DETERMINATION OF THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF LIROCONITE CU2A1[As04] (OH)4.4H20 R. V. Kolesova and E. G. Fesenko
|
|
|
- Alexina Craig
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SOVET PHYSCS - CRYSTALLOGRAPHY VOL. 13, NO.3 NOV.-DEC., 1968 DETERMNATON OF THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF LROCONTE CU2A1[As04] (OH)4.4H20 R. V. Kolesova and E. G. Fesenko Rostov University Translated from Kristallografiya, VoL 13, No.3, pp , May-June, 1968 Original article submitted February 20, 1967 Projections and sections of the Patterson function are used to determine the positions of the heavy atoms. The coordinates of the light atoms are derived from the three-dimensional electron-density distribution. The structure may be represented as a chain of Al octahedra linked by vertices to As tetrahedra, which are joined via paired Cu bipyramids. This greenish-blue mineral belongs to the torquoise group. Our specimens (from Cornwall, Britain) were crystalline fragments of size 0.2 to 0.8 mm. Rotation and layer-line patterns (weissenberg goniometer, Mo Ka and C u Ka) gave the cell parameters as a = 12.64, b = 7.50, c = 9.86 A, {3 = 91 18', which agree well with the values of [1,2]. The unit cell contains four C u:0l [As04 ](OH)4. 4HP formula units. The absences indicate the x-ray group as 2/ml-/a, which includes space groups l2/a and la. The statistics of the reflections of general type indicated the presence of a center of symmetry, which led us to choose group l2/a. The As and Cu atoms led to hope that the Patterson function would solve the structure. The four As atoms can have only special positions in group 12/ a, the most likely ones being on twofold axes. The p(uw) Patterson projection (Fig. 1) showed that CU lies in a general eightfold position with xcu = 0.129, zcu = The y coordinates of Cu and As were derived approximately from p(uv). The strong peaks on the lines u = 0, u = 0.121, and u = confirmed the x coordinates of the heavy atoms, but the y coor~ dinates were found only roughly, because the two Cu-As peaks on the u = line are replaced by one very strong one, from overlap of the two; this had v ~ 0.208, which gives YCu ~ and YAs ~ This explained why the lines u = 0 and u = did not have two Cu-Cu' peaks, which both have v = Y2-2yCu but which differ by a factor two in weight: one of them coincides with the peak at the origin, and the other with the parameterless Fig. 1. The p(uv) Patterson projecrion for liroconire. (for this xcu) Cu -Cu' peak at u = 0.242, v = 0 (Fig. 2, a and b). The As-As' peak on u = 0 is represented by a peak of suitable height at v = 0.402, which gives y As = Further information was obtained from sections P(%v 0) and P(O,121 v 0.250) of the three-dimensional Patterson function. The y coordinates given by these were (As) and (Cu). Ordinary (xz), (xy) and weighted k(xz) (K = 1, 2,3,4) projections of the electron 324
2 CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF LROCONTE 325 a Fig. 2. a) p(uv) Patterson projection for liroconite, b) symmetry of the projection and disposition of the peaks. density allowed us to locate the Ai and four of the six independent atoms, leaving the positions of two 0 still uncertain. Weighted projections were used [3] to construct the three-dimensional electron density, which gave the coordinates of these last two atoms and also refined values for the others. At this stage Rhkl = Least-squares refinement reduced this to Rhkl = The discrepancies t:. =[(Fo - F~/Fol]'100%weredistributed as follows: 0 ~ t:. ~ 10 for 56.5% of the total nonzero reflections, 10 < t:. ~ 20,24.4%,20 < t:. ~ 30, 10.2%,30 < t:. ~ 40, 4.9%, 40 < t:. ~ 50,1.8%, and t:. > 50, 2.2%. That is, discrepancies exceeding 20% occur for 97 reflections out of 508, and for these 97, 44 had intensities estimated as less than 10 (the weakest density was 3, the strongest 400), 18 had 10 to 15, nine had 15 to 20, seven 20 to 25, and four over 160. Thus, 82 of the 97 reflections with discrepancies over 20% were very weak, while four were very strong which naturally increased the error of measurement for these. The remaining 15 had intensities as follows: seven between 25 and 30, and the other eight between 30 and 110, of which only two gave discrepancies greater than 31%: for 400, t:. = 56; for , t:. = 33%. Table 1 gives the numbers of finite reflections for various layer lines, and also R1 (reliability factor taking account only of As and Cu), R2 (from coordinates of all atoms from the three~imensional electron-density synthesis), and Rs (after leastsquares refinement). The table also gives the corresponding isotropic temperature factors Bi and max (sin ea). Table 2 gives the final values for the coordinates of the basic atoms. The Ai atoms lie at inversion centers; as in many other structures, the nearest neighbors are six atoms (Fig. 3a), which form an octahedron. The cation-anion distances are: Al-01(0'1) = 1.89; Al-Os(O~) = 1.95; Al-04(0~) =1.80 A; the first four agree well with known values, e.g., for epidote [4], where the Al-O bond lengths are A, corundum [5], where three Al-O distances are 2.0 A and the other three 1. 9 A, etc. The other two are somewhat shorter. The 0-0 here and subsequently are shown in the figures. The bond angles are: 01-Al-04 = 85 57', 0s-Al-04 = 87 57', 01-0S-0'1 = 88 24'. TABLE 1. Reliability Factors for Layer Lines Ref. No. of Fol ~ 0 B, max sin 3/'1. ho 128 0,37 0 0,18 0,4 0,11 0,57 1,146 Ml 112 0,36 0,11.1,4 0,08 i,4 0,636 h ,37 0 0,18 0,6 0,11 0,4 0,774 h ,37 0 0,17 0,4 0,11 0,4 0,713 h ,32 0 0,18 1,6 0,12 1,11 0,554 hko 49 0,29 0 0,16 1,0 0,13 0,75 0,711
3 326 R. V. KOLESOVA AND E. G. FESENKO TABLE 2. Coordinates of the Basic Atoms in Liroconite Atom xla Vlb zle A tom xla Ylb zle As Cn , Al O rl, a b Fig. 3. Coordination polyhedra in liroconite. Primes denote atoms related to the basis ones by symmerry operations. The As atoms lie on twofold axes, each having an oxygen tetrahedron (Fig. 3b) with As -Ot (Ot") = 1.56; As - 2( 2') = 1.59 A. The As -0 bond lengths are appreciably less than those in clinoclasite, where two As-O distances have an average of 1.73A and the other two have 1.68 A [6], but they are only slightly less than for the corresponding in simplesite Fe3(As04)2. 8HP, where As -Ot = 1.60; As -02 = 1.63, and As -03 ( 3') = 1.69 A [7]. t may be that this is due to replacement of part of As in liroconite by P, which has a smaller ionic radius. A chemical analysis was not possible, as only a little material was available. The bond angles fall into two groups: 0t-As -02'(Ot'-As -02) = '; 0t-As -02(Ot' -As - 2') = 105,51' for the first and 0t-AS-Ol = '; 02-As-02' = ' for the second. The four oxygen atoms (02' 3, 4, 02") nearest the Cu (Fig. 3c) li-e at 2.00,1.87,2.02,2.01 A, respectively; they lie roughly in a plane and form a quadrilateral, or rather two triangles 030P2" and with 0302" as common side, the planes of the 3 4 2" two lying at '. The angles are: = 89 17', " = 89 57, 02-02"-Ol = 94 24',and 02" = 86 24'. The Cu atom lies above this plane by A. The coordination number is brought up to that most favorable as regards energy and most commonly found with divalent copper [81 by Os and Os' which lie at 2.75 and 2.55 A,respectively.from the copper. The bond angles are: 02-Cu-OS = 80 02', 02-Cu-0s = 77 49', 03- Cu-Os = 89 57', 03-Cu-OS = 82 04', 04-Cu-OS = ', 04-Cu-OS = ', 02"-Cu-Os =91.58, 0t-Cu-Os = 94 51'. The displacement of the plane of the quadrilateral towards Os shortens that bond relative to Cu -Os' which indicates a tendency to fivefold coordination (tetragonal pyramid). The unit cell has eight Cu polyhedra linked via common 02-02" edges into four pairs via centers of symmetry, as in clinoclasite and cornetite [91. This 02-02" edge is much shorter than the other sides of the quadrilateral. The C u -C u dis tance in a pair is 3.03 A, while the angle between the planes of the two quadrilaterals is about 180. Figures 4-6 show projections on the three coordinate planes, while Fig. 7 shows an axonometric projection. The Al octahedra and As tetrahedra are linked via common 0t vertices and form chains along the a axis. Three such chains (xoo;xy2%; xll)are linked by two groups of paired Cu
4 CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF LROCONTE 327 Fig.4. Projection of the structure of liroconite 011the xz plane. Fig. 7. Axonometric projection of the structure of liroconite. Fig. 5. Projection of the structure of liroconite on the yz plane. polyhedra so that the common vertices 02 and 02" of two Cu polyhedra are simultaneously vertices of two As tetrahedra, while 03 and 04 in the quadrilateral around Cu also belong to two Al octahedra. The other two groups of paired Cu polyhedra similarly link x1f21f2, xl0, and xol chains. The protons were distributed between the oxygen atoms to form OH groups and H20 molecules from the valency balance derived from Pauling's second rule. The sum of the bond strengths at 01 is 1.75, while that at 02 is 1.91; those at 03 and 04 are 0.83, and those at Os and 06 are Hence 03 and 04 are identified as OH groups, while Os and 06 are HP molecules. The bonds are obviously longer for the last two, which confirms this conclusion, since HP lies before OH in the series of increasing addend field strength [8]. Figures 5 and 6 show that the water molecules lie in channels parallel to the a and c axes, the minimum distance between water molecules being 2.80 A. The structure explains the imperfect cleavage [1] or (110) and (011). The packing coefficient is 0.56, so the bonds have a considerable proportion of homopolarity. Representation of the atoms as spheres in this case is purely formal, but if we do this and calculate the packing coefficients for major planes (Table 3), we get maximal values for (110) and (011), the values being much higher than for the TABLE 3. Packing Coefficients for Major Planes in Liroconite Plane (too) (001) (010) (011) (110) (110) (Jot) (111) Fig. 6. Projection of the structure of liroconite on the xy plane. k r;
5 328 R. V. KOLESOVA AND E. G. FESENKO other planes (the bar is connected with the choice of coordinate origin). Figures 5 and 6 illustrate this. The grouping of many atoms close to these planes leads to stronger bonds in directions parallel to the planes and weaker ones perpendicular to them. The cleavage is imperfect because the centers do not lie exactly in these planes, and also because between the planes lie some of the atoms, which are linked to atoms in the planes. The commonest {110} and {011 }forms [1] are formed by the most densely populated planes. We are indebted to r. M. Rumanova for providing the crystals and for valuable advice, and to L. O. A tovmyan, N. r. Golovina, and G. F. Klitskaya for collaboration in the computations. LTERATURE CTED 1. L. G. Berry, Amer. Mineralogist, 36, 484 (1951). 2. V. r. Mikheev, X-Ray dentification of Minerals [in Russian], Gosgeoltekhizdat, Moscow (1957). 3. B. K. Vainshtein and G. N. Tishchenko, Trudy nst. Kristallogr. AN SSSR, g, 68 (1955). 4. N. V. Belov and r. M. Rumanova, Trudy nst. kristallogr. AN SSSR, ~, 103 (1954). 5. B. F. Ormont, Structures of norganic Compounds [in Russian], zd. tekh.-teor. lit., Moscow (1950). 6. S. Chose, M. Fenlmann, and M. Sundaralingam, Acta Cryst., 18, (1965). 7. Coll.: New Research on Crystallography and Crystallochemis try. N. Crystal structures [Russian translation], zd. in lit., Moscow (1951), p M. A. Porai-Koshits, Zh. Strukt. khimii,~, 2, 218 (1961). 9. M. Fenlmann, S. Chose, and J. S. Finney, J. Chern. Phys., 47,7, (1963).
The Crystal Structure of Sodium Pentafluorodistannate(II), NaSn2Fs*
 1104 Acta Cryst. (1964). 17, 1104 The Crystal Structure of Sodium Pentafluorodistannate(II), NaSn2Fs* :BY ROBERT R. MCDONALD,'~ ALLEN C. I~RSON, AND Do~ T. CROMER University of California, Los Alamos Scientific
1104 Acta Cryst. (1964). 17, 1104 The Crystal Structure of Sodium Pentafluorodistannate(II), NaSn2Fs* :BY ROBERT R. MCDONALD,'~ ALLEN C. I~RSON, AND Do~ T. CROMER University of California, Los Alamos Scientific
XVI. The Crystal Structure of Benitoite, BaTiSia09.
 139 XV. The Crystal Structure of Benitoite, BaTiSia09. By w. H. Zachariasen (Oslo - Manchester). (With 2 figures.) 1. ntroduction. The mineral Benitoite from St. Benito in California has the composition
139 XV. The Crystal Structure of Benitoite, BaTiSia09. By w. H. Zachariasen (Oslo - Manchester). (With 2 figures.) 1. ntroduction. The mineral Benitoite from St. Benito in California has the composition
Crystal Structure and Chemistry
 Crystal Structure and Chemistry Controls on Crystal Structure Metallic bonding closest packing Covalent bonding depends on orbital overlap and geometry Ionic bonding Pauling s Rules Coordination Principle
Crystal Structure and Chemistry Controls on Crystal Structure Metallic bonding closest packing Covalent bonding depends on orbital overlap and geometry Ionic bonding Pauling s Rules Coordination Principle
Lecture 4! ü Review on atom/ion size! ü Crystal structure (Chap 4 of Nesseʼs book)!
 Lecture 4! ü Review on atom/ion size! ü Crystal structure (Chap 4 of Nesseʼs book)! 15 C 4+ 42 Si 4+ Size of atoms! Hefferan and O Brien, 2010; Earth Materials Force balance! Crystal structure (Chap. 4)!
Lecture 4! ü Review on atom/ion size! ü Crystal structure (Chap 4 of Nesseʼs book)! 15 C 4+ 42 Si 4+ Size of atoms! Hefferan and O Brien, 2010; Earth Materials Force balance! Crystal structure (Chap. 4)!
CHAPTER 4. Crystal Structure
 CHAPTER 4 Crystal Structure We can assume minerals to be made of orderly packing of atoms or rather ions or molecules. Many mineral properties like symmetry, density etc are dependent on how the atoms
CHAPTER 4 Crystal Structure We can assume minerals to be made of orderly packing of atoms or rather ions or molecules. Many mineral properties like symmetry, density etc are dependent on how the atoms
Geol /19/06 Labs 5 & 6 Crystal Chemistry Ionic Coordination and Mineral Structures
 Geol 2311 9/19/0 Labs 5 & Crystal Chemistry Ionic Coordination and Mineral Structures Handout Oral Mineral Tray Report Samples Ionic Coordination Exercise Investigating Mineral Structures using XtalDraw
Geol 2311 9/19/0 Labs 5 & Crystal Chemistry Ionic Coordination and Mineral Structures Handout Oral Mineral Tray Report Samples Ionic Coordination Exercise Investigating Mineral Structures using XtalDraw
Review questions CHAPTER 5. Practice exercises 5.1 F F 5.3
 CHAPTER 5 Practice exercises 5.1 S 5.3 5.5 Ethane is symmetrical, so does not have a dipole moment. However, ethanol has a polar H group at one end and so has a dipole moment. 5.7 xygen has the valence
CHAPTER 5 Practice exercises 5.1 S 5.3 5.5 Ethane is symmetrical, so does not have a dipole moment. However, ethanol has a polar H group at one end and so has a dipole moment. 5.7 xygen has the valence
Synthesis and Crystal Structure of Na 3 (H 3 O)[UO 2 (SeO 3 ) 2 ] 2 H 2 O
![Synthesis and Crystal Structure of Na 3 (H 3 O)[UO 2 (SeO 3 ) 2 ] 2 H 2 O Synthesis and Crystal Structure of Na 3 (H 3 O)[UO 2 (SeO 3 ) 2 ] 2 H 2 O](/thumbs/72/67560913.jpg) ISSN 1063-7745, Crystallography Reports, 009, Vol. 54, No. 5, pp. 85 857. Pleiades Publishing, Inc., 009. Original Russian Text L.B. Serezhkina, A.V. Vologzhanina, A.V. Marukhnov, D.V. Pushkin, V.N. Serezhkin,
ISSN 1063-7745, Crystallography Reports, 009, Vol. 54, No. 5, pp. 85 857. Pleiades Publishing, Inc., 009. Original Russian Text L.B. Serezhkina, A.V. Vologzhanina, A.V. Marukhnov, D.V. Pushkin, V.N. Serezhkin,
Silicate Structures. Silicate Minerals: Pauling s s Rules and. Elemental Abundance in Crust. Elemental Abundance in Crust: Pauling s s Rules
 Silicate Minerals: Pauling s s Rules and Silicate Structures February 6, 2007 Elemental Abundance in Crust Fe Ion O 2- Si 4+ Al 3+, 3+ Ca Na + K + Mg mol % 2.6 1.4 mol% x charge 4.8 3.8 2.6 1.4 3.8 Sum
Silicate Minerals: Pauling s s Rules and Silicate Structures February 6, 2007 Elemental Abundance in Crust Fe Ion O 2- Si 4+ Al 3+, 3+ Ca Na + K + Mg mol % 2.6 1.4 mol% x charge 4.8 3.8 2.6 1.4 3.8 Sum
: Bond Order = 1.5 CHAPTER 5. Practice Questions
 CAPTER 5 Practice Questions 5.1 5.3 S 5.5 Ethane is symmetrical, so does not have a dipole moment. owever, ethanol has a polar group at one end and so has a dipole moment. 5.7 xygen has the valence electron
CAPTER 5 Practice Questions 5.1 5.3 S 5.5 Ethane is symmetrical, so does not have a dipole moment. owever, ethanol has a polar group at one end and so has a dipole moment. 5.7 xygen has the valence electron
Advanced Ceramics for Strategic Applications Prof. H. S. Maiti Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Advanced Ceramics for Strategic Applications Prof. H. S. Maiti Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture -3 Crystal Structure Having made some introductory
Advanced Ceramics for Strategic Applications Prof. H. S. Maiti Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture -3 Crystal Structure Having made some introductory
CRYSTAL CHEMISTRY OF THE BASIC MANGANESE ARSENATES: III. The CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF EVEITE, Mn 2 (OH) (AsO 4 )
 THE AMERICAN MINERALOGIST, VOL. 53, NOVEMBER-DECEMBER, 1968 CRYSTAL CHEMISTRY OF THE BASIC MANGANESE ARSENATES: III. The CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF EVEITE, Mn 2 (OH) (AsO 4 ) PAUL B. MOORE and JOSEPH R. SMYTH,
THE AMERICAN MINERALOGIST, VOL. 53, NOVEMBER-DECEMBER, 1968 CRYSTAL CHEMISTRY OF THE BASIC MANGANESE ARSENATES: III. The CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF EVEITE, Mn 2 (OH) (AsO 4 ) PAUL B. MOORE and JOSEPH R. SMYTH,
The Crystal Structure of Iron Pentacarbonyl: Space Group and Refinement of the Structure
 JAN H. VAN DEN HENDE AND HENRI BOUTIN 663 neighbors within 3.2/l and it is not involved in any hydrogen bonding. The short S-O(3) distance suggests a double bond. If there were no such double bond and
JAN H. VAN DEN HENDE AND HENRI BOUTIN 663 neighbors within 3.2/l and it is not involved in any hydrogen bonding. The short S-O(3) distance suggests a double bond. If there were no such double bond and
Experiment 7: Understanding Crystal Structures
 Experiment 7: Understanding Crystal Structures To do well in this laboratory experiment you need to be familiar with the concepts of lattice, crystal structure, unit cell, coordination number, the different
Experiment 7: Understanding Crystal Structures To do well in this laboratory experiment you need to be familiar with the concepts of lattice, crystal structure, unit cell, coordination number, the different
If you put an electron into the t 2g, like that for Ti 3+, then you stabilize the barycenter of the d orbitals by 0.4 D o.
 Crystal Field Stabilization Energy Week 2-1 Octahedral Symmetry (O h ) If you put an electron into the t 2g, like that for Ti 3+, then you stabilize the barycenter of the d orbitals by 0.4 D o. Each additional
Crystal Field Stabilization Energy Week 2-1 Octahedral Symmetry (O h ) If you put an electron into the t 2g, like that for Ti 3+, then you stabilize the barycenter of the d orbitals by 0.4 D o. Each additional
CHAPTER 3. Crystallography
 CHAPTER 3 Crystallography Atomic Structure Atoms are made of Protons: mass 1.00728 amu, +1 positive charge Neutrons: mass of 1.00867 amu, neutral Electrons: mass of 0.00055 amu, -1 negative charge (1 amu
CHAPTER 3 Crystallography Atomic Structure Atoms are made of Protons: mass 1.00728 amu, +1 positive charge Neutrons: mass of 1.00867 amu, neutral Electrons: mass of 0.00055 amu, -1 negative charge (1 amu
Earth Solid Earth Rocks Minerals Atoms. How to make a mineral from the start of atoms?
 Earth Solid Earth Rocks Minerals Atoms How to make a mineral from the start of atoms? Formation of ions Ions excess or deficit of electrons relative to protons Anions net negative charge Cations net
Earth Solid Earth Rocks Minerals Atoms How to make a mineral from the start of atoms? Formation of ions Ions excess or deficit of electrons relative to protons Anions net negative charge Cations net
The Crystal and Molecular Structures of Hydrazine Adducts with Isomeric Pyrazine Dicarboxylic Acids
 The Open Crystallography Journal, 2008, 1, 31-36 31 Open Access The Crystal and Molecular Structures of Hydrazine Adducts with Isomeric Pyrazine Dicarboxylic Acids Wojciech Starosta and Janusz Leciejewicz*
The Open Crystallography Journal, 2008, 1, 31-36 31 Open Access The Crystal and Molecular Structures of Hydrazine Adducts with Isomeric Pyrazine Dicarboxylic Acids Wojciech Starosta and Janusz Leciejewicz*
130 points on 6 pages + a useful page 7
 Name KEY Chemistry 350 Spring 2012 Exam #2, March 30, 2012 50 minutes 130 points on 6 pages + a useful page 7 1. Circle the element/compound most likely to have the desired property. Briefly explain your
Name KEY Chemistry 350 Spring 2012 Exam #2, March 30, 2012 50 minutes 130 points on 6 pages + a useful page 7 1. Circle the element/compound most likely to have the desired property. Briefly explain your
Earth Materials I Crystal Structures
 Earth Materials I Crystal Structures Isotopes same atomic number, different numbers of neutrons, different atomic mass. Ta ble 1-1. Su mmar y of quantu m num bers Name Symbol Values Principal n 1, 2,
Earth Materials I Crystal Structures Isotopes same atomic number, different numbers of neutrons, different atomic mass. Ta ble 1-1. Su mmar y of quantu m num bers Name Symbol Values Principal n 1, 2,
Atomic Arrangement. Primer in Materials Spring
 Atomic Arrangement Primer in Materials Spring 2017 30.4.2017 1 Levels of atomic arrangements No order In gases, for example the atoms have no order, they are randomly distributed filling the volume to
Atomic Arrangement Primer in Materials Spring 2017 30.4.2017 1 Levels of atomic arrangements No order In gases, for example the atoms have no order, they are randomly distributed filling the volume to
Chapter 6 Molecular Structure
 hapter 6 Molecular Structure 1. Draw the Lewis structure of each of the following ions, showing all nonzero formal charges. Indicate whether each ion is linear or bent. If the ion is bent, what is the
hapter 6 Molecular Structure 1. Draw the Lewis structure of each of the following ions, showing all nonzero formal charges. Indicate whether each ion is linear or bent. If the ion is bent, what is the
Atomic Arrangement. Primer Materials For Science Teaching Spring
 Atomic Arrangement Primer Materials For Science Teaching Spring 2016 31.3.2015 Levels of atomic arrangements No order In gases, for example the atoms have no order, they are randomly distributed filling
Atomic Arrangement Primer Materials For Science Teaching Spring 2016 31.3.2015 Levels of atomic arrangements No order In gases, for example the atoms have no order, they are randomly distributed filling
 VSEPR Theory, Valence Bond Theory, Characteristic of Covalent Compounds 1. Which of the following is not correct? 1. A sigma bond is weaker than pi bond. 2. A sigma bond is stronger than pi bond.. A double
VSEPR Theory, Valence Bond Theory, Characteristic of Covalent Compounds 1. Which of the following is not correct? 1. A sigma bond is weaker than pi bond. 2. A sigma bond is stronger than pi bond.. A double
The Crystal Structure of Dihydroxyfulnarie. BY M.P. GUPTA AND N. P. GOPTA Department of Physics, Ranchi University, Ranchi, India
 W. G. MUMME AND A. F. REID 631 HAMILTON, W. C. (1964). Statistics in Physical Science, New York: The Ronald Press. HAMILTON, W. C. (1965). Acta Cryst. 18, 502. HILL, P. M., PEISER, H. S. & RAIT, J. R.
W. G. MUMME AND A. F. REID 631 HAMILTON, W. C. (1964). Statistics in Physical Science, New York: The Ronald Press. HAMILTON, W. C. (1965). Acta Cryst. 18, 502. HILL, P. M., PEISER, H. S. & RAIT, J. R.
Periodic Trends. Homework: Lewis Theory. Elements of his theory:
 Periodic Trends There are various trends on the periodic table that need to be understood to explain chemical bonding. These include: Atomic/Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity Electron Affinity
Periodic Trends There are various trends on the periodic table that need to be understood to explain chemical bonding. These include: Atomic/Ionic Radius Ionization Energy Electronegativity Electron Affinity
For more info visit Chemical bond is the attractive force which holds various constituents together in a molecule.
 Chemical bond:- Chemical bond is the attractive force which holds various constituents together in a molecule. There are three types of chemical bonds: Ionic Bond, Covalent Bond, Coordinate Bond. Octet
Chemical bond:- Chemical bond is the attractive force which holds various constituents together in a molecule. There are three types of chemical bonds: Ionic Bond, Covalent Bond, Coordinate Bond. Octet
Bonding. Bringing the atoms together
 Bonding Bringing the atoms together More than one atom Until now, we have been consumed with describing individual atoms of elements. However, isolating individual atoms in most elements is an arduous
Bonding Bringing the atoms together More than one atom Until now, we have been consumed with describing individual atoms of elements. However, isolating individual atoms in most elements is an arduous
THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF BORAX*
 MINERALOGICAL JOURNAL, VOL. 2, No. 1, pp. 1-18, DEC., 1956 THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF BORAX* NOBUO MORIMOTO Mineralogical Institute, University of Tokyo ABSTRACT The crystal structure of borax, Na2B4O7 E10H2O,
MINERALOGICAL JOURNAL, VOL. 2, No. 1, pp. 1-18, DEC., 1956 THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF BORAX* NOBUO MORIMOTO Mineralogical Institute, University of Tokyo ABSTRACT The crystal structure of borax, Na2B4O7 E10H2O,
Earth and Planetary Materials
 Earth and Planetary Materials Spring 2013 Lecture 3 2013.01.14 14 1 Close Packed Anion Arrays Closest Packing Coordination number (C.N.) : number of anions bonded to a cation larger cation, higher C.N.
Earth and Planetary Materials Spring 2013 Lecture 3 2013.01.14 14 1 Close Packed Anion Arrays Closest Packing Coordination number (C.N.) : number of anions bonded to a cation larger cation, higher C.N.
CHAPTER 9 COVALENT BONDING: ORBITALS 323
 APTER 9 OVALET BODIG: ORBITALS 323 2 3 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 3 2 3 O * * 2 o; most of the carbons are not in the same plane since a majority of carbon atoms exhibit a tetrahedral structure (19.5 bond angles).
APTER 9 OVALET BODIG: ORBITALS 323 2 3 2 2 2 3 3 2 2 3 2 3 O * * 2 o; most of the carbons are not in the same plane since a majority of carbon atoms exhibit a tetrahedral structure (19.5 bond angles).
Chemical bonds. In some minerals, other (less important) bond types include:
 Chemical bonds Chemical bond: force of attraction between two or more atoms/ions Types of bonds in crystals: Ionic bond: electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged ions. This type of bond
Chemical bonds Chemical bond: force of attraction between two or more atoms/ions Types of bonds in crystals: Ionic bond: electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged ions. This type of bond
The crystal structure of BiOCI
 Zeitschrift fur Kristallographie 205, 35-40 (1993) COby R. Oldenbourg Verlag, Munchen 1993-0044-2968/93 $ 3.00+0.00 The crystal structure of BiO K. G. Keramidas, G. P. Voutsas, and P. 1. Rentzeperis Applied
Zeitschrift fur Kristallographie 205, 35-40 (1993) COby R. Oldenbourg Verlag, Munchen 1993-0044-2968/93 $ 3.00+0.00 The crystal structure of BiO K. G. Keramidas, G. P. Voutsas, and P. 1. Rentzeperis Applied
Inorganic Exam 1 Chm October 2010
 Inorganic Exam 1 Chm 451 28 October 2010 Name: Instructions. Always show your work where required for full credit. 1. In the molecule CO 2, the first step in the construction of the MO diagram was to consider
Inorganic Exam 1 Chm 451 28 October 2010 Name: Instructions. Always show your work where required for full credit. 1. In the molecule CO 2, the first step in the construction of the MO diagram was to consider
Chem Spring, 2017 Assignment 5 - Solutions
 Page 1 of 10 Chem 370 - Spring, 2017 Assignment 5 - Solutions 5.1 Additional combinations are p z ± d z 2, p x ±d xz, and p y ±d yz. p z ± d z 2 p x ±d xz or p y ±d yz 5.2 a. Li 2 has the configuration
Page 1 of 10 Chem 370 - Spring, 2017 Assignment 5 - Solutions 5.1 Additional combinations are p z ± d z 2, p x ±d xz, and p y ±d yz. p z ± d z 2 p x ±d xz or p y ±d yz 5.2 a. Li 2 has the configuration
Ionic Coordination and Silicate Structures
 Ionic Coordination and Silicate Structures Pauling s Rules A coordination polyhedron of anions forms around a cation Ionic distance determined by radii Coordination number determined by radius ratio. May
Ionic Coordination and Silicate Structures Pauling s Rules A coordination polyhedron of anions forms around a cation Ionic distance determined by radii Coordination number determined by radius ratio. May
Structure and Non-linear Optical Properties of b-barium Borate
 652 Acta Cryst. (1998). B54, 652±656 Structure and Non-linear Optical Properties of b-barium Borate D. F. Xue and S. Y. Zhang* Laboratory of Rare Earth Chemistry and Physics, Changchun Institute of Applied
652 Acta Cryst. (1998). B54, 652±656 Structure and Non-linear Optical Properties of b-barium Borate D. F. Xue and S. Y. Zhang* Laboratory of Rare Earth Chemistry and Physics, Changchun Institute of Applied
Remember the purpose of this reading assignment is to prepare you for class. Reading for familiarity not mastery is expected.
 Remember the purpose of this reading assignment is to prepare you for class. Reading for familiarity not mastery is expected. After completing this reading assignment and reviewing the intro video you
Remember the purpose of this reading assignment is to prepare you for class. Reading for familiarity not mastery is expected. After completing this reading assignment and reviewing the intro video you
EGN 3365 Review on Bonding & Crystal Structures by Zhe Cheng
 EGN 3365 Review on Bonding & Crystal Structures 2017 by Zhe Cheng Expectations on Chapter 1 Chapter 1 Understand materials can be classified in different ways by composition, property, application, or
EGN 3365 Review on Bonding & Crystal Structures 2017 by Zhe Cheng Expectations on Chapter 1 Chapter 1 Understand materials can be classified in different ways by composition, property, application, or
Covalent Bonding. In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons
 In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. They are monatomic - consist of single atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons To form ionic compounds Some elements share
In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. They are monatomic - consist of single atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons To form ionic compounds Some elements share
Molecular Geometry and Electron Domain Theory *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m12594 1 Molecular Geometry and Electron Domain Theory * John S. Hutchinson This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 2.0 1
OpenStax-CNX module: m12594 1 Molecular Geometry and Electron Domain Theory * John S. Hutchinson This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 2.0 1
1a. (2 pts) Sketch the general trends (one big arrow across top and one down the side) for the first ionization energies on the periodic table
 Chm 451 Fall 2007 Exam 1 Name: First ionization energy. 1a. (2 pts) Sketch the general trends (one big arrow across top and one down the side) for the first ionization energies on the periodic table 1b.
Chm 451 Fall 2007 Exam 1 Name: First ionization energy. 1a. (2 pts) Sketch the general trends (one big arrow across top and one down the side) for the first ionization energies on the periodic table 1b.
Chapter 6 Test. name. The Structure of Matter
 Chapter 6 Test The Structure of Matter MULTIPLE CHOICE. Write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question on the answer sheet provided. 1. A compound
Chapter 6 Test The Structure of Matter MULTIPLE CHOICE. Write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question on the answer sheet provided. 1. A compound
Covalent Bonding. In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons
 In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. They are monatomic - consist of single atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons To form ionic compounds Some elements share
In nature, only the noble gas elements exist as uncombined atoms. They are monatomic - consist of single atoms. All other elements need to lose or gain electrons To form ionic compounds Some elements share
A refinement of the crystal of covellite, CuS
 MINERALOGICAL JOURNAL, VOL. 8, No.6, PP. 311-319, APRIL 1977 A refinement of the crystal of covellite, CuS structure MASAAKI OHMASA*, MASATOSHI SUZUKI and YOSHIO TAKEUCHI Mineralogical Insti(ute, Faculty
MINERALOGICAL JOURNAL, VOL. 8, No.6, PP. 311-319, APRIL 1977 A refinement of the crystal of covellite, CuS structure MASAAKI OHMASA*, MASATOSHI SUZUKI and YOSHIO TAKEUCHI Mineralogical Insti(ute, Faculty
10.2,3,4. Vectors in 3D, Dot products and Cross Products
 Name: Section: 10.2,3,4. Vectors in 3D, Dot products and Cross Products 1. Sketch the plane parallel to the xy-plane through (2, 4, 2) 2. For the given vectors u and v, evaluate the following expressions.
Name: Section: 10.2,3,4. Vectors in 3D, Dot products and Cross Products 1. Sketch the plane parallel to the xy-plane through (2, 4, 2) 2. For the given vectors u and v, evaluate the following expressions.
Chm October Molecular Orbitals. Instructions. Always show your work for full credit.
 Inorganic Exam 2 Chm 451 29 October 2009 Name: Instructions. Always show your work for full credit. Molecular Orbitals 1. (4 pts) An unusual structure, and one for which there are probably no real examples
Inorganic Exam 2 Chm 451 29 October 2009 Name: Instructions. Always show your work for full credit. Molecular Orbitals 1. (4 pts) An unusual structure, and one for which there are probably no real examples
Chapter 3. The structure of crystalline solids 3.1. Crystal structures
 Chapter 3. The structure of crystalline solids 3.1. Crystal structures 3.1.1. Fundamental concepts 3.1.2. Unit cells 3.1.3. Metallic crystal structures 3.1.4. Ceramic crystal structures 3.1.5. Silicate
Chapter 3. The structure of crystalline solids 3.1. Crystal structures 3.1.1. Fundamental concepts 3.1.2. Unit cells 3.1.3. Metallic crystal structures 3.1.4. Ceramic crystal structures 3.1.5. Silicate
Further refinement of the goyazite structure
 MNERALOGCAL JOURNAL, VOL. 13, NO.6, PP. 390-396, APRL 1987 Short Communication Further refinement of the goyazite structure Toshio KATO nstitute of Earth Sciences, Faculty of Liberal Arts, Yamaguchi University,
MNERALOGCAL JOURNAL, VOL. 13, NO.6, PP. 390-396, APRL 1987 Short Communication Further refinement of the goyazite structure Toshio KATO nstitute of Earth Sciences, Faculty of Liberal Arts, Yamaguchi University,
Chem 728 Introduction to Solid Surfaces
 Chem 728 Introduction to Solid Surfaces Solids: hard; fracture; not compressible; molecules close to each other Liquids: molecules mobile, but quite close to each other Gases: molecules very mobile; compressible
Chem 728 Introduction to Solid Surfaces Solids: hard; fracture; not compressible; molecules close to each other Liquids: molecules mobile, but quite close to each other Gases: molecules very mobile; compressible
CHEMICAL BONDING IONIC BONDS COVALENT BONDS HYDROGEN BONDS METALLIC BONDS
 CHEMICAL BONDING IONIC BONDS COVALENT BONDS HYDROGEN BONDS METALLIC BONDS IONIC BONDING When an atom of a nonmetal takes one or more electrons from an atom of a metal so both atoms end up with eight valence
CHEMICAL BONDING IONIC BONDS COVALENT BONDS HYDROGEN BONDS METALLIC BONDS IONIC BONDING When an atom of a nonmetal takes one or more electrons from an atom of a metal so both atoms end up with eight valence
STRUCTURES OF MERCURY MERCAPTIDES
 STRUCTURES OF MERCURY MERCAPTIDES PART 11. X-RAY STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF MERCURY ETHYLMERCAPTIDE D. C. BRADLEY~ AND N. R. KUNCHUR~ Department of Chemistry, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario
STRUCTURES OF MERCURY MERCAPTIDES PART 11. X-RAY STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS OF MERCURY ETHYLMERCAPTIDE D. C. BRADLEY~ AND N. R. KUNCHUR~ Department of Chemistry, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario
Chapter 6. Preview. Objectives. Molecular Compounds
 Section 2 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Compounds Preview Objectives Molecular Compounds Formation of a Covalent Bond Characteristics of the Covalent Bond The Octet Rule Electron-Dot Notation Lewis Structures
Section 2 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Compounds Preview Objectives Molecular Compounds Formation of a Covalent Bond Characteristics of the Covalent Bond The Octet Rule Electron-Dot Notation Lewis Structures
 CHAPTER 6 CHEMICAL BONDING SHORT QUESTION WITH ANSWERS Q.1 Dipole moments of chlorobenzene is 1.70 D and of chlorobenzene is 2.5 D while that of paradichlorbenzene is zero; why? Benzene has zero dipole
CHAPTER 6 CHEMICAL BONDING SHORT QUESTION WITH ANSWERS Q.1 Dipole moments of chlorobenzene is 1.70 D and of chlorobenzene is 2.5 D while that of paradichlorbenzene is zero; why? Benzene has zero dipole
How to study minerals?!
 How to study minerals?! ü What tools did scientists have from pre-history to Renaissance? Eyes and measuring devices Calcite Crystal faces! ü One of the most spectacular aspect of minerals ü NOTE: No mention
How to study minerals?! ü What tools did scientists have from pre-history to Renaissance? Eyes and measuring devices Calcite Crystal faces! ü One of the most spectacular aspect of minerals ü NOTE: No mention
3.014 Materials Laboratory Fall LABORATORY 2: Module β 1. Radius Ratios and Symmetry in Ionic Crystals
 3.014 Materials Laboratory Fall 2006 LABORATORY 2: Module β 1 Radius Ratios and Symmetry in Ionic Crystals Instructor: Francesco Stellacci Objectives Discover principles of X-ray diffraction from crystalline
3.014 Materials Laboratory Fall 2006 LABORATORY 2: Module β 1 Radius Ratios and Symmetry in Ionic Crystals Instructor: Francesco Stellacci Objectives Discover principles of X-ray diffraction from crystalline
Chapter 6. Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 6 Chemical Bonding Section 6.1 Intro to Chemical Bonding 6.1 Objectives Define chemical bond. Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds. Describe ionic and covalent bonding. Explain why most chemical
Chapter 6 Chemical Bonding Section 6.1 Intro to Chemical Bonding 6.1 Objectives Define chemical bond. Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds. Describe ionic and covalent bonding. Explain why most chemical
Molecular Orbitals of Ethene
 Molecular Orbitals of Ethene 1 Molecular Orbital Analysis of Ethene Dimerisation the reaction is said to be a "symmetry forbidden" interestingly, this reaction is rare and very slow! Molecular Orbitals
Molecular Orbitals of Ethene 1 Molecular Orbital Analysis of Ethene Dimerisation the reaction is said to be a "symmetry forbidden" interestingly, this reaction is rare and very slow! Molecular Orbitals
Lecture 05 Structure of Ceramics 2 Ref: Barsoum, Fundamentals of Ceramics, Ch03, McGraw-Hill, 2000.
 MME 467 Ceramics for Advanced Applications Lecture 05 Structure of Ceramics 2 Ref: Barsoum, Fundamentals of Ceramics, Ch03, McGraw-Hill, 2000. Prof. A. K. M. Bazlur Rashid Department of MME, BUET, Dhaka
MME 467 Ceramics for Advanced Applications Lecture 05 Structure of Ceramics 2 Ref: Barsoum, Fundamentals of Ceramics, Ch03, McGraw-Hill, 2000. Prof. A. K. M. Bazlur Rashid Department of MME, BUET, Dhaka
CHAPTER 6 CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A DEHYDROACETIC ACID SUBSTITUTED SCHIFF BASE DERIVATIVE
 139 CHAPTER 6 CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A DEHYDROACETIC ACID SUBSTITUTED SCHIFF BASE DERIVATIVE 6.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter describes the crystal and molecular structure of a dehydroacetic acid substituted
139 CHAPTER 6 CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A DEHYDROACETIC ACID SUBSTITUTED SCHIFF BASE DERIVATIVE 6.1 INTRODUCTION This chapter describes the crystal and molecular structure of a dehydroacetic acid substituted
A STATISTICAL MODEL FOR THE CRYSTAL. S. Durovic
 SOVET PHYSCS - CRYSTALLOGRAPHY VOL. 7, NO.3 NOVEMBER-DECEMBER,1962 A STATSTCAL MODEL FOR THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE S. Durovic OF MULLTE Refractory Materials Research nstitute, Komenski University, Bratislava,
SOVET PHYSCS - CRYSTALLOGRAPHY VOL. 7, NO.3 NOVEMBER-DECEMBER,1962 A STATSTCAL MODEL FOR THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE S. Durovic OF MULLTE Refractory Materials Research nstitute, Komenski University, Bratislava,
Competition between face-centered cubic and icosahedral cluster structures
 Competition between face-centered cubic and icosahedral cluster structures R. S. Berry University of Chicago, Chicago, IL 60637, USA B. M. Smyrnov, and A. Yu. Strizhev High-Temperatures Institute, Russian
Competition between face-centered cubic and icosahedral cluster structures R. S. Berry University of Chicago, Chicago, IL 60637, USA B. M. Smyrnov, and A. Yu. Strizhev High-Temperatures Institute, Russian
One Q partial negative, the other partial negative Ø H- bonding particularly strong. Abby Carroll 2
 Chemistry Notes v Polarity Experiment Ø Things involved Polarity Solubility Dispersion Ø Polarity Shaving cream has soap steric acid Water is polar Food coloring is polar/ionic because dissolved Like dissolves
Chemistry Notes v Polarity Experiment Ø Things involved Polarity Solubility Dispersion Ø Polarity Shaving cream has soap steric acid Water is polar Food coloring is polar/ionic because dissolved Like dissolves
Microsystem Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Automation School of Electrical Engineering
 Periodic table Key to understand trends in the periodic table is the concept of effective nuclear charge Z eff. Z eff is the nuclear charge of an atom minus the screening constant, which takes into account
Periodic table Key to understand trends in the periodic table is the concept of effective nuclear charge Z eff. Z eff is the nuclear charge of an atom minus the screening constant, which takes into account
Chem 673, Problem Set 5 Due Thursday, December 1, 2005
 otton, Problem 9.3 (assume D 4h symmetry) Additional Problems: hem 673, Problem Set 5 Due Thursday, December 1, 2005 (1) Infrared and Raman spectra of Benzene (a) Determine the symmetries (irreducible
otton, Problem 9.3 (assume D 4h symmetry) Additional Problems: hem 673, Problem Set 5 Due Thursday, December 1, 2005 (1) Infrared and Raman spectra of Benzene (a) Determine the symmetries (irreducible
arxiv: v4 [cond-mat.supr-con] 22 Jun 2013
![arxiv: v4 [cond-mat.supr-con] 22 Jun 2013 arxiv: v4 [cond-mat.supr-con] 22 Jun 2013](/thumbs/73/68953311.jpg) arxiv:1302.6002v4 [cond-mat.supr-con] 22 Jun 2013 Highly Correlated Electron State and High-Temperature Superconductivity in Iron Pnictides M.V.Krasinkova Ioffe Physico-Technical Institute, Russian Academy
arxiv:1302.6002v4 [cond-mat.supr-con] 22 Jun 2013 Highly Correlated Electron State and High-Temperature Superconductivity in Iron Pnictides M.V.Krasinkova Ioffe Physico-Technical Institute, Russian Academy
Big Idea: Ionic Bonds: Ionic Bonds: Metals: Nonmetals: Covalent Bonds: Ionic Solids: What ions do atoms form? Electron Electron
 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
GEOLOGY 284: MINERALOGY
 Dr. Helen Lang Dept. of Geology & Geography West Virginia University FALL 2010 GEOLOGY 284: MINERALOGY Mineralogy and the Development of Modern Chemistry A Bit of History Mineral processing and isolation
Dr. Helen Lang Dept. of Geology & Geography West Virginia University FALL 2010 GEOLOGY 284: MINERALOGY Mineralogy and the Development of Modern Chemistry A Bit of History Mineral processing and isolation
Cartoon courtesy of NearingZero.net. Unit 3: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
 Cartoon courtesy of NearingZero.net Unit 3: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Bonds Forces that hold groups of atoms together and make them function as a unit. Ionic bonds transfer of electrons
Cartoon courtesy of NearingZero.net Unit 3: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Bonds Forces that hold groups of atoms together and make them function as a unit. Ionic bonds transfer of electrons
Rachel R. Henderson, Hexiong Yang, Robert T. Downs and Robert A. Jenkins
 ISSN 1600-5368 Inorganic compounds Metal-organic compounds Organic compounds Acta Crystallographica Section E Structure Reports Online ISSN 1600-5368 Editors: W. Clegg and D. G. Watson Redetermination
ISSN 1600-5368 Inorganic compounds Metal-organic compounds Organic compounds Acta Crystallographica Section E Structure Reports Online ISSN 1600-5368 Editors: W. Clegg and D. G. Watson Redetermination
Atomic and Molecular Dimensions
 1 Atomic and Molecular Dimensions Equilibrium Interatomic Distances When two atoms approach each other, their positively charged nuclei and negatively charged electronic clouds interact. The total interaction
1 Atomic and Molecular Dimensions Equilibrium Interatomic Distances When two atoms approach each other, their positively charged nuclei and negatively charged electronic clouds interact. The total interaction
CRYSTAL STRUCTURES WITH CUBIC UNIT CELLS
 CRYSTAL STRUCTURES WITH CUBIC UNIT CELLS Crystalline solids are a three dimensional collection of individual atoms, ions, or whole molecules organized in repeating patterns. These atoms, ions, or molecules
CRYSTAL STRUCTURES WITH CUBIC UNIT CELLS Crystalline solids are a three dimensional collection of individual atoms, ions, or whole molecules organized in repeating patterns. These atoms, ions, or molecules
Lecture 2: Bonding in solids
 Lecture 2: Bonding in solids Electronegativity Van Arkel-Ketalaar Triangles Atomic and ionic radii Band theory of solids Molecules vs. solids Band structures Analysis of chemical bonds in Reciprocal space
Lecture 2: Bonding in solids Electronegativity Van Arkel-Ketalaar Triangles Atomic and ionic radii Band theory of solids Molecules vs. solids Band structures Analysis of chemical bonds in Reciprocal space
A simple example of a polyhedral network or polynet, constructed from truncated octahedra and hexagonal prisms.
 Polyhedral Nets A simple example of a polyhedral network or polynet, constructed from truncated octahedra and hexagonal prisms. The building process indicated produces a labyrinth. The labyrinth graph
Polyhedral Nets A simple example of a polyhedral network or polynet, constructed from truncated octahedra and hexagonal prisms. The building process indicated produces a labyrinth. The labyrinth graph
Chemistry 101 Chapter 9 CHEMICAL BONDING. Chemical bonds are strong attractive force that exists between the atoms of a substance
 CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical bonds are strong attractive force that exists between the atoms of a substance Chemical Bonds are commonly classified into 3 types: 1. IONIC BONDING Ionic bonds usually form between
CHEMICAL BONDING Chemical bonds are strong attractive force that exists between the atoms of a substance Chemical Bonds are commonly classified into 3 types: 1. IONIC BONDING Ionic bonds usually form between
Lecture 04 Structure of Ceramics 1 Ref: Barsoum, Fundamentals of Ceramics, Ch03, McGraw-Hill, 2000.
 MME 467 Ceramics for Advanced Applications Lecture 04 Structure of Ceramics 1 Ref: Barsoum, Fundamentals of Ceramics, Ch03, McGraw-Hill, 2000. Prof. A. K. M. Bazlur Rashid Department of MME, BUET, Dhaka
MME 467 Ceramics for Advanced Applications Lecture 04 Structure of Ceramics 1 Ref: Barsoum, Fundamentals of Ceramics, Ch03, McGraw-Hill, 2000. Prof. A. K. M. Bazlur Rashid Department of MME, BUET, Dhaka
CHAPTER 12 CHEMICAL BONDING
 CHAPTER 12 CHEMICAL BONDING Core electrons are found close to the nucleus, whereas valence electrons are found in the most distant s and p energy subshells. The valence electrons are responsible for holding
CHAPTER 12 CHEMICAL BONDING Core electrons are found close to the nucleus, whereas valence electrons are found in the most distant s and p energy subshells. The valence electrons are responsible for holding
Nanomaterial: Look at the Earth
 Nanomaterial: Look at the Earth Siddhartha S. Mukhopadhyay Electron Microscopy and Nanoscience Laboratory, Punjab Agricultural University Ludhiana Why clay? The unit cell dimensions of clay minerals are
Nanomaterial: Look at the Earth Siddhartha S. Mukhopadhyay Electron Microscopy and Nanoscience Laboratory, Punjab Agricultural University Ludhiana Why clay? The unit cell dimensions of clay minerals are
A and 4 molecules in the unit cell. Final atomic parameters have been obtained from a blockdiagonal
 Crystal and molecular structure of the m-bromobenzoate derivative of bisnorquassin H. LYNTON Department of Chemistry, Uniuersity of New Brunswick, Fredericton, New Britns~vick Received July 4, 1969 The
Crystal and molecular structure of the m-bromobenzoate derivative of bisnorquassin H. LYNTON Department of Chemistry, Uniuersity of New Brunswick, Fredericton, New Britns~vick Received July 4, 1969 The
Ceramic Bonding. CaF 2 : large SiC: small
 Recall ceramic bonding: - Mixed ionic and covalent. - % ionic character ( f ) increases with difference in electronegativity Large vs small ionic bond character: Ceramic Bonding CaF : large SiC: small
Recall ceramic bonding: - Mixed ionic and covalent. - % ionic character ( f ) increases with difference in electronegativity Large vs small ionic bond character: Ceramic Bonding CaF : large SiC: small
8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds List and define three types of bonding. chapter 8 Bonding General Concepts.notebook. September 10, 2015
 chapter 8 Bonding General Concepts.notebook Chapter 8: Bonding: General Concepts Mar 13 11:15 AM 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds List and define three types of bonding. Bonds are forces that hold groups of
chapter 8 Bonding General Concepts.notebook Chapter 8: Bonding: General Concepts Mar 13 11:15 AM 8.1 Types of Chemical Bonds List and define three types of bonding. Bonds are forces that hold groups of
Chapter 13: Phenomena
 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chemical Bonding. Section 1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding. Section 2 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Compounds
 Chemical Bonding Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Section 2 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Compounds Section 3 Ionic Bonding and Ionic Compounds Section 4 Metallic Bonding Section
Chemical Bonding Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Chemical Bonding Section 2 Covalent Bonding and Molecular Compounds Section 3 Ionic Bonding and Ionic Compounds Section 4 Metallic Bonding Section
EPSC501 Crystal Chemistry WEEK 5
 EPSC501 Crystal Chemistry WEEK 5 Oxidation states of transition elements (many more in aqueous solutions than in the common rock-forming minerals) Notice that almost every transition metal has a +2 oxidation
EPSC501 Crystal Chemistry WEEK 5 Oxidation states of transition elements (many more in aqueous solutions than in the common rock-forming minerals) Notice that almost every transition metal has a +2 oxidation
Redetermination of Crystal Structure of Bis(2,4-pentanedionato)copper(II)
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 20, No. 8 (2008), 5834-5838 Redetermination of Crystal Structure of Bis(2,4-pentanedionato)copper(II) HAMID GLCHUBIAN Department of Chemistry, Mazandaran University, P..
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 20, No. 8 (2008), 5834-5838 Redetermination of Crystal Structure of Bis(2,4-pentanedionato)copper(II) HAMID GLCHUBIAN Department of Chemistry, Mazandaran University, P..
Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule For Lewis structures of covalent compounds least electronegative
 Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule Lewis structures are a basic representation of how atoms are arranged in compounds based on bond formation by the valence electrons. A Lewis dot symbol of an atom
Helpful Hints Lewis Structures Octet Rule Lewis structures are a basic representation of how atoms are arranged in compounds based on bond formation by the valence electrons. A Lewis dot symbol of an atom
Chemical Bonding: Chemical Formulas HL
 Name: Chemical Bonding 5. Chemical Bonding: Chemical Formulas Ionic Bonding Covalent Bonding Electronegativity Shapes of Molecules and Intermolecular Forces Objectives -understand that compounds can be
Name: Chemical Bonding 5. Chemical Bonding: Chemical Formulas Ionic Bonding Covalent Bonding Electronegativity Shapes of Molecules and Intermolecular Forces Objectives -understand that compounds can be
Atoms with a complete outer shell do not react with other atoms. The outer shell is called the valence shell. Its electrons are valence electrons.
 Bonding and the Outer Shell Use this table for reference: http://www.dreamwv.com/primer/page/s_pertab.html Atoms with incomplete shells react with others in a way that allows it to complete the outer shell.
Bonding and the Outer Shell Use this table for reference: http://www.dreamwv.com/primer/page/s_pertab.html Atoms with incomplete shells react with others in a way that allows it to complete the outer shell.
Chapter 13: Phenomena
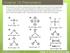 Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
Chapter 13: Phenomena Phenomena: Scientists measured the bond angles of some common molecules. In the pictures below each line represents a bond that contains 2 electrons. If multiple lines are drawn together
EPSC 233. Compositional variation in minerals. Recommended reading: PERKINS, p. 286, 41 (Box 2-4).
 EPSC 233 Compositional variation in minerals Recommended reading: PERKINS, p. 286, 41 (Box 2-4). Some minerals are nearly pure elements. These are grouped under the category of native elements. This includes
EPSC 233 Compositional variation in minerals Recommended reading: PERKINS, p. 286, 41 (Box 2-4). Some minerals are nearly pure elements. These are grouped under the category of native elements. This includes
Chapter 8 Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 8 Chemical Bonding Types of Bonds Ionic Bonding Covalent Bonding Shapes of Molecules 8-1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Table 8.1 Two
Chapter 8 Chemical Bonding Types of Bonds Ionic Bonding Covalent Bonding Shapes of Molecules 8-1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Table 8.1 Two
Periodic Table trends
 2017/2018 Periodic Table trends Mohamed Ahmed Abdelbari Atomic Radius The size of an atom is defined by the edge of its orbital. However, orbital boundaries are fuzzy and in fact are variable under different
2017/2018 Periodic Table trends Mohamed Ahmed Abdelbari Atomic Radius The size of an atom is defined by the edge of its orbital. However, orbital boundaries are fuzzy and in fact are variable under different
Structure of Crystalline Solids
 Structure of Crystalline Solids Solids- Effect of IMF s on Phase Kinetic energy overcome by intermolecular forces C 60 molecule llotropes of Carbon Network-Covalent solid Molecular solid Does not flow
Structure of Crystalline Solids Solids- Effect of IMF s on Phase Kinetic energy overcome by intermolecular forces C 60 molecule llotropes of Carbon Network-Covalent solid Molecular solid Does not flow
Lecture 6 - Bonding in Crystals
 Lecture 6 onding in Crystals inding in Crystals (Kittel Ch. 3) inding of atoms to form crystals A crystal is a repeated array of atoms Why do they form? What are characteristic bonding mechanisms? How
Lecture 6 onding in Crystals inding in Crystals (Kittel Ch. 3) inding of atoms to form crystals A crystal is a repeated array of atoms Why do they form? What are characteristic bonding mechanisms? How
Chemistry primer. Atom = the smallest unit of an element. Element determined by the number of protons in the nucleus
 Chemistry primer Atom = the smallest unit of an element Element determined by the number of protons in the nucleus E- is an electron, P+ is a proton, N is a neutron Carbon atom Electron cloud Nucleus Carbon
Chemistry primer Atom = the smallest unit of an element Element determined by the number of protons in the nucleus E- is an electron, P+ is a proton, N is a neutron Carbon atom Electron cloud Nucleus Carbon
Crystal Models. Figure 1.1 Section of a three-dimensional lattice.
 Crystal Models The Solid-State Structure of Metals and Ionic Compounds Objectives Understand the concept of the unit cell in crystalline solids. Construct models of unit cells for several metallic and
Crystal Models The Solid-State Structure of Metals and Ionic Compounds Objectives Understand the concept of the unit cell in crystalline solids. Construct models of unit cells for several metallic and
Mo 2+, Mo 2+, Cr electrons. Mo-Mo quadruple bond.
 Problem 1 (2 points) 1. Consider the MoMoCr heterotrimetallic complex shown below (Berry, et. al. Inorganica Chimica Acta 2015, p. 241). Metal-metal bonds are not drawn. The ligand framework distorts this
Problem 1 (2 points) 1. Consider the MoMoCr heterotrimetallic complex shown below (Berry, et. al. Inorganica Chimica Acta 2015, p. 241). Metal-metal bonds are not drawn. The ligand framework distorts this
Critical Temperature - the temperature above which the liquid state of a substance no longer exists regardless of the pressure.
 Critical Temperature - the temperature above which the liquid state of a substance no longer exists regardless of the pressure. Critical Pressure - the vapor pressure at the critical temperature. Properties
Critical Temperature - the temperature above which the liquid state of a substance no longer exists regardless of the pressure. Critical Pressure - the vapor pressure at the critical temperature. Properties
CHEM 3013 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I LECTURE NOTES
 M 3013 OAI MIST I LTU OTS 1 APT 1 1. Atomic orbitals a. eisenberg Uncertainty Principle The exact position of an electron cannot be specified; only the probability that it occupies a certain position of
M 3013 OAI MIST I LTU OTS 1 APT 1 1. Atomic orbitals a. eisenberg Uncertainty Principle The exact position of an electron cannot be specified; only the probability that it occupies a certain position of
Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Ms. Grobsky
 Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Ms. Grobsky What Determines the Type of Bonding in Any Substance? Why do Atoms Bond? The key to answering the first question are found in the electronic structure of the atoms
Chemical Bonding AP Chemistry Ms. Grobsky What Determines the Type of Bonding in Any Substance? Why do Atoms Bond? The key to answering the first question are found in the electronic structure of the atoms
