndnt n th bam nrgy and drift spac lngth. Fr dsign purpss, thrfr, it is f intrst t dtrmin hw th bam dflctin is affctd by dpartur frm ths ptima, du t a mchanical r Q valu rstrictin r a majr chang in bam nrgy. This is indicatd by th graphs f bam dflctin vrsus cavity ''h'' dimnsin shwn plttd in Figur 17 fr th abv mntind bam nrgis and a fixd drift distanc f cm. Ths xampls wr cmputd fr 856 MHz cppr cavitis having 9 pr cnt f th ihrtical Q valu and an input r-f pwr lvl f 4 kw. Th dflctin rducing influnc f th bam aprturs n th cavity filds wa nt takn int accunt. Th Figur 17 curvs als dpict an aspct which is j particular valu in crtain bam dflctin applicatins: namly, that fr a givn md and a givn valu f "h", th bam nrgy can b varid as much as tw t n whil th bam dflctin rmains ssntially cnstant,.g. in th TMUO md, fr S = cm and h = 3.8 cm, X changs by nly:!: -1/ pr cnt as th bam nrgy is varid vr th rang 7 t 15 ky. 3. Equatins f ]\Jtin Including th Effcts f Magntic and Elctric Fild Variatin Alng th Dflctin Trajctry f th Particl Th simplifid prcding analysis disrgardd th spatial variatin f th dflcting magntic fild xprincd by th particl during divrgnc frm trajctris initially dirctd prpndicular t th rgin f maximum dflcting magntic fild. With th transit tims nrmally ncuntrd in practical dvics, th crrctin t th magnitud f th dflctin du t this spatial variatin is f littl cnsqunc. On th thr 318
17 hand, if it is ncssary t invstigat changs in bam crss- sctin during dflctin, allwanc must b mad fr th spatial and tmpral variatins f all th fild cmpnnts. This is particularly th cas fr bams which hav rlativly larg crss-sctins with rspct t th cavity fr spac wavlngth. Qualitativ cntributins t bam abrratin, du t th lctric filds, hav bn discussd in Sctin.4. Apart frm th lngitudinal lctric fild ffcts, hwvr, all f th particls undrging dflctin will xprinc additinal vlcity mdulatin cntributins du t frcs which aris frm th transvrs vlcity crss prducts. Als, fr particls which ar rmt frm th cntrally lcatd transvrs plan passing thrugh th rgin f pak dflcting magntic fild, th crss prduct vlcity mdulatin ffcts will b accmpanid by fcusing (and dfcusing) frcs, i.., th rthgnal magntic fild cmpnnts giv ris t rthgnal transvrs displacmnts as wll as vlcity mdulating frcs Cylindrical and Rctangular Cartsian Crdinat Systms. Fr a singl lctrn ( = - q) travling at vlcity thrugh lctric () and magntic filds ( = J.l.!!) th quatin f mtin may b writtn (ym v)=re + v x J.l!.l.] dt - L'-- (3.31) and sinc w btain d dt (y m)!: [v r t v = rv + cp v + zv - r - cp - z (ym ) + ym dv r dt ct ] ym Vcp dt d + cp [v dt (ym + ym v - cp ) + ym dt r Equating Equatin (3.34) t (3.3) and substituting v r givs r, v z and ct. v = r - = rcp cp dt - dr (ym r) = E + J.l rh cp -J.l H i. J + ym r dt r z cp dcp] dt (3.35) In cylindrical c-rdinats, v x J.l!l = J.l.!: : Z thrfr [ + v V \. r cp z II H II r 6 Z J.l!: cp 1I z - v z 1I cp) -J.lCP(VH - r Z - v Z H) r +J.lZ('H.-VH) -1'6 cpr v x J.l!!]=!: /E + J.lV II - J.lV H",). r z Z '+' + : IE - J.l v H + J.l v H ) \ rz zr + z + J.lVrHcp - J.lVcpHr) (3.3) Als, sinc re +J.lrH -J.lr<PH] (3.37) L Z </> r.. ';' z+r+r'+' y = 1 - [ ] -V (3.38) xpanding th drivativs and multiplying Equatin (3.35) by r, (3.36) by and (3.37) by z, and thn adding, lads t y m E (3.39) Fr th lft hand sid f Equatin (3.31), bcaus y is a variabl (3.33) Substituting Equatin (3.39) int th xpandd drivativs f Equatins (3.35), (3.36) and (3.37), and fr th TMOIO, TM llo mds ltting E =E =H = cp r z 319
18 givs th fllwing quatins (which can b slvd numrically) : yi + z y = 111 f..iyu x (3.49) (3.4) Als, sinc.. [ r = -- f..ih E z ] Z rm y r c ' r z + f..ih i: - f..ih r my z r i: r Z c EJ (3.41) (3.4) Y=. y = -- ye m c y and th abv quatins bcm (3.5) Y = E Z z mc (3.43) x y m y (3.51) In rctangular cartsian c-rdinats v x f..i!! = f..i r y m y v v v x y z H H H x Y z z y m y (3.53) = f..ix(v H - v H ) + f..i(v H - v H ) + f..i z(v H - v H ) -yz zy zx xz -xy yx and Equatin (3.31) can b writtn With initial cnditins, x ' z' V ' x ' Y' Z and, fr xampl, with a paraxial bam, v =;> y d (y m v ) = [E + f..i (v H d t x x yz - v H )] z Y (3.44) th abv quatins can b slvd numrically fr a givn tim dpndnc f th sinusidal filds. d (ym v) = re + f..i (v H d t z LZ xy Fr th TE11, TE 1 mds, and ltting v x, x E x v y E z y H Y and - v H )] Y x v z (3.45) (3.46) th Equatins (3.44), (3.45), and (3.46) can b writtn 3.. Rlatinship f Spatial C-rdinats with R- F Fild Tim Dpndnc. Th TEI md will b th nly cas discussd in this sctin, but sinc th rlatinship is cmmn t all cnfiguratins th rsults can b radily applid t th thr mds f intrst. Multiplying th TEI fild Equatins (.54). (.55) and (.56) by a cmplx tim dpndnc w btain 1fX sin a sin d } a 1] H sin 1fx sin 1fz sin f(t) ;\ z a d 1fz jf(t (3. 3) yx + xy = m f..iyu (3.47) z rrx itz H R (Il cs sin jf(t)) z z a d yy + yy [E + f..i (zu - xu )] (3.48) m y x z 1fx 1fz II cs sin cs f(t) z a d p. :'5) 3
19 H R (- a H sin 7fX 7fZ jf(tj cs d X d z a a 7fX 7f Z = - - H sin -;- cs d cs f(t) (3.56) d z Rfrring t th c-rdinat systm shwn in Figur 8(b), and dfining a psitiv Hx dflcting fild in th cntr f th cavity fr th first half cycl, thn, t satisfy th cnditins, d 3d H > fr < z < - x 4 4 d 3d H < < z < - < z < d x 4 ' 4 d x = H > < z < z d H < < z < d z d x=a H < < z < z H > s! < z < d, z f(t) must qual = (wt - 7f /) fr < wt < 7f, i.., H x a H sin 7fx COE 7fz sinwt d z a d and, chsing th uppr sign, giving and E Y E < fr y E > fr y a1) H sin 7fX sin 7f z (t _ - 7f ) A z a d sin 7f < z < d and < wt < ' d < z < d and 7f < wt < (3.57) (3.58) 3.3 Abrratin Cmputatins fr Larg Bam Crss Sctins and Dflctins Th rsults f applying th Sctin 3. quatins t TE11 and TE1 cppr cavitis ar discussd blw. Th paramtrs chsn fr ths xampls wr i\=.15m, PL=4kW, S=.m, bam diamtrs f O.lA and.a,and bam nrgis f 7 and 15kV. Th cmputatins wr basd n an initially cylindrical bam having ngligibl spac charg; and n allwanc was mad fr fild prturbatin du t th bam aprturs Bam Enrgy and Crss-Sctin Variatins at a Givn Drift Distanc fr TE 1 Md Dflctins. Figur 18 shws bam crss-sctin diagrams fr svral dflctin xampls and an initially paralll bam f circular crss-sctin which ntrs th cntral rgin f a TE1 cavity, dirctd alng th "y" axis (Figur 8b), prpndicular t th Hx and Hy filds. Th diagrams wr cnstructd with th psitin f th dflctd cntral ray (N.1), fr ach cas, nrmalizd t a cmmn pint. Th crss-sctins markd A shw th abrratin ffcts at th nd f a cm drift distanc fr a 7 kv,. AO diamtr bam and "h" dimnsins f 1.6 and.4 cm. Th diagrams markd B cmpar 7 and 15 k V,.1 AO and. AO diamtr bams fr a cm drift lngth and ptimum valus f "h". Th crsssctins A and B ar fr particls which rach th cntr f th cavity (y = h/) whn th dflcting magntic fild (Hx) passs thrugh pak psitiv and ngativ valus, rspctivly. A fatur which is cmmn t all cass is an lliptic distrtin f th bam crss-sctin du t a nt fcusing frc in th plan f dflctin and a wak dfcusing frc in th rthgnal plan. Furthrmr, it can b ntd that th cntrid f charg (assuming an initially symmtric radial distributin) has a tndncy t migrat utward in th dirctin f dflctin, as indicatd by th mdifid lcatin f th initial vrtical cntral plan shwn n th B crss- sctins. Th fcusing ffct and cntrid migratin, in th dirctin f dflctin, ar causd prdminatly by vlcity mdulatin frcs du t Ey and Z/1Hx variatins as intgratd vr th dflctin trajctry f th particl ( S Y S h). Th wak dfcusing frc ariss mainly frm th ff-axis ( x I a/) crss prduct cmpnnt Y /1 Hz Th bam nrgy variatins fr svral f th Figur 18 rbit xampls ar listd in Tabl VII tgthr with dflctin valus basd n th thrtical Q. Th Tabl VII ntry angls and transit tims crrspnd t maximum dflctin cnditins, and th data will, f curs, b mdifid fr thr tims during th r-f cycl. Bam nrgy infrmatin f this natur whn intgratd vr th r-f cycl and cmbind with th charg distributin nabls th bam cupling charactristics f th md t b valuatd TE11 Md Bam Dflctin Abrratin Charactristics. Th TE 11 md abrratin ffcts fr 7 and 15 kv dflctd bams f.1 and. AO diamtr ar shwn in Figur 19. Th initial bam cnditins wr chsn as in Sctin , hwvr, in rdr t tak advantag f th pak Hz dflcting fild (s Figur (b)), th "y" dirctd bam was ff- st such that th utr priphry (rbit N.4) was lcatd 31
20 cls t th sid wall. T avid bam cllisin with th cavity wall, du t dflctins f apprximatly mm within th cavity, th ntry psitin f th bam was basd n ntry c-rdinats fr rbit N.4 f X =.5 m and Z = d/ fr all xampls. In rdr t illustrat vrlap charactristics f th larg diamtr bam, th dflctin crss-sctin diagrams A, B and C f Figur 19 wr cnstructd dirctly frm th dflctin valus; and unlik th cas f Figur 18 ths valus wr nt nrmalizd t a cmmn pint. Fr ntry angls (wt), which prduc maximum particl dflctin in th -x dirctin (a pak psitiv Hz fild whn th bam rachs th cntr f th cavity), th crss-sctin diagrams markd A shw a cnsidrabl dfcusing spcially in th dirctin f dflctin. Th B diagrams, crrspnding t th "straight ahad" cndi tin with ntry phass f (wt + IT /), als xhibit this dfcusing charactristic but t a lssr dgr. Unlik A and B, th C diagrams at th thr dflctin xtrmity (wt + IT) indicat th prsnc f strng fcusing frcs in th dirctin f dflctin. Th riginal circular crss-sctin f. 11. diamtr transfrms thrugh an lliptic stag, shwn at S = 1 cm, int a grssly distrtd prfil at S = cm. This ffct is du t th rlativly larg ara ccupid by th bam within th cavity. Th N. rbit bing in a lw dflcting magntic fild nvirnmnt gains lss than half f th transvrs mmntmn rcivd by th N.4 rbit. In th cas f th 7 kv bam, this diffrnc is sufficint t caus a dflctin crss-vr prir t travrsal f th cm drift distanc. Th wid sprad in mrgnt nrgy, causd by larg lctric fild gradints du t th ff-st bam gmtry, als cntributs t th prfil distrtin. Bam nrgy and dflctin valus fr svral f th Figur 19 bam crss-sctin xampls ar listd in Tabl VIII fr diffrnt tims during th r-f cycl. As prdictd by th Tabl V data, th TE11 md cmpars vry unfavrably with th TE1 md fr dflctin f larg diamtr bams. Th Figur bam diamtr xampls shw that at n xtrmity f th swp (wt) vn thugh th N.4 rbit dflctin is much gratr than th ntry bam diamtr th rsulting dfcusing is sufficint t caus vrlap with th straight ahad bam psitin (wt + IT/). At S = cm an initial.1 cm diamtr sprads t 4.63 and 4. cm in th dirctin f dflctin fr 7 and 15 k V bams, rspctivly. Evn thugh th dflctd bam charg dnsity is cnsidrably rducd in th vrlap rgin, as indicatd by th displacmnt f th cntrid plan, abrratin f this typ wuld b unaccptabl fr applicatins which rquir cmplt cut-ff. On th thr hand, at th thr dflctin xtrmity (wt + IT) th strng r-f fcusing and vlcity mdulatin charactristics may wll b xplitd (within th bunds f spac charg) by incrpratin f th cavity in an apprpriat systm. 3.:53 TE11!ind TE1 Bam Lading Charactristics During Dflctin. Valus f mrgnt bam ttal nrgy at varius tims during th r-f cycl fr th TE11 and TE 1 cavity xampls f Figurs 19 and 18 ar listd in Tabls IX and X, rspctivly. Th listd valus (applicabl t 7 kv ntry nrgy) indicat th mannr in which nrgy is transfrrd btwn th r-f filds and th varius bam trajctris. Thus, by apprpriatly wighting th rbital data in accrdanc with a givn crss-sctinal charg distributin, it is pssibl t dtrmin th bam lading charactristics f th systm. Th apparnt nt incras in bam nrgy fr ths xampls suggsts psitiv bam lading cnditins and supprts th thry that bam inducd dflctin filds can b radily stablishd undr bunchd bam cnditins. This is f particular intrst whn cnsidring th TE1\lU puls brak-up md in linar acclratr structurs; and th abv tchniqu prvids a mans f studying th starting-up and nrgy transfr mchanisms fr this phnmnn. This is spcially applicabl t th cas f band dg intractin* whr th vp = clin intrscts highr pass band w-p curvs in cls prximity t th zr grup vlcity cut-ff pint (pd = IT). Undr ths cnditins small transvrs dflctin filds can b prducd by th bam in individual cavitis within a wavguid sctin; as distinct frm th rgnrativ backward wav mchanism. Shrt intrval stps in azimuthal rtatin f th dfrmatin plan (tuning plungrs) during wavguid tuning, as prfrmd n sm high currnt and lng wavguid dsigns, will tnd t avid md plarizatin and prvnt this transvrs disturbanc frm chrntly cupling t th bam within subsquntly lcatd idntical dsign sctins. 1\1r pwrful supprssin tchniqus includ (a) diffrntial absrptin f th highr rdr mds by intrnal lading r cupling int xtrnal lads and (b) th us f structurs which pssss highr rdr md _plit pas8-band charactristics in th vicinity f th vp = c intrcpt. :3.4 Sm Slctd Exampls f Transvrs 1\lagntic Dflctin Cavitis A dtaild discus8in rlating t applicatins f th cavitis prsntd in this sctin may b fund lswhr. z Figur shws a typical TE1 S-band chppr cavity and gilll and assmbly fr an injctr chppr-prbunchr systm. A ladd Q f 8 (with critical cupling) was btaind with this cavity by u8ing nn-magntic stl fr fiv f th wall surfacs and OFHC cppr (and plat) fr th thr. Th cling tubs, r-f input cuplr and tunr (bllws) ar clarly indicatd. Watr jts fr and cling and magnt pl pics fr d-c-biasing f th bam ar lcatd in th aprturs arund th priphry f th and plat. Figur 1(a) shws tw nd caps and an intgral blck assmbly which cntains tw TE1 cavitis rintd at right angls t ach thr. Th pattrns n th innr surfacs ar multipactr supprssin grvs. Th 3
21 tungstn scrn bam tracs dpictd in Figur 1(b) wr btaind by driving ths cavitis in phas quadratur t prvid (a) r-f rtatin f a transmittd 1 kl'v, 3A unchppd bam and (b) bunch mnitring f th bam aftr bing subjctd t prgrssivly incrasd chpping actin prducd by a sparat TE lo cavity similar t that shwn in Figur. Figur shws a 476 MHz, TE 11 chppr cavity fr 1 bunch in 6 slctin as usd in th injctin systm f a 856 MHz linar acclratr fr synchrtrn injctin. Th bam aprtur, lcatd in a rgin f maximum transvrs magntic fild, can b ntd at th priphry f th cavity. Th authr wishs t thank his cllagus fr thir ncuragmnt and supprt during th curs f ths prjcts and Varian Assciats fr prmissin t prsnt this matrial. Rfrncs 1. J. Haimsn, IRE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 9, 3 (196).. J. Haimsn, Varian Rprt TMO-9 (Fb. 1966). 3. W. K. H. Panfsky and W. A. Wnzl, Rv. Sci. Inst. 7, 967, (1956). 4. Filds and Wavs in Mdrn Radi, S. Ram and J. R. Whinnry, (1953). 5. Radiatin Labratry Sris N. 11, Ed., C. G. Mntgmry, (1947). 6. J. Haimsn, Nucl. Instr. Mth., 33, 93 (1965). *Rfr IEEE, Trans. Nucl. Sci. Vl. NS-1, Pag 997, Jun TABLE I COMPARISON OF OPTIMIZED H FIELD MAXIMA FOR THE TM 1 AND TE 11 MODES h ī\ a i\ TM 1 TE 11 H i\ a d - H i\ cpm P d i\ i\ zm P L L Jt; H i\ xm P L TABLE II COMPARISON OF Q VALUES FOR THE TM 1 AND TE 11 MODES QR Q in cppr at f = 856 MHz s h ī\ Optimum Optimum TM TE TM TE
22 h - A A O. : TABLE!l COMPARISON OF OPTIMIZED H FIELD 11AXIMA FOR THE TM IIO AND TE I 11DES TM 11 TE 1!L H A -.!'. H A -. CPM P d A zm P A L L ' ;lgl * 1. 31' O. :l:!7 O. GO:I ' 1.45" (;:1 1. OJ 5* O. IG '" Maximizd valus II xm A P L.851.7HH H' 1.78' 1.11' TABLE IV COMPARISON OF Q VALUES FOR THE TM llo AND TE I MODES QR s Q in cppr at 856 MHz h - Optimum TE Optimum TE A 1 1 TM 11 HzM HxM TM llo HzM HxM TABLE V PERCENTAGE (BIN) VARIATION OF H FIELD ACROSS THE BEAM DIAMETER IN THE DIRECTIO:-; OF DEFLECTION. TM 1 " TE TE UO TE 1 TE 1 Bam Diamtr HcpM(r) HZI(X) (a d) HcpM 1r ) HzM(x) H xm 1z ) H H z x..5a O.lOA A A Rlativ H O. 74 Maxima Symmtric H fild distributin abut th bam cntr-lin. 34
23 TABLE VI COMPARISON OF OPTIMIZED E FIELD MAXIMA E zm S s h h#c ry P EyM ry P L L l!.- h TM TM TE TE 1 TE 1 fr HzM fr H zm fr HxM TABLE VII COMPARISON OF TE I MODE DEFLECTION AND BEAM ENERGY FOR VARIOUS BEAM POSITIONS Entry Angl Figur 18 Ttal Enrgy (kv) at Elctrn Bam Orbit z h y=- y = Paramtrs N. (m) h Enrgy (kv) COITC'spnding t y Bam Psitin Aftr Dflctin at S = m z (m) (wt ) = 3.3 V =7kV 1 G.O 1 G dia =.1 ho 11 {j fi V= 7 ky dia =.1, V = 15 ky : di. =.1 ho : V = 15 ky dia =. ho :l V= 7 kv dia =.1 A Cavity dimnsins, a =.16 m, d = 18 m and h = 41 m fr th 7 ky xampls, and a = 164 m, d = 17 m and h = 91 m fr th 15 ky xampls. TABLE VIII COMPARISON OF TE IOI MODE DEFLECTION AND BEAM ENERGY FOR VARIOUS BEAM POSITIONS Entry Angl Figur 1!l Ttal Enrgy (kv) at Elctrn Enrgy (kv) Bam Orbit Xc h Crrspnding Y = h Paramtrs N. (m) y = - t y Bam Psitin Aftr Dflctin at S = m x (m) (wt ) =8. V = 7 ky dia= O.lA V = 7 ky dia =. A.3fi :1O V = 15 ky 4 O.S '1.4 dia =.1 A :lO OS : V = 15 ky G dia =. A. :ls l.:lo V=7kV dia=.a R V =15kV dia:=-. \( V= 15kV dia=o , , Cavity dimnsins, a =.617 m, d =.1 m and h =.3 m fr th 7 ky xampls, and a =.619m, d =.99 m and h =.39 m fr th 15 ky xampls. 35
24 TABLE IX VARIA TION OF BEAM ENERGY WITH TIME DURING THE R-F CYCLE FOR THE TE 11 MODE Figur 19 Ttal Bam Enrgy (kv) Entry Angl Orbit N wt wt + rr/ wt + rr : wt + 3rr/ TABLE X VARIA TION OF BEAM ENERGY WITH TIME.:::D...:Uc.:;R.:.::I;:.:N-=G'-T=-H=E-=R:..:.---=F:...::C...:Y:...:C:c.::L=E=--=F--=O::..::R..:...:T-=H=-=ETE 1 _M_O_D_E Figur 18 Ttal Bam Enrgy (kv) Bam Entry Diamtr Angl Orbit N A wt wt + rr/ wt + rr wt + 3rr/ Orbit N A- wt wt + rr/ wt +rr wt + 3rr/ I I , " / \ I... -, I / I..., I I -7":. I I I \ \ " I \' ,ri-f I a H,-... I li_'_-_?_-_/ "...;: Fig. la) Circular cylindrical cavity TM md. 1 m p a x d Fig. l(b) Rctangular wavguid cavity TE md. 1l I Prcdings f th 1966 Linar Acclratr Cnfrnc, Ls Alams, Nw Mxic, USA 36
25 N '" 1. H.,. H' 1M 1. HIM I +,,\.,\O.9 H H Ol x.' 'a dl -...,. ;H..,...8 D.6 '/>"\\ H,M.3'1.., "" 'f;j\o d..7 H",Irl.' 5- HOI! c.6,.. ',., x- u,.,,. rt 'i.5 c z-t z I D.. U.. 1- ) Fig.. Magntic fild distributins H (r), H (x).4 & Fig. 5. Variatin f Q.R s with (h/ ") Z and Hx(z). fr th TlO and UO.3 mds..' li'i1j 1(''... D.I.l[( )' f' - 1, 1 D.l, li'o,j.n..5 "' I--,. ) H, ' a.., H. r r'l I H, l. zd... Fig. 4. Cmparisn f magntic fild li'i1,j gradints in th dirctin f "3 bam dflctin fr lo and TE 1l mds...., ".3 D.4.., () QflI.-k :; m OIl, r'o 15 ". m.. Fig. 3. Optimum (a/d) rati vrsus (h/ A ) fr TE 1l U;)- and TE mds. 1 Fig. 6. Variatin f AR and pak magntic fild ith (a/a) fr th TE md. 1l "". 1m", Prcdings f th 1966 Linar Acclratr Cnfrnc, Ls Alams, Nw Mxic, USA 37
26 -g. :., i!: Ji' '"!i f '" II 5 Fig. 7. frq-llxxxi, - l56mhz,'1_" Q l Q, Fr Othr V.luts f Q r, lh Q,,.,. Build-up TIn, I -It Ir(MHz) Wi" It1j,lWtI Magntic fild strngth build-up tim charactristic. 4t-! (b) TEI Md Fig. 8. O and TE 1 md fild pattrns. L !H..,lrl!, - Ind 'r / / I.lt l /.;/ (i) Fig. 9. TM llo magntic fild distributins Hr(r) in th <t> = plan and H<t>(r) in th <t> = TI/ plan (tj I ;;, O! H" O., 13 TI! MaW 1 11 U;}1 ['W"I( L IOO II Fig. 1. Variatin f QRsnand pak magntic filds with (a/a) fr th TE15 md and (h/a) = O.. O., / / / / / / / / Prcdings f th 1966 Linar Acclratr Cnfrnc, Ls Alams, Nw Mxic, USA 38
27 1.r---r---r---r---r---r---r---r---r---r---r---r----, Imm I. Smm Cramlc Bud Dr,.,n Thrugh Thl lng A.xis I.,., Tt 1 Md d"z. ),'Olmm Fig Gradints f ptimizd magntic filds in th dirctin f bam dflctin fr lo and TE 1 mds.. TMaw r 1.. Cpptr Plald Smm 8.11 kam Drawn Paraml1y Thrugh Cntrlin Bam Apr1uf "lng / Vanus "xu " / " 1 Prun1 vn. Tnnsmlssln "I Tt I Mtt 76 n.. d. "' 15m Axn BlndO Bam Cnt.rllnt 1.5.c;DI" 1..5 TMllO(; ) 16mm 1. "pr1uff With [dnnal Drift Tubs INaI T 5,,11) IOO-"l-"' '><--' A..I,IPslllnOIB.ltltml_ Fig. 1. TE 1 cavity bad prturbatin xprimntal data. Fig ()..7 Radial dpndnc f lngitudinal lctric fild (E z ) fr th TM 1 and lo mds. x!! 3. ; Q! i. & ; TMllO - C_rCvlty(9OI 1l1 ),.lmm P L 'kw U9 1 3 Drift DlsRn S(cm) Fig. 15. TM llo cavity bam dflctin vrsus drift lngth. Fig. 14. lo cavity and bam dflctin paths. 39
28 ---1I 11 UO I 1 1 A.lm N illlwallc has bhn mad tr b,m apnur Irlng fild ffcts.... m Dilm.ur --..' ' Olmum "h" Dimnsin lml -- Fig. 16. TlO' TE IOl and TE ptimum "h" dimnsin vrsus drift lngth fr varius I bam nrgis at 856 MHz. l, z la y, ---liioi ' O.11l) m S" 1I.Om Q' 9(r.thrkaIVJlu, fr cppr Pt'4fIW Naliwanc hu bn rnaclt fr bum IPIrtur'rlngtfl.kI.f1tcb Cavity "11" Dimnsin (m) Fig. 17. Bam dflctin vrsus "h" dimnsin fr a givn drift lngth and input R-F pwr and varius bam nrgis. B -r.v h' O.cw. -- lso.vh'q.oln!,,-»' Fr:::... " Q.1Q5 WI S-.111 'L' 4IIW 1.V h D.4m C 7D.Vh O.OUIII Fig. 18. Bam crss-sctin variatins fr TE I cavity dflctins. 8lm OI.rMt.r,\. y. Y' h + 51 Fig Q -1-- Bam crss-sctin variatins fr TE IOl cavity dflctins D l5tv h' O.OJlm --.3/. 33
29 Fig.. Elctrn gun and and chppr cavity assmbly during cnstructin. - Fig. la. Transvrs dflctin highr rdr md dual cavity assmbly fr bam rtatin and mnitring f R-F bunch lngth. l(b) (b) 3 (b) 4(b) Fig. lb. Tungstn scrn pbqtgraphs shwing bam rtatin and R-F chpping at S-band frquncy. Fig MHz, TE 1l transvrs magntic chppr cavity fr n in six bunch slctin. 331
Lecture 26: Quadrature (90º) Hybrid.
 Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 26 Pag f Lctur 26: Quadratur (9º) Hybrid. Back in Lctur 23, w bgan ur discussin f dividrs and cuplrs by cnsidring imprtant gnral prprtis f thrand fur-prt ntwrks. This was fllwd by
Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 26 Pag f Lctur 26: Quadratur (9º) Hybrid. Back in Lctur 23, w bgan ur discussin f dividrs and cuplrs by cnsidring imprtant gnral prprtis f thrand fur-prt ntwrks. This was fllwd by
. This is made to keep the kinetic energy at outlet a minimum.
 Runnr Francis Turbin Th shap th blads a Francis runnr is cmplx. Th xact shap dpnds n its spciic spd. It is bvius rm th quatin spciic spd (Eq.5.8) that highr spciic spd mans lwr had. This rquirs that th
Runnr Francis Turbin Th shap th blads a Francis runnr is cmplx. Th xact shap dpnds n its spciic spd. It is bvius rm th quatin spciic spd (Eq.5.8) that highr spciic spd mans lwr had. This rquirs that th
A Unified Theory of rf Plasma Heating. J.e. Sprott. July 1968
 A Unifid Thry f rf Plasma Hating by J.. Sprtt July 968 PLP 3 Plasma Studis Univrsity f iscnsin INTRODUCfION In this papr, th majr rsults f PLP's 86 and 07 will b drivd in a mr cncis and rigrus way, and
A Unifid Thry f rf Plasma Hating by J.. Sprtt July 968 PLP 3 Plasma Studis Univrsity f iscnsin INTRODUCfION In this papr, th majr rsults f PLP's 86 and 07 will b drivd in a mr cncis and rigrus way, and
LECTURE 5 Guassian Wave Packet
 LECTURE 5 Guassian Wav Pact 1.5 Eampl f a guassian shap fr dscribing a wav pact Elctrn Pact ψ Guassian Assumptin Apprimatin ψ As w hav sn in QM th wav functin is ftn rprsntd as a Furir transfrm r sris.
LECTURE 5 Guassian Wav Pact 1.5 Eampl f a guassian shap fr dscribing a wav pact Elctrn Pact ψ Guassian Assumptin Apprimatin ψ As w hav sn in QM th wav functin is ftn rprsntd as a Furir transfrm r sris.
Lecture 27: The 180º Hybrid.
 Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 7 Pag f 0 Lctur 7: Th 80º Hybrid. Th scnd rciprcal dirctinal cuplr w will discuss is th 80º hybrid. As th nam implis, th utputs frm such a dvic can b 80º ut f phas. Thr ar tw primary
Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 7 Pag f 0 Lctur 7: Th 80º Hybrid. Th scnd rciprcal dirctinal cuplr w will discuss is th 80º hybrid. As th nam implis, th utputs frm such a dvic can b 80º ut f phas. Thr ar tw primary
Topic 5: Discrete-Time Fourier Transform (DTFT)
 ELEC36: Signals And Systms Tpic 5: Discrt-Tim Furir Transfrm (DTFT) Dr. Aishy Amr Cncrdia Univrsity Elctrical and Cmputr Enginring DT Furir Transfrm Ovrviw f Furir mthds DT Furir Transfrm f Pridic Signals
ELEC36: Signals And Systms Tpic 5: Discrt-Tim Furir Transfrm (DTFT) Dr. Aishy Amr Cncrdia Univrsity Elctrical and Cmputr Enginring DT Furir Transfrm Ovrviw f Furir mthds DT Furir Transfrm f Pridic Signals
Another Explanation of the Cosmological Redshift. April 6, 2010.
 Anthr Explanatin f th Csmlgical Rdshift April 6, 010. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 4605 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s h lss f nrgy f th phtn with th tim by missin f
Anthr Explanatin f th Csmlgical Rdshift April 6, 010. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 4605 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s h lss f nrgy f th phtn with th tim by missin f
Chapter 2 Linear Waveshaping: High-pass Circuits
 Puls and Digital Circuits nkata Ra K., Rama Sudha K. and Manmadha Ra G. Chaptr 2 Linar Wavshaping: High-pass Circuits. A ramp shwn in Fig.2p. is applid t a high-pass circuit. Draw t scal th utput wavfrm
Puls and Digital Circuits nkata Ra K., Rama Sudha K. and Manmadha Ra G. Chaptr 2 Linar Wavshaping: High-pass Circuits. A ramp shwn in Fig.2p. is applid t a high-pass circuit. Draw t scal th utput wavfrm
Modern Physics. Unit 5: Schrödinger s Equation and the Hydrogen Atom Lecture 5.6: Energy Eigenvalues of Schrödinger s Equation for the Hydrogen Atom
 Mdrn Physics Unit 5: Schrödingr s Equatin and th Hydrgn Atm Lctur 5.6: Enrgy Eignvalus f Schrödingr s Equatin fr th Hydrgn Atm Rn Rifnbrgr Prfssr f Physics Purdu Univrsity 1 Th allwd nrgis E cm frm th
Mdrn Physics Unit 5: Schrödingr s Equatin and th Hydrgn Atm Lctur 5.6: Enrgy Eignvalus f Schrödingr s Equatin fr th Hydrgn Atm Rn Rifnbrgr Prfssr f Physics Purdu Univrsity 1 Th allwd nrgis E cm frm th
Chapter 33 Gauss s Law
 Chaptr 33 Gauss s Law 33 Gauss s Law Whn askd t find th lctric flux thrugh a clsd surfac du t a spcifid nn-trivial charg distributin, flks all t ftn try th immnsly cmplicatd apprach f finding th lctric
Chaptr 33 Gauss s Law 33 Gauss s Law Whn askd t find th lctric flux thrugh a clsd surfac du t a spcifid nn-trivial charg distributin, flks all t ftn try th immnsly cmplicatd apprach f finding th lctric
Lecture 2a. Crystal Growth (cont d) ECE723
 Lctur 2a rystal Grwth (cnt d) 1 Distributin f Dpants As a crystal is pulld frm th mlt, th dping cncntratin incrpratd int th crystal (slid) is usually diffrnt frm th dping cncntratin f th mlt (liquid) at
Lctur 2a rystal Grwth (cnt d) 1 Distributin f Dpants As a crystal is pulld frm th mlt, th dping cncntratin incrpratd int th crystal (slid) is usually diffrnt frm th dping cncntratin f th mlt (liquid) at
MHT-CET 5 (PHYSICS) PHYSICS CENTERS : MUMBAI /DELHI /AKOLA /LUCKNOW / NASHIK /PUNE /NAGPUR / BOKARO / DUBAI # 1
 1. (D) Givn, mass f th rckts, m = 5000 kg; Exhaust spd, v = 800 m/s Acclratin, a = 0 m/s m Lt is amunt f gas pr scnd, t Frc = m (a + g) mu m a g t m 800 m a g t 5000 10 0 5000 0 m 5000 0 187.5 kg sc t
1. (D) Givn, mass f th rckts, m = 5000 kg; Exhaust spd, v = 800 m/s Acclratin, a = 0 m/s m Lt is amunt f gas pr scnd, t Frc = m (a + g) mu m a g t m 800 m a g t 5000 10 0 5000 0 m 5000 0 187.5 kg sc t
22/ Breakdown of the Born-Oppenheimer approximation. Selection rules for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branches.
 Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
5 Curl-free fields and electrostatic potential
 5 Curl-fr filds and lctrstatic tntial Mathmaticall, w can gnrat a curl-fr vctr fild E(,, ) as E = ( V, V, V ), b taking th gradint f an scalar functin V (r) =V (,, ). Th gradint f V (,, ) is dfind t b
5 Curl-fr filds and lctrstatic tntial Mathmaticall, w can gnrat a curl-fr vctr fild E(,, ) as E = ( V, V, V ), b taking th gradint f an scalar functin V (r) =V (,, ). Th gradint f V (,, ) is dfind t b
FUNDAMENTAL AND SECOND HARMONIC AMPLITUDES IN A COLLISIONAL MAGNETOACTIVE PLASMA UDC B. M. Jovanović, B. Živković
 FACTA UNIVERSITATIS Sris: Physics, Chmistry and Tchnlgy Vl., N 5, 3, pp. 45-51 FUNDAMENTAL AND SECOND HARMONIC AMPLITUDES IN A COLLISIONAL MAGNETOACTIVE PLASMA UDC 533.9 B. M. Jvanvić, B. Živkvić Dpartmnt
FACTA UNIVERSITATIS Sris: Physics, Chmistry and Tchnlgy Vl., N 5, 3, pp. 45-51 FUNDAMENTAL AND SECOND HARMONIC AMPLITUDES IN A COLLISIONAL MAGNETOACTIVE PLASMA UDC 533.9 B. M. Jvanvić, B. Živkvić Dpartmnt
6. Negative Feedback in Single- Transistor Circuits
 Lctur 8: Intrductin t lctrnic analg circuit 36--366 6. Ngativ Fdback in Singl- Tranitr ircuit ugn Paprn, 2008 Our aim i t tudy t ffct f ngativ fdback n t mall-ignal gain and t mall-ignal input and utput
Lctur 8: Intrductin t lctrnic analg circuit 36--366 6. Ngativ Fdback in Singl- Tranitr ircuit ugn Paprn, 2008 Our aim i t tudy t ffct f ngativ fdback n t mall-ignal gain and t mall-ignal input and utput
SERBIATRIB th International Conference on Tribology. Kragujevac, Serbia, May 2011
 Srbian Triblgy Scity SERBIATRIB 11 1 th Intrnatinal Cnfrnc n Triblgy Kragujvac, Srbia, 11 13 May 11 Faculty f Mchanical Enginring in Kragujvac EFFECT OF CHANGES OF VISCOSITY OF MINERA OI IN THE FUNCTION
Srbian Triblgy Scity SERBIATRIB 11 1 th Intrnatinal Cnfrnc n Triblgy Kragujvac, Srbia, 11 13 May 11 Faculty f Mchanical Enginring in Kragujvac EFFECT OF CHANGES OF VISCOSITY OF MINERA OI IN THE FUNCTION
ME 354, MECHANICS OF MATERIALS LABORATORY COMPRESSION AND BUCKLING
 ME 354, MECHANICS OF MATERIALS LABATY COMPRESSION AND BUCKLING 01 January 000 / mgj PURPOSE Th purps f this xrcis is t study th ffcts f nd cnditins, clumn lngth, and matrial prprtis n cmprssiv bhaviur
ME 354, MECHANICS OF MATERIALS LABATY COMPRESSION AND BUCKLING 01 January 000 / mgj PURPOSE Th purps f this xrcis is t study th ffcts f nd cnditins, clumn lngth, and matrial prprtis n cmprssiv bhaviur
Fourier Transforms and the Wave Equation. Key Mathematics: More Fourier transform theory, especially as applied to solving the wave equation.
 Lur 7 Fourir Transforms and th Wav Euation Ovrviw and Motivation: W first discuss a fw faturs of th Fourir transform (FT), and thn w solv th initial-valu problm for th wav uation using th Fourir transform
Lur 7 Fourir Transforms and th Wav Euation Ovrviw and Motivation: W first discuss a fw faturs of th Fourir transform (FT), and thn w solv th initial-valu problm for th wav uation using th Fourir transform
ELEC 372 LECTURE NOTES, WEEK 11 Dr. Amir G. Aghdam Concordia University
 ELEC 37 LECTURE NOTES, WEE Dr Amir Aghdam Cncrdia Univrity Part f th nt ar adaptd frm th matrial in th fllwing rfrnc: Mdrn Cntrl Sytm by Richard C Drf and Rbrt H Bihp, Prntic Hall Fdback Cntrl f Dynamic
ELEC 37 LECTURE NOTES, WEE Dr Amir Aghdam Cncrdia Univrity Part f th nt ar adaptd frm th matrial in th fllwing rfrnc: Mdrn Cntrl Sytm by Richard C Drf and Rbrt H Bihp, Prntic Hall Fdback Cntrl f Dynamic
Why is a E&M nature of light not sufficient to explain experiments?
 1 Th wird world of photons Why is a E&M natur of light not sufficint to xplain xprimnts? Do photons xist? Som quantum proprtis of photons 2 Black body radiation Stfan s law: Enrgy/ ara/ tim = Win s displacmnt
1 Th wird world of photons Why is a E&M natur of light not sufficint to xplain xprimnts? Do photons xist? Som quantum proprtis of photons 2 Black body radiation Stfan s law: Enrgy/ ara/ tim = Win s displacmnt
A Propagating Wave Packet Group Velocity Dispersion
 Lctur 8 Phys 375 A Propagating Wav Packt Group Vlocity Disprsion Ovrviw and Motivation: In th last lctur w lookd at a localizd solution t) to th 1D fr-particl Schrödingr quation (SE) that corrsponds to
Lctur 8 Phys 375 A Propagating Wav Packt Group Vlocity Disprsion Ovrviw and Motivation: In th last lctur w lookd at a localizd solution t) to th 1D fr-particl Schrödingr quation (SE) that corrsponds to
Revision: August 21, E Main Suite D Pullman, WA (509) Voice and Fax
 2.7.1: Sinusidal signals, cmplx xpnntials, and phasrs Rvisin: ugust 21, 2010 215 E Main Suit D ullman, W 99163 (509 334 6306 ic and Fax Ovrviw In this mdul, w will rviw prprtis f sinusidal functins and
2.7.1: Sinusidal signals, cmplx xpnntials, and phasrs Rvisin: ugust 21, 2010 215 E Main Suit D ullman, W 99163 (509 334 6306 ic and Fax Ovrviw In this mdul, w will rviw prprtis f sinusidal functins and
Performance of Microstrip Directional Coupler Using Synthesis Technique
 ISSN: 78 8875 Vl., Issu, March 0 Prrmanc Micrstrip Dirctinal uplr Using Synthsis Tchniqu Vijayan T Asst. Prssr, Dpt E&I, Bharath Univrsity, hnnai-60007, India ABSTRAT: Th intrducd dsign mthd rquirs nly
ISSN: 78 8875 Vl., Issu, March 0 Prrmanc Micrstrip Dirctinal uplr Using Synthsis Tchniqu Vijayan T Asst. Prssr, Dpt E&I, Bharath Univrsity, hnnai-60007, India ABSTRAT: Th intrducd dsign mthd rquirs nly
AS 5850 Finite Element Analysis
 AS 5850 Finit Elmnt Analysis Two-Dimnsional Linar Elasticity Instructor Prof. IIT Madras Equations of Plan Elasticity - 1 displacmnt fild strain- displacmnt rlations (infinitsimal strain) in matrix form
AS 5850 Finit Elmnt Analysis Two-Dimnsional Linar Elasticity Instructor Prof. IIT Madras Equations of Plan Elasticity - 1 displacmnt fild strain- displacmnt rlations (infinitsimal strain) in matrix form
Exam 1. It is important that you clearly show your work and mark the final answer clearly, closed book, closed notes, no calculator.
 Exam N a m : _ S O L U T I O N P U I D : I n s t r u c t i o n s : It is important that you clarly show your work and mark th final answr clarly, closd book, closd nots, no calculator. T i m : h o u r
Exam N a m : _ S O L U T I O N P U I D : I n s t r u c t i o n s : It is important that you clarly show your work and mark th final answr clarly, closd book, closd nots, no calculator. T i m : h o u r
Chapter 6: Polarization and Crystal Optics
 Chaptr 6: Polarization and Crystal Optics * P6-1. Cascadd Wav Rtardrs. Show that two cascadd quartr-wav rtardrs with paralll fast axs ar quivalnt to a half-wav rtardr. What is th rsult if th fast axs ar
Chaptr 6: Polarization and Crystal Optics * P6-1. Cascadd Wav Rtardrs. Show that two cascadd quartr-wav rtardrs with paralll fast axs ar quivalnt to a half-wav rtardr. What is th rsult if th fast axs ar
Extraction of Doping Density Distributions from C-V Curves
 Extraction of Doping Dnsity Distributions from C-V Curvs Hartmut F.-W. Sadrozinski SCIPP, Univ. California Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA 9564 USA 1. Connction btwn C, N, V Start with Poisson quation d V =
Extraction of Doping Dnsity Distributions from C-V Curvs Hartmut F.-W. Sadrozinski SCIPP, Univ. California Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA 9564 USA 1. Connction btwn C, N, V Start with Poisson quation d V =
Even/Odd Mode Analysis of the Wilkinson Divider
 //9 Wilkinn Dividr Evn and Odd Md Analyi.dc / Evn/Odd Md Analyi f th Wilkinn Dividr Cnidr a matchd Wilkinn pwr dividr, with a urc at prt : Prt Prt Prt T implify thi chmatic, w rmv th grund plan, which
//9 Wilkinn Dividr Evn and Odd Md Analyi.dc / Evn/Odd Md Analyi f th Wilkinn Dividr Cnidr a matchd Wilkinn pwr dividr, with a urc at prt : Prt Prt Prt T implify thi chmatic, w rmv th grund plan, which
Einstein Equations for Tetrad Fields
 Apiron, Vol 13, No, Octobr 006 6 Einstin Equations for Ttrad Filds Ali Rıza ŞAHİN, R T L Istanbul (Turky) Evry mtric tnsor can b xprssd by th innr product of ttrad filds W prov that Einstin quations for
Apiron, Vol 13, No, Octobr 006 6 Einstin Equations for Ttrad Filds Ali Rıza ŞAHİN, R T L Istanbul (Turky) Evry mtric tnsor can b xprssd by th innr product of ttrad filds W prov that Einstin quations for
Chapter 2: Examples of Mathematical Models for Chemical Processes
 Chaptr 2: Exampls Mathmatical Mdls r Chmical Prcsss In this chaptr w dvlp mathmatical mdls r a numbr lmntary chmical prcsss that ar cmmnly ncuntrd in practic. W will apply th mthdlgy discussd in th prvius
Chaptr 2: Exampls Mathmatical Mdls r Chmical Prcsss In this chaptr w dvlp mathmatical mdls r a numbr lmntary chmical prcsss that ar cmmnly ncuntrd in practic. W will apply th mthdlgy discussd in th prvius
OPTICAL OSCILLATOR STRENGTHS FOR THE ELECTRON QUANTUM TRANSITIONS IN ELLIPTIC NANOTUBES
 OPTICAL OSCILLATOR STRENGTHS FOR THE ELECTRON QUANTUM TRANSITIONS IN ELLIPTIC NANOTUBES V. A. HOLOVATSKY, O. M. VOITSEKHIVSKA, V. I. GUTSUL Chrnivtsi Natinal Univrsity, Chrnivtsi, 58012, Ukrain, thrphys@chnu.cv.ua
OPTICAL OSCILLATOR STRENGTHS FOR THE ELECTRON QUANTUM TRANSITIONS IN ELLIPTIC NANOTUBES V. A. HOLOVATSKY, O. M. VOITSEKHIVSKA, V. I. GUTSUL Chrnivtsi Natinal Univrsity, Chrnivtsi, 58012, Ukrain, thrphys@chnu.cv.ua
Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors
 Snsrs and Actuatrs Intrductin t snsrs Sandr Stuijk (s.stuijk@tu.nl) Dpartmnt f Elctrical Enginring Elctrnic Systms APAITIVE IUITS (haptr., 7., 9., 0.6,.,.) apaciti snsr capacitanc dpnds n physical prprtis
Snsrs and Actuatrs Intrductin t snsrs Sandr Stuijk (s.stuijk@tu.nl) Dpartmnt f Elctrical Enginring Elctrnic Systms APAITIVE IUITS (haptr., 7., 9., 0.6,.,.) apaciti snsr capacitanc dpnds n physical prprtis
MAGNETIC MONOPOLE THEORY
 AGNETIC ONOPOLE THEORY S HUSSAINSHA Rsarch schlar f ECE, G.Pullaiah Cllg f Enginring and Tchnlgy, Kurnl, Andhra Pradsh, India Eail: ssshaik80@gail.c Cll: +91 9000390153 Abstract: Th principal bjctiv f
AGNETIC ONOPOLE THEORY S HUSSAINSHA Rsarch schlar f ECE, G.Pullaiah Cllg f Enginring and Tchnlgy, Kurnl, Andhra Pradsh, India Eail: ssshaik80@gail.c Cll: +91 9000390153 Abstract: Th principal bjctiv f
Search sequence databases 3 10/25/2016
 Sarch squnc databass 3 10/25/2016 Etrm valu distribution Ø Suppos X is a random variabl with probability dnsity function p(, w sampl a larg numbr S of indpndnt valus of X from this distribution for an
Sarch squnc databass 3 10/25/2016 Etrm valu distribution Ø Suppos X is a random variabl with probability dnsity function p(, w sampl a larg numbr S of indpndnt valus of X from this distribution for an
Design Guidelines for Quartz Crystal Oscillators. R 1 Motional Resistance L 1 Motional Inductance C 1 Motional Capacitance C 0 Shunt Capacitance
 TECHNICAL NTE 30 Dsign Guidlins for Quartz Crystal scillators Introduction A CMS Pirc oscillator circuit is wll known and is widly usd for its xcllnt frquncy stability and th wid rang of frquncis ovr which
TECHNICAL NTE 30 Dsign Guidlins for Quartz Crystal scillators Introduction A CMS Pirc oscillator circuit is wll known and is widly usd for its xcllnt frquncy stability and th wid rang of frquncis ovr which
Definition1: The ratio of the radiation intensity in a given direction from the antenna to the radiation intensity averaged over all directions.
 Dirctivity or Dirctiv Gain. 1 Dfinition1: Dirctivity Th ratio of th radiation intnsity in a givn dirction from th antnna to th radiation intnsity avragd ovr all dirctions. Dfinition2: Th avg U is obtaind
Dirctivity or Dirctiv Gain. 1 Dfinition1: Dirctivity Th ratio of th radiation intnsity in a givn dirction from th antnna to th radiation intnsity avragd ovr all dirctions. Dfinition2: Th avg U is obtaind
N J of oscillators in the three lowest quantum
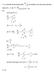 . a) Calculat th fractinal numbr f scillatrs in th thr lwst quantum stats (j,,,) fr fr and Sl: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ).6.98. fr usth sam apprach fr fr j fr frm q. b) .) a) Fr a systm f lcalizd distinguishabl
. a) Calculat th fractinal numbr f scillatrs in th thr lwst quantum stats (j,,,) fr fr and Sl: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ).6.98. fr usth sam apprach fr fr j fr frm q. b) .) a) Fr a systm f lcalizd distinguishabl
Math 34A. Final Review
 Math A Final Rviw 1) Us th graph of y10 to find approimat valus: a) 50 0. b) y (0.65) solution for part a) first writ an quation: 50 0. now tak th logarithm of both sids: log() log(50 0. ) pand th right
Math A Final Rviw 1) Us th graph of y10 to find approimat valus: a) 50 0. b) y (0.65) solution for part a) first writ an quation: 50 0. now tak th logarithm of both sids: log() log(50 0. ) pand th right
Microwave Engineering
 Micrwav Enginring hng-hsing Hsu Dpartmnt f Elctrical Enginring Natinal Unitd Univrsity Outlin. Transmissin Lin Thry. Transmissin Lins and Wavguids Gnral lutins fr TEM, TE, and TM wavs ; Paralll Plat wavguid
Micrwav Enginring hng-hsing Hsu Dpartmnt f Elctrical Enginring Natinal Unitd Univrsity Outlin. Transmissin Lin Thry. Transmissin Lins and Wavguids Gnral lutins fr TEM, TE, and TM wavs ; Paralll Plat wavguid
120~~60 o D 12~0 1500~30O, 15~30 150~30. ..,u 270,,,, ~"~"-4-~qno 240 2~o 300 v 240 ~70O 300
 1 Find th plar crdinats that d nt dscrib th pint in th givn graph. (-2, 30 ) C (2,30 ) B (-2,210 ) D (-2,-150 ) Find th quatin rprsntd in th givn graph. F 0=3 H 0=2~ G r=3 J r=2 0 :.1 2 3 ~ 300 2"~ 2,
1 Find th plar crdinats that d nt dscrib th pint in th givn graph. (-2, 30 ) C (2,30 ) B (-2,210 ) D (-2,-150 ) Find th quatin rprsntd in th givn graph. F 0=3 H 0=2~ G r=3 J r=2 0 :.1 2 3 ~ 300 2"~ 2,
Brief Introduction to Statistical Mechanics
 Brif Introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Purpos: Ths nots ar intndd to provid a vry quick introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Th fild is of cours far mor vast than could b containd in ths fw pags.
Brif Introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Purpos: Ths nots ar intndd to provid a vry quick introduction to Statistical Mchanics. Th fild is of cours far mor vast than could b containd in ths fw pags.
Title: Vibrational structure of electronic transition
 Titl: Vibrational structur of lctronic transition Pag- Th band spctrum sn in th Ultra-Violt (UV) and visibl (VIS) rgions of th lctromagntic spctrum can not intrprtd as vibrational and rotational spctrum
Titl: Vibrational structur of lctronic transition Pag- Th band spctrum sn in th Ultra-Violt (UV) and visibl (VIS) rgions of th lctromagntic spctrum can not intrprtd as vibrational and rotational spctrum
The pn junction: 2 Current vs Voltage (IV) characteristics
 Th pn junction: Currnt vs Voltag (V) charactristics Considr a pn junction in quilibrium with no applid xtrnal voltag: o th V E F E F V p-typ Dpltion rgion n-typ Elctron movmnt across th junction: 1. n
Th pn junction: Currnt vs Voltag (V) charactristics Considr a pn junction in quilibrium with no applid xtrnal voltag: o th V E F E F V p-typ Dpltion rgion n-typ Elctron movmnt across th junction: 1. n
A Brief and Elementary Note on Redshift. May 26, 2010.
 A Brif and Elmntary Nt n Rdshift May 26, 2010. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 46025 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s Abstract A rasnabl xplanatin f bth rdshifts: csmlgical
A Brif and Elmntary Nt n Rdshift May 26, 2010. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 46025 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s Abstract A rasnabl xplanatin f bth rdshifts: csmlgical
PHYS-333: Problem set #2 Solutions
 PHYS-333: Problm st #2 Solutions Vrsion of March 5, 2016. 1. Visual binary 15 points): Ovr a priod of 10 yars, two stars sparatd by an angl of 1 arcsc ar obsrvd to mov through a full circl about a point
PHYS-333: Problm st #2 Solutions Vrsion of March 5, 2016. 1. Visual binary 15 points): Ovr a priod of 10 yars, two stars sparatd by an angl of 1 arcsc ar obsrvd to mov through a full circl about a point
Coupled Pendulums. Two normal modes.
 Tim Dpndnt Two Stat Problm Coupld Pndulums Wak spring Two normal mods. No friction. No air rsistanc. Prfct Spring Start Swinging Som tim latr - swings with full amplitud. stationary M +n L M +m Elctron
Tim Dpndnt Two Stat Problm Coupld Pndulums Wak spring Two normal mods. No friction. No air rsistanc. Prfct Spring Start Swinging Som tim latr - swings with full amplitud. stationary M +n L M +m Elctron
Cosmology. Outline. Relativity and Astrophysics Lecture 17 Terry Herter. Redshift (again) The Expanding Universe Applying Hubble s Law
 Csmlgy Csmlgy Rlativity and Astrphysics ctur 17 Trry Hrtr Outlin Rdshit (again) Th Expanding Univrs Applying Hubbl s aw Distanc rm Rdshit Csmlgical Principl Olbrs Paradx A90-17 Csmlgy A90-17 1 Csmlgy Rdshit
Csmlgy Csmlgy Rlativity and Astrphysics ctur 17 Trry Hrtr Outlin Rdshit (again) Th Expanding Univrs Applying Hubbl s aw Distanc rm Rdshit Csmlgical Principl Olbrs Paradx A90-17 Csmlgy A90-17 1 Csmlgy Rdshit
Background: We have discussed the PIB, HO, and the energy of the RR model. In this chapter, the H-atom, and atomic orbitals.
 Chaptr 7 Th Hydrogn Atom Background: W hav discussd th PIB HO and th nrgy of th RR modl. In this chaptr th H-atom and atomic orbitals. * A singl particl moving undr a cntral forc adoptd from Scott Kirby
Chaptr 7 Th Hydrogn Atom Background: W hav discussd th PIB HO and th nrgy of th RR modl. In this chaptr th H-atom and atomic orbitals. * A singl particl moving undr a cntral forc adoptd from Scott Kirby
2. Background Material
 S. Blair Sptmbr 3, 003 4. Background Matrial Th rst of this cours dals with th gnration, modulation, propagation, and ction of optical radiation. As such, bic background in lctromagntics and optics nds
S. Blair Sptmbr 3, 003 4. Background Matrial Th rst of this cours dals with th gnration, modulation, propagation, and ction of optical radiation. As such, bic background in lctromagntics and optics nds
Classical Magnetic Dipole
 Lctur 18 1 Classical Magntic Dipol In gnral, a particl of mass m and charg q (not ncssarily a point charg), w hav q g L m whr g is calld th gyromagntic ratio, which accounts for th ffcts of non-point charg
Lctur 18 1 Classical Magntic Dipol In gnral, a particl of mass m and charg q (not ncssarily a point charg), w hav q g L m whr g is calld th gyromagntic ratio, which accounts for th ffcts of non-point charg
surface of a dielectric-metal interface. It is commonly used today for discovering the ways in
 Surfac plasmon rsonanc is snsitiv mchanism for obsrving slight changs nar th surfac of a dilctric-mtal intrfac. It is commonl usd toda for discovring th was in which protins intract with thir nvironmnt,
Surfac plasmon rsonanc is snsitiv mchanism for obsrving slight changs nar th surfac of a dilctric-mtal intrfac. It is commonl usd toda for discovring th was in which protins intract with thir nvironmnt,
Ring Resonators for Integrated Optics Applications
 Ring Rsnatrs fr Intgratd Optics Applicatins by Michal Gad A thsis prsntd t th Univrsity f Watrl in fulfillmnt f th thsis rquirmnt fr th dgr f Dctr f Philsphy in Physics Watrl, Ontari, Canada, 0 Michal
Ring Rsnatrs fr Intgratd Optics Applicatins by Michal Gad A thsis prsntd t th Univrsity f Watrl in fulfillmnt f th thsis rquirmnt fr th dgr f Dctr f Philsphy in Physics Watrl, Ontari, Canada, 0 Michal
SCALING OF SYNCHROTRON RADIATION WITH MULTIPOLE ORDER. J. C. Sprott
 SCALING OF SYNCHROTRON RADIATION WITH MULTIPOLE ORDER J. C. Sprott PLP 821 Novmbr 1979 Plasma Studis Univrsity of Wisconsin Ths PLP Rports ar informal and prliminary and as such may contain rrors not yt
SCALING OF SYNCHROTRON RADIATION WITH MULTIPOLE ORDER J. C. Sprott PLP 821 Novmbr 1979 Plasma Studis Univrsity of Wisconsin Ths PLP Rports ar informal and prliminary and as such may contain rrors not yt
ECE 344 Microwave Fundamentals
 ECE 44 Microwav Fundamntals Lctur 08: Powr Dividrs and Couplrs Part Prpard By Dr. hrif Hkal 4/0/08 Microwav Dvics 4/0/08 Microwav Dvics 4/0/08 Powr Dividrs and Couplrs Powr dividrs, combinrs and dirctional
ECE 44 Microwav Fundamntals Lctur 08: Powr Dividrs and Couplrs Part Prpard By Dr. hrif Hkal 4/0/08 Microwav Dvics 4/0/08 Microwav Dvics 4/0/08 Powr Dividrs and Couplrs Powr dividrs, combinrs and dirctional
u 3 = u 3 (x 1, x 2, x 3 )
 Lctur 23: Curvilinar Coordinats (RHB 8.0 It is oftn convnint to work with variabls othr than th Cartsian coordinats x i ( = x, y, z. For xampl in Lctur 5 w mt sphrical polar and cylindrical polar coordinats.
Lctur 23: Curvilinar Coordinats (RHB 8.0 It is oftn convnint to work with variabls othr than th Cartsian coordinats x i ( = x, y, z. For xampl in Lctur 5 w mt sphrical polar and cylindrical polar coordinats.
4.2 Design of Sections for Flexure
 4. Dsign of Sctions for Flxur This sction covrs th following topics Prliminary Dsign Final Dsign for Typ 1 Mmbrs Spcial Cas Calculation of Momnt Dmand For simply supportd prstrssd bams, th maximum momnt
4. Dsign of Sctions for Flxur This sction covrs th following topics Prliminary Dsign Final Dsign for Typ 1 Mmbrs Spcial Cas Calculation of Momnt Dmand For simply supportd prstrssd bams, th maximum momnt
Hydrogen Atom and One Electron Ions
 Hydrogn Atom and On Elctron Ions Th Schrödingr quation for this two-body problm starts out th sam as th gnral two-body Schrödingr quation. First w sparat out th motion of th cntr of mass. Th intrnal potntial
Hydrogn Atom and On Elctron Ions Th Schrödingr quation for this two-body problm starts out th sam as th gnral two-body Schrödingr quation. First w sparat out th motion of th cntr of mass. Th intrnal potntial
Effect of Warm Ionized Plasma Medium on Radiation Properties of Mismatched Microstrip Termination
 J. Elctrmagntic Analysis & Alicatins, 9, 3: 181-186 di:1.436/jmaa.9.137 Publishd Onlin Stmbr 9 (www.scip.rg/jurnal/jmaa) 181 Effct f Warm Inizd Plasma Mdium n adiatin Prrtis f Mismatchd Micrstri Trminatin
J. Elctrmagntic Analysis & Alicatins, 9, 3: 181-186 di:1.436/jmaa.9.137 Publishd Onlin Stmbr 9 (www.scip.rg/jurnal/jmaa) 181 Effct f Warm Inizd Plasma Mdium n adiatin Prrtis f Mismatchd Micrstri Trminatin
Reflector Antennas. Contents
 Rlctr Antnnas Mtivatin: - incras th aprtur ara and, thrr, incras dirctivity - cllimat nrgy in n dirctin - rduc th siz th antnna systm - us th rlctr (and subrlctr) r bam shaping Cntnts 1. Intrductin. Crnr
Rlctr Antnnas Mtivatin: - incras th aprtur ara and, thrr, incras dirctivity - cllimat nrgy in n dirctin - rduc th siz th antnna systm - us th rlctr (and subrlctr) r bam shaping Cntnts 1. Intrductin. Crnr
1.2 Faraday s law A changing magnetic field induces an electric field. Their relation is given by:
 Elctromagntic Induction. Lorntz forc on moving charg Point charg moving at vlocity v, F qv B () For a sction of lctric currnt I in a thin wir dl is Idl, th forc is df Idl B () Elctromotiv forc f s any
Elctromagntic Induction. Lorntz forc on moving charg Point charg moving at vlocity v, F qv B () For a sction of lctric currnt I in a thin wir dl is Idl, th forc is df Idl B () Elctromotiv forc f s any
Mathematics. Complex Number rectangular form. Quadratic equation. Quadratic equation. Complex number Functions: sinusoids. Differentiation Integration
 Mathmatics Compl numbr Functions: sinusoids Sin function, cosin function Diffrntiation Intgration Quadratic quation Quadratic quations: a b c 0 Solution: b b 4ac a Eampl: 1 0 a= b=- c=1 4 1 1or 1 1 Quadratic
Mathmatics Compl numbr Functions: sinusoids Sin function, cosin function Diffrntiation Intgration Quadratic quation Quadratic quations: a b c 0 Solution: b b 4ac a Eampl: 1 0 a= b=- c=1 4 1 1or 1 1 Quadratic
Operating parameters for representative BWR and PWR designs are given below. For the PWR hot channel and the BWR average channel compute and plot:
 Opratin paramtrs r rprsntativ BWR an PWR sins ar ivn blw. Fr t PWR t cannl an t BWR avra cannl cmput an plt: 1) t vi an quality istributins ) Dtrmin t iniviual cmpnnts an t ttal prssur rp Cmpar t rsults
Opratin paramtrs r rprsntativ BWR an PWR sins ar ivn blw. Fr t PWR t cannl an t BWR avra cannl cmput an plt: 1) t vi an quality istributins ) Dtrmin t iniviual cmpnnts an t ttal prssur rp Cmpar t rsults
15. Stress-Strain behavior of soils
 15. Strss-Strain bhavior of soils Sand bhavior Usually shard undr draind conditions (rlativly high prmability mans xcss por prssurs ar not gnratd). Paramtrs govrning sand bhaviour is: Rlativ dnsity Effctiv
15. Strss-Strain bhavior of soils Sand bhavior Usually shard undr draind conditions (rlativly high prmability mans xcss por prssurs ar not gnratd). Paramtrs govrning sand bhaviour is: Rlativ dnsity Effctiv
Types of Communication
 Tps f Cmmunicatin Analg: cntinuus ariabls with nis {rrr 0} 0 (imprfct) Digital: dcisins, discrt chics, quantizd, nis {rrr} 0 (usuall prfct) Mssag S, S, r S M Mdulatr (t) channl; adds nis and distrtin M-ar
Tps f Cmmunicatin Analg: cntinuus ariabls with nis {rrr 0} 0 (imprfct) Digital: dcisins, discrt chics, quantizd, nis {rrr} 0 (usuall prfct) Mssag S, S, r S M Mdulatr (t) channl; adds nis and distrtin M-ar
... = ρi. Tmin. Tmax. 1. Time Lag 2. Decrement Factor 3. Relative humidity 4. Moisture content
 9//8 9//9 9/7/ 56-5 9 * - - midvar@sutch.ac.ir 7555- * -...... : «Rsarch Nt» Effct f mistur cntnt f building matrials n thrmal prfrmanc f xtrir building walls A. Omidvar *, B. Rsti - Assist. Prf., Mch.
9//8 9//9 9/7/ 56-5 9 * - - midvar@sutch.ac.ir 7555- * -...... : «Rsarch Nt» Effct f mistur cntnt f building matrials n thrmal prfrmanc f xtrir building walls A. Omidvar *, B. Rsti - Assist. Prf., Mch.
Elements of Statistical Thermodynamics
 24 Elmnts of Statistical Thrmodynamics Statistical thrmodynamics is a branch of knowldg that has its own postulats and tchniqus. W do not attmpt to giv hr vn an introduction to th fild. In this chaptr,
24 Elmnts of Statistical Thrmodynamics Statistical thrmodynamics is a branch of knowldg that has its own postulats and tchniqus. W do not attmpt to giv hr vn an introduction to th fild. In this chaptr,
COLLECTOR SELECTION FOR SOLAR EJECTOR COOLING SYSTEM
 Slar Enrgy Vl. 71, N. 4, pp. 69 74, 001 Prgamn P II: S0038 09X(01)0004 1 001 Publishd by Elsvir Scinc Ltd Printd in Grat Britain 0038-09X/01/$ - s frnt mattr www.lsvir.cm/ lcat/ slnr COLLECTOR SELECTION
Slar Enrgy Vl. 71, N. 4, pp. 69 74, 001 Prgamn P II: S0038 09X(01)0004 1 001 Publishd by Elsvir Scinc Ltd Printd in Grat Britain 0038-09X/01/$ - s frnt mattr www.lsvir.cm/ lcat/ slnr COLLECTOR SELECTION
The van der Waals interaction 1 D. E. Soper 2 University of Oregon 20 April 2012
 Th van dr Waals intraction D. E. Sopr 2 Univrsity of Orgon 20 pril 202 Th van dr Waals intraction is discussd in Chaptr 5 of J. J. Sakurai, Modrn Quantum Mchanics. Hr I tak a look at it in a littl mor
Th van dr Waals intraction D. E. Sopr 2 Univrsity of Orgon 20 pril 202 Th van dr Waals intraction is discussd in Chaptr 5 of J. J. Sakurai, Modrn Quantum Mchanics. Hr I tak a look at it in a littl mor
Performance Analysis of Rotor Tip Shapes in Hover Using Computational Fluid Dynamics
 Prfrmanc Analysis f Rtr Tip Shaps in Hvr Using Cmputatinal Fluid Dynamics by Alan Brcklhurst and Grg Baraks Prsntd at th Burn 7-8 April 26 INTRODUCTION Aims and Objctivs Validatin UH-6A Cmparisn with Mdl
Prfrmanc Analysis f Rtr Tip Shaps in Hvr Using Cmputatinal Fluid Dynamics by Alan Brcklhurst and Grg Baraks Prsntd at th Burn 7-8 April 26 INTRODUCTION Aims and Objctivs Validatin UH-6A Cmparisn with Mdl
Frequency Response. Lecture #12 Chapter 10. BME 310 Biomedical Computing - J.Schesser
 Frquncy Rspns Lcur # Chapr BME 3 Bimdical Cmpuing - J.Schssr 99 Idal Filrs W wan sudy Hω funcins which prvid frquncy slciviy such as: Lw Pass High Pass Band Pass Hwvr, w will lk a idal filring, ha is,
Frquncy Rspns Lcur # Chapr BME 3 Bimdical Cmpuing - J.Schssr 99 Idal Filrs W wan sudy Hω funcins which prvid frquncy slciviy such as: Lw Pass High Pass Band Pass Hwvr, w will lk a idal filring, ha is,
Lecture Outline. Skin Depth Power Flow 8/7/2018. EE 4347 Applied Electromagnetics. Topic 3e
 8/7/018 Cours Instructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Offic: A 337 Phon: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utp.du EE 4347 Applid Elctromagntics Topic 3 Skin Dpth & Powr Flow Skin Dpth Ths & Powr nots Flow may contain
8/7/018 Cours Instructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Offic: A 337 Phon: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utp.du EE 4347 Applid Elctromagntics Topic 3 Skin Dpth & Powr Flow Skin Dpth Ths & Powr nots Flow may contain
DIELECTRIC AND MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
 DILCTRIC AD MAGTIC PROPRTIS OF MATRIALS Dilctric Proprtis: Dilctric matrial Dilctric constant Polarization of dilctric matrials, Typs of Polarization (Polarizability). quation of intrnal filds in liquid
DILCTRIC AD MAGTIC PROPRTIS OF MATRIALS Dilctric Proprtis: Dilctric matrial Dilctric constant Polarization of dilctric matrials, Typs of Polarization (Polarizability). quation of intrnal filds in liquid
Division of Mechanics Lund University MULTIBODY DYNAMICS. Examination Name (write in block letters):.
 Division of Mchanics Lund Univrsity MULTIBODY DYNMICS Examination 7033 Nam (writ in block lttrs):. Id.-numbr: Writtn xamination with fiv tasks. Plas chck that all tasks ar includd. clan copy of th solutions
Division of Mchanics Lund Univrsity MULTIBODY DYNMICS Examination 7033 Nam (writ in block lttrs):. Id.-numbr: Writtn xamination with fiv tasks. Plas chck that all tasks ar includd. clan copy of th solutions
orbiting electron turns out to be wrong even though it Unfortunately, the classical visualization of the
 Lctur 22-1 Byond Bohr Modl Unfortunatly, th classical visualization of th orbiting lctron turns out to b wrong vn though it still givs us a simpl way to think of th atom. Quantum Mchanics is ndd to truly
Lctur 22-1 Byond Bohr Modl Unfortunatly, th classical visualization of th orbiting lctron turns out to b wrong vn though it still givs us a simpl way to think of th atom. Quantum Mchanics is ndd to truly
A Redshift Phenomenon in Relativistic Binary System
 J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Rs. 3(8)-7 03 03 TxtRad Pulicatin ISSN 090-4304 Jurnal f Basic and Applid Scintific Rsarch www.txtrad.cm A Rdshift Phnmnn in Rlativistic Binary Systm A.B.Mrcs 34 Dpartmnt f Astrnmy
J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Rs. 3(8)-7 03 03 TxtRad Pulicatin ISSN 090-4304 Jurnal f Basic and Applid Scintific Rsarch www.txtrad.cm A Rdshift Phnmnn in Rlativistic Binary Systm A.B.Mrcs 34 Dpartmnt f Astrnmy
COMPUTER GENERATED HOLOGRAMS Optical Sciences 627 W.J. Dallas (Monday, April 04, 2005, 8:35 AM) PART I: CHAPTER TWO COMB MATH.
 C:\Dallas\0_Courss\03A_OpSci_67\0 Cgh_Book\0_athmaticalPrliminaris\0_0 Combath.doc of 8 COPUTER GENERATED HOLOGRAS Optical Scincs 67 W.J. Dallas (onday, April 04, 005, 8:35 A) PART I: CHAPTER TWO COB ATH
C:\Dallas\0_Courss\03A_OpSci_67\0 Cgh_Book\0_athmaticalPrliminaris\0_0 Combath.doc of 8 COPUTER GENERATED HOLOGRAS Optical Scincs 67 W.J. Dallas (onday, April 04, 005, 8:35 A) PART I: CHAPTER TWO COB ATH
ELEG 413 Lecture #6. Mark Mirotznik, Ph.D. Professor The University of Delaware
 LG 43 Lctur #6 Mrk Mirtnik, Ph.D. Prfssr Th Univrsity f Dlwr mil: mirtni@c.udl.du Wv Prpgtin nd Plritin TM: Trnsvrs lctrmgntic Wvs A md is prticulr fild cnfigurtin. Fr givn lctrmgntic bundry vlu prblm,
LG 43 Lctur #6 Mrk Mirtnik, Ph.D. Prfssr Th Univrsity f Dlwr mil: mirtni@c.udl.du Wv Prpgtin nd Plritin TM: Trnsvrs lctrmgntic Wvs A md is prticulr fild cnfigurtin. Fr givn lctrmgntic bundry vlu prblm,
cycle that does not cross any edges (including its own), then it has at least
 W prov th following thorm: Thorm If a K n is drawn in th plan in such a way that it has a hamiltonian cycl that dos not cross any dgs (including its own, thn it has at last n ( 4 48 π + O(n crossings Th
W prov th following thorm: Thorm If a K n is drawn in th plan in such a way that it has a hamiltonian cycl that dos not cross any dgs (including its own, thn it has at last n ( 4 48 π + O(n crossings Th
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION
 MD DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION Sllabus : Ordinar diffrntial quations, thir ordr and dgr. Formation of diffrntial quations. Solution of diffrntial quations b th mthod of sparation of variabls, solution of homognous
MD DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION Sllabus : Ordinar diffrntial quations, thir ordr and dgr. Formation of diffrntial quations. Solution of diffrntial quations b th mthod of sparation of variabls, solution of homognous
High Energy Physics. Lecture 5 The Passage of Particles through Matter
 High Enrgy Physics Lctur 5 Th Passag of Particls through Mattr 1 Introduction In prvious lcturs w hav sn xampls of tracks lft by chargd particls in passing through mattr. Such tracks provid som of th most
High Enrgy Physics Lctur 5 Th Passag of Particls through Mattr 1 Introduction In prvious lcturs w hav sn xampls of tracks lft by chargd particls in passing through mattr. Such tracks provid som of th most
The failure of the classical mechanics
 h failur of th classical mchanics W rviw som xprimntal vidncs showing that svral concpts of classical mchanics cannot b applid. - h blac-body radiation. - Atomic and molcular spctra. - h particl-li charactr
h failur of th classical mchanics W rviw som xprimntal vidncs showing that svral concpts of classical mchanics cannot b applid. - h blac-body radiation. - Atomic and molcular spctra. - h particl-li charactr
Derivation of Electron-Electron Interaction Terms in the Multi-Electron Hamiltonian
 Drivation of Elctron-Elctron Intraction Trms in th Multi-Elctron Hamiltonian Erica Smith Octobr 1, 010 1 Introduction Th Hamiltonian for a multi-lctron atom with n lctrons is drivd by Itoh (1965) by accounting
Drivation of Elctron-Elctron Intraction Trms in th Multi-Elctron Hamiltonian Erica Smith Octobr 1, 010 1 Introduction Th Hamiltonian for a multi-lctron atom with n lctrons is drivd by Itoh (1965) by accounting
0WAVE PROPAGATION IN MATERIAL SPACE
 0WAVE PROPAGATION IN MATERIAL SPACE All forms of EM nrgy shar thr fundamntal charactristics: 1) thy all tral at high locity 2) In traling, thy assum th proprtis of was 3) Thy radiat outward from a sourc
0WAVE PROPAGATION IN MATERIAL SPACE All forms of EM nrgy shar thr fundamntal charactristics: 1) thy all tral at high locity 2) In traling, thy assum th proprtis of was 3) Thy radiat outward from a sourc
2. Laser physics - basics
 . Lasr physics - basics Spontanous and stimulatd procsss Einstin A and B cofficints Rat quation analysis Gain saturation What is a lasr? LASER: Light Amplification by Stimulatd Emission of Radiation "light"
. Lasr physics - basics Spontanous and stimulatd procsss Einstin A and B cofficints Rat quation analysis Gain saturation What is a lasr? LASER: Light Amplification by Stimulatd Emission of Radiation "light"
Module 8 Non equilibrium Thermodynamics
 Modul 8 Non quilibrium hrmodynamics ctur 8.1 Basic Postulats NON-EQUIIRIBIUM HERMODYNAMICS Stady Stat procsss. (Stationary) Concpt of ocal thrmodynamic qlbm Extnsiv proprty Hat conducting bar dfin proprtis
Modul 8 Non quilibrium hrmodynamics ctur 8.1 Basic Postulats NON-EQUIIRIBIUM HERMODYNAMICS Stady Stat procsss. (Stationary) Concpt of ocal thrmodynamic qlbm Extnsiv proprty Hat conducting bar dfin proprtis
Square shaped flat-top beam in refractive beam shapers
 Squar shapd flat-tp bam in rfractiv bam shaprs Alxandr Laskin a, Vadim Laskin a, Alksi Ostrun b a AdlOptica GmbH, Rudwr Chauss 29, 12489 Brlin, Grmany b St. Ptrsburg Natinal Rsarch Univrsity f Infrmatin
Squar shapd flat-tp bam in rfractiv bam shaprs Alxandr Laskin a, Vadim Laskin a, Alksi Ostrun b a AdlOptica GmbH, Rudwr Chauss 29, 12489 Brlin, Grmany b St. Ptrsburg Natinal Rsarch Univrsity f Infrmatin
Unit 2 Part 2 Particles, Bonding and Structure Interatomic and Intermolecular Bonding UNIT 2 PARTICLES, BONDING AND STRUCTURE
 Unit 2 Part 2 Particls, nding and Structur Intratmic and Intrmlcular nding UNIT 2 PARTICLES, NDING AND STRUCTURE PART 2 INTERATMIC AND INTERMLECULAR NDING Cntnts 1. Inic nding 2. Cvalnt nding 3. Mtallic
Unit 2 Part 2 Particls, nding and Structur Intratmic and Intrmlcular nding UNIT 2 PARTICLES, NDING AND STRUCTURE PART 2 INTERATMIC AND INTERMLECULAR NDING Cntnts 1. Inic nding 2. Cvalnt nding 3. Mtallic
GEOMETRICAL PHENOMENA IN THE PHYSICS OF SUBATOMIC PARTICLES. Eduard N. Klenov* Rostov-on-Don, Russia
 GEOMETRICAL PHENOMENA IN THE PHYSICS OF SUBATOMIC PARTICLES Eduard N. Klnov* Rostov-on-Don, Russia Th articl considrs phnomnal gomtry figurs bing th carrirs of valu spctra for th pairs of th rmaining additiv
GEOMETRICAL PHENOMENA IN THE PHYSICS OF SUBATOMIC PARTICLES Eduard N. Klnov* Rostov-on-Don, Russia Th articl considrs phnomnal gomtry figurs bing th carrirs of valu spctra for th pairs of th rmaining additiv
section 1 Influencing Change Toolkit How to: Influence People
 Influncing Chang Tlkit Hw t: Influnc Ppl Influncing ppl mans having an ffct n thm, changing r mdifying thir viw. In rdr t influnc chang, w nd t influnc th ppl wh ar in a psitin t mak that chang happn.
Influncing Chang Tlkit Hw t: Influnc Ppl Influncing ppl mans having an ffct n thm, changing r mdifying thir viw. In rdr t influnc chang, w nd t influnc th ppl wh ar in a psitin t mak that chang happn.
Answer Homework 5 PHA5127 Fall 1999 Jeff Stark
 Answr omwork 5 PA527 Fall 999 Jff Stark A patint is bing tratd with Drug X in a clinical stting. Upon admiion, an IV bolus dos of 000mg was givn which yildd an initial concntration of 5.56 µg/ml. A fw
Answr omwork 5 PA527 Fall 999 Jff Stark A patint is bing tratd with Drug X in a clinical stting. Upon admiion, an IV bolus dos of 000mg was givn which yildd an initial concntration of 5.56 µg/ml. A fw
CO-ORDINATION OF FAST NUMERICAL RELAYS AND CURRENT TRANSFORMERS OVERDIMENSIONING FACTORS AND INFLUENCING PARAMETERS
 CO-ORDINATION OF FAST NUMERICAL RELAYS AND CURRENT TRANSFORMERS OVERDIMENSIONING FACTORS AND INFLUENCING PARAMETERS Stig Holst ABB Automation Products Swdn Bapuji S Palki ABB Utilitis India This papr rports
CO-ORDINATION OF FAST NUMERICAL RELAYS AND CURRENT TRANSFORMERS OVERDIMENSIONING FACTORS AND INFLUENCING PARAMETERS Stig Holst ABB Automation Products Swdn Bapuji S Palki ABB Utilitis India This papr rports
General Notes About 2007 AP Physics Scoring Guidelines
 AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Gnral Nots About 2007 AP Physics Scoring Guidlins 1. Th solutions contain th most common mthod of solving th fr-rspons qustions and th allocation
AP PHYSICS C: ELECTRICITY AND MAGNETISM 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Gnral Nots About 2007 AP Physics Scoring Guidlins 1. Th solutions contain th most common mthod of solving th fr-rspons qustions and th allocation
Chapter 2 GAUSS LAW Recommended Problems:
 Chapter GAUSS LAW Recmmended Prblems: 1,4,5,6,7,9,11,13,15,18,19,1,7,9,31,35,37,39,41,43,45,47,49,51,55,57,61,6,69. LCTRIC FLUX lectric flux is a measure f the number f electric filed lines penetrating
Chapter GAUSS LAW Recmmended Prblems: 1,4,5,6,7,9,11,13,15,18,19,1,7,9,31,35,37,39,41,43,45,47,49,51,55,57,61,6,69. LCTRIC FLUX lectric flux is a measure f the number f electric filed lines penetrating
Sundials and Linear Algebra
 Sundials and Linar Algbra M. Scot Swan July 2, 25 Most txts on crating sundials ar dirctd towards thos who ar solly intrstd in making and using sundials and usually assums minimal mathmatical background.
Sundials and Linar Algbra M. Scot Swan July 2, 25 Most txts on crating sundials ar dirctd towards thos who ar solly intrstd in making and using sundials and usually assums minimal mathmatical background.
Solution: APPM 1360 Final (150 pts) Spring (60 pts total) The following parts are not related, justify your answers:
 APPM 6 Final 5 pts) Spring 4. 6 pts total) Th following parts ar not rlatd, justify your answrs: a) Considr th curv rprsntd by th paramtric quations, t and y t + for t. i) 6 pts) Writ down th corrsponding
APPM 6 Final 5 pts) Spring 4. 6 pts total) Th following parts ar not rlatd, justify your answrs: a) Considr th curv rprsntd by th paramtric quations, t and y t + for t. i) 6 pts) Writ down th corrsponding
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics. Thermodynamics & Statistical Mechanics Qualifying Examination
 Univrsity of Illinois at Chicago Dpartmnt of hysics hrmodynamics & tatistical Mchanics Qualifying Eamination January 9, 009 9.00 am 1:00 pm Full crdit can b achivd from compltly corrct answrs to 4 qustions.
Univrsity of Illinois at Chicago Dpartmnt of hysics hrmodynamics & tatistical Mchanics Qualifying Eamination January 9, 009 9.00 am 1:00 pm Full crdit can b achivd from compltly corrct answrs to 4 qustions.
Ch. 24 Molecular Reaction Dynamics 1. Collision Theory
 Ch. 4 Molcular Raction Dynamics 1. Collision Thory Lctur 16. Diffusion-Controlld Raction 3. Th Matrial Balanc Equation 4. Transition Stat Thory: Th Eyring Equation 5. Transition Stat Thory: Thrmodynamic
Ch. 4 Molcular Raction Dynamics 1. Collision Thory Lctur 16. Diffusion-Controlld Raction 3. Th Matrial Balanc Equation 4. Transition Stat Thory: Th Eyring Equation 5. Transition Stat Thory: Thrmodynamic
NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y. C o m m o n P r a c t i c e T e s t 1 6 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Date: PHYSIS HEMISTRY MTHEMTIS
![NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y. C o m m o n P r a c t i c e T e s t 1 6 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Date: PHYSIS HEMISTRY MTHEMTIS NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y. C o m m o n P r a c t i c e T e s t 1 6 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Date: PHYSIS HEMISTRY MTHEMTIS](/thumbs/79/79886930.jpg) . (D). (A). (D). (D) 5. (B) 6. (A) 7. (A) 8. (A) 9. (B). (A). (D). (B). (B). (C) 5. (D) NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y C o m m o n P r a c t i c T s t 6 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Dat: 8.8.6 ANSWER PHYSIS
. (D). (A). (D). (D) 5. (B) 6. (A) 7. (A) 8. (A) 9. (B). (A). (D). (B). (B). (C) 5. (D) NARAYANA I I T / P M T A C A D E M Y C o m m o n P r a c t i c T s t 6 XII STD BATCHES [CF] Dat: 8.8.6 ANSWER PHYSIS
Electromagnetism Physics 15b
 lctromagntism Physics 15b Lctur #8 lctric Currnts Purcll 4.1 4.3 Today s Goals Dfin lctric currnt I Rat of lctric charg flow Also dfin lctric currnt dnsity J Charg consrvation in a formula Ohm s Law vryon
lctromagntism Physics 15b Lctur #8 lctric Currnts Purcll 4.1 4.3 Today s Goals Dfin lctric currnt I Rat of lctric charg flow Also dfin lctric currnt dnsity J Charg consrvation in a formula Ohm s Law vryon
