Synthesis of Magnetic Nanoparticles Coated with Covalently Bonded Carboxymethyl Cellulose
|
|
|
- Anthony Hunt
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of ChemTech Research CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: , ISSN(Online): Vol.9, No.05 pp , 2016 Synthesis of Magnetic Nanoparticles Coated with Covalently Bonded Carboxymethyl Cellulose Herrera A*, Vela L, Morales G Multifunctional Nanomaterials Research Group. Chemical Engineering Program.Faculty of Engineering.Universidad de Cartagena, Campus Piedra de Bolivar. Street 30 # Office D-307. Cartagena, Colombia.Tel (575) ext. 214 Abstract : Magnetite nanoparticles (MNP) were synthesized through the coprecipitation method and then modified with carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) by using carbodiimide chemistry. These nanoparticles exhibited a crystal size of 30 ± 20 nm and a magnetization saturation of 48 emu/g. FTIR was used to determine the grafting of the CMC molecules, observing a peak at 1507 cm -1, which suggest the covalent bond of this hydrophilic polymer onto the magnetic nanoparticles. These nanoparticles exhibited a hydrodynamic size of about 173± 53 nm after suspension in distilled water, as estimated from DLS.Additionally from TGA, a 16% of organic material was estimated to be grafted onto the nanoparticles, indicating the possibility of a crosslink between a CMC molecule and several nanoparticles, as CMC has about 388 COO - groups per chain.this crosslink can yieldagglomerated nanoparticles, as observed from SEM measurements. Despite agglomeration, modification of magnetic nanoparticles with CMC rendshigh hydrophilic nanoparticles that can be suspended in aqueous media forming a stable colloidal solution. Keywords : Magnetite nanoparticles, carboxymethylcellulose, Carbodiimide chemistry. Introduction Magnetite (Fe 3 O 4 ) nanoparticles belong to the group of nanomaterials that have received great acceptance within the scientific community due to their magnetic properties and their nano-scale size features. These properties make them highly attractive for a wide variety of applications, such as water treatment, biotechnology, ferrofluids, and biomedical applications, especially as agents for MRI and targeted drug delivery 1-5.For these applications, it is important to modify the magnetic nanoparticles with functional molecules that allow their suspension in aqueous or organic media 4-6. Among these materials, natural polymers, such as polysaccharides are considered the most popular ones due to the fact that they have a low cost, they are safe and biocompatible 7-9. Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) is a versatile natural polysaccharide that could be used for the modification of magnetite nanoparticles, because their functional carboxylate anions can be physically adsorbed onto the iron atoms present in the magnetic nanoparticles 7.This methodology has the disadvantage that nanoparticles can be desorbed from the polymer matrix by changing the ph of the suspension media. This research is focused on the synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles coated with covalently bonded CMC molecules. In this methodology, magnetite nanoparticles were first synthesized through the coprecipitation method, and then they were encapsulated on a polysiloxane matrix by condensation of
2 Herrera A et al /International Journal of ChemTech Research, 2016,9(5),pp aminopropyl silane molecules (APS).Afterwards, CMC molecules could be attached to the magnetic nanoparticles by linking the carboxylate anions present in the CMC molecule and the amine groups previously grafted around the nanoparticle s surface.this covalent bond is achieved by using carbodiimide chemistry in an acid aqueous media.the physical-chemical properties of the synthesized nanoparticles were characterized by different techniques, such as FTIR, TGA, dynamic light scattering, and scanning electron microscopy. Modification of magnetic nanoparticles with CMC rends high hydrophilic nanoparticles that can be suspended in aqueous media forming a stable colloidal suspension. Methodology Materials All chemical reagents were used as supplied.iron (II) chloride 99%, iron (III) chloride 97%, (3- aminopropyl)triethoxysilane (APS) 98%, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) 90 kda, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) 99%, and ammonium hydroxide 29%v/v were acquired from Alfa Aesar.1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethyl aminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC)and N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) 98%were purchased from Sigma Aldrich. Preparationof magnetic nanoparticles decorated with functional amine groups Magnetite nanoparticles were synthetized by the co-precipitation method 3. In a typical procedure, 30 ml of a ferric solution (0.36 M) was mixed with 30 ml of a ferroussolution (0.18 M). This mixture was stirred at 100 rpm and heated up to 70 C. Then, 9 ml of NH 4 OH were added, which produced a black coloration, indicative of magnetite formation. Synthesis was carried out at ph 8.0 for one hour at 80 C. Afterwards, nanoparticles were decanted using a magnet, washed four times with distilled water and dried at 80 C. Magnetic nanoparticles (1.5 g) were peptized with nitric acid (2 M)and then suspended in 80 ml of DMSO. To graft the amine (NH 2 ) groups onto the magnetic nanoparticle surface, 5 ml of APS, 1.25 ml of deionized water and 0.1 ml of acetic acid were added to the magnetic nanoparticle suspension 9.Reaction was carried out at room temperature using a shaker at 125 rpm for 3 days. It has been reported that long agitation times ensure the hydrolysis/condensation mechanism of the APS molecules, allowing the encapsulation of the magnetic nanoparticles in a siloxane (Si-O) matrix, which exhibits functional amine groups 9.Afterwards, functionalized nanoparticles were removed from magnetic decantation, washed twice with ethanol, and dried at room temperature. Finally, magnetic-aps nanoparticles (0.1 g) were suspended in 10 ml of deionized water at ph 4.0 using an ultrasonic bath for 15 minutes. This colloidal suspension was stored at 4 C for further modification with CMC molecules. Modification of magnetic-aps nanoparticles with covalently bonded CMC Commercial CMC was acquired with a degree of substitution DS of 0.7 carboxymethyl groups per anhydroglucose unit. Number of carboxylate anions(coo - ) present per CMC chain can be estimated by (10): where, M w-cmc is the molecular weight of the CMC (90,000 g/mol) and M w-agu is the molecular weight of an anhydroglucose unit (162 g/mol).from this relationship, a number of ~388 COO - /CMC chain were estimated. These carboxylate anionscan be used to covalently attach the CMC molecules onto the magnetic nanoparticles through a link with the amine groups (NH 2 ) previously grafted around the nanoparticle surface 11. To this end, 0.1 g of CMC was suspended in 7.5 ml of deionized water at ph 5.0. Then, 12.5 mg of EDC and 7.5 mg of NHS were added. The activated carboxylic solution was subsequently mixed with the aqueous suspension of magnetic-aps nanoparticles prepared at 4 C.This reaction mixture was shaken at 125 rpm for 2 days at room temperature. Afterwards, modified magnetite-aps-cmc nanoparticles were separated by magnetic decantation, washed twice with ethanol, and dried at room temperature.
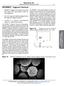
3 Herrera A et al /International Journal of ChemTech Research, 2016,9(5),pp Characterization Size and crystalline structure were characterized through X-ray diffraction using an X Pert PRO equipped with a PW3050/60 goniometer. Magnetic properties were determined from a Vibration Sample Magnetometer VSM-7400.An FTIR NICOLET 6700 was used to determine the functional groups grafted around the nanoparticles. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was performed to determine the amount of CMC attached onto the nanoparticle s surface.this measurement was performed using the TGA Q500 V20.8 Build 43 equipment under air with a heating rate of 20 C/min. The hydrodynamic diameter of the CMC coated magnetic nanoparticles was determined by dynamic light scattering DLS using the HORIBA LB-550 equipment. Additionally, images of the functionalized nanoparticles were recorded by scanning electron microscope SEM using the JEOL JSM-6490LV equipment coupled to an energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). Results and discussion Crystal size and magnetic properties Figure 1.ashows the diffraction pattern obtained for the synthesized magnetite nanoparticles, which exhibited an inverse cubic spline crystalline structure in accordance with the information reported in literature 11, 12. An average crystal size of 30 ± 20 nm was determined from the Scherrer s equation 12 : Where D represents the crystal size,k is a constant (0.9), lis the X-ray wavelength (0.154 nm), bis the full width at the half maximum intensity, and is the Bragg angle. Magnetic properties were determined by measuring the magnetization of the sample M as a function of the applied magnetic field H 12. Figure 1.b displays this measurement, from which a magnetization saturation M s of 48 emu/g was established. This valueis in agreement with the one reported for magnetite nanoparticles (46.7 emu/g) 12. The magnetic core size was determined from the Langevin function and the magnetic response of the nanoparticles at low and high magnetic fields 9.From this analysis, a magnetic core size of 4.0 ± 1.0 nm was estimated for the synthesized magnetite nanoparticles. Figure 1. X-ray diffraction pattern (a) and magnetization response (b) displayed for magnetite nanoparticles synthesized from the co-precipitation method. Modification with CMC molecules Figure 2.a shows the FTIR spectra recorded for magnetite nanoparticles coated with APS and modified with CMC molecules. From these measurements, vibrations peaks were observed at 2900, 1645, and 1100 cm -1, for the sample of magnetite-aps nanoparticles, which correspond to the functional groups CH 2, NH 2, and Si-O- Si, present in the chemical structure of the APS molecule 11.In the case of magnetite-cmc nanoparticles the
4 Herrera A et al /International Journal of ChemTech Research, 2016,9(5),pp presence of peaks at 3600 cm -1 and 1700 cm -1 was observed. These peaks are related to the vibrations of the functional groups OH and C=O, respectively, which form part of the hydrophilic CMC polymer. Additionally, a peak at 1507 cm -1 was observed for the magnetite-cmc nanoparticles, suggesting the covalent bond between carboxylates and amines after activation with the carbodiimide agent EDC in presence of NHS 11. Figure 2. (a) FTIR spectra for magnetite nanoparticles coated with APS and CMC molecules; and(b) TGA analysis for magnetite nanoparticles after modification with CMC. A TGA analysis was performed to determine the organic content of the hydrophilic polymer attached onto the magnetite nanoparticles. Figure 2.b displays this measurement, in which three significant weight loss stages can be observed. The first one occurs at 50 C, and corresponds to the loss of humidity contained in the sample (4%). The other weight loss stages were observed at 261 C and 300 C, which can be attributed mainly to the decomposition of CMC molecules (M w-cmc 90,000 g/mol), as the APS is a very small organic molecule (M w-aps 221 g/mol).this weight loss corresponds to a 16% of the initial sample weight. Therefore, it is inferred that the remaining 80% can be associated to the weight of the inorganic iron oxide material present in the magnetite nanoparticles. Hydrodynamic size and size distribution The hydrodynamic size distribution of the magnetite nanoparticles coated with carboxymethylcellulose was determined by dynamic light scattering (DLS).For this measurement a sample of the MNP-CMC nanoparticles was suspended in distilled water at room temperature. Figure 3 shows this result, from which it was possible to calculate an average hydrodynamic diameter of 173 ± 53 nm by: where D is the particle size obtained from the multimodal size distribution (MSD) function of the instrument,g d is the relative intensity showed in the histogram, and sis the standard deviation of the data 11. Figure 3. DLS measurement for magnetite-cmc nanoparticles suspended in distilled water. The wide size distribution observed from DLS can be attributed to the fact that magnetite nanoparticles were synthesized by means of the co-precipitation method, which has been reported to produce small
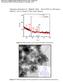
5 Herrera A et al /International Journal of ChemTech Research, 2016,9(5),pp agglomerates instead of monodisperse nanoparticles 9.This feature, along with the few amount of CMC that was found to be grafted onto the surface of the nanoparticles (16% according to TGA), can be explained by two proposed case scenarios: (i) a single chain of CMC was grafted around a cluster of agglomerated nanoparticles by linking its carboxylate anions (COO - ) to the previously condensed amine (NH 2 )groups present in the magnetite-aps nanoparticles; or (ii) CMC moleculescan form a crosslink between clusters of magnetite nanoparticles, by connecting them through their amine groups, building a much bigger structure, as an amount of approximately 388 carboxylic groups per CMC chain was estimated. Figure 4 illustrates both possible scenarios. Figure 4. Possible spatial configuration of a CMC chain around magnetic nanoparticles.(a) A single CMC chain surrounding a cluster of MNPs; and (b) Crosslink of CMC and clusters of MNPs. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to obtain images of the magnetite nanoparticles after modification with CMC molecules. Figure 5 shows these photographs, and there agglomeration of the magnetite nanoparticles coated with the CMC can be observed, as previously hypothesized. In addition, EDS spectroscopy indicated an elemental composition for magnetite-cmc nanoparticles of about 15.4% of carbon, 39.4% of oxygen, 1.3% of silicon, and 43.9% of iron. This suggests a low content of CMC molecules as compared with the magnetite nanoparticles. This result is in agreement with the results obtained from TGA measurements, which showed an inorganic content of about 80% related to the iron oxide material present in the magnetite nanoparticles. Moreover, it endorses the possible second scenario proposed to explain the spatial configuration of the CMC molecules forming a crosslink with several clusters of magnetite nanoparticles. Figure 5. SEM images of magnetic nanoparticles coated with covalently bonded CMC.(a) magnification at X20,000; and (b) magnification at X50,000 Conclusions An easy and economical method to obtain magnetite nanoparticles modified with covalently bonded CMC was presented. This hydrophilic polymer allows the suspension of magnetic nanoparticles in aqueous media, rendering high stable colloidal solutions. In addition, CMC is a natural polymer that exhibits a high density of carboxylate ions per chain. These functional groups could be used for further modifications to graft other molecules of interest, such as proteins or antibodies. From this point, it could be possible to design a smart platform for different applications, such as biomedicine, sensors, and magnetic actuators.
6 Herrera A et al /International Journal of ChemTech Research, 2016,9(5),pp Acknowledgments We would like to thank the Chemical Engineering Program of the University of Cartagena for allowing the use of the Materials Science Lab for the synthesis, modification, and characterization of the magnetite-cmc nanoparticles. References 1. Tang S. and Lo I., Magnetic nanoparticles: Essential factors for sustainable environmental applications, Water Res.,2013, 47, Mohanpuria P., Rana N., Yadav S., Biosynthesis of nanoparticles: technological concepts and future applications, J. Nanopart. Res.,2008, 10, Correa J., Bordallo E., Canetti D., León V., Otero-Díaz L., Negro C., Gómez A., Sáez-Puche R., Structure and superparamagnetic behaviour of magnetite nanoparticles in cellulose beads, Mater. Res. Bull.,2010, 45, Tóth I., Illés E., Szekeres M., Tombácz E., Preparation and characterization of chondroitin-sulfate-a-coated magnetite nanoparticles for biomedical applications, J. Magn. Magn. Mater.,2015, 380, Illés E., Tombácz E., Szekeres M., Tóth I., Szabó Á., Iván B., Novel carboxylated PEG-coating on magnetite nanoparticles designed for biomedical applications, J. Magn. Magn. Mater.,2015, 380, Maccarini M., Atrei A., Innocenti C., Barbucci R., Interactions at the CMC/magnetite interface: Implications for the stability of aqueous dispersions and the magnetic properties of magnetite nanoparticles, Colloid.Surface. A., 2014, 462, Habibi N., Preparation of biocompatible magnetite-carboxymethyl cellulose nanocomposite: Characterization of nanocomposite by FTIR, XRD, FESEM and TEM, Spectrochim. Acta A., 2014, 131, Butun S., Ince F., Erdugah H., Sahiner N., One-step fabrication of biocompatible carboxymethyl cellulose polymeric particles for drug delivery systems, Carbohyd. Polym.,2011, 86, Herrera A., Barrera C., Rinaldi C., Synthesis and functionalization of magnetite nanoparticles with aminopropylsilane and carboxymethyldextran. J. Mater. Chem.,2008, 18, Bono A., Ying P., Yan F., Muei C., Sarbatly R., Krishnaiah D., Synthesis and Characterization of Carboxymethyl Cellulose from Palm Kernel Cake, Adv. Nat. Appl. Sci.,2009, 3, Barrera C., Herrera A., Zayas Y., Rinaldi C., Surface modification of magnetite nanoparticles for biomedical applications, J. Magn. Magn. Mater.,2009, 321, Ghandoor H., Zidan H., Khalil M., Ismail M., Synthesis and Some Physical Properties of Magnetite (Fe 3 O 4 ) Nanoparticles, Intern. J. Electr. Sci.,2012, 7, *****
MAGNETIC NANOPARTICLES FOR HYPERTHERMIA APPLICATIONS. Mohamed DARWISH and Ivan STIBOR
 MAGNETIC NANOPARTICLES FOR HYPERTHERMIA APPLICATIONS Mohamed DARWISH and Ivan STIBOR Institute for Nanomaterials, Advanced Technology and Innovation, Technical University of Liberec, 461 17Liberec, Czech
MAGNETIC NANOPARTICLES FOR HYPERTHERMIA APPLICATIONS Mohamed DARWISH and Ivan STIBOR Institute for Nanomaterials, Advanced Technology and Innovation, Technical University of Liberec, 461 17Liberec, Czech
Preparation of Fe 3 O 2 Nanostructures via Inverse Micelle Method and Study of Their Magnetic Properties for Biological Applications
 International Journal of Bio-Inorganic Hybrid Nanomaterials Preparation of Fe 3 O 4 @SiO 2 Nanostructures via Inverse Micelle Method and Study of Their Magnetic Properties for Biological Applications Afsaneh
International Journal of Bio-Inorganic Hybrid Nanomaterials Preparation of Fe 3 O 4 @SiO 2 Nanostructures via Inverse Micelle Method and Study of Their Magnetic Properties for Biological Applications Afsaneh
(APTES), 3- mercaptopropyltrimethoxysilane (MPTMS), tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS), N,Ndimethylformamide
 SUPPRTING INFRMATIN Materials: Iron (II) chloride hydrate ( FeCl 2,4H 2, 99%) was purchased from Alfa Aesar ( Ward Hill, MA). Iron (III) chloride hexahydrate ( FeCl 3,6H 2, 97%), (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane
SUPPRTING INFRMATIN Materials: Iron (II) chloride hydrate ( FeCl 2,4H 2, 99%) was purchased from Alfa Aesar ( Ward Hill, MA). Iron (III) chloride hexahydrate ( FeCl 3,6H 2, 97%), (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane
Available online at ScienceDirect. Procedia Materials Science 11 (2015 )
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Materials Science 11 (2015 ) 282 286 5th International Biennial Conference on Ultrafine Grained and Nanostructured Materials, UFGNSM15 Prepartion
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Materials Science 11 (2015 ) 282 286 5th International Biennial Conference on Ultrafine Grained and Nanostructured Materials, UFGNSM15 Prepartion
Magnetically-driven selective synthesis of Au clusters on Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications Magnetically-driven selective synthesis of Au clusters on Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles Víctor Sebastian, M. Pilar Calatayud, Gerardo F. Goya
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications Magnetically-driven selective synthesis of Au clusters on Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles Víctor Sebastian, M. Pilar Calatayud, Gerardo F. Goya
ANTIBIOTIC COATED MAGNETITE NANOPARTICLES FOR BIOLOGICAL APPLICATIONS
 ANTIBIOTIC COATED MAGNETITE NANOPARTICLES FOR BIOLOGICAL APPLICATIONS E.L. Foca-nici Ciurlica a, C. Nadejde a, D.E. Creanga a, A. Carlescu a and V. Badescu b a Faculty of Physics, Alexandru Ioan Cuza University
ANTIBIOTIC COATED MAGNETITE NANOPARTICLES FOR BIOLOGICAL APPLICATIONS E.L. Foca-nici Ciurlica a, C. Nadejde a, D.E. Creanga a, A. Carlescu a and V. Badescu b a Faculty of Physics, Alexandru Ioan Cuza University
Adsorption of Amino Acids, Aspartic Acid and Lysine onto Iron-Oxide Nanoparticles
 Supporting Information Adsorption of Amino Acids, Aspartic Acid and Lysine onto Iron-Oxide Nanoparticles Klementina Pušnik, Mojca Peterlin, Irena Kralj Cigić, Gregor Marolt, Ksenija Kogej, Alenka Mertelj,
Supporting Information Adsorption of Amino Acids, Aspartic Acid and Lysine onto Iron-Oxide Nanoparticles Klementina Pušnik, Mojca Peterlin, Irena Kralj Cigić, Gregor Marolt, Ksenija Kogej, Alenka Mertelj,
Fabrication and characterization of poly (ethylene oxide) templated nickel oxide nanofibers for dye degradation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Environmental Science: Nano. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Fabrication and characterization of poly (ethylene
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Environmental Science: Nano. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supplementary Information Fabrication and characterization of poly (ethylene
SCIENTIFIC REPORT. regarding the implementation of the project between May December 2014
 SCIENTIFIC REPORT regarding the implementation of the project between May 2013 - December 2014 Title of the project: DETECTION AND IDENTIFICATION OF BIOMOLECULES OF MEDICAL INTEREST BY USING MAGNETIC AND
SCIENTIFIC REPORT regarding the implementation of the project between May 2013 - December 2014 Title of the project: DETECTION AND IDENTIFICATION OF BIOMOLECULES OF MEDICAL INTEREST BY USING MAGNETIC AND
Supporting Information. for. Advanced Materials, adma Wiley-VCH 2006
 Supporting Information for Advanced Materials, adma.200601546 Wiley-VCH 2006 69451 Weinheim, Germany Supporting Information Synthesis of Magnetic Microspheres with Immobilized Metal Ions for Enrichment
Supporting Information for Advanced Materials, adma.200601546 Wiley-VCH 2006 69451 Weinheim, Germany Supporting Information Synthesis of Magnetic Microspheres with Immobilized Metal Ions for Enrichment
Facile synthesis of yolk-shell structured Si-C nanocomposites as anode for lithium-ion battery 1. Experimental 1.1 Chemicals
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Facile synthesis of yolk-shell structured Si-C nanocomposites as anode for lithium-ion battery
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Facile synthesis of yolk-shell structured Si-C nanocomposites as anode for lithium-ion battery
Synthesis of 12 nm iron oxide nanoparticles
 Electronic Supporting Information for Dendronized iron oxide nanoparticles as contrast agent for MRI Brice Basly, a Delphine Felder-Flesch,* a Pascal Perriat, b Claire Billotey, c Jacqueline Taleb, c Geneviève
Electronic Supporting Information for Dendronized iron oxide nanoparticles as contrast agent for MRI Brice Basly, a Delphine Felder-Flesch,* a Pascal Perriat, b Claire Billotey, c Jacqueline Taleb, c Geneviève
Chapter 6 Magnetic nanoparticles
 Chapter 6 Magnetic nanoparticles Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) are a class of nanoparticle which can be manipulated using magnetic field gradients. Such particles commonly consist of magnetic elements
Chapter 6 Magnetic nanoparticles Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) are a class of nanoparticle which can be manipulated using magnetic field gradients. Such particles commonly consist of magnetic elements
Growth of silver nanocrystals on graphene by simultaneous reduction of graphene oxide and silver ions with a rapid and efficient one-step approach
 Growth of silver nanocrystals on graphene by simultaneous reduction of graphene oxide and silver ions with a rapid and efficient one-step approach Xiu-Zhi Tang, a Zongwei Cao, b Hao-Bin Zhang, a Jing Liu
Growth of silver nanocrystals on graphene by simultaneous reduction of graphene oxide and silver ions with a rapid and efficient one-step approach Xiu-Zhi Tang, a Zongwei Cao, b Hao-Bin Zhang, a Jing Liu
Supplementary Information. Seeding Approach to Noble Metal Decorated Conducting Polymer Nanofiber Network
 Supplementary Information Seeding Approach to Noble Metal Decorated Conducting Polymer Nanofiber Network Zhen Liu, Selcuk Poyraz, Yang Liu, Xinyu Zhang* Department of Polymer and Fiber Engineering, Auburn
Supplementary Information Seeding Approach to Noble Metal Decorated Conducting Polymer Nanofiber Network Zhen Liu, Selcuk Poyraz, Yang Liu, Xinyu Zhang* Department of Polymer and Fiber Engineering, Auburn
Research Article Synthesis and Characterization of Magnetic Nanosized Fe 3 O 4 /MnO 2 Composite Particles
 Nanomaterials Volume 29, rticle ID 34217, 5 pages doi:1.1155/29/34217 Research rticle Synthesis and Characterization of Magnetic Nanosized /MnO 2 Composite Particles Zhang Shu and Shulin Wang Department
Nanomaterials Volume 29, rticle ID 34217, 5 pages doi:1.1155/29/34217 Research rticle Synthesis and Characterization of Magnetic Nanosized /MnO 2 Composite Particles Zhang Shu and Shulin Wang Department
STRUCTURE AND MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF SiO 2 COATED Fe 2 NANOPARTICLES SYNTHESIZED BY CHEMICAL VAPOR CONDENSATION PROCESS
 Rev.Adv.Mater.Sci. Structure and magnetic 4 (2003) properties 55-59 of coated 55 STRUCTURE AND MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF COATED NANOPARTICLES SYNTHESIZED BY CHEMICAL VAPOR CONDENSATION PROCESS Ji-Hun Yu,
Rev.Adv.Mater.Sci. Structure and magnetic 4 (2003) properties 55-59 of coated 55 STRUCTURE AND MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF COATED NANOPARTICLES SYNTHESIZED BY CHEMICAL VAPOR CONDENSATION PROCESS Ji-Hun Yu,
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 3, March-2014 ISSN
 156 Copper Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis Characterization Y.Suresh*1, S.Annapurna*2, G.Bhikshamaiah*3, A.K.Singh#4 Abstract Present work describes the synthesis nanoparticles using papaya extract as a
156 Copper Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis Characterization Y.Suresh*1, S.Annapurna*2, G.Bhikshamaiah*3, A.K.Singh#4 Abstract Present work describes the synthesis nanoparticles using papaya extract as a
Encapsulation of enzyme in metal ion-surfactant nanocomposites for
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting information for Encapsulation of enzyme in metal ion-surfactant nanocomposites for catalysis
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting information for Encapsulation of enzyme in metal ion-surfactant nanocomposites for catalysis
Rapid, Efficient Phase Pure Synthesis of Ca 2 AlNO 3 Layered Double Hydroxide
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Rapid, Efficient Phase Pure Synthesis of Ca 2 AlNO
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Rapid, Efficient Phase Pure Synthesis of Ca 2 AlNO
O-Allylation of phenols with allylic acetates in aqueous medium using a magnetically separable catalytic system
 Supporting information for -Allylation of phenols with allylic acetates in aqueous medium using a magnetically separable catalytic system Amit Saha, John Leazer* and Rajender S. Varma* Sustainable Technology
Supporting information for -Allylation of phenols with allylic acetates in aqueous medium using a magnetically separable catalytic system Amit Saha, John Leazer* and Rajender S. Varma* Sustainable Technology
Formation and Surface Modification of Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles by Co-precipitation and Sol-gel Method
 J. Ind. Eng. Chem., Vol. 13, No. 7, (2007) 1137-1141 Formation and Surface Modification of Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles by Co-precipitation and Sol-gel Method Ki Do Kim, Sung Soo Kim, Yong-Ho Choa, and Hee Taik
J. Ind. Eng. Chem., Vol. 13, No. 7, (2007) 1137-1141 Formation and Surface Modification of Fe 3 O 4 Nanoparticles by Co-precipitation and Sol-gel Method Ki Do Kim, Sung Soo Kim, Yong-Ho Choa, and Hee Taik
Preparation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Mixed with Calcinated Laterite for Arsenic Removal
 Preparation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Mixed with Calcinated Laterite for Arsenic Removal Wint Myat Shwe 1, Dr. Mya Mya Oo 2, Dr. Su Su Hlaing 3 Abstract-- To overcome arsenic toxicity; which has become
Preparation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Mixed with Calcinated Laterite for Arsenic Removal Wint Myat Shwe 1, Dr. Mya Mya Oo 2, Dr. Su Su Hlaing 3 Abstract-- To overcome arsenic toxicity; which has become
The Preparation of Gold Magnetic Nanoparticles Through Layer-by- Layer Assembly Technique
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS The Preparation of Gold Magnetic Nanoparticles Through Layer-by- Layer Assembly Technique To cite this article: Qi Yao Cui et
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS The Preparation of Gold Magnetic Nanoparticles Through Layer-by- Layer Assembly Technique To cite this article: Qi Yao Cui et
Supplementary Information. Core-Shell Silver/Polymeric Nanoparticles-Based Combinatorial Therapy against Breast Cancer In-vitro
 Supplementary Information Core-Shell Silver/Polymeric Nanoparticles-Based Combinatorial Therapy against Breast Cancer In-vitro Nancy M. El-Baz 1,2, Laila Ziko 1,3, Rania Siam 1,3, Wael Mamdouh 1,2 * 1
Supplementary Information Core-Shell Silver/Polymeric Nanoparticles-Based Combinatorial Therapy against Breast Cancer In-vitro Nancy M. El-Baz 1,2, Laila Ziko 1,3, Rania Siam 1,3, Wael Mamdouh 1,2 * 1
A General Synthesis of Discrete Mesoporous Carbon Microspheres through a Confined Self- Assembly Process in Inverse Opals
 A General Synthesis of Discrete Mesoporous Carbon Microspheres through a Confined Self- Assembly Process in Inverse Opals Zhenkun Sun,, Yong Liu, Bin Li, Jing Wei, Minghong Wang, Qin Yue, Yonghui Deng,
A General Synthesis of Discrete Mesoporous Carbon Microspheres through a Confined Self- Assembly Process in Inverse Opals Zhenkun Sun,, Yong Liu, Bin Li, Jing Wei, Minghong Wang, Qin Yue, Yonghui Deng,
The sacrificial role of graphene oxide in stabilising Fenton-like catalyst GO Fe 3 O 4
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 The sacrificial role of graphene oxide in stabilising Fenton-like catalyst GO Fe 3 O 4 Nor Aida
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 The sacrificial role of graphene oxide in stabilising Fenton-like catalyst GO Fe 3 O 4 Nor Aida
Double Mesoporous Silica Shelled Spherical/Ellipsoidal Nanostructures: Synthesis and Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Anticancer Drug Delivery
 Supporting information for Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry Double Mesoporous Silica Shelled Spherical/Ellipsoidal Nanostructures: Synthesis and Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Anticancer
Supporting information for Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry Double Mesoporous Silica Shelled Spherical/Ellipsoidal Nanostructures: Synthesis and Hydrophilic/Hydrophobic Anticancer
Synthesis of Nanoparticles and Surface Modifications
 Synthesis of Nanoparticles and Surface Modifications Self-Assembly Static assembly Dynamic assembly RT = 8.314 J/mol x 300 = 2.4 kj/mol Driving forces Chemisorption Surface effect Hydrophobic-hydrophilic
Synthesis of Nanoparticles and Surface Modifications Self-Assembly Static assembly Dynamic assembly RT = 8.314 J/mol x 300 = 2.4 kj/mol Driving forces Chemisorption Surface effect Hydrophobic-hydrophilic
Synthesis and Characterization of Janus Magnetic Nanoparticles and its Application as an Adsorbent
 64 Journal of Chemical Engineering, IEB Synthesis and Characterization of Magnetic Nanoparticles and its Application as an Adsorbent Abstract Zayed Bin Zakir Shawon Department of Chemical and Biomolecular
64 Journal of Chemical Engineering, IEB Synthesis and Characterization of Magnetic Nanoparticles and its Application as an Adsorbent Abstract Zayed Bin Zakir Shawon Department of Chemical and Biomolecular
Magnetic Janus Nanorods for Efficient Capture, Separation. and Elimination of Bacteria
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Magnetic Janus Nanorods for Efficient Capture, Separation and Elimination of Bacteria Zhi-min
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Magnetic Janus Nanorods for Efficient Capture, Separation and Elimination of Bacteria Zhi-min
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Materials Graphite powder (SP-1 graphite) was obtained from Bay carbon.
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Materials Graphite powder (SP-1 graphite) was obtained from Bay carbon.
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Au nanoparticles supported on magnetically separable Fe 2 O 3 - graphene
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Au nanoparticles supported on magnetically separable Fe 2 O 3 - graphene
Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Long Wavelength Photoinitiators for Free Radical Polymerization
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Polymer Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Long Wavelength Photoinitiators
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Polymer Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Long Wavelength Photoinitiators
Selective Removal of Lead (II) Ion from Wastewater Using Superparamagnetic Monodispersed Iron Oxide (Fe 3. ) Nanoparticles as a Effective Adsorbent
 Int. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., Vol. 9, No. 2, June 2013, pp. 109-114 Short Communication Selective Removal of Lead (II) Ion from Wastewater Using Superparamagnetic Monodispersed Iron Oxide ( ) Nanoparticles
Int. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol., Vol. 9, No. 2, June 2013, pp. 109-114 Short Communication Selective Removal of Lead (II) Ion from Wastewater Using Superparamagnetic Monodispersed Iron Oxide ( ) Nanoparticles
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information One-Step Synthesis of Amine-Functionalized Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Efficient Antibacterial and Anticancer Materials Nanjing Hao, Kalana W. Jayawardana, Xuan Chen
Supporting Information One-Step Synthesis of Amine-Functionalized Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as Efficient Antibacterial and Anticancer Materials Nanjing Hao, Kalana W. Jayawardana, Xuan Chen
Preparation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Mixed with Calcinated Laterite for Arsenic Removal
 Preparation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Mixed with Calcinated Laterite for Arsenic Removal Wint Myat Shwe 1, Su Su Hlaing 2, Mya Mya Oo 3 Abstract-- This paper was studied about a simple and efficient
Preparation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Mixed with Calcinated Laterite for Arsenic Removal Wint Myat Shwe 1, Su Su Hlaing 2, Mya Mya Oo 3 Abstract-- This paper was studied about a simple and efficient
Electronic Supplementary Information. Facile Synthesis of Germanium-Graphene Nanocomposites. and Their Application as Anode Material for Lithium Ion
 Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngCommunity This journal is (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry 2011 Electronic Supplementary Information Facile Synthesis of Germanium-Graphene Nanocomposites and
Supplementary Material (ESI) for CrystEngCommunity This journal is (c) The Royal Society of Chemistry 2011 Electronic Supplementary Information Facile Synthesis of Germanium-Graphene Nanocomposites and
Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy
 Supporting Information Core/Shell to Yolk/Shell Nanostructures by a Novel Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy Jie Han, Rong Chen and Rong Guo* School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University,
Supporting Information Core/Shell to Yolk/Shell Nanostructures by a Novel Sacrifical Template-Free Strategy Jie Han, Rong Chen and Rong Guo* School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Yangzhou University,
An investigation on the optimum conditions of synthesizing a magnetite based ferrofluid as MRI contrast agent using Taguchi method
 Materials Science-Poland, 31(2), 2013, pp. 253-258 http://www.materialsscience.pwr.wroc.pl/ DOI: 10.2478/s13536-012-0098-9 An investigation on the optimum conditions of synthesizing a magnetite based ferrofluid
Materials Science-Poland, 31(2), 2013, pp. 253-258 http://www.materialsscience.pwr.wroc.pl/ DOI: 10.2478/s13536-012-0098-9 An investigation on the optimum conditions of synthesizing a magnetite based ferrofluid
Supporting Information. Self-assembled nanofibers from Leucine Derived Amphiphiles as Nanoreactors for Growth of ZnO Nanoparticles
 Supporting Information Self-assembled nanofibers from Leucine Derived Amphiphiles as Nanoreactors for Growth of ZnO Nanoparticles Karen T. Johnson, Theodore E. Gribb, Evan M. Smoak, and Ipsita A. Banerjee*
Supporting Information Self-assembled nanofibers from Leucine Derived Amphiphiles as Nanoreactors for Growth of ZnO Nanoparticles Karen T. Johnson, Theodore E. Gribb, Evan M. Smoak, and Ipsita A. Banerjee*
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Photoinduced Postsynthetic Polymerization of a Metal Organic Framework toward a Flexible Stand-Alone Membrane** Yuanyuan Zhang, Xiao Feng,* Haiwei Li, Yifa Chen, Jingshu Zhao, Shan
Supporting Information Photoinduced Postsynthetic Polymerization of a Metal Organic Framework toward a Flexible Stand-Alone Membrane** Yuanyuan Zhang, Xiao Feng,* Haiwei Li, Yifa Chen, Jingshu Zhao, Shan
Hybrid Gold Superstructures: Synthesis and. Specific Cell Surface Protein Imaging Applications
 Supporting Information Hybrid Gold Nanocube@Silica@Graphene-Quantum-Dot Superstructures: Synthesis and Specific Cell Surface Protein Imaging Applications Liu Deng, Ling Liu, Chengzhou Zhu, Dan Li and Shaojun
Supporting Information Hybrid Gold Nanocube@Silica@Graphene-Quantum-Dot Superstructures: Synthesis and Specific Cell Surface Protein Imaging Applications Liu Deng, Ling Liu, Chengzhou Zhu, Dan Li and Shaojun
Pre-seeding -assisted synthesis of high performance polyamide-zeolite nanocomposie membrane for water purification
 Electronic Supporting Information: Pre-seeding -assisted synthesis of high performance polyamide-zeolite nanocomposie membrane for water purification Chunlong Kong, a Takuji Shintani b and Toshinori Tsuru*
Electronic Supporting Information: Pre-seeding -assisted synthesis of high performance polyamide-zeolite nanocomposie membrane for water purification Chunlong Kong, a Takuji Shintani b and Toshinori Tsuru*
Hetero-crystals with Enhanced Photocatalytic Properties and Stabilities
 Supporting Information for Facile Synthesis of Rhombic Dodecahedral AgX/Ag 3 PO 4 (X=Cl, Br, I) Hetero-crystals with Enhanced Photocatalytic Properties and Stabilities Yingpu Bi, Shuxin Ouyang, Junyu Cao,
Supporting Information for Facile Synthesis of Rhombic Dodecahedral AgX/Ag 3 PO 4 (X=Cl, Br, I) Hetero-crystals with Enhanced Photocatalytic Properties and Stabilities Yingpu Bi, Shuxin Ouyang, Junyu Cao,
Novel fluorescent matrix embedded carbon quantum dots enrouting stable gold and silver hydrosols
 Novel fluorescent matrix embedded carbon quantum dots enrouting stable gold and silver hydrosols Shouvik Mitra a, Sourov Chandra b, Prasun Patra a, Panchanan Pramanik b *, Arunava Goswami a * a AERU, Biological
Novel fluorescent matrix embedded carbon quantum dots enrouting stable gold and silver hydrosols Shouvik Mitra a, Sourov Chandra b, Prasun Patra a, Panchanan Pramanik b *, Arunava Goswami a * a AERU, Biological
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Au-HKUST-1 Composite Nanocapsules: Synthesis with a Coordination Replication Strategy and Catalysis on CO Oxidation Yongxin Liu, 1 Jiali Zhang, 1 Lingxiao Song, 1 Wenyuan Xu, 1 Zanru
Supporting Information Au-HKUST-1 Composite Nanocapsules: Synthesis with a Coordination Replication Strategy and Catalysis on CO Oxidation Yongxin Liu, 1 Jiali Zhang, 1 Lingxiao Song, 1 Wenyuan Xu, 1 Zanru
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Materials Multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs, φ = 10-30 nm) were purchased from Nanotech Port Co. Ltd. (Shenzhen, China). Tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS, >98 %), Triton X-100 and
Supporting Information Materials Multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWNTs, φ = 10-30 nm) were purchased from Nanotech Port Co. Ltd. (Shenzhen, China). Tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS, >98 %), Triton X-100 and
Detonation Nanodiamond Suspensions
 PRODUCT SHEET Rev. 10/17, v3.0 Detonation Nanodiamond Suspensions Colloidal suspensions of detonation nanodiamond (DND) in both and a variety of organic solvents have a wide range of uses, including: (1)
PRODUCT SHEET Rev. 10/17, v3.0 Detonation Nanodiamond Suspensions Colloidal suspensions of detonation nanodiamond (DND) in both and a variety of organic solvents have a wide range of uses, including: (1)
SPHERO TM Magnetic Particles
 SPHER TM Magnetic Particles SPHER TM Magnetic Microparticles provide high quality and reproducible results for your application Allow for rapid and reliable binding between the target and magnetic particle
SPHER TM Magnetic Particles SPHER TM Magnetic Microparticles provide high quality and reproducible results for your application Allow for rapid and reliable binding between the target and magnetic particle
Synthesis and Characterization of Iron-Oxide (Hematite) Nanocrystals. Z.H. Lee
 ABSTRACT Synthesis and Characterization of Iron-Oxide (Hematite) Nanocrystals Z.H. Lee Engineering Science Programme, National University of Singapore Kent Ridge, Singapore 119260 Monodispersed iron oxide
ABSTRACT Synthesis and Characterization of Iron-Oxide (Hematite) Nanocrystals Z.H. Lee Engineering Science Programme, National University of Singapore Kent Ridge, Singapore 119260 Monodispersed iron oxide
Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different Proportions
 2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
2015 2 nd International Conference on Material Engineering and Application (ICMEA 2015) ISBN: 978-1-60595-323-6 Adsorption of Methylene Blue on Mesoporous SBA 15 in Ethanol water Solution with Different
International Journal of Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences
 F. Fathi et al IJCPS, 2014, Vol.2(4): 760-764 Research Article ISSN: 2321-3132 International Journal of Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijcps Synthesis and Surface modification
F. Fathi et al IJCPS, 2014, Vol.2(4): 760-764 Research Article ISSN: 2321-3132 International Journal of Chemistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijcps Synthesis and Surface modification
Doxorubicin loaded on aminosilane modified superparamagnetic magnetic nanoparticles and its characterization
 American Journal of Oil and Chemical Technologies: Volume 4. Issue 3. May 2016 Petrotex Library Archive American Journal of Oil and Chemical Technologies Journal Website: http://www.petrotex.us/ Doxorubicin
American Journal of Oil and Chemical Technologies: Volume 4. Issue 3. May 2016 Petrotex Library Archive American Journal of Oil and Chemical Technologies Journal Website: http://www.petrotex.us/ Doxorubicin
SUPPORTING INFORMATION. A New Approach for the Surface Enhanced Resonance Raman Scattering (SERRS)
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION A New Approach for the Surface Enhanced Resonance Raman Scattering (SERRS) Detection of Dopamine at Picomolar (pm) Levels in the Presence of Ascorbic Acid Murat Kaya, Mürvet Volkan
SUPPORTING INFORMATION A New Approach for the Surface Enhanced Resonance Raman Scattering (SERRS) Detection of Dopamine at Picomolar (pm) Levels in the Presence of Ascorbic Acid Murat Kaya, Mürvet Volkan
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) using gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles as dispersible electrodes Kyloon Chuah, Leo M. H. Lai, Ian
Supplementary Information Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) using gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles as dispersible electrodes Kyloon Chuah, Leo M. H. Lai, Ian
Supporting Information. Capping Nanoparticles with Graphene Quantum Dots for Enhanced Thermoelectric Performance
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Capping Nanoparticles with Graphene Quantum Dots for Enhanced Thermoelectric
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Capping Nanoparticles with Graphene Quantum Dots for Enhanced Thermoelectric
Synthesis and Characterization of Polymeric Composites Embeded with Silver Nanoparticles
 World Journal of Nano Science and Engineering, 2012, 2, 19-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/wjnse.2012.21004 Published Online March 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjnse) 19 Synthesis and Characterization
World Journal of Nano Science and Engineering, 2012, 2, 19-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/wjnse.2012.21004 Published Online March 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/wjnse) 19 Synthesis and Characterization
Surface Modification of PTMS Particles with Organosilanes: TEOS-, VTMS-, and MTMS-Modified Particles
 Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology 31, 117 121, 2004 c 2004 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The United States. Surface Modification of PTMS Particles with Organosilanes: TEOS-, VTMS-,
Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology 31, 117 121, 2004 c 2004 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The United States. Surface Modification of PTMS Particles with Organosilanes: TEOS-, VTMS-,
Facile synthesis of polymer and carbon spheres decorated with highly dispersed metal nanoparticles
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 1 Facile synthesis of polymer and carbon spheres decorated with highly dispersed metal nanoparticles
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 1 Facile synthesis of polymer and carbon spheres decorated with highly dispersed metal nanoparticles
A Systematic Study of the Synthesis of Silver Nanoplates: Is Citrate a. "Magic" Reagent?
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION A Systematic Study of the Synthesis of Silver Nanoplates: Is Citrate a "Magic" Reagent? Qiao Zhang, Na Li,, James Goebl, Zhenda Lu, Yadong Yin*, Department of Chemistry, University
SUPPORTING INFORMATION A Systematic Study of the Synthesis of Silver Nanoplates: Is Citrate a "Magic" Reagent? Qiao Zhang, Na Li,, James Goebl, Zhenda Lu, Yadong Yin*, Department of Chemistry, University
Gas Sensors Based on Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes Decorated with. Different Metal Oxides Nanoparticles.
 Gas Sensors Based on Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes Decorated with Different Metal Oxides Nanoparticles. A. Abbaspourrad, C. Verissimo, R.V. Gelamo, M. M. da Silva, A. R. Vaz, F. P. M. Rouxinol, O. L. Alves,
Gas Sensors Based on Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes Decorated with Different Metal Oxides Nanoparticles. A. Abbaspourrad, C. Verissimo, R.V. Gelamo, M. M. da Silva, A. R. Vaz, F. P. M. Rouxinol, O. L. Alves,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Decorating Graphene Sheets with Gold Nanoparticles Ryan Muszynski, Brian Seeger and, Prashant V. Kamat* Radiation Laboratory, Departments of Chemistry & Biochemistry and Chemical
Supporting Information Decorating Graphene Sheets with Gold Nanoparticles Ryan Muszynski, Brian Seeger and, Prashant V. Kamat* Radiation Laboratory, Departments of Chemistry & Biochemistry and Chemical
Facile Synthesis and Catalytic Properties of CeO 2 with Tunable Morphologies from Thermal Transformation of Cerium Benzendicarboxylate Complexes
 Electronic Supplementary Information Facile Synthesis and Catalytic Properties of CeO 2 with Tunable Morphologies from Thermal Transformation of Cerium Benzendicarboxylate Complexes Yuhua Zheng, Kai Liu,
Electronic Supplementary Information Facile Synthesis and Catalytic Properties of CeO 2 with Tunable Morphologies from Thermal Transformation of Cerium Benzendicarboxylate Complexes Yuhua Zheng, Kai Liu,
Supplementary Information for
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information for Cu Nanowires Shelled with NiFe Layered Double
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Energy & Environmental Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information for Cu Nanowires Shelled with NiFe Layered Double
Supporting Information. Solution-Phase Synthesis of Highly Conductive Tungsten Diselenide Nanosheets
 Supporting Information Solution-Phase Synthesis of Highly Conductive Tungsten Diselenide Nanosheets Priscilla D. Antunez, David H. Webber, and Richard L. Brutchey* Department of Chemistry and the Center
Supporting Information Solution-Phase Synthesis of Highly Conductive Tungsten Diselenide Nanosheets Priscilla D. Antunez, David H. Webber, and Richard L. Brutchey* Department of Chemistry and the Center
Synthesis and characterization of silica titania core shell particles
 PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 65, No. 5 journal of November 2005 physics pp. 787 791 Synthesis and characterization of silica titania core shell particles SUCHITA KALELE 1, RAVI DEY 1, NEHA
PRAMANA c Indian Academy of Sciences Vol. 65, No. 5 journal of November 2005 physics pp. 787 791 Synthesis and characterization of silica titania core shell particles SUCHITA KALELE 1, RAVI DEY 1, NEHA
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Polymer-coated spherical mesoporous silica for ph-controlled delivery of insulin Sae Rom Choi a,, Dong-jin Jang b,, Sanghyun Kim a, Sunhyung An c, Jinwoo Lee c, Euichaul
Electronic Supplementary Information Polymer-coated spherical mesoporous silica for ph-controlled delivery of insulin Sae Rom Choi a,, Dong-jin Jang b,, Sanghyun Kim a, Sunhyung An c, Jinwoo Lee c, Euichaul
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
Supplementary Information Fabrication of Novel Rattle-Type Magnetic Mesoporous carbon Microspheres for Removal of Microcystins Xinghua Zhang and Long Jiang* Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Science
enzymatic cascade system
 Electronic Supplementary Information Fe 3 O 4 -Au@mesoporous SiO 2 microsphere: an ideal artificial enzymatic cascade system Xiaolong He, a,c Longfei Tan, a Dong Chen,* b Xiaoli Wu, a,c Xiangling Ren,
Electronic Supplementary Information Fe 3 O 4 -Au@mesoporous SiO 2 microsphere: an ideal artificial enzymatic cascade system Xiaolong He, a,c Longfei Tan, a Dong Chen,* b Xiaoli Wu, a,c Xiangling Ren,
Preparation of Aminated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles (MSNs) by Delayed Co-condensation Technique
 Extra Supporting Information (ESI) Experimental Procedures General All chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich and used as received, unless otherwise specified. 2,2',2''-(10-(2-((2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)oxy)-2-oxoethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7-
Extra Supporting Information (ESI) Experimental Procedures General All chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich and used as received, unless otherwise specified. 2,2',2''-(10-(2-((2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl)oxy)-2-oxoethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7-
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplementary Information Multifunctional Fe 2 O 3 /CeO 2 Nanocomposites for Free Radical Scavenging
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplementary Information Multifunctional Fe 2 O 3 /CeO 2 Nanocomposites for Free Radical Scavenging
The materials used in this study were Iron (III) chloride hexahydrate (AR grade) and
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Synthesis of Metastable Hard-Magnetic ε-fe 2 O 3 Nanoparticles from Silica-Coated
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information Synthesis of Metastable Hard-Magnetic ε-fe 2 O 3 Nanoparticles from Silica-Coated
Permeable Silica Shell through Surface-Protected Etching
 Permeable Silica Shell through Surface-Protected Etching Qiao Zhang, Tierui Zhang, Jianping Ge, Yadong Yin* University of California, Department of Chemistry, Riverside, California 92521 Experimental Chemicals:
Permeable Silica Shell through Surface-Protected Etching Qiao Zhang, Tierui Zhang, Jianping Ge, Yadong Yin* University of California, Department of Chemistry, Riverside, California 92521 Experimental Chemicals:
Etching-limited branching growth of cuprous oxide during ethanol-assisted. solution synthesis
 Electronic supplementary information Etching-limited branching growth of cuprous oxide during ethanol-assisted solution synthesis Shaodong Sun, Hongjun You, Chuncai Kong, Xiaoping Song, Bingjun Ding, and
Electronic supplementary information Etching-limited branching growth of cuprous oxide during ethanol-assisted solution synthesis Shaodong Sun, Hongjun You, Chuncai Kong, Xiaoping Song, Bingjun Ding, and
Three Dimensional Nano-assemblies of Noble Metal. Nanoparticles-Infinite Coordination Polymers as a Specific
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Three Dimensional Nano-assemblies of Noble Metal Nanoparticles-Infinite
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information Three Dimensional Nano-assemblies of Noble Metal Nanoparticles-Infinite
PREPARATION, CHARACTERISATION AND PHOTOCATALYTIC ACTIVITY OF TERNARY GRAPHENE-Fe 3 O 4 :TiO 2 NANOCOMPOSITES
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 13, No. 2, April - June 2018, p. 499-504 PREPARATION, CHARACTERISATION AND PHOTOCATALYTIC ACTIVITY OF TERNARY GRAPHENE-Fe 3 O 4 :TiO 2 NANOCOMPOSITES
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 13, No. 2, April - June 2018, p. 499-504 PREPARATION, CHARACTERISATION AND PHOTOCATALYTIC ACTIVITY OF TERNARY GRAPHENE-Fe 3 O 4 :TiO 2 NANOCOMPOSITES
Pickering emulsion engineering: Fabrication of materials with multiple cavities
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 014 Electronic Supplementary Infomaton Pickering emulsion engineering: Fabrication of materials
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 014 Electronic Supplementary Infomaton Pickering emulsion engineering: Fabrication of materials
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Visible Light-Driven BiOI-Based Janus Micromotors in Pure Water Renfeng Dong, a Yan Hu, b Yefei Wu, b Wei Gao, c Biye Ren, b* Qinglong Wang, a Yuepeng Cai a* a School of Chemistry
Supporting Information Visible Light-Driven BiOI-Based Janus Micromotors in Pure Water Renfeng Dong, a Yan Hu, b Yefei Wu, b Wei Gao, c Biye Ren, b* Qinglong Wang, a Yuepeng Cai a* a School of Chemistry
Supporting Information:
 Supporting Information: In Situ Synthesis of Magnetically Recyclable Graphene Supported Pd@Co Core-Shell Nanoparticles as Efficient Catalysts for Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane Jun Wang,
Supporting Information: In Situ Synthesis of Magnetically Recyclable Graphene Supported Pd@Co Core-Shell Nanoparticles as Efficient Catalysts for Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane Jun Wang,
Research Article Preparation of γ-fe 2 O 3 /Ni 2 O 3 /FeCl 3 (FeCl 2 ) Composite Nanoparticles by Hydrothermal Process Useful for Ferrofluids
 Smart Materials Research Volume 2011, Article ID 351072, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/351072 Research Article Preparation of γ-fe 2 O 3 /Ni 2 O 3 /FeCl 3 (FeCl 2 ) Composite Nanoparticles by Hydrothermal Process
Smart Materials Research Volume 2011, Article ID 351072, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/351072 Research Article Preparation of γ-fe 2 O 3 /Ni 2 O 3 /FeCl 3 (FeCl 2 ) Composite Nanoparticles by Hydrothermal Process
Magnetic Silica Particles for Catalysis
 4 Magnetic Silica Particles for atalysis Abstract Monodisperse magnetizable colloidal silica particles in a stable dispersion have been functionalized with a homogeneous catalyst: a PP-pincer Pd-complex.
4 Magnetic Silica Particles for atalysis Abstract Monodisperse magnetizable colloidal silica particles in a stable dispersion have been functionalized with a homogeneous catalyst: a PP-pincer Pd-complex.
nanocomposites: synthesis and characterization
 National Institute for Research and Development of Isotopic and Molecular Technologies Cluj-Napoca Romania Carbon nanotubes-polypyrrole nanocomposites: synthesis and characterization R. Turcu a, O. Pana
National Institute for Research and Development of Isotopic and Molecular Technologies Cluj-Napoca Romania Carbon nanotubes-polypyrrole nanocomposites: synthesis and characterization R. Turcu a, O. Pana
MOPHOLOGY OF POLYANILINE NANOTUBE WITH VARIOUS LEVEL OF Fe3O4 NANOPARTICLES AND THEIR ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITIES BY ULTRASONIC DISPERSION METHOD
 MOPHOLOGY OF POLYANILINE NANOTUBE WITH VARIOUS LEVEL OF Fe3O4 NANOPARTICLES AND THEIR ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITIES BY ULTRASONIC DISPERSION METHOD Mahmoud Auwal Adamu, M. K. Mustafa and Nurun Najwa Binti
MOPHOLOGY OF POLYANILINE NANOTUBE WITH VARIOUS LEVEL OF Fe3O4 NANOPARTICLES AND THEIR ELECTRICAL CONDUCTIVITIES BY ULTRASONIC DISPERSION METHOD Mahmoud Auwal Adamu, M. K. Mustafa and Nurun Najwa Binti
Supporting information for Magnetic Paper - Based ELISA for IgM-dengue detection by G.A. Ortega, S. Pérez and E. Reguera
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting information for Magnetic Paper - Based ELISA for IgM-dengue detection by G.A. Ortega,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting information for Magnetic Paper - Based ELISA for IgM-dengue detection by G.A. Ortega,
Magnetic Particles for Phosphorus Adsorption in Simulated Phosphate Solution
 215 4th International Conference on Informatics, Environment, Energy and Applications Volume 82 of IPCBEE (215) DOI: 1.7763/IPCBEE. 215.V82.28 Magnetic Particles for Phosphorus Adsorption in Simulated
215 4th International Conference on Informatics, Environment, Energy and Applications Volume 82 of IPCBEE (215) DOI: 1.7763/IPCBEE. 215.V82.28 Magnetic Particles for Phosphorus Adsorption in Simulated
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information of Appointed exploding microcapsules as drug carriers By Jing Zhang, Cao Li, Ya Wang, Ren-Xi Zhuo and Xian-Zheng Zhang * Materials Propargyl alcohol (PA-OH), dextran (M w ~20 k &
Supporting Information of Appointed exploding microcapsules as drug carriers By Jing Zhang, Cao Li, Ya Wang, Ren-Xi Zhuo and Xian-Zheng Zhang * Materials Propargyl alcohol (PA-OH), dextran (M w ~20 k &
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Facile Synthesis of Ag@Pd Satellites-Fe 3 O 4 Core Nanocomposite as Efficient and Reusable Hydrogenation Catalysts Kun Jiang, a Han-Xuan Zhang, a Yao-Yue Yang a, Robert Mothes, b
Supporting Information Facile Synthesis of Ag@Pd Satellites-Fe 3 O 4 Core Nanocomposite as Efficient and Reusable Hydrogenation Catalysts Kun Jiang, a Han-Xuan Zhang, a Yao-Yue Yang a, Robert Mothes, b
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Study of molecular conformation and activity-related properties of lipase immobilized onto core-shell structured polyacrylic acid-coated magnetic silica nanocomposite particles Parvaneh
Supporting Information Study of molecular conformation and activity-related properties of lipase immobilized onto core-shell structured polyacrylic acid-coated magnetic silica nanocomposite particles Parvaneh
Carbon nanotube coated snowman-like particles and their electro-responsive characteristics. Ke Zhang, Ying Dan Liu and Hyoung Jin Choi
 Supporting Information: Carbon nanotube coated snowman-like particles and their electro-responsive characteristics Ke Zhang, Ying Dan Liu and Hyoung Jin Choi Experimental Section 1.1 Materials The MWNT
Supporting Information: Carbon nanotube coated snowman-like particles and their electro-responsive characteristics Ke Zhang, Ying Dan Liu and Hyoung Jin Choi Experimental Section 1.1 Materials The MWNT
Synthesis and characterization of hybride polyaniline / polymethacrylic acid/ Fe 3 O 4 nanocomposites
 Synthesis and characterization of hybride polyaniline / polymethacrylic acid/ Fe 3 O 4 nanocomposites Mohammad Reza Saboktakin*, Abel Maharramov, Mohammad Ali Ramazanov Department of Chemistry, Baku State
Synthesis and characterization of hybride polyaniline / polymethacrylic acid/ Fe 3 O 4 nanocomposites Mohammad Reza Saboktakin*, Abel Maharramov, Mohammad Ali Ramazanov Department of Chemistry, Baku State
Removal efficiency on magnetite (Fe 3 O 4 ) of some multicomponent systems present in synthetic aqueous solutions
 Removal efficiency on magnetite (Fe 3 O 4 ) of some multicomponent systems present in synthetic aqueous solutions Andra Predescu, Ecaterina Matei, Andrei Predescu, Andrei Berbecaru Faculty of Materials
Removal efficiency on magnetite (Fe 3 O 4 ) of some multicomponent systems present in synthetic aqueous solutions Andra Predescu, Ecaterina Matei, Andrei Predescu, Andrei Berbecaru Faculty of Materials
Facile Synthesis of Gold Wavy Nanowires and Investigation of
 Supporting Information for Facile Synthesis of Gold Wavy Nanowires and Investigation of Their Growth Mechanism Cun Zhu,, Hsin-Chieh Peng, Jie Zeng, Jingyue Liu, Zhongze Gu and Younan Xia,,* The Wallace
Supporting Information for Facile Synthesis of Gold Wavy Nanowires and Investigation of Their Growth Mechanism Cun Zhu,, Hsin-Chieh Peng, Jie Zeng, Jingyue Liu, Zhongze Gu and Younan Xia,,* The Wallace
Monodisperse magnetite nanoparticles with nearly ideal saturation magnetization
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information for Monodisperse magnetite nanoparticles with nearly ideal saturation
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supporting Information for Monodisperse magnetite nanoparticles with nearly ideal saturation
CHAPTER 3. FABRICATION TECHNOLOGIES OF CdSe/ZnS / Au NANOPARTICLES AND NANODEVICES. 3.1 THE SYNTHESIS OF Citrate-Capped Au NANOPARTICLES
 CHAPTER 3 FABRICATION TECHNOLOGIES OF CdSe/ZnS / Au NANOPARTICLES AND NANODEVICES 3.1 THE SYNTHESIS OF Citrate-Capped Au NANOPARTICLES Au NPs with ~ 15 nm were prepared by citrate reduction of HAuCl 4
CHAPTER 3 FABRICATION TECHNOLOGIES OF CdSe/ZnS / Au NANOPARTICLES AND NANODEVICES 3.1 THE SYNTHESIS OF Citrate-Capped Au NANOPARTICLES Au NPs with ~ 15 nm were prepared by citrate reduction of HAuCl 4
Supporting Information Supramolecular Polymerization at Interface: Layer-by-layer Assembly Driven by Host-enhanced π-π Interaction
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Supramolecular Polymerization at Interface: Layer-by-layer Assembly Driven
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Supramolecular Polymerization at Interface: Layer-by-layer Assembly Driven
2017 Reaction of cinnamic acid chloride with ammonia to cinnamic acid amide
 217 Reaction of cinnamic acid chloride with ammonia to cinnamic acid amide O O Cl NH 3 NH 2 C 9 H 7 ClO (166.6) (17.) C 9 H 9 NO (147.2) Classification Reaction types and substance classes reaction of
217 Reaction of cinnamic acid chloride with ammonia to cinnamic acid amide O O Cl NH 3 NH 2 C 9 H 7 ClO (166.6) (17.) C 9 H 9 NO (147.2) Classification Reaction types and substance classes reaction of
Switching shape of hollow layer-by-layer hydrogel microcontainers
 Electronic Supplementary Information Switching shape of hollow layer-by-layer hydrogel microcontainers Veronika Kozlovskaya, William Higgins, Jun Chen and Eugenia Kharlampieva* University of Alabama at
Electronic Supplementary Information Switching shape of hollow layer-by-layer hydrogel microcontainers Veronika Kozlovskaya, William Higgins, Jun Chen and Eugenia Kharlampieva* University of Alabama at
In Situ synthesis of architecture for Strong Light-Matter Interactions
 In Situ synthesis of Ag@Cu2O-rGO architecture for Strong Light-Matter Interactions Shuang Guo 1, 2, Yaxin Wang 1, *, Fan Zhang 1, Renxian Gao 1, Maomao Liu 1, Lirong Dong 1, Yang Liu 2, Yongjun Zhang 2,
In Situ synthesis of Ag@Cu2O-rGO architecture for Strong Light-Matter Interactions Shuang Guo 1, 2, Yaxin Wang 1, *, Fan Zhang 1, Renxian Gao 1, Maomao Liu 1, Lirong Dong 1, Yang Liu 2, Yongjun Zhang 2,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Superparamagnetic luminescent MOF@Fe 3 O 4 /SiO 2 composite particles for signal augmentation by magnetic harvesting as potential water detectors Tobias Wehner, Karl Mandel *, Michael
Supporting Information Superparamagnetic luminescent MOF@Fe 3 O 4 /SiO 2 composite particles for signal augmentation by magnetic harvesting as potential water detectors Tobias Wehner, Karl Mandel *, Michael
