Molecular Orbitals in Inorganic Chemistry. Dr. P. Hunt Rm 167 (Chemistry)
|
|
|
- Scott Blankenship
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Molecular rbitals in Inorganic Chemistry Dr. P. unt Rm 167 (Chemistry)
2 Lecture 2 utline L2 build a M diagram to show you the process quick revision stage 1: basic M diagram for 2 stage 2: include M mixing real Ms (how good are qualitative diagrams) Walsh or correlation diagrams L3 come back and look closely at the details
3 Revision M are combinations of As Fig. 1 details: Maths lectures with Joao Malhado Foundation from last year atomic orbitals radial and angular components radial: as quantum shell increases inner nodes radius max density increases cartoons represent outer portion shaded part represents negative part of function angular nature represented by the lobes the rbitron link from my website removed due to copyright ψ 1s R 1s Y 1s 2Z 3 2 e ρ 2!#" # $ (1 4π )1 2!#" # $ R 1s Y 1s z θ y=ax 2 +bx+c positive θ x negative sign change with θ Fig. 2 Fig. 3
4 Setting Up determine the shape of the molecule Lecture 1 find the point group of the molecule: C2v define the axial system find all of the symmetry elements C 2v A 1 E C 2 σ v (xz) σ v '(yz) h= z y z C 2 (z) x σ v (yz) 1 2 σ v (xz) A Fig. 4 B 1 B x y your character tables
5 Fragments map onto each other under the symmetry operations atoms map onto each other atom maps onto its self 2 and atom are the fragments use place holders! z x y 2 fragment place holder whole molecule place holder fragment Fig. 5
6 Fragments map onto each other under the symmetry operations atoms map onto each other atom maps onto its self 2 and atom are the fragments use place holders! z x y 2 fragment place holder whole molecule place holder fragment reproduce the whole of the molecular structure in the M fragment orbitals 2 orbitals atom orbitals 2 orbitals (s and p) orbitals Fig. 6
7 Set Up M Diagram Important! vertical axis: Energy 1s A position As more electronegative than so valence orbitals lie below 1s reference orbital atoms are further apart than in 2 so stablilsation and destabilsation are less ie splitting energy is less more on this next lecture! y z x??? 2 p y p x p z s Fig. 6
8 Fragment rbital Symmetry ow does each orbital transform under the symmetry operations of the group? orbital is unchanged => character = 1 a sign change => character = -1 check against the character table σ v (yz) Lecture 1 No change under σ χ = 1 v σ v C 2v E C 2 σ v (xz) σ v '(yz) Short-Cut! Γ Fig. 7 totally bonding orbitals are always totally symmetric which is the first symmetry label listed for all point groups for C2v this is the a1 irreducible representation
9 Short Cuts! look in the last columns of the character table find Tx, Ty, Tz sometimes also written as just x, y, z gives you the axis symmetry label Short-Cut! C 2v A 1 E C 2 σv (xz) σ v '(yz) h=4 T z Important! A 2 B 1 B T x T y Fig. 7
10 Fragment rbitals look for similarities in the phase of orbitals and the cartesian axes Short-Cut! Γ C 2v E C 2 σ v (xz) σ v '(yz) T y b 2 x Γ Γ T x T z b 1 2 C 2v E C 2 σ v (xz) σ v '(yz) Γ Γ b 1 Fig. 7 Fig. 8 look for similarity in phase patterns!
11 Fragment rbitals look for similarities in the phase of orbitals and the cartesian axes Short-Cut! C 2v E C 2 σ v (xz) σ v '(yz) Γ p y b 2 Γ p x b 1 Γ p z Fig. 7
12 Add symmetry labels to M diagram Fig. 9
13 Form the Ms work out Ms first then the splitting Important! nly fragment orbitals (Fs) of the same symmetry can combine for water: a1 and b1 F can only combine NCE more than one F of same symmetry? then combine the lowest energy two leave the last one non-bonding (for now!) Form Ms by adding Fs together as is adding Fs with NE F phase inverted + + b 1 Fig 10
14 Stage ne M Diagram b 1 Evaluate splitting b 2 b 1 Fs far apart in energy interact only weakly in-phase interactions are bonding destabilisation is always larger more on this next lecture! TEN Ms on the diagram z x y 2 Fig 11/12
15 Stage ne 2b 1 M Diagram b 1 Evaluate splitting b 2 b 1 Fs closer in energy interact more destabilisation is always larger more on this next lecture! TEN Ms on the diagram z x y 2 Fig 11/12
16 Stage ne 2b 1 M Diagram 4 b 1 Label Ms 1b 2 b 2 b 1 number within symmetry label count the core orbitals only if molecule is small 3 1b 1 2 z x y 2 Fig 11/12
17 Stage ne antibonding M is always destabilised more than the bonding M is stabilised 2b 1 M Diagram 4 b 1 Annotate your diagrams! Important! F left nonbonding in the first stage diagram 1b 2 3 1b 1 b 2 Fs are closer in energy and so the interaction between the orbitals is larger for the b 1 M b 1 do not repeat information z 2 1 is the 1sA which is not shown because this is a valence M diagram x y Fig 11/12
18 Stage ne antibonding M is always destabilised more than the bonding M is stabilised 2b 1 M Diagram 4 b 1 add the electrons! fill sequentially F left nonbonding in the first stage diagram 1b 2 3 b 2 b 1 1b 1 Fs are closer in energy and so the interaction between the orbitals is larger for the b 1 M 2 z 1 is the 1sA which is not shown because this is a valence M diagram x y 2 valence e 6 valence e Fig 11/12
19 Stage 2: M Mixing necessary conditions NLY Ms of the same symmetry can mix to occur mixing MUST stabilise the total energy mixing tends to be large when: Ms are close in energy one M is non-bonding or unoccupied orbitals are in M-LUM region Important!
20 M Mixing mixing orbitals add Ms together as is 0 add Ms with NE M phase inverted inspect to determine which is the bonding mixed M occupied + unoccupied antibonding due to increased out-ofphase interaction ψ (3 ) ψ (4 ) ψ 1 = ψ (3 ) + ψ (4 ) antibonding M Fig 13
21 In-Class Activity mixing orbitals add Ms together as is add Ms with NE M phase inverted 0 inspect to determine which is the bonding mixed M form -ψ(3 )+ψ(4 ) Fig 14
22 In-Class Activity mixing orbitals add Ms together as is add Ms with NE M phase inverted 0 inspect to determine which is the bonding mixed M form -ψ(3 )+ψ(4 ) + bonding due to increased inphase interaction ψ (3 ) ψ (4 ) ψ 2 = ( ψ (3 )) + ψ (4 ) = ψ (4 ) ψ (3 ) "non-bonding" or slightly antibonding M Fig 14
23 4 Mixing 2b 1 strong mixing: 4a1 M unoccupied 3a1 M non-bonding in M/LUM region close in energy occupied M is stabilised b 1 1b 2 3 1b 1 b 2 b 1 significant mixing drives 3 M down in energy and chanes the shape of the M extra lines drawn to show the main mixing interaction 2 z x y 2 valence e 2 6 valence e Fig 15
24 4 Final M antibonding M is always destabilised more than the bonding M is stabilised 2b 1 Diagram of the 4 lies above the 2b 1 M because there is strong directional antibonding overlap in the 4 M and weaker less directional overlap in the 2b 1 M 2 b 1 b 2 F left nonbonding as there is no other F of this symmetry for it to interact with Fs are closer in energy and so the interaction between the orbitals is larger for the 1b 1 than the 2 M 1b 2 3 1b 1 2 b 2 b 1 significant mixing drives 3 M down in energy and chanes the shape of the M z 1 is the 1sA which is not shown because this is a valence M diagram x y 2 valence e 2 6 valence e Fig 15
25 Real Ms computed molecular orbitals 2 1b 1 we have solved the Schrödinger equation!!! 3 b 2 Fig 16
26 Experimental Evidence Photoelectron spectrum energy required to eject an electron from its orbital traditional theory: expect 2 equivalent bonds and 2 equivalent lone pairs for water = 2 lines in photo-electron spectrum removed due to copyright Fig 17 BUT have 3 lines in photo-electron spectrum which relate to delocalised 1b1, 3a1 and 1b2 Ms Fig 18
27 Delocalisation Ms are delocalised not 2 center 2 electron most of Ms extend over ALL atoms in molecule there are no bonds where have the bonds gone??? Bonds represent a build up of the TTAL electron density We keep ideas of hybridisation and 2c-2e bonds because they are USEFUL
28 Analysis 4 M diagrams are transferable 2b 1 one diagram is good for many molecules or fragments! molecules Be2 (homework), 2S fragments C2 (lecture 4), N2 we can even treat metal fragments: M2 b 1 1b 2 3 b 2 b 1 general formula A2 1b 1 A=main group element, M=metal slight modifications: different numbers of electrons slightly different position of the fragment orbitals z x y 2 valence e valence e
29 Correlation Diagram Walsh diagram: change one geometric parameter and examine changes in Ms and energies normally a bond distance or angle link the Ms for two extreme geometries removed due to copyright example: Why is 2 bent? start with high symmetry Fig 21 C 2v 105º 180º D h Prof. A.D Walsh University of Dundee from: scientists.htm end with lower symmetry -- angle
30 Walsh Diagram typically start from the highest symmetry I ve constructed the M diagram for linear 2 for you (Self-study for you to reproduce) Fig 21
31 Walsh Diagram then examine how Ms change under geometric distortion Qualitative not Quantitative! Fig 21
32 Energy of Ms then examine how Ms change under geometric distortion 2σ g + (2a1) stabilised BNDED overlap dominates directed & overlap is stronger in linear structure on bending - bonding overlap ALS... through space bonding overlap net result small stabilisation Fig 21
33 Energy of Ms then examine how Ms change under geometric distortion 1σ u + (1b1) destabilised - bonding overlap ALS... through space antibonding net result destabilisation Fig 21
34 Energy of Ms then examine how Ms change under geometric distortion 1π u (1b2) no change non-bonding orbital Fig 21
35 Energy of Ms then examine how Ms change under geometric distortion 2σ u + (2b1) stabilised socrative quiz! WZ9KBWC3 Fig 21
36 Energy of Ms then examine how Ms change under geometric distortion 2σ u + (2b1) stabilised - antibonding overlap also... through space antibonding BNDED overlap dominates net result destabilisation Fig 21
37 Energy of Ms then examine how Ms change under geometric distortion 1π u 3σ g + / or 3a1/4a1 special as planar molecule 1πu and 3σg + cannot mix (not same symmetry) when molecule distorts they become the same symmetry: mixing occurs 1πu goes to 3a1 3σg + goes to 4a1 on mixing the 1πu ( 3a1) is stabilised Important! Fig 21 18
38 Change of Axes When the symmetry point group changes the axial definition changes! y z x y z x y x z y x z z-axis reorientated orbital remains the same only labels change then follow with mixing 4 2σ g + 3 1π u mixing Fig 22
39 Walsh Diagram rbital changes As move with the atoms form or shape of As remains constant!! except for Ms which undergo mixing Molecular stability examine how occupied Ms change under geometric distortion look for occupied Ms which show a large change in energy these orbitals drive the change in shape self-study questions Fig 22
40 Symmetry Breaking But how does the drop in symmetry start? nuclear vibrations provide infinitesimal distortion required for M mixing vibronic coupling = coupling of electronic and nuclear motions breakdown of the Born-ppenheimer approximation! collapse of a VERY fundamental approximation more common than you think! of which Jahn-Teller theorem is a special case
41 Symmetry Breaking symmetry & symmetry breaking underlies many theories in physics and chemistry Noether s Theorem Shows that a conservation law can be derived from any continuous symmetry. invariance with respect to translation gives the law of conservation of linear momentum invariance with respect to time translation gives the law of conservation of energy general relativity magnetism standard model of particle physics superconductivity Serious Stuff! existence of iggs particle eisenberg Uncertainty Principle field theory removed due to copyright Emmy Noether source: Image:Noether.jpg accessed 17/08/07
42 M checklist steps we have used today to form a M diagram VERY Important! Steps to construct a M diagram determine the molecular shape and identify the point group define the axial system and all of the symmetry operations identify the chemical fragments, put them on the bottom of the diagram determine the energy levels and symmetry labels of the fragment orbitals (use 1s as a reference) combine fragment orbitals of the same symmetry, determine the Ms and then estimate the splitting energy; draw in the M energy levels and Ms (in pencil!) determine the number of electrons in each fragment and hence the central M region, add them to the diagram identify if any M mixing occurs, determine the mixed orbitals and redraw the M diagram with shifted energy levels and the mixed Ms annotate your diagram use the M diagram to understand the structure, bonding and chemistry of the molecule
43 Key Points be able to form M diagrams for molecules with the general formula A2 and A3 (tutorial) where A= main group element or a metal be able to explain and illustrate M mixing be able to critically evaluate VSEPR theory, localised 2c-2e bonding and the delocalised M picture of bonding be able to describe how a PES is formed and be able to relate a spectrum to the Ms, and M diagram of a molecule be able to form correlation diagrams and explain why a particular geometry is more stable than another with reference to the stability of the Ms be able to discuss symmetry breaking and vibronic coupling be able to describe the process of forming a M diagram (the M checklist)
44 Finally See my web-site notes AND slides link to panopto when it becomes available optional background support for beginners optional material to take you a little further links to interesting people and web-sites links to relevant research papers on Ms model answers!!
Molecular Orbitals in Inorganic Chemistry. Dr. P. Hunt Rm 167 (Chemistry)
 Molecular Orbitals in Inorganic Chemistr Dr. P. unt p.hunt@imperial.ac.uk Rm 167 (Chemistr) http://www.ch.ic.ac.uk/hunt/ Outline choosing fragments orbital smmetr (again!) bonding and antibonding character
Molecular Orbitals in Inorganic Chemistr Dr. P. unt p.hunt@imperial.ac.uk Rm 167 (Chemistr) http://www.ch.ic.ac.uk/hunt/ Outline choosing fragments orbital smmetr (again!) bonding and antibonding character
Lecture 4 Model Answers to Problems
 Self-Study Problems / Exam Preparation Construct and annotate a valence MO diagram for H 2 CN -. Use your diagram to explain why the neutral radical is more stable than the anion. (this is an old exam
Self-Study Problems / Exam Preparation Construct and annotate a valence MO diagram for H 2 CN -. Use your diagram to explain why the neutral radical is more stable than the anion. (this is an old exam
Molecular Orbitals in Inorganic Chemistry
 Outline Molecular Orbitals in Inorganic hemistr Dr. P. unt p.hunt@imperial.ac.uk Rm 167 (hemistr) http://www.ch.ic.ac.uk/hunt/ choosing fragments orbital smmetr (again!) bonding and antibonding character
Outline Molecular Orbitals in Inorganic hemistr Dr. P. unt p.hunt@imperial.ac.uk Rm 167 (hemistr) http://www.ch.ic.ac.uk/hunt/ choosing fragments orbital smmetr (again!) bonding and antibonding character
Molecular Orbitals in Inorganic Chemistry. Dr. P. Hunt Rm 167 (Chemistry)
 Molecular Orbitals in Inorganic Chemistry Dr. P. Hunt p.hunt@imperial.ac.uk Rm 167 (Chemistry http://www.ch.ic.ac.uk/hunt/ Outline LCAO theory orbital size matters where to put the FO energy levels the
Molecular Orbitals in Inorganic Chemistry Dr. P. Hunt p.hunt@imperial.ac.uk Rm 167 (Chemistry http://www.ch.ic.ac.uk/hunt/ Outline LCAO theory orbital size matters where to put the FO energy levels the
Molecular Orbitals in Inorganic Chemistry. Dr. P. Hunt Rm 167 (Chemistry)
 Molecular Orbitals in Inorganic Chemistry Dr. P. unt p.hunt@imperial.ac.uk Rm 167 (Chemistry) http://www.ch.ic.ac.uk/hunt/ Resources Web notes AND slides link to panopto when it becomes available model
Molecular Orbitals in Inorganic Chemistry Dr. P. unt p.hunt@imperial.ac.uk Rm 167 (Chemistry) http://www.ch.ic.ac.uk/hunt/ Resources Web notes AND slides link to panopto when it becomes available model
The symmetry properties & relative energies of atomic orbitals determine how they react to form molecular orbitals. These molecular orbitals are then
 1 The symmetry properties & relative energies of atomic orbitals determine how they react to form molecular orbitals. These molecular orbitals are then filled with the available electrons according to
1 The symmetry properties & relative energies of atomic orbitals determine how they react to form molecular orbitals. These molecular orbitals are then filled with the available electrons according to
x find all of the symmetry operations/elements: o character table headings: E, 2C φ σ v, i, S φ C 2 φ
 Construct and annotate a valence molecular orbital diagram for the linear molecule Mg 2. Assume the 3pAOs lie deeper in energ than the Mg 3sAO and that the Mg and orbitals interact onl slightl. Mg is a
Construct and annotate a valence molecular orbital diagram for the linear molecule Mg 2. Assume the 3pAOs lie deeper in energ than the Mg 3sAO and that the Mg and orbitals interact onl slightl. Mg is a
Figure 1 Correlation diagram for BeH 2
 Self-Stud Problems / Eam Preparation revise our computational chemistr workshop from last ear: http://www.huntresearchgroup.org.uk/teaching/ear1_lab_start.html o make sure ou have checked that the molecule
Self-Stud Problems / Eam Preparation revise our computational chemistr workshop from last ear: http://www.huntresearchgroup.org.uk/teaching/ear1_lab_start.html o make sure ou have checked that the molecule
Chem 673, Problem Set 5 Due Tuesday, December 2, 2008
 Chem 673, Problem Set 5 Due Tuesday, December 2, 2008 (1) (a) Trigonal bipyramidal (tbp) coordination is fairly common. Calculate the group overlaps of the appropriate SALCs for a tbp with the 5 d-orbitals
Chem 673, Problem Set 5 Due Tuesday, December 2, 2008 (1) (a) Trigonal bipyramidal (tbp) coordination is fairly common. Calculate the group overlaps of the appropriate SALCs for a tbp with the 5 d-orbitals
Chem Spring, 2017 Assignment 5 - Solutions
 Page 1 of 10 Chem 370 - Spring, 2017 Assignment 5 - Solutions 5.1 Additional combinations are p z ± d z 2, p x ±d xz, and p y ±d yz. p z ± d z 2 p x ±d xz or p y ±d yz 5.2 a. Li 2 has the configuration
Page 1 of 10 Chem 370 - Spring, 2017 Assignment 5 - Solutions 5.1 Additional combinations are p z ± d z 2, p x ±d xz, and p y ±d yz. p z ± d z 2 p x ±d xz or p y ±d yz 5.2 a. Li 2 has the configuration
Mo 2+, Mo 2+, Cr electrons. Mo-Mo quadruple bond.
 Problem 1 (2 points) 1. Consider the MoMoCr heterotrimetallic complex shown below (Berry, et. al. Inorganica Chimica Acta 2015, p. 241). Metal-metal bonds are not drawn. The ligand framework distorts this
Problem 1 (2 points) 1. Consider the MoMoCr heterotrimetallic complex shown below (Berry, et. al. Inorganica Chimica Acta 2015, p. 241). Metal-metal bonds are not drawn. The ligand framework distorts this
Chapter 5. Molecular Orbitals
 Chapter 5. Molecular Orbitals MO from s, p, d, orbitals: - Fig.5.1, 5.2, 5.3 Homonuclear diatomic molecules: - Fig. 5.7 - Para- vs. Diamagnetic Heteronuclear diatomic molecules: - Fig. 5.14 - ex. CO Hybrid
Chapter 5. Molecular Orbitals MO from s, p, d, orbitals: - Fig.5.1, 5.2, 5.3 Homonuclear diatomic molecules: - Fig. 5.7 - Para- vs. Diamagnetic Heteronuclear diatomic molecules: - Fig. 5.14 - ex. CO Hybrid
5.80 Small-Molecule Spectroscopy and Dynamics
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.80 Small-Molecule Spectroscopy and Dynamics Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 5.80 Lecture
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.80 Small-Molecule Spectroscopy and Dynamics Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 5.80 Lecture
Chemistry: The Central Science. Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theory
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theory The shape and size of a molecule of a particular substance, together with the strength and polarity of its bonds, largely
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theory The shape and size of a molecule of a particular substance, together with the strength and polarity of its bonds, largely
Chemistry 543--Final Exam--Keiderling May 5, pm SES
 Chemistry 543--Final Exam--Keiderling May 5,1992 -- 1-5pm -- 174 SES Please answer all questions in the answer book provided. Make sure your name is clearly indicated and that the answers are clearly numbered,
Chemistry 543--Final Exam--Keiderling May 5,1992 -- 1-5pm -- 174 SES Please answer all questions in the answer book provided. Make sure your name is clearly indicated and that the answers are clearly numbered,
Spectroscopy and Characterisation. Dr. P. Hunt Rm 167 (Chemistry) web-site:
 Spectroscop and Characterisation Dr. P. unt p.hunt@imperial.ac.uk Rm 167 (Chemistr) web-site: http://www.ch.ic.ac.uk/hunt Resources Web copies course notes download slides model answers links to good web-sites
Spectroscop and Characterisation Dr. P. unt p.hunt@imperial.ac.uk Rm 167 (Chemistr) web-site: http://www.ch.ic.ac.uk/hunt Resources Web copies course notes download slides model answers links to good web-sites
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
SHAPES OF MOLECULES (VSEPR MODEL)
 1 SAPES MLEULES (VSEPR MDEL) Valence Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion model - Electron pairs surrounding atom spread out as to minimize repulsion. - Electron pairs can be bonding pairs (including multiple
1 SAPES MLEULES (VSEPR MDEL) Valence Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion model - Electron pairs surrounding atom spread out as to minimize repulsion. - Electron pairs can be bonding pairs (including multiple
1s atomic orbital 2s atomic orbital 2s atomic orbital (with node) 2px orbital 2py orbital 2pz orbital
 Atomic Orbitals 1s atomic orbital 2s atomic orbital 2s atomic orbital (with node) 2px orbital 2py orbital 2pz orbital Valence Bond Theory and ybridized Atomic Orbitals Bonding in 2 1s 1s Atomic Orbital
Atomic Orbitals 1s atomic orbital 2s atomic orbital 2s atomic orbital (with node) 2px orbital 2py orbital 2pz orbital Valence Bond Theory and ybridized Atomic Orbitals Bonding in 2 1s 1s Atomic Orbital
Be H. Delocalized Bonding. Localized Bonding. σ 2. σ 1. Two (sp-1s) Be-H σ bonds. The two σ bonding MO s in BeH 2. MO diagram for BeH 2
 The Delocalized Approach to Bonding: The localized models for bonding we have examined (Lewis and VBT) assume that all electrons are restricted to specific bonds between atoms or in lone pairs. In contrast,
The Delocalized Approach to Bonding: The localized models for bonding we have examined (Lewis and VBT) assume that all electrons are restricted to specific bonds between atoms or in lone pairs. In contrast,
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Geometry James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Shapes Lewis Structures show bonding and lone pairs, but do not denote shape. However, we use Lewis Structures to
Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Geometry James F. Kirby Quinnipiac University Hamden, CT Shapes Lewis Structures show bonding and lone pairs, but do not denote shape. However, we use Lewis Structures to
Molecular Orbital Theory
 Molecular Orbital Theory 1. MO theory suggests that atomic orbitals of different atoms combine to create MOLECULAR ORBITALS 2. Electrons in these MOLECULAR ORBITALS belong to the molecule as whole 3. This
Molecular Orbital Theory 1. MO theory suggests that atomic orbitals of different atoms combine to create MOLECULAR ORBITALS 2. Electrons in these MOLECULAR ORBITALS belong to the molecule as whole 3. This
Valence Bond Model and Hybridization
 Valence Bond Model and ybridization APPENDIX 4 1 Concepts The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page reference VSEPR theory 65 More advanced ideas about electronic structure
Valence Bond Model and ybridization APPENDIX 4 1 Concepts The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page reference VSEPR theory 65 More advanced ideas about electronic structure
Molecular Orbitals. Chapter 9. Sigma bonding orbitals. Sigma bonding orbitals. Pi bonding orbitals. Sigma and pi bonds
 Molecular Orbitals Chapter 9 Orbitals and Covalent Bond The overlap of atomic orbitals from separate atoms makes molecular orbitals Each molecular orbital has room for two electrons Two types of MO Sigma
Molecular Orbitals Chapter 9 Orbitals and Covalent Bond The overlap of atomic orbitals from separate atoms makes molecular orbitals Each molecular orbital has room for two electrons Two types of MO Sigma
Where have we been? Lectures 1 and 2 Bohr s Model/ Wave Mechanics/ Radial and Angular Wavefunctions/ Radial Distribution Functions/ s and p orbitals
 Where have we been? Lectures 1 and 2 Bohr s Model/ Wave Mechanics/ Radial and Angular Wavefunctions/ Radial Distribution unctions/ s and p orbitals Where are we going? Lecture 3 Brief wavefunction considerations:
Where have we been? Lectures 1 and 2 Bohr s Model/ Wave Mechanics/ Radial and Angular Wavefunctions/ Radial Distribution unctions/ s and p orbitals Where are we going? Lecture 3 Brief wavefunction considerations:
Lecture January 18, Quantum Numbers Electronic Configurations Ionization Energies Effective Nuclear Charge Slater s Rules
 Lecture 3 362 January 18, 2019 Quantum Numbers Electronic Configurations Ionization Energies Effective Nuclear Charge Slater s Rules Inorganic Chemistry Chapter 1: Figure 1.4 Time independent Schrödinger
Lecture 3 362 January 18, 2019 Quantum Numbers Electronic Configurations Ionization Energies Effective Nuclear Charge Slater s Rules Inorganic Chemistry Chapter 1: Figure 1.4 Time independent Schrödinger
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories PART I Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories PART I Molecular Shapes Lewis structures give atomic connectivity: they tell us which atoms are physically connected to which atoms. The shape of a molecule
Symmetry Adapted Orbitals
 Symmetry Adapted Orbitals z B x y e a Figure Symmetry adapted fragment orbitals for 3 L= ML 3 M C is isolobal with P 3 P Figure 2 Isolobal relationship Introduction so far the fragments used in forming
Symmetry Adapted Orbitals z B x y e a Figure Symmetry adapted fragment orbitals for 3 L= ML 3 M C is isolobal with P 3 P Figure 2 Isolobal relationship Introduction so far the fragments used in forming
Chapter 8. Molecular Shapes. Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR) What Determines the Shape of a Molecule?
 PowerPoint to accompany Molecular Shapes Chapter 8 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Figure 8.2 The shape of a molecule plays an important role in its reactivity. By noting the number of bonding
PowerPoint to accompany Molecular Shapes Chapter 8 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Figure 8.2 The shape of a molecule plays an important role in its reactivity. By noting the number of bonding
Chapter 4 Symmetry and Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 4 Symmetry and Chemical Bonding 4.1 Orbital Symmetries and Overlap 4.2 Valence Bond Theory and Hybrid Orbitals 4.3 Localized and Delocalized Molecular Orbitals 4.4 MX n Molecules with Pi-Bonding
Chapter 4 Symmetry and Chemical Bonding 4.1 Orbital Symmetries and Overlap 4.2 Valence Bond Theory and Hybrid Orbitals 4.3 Localized and Delocalized Molecular Orbitals 4.4 MX n Molecules with Pi-Bonding
LECTURE 2 DEGENERACY AND DESCENT IN SYMMETRY: LIGAND FIELD SPLITTINGS AND RELATED MATTERS
 SYMMETRY II. J. M. GOICOECHEA. LECTURE 2. 1 LECTURE 2 DEGENERACY AND DESCENT IN SYMMETRY: LIGAND FIELD SPLITTINGS AND RELATED MATTERS 2.1 Degeneracy When dealing with non-degenerate symmetry adapted wavefunctions
SYMMETRY II. J. M. GOICOECHEA. LECTURE 2. 1 LECTURE 2 DEGENERACY AND DESCENT IN SYMMETRY: LIGAND FIELD SPLITTINGS AND RELATED MATTERS 2.1 Degeneracy When dealing with non-degenerate symmetry adapted wavefunctions
Lecture 14 Chemistry 362 M. Darensbourg 2017 Spring term. Molecular orbitals for diatomics
 Lecture 14 Chemistry 362 M. Darensbourg 2017 Spring term Molecular orbitals for diatomics Molecular Orbital Theory of the Chemical Bond Simplest example - H 2 : two H atoms H A and H B Only two a.o.'s
Lecture 14 Chemistry 362 M. Darensbourg 2017 Spring term Molecular orbitals for diatomics Molecular Orbital Theory of the Chemical Bond Simplest example - H 2 : two H atoms H A and H B Only two a.o.'s
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Geometries -Bond angles: angles made by the lines joining the nuclei of the atoms in a molecule -Bond angles determine overall shape of
Chapter 9: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.1 Molecular Geometries -Bond angles: angles made by the lines joining the nuclei of the atoms in a molecule -Bond angles determine overall shape of
Shapes of Molecules. Lewis structures are useful but don t allow prediction of the shape of a molecule.
 Shapes of Molecules Lewis structures are useful but don t allow prediction of the shape of a molecule. H O H H O H Can use a simple theory based on electron repulsion to predict structure (for non-transition
Shapes of Molecules Lewis structures are useful but don t allow prediction of the shape of a molecule. H O H H O H Can use a simple theory based on electron repulsion to predict structure (for non-transition
Chapter 9. Covalent Bonding: Orbitals
 Chapter 9. Covalent onding: Orbitals Models to explain the structures and/or energies of the covalent molecules Localized Electron (LE) onding Model Lewis Structure Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
Chapter 9. Covalent onding: Orbitals Models to explain the structures and/or energies of the covalent molecules Localized Electron (LE) onding Model Lewis Structure Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion
Molecular Orbitals. Based on Inorganic Chemistry, Miessler and Tarr, 4 th edition, 2011, Pearson Prentice Hall
 Molecular Orbitals Based on Inorganic Chemistry, Miessler and Tarr, 4 th edition, 2011, Pearson Prentice Hall Images from Miessler and Tarr Inorganic Chemistry 2011 obtained from Pearson Education, Inc.
Molecular Orbitals Based on Inorganic Chemistry, Miessler and Tarr, 4 th edition, 2011, Pearson Prentice Hall Images from Miessler and Tarr Inorganic Chemistry 2011 obtained from Pearson Education, Inc.
Chapter 9. Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Topics Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry and Polarity Valence Bond Theory Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Hybridization in Molecules
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories Topics Molecular Geometry Molecular Geometry and Polarity Valence Bond Theory Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Hybridization in Molecules
Be H. Delocalized Bonding. Localized Bonding. σ 2. σ 1. Two (sp-1s) Be-H σ bonds. The two σ bonding MO s in BeH 2. MO diagram for BeH 2
 The Delocalized Approach to Bonding: The localized models for bonding we have examined (Lewis and VBT) assume that all electrons are restricted to specific bonds between atoms or in lone pairs. In contrast,
The Delocalized Approach to Bonding: The localized models for bonding we have examined (Lewis and VBT) assume that all electrons are restricted to specific bonds between atoms or in lone pairs. In contrast,
NH 3 H 2 O N 2. Why do they make chemical bonds? Molecular Orbitals
 N 2 NH 3 H 2 O Why do they make chemical bonds? 5 Molecular Orbitals Why do they make chemical bonds? Stabilization Bond energy Types of Chemical Bonds Metallic Bond Ionic Bond Covalent Bond Covalent Bond
N 2 NH 3 H 2 O Why do they make chemical bonds? 5 Molecular Orbitals Why do they make chemical bonds? Stabilization Bond energy Types of Chemical Bonds Metallic Bond Ionic Bond Covalent Bond Covalent Bond
Chapter 9. Covalent Bonding: Orbitals. Copyright 2017 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved.
 Chapter 9 Covalent Bonding: Orbitals Chapter 9 Table of Contents (9.1) (9.2) (9.3) (9.4) (9.5) (9.6) Hybridization and the localized electron model The molecular orbital model Bonding in homonuclear diatomic
Chapter 9 Covalent Bonding: Orbitals Chapter 9 Table of Contents (9.1) (9.2) (9.3) (9.4) (9.5) (9.6) Hybridization and the localized electron model The molecular orbital model Bonding in homonuclear diatomic
Molecular Orbitals in Inorganic Chemistry
 Resources Molecular rbitals in Inorganic Chemistr Dr. P. unt p.hunt@imperial.ac.uk Rm 67 (Chemistr) http://www.ch.ic.ac.uk/hunt/ Web notes AND slides link to panopto when it becomes available model answers
Resources Molecular rbitals in Inorganic Chemistr Dr. P. unt p.hunt@imperial.ac.uk Rm 67 (Chemistr) http://www.ch.ic.ac.uk/hunt/ Web notes AND slides link to panopto when it becomes available model answers
Molecular shape is only discussed when there are three or more atoms connected (diatomic shape is obvious).
 Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry (Ch9 Jespersen, Ch10 Chang) The arrangement of the atoms of a molecule in space is the molecular geometry. This is what gives the molecules their shape. Molecular shape is
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry (Ch9 Jespersen, Ch10 Chang) The arrangement of the atoms of a molecule in space is the molecular geometry. This is what gives the molecules their shape. Molecular shape is
Vibrational Autoionization in Polyatomic molecules
 Vibrational Autoionization in Polyatomic molecules S.T. Pratt Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2005. 56:281-308 2006. 12. 4. Choi, Sunyoung 1 Schedule 12/4 (Mon) - Introduction - Theoretical background 12/6 (Wed)
Vibrational Autoionization in Polyatomic molecules S.T. Pratt Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2005. 56:281-308 2006. 12. 4. Choi, Sunyoung 1 Schedule 12/4 (Mon) - Introduction - Theoretical background 12/6 (Wed)
Chapter 10: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes; VSEPR, Valence Bond and Molecular Orbital Theories
 C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 1 0 P a g e 1 Chapter 10: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes; VSEPR, Valence Bond and Molecular Orbital Theories Homework: Read Chapter 10: Work out sample/practice
C h e m i s t r y 1 A : C h a p t e r 1 0 P a g e 1 Chapter 10: Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes; VSEPR, Valence Bond and Molecular Orbital Theories Homework: Read Chapter 10: Work out sample/practice
Chapter 10. Structure Determines Properties! Molecular Geometry. Chemical Bonding II
 Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II Structure Determines Properties! Properties of molecular substances depend on the structure of the molecule The structure includes many factors, including: the skeletal arrangement
Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II Structure Determines Properties! Properties of molecular substances depend on the structure of the molecule The structure includes many factors, including: the skeletal arrangement
Orbitals and energetics
 Orbitals and energetics Bonding and structure Molecular orbital theory Crystal field theory Ligand field theory Provide fundamental understanding of chemistry dictating radionuclide complexes Structure
Orbitals and energetics Bonding and structure Molecular orbital theory Crystal field theory Ligand field theory Provide fundamental understanding of chemistry dictating radionuclide complexes Structure
Lecture 1: Chemistry of the Carbonyl Group
 Lecture 1: Chemistry of the Carbonyl Group bjectives: By the end of this lecture you will be able to: 1. identify and name all major carbonyl functional groups; 2. use a molecular orbital approach to describe
Lecture 1: Chemistry of the Carbonyl Group bjectives: By the end of this lecture you will be able to: 1. identify and name all major carbonyl functional groups; 2. use a molecular orbital approach to describe
Figure 1 Setting the charge in HF 2 -.
 Self-Stud Problems / Eam Preparation compute the orbitals for (linear) -, draw and annotate a MO diagram consistent with the MOs ou observe o if ou have problems setting up the calculation, select Be and
Self-Stud Problems / Eam Preparation compute the orbitals for (linear) -, draw and annotate a MO diagram consistent with the MOs ou observe o if ou have problems setting up the calculation, select Be and
Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT)
 Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) In this section, There are another approach to the bonding in metal complexes: the use of molecular orbital theory (MOT). In contrast to crystal field theory, the molecular
Molecular Orbital Theory (MOT) In this section, There are another approach to the bonding in metal complexes: the use of molecular orbital theory (MOT). In contrast to crystal field theory, the molecular
Section 2 Simple Molecular Orbital Theory
 Section 2 Simple Molecular Orbital Theory In this section, the conceptual framework of molecular orbital theory is developed. Applications are presented and problems are given and solved within qualitative
Section 2 Simple Molecular Orbital Theory In this section, the conceptual framework of molecular orbital theory is developed. Applications are presented and problems are given and solved within qualitative
Molecular Geometry. Dr. Williamson s Molecular Geometry Notes. VSEPR: Definition of Terms. Dr. V.M. Williamson Texas A & M University Student Version
 Molecular Geometry Dr. V.M. Williamson Texas A & M University Student Version Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion- VSEPR 1. Valence e- to some extent 2. Electron pairs move as far away as possible to
Molecular Geometry Dr. V.M. Williamson Texas A & M University Student Version Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion- VSEPR 1. Valence e- to some extent 2. Electron pairs move as far away as possible to
Molecular Geometry. Dr. Williamson s Molecular Geometry Notes. VSEPR: Definition of Terms. VSEPR: Electronic Geometries VSEPR
 Molecular Geometry Dr. V.M. Williamson Texas A & M University Student Version Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion- VSEPR 1. Valence e- to some extent 2. Electron pairs move as far away as possible to
Molecular Geometry Dr. V.M. Williamson Texas A & M University Student Version Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion- VSEPR 1. Valence e- to some extent 2. Electron pairs move as far away as possible to
RDCH 702 Lecture 4: Orbitals and energetics
 RDCH 702 Lecture 4: Orbitals and energetics Molecular symmetry Bonding and structure Molecular orbital theory Crystal field theory Ligand field theory Provide fundamental understanding of chemistry dictating
RDCH 702 Lecture 4: Orbitals and energetics Molecular symmetry Bonding and structure Molecular orbital theory Crystal field theory Ligand field theory Provide fundamental understanding of chemistry dictating
QUANTUM MECHANICS AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
 6 QUANTUM MECHANICS AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE 6.1 Quantum Picture of the Chemical Bond 6.2 Exact Molecular Orbital for the Simplest Molecule: H + 2 6.3 Molecular Orbital Theory and the Linear Combination
6 QUANTUM MECHANICS AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE 6.1 Quantum Picture of the Chemical Bond 6.2 Exact Molecular Orbital for the Simplest Molecule: H + 2 6.3 Molecular Orbital Theory and the Linear Combination
C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 6 THE PERIODIC TABLE & ATOMIC STRUCTURE INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH
 C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 6 THE PERIODIC TABLE & ATOMIC STRUCTURE 0 1 INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH CHAPTER 6 THE PERIODIC TABLE & ATOMIC STRUCTURE The Electromagnetic Spectrum The Wave
C H E M 1 CHEM 101-GENERAL CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 6 THE PERIODIC TABLE & ATOMIC STRUCTURE 0 1 INSTR : FİLİZ ALSHANABLEH CHAPTER 6 THE PERIODIC TABLE & ATOMIC STRUCTURE The Electromagnetic Spectrum The Wave
CHEMISTRY - ZUMDAHL 2E CH.4 - MOLECULAR STRUCTURE AND ORBITALS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTRONIC GEOMETRY When drawing a compound you have to take into account two different systems of geometrical shape. The simpler system known as electronic geometry or shape
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTRONIC GEOMETRY When drawing a compound you have to take into account two different systems of geometrical shape. The simpler system known as electronic geometry or shape
Chapter 10. Geometry
 Chapter 10 Molec cular Geometry 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE Molecular Geometry Molecular Polarity VSEPR Model Summary of Molecular Shapes Hybridization Molecular Orbital Theory Bond Angles 2 MOLECULAR GEOMETRY Molecular
Chapter 10 Molec cular Geometry 1 CHAPTER OUTLINE Molecular Geometry Molecular Polarity VSEPR Model Summary of Molecular Shapes Hybridization Molecular Orbital Theory Bond Angles 2 MOLECULAR GEOMETRY Molecular
CHEMISTRY - MCMURRY 7E CH.7 - COVALENT BONDING AND ELECTRON DOT STRUCTURES
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTRONIC GEOMETRY When drawing a compound you have to take into account two different systems of geometrical shape. The simpler system known as electronic geometry or shape
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ELECTRONIC GEOMETRY When drawing a compound you have to take into account two different systems of geometrical shape. The simpler system known as electronic geometry or shape
Lecture Presentation. Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, Valence Bond Theory, and Molecular Orbital Theory
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, Valence Bond Theory, and Molecular Orbital Theory Predicting Molecular Geometry 1. Draw the Lewis structure. 2. Determine the number
Lecture Presentation Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes, Valence Bond Theory, and Molecular Orbital Theory Predicting Molecular Geometry 1. Draw the Lewis structure. 2. Determine the number
Chapter 10. VSEPR Model: Geometries
 Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry VSEPR Model: Geometries Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Electron pairs repel and get as far apart as possible Example: Water Four electron pairs Farthest apart
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry VSEPR Model: Geometries Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Electron pairs repel and get as far apart as possible Example: Water Four electron pairs Farthest apart
Drawing Good Lewis Structures. Molecular Shape
 3//05 Drawing Good Lewis Structures. # valence e in atoms (± charge) must = # e in structure ; always. determine connectivity: least EN usually central; avoid small rings; always terminal ( e ); work out
3//05 Drawing Good Lewis Structures. # valence e in atoms (± charge) must = # e in structure ; always. determine connectivity: least EN usually central; avoid small rings; always terminal ( e ); work out
Chemistry 2. Lecture 1 Quantum Mechanics in Chemistry
 Chemistry 2 Lecture 1 Quantum Mechanics in Chemistry Your lecturers 8am Assoc. Prof Timothy Schmidt Room 315 timothy.schmidt@sydney.edu.au 93512781 12pm Assoc. Prof. Adam J Bridgeman Room 222 adam.bridgeman@sydney.edu.au
Chemistry 2 Lecture 1 Quantum Mechanics in Chemistry Your lecturers 8am Assoc. Prof Timothy Schmidt Room 315 timothy.schmidt@sydney.edu.au 93512781 12pm Assoc. Prof. Adam J Bridgeman Room 222 adam.bridgeman@sydney.edu.au
Andrew Rosen *Note: If you can rotate a molecule to have one isomer equal to another, they are both the same
 *Note: If you can rotate a molecule to have one isomer equal to another, they are both the same *Note: For hybridization, if an SP 2 is made, there is one unhybridized p orbital (because p usually has
*Note: If you can rotate a molecule to have one isomer equal to another, they are both the same *Note: For hybridization, if an SP 2 is made, there is one unhybridized p orbital (because p usually has
Lecture 17 - Covalent Bonding. Lecture 17 - VSEPR and Molecular Shape. Lecture 17 - Introduction. Lecture 17 - VSEPR and Molecular Shape
 Chem 103, Section F0F Unit VI - Compounds Part II: Covalent Compounds Lecture 17 Using the Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory to predict molecular shapes Molecular shape and polarity
Chem 103, Section F0F Unit VI - Compounds Part II: Covalent Compounds Lecture 17 Using the Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory to predict molecular shapes Molecular shape and polarity
Chemistry Lecture Notes
 Molecular orbital theory Valence bond theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding. Useful for predicting shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations
Molecular orbital theory Valence bond theory gave us a qualitative picture of chemical bonding. Useful for predicting shapes of molecules, bond strengths, etc. It fails to describe some bonding situations
VALENCE Hilary Term 2018
 VALENCE Hilary Term 2018 8 Lectures Prof M. Brouard Valence is the theory of the chemical bond Outline plan 1. The Born-Oppenheimer approximation 2. Bonding in H + 2 the LCAO approximation 3. Many electron
VALENCE Hilary Term 2018 8 Lectures Prof M. Brouard Valence is the theory of the chemical bond Outline plan 1. The Born-Oppenheimer approximation 2. Bonding in H + 2 the LCAO approximation 3. Many electron
Lecture 9 Electronic Spectroscopy
 Lecture 9 Electronic Spectroscopy Molecular Orbital Theory: A Review - LCAO approximaton & AO overlap - Variation Principle & Secular Determinant - Homonuclear Diatomic MOs - Energy Levels, Bond Order
Lecture 9 Electronic Spectroscopy Molecular Orbital Theory: A Review - LCAO approximaton & AO overlap - Variation Principle & Secular Determinant - Homonuclear Diatomic MOs - Energy Levels, Bond Order
Chemistry 3211 Coordination Chemistry Part 3 Ligand Field and Molecular Orbital Theory
 Chemistry 3211 Coordination Chemistry Part 3 Ligand Field and Molecular Orbital Theory Electronic Structure of Six and Four-Coordinate Complexes Using Crystal Field Theory, we can generate energy level
Chemistry 3211 Coordination Chemistry Part 3 Ligand Field and Molecular Orbital Theory Electronic Structure of Six and Four-Coordinate Complexes Using Crystal Field Theory, we can generate energy level
Quiz 5 R = lit-atm/mol-k 1 (25) R = J/mol-K 2 (25) 3 (25) c = X 10 8 m/s 4 (25)
 ADVANCED INORGANIC CHEMISTRY QUIZ 5 and FINAL December 18, 2012 INSTRUCTIONS: PRINT YOUR NAME > NAME. QUIZ 5 : Work 4 of 1-5 (The lowest problem will be dropped) FINAL: #6 (10 points ) Work 6 of 7 to 14
ADVANCED INORGANIC CHEMISTRY QUIZ 5 and FINAL December 18, 2012 INSTRUCTIONS: PRINT YOUR NAME > NAME. QUIZ 5 : Work 4 of 1-5 (The lowest problem will be dropped) FINAL: #6 (10 points ) Work 6 of 7 to 14
Bonding in Molecules Prof John McGrady Michaelmas Term 2009
 Bonding in Molecules Prof John McGrady Michaelmas Term 2009 6 lectures building on material presented in Introduction to Molecular Orbitals (HT Year 1). Provides a basis for analysing the shapes, properties,
Bonding in Molecules Prof John McGrady Michaelmas Term 2009 6 lectures building on material presented in Introduction to Molecular Orbitals (HT Year 1). Provides a basis for analysing the shapes, properties,
Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II
 Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II Valence Bond Theory Valence Bond Theory: A quantum mechanical model which shows how electron pairs are shared in a covalent bond. Bond forms between two atoms when the following
Chapter 10 Chemical Bonding II Valence Bond Theory Valence Bond Theory: A quantum mechanical model which shows how electron pairs are shared in a covalent bond. Bond forms between two atoms when the following
Chapter 4 Symmetry and Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 4 Symmetry and Chemical Bonding 4.1 Orbital Symmetries and Overlap 4.2 Valence Bond Theory and Hybrid Orbitals 4.3 Localized and Delocalized Molecular Orbitals 4.4 MX n Molecules with Pi-Bonding
Chapter 4 Symmetry and Chemical Bonding 4.1 Orbital Symmetries and Overlap 4.2 Valence Bond Theory and Hybrid Orbitals 4.3 Localized and Delocalized Molecular Orbitals 4.4 MX n Molecules with Pi-Bonding
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories. Lecture Presentation. John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Shapes The shape of a molecule plays an important role in its reactivity. By noting the number of
Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Shapes The shape of a molecule plays an important role in its reactivity. By noting the number of
Ch. 9- Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Ch. 9- Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.0 Introduction A. Lewis structures do not show one of the most important aspects of molecules- their overall shapes B. The shape and size of molecules-
Ch. 9- Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories 9.0 Introduction A. Lewis structures do not show one of the most important aspects of molecules- their overall shapes B. The shape and size of molecules-
5.04 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry II
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.04 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry II Fall 008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 5.04, Principles
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 5.04 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry II Fall 008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. 5.04, Principles
In this lecture we will understand how the molecular orbitals are formed from the interaction of atomic orbitals.
 Lecture 7 Title: Understanding of Molecular Orbital Page-1 In this lecture we will understand how the molecular orbitals are formed from the interaction of atomic orbitals. We will see how the electrons
Lecture 7 Title: Understanding of Molecular Orbital Page-1 In this lecture we will understand how the molecular orbitals are formed from the interaction of atomic orbitals. We will see how the electrons
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories
 Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories MOLECULAR SHAPES 2 Molecular Shapes Lewis Structures show bonding and lone pairs do not denote shape Use Lewis Structures to determine shapes Molecular
Chapter 9 Molecular Geometry and Bonding Theories MOLECULAR SHAPES 2 Molecular Shapes Lewis Structures show bonding and lone pairs do not denote shape Use Lewis Structures to determine shapes Molecular
Lecture 30 Chapter 10 Sections 1-2. Orbital overlap = bonding Molecular orbitals Hybrid orbitals
 Lecture 30 Chapter 10 Sections 1-2 Orbital overlap = bonding Molecular orbitals Hybrid orbitals Announcements CAPA #17 due tomorrow Seminar Friday 3:00 Seminar Tuesday 11:00 Bond Lengths and Energies Bond
Lecture 30 Chapter 10 Sections 1-2 Orbital overlap = bonding Molecular orbitals Hybrid orbitals Announcements CAPA #17 due tomorrow Seminar Friday 3:00 Seminar Tuesday 11:00 Bond Lengths and Energies Bond
Lab Lecture on VSEPR and SPARTAN Chem 141 Lab Dr Abrash 10/3/2011
 Q: What is the purpose of this lab? Lab Lecture on VSEPR and SPARTAN Chem 141 Lab Dr Abrash 10/3/2011 To learn two methods to study and predict the shapes of molecules. One is a rule based paper method
Q: What is the purpose of this lab? Lab Lecture on VSEPR and SPARTAN Chem 141 Lab Dr Abrash 10/3/2011 To learn two methods to study and predict the shapes of molecules. One is a rule based paper method
Goals for Today. Clarify some Rydberg Concepts Absorption vs. emission
 Note: Due to recent changes the exam 2 material for these slides ends at Ionization Energy Exceptions. You can omit Lewis Structures through General Formal Charge Rules. CH301 Unit 2 QUANTUM NUMBERS AND
Note: Due to recent changes the exam 2 material for these slides ends at Ionization Energy Exceptions. You can omit Lewis Structures through General Formal Charge Rules. CH301 Unit 2 QUANTUM NUMBERS AND
: Bond Order = 1.5 CHAPTER 5. Practice Questions
 CAPTER 5 Practice Questions 5.1 5.3 S 5.5 Ethane is symmetrical, so does not have a dipole moment. owever, ethanol has a polar group at one end and so has a dipole moment. 5.7 xygen has the valence electron
CAPTER 5 Practice Questions 5.1 5.3 S 5.5 Ethane is symmetrical, so does not have a dipole moment. owever, ethanol has a polar group at one end and so has a dipole moment. 5.7 xygen has the valence electron
Chapter 13: Phenomena
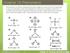 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chemical Bonding. Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory
 Chemical Bonding Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Problems with Valence Bond Theory VB theory predicts properties better than Lewis theory bonding schemes, bond strengths,
Chemical Bonding Lewis Theory-VSEPR Valence Bond Theory Molecular Orbital Theory Problems with Valence Bond Theory VB theory predicts properties better than Lewis theory bonding schemes, bond strengths,
Chapter 11 Answers. Practice Examples
 hapter Answers Practice Examples a. There are three half-filled p orbitals on, and one half-filled 5p orbital on I. Each halffilled p orbital from will overlap with one half-filled 5p orbital of an I.
hapter Answers Practice Examples a. There are three half-filled p orbitals on, and one half-filled 5p orbital on I. Each halffilled p orbital from will overlap with one half-filled 5p orbital of an I.
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules
 Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules +e r n = 3 n = 2 n = 1 +e +e r y even Lecture 19, p 1 Today Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Using RF photons to drive transitions between nuclear spin orientations in
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules +e r n = 3 n = 2 n = 1 +e +e r y even Lecture 19, p 1 Today Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Using RF photons to drive transitions between nuclear spin orientations in
MODULE 213 BASIC INORGANIC CHEMISTRY UNIT 1 ATOMIC STRUCTURE AND BONDING II
 Course Title: Basic Inorganic Chemistry 1 Course Code: CHEM213 Credit Hours: 2.0 Requires: 122 Required for: 221 Course Outline: Wave-particle duality: what are the typical properties of particles? What
Course Title: Basic Inorganic Chemistry 1 Course Code: CHEM213 Credit Hours: 2.0 Requires: 122 Required for: 221 Course Outline: Wave-particle duality: what are the typical properties of particles? What
Chapter 9. Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories. Lecture Presentation. John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Shapes The shape of a molecule plays an important role in its reactivity. By noting the number of
Lecture Presentation Chapter 9 Theories John D. Bookstaver St. Charles Community College Cottleville, MO Shapes The shape of a molecule plays an important role in its reactivity. By noting the number of
Molecular shape is determined by the number of bonds that form around individual atoms.
 Chapter 9 CH 180 Major Concepts: Molecular shape is determined by the number of bonds that form around individual atoms. Sublevels (s, p, d, & f) of separate atoms may overlap and result in hybrid orbitals
Chapter 9 CH 180 Major Concepts: Molecular shape is determined by the number of bonds that form around individual atoms. Sublevels (s, p, d, & f) of separate atoms may overlap and result in hybrid orbitals
Chapter Molecules are 3D. Shapes and Bonds. Chapter 9 1. Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
 Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure 1 Shape 9.1 Molecules are 3D Angle Linear 180 Planar triangular (trigonal planar) 120 Tetrahedral 109.5 2 Shapes and Bonds Imagine a molecule where the
Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure 1 Shape 9.1 Molecules are 3D Angle Linear 180 Planar triangular (trigonal planar) 120 Tetrahedral 109.5 2 Shapes and Bonds Imagine a molecule where the
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules
 Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules +e r n = 3 n = 2 n = 1 +e +e r ψ even Lecture 19, p 1 Today Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Using RF photons to drive transitions between nuclear spin orientations in
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules +e r n = 3 n = 2 n = 1 +e +e r ψ even Lecture 19, p 1 Today Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Using RF photons to drive transitions between nuclear spin orientations in
Periodic Trends. Homework: Lewis Theory. Elements of his theory:
 Periodic Trends There are various trends on the periodic table that need to be understood to explain chemical bonding. These include: Atomic/Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity Electron Affinity
Periodic Trends There are various trends on the periodic table that need to be understood to explain chemical bonding. These include: Atomic/Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity Electron Affinity
Bonding in Molecules Covalent Bonding
 Bonding in Molecules Covalent Bonding The term covalent implies sharing of electrons between atoms. Valence electrons and valence shell orbitals - nly valence electrons are used for bonding: ns, np, nd
Bonding in Molecules Covalent Bonding The term covalent implies sharing of electrons between atoms. Valence electrons and valence shell orbitals - nly valence electrons are used for bonding: ns, np, nd
CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications. CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications
 CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications Crystal Structure: XRD XRD: Diffraction Peak Positions Centering Allowed Peaks I-centered h+k+l is an even number F-centered hkl either all even or
CH676 Physical Chemistry: Principles and Applications Crystal Structure: XRD XRD: Diffraction Peak Positions Centering Allowed Peaks I-centered h+k+l is an even number F-centered hkl either all even or
The wavefunction that describes a bonding pair of electrons:
 4.2. Molecular Properties from VB Theory a) Bonding and Bond distances The wavefunction that describes a bonding pair of electrons: Ψ b = a(h 1 ) + b(h 2 ) where h 1 and h 2 are HAOs on adjacent atoms
4.2. Molecular Properties from VB Theory a) Bonding and Bond distances The wavefunction that describes a bonding pair of electrons: Ψ b = a(h 1 ) + b(h 2 ) where h 1 and h 2 are HAOs on adjacent atoms
Lecture outline: Section 9. theory 2. Valence bond theory 3. Molecular orbital theory. S. Ensign, Chem. 1210
 Lecture outline: Section 9 Molecular l geometry and bonding theories 1. Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory 2. Valence bond theory 3. Molecular orbital theory 1 Ionic bonding Covalent bonding
Lecture outline: Section 9 Molecular l geometry and bonding theories 1. Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory 2. Valence bond theory 3. Molecular orbital theory 1 Ionic bonding Covalent bonding
Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure
 CHM 123 Chapter 8 Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure 8.1 Molecular shapes and VSEPR theory VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of
CHM 123 Chapter 8 Covalent Compounds: Bonding Theories and Molecular Structure 8.1 Molecular shapes and VSEPR theory VSEPR theory proposes that the geometric arrangement of terminal atoms, or groups of
VSEPR Theory. Shapes of Molecules. Molecular Structure or Molecular Geometry
 VSEPR Theory VSEPR Theory Shapes of Molecules Molecular Structure or Molecular Geometry The 3-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that make-up a molecule. Determines several properties of a substance,
VSEPR Theory VSEPR Theory Shapes of Molecules Molecular Structure or Molecular Geometry The 3-dimensional arrangement of the atoms that make-up a molecule. Determines several properties of a substance,
Review questions CHAPTER 5. Practice exercises 5.1 F F 5.3
 CHAPTER 5 Practice exercises 5.1 S 5.3 5.5 Ethane is symmetrical, so does not have a dipole moment. However, ethanol has a polar H group at one end and so has a dipole moment. 5.7 xygen has the valence
CHAPTER 5 Practice exercises 5.1 S 5.3 5.5 Ethane is symmetrical, so does not have a dipole moment. However, ethanol has a polar H group at one end and so has a dipole moment. 5.7 xygen has the valence
bond energy- energy required to break a chemical bond -We can measure bond energy to determine strength of interaction
 bond energy- energy required to break a chemical bond -We can measure bond energy to determine strength of interaction ionic compound- a metal reacts with a nonmetal Ionic bonds form when an atom that
bond energy- energy required to break a chemical bond -We can measure bond energy to determine strength of interaction ionic compound- a metal reacts with a nonmetal Ionic bonds form when an atom that
Chapter 10. VSEPR Model: Geometries
 Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry VSEPR Model: Geometries Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Electron pairs repel and get as far apart as possible Example: Water Four electron pairs Two bonds Two
Chapter 10 Molecular Geometry VSEPR Model: Geometries Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory Electron pairs repel and get as far apart as possible Example: Water Four electron pairs Two bonds Two
