Proteins. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of medicine University of Szeged
|
|
|
- Suzanna Flynn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Proteins
2 Classification Function Structure Connecting peptide parts
3 Synthesis Transcription - nucleus Translation - cytoplasma Posttranslation changes (folding) - endoplasmatic reticulum
4 Amino acids
5 Amino acids
6 Amino acids
7 Structure Primer= order of the aminoacids Secunder= the conformation of the peptide chain alfa-helix, beta-sheet, beta-turn, random coil
8 Structure Suprasecunder: the location of the domains inside the tertier structure Tertier= shape of the peptide chain globular, fibrillar
9 Structure Quaterner= location of the subunits (peptide chains)
10 Folding, Denaturation Protein folding: formation of the native conformation - chaperons features and roles Denaturation: loss of native structure - reasons - reversible (tertier, quaterner structure) - irreversible (secunder)
11 Bioenergetics
12 Termodynamics Isolated system Closed system Open system: material-, energy- and informationtransport, if the entropy level is low - Energy source: C-atom (oxidation)
13 Free entalpy-change A + B C + D G = Go + RT ln ( [C] [D] / [A] [B] ) = Go + RT lnk G = Gproducts - Gstarting materials +: endergon; 0: balance; -: exergon
14
15 Linked reactions
16 Role of the enzymes: the decrease of the activation energy
17 Macroerg compounds Macroerg binding (>30kJ) containing molecules Carbamil-phosphate phosphoenol-piruvate
18 Macroerg compounds 1,3-bifosphoglycerate Creatine-phosphate
19 Macroerg compounds Cyclic adenosine-monophosphate Adenosine-triphosphate
20 Enzymes
21 General features Biocatalisator Definers of velocity, specificity, direction of the reaction Conditions of the optimal work: temperature, ph, ions
22 Models of substrate binding A: Lock and key model B: Induced fit C: Fluktuation
23 Types of enzyme catalysis Kovalent catalysis - temporary kovalent binding (side chains) instabile intermedier - eg.: trypsin, etc.
24 Types of enzyme catalysis Acid-basis - H+ absorbation/adsorbation (acidic and basical side chains) - eg.: ribonuclease
25 Types of enzymecatalysis Metal ione-catalysis - temporary binding to a metal ion deformation, tension of the binding - carbonic acid-anhydrase Entropy-effect - temporary decrease of the entropy the chance of the proper collision is elevated
26 Enzyme classes Nomenclature: 1. class - 2. subclass - 3. group - 4. concrete enzyme 1.: Oxydoreductases - oxidases, oxigenases, reductases, etc. - eg.:glycerine aldehide-3-phosphatedehydrogenase 2.: Transferases - kinases, transaldolases, transketolases, transferases - eg.: hexokinase, glucokinase
27 Enzyme classes Hidrolases - phosphatases, esterases, etc. - eg.: glucose-6-phoszphatase Liases - C-C, C-O, C-N, C-S, C-O liases, subtypes - eg.: aldolase
28 Enzyme classes Isomerases - cis-trans isomerases, intramolecular isomerases, etc. - eg.: triose phosphate-isomerase Ligases - C-O, C-S, C-N, C-C, P-ester, N-Me binding producers - eg.: piruvate-carboxylase
29 Coenzymes Necessary for the enzyme s work, but not protein Role: energytransfer, chargetransfer, acilgroup transfer Prostetic group
30 Nutritients with coenzyme-function Metal ions and atoms - eg.: Fe2+ - cytocrome-oxydase, Mg2+ - glucokinase, Se glutatione-peroxydase Vitamins - eg.: B1-vitamine (tiamin) tiamin-pirophosphate aldehids piruvate acid-dehydrogenase Folic acid (B9) - tetrahidrofolate (THF) one C atomic groups timidilate synthase
31 Coenzymes of oxydoreductases 1. Nicotinamide-adenin-dinucleotide (-phosphate; NAD + & NADP + ; vitamine B 3, niacin) eg. -alcohol dehydrogenase -lactate dehydrogenase
32 2. a) Flavin-mononucleotide (FMN; vitamine B 2, riboflavin) eg. -NADH dehydrogenase 2. b) Flavin-adenin-dinucleotide (FAD) eg. -succinate dehydrogenase -acyl-coa-dehydrogenase Faculty riboflavin medicine
33 3. Lipoic acid (dithio octanic acid) eg. -pyruvate dehydrogenase Dihydro lipoic acid 4. Tetrahydrobiopteryn (THB, BH 4 ) eg. -tyrosine hydroxylase -nitrogen monoxide synthase
34 5. Coenzyme Q (Q9 or Q10 coenzyme, ubiquinone) eg. mtchrial respiratory chain Complex I & II
35 1. S-adenosyl-methionine (SAM) eg. -choline acetyl transferase Coenzymes for transferases 2. Tetrahydrofolate (THF, FH 4 ; folate, pteroylglutamate, vitamine B 9 ) methylmethylenemethenylformylformimino- THF Eg.: thymidilate synthase -purine nucleotide synthesis
36 3. biotin (vitamine H) eg. -pyruvate carboxylase -acetyl-coa carboxylase -propionyl-coa carboxylase 4. Thiamine pirophosphate (TPP; thiamine, vitamine B 1 ) eg. -Pyruvate dehydrogenase
37 5. Coenzyme A (CoA; panthotenic acid, vitamine B 5 ) adenosine panthotenic acid thioethanolamine eg. -fatty acid/ketone body/cholesterol synthesis -pyruvate dehydrogenase 6. Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP; adermine, vitamine B 6 ) eg. -transaminase reactions: - Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) - Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
38 7. adenosine-triphosphate (ATP) eg. -hexokinase 9. cytidine triphosphate (CTP) eg. -CTP:phosphocholine cytidil transferase 8. cyclic adenosine monophosphate (camp) 10. uridine triphosphate (UTP) eg. -UDP glucuronyl transferase
39 phosphoadenosine-5 -phosphosulfate (PAPS; active sulfate) eg. -sulfotransferases 12. Cobalamine (vitamine B12) eg. -methyl malonyl CoA mutase -homocystein methyl transferase
40 Coenzymes for lyases 1. thiamine PP 2. pyridoxal P (see at transferases) 3. biotin Coenzymes for isomerases 1. NADH (see at oxidoreductases) 2. cobalamine (see at transferases) 3. pyridoxal phosphate (see at transferases) Coenzymes for ligases 1. Nucleoside triphosphates (ATP, GTP, UTP, CTP; see at transferases) 2. NADH (see at oxidoreductases)
41 Multienzyme system Meaning: Entirety of closely working enzymes that catalyses different steps of the same reaction chain. Closely placed in the space eg.: fatty acid synthase S A B C P E1 E2 E3 E4
42 Kinetics of the enzyme reaction 0 order: the velocity of the reaction is not affected by the concentration 1st order: the velocity affected by the starting concentration 2nd order: the velocity is affected by the concentration of two materials
43 The kinetics of the enzyme reaction Michaelis-Menten model: the velocity of the reaction depends on the S concentration - saturation curve k 1 E + S ES E + P K -1 Conditions: -. At the beginning the [P] is small, thus velocity (v) of the backforming is minimal, k 2 process occurs irreversible - [S]>>[E] - free [S] = initial [S] (for the initial [S] to [P] is minimal) k 2
44 The kinetics of the enzyme reaction v of ES production V of ES elimination k 1 [E][S] = k -1 [ES] + k 2 [ES] k 1 [E][S] = (k -1 + k 2 )[ES] [E][S] = (k -1 + k 2 )[ES] k 1 K M = [S], where the v is the half of v max Briggs-Halden formula: v = v max [S] [S] + K M
45 The kinetics of the enzyme reactionthe direct linearisation
46 The kinetics of the enzyme reaction Linewaver-Burk form Take the reciproke 1 K M + [S] v [S]v max
47 Regulation of the enzyme-function Kovalens modification Limited proteolysis Gene induction Allosterical regulation Compartmentalisation Inhibition
48 Modulation of the enzyme activity Competitive - substrate (S) & inhibitor (I) contest for the same site - K M, v max ø - pl.: phrosphofructokinase ATP E + S ES E + P + I EI
49 Modulation of the enzyme activity nonkompetitive - inhibitor inhibits the catalysis by binding to another site - KM ø, vmax - eg.: metal ions (Zn 2+ carbonic acid anhydrase) E + S ES E + P + I + I EI + S EIS
50 Modulation of the enzyme activity uncompetitive - inhibitor binds to an alternative form of the enzyme - KM, vmax E + S ES E + P + I EIS
Chapter 6: Outline-2. Chapter 6: Outline Properties of Enzymes. Introduction. Activation Energy, E act. Activation Energy-2
 Chapter 6: Outline- Properties of Enzymes Classification of Enzymes Enzyme inetics Michaelis-Menten inetics Lineweaver-Burke Plots Enzyme Inhibition Catalysis Catalytic Mechanisms Cofactors Chapter 6:
Chapter 6: Outline- Properties of Enzymes Classification of Enzymes Enzyme inetics Michaelis-Menten inetics Lineweaver-Burke Plots Enzyme Inhibition Catalysis Catalytic Mechanisms Cofactors Chapter 6:
Chapter 8 Metabolism: Energy, Enzymes, and Regulation
 Chapter 8 Metabolism: Energy, Enzymes, and Regulation Energy: Capacity to do work or cause a particular change. Thus, all physical and chemical processes are the result of the application or movement of
Chapter 8 Metabolism: Energy, Enzymes, and Regulation Energy: Capacity to do work or cause a particular change. Thus, all physical and chemical processes are the result of the application or movement of
Catalysis. Instructor: Dr. Tsung-Lin Li Genomics Research Center Academia Sinica
 Catalysis Instructor: Dr. Tsung-Lin Li Genomics Research Center Academia Sinica References: Biochemistry" by Donald Voet and Judith G. Voet Biochemistry" by Christopher K. Mathews, K. E. Van Hold and Kevin
Catalysis Instructor: Dr. Tsung-Lin Li Genomics Research Center Academia Sinica References: Biochemistry" by Donald Voet and Judith G. Voet Biochemistry" by Christopher K. Mathews, K. E. Van Hold and Kevin
Biologic catalysts 1. Shared properties with chemical catalysts a. Enzymes are neither consumed nor produced during the course of a reaction. b.
 Enzyme definition Enzymes are protein catalysts that increase the velocity of a chemical reaction and are not consumed during the reaction they catalyze. [Note: Some types of RNA can act like enzymes,
Enzyme definition Enzymes are protein catalysts that increase the velocity of a chemical reaction and are not consumed during the reaction they catalyze. [Note: Some types of RNA can act like enzymes,
ENZYMES. by: Dr. Hadi Mozafari
 ENZYMES by: Dr. Hadi Mozafari 1 Specifications Often are Polymers Have a protein structures Enzymes are the biochemical reactions Katalyzers Enzymes are Simple & Complex compounds 2 Enzymatic Reactions
ENZYMES by: Dr. Hadi Mozafari 1 Specifications Often are Polymers Have a protein structures Enzymes are the biochemical reactions Katalyzers Enzymes are Simple & Complex compounds 2 Enzymatic Reactions
Biochemistry 462a - Enzyme Kinetics Reading - Chapter 8 Practice problems - Chapter 8: (not yet assigned); Enzymes extra problems
 Biochemistry 462a - Enzyme Kinetics Reading - Chapter 8 Practice problems - Chapter 8: (not yet assigned); Enzymes extra problems Introduction Enzymes are Biological Catalysis A catalyst is a substance
Biochemistry 462a - Enzyme Kinetics Reading - Chapter 8 Practice problems - Chapter 8: (not yet assigned); Enzymes extra problems Introduction Enzymes are Biological Catalysis A catalyst is a substance
Unit 3. Enzymes. Catalysis and enzyme kinetics.
 Unit 3 Enzymes. Catalysis and enzyme kinetics. OUTLINE 3.1. Characteristics of biological catalysts. Coenzymes, cofactors, vitamins Enzyme nomenclature and classification 3.2. Enzyme catalysis. Transition
Unit 3 Enzymes. Catalysis and enzyme kinetics. OUTLINE 3.1. Characteristics of biological catalysts. Coenzymes, cofactors, vitamins Enzyme nomenclature and classification 3.2. Enzyme catalysis. Transition
What is an enzyme? Lecture 12: Enzymes & Kinetics I Introduction to Enzymes and Kinetics. Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 KEY FEATURES OF ENZYMES
 Lecture 12: Enzymes & Kinetics I Introduction to Enzymes and Kinetics Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 What is an enzyme? General Properties Mostly proteins, but some are actually RNAs Biological catalysts
Lecture 12: Enzymes & Kinetics I Introduction to Enzymes and Kinetics Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2004 What is an enzyme? General Properties Mostly proteins, but some are actually RNAs Biological catalysts
What is an enzyme? Lecture 12: Enzymes & Kinetics I Introduction to Enzymes and Kinetics. Margaret A. Daugherty Fall General Properties
 Lecture 12: Enzymes & Kinetics I Introduction to Enzymes and Kinetics Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 ENZYMES: Why, what, when, where, how? All but the who! What: proteins that exert kinetic control over
Lecture 12: Enzymes & Kinetics I Introduction to Enzymes and Kinetics Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 ENZYMES: Why, what, when, where, how? All but the who! What: proteins that exert kinetic control over
Chapter 8: Energy and Metabolism
 Chapter 8: Energy and Metabolism Why do organisms need energy? How do organisms manage their energy needs? Defining terms and issues: energy and thermodynamics metabolic reactions and energy transfers
Chapter 8: Energy and Metabolism Why do organisms need energy? How do organisms manage their energy needs? Defining terms and issues: energy and thermodynamics metabolic reactions and energy transfers
Lecture 7: Enzymes and Energetics
 Lecture 7: Enzymes and Energetics I. Biological Background A. Biological work requires energy 1. Energy is the capacity to do work a. Energy is expressed in units of work (kilojoules) or heat energy (kilocalories)
Lecture 7: Enzymes and Energetics I. Biological Background A. Biological work requires energy 1. Energy is the capacity to do work a. Energy is expressed in units of work (kilojoules) or heat energy (kilocalories)
Enzymes I. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester,
 Enzymes I Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources Mark's Basic Medical Biochemistry Other resources NCBI Bookshelf: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=books The Medical Biochemistry
Enzymes I Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources Mark's Basic Medical Biochemistry Other resources NCBI Bookshelf: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=books The Medical Biochemistry
I. Enzymes as Catalysts Chapter 4
 8/29/11 I. Enzymes as Catalysts Chapter 4 Enzymes and Energy Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Enzymes Activation Energy A class
8/29/11 I. Enzymes as Catalysts Chapter 4 Enzymes and Energy Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Enzymes Activation Energy A class
Part II => PROTEINS and ENZYMES. 2.5 Enzyme Properties 2.5a Enzyme Nomenclature 2.5b Transition State Theory
 Part II => PROTEINS and ENZYMES 2.5 Enzyme Properties 2.5a Enzyme Nomenclature 2.5b Transition State Theory Section 2.5a: Enzyme Nomenclature Synopsis 2.5a - Enzymes are biological catalysts they are almost
Part II => PROTEINS and ENZYMES 2.5 Enzyme Properties 2.5a Enzyme Nomenclature 2.5b Transition State Theory Section 2.5a: Enzyme Nomenclature Synopsis 2.5a - Enzymes are biological catalysts they are almost
Enzymes and kinetics. Eva Samcová and Petr Tůma
 Enzymes and kinetics Eva Samcová and Petr Tůma Termodynamics and kinetics Equilibrium state ΔG 0 = -RT lnk eq ΔG < 0 products predominate ΔG > 0 reactants predominate Rate of a chemical reaction Potential
Enzymes and kinetics Eva Samcová and Petr Tůma Termodynamics and kinetics Equilibrium state ΔG 0 = -RT lnk eq ΔG < 0 products predominate ΔG > 0 reactants predominate Rate of a chemical reaction Potential
Basic Concepts of Enzyme Action. Enzymes. Rate Enhancement 9/17/2015. Stryer Short Course Chapter 6
 Basic Concepts of Enzyme Action Stryer Short Course Chapter 6 Enzymes Biocatalysts Active site Substrate and product Catalyzed rate Uncatalyzed rate Rate Enhancement Which is a better catalyst, carbonic
Basic Concepts of Enzyme Action Stryer Short Course Chapter 6 Enzymes Biocatalysts Active site Substrate and product Catalyzed rate Uncatalyzed rate Rate Enhancement Which is a better catalyst, carbonic
CHAPTER 15 Metabolism: Basic Concepts and Design
 CHAPTER 15 Metabolism: Basic Concepts and Design Chapter 15 An overview of Metabolism Metabolism is the sum of cellular reactions - Metabolism the entire network of chemical reactions carried out by living
CHAPTER 15 Metabolism: Basic Concepts and Design Chapter 15 An overview of Metabolism Metabolism is the sum of cellular reactions - Metabolism the entire network of chemical reactions carried out by living
Enzyme Catalysis & Biotechnology
 L28-1 Enzyme Catalysis & Biotechnology Bovine Pancreatic RNase A Biochemistry, Life, and all that L28-2 A brief word about biochemistry traditionally, chemical engineers used organic and inorganic chemistry
L28-1 Enzyme Catalysis & Biotechnology Bovine Pancreatic RNase A Biochemistry, Life, and all that L28-2 A brief word about biochemistry traditionally, chemical engineers used organic and inorganic chemistry
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY SEMMELWEIS CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY SEMMELWEIS CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Chapter 8. Enzymes: basic concept and kinetics
 Chapter 8 Enzymes: basic concept and kinetics Learning objectives: mechanism of enzymatic catalysis Michaelis -Menton Model Inhibition Single Molecule of Enzymatic Reaction Enzymes: catalysis chemical
Chapter 8 Enzymes: basic concept and kinetics Learning objectives: mechanism of enzymatic catalysis Michaelis -Menton Model Inhibition Single Molecule of Enzymatic Reaction Enzymes: catalysis chemical
Enzymes. Dr.Anupam Porwal Assistant Professor Dept. Of Biotechnology
 1 Enzymes Dr.Anupam Porwal Assistant Professor Dept. Of Biotechnology 2 What Are Enzymes? Most enzymes are Proteins (tertiary and quaternary structures) except for a class of RNA modifying catalysts known
1 Enzymes Dr.Anupam Porwal Assistant Professor Dept. Of Biotechnology 2 What Are Enzymes? Most enzymes are Proteins (tertiary and quaternary structures) except for a class of RNA modifying catalysts known
Chapter 6 Overview. Enzymes. Catalysis most important function of proteins. Globular protein Increase rate of metabolic processes
 Chapter 6 Overview Enzymes Catalysis most important function of proteins n Enzymes protein catalysts Globular protein Increase rate of metabolic processes Enzymes kinetics info on reaction rates & measure
Chapter 6 Overview Enzymes Catalysis most important function of proteins n Enzymes protein catalysts Globular protein Increase rate of metabolic processes Enzymes kinetics info on reaction rates & measure
Outline. Metabolism: Energy and Enzymes. Forms of Energy. Chapter 6
 Metabolism: Energy and Enzymes Chapter 6 Forms of Energy Outline Laws of Thermodynamics Metabolic Reactions ATP Metabolic Pathways Energy of Activation Enzymes Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration 1 2 Forms
Metabolism: Energy and Enzymes Chapter 6 Forms of Energy Outline Laws of Thermodynamics Metabolic Reactions ATP Metabolic Pathways Energy of Activation Enzymes Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration 1 2 Forms
Photosynthetic autotrophs use the energy of sunlight to convert low-g CO 2 and H 2 O into energy-rich complex sugar molecules.
 Chapters 7 & 10 Bioenergetics To live, organisms must obtain energy from their environment and use it to do the work of building and organizing cell components such as proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids,
Chapters 7 & 10 Bioenergetics To live, organisms must obtain energy from their environment and use it to do the work of building and organizing cell components such as proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids,
P. Wipf - Chem /8/2006. Boger Notes: p (Chapters IV & V) Carey/Sundberg: B p (Chapter B )
 P. Wipf - Chem 2320 1 2/8/2006 I. Basic Principles ID. Oxidation Reactions - Continued Boger Notes: p. 41-94 (Chapters IV & V) Carey/Sundberg: B p. 757-820 (Chapter B 12.2-12.7) Phenol Oxidation [PhI(OAc)
P. Wipf - Chem 2320 1 2/8/2006 I. Basic Principles ID. Oxidation Reactions - Continued Boger Notes: p. 41-94 (Chapters IV & V) Carey/Sundberg: B p. 757-820 (Chapter B 12.2-12.7) Phenol Oxidation [PhI(OAc)
Enzymes and Enzyme Kinetics I. Dr.Nabil Bashir
 Enzymes and Enzyme Kinetics I Dr.Nabil Bashir Enzymes and Enzyme Kinetics I: Outlines Enzymes - Basic Concepts and Kinetics Enzymes as Catalysts Enzyme rate enhancement / Enzyme specificity Enzyme cofactors
Enzymes and Enzyme Kinetics I Dr.Nabil Bashir Enzymes and Enzyme Kinetics I: Outlines Enzymes - Basic Concepts and Kinetics Enzymes as Catalysts Enzyme rate enhancement / Enzyme specificity Enzyme cofactors
(kilo ) or heat energy (kilo ) C. Organisms carry out conversions between potential energy and kinetic energy 1. Potential energy is energy;
 I. Biological work requires energy A. Energy is the to do work B. Energy is expressed in units of work (kilo ) or heat energy (kilo ) C. Organisms carry out conversions between potential energy and kinetic
I. Biological work requires energy A. Energy is the to do work B. Energy is expressed in units of work (kilo ) or heat energy (kilo ) C. Organisms carry out conversions between potential energy and kinetic
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 8
 Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 8 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University January 28, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 8 January 28, 2013 1 / 33 Outline Questions and answers Energy and
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 8 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University January 28, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 8 January 28, 2013 1 / 33 Outline Questions and answers Energy and
The products have more enthalpy and are more ordered than the reactants.
 hapters 7 & 10 Bioenergetics To live, organisms must obtain energy from their environment and use it to do the work of building and organizing cell components such as proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids,
hapters 7 & 10 Bioenergetics To live, organisms must obtain energy from their environment and use it to do the work of building and organizing cell components such as proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids,
Introduction to Enzymes
 Introduction to Enzymes Lysozyme active site Chapter 8 Part 1 HIV-1 Protease with bound Inhibitor Dr. Ray How Enzymes Function What structural features allow an enzyme to have its unique biochemical function?
Introduction to Enzymes Lysozyme active site Chapter 8 Part 1 HIV-1 Protease with bound Inhibitor Dr. Ray How Enzymes Function What structural features allow an enzyme to have its unique biochemical function?
Enzymes and Protein Structure
 Enzymes and Protein Structure Last Week PTM s We (Re)Learned About Primary Structure And Tertiary Structure S-Q-D-A-G-M-Q-Q-G-A-D-M-D-Q-V-S-A Secondary Structure Enzymes What are these crazy things called
Enzymes and Protein Structure Last Week PTM s We (Re)Learned About Primary Structure And Tertiary Structure S-Q-D-A-G-M-Q-Q-G-A-D-M-D-Q-V-S-A Secondary Structure Enzymes What are these crazy things called
Chapter 5. Energy Flow in the Life of a Cell
 Chapter 5 Energy Flow in the Life of a Cell Including some materials from lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Ammended by John Crocker Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.. Review
Chapter 5 Energy Flow in the Life of a Cell Including some materials from lectures by Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida Ammended by John Crocker Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.. Review
C. Incorrect! Catalysts themselves are not altered or consumed during the reaction.
 Human Physiology - Problem Drill 04: Enzymes and Energy Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed, (3) Pick the answer,
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 04: Enzymes and Energy Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as needed, (3) Pick the answer,
Energy and Cellular Metabolism
 1 Chapter 4 About This Chapter Energy and Cellular Metabolism 2 Energy in biological systems Chemical reactions Enzymes Metabolism Figure 4.1 Energy transfer in the environment Table 4.1 Properties of
1 Chapter 4 About This Chapter Energy and Cellular Metabolism 2 Energy in biological systems Chemical reactions Enzymes Metabolism Figure 4.1 Energy transfer in the environment Table 4.1 Properties of
BCMB 3100 Chapters 6,7,8 Enzyme Basics. Six Classes (IUBMB) Kinetics Michaelis-Menten Equation Vo, Km, Vmax, Kcat Lineweaver-Burk Plot
 BCMB 3100 Chapters 6,7,8 Enzyme Basics Six Classes (IUBMB) Kinetics Enzymes are biological macromolecules that increase the rate of the reaction. Six major groups of enzymes (pgs. 94-95/98-99) Oxidoreductases:
BCMB 3100 Chapters 6,7,8 Enzyme Basics Six Classes (IUBMB) Kinetics Enzymes are biological macromolecules that increase the rate of the reaction. Six major groups of enzymes (pgs. 94-95/98-99) Oxidoreductases:
Introduction and. Properties of Enzymes
 Unit-III Enzymes Contents 1. Introduction and Properties of enzymes 2. Nomenclature and Classification 3. Mechanism of enzyme-catalyzed reactions 4. Kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions 5. Inhibition
Unit-III Enzymes Contents 1. Introduction and Properties of enzymes 2. Nomenclature and Classification 3. Mechanism of enzyme-catalyzed reactions 4. Kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions 5. Inhibition
BCMB 3100 Chapters 6,7,8 Enzyme Basics. Six Classes (IUBMB) Kinetics Michaelis-Menten Equation Vo, Km, Vmax, Kcat Lineweaver-Burk Plot
 BCMB 3100 Chapters 6,7,8 Enzyme Basics Six Classes (IUBMB) Kinetics Michaelis-Menten Equation Vo, Km, Vmax, Kcat Lineweaver-Burk Plot Enzymes are biological macromolecules that increase the rate of the
BCMB 3100 Chapters 6,7,8 Enzyme Basics Six Classes (IUBMB) Kinetics Michaelis-Menten Equation Vo, Km, Vmax, Kcat Lineweaver-Burk Plot Enzymes are biological macromolecules that increase the rate of the
BCMB 3100 Chapters 6,7,8 Enzyme Basics. Six Classes (IUBMB) Kinetics Michaelis-Menten Equation Vo, Km, Vmax, Kcat Lineweaver-Burk Plot
 BCMB 3100 Chapters 6,7,8 Enzyme Basics Six Classes (IUBMB) Kinetics Michaelis-Menten Equation Vo, Km, Vmax, Kcat Lineweaver-Burk Plot Enzymes are biological macromolecules that increase the rate of the
BCMB 3100 Chapters 6,7,8 Enzyme Basics Six Classes (IUBMB) Kinetics Michaelis-Menten Equation Vo, Km, Vmax, Kcat Lineweaver-Burk Plot Enzymes are biological macromolecules that increase the rate of the
I. Flow of Energy in Living Things II. Laws of Thermodynamics & Free Energy III. Activation Energy IV. Enzymes V. Reaction Coupling VI.
 Chapter 6 Energy & Metabolism I. Flow of Energy in Living Things II. Laws of Thermodynamics & Free Energy III. Activation Energy IV. Enzymes V. Reaction Coupling VI. Metabolism I. Flow of Energy in Living
Chapter 6 Energy & Metabolism I. Flow of Energy in Living Things II. Laws of Thermodynamics & Free Energy III. Activation Energy IV. Enzymes V. Reaction Coupling VI. Metabolism I. Flow of Energy in Living
BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE. Lecture Presentation by Cindy S. Malone, PhD, California State University Northridge. FIFTH EDITION Freeman Quillin Allison
 BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE FIFTH EDITION Freeman Quillin Allison 8 Lecture Presentation by Cindy S. Malone, PhD, California State University Northridge Roadmap 8 In this chapter you will learn how Enzymes use
BIOLOGICAL SCIENCE FIFTH EDITION Freeman Quillin Allison 8 Lecture Presentation by Cindy S. Malone, PhD, California State University Northridge Roadmap 8 In this chapter you will learn how Enzymes use
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of Lethbridge. Biochemistry II. Bioenergetics
 Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of Lethbridge II. Bioenergetics Slide 1 Bioenergetics Bioenergetics is the quantitative study of energy relationships and energy conversion in biological
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of Lethbridge II. Bioenergetics Slide 1 Bioenergetics Bioenergetics is the quantitative study of energy relationships and energy conversion in biological
ATP ATP. The energy needs of life. Living economy. Where do we get the energy from? 9/11/2015. Making energy! Organisms are endergonic systems
 Making energy! ATP The energy needs of life rganisms are endergonic systems What do we need energy for? synthesis building biomolecules reproduction movement active transport temperature regulation 2007-2008
Making energy! ATP The energy needs of life rganisms are endergonic systems What do we need energy for? synthesis building biomolecules reproduction movement active transport temperature regulation 2007-2008
Biological Chemistry and Metabolic Pathways
 Biological Chemistry and Metabolic Pathways 1. Reaction a. Thermodynamics b. Kinetics 2. Enzyme a. Structure and Function b. Regulation of Activity c. Kinetics d. Inhibition 3. Metabolic Pathways a. REDOX
Biological Chemistry and Metabolic Pathways 1. Reaction a. Thermodynamics b. Kinetics 2. Enzyme a. Structure and Function b. Regulation of Activity c. Kinetics d. Inhibition 3. Metabolic Pathways a. REDOX
Chapter Cells and the Flow of Energy A. Forms of Energy 1. Energy is capacity to do work; cells continually use energy to develop, grow,
 Chapter 6 6.1 Cells and the Flow of Energy A. Forms of Energy 1. Energy is capacity to do work; cells continually use energy to develop, grow, repair, reproduce, etc. 2. Kinetic energy is energy of motion;
Chapter 6 6.1 Cells and the Flow of Energy A. Forms of Energy 1. Energy is capacity to do work; cells continually use energy to develop, grow, repair, reproduce, etc. 2. Kinetic energy is energy of motion;
GO ID GO term Number of members GO: translation 225 GO: nucleosome 50 GO: calcium ion binding 76 GO: structural
 GO ID GO term Number of members GO:0006412 translation 225 GO:0000786 nucleosome 50 GO:0005509 calcium ion binding 76 GO:0003735 structural constituent of ribosome 170 GO:0019861 flagellum 23 GO:0005840
GO ID GO term Number of members GO:0006412 translation 225 GO:0000786 nucleosome 50 GO:0005509 calcium ion binding 76 GO:0003735 structural constituent of ribosome 170 GO:0019861 flagellum 23 GO:0005840
A. Reaction Mechanisms and Catalysis (1) proximity effect (2) acid-base catalysts (3) electrostatic (4) functional groups (5) structural flexibility
 (P&S Ch 5; Fer Ch 2, 9; Palm Ch 10,11; Zub Ch 9) A. Reaction Mechanisms and Catalysis (1) proximity effect (2) acid-base catalysts (3) electrostatic (4) functional groups (5) structural flexibility B.
(P&S Ch 5; Fer Ch 2, 9; Palm Ch 10,11; Zub Ch 9) A. Reaction Mechanisms and Catalysis (1) proximity effect (2) acid-base catalysts (3) electrostatic (4) functional groups (5) structural flexibility B.
Principles of Bioenergetics. Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 14
 1 Principles of Bioenergetics Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 14 2 Metabolism A highly coordinated cellular activity aimed at achieving the following goals: Obtain chemical energy. Convert nutrient molecules
1 Principles of Bioenergetics Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 14 2 Metabolism A highly coordinated cellular activity aimed at achieving the following goals: Obtain chemical energy. Convert nutrient molecules
2054, Chap. 8, page 1
 2054, Chap. 8, page 1 I. Metabolism: Energetics, Enzymes, and Regulation (Chapter 8) A. Energetics and work 1. overview a. energy = ability to do work (1) chemical, transport, mechanical (2) ultimate source
2054, Chap. 8, page 1 I. Metabolism: Energetics, Enzymes, and Regulation (Chapter 8) A. Energetics and work 1. overview a. energy = ability to do work (1) chemical, transport, mechanical (2) ultimate source
BIOCHEMISTRY. František Vácha. JKU, Linz.
 BIOCHEMISTRY František Vácha http://www.prf.jcu.cz/~vacha/ JKU, Linz Recommended reading: D.L. Nelson, M.M. Cox Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry D.J. Voet, J.G. Voet, C.W. Pratt Principles of Biochemistry
BIOCHEMISTRY František Vácha http://www.prf.jcu.cz/~vacha/ JKU, Linz Recommended reading: D.L. Nelson, M.M. Cox Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry D.J. Voet, J.G. Voet, C.W. Pratt Principles of Biochemistry
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Metabolism*
 Chapter 6- An Introduction to Metabolism* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. The Energy of Life
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Metabolism* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. The Energy of Life
BIOCHEMISTRY/MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 Enzymes Activation Energy Chemical reactions require an initial input of energy activation energy large biomolecules are stable must absorb energy to break bonds cellulose energy CO 2 + H 2 O + heat Activation
Enzymes Activation Energy Chemical reactions require an initial input of energy activation energy large biomolecules are stable must absorb energy to break bonds cellulose energy CO 2 + H 2 O + heat Activation
Chemistry 1506: Allied Health Chemistry 2. Section 10: Enzymes. Biochemical Catalysts. Outline
 Chemistry 1506 Dr. Hunter s Class Section 10 Notes - Page 1/14 Chemistry 1506: Allied Health Chemistry 2 Section 10: Enzymes Biochemical Catalysts. Outline SECTION 10.1 INTRODUCTION...2 SECTION SECTION
Chemistry 1506 Dr. Hunter s Class Section 10 Notes - Page 1/14 Chemistry 1506: Allied Health Chemistry 2 Section 10: Enzymes Biochemical Catalysts. Outline SECTION 10.1 INTRODUCTION...2 SECTION SECTION
CHAPTER 8. An Introduction to Metabolism
 CHAPTER 8 An Introduction to Metabolism WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW: Examples of endergonic and exergonic reactions. The key role of ATP in energy coupling. That enzymes work by lowering the energy of activation.
CHAPTER 8 An Introduction to Metabolism WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW: Examples of endergonic and exergonic reactions. The key role of ATP in energy coupling. That enzymes work by lowering the energy of activation.
BIOCHEMISTRY - CLUTCH REVIEW 2.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BINDING AFFINITY Protein-ligand binding is reversible, like a chemical equilibrium [S] substrate concentration [E] enzyme concentration Ligands bind to proteins via the same
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BINDING AFFINITY Protein-ligand binding is reversible, like a chemical equilibrium [S] substrate concentration [E] enzyme concentration Ligands bind to proteins via the same
Enzyme Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of
 Enzyme Enzyme Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme
Enzyme Enzyme Enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts. Enzymes accelerate, or catalyze, chemical reactions. The molecules at the beginning of the process are called substrates and the enzyme
Metabolism and Enzymes
 Energy Basics Metabolism and Enzymes Chapter 5 Pgs. 77 86 Chapter 8 Pgs. 142 162 Energy is the capacity to cause change, and is required to do work. Very difficult to define quantity. Two types of energy:
Energy Basics Metabolism and Enzymes Chapter 5 Pgs. 77 86 Chapter 8 Pgs. 142 162 Energy is the capacity to cause change, and is required to do work. Very difficult to define quantity. Two types of energy:
Basic Concepts of Metabolism. Stages of Catabolism. Key intermediates 10/12/2015. Chapter 15, Stryer Short Course
 Basic Concepts of Metabolism Chapter 15, Stryer Short Course Digestion Formation of key intermediate small molecules Formation of ATP Stages of Catabolism Key intermediates 1 Fundamental Needs for Energy
Basic Concepts of Metabolism Chapter 15, Stryer Short Course Digestion Formation of key intermediate small molecules Formation of ATP Stages of Catabolism Key intermediates 1 Fundamental Needs for Energy
Biochemistry 3300 Problems (and Solutions) Metabolism I
 (1) Provide a reasonable systematic name for an enzyme that catalyzes the following reaction: fructose + ATP > fructose-1 phosphate + ADP (2) The IUBMB has a developed a set of rules for classifying enzymes
(1) Provide a reasonable systematic name for an enzyme that catalyzes the following reaction: fructose + ATP > fructose-1 phosphate + ADP (2) The IUBMB has a developed a set of rules for classifying enzymes
Life 21 - Aerobic respiration Raven & Johnson Chapter 9 (parts)
 1 Life 21 - Aerobic respiration Raven & Johnson Chapter 9 (parts) Objectives 1: Describe the overall action of the Krebs cycle in generating ATP, NADH and FADH 2 from acetyl-coa 2: Understand the generation
1 Life 21 - Aerobic respiration Raven & Johnson Chapter 9 (parts) Objectives 1: Describe the overall action of the Krebs cycle in generating ATP, NADH and FADH 2 from acetyl-coa 2: Understand the generation
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
 Lecture 13 9/30/05 I. General Principles Cellular Respiration: arvesting Chemical Energy Chapter 9 Lecture utline 1. Regulation of Enzymes: competitive, allosteric, phosphorylation 2. Equilibrium 3. Digestion
Lecture 13 9/30/05 I. General Principles Cellular Respiration: arvesting Chemical Energy Chapter 9 Lecture utline 1. Regulation of Enzymes: competitive, allosteric, phosphorylation 2. Equilibrium 3. Digestion
Metabolism and enzymes
 Metabolism and enzymes 4-11-16 What is a chemical reaction? A chemical reaction is a process that forms or breaks the chemical bonds that hold atoms together Chemical reactions convert one set of chemical
Metabolism and enzymes 4-11-16 What is a chemical reaction? A chemical reaction is a process that forms or breaks the chemical bonds that hold atoms together Chemical reactions convert one set of chemical
Chem Lecture 4 Enzymes Part 1
 Chem 452 - Lecture 4 Enzymes Part 1 Question of the Day: Enzymes are biological catalysts. Based on your general understanding of catalysts, what does this statement imply about enzymes? Introduction Enzymes
Chem 452 - Lecture 4 Enzymes Part 1 Question of the Day: Enzymes are biological catalysts. Based on your general understanding of catalysts, what does this statement imply about enzymes? Introduction Enzymes
Ch 4: Cellular Metabolism, Part 1
 Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Ch 4: Cellular Metabolism, Part 1 Energy as it relates to Biology Energy for synthesis and movement Energy transformation Enzymes and how they speed reactions Metabolism
Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Ch 4: Cellular Metabolism, Part 1 Energy as it relates to Biology Energy for synthesis and movement Energy transformation Enzymes and how they speed reactions Metabolism
Exam 4 April 15, 2005 CHEM 3511 Print Name: KEY Signature
 1) (8 pts) General Properties of Enzymes. Give four properties of enzymaticallycatalyzed reactions. The answers should indicate how enzymatic reactions differ from non-enzymatic reactions. Write four only
1) (8 pts) General Properties of Enzymes. Give four properties of enzymaticallycatalyzed reactions. The answers should indicate how enzymatic reactions differ from non-enzymatic reactions. Write four only
BMB Lecture 9
 BMB 178 2018 Lecture 9 Class 11, November 7, 2018 Steady-state kinetics (I) Case 3. Viscosity Variation If k cat /K m decreases with increasing viscosity, then the reaction is diffusion-limited (S binding
BMB 178 2018 Lecture 9 Class 11, November 7, 2018 Steady-state kinetics (I) Case 3. Viscosity Variation If k cat /K m decreases with increasing viscosity, then the reaction is diffusion-limited (S binding
Flow of Energy. Flow of Energy. Energy and Metabolism. Chapter 6
 Energy and Metabolism Chapter 6 Flow of Energy Energy: the capacity to do work -kinetic energy: the energy of motion -potential energy: stored energy Energy can take many forms: mechanical electric current
Energy and Metabolism Chapter 6 Flow of Energy Energy: the capacity to do work -kinetic energy: the energy of motion -potential energy: stored energy Energy can take many forms: mechanical electric current
It is generally believed that the catalytic reactions occur in at least two steps.
 Lecture 16 MECHANISM OF ENZYME ACTION A chemical reaction such as A ----> P takes place because a certain fraction of the substrate possesses enough energy to attain an activated condition called the transition
Lecture 16 MECHANISM OF ENZYME ACTION A chemical reaction such as A ----> P takes place because a certain fraction of the substrate possesses enough energy to attain an activated condition called the transition
Biochemistry Enzyme kinetics
 1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name Module Name/Title Enzyme Kinetics Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj 2 1. Objectives 2. Enzymes as biological catalyst 3. Enzyme Catalysis 4. Understanding
1 Description of Module Subject Name Paper Name Module Name/Title Enzyme Kinetics Dr. Vijaya Khader Dr. MC Varadaraj 2 1. Objectives 2. Enzymes as biological catalyst 3. Enzyme Catalysis 4. Understanding
Lecture Series 9 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy
 Lecture Series 9 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy Reading Assignments Review Chapter 3 Energy, Catalysis, & Biosynthesis Read Chapter 13 How Cells obtain Energy from Food Read Chapter 14
Lecture Series 9 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy Reading Assignments Review Chapter 3 Energy, Catalysis, & Biosynthesis Read Chapter 13 How Cells obtain Energy from Food Read Chapter 14
f) Adding an enzyme does not change the Gibbs free energy. It only increases the rate of the reaction by lowering the activation energy.
 Problem Set 2-Answer Key BILD1 SP16 1) How does an enzyme catalyze a chemical reaction? Define the terms and substrate and active site. An enzyme lowers the energy of activation so the reaction proceeds
Problem Set 2-Answer Key BILD1 SP16 1) How does an enzyme catalyze a chemical reaction? Define the terms and substrate and active site. An enzyme lowers the energy of activation so the reaction proceeds
Reading for today: Chapter 16 (selections from Sections A, B and C) Friday and Monday: Chapter 17 (Diffusion)
 Lecture 29 Enzymes Reading for today: Chapter 6 (selections from Sections, B and C) Friday and Monday: Chapter 7 (Diffusion) 4/3/6 Today s Goals Michaelis-Menten mechanism for simple enzyme reactions:
Lecture 29 Enzymes Reading for today: Chapter 6 (selections from Sections, B and C) Friday and Monday: Chapter 7 (Diffusion) 4/3/6 Today s Goals Michaelis-Menten mechanism for simple enzyme reactions:
Prerequisites Properties of allosteric enzymes. Basic mechanisms involving regulation of metabolic pathways.
 Case 16 Allosteric Regulation of ATCase Focus concept An enzyme involved in nucleotide synthesis is subject to regulation by a variety of combinations of nucleotides. Prerequisites Properties of allosteric
Case 16 Allosteric Regulation of ATCase Focus concept An enzyme involved in nucleotide synthesis is subject to regulation by a variety of combinations of nucleotides. Prerequisites Properties of allosteric
Biological Process Term Enrichment
 Biological Process Term Enrichment cellular protein localization cellular macromolecule localization intracellular protein transport intracellular transport generation of precursor metabolites and energy
Biological Process Term Enrichment cellular protein localization cellular macromolecule localization intracellular protein transport intracellular transport generation of precursor metabolites and energy
Electron Transport Chain (Respiratory Chain) - exercise - Vladimíra Kvasnicová
 Electron Transport Chain (Respiratory Chain) - exercise - Vladimíra Kvasnicová Respiratory chain (RCH) a) is found in all cells b) is located in a mitochondrion c) includes enzymes integrated in the inner
Electron Transport Chain (Respiratory Chain) - exercise - Vladimíra Kvasnicová Respiratory chain (RCH) a) is found in all cells b) is located in a mitochondrion c) includes enzymes integrated in the inner
Cell and Molecular Biology
 Cell and Molecular Biology (3000719): academic year 2013 Content & Objective :Cell Chemistry and Biosynthesis 3 rd Edition, 1994, pp. 41-88. 4 th Edition, 2002, pp. 47-127. 5 th Edition, 2008, pp. 45-124.
Cell and Molecular Biology (3000719): academic year 2013 Content & Objective :Cell Chemistry and Biosynthesis 3 rd Edition, 1994, pp. 41-88. 4 th Edition, 2002, pp. 47-127. 5 th Edition, 2008, pp. 45-124.
Bioenergetics, or biochemical thermodynamics, is the study of the energy changes accompanying biochemical reactions. Biologic systems are essentially
 Bioenergetics Bioenergetics, or biochemical thermodynamics, is the study of the energy changes accompanying biochemical reactions. Biologic systems are essentially isothermic and use chemical energy to
Bioenergetics Bioenergetics, or biochemical thermodynamics, is the study of the energy changes accompanying biochemical reactions. Biologic systems are essentially isothermic and use chemical energy to
Introduction to Metabolism (Or Energy Management) Chapter 8
 Introduction to Metabolism (Or Energy Management) Chapter 8 Metabolism of the chemical reactions in the organism Building up molecules Breaking down molecules Managing energy and materials Route to end-product
Introduction to Metabolism (Or Energy Management) Chapter 8 Metabolism of the chemical reactions in the organism Building up molecules Breaking down molecules Managing energy and materials Route to end-product
Metabolism: Energy and Enzymes. February 24 th, 2012
 Metabolism: Energy and Enzymes February 24 th, 2012 1 Outline Forms of Energy Laws of Thermodynamics Metabolic Reactions ATP Metabolic Pathways Energy of Activation Enzymes Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration
Metabolism: Energy and Enzymes February 24 th, 2012 1 Outline Forms of Energy Laws of Thermodynamics Metabolic Reactions ATP Metabolic Pathways Energy of Activation Enzymes Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration
Exam 3 Review (4/12/2011) Lecture note excerpt covering lectures (Exam 3 topics: Chapters 8, 12, 14 & 15)
 Exam 3 Review (4/12/2011) Lecture note excerpt covering lectures 17-23 (Exam 3 topics: Chapters 8, 12, 14 & 15) Enzyme Kinetics, Inhibition, and Regulation Chapter 12 Enzyme Kinetics When the concentration
Exam 3 Review (4/12/2011) Lecture note excerpt covering lectures 17-23 (Exam 3 topics: Chapters 8, 12, 14 & 15) Enzyme Kinetics, Inhibition, and Regulation Chapter 12 Enzyme Kinetics When the concentration
Chapter 6: Energy Flow in the Life of a Cell
 Chapter 6: Energy Flow in the Life of a Cell What is Energy? Answer: The capacity to do work Types of Energy: 1) Potential Energy = Stored energy Positional (stored in location of object) Chemical (stored
Chapter 6: Energy Flow in the Life of a Cell What is Energy? Answer: The capacity to do work Types of Energy: 1) Potential Energy = Stored energy Positional (stored in location of object) Chemical (stored
C a h p a t p e t r e r 6 E z n y z m y e m s
 Chapter 6 Enzymes 4. Examples of enzymatic reactions acid-base catalysis: give and take protons covalent catalysis: a transient covalent bond is formed between the enzyme and the substrate metal ion catalysis:
Chapter 6 Enzymes 4. Examples of enzymatic reactions acid-base catalysis: give and take protons covalent catalysis: a transient covalent bond is formed between the enzyme and the substrate metal ion catalysis:
Pyruvate is reduced to lactate in anaerobic metabolism in muscle cells
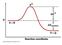 Pyruvate is reduced to lactate in anaerobic metabolism in muscle cells Transferases and hydrolases catalyze group transfer reactions Acyl transfer: Hexokinase catalyzes a phosphoryl transfer from ATP to
Pyruvate is reduced to lactate in anaerobic metabolism in muscle cells Transferases and hydrolases catalyze group transfer reactions Acyl transfer: Hexokinase catalyzes a phosphoryl transfer from ATP to
Lecture #8 9/21/01 Dr. Hirsh
 Lecture #8 9/21/01 Dr. Hirsh Types of Energy Kinetic = energy of motion - force x distance Potential = stored energy In bonds, concentration gradients, electrical potential gradients, torsional tension
Lecture #8 9/21/01 Dr. Hirsh Types of Energy Kinetic = energy of motion - force x distance Potential = stored energy In bonds, concentration gradients, electrical potential gradients, torsional tension
NUCLEOTIDE BINDING ENZYMES
 NUCLEOTIDE BINDING ENZYMES The Rossmann fold Relationship between sequence, structure and function. Anna Casas, Júlia Gasull and Nerea Vega Index 1. Introduction: Adenine nucleotides 1. The most commonly
NUCLEOTIDE BINDING ENZYMES The Rossmann fold Relationship between sequence, structure and function. Anna Casas, Júlia Gasull and Nerea Vega Index 1. Introduction: Adenine nucleotides 1. The most commonly
20. Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation
 20. Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation 20.1 What Role Does Electron Transport Play in Metabolism? Electron transport - Role of oxygen in metabolism as final acceptor of electrons - In inner
20. Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation 20.1 What Role Does Electron Transport Play in Metabolism? Electron transport - Role of oxygen in metabolism as final acceptor of electrons - In inner
Welcome to Class 8! Introductory Biochemistry! Announcements / Reminders! Midterm TA led Review Sessions!
 Announcements / Reminders Midterm TA led Review Sessions Welcome to Class 8 Sunday, February 23 from 8-10pm Location: Science Center Main Room (315) Office Hours Prof Salomon: SFH 270 on Thursday Feb 20,
Announcements / Reminders Midterm TA led Review Sessions Welcome to Class 8 Sunday, February 23 from 8-10pm Location: Science Center Main Room (315) Office Hours Prof Salomon: SFH 270 on Thursday Feb 20,
Proteins Act As Catalysts
 Proteins Act As Catalysts Properties of Enzymes Catalyst - speeds up attainment of reaction equilibrium Enzymatic reactions -10 3 to 10 17 faster than the corresponding uncatalyzed reactions Substrates
Proteins Act As Catalysts Properties of Enzymes Catalyst - speeds up attainment of reaction equilibrium Enzymatic reactions -10 3 to 10 17 faster than the corresponding uncatalyzed reactions Substrates
Overview of Kinetics
 Overview of Kinetics [P] t = ν = k[s] Velocity of reaction Conc. of reactant(s) Rate of reaction M/sec Rate constant sec -1, M -1 sec -1 1 st order reaction-rate depends on concentration of one reactant
Overview of Kinetics [P] t = ν = k[s] Velocity of reaction Conc. of reactant(s) Rate of reaction M/sec Rate constant sec -1, M -1 sec -1 1 st order reaction-rate depends on concentration of one reactant
Giving you the energy you need!
 Giving you the energy you need! Use your dominant hand Open and close the pin (with your thumb and forefinger) as many times as you can for 20 seconds while holding the other fingers straight out! Repeat
Giving you the energy you need! Use your dominant hand Open and close the pin (with your thumb and forefinger) as many times as you can for 20 seconds while holding the other fingers straight out! Repeat
Oxidative Phosphorylation versus. Photophosphorylation
 Photosynthesis Oxidative Phosphorylation versus Photophosphorylation Oxidative Phosphorylation Electrons from the reduced cofactors NADH and FADH 2 are passed to proteins in the respiratory chain. In eukaryotes,
Photosynthesis Oxidative Phosphorylation versus Photophosphorylation Oxidative Phosphorylation Electrons from the reduced cofactors NADH and FADH 2 are passed to proteins in the respiratory chain. In eukaryotes,
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Nafeth Abu Tarboush
 number 6 Done by أنس القيشاوي Corrected by Zaid Emad Doctor Nafeth Abu Tarboush 1 P a g e In the previous lecture, we talked about redox reactions and the reduction potential briefly and how it can help
number 6 Done by أنس القيشاوي Corrected by Zaid Emad Doctor Nafeth Abu Tarboush 1 P a g e In the previous lecture, we talked about redox reactions and the reduction potential briefly and how it can help
Ch. 3 Metabolism and Enzymes
 Ch. 3 Metabolism and Enzymes Originally prepared by Kim B. Foglia. Revised and adapted by Nhan A. Pham Flow of energy through life Life is built on chemical reactions that enable energy to flow through
Ch. 3 Metabolism and Enzymes Originally prepared by Kim B. Foglia. Revised and adapted by Nhan A. Pham Flow of energy through life Life is built on chemical reactions that enable energy to flow through
Bioenergetics and high-energy compounds
 Bioenergetics and high-energy compounds Tomáš Kučera tomas.kucera@lfmotol.cuni.cz Department of Medical Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Charles University in Prague and Motol
Bioenergetics and high-energy compounds Tomáš Kučera tomas.kucera@lfmotol.cuni.cz Department of Medical Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Charles University in Prague and Motol
13 Enzymes Kinetics. and Specificity + 6 O 2 ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS KEY QUESTIONS
 3 Enzymes Kinetics and Specificity Mark M. Lawrence/CRBIS ESSENTIAL QUESTINS At any moment, thousands of chemical reactions are taking place in any living cell. Enzymes are essential for these reactions
3 Enzymes Kinetics and Specificity Mark M. Lawrence/CRBIS ESSENTIAL QUESTINS At any moment, thousands of chemical reactions are taking place in any living cell. Enzymes are essential for these reactions
Catalysis is Necessary for Life. Chapter 6 Enzymes. Why Study Enzymes? Enzymes are Biological Catalysts
 Chapter 6 Enzymes Catalysis is Necessary for Life Definition: a catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction, while emerging unchanged at the end Corollary A: a catalyst is never used up,
Chapter 6 Enzymes Catalysis is Necessary for Life Definition: a catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction, while emerging unchanged at the end Corollary A: a catalyst is never used up,
Chapter 13 Principles of Bioenergetics
 Chapter 13 Principles of Bioenergetics 1. Cells need energy to do all their work To generate and maintain its highly ordered structure (biosynthesis of macromolecules) To generate all kinds of movement
Chapter 13 Principles of Bioenergetics 1. Cells need energy to do all their work To generate and maintain its highly ordered structure (biosynthesis of macromolecules) To generate all kinds of movement
CHEM April 10, Exam 3
 Name CHEM 3511 April 10, 2009 Exam 3 Name Page 1 1. (12 points) Give the name of your favorite Tech professor and in one sentence describe why you like him/her. 2. (10 points) An enzyme cleaves a chemical
Name CHEM 3511 April 10, 2009 Exam 3 Name Page 1 1. (12 points) Give the name of your favorite Tech professor and in one sentence describe why you like him/her. 2. (10 points) An enzyme cleaves a chemical
Pathways that Harvest and Store Chemical Energy
 6 Pathways that Harvest and Store Chemical Energy Energy is stored in chemical bonds and can be released and transformed by metabolic pathways. Chemical energy available to do work is termed free energy
6 Pathways that Harvest and Store Chemical Energy Energy is stored in chemical bonds and can be released and transformed by metabolic pathways. Chemical energy available to do work is termed free energy
CHAPTER 1: ENZYME KINETICS AND APPLICATIONS
 CHAPTER 1: ENZYME KINETICS AND APPLICATIONS EM 1 2012/13 ERT 317 BIOCHEMICAL ENGINEERING Course details Credit hours/units : 4 Contact hours : 3 hr (L), 3 hr (P) and 1 hr (T) per week Evaluations Final
CHAPTER 1: ENZYME KINETICS AND APPLICATIONS EM 1 2012/13 ERT 317 BIOCHEMICAL ENGINEERING Course details Credit hours/units : 4 Contact hours : 3 hr (L), 3 hr (P) and 1 hr (T) per week Evaluations Final
Chemistry 5.07SC Biological Chemistry I Fall Semester, 2013
 Chemistry 5.07SC Biological Chemistry I Fall Semester, 2013 Lecture 10. Biochemical Transformations II. Phosphoryl transfer and the kinetics and thermodynamics of energy currency in the cell: ATP and GTP.
Chemistry 5.07SC Biological Chemistry I Fall Semester, 2013 Lecture 10. Biochemical Transformations II. Phosphoryl transfer and the kinetics and thermodynamics of energy currency in the cell: ATP and GTP.
