Study on the Catalytic Effect of Nitric Acid Activated Myanmar Natural Clay for the Degradation of Plastic Wastes
|
|
|
- Silvester Benson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Study on the Catalytic Effect of Nitric Acid Activated Myanmar Natural Clay for the Degradation of Plastic Wastes Amie Thant, Chaw Su Su Hmwe Abstract In this study, the performance of different acid treated Myanmar Natural Clay (Mabisian) was conducted the pyrolysis of mixed plastic wastes, 40% high density polyethylene, 30% polypropylene, 25% low density polyethylene and 5% polystyrene. Mabisian clay was refluxed with different concentration of nitric acid (2M, 4M, 6M, 8M, 10M, 12M and 14M) at 100ºC for 3hrs followed by calcination at 500ºC for 1hr. The physico-chemical characteristics of resulted leached clay were studied by X-Ray Fluoresence spectroscopy (XRF), X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) and Fourier Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR). The pyrolytic oil was characterized by Gas Chromatography mass spectopy (GC-MS). XRF and FTIR studies indicated that acid treatment under reflux condition lead to the removal of octahedral Al 3+ cations along with other impurities. The chemical treatment increased the Si/Al ratio. The maximum liquid yield (75%) was obtained at 12 M nitric acid, 3hr reaction time and 100 º C reaction temperatures. In addition, the percent peak area of gasoline range hydrocarbon was obtained 55.6% at optimum condition. Thus, the treated clay can be used as promising as catalyst support. Index Terms Acid Activation; Mabisian Clay; Nitric Acid; Pyrolysis; Plastic Wastes; Physico-Chemical Character; Catalyst Support. I. INTRODUCTION Nowadays, the industrialization and population was growing. It makes the problem for disposing the solid waste around the world. The more the world population rapidly grows the more consumption of the plastics increase. Plastics materials are utilized from domestic appliances to agricultural because of their effective ways such as light weight characteristics, high chemical stability and low degradability. Plastic wastes can be turned into valuable energy since they are derived from petrochemical source which having significant calorific value. Municipal and industrial wastes are disposed by landfilling, incineration, true material recycling, and chemical recovery. The emission of air bone particles and carbon dioxide into the atmosphere can cause the dangerous air pollution problems by landfill treatment and incineration [1]. Chemical recycling is more suitable than any other materials recycling method around the world. Pyrolysis Published on August 31, A. Thant is a lecturer at Mandalay Technological University, Mandalay, Myanmar. She completed her BE at Technological University, Mandalay and M.E at De La Salle University, Manila, Philippines. ( amythant81@ gmail.com). C. S. S. Hmwe is a Professor at Mandalay Technological University, Mandalay, Myanmar. She completed her BE and PhD at the same University and she completed her ME at Yangon Technological University, Yangon, Myanmar ( chawsu2hmwe@gmail.com). means thermal cracking of high molecular weight hydrocarbon turns into low molecular weight hydrocarbon under absent of oxygen atmosphere. The three major products of pyrolysis process are oil, gas and char. The liquid product can be used in furnace, boiler, turbine and diesel engines without upgrading or treatment [2],[3]. In the study of catalytic cracking and thermal cracking, the catalyst cost is found as an important factor. The thermal cracking requires the high temperature and longer reaction time and produces the higher molecular chain while the catalytic cracking can reduce the reaction temperature and reaction time [4]. In cracking of plastic wastes, natural and synthesis catalyst can be utilized. Natural catalysts are cheaper than synthesis catalysts. Ferric carbonate catalyst and waste plastic mixture to fuel production reports showed that higher percentage catalyst adding fuel conversion rate is increasing. High percentage catalyst added increased the light gas production percentage and produced light gas can be used for heat source when large scale production starts. However, high percentage catalyst added to fuel production cost will be increase because catalyst has to buy from market and it adding extra cost also during production period [5]. The use of clay-type aluminosilicates in heterogeneous catalysis as solid acid catalysts is almost as old as the catalysis concept itself. In modern petrochemical processes, the zeolite acid catalyst is employed. However, acid modified clays are more attractive due to their low cost and their suitable pore structure than zeolite for the degradation of long chain molecules [6]. Although it has a very low catalyze ability reaction in natural clay, various activation methods can change the structural properties of natural clay to generate catalysts with high acidity, surface area, porosity and thermal stability. [7]. Acid modification is widely accepted as an effective method to create active materials for adsotption and catalysis purposes. The increasement of Si/Al ratio will improve not only the stability of the crystal framework but also reduce the coke formation during the catalytic cracking [8]. The study on the effect of sulphuric acid treatment on the physico-chemical characteristics of kaolin clay under refluxed condition has been concluded that sulphuric acid treatment at and above 5M concentration almost destroys the crystalline structure and other properties to a considerable extent [9]. The present work studied the effect of nitric acid treated Myanmar natural clay on distribution of liquid hydrocarbon products. DOI: 56
2 II. MATERIAL AND EXPERIMENTAL A. Materials In this study, Myanmar Natural Clay (Mabisian) was used as a catalyst support. It was collected from Department of Research and Innovation. Raw materials used for this study are mixed plastic wastes (High density polyethylene, Low density polyethylene, Polypropylene and Polystyrene) natural catalysts and starch powder. Plastics wastes were cut into smaller sizes (6mm x 6mm). All chemicals used were analytical reagent grade, obtained from Able Chemical, Mandalay. B. Acid Modification The experimental set-up for the acid activation process was shown in Fig. 1. The acid activation was carried out by adding 30 g of the clay put into 500 ml of two- neck flat bottom flask. And then 300 ml of various concentration of nitric acid solution (2 M, 4 M, 6M, 8M, 10M,12M and 14 M) was poured into the reactor equipped with a reflux condenser under stirring condition at 100ºCfor 3hr. The resulting clay suspension was then rapidly quenched by adding 500 ml of ice cold water. The slurry was washed repeatedly with distilled water until neutral point was obtained. The washed clay was dried in an oven. After that the dried clay was calcined at 500ºC for 2 hr and ground in a mortar and pestle to get powder form. The untreated sample is referred to as NH and treated samples are referred to as NH1, NH2, NH3, NH4, NH5, NH6 and NH7 in the subsequent text where the numbers refer to the different concentration of acid used. Reflux Condenser staged condenser was used. The inlet and outlet temperature of hot water from 95ºC to 70ºC for the first stage condenser while The inlet and outlet temperature of cold water in shell side were 10 ºC and 27 ºC for second stage condenser. The reactor was heated with an electric furnace at a rate of 5ºC min-1 to reach the desired temperature. The reactor temperature was controlled and monitored by a set of temperature controller and thermocouple. The temperature range was maintained at from 200ºC to 400ºC. Crude liquid fuel and waxes flowed into the collector and the light gases were stored by the gas bag. The liquid fuel was characterized by gas chromatography mass spectrometer (GC-MS). submission. Fig. 2. Process of Catalytic Pyrolysis (1) N 2, (2) thermal reactor, (3) Electronic Heater, (4) first stage condenser, (5) second-stage condenser, (6) liquid collector, (7) gas collector. D. Characterization Methods The untreated and acid treated Mabisian clay materials were characterized by X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The condensable gas in the form of liquid was analyzed by gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry detector (GC-MS). The set up parameters are given in Table I. Cooling Bath Thermomete Reactor TABLE I: GC-MS METHOD CHARACTERISTIC Column Carrier gas H 2 Carrier gas flow 1.0 ml/min Initial temperature/initial time 50ºC/ 2min Heating rate 10ºC/min Final temperature/final time 300ºC/10 min Injection temperature 250ºC Injection volume <1.0ml Fig. 1. Acid activation process Heater with Stirrer C. Pyrolysis of Mixed Plastic Wastes The experimental set-up for pyrolysis process was shown in Fig. 2. The experiment was carried out by loading 200 g of mixed plastic wastes such as 40% HDPE, 30% PP, 25% LDPE and 5% PS into the fixed bed reactor and 20 g of catalyst into the catalyst bed. Before starting experiment, nitrogen was flowed to the reactor to wash out oxygen from the reaction medium. In the catalytic pyrolysis process, two- XRF analyses of the samples were done using a Model- PW2400 of Phillips make, with X-ray tube of rhodium anode and scintillation detector with a current 40 ma and voltage 40 mv. The X-ray diffraction data was collected using Rigaku Geigerflex RADIA, Japan, X-ray Cu k-alpha 1/40kv/25MA, scan range deg, scan speed 4 deg/min. FTIR spectra were recorded on a Perkin-Elmer infrared spectrophotometer as KBr pellets with resolution of 4 cm 1, in the range of cm -1. DOI: 57
3 III. RESULT AND DISCUSSION A. XRF Characterization The chemical composition changes that the effect of nitric acid treated Myanmar Natural clay was analyzed using XRF. The changes in the chemical composition of the natural and acid activated Myanmar Natural clay at different acid concentrations are shown in Table II. Si and Al are major components of the mabisian clay with trace amount of Na, Mg, Ca, Fe and others. The Si/Al ratio was increased as the acid concentration increased up to 12M(NH6) and decreased with further increase in acid concentration. The content of Fe, Mg, Ca, Na in the clay decrease as an acid concentration increased while the Cr content did not change for any acid concentration. However, the composition of Al decreases up to 12M of acid concentration and increase with the father increase in acid concentration. The conduct showed by the Al, Fe, and Mg contents with progressive acid treatment is related to the progressive dissolution of the clay mineral. TABLE II: CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF UNTREATED AND ACID TREATED MABISIAN CLAY Chem -ical Conte -nt (wt%) Materials NH0 NH1 NH2 NH3 NH4 NH5 NH6 NH7 O Na Mg Al Si P S K Ca Ti Fe Cr Zr Rb Si/Al B. XRD Characterization X-ray diffraction method was used to study the structural changes of the untreated and acid treated Myanmar Natural Clay. The important mineralogical changes of the different concentration of nitric acid treated Myanmar Natural Clay (Mabisian) clays were shown in Fig. 3. Leaching of the Mabisian clay with nitric acid produces important mineralogical changes as seen in XRD patterns. The untreated clay shows well-defined reflections at 2θ value of º, º, and º which are typical characteristic peaks of kaolinite. After the acid treatment, the intensity of the clay moderately increases up to 12M and decrease in further increase in acid concentration. The acid activation process can effect on the crystalinity of the Mabisian clay. The increase of crystallite size depends on the intensity increase while the decreases of the mean lattic strain. Fig. 3. X-ray diffraction patterns of the natural and acid-treated Mabisian Clay C. FTIR Characterization In order to study the effect of acid leaching on the mabisian clay, FTIR analysis technique was used in the range from cm -1. The FTIR spetra of the raw and acid leached samples are shown in Fig. 4. This indicates that the functional groups change during the acid activation process. During the acid-leaching of the clay samples the cations from the acid medium penetrate into the clay structures attacking the OH groups thereby causing the alteration in the adsorption bands attributed to the OH vibrations and octahedral cations. The untreated sample shows absorption band 547.8, , , 911.4, , , , , , cm -1. In the O-H stretching region, the parent and acid treated clay show two prominent bands at , cm -1 corresponds to Al-OH stretching]. The intensity of absorption band was decrease at 3620 cm -1 after acid activation. It is due to the removal of octahedral cations, causing the loss of water. The band at , 1051 and cm -1 disappeared after the acid treatment of the clay sample. Again, strong bands are found in the cm -1 related to Al-Al-OH stretching and in the cm -1 DOI: 58
4 Peak Area ( %) Yield (wt%) corresponds to Al-Mg-OH stretching in untreated and treated clay. D. Product Oil Yield and Oil Composition The catalytic cracking of mixed plastic wastes (HDPE, PP, LDPE, PS) over acid-treated Mabisian clay was studied in the fixed bed reactor. The ratio of plastic to catalyst used was 10:1. The pyrolytic product yields related to the various acid concentrations was shown in Fig. 5. A yield of liquid product increased when the acid concentration increased up to 12M (NH6) and decreased in further increased in acid concentration. However, the yield of oil was not significant difference on the acid concentration. In addition, the coke formation slightly decreased when acid concentration increased. The composition of crude pyrolytic oil (liquid fuel) was characterized by using GC-MS. The quality of condensable gases (liquid fuel) derived from pyrolysis of mixed plastics waste using various concentration of nitric acid treated clay was calculated in term of gasoline range hydrocarbon. According to the GC-MS result, the composition of pyrolytic oil was influence on the various concentration of nitric acid. The relationship between the composition of the product oil and different acid concentration was shown in Fig. 6. In this figure, the range from C 7 C 12 indicates the gasoline range hydrocarbon and and > C 13+ was describe the higher molecular weight. It can be seen that the gasoline range hydrocarbons increased with the acid concentration increased up to 12M of nitric acid. However, the composition of gasoline range hydrocarbons decreased with any further increase of nitric acid was used Liquid Gas Coke Fig. 4. FTIR Result of Untreated and Acid Treated Clay Acid concentration Fig. 5. Product Yield from Catalytic Pyrolysis of Mixed Plastic Wastes by using Natural and Different Acid Treated Clay as a catalyst support C7-C12 (Gasoline range H/C) >C13 (Higher MW H/C) Acid Concentration Fig. 6. Influence of Natural and Different Acid Treated Clay on the Distribution of Gasoline Range and High Molecular Weight Hydrocarbon from Catalytic Pyrolysis of Mixed Plastic Wastes. DOI: 59
5 IV. CONCLUSION In this study, the catalytic degradation of mixed plastic using acid activated Mabisian clay was conducted. The XRF and FTIR study indicated that acid treatment under reflux condition lead to the removal of octahedral Al 3+ cations along with other impurities. The chemical treatment increases the Si/Al ratio from 1.39 to According to XRD result, the intensity of the clay moderately increases up to 12M and decrease in further increase in acid concentration. The FTIR results indicate that the functional groups of the Myanmar Natural Clay change during the acid activation process. The acid activation process can effect on the crystalinity of the Mabisian clay. The oil product obtained from catalytic pyrolysis of mixed plastic wastes (HDPE, LDPE, PP and PS) over acid treated clay showed only small difference in gas and oil yield in relation to the natural and different acid treated clay used. However, there was a significant difference in the composition of liquid fuel. The gasoline range hydrocarbon increased when the acid concentration increased up to 12 M which is NH6. The catalytic cracking of mixed plastic wastes using the acid treated clay at 12 M nitric acid, 3hr reaction time and 100 º C reaction temperatures as a catalyst support was given the maximum liquid yield (75%). In addition, the percent peak area of gasoline range hydrocarbon was obtained 55.6% at optimum condition. Therefore, pyrolysis of mixed plastics waste using acid treated Myanmar Natural clay not only reduces the plastic waste problem which causes the environmental pollution but also can produce the liquid fuel. Thus, the treated clay can be used as promising as catalyst support. ACKNOWLEDGMENT The author wishes to express all teachers and staff, Technological University, Myanmar for their kind help and valuable suggestions REFERENCES [1] Mohammad, N. S. and Halim, H. R. (2009). Catalytic coprocessing of waste plastics and petroleum residue into liquid fuel oils. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis. Vol.86, pp [2] Hwang, E.Y. Kim, J.R. and Chio, J. K, (2002). Performance of acid treated natural zeolites in catalytic degradation of polypropylene. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis. Vol.62, pp [3] Rezvanipour, M, Alikhani Hesari, F. and Pazouki, M. (2014). Catalytic Pyrolysis of General Purpose Polystyrene Using Red Mud as a Catalyst. Iranian Journal of Chemical Engineering, Vol. 11, No.4, pp [4] Ali, S and Uemichi, Y, (2002). Polymer waste recycling over used catalysts. Catalysis Today, Vol.75, pp [5] Lenarda, M. Storaro, L., Talona, A., Moretti, E., Riello, P., (2007). Solid acid catalysts from clays: preparation of mesoporous catalysts by chemical activation of metakaolin under acid conditions. Journal of Colloid Interface Sci. Vol. 311, pp [6] Tae, J.W., Jang, B.S., Kin, J.R. and Park, D.W., (2004). Catalytic degradation of polystyrene using acid-treated halloysite clays. Solid State Ionics, Vol.172, pp [7] Syamsiro M., Cheng S. and Saptoadi H., (2014). Liquid and Gaseous fuels from Waste Plastics by Sequential Pyrolysis and Catalytic Reforming Processes over Indonesian Natural Zeolite Catalysts. Waste Technology. Vol.2, No.2, pp [8] Delhez,R, Keijser, T.H., Mittemeijer, E.J., Fresenius, Z., (1982). Determination of crystallite size and lattice distortions through X-ray diffraction line profile analysis. Analytical Chemistry. Vol.312, pp [9] Achyut P.K., Mishra, B.G., Mishra D.K., and Singh, R.K., (2010). Effect of sulphuric acid treatment on the physico-chemical characteristics of kaolin clay. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects, Vol:363, pp Amie Thant was born in 1983 in Myanmar. She received her BE (Chemical) from Department of Chemical Engineering, Technological University (Mandalay) Myanmar in She got her Master of Sciences in Chemical Engineering degree from De La Salle University, Manila, Philippines in Right now she is doing the research for her PhD (Thesis) in Mandalay Technological University in Myanmar. Chaw Su Su Hmwe has been working in Technological University. She was born in 1981 in Myanmar. She received her B.E (Chemical) from Technological University (MTU), Myanmar in She received her M.E (Chemical) from Department of Chemical Engineering, Yangon Technological University, Myanmar in She received her PhD (Chemical) from Technological University, Myanmar in She has been doing the research of conversion of mixed plastic wastes into liquid hydrocarbon fuel. Now she doing the research in the field of Waste Water Treatment.. DOI: 60
Second International Seminar on Environmental Chemistry and Toxicology, April 26-27, 2005, Jogjakarta, Indonesia
 Optimization of Catalytic degradation of Plastic to Aromatics Over HY Zeolite Didi Dwi Anggoro Chemical Engineering Department, Diponegoro University Jl. Prof Sudharto SH, Tembalang, Semarang 50239, Indonesia
Optimization of Catalytic degradation of Plastic to Aromatics Over HY Zeolite Didi Dwi Anggoro Chemical Engineering Department, Diponegoro University Jl. Prof Sudharto SH, Tembalang, Semarang 50239, Indonesia
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information Metal-Organic Framework-Templated Synthesis of γ-fe 2 O 3
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information Metal-Organic Framework-Templated Synthesis of γ-fe 2 O 3
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Catalytic performance of Keplerate polyoxomolybdates in green epoxidation of alkenes with hydrogen
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Catalytic performance of Keplerate polyoxomolybdates in green epoxidation of alkenes with hydrogen
Removal of Cu 2+, Cd 2+, Hg 2+, and Ag + from Industrial Wastewater by Using Thiol-Loaded Silica Gel
 Universities Research Journal 2011, Vol. 4, No. 3 Removal of Cu 2+, Cd 2+, Hg 2+, and Ag + from Industrial Wastewater by Using Thiol-Loaded Silica Gel Aye Aye Myat 1, Kyaw Naing 2 and San San Myint 1 Abstract
Universities Research Journal 2011, Vol. 4, No. 3 Removal of Cu 2+, Cd 2+, Hg 2+, and Ag + from Industrial Wastewater by Using Thiol-Loaded Silica Gel Aye Aye Myat 1, Kyaw Naing 2 and San San Myint 1 Abstract
Effect of acid modification on physicochemical characteristics of Kpautagi clay
 Leonardo Journal of Sciences ISSN 1583-0233 Issue 28, January-June 2016 p. 87-94 Effect of acid modification on physicochemical characteristics of Kpautagi clay Matthew A. ONU 1,*, Joseph O. OKAFOR 1,
Leonardo Journal of Sciences ISSN 1583-0233 Issue 28, January-June 2016 p. 87-94 Effect of acid modification on physicochemical characteristics of Kpautagi clay Matthew A. ONU 1,*, Joseph O. OKAFOR 1,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Zeolitic Imidzolate Framework-8 as Efficient ph-sensitive Drug Delivery Vehicle Chun-Yi Sun, Chao Qin, Xin-Long Wang,* Guang-Sheng Yang, Kui-Zhan Shao, Ya-Qian Lan, Zhong-Min Su,*
Supporting Information Zeolitic Imidzolate Framework-8 as Efficient ph-sensitive Drug Delivery Vehicle Chun-Yi Sun, Chao Qin, Xin-Long Wang,* Guang-Sheng Yang, Kui-Zhan Shao, Ya-Qian Lan, Zhong-Min Su,*
OBTAINING OF LIQUID FUEL FROM COAL IN THE PRESENCE OF THE POLYMERS
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 14(1), 2016, 261-268 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com OBTAINING OF LIQUID FUEL FROM COAL IN THE PRESENCE OF THE POLYMERS D. A. BAISEITOV, SH. E. GABDRASHOVA, A. K. AKYLBAI,
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 14(1), 2016, 261-268 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com OBTAINING OF LIQUID FUEL FROM COAL IN THE PRESENCE OF THE POLYMERS D. A. BAISEITOV, SH. E. GABDRASHOVA, A. K. AKYLBAI,
A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with. Aliphatic Alcohols in the Presence of Molecular Oxygen. Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with Aliphatic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 A Tunable Process: Catalytic Transformation of Renewable Furfural with Aliphatic
Pd-P nanoalloys supported on porous carbon frame as efficient catalyst for benzyl alcohol oxidation
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting information Pd-P nanoalloys supported on porous carbon frame as
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting information Pd-P nanoalloys supported on porous carbon frame as
A Highly efficient Iron doped BaTiO 3 nanocatalyst for the catalytic reduction of nitrobenzene to azoxybenzene
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 A Highly efficient Iron doped BaTiO 3 nanocatalyst for the catalytic reduction of nitrobenzene
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 A Highly efficient Iron doped BaTiO 3 nanocatalyst for the catalytic reduction of nitrobenzene
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information MgFeCe ternary layered double hydroxide as highly efficient and recyclable heterogeneous base catalyst for synthesis of dimethyl carbonate by transesterification Nayana T. Nivangune
Supporting Information MgFeCe ternary layered double hydroxide as highly efficient and recyclable heterogeneous base catalyst for synthesis of dimethyl carbonate by transesterification Nayana T. Nivangune
Optimization of Process Parameters by Taguchi Method: Catalytic Degradation of Polypropylene to Liquid Fuel
 International Journal of Multidisciplinary and urrent Research Research rticle ISSN: -4 vailable at: http://ijmcr.com Optimization of Process Parameters by aguchi Method: atalytic Degradation of Polypropylene
International Journal of Multidisciplinary and urrent Research Research rticle ISSN: -4 vailable at: http://ijmcr.com Optimization of Process Parameters by aguchi Method: atalytic Degradation of Polypropylene
Development of process for the Catalytic Degradation of synthetic polymers.
 Development of process for the Catalytic Degradation of synthetic polymers. A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfilment for the Award of the Degree Of MASTER OF SCIENCE In CHEMISTRY By ASHISH SACHAN Under
Development of process for the Catalytic Degradation of synthetic polymers. A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfilment for the Award of the Degree Of MASTER OF SCIENCE In CHEMISTRY By ASHISH SACHAN Under
Preparation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Mixed with Calcinated Laterite for Arsenic Removal
 Preparation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Mixed with Calcinated Laterite for Arsenic Removal Wint Myat Shwe 1, Dr. Mya Mya Oo 2, Dr. Su Su Hlaing 3 Abstract-- To overcome arsenic toxicity; which has become
Preparation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Mixed with Calcinated Laterite for Arsenic Removal Wint Myat Shwe 1, Dr. Mya Mya Oo 2, Dr. Su Su Hlaing 3 Abstract-- To overcome arsenic toxicity; which has become
Catalytic degradation of polyethylene over SBA-16
 Korean J. Chem. Eng., 27(5), 1446-1451 (2010) DOI: 1007/s11814-010-0281-9 INVITED REVIEW PAPER Catalytic degradation of polyethylene over SBA-16 Suek Joo Choi*, Young-Kwon Park*, **,, Kwang-Eun Jeong***,
Korean J. Chem. Eng., 27(5), 1446-1451 (2010) DOI: 1007/s11814-010-0281-9 INVITED REVIEW PAPER Catalytic degradation of polyethylene over SBA-16 Suek Joo Choi*, Young-Kwon Park*, **,, Kwang-Eun Jeong***,
Experiment 24. Chemical recycling of poly(ethylene) terephthalate (PET)
 Methods of pollution control and waste management Experiment 24 Chemical recycling of poly(ethylene) terephthalate (PET) Manual Department of Chemical Technology The aim of this experiment is to gain knowledge
Methods of pollution control and waste management Experiment 24 Chemical recycling of poly(ethylene) terephthalate (PET) Manual Department of Chemical Technology The aim of this experiment is to gain knowledge
Synthesis gas production via the biogas reforming reaction over Ni/MgO-Al 2 O 3 and Ni/CaO-Al 2 O 3 catalysts
 Synthesis gas production via the biogas reforming reaction over Ni/MgO-Al 2 O 3 and Ni/CaO-Al 2 O 3 catalysts N.D. Charisiou 1,2, A. Baklavaridis 1, V.G. Papadakis 2, M.A. Goula 1 1 Department of Environmental
Synthesis gas production via the biogas reforming reaction over Ni/MgO-Al 2 O 3 and Ni/CaO-Al 2 O 3 catalysts N.D. Charisiou 1,2, A. Baklavaridis 1, V.G. Papadakis 2, M.A. Goula 1 1 Department of Environmental
4023 Synthesis of cyclopentanone-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester from adipic acid diethyl ester
 NP 4023 Synthesis of cyclopentanone-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester from adipic acid diethyl ester NaEt C 10 H 18 4 Na C 2 H 6 C 8 H 12 3 (202.2) (23.0) (46.1) (156.2) Classification Reaction types and substance
NP 4023 Synthesis of cyclopentanone-2-carboxylic acid ethyl ester from adipic acid diethyl ester NaEt C 10 H 18 4 Na C 2 H 6 C 8 H 12 3 (202.2) (23.0) (46.1) (156.2) Classification Reaction types and substance
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2008 69451 Weinheim, Germany Iridium-Catalyzed Dehydrocoupling of Primary Amine-Borane Adducts: A Route to High Molecular Weight Polyaminoboranes, Boron-Nitrogen Analogues
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2008 69451 Weinheim, Germany Iridium-Catalyzed Dehydrocoupling of Primary Amine-Borane Adducts: A Route to High Molecular Weight Polyaminoboranes, Boron-Nitrogen Analogues
EFFECTS OF POST-TREATMENT STEAMING ON CATALYTIC PERFORMANCE OF MODIFIED HZSM-5 CATALYSTS FOR THE CONVERSION OF n-pentane TO AROMATICS
 EFFECTS OF POST-TREATMENT STEAMING ON CATALYTIC PERFORMANCE OF MODIFIED HZSM-5 CATALYSTS FOR THE CONVERSION OF n-pentane TO AROMATICS Chaninwut Kalajuck a, Siriporn Jongpatiwut*,a,b, Thirasak Rirksomboon
EFFECTS OF POST-TREATMENT STEAMING ON CATALYTIC PERFORMANCE OF MODIFIED HZSM-5 CATALYSTS FOR THE CONVERSION OF n-pentane TO AROMATICS Chaninwut Kalajuck a, Siriporn Jongpatiwut*,a,b, Thirasak Rirksomboon
Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO
 Supporing Information Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO Chun-Jiang Jia, Yong Liu, Hans Bongard, Ferdi Schüth* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung,
Supporing Information Very low temperature CO oxidation over colloidally deposited gold nanoparticles on Mg(OH) 2 and MgO Chun-Jiang Jia, Yong Liu, Hans Bongard, Ferdi Schüth* Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung,
Studies on Mo/HZSM-5 Complex catalyst for Methane Aromatization
 Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 13(2004)36 40 Studies on Mo/HZSM-5 Complex catalyst for Methane Aromatization Qun Dong 1, Xiaofei Zhao 1, Jian Wang 1, M Ichikawa 2 1. Department of Petrochemical Engineering,
Journal of Natural Gas Chemistry 13(2004)36 40 Studies on Mo/HZSM-5 Complex catalyst for Methane Aromatization Qun Dong 1, Xiaofei Zhao 1, Jian Wang 1, M Ichikawa 2 1. Department of Petrochemical Engineering,
Supplementary Information. ZIF-8 Immobilized Ni(0) Nanoparticles: Highly Effective Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane
 Supplementary Information ZIF-8 Immobilized Ni() Nanoparticles: Highly Effective Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane Pei-Zhou Li, a,b Kengo Aranishi, a and Qiang Xu* a,b
Supplementary Information ZIF-8 Immobilized Ni() Nanoparticles: Highly Effective Catalysts for Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane Pei-Zhou Li, a,b Kengo Aranishi, a and Qiang Xu* a,b
A triazine-based covalent organic polymer for efficient CO 2 adsorption
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information A triazine-based covalent organic polymer for efficient CO
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information A triazine-based covalent organic polymer for efficient CO
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Designed Copper-amine Complex as an Efficient Template for One-pot Synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13 Zeolite with Excellent Activity for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by
Electronic Supplementary Information Designed Copper-amine Complex as an Efficient Template for One-pot Synthesis of Cu-SSZ-13 Zeolite with Excellent Activity for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by
Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using
 Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using Hierarchical Mesoporous Zeolites Deepak Verma, Rohit Kumar, Bharat S. Rana, Anil K. Sinha* CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun-2485,
Aviation Fuel Production from Lipids by a Single-Step Route using Hierarchical Mesoporous Zeolites Deepak Verma, Rohit Kumar, Bharat S. Rana, Anil K. Sinha* CSIR-Indian Institute of Petroleum, Dehradun-2485,
Selective aerobic oxidation of biomass-derived HMF to 2,5- diformylfuran using a MOF-derived magnetic hollow Fe-Co
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Selective aerobic oxidation of biomass-derived HMF to 2,5- diformylfuran using a MOF-derived
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Selective aerobic oxidation of biomass-derived HMF to 2,5- diformylfuran using a MOF-derived
Biogasoline from Catalytic Cracking of Refined Palm Oil using H-ZSM-5 Catalyst
 Int l Journal of Advances in Chemical Engg., & Biological Sciences (IJACEBS) Vol., Issue (04) ISSN 49-507 EISSN 49-55 Biogasoline from Catalytic Cracking of Refined Palm Oil using H-ZSM-5 Catalyst Jiratchaya
Int l Journal of Advances in Chemical Engg., & Biological Sciences (IJACEBS) Vol., Issue (04) ISSN 49-507 EISSN 49-55 Biogasoline from Catalytic Cracking of Refined Palm Oil using H-ZSM-5 Catalyst Jiratchaya
Supporting Information for
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information for Microwave-enhanced catalytic wet peroxide oxidation of quinoline:
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information for Microwave-enhanced catalytic wet peroxide oxidation of quinoline:
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Polyoxometalate-based crystalline tubular microreactor: redox-active inorganic-organic hybrid materials producing gold nanoparticles and catalytic properties Dong-Ying Du, Jun-Sheng
Supporting Information Polyoxometalate-based crystalline tubular microreactor: redox-active inorganic-organic hybrid materials producing gold nanoparticles and catalytic properties Dong-Ying Du, Jun-Sheng
CuH-ZSM-5 as Hydrocarbon Trap under cold. start conditions
 CuH-ZSM-5 as Hydrocarbon Trap under cold start conditions M. Navlani-García a, B. Puértolas b, D. Lozano-Castelló a, *, D. Cazorla-Amorós a, M. V. Navarro b, T. García b a Instituto Universitario de Materiales,
CuH-ZSM-5 as Hydrocarbon Trap under cold start conditions M. Navlani-García a, B. Puértolas b, D. Lozano-Castelló a, *, D. Cazorla-Amorós a, M. V. Navarro b, T. García b a Instituto Universitario de Materiales,
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 Supporting Information Lei Liu, ab Yijie Xia, b Jie Zhang* b a) China Center for Modernization
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 214 Supporting Information Lei Liu, ab Yijie Xia, b Jie Zhang* b a) China Center for Modernization
One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene Peipei Zhang,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting Information One-pass Selective Conversion of Syngas to para-xylene Peipei Zhang,
Preparation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Mixed with Calcinated Laterite for Arsenic Removal
 Preparation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Mixed with Calcinated Laterite for Arsenic Removal Wint Myat Shwe 1, Su Su Hlaing 2, Mya Mya Oo 3 Abstract-- This paper was studied about a simple and efficient
Preparation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Mixed with Calcinated Laterite for Arsenic Removal Wint Myat Shwe 1, Su Su Hlaing 2, Mya Mya Oo 3 Abstract-- This paper was studied about a simple and efficient
Characteristics of Metal Supported-Zeolite Catalysts for Hydrocracking of Polyethylene Terephthalat
 IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC) e-issn: 2278-5736. Volume 3, Issue 4 (Jan. Feb. 2013), PP 29-34 Characteristics of Metal Supported-Zeolite Catalysts for Hydrocracking of Polyethylene Terephthalat
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC) e-issn: 2278-5736. Volume 3, Issue 4 (Jan. Feb. 2013), PP 29-34 Characteristics of Metal Supported-Zeolite Catalysts for Hydrocracking of Polyethylene Terephthalat
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Controllable integration of ultrasmall noble metal nanoparticles
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Controllable integration of ultrasmall noble metal nanoparticles
PREPARATION, CHARACTERIZATION OF OXIDATION-REDUCTION PROPERTIES AND APPLICATION OF Fe-ZSM-5 CATALYSTS
 PREPARATION, CHARACTERIZATION OF OXIDATION-REDUCTION PROPERTIES AND APPLICATION OF Fe-ZSM-5 CATALYSTS D. Szalay*, G. Horváth**, J. Halász** and I. Kiricsi** Department of Environmental Engineering, Széchenyi
PREPARATION, CHARACTERIZATION OF OXIDATION-REDUCTION PROPERTIES AND APPLICATION OF Fe-ZSM-5 CATALYSTS D. Szalay*, G. Horváth**, J. Halász** and I. Kiricsi** Department of Environmental Engineering, Széchenyi
Supporting Information. Highly Efficient Aerobic Oxidation of Various Amines Using Pd 3 Pb Intermetallic Compound Catalysts
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Highly Efficient Aerobic Oxidation of Various Amines Using Pd 3 Pb Intermetallic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Highly Efficient Aerobic Oxidation of Various Amines Using Pd 3 Pb Intermetallic
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Characterization of pure CaO and Zr-TiO 2 /CaO nanocomposite
 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 4.1. Characterization of pure CaO and Zr-TiO 2 /CaO nanocomposite 4.1.1. Scanning electron microscopy analysis (SEM) SEM images of prepared CaO are shown in Fig. 4.1 (a and b). CaO
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 4.1. Characterization of pure CaO and Zr-TiO 2 /CaO nanocomposite 4.1.1. Scanning electron microscopy analysis (SEM) SEM images of prepared CaO are shown in Fig. 4.1 (a and b). CaO
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Cu-SSZ-39, an active and hydrothermally stable catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx Manuel Moliner, *a Cristina Franch, a Eduardo Palomares,
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Cu-SSZ-39, an active and hydrothermally stable catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx Manuel Moliner, *a Cristina Franch, a Eduardo Palomares,
Supporting Information:
 Supporting Information: In Situ Synthesis of Magnetically Recyclable Graphene Supported Pd@Co Core-Shell Nanoparticles as Efficient Catalysts for Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane Jun Wang,
Supporting Information: In Situ Synthesis of Magnetically Recyclable Graphene Supported Pd@Co Core-Shell Nanoparticles as Efficient Catalysts for Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane Jun Wang,
Mesostructured Zeolite Y - High Hydrothermal Stability and Superior FCC Catalytic Performance
 Supporting Information Mesostructured Zeolite Y - High Hydrothermal Stability and Superior FCC Catalytic Performance Javier García-Martínez,* Marvin Johnson, Julia Valla, Kunhao Li, and Jackie Y. Ying*
Supporting Information Mesostructured Zeolite Y - High Hydrothermal Stability and Superior FCC Catalytic Performance Javier García-Martínez,* Marvin Johnson, Julia Valla, Kunhao Li, and Jackie Y. Ying*
One-pot Solvent-free Synthesis of Sodium Benzoate from the Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol over Novel Efficient AuAg/TiO 2 Catalysts
 Electronic Supplementary Information One-pot Solvent-free Synthesis of Sodium Benzoate from the Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol over Novel Efficient AuAg/TiO 2 Catalysts Ying Wang, Jia-Min Zheng, Kangnian
Electronic Supplementary Information One-pot Solvent-free Synthesis of Sodium Benzoate from the Oxidation of Benzyl Alcohol over Novel Efficient AuAg/TiO 2 Catalysts Ying Wang, Jia-Min Zheng, Kangnian
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2008 69451 Weinheim, Germany Supporting information: Iron Nanoparticle Catalyzed Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane for Chemical Hydrogen Storage Jun-Min Yan,
Supporting Information Wiley-VCH 2008 69451 Weinheim, Germany Supporting information: Iron Nanoparticle Catalyzed Hydrolytic Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane for Chemical Hydrogen Storage Jun-Min Yan,
Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate
 Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate An-Yuan Yin, Xiao-Yang Guo, Wei-Lin Dai*, Kang-Nian Fan Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular
Supporting Information High Activity and Selectivity of Ag/SiO 2 Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Dimethyloxalate An-Yuan Yin, Xiao-Yang Guo, Wei-Lin Dai*, Kang-Nian Fan Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular
Supporting Information. Mesostructured Y Zeolite as Superior FCC Catalyst -- From Lab to Refinery
 Supporting Information Mesostructured Y Zeolite as Superior FCC Catalyst -- From Lab to Refinery Javier Garcia-Martinez,* a,b Kunhao Li a and Gautham Krishnaiah a a Rive Technology, Inc., Monmouth Junction,
Supporting Information Mesostructured Y Zeolite as Superior FCC Catalyst -- From Lab to Refinery Javier Garcia-Martinez,* a,b Kunhao Li a and Gautham Krishnaiah a a Rive Technology, Inc., Monmouth Junction,
Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of Phenol
 http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2015.952 2015, 4(2), 438-442 RESEARCH ARTICLE Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of
http://www.e-journals.in Chemical Science Transactions DOI:10.7598/cst2015.952 2015, 4(2), 438-442 RESEARCH ARTICLE Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Activity of MCM-41 Catalyst for Nitration of
FUEL PRODUCTION FROM WASTE PLASTIC USING CLAY CATALYST Keerthi J 1, Roopa Farshi 2, Ravi Shankar R 3, M. A. L. Antony Raj 4
 FUEL PRODUCTION FROM WASTE PLASTIC USING CLAY CATALYST Keerthi J 1, Roopa Farshi 2, Ravi Shankar R 3, M. A. L. Antony Raj 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Keerthi J, Roopa Farshi, Ravi Shankar R, M. A. L. Antony
FUEL PRODUCTION FROM WASTE PLASTIC USING CLAY CATALYST Keerthi J 1, Roopa Farshi 2, Ravi Shankar R 3, M. A. L. Antony Raj 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Keerthi J, Roopa Farshi, Ravi Shankar R, M. A. L. Antony
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 5, Issue 3, March-2014 ISSN
 156 Copper Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis Characterization Y.Suresh*1, S.Annapurna*2, G.Bhikshamaiah*3, A.K.Singh#4 Abstract Present work describes the synthesis nanoparticles using papaya extract as a
156 Copper Nanoparticles: Green Synthesis Characterization Y.Suresh*1, S.Annapurna*2, G.Bhikshamaiah*3, A.K.Singh#4 Abstract Present work describes the synthesis nanoparticles using papaya extract as a
SYNTHESIS OF ZEOLITE FROM
 SYNTHESIS OF ZEOLITE FROM COAL FLY ASH: ITS APPLICATION AS WATER SORBENT Thepparat Klamrassamee 1, Prasert Pavasant 2 and Navadol Laosiripojana 1 * 1 The Joint Graduate School of Energy and Environment,
SYNTHESIS OF ZEOLITE FROM COAL FLY ASH: ITS APPLICATION AS WATER SORBENT Thepparat Klamrassamee 1, Prasert Pavasant 2 and Navadol Laosiripojana 1 * 1 The Joint Graduate School of Energy and Environment,
Supporting Information for: Three-Dimensional Cuprous Oxide Microtube Lattices with High Catalytic
 Supporting Information for: Three-Dimensional Cuprous Oxide Microtube Lattices with High Catalytic Activity Templated by Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers Guigao Liu, Fang He*, Xiaoqing Li, Sihui Wang, Lijun
Supporting Information for: Three-Dimensional Cuprous Oxide Microtube Lattices with High Catalytic Activity Templated by Bacterial Cellulose Nanofibers Guigao Liu, Fang He*, Xiaoqing Li, Sihui Wang, Lijun
Clean synthesis of propylene carbonate from urea and 1,2-propylene glycol over zinc iron double oxide catalyst
 Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:794 798 (2006) DOI: 10.1002/jctb.1412 Clean synthesis of propylene carbonate from urea and 1,2-propylene glycol over zinc iron
Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology J Chem Technol Biotechnol 81:794 798 (2006) DOI: 10.1002/jctb.1412 Clean synthesis of propylene carbonate from urea and 1,2-propylene glycol over zinc iron
Plasma driven ammonia decomposition on Fe-catalyst: eliminating surface nitrogen poisoning
 Supporting Information for Plasma driven ammonia decomposition on Fe-catalyst: eliminating surface nitrogen poisoning Contents: 1. Scheme of the DBD plasma-driven catalysis reactor, Scheme S1. 2. XRF analysis
Supporting Information for Plasma driven ammonia decomposition on Fe-catalyst: eliminating surface nitrogen poisoning Contents: 1. Scheme of the DBD plasma-driven catalysis reactor, Scheme S1. 2. XRF analysis
Synthesis of Carbon Nanoparticles from Polystyrene Wastes
 Synthesis of Carbon Nanoparticles from Polystyrene Wastes Davood Kaviani 1, Payam Pirmohamadi 2, Majid Saghi 3, Behzad Padidaran 4, Mohammad Hosein Bigtan 5 1 Department of chemistry, Science and research
Synthesis of Carbon Nanoparticles from Polystyrene Wastes Davood Kaviani 1, Payam Pirmohamadi 2, Majid Saghi 3, Behzad Padidaran 4, Mohammad Hosein Bigtan 5 1 Department of chemistry, Science and research
Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite) catalyst
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite)
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Synthesis of isoalkanes over core (Fe-Zn-Zr)-shell (zeolite)
Supplementary Figure S1 Reactor setup Calcined catalyst (0.40 g) and silicon carbide powder (0.4g) were mixed thoroughly and inserted into a 4 mm
 Supplementary Figure S1 Reactor setup Calcined catalyst (.4 g) and silicon carbide powder (.4g) were mixed thoroughly and inserted into a 4 mm diameter silica reactor (G). The powder mixture was sandwiched
Supplementary Figure S1 Reactor setup Calcined catalyst (.4 g) and silicon carbide powder (.4g) were mixed thoroughly and inserted into a 4 mm diameter silica reactor (G). The powder mixture was sandwiched
Electronic Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Information Formation of MS-Ag and MS (M=Pb, Cd, Zn) nanotubes via microwave-assisted cation exchange and their enhanced photocatalytic activities Yanrong Wang, a Wenlong Yang,
Electronic Supplementary Information Formation of MS-Ag and MS (M=Pb, Cd, Zn) nanotubes via microwave-assisted cation exchange and their enhanced photocatalytic activities Yanrong Wang, a Wenlong Yang,
Novel fungus-titanate bio-nano composites as high performance. absorbents for the efficient removal of radioactive ions from.
 This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 0 Electronic Supplementary Information For Novel fungus-titanate bio-nano composites as high performance absorbents for the efficient removal of radioactive
This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 0 Electronic Supplementary Information For Novel fungus-titanate bio-nano composites as high performance absorbents for the efficient removal of radioactive
Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of High Density Poly Ethylene Catalytic Cracking Reactor
 American Journal of Oil and Chemical Technologies Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of High Density Poly Ethylene Catalytic Cracking Reactor Bagher Anvaripour Mohammad Shah Bin Zahra Maghareh Chemical
American Journal of Oil and Chemical Technologies Computational Fluid Dynamics Modeling of High Density Poly Ethylene Catalytic Cracking Reactor Bagher Anvaripour Mohammad Shah Bin Zahra Maghareh Chemical
Catalytic Decomposition of Formaldehyde on Nanometer Manganese Dioxide
 Modern Applied Science April, 29 Catalytic Decomposition of Formaldehyde on Nanometer Manganese Dioxide Xiujuan Chu & Hua Zhang (Corresponding author) Tianjin Municipal Key Lab of Fibres Modification and
Modern Applied Science April, 29 Catalytic Decomposition of Formaldehyde on Nanometer Manganese Dioxide Xiujuan Chu & Hua Zhang (Corresponding author) Tianjin Municipal Key Lab of Fibres Modification and
Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for production of hydrogen from methanol steam reforming
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Strategic use of CuAlO 2 as a sustained release catalyst for
Efficient Co-Fe layered double hydroxide photocatalysts for water oxidation under visible light
 Supplementary Information Efficient Co-Fe layered double hydroxide photocatalysts for water oxidation under visible light Sang Jun Kim, a Yeob Lee, a Dong Ki Lee, a Jung Woo Lee a and Jeung Ku Kang* a,b
Supplementary Information Efficient Co-Fe layered double hydroxide photocatalysts for water oxidation under visible light Sang Jun Kim, a Yeob Lee, a Dong Ki Lee, a Jung Woo Lee a and Jeung Ku Kang* a,b
Supporting Information. for. A Sustainable Protocol for the Spontaneous Synthesis of Zinc-Glutamate. Wet Conditions
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information for A Sustainable Protocol for the Spontaneous Synthesis of Zinc-Glutamate
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information for A Sustainable Protocol for the Spontaneous Synthesis of Zinc-Glutamate
Catalytic Cracking of Polyolefins in the Molten Phase Basic Study for the Process Development of Waste Plastics Liquefaction
 Journal of Environmental Science and Engineering B 6 (2017) 352-361 doi:10.17265/2162-5263/2017.07.002 D DAVID PUBLISHING Catalytic Cracking of Polyolefins in the Molten Phase Basic Study for the Process
Journal of Environmental Science and Engineering B 6 (2017) 352-361 doi:10.17265/2162-5263/2017.07.002 D DAVID PUBLISHING Catalytic Cracking of Polyolefins in the Molten Phase Basic Study for the Process
Effects of Different Processing Parameters on Divinylbenzene (DVB) Production Rate
 1 Effects of Different Processing Parameters on Divinylbenzene (DVB) Production Rate ME Zeynali Petrochemical Synthesis Group, Petrochemical Faculty, Iran Polymer and Petrochemical Institute (IPPI), P.O.
1 Effects of Different Processing Parameters on Divinylbenzene (DVB) Production Rate ME Zeynali Petrochemical Synthesis Group, Petrochemical Faculty, Iran Polymer and Petrochemical Institute (IPPI), P.O.
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets Lan Wang, a Ling Zang, b Jincai Zhao c and Chuanyi Wang*
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Green synthesis of shape-defined anatase TiO 2 nanocrystals wholly exposed with {001} and {100} facets Lan Wang, a Ling Zang, b Jincai Zhao c and Chuanyi Wang*
Immobilization of BiOX (X=Cl, Br) on activated carbon fibers as
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Immobilization of BiOX (X=Cl, Br) on activated carbon fibers as recycled photocatalysts
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Dalton Transactions. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Immobilization of BiOX (X=Cl, Br) on activated carbon fibers as recycled photocatalysts
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Multi-scale promoting effects
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Catalysis Science & Technology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Multi-scale promoting effects
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/321/5894/1331/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Identification of Active Gold Nanoclusters on Iron Oxide Supports for CO Oxidation Andrew A. Herzing, Christopher J.
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/321/5894/1331/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Identification of Active Gold Nanoclusters on Iron Oxide Supports for CO Oxidation Andrew A. Herzing, Christopher J.
Facile Synthesis and Catalytic Properties of CeO 2 with Tunable Morphologies from Thermal Transformation of Cerium Benzendicarboxylate Complexes
 Electronic Supplementary Information Facile Synthesis and Catalytic Properties of CeO 2 with Tunable Morphologies from Thermal Transformation of Cerium Benzendicarboxylate Complexes Yuhua Zheng, Kai Liu,
Electronic Supplementary Information Facile Synthesis and Catalytic Properties of CeO 2 with Tunable Morphologies from Thermal Transformation of Cerium Benzendicarboxylate Complexes Yuhua Zheng, Kai Liu,
The School For Excellence 2018 Unit 3 & 4 Chemistry Topic Notes Page 1
 The term fractional distillation refers to a physical method used to separate various components of crude oil. Fractional distillation uses the different boiling temperatures of each component, or fraction,
The term fractional distillation refers to a physical method used to separate various components of crude oil. Fractional distillation uses the different boiling temperatures of each component, or fraction,
LEAD (Colorimetric) 2. Muffle Furnace: Equipped with pyrometer and capable of operating at controlled temperatures up to 500 C
 LEADX.01-1 LEAD (Colorimetric) PRINCIPLE SCOPE Organic matter in the sample is destroyed by ignition in the presence of sulfuric acid. The residue is dissolved in dilute acid, and the lead is complexed
LEADX.01-1 LEAD (Colorimetric) PRINCIPLE SCOPE Organic matter in the sample is destroyed by ignition in the presence of sulfuric acid. The residue is dissolved in dilute acid, and the lead is complexed
Ligand-free coupling of phenols and alcohols with aryl halides by a recyclable heterogeneous copper catalyst
 Supporting Information Ligand-free coupling of phenols and alcohols with aryl halides by a recyclable heterogeneous copper catalyst Man Wang, Bizhen Yuan, Tongmei Ma, Huanfeng Jiang and Yingwei Li* School
Supporting Information Ligand-free coupling of phenols and alcohols with aryl halides by a recyclable heterogeneous copper catalyst Man Wang, Bizhen Yuan, Tongmei Ma, Huanfeng Jiang and Yingwei Li* School
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Facile preparation of superhydrophobic coating by spraying a fluorinated acrylic random copolymer micelle solution Hui Li, a,b Yunhui Zhao a and Xiaoyan Yuan* a a School of Materials
Supplementary Information Facile preparation of superhydrophobic coating by spraying a fluorinated acrylic random copolymer micelle solution Hui Li, a,b Yunhui Zhao a and Xiaoyan Yuan* a a School of Materials
Characterization of zeolites by advanced SEM/STEM techniques
 SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENT NEWS 2016 Vol. 7 SEPTEMBER Technical magazine of Electron Microscope and Analytical Instruments. Article Characterization of zeolites by advanced SEM/STEM techniques Toshiyuki Yokoi
SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENT NEWS 2016 Vol. 7 SEPTEMBER Technical magazine of Electron Microscope and Analytical Instruments. Article Characterization of zeolites by advanced SEM/STEM techniques Toshiyuki Yokoi
Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Long Wavelength Photoinitiators for Free Radical Polymerization
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Polymer Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Long Wavelength Photoinitiators
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Polymer Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Long Wavelength Photoinitiators
Comparison of acid catalysts for the dehydration of methanol to dimethyl ether
 Proceedings of European Congress of Chemical Engineering (ECCE-6) Copenhagen, 16-2 September 27 Comparison of acid catalysts for the dehydration of methanol to dimethyl ether I. Sierra, J. Ereña, A. T.
Proceedings of European Congress of Chemical Engineering (ECCE-6) Copenhagen, 16-2 September 27 Comparison of acid catalysts for the dehydration of methanol to dimethyl ether I. Sierra, J. Ereña, A. T.
In Situ synthesis of architecture for Strong Light-Matter Interactions
 In Situ synthesis of Ag@Cu2O-rGO architecture for Strong Light-Matter Interactions Shuang Guo 1, 2, Yaxin Wang 1, *, Fan Zhang 1, Renxian Gao 1, Maomao Liu 1, Lirong Dong 1, Yang Liu 2, Yongjun Zhang 2,
In Situ synthesis of Ag@Cu2O-rGO architecture for Strong Light-Matter Interactions Shuang Guo 1, 2, Yaxin Wang 1, *, Fan Zhang 1, Renxian Gao 1, Maomao Liu 1, Lirong Dong 1, Yang Liu 2, Yongjun Zhang 2,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Au-HKUST-1 Composite Nanocapsules: Synthesis with a Coordination Replication Strategy and Catalysis on CO Oxidation Yongxin Liu, 1 Jiali Zhang, 1 Lingxiao Song, 1 Wenyuan Xu, 1 Zanru
Supporting Information Au-HKUST-1 Composite Nanocapsules: Synthesis with a Coordination Replication Strategy and Catalysis on CO Oxidation Yongxin Liu, 1 Jiali Zhang, 1 Lingxiao Song, 1 Wenyuan Xu, 1 Zanru
An unprecedented 2D 3D metal-organic polyrotaxane. framework constructed from cadmium and flexible star-like
 Electronic Supplementary Information An unprecedented 2D 3D metal-organic polyrotaxane framework constructed from cadmium and flexible star-like ligand Hua Wu, a,b Hai-Yan Liu, a Ying-Ying Liu, a Jin Yang,*
Electronic Supplementary Information An unprecedented 2D 3D metal-organic polyrotaxane framework constructed from cadmium and flexible star-like ligand Hua Wu, a,b Hai-Yan Liu, a Ying-Ying Liu, a Jin Yang,*
Supporting information
 Supporting information Temperature and ph-dual Responsive AIE-Active Core Crosslinked Polyethylene Poly(methacrylic acid) Multimiktoarm Star Copolymers ` Zhen Zhang,*,, and Nikos Hadjichristidis*, School
Supporting information Temperature and ph-dual Responsive AIE-Active Core Crosslinked Polyethylene Poly(methacrylic acid) Multimiktoarm Star Copolymers ` Zhen Zhang,*,, and Nikos Hadjichristidis*, School
DEVELOPMENT OF CATALYSTS FOR ETHANE EPOXIDATION REACTION. Keywords: Ethylene oxide, Partial oxidation, Ethane epoxidation, Second metal.
 DEVELOPMENT OF CATALYSTS FOR ETHANE EPOXIDATION REACTION Kingsuda Mahunee a, Krittiya Pornmai a, Sitthiphong Pengpanich c, Sumaeth Chavade j* a,b a The Petroleum and Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn
DEVELOPMENT OF CATALYSTS FOR ETHANE EPOXIDATION REACTION Kingsuda Mahunee a, Krittiya Pornmai a, Sitthiphong Pengpanich c, Sumaeth Chavade j* a,b a The Petroleum and Petrochemical College, Chulalongkorn
Efficient Molybdenum (VI) Modified Zr-MOF Catalyst for
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Efficient Molybdenum (VI) Modified Zr-MOF Catalyst for Epoxidation of Olefins Jia Tang, a Wenjun
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Efficient Molybdenum (VI) Modified Zr-MOF Catalyst for Epoxidation of Olefins Jia Tang, a Wenjun
driving agent and study of photocatalytic activity Mohammad Salehi Department of Chemistry, Iran University of Science and Technology, Narmak, Tehran
 A simplified microwave-assisted synthesis of NiMoO 4 nanoparticles by using organic driving agent and study of photocatalytic activity Azadeh Tadjarodi *, Raheleh Pradehkhorram, Mina Imani, Samaneh Ebrahimi,
A simplified microwave-assisted synthesis of NiMoO 4 nanoparticles by using organic driving agent and study of photocatalytic activity Azadeh Tadjarodi *, Raheleh Pradehkhorram, Mina Imani, Samaneh Ebrahimi,
Supporting Information. Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with. Controlled Mesoporosity and Size
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with Controlled
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting Information Nanoscale Kirkendall Growth of Silicalite-1 Zeolite Mesocrystals with Controlled
Electronic supplementary information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic supplementary information Heterogeneous nucleation and growth of highly crystalline
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic supplementary information Heterogeneous nucleation and growth of highly crystalline
A General Synthesis of Discrete Mesoporous Carbon Microspheres through a Confined Self- Assembly Process in Inverse Opals
 A General Synthesis of Discrete Mesoporous Carbon Microspheres through a Confined Self- Assembly Process in Inverse Opals Zhenkun Sun,, Yong Liu, Bin Li, Jing Wei, Minghong Wang, Qin Yue, Yonghui Deng,
A General Synthesis of Discrete Mesoporous Carbon Microspheres through a Confined Self- Assembly Process in Inverse Opals Zhenkun Sun,, Yong Liu, Bin Li, Jing Wei, Minghong Wang, Qin Yue, Yonghui Deng,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Oxygen Reduction on Graphene-Carbon Nanotube Composites Doped Sequentially with Nitrogen and Sulfur Drew C. Higgins, Md Ariful Hoque, Fathy Hassan, Ja-Yeon Choi, Baejung Kim, Zhongwei
Supporting Information Oxygen Reduction on Graphene-Carbon Nanotube Composites Doped Sequentially with Nitrogen and Sulfur Drew C. Higgins, Md Ariful Hoque, Fathy Hassan, Ja-Yeon Choi, Baejung Kim, Zhongwei
Supporting information for Mesoporous Nitrogen-Doped Carbons with High Nitrogen Content and
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information for Mesoporous Nitrogen-Doped Carbons with High Nitrogen Content
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Green Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Supporting information for Mesoporous Nitrogen-Doped Carbons with High Nitrogen Content
Electronic Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supporting Information 3D ordered macroporous TiO 2 -supported
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry A. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Electronic Supporting Information 3D ordered macroporous TiO 2 -supported
Red Color CPL Emission of Chiral 1,2-DACH-based Polymers via. Chiral Transfer of the Conjugated Chain Backbone Structure
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Polymer Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Red Color CPL Emission of Chiral 1,2-DACH-based Polymers via Chiral Transfer of the Conjugated
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Polymer Chemistry. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Red Color CPL Emission of Chiral 1,2-DACH-based Polymers via Chiral Transfer of the Conjugated
The effect of acid leaching time in modifying natural zeolite as catalyst for toluene steam reforming
 The effect of acid leaching time in modifying natural zeolite as catalyst for toluene steam reforming Joko Waluyo 1,2, I.G.B.N. Makertihartha 1, Herri Susanto 1,* 1 Department of Chemical Engineering,
The effect of acid leaching time in modifying natural zeolite as catalyst for toluene steam reforming Joko Waluyo 1,2, I.G.B.N. Makertihartha 1, Herri Susanto 1,* 1 Department of Chemical Engineering,
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information A difunctional metal organic framework with Lewis
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Journal of Materials Chemistry C. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information A difunctional metal organic framework with Lewis
Influence of Functional Sulfonic Acid Group on Pyrolysis Characteristics for Cation
 Journal of NUCLEAR SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY, 24[2], pp. 124~128 (February 1987) Influence of Functional Sulfonic Acid Group on Pyrolysis Characteristics for Cation Exchange Resin Masami MATSUDA, Kiyomi FUNABASHI,
Journal of NUCLEAR SCIENCE and TECHNOLOGY, 24[2], pp. 124~128 (February 1987) Influence of Functional Sulfonic Acid Group on Pyrolysis Characteristics for Cation Exchange Resin Masami MATSUDA, Kiyomi FUNABASHI,
Electronic Supporting Information (ESI) Porous Carbon Materials with Controllable Surface Area Synthsized from Metal-Organic Frameworks
 Electronic Supporting Information (ESI) Porous Carbon Materials with Controllable Surface Area Synthsized from Metal-Organic Frameworks Seunghoon Lim, Kyungwon Suh, Yelin Kim, Minyoung Yoon, Hyeran Park,
Electronic Supporting Information (ESI) Porous Carbon Materials with Controllable Surface Area Synthsized from Metal-Organic Frameworks Seunghoon Lim, Kyungwon Suh, Yelin Kim, Minyoung Yoon, Hyeran Park,
Room Temperature Hydrogen Generation from Hydrous Hydrazine for Chemical Hydrogen Storage
 (Supporting Information) Room Temperature Hydrogen Generation from Hydrous Hydrazine for Chemical Hydrogen Storage Sanjay Kumar Singh, Xin-Bo Zhang, and Qiang Xu* National Institute of Advanced Industrial
(Supporting Information) Room Temperature Hydrogen Generation from Hydrous Hydrazine for Chemical Hydrogen Storage Sanjay Kumar Singh, Xin-Bo Zhang, and Qiang Xu* National Institute of Advanced Industrial
3.2 Alkanes. Refining crude oil. N Goalby chemrevise.org 40 C 110 C 180 C. 250 C fuel oil 300 C 340 C. Fractional Distillation: Industrially
 3.2 Alkanes Refining crude oil Fractional Distillation: Industrially Petroleum is a mixture consisting mainly of alkane hydrocarbons Petroleum fraction: mixture of hydrocarbons with a similar chain length
3.2 Alkanes Refining crude oil Fractional Distillation: Industrially Petroleum is a mixture consisting mainly of alkane hydrocarbons Petroleum fraction: mixture of hydrocarbons with a similar chain length
Figure : SEM image of all adsorbent (A)Coal dust, (B)Bentonite, (C)Fly ash, (D)Laterite soil and (E)Sodium zeolite
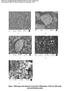 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 A B C D E Figure : SEM image of all adsorbent (A)Coal dust, (B)Bentonite, (C)Fly ash, (D)Laterite
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 A B C D E Figure : SEM image of all adsorbent (A)Coal dust, (B)Bentonite, (C)Fly ash, (D)Laterite
Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment
 Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment Ming Zhou,* Ali A. Rownaghi, and Jonas Hedlund,* *Chemical Technology, Luleå University of Technology, SE-971 87 Luleå,
Synthesis of Mesoporous ZSM-5 Zeolite Crystals by Conventional Hydrothermal Treatment Ming Zhou,* Ali A. Rownaghi, and Jonas Hedlund,* *Chemical Technology, Luleå University of Technology, SE-971 87 Luleå,
Catalytic activity of the beta zeolite with enhanced textural properties in the Friedel-Crafts acylation of aromatic compounds
 Zeolites and Related Materials: Trends, Targets and Challenges Proceedings of 4 th International FEZA Conference A. Gedeon, P. Massiani and F. Babboneau (Editors) 28 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Zeolites and Related Materials: Trends, Targets and Challenges Proceedings of 4 th International FEZA Conference A. Gedeon, P. Massiani and F. Babboneau (Editors) 28 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
