! "#$%&'$!()! *+&$(,)#$! *+&$(,)#$! *+&$(,)#$!
|
|
|
- Aubrey Bell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Learning Checkpoint, p A solution with a ph of 11 is basic. 2. A solution with a ph of 5 is acidic. 3. The ph of pure water is 7 (neutral).! "#$%&'$!()! *+&$(,)#$! 4. No, litmus paper does not determine a specific ph value. It only indicates whether the solution is acidic or basic. 5. A universal indicator allows you to determine a specific ph value. Learning Checkpoint, p (a) Hydrochloric acid (b) Nitric acid (c) Acetic (or ethanoic) acid 2. (a) The polyatomic ion is sulphate. (b) The polyatomic ion is nitrate.! "#$%&'$!()! *+&$(,)#$! Learning Checkpoint, p (a) Potassium hydroxide (b) Calcium hydroxide (c) Magnesium hydroxide (d) Ammonium hydroxide! "#$%&'$!()! *+&$(,)#$! 2. Hydroxide (the OH ) is the polyatomic group that is found at the end of the chemical formula for most bases.
2 !"#$ Key Concept Review 1. An acid is a substance that produces a solution with a ph less than 7. Several types of acids are citric acid, ascorbic acid (vitamin C), hydrochloric acid, lactic acid, and sulphuric acid. 2. A base is a substance that produces a solution with a ph greater than 7. Two examples of bases are sodium hydroxide and ammonium hydroxide (see Table 5.6, student book page 201). 3. (a) The solution is basic. (b) The solution is acidic. (c) The solution is acidic. (d) The solution is acidic. (e) The solution is basic. 4. A solution that contains dissolved calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH 2 ), would be basic because bases include the hydroxide (OH ) ion. 5. Acids are similar to bases in that they dissolve in water, conduct electricity in aqueous solution, and can irritate or burn skin. Acids are different from bases in that acids taste sour (while bases taste bitter), have a ph less than 7 (while bases have a ph greater than 7), turn blue litmus paper red (whereas bases turn red litmus paper blue), and corrode metals (bases do not corrode metals). 6. An acid-base indicator is any substance that changes colour in the presence of an acid or a base. 7. (a) KOH(aq) is basic. (b) Al(OH) 3 (aq) is basic. (c) HCl(aq) is an acid. (d) C 6 H 5 COOH(aq) is an acid. 8. (a) HNO 3 (aq) (b) CsOH (c) HCl(aq) (d) H 3 PO 4 (aq) (e) potassium hydroxide (f) sulphuric acid or aqueous hydrogen sulphate 9. (a) Mg(OH) 2 (b) KOH (c) Al(OH) 3
3 11. For litmus paper, BLUE + Acid RED. Therefore, the upper of the two strips in the photograph was dipped into the lemon juice. The lower of the two strips was dipped into the solution of baking soda and water. 12. We cannot use 100% acetic acid on foods because the acid would be so concentrated that it would burn the tongue, mouth, and digestive system. 13. Litmus paper provides only a narrow range of colours to indicate ph (typically pink and blue) and is capable of indicating only if a solution is acidic or basic. A universal indicator is more useful than litmus paper because it indicates specific ph values. 14. Students will use the information in this section (and possibly their own additional ideas) to construct and complete a chart. Uses for Acids DNA passes on genetic characteristics. Hydrochloric acid in the stomach digests food. Vinegar is used as an ingredient to flavour food. To conduct electricity in car batteries To etch glass To produce dyes for clothing Students may include information from Table 5.4, student book page 200. Uses for Bases Soaps and cleaners Making plastic and textiles Making glass, cement, and steel Treating indigestion Students may include other uses from Table 5.6, student book page 201.
4 Answers to Practice Problems 5.1, p HBr(aq) + KOH(aq) KBr(aq) + H 2 O(l). 2. H 2 SO 4 (aq) + Mg(OH) 2 (aq) MgSO 4 (aq) + 2H 2 O(l). 3. H 3 PO 4 (aq) + 3NaOH(aq) Na 3 PO 4 (aq) + 3H 2 O(l). Learning Checkpoint, p. 209! "#$%&'$!()! *+&$(,)#$! 1. Sulphur oxides (SO 2 and SO 3 ) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) are the main gases that cause acid precipitation. NOx refers to the fact that there are several different gases made of nitrogen and oxygen. 2. Nitrogen oxides are gases composed of nitrogen atom(s) and one or more oxygen atoms. Examples are NO 2, N 2 O, and N 2 O Two chemical equations for reactions that cause acid precipitation are: 2SO 2 (g) + O 2 (g) 2SO 3 (g) SO 3 (g) + H 2 O(l) H 2 SO 4 (aq) 4. The source of water is water vapour in the air. Students might also name the source as rain or water evaporated from Earth s surface. 5. Students answers will vary but will include two of the following industries or human activities that contribute to acid precipitation: coal-fired power plants, iron and steel production, smelting of metals (such as zinc, nickel, and copper), fertilizer production, pulp and paper production, and automobile emissions.
5 Learning Checkpoint, p. 210! "#$%&'$!()! *+&$(,)#$! 1. Two effects that acid precipitation has on the environment are that lakes become more acidic, affecting organisms that live in the water, and acid precipitation changes the ph of the soil, which can cause trees and other plant species to die. 2. The ph of an acidic lake can be increased by adding bases such as lime (Ca(OH) 2 ) to the source of the lake or directly to the lake itself. 3. Lakes on limestone rock are less affected by acid rain because the limestone rock neutralizes the acid in the rain that falls on the lake or enters the lake through rivers. 4. Scrubbers are devices found in smokestacks of industries such as coal-fired power plants and ore-smelting facilities that release sulphur dioxide gas and nitrogen oxide gases. Scrubbers, a specially formulated chemical mixture, remove these gases by reacting with the emissions. 5. The chemical equation for the reaction in catalytic converters is: 2N 2 O 3 (g) 2N 2 (g) + 3O 2 (g).
6 !"#$ Key Concept Review 1. Neutralization is a chemical reaction between an acid and a base that produces water (H 2 O) and a salt. 2. The products of a neutralization reaction are a salt (an ionic compound) and water. 3. Antacids are composed of bases, which undergo a neutralization reaction with some of the hydrochloric acid in the stomach. This makes the stomach contents less acidic and less painful. 4. Acid precipitation is rain, snow, fog, or dew that has a ph less than Two gases that contribute to acid precipitation are sulphur dioxide (SO 2 ) (and also SO 3 ), and nitrogen oxides (NOx). NOx refers to the fact that there are several different gases made of nitrogen and oxygen. 6. Acid leaching is a process in which acids (from acid precipitation or contaminated groundwater) dissolve metals found in soil. For example, mine tailings that produce iron sulphide can produce sulphuric acid when exposed to air and water. This acid solution can enter the water system and dissolve heavy metals in the soil. Once they are released, they can contaminate the water supply. Connect Your Understanding 7. Chemical reaction (b) is a neutralization reaction because the reactants include an acid (H 3 PO 4 ) and a base (NaOH) and because the products are a salt (Na 3 PO 4 ) and water (H 2 O). 8. The completed word equations are: (a) sulphuric acid + calcium hydroxide water + calcium sulphate (b) hydrogen bromide + sodium hydroxide water + sodium bromide (c) hydrochloric acid + sodium hydroxide water + sodium chloride 9. The skeleton equations for the neutralization reactions in question 8 are: (a) H 2 SO 4 + Ca(OH) 2 H 2 O + CaSO 4 (b) HBr + NaOH H 2 O + NaBr (c) HCl + NaOH H 2 O + NaCl
7 10. The balanced chemical equations for the neutralization reactions in question 8 are: (a) H 2 SO 4 + Ca(OH) 2 2H 2 O + CaSO 4 (b) HBr + NaOH H 2 O + NaBr (same as the skeleton equation) (c) HCl + NaOH H 2 O + NaCl (same as the skeleton equation) 11. The classmate s conclusion is incorrect because the products of a neutralization reaction are water and a salt. If the salt dissolved, the solution would be clear. An example would be chemical reaction (c) in question 8. A chemical reaction has happened, but there is no visible evidence of it. 12. Two or more reasons to avoid using an antacid regularly are that long-term use of an antacid might have side effects that could affect your health, and long-term use could mask a more serious problem in the digestive system. Students may find this question challenging. 13. Acid rain can be a problem anywhere metals are used out of doors, such as in support reinforcing bars for concrete roads, cars and structures (buildings and bridges), and public artwork (statues). The acids react with the metals and corrode them. Also, if precipitation is acidic enough, it may cause acid leaching of metals into the soil, which can contaminate water supplies. 14. Acid rain is a costly result of human activities because we constantly need to monitor and replace metals, stone, and concrete used in building and roads. The damaged statue in the photograph is an illustration of the harmful effects of acid precipitation. The statue cannot be repaired, so if acid rain continues, the statue, a cultural artefact, will be lost forever. 15. Acid precipitation affects the water in lakes by making the lake water more acidic. The lowering of the ph can cause fish and other water organisms to die. Acidic lakes also cannot support the same variety of organisms as healthy lakes. 16. If a lake has formed on limestone, the limestone can protect the lake from acidification by neutralizing excess acid in the lake s water. 17. A negative effect of acid leaching is the acid leaching of heavy metals from soil in areas surrounding abandoned mine sites. The acid and metals can reach water systems, and both the metals and the acids can harm organisms. On the other hand, soils contaminated by heavy metals can be cleaned of contaminants by using acid leaching to remove them.
8 !" Key Concept Review 1. The following Venn diagram shows the similarities and differences between acids and bases. Students may choose another graphic organizer. 2. Litmus paper is blue or red litmus dried onto strips of paper. Red litmus paper turns blue when it is dipped into a basic solution. Blue litmus paper turns red when it is dipped in an acidic solution. 3. The ph scale is a number scale that can be used to classify solutions as acidic, basic, or neutral. Any substance in an aqueous solution with a ph of 7 is neutral. An acid is a substance that produces a solution with a ph less than 7. A base is a substance that produces a solution with a ph greater than (a) This solution is acidic. (b) This solution is neutral. (c) This solution is neutral. (d) This solution is basic. (e) This solution is basic.
9 Connect Your Understanding 5. The normal ph of blood is slightly basic. We know this because ph values for basic solutions are greater than You could safely test the liquid to determine if it is an acid (or a base) by using litmus paper, ph paper, or universal indicator solution. 7. Since each step on the ph scale represents a tenfold change in concentration, the first solution is 10! 10 = 100 times more concentrated, thus 100 times more acidic, than the second solution. 8. The girl appears to find the lemon sour. Sourness is a property of acids, so the lemon is probably acidic.
10 9. (a) H 2 SO 4 (aq) is an acid because it starts with hydrogen. (b) CH 3 COOH(aq) is an acid because it ends with COOH (carboxyl polyatomic group). (c) Mg(OH) 2 (aq) is a base because it contains the OH ion. 10. (a) H 2 SO 4 (aq); acid (b) Ca(OH) 2 (aq); base (c) HBr(aq); acid (d) magnesium hydroxide solution: Mg(OH) 2 (aq); base 11. (a) hydrofluoric acid (aqueous hydrogen fluoride); acid (b) nitric acid (aqueous hydrogen nitrate); acid (c) sodium hydroxide; base (d) ammonium hydroxide; base (e) acetic acid (ethanoic acid); acid (f) phosphoric acid (aqueous hydrogen phosphate); acid (g) calcium hydroxide; base 12. Two ways that human activities could disrupt the normal ph of bodies of water and cause harm to fish are acid precipitation, caused by emissions from coal-fired power plants and other industries and by automobile emissions, and acid leaching from mine tailings (waste rock). Both of these lower the ph in bodies of water. If the ph is low enough, it will harm or even kill fish. 13. (a) Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is an acid. Sodium hydroxide, NaOH, is a base. As NaOH is added to the beaker, the ph reading on the meter will rise. (b) As the base is added to the acid, it enters into a neutralization reaction with the acid, which makes the solution less acidic, so the ph rises. 14. (a) Your body can get rid of excess acids by converting them into less harmful substances or by producing bases to neutralize them. They could also excrete them in their urine. (b) A lab technician could test a urine sample to determine its ph using ph paper, a ph meter, or universal indicator. (Note that litmus paper is not a good answer here as it does not provide the actual ph of a solution.) 15. (a) Teeth are strongly susceptible to attack by acids, and basic saliva prevents acids from damaging them. Saliva can help to neutralize acids in the food we eat, such as those in lemons. (b) Drinking a lot of acidic soft drinks will expose your teeth to excess amounts of acid. Eventually the acids will corrode the tooth enamel, which will lead to cavities.
11 16. Student answers will vary but may include some of the following positive aspects of being an environmental chemist: gaining a greater understanding of the acids, bases, and chemical processes in nature; assisting in the remediation of polluted areas in the environment; researching ways to decrease pollution; and studying the effects of chemicals on plants and animals to gain a greater understanding of its effects on humans. 17. Students will select one of the acids or bases in this chapter and use it to write a story in the first person using facts from this chapter and information gained through Internet or library research. 18. Students will select one of the acids and one of the bases in this chapter and write a dialogue between them using facts from this chapter and information gained through Internet or library research. 19. Students will design a visual device to remember the differences between acids and bases (one such device is provided earlier on page 197). 20. (a) Coal-fired plants can release sulphur oxide gases (SO 2 and SO 3 ) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) gases into the atmosphere. These combine with water vapour to produce sulphuric acid (H 2 SO 4 (aq)) and nitric acid (HNO 3 (aq)) (b) Scrubbers are devices that are found in tall industrial smokestacks of industries, such as coal-fuelled power plants and ore smelting facilities, that release sulphur dioxide gas and nitrogen oxide gases. A specially formulated chemical mixture in the scrubber combines with these gases in chemical reactions, and the products of the reaction can be removed and recycled.
Classifying Substances
 Classifying Substances There are other ways you can use to classify compounds. For example, you can classify some compounds as acids or bases. You are very familiar with acids and bases because you see
Classifying Substances There are other ways you can use to classify compounds. For example, you can classify some compounds as acids or bases. You are very familiar with acids and bases because you see
Topic 5 National Chemistry Summary Notes. Acids and Alkalis
 Topic 5 National Chemistry Summary Notes Acids and Alkalis Experiment Collect some samples of rain water LI 1 The ph Scale The ph scale is a continuous range of numbers from below 0 to above 14. Acids
Topic 5 National Chemistry Summary Notes Acids and Alkalis Experiment Collect some samples of rain water LI 1 The ph Scale The ph scale is a continuous range of numbers from below 0 to above 14. Acids
Downloaded from
 1 X Chemistry Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts Chapter Notes Top concepts: 1. Definition of acids, bases and salts: Acids Bases Salts Sour in taste Bitter in taste & soapy to touch Acid + Base Salt + Water
1 X Chemistry Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts Chapter Notes Top concepts: 1. Definition of acids, bases and salts: Acids Bases Salts Sour in taste Bitter in taste & soapy to touch Acid + Base Salt + Water
Science 10. Unit 2: Chemistry. Book 5: Acid -Base Chemistry & the ph Scale. Block: Name:
 Science 10 Unit 2: Chemistry Book 5: Acid -Base Chemistry & the ph Scale Name: Block: 1 Classifying Substances There are other ways you can use to classify compounds. For example, you can classify some
Science 10 Unit 2: Chemistry Book 5: Acid -Base Chemistry & the ph Scale Name: Block: 1 Classifying Substances There are other ways you can use to classify compounds. For example, you can classify some
Everyday you encounter a variety of different acids and bases. Below is a list of som common acids and bases
 Acids and Bases Everyday you encounter a variety of different acids and bases. Below is a list of som common acids and bases Milk carbonic acid (H 2 CO 3 ) calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH) s ) sodium hydroxide
Acids and Bases Everyday you encounter a variety of different acids and bases. Below is a list of som common acids and bases Milk carbonic acid (H 2 CO 3 ) calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH) s ) sodium hydroxide
Acids, Bases & Salts
 Introduction Acids, Bases & Salts Elements combine to form numerous compounds. On the basis of their chemical properties, compounds can be classified into three categories: Acids Bases Salts Acids and
Introduction Acids, Bases & Salts Elements combine to form numerous compounds. On the basis of their chemical properties, compounds can be classified into three categories: Acids Bases Salts Acids and
SNC2D CHEMISTRY 2/24/2013. CHEMICAL REACTIONS L Acids & Bases (P ) Activity: Introduction to (2DCHEM-ASG3) Introduction to Acids & Bases
 SNC2D CHEMISTRY CHEMICAL REACTIONS L Acids & Bases (P.198-201) Activity: Introduction to (2DCHEM-ASG3) INSTRUCTIONS A. Read the activity 2DCHEM - ASG3 (Introduction to Acids & Bases). B. Follow the instructions
SNC2D CHEMISTRY CHEMICAL REACTIONS L Acids & Bases (P.198-201) Activity: Introduction to (2DCHEM-ASG3) INSTRUCTIONS A. Read the activity 2DCHEM - ASG3 (Introduction to Acids & Bases). B. Follow the instructions
Understand what acids and alkalis are, and where they are found.
 Lesson Aims- Understand what acids and alkalis are, and where they are found. Test a range of household products with litmus indicator to see whether they are acidic or alkaline. Found in citrus fruit
Lesson Aims- Understand what acids and alkalis are, and where they are found. Test a range of household products with litmus indicator to see whether they are acidic or alkaline. Found in citrus fruit
Chapter 5 Notes Science 10 Name:
 5.1 Acids and Bases Many familiar compounds are acids or bases. o Classification as acids or bases is based on chemical composition. Acids and bases can be very dangerous. o Both can be very. o NEVER try
5.1 Acids and Bases Many familiar compounds are acids or bases. o Classification as acids or bases is based on chemical composition. Acids and bases can be very dangerous. o Both can be very. o NEVER try
SNC2D CHEMISTRY 3/12/2013. CHEMICAL REACTIONS L Neutralization Reactions (P ) ph & Plants. ph & Plants
 SNC2D CHEMISTRY CHEMICAL REACTIONS L Reactions (P.204-212) ph & Plants Growing plants for a living can be risky. Many factors can affect the success of a crop, from weather conditions to the nutrient content
SNC2D CHEMISTRY CHEMICAL REACTIONS L Reactions (P.204-212) ph & Plants Growing plants for a living can be risky. Many factors can affect the success of a crop, from weather conditions to the nutrient content
Unit 13 Acids and Bases E.Q. What are the differences between acids and bases?
 Unit 13 Acids and Bases E.Q. What are the differences between acids and bases? What are Properties of Acids? They taste sour (don t try this in lab). They can conduct electricity. Can be strong or weak
Unit 13 Acids and Bases E.Q. What are the differences between acids and bases? What are Properties of Acids? They taste sour (don t try this in lab). They can conduct electricity. Can be strong or weak
Name: Date: Number: Acids
 Acids The sour taste of the lemon juice tells us that it is an acid. Acids are special kinds of chemicals. They are common in everyday life. Some are helpful, others are harmful. There are some that are
Acids The sour taste of the lemon juice tells us that it is an acid. Acids are special kinds of chemicals. They are common in everyday life. Some are helpful, others are harmful. There are some that are
UNIT 10 COMMON ACIDS AND ALKALIS
 ABLE EDUCATION CENTRE UNIT 10 COMMON ACIDS AND ALKALIS A Multiple-choice questions 1 Which of the following are the properties of alkalis? (1) They taste sour. (2) They are slippery. (3) They can turn
ABLE EDUCATION CENTRE UNIT 10 COMMON ACIDS AND ALKALIS A Multiple-choice questions 1 Which of the following are the properties of alkalis? (1) They taste sour. (2) They are slippery. (3) They can turn
the universal solvent
 Chapter 7: Acids, Bases, and Solutions Solution a homogeneous mixture Solutions have the same properties throughout, containing solute particles (molecules or ions) that are too small to see Solvent the
Chapter 7: Acids, Bases, and Solutions Solution a homogeneous mixture Solutions have the same properties throughout, containing solute particles (molecules or ions) that are too small to see Solvent the
Have a ph value less than ph 7 Turn blue litmus indicator red Can neutralise an alkali Have a sour taste (WARNING: never taste any chemicals)
 Acids and Alkalis ACIDS (acidic solutions) Acids have the following properties: Have a ph value less than ph 7 Turn blue litmus indicator red Can neutralise an alkali Have a sour taste (WARNING: never
Acids and Alkalis ACIDS (acidic solutions) Acids have the following properties: Have a ph value less than ph 7 Turn blue litmus indicator red Can neutralise an alkali Have a sour taste (WARNING: never
Chapter 14: Acids and Bases
 Chapter 14: Acids and Bases Properties of Acids and Bases What is an acid? Some examples of common items containing acids: Vinegar contains acetic acid; lemons and citrus fruits contain citric acid; many
Chapter 14: Acids and Bases Properties of Acids and Bases What is an acid? Some examples of common items containing acids: Vinegar contains acetic acid; lemons and citrus fruits contain citric acid; many
Written by: - SHAHZAD IFTIKHAR Contact # Website: s:
 SHORT QUESTION >> Question: What is Self Ionization of Water? Write the equation for self ionization of water? The reaction in which two water molecules produce ions is called as the self ionization or
SHORT QUESTION >> Question: What is Self Ionization of Water? Write the equation for self ionization of water? The reaction in which two water molecules produce ions is called as the self ionization or
Lab: Cabbages in Chemistry 3pts ec printing in COLOR / 2pts B&W
 Lab: Cabbages in Chemistry 3pts ec printing in COLOR / 2pts B&W Telltale Colors 1. In the mixing tray, place 5 drops of the chemical in 13 compartments 2. DIP test the ph paper & record the ph measurement
Lab: Cabbages in Chemistry 3pts ec printing in COLOR / 2pts B&W Telltale Colors 1. In the mixing tray, place 5 drops of the chemical in 13 compartments 2. DIP test the ph paper & record the ph measurement
Lesson Five: Acids, Bases, ph, and Buffers
 Lesson Five: Acids, Bases, ph, and Buffers Arrhenius Acids and Bases Acids and bases can be defined a number of ways. One of the oldest and most common ways is the definition according to Arrhenius, named
Lesson Five: Acids, Bases, ph, and Buffers Arrhenius Acids and Bases Acids and bases can be defined a number of ways. One of the oldest and most common ways is the definition according to Arrhenius, named
Acids, Bases and Salts
 Acids, Bases and Salts Synopsis Substances are classified into acids, bases and salts depending on their chemical behavior and properties. Acids are of sour taste and turn blue litmus to red. Bases are
Acids, Bases and Salts Synopsis Substances are classified into acids, bases and salts depending on their chemical behavior and properties. Acids are of sour taste and turn blue litmus to red. Bases are
Chapter 19 Acids and Bases
 Chapter 19 Acids and Bases p.1/11 19.1 Introducing Acids and Alkalis Acids and bases are common stuff in everyday life. Domestic Acids and Alkalis Common domestic acids Many foods and drinks contain acids.
Chapter 19 Acids and Bases p.1/11 19.1 Introducing Acids and Alkalis Acids and bases are common stuff in everyday life. Domestic Acids and Alkalis Common domestic acids Many foods and drinks contain acids.
5.1. ? Create a Quiz. Acids and Bases. Before You Read. What are acids and bases? What is ph? What are ph indicators?
 Acids and Bases Textbook pages 220 233 Section 5.1 Summary Before You Read Many acids and bases can be found in your home. Describe one acid and one base that you are familiar with. Record your answer
Acids and Bases Textbook pages 220 233 Section 5.1 Summary Before You Read Many acids and bases can be found in your home. Describe one acid and one base that you are familiar with. Record your answer
Name Date Class STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY
 Chemical Reactions Section 10.1 Reactions and Equations In your textbook, read about evidence of chemical reactions. For each statement, write yes if evidence of a chemical reaction is present. Write no
Chemical Reactions Section 10.1 Reactions and Equations In your textbook, read about evidence of chemical reactions. For each statement, write yes if evidence of a chemical reaction is present. Write no
What are Acids and Bases? What are some common acids you know? What are some common bases you know? Where is it common to hear about ph balanced
 What are Acids and Bases? What are some common acids you know? What are some common bases you know? Where is it common to hear about ph balanced materials? Historically, classified by their observable
What are Acids and Bases? What are some common acids you know? What are some common bases you know? Where is it common to hear about ph balanced materials? Historically, classified by their observable
Form 4 Chapter 7: Acid and Bases
 Form 4 Chapter 7: Acid and Bases The ph Scale Properties Acids Alkalis Physical. Substances that ionized in water to produce hydrogen ions.. Sour taste.. Turn blue litmus paper red. 4. Give a ph value
Form 4 Chapter 7: Acid and Bases The ph Scale Properties Acids Alkalis Physical. Substances that ionized in water to produce hydrogen ions.. Sour taste.. Turn blue litmus paper red. 4. Give a ph value
Which other compounds react with acids to produce salts? Acids can also react with metals and carbonates to produce salts.
 Salts Textbook pages 234 243 Section 5.2 Summary Before You Read How many different uses for salts can you name? Write your answers on the lines below. What are salts? In chemistry, salts are a class of
Salts Textbook pages 234 243 Section 5.2 Summary Before You Read How many different uses for salts can you name? Write your answers on the lines below. What are salts? In chemistry, salts are a class of
Unit 1: Chemistry in Action
 Unit 1: Chemistry in Action Intermediate 1 Chemistry Learning Outcomes Substances Elements Everything in the world is made from about 100 elements. Each element has a name and a symbol. Chemists have arranged
Unit 1: Chemistry in Action Intermediate 1 Chemistry Learning Outcomes Substances Elements Everything in the world is made from about 100 elements. Each element has a name and a symbol. Chemists have arranged
Choose the correct answer. velocity changes in every two seconds by ms -1
 Acceleration Q I Choose the correct answer 1. If a body moves with uniform velocity its acceleration is -----zero. 2. Acceleration of a body is the rate of change of ----velocity 3. The acceleration of
Acceleration Q I Choose the correct answer 1. If a body moves with uniform velocity its acceleration is -----zero. 2. Acceleration of a body is the rate of change of ----velocity 3. The acceleration of
Acids Neutral Bases. See pages
 5.1 Acids and Bases 5.1 Acids and Bases Many familiar compounds are acids or bases. Classification as acids or bases is based on chemical composition. Acids and bases can be very dangerous. Both can be
5.1 Acids and Bases 5.1 Acids and Bases Many familiar compounds are acids or bases. Classification as acids or bases is based on chemical composition. Acids and bases can be very dangerous. Both can be
Reactions with Acids. Chemistry 10 Mrs. Page
 Reactions with Acids Chemistry 10 Mrs. Page Learning Objectives Predict the products and balance chemical equations for the reactions with acids involving; reactive metals, metal oxides, metal hydroxides,
Reactions with Acids Chemistry 10 Mrs. Page Learning Objectives Predict the products and balance chemical equations for the reactions with acids involving; reactive metals, metal oxides, metal hydroxides,
5.2. Neutralization Reactions. ph and Plants
 5.2 Neutralization Reactions Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Neutralization is a type of chemical reaction that occurs between an acid and a base and produces water and a salt.
5.2 Neutralization Reactions Here is a summary of what you will learn in this section: Neutralization is a type of chemical reaction that occurs between an acid and a base and produces water and a salt.
Chemical Reactions. Chemical Reactions Chemical reactions have a standard format when written:
 0.3.notebook A chemical property is a behaviour that occurs when substances change to create a new substance. When a new substance is created, a chemical change has occurred. New colour Evidence of chemical
0.3.notebook A chemical property is a behaviour that occurs when substances change to create a new substance. When a new substance is created, a chemical change has occurred. New colour Evidence of chemical
4.2. Double Displacement Reactions. Characteristics of Double Displacement Reactions SECTION. Key Terms
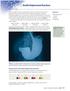 SECTION 4.2 Double Displacement Reactions X rays are highly useful for creating images of bones in the human body, but they generally do not show soft tissues clearly. To help doctors diagnose conditions
SECTION 4.2 Double Displacement Reactions X rays are highly useful for creating images of bones in the human body, but they generally do not show soft tissues clearly. To help doctors diagnose conditions
Acids and Bases. Properties, Reactions, ph, and Titration
 Acids and Bases Properties, Reactions, ph, and Titration C-19 2017 Properties of acids 1. Taste Sour (don t try this except with foods). 2. Are electrolytes (conduct electricity). Some are strong, some
Acids and Bases Properties, Reactions, ph, and Titration C-19 2017 Properties of acids 1. Taste Sour (don t try this except with foods). 2. Are electrolytes (conduct electricity). Some are strong, some
ELECTROLYTES & NEUTRALIZATION
 ELECTROLYTES & NEUTRALIZATION BUT FIRST LET S REVIEW IONS AND BONDING What is the Lewis dot diagram for Magnesium? Mg 2 2- S What is the Lewis dot diagram for Sulfur? How would these 2 elements bond? What
ELECTROLYTES & NEUTRALIZATION BUT FIRST LET S REVIEW IONS AND BONDING What is the Lewis dot diagram for Magnesium? Mg 2 2- S What is the Lewis dot diagram for Sulfur? How would these 2 elements bond? What
Ch. 8 - Solutions, Acids & Bases. Solution = a homogeneous mixture of 2 or more substances
 Ch. 8 - Solutions, Acids & Bases Solution = a homogeneous mixture of 2 or more substances Solute substance whose particles are dissolved in a solution Solvent substance in which the solute dissolves in
Ch. 8 - Solutions, Acids & Bases Solution = a homogeneous mixture of 2 or more substances Solute substance whose particles are dissolved in a solution Solvent substance in which the solute dissolves in
ACIDS & BASES PROPERTIES OF ACIDS ACIDS PROPERTIES OF ACIDS PROPERTIES OF ACIDS 11/1/2016
 SC STANDARD COVERED ACIDS & BASES Standard PS-3.7 Classify various solutions as acids or bases according to their physical properties, chemical properties (including neutralization and reaction with metals),
SC STANDARD COVERED ACIDS & BASES Standard PS-3.7 Classify various solutions as acids or bases according to their physical properties, chemical properties (including neutralization and reaction with metals),
Chapter 14: Acids and Bases
 Chemistry 12 Ch 1 4 : Acids and Bases Page 1 Chapter 14: Acids and Bases Check MasteringChemistry Deadlines Acids and Bases: The sour taste of lemons and lime, the bite of sourdough bread, and the tang
Chemistry 12 Ch 1 4 : Acids and Bases Page 1 Chapter 14: Acids and Bases Check MasteringChemistry Deadlines Acids and Bases: The sour taste of lemons and lime, the bite of sourdough bread, and the tang
4.5: Acids and Bases. SCH3U: Solutions and Solubility. Properties of Pure and Aqueous Substances. Arrhenius Theory. Acid:
 4.5: Acids and Bases Properties of Pure and Aqueous Substances Arrhenius Theory Acid: Acids are sour tasting and corrosive. They react readily with active metals such as Zn, Ca, Mg and carbonate-based
4.5: Acids and Bases Properties of Pure and Aqueous Substances Arrhenius Theory Acid: Acids are sour tasting and corrosive. They react readily with active metals such as Zn, Ca, Mg and carbonate-based
Acids, Bases, and Salts
 Acids, Bases, and Salts 1 An acid is a substance that releases hydrogen ions when it dissociates. H +1 Cl -1 Cl -1 H +1 2 An acid is a substance that releases hydrogen ions when it dissociates in water.
Acids, Bases, and Salts 1 An acid is a substance that releases hydrogen ions when it dissociates. H +1 Cl -1 Cl -1 H +1 2 An acid is a substance that releases hydrogen ions when it dissociates in water.
REACTIONS OF ACIDS. J:\Science\Chemistry\Stage 1 Notes\Acids & Bases\Reactionsofacids.doc
 REACTIONS OF ACIDS 1. Acids taste sour We do not attempt to taste strong acids as they are too dangerous. They do taste sour, but then they proceed to destroy cells on your tongue and mouth. If you vomit,
REACTIONS OF ACIDS 1. Acids taste sour We do not attempt to taste strong acids as they are too dangerous. They do taste sour, but then they proceed to destroy cells on your tongue and mouth. If you vomit,
8.1 Classifying Inorganic Compounds
 8.1 Classifying Inorganic Compounds You know that compounds can be ionic or molecular based on how their elements are bonded. But all compounds can also be organic or inorganic, depending on the kinds
8.1 Classifying Inorganic Compounds You know that compounds can be ionic or molecular based on how their elements are bonded. But all compounds can also be organic or inorganic, depending on the kinds
Acids and Bases. Acids
 1 Acids and Bases Acids Although some acids can burn and are dangerous to handle, most acids in foods are safe to eat. What acids have in common, however, is that they contain at least one hydrogen atom
1 Acids and Bases Acids Although some acids can burn and are dangerous to handle, most acids in foods are safe to eat. What acids have in common, however, is that they contain at least one hydrogen atom
Acids and Alkalis. Looking at acids and alkalis. 1 hydrochloric. 2 sour. 3 bases. 4 ionize, ionization. 5 hydrogen. 6 mobile ions.
 Topic 4 Acids and Alkalis Section A Fill in the blanks Unit 1 Looking at acids and alkalis 1 hydrochloric 2 sour bases 4 ionize, ionization 5 hydrogen 6 mobile ions 7 basicity 8 monobasic 9 dibasic 10
Topic 4 Acids and Alkalis Section A Fill in the blanks Unit 1 Looking at acids and alkalis 1 hydrochloric 2 sour bases 4 ionize, ionization 5 hydrogen 6 mobile ions 7 basicity 8 monobasic 9 dibasic 10
Elements and Their Oxides
 Elements and Their Oxides An oxide is a. Oxides can form when an element reacts with oxygen, often in air. This reaction can be rapid with the release of a great deal of energy, as in the combustion of
Elements and Their Oxides An oxide is a. Oxides can form when an element reacts with oxygen, often in air. This reaction can be rapid with the release of a great deal of energy, as in the combustion of
Chemical Reaction Defn: Chemical Reaction: when starting chemical species form different chemicals.
 Chemical Reaction Defn: Chemical Reaction: when starting chemical species form different chemicals. Evidence to indicate that a chemical reaction has occurred: Temperature change Different coloured materials
Chemical Reaction Defn: Chemical Reaction: when starting chemical species form different chemicals. Evidence to indicate that a chemical reaction has occurred: Temperature change Different coloured materials
5.1. Acids and Doses. Before You Read. Section. Summary. What are acids and bases? What is ph?
 Acids and Doses Textbook pages 220-233 5.1 Summary Before You Read Many acids and bases can be found in your home. Describe one acid and one base that you are familiar with. Record your answer in the lines
Acids and Doses Textbook pages 220-233 5.1 Summary Before You Read Many acids and bases can be found in your home. Describe one acid and one base that you are familiar with. Record your answer in the lines
Acids and Bases. Chapter 11
 Acids and Bases Chapter 11 Acids and Bases in our Lives Acids and bases are important substance in health, industry, and the environment. One of the most common characteristics of acids is their sour taste.
Acids and Bases Chapter 11 Acids and Bases in our Lives Acids and bases are important substance in health, industry, and the environment. One of the most common characteristics of acids is their sour taste.
Acids and Doses. Before You Read. Section 5.1. Summary. What are acids and bases? What is ph?
 Acids and Doses Textbook pages 220-233 5.1 Before You Read Many acids and bases can be found in your home. Describe one acid and one base that you are familiar with. Record your answer in the lines below.
Acids and Doses Textbook pages 220-233 5.1 Before You Read Many acids and bases can be found in your home. Describe one acid and one base that you are familiar with. Record your answer in the lines below.
I. What Are the Properties of Acids?
 Chapter 6.3 DESCRIBING ACIDS AND BASES I. What Are the Properties of Acids? I. An Acid reacts with metals, reacts wth carbonates, tastes sour, and turns blue litmus paper red. A. REACTIONS WITH METALS
Chapter 6.3 DESCRIBING ACIDS AND BASES I. What Are the Properties of Acids? I. An Acid reacts with metals, reacts wth carbonates, tastes sour, and turns blue litmus paper red. A. REACTIONS WITH METALS
Acids and Bases Unit 13
 Acids and Bases Unit 13 Chemistry of Acids and Bases 1. Watch video and complete worksheet Standard Deviants Teaching Systems: Chemistry: Module 05: Acids and Bases http://app.discoveryeducation.com/player/view/asset
Acids and Bases Unit 13 Chemistry of Acids and Bases 1. Watch video and complete worksheet Standard Deviants Teaching Systems: Chemistry: Module 05: Acids and Bases http://app.discoveryeducation.com/player/view/asset
Practice Examination #8B
 Practice Examination #8B Name: Date: 1. Equal volumes of 0.5 M HCl and 0.5 M NaOH are mixed. The total volume of the resulting mixture is 2 liters. The ph of the resulting solution is 1. A. 1 B. 2 C. 7
Practice Examination #8B Name: Date: 1. Equal volumes of 0.5 M HCl and 0.5 M NaOH are mixed. The total volume of the resulting mixture is 2 liters. The ph of the resulting solution is 1. A. 1 B. 2 C. 7
Downloaded from
 CHAPTER 2--ACIDS, BASES AND SALTS Acids: Substances which turn blue litmus solution red are called acids. Acids are sour in taste Bases: Substances which change red litmus solution blue are called bases.
CHAPTER 2--ACIDS, BASES AND SALTS Acids: Substances which turn blue litmus solution red are called acids. Acids are sour in taste Bases: Substances which change red litmus solution blue are called bases.
Acids and Bases. Acids and Bases in our Lives. Chapter 11
 Acids and Bases Chapter 11 Acids and Bases in our Lives Acids and bases are important substance in health, industry, and the environment. One of the most common characteristics of acids is their sour taste.
Acids and Bases Chapter 11 Acids and Bases in our Lives Acids and bases are important substance in health, industry, and the environment. One of the most common characteristics of acids is their sour taste.
ie) HCl (aq) H + (aq) + Cl - (aq) *Like all equations, dissociation equations are written in balanced form
 Acids and Bases Acids - substances which dissolve in water to form H + ions in solution ie) HCl (aq) H + (aq) + Cl - (aq) *Like all equations, dissociation equations are written in balanced form a) contain
Acids and Bases Acids - substances which dissolve in water to form H + ions in solution ie) HCl (aq) H + (aq) + Cl - (aq) *Like all equations, dissociation equations are written in balanced form a) contain
Do Now April 24, 2017
 Do Now April 24, 2017 Obj: Observe and describe neutralization reactions. Copy: Neutralization is when an acid and base react to product a salt and water. e.g. HCl + NaOH NaCl + H 2 O acid base salt water
Do Now April 24, 2017 Obj: Observe and describe neutralization reactions. Copy: Neutralization is when an acid and base react to product a salt and water. e.g. HCl + NaOH NaCl + H 2 O acid base salt water
ADEng. Programme Chemistry for Engineers Prepared by M. J. McNeil, MPhil.
 ADEng. Programme Chemistry for Engineers Prepared by M. J. McNeil, MPhil. Department of Pure and Applied Sciences Portmore Community College Main Campus 1 LECTURE OBJECTIVES Define acid, bases, alkali,
ADEng. Programme Chemistry for Engineers Prepared by M. J. McNeil, MPhil. Department of Pure and Applied Sciences Portmore Community College Main Campus 1 LECTURE OBJECTIVES Define acid, bases, alkali,
Neutralisation. November 29, neutral
 Neutralisation November 29, 2015 neutral STARTER Decide if the statements are true or false. 1. Vinegar is an example of an alkali. FALSE 2. Tea contains tannic acid. TRUE 3. Coke is an alkali. FALSE 4.
Neutralisation November 29, 2015 neutral STARTER Decide if the statements are true or false. 1. Vinegar is an example of an alkali. FALSE 2. Tea contains tannic acid. TRUE 3. Coke is an alkali. FALSE 4.
ACIDS & BASES. Acids & Bases 1
 ACIDS & BASES Acids and bases have real-life significance. The human body functions properly only when delicate acid-base balances are maintained and crops grow best in soil with the proper ph. In addition,
ACIDS & BASES Acids and bases have real-life significance. The human body functions properly only when delicate acid-base balances are maintained and crops grow best in soil with the proper ph. In addition,
2. What characteristic of water makes it the universal solvent? Nonpolar large molecules long-chain hydrocarbon molecules polar
 PS Chemistry Chapter 22 & 23 Review Test Date Chapter 22 Suggestions for Studying Section 1 Know that a solution is made up of a solute and solvent. Be able to provide an example of a solute and a solvent.
PS Chemistry Chapter 22 & 23 Review Test Date Chapter 22 Suggestions for Studying Section 1 Know that a solution is made up of a solute and solvent. Be able to provide an example of a solute and a solvent.
Page 2. Q1.A student investigated food dyes using paper chromatography. This is the method used.
 Q1.A student investigated food dyes using paper chromatography. This is the method used. 1. Put a spot of food colouring X on the start line. 2. Put spots of four separate dyes, A, B, C and D, on the start
Q1.A student investigated food dyes using paper chromatography. This is the method used. 1. Put a spot of food colouring X on the start line. 2. Put spots of four separate dyes, A, B, C and D, on the start
Write down everything that the word equation tells you about the reaction (Total 4 marks)
 Q1. Here is a word equation for a chemical reaction. copper oxide + sulphuric acid copper sulphate + water Write down everything that the word equation tells you about the reaction.......... (Total 4 marks)
Q1. Here is a word equation for a chemical reaction. copper oxide + sulphuric acid copper sulphate + water Write down everything that the word equation tells you about the reaction.......... (Total 4 marks)
Lesson-5 Acids, bases and salts
 NAME: Grade -7(CHEMISTRY) Worksheet Roll No: Lesson-5 Acids, bases and salts Q.1 Write properties of acid. Ans: Acids have sour taste. Acids turns blue litmus into red. Acids react with metals and release
NAME: Grade -7(CHEMISTRY) Worksheet Roll No: Lesson-5 Acids, bases and salts Q.1 Write properties of acid. Ans: Acids have sour taste. Acids turns blue litmus into red. Acids react with metals and release
Unit 4 Toxins, Section IV, L17-22
 Unit 4 Toxins, Section IV, L17-22 Lesson 17 Heartburn Lesson 18 Pass the Proton Lesson 19 phooey! Lesson 20 Watered Down Lesson 21 Neutral Territory Lesson 22 Drip Drop Acids and Bases What are the properties
Unit 4 Toxins, Section IV, L17-22 Lesson 17 Heartburn Lesson 18 Pass the Proton Lesson 19 phooey! Lesson 20 Watered Down Lesson 21 Neutral Territory Lesson 22 Drip Drop Acids and Bases What are the properties
O + (aq) In this reaction, the water molecule is a Brønsted-Lowry base. It accepts a proton from HF to form H 3
 AcidBase Reactions Key Terms conjugate base conjugate acid amphoteric neutralization salt In the previous sections, you learned about three acidbase theories: Arrhenius, BrønstedLowry, and Lewis. The BrønstedLowry
AcidBase Reactions Key Terms conjugate base conjugate acid amphoteric neutralization salt In the previous sections, you learned about three acidbase theories: Arrhenius, BrønstedLowry, and Lewis. The BrønstedLowry
Water, the SPECIAL Equilibrium
 THE ACID TEST Water, the SPECIAL Equilibrium I. Characteristics of Water A. Water are highly. B. They are in continuous. C. Always. D. Water is dense in the solid phase than in the phase. i.e. ice floats
THE ACID TEST Water, the SPECIAL Equilibrium I. Characteristics of Water A. Water are highly. B. They are in continuous. C. Always. D. Water is dense in the solid phase than in the phase. i.e. ice floats
Acids, Bases, & Neutralization Chapter 20 & 21 Assignment & Problem Set
 Acids, Bases, & Neutralization Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. Acids, Bases, & Neutralization 2 Study Guide: Things You Must Know
Acids, Bases, & Neutralization Name Warm-Ups (Show your work for credit) Date 1. Date 2. Date 3. Date 4. Date 5. Date 6. Date 7. Date 8. Acids, Bases, & Neutralization 2 Study Guide: Things You Must Know
Student Notes Acids and Bases
 Name: Class: Date: Student Notes Acids and Bases Many foods that we eat contain acids, such as lemons, oranges, apples, vinegar, grapes, and soda pop. Lemons and oranges contain citric acid, while apples
Name: Class: Date: Student Notes Acids and Bases Many foods that we eat contain acids, such as lemons, oranges, apples, vinegar, grapes, and soda pop. Lemons and oranges contain citric acid, while apples
DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT REACTIONS. Double your pleasure, double your fun
 DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT REACTIONS Double your pleasure, double your fun Industrial processes produce unwanted by-products. Dissolved toxic metal ions-copper, mercury, and cadmium-are common leftovers in the
DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT REACTIONS Double your pleasure, double your fun Industrial processes produce unwanted by-products. Dissolved toxic metal ions-copper, mercury, and cadmium-are common leftovers in the
Science 10: Chemistry II Practice Test
 Science 10: Chemistry II Practice Test Name: Multiple Choice: Circle the letter of the best answer. You may refer to a periodic table and an ion chart. 1. What type of reaction is the following? silver
Science 10: Chemistry II Practice Test Name: Multiple Choice: Circle the letter of the best answer. You may refer to a periodic table and an ion chart. 1. What type of reaction is the following? silver
Acids and Bases 2 Science Notes JC-Learn. JC-Learn. Science Notes Acids and Bases 2. 1 P a g e
 JC-Learn Science Notes Acids and Bases 2 1 P a g e Acids and Bases 2 The two most common laboratory acids are hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4). The two most common laboratory bases are
JC-Learn Science Notes Acids and Bases 2 1 P a g e Acids and Bases 2 The two most common laboratory acids are hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4). The two most common laboratory bases are
5 ACIDS, BASES AND SALTS
 5 ACIDS, BASES AND SALTS TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. Taste the following substances and enter the result in the following table : Substance Taste (Sour / bitter / any other) Lemon juice Orange
5 ACIDS, BASES AND SALTS TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. Taste the following substances and enter the result in the following table : Substance Taste (Sour / bitter / any other) Lemon juice Orange
Acids and Bases. Acids and Bases in. our Lives. Acids and Bases in our Lives. Acids and Bases in our Lives. Chapter 11
 Acids and Bases Chapter 11 Acids and Bases in our Lives We produce lactic acid in our muscles when we exercise. Acid from bacteria turns milks sour in the products of yogurt and cottage cheese. We have
Acids and Bases Chapter 11 Acids and Bases in our Lives We produce lactic acid in our muscles when we exercise. Acid from bacteria turns milks sour in the products of yogurt and cottage cheese. We have
CHAPTER 19. Acids, Bases, and Salts Acid Base Theories
 CHAPTER 19 Acids, Bases, and Salts 19.1 Acid Base Theories ACIDS tart or sour taste Electrolytes Strong acids are corrosive Acid Facts... indicators will change color Blue litmus paper turns pink react
CHAPTER 19 Acids, Bases, and Salts 19.1 Acid Base Theories ACIDS tart or sour taste Electrolytes Strong acids are corrosive Acid Facts... indicators will change color Blue litmus paper turns pink react
The grade 5 English science unit, Acids and Bases, meets the academic content standards set in the Korean curriculum, which state students should:
 This area addresses ph among different characteristics of solutions. It will be interesting for students to classify a variety of solutions into acids and bases by using the characteristics of the solutions.
This area addresses ph among different characteristics of solutions. It will be interesting for students to classify a variety of solutions into acids and bases by using the characteristics of the solutions.
How do Metal Carbonates and Metal Hydrogencarbonates React
 Acids, Bases, and Salts] This chapter is about: Reaction of acids and bases, how acids and bases cancel out each other s effects and many more interesting things that we use and see in our day-to-day life.
Acids, Bases, and Salts] This chapter is about: Reaction of acids and bases, how acids and bases cancel out each other s effects and many more interesting things that we use and see in our day-to-day life.
Acids and Bases. Part A Unit-based exercise. Topic 4. Unit 14 Acids and alkalis. Fill in the blanks. 1 hydrochloric. 2 Sulphuric. 3 Ethanoic.
 Topic 4 Acids and Bases Part A Unit-based exercise Unit 14 Acids and alkalis Fill in the blanks 1 hydrochloric 2 Sulphuric 3 Ethanoic 4 sour 5 red; yellow 6 colourless; red 7 bases 8 dissociate; dissociation
Topic 4 Acids and Bases Part A Unit-based exercise Unit 14 Acids and alkalis Fill in the blanks 1 hydrochloric 2 Sulphuric 3 Ethanoic 4 sour 5 red; yellow 6 colourless; red 7 bases 8 dissociate; dissociation
An acidic substance always contains (1) in its name. An (2) is a chemical that changes colour to tell you
 Test Part A Fill in the gaps An acidic substance always contains (1) in its name. An (2) is a chemical that changes colour to tell you whether a substance is an acid or a (3). Another name for (4)/(5)
Test Part A Fill in the gaps An acidic substance always contains (1) in its name. An (2) is a chemical that changes colour to tell you whether a substance is an acid or a (3). Another name for (4)/(5)
Definition of Acid. HCl + H 2 O H 3 O + + Cl
 Acids Definition of Acid Acids are substances that contain H + ions that ionize when dissolved in water. Arrhenius acid: a compound that increases the concentration of H + ions that are present when added
Acids Definition of Acid Acids are substances that contain H + ions that ionize when dissolved in water. Arrhenius acid: a compound that increases the concentration of H + ions that are present when added
Wherever chemical solutions are involved, ph matters. Some
 47 Acids, Bases, and the ph Scale R EA D I N G Wherever chemical solutions are involved, ph matters. Some important chemical reactions, such as those involved in corrosion of iron or digestion of food,
47 Acids, Bases, and the ph Scale R EA D I N G Wherever chemical solutions are involved, ph matters. Some important chemical reactions, such as those involved in corrosion of iron or digestion of food,
Chapter 13 Acids and Bases: The Molecules Responsible for Sour and Bitter
 Nivaldo J. Tro http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/tro Chapter 13 Acids and Bases: The Molecules Responsible for Sour and Bitter Mark Erickson Hartwick College Acids Sourness in foods is caused by acids,
Nivaldo J. Tro http://www.cengage.com/chemistry/tro Chapter 13 Acids and Bases: The Molecules Responsible for Sour and Bitter Mark Erickson Hartwick College Acids Sourness in foods is caused by acids,
Acids and Bases. Say Thanks to the Authors Click (No sign in required)
 Acids and Bases Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org
Acids and Bases Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org
Chapter 9 Acid-base reactions
 CHEM, 2nd edition Cengage Learning Chapter 9 Acid-base reactions Acids and bases are chemical compounds that occur regularly in 'everyday life'. These two types of substances have opposite properties.
CHEM, 2nd edition Cengage Learning Chapter 9 Acid-base reactions Acids and bases are chemical compounds that occur regularly in 'everyday life'. These two types of substances have opposite properties.
Chemistry and Reactions Year 9 Extension Science. 1 GZ Science Resources 2014
 Chemistry and Reactions Year 9 Extension Science 1 GZ Science Resources 2014 1a Reactants join together to form new products during chemical reactions The atoms present in the reactants rearrange themselves
Chemistry and Reactions Year 9 Extension Science 1 GZ Science Resources 2014 1a Reactants join together to form new products during chemical reactions The atoms present in the reactants rearrange themselves
Unit 4: ACIDS, BASES AND SALTS
 ABS - 1 Unit 4: ACIDS, BASES AND SALTS 4.1 Arrhenius Acids and Bases Acids release H + in water Bases release OH - in water Salts are products of an acid-base neutralization reaction. The salt is an ionic
ABS - 1 Unit 4: ACIDS, BASES AND SALTS 4.1 Arrhenius Acids and Bases Acids release H + in water Bases release OH - in water Salts are products of an acid-base neutralization reaction. The salt is an ionic
Double replacement reactions
 1. Learn to predict Double replacement reaction If and when a reaction occurs, what are the products? 2. Learn to write Double replacement reaction: (i) Balanced chemical reaction (ii) Net ionicreaction
1. Learn to predict Double replacement reaction If and when a reaction occurs, what are the products? 2. Learn to write Double replacement reaction: (i) Balanced chemical reaction (ii) Net ionicreaction
Section Four Structured questions
 Section Four Structured questions 1 For each of the following experiments, state ONE observable change and write a chemical equation for the reaction involved. a) Magnesium strip is added to dilute hydrochloric
Section Four Structured questions 1 For each of the following experiments, state ONE observable change and write a chemical equation for the reaction involved. a) Magnesium strip is added to dilute hydrochloric
BUT FIRST LET S REVIEW IONS AND BONDING. What is the Lewis dot diagram for Magnesium? 2+ 2-
 ELECTROLYTES BUT FIRST LET S REVIEW IONS AND BONDING What is the Lewis dot diagram for Magnesium? Mg 2 2- S What is the Lewis dot diagram for Sulfur? How would these 2 elements complete the octet rule?
ELECTROLYTES BUT FIRST LET S REVIEW IONS AND BONDING What is the Lewis dot diagram for Magnesium? Mg 2 2- S What is the Lewis dot diagram for Sulfur? How would these 2 elements complete the octet rule?
Definition of Acid. HCl + H 2 O H 3 O + + Cl
 Acids Definition of Acid Acids are substances that contain H + ions that ionize when dissolved in water. Arrhenius acid: a compound that increases the concentration of H + ions that are present when added
Acids Definition of Acid Acids are substances that contain H + ions that ionize when dissolved in water. Arrhenius acid: a compound that increases the concentration of H + ions that are present when added
Families of Chemical Compounds. Chapter 9
 Families of Chemical Compounds Chapter 9 Groups of Compounds Compounds are grouped based on physical and chemical properties Types: Organic, Acids, Bases, and Salts Acids and Bases Examples of Acids Aspirin
Families of Chemical Compounds Chapter 9 Groups of Compounds Compounds are grouped based on physical and chemical properties Types: Organic, Acids, Bases, and Salts Acids and Bases Examples of Acids Aspirin
Unit 5 Lesson 3 Measuring ph. Copyright Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company
 What s Your Number? What is the ph scale? The ph of a solution is a measure of how acidic or basic a solution is. A solution that has a ph value of exactly 7 is neutral neither acidic nor basic. A solution
What s Your Number? What is the ph scale? The ph of a solution is a measure of how acidic or basic a solution is. A solution that has a ph value of exactly 7 is neutral neither acidic nor basic. A solution
Chemical Reaction Defn: Chemical Reaction: when starting chemical species form different chemicals.
 Chemistry 11 Notes on Chemical Reactions Chemical Reaction Defn: Chemical Reaction: when starting chemical species form different chemicals. Evidence to indicate that a chemical reaction has occurred:
Chemistry 11 Notes on Chemical Reactions Chemical Reaction Defn: Chemical Reaction: when starting chemical species form different chemicals. Evidence to indicate that a chemical reaction has occurred:
Page 1 of 14. Website: Mobile:
 Question 1: You have been provided with three test tubes. One of them contains distilled water and the other two contain an acidic solution and a basic solution, respectively. If you are given only red
Question 1: You have been provided with three test tubes. One of them contains distilled water and the other two contain an acidic solution and a basic solution, respectively. If you are given only red
Unit 5 ACIDS, BASES & SALTS
 Chemistry Form 3 Page 50 Ms. R. Buttigieg Unit 5 ACIDS, BASES & SALTS See Chemistry for You Chapter 12 pg. 142 onwards. See GCSE Chemistry Chapter 7 pg. 95 onwards INTRODUCTION ACIDS Acids have a ph less
Chemistry Form 3 Page 50 Ms. R. Buttigieg Unit 5 ACIDS, BASES & SALTS See Chemistry for You Chapter 12 pg. 142 onwards. See GCSE Chemistry Chapter 7 pg. 95 onwards INTRODUCTION ACIDS Acids have a ph less
SUBJECT SCIENCE CLASS VII CHAPTER 4, HEAT
 SUBJECT SCIENCE CLASS VII CHAPTER 4, HEAT 1. What is temperature? Temperature is the reliable measure of the hotness of an object. 2. What is thermometer? Thermometer is a device which is used to measure
SUBJECT SCIENCE CLASS VII CHAPTER 4, HEAT 1. What is temperature? Temperature is the reliable measure of the hotness of an object. 2. What is thermometer? Thermometer is a device which is used to measure
Ch 7 Chemical Reactions Study Guide Accelerated Chemistry SCANTRON
 Ch 7 Chemical Reactions Study Guide Accelerated Chemistry SCANTRON Name /80 TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. Correct the False statments by changing the
Ch 7 Chemical Reactions Study Guide Accelerated Chemistry SCANTRON Name /80 TRUE/FALSE. Write 'T' if the statement is true and 'F' if the statement is false. Correct the False statments by changing the
SNC2D1: Grade 10 Academic Science
 SNC2D1: Grade 10 Academic Science Chemistry Test date: Monday, March 24 Study tips: apple Read through your notes apple Make point form notes to summarize the topics apple Complete the review sheet apple
SNC2D1: Grade 10 Academic Science Chemistry Test date: Monday, March 24 Study tips: apple Read through your notes apple Make point form notes to summarize the topics apple Complete the review sheet apple
A salt is a neutral ionic compound composed of cations and anions. It is the result of an acid-base neutralisation reaction.
 Acid-base reactions When an acid and a base react, they form a salt. If the base contains hydroxide (OH ) ions, then water will also be formed. The word salt is a general term which applies to the products
Acid-base reactions When an acid and a base react, they form a salt. If the base contains hydroxide (OH ) ions, then water will also be formed. The word salt is a general term which applies to the products
Name: Block: Date: Student Notes
 Name: Block: Date: LCPS Core Experience Acids and Bases Student Notes OBJECTIVES Students will: recognize some acids and bases as common and familiar household chemicals. realize that acids and bases are
Name: Block: Date: LCPS Core Experience Acids and Bases Student Notes OBJECTIVES Students will: recognize some acids and bases as common and familiar household chemicals. realize that acids and bases are
Metal + water -> metal hydroxide + hydrogen Metal + acid -> metal salt + hydrogen
 Name of Formula Formula of ion Name of salt Hydrochloric Sulphuric HCl Cl - Chloride H 2 SO 4 SO 4-2 Sulphate Key words: Oxidation: loss of electrons Reduction: gain of electrons Displacement reaction:
Name of Formula Formula of ion Name of salt Hydrochloric Sulphuric HCl Cl - Chloride H 2 SO 4 SO 4-2 Sulphate Key words: Oxidation: loss of electrons Reduction: gain of electrons Displacement reaction:
