Study of Refractive Index of Potassium Dichromate Solution as a Function of its Concentration
|
|
|
- Gabriella Powell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Study of Refractive Index of Potassium Dichromate Solution as a Function of its Concentration N.V.Wani 1,S.M. Dongarge 2 andu.v. Biradar 3 1,2,3 Department of Physics, Mahatma Basweshwar Mahavidyalaya, Latur, Maharashtra. (India) ABSTRACT : There are numerous methods to determine the refractive index of salt solution. These methods are quite tedious. The most suitable and easiest method of measuring the refractive index of salt solution is reported in this paper. A method is developed by developing mathematical equation for salt solutions. The technique was employed to study therefractive index of saltsolution as a function of concentration. Aequilateral hollow prism is used along with optical spectrometer at room temperature to determine refractive index ofpotassium dichromate(k 2Cr 2O 7) solution. The experimental results were compared with the results obtained from theoretical consideration and it was found that this technique is quite reliable and can be safely used in the study of the optical properties of any soluble salt solution. 1.INTRODUCTION:- Refractive index is one of the most important optical properties of a medium. It plays an important role in many areas of material science with special reference to thin film technology and fiber optics. Similarly, measurement of refractive index is widely used in analytical chemistry to determine the concentration of solutions. Recent studies [Schwartz 1999, Olesberg 2000, Shlichta 1986] provide more detailed discussion on the concentration mapping by the measurement of refractive index of liquids.several techniques are reported in literature for the measurement of concentration dependence of refractive index of liquids [McPherson 1999, Garcia 1999, Otalora 1999, Miyashita 1994]. The present paper reports a relatively simple and reliable technique, which can be used to measure the refractive index of salt solution as a function of concentrations. M.T. Teli developed the equation for volume shrinkage of salt when added to water which is taken into account for this experiment[1997 Radiation physics and chemistry].recently U V Biradaretal. Measured the refractive index of KCl in Vol 6, issue 2. A prism divides white light into its constituent spectral colours. For a given colour, the refractive index of a medium depends on the density of the medium. The absolute refractive index of a medium is the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in the medium. The relative refractive index is the ratio of the speed of light in first medium to that in the second medium. Refraction occurs with all types of waves but is most familiar with light waves. The refractive index of a medium differs with frequency. 2.EQUIPMENT USED FOR THE STUDY:- 2.1 Spectrometer: An optical spectrometer is an instrument used for obtaining a pure spectrum. It is used for the study of spectra and for finding the refractive index of a material in the form of a prism. In its simplest form it has following main parts. a) Collimator:- A collimator is a device forproducing a parallel beam of light. It consists of a horizontal tube of variable length with adjustment slit at one end and converging achromatic lens at the other end. The focal length of the lens is almost equal to the length of collimator tube. The distance between the slit and the lens can be changed by a 177 N.V.Wani, S.M. Dongarge and U.V. Biradar
2 rack and pinion arrangement or by sliding the inner tube to obtain parallel rays. The tube rests on two screws by which it can be slightly tilted up or down if necessary as shown in figure1. ( Fig 1. Optical spectrometer with hollow prism) b) Slit:- It consists of two sharp edges. One of the edges is fixed while the other can be moved parallel to it by working the screw provided at its side as shown in figure 1. c)telescope:- It is an astronomical telescope fitted with a Ramsden s eye-piece(an optical instrument consists of two planoconvex lenses)and cross wires. It is mounted on another arm fixed rigidly to the circular scale in half degrees. The telescope along with scale can be turned round a vertical axis passing through the centre of the spectrometer. It can be fixed in any position by screw and then can be given a slow rotation or fine adjustment by a tangent screw. The position of the telescope can be read by the two vernier V 1 and V 2,180 o apart fixed to the prism table. The telescope rests on the screws by which it can be slightly tilted up or down, for adjustment of its axis if necessary. A rack and pinion arrangement is provided on the side of the telescope for focusing. d) Prism table: - It consists of an upper plate and a lower plate separated by three spring through which passes the leveling screws. A set of parallel equidistant lines are engraved on the upper plate. These lines are parallel to the line joining any two of the screws. The prism is always placed with one of its reflecting faces perpendicular to these lines. A series of circles concentric with the axis of rotation of the prism are also ruled on this plate. This help in placing the prism correctly. The height of prism table can be adjusted by camping screw, which is used to fix the prism table to the vernier V 1 and V 2. The table can rotate about vertical axes and may be fixed in any desired position by means of the screw. When fixed by the screw, it can be turned very slowly by a tangent screw placed at a base of the spectrometer. The position of table can be accurately read by vernier moving on the circular scale. 3.THEORY DEVELOPED FOR THE DETERMINATION OF R.I.OF SALT SOLUTION:- A convenient formula for refractive index is obtained in the minimum deviation case when a ray of light suffers deviation while passing through a prism. The deviation produced by the prism depends on the angle of incidence. For a certain value of the angle of incidence, the angle of deviation is minimum. If m denotes the angle of minimum deviation for a given prism of refractive angle A, then the refractive index of the material of the prism is given by = sin[(a+ m)/2] sin(a/2) (i) Equation (i) have been employed to calculate the experimental values of refractive index of the salt solutionfor any concentration of solution.these values are given in table 1. Where A is angle of hollow prism and mis angle of minimum deviation. 178 N.V.Wani, S.M. Dongarge and U.V. Biradar
3 If we consider V w as the volume of water taken in the hollow prism and V sis the volume ofpotassium dichromate(k 2Cr 2O 7)added to the water.then total volume (V s+v w) in the hollow prism is V = V s + V w When the potassium dichromate(k 2Cr 2O 7)is added to the water then there will be shrinkage of volume( V) in the potassium dichromate(k 2Cr 2O 7)which is to be considered by Teli s equation not by the above equation V =V V i.e.v = V V =V(1 V / V)=V(1- ) Where, = V / V=(V V )/V =Degree of shrinkage If we consider this equation for the solution for determining refractive index combining together[potassium dichromate(k 2Cr 2O 7)and water] for different concentrations we get an equation of straight line in the following form. = w + ( s w) V s /V (ii) Where is the refractive index of solution, w is the refractive index of the water and s is the refractive index of the potassium dichromate(k 2Cr 2O 7).Equation(ii) has been employed to calculate the theoretical values of refractive index of the salt solution for any concentration of solution. These values are given in table EXPERIMENTAL SET-UP FOR THE MEASUREMENT OF REFRACTIVE INDEX BY AN OPTICAL SPECTROMETER : Experimental arrangement used in our study is shown in fig1.specially constructed equilateral hollow prism was used to measure the refractive index of liquid with the help of an optical spectrometer. A mercury lamp was used as a source of light and a collimated beam was allowed to fall on onesurface of the prism filled with liquid and the angle of minimum deviation was determined for different concentrations.mean of two values are taken for each angle of minimum deviation( m). To study the refractive index of potassium dichromate(k 2Cr 2O 7)solution as a function of concentration, an electronic balance was used to measure the mass of potassium dichromate(k 2Cr 2O 7) and solutions of required concentration were prepared by dissolving the 2 gram of potassium dichromate(k 2Cr 2O 7) in 8 ml of water. Thus, prepared solutions were filtered before pouring into the hollow prism. The hollow prism was rinsed carefully after every measurement. Solutions of lower concentrations were made by adding the water of different volume with proper mass of salt. Accordingly the volume was converted to concentration as required in formula. The values of different concentrations are given in table(1). Refractive index of potassium dichromate(k 2Cr 2O 7)solution as a function of concentration is shown in fig(2). For concentratedsolution, refractive index is as high as 1.365, which reduces to when the solution is diluted to a concentration of With the decrease in concentration, the density of the solution also decreases and also refractive index decreases. The results showed that the refractive index of the solution of concentration less than 0.04measures nearly the same as that of the pure water. The resultindicates that the effect of concentration on refractive index is dominant up to the concentration of 0.04 M. 5. CONCLUSIONS :- In this paper,refractive index have been measured for different concentration at room temperature and good accordance has been found between experimental and theoretical values. Here the study of refractive index of salt solution as a function of a concentration is not only carried out but also the refractive indexof salts whichare dissolved in water are also calculated. This is an alternate method to determine the R.I. of crystalline material without taking them into prism form. 6. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT :- We are thankful to Prof. Dr. J S Dargad, Principal, Dayanand Science College, Latur for providing facility to carry out work in their research laboratory. 179 N.V.Wani, S.M. Dongarge and U.V. Biradar
4 Table(1):Theoretical and experimental values of refractive index of potassium dichromate as a function of concentration Sr. No. Concentration V s/v s+v w Vernier- I Vernier II Refractive Index( ) (Experimental) Refractive Index ( ) (Theoretical) s Refractive index of K 2 Cr 2 O 7 solution as a function of concentration R.I. of K 2 Cr 2 O 7 Solution (Theo.) (Pract.) Concentration V s /V s +V w Fig.(2): Theoretical and experimental values of refractive index as a function of concentration 180 N.V.Wani, S.M. Dongarge and U.V. Biradar
5 A graph between refractive index and concentration of potassium dichromate(k 2Cr 2O 7) solution gives the slope of refractive index of solution [potassium dichromate(k 2Cr 2O 7) and water]and By using above mathematical equations we can calculate refractive index of potassium dichromate(k 2Cr 2O 7) and water ( w) by using graph as shown in fig.(2). intercept gives the refractive index of water. By subtracting intercept from slope we get refractive index. ofpotassium dichromate(k 2Cr 2O 7). For this purpose, we made the calculations mentioned in table (1). It requires to be converted in V s and V wform. For this we have considered least square method. The refractive index of potassium dichromate(k 2Cr 2O 7)is and water is Both these values are within the acceptable limit, which satisfies our experimental and theoretical results. 7. REFERENCES:- [1] U.V. Biradar, S.M. Dongarge and N.V. Wani, Refractive Index of Salt (KCl) from Aqueous Solution, International Journal of Computer& Mathematical Sciences Volume 6, Issue 2 February [2] U.V. Biradar and S.M. Dongarge, Refractive Index of Salt (NaCl) from Aqueous Solution, International Journal of Computer & Mathematical Sciences Volume 4, Issue 12 December [3] Olesberg, J.T, Arnold, M.A, Hu, S-Y.B., Wiencek, J.M., Temperature insensitive near infrared method for determination of protein concentration during protein crystal growth.analytical Chemistry, 72, [4] Schwartz, A.M., Berglund, K.A., The use of Raman spectroscopy for in situ monitoring of lysozyme concentration during crystallization in a hanging drop. J. Crystal Growth, 203, 599. [5] McPherson, A., Malkin, A. J., Kuznetsov, Y. G., Koszelak, S., Wells, M., Jenkins, G., Howard, J., Lawson, G., Effects of microgravity on protein crystallization: evidence for concentration gradients around growing crystals, J. Crystal Growth, 196, 572. [6] Garcia-Ruiz, J. M., Novella, M. L., Otalora, F., Supersaturation patterns in counter-diffusion crystallisation methods followed by Mach-Zehnder interferometry, Crystal Growth, 196, [7] Otalora F, Novella ML, Rondon D, Garcia-Ruiz JM, Growth of lysozyme crystals under micro gravity conditions in the LMS (STS-78) mission Journal of Crystal Growth, 196, 649. [8] Miyashita, S., Komatsu, H., Suzuki, Y., Nakada, T., Observation of the concentration distribution around a growing lysozyme crystal, J. Crystal Growth, 141, 419. [9] Shlichta, P. J., Feasibility of mapping solution properties during the growth of protein crystals. J. Crystal Growth, 76, 656. [10] J. D. Bass and D. J. Weidner, "Method for Measuring the Refractive Index of Transparent Solids," Rev. Sci. Instrum. 55, 1569 (1984). s [11] D. D. Jenkin, "Refractive Index of Solution," Phys. Educ. 17, 82 (1982). [12] Miller, A., Hussmann, E. K., McLaughlin, W. L., Interferometer for measuring fast changes of refractive index and temperature in transparent liquids Review of Scientific instruments, 46, N.V.Wani, S.M. Dongarge and U.V. Biradar
Refractive Index of Salt (KCl) From Aqueous Solution
 Refractive Index of Salt (KCl) From Aqueous Solution U.V. Biradar 1, S.M. Dongarge 2 and N.V.Wani 3 1 Department of Physics, Mahatma Basweshwar Mahavidyalaya, Latur, Maharashtra (India) 2 Department of
Refractive Index of Salt (KCl) From Aqueous Solution U.V. Biradar 1, S.M. Dongarge 2 and N.V.Wani 3 1 Department of Physics, Mahatma Basweshwar Mahavidyalaya, Latur, Maharashtra (India) 2 Department of
Refractive Index of Salt (NaCl) from Aquous Solution
 Refractive Index of Salt (NaCl) from Aquous Solution Department of Physics, Mahatma Basweshwar Mahavidyalaya Latur 413512 (M.S.)INDIA. ABSTRACT There are different methods to determine the refractive index
Refractive Index of Salt (NaCl) from Aquous Solution Department of Physics, Mahatma Basweshwar Mahavidyalaya Latur 413512 (M.S.)INDIA. ABSTRACT There are different methods to determine the refractive index
RESEARCH ON STUDY OF CONCENTRATION DEPENDENCE OF REFRACTIVE INDEX OF OIL USING A NOVEL TECHNIQUE
 RESEARCH ON STUDY OF CONCENTRATION DEPENDENCE OF REFRACTIVE INDEX OF OIL USING A NOVEL TECHNIQUE Department of Physics, Mid Western University, Campus of Science and Technology email:dhakaldharma605@gmail.com
RESEARCH ON STUDY OF CONCENTRATION DEPENDENCE OF REFRACTIVE INDEX OF OIL USING A NOVEL TECHNIQUE Department of Physics, Mid Western University, Campus of Science and Technology email:dhakaldharma605@gmail.com
Experiment #4: Optical Spectrometer and the Prism Deviation
 Experiment #4: Optical Spectrometer and the Prism Deviation Carl Adams October 2, 2011 1 Purpose In the first part of this lab you will set up and become familiar with an optical spectrometer. In the second
Experiment #4: Optical Spectrometer and the Prism Deviation Carl Adams October 2, 2011 1 Purpose In the first part of this lab you will set up and become familiar with an optical spectrometer. In the second
Optical Characterization of Sucrose (C 12 H 21 O 11 ) at Different Temperatures
 Optical Characterization of Sucrose (C 12 H 21 O 11 ) at Different Temperatures N. K. Wagholikar 1, S. B. Jagtap 2 * Asst. Professor, Dept. of Physics, Sir Parashurambhau College, Pune, Maharashtra State,
Optical Characterization of Sucrose (C 12 H 21 O 11 ) at Different Temperatures N. K. Wagholikar 1, S. B. Jagtap 2 * Asst. Professor, Dept. of Physics, Sir Parashurambhau College, Pune, Maharashtra State,
Determination of Cauchy s Contants
 8. Determination of Cauchy s Contants 8.1 Objective: To determine Cauchy s Constants using a prism and spectrometer. Apparatus: Glass prism, spectrometer and mercury vapour lamp. 8. Theory: The wavelength
8. Determination of Cauchy s Contants 8.1 Objective: To determine Cauchy s Constants using a prism and spectrometer. Apparatus: Glass prism, spectrometer and mercury vapour lamp. 8. Theory: The wavelength
DISPERSION OF A GLASS PRISM
 PH2 page 1 DISPERSION OF A GLASS PRISM OBJECTIVE The objective of this experiment is to analyze the emission spectrum of helium and to analyze the dispersion of a glass prism by measuring the index of
PH2 page 1 DISPERSION OF A GLASS PRISM OBJECTIVE The objective of this experiment is to analyze the emission spectrum of helium and to analyze the dispersion of a glass prism by measuring the index of
Study of concentration dependence of Refractive index of Sugar and Salt Solution
 KATHMANDU UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCE (PHYSICS) Study of concentration dependence of Refractive index of Sugar and Salt Solution A 2 nd Year 1 st Semester Project Report
KATHMANDU UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCE (PHYSICS) Study of concentration dependence of Refractive index of Sugar and Salt Solution A 2 nd Year 1 st Semester Project Report
Measurement of Temperature and Concentration Dependences of. Refractive Index of Hen-egg-white Lysozyme Solution
 Measurement of Temperature and Concentration Dependences of Refractive Index of Hen-egg-white Lysozyme Solution Corresponding author: Y. Inatomi Postal Address: Space Utilization Research Center, The Institute
Measurement of Temperature and Concentration Dependences of Refractive Index of Hen-egg-white Lysozyme Solution Corresponding author: Y. Inatomi Postal Address: Space Utilization Research Center, The Institute
To determine the wavelengths of light emitted by a mercury vapour lamp by using a diffraction grating.
 12. Diffraction grating OBJECT To determine the wavelengths of light emitted by a mercury vapour lamp by using a diffraction grating. INTRODUCTION: Consider a light beam transmitted through an aperture
12. Diffraction grating OBJECT To determine the wavelengths of light emitted by a mercury vapour lamp by using a diffraction grating. INTRODUCTION: Consider a light beam transmitted through an aperture
Optics. Measuring the line spectra of inert gases and metal vapors using a prism spectrometer. LD Physics Leaflets P
 Optics Spectrometer Prism spectrometer LD Physics Leaflets P5.7.1.1 Measuring the line spectra of inert gases and metal vapors using a prism spectrometer Objects of the experiment Adjusting the prism spectrometer.
Optics Spectrometer Prism spectrometer LD Physics Leaflets P5.7.1.1 Measuring the line spectra of inert gases and metal vapors using a prism spectrometer Objects of the experiment Adjusting the prism spectrometer.
Any first year text, sections on atomic structure, spectral lines and spectrometers
 Physics 33 Experiment 5 Atomic Spectra References Any first year text, sections on atomic structure, spectral lines and spectrometers Any modern physics text, eg F.K. Richtmeyer, E.H. Kennard and J.N.
Physics 33 Experiment 5 Atomic Spectra References Any first year text, sections on atomic structure, spectral lines and spectrometers Any modern physics text, eg F.K. Richtmeyer, E.H. Kennard and J.N.
DISPERSION AND SPECTRA CHAPTER 20
 CHAPTER 20 DISPERSION AND SPECTRA 20.1 DISPERSION As mentioned earlier, the refractive index of a material depends slightly on the wavelength of light. The relation between the two may be approximately
CHAPTER 20 DISPERSION AND SPECTRA 20.1 DISPERSION As mentioned earlier, the refractive index of a material depends slightly on the wavelength of light. The relation between the two may be approximately
Laboratory #29: Spectrometer
 INDIANA UNIVERSITY, DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS, P309 LABORATORY Laboratory #29: Spectrometer Goal: Learn to adjust an optical spectrometer, use a transmission grating to measure known spectral lines of mercury,
INDIANA UNIVERSITY, DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS, P309 LABORATORY Laboratory #29: Spectrometer Goal: Learn to adjust an optical spectrometer, use a transmission grating to measure known spectral lines of mercury,
EXPERIMENT 5:Determination of the refractive index (µ) of the material of a prism using sprectometer
 EXPERIMENT 5:Determination of the refractive index (µ) of the material of a prism using sprectometer Debangshu Mukherjee B.Sc Physics,1st year Chennai Mathematical Institute 17.10.008 1 Aim of Experiment
EXPERIMENT 5:Determination of the refractive index (µ) of the material of a prism using sprectometer Debangshu Mukherjee B.Sc Physics,1st year Chennai Mathematical Institute 17.10.008 1 Aim of Experiment
Dispersion and resolving power of the prism and grating spectroscope (Item No.: P )
 Dispersion and resolving power of the prism and grating spectroscope (Item No.: P2210300) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Education Level: University Topic: Light and Optics Subtopic: Diffraction
Dispersion and resolving power of the prism and grating spectroscope (Item No.: P2210300) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Education Level: University Topic: Light and Optics Subtopic: Diffraction
THE DIFFRACTION GRATING SPECTROMETER
 Purpose Theory THE DIFFRACTION GRATING SPECTROMETER a. To study diffraction of light using a diffraction grating spectrometer b. To measure the wavelengths of certain lines in the spectrum of the mercury
Purpose Theory THE DIFFRACTION GRATING SPECTROMETER a. To study diffraction of light using a diffraction grating spectrometer b. To measure the wavelengths of certain lines in the spectrum of the mercury
Instruments and Related Topics
 1. Traveling Microscope The traveling microscope [Fig.1] is an instrument well-suited for the purpose of measuring small vertical or horizontal distances with high accuracy. It consists of a compound microscope
1. Traveling Microscope The traveling microscope [Fig.1] is an instrument well-suited for the purpose of measuring small vertical or horizontal distances with high accuracy. It consists of a compound microscope
Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 224. Your name Lab section
 Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 224 THE DIFFRACTION GRATING AND THE OPTICAL SPECTRUM Your name Lab section 1. What are the goals of this experiment? 2. If the period of a diffraction grating is d = 1,000 nm, where the
Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 224 THE DIFFRACTION GRATING AND THE OPTICAL SPECTRUM Your name Lab section 1. What are the goals of this experiment? 2. If the period of a diffraction grating is d = 1,000 nm, where the
Ph 3455/MSE 3255 Experiment 2: Atomic Spectra
 Ph 3455/MSE 3255 Experiment 2: Atomic Spectra Background Reading: Tipler, Llewellyn pp. 163-165 Apparatus: Spectrometer, sodium lamp, hydrogen lamp, mercury lamp, diffraction grating, watchmaker eyeglass,
Ph 3455/MSE 3255 Experiment 2: Atomic Spectra Background Reading: Tipler, Llewellyn pp. 163-165 Apparatus: Spectrometer, sodium lamp, hydrogen lamp, mercury lamp, diffraction grating, watchmaker eyeglass,
ARC SPECTRUM OF IRON /COPPER / BRASS
 ARC PECTRUM OF IRON /COPPER / BRA Aim : To determine the wavelength of prominent lines in the emission spectrum of iron/ copper/ brass. Apparatus : Constant deviation spectrometer, dc voltage source, metal
ARC PECTRUM OF IRON /COPPER / BRA Aim : To determine the wavelength of prominent lines in the emission spectrum of iron/ copper/ brass. Apparatus : Constant deviation spectrometer, dc voltage source, metal
Atomic emission spectra experiment
 Atomic emission spectra experiment Contents 1 Overview 1 2 Equipment 1 3 Measuring the grating spacing using the sodium D-lines 4 4 Measurement of hydrogen lines and the Rydberg Constant 5 5 Measurement
Atomic emission spectra experiment Contents 1 Overview 1 2 Equipment 1 3 Measuring the grating spacing using the sodium D-lines 4 4 Measurement of hydrogen lines and the Rydberg Constant 5 5 Measurement
E. K. A. ADVANCED PHYSICS LABORATORY PHYSICS 3081, 4051 FRAUNHOFER DIFFRACTION
 E. K. A. ADVANCED PHYSICS LABORATORY PHYSICS 3081, 4051 FRAUNHOFER DIFFRACTION References for Fraunhofer Diffraction 1. Jenkins and White Fundamentals of Optics. Chapters on Fraunhofer diffraction and
E. K. A. ADVANCED PHYSICS LABORATORY PHYSICS 3081, 4051 FRAUNHOFER DIFFRACTION References for Fraunhofer Diffraction 1. Jenkins and White Fundamentals of Optics. Chapters on Fraunhofer diffraction and
Lab 5: Spectroscopy & the Hydrogen Atom Phy248 Spring 2009
 Lab 5: Spectroscopy & the Hydrogen Atom Phy248 Spring 2009 Name Section Return this spreadsheet to your TA that will use it to score your lab. To receive full credit you must use complete sentences and
Lab 5: Spectroscopy & the Hydrogen Atom Phy248 Spring 2009 Name Section Return this spreadsheet to your TA that will use it to score your lab. To receive full credit you must use complete sentences and
n(λ) = c/v(λ). Figure 1: Dispersion curves for some common optical glass types.
 Physics 2310 Lab 2: The Dispersion of Optical Glass Dr. Michael Pierce (Univ. of Wyoming) Based on a lab by Dr. M. Kruger (Univ. of Missouri, Kansas City) Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to introduce
Physics 2310 Lab 2: The Dispersion of Optical Glass Dr. Michael Pierce (Univ. of Wyoming) Based on a lab by Dr. M. Kruger (Univ. of Missouri, Kansas City) Purpose: The purpose of this lab is to introduce
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT. Physics 211 E&M and Quantum Physics Spring Lab #9: Diffraction Spectroscopy
 NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT Physics 211 E&M and Quantum Physics Spring 2018 Lab #9: Diffraction Spectroscopy Lab Writeup Due: Mon/Wed/Thu/Fri, April 30/ May 2/3/4, 2018 Background All
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT Physics 211 E&M and Quantum Physics Spring 2018 Lab #9: Diffraction Spectroscopy Lab Writeup Due: Mon/Wed/Thu/Fri, April 30/ May 2/3/4, 2018 Background All
EXPERIMENT NO. 6. OBJECT: To determine the wavelength of any three lines of mercury light by diffraction grating in1 st and 2 nd order spectrum.
 EXPEIMENT NO. 6 OBJECT: To determine the wavelength of any three lines of mercury light by diffraction grating in1 st and 2 nd order spectrum. APPAATUS: A diffraction grating, Spectrometer, spirit level,
EXPEIMENT NO. 6 OBJECT: To determine the wavelength of any three lines of mercury light by diffraction grating in1 st and 2 nd order spectrum. APPAATUS: A diffraction grating, Spectrometer, spirit level,
Experiment #5: Cauchy s Formula
 Experiment #5: Cauchy s Formula Carl Adams October 14, 2011 1 Purpose This experiment is a continuation of Experiment #4. It is assumed you have an aligned spectrometer. 2 Safety/Protocol 1. The gas discharge
Experiment #5: Cauchy s Formula Carl Adams October 14, 2011 1 Purpose This experiment is a continuation of Experiment #4. It is assumed you have an aligned spectrometer. 2 Safety/Protocol 1. The gas discharge
For more sample papers visit :
 PHYSICS (THEORY) (Three hours) For more sample papers visit : www.4ono.com Answer all questions in Part I and six questions from Part II, choosing two questions from each of the Sections A, B and C. All
PHYSICS (THEORY) (Three hours) For more sample papers visit : www.4ono.com Answer all questions in Part I and six questions from Part II, choosing two questions from each of the Sections A, B and C. All
LAB 10: OPTICAL MATERIALS AND DISPERSION I
 OPTI 202L - Geometrical and Instrumental Optics Lab LAB 10: OPTICAL MATERIALS AND DISPERSION I 10-1 Measuring the refractive index of a material is one of the most fundamental optical measurements, and
OPTI 202L - Geometrical and Instrumental Optics Lab LAB 10: OPTICAL MATERIALS AND DISPERSION I 10-1 Measuring the refractive index of a material is one of the most fundamental optical measurements, and
Dispersion of light by a prism
 Dispersion of light by a prism Aim: (i) To calculate refractive index µ of a prism for various wavelengths (λ) of Hg and to find dispersive power of the material of the prism (ii) To plot µ-/λ curve and
Dispersion of light by a prism Aim: (i) To calculate refractive index µ of a prism for various wavelengths (λ) of Hg and to find dispersive power of the material of the prism (ii) To plot µ-/λ curve and
Operating Instructions Spectro-Goniometer Student. 1 Functional Elements. 2 Safety Precautions. Figure 1: Spectro-Goniometer Student
 Operating Instructions Spectro-Goniometer Student 1 Functional Elements Figure 1: Spectro-Goniometer Student 1. Adjustable entrance slit, holding screw for slit cover 2. Lock ring fixing entrance slit
Operating Instructions Spectro-Goniometer Student 1 Functional Elements Figure 1: Spectro-Goniometer Student 1. Adjustable entrance slit, holding screw for slit cover 2. Lock ring fixing entrance slit
INTERFEROMETERS. There are 4 principal types of measurements that can be made with this type of interferometer.
 INTERFEROMETERS NOTE: Most mirrors in the apparatus are front surface aluminized. Do not touch the surfaces nor wipe them. they can be easily permanently damaged. Introduction This experiment provides
INTERFEROMETERS NOTE: Most mirrors in the apparatus are front surface aluminized. Do not touch the surfaces nor wipe them. they can be easily permanently damaged. Introduction This experiment provides
LABORATORY WRITE-UP MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER LAB AUTHOR S NAME GOES HERE STUDENT NUMBER:
 LABORATORY WRITE-UP MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER LAB AUTHOR S NAME GOES HERE STUDENT NUMBER: 111-22-3333 MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER 1. PURPOSE The purpose of this experiment is to give some practice in using
LABORATORY WRITE-UP MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER LAB AUTHOR S NAME GOES HERE STUDENT NUMBER: 111-22-3333 MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER 1. PURPOSE The purpose of this experiment is to give some practice in using
The Quantum Model of the Hydrogen Atom
 Physics 109 Science 1 Experiment 1 1 The Quantum Model of the Hydrogen Atom In this experiment you will use a spectrometer to determine the wavelengths of the visible lines of atomic hydrogen. The goal
Physics 109 Science 1 Experiment 1 1 The Quantum Model of the Hydrogen Atom In this experiment you will use a spectrometer to determine the wavelengths of the visible lines of atomic hydrogen. The goal
PC1144 Physics IV. Atomic Spectra
 PC1144 Physics IV Atomic Spectra 1 Objectives Investigate how well the visible light wavelengths of hydrogen predicted by the Bohr theory agree with experimental values. Determine an experimental value
PC1144 Physics IV Atomic Spectra 1 Objectives Investigate how well the visible light wavelengths of hydrogen predicted by the Bohr theory agree with experimental values. Determine an experimental value
Spectroscopic Measurements of Optical Elements For Submillimeter Receivers
 5- Abstract Spectroscopic Measurements of Optical Elements For Submillimeter Receivers J. Kawamura, S. Paine, and D. C. Papa Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics 60 Garden Street Cambridge, Massachusetts
5- Abstract Spectroscopic Measurements of Optical Elements For Submillimeter Receivers J. Kawamura, S. Paine, and D. C. Papa Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics 60 Garden Street Cambridge, Massachusetts
EXPERIMENT 12 THE GRATING SPECTROMETER AND ATOMIC SPECTRA
 OBJECTIVES Learn the theory of the grating spectrometer Observe the spectrum of mercury and hydrogen Measure the grating constant of a diffraction grating Measure the Rydberg Constant EXPERIMENT THE GRATING
OBJECTIVES Learn the theory of the grating spectrometer Observe the spectrum of mercury and hydrogen Measure the grating constant of a diffraction grating Measure the Rydberg Constant EXPERIMENT THE GRATING
Speed of Light in Glass
 Experiment (1) Speed of Light in Glass Objective:- This experiment is used to determine the speed of propagation of light waves in glass. Apparatus:- Prism, spectrometer, Halogen lamp source. Theory:-
Experiment (1) Speed of Light in Glass Objective:- This experiment is used to determine the speed of propagation of light waves in glass. Apparatus:- Prism, spectrometer, Halogen lamp source. Theory:-
Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model SP E 2/96 STUDENT SPECTROMETER. Copyright January 1991 $7.
 Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model SP-9268 012-02135E 2/96 STUDENT SPECTROMETER Copyright January 1991 $7.50 012-02135E Spectrometer Table of Contents Section Page
Instruction Manual and Experiment Guide for the PASCO scientific Model SP-9268 012-02135E 2/96 STUDENT SPECTROMETER Copyright January 1991 $7.50 012-02135E Spectrometer Table of Contents Section Page
MOLEBIO LAB #4: Using a Spectrophotometer
 Introduction: Spectrophotometry MOLEBIO LAB #4: Using a Spectrophotometer Many kinds of molecules interact with or absorb specific types of radiant energy in a predictable fashion. For example, when while
Introduction: Spectrophotometry MOLEBIO LAB #4: Using a Spectrophotometer Many kinds of molecules interact with or absorb specific types of radiant energy in a predictable fashion. For example, when while
Lab report 30 EXPERIMENT 4. REFRACTION OF LIGHT
 30 EXPERIMENT 4. REFRACTION OF LIGHT Lab report Go to your course homepage on Sakai (Resources, Lab templates) to access the online lab report worksheet for this experiment. The worksheet has to be completed
30 EXPERIMENT 4. REFRACTION OF LIGHT Lab report Go to your course homepage on Sakai (Resources, Lab templates) to access the online lab report worksheet for this experiment. The worksheet has to be completed
Planck's "quantum of action" and external photoelectric effect (Item No.: P )
 Planck's "quantum of action" and external photoelectric effect (Item No.: P2510502) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Education Level: University Topic: Modern Physics Subtopic: Quantum Physics
Planck's "quantum of action" and external photoelectric effect (Item No.: P2510502) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Education Level: University Topic: Modern Physics Subtopic: Quantum Physics
IO.5 Elliptically Polarized Light
 1. Purpose: IO.5 Elliptically Polarized Light Analyze elliptically polarized light; determine the orientation of the vibration ellipse and the ratio of its semi-axes. 2. Apparatus: Gaertner Scientific
1. Purpose: IO.5 Elliptically Polarized Light Analyze elliptically polarized light; determine the orientation of the vibration ellipse and the ratio of its semi-axes. 2. Apparatus: Gaertner Scientific
PHYSICS PAPER 1 (THEORY) (Three hours)
 PHYSICS PAPER 1 (THEORY) (Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must OT start writing during this time.) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PHYSICS PAPER 1 (THEORY) (Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must OT start writing during this time.) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Final Practice Problems
 Final Practice Problems 1. The figure below shows a snapshot graph at t = 0 s of a sinusoidal wave traveling to the right along a string at 50 m/s. (a) Write the equation that describes the displacement
Final Practice Problems 1. The figure below shows a snapshot graph at t = 0 s of a sinusoidal wave traveling to the right along a string at 50 m/s. (a) Write the equation that describes the displacement
Dr. Radhakrishnan A N Assistant Professor of Physics GPTC, Vechoochira
 CONTENTS. Vernier Calipers. Screw Gauge. Simple Pendulum 7. Moment Bar 9. Convex Lens Appendix Vernier Calipers Exp. No: Date: Aim (i) To nd the volume of the given cylinder by measuring its length and
CONTENTS. Vernier Calipers. Screw Gauge. Simple Pendulum 7. Moment Bar 9. Convex Lens Appendix Vernier Calipers Exp. No: Date: Aim (i) To nd the volume of the given cylinder by measuring its length and
Chapter 4. Dispersion of Glass. 4.1 Introduction. 4.2 Apparatus
 Chapter 4 Dispersion of Glass 4.1 Introduction This experiment will develop skills in choosing a suitable fit for data and plotting the resulting curve. Curve fitting will count for a big chunk of the
Chapter 4 Dispersion of Glass 4.1 Introduction This experiment will develop skills in choosing a suitable fit for data and plotting the resulting curve. Curve fitting will count for a big chunk of the
Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Vermaa Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee
 Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Vermaa Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee Module-04 Lecture-02 Diffraction Part - 02 In the previous lecture I discussed single slit and double
Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Vermaa Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee Module-04 Lecture-02 Diffraction Part - 02 In the previous lecture I discussed single slit and double
University of Massachusetts, Amherst
 PHYSICS 286: Modern Physics Laboratory SPRING 2010 (A. Dinsmore and K. Kumar) Feb 2009 Experiment 4: THE FRANCK HERTZ EXPERIMENT Electronic Excitations of a Gas, and Evidence for the Quantization of Atomic
PHYSICS 286: Modern Physics Laboratory SPRING 2010 (A. Dinsmore and K. Kumar) Feb 2009 Experiment 4: THE FRANCK HERTZ EXPERIMENT Electronic Excitations of a Gas, and Evidence for the Quantization of Atomic
Protokoll. Grundpraktikum II - Optical Spectroscopy
 Protokoll Grundpraktikum II - Optical Spectroscopy 1 Elaboration 1.1 Optical Spectroscopy Student: Hauke Rasch, Martin Borchert Tutor: Madsen Date: 22.October2014 This experiment is about the fundamental
Protokoll Grundpraktikum II - Optical Spectroscopy 1 Elaboration 1.1 Optical Spectroscopy Student: Hauke Rasch, Martin Borchert Tutor: Madsen Date: 22.October2014 This experiment is about the fundamental
Lab 10: Spectroscopy & the Hydrogen Atom Phy208 Fall 2008
 Lab 10: Spectroscopy & the Hydrogen Atom Phy208 Fall 2008 Name Section This sheet is the lab document your TA will use to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. To receive full credit
Lab 10: Spectroscopy & the Hydrogen Atom Phy208 Fall 2008 Name Section This sheet is the lab document your TA will use to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. To receive full credit
Telescopes (Chapter 6)
 Telescopes (Chapter 6) Based on Chapter 6 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 7 and 10 on Our planetary system and Jovian planet systems Chapter 5 on Light will be useful for understanding
Telescopes (Chapter 6) Based on Chapter 6 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 7 and 10 on Our planetary system and Jovian planet systems Chapter 5 on Light will be useful for understanding
Einstein Classes, Unit No. 102, 103, Vardhman Ring Road Plaza, Vikas Puri Extn., Outer Ring Road New Delhi , Ph. : ,
 1 O P T I C S 1. Define resolving power of a telescope & microscope and give the expression for its resolving power. 2. Explain briefly the formation of mirage in deserts. 3. The radii of curvature of
1 O P T I C S 1. Define resolving power of a telescope & microscope and give the expression for its resolving power. 2. Explain briefly the formation of mirage in deserts. 3. The radii of curvature of
DAY LABORATORY EXERCISE: SPECTROSCOPY
 AS101 - Day Laboratory: Spectroscopy Page 1 DAY LABORATORY EXERCISE: SPECTROSCOPY Goals: To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are
AS101 - Day Laboratory: Spectroscopy Page 1 DAY LABORATORY EXERCISE: SPECTROSCOPY Goals: To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are
PHYSICS PAPER 1 (THEORY)
 PHYSICS PAPER 1 (THEORY) (Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
PHYSICS PAPER 1 (THEORY) (Three hours) (Candidates are allowed additional 15 minutes for only reading the paper. They must NOT start writing during this time.) ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The Michelson Interferometer
 Experiment #33 The Michelson Interferometer References 1. Your first year physics textbook. 2. Hecht, Optics, Addison Wesley - Chapter 9 in the 4th Ed. (2001). 3. Jenkins and White, Fundamentals of Optics
Experiment #33 The Michelson Interferometer References 1. Your first year physics textbook. 2. Hecht, Optics, Addison Wesley - Chapter 9 in the 4th Ed. (2001). 3. Jenkins and White, Fundamentals of Optics
Determination of the Thickness and the Orientation of a Calcite Plate by Interference Fringes.
 Determination of the Thickness and the Orientation of a Calcite Plate by Interference Fringes. S. T. NAKAMURA AND R. TADIME. [READ SEPTEMBER 19, 1914.] For the explanation of the interference figures by
Determination of the Thickness and the Orientation of a Calcite Plate by Interference Fringes. S. T. NAKAMURA AND R. TADIME. [READ SEPTEMBER 19, 1914.] For the explanation of the interference figures by
Experiment O-2. The Michelson Interferometer
 Experiment O-2 The Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the best known and historically important interferometers. It is a very accurate length-measuring device and has been
Experiment O-2 The Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the best known and historically important interferometers. It is a very accurate length-measuring device and has been
The Grating Spectrometer and Atomic Spectra
 PHY 192 Grating Spectrometer Spring 2012 1 The Grating Spectrometer and Atomic Spectra Introduction In the previous experiment diffraction and interference were discussed and at the end a diffraction grating
PHY 192 Grating Spectrometer Spring 2012 1 The Grating Spectrometer and Atomic Spectra Introduction In the previous experiment diffraction and interference were discussed and at the end a diffraction grating
Atomic and nuclear physics
 Atomic and nuclear physics Atomic shell Normal Zeeman effect LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets Observing the normal Zeeman effect in transverse and longitudinal Objects of the experiment Observing the line triplet
Atomic and nuclear physics Atomic shell Normal Zeeman effect LEYBOLD Physics Leaflets Observing the normal Zeeman effect in transverse and longitudinal Objects of the experiment Observing the line triplet
Measurement of linear and mass attenuation coefficient of alcohol soluble compound for gamma rays at energy MeV
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Archives of Applied Science Research, 2012, 4 (4):1748-1752 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X CODEN (USA) AASRC9 Measurement
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Archives of Applied Science Research, 2012, 4 (4):1748-1752 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X CODEN (USA) AASRC9 Measurement
AS 101: Day Lab #2 Summer Spectroscopy
 Spectroscopy Goals To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are related To see spectral lines from different elements in emission and
Spectroscopy Goals To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are related To see spectral lines from different elements in emission and
filled with water of refractive index 4/3. The water between them forms a thin equi-concave lens. Find the focal length of the combination of glass an
 LIKELY PROBLEMS IN PHYSICS FOR II PUC 1. A ray of light is incident at an angle of 30 0 on one side of a glass slab of thickness 0.05 m. The lateral shift of the ray on passing through the slab is 0.01
LIKELY PROBLEMS IN PHYSICS FOR II PUC 1. A ray of light is incident at an angle of 30 0 on one side of a glass slab of thickness 0.05 m. The lateral shift of the ray on passing through the slab is 0.01
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 9, Issue 1, January ISSN
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 9, Issue 1, January-2018 853 Linear and mass absorption coefficient of methanol solution of oxalic acid by varying concentration at 0.662
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 9, Issue 1, January-2018 853 Linear and mass absorption coefficient of methanol solution of oxalic acid by varying concentration at 0.662
Visible Spectrometer
 Visible Spectrometer Experiment VIS University of Florida Department of Physics PHY4803L Advanced Physics Laboratory Objective The Balmer spectral lines from a hydrogen discharge lamp are observed with
Visible Spectrometer Experiment VIS University of Florida Department of Physics PHY4803L Advanced Physics Laboratory Objective The Balmer spectral lines from a hydrogen discharge lamp are observed with
Optics and Telescopes
 Optics and Telescopes Guiding Questions 1. Why is it important that telescopes be large? 2. Why do most modern telescopes use a large mirror rather than a large lens? 3. Why are observatories in such remote
Optics and Telescopes Guiding Questions 1. Why is it important that telescopes be large? 2. Why do most modern telescopes use a large mirror rather than a large lens? 3. Why are observatories in such remote
Fully achromatic nulling interferometer (FANI) for high SNR exoplanet characterization
 Fully achromatic nulling interferometer (FANI) for high SNR exoplanet characterization François Hénault Institut de Planétologie et d Astrophysique de Grenoble Université Joseph Fourier Centre National
Fully achromatic nulling interferometer (FANI) for high SNR exoplanet characterization François Hénault Institut de Planétologie et d Astrophysique de Grenoble Université Joseph Fourier Centre National
Leveling. 3.1 Definitions
 Leveling 3.1 Definitions Leveling is the procedure used to determine differences in elevation between points that are remote from each other. Elevation is a vertical distance above or below a reference
Leveling 3.1 Definitions Leveling is the procedure used to determine differences in elevation between points that are remote from each other. Elevation is a vertical distance above or below a reference
Photoelectric Effect Experiment
 Experiment 1 Purpose The photoelectric effect is a key experiment in modern physics. In this experiment light is used to excite electrons that (given sufficient energy) can escape from a material producing
Experiment 1 Purpose The photoelectric effect is a key experiment in modern physics. In this experiment light is used to excite electrons that (given sufficient energy) can escape from a material producing
Diffraction Gratings, Atomic Spectra. Prof. Shawhan (substituting for Prof. Hall) November 14, 2016
 Diffraction Gratings, Atomic Spectra Prof. Shawhan (substituting for Prof. Hall) November 14, 2016 1 Increase number of slits: 2 Visual Comparisons 3 4 8 2 Diffraction Grating Note: despite the name, this
Diffraction Gratings, Atomic Spectra Prof. Shawhan (substituting for Prof. Hall) November 14, 2016 1 Increase number of slits: 2 Visual Comparisons 3 4 8 2 Diffraction Grating Note: despite the name, this
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 1 of 38
 F UNDAMENTALS OF PHOTONICS Module 1.1 Nature and Properties of Light Linda J. Vandergriff Director of Photonics System Engineering Science Applications International Corporation McLean, Virginia Light
F UNDAMENTALS OF PHOTONICS Module 1.1 Nature and Properties of Light Linda J. Vandergriff Director of Photonics System Engineering Science Applications International Corporation McLean, Virginia Light
10. Wavelength measurement using prism spectroscopy
 Spk 0. Wavelength measurement using prism spectroscopy 0. Introduction The study of emitted spectra of electromagnetic waves by excited atoms makes for one of the most important methods to investigate
Spk 0. Wavelength measurement using prism spectroscopy 0. Introduction The study of emitted spectra of electromagnetic waves by excited atoms makes for one of the most important methods to investigate
DELHI PUBLIC SCHOOL, BAHADURGARH Sample Paper 1 PHYSICS CLASS-XII Date- Duration:3hr
 SET: 1 General Instructions:- DELHI PUBLIC SCHOOL, BAHADURGARH Sample Paper 1 PHYSICS CLASS-XII Date- Duration:3hr All questions are compulsory. There are 30 questions in total. Questions 1 to 8 carry
SET: 1 General Instructions:- DELHI PUBLIC SCHOOL, BAHADURGARH Sample Paper 1 PHYSICS CLASS-XII Date- Duration:3hr All questions are compulsory. There are 30 questions in total. Questions 1 to 8 carry
UNIT-5 EM WAVES UNIT-6 RAY OPTICS
 UNIT-5 EM WAVES 2 Marks Question 1. To which regions of electromagnetic spectrum do the following wavelengths belong: (a) 250 nm (b) 1500 nm 2. State any one property which is common to all electromagnetic
UNIT-5 EM WAVES 2 Marks Question 1. To which regions of electromagnetic spectrum do the following wavelengths belong: (a) 250 nm (b) 1500 nm 2. State any one property which is common to all electromagnetic
HYDROGEN SPECTRUM. Figure 1 shows the energy level scheme for the hydrogen atom as calculated from equation. Figure 1 Figure 2
 15 Jul 04 Hydrogen.1 HYDROGEN SPECTRUM In this experiment the wavelengths of the visible emission lines of hydrogen (Balmer series) will be measured and compared to the values predicted by Bohr s quantum
15 Jul 04 Hydrogen.1 HYDROGEN SPECTRUM In this experiment the wavelengths of the visible emission lines of hydrogen (Balmer series) will be measured and compared to the values predicted by Bohr s quantum
Sodium Chloride - Analytical Standard
 Sodium Chloride - Analytical Standard Determination of Total Mercury Former numbering: ECSS/CN 312-1982 & ESPA/CN-E-106-1994 1. SCOPE AND FIELD OF APPLICATION The present EuSalt Analytical Standard describes
Sodium Chloride - Analytical Standard Determination of Total Mercury Former numbering: ECSS/CN 312-1982 & ESPA/CN-E-106-1994 1. SCOPE AND FIELD OF APPLICATION The present EuSalt Analytical Standard describes
Fig. 8.1 illustrates the three measurements. air medium A. ray 1. air medium A. ray 2. air medium A. ray 3. Fig For Examiner s Use
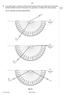 9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
5 TH ERMAL GRADIENT INTERFEROMETRIC MEASUREMENT
 5 TH ERMAL GRADIENT INTERFEROMETRIC MEASUREMENT Gradient Index Measurement with Temperature MODEL OEK-100 PROJECT #4 50 5.1 Introduction It is possible to measure the change in index of refraction of a
5 TH ERMAL GRADIENT INTERFEROMETRIC MEASUREMENT Gradient Index Measurement with Temperature MODEL OEK-100 PROJECT #4 50 5.1 Introduction It is possible to measure the change in index of refraction of a
JRE Group of Institutions ASSIGNMENT # 1 Special Theory of Relativity
 ASSIGNMENT # 1 Special Theory of Relativity 1. What was the objective of conducting the Michelson-Morley experiment? Describe the experiment. How is the negative result of the experiment interpreted? 2.
ASSIGNMENT # 1 Special Theory of Relativity 1. What was the objective of conducting the Michelson-Morley experiment? Describe the experiment. How is the negative result of the experiment interpreted? 2.
Laboratory Exercise 7 MEASUREMENTS IN ASTRONOMY
 Laboratory Exercise 7 MEASUREMENTS IN ASTRONOMY Introduction Part A: The angular resolution of telescopes For astronomical observations, reflecting telescopes have replaced the refracting type of instrument.
Laboratory Exercise 7 MEASUREMENTS IN ASTRONOMY Introduction Part A: The angular resolution of telescopes For astronomical observations, reflecting telescopes have replaced the refracting type of instrument.
NEW STANDARD SEXTANT OF THE U. S. NAVY
 NEW STANDARD SEXTANT OF THE U. S. NAVY Director of the United States of America Hydrographic Office has sent to the International Hydrographic Bureau the following data relating to the new Standard Sextant
NEW STANDARD SEXTANT OF THE U. S. NAVY Director of the United States of America Hydrographic Office has sent to the International Hydrographic Bureau the following data relating to the new Standard Sextant
Practical 1P4 Energy Levels and Band Gaps
 Practical 1P4 Energy Levels and Band Gaps What you should learn from this practical Science This practical illustrates some of the points from the lecture course on Elementary Quantum Mechanics and Bonding
Practical 1P4 Energy Levels and Band Gaps What you should learn from this practical Science This practical illustrates some of the points from the lecture course on Elementary Quantum Mechanics and Bonding
An accessory to the polarizing microscope for the optical examination of crystals.
 513 An accessory to the polarizing microscope for the optical examination of crystals. By H. C. G. VINCENT, M.A., F.G.S. Department of Geology, University of Cape Town. [Taken as read November 4, 1954.]
513 An accessory to the polarizing microscope for the optical examination of crystals. By H. C. G. VINCENT, M.A., F.G.S. Department of Geology, University of Cape Town. [Taken as read November 4, 1954.]
Astronomy 203 practice final examination
 Astronomy 203 practice final examination Fall 1999 If this were a real, in-class examination, you would be reminded here of the exam rules, which are as follows: You may consult only one page of formulas
Astronomy 203 practice final examination Fall 1999 If this were a real, in-class examination, you would be reminded here of the exam rules, which are as follows: You may consult only one page of formulas
Dispersive power. of Prism
 Dispersive power of Pris 1 Dispersive Power of Pris Experient No. Object : To deterine the dispersive power of the aterial of a pris by spectroeter. Apparatus : Spectroeter, pris, spirit level, reading
Dispersive power of Pris 1 Dispersive Power of Pris Experient No. Object : To deterine the dispersive power of the aterial of a pris by spectroeter. Apparatus : Spectroeter, pris, spirit level, reading
Study of Interdiffusion of Calcium Chloride-Water system Using Laser Beam Deflection Sensor
 STUDENT JOURNAL OF PHYSICS Study of Interdiffusion of Calcium Chloride-Water system Using Laser Beam Deflection Sensor T.M. Sreedevi 1, N.P. Dhanya 2, P.R. Sasikumar 3 1 M Sc (Physics, Fourth Semester)
STUDENT JOURNAL OF PHYSICS Study of Interdiffusion of Calcium Chloride-Water system Using Laser Beam Deflection Sensor T.M. Sreedevi 1, N.P. Dhanya 2, P.R. Sasikumar 3 1 M Sc (Physics, Fourth Semester)
Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry. Presentation by, Mrs. Sangita J. Chandratre Department of Microbiology M. J. college, Jalgaon
 Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry Presentation by, Mrs. Sangita J. Chandratre Department of Microbiology M. J. college, Jalgaon Defination In analytical chemistry, Atomic absorption spectroscopy is a
Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry Presentation by, Mrs. Sangita J. Chandratre Department of Microbiology M. J. college, Jalgaon Defination In analytical chemistry, Atomic absorption spectroscopy is a
Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations
 Name: Date: Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations 1. A source produces water waves of frequency 10 Hz. The graph shows the variation with horizontal position of the vertical displacement of the surface
Name: Date: Topic 4 &11 Review Waves & Oscillations 1. A source produces water waves of frequency 10 Hz. The graph shows the variation with horizontal position of the vertical displacement of the surface
Interference- Michelson Interferometer. Interference lecture by Dr. T.Vishwam
 Interference- Michelson Interferometer Interference lecture by Dr. T.Vishwam * Measurement of the coherence length of a spectral line * Measurement of thickness of thin transparent flakes * Measurement
Interference- Michelson Interferometer Interference lecture by Dr. T.Vishwam * Measurement of the coherence length of a spectral line * Measurement of thickness of thin transparent flakes * Measurement
MHS. Physics. Sample Questions. Exam to go from grade 10 to grade 11
 MHS Physics Exam to go from grade 10 to grade 11 Sample Questions 1. non-luminous source of light is one which: 1. emits light by itself 2. carries light inside 3. reflects light coming from other objects
MHS Physics Exam to go from grade 10 to grade 11 Sample Questions 1. non-luminous source of light is one which: 1. emits light by itself 2. carries light inside 3. reflects light coming from other objects
DISPERSION VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS. Two identical prisms made of the same material placed with their based on opposite sides (of the
 DISPERSION VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS Q-1. What will be the spectrum of sun during a total solar eclipse? Q-2. Why the secondary rainbow is always fainter than the primary rainbow? Q-3. Two identical
DISPERSION VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS Q-1. What will be the spectrum of sun during a total solar eclipse? Q-2. Why the secondary rainbow is always fainter than the primary rainbow? Q-3. Two identical
Grade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics Chapters 4, 5 and 6
 Grade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics Chapters 4, 5 and 6 At the end of this unit, students will be expected to 1. Provide examples of ideas and theories of light used in the past to explain observed properties.
Grade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics Chapters 4, 5 and 6 At the end of this unit, students will be expected to 1. Provide examples of ideas and theories of light used in the past to explain observed properties.
Experiment 24: Spectroscopy
 Experiment 24: Spectroscopy Figure 24.1: Spectroscopy EQUIPMENT High Voltage Power Supply Incandescent Light Source (3) Gas Discharge Tubes: 1. Helium 2. Hydrogen 3. Unknown Element Spectrometer Felt (1)
Experiment 24: Spectroscopy Figure 24.1: Spectroscopy EQUIPMENT High Voltage Power Supply Incandescent Light Source (3) Gas Discharge Tubes: 1. Helium 2. Hydrogen 3. Unknown Element Spectrometer Felt (1)
Solution 3: A glass prism deviates the violet light most and the red light least.
 EXERCISE- 6 (A) Question 1: Name three factors on which the deviation produces by a prism depends and state how does it depend on the factors stated by you. Solution 1: The deviation produced by the prism
EXERCISE- 6 (A) Question 1: Name three factors on which the deviation produces by a prism depends and state how does it depend on the factors stated by you. Solution 1: The deviation produced by the prism
Diffraction of light by a grating
 (ta initials) first name (print) last name (print) brock id (ab17cd) (lab date) Experiment 5 Diffraction of light by a grating In this Experiment you will learn the geometical analysis of a diffraction
(ta initials) first name (print) last name (print) brock id (ab17cd) (lab date) Experiment 5 Diffraction of light by a grating In this Experiment you will learn the geometical analysis of a diffraction
THE ZEEMAN EFFECT PHYSICS 359E
 THE ZEEMAN EFFECT PHYSICS 359E INTRODUCTION The Zeeman effect is a demonstration of spatial quantization of angular momentum in atomic physics. Since an electron circling a nucleus is analogous to a current
THE ZEEMAN EFFECT PHYSICS 359E INTRODUCTION The Zeeman effect is a demonstration of spatial quantization of angular momentum in atomic physics. Since an electron circling a nucleus is analogous to a current
The Grating Spectrometer and Atomic Spectra
 PHY 192 Grating Spectrometer 1 The Grating Spectrometer and Atomic Spectra Introduction In the previous experiment diffraction and interference were discussed and at the end a diffraction grating was introduced.
PHY 192 Grating Spectrometer 1 The Grating Spectrometer and Atomic Spectra Introduction In the previous experiment diffraction and interference were discussed and at the end a diffraction grating was introduced.
Phys102 Lecture Diffraction of Light
 Phys102 Lecture 31-33 Diffraction of Light Key Points Diffraction by a Single Slit Diffraction in the Double-Slit Experiment Limits of Resolution Diffraction Grating and Spectroscopy Polarization References
Phys102 Lecture 31-33 Diffraction of Light Key Points Diffraction by a Single Slit Diffraction in the Double-Slit Experiment Limits of Resolution Diffraction Grating and Spectroscopy Polarization References
CBSE QUESTION PAPER. PHYSICS (Theory)
 CBSE QUESTION PAPER PHYSICS (Theory) Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 70 General Instructions: (i) (ii) (iii) All questions are compulsory. There are 30 questions in total. Questions 1 to 8 carry
CBSE QUESTION PAPER PHYSICS (Theory) Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 70 General Instructions: (i) (ii) (iii) All questions are compulsory. There are 30 questions in total. Questions 1 to 8 carry
