Coding sequence array Office hours Wednesday 3-4pm 304A Stanley Hall
|
|
|
- Morgan Hunter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Coding sequence array Office hours Wednesday 3-4pm 304A Stanley Hall Review session 5pm Thursday, Dec. 11 GPB100 Fig RNA-seq Expression effects of cancer AAAAA AAAAA AAAAA Solexa sequencing counts seq maps TCGTTCACTTGTATTGG TCTCTACTGGTGGTGGT GACAAACTGTCGCTGTC TCTCTACCGGTGGTGGT TCGTTCACTTGTAATGG TTGAAGCTACCACCAAC TGTCCTTATCTATGTGT CGTACTTTTTTAATTGT ATCATTGTTCCAGAAAT TTATCAGAGGTGCTGGT CAAAGACCTCATTTAAT AGGAGGGTATATATGCT R0 genome pos sbaysum.fsa chr03.fsa orient R F sbaysum.fsa chr04.fsa F R sbaysum.fsa chr11.fsa R F chr14.fsa sbaysum.fsa chr14.fsa R R R R0 U1 R0 Diagnosis via transcriptional profile Diagnosis via transcriptional profile patient samples transcripts 1
2 Marker is linked to polymorphism in expression regulation cascade Linkage mapping of mrna levels Black 6 mouse x DBA mouse G 111 F2 progeny kinase TF Microarray each F2 liver TF Genotype each F2 TF ORF G Looking for linkage (coinheritance) between marker and mrna level. G Locally acting polymorphisms Nonlocal polymorphisms ~25% of varying mrnas are caused by locally acting polymorphism Polymorphism responsible for mrna difference is at the locus of the gene itself Nonlocal polymorphisms Black 6 mouse x DBA mouse 111 F2 progeny One polymorphism in a key regulator can affect a regulon: 100 s of related mrnas. Microarray each F2 liver Genotype each F2 Measure fat pad each F2 2
3 Colored curves = fat mass at different body locations Finding polymorphism responsible for difference in macroscopic phenotype is hard Finding polymorphism responsible for difference in macroscopic phenotype is hard If mrnas change too, can learn mechanism from known function of encoded proteins 3
4 Counts allele 1/allele 2, cases Counts allele 1/allele 2, controls = 1.5 Marker predicts quantitative expression level = association Linkage of human transcripts Can we map expression traits first, disease afterward? 4
5 Linkage of human transcripts Association of human transcripts Association of human transcripts Association in multiple populations linkage (families) assoc (unrelated) European-Americans in Utah Han Chinese and Japanese Association in multiple populations A new brand of genetic variation 5
6 Translation Translation Fig Fig PSI+ yeast read through STOPs PSI+ yeast read through STOPs PSI+ yeast read through STOPs Weird genetics of read-through Haploid PSI+ Haploid psi- Diploid PSI bp 6
7 Weird genetics of read-through Weird genetics of read-through Haploid PSI+ Haploid psi- Haploid PSI+ Haploid psi- Diploid PSI+ sporulate Diploid PSI+ sporulate But why wouldn t it get diluted over many divisions? Haploid PSI+ Haploid PSI+ Haploid PSI+ Haploid PSI+ Haploid PSI+ Haploid PSI+ Haploid PSI+ Haploid PSI+ Cytoplasmic aggregates of Sup35 Cytoplasmic aggregates of Sup35 How would this explain the results? Hard to make aggregate, easy to join Protein inheritance 7
8 Protein inheritance PSI+ begets more PSI+ Original from PSI+ nucleates in all progeny Not due to dominant genetics in the usual way. Nucleating prions in mad cow disease Is PSI+ the yeast analog of mad cow or Alzheimer s? If bad, would be lost If bad, would be lost (Pichia methanolica vs. S. cerevisiae) 8
9 Genetically distinct S. cerevisiae strains Genetically distinct S. cerevisiae strains Genetically distinct S. cerevisiae strains Genetically distinct S. cerevisiae strains 50 C Why would aggregates result in so many novel abilities and traits?? 50 C 9
10 The clincher Why would aggregates result in so many novel abilities and traits?? Apparently does not happen in Alzheimer s The clincher (partial LOF) The clincher (partial LOF) What do you conclude? A. Sup35 does not cause resistance to paraquat. B. Prions do not cause resistance to paraquat. C. Aggregation is not necessary to cause resistance to paraquat. D. Aggregation is not sufficient to cause resistance to paraquat. The clincher (partial LOF) The clincher (partial LOF) Aggregates per se don t cause resistance. Aggregates per se don t cause resistance. Losing function of sup35 does. 10
11 Aggregation = more read-through Aggregation = more read-through New extra-long forms of proteins cause new traits. PSI+ allows epigenetic change in protein sequence. Genetically distinct S. cerevisiae strains Genetic effects? Phenotypes varied between genetically diverse PSI+ strains. Genetic effects? Aggregation = more read-through Genetically distinct S. cerevisiae strains Phenotypes varied between genetically diverse PSI+ strains. How can the cause be genetic and non-genetic (protein aggregates) at the same time? 11
12 Aggregation = more read-through Aggregation = more read-through UTR mutations usually occur and have no effect UTR mutations usually occur and have no effect, so organism doesn t die and allele is maintained. Aggregation = more read-through Aggregation = more read-through UTR mutations usually occur and have no effect, so organism doesn t die and allele is maintained. Now in PSI+, they manifest! Sequence differences in readthrough region cause phenotypic differences between PSI+ strains. Cryptic variation: DNA sequence differences between individuals that are usually not expressed 12
Expression QTLs and Mapping of Complex Trait Loci. Paul Schliekelman Statistics Department University of Georgia
 Expression QTLs and Mapping of Complex Trait Loci Paul Schliekelman Statistics Department University of Georgia Definitions: Genes, Loci and Alleles A gene codes for a protein. Proteins due everything.
Expression QTLs and Mapping of Complex Trait Loci Paul Schliekelman Statistics Department University of Georgia Definitions: Genes, Loci and Alleles A gene codes for a protein. Proteins due everything.
A complementation test would be done by crossing the haploid strains and scoring the phenotype in the diploids.
 Problem set H answers 1. To study DNA repair mechanisms, geneticists isolated yeast mutants that were sensitive to various types of radiation; for example, mutants that were more sensitive to UV light.
Problem set H answers 1. To study DNA repair mechanisms, geneticists isolated yeast mutants that were sensitive to various types of radiation; for example, mutants that were more sensitive to UV light.
GENETICS - CLUTCH CH.1 INTRODUCTION TO GENETICS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: HISTORY OF GENETICS The earliest use of genetics was through of plants and animals (8000-1000 B.C.) Selective breeding (artificial selection) is the process of breeding organisms
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: HISTORY OF GENETICS The earliest use of genetics was through of plants and animals (8000-1000 B.C.) Selective breeding (artificial selection) is the process of breeding organisms
UNIT 8 BIOLOGY: Meiosis and Heredity Page 148
 UNIT 8 BIOLOGY: Meiosis and Heredity Page 148 CP: CHAPTER 6, Sections 1-6; CHAPTER 7, Sections 1-4; HN: CHAPTER 11, Section 1-5 Standard B-4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the molecular
UNIT 8 BIOLOGY: Meiosis and Heredity Page 148 CP: CHAPTER 6, Sections 1-6; CHAPTER 7, Sections 1-4; HN: CHAPTER 11, Section 1-5 Standard B-4: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the molecular
GSBHSRSBRSRRk IZTI/^Q. LlML. I Iv^O IV I I I FROM GENES TO GENOMES ^^^H*" ^^^^J*^ ill! BQPIP. illt. goidbkc. itip31. li4»twlil FIFTH EDITION
 FIFTH EDITION IV I ^HHk ^ttm IZTI/^Q i I II MPHBBMWBBIHB '-llwmpbi^hbwm^^pfc ' GSBHSRSBRSRRk LlML I I \l 1MB ^HP'^^MMMP" jflp^^^^^^^^st I Iv^O FROM GENES TO GENOMES %^MiM^PM^^MWi99Mi$9i0^^ ^^^^^^^^^^^^^V^^^fii^^t^i^^^^^
FIFTH EDITION IV I ^HHk ^ttm IZTI/^Q i I II MPHBBMWBBIHB '-llwmpbi^hbwm^^pfc ' GSBHSRSBRSRRk LlML I I \l 1MB ^HP'^^MMMP" jflp^^^^^^^^st I Iv^O FROM GENES TO GENOMES %^MiM^PM^^MWi99Mi$9i0^^ ^^^^^^^^^^^^^V^^^fii^^t^i^^^^^
KEY: Chapter 9 Genetics of Animal Breeding.
 KEY: Chapter 9 Genetics of Animal Breeding. Answer each question using the reading assigned to you. You can access this information by clicking on the following URL: https://drive.google.com/a/meeker.k12.co.us/file/d/0b1yf08xgyhnad08xugxsnfvba28/edit?usp=sh
KEY: Chapter 9 Genetics of Animal Breeding. Answer each question using the reading assigned to you. You can access this information by clicking on the following URL: https://drive.google.com/a/meeker.k12.co.us/file/d/0b1yf08xgyhnad08xugxsnfvba28/edit?usp=sh
Designer Genes C Test
 Northern Regional: January 19 th, 2019 Designer Genes C Test Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Rank: Score: Directions: You will have 50 minutes to complete the test. You may not write on the
Northern Regional: January 19 th, 2019 Designer Genes C Test Name(s): Team Name: School Name: Team Number: Rank: Score: Directions: You will have 50 minutes to complete the test. You may not write on the
Formative/Summative Assessments (Tests, Quizzes, reflective writing, Journals, Presentations)
 Biology Curriculum Map 2017-18 2 Weeks- Introduction to Biology: Scientific method, lab safety, organizing and analyzing data, and psuedoscience. This unit establishes the fundamental nature of scientific
Biology Curriculum Map 2017-18 2 Weeks- Introduction to Biology: Scientific method, lab safety, organizing and analyzing data, and psuedoscience. This unit establishes the fundamental nature of scientific
2. Der Dissertation zugrunde liegende Publikationen und Manuskripte. 2.1 Fine scale mapping in the sex locus region of the honey bee (Apis mellifera)
 2. Der Dissertation zugrunde liegende Publikationen und Manuskripte 2.1 Fine scale mapping in the sex locus region of the honey bee (Apis mellifera) M. Hasselmann 1, M. K. Fondrk², R. E. Page Jr.² und
2. Der Dissertation zugrunde liegende Publikationen und Manuskripte 2.1 Fine scale mapping in the sex locus region of the honey bee (Apis mellifera) M. Hasselmann 1, M. K. Fondrk², R. E. Page Jr.² und
Genetics 275 Notes Week 7
 Cytoplasmic Inheritance Genetics 275 Notes Week 7 Criteriafor recognition of cytoplasmic inheritance: 1. Reciprocal crosses give different results -mainly due to the fact that the female parent contributes
Cytoplasmic Inheritance Genetics 275 Notes Week 7 Criteriafor recognition of cytoplasmic inheritance: 1. Reciprocal crosses give different results -mainly due to the fact that the female parent contributes
Exam 1 PBG430/
 1 Exam 1 PBG430/530 2014 1. You read that the genome size of maize is 2,300 Mb and that in this species 2n = 20. This means that there are 2,300 Mb of DNA in a cell that is a. n (e.g. gamete) b. 2n (e.g.
1 Exam 1 PBG430/530 2014 1. You read that the genome size of maize is 2,300 Mb and that in this species 2n = 20. This means that there are 2,300 Mb of DNA in a cell that is a. n (e.g. gamete) b. 2n (e.g.
Solutions to Problem Set 4
 Question 1 Solutions to 7.014 Problem Set 4 Because you have not read much scientific literature, you decide to study the genetics of garden peas. You have two pure breeding pea strains. One that is tall
Question 1 Solutions to 7.014 Problem Set 4 Because you have not read much scientific literature, you decide to study the genetics of garden peas. You have two pure breeding pea strains. One that is tall
Objective 3.01 (DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis)
 Objective 3.01 (DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis) DNA Structure o Discovered by Watson and Crick o Double-stranded o Shape is a double helix (twisted ladder) o Made of chains of nucleotides: o Has four types
Objective 3.01 (DNA, RNA and Protein Synthesis) DNA Structure o Discovered by Watson and Crick o Double-stranded o Shape is a double helix (twisted ladder) o Made of chains of nucleotides: o Has four types
Parts 2. Modeling chromosome segregation
 Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 2 Meiosis Goals: To increase your familiarity with the molecular control of meiosis, outcomes of meiosis, and the important role of crossing over in generating genetic
Genome 371, Autumn 2018 Quiz Section 2 Meiosis Goals: To increase your familiarity with the molecular control of meiosis, outcomes of meiosis, and the important role of crossing over in generating genetic
Chapter 2: Extensions to Mendel: Complexities in Relating Genotype to Phenotype.
 Chapter 2: Extensions to Mendel: Complexities in Relating Genotype to Phenotype. please read pages 38-47; 49-55;57-63. Slide 1 of Chapter 2 1 Extension sot Mendelian Behavior of Genes Single gene inheritance
Chapter 2: Extensions to Mendel: Complexities in Relating Genotype to Phenotype. please read pages 38-47; 49-55;57-63. Slide 1 of Chapter 2 1 Extension sot Mendelian Behavior of Genes Single gene inheritance
1. Contains the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose. 2. Single-stranded instead of double stranded. 3. Contains uracil in place of thymine.
 Protein Synthesis & Mutations RNA 1. Contains the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose. 2. Single-stranded instead of double stranded. 3. Contains uracil in place of thymine. RNA Contains: 1. Adenine 2.
Protein Synthesis & Mutations RNA 1. Contains the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose. 2. Single-stranded instead of double stranded. 3. Contains uracil in place of thymine. RNA Contains: 1. Adenine 2.
Lecture 7 (FW) February 11, 2009 Phenotype and Genotype Reading: pp
 Lecture 7 (FW) February 11, 2009 Phenotype and Genotype Reading: pp. 51-62 Annoucement: A review session for the first mid term will be held on Tuesday, 2/24, from 5-6:30 PM in 159 Mulford Hall. The mid
Lecture 7 (FW) February 11, 2009 Phenotype and Genotype Reading: pp. 51-62 Annoucement: A review session for the first mid term will be held on Tuesday, 2/24, from 5-6:30 PM in 159 Mulford Hall. The mid
Linear Regression (1/1/17)
 STA613/CBB540: Statistical methods in computational biology Linear Regression (1/1/17) Lecturer: Barbara Engelhardt Scribe: Ethan Hada 1. Linear regression 1.1. Linear regression basics. Linear regression
STA613/CBB540: Statistical methods in computational biology Linear Regression (1/1/17) Lecturer: Barbara Engelhardt Scribe: Ethan Hada 1. Linear regression 1.1. Linear regression basics. Linear regression
Mitosis & Meiosis Practice Test
 Name: DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST Class: ALL ID: A Mitosis & Meiosis Practice Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make
Name: DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST Class: ALL ID: A Mitosis & Meiosis Practice Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make
Parts 2. Modeling chromosome segregation
 Genome 371, Autumn 2017 Quiz Section 2 Meiosis Goals: To increase your familiarity with the molecular control of meiosis, outcomes of meiosis, and the important role of crossing over in generating genetic
Genome 371, Autumn 2017 Quiz Section 2 Meiosis Goals: To increase your familiarity with the molecular control of meiosis, outcomes of meiosis, and the important role of crossing over in generating genetic
Computational Biology: Basics & Interesting Problems
 Computational Biology: Basics & Interesting Problems Summary Sources of information Biological concepts: structure & terminology Sequencing Gene finding Protein structure prediction Sources of information
Computational Biology: Basics & Interesting Problems Summary Sources of information Biological concepts: structure & terminology Sequencing Gene finding Protein structure prediction Sources of information
Related Courses He who asks is a fool for five minutes, but he who does not ask remains a fool forever.
 CSE 527 Computational Biology http://www.cs.washington.edu/527 Lecture 1: Overview & Bio Review Autumn 2004 Larry Ruzzo Related Courses He who asks is a fool for five minutes, but he who does not ask remains
CSE 527 Computational Biology http://www.cs.washington.edu/527 Lecture 1: Overview & Bio Review Autumn 2004 Larry Ruzzo Related Courses He who asks is a fool for five minutes, but he who does not ask remains
AP Biology Unit 6 Practice Test 1. A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following mitosis and is found to have an average of 8
 AP Biology Unit 6 Practice Test Name: 1. A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following mitosis and is found to have an average of 8 picograms of DNA per nucleus. How many picograms
AP Biology Unit 6 Practice Test Name: 1. A group of cells is assayed for DNA content immediately following mitosis and is found to have an average of 8 picograms of DNA per nucleus. How many picograms
Reinforcement Unit 3 Resource Book. Meiosis and Mendel KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have.
 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. Your body is made of two basic cell types. One basic type are somatic cells, also called body cells,
6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. Your body is made of two basic cell types. One basic type are somatic cells, also called body cells,
Principles of Genetics
 Principles of Genetics Snustad, D ISBN-13: 9780470903599 Table of Contents C H A P T E R 1 The Science of Genetics 1 An Invitation 2 Three Great Milestones in Genetics 2 DNA as the Genetic Material 6 Genetics
Principles of Genetics Snustad, D ISBN-13: 9780470903599 Table of Contents C H A P T E R 1 The Science of Genetics 1 An Invitation 2 Three Great Milestones in Genetics 2 DNA as the Genetic Material 6 Genetics
Name: Period: EOC Review Part F Outline
 Name: Period: EOC Review Part F Outline Mitosis and Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences
Name: Period: EOC Review Part F Outline Mitosis and Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences
9 Genetic diversity and adaptation Support. AQA Biology. Genetic diversity and adaptation. Specification reference. Learning objectives.
 Genetic diversity and adaptation Specification reference 3.4.3 3.4.4 Learning objectives After completing this worksheet you should be able to: understand how meiosis produces haploid gametes know how
Genetic diversity and adaptation Specification reference 3.4.3 3.4.4 Learning objectives After completing this worksheet you should be able to: understand how meiosis produces haploid gametes know how
Lecture 18 June 2 nd, Gene Expression Regulation Mutations
 Lecture 18 June 2 nd, 2016 Gene Expression Regulation Mutations From Gene to Protein Central Dogma Replication DNA RNA PROTEIN Transcription Translation RNA Viruses: genome is RNA Reverse Transcriptase
Lecture 18 June 2 nd, 2016 Gene Expression Regulation Mutations From Gene to Protein Central Dogma Replication DNA RNA PROTEIN Transcription Translation RNA Viruses: genome is RNA Reverse Transcriptase
Lesson 4: Understanding Genetics
 Lesson 4: Understanding Genetics 1 Terms Alleles Chromosome Co dominance Crossover Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA Dominant Genetic code Genome Genotype Heredity Heritability Heritability estimate Heterozygous
Lesson 4: Understanding Genetics 1 Terms Alleles Chromosome Co dominance Crossover Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA Dominant Genetic code Genome Genotype Heredity Heritability Heritability estimate Heterozygous
The phenotype of this worm is wild type. When both genes are mutant: The phenotype of this worm is double mutant Dpy and Unc phenotype.
 Series 2: Cross Diagrams - Complementation There are two alleles for each trait in a diploid organism In C. elegans gene symbols are ALWAYS italicized. To represent two different genes on the same chromosome:
Series 2: Cross Diagrams - Complementation There are two alleles for each trait in a diploid organism In C. elegans gene symbols are ALWAYS italicized. To represent two different genes on the same chromosome:
Biology I Level - 2nd Semester Final Review
 Biology I Level - 2nd Semester Final Review The 2 nd Semester Final encompasses all material that was discussed during second semester. It s important that you review ALL notes and worksheets from the
Biology I Level - 2nd Semester Final Review The 2 nd Semester Final encompasses all material that was discussed during second semester. It s important that you review ALL notes and worksheets from the
Meiosis and Mendel. Chapter 6
 Meiosis and Mendel Chapter 6 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS Key Concept Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. Body Cells vs. Gametes You have body cells and gametes body cells
Meiosis and Mendel Chapter 6 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS Key Concept Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. Body Cells vs. Gametes You have body cells and gametes body cells
The phenotype of this worm is wild type. When both genes are mutant: The phenotype of this worm is double mutant Dpy and Unc phenotype.
 Series 1: Cross Diagrams There are two alleles for each trait in a diploid organism In C. elegans gene symbols are ALWAYS italicized. To represent two different genes on the same chromosome: When both
Series 1: Cross Diagrams There are two alleles for each trait in a diploid organism In C. elegans gene symbols are ALWAYS italicized. To represent two different genes on the same chromosome: When both
that does not happen during mitosis?
 Review! What is a somatic cell?! What is a sex cell?! What is a haploid cell?! What is a diploid cell?! Why is cell division important?! What are the different types of cell division?! What are these useful
Review! What is a somatic cell?! What is a sex cell?! What is a haploid cell?! What is a diploid cell?! Why is cell division important?! What are the different types of cell division?! What are these useful
Untitled Document. A. antibiotics B. cell structure C. DNA structure D. sterile procedures
 Name: Date: 1. The discovery of which of the following has most directly led to advances in the identification of suspects in criminal investigations and in the identification of genetic diseases? A. antibiotics
Name: Date: 1. The discovery of which of the following has most directly led to advances in the identification of suspects in criminal investigations and in the identification of genetic diseases? A. antibiotics
Interphase & Cell Division
 1 Interphase & Cell Division 2 G1 = cell grows and carries out its normal job. S phase = DNA is copied (replicated/duplicated) G2 = Cell prepares for division 3 During mitosis, the nuclear membrane breaks
1 Interphase & Cell Division 2 G1 = cell grows and carries out its normal job. S phase = DNA is copied (replicated/duplicated) G2 = Cell prepares for division 3 During mitosis, the nuclear membrane breaks
- mutations can occur at different levels from single nucleotide positions in DNA to entire genomes.
 February 8, 2005 Bio 107/207 Winter 2005 Lecture 11 Mutation and transposable elements - the term mutation has an interesting history. - as far back as the 17th century, it was used to describe any drastic
February 8, 2005 Bio 107/207 Winter 2005 Lecture 11 Mutation and transposable elements - the term mutation has an interesting history. - as far back as the 17th century, it was used to describe any drastic
Chapter 17. From Gene to Protein. Biology Kevin Dees
 Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein DNA The information molecule Sequences of bases is a code DNA organized in to chromosomes Chromosomes are organized into genes What do the genes actually say??? Reflecting
Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein DNA The information molecule Sequences of bases is a code DNA organized in to chromosomes Chromosomes are organized into genes What do the genes actually say??? Reflecting
When one gene is wild type and the other mutant:
 Series 2: Cross Diagrams Linkage Analysis There are two alleles for each trait in a diploid organism In C. elegans gene symbols are ALWAYS italicized. To represent two different genes on the same chromosome:
Series 2: Cross Diagrams Linkage Analysis There are two alleles for each trait in a diploid organism In C. elegans gene symbols are ALWAYS italicized. To represent two different genes on the same chromosome:
Chromosome duplication and distribution during cell division
 CELL DIVISION AND HEREDITY Student Packet SUMMARY IN EUKARYOTES, HERITABLE INFORMATION IS PASSED TO THE NEXT GENERATION VIA PROCESSES THAT INCLUDE THE CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS /MEIOSIS AND FERTILIZATION Mitosis
CELL DIVISION AND HEREDITY Student Packet SUMMARY IN EUKARYOTES, HERITABLE INFORMATION IS PASSED TO THE NEXT GENERATION VIA PROCESSES THAT INCLUDE THE CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS /MEIOSIS AND FERTILIZATION Mitosis
BTRY 7210: Topics in Quantitative Genomics and Genetics
 BTRY 7210: Topics in Quantitative Genomics and Genetics Jason Mezey Biological Statistics and Computational Biology (BSCB) Department of Genetic Medicine jgm45@cornell.edu February 12, 2015 Lecture 3:
BTRY 7210: Topics in Quantitative Genomics and Genetics Jason Mezey Biological Statistics and Computational Biology (BSCB) Department of Genetic Medicine jgm45@cornell.edu February 12, 2015 Lecture 3:
Verification of the Principles of Genetics by Manipulating Saccharomyces Cerevisiae and Observing Meiotic Products ABSTRACT
 November 27, 2002 Bio251 Dr. Calhoon Verification of the Principles of Genetics by Manipulating Saccharomyces Cerevisiae and Observing Meiotic Products ABSTRACT The experiment was conducted to verify the
November 27, 2002 Bio251 Dr. Calhoon Verification of the Principles of Genetics by Manipulating Saccharomyces Cerevisiae and Observing Meiotic Products ABSTRACT The experiment was conducted to verify the
Variation of Traits. genetic variation: the measure of the differences among individuals within a population
 Genetic variability is the measure of the differences among individuals within a population. Because some traits are more suited to certain environments, creating particular niches and fits, we know that
Genetic variability is the measure of the differences among individuals within a population. Because some traits are more suited to certain environments, creating particular niches and fits, we know that
Development. biologically-inspired computing. lecture 16. Informatics luis rocha x x x. Syntactic Operations. biologically Inspired computing
 lecture 16 -inspired S S2 n p!!! 1 S Syntactic Operations al Code:N Development x x x 1 2 n p S Sections I485/H400 course outlook Assignments: 35% Students will complete 4/5 assignments based on algorithms
lecture 16 -inspired S S2 n p!!! 1 S Syntactic Operations al Code:N Development x x x 1 2 n p S Sections I485/H400 course outlook Assignments: 35% Students will complete 4/5 assignments based on algorithms
genome a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another gene the passing of traits from one generation to the next
 genetics the study of heredity heredity sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait genome a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another gene trait the passing
genetics the study of heredity heredity sequence of DNA that codes for a protein and thus determines a trait genome a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another gene trait the passing
Learning Objectives:
 Review! Why is cell division important?! What are the different types of cell division?! What are these useful for?! What are the products?! What is a somatic cell?! What is a sex cell?! What is a haploid
Review! Why is cell division important?! What are the different types of cell division?! What are these useful for?! What are the products?! What is a somatic cell?! What is a sex cell?! What is a haploid
Name. Diversity of Life
 Review Guide Semester 1 End of Course Exam in Biology Name Diversity of Life Vocabulary to know and be able to apply: Prokaryotic, eukaryotic, unicellular, multicellular, sexual reproduction, asexual reproduction,
Review Guide Semester 1 End of Course Exam in Biology Name Diversity of Life Vocabulary to know and be able to apply: Prokaryotic, eukaryotic, unicellular, multicellular, sexual reproduction, asexual reproduction,
Describe the process of cell division in prokaryotic cells. The Cell Cycle
 The Cell Cycle Objective # 1 In this topic we will examine the cell cycle, the series of changes that a cell goes through from one division to the next. We will pay particular attention to how the genetic
The Cell Cycle Objective # 1 In this topic we will examine the cell cycle, the series of changes that a cell goes through from one division to the next. We will pay particular attention to how the genetic
Introduction to Bioinformatics
 CSCI8980: Applied Machine Learning in Computational Biology Introduction to Bioinformatics Rui Kuang Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Minnesota kuang@cs.umn.edu History of Bioinformatics
CSCI8980: Applied Machine Learning in Computational Biology Introduction to Bioinformatics Rui Kuang Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of Minnesota kuang@cs.umn.edu History of Bioinformatics
Genetics (patterns of inheritance)
 MENDELIAN GENETICS branch of biology that studies how genetic characteristics are inherited MENDELIAN GENETICS Gregory Mendel, an Augustinian monk (1822-1884), was the first who systematically studied
MENDELIAN GENETICS branch of biology that studies how genetic characteristics are inherited MENDELIAN GENETICS Gregory Mendel, an Augustinian monk (1822-1884), was the first who systematically studied
Peddie Summer Day School
 Peddie Summer Day School Course Syllabus: BIOLOGY Teacher: Mr. Jeff Tuliszewski Text: Biology by Miller and Levine, Prentice Hall, 2010 edition ISBN 9780133669510 Guided Reading Workbook for Biology ISBN
Peddie Summer Day School Course Syllabus: BIOLOGY Teacher: Mr. Jeff Tuliszewski Text: Biology by Miller and Levine, Prentice Hall, 2010 edition ISBN 9780133669510 Guided Reading Workbook for Biology ISBN
Name Class Date. KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have.
 Section 1: Chromosomes and Meiosis KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. VOCABULARY somatic cell autosome fertilization gamete sex chromosome diploid homologous
Section 1: Chromosomes and Meiosis KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. VOCABULARY somatic cell autosome fertilization gamete sex chromosome diploid homologous
Lecture 2: Read about the yeast MAT locus in Molecular Biology of the Gene. Watson et al. Chapter 10. Plus section on yeast as a model system Read
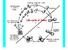 Lecture 2: Read about the yeast MAT locus in Molecular Biology of the Gene. Watson et al. Chapter 10. Plus section on yeast as a model system Read chapter 22 and chapter 10 [section on MATing type gene
Lecture 2: Read about the yeast MAT locus in Molecular Biology of the Gene. Watson et al. Chapter 10. Plus section on yeast as a model system Read chapter 22 and chapter 10 [section on MATing type gene
1. Draw, label and describe the structure of DNA and RNA including bonding mechanisms.
 Practicing Biology BIG IDEA 3.A 1. Draw, label and describe the structure of DNA and RNA including bonding mechanisms. 2. Using at least 2 well-known experiments, describe which features of DNA and RNA
Practicing Biology BIG IDEA 3.A 1. Draw, label and describe the structure of DNA and RNA including bonding mechanisms. 2. Using at least 2 well-known experiments, describe which features of DNA and RNA
G C T G U A. template strand
 A 5 w 3 3 c 5 mrna RNA polymerase T G C A G C C T G U A coding or sense st AUG?? template strand The triplet code 3 bases = 1 amino acid Punctuation: sta rt: sto p: AUGA CUU CAGUAAC AU U AA C C AUG = methionine,
A 5 w 3 3 c 5 mrna RNA polymerase T G C A G C C T G U A coding or sense st AUG?? template strand The triplet code 3 bases = 1 amino acid Punctuation: sta rt: sto p: AUGA CUU CAGUAAC AU U AA C C AUG = methionine,
Biology EOC Review Study Questions
 Biology EOC Review Study Questions Microscopes and Characteristics of Life 1. How do you calculate total magnification on a compound light microscope? 2. What is the basic building block of all living
Biology EOC Review Study Questions Microscopes and Characteristics of Life 1. How do you calculate total magnification on a compound light microscope? 2. What is the basic building block of all living
Unit 3 - Molecular Biology & Genetics - Review Packet
 Name Date Hour Unit 3 - Molecular Biology & Genetics - Review Packet True / False Questions - Indicate True or False for the following statements. 1. Eye color, hair color and the shape of your ears can
Name Date Hour Unit 3 - Molecular Biology & Genetics - Review Packet True / False Questions - Indicate True or False for the following statements. 1. Eye color, hair color and the shape of your ears can
Introduc)on to Gene)cs How to Analyze Your Own Genome Fall 2013
 Introduc)on to Gene)cs 02-223 How to Analyze Your Own Genome Fall 2013 Overview Primer on gene
Introduc)on to Gene)cs 02-223 How to Analyze Your Own Genome Fall 2013 Overview Primer on gene
CHAPTER 23 THE EVOLUTIONS OF POPULATIONS. Section C: Genetic Variation, the Substrate for Natural Selection
 CHAPTER 23 THE EVOLUTIONS OF POPULATIONS Section C: Genetic Variation, the Substrate for Natural Selection 1. Genetic variation occurs within and between populations 2. Mutation and sexual recombination
CHAPTER 23 THE EVOLUTIONS OF POPULATIONS Section C: Genetic Variation, the Substrate for Natural Selection 1. Genetic variation occurs within and between populations 2. Mutation and sexual recombination
Name: Per: Task: To create a model that explains how bi-racial parents can have black and white twins
 Name: Per: Genetics Test Review Task: To create a model that explains how bi-racial parents can have black and white twins Part 1: DNA to Protein to Trait LT15 (Protein and Traits) - Proteins express inherited
Name: Per: Genetics Test Review Task: To create a model that explains how bi-racial parents can have black and white twins Part 1: DNA to Protein to Trait LT15 (Protein and Traits) - Proteins express inherited
Prof. Fahd M. Nasr. Lebanese university Faculty of sciences I Department of Natural Sciences.
 Prof. Fahd M. Nasr Lebanese university Faculty of sciences I Department of Natural Sciences fnasr@ul.edu.lb B3206 Microbial Genetics Eukaryotic M. G. The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a genetic model
Prof. Fahd M. Nasr Lebanese university Faculty of sciences I Department of Natural Sciences fnasr@ul.edu.lb B3206 Microbial Genetics Eukaryotic M. G. The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a genetic model
Three different fusions led to three basic ideas: 1) If one fuses a cell in mitosis with a cell in any other stage of the cell cycle, the chromosomes
 Section Notes The cell division cycle presents an interesting system to study because growth and division must be carefully coordinated. For many cells it is important that it reaches the correct size
Section Notes The cell division cycle presents an interesting system to study because growth and division must be carefully coordinated. For many cells it is important that it reaches the correct size
Full file at CHAPTER 2 Genetics
 CHAPTER 2 Genetics MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Chromosomes are a. small linear bodies. b. contained in cells. c. replicated during cell division. 2. A cross between true-breeding plants bearing yellow seeds produces
CHAPTER 2 Genetics MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Chromosomes are a. small linear bodies. b. contained in cells. c. replicated during cell division. 2. A cross between true-breeding plants bearing yellow seeds produces
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK. COURSE OUTLINE BIOL 310 The Human Genome. Prepared By: Ron Tavernier
 STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE BIOL 310 The Human Genome Prepared By: Ron Tavernier SCHOOL OF SCIENCE, HEALTH & CRIMINAL JUSTICE SCIENCE DEPARTMENT May
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK COURSE OUTLINE BIOL 310 The Human Genome Prepared By: Ron Tavernier SCHOOL OF SCIENCE, HEALTH & CRIMINAL JUSTICE SCIENCE DEPARTMENT May
Module B Unit 5 Cell Growth and Reproduction. Mr. Mitcheltree
 Module B Unit 5 Cell Growth and Reproduction Mr. Mitcheltree DNA and Genetics - The Cell and Inheritance Gene = group of codons that code for a specific protein Allele = alternate form of a gene A dominant,
Module B Unit 5 Cell Growth and Reproduction Mr. Mitcheltree DNA and Genetics - The Cell and Inheritance Gene = group of codons that code for a specific protein Allele = alternate form of a gene A dominant,
Introduction to population genetics & evolution
 Introduction to population genetics & evolution Course Organization Exam dates: Feb 19 March 1st Has everybody registered? Did you get the email with the exam schedule Summer seminar: Hot topics in Bioinformatics
Introduction to population genetics & evolution Course Organization Exam dates: Feb 19 March 1st Has everybody registered? Did you get the email with the exam schedule Summer seminar: Hot topics in Bioinformatics
A Few Terms: When and where do you want your cells to divide?
 Today: - Lab 4 Debrief - Mitosis - Lunch -Meiosis Other: Blood Drive Today! TIME: 11:00am 1:00pm + 2:00pm 5:00pm PLACE: Baxter Events Center Thinking About Mitosis When and where do you want your cells
Today: - Lab 4 Debrief - Mitosis - Lunch -Meiosis Other: Blood Drive Today! TIME: 11:00am 1:00pm + 2:00pm 5:00pm PLACE: Baxter Events Center Thinking About Mitosis When and where do you want your cells
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005
 7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
Chapter 15 Active Reading Guide Regulation of Gene Expression
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 15 Active Reading Guide Regulation of Gene Expression The overview for Chapter 15 introduces the idea that while all cells of an organism have all genes in the genome,
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 15 Active Reading Guide Regulation of Gene Expression The overview for Chapter 15 introduces the idea that while all cells of an organism have all genes in the genome,
Eukaryotic Gene Expression
 Eukaryotic Gene Expression Lectures 22-23 Several Features Distinguish Eukaryotic Processes From Mechanisms in Bacteria 123 Eukaryotic Gene Expression Several Features Distinguish Eukaryotic Processes
Eukaryotic Gene Expression Lectures 22-23 Several Features Distinguish Eukaryotic Processes From Mechanisms in Bacteria 123 Eukaryotic Gene Expression Several Features Distinguish Eukaryotic Processes
Control of Gene Expression
 Control of Gene Expression Mechanisms of Gene Control Gene Control in Eukaryotes Master Genes Gene Control In Prokaryotes Epigenetics Gene Expression The overall process by which information flows from
Control of Gene Expression Mechanisms of Gene Control Gene Control in Eukaryotes Master Genes Gene Control In Prokaryotes Epigenetics Gene Expression The overall process by which information flows from
Hypothesis. Levels of organization. Theory. Controlled experiment. Homeostasis. ph scale. Characteristics of living things
 Hypothesis Quantitative & Qualitative observations Theory Levels of organization Controlled experiment Homeostasis Characteristics of living things ph scale Quantitative- involves numbers, counting, measuring
Hypothesis Quantitative & Qualitative observations Theory Levels of organization Controlled experiment Homeostasis Characteristics of living things ph scale Quantitative- involves numbers, counting, measuring
Genomes and Their Evolution
 Chapter 21 Genomes and Their Evolution PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 21 Genomes and Their Evolution PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Name: Test date: Per:
 Name: Test date: Per: Cell Cycle/Protein Synthesis Unit 1 Study Guide Always remember to use your notes/lectures first, then book, then other sources to help you find the right answers. Be as thorough
Name: Test date: Per: Cell Cycle/Protein Synthesis Unit 1 Study Guide Always remember to use your notes/lectures first, then book, then other sources to help you find the right answers. Be as thorough
Evolutionary analysis of the well characterized endo16 promoter reveals substantial variation within functional sites
 Evolutionary analysis of the well characterized endo16 promoter reveals substantial variation within functional sites Paper by: James P. Balhoff and Gregory A. Wray Presentation by: Stephanie Lucas Reviewed
Evolutionary analysis of the well characterized endo16 promoter reveals substantial variation within functional sites Paper by: James P. Balhoff and Gregory A. Wray Presentation by: Stephanie Lucas Reviewed
Ch 11.4, 11.5, and 14.1 Review. Game
 Ch 11.4, 11.5, and 14.1 Review Game What happens to the chromosome number during meiosis? A It doubles B It stays the same C It halves D It becomes diploid Ans: C Gametes are A Sex cells B Sperm and eggs
Ch 11.4, 11.5, and 14.1 Review Game What happens to the chromosome number during meiosis? A It doubles B It stays the same C It halves D It becomes diploid Ans: C Gametes are A Sex cells B Sperm and eggs
UNIT 5. Protein Synthesis 11/22/16
 UNIT 5 Protein Synthesis IV. Transcription (8.4) A. RNA carries DNA s instruction 1. Francis Crick defined the central dogma of molecular biology a. Replication copies DNA b. Transcription converts DNA
UNIT 5 Protein Synthesis IV. Transcription (8.4) A. RNA carries DNA s instruction 1. Francis Crick defined the central dogma of molecular biology a. Replication copies DNA b. Transcription converts DNA
The geneticist s questions. Deleting yeast genes. Functional genomics. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Functional genomics..is a field of molecular biology that attempts to make use of the vast wealth of data produced by genomic projects (such as genome sequencing projects)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Functional genomics..is a field of molecular biology that attempts to make use of the vast wealth of data produced by genomic projects (such as genome sequencing projects)
Mitosis and Meiosis. 2. The distribution of chromosomes in one type of cell division is shown in the diagram below.
 Name: Date: 1. Jack bought a small turtle. Three months later, the turtle had grown to twice its original size. Which of the following statements best describes why Jack s turtle got bigger? A. Parts of
Name: Date: 1. Jack bought a small turtle. Three months later, the turtle had grown to twice its original size. Which of the following statements best describes why Jack s turtle got bigger? A. Parts of
1. The diagram below shows two processes (A and B) involved in sexual reproduction in plants and animals.
 1. The diagram below shows two processes (A and B) involved in sexual reproduction in plants and animals. Which statement best explains how these processes often produce offspring that have traits not
1. The diagram below shows two processes (A and B) involved in sexual reproduction in plants and animals. Which statement best explains how these processes often produce offspring that have traits not
BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Week of Oct 3 Additional Practice Problems for Section. A/a ; B/B ; d/d X A/a ; b/b ; D/d
 BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Week of Oct 3 Additional Practice Problems for Section 1. In the following cross, all genes are on separate chromosomes. A is dominant to a, B is dominant to b and D is dominant
BS 50 Genetics and Genomics Week of Oct 3 Additional Practice Problems for Section 1. In the following cross, all genes are on separate chromosomes. A is dominant to a, B is dominant to b and D is dominant
2. Yeast two-hybrid system
 2. Yeast two-hybrid system I. Process workflow a. Mating of haploid two-hybrid strains on YPD plates b. Replica-plating of diploids on selective plates c. Two-hydrid experiment plating on selective plates
2. Yeast two-hybrid system I. Process workflow a. Mating of haploid two-hybrid strains on YPD plates b. Replica-plating of diploids on selective plates c. Two-hydrid experiment plating on selective plates
What is a sex cell? How are sex cells made? How does meiosis help explain Mendel s results?
 CHAPTER 6 3 Meiosis SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a sex cell? How are sex cells made? How does meiosis help explain
CHAPTER 6 3 Meiosis SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a sex cell? How are sex cells made? How does meiosis help explain
Cells and Their Processes. 1. What element do organic compounds have that inorganic compounds do not?
 Name: Date: Cells and Their Processes 1. What element do organic compounds have that inorganic compounds do not? 2. List the four types of organic compounds, describe the function of each AND list a food
Name: Date: Cells and Their Processes 1. What element do organic compounds have that inorganic compounds do not? 2. List the four types of organic compounds, describe the function of each AND list a food
Gene Expression and Signal Transduction Shane Burgess CVM
 Gene Expression and Signal Transduction Shane Burgess CVM Why Gene Expression and Signal Transduction? Fundamental to all biology A. Biological basics and paradigms B. Gene Expression C. Signaling A. BIOLOGICAL
Gene Expression and Signal Transduction Shane Burgess CVM Why Gene Expression and Signal Transduction? Fundamental to all biology A. Biological basics and paradigms B. Gene Expression C. Signaling A. BIOLOGICAL
Single nucleotide variants in transcription factors associate more tightly with phenotype than with gene expression
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2014 Single nucleotide variants in transcription factors associate more tightly with phenotype than with gene expression
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2014 Single nucleotide variants in transcription factors associate more tightly with phenotype than with gene expression
Bi 1x Spring 2014: LacI Titration
 Bi 1x Spring 2014: LacI Titration 1 Overview In this experiment, you will measure the effect of various mutated LacI repressor ribosome binding sites in an E. coli cell by measuring the expression of a
Bi 1x Spring 2014: LacI Titration 1 Overview In this experiment, you will measure the effect of various mutated LacI repressor ribosome binding sites in an E. coli cell by measuring the expression of a
Chromosome Chr Duplica Duplic t a ion Pixley
 Chromosome Duplication Pixley Figure 4-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Figure 4-72 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Interphase During mitosis (cell division),
Chromosome Duplication Pixley Figure 4-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Figure 4-72 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Interphase During mitosis (cell division),
Heredity and Genetics WKSH
 Chapter 6, Section 3 Heredity and Genetics WKSH KEY CONCEPT Mendel s research showed that traits are inherited as discrete units. Vocabulary trait purebred law of segregation genetics cross MAIN IDEA:
Chapter 6, Section 3 Heredity and Genetics WKSH KEY CONCEPT Mendel s research showed that traits are inherited as discrete units. Vocabulary trait purebred law of segregation genetics cross MAIN IDEA:
Chapter 6 Meiosis and Mendel
 UNIT 3 GENETICS Chapter 6 Meiosis and Mendel 1 hairy ears (hypertrichosis)- due to holandric gene. (Y chromosome)-only occurs in males. Appears in all sons. 2 Polydactyly- having extra fingers Wendy the
UNIT 3 GENETICS Chapter 6 Meiosis and Mendel 1 hairy ears (hypertrichosis)- due to holandric gene. (Y chromosome)-only occurs in males. Appears in all sons. 2 Polydactyly- having extra fingers Wendy the
AGREE or DISAGREE? What s your understanding of EVOLUTION?
 AGREE or DISAGREE? What s your understanding of EVOLUTION? Statement 1. Humans evolved from monkeys. Reasons for AGREE 0% Reasons for DISAGREE 100% Outcompeted by humans Humans and monkeys are evolving
AGREE or DISAGREE? What s your understanding of EVOLUTION? Statement 1. Humans evolved from monkeys. Reasons for AGREE 0% Reasons for DISAGREE 100% Outcompeted by humans Humans and monkeys are evolving
A Case Study -- Chu et al. The Transcriptional Program of Sporulation in Budding Yeast. What is Sporulation? CSE 527, W.L. Ruzzo 1
 A Case Study -- Chu et al. An interesting early microarray paper My goals Show arrays used in a real experiment Show where computation is important Start looking at analysis techniques The Transcriptional
A Case Study -- Chu et al. An interesting early microarray paper My goals Show arrays used in a real experiment Show where computation is important Start looking at analysis techniques The Transcriptional
Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2014
 Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2014 Biomolecules and Enzymes (Chapter 2) 8 questions Macromolecules, Biomolecules, Organic Compunds Elements *From the Periodic Table of Elements Subunits Monomers,
Biology I Fall Semester Exam Review 2014 Biomolecules and Enzymes (Chapter 2) 8 questions Macromolecules, Biomolecules, Organic Compunds Elements *From the Periodic Table of Elements Subunits Monomers,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Discussion Rationale for using maternal ythdf2 -/- mutants as study subject To study the genetic basis of the embryonic developmental delay that we observed, we crossed fish with different
Supplementary Discussion Rationale for using maternal ythdf2 -/- mutants as study subject To study the genetic basis of the embryonic developmental delay that we observed, we crossed fish with different
GENETICS UNIT VOCABULARY CHART. Word Definition Word Part Visual/Mnemonic Related Words 1. adenine Nitrogen base, pairs with thymine in DNA and uracil
 Word Definition Word Part Visual/Mnemonic Related Words 1. adenine Nitrogen base, pairs with thymine in DNA and uracil in RNA 2. allele One or more alternate forms of a gene Example: P = Dominant (purple);
Word Definition Word Part Visual/Mnemonic Related Words 1. adenine Nitrogen base, pairs with thymine in DNA and uracil in RNA 2. allele One or more alternate forms of a gene Example: P = Dominant (purple);
Number of questions TEK (Learning Target) Biomolecules & Enzymes
 Unit Biomolecules & Enzymes Number of questions TEK (Learning Target) on Exam 8 questions 9A I can compare and contrast the structure and function of biomolecules. 9C I know the role of enzymes and how
Unit Biomolecules & Enzymes Number of questions TEK (Learning Target) on Exam 8 questions 9A I can compare and contrast the structure and function of biomolecules. 9C I know the role of enzymes and how
Patterns of inheritance
 Patterns of inheritance Learning goals By the end of this material you would have learnt about: How traits and characteristics are passed on from one generation to another The different patterns of inheritance
Patterns of inheritance Learning goals By the end of this material you would have learnt about: How traits and characteristics are passed on from one generation to another The different patterns of inheritance
Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1
 Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1 Almost all the cells in your body were produced by mitosis. The only exceptions are the gametes sperm or eggs which are produced by a different
Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1 Almost all the cells in your body were produced by mitosis. The only exceptions are the gametes sperm or eggs which are produced by a different
Translation Part 2 of Protein Synthesis
 Translation Part 2 of Protein Synthesis IN: How is transcription like making a jello mold? (be specific) What process does this diagram represent? A. Mutation B. Replication C.Transcription D.Translation
Translation Part 2 of Protein Synthesis IN: How is transcription like making a jello mold? (be specific) What process does this diagram represent? A. Mutation B. Replication C.Transcription D.Translation
Videos. Bozeman, transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Crashcourse: Transcription and Translation - https://youtu.
 Translation Translation Videos Bozeman, transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Crashcourse: Transcription and Translation - https://youtu.be/itsb2sqr-r0 Translation Translation The
Translation Translation Videos Bozeman, transcription and translation: https://youtu.be/h3b9arupxzg Crashcourse: Transcription and Translation - https://youtu.be/itsb2sqr-r0 Translation Translation The
