BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination June, 2018
|
|
|
- Randell Harper
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 No. of Printed Pages : 12 I CHE-04 C C1 BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination June, 2018 CHEMISTRY CHE-04 : PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 Note : Attempt all the parts. Answer five questions from each of the parts A, B, C and D. Use of log tables is permitted. Use of non-programmable calculators is allowed. PART A Answer any five of the following questions : 5x1=5 1. State Trouton's rule Define an adiabatic process What is meant by entropy of a system? 1 4. Define Chemiluminescence. 1 CHE-04 1 P.T.O.
2 5. Give the phase rule equation. 6. Name the methods for finding the transport number. 7. What are the units of second order rate constant? CHE-04 2
3 PART B Answer any five of the following questions : 5x2=10 8. The gas supplied for household use is mostly a mixture of propane and butane. Are the critical temperatures of these gases higher than 298 K? Justify your answer Rice, dal and vegetables are cooked faster inside a pressure cooker than in an open vessel. Explain the reason What are buffer solutions? Give an example Express the equilibrium constant for the reaction CO (g) + 2H 2 (g) CH3OH (g) in terms of extent of reaction, 12. Draw and explain the titration curve for conducto-metric titration for Strong Acid vs Strong Base State Hess's law of constant heat summation. 14. Can azeotropes be separated into pure components by fractional distillation? Justify your answer. 2 CHE-04 3 P.T.Q.
4 PART C Answer any five of the following questions : 5x3= Starting from du = TdS -pdv, derive rar± 117)s = (Z)v Derive Bragg's equation : n2 = 2d sin What is common ion effect? Explain its role in precipitation of cations in qualitative analysis Predict which of the following reactions will be spontaneous, with the help of standard potential values : 3 (a) Fe + 2H+ ---> Fe 2+ + H2 E = 0.44 V Fe2+/Fe (b) Cu + 2H+ ---> Cu + H2 E = V (c) 2Fe > 2Fe E = V I 2/I E = V Fe 3+/Fe` ± CHE-04 4
5 19. Derive Nernst's distribution law thermodynamically. 20. Using the value of p c = x le Pa, Vc = 99.0 x 106 m3 mo1-1, calculate the reduced temperature of a gas if it occupies 5 x 10-2 m3 5 Pa. space at x Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of boiling points : Ethanol, glycerol and ethylene glycol Justify your answer. 3 CHE-04 5 P.T.O.
6 PART D Answer any five of the following questions : 5x4= Derive the following expression for an ideal gas : 4 1 _ pv = 3 m N u 23. Explain the difference between fluorescence and phosphorescence. 24. Describe the Lindemann and Hinshelwood mechanism to explain the unimolecular decomposition reaction Draw and explain the phase diagram of sulphur Derive the expression for Langmuir adsorption isotherm Calculate the entropy of mixing of 1 mol of 112 with 2 mol of 02. Assume that no chemical reaction occurs. 28. The boiling point of chloroform was raised by K when 5.15 x 10-4 kg of an organic compound was dissolved in 3.5 x 10-2 kg of chloroform. Calculate the molar mass of the organic compound. Molar Elevation constant for chloroform is 3.90 K kg morl. 4 CHE-04 6
7 din ti Inch (41.7r Tft. ) Tr-I-M.76v T-4, 2018 TRIER Ido in 4% : Tfrgi4 04,14 : 2 EITTJ 3#11W6 37 al*w : 50 Tie. : gift 37 3R?" er-47 l w, Zs7, 7T ark RR* 1PT lifw-glw Nr4.77 JR? j1/ IRfIT fll(pled HP/ 41 37Y/Td. */ 31thrArltel 4,e-g)rie(?* Ptirf 1 ari-ga / A..il(Wort # TIN. TR-4T 4- JR?' e-r-4q : 5x feur 1 2. tog mstoi merr ti* 3. cran TEFF 311f? 4. titheipth t.i41 tr-4 CHE-04 7 P.T.O.
8 5. mier-9-tt 14H w-ncniut A-dT-4 I 6. 3TrITT14-44* fetpal TIT fo -FuR 7. t#4.111 itzrd**eff 1114)? CHE-04 8
9 Pi-ifCiRoa # 4 ATef - drit 5x2=10 8. It d kit1) 41 * t 3T111-*7( M A vl-7 T wrr1.11 Wftf 298 K 3TR-T? T *r W-47 I 9. 3cm vaci, 3R 1T Ac-41 t 4.) oeutsen *INR I fiWt f4fzir TM.? dcwul tr4r I TWAT CO (g) (g) CH3OH (g) FT "Fq Trp:Er oem Ar--4R c1 3 TCF 3 74F k-tt1 * KichcArne4 31illTER * 391:17R Witrff Ai* dticn *I-N7 I 'f W2TK daiii-kichcl-i l H -PAR 14. Tf -PaTRzfraft *WI SEITTIt 31T1M TKT d-14 lidct>1 TraTT 6eil? 3 3fft *A7 CHE-04 9 P.T.O.
10 UM TT 14s-i drit 007. : 5x3= du = TdS - pdv 34T4T cht AH WA-R : a), - ( ys)v 16. ATI chtui, na= 2d sin e "09-01W *1177 ( T11: R NITT4 clqc)tiul 4 at44crur *k-41 itrwr *1-044Kgen WA -R i-lcb 1-41-T4 Trr-41 4't ieiril wa-r-4-r PiHroRgo A t al-r : 6 : (a) Fe + 2H+ Fe2+ + H2 E Fe 2+/ = 0.44 V (b) Cu + 2H+ Cu2+ + H2 E 0 c11 4-V al = V (c) 2Fe3+ + 2F 2Fe E 1 2 /1- = V E = V Fe 3+/Fe 2+ CHE-04 10
11 19. 4 ikdtat 3aiiii6bi:9-eciff WA I *fit ti pc = x le Pa at Vc = 99.0 x 106 -m3 mor1 *TR "*1 3RIITT cbt; x 105 Pa tft 3ticbi 1:11:14rd TV' N cict A.N7, zft 5 x 10-2 m3 3iTzrd'9 kt PH ci ctzir10 314) rsit3i4 oticiplo *P4R : 3T:A -R2Wra ', fir kikto Wall q Aziwtai CHE P.T.O. J
12 (-Hort A7-f qfw5r-j drl< 5x4= %7413JT ker PHRIRsid t1i(14)tu1 mj-ezrff AT-4R : pv.- 3 mnu 23. Sfr-dāft:i atit PF-dtRF Atq' 34( *1' 00-11(sAi *Ii-47 I 24. L q I1,3'act.) atcrern atrtftzfr *1 - oii(9,41* R1 rrl ~~li ~l atit fr4wg -Wirr-4RT 0* I 25. TTY 5T 1TaTiliZi A od ill ATTIT alfilatfur (1 1-1(114 co-1 71ch 9c:ff *I* I ztx1 H -k wr( ml twitipieb 34141*-41. Ter 6icn t, 1 4.1)C1 H2 *I. 2 ii)ci 02 f43p4-7-4flft 1-11kct)R1C1 4:11-47 I x 10-2 kg crk-q x 10-4 kg chicipich Art- 'El)--M4 ct.--n14;14 wzi-qk K A-4 TRIT I cblench zrift kirci, *li* ct\-q,4,74 dw.1.1 W2R-k 3.90 K kg morl t I 4 CHE ,500
BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination June, 2015
 No. of Printed Pages : 12 04668 BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination June, 2015 CHEMISTRY CHE-04 : PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY CHE-04 Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 Note : Attempt all parts. Answer
No. of Printed Pages : 12 04668 BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination June, 2015 CHEMISTRY CHE-04 : PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY CHE-04 Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 Note : Attempt all parts. Answer
BACHELOR'S DEGREE PROGRAMME (BDP) Term-End Examination December, 2014 ELECTIVE COURSE : MATHEMATICS MTE-06 : ABSTRACT ALGEBRA
 072 A0.2 No. of Printed Pages : 8 BACHELOR'S DEGREE PROGRAMME (BDP) Term-End Examination December, 2014 ELECTIVE COURSE : MATHEMATICS MTE-06 : ABSTRACT ALGEBRA MTE-06 Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50
072 A0.2 No. of Printed Pages : 8 BACHELOR'S DEGREE PROGRAMME (BDP) Term-End Examination December, 2014 ELECTIVE COURSE : MATHEMATICS MTE-06 : ABSTRACT ALGEBRA MTE-06 Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50
REMOVE THIS PAGE PRIOR TO STARTING EXAM.
 REMOVE THIS PAGE PRIOR TO STARTING EXAM. 1 2 ANSWER KEY CHEMISTRY F14O3 SECOND EXAM 11/10/99 PROFESSOR J. MORROW PRINT NAME, LAST: FIRST: I.D.# : MAXIMUM POINT VALUE IS IN PARENTHESES 1. (15) 9. (15) 17.
REMOVE THIS PAGE PRIOR TO STARTING EXAM. 1 2 ANSWER KEY CHEMISTRY F14O3 SECOND EXAM 11/10/99 PROFESSOR J. MORROW PRINT NAME, LAST: FIRST: I.D.# : MAXIMUM POINT VALUE IS IN PARENTHESES 1. (15) 9. (15) 17.
BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination
 No. of Printed Pages : 8 PHE-06 BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination June, 2016 PHYSICS PHE-06 : THERMODYNAMICS AND STATISTICAL MECHANICS Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 Note : All questions
No. of Printed Pages : 8 PHE-06 BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination June, 2016 PHYSICS PHE-06 : THERMODYNAMICS AND STATISTICAL MECHANICS Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 Note : All questions
Lecture 3 Evaluation of Entropy
 Lecture 3 Evaluation of Entropy If we wish to designate S by a proper name we can say of it that it is the transformation content of the body, in the same way that we say of the quantity U that it is the
Lecture 3 Evaluation of Entropy If we wish to designate S by a proper name we can say of it that it is the transformation content of the body, in the same way that we say of the quantity U that it is the
BACHELOR'S DEGREE PROGRAMME (BDP) Term-End Examination
 No. of Printed Pages : 12 MTE-03 BACHELOR'S DEGREE PROGRAMME (BDP) Term-End Examination 1,4* :ert June, 2015 ELECTIVE COURSE : MATHEMATICS MTE-03 : MATHEMATICAL METHODS Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50
No. of Printed Pages : 12 MTE-03 BACHELOR'S DEGREE PROGRAMME (BDP) Term-End Examination 1,4* :ert June, 2015 ELECTIVE COURSE : MATHEMATICS MTE-03 : MATHEMATICAL METHODS Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50
BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination June, B.Sc. EXAMINATION CHE-1 : ATOMS AND MOLECULES AND CHE-2 : INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 No. of Printed Pages : 15 00881 CHE-1 BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination June, 2010 CHEMISTRY CHE-1 : ATOMS AND MOLECULES Time : 1 hour Maximum Marks : 25 B.Sc. EXAMINATION Instructions :
No. of Printed Pages : 15 00881 CHE-1 BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination June, 2010 CHEMISTRY CHE-1 : ATOMS AND MOLECULES Time : 1 hour Maximum Marks : 25 B.Sc. EXAMINATION Instructions :
UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA, DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY Chemistry 2290, Winter 2011, Dr. H. Georg Schreckenbach. Final Examination April 12, 2011 (3 hours)
 Comments 2012: - This exam turned out to be too short almost all of the class had left after 2 ½ hours or so. For this year, then, expect a somewhat longer exam (with a few more questions and/or somewhat
Comments 2012: - This exam turned out to be too short almost all of the class had left after 2 ½ hours or so. For this year, then, expect a somewhat longer exam (with a few more questions and/or somewhat
Chapter 15 Thermal Properties of Matter
 Chapter 15 Thermal Properties of Matter To understand the mole and Avogadro's number. To understand equations of state. To study the kinetic theory of ideal gas. To understand heat capacity. To learn and
Chapter 15 Thermal Properties of Matter To understand the mole and Avogadro's number. To understand equations of state. To study the kinetic theory of ideal gas. To understand heat capacity. To learn and
Problem: Calculate the entropy change that results from mixing 54.0 g of water at 280 K with 27.0 g of water at 360 K in a vessel whose walls are
 Problem: Calculate the entropy change that results from mixing 54.0 g of water at 280 K with 27.0 g of water at 360 K in a vessel whose walls are perfectly insulated from the surroundings. Is this a spontaneous
Problem: Calculate the entropy change that results from mixing 54.0 g of water at 280 K with 27.0 g of water at 360 K in a vessel whose walls are perfectly insulated from the surroundings. Is this a spontaneous
Subject : Chemistry Class : XII Chapter-2.Solutions Work Sheet ( WS 2. 1) Topic- 2.1 Henry s & Raoult s Laws
 Work Sheet ( WS 2. 1) Topic- 2.1 Henry s & Raoult s Laws Name -. Class/ sec.. Roll No.. A. Fill in the blanks: 1. Solutions are mixtures of two or more than two components. 2. Generally, the component
Work Sheet ( WS 2. 1) Topic- 2.1 Henry s & Raoult s Laws Name -. Class/ sec.. Roll No.. A. Fill in the blanks: 1. Solutions are mixtures of two or more than two components. 2. Generally, the component
Hence. The second law describes the direction of energy transfer in spontaneous processes
 * Heat and Work The first law of thermodynamics states that: Although energy has many forms, the total quantity of energy is constant. When energy disappears in one form, it appears simultaneously in other
* Heat and Work The first law of thermodynamics states that: Although energy has many forms, the total quantity of energy is constant. When energy disappears in one form, it appears simultaneously in other
Chapter 5. Simple Mixtures Fall Semester Physical Chemistry 1 (CHM2201)
 Chapter 5. Simple Mixtures 2011 Fall Semester Physical Chemistry 1 (CHM2201) Contents The thermodynamic description of mixtures 5.1 Partial molar quantities 5.2 The thermodynamic of Mixing 5.3 The chemical
Chapter 5. Simple Mixtures 2011 Fall Semester Physical Chemistry 1 (CHM2201) Contents The thermodynamic description of mixtures 5.1 Partial molar quantities 5.2 The thermodynamic of Mixing 5.3 The chemical
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY CHEM330
 PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY CHEM330 Duration: 3 hours Total Marks: 100 Internal Examiner: External Examiner: Professor B S Martincigh Professor J C Swarts University of the Free State INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Answer five
PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY CHEM330 Duration: 3 hours Total Marks: 100 Internal Examiner: External Examiner: Professor B S Martincigh Professor J C Swarts University of the Free State INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Answer five
ELECTIVE COURSE : MATHEMATICS MTE-08 : DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 No. of Printed Pages : 8 MTE-08 BACHELOR'S DEGREE PROGRAMME (BDP) Term-End Examination December, 2014 ELECTIVE COURSE : MATHEMATICS MTE-08 : DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 (Weightage
No. of Printed Pages : 8 MTE-08 BACHELOR'S DEGREE PROGRAMME (BDP) Term-End Examination December, 2014 ELECTIVE COURSE : MATHEMATICS MTE-08 : DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 (Weightage
No. of Printed Pages : 8
 No. of Printed Pages : 8 BP11E-106/PHE-06 BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination June, 2018 PHYSICS BPHE-106/PHE-06 : THERMODYNAMICS AND STATISTICAL MECHANICS Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50
No. of Printed Pages : 8 BP11E-106/PHE-06 BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination June, 2018 PHYSICS BPHE-106/PHE-06 : THERMODYNAMICS AND STATISTICAL MECHANICS Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50
BACHELOR'S DEGREE PROGRAMME (BDP) Term-End Examination December, Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 (Weightage : 70%)
 01287 No. of Printed Pages : 12 MTE-10 BACHELOR'S DEGREE PROGRAMME (BDP) Term-End Examination December, 2014 ELECTIVE COURSE : MATHEMATICS MTE-10 : NUMERICAL ANALYSIS Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50
01287 No. of Printed Pages : 12 MTE-10 BACHELOR'S DEGREE PROGRAMME (BDP) Term-End Examination December, 2014 ELECTIVE COURSE : MATHEMATICS MTE-10 : NUMERICAL ANALYSIS Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50
BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination June, 2015
 No. of Printed Pages : 12 CHE-05 BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination June, 2015 CHEMISTRY CHE-05 : ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 Note : Attempt all the four questions.
No. of Printed Pages : 12 CHE-05 BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination June, 2015 CHEMISTRY CHE-05 : ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 Note : Attempt all the four questions.
Lecture 5. PHYC 161 Fall 2016
 Lecture 5 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Ch. 19 First Law of Thermodynamics In a thermodynamic process, changes occur in the state of the system. Careful of signs! Q is positive when heat flows into a system. W is
Lecture 5 PHYC 161 Fall 2016 Ch. 19 First Law of Thermodynamics In a thermodynamic process, changes occur in the state of the system. Careful of signs! Q is positive when heat flows into a system. W is
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING DESIGN & SAFETY
 CHEMICAL ENGINEERING DESIGN & SAFETY CHE 4253 Prof. Miguel Bagajewicz Explosions Explained EXPLOSION A rapid and uniform expansion Expanding Shock wave Initial System Boundary EXPLOSION The expansion ends
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING DESIGN & SAFETY CHE 4253 Prof. Miguel Bagajewicz Explosions Explained EXPLOSION A rapid and uniform expansion Expanding Shock wave Initial System Boundary EXPLOSION The expansion ends
No. of Printed Pages : 8
 No. of Printed Pages : 8 BACHELOR'S DEGREE PROGRAMME (BDP) Term-End Examination ---E - December, 2016 I MTE-08 ELECTIVE COURSE : MATHEMATICS MTE-08 : DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS - Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks
No. of Printed Pages : 8 BACHELOR'S DEGREE PROGRAMME (BDP) Term-End Examination ---E - December, 2016 I MTE-08 ELECTIVE COURSE : MATHEMATICS MTE-08 : DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS - Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks
Energy, Enthalpy and Thermochemistry. Energy: The capacity to do work or to produce heat
 9 Energy, Enthalpy and Thermochemistry Energy: The capacity to do work or to produce heat The law of conservation of energy Energy can be converted but the total is a constant Two types of energy: Kinetic
9 Energy, Enthalpy and Thermochemistry Energy: The capacity to do work or to produce heat The law of conservation of energy Energy can be converted but the total is a constant Two types of energy: Kinetic
Some properties of the Helmholtz free energy
 Some properties of the Helmholtz free energy Energy slope is T U(S, ) From the properties of U vs S, it is clear that the Helmholtz free energy is always algebraically less than the internal energy U.
Some properties of the Helmholtz free energy Energy slope is T U(S, ) From the properties of U vs S, it is clear that the Helmholtz free energy is always algebraically less than the internal energy U.
1. Read all questions thoroughly and answer each question completely. ALL WORK MUST BE SHOWN IN ORDER TO RECEIVE ANY CREDIT.
 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Read all questions thoroughly and answer each question completely. ALL WORK MUST BE SHOWN IN ORDER TO RECEIVE ANY CREDIT. 2. You will be allowed to use only the given sheet of thermodynamic
INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Read all questions thoroughly and answer each question completely. ALL WORK MUST BE SHOWN IN ORDER TO RECEIVE ANY CREDIT. 2. You will be allowed to use only the given sheet of thermodynamic
7. (2) Of these elements, which has the greatest number of atoms in a mole? a. hydrogen (H) b. oxygen (O) c. iron (Fe) d. gold (Au) e. all tie.
 General Physics I Exam 5 - Chs. 13,14,15 - Heat, Kinetic Theory, Thermodynamics Dec. 14, 2010 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used, essential
General Physics I Exam 5 - Chs. 13,14,15 - Heat, Kinetic Theory, Thermodynamics Dec. 14, 2010 Name Rec. Instr. Rec. Time For full credit, make your work clear to the grader. Show formulas used, essential
BACHELOR OP SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination June, 2018
 No. of Printed Pages : 8 I CHE-06 01006 BACHELOR OP SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination June, 2018 CHEMISTRY CHE-06 : ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISM Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 Note : Answer any five
No. of Printed Pages : 8 I CHE-06 01006 BACHELOR OP SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination June, 2018 CHEMISTRY CHE-06 : ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISM Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 Note : Answer any five
3.012 PS Issued: Fall 2004 Due: pm
 3.012 PS 2 3.012 Issued: 09.15.04 Fall 2004 Due: 09.22.04 5pm Graded problems: 1. In discussing coordination numbers and deriving the permitted range of radius ratio, R A / R B, allowed for each ( where
3.012 PS 2 3.012 Issued: 09.15.04 Fall 2004 Due: 09.22.04 5pm Graded problems: 1. In discussing coordination numbers and deriving the permitted range of radius ratio, R A / R B, allowed for each ( where
BACHELOR'S DEGREE PROGRAMME (BDP) Term-End Examination. June, 2018 ELECTIVE COURSE : MATHEMATICS MTE-02 : LINEAR ALGEBRA
 No. of Printed Pages : 8 1MTE-021 BACHELOR'S DEGREE PROGRAMME (BDP) Term-End Examination 046OB June, 2018 ELECTIVE COURSE : MATHEMATICS MTE-02 : LINEAR ALGEBRA Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 (Weightage
No. of Printed Pages : 8 1MTE-021 BACHELOR'S DEGREE PROGRAMME (BDP) Term-End Examination 046OB June, 2018 ELECTIVE COURSE : MATHEMATICS MTE-02 : LINEAR ALGEBRA Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 (Weightage
BACHELOR'S DEGREE PROGRAMME (BDP) Term-End Examination ELECTIVE COURSE : MATHEMATICS MTE-02 : LINEAR ALGEBRA
 No. of Printed Pages : 8 MTE-021 BACHELOR'S DEGREE PROGRAMME (BDP) Term-End Examination 01-2. 0 6 June, 2016 ELECTIVE COURSE : MATHEMATICS MTE-02 : LINEAR ALGEBRA Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 (Weightage
No. of Printed Pages : 8 MTE-021 BACHELOR'S DEGREE PROGRAMME (BDP) Term-End Examination 01-2. 0 6 June, 2016 ELECTIVE COURSE : MATHEMATICS MTE-02 : LINEAR ALGEBRA Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 (Weightage
No. of Printed Pages : 8
 No. of Printed Pages : 8 BACHELOR'S DEGREE PROGRAMME (BDP) Term-End Examination December, 2017 ELECTIVE COURSE : MATHEMATICS MTE-02 : LINEAR ALGEBRA mte-02 Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 (Weightage
No. of Printed Pages : 8 BACHELOR'S DEGREE PROGRAMME (BDP) Term-End Examination December, 2017 ELECTIVE COURSE : MATHEMATICS MTE-02 : LINEAR ALGEBRA mte-02 Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 (Weightage
Overview. Types of Solutions. Intermolecular forces in solution. Concentration terms. Colligative properties. Osmotic Pressure 2 / 46
 1 / 46 2 / 46 Overview Types of Solutions. Intermolecular forces in solution Concentration terms Colligative properties Osmotic Pressure 3 / 46 Solutions and Colloids A solution is a homogeneous mixture
1 / 46 2 / 46 Overview Types of Solutions. Intermolecular forces in solution Concentration terms Colligative properties Osmotic Pressure 3 / 46 Solutions and Colloids A solution is a homogeneous mixture
The first law of thermodynamics continued
 Lecture 7 The first law of thermodynamics continued Pre-reading: 19.5 Where we are The pressure p, volume V, and temperature T are related by an equation of state. For an ideal gas, pv = nrt = NkT For
Lecture 7 The first law of thermodynamics continued Pre-reading: 19.5 Where we are The pressure p, volume V, and temperature T are related by an equation of state. For an ideal gas, pv = nrt = NkT For
Chapter Solutions. MockTime.com. (a) M urea (b) 0.01 M KNO3 (c) 0.01 M Na2 SO4 (d) M glucose Ans: (c)
 47 Chapter Solutions 1. Freezing point of an aqueous solution is ( 0.186) C. Elevation of boiling point of the same solution is K b = 0.512 C,Kf = 1.86 C, find the increase in boiling point. [2002] (a)
47 Chapter Solutions 1. Freezing point of an aqueous solution is ( 0.186) C. Elevation of boiling point of the same solution is K b = 0.512 C,Kf = 1.86 C, find the increase in boiling point. [2002] (a)
Chemistry 112, Fall 2006, Section 1 (Garman and Heuck) Final Exam A (100 points) 19 Dec 2006
 Chemistry 112, Fall 2006, Section 1 (Garman and Heuck) (100 points) 19 Dec 2006 Name: YOU MUST: Put your name and student ID on the bubble sheet correctly. Put the exam version on the bubble sheet on the
Chemistry 112, Fall 2006, Section 1 (Garman and Heuck) (100 points) 19 Dec 2006 Name: YOU MUST: Put your name and student ID on the bubble sheet correctly. Put the exam version on the bubble sheet on the
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON. University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS. For The Following Qualifications:-
 UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS For The Following Qualifications:- B.Sc. M.Sci. Statistical Thermodynamics COURSE CODE : PHAS2228 UNIT VALUE : 0.50 DATE
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS For The Following Qualifications:- B.Sc. M.Sci. Statistical Thermodynamics COURSE CODE : PHAS2228 UNIT VALUE : 0.50 DATE
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON. University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS. For The Following Qualifications:-
 UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS For The Following Qualifications:- B.Sc. M.Sci. Physics 1B28: Thermal Physics COURSE CODE : PHYSIB28 UNIT VALUE : 0.50 DATE
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS For The Following Qualifications:- B.Sc. M.Sci. Physics 1B28: Thermal Physics COURSE CODE : PHYSIB28 UNIT VALUE : 0.50 DATE
Chem 102H Exam 2 - Spring 2005
 Name I.D. # Chem 102H Exam 2 - Spring 2005 PHYSICAL CNSTANTS/CNVERSIN FACTRS Speed of light = 3.00! 10 8 m/s Planck!s const. = 6.63! 10-34 J s Avagadro!s Number = 6.02! 10 23 Electron charge = 1.602! 10-19
Name I.D. # Chem 102H Exam 2 - Spring 2005 PHYSICAL CNSTANTS/CNVERSIN FACTRS Speed of light = 3.00! 10 8 m/s Planck!s const. = 6.63! 10-34 J s Avagadro!s Number = 6.02! 10 23 Electron charge = 1.602! 10-19
PSI AP Chemistry Solutions Practice Problems
 PSI AP Chemistry Solutions Practice Problems Name Solutions: Mixtures, Solubility and Concentration Classwork 1. A student determined that there were 0.032 grams of oxygen gas dissolved in a 200.0 ml sample
PSI AP Chemistry Solutions Practice Problems Name Solutions: Mixtures, Solubility and Concentration Classwork 1. A student determined that there were 0.032 grams of oxygen gas dissolved in a 200.0 ml sample
Entropy Changes & Processes
 Entropy Changes & Processes Chapter 4 of Atkins: The Second Law: The Concepts Section 4.4-4.7 Third Law of Thermodynamics Nernst Heat Theorem Third- Law Entropies Reaching Very Low Temperatures Helmholtz
Entropy Changes & Processes Chapter 4 of Atkins: The Second Law: The Concepts Section 4.4-4.7 Third Law of Thermodynamics Nernst Heat Theorem Third- Law Entropies Reaching Very Low Temperatures Helmholtz
Unit - 2 SOLUTIONS VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 1. Give an example of liquid in solid type solution.
 Unit - 2 SOLUTIONS VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 1. Give an example of liquid in solid type solution. 2. Which type of solid solution will result by mixing two solid components with large difference
Unit - 2 SOLUTIONS VSA QUESTIONS (1 - MARK QUESTIONS) 1. Give an example of liquid in solid type solution. 2. Which type of solid solution will result by mixing two solid components with large difference
P a g e 5 1 of R e p o r t P B 4 / 0 9
 P a g e 5 1 of R e p o r t P B 4 / 0 9 J A R T a l s o c o n c l u d e d t h a t a l t h o u g h t h e i n t e n t o f N e l s o n s r e h a b i l i t a t i o n p l a n i s t o e n h a n c e c o n n e
P a g e 5 1 of R e p o r t P B 4 / 0 9 J A R T a l s o c o n c l u d e d t h a t a l t h o u g h t h e i n t e n t o f N e l s o n s r e h a b i l i t a t i o n p l a n i s t o e n h a n c e c o n n e
Phase Changes and Latent Heat
 Review Questions Why can a person remove a piece of dry aluminum foil from a hot oven with bare fingers without getting burned, yet will be burned doing so if the foil is wet. Equal quantities of alcohol
Review Questions Why can a person remove a piece of dry aluminum foil from a hot oven with bare fingers without getting burned, yet will be burned doing so if the foil is wet. Equal quantities of alcohol
CHEM 108 (Spring-2008) Exam. 3 (105 pts)
 CHEM 08 (Spring-008) Exam. (05 pts) Name: --------------------------------------------------------------------------, CLID # -------------------------------- LAST NAME, First (Circle the alphabet segment
CHEM 08 (Spring-008) Exam. (05 pts) Name: --------------------------------------------------------------------------, CLID # -------------------------------- LAST NAME, First (Circle the alphabet segment
Solution KEY CONCEPTS
 Solution KEY CONCEPTS Solution is the homogeneous mixture of two or more substances in which the components are uniformly distributed into each other. The substances which make the solution are called
Solution KEY CONCEPTS Solution is the homogeneous mixture of two or more substances in which the components are uniformly distributed into each other. The substances which make the solution are called
Thermodynamics of solids 5. Unary systems. Kwangheon Park Kyung Hee University Department of Nuclear Engineering
 Thermodynamics of solids 5. Unary systems Kwangheon ark Kyung Hee University Department of Nuclear Engineering 5.1. Unary heterogeneous system definition Unary system: one component system. Unary heterogeneous
Thermodynamics of solids 5. Unary systems Kwangheon ark Kyung Hee University Department of Nuclear Engineering 5.1. Unary heterogeneous system definition Unary system: one component system. Unary heterogeneous
PHE-5 : MATHEMATICAL METHODS IN PHYSICS-II Instructions : 7. Students registered for both PHE-4 & PHE-5 courses
 No. of Printed Pages : 15 00 (.0 BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination June, 2010 PHYSICS PHE- I PHE- : MATHEMATICAL METHODS IN PHYSICS-I Time : 1 1/2 hours Maximum Marks : 25 B.Sc. EXAMINATION,
No. of Printed Pages : 15 00 (.0 BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination June, 2010 PHYSICS PHE- I PHE- : MATHEMATICAL METHODS IN PHYSICS-I Time : 1 1/2 hours Maximum Marks : 25 B.Sc. EXAMINATION,
FIRST PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Trinity Term Preliminary Examination in Chemistry SUBJECT 3: PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY. Time allowed: 2 ½ hours
 FIRST PUBLIC EXAMINATION Trinity Term 004 Preliminary Examination in Chemistry SUBJECT 3: PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY Wednesday, June 9 th 004, 9.30 a.m. to 1 noon Time allowed: ½ hours Candidates should answer
FIRST PUBLIC EXAMINATION Trinity Term 004 Preliminary Examination in Chemistry SUBJECT 3: PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY Wednesday, June 9 th 004, 9.30 a.m. to 1 noon Time allowed: ½ hours Candidates should answer
Chem 1100 Pre-Test 3. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chem 1100 Pre-Test 3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. An open-tube manometer is used to measure the pressure in a flask. The atmospheric
Chem 1100 Pre-Test 3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. An open-tube manometer is used to measure the pressure in a flask. The atmospheric
where R = universal gas constant R = PV/nT R = atm L mol R = atm dm 3 mol 1 K 1 R = J mol 1 K 1 (SI unit)
 Ideal Gas Law PV = nrt where R = universal gas constant R = PV/nT R = 0.0821 atm L mol 1 K 1 R = 0.0821 atm dm 3 mol 1 K 1 R = 8.314 J mol 1 K 1 (SI unit) Standard molar volume = 22.4 L mol 1 at 0 C and
Ideal Gas Law PV = nrt where R = universal gas constant R = PV/nT R = 0.0821 atm L mol 1 K 1 R = 0.0821 atm dm 3 mol 1 K 1 R = 8.314 J mol 1 K 1 (SI unit) Standard molar volume = 22.4 L mol 1 at 0 C and
UNIVESITY OF SWAZILAND FACl.JLTY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS
 UNIVESITY OF SWAZILAND FACl.LTY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS Main Examination 2016/2017. COURSE NAME: Thermodynamics/Thermofluids COURSE CODE: PHY242/EEE202 TIME ALLOWED: 3 hours ANSWER
UNIVESITY OF SWAZILAND FACl.LTY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS Main Examination 2016/2017. COURSE NAME: Thermodynamics/Thermofluids COURSE CODE: PHY242/EEE202 TIME ALLOWED: 3 hours ANSWER
Equations: q trans = 2 mkt h 2. , Q = q N, Q = qn N! , < P > = kt P = , C v = < E > V 2. e 1 e h /kt vib = h k = h k, rot = h2.
 Constants: R = 8.314 J mol -1 K -1 = 0.08206 L atm mol -1 K -1 k B = 0.697 cm -1 /K = 1.38 x 10-23 J/K 1 a.m.u. = 1.672 x 10-27 kg 1 atm = 1.0133 x 10 5 Nm -2 = 760 Torr h = 6.626 x 10-34 Js For H 2 O
Constants: R = 8.314 J mol -1 K -1 = 0.08206 L atm mol -1 K -1 k B = 0.697 cm -1 /K = 1.38 x 10-23 J/K 1 a.m.u. = 1.672 x 10-27 kg 1 atm = 1.0133 x 10 5 Nm -2 = 760 Torr h = 6.626 x 10-34 Js For H 2 O
Entropy in Macroscopic Systems
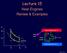 Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Review Entropy in Macroscopic Systems
Lecture 15 Heat Engines Review & Examples p p b b Hot reservoir at T h p a a c adiabats Heat leak Heat pump Q h Q c W d V 1 V 2 V Cold reservoir at T c Lecture 15, p 1 Review Entropy in Macroscopic Systems
Department of Chemistry Memorial University of Newfoundland Chemistry 1050
 Department of Chemistry Memorial University of Newfoundland Chemistry 1050 FINAL EXAMINATION Fall 017 TIME: 3 hours READ TE FOLLOWING CAREFULLY 1. This examination consists of 13 pages including a Data
Department of Chemistry Memorial University of Newfoundland Chemistry 1050 FINAL EXAMINATION Fall 017 TIME: 3 hours READ TE FOLLOWING CAREFULLY 1. This examination consists of 13 pages including a Data
AP* General Equilibrium Free Response Questions page 1
 AP* General Equilibrium Free Response Questions page 1 General Equilibrium Problems 1983 Sulfuryl chloride, SO 2 Cl 2, is a highly reactive gaseous compound. When heated, it decomposes as follows: SO 2
AP* General Equilibrium Free Response Questions page 1 General Equilibrium Problems 1983 Sulfuryl chloride, SO 2 Cl 2, is a highly reactive gaseous compound. When heated, it decomposes as follows: SO 2
18:00-21:00, 13 January, 2017 (Total Score: 118 points)
 Chemistry I Final Exam 18:00-21:00, 13 January, 2017 (Total Score: 118 points) R = 8.314 J K -1 mol -1 1. The ionic character of the bond in a diatomic molecule can be estimated by the formula: ( /ed )
Chemistry I Final Exam 18:00-21:00, 13 January, 2017 (Total Score: 118 points) R = 8.314 J K -1 mol -1 1. The ionic character of the bond in a diatomic molecule can be estimated by the formula: ( /ed )
The Second Law of Thermodynamics (Chapter 4)
 The Second Law of Thermodynamics (Chapter 4) First Law: Energy of universe is constant: ΔE system = - ΔE surroundings Second Law: New variable, S, entropy. Changes in S, ΔS, tell us which processes made
The Second Law of Thermodynamics (Chapter 4) First Law: Energy of universe is constant: ΔE system = - ΔE surroundings Second Law: New variable, S, entropy. Changes in S, ΔS, tell us which processes made
Practice Final CH142, Spring 2012
 Practice Final CH142, Spring 2012 First here are a group of practice problems on Latimer Diagrams: 1. The Latimer diagram for nitrogen oxides in given below. Is NO stable with respect to disproportionation
Practice Final CH142, Spring 2012 First here are a group of practice problems on Latimer Diagrams: 1. The Latimer diagram for nitrogen oxides in given below. Is NO stable with respect to disproportionation
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON VERY IMPORTANT NOTE. Section A answers MUST BE in a separate blue answer book. If any blue
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2011/12 ENERGY AND MATTER SOLUTIONS Duration: 120 MINS VERY IMPORTANT NOTE Section A answers MUST BE in a separate blue answer book. If any blue
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHAMPTON PHYS1013W1 SEMESTER 2 EXAMINATION 2011/12 ENERGY AND MATTER SOLUTIONS Duration: 120 MINS VERY IMPORTANT NOTE Section A answers MUST BE in a separate blue answer book. If any blue
10-1 Heat 10-2 Calorimetry 10-3 Enthalpy 10-4 Standard-State Enthalpies 10-5 Bond Enthalpies 10-6 The First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 10 Thermochemistry 10-1 Heat 10-2 Calorimetry 10-3 Enthalpy 10-4 Standard-State Enthalpies 10-5 Bond Enthalpies 10-6 The First Law of Thermodynamics OFB Chap. 10 1 OFB Chap. 10 2 Thermite Reaction
Chapter 10 Thermochemistry 10-1 Heat 10-2 Calorimetry 10-3 Enthalpy 10-4 Standard-State Enthalpies 10-5 Bond Enthalpies 10-6 The First Law of Thermodynamics OFB Chap. 10 1 OFB Chap. 10 2 Thermite Reaction
Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Reactions
 Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Reactions Outline thermodynamics internal energy definition, first law enthalpy definition, energy diagrams, calorimetry, theoretical calculation (heats of formation
Thermochemistry: Energy Flow and Chemical Reactions Outline thermodynamics internal energy definition, first law enthalpy definition, energy diagrams, calorimetry, theoretical calculation (heats of formation
Tutorial 1 (not important for 2015)
 Tutorial 1 (not important for 2015) 1 st Law of thermodynamics and other basic concepts Do No. 5 (05-03-2015) 1. One mole of an ideal gas is allowed to expand against a piston which supports 41 atm pressures.
Tutorial 1 (not important for 2015) 1 st Law of thermodynamics and other basic concepts Do No. 5 (05-03-2015) 1. One mole of an ideal gas is allowed to expand against a piston which supports 41 atm pressures.
Lesson 01: Atomic Masses and Avogadro s Hypothesis. 01 Counting Atoms and Molecules
 Chemistry 11, Mole Concept, Unit 04 1 Lesson 01: Atomic Masses and Avogadro s Hypothesis 01 Counting Atoms and Molecules The chemical changes we observe always involve a certain number of atoms that rearrange
Chemistry 11, Mole Concept, Unit 04 1 Lesson 01: Atomic Masses and Avogadro s Hypothesis 01 Counting Atoms and Molecules The chemical changes we observe always involve a certain number of atoms that rearrange
 The underlying prerequisite to the application of thermodynamic principles to natural systems is that the system under consideration should be at equilibrium. http://eps.mcgill.ca/~courses/c220/ Reversible
The underlying prerequisite to the application of thermodynamic principles to natural systems is that the system under consideration should be at equilibrium. http://eps.mcgill.ca/~courses/c220/ Reversible
O CHE-1 : ATOMS AND MOLECULES
 CHE-1 I BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) O Term-End Examination December, 2009 00 CHEMISTRY. O CHE-1 : ATOMS AND MOLECULES Time : 1 hour Maximum Marks : 25 Note : Answer all the five questions. Instructions
CHE-1 I BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) O Term-End Examination December, 2009 00 CHEMISTRY. O CHE-1 : ATOMS AND MOLECULES Time : 1 hour Maximum Marks : 25 Note : Answer all the five questions. Instructions
Chapter 3. The Second Law Fall Semester Physical Chemistry 1 (CHM2201)
 Chapter 3. The Second Law 2011 Fall Semester Physical Chemistry 1 (CHM2201) Contents The direction of spontaneous change 3.1 The dispersal of energy 3.2 The entropy 3.3 Entropy changes accompanying specific
Chapter 3. The Second Law 2011 Fall Semester Physical Chemistry 1 (CHM2201) Contents The direction of spontaneous change 3.1 The dispersal of energy 3.2 The entropy 3.3 Entropy changes accompanying specific
Thermo. Dr. Nuri Solak, Asst. Prof.
 Thermo Dr. Nuri Solak, Asst. Prof. http://web.itu.edu.tr/solaknu/ www.ninova.itu.edu.tr http://web.itu.edu.tr/solaknu/ 1 11.09.2014 => Introduction, Definition of terms, Importance of thermodynamics
Thermo Dr. Nuri Solak, Asst. Prof. http://web.itu.edu.tr/solaknu/ www.ninova.itu.edu.tr http://web.itu.edu.tr/solaknu/ 1 11.09.2014 => Introduction, Definition of terms, Importance of thermodynamics
BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination December, 2009 PHYSICS PHE-15 : ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS
 BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination December, 2009 PHYSICS PHE-15 : ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS I PHE-15 Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 Note : Attempt all questions. The marks for each questions
BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination December, 2009 PHYSICS PHE-15 : ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS I PHE-15 Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 Note : Attempt all questions. The marks for each questions
LESSON 11. Glossary: Solutions. Boiling-point elevation
 LESSON 11 Glossary: Solutions Boiling-point elevation Colligative properties Freezing-point depression Molality Molarity (M) Mole (mol) Mole fraction Saturated solution a colligative property of a solution
LESSON 11 Glossary: Solutions Boiling-point elevation Colligative properties Freezing-point depression Molality Molarity (M) Mole (mol) Mole fraction Saturated solution a colligative property of a solution
evidyarthi.in Thermodynamics Q 1.
 SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. Thermodynamics The enthalpy for the following reaction ( H o ) at 25 o C are given below: (i) 1/2 H 2 (g) + 1/2 O 2 (g) OH(g) 10.06 kcal (ii) H 2 (g) 2H(g) 104.18 kcal (iii) O
SUBJECTIVE PROBLEMS: Q 1. Thermodynamics The enthalpy for the following reaction ( H o ) at 25 o C are given below: (i) 1/2 H 2 (g) + 1/2 O 2 (g) OH(g) 10.06 kcal (ii) H 2 (g) 2H(g) 104.18 kcal (iii) O
PSI AP Chemistry: Solutions Practice Problems
 PSI AP Chemistry: Solutions Practice Problems Name Solutions: Mixtures, Solubility and Concentration Classwork 1. A student determined that there were 0.032 grams of oxygen gas dissolved in a 200.0 ml
PSI AP Chemistry: Solutions Practice Problems Name Solutions: Mixtures, Solubility and Concentration Classwork 1. A student determined that there were 0.032 grams of oxygen gas dissolved in a 200.0 ml
8. Relax and do well.
 CHEM 1515 Exam II John II. Gelder October 14, 1993 Name TA's Name Lab Section INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This examination consists of a total of 8 different pages. The last two pages include a periodic table, a
CHEM 1515 Exam II John II. Gelder October 14, 1993 Name TA's Name Lab Section INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This examination consists of a total of 8 different pages. The last two pages include a periodic table, a
ADIABATIC PROCESS Q = 0
 THE KINETIC THEORY OF GASES Mono-atomic Fig.1 1 3 Average kinetic energy of a single particle Fig.2 INTERNAL ENERGY U and EQUATION OF STATE For a mono-atomic gas, we will assume that the total energy
THE KINETIC THEORY OF GASES Mono-atomic Fig.1 1 3 Average kinetic energy of a single particle Fig.2 INTERNAL ENERGY U and EQUATION OF STATE For a mono-atomic gas, we will assume that the total energy
Last Name or Student ID
 10/06/08, Chem433 Exam # 1 Last Name or Student ID 1. (3 pts) 2. (3 pts) 3. (3 pts) 4. (2 pts) 5. (2 pts) 6. (2 pts) 7. (2 pts) 8. (2 pts) 9. (6 pts) 10. (5 pts) 11. (6 pts) 12. (12 pts) 13. (22 pts) 14.
10/06/08, Chem433 Exam # 1 Last Name or Student ID 1. (3 pts) 2. (3 pts) 3. (3 pts) 4. (2 pts) 5. (2 pts) 6. (2 pts) 7. (2 pts) 8. (2 pts) 9. (6 pts) 10. (5 pts) 11. (6 pts) 12. (12 pts) 13. (22 pts) 14.
Heat and Thermodynamics. February. 2, Solution of Recitation 2. Consider the first case when air is allowed to expand isothermally.
 Heat and Thermodynamics. February., 0 Solution of Recitation Answer : We have given that, Initial volume of air = = 0.4 m 3 Initial pressure of air = P = 04 kpa = 04 0 3 Pa Final pressure of air = P =
Heat and Thermodynamics. February., 0 Solution of Recitation Answer : We have given that, Initial volume of air = = 0.4 m 3 Initial pressure of air = P = 04 kpa = 04 0 3 Pa Final pressure of air = P =
4. All questions are NOT ofequal value. Marks available for each question are shown in the examination paper.
 THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES SCHOOL OF PHYSICS \1111~11\llllllllllllftllll~flrllllllllll\11111111111111111 >014407892 PHYS2060 THER1\1AL PHYSICS FINAL EXAMINATION SESSION 2 - NOVEMBER 2010 I. Time
THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES SCHOOL OF PHYSICS \1111~11\llllllllllllftllll~flrllllllllll\11111111111111111 >014407892 PHYS2060 THER1\1AL PHYSICS FINAL EXAMINATION SESSION 2 - NOVEMBER 2010 I. Time
 Physical Chemistry Physical chemistry is the branch of chemistry that establishes and develops the principles of Chemistry in terms of the underlying concepts of Physics Physical Chemistry Main book: Atkins
Physical Chemistry Physical chemistry is the branch of chemistry that establishes and develops the principles of Chemistry in terms of the underlying concepts of Physics Physical Chemistry Main book: Atkins
Data Provided: A formula sheet and table of physical constants are attached to this paper.
 Data Provided: A formula sheet and table of physical constants are attached to this paper. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND ASTRONOMY Spring Semester (2016-2017) From Thermodynamics to Atomic and Nuclear Physics
Data Provided: A formula sheet and table of physical constants are attached to this paper. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND ASTRONOMY Spring Semester (2016-2017) From Thermodynamics to Atomic and Nuclear Physics
Topic 1.2 AMOUNT OF SUBSTANCE
 Topic 1.2 AMOUNT OF SUBSTANCE The mole Reacting masses and atom economy Solutions and titrations The ideal gas equation Empirical and molecular formulae Ionic equations Mill Hill County High School THE
Topic 1.2 AMOUNT OF SUBSTANCE The mole Reacting masses and atom economy Solutions and titrations The ideal gas equation Empirical and molecular formulae Ionic equations Mill Hill County High School THE
Name (Print) Section # or TA. 1. You may use a crib sheet which you prepared in your own handwriting. This may be
 Name (Print) Section # or TA 1. You may use a crib sheet which you prepared in your own handwriting. This may be one 8-1/2 by 11 inch sheet of paper with handwriting only on one side. 2. You may use a
Name (Print) Section # or TA 1. You may use a crib sheet which you prepared in your own handwriting. This may be one 8-1/2 by 11 inch sheet of paper with handwriting only on one side. 2. You may use a
OKANAGAN UNIVERSITY COLLEGE FINAL EXAMINATION CHEMISTRY 121
 Name (Print) Surname Given Names Student Number Centre OKANAGAN UNIVERSITY COLLEGE FINAL EXAMINATION CHEMISTRY 2 Professor: Nigel Eggers, Renee Van Poppelen, Stephen McNeil April 5, 2004 Duration: 3 hours
Name (Print) Surname Given Names Student Number Centre OKANAGAN UNIVERSITY COLLEGE FINAL EXAMINATION CHEMISTRY 2 Professor: Nigel Eggers, Renee Van Poppelen, Stephen McNeil April 5, 2004 Duration: 3 hours
Chapter 18 Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 18 Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics Heat is the transfer of energy due to the difference in temperature. The internal energy is the total energy of the object in its centerofmass reference
Chapter 18 Heat and the First Law of Thermodynamics Heat is the transfer of energy due to the difference in temperature. The internal energy is the total energy of the object in its centerofmass reference
5. We use the following relation derived in Sample Problem Entropy change of two blocks coming to equilibrium:
 Chapter 20 5. We use the following relation derived in Sample Problem Entropy change of two blocks coming to equilibrium: Tf S = mc ln. Ti (a) The energy absorbed as heat is given by Eq. 19-14. Using Table
Chapter 20 5. We use the following relation derived in Sample Problem Entropy change of two blocks coming to equilibrium: Tf S = mc ln. Ti (a) The energy absorbed as heat is given by Eq. 19-14. Using Table
No. of Printed Pages : 12 I cite-o4 1
 No. of Printed Pages : 12 I cite-o4 1 taa. BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination December, 2017 CHEMISTRY CHE-04 : PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 Note : Attempt all the
No. of Printed Pages : 12 I cite-o4 1 taa. BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination December, 2017 CHEMISTRY CHE-04 : PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 Note : Attempt all the
PHYSICS PHE-14 : MATHEMATICAL METHODS IN PHYSICS-III
 00 74 3 No. of Printed Pages : 8 I PHE-14 BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination December, 2014 PHYSICS PHE-14 : MATHEMATICAL METHODS IN PHYSICS-III Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 Note : All
00 74 3 No. of Printed Pages : 8 I PHE-14 BACHELOR OF SCIENCE (B.Sc.) Term-End Examination December, 2014 PHYSICS PHE-14 : MATHEMATICAL METHODS IN PHYSICS-III Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 Note : All
Chem 75 Winter, 2017 Practice Exam 3
 1. The Handbook of Chemistry and Physics says that PbBr 2 is soluble in water to the tune of 8.441 g per kg of water at 25 C. The molar mass of PbBr 2 is 367 g mol 1. (a) What is the ionic strength of
1. The Handbook of Chemistry and Physics says that PbBr 2 is soluble in water to the tune of 8.441 g per kg of water at 25 C. The molar mass of PbBr 2 is 367 g mol 1. (a) What is the ionic strength of
CHEM 108 (Spring-2008)
 CHEM 108 (Spring-2008) Final Exam (106 pts) Name: --------------------------------------------------------------------------, CLID # -------------------------------- LAST NAME, First (Circle the alphabet
CHEM 108 (Spring-2008) Final Exam (106 pts) Name: --------------------------------------------------------------------------, CLID # -------------------------------- LAST NAME, First (Circle the alphabet
CLASS TEST GRADE 11. PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY Test 4: Matter and materials 1
 CLASS TEST GRADE PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY Test 4: Matter and materials MARKS: 45 TIME: hour INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION. Answer ALL the questions. 2. You may use non-programmable calculators. 3. You
CLASS TEST GRADE PHYSICAL SCIENCES: CHEMISTRY Test 4: Matter and materials MARKS: 45 TIME: hour INSTRUCTIONS AND INFORMATION. Answer ALL the questions. 2. You may use non-programmable calculators. 3. You
Thermodynamics. Chem 36 Spring The study of energy changes which accompany physical and chemical processes
 Thermodynamics Chem 36 Spring 2002 Thermodynamics The study of energy changes which accompany physical and chemical processes Why do we care? -will a reaction proceed spontaneously? -if so, to what extent?
Thermodynamics Chem 36 Spring 2002 Thermodynamics The study of energy changes which accompany physical and chemical processes Why do we care? -will a reaction proceed spontaneously? -if so, to what extent?
Chemistry 123: Physical and Organic Chemistry Topic 2: Thermochemistry
 Recall the equation. w = -PΔV = -(1.20 atm)(1.02 L)( = -1.24 10 2 J -101 J 1 L atm Where did the conversion factor come from? Compare two versions of the gas constant and calculate. 8.3145 J/mol K 0.082057
Recall the equation. w = -PΔV = -(1.20 atm)(1.02 L)( = -1.24 10 2 J -101 J 1 L atm Where did the conversion factor come from? Compare two versions of the gas constant and calculate. 8.3145 J/mol K 0.082057
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Entropy and free energy
 Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Entropy and free energy Learning goals and key skills: Understand the meaning of spontaneous process, reversible process, irreversible process, and isothermal process.
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Entropy and free energy Learning goals and key skills: Understand the meaning of spontaneous process, reversible process, irreversible process, and isothermal process.
8. Relax and do well.
 CHEM 15 Exam II John II. Gelder March 4, 1999 Name TA's Name Lab Section INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This examination consists of a total of 7 different pages. The last two pages includes a periodic table, a solubility
CHEM 15 Exam II John II. Gelder March 4, 1999 Name TA's Name Lab Section INSTRUCTIONS: 1. This examination consists of a total of 7 different pages. The last two pages includes a periodic table, a solubility
Chemistry. TOPIC : Solution and colligative properties
 TOPIC : Solution and colligative properties Date : Marks : 20 mks Time : ½ hr. If 5.85 g of NaCl (molecular weight 58.5) is dissolved in water and the solution is made up to 0.5 litre, the molarity of
TOPIC : Solution and colligative properties Date : Marks : 20 mks Time : ½ hr. If 5.85 g of NaCl (molecular weight 58.5) is dissolved in water and the solution is made up to 0.5 litre, the molarity of
Our country, our future 525/1 S6 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 DURATION: 2 HOUR 45 MINUTES
 1 Our country, our future 525/1 S6 CHEMISTRY Exam 10 PAPER 1 DURATION: 2 HOUR 45 MINUTES For Marking guide contact and consultations: Dr. Bbosa Science 0776 802709, Instructions - This paper consists of
1 Our country, our future 525/1 S6 CHEMISTRY Exam 10 PAPER 1 DURATION: 2 HOUR 45 MINUTES For Marking guide contact and consultations: Dr. Bbosa Science 0776 802709, Instructions - This paper consists of
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
 Chapter 19. Chemical Thermodynamics Sample Exercise 19.2 (p. 819) Elemental mercury is a silver liquid at room temperature. Its normal freezing point is -38.9 o C, and its molar enthalpy of fusion is H
Chapter 19. Chemical Thermodynamics Sample Exercise 19.2 (p. 819) Elemental mercury is a silver liquid at room temperature. Its normal freezing point is -38.9 o C, and its molar enthalpy of fusion is H
Chemical Thermodynamics
 Quiz A 42.8 ml solution of ammonia (NH 3 ) is titrated with a solution of 0.9713 M hydrochloric acid. The initial reading on the buret containing the HCl was 47.13 ml and the final reading when the endpoint
Quiz A 42.8 ml solution of ammonia (NH 3 ) is titrated with a solution of 0.9713 M hydrochloric acid. The initial reading on the buret containing the HCl was 47.13 ml and the final reading when the endpoint
Downloaded from
 : Bhubaneswar Region CHAPTER 2-SOLUTIONS 1 MARK QUESTIONS 1 What is molarity? 2 What do you understand by saying that molality of a solution is 0.2? 3 Why is the vapour pressure of a liquid remains constant
: Bhubaneswar Region CHAPTER 2-SOLUTIONS 1 MARK QUESTIONS 1 What is molarity? 2 What do you understand by saying that molality of a solution is 0.2? 3 Why is the vapour pressure of a liquid remains constant
Chem 112, Fall 05 (Garman/Weis) Final Exam A, 12/20/2005 (Print Clearly) +2 points
 +2 points Before you begin, make sure that your exam has all 10 pages. There are 24 required problems worth 4 points apiece, unless otherwise noted, and two 4-point extra credit problems. Stay focused,
+2 points Before you begin, make sure that your exam has all 10 pages. There are 24 required problems worth 4 points apiece, unless otherwise noted, and two 4-point extra credit problems. Stay focused,
Chapter 19: The Kinetic Theory of Gases Questions and Example Problems
 Chapter 9: The Kinetic Theory of Gases Questions and Example Problems N M V f N M Vo sam n pv nrt Nk T W nrt ln B A molar nmv RT k T rms B p v K k T λ rms avg B V M m πd N/V Q nc T Q nc T C C + R E nc
Chapter 9: The Kinetic Theory of Gases Questions and Example Problems N M V f N M Vo sam n pv nrt Nk T W nrt ln B A molar nmv RT k T rms B p v K k T λ rms avg B V M m πd N/V Q nc T Q nc T C C + R E nc
Practice Examinations Chem 393 Fall 2005 Time 1 hr 15 min for each set.
 Practice Examinations Chem 393 Fall 2005 Time 1 hr 15 min for each set. The symbols used here are as discussed in the class. Use scratch paper as needed. Do not give more than one answer for any question.
Practice Examinations Chem 393 Fall 2005 Time 1 hr 15 min for each set. The symbols used here are as discussed in the class. Use scratch paper as needed. Do not give more than one answer for any question.
Transition Theory Abbreviated Derivation [ A - B - C] # E o. Reaction Coordinate. [ ] # æ Æ
![Transition Theory Abbreviated Derivation [ A - B - C] # E o. Reaction Coordinate. [ ] # æ Æ Transition Theory Abbreviated Derivation [ A - B - C] # E o. Reaction Coordinate. [ ] # æ Æ](/thumbs/79/79511213.jpg) Transition Theory Abbreviated Derivation A + BC æ Æ AB + C [ A - B - C] # E A BC D E o AB, C Reaction Coordinate A + BC æ æ Æ æ A - B - C [ ] # æ Æ æ A - B + C The rate of reaction is the frequency of
Transition Theory Abbreviated Derivation A + BC æ Æ AB + C [ A - B - C] # E A BC D E o AB, C Reaction Coordinate A + BC æ æ Æ æ A - B - C [ ] # æ Æ æ A - B + C The rate of reaction is the frequency of
