With Realistic Parameters the Basic Real Business Cycle Model Acts Like the Solow Growth Model
|
|
|
- Ashley Jones
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Preliminary Draft With Realistic Parameters the Basic Real Business ycle Model Acts Like the Solow Growth Model Miles Kimball Shanthi P. Ramnath University of Michigan ABSTRAT The business cycle aspect of the real business cycle model was driven by unrealisitic values chosen for parameters. When empirical measures of key exogenous parameters are incorporated into the real business cycle model, the model responds to a technology shock with strikingly similarity to the Solow growth model. The similarity results from labor hours and the investment to output ratio remaining fixed. We argue that these key parameters include the technology process, the elasticity of intertemporal substitution, and the utility function. Based on prior empirical studies, technology shocks are found to be permanent while the elasticity of intertemporal substitution is estimated to be low. Also, King-Plosser-Rebello preferences are constructed to match the data which shows no long-run trend in labor hours. After imposing these three facts through a recalibration of parameters, the RB model behaves identically to the Solow model with respect to the adjustment of capital in response to a technology shock. What s more, these conclusions do not depend on the size of the labor supply elasticity. 1. Introduction By endogenizing labor supply and introducing mean-reverting technology shocks, the real business cycle model provided a mechanism that successfully replicated various features of a business cycle. Though puzzles remained, there was a marked change in the way growth theory and business
2 2 cycle theory were viewed. But soon the classic Prescott model became the target of criticism for what seemed to be an arbitrary methodology. Watson (1993) describes the RB methodology and aruges since the economic model does not provide a complete probability structure, inference procedures lack statistical foundations and are necessarily ad hoc. Various parameter values came under attack, including the largely disputed labor supply elasticity, which was said to be much larger than empirical results suggested. In the sections to follow, we will discuss three key parameters that drive the results and what their proper estimates should be. We will also discuss the irrelevance of the labor supply elasticity once the other parameters are chosen to have empirically sound values. 2. Realistic alibration of RB Parameters 2.1. Permanent versus Temporary Technology Shocks The RB model, as Prescott formulated it, assumes that technology shocks follow a persistent autoregressive process. Intuitively, this assumption is unrealistic. A technological improvement should not be temporary for the same reason good ideas should not be forgotten. And this intuition indeed appears in the data. It s true empirically that the Solow residual often mimics a business cycle and thus it seems plausible that technology shocks are autoregressive. However, the cyclicality of the Solow residual comes from changes in utilization and hence is the result of mismeasurement. Basu, Fernald, Kimball (2006) account for this mismeasurement by cleaning up the Solow residual. After estimating a purified technology series they find that after controlling for non-technological factors in measured aggregate total factor producitivity, technology shocks are in fact permanent. But permanent technology shocks do not produce business cycles. ogley and Nason (1995) find that standard RB models must rely heavily on exogenous sources of dynamics and output dynamics are essentially the same as impulse dynamics. This suggests that business cycles produced by the RB model are largely driven by the autoregressive technology process, which is not substantiated in the data. Permanent technology shocks are also supported by the existance of a unit root in output data.
3 3 If US gross domestic product contains a unit root, then shocks to GDP are permanent and the shocks likely to affect GDP are technological improvements. There has been some debate in the past as to whether output data is can be described by cyclical fluctuations around a deterministic trend, or whether output data is a non-stationary process. The first view is consistent with business cycle theory in that once data is detrended, the residual component is interpreted as a business cycle. ampbell and Mankiw (1987) question this traditional view and find that shocks to GDP in postwar US data are largely permanent, suggesting output data is non-stationary. Nelson and Plosser (1982) find that the existence of a unit root cannot be rejected in various US aggregate times series data. hristiano and Eichenbaum (1990) dismiss ampbell and Mankiw s (1987) methodology, however they conclude that whether or not output data has a unit root is indeed uncertain. The use of permanent technology shocks is now more accepted in the literature. Rotemberg and Woodford (1996) argue that technology shocks must be permanent in order for the model, rather than an exogenous factor, to explain growth. Gali (1999) also assumes permament technolgy shocks when identifying the effect of technology shocks on labor hours. The identifying assumption is that only a permanent techology shock can affect labor productivity in the long run King-Plosser-Rebello Preferences Much research has found that the long-run labor supply elasticity is zero. In other words, in the long run, income and substitution effects cancel. In light of this evidence, King-Plosser-Rebello preferences are appropriate to model consumer utility. KPR preferences are constructed such that income and substitution effects cancel and they allow for nonseparability of consumption and labor. Kimball and Shapiro (2004) argue for the use of KPR preferences to assure key features of the data are maintained in preferences.
4 Low Elasticity of Intertemporal Substitution The RB model uses the elasticity of intertemporal substitution as its internal propogation mechanism. A low elasticity of intertemporal substitution implies that consumption responds modestly to changes in the interest rate. Thus in order to incite dynamics, higher values are more favorable in RB models. However, empirical estimates of the elasticity of intertemporal substitution tend to be low. Hall (1988) estimates the elasticity by looking at changes in consumption with respect to changes in the real interest rate. The elasticity of substitution with respect to Treasury bills and savings accounts are inconclusive. Stock market estimates reveal an elasticty close to zero. Basu and Kimball (2002) find similar results that the elasticity of intertemporal substitution is small. They measure an elasticity of 0.50 that is significantly different than zero The Debate over Labor Supply Elasticity The labor supply elasticity parameter used by Prescott has been often criticized for being too high. In macroeconimics, a high labor supply elasticity is preferable since it implies a large labor response to technology shocks thereby amplifying the business cycle produced through simulation. But labor economists have done numerous studies to estimate labor supply elasticities and tend to estimate values much lower than the macroeconomist hopes for. In Pencavel s handbook chapter on male labor supply, he reports that using US data, Ashenfelter and Heckman (1973) estimate a male income-compensated wage elasticity of Hausman and Ruud (1984) estimate a response of 0.55, while Wales and Woodland (1979) estimate the highest elasticity of These estimates are much lower than the calibration that typical RB models use for labor supply elasticity, which can range anywhere from a value of 3 to infinite. Once empirical estimates for the key parameters we discuss above are used to calibrate the basic RB model, the magnitude of the labor supply elasticity becomes irrelevant. In fact, when empirical parameters are used, labor is constant after a technology shock.
5 5 3. Analyzing Basic Real Business ycle Models The basic real business cycle model begins with a representative agent maximizing the stream of present-value discounted utility. There is a representative firm seeking to maximize profits subject to a material balance condition and an equation of motion for capital. We will consider the centralized problem, where the representative agent owns the capital and labor. We will impose KPR preferences and for simplicity, assume a obb-douglas production function. The problem is then to maximize subject to the constraint that U = 0 e ρt 1 1 s 1 1 e [( 1 s 1)v(N)] s = ZK α N 1 α and the materials balance constraint, = + I + G. apital evolves according to following the equation of motion, K = I δk. For now, we will assume that there is no government spending, giving us the current-value Hamiltonian, H = 1 1 s 1 1 e ( 1 s 1)v(N) + Λ[ZK α N 1 α δk]. s Taking first order conditions we get equilibrium conditions giving us the H : 1 s e ( 1 s 1)v(N) = Λ H N : 1 1 s e [( 1 s 1)v(N)] v (N) = ΛW Λ = ρλ R + δ. King-Plosser-Rebello utility is constructed such that the real wage is is equivalent the disutility of labor scaled by consumption. In other words, v (N) = w where w is the real wage, is
6 6 consumption and v (N) is the marginal disutility from working. Using KPR utility and obb Douglas technology we show that labor is fully characterized by the consumption to output ratio. Proposition 1. With obb Douglas technology and King-Plosser-Rebello utility N monotonically relates to /. Proof. v (N) = w Nv (N) = wn Nv (N) = wn Nv (N) = Nv (N) = wn wn obb-douglas production implies that wn = 1 α where α is capital s share in production and 1 α labor s share. This implies that, Nv (N) = 1 α. (1) Note that v (N) is the marginal disutility from working and increasing in N. If / is constant, then N will also remain constant. However, if / rises (income effect dominates), then N must fall and if / falls (substitution effect dominates), then N must rise. This is will prove to be a useful result for the rest of our analysis. 4. Steady-State and Deviations from We will now derive the steady-state equations for all contemporanous variables in terms of capital, labor, and the marginal value of capital. We start by deriving the steady-state values for
7 7 / and I/ in terms of parameters. I = δk = δα R = δα ρ + δ = I W N + RK I = W N + RK I = (1 α) + RK I = (1 α) + (ρ + δ ρ + δ )α = (1 α) + ρδ ρ + δ δα ρ + δ To begin we can derive the log-linarized equilibrium equations. onsumption: Substituting in Output: 1 α (/ ) 1 s e ( 1 s 1)v(N) = Λ 1 s + ( 1 1)ṽ(N) = Λ s 1 s c + (1 s 1)v (N) = λ for Nv (N) we finally get an expression for the log deviation of consumption, c = (1 α) (1 α) + ( ρ s)n λs (2) ρ+δ )α(1 y = αk + (1 α)n + z Investment: i = y( I ) c( I ) i = αk + (1 α)n + z( I ) ( (1 α) (1 α) + ( ρ ρ+δ )α(1 s)n λs)( I ) Rental rate: marginal product of capital r = (α 1)k + (1 α)n + z
8 8 Labor demand: and the price measure of the solow residual, n + z k = σ KN (r + z w) (1 α)z = α r+(1 α)wassuming obb-douglas and normalizing prices to 1, y = αk + (1 α)(n + z) and, and so we get, 0 = αr + (1 α)(w z) n + z + k = σ KN (r + z w). If we assume technology is not changing and therefore = 0, then demand and supply for capital becomes, r = 1 α (w z). α To get labor demand eliminate r from the equation to get, n + z + k = σ KN [ 1 α (w z) + z w] α n = k + ( σ KN α 1)z σ KN α w. (3) Labor supply: H N : 1 1 s e [( 1 s 1)v(N)] v (N) = ΛW n = η(w + sλ) (4) factors] [Here is where I would set up the table to summarize variables in terms of n, λ, and exogenous
9 9 By setting labor supply equal to labor demand, we can solve for the optimal amount of labor, n and the wage rate, w. Multiplying equation 1 by σ α and equation 2 by η and adding them together we get: ( σ α + η)n = σ α sλ + +η( σ α 1)z n = s σ α λ + +η( σ α 1)z σ α + η Subtracting second equation from the first gives, n = η(w + sλ) n = k + ( σ α 1)z σ α w 0 = sηλ k ( σ α 1)z + σ α w + wη k + ( σ α 1)z sηλ = ( σ α + η)w w = k + ( σ α 1)z sηλ σ α + η. With our equation for n we can now substitute back in, to solve for our contemporaneous variables in terms of k and λ. In doing so we will then solve for our two log-linearized equations of motion. 5. Empirical Parameter Estimates and Simulations 5.1. Results 6. onclusion
DSGE-Models. Calibration and Introduction to Dynare. Institute of Econometrics and Economic Statistics
 DSGE-Models Calibration and Introduction to Dynare Dr. Andrea Beccarini Willi Mutschler, M.Sc. Institute of Econometrics and Economic Statistics willi.mutschler@uni-muenster.de Summer 2012 Willi Mutschler
DSGE-Models Calibration and Introduction to Dynare Dr. Andrea Beccarini Willi Mutschler, M.Sc. Institute of Econometrics and Economic Statistics willi.mutschler@uni-muenster.de Summer 2012 Willi Mutschler
1 The Basic RBC Model
 IHS 2016, Macroeconomics III Michael Reiter Ch. 1: Notes on RBC Model 1 1 The Basic RBC Model 1.1 Description of Model Variables y z k L c I w r output level of technology (exogenous) capital at end of
IHS 2016, Macroeconomics III Michael Reiter Ch. 1: Notes on RBC Model 1 1 The Basic RBC Model 1.1 Description of Model Variables y z k L c I w r output level of technology (exogenous) capital at end of
Public Economics The Macroeconomic Perspective Chapter 2: The Ramsey Model. Burkhard Heer University of Augsburg, Germany
 Public Economics The Macroeconomic Perspective Chapter 2: The Ramsey Model Burkhard Heer University of Augsburg, Germany October 3, 2018 Contents I 1 Central Planner 2 3 B. Heer c Public Economics: Chapter
Public Economics The Macroeconomic Perspective Chapter 2: The Ramsey Model Burkhard Heer University of Augsburg, Germany October 3, 2018 Contents I 1 Central Planner 2 3 B. Heer c Public Economics: Chapter
Foundation of (virtually) all DSGE models (e.g., RBC model) is Solow growth model
 THE BASELINE RBC MODEL: THEORY AND COMPUTATION FEBRUARY, 202 STYLIZED MACRO FACTS Foundation of (virtually all DSGE models (e.g., RBC model is Solow growth model So want/need/desire business-cycle models
THE BASELINE RBC MODEL: THEORY AND COMPUTATION FEBRUARY, 202 STYLIZED MACRO FACTS Foundation of (virtually all DSGE models (e.g., RBC model is Solow growth model So want/need/desire business-cycle models
Econ 5110 Solutions to the Practice Questions for the Midterm Exam
 Econ 50 Solutions to the Practice Questions for the Midterm Exam Spring 202 Real Business Cycle Theory. Consider a simple neoclassical growth model (notation similar to class) where all agents are identical
Econ 50 Solutions to the Practice Questions for the Midterm Exam Spring 202 Real Business Cycle Theory. Consider a simple neoclassical growth model (notation similar to class) where all agents are identical
Advanced Macroeconomics II. Real Business Cycle Models. Jordi Galí. Universitat Pompeu Fabra Spring 2018
 Advanced Macroeconomics II Real Business Cycle Models Jordi Galí Universitat Pompeu Fabra Spring 2018 Assumptions Optimization by consumers and rms Perfect competition General equilibrium Absence of a
Advanced Macroeconomics II Real Business Cycle Models Jordi Galí Universitat Pompeu Fabra Spring 2018 Assumptions Optimization by consumers and rms Perfect competition General equilibrium Absence of a
(a) Write down the Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman (HJB) Equation in the dynamic programming
 1. Government Purchases and Endogenous Growth Consider the following endogenous growth model with government purchases (G) in continuous time. Government purchases enhance production, and the production
1. Government Purchases and Endogenous Growth Consider the following endogenous growth model with government purchases (G) in continuous time. Government purchases enhance production, and the production
Small Open Economy RBC Model Uribe, Chapter 4
 Small Open Economy RBC Model Uribe, Chapter 4 1 Basic Model 1.1 Uzawa Utility E 0 t=0 θ t U (c t, h t ) θ 0 = 1 θ t+1 = β (c t, h t ) θ t ; β c < 0; β h > 0. Time-varying discount factor With a constant
Small Open Economy RBC Model Uribe, Chapter 4 1 Basic Model 1.1 Uzawa Utility E 0 t=0 θ t U (c t, h t ) θ 0 = 1 θ t+1 = β (c t, h t ) θ t ; β c < 0; β h > 0. Time-varying discount factor With a constant
The Real Business Cycle Model
 The Real Business Cycle Model Macroeconomics II 2 The real business cycle model. Introduction This model explains the comovements in the fluctuations of aggregate economic variables around their trend.
The Real Business Cycle Model Macroeconomics II 2 The real business cycle model. Introduction This model explains the comovements in the fluctuations of aggregate economic variables around their trend.
Equilibrium Conditions (symmetric across all differentiated goods)
 MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION IN A DSGE MODEL: PART II SEPTEMBER 30, 200 Canonical Dixit-Stiglitz Model MONOPOLISTICALLY-COMPETITIVE EQUILIBRIUM Equilibrium Conditions (symmetric across all differentiated goods)
MONOPOLISTIC COMPETITION IN A DSGE MODEL: PART II SEPTEMBER 30, 200 Canonical Dixit-Stiglitz Model MONOPOLISTICALLY-COMPETITIVE EQUILIBRIUM Equilibrium Conditions (symmetric across all differentiated goods)
4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models. Basic Economic Models
 4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models Basic Economic Models In Economics, we use theoretical models to explain the economic processes in the real world. These models de ne a relation
4- Current Method of Explaining Business Cycles: DSGE Models Basic Economic Models In Economics, we use theoretical models to explain the economic processes in the real world. These models de ne a relation
problem. max Both k (0) and h (0) are given at time 0. (a) Write down the Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman (HJB) Equation in the dynamic programming
 1. Endogenous Growth with Human Capital Consider the following endogenous growth model with both physical capital (k (t)) and human capital (h (t)) in continuous time. The representative household solves
1. Endogenous Growth with Human Capital Consider the following endogenous growth model with both physical capital (k (t)) and human capital (h (t)) in continuous time. The representative household solves
Macroeconomics Theory II
 Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco FEUNL February 2011 Francesco Franco Macroeconomics Theory II 1/34 The log-linear plain vanilla RBC and ν(σ n )= ĉ t = Y C ẑt +(1 α) Y C ˆn t + K βc ˆk t 1 + K
Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco FEUNL February 2011 Francesco Franco Macroeconomics Theory II 1/34 The log-linear plain vanilla RBC and ν(σ n )= ĉ t = Y C ẑt +(1 α) Y C ˆn t + K βc ˆk t 1 + K
Topic 3. RBCs
 14.452. Topic 3. RBCs Olivier Blanchard April 8, 2007 Nr. 1 1. Motivation, and organization Looked at Ramsey model, with productivity shocks. Replicated fairly well co-movements in output, consumption,
14.452. Topic 3. RBCs Olivier Blanchard April 8, 2007 Nr. 1 1. Motivation, and organization Looked at Ramsey model, with productivity shocks. Replicated fairly well co-movements in output, consumption,
Chapter 11 The Stochastic Growth Model and Aggregate Fluctuations
 George Alogoskoufis, Dynamic Macroeconomics, 2016 Chapter 11 The Stochastic Growth Model and Aggregate Fluctuations In previous chapters we studied the long run evolution of output and consumption, real
George Alogoskoufis, Dynamic Macroeconomics, 2016 Chapter 11 The Stochastic Growth Model and Aggregate Fluctuations In previous chapters we studied the long run evolution of output and consumption, real
Neoclassical Business Cycle Model
 Neoclassical Business Cycle Model Prof. Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2015 1 / 36 Production Economy Last time: studied equilibrium in an endowment economy Now: study equilibrium in an economy
Neoclassical Business Cycle Model Prof. Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2015 1 / 36 Production Economy Last time: studied equilibrium in an endowment economy Now: study equilibrium in an economy
Graduate Macroeconomics - Econ 551
 Graduate Macroeconomics - Econ 551 Tack Yun Indiana University Seoul National University Spring Semester January 2013 T. Yun (SNU) Macroeconomics 1/07/2013 1 / 32 Business Cycle Models for Emerging-Market
Graduate Macroeconomics - Econ 551 Tack Yun Indiana University Seoul National University Spring Semester January 2013 T. Yun (SNU) Macroeconomics 1/07/2013 1 / 32 Business Cycle Models for Emerging-Market
Lecture 4 The Centralized Economy: Extensions
 Lecture 4 The Centralized Economy: Extensions Leopold von Thadden University of Mainz and ECB (on leave) Advanced Macroeconomics, Winter Term 2013 1 / 36 I Motivation This Lecture considers some applications
Lecture 4 The Centralized Economy: Extensions Leopold von Thadden University of Mainz and ECB (on leave) Advanced Macroeconomics, Winter Term 2013 1 / 36 I Motivation This Lecture considers some applications
New Notes on the Solow Growth Model
 New Notes on the Solow Growth Model Roberto Chang September 2009 1 The Model The firstingredientofadynamicmodelisthedescriptionofthetimehorizon. In the original Solow model, time is continuous and the
New Notes on the Solow Growth Model Roberto Chang September 2009 1 The Model The firstingredientofadynamicmodelisthedescriptionofthetimehorizon. In the original Solow model, time is continuous and the
Practice Questions for Mid-Term I. Question 1: Consider the Cobb-Douglas production function in intensive form:
 Practice Questions for Mid-Term I Question 1: Consider the Cobb-Douglas production function in intensive form: y f(k) = k α ; α (0, 1) (1) where y and k are output per worker and capital per worker respectively.
Practice Questions for Mid-Term I Question 1: Consider the Cobb-Douglas production function in intensive form: y f(k) = k α ; α (0, 1) (1) where y and k are output per worker and capital per worker respectively.
Deep Habits: Technical Notes
 Deep Habits: Technical Notes Morten Ravn Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé Martín Uribe October 18, 2004 This note derives in detail the model, its associated equilibrium conditions, the steadystate equilibrium,
Deep Habits: Technical Notes Morten Ravn Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé Martín Uribe October 18, 2004 This note derives in detail the model, its associated equilibrium conditions, the steadystate equilibrium,
Graduate Macro Theory II: Notes on Quantitative Analysis in DSGE Models
 Graduate Macro Theory II: Notes on Quantitative Analysis in DSGE Models Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Spring 2011 This note describes very briefly how to conduct quantitative analysis on a linearized
Graduate Macro Theory II: Notes on Quantitative Analysis in DSGE Models Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Spring 2011 This note describes very briefly how to conduct quantitative analysis on a linearized
Cointegration and the Ramsey Model
 RamseyCointegration, March 1, 2004 Cointegration and the Ramsey Model This handout examines implications of the Ramsey model for cointegration between consumption, income, and capital. Consider the following
RamseyCointegration, March 1, 2004 Cointegration and the Ramsey Model This handout examines implications of the Ramsey model for cointegration between consumption, income, and capital. Consider the following
The Ramsey Model. (Lecture Note, Advanced Macroeconomics, Thomas Steger, SS 2013)
 The Ramsey Model (Lecture Note, Advanced Macroeconomics, Thomas Steger, SS 213) 1 Introduction The Ramsey model (or neoclassical growth model) is one of the prototype models in dynamic macroeconomics.
The Ramsey Model (Lecture Note, Advanced Macroeconomics, Thomas Steger, SS 213) 1 Introduction The Ramsey model (or neoclassical growth model) is one of the prototype models in dynamic macroeconomics.
Lecture notes on modern growth theory
 Lecture notes on modern growth theory Part 2 Mario Tirelli Very preliminary material Not to be circulated without the permission of the author October 25, 2017 Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Optimal economic
Lecture notes on modern growth theory Part 2 Mario Tirelli Very preliminary material Not to be circulated without the permission of the author October 25, 2017 Contents 1. Introduction 1 2. Optimal economic
Permanent Income Hypothesis Intro to the Ramsey Model
 Consumption and Savings Permanent Income Hypothesis Intro to the Ramsey Model Lecture 10 Topics in Macroeconomics November 6, 2007 Lecture 10 1/18 Topics in Macroeconomics Consumption and Savings Outline
Consumption and Savings Permanent Income Hypothesis Intro to the Ramsey Model Lecture 10 Topics in Macroeconomics November 6, 2007 Lecture 10 1/18 Topics in Macroeconomics Consumption and Savings Outline
Relative Deep Habits
 Relative Deep Habits Morten Ravn Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé Martín Uribe May 5, 25 Abstract This note presents a detailed formal derivation of the equilibrium conditions of a variation of the deep habit model
Relative Deep Habits Morten Ravn Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé Martín Uribe May 5, 25 Abstract This note presents a detailed formal derivation of the equilibrium conditions of a variation of the deep habit model
Taylor Rules and Technology Shocks
 Taylor Rules and Technology Shocks Eric R. Sims University of Notre Dame and NBER January 17, 2012 Abstract In a standard New Keynesian model, a Taylor-type interest rate rule moves the equilibrium real
Taylor Rules and Technology Shocks Eric R. Sims University of Notre Dame and NBER January 17, 2012 Abstract In a standard New Keynesian model, a Taylor-type interest rate rule moves the equilibrium real
Economic Growth: Lecture 8, Overlapping Generations
 14.452 Economic Growth: Lecture 8, Overlapping Generations Daron Acemoglu MIT November 20, 2018 Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Economic Growth Lecture 8 November 20, 2018 1 / 46 Growth with Overlapping Generations
14.452 Economic Growth: Lecture 8, Overlapping Generations Daron Acemoglu MIT November 20, 2018 Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Economic Growth Lecture 8 November 20, 2018 1 / 46 Growth with Overlapping Generations
Economic Growth: Lecture 9, Neoclassical Endogenous Growth
 14.452 Economic Growth: Lecture 9, Neoclassical Endogenous Growth Daron Acemoglu MIT November 28, 2017. Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Economic Growth Lecture 9 November 28, 2017. 1 / 41 First-Generation Models
14.452 Economic Growth: Lecture 9, Neoclassical Endogenous Growth Daron Acemoglu MIT November 28, 2017. Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Economic Growth Lecture 9 November 28, 2017. 1 / 41 First-Generation Models
Assumption 5. The technology is represented by a production function, F : R 3 + R +, F (K t, N t, A t )
 6. Economic growth Let us recall the main facts on growth examined in the first chapter and add some additional ones. (1) Real output (per-worker) roughly grows at a constant rate (i.e. labor productivity
6. Economic growth Let us recall the main facts on growth examined in the first chapter and add some additional ones. (1) Real output (per-worker) roughly grows at a constant rate (i.e. labor productivity
Macroeconomics Field Exam. August 2007
 Macroeconomics Field Exam August 2007 Answer all questions in the exam. Suggested times correspond to the questions weights in the exam grade. Make your answers as precise as possible, using graphs, equations,
Macroeconomics Field Exam August 2007 Answer all questions in the exam. Suggested times correspond to the questions weights in the exam grade. Make your answers as precise as possible, using graphs, equations,
Advanced Macroeconomics II The RBC model with Capital
 Advanced Macroeconomics II The RBC model with Capital Lorenza Rossi (Spring 2014) University of Pavia Part of these slides are based on Jordi Galì slides for Macroeconomia Avanzada II. Outline Real business
Advanced Macroeconomics II The RBC model with Capital Lorenza Rossi (Spring 2014) University of Pavia Part of these slides are based on Jordi Galì slides for Macroeconomia Avanzada II. Outline Real business
The Solow Model. Prof. Lutz Hendricks. January 26, Econ520
 The Solow Model Prof. Lutz Hendricks Econ520 January 26, 2017 1 / 28 Issues The production model measures the proximate causes of income gaps. Now we start to look at deep causes. The Solow model answers
The Solow Model Prof. Lutz Hendricks Econ520 January 26, 2017 1 / 28 Issues The production model measures the proximate causes of income gaps. Now we start to look at deep causes. The Solow model answers
Can News be a Major Source of Aggregate Fluctuations?
 Can News be a Major Source of Aggregate Fluctuations? A Bayesian DSGE Approach Ippei Fujiwara 1 Yasuo Hirose 1 Mototsugu 2 1 Bank of Japan 2 Vanderbilt University August 4, 2009 Contributions of this paper
Can News be a Major Source of Aggregate Fluctuations? A Bayesian DSGE Approach Ippei Fujiwara 1 Yasuo Hirose 1 Mototsugu 2 1 Bank of Japan 2 Vanderbilt University August 4, 2009 Contributions of this paper
A Summary of Economic Methodology
 A Summary of Economic Methodology I. The Methodology of Theoretical Economics All economic analysis begins with theory, based in part on intuitive insights that naturally spring from certain stylized facts,
A Summary of Economic Methodology I. The Methodology of Theoretical Economics All economic analysis begins with theory, based in part on intuitive insights that naturally spring from certain stylized facts,
Solving a Dynamic (Stochastic) General Equilibrium Model under the Discrete Time Framework
 Solving a Dynamic (Stochastic) General Equilibrium Model under the Discrete Time Framework Dongpeng Liu Nanjing University Sept 2016 D. Liu (NJU) Solving D(S)GE 09/16 1 / 63 Introduction Targets of the
Solving a Dynamic (Stochastic) General Equilibrium Model under the Discrete Time Framework Dongpeng Liu Nanjing University Sept 2016 D. Liu (NJU) Solving D(S)GE 09/16 1 / 63 Introduction Targets of the
Solow Growth Model. Michael Bar. February 28, Introduction Some facts about modern growth Questions... 4
 Solow Growth Model Michael Bar February 28, 208 Contents Introduction 2. Some facts about modern growth........................ 3.2 Questions..................................... 4 2 The Solow Model 5
Solow Growth Model Michael Bar February 28, 208 Contents Introduction 2. Some facts about modern growth........................ 3.2 Questions..................................... 4 2 The Solow Model 5
Real Business Cycle Model (RBC)
 Real Business Cycle Model (RBC) Seyed Ali Madanizadeh November 2013 RBC Model Lucas 1980: One of the functions of theoretical economics is to provide fully articulated, artificial economic systems that
Real Business Cycle Model (RBC) Seyed Ali Madanizadeh November 2013 RBC Model Lucas 1980: One of the functions of theoretical economics is to provide fully articulated, artificial economic systems that
Population growth and technological progress in the optimal growth model
 Quantitative Methods in Economics Econ 600 Fall 2016 Handout # 5 Readings: SLP Sections 3.3 4.2, pages 55-87; A Ch 6 Population growth and technological progress in the optimal growth model In the optimal
Quantitative Methods in Economics Econ 600 Fall 2016 Handout # 5 Readings: SLP Sections 3.3 4.2, pages 55-87; A Ch 6 Population growth and technological progress in the optimal growth model In the optimal
Indeterminacy, Aggregate Demand, and the Real Business Cycle
 Indeterminacy, Aggregate Demand, and the Real Business Cycle Jess Benhabib Department of Economics New York University jess.benhabib@nyu.edu Yi Wen Department of Economics Cornell University Yw57@cornell.edu
Indeterminacy, Aggregate Demand, and the Real Business Cycle Jess Benhabib Department of Economics New York University jess.benhabib@nyu.edu Yi Wen Department of Economics Cornell University Yw57@cornell.edu
Equilibrium in a Production Economy
 Equilibrium in a Production Economy Prof. Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2012 Sims (ND) Equilibrium in a Production Economy Fall 2012 1 / 23 Production Economy Last time: studied equilibrium in
Equilibrium in a Production Economy Prof. Eric Sims University of Notre Dame Fall 2012 Sims (ND) Equilibrium in a Production Economy Fall 2012 1 / 23 Production Economy Last time: studied equilibrium in
A Modern Equilibrium Model. Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania
 A Modern Equilibrium Model Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania 1 Household Problem Preferences: max E X β t t=0 c 1 σ t 1 σ ψ l1+γ t 1+γ Budget constraint: c t + k t+1 = w t l t + r t
A Modern Equilibrium Model Jesús Fernández-Villaverde University of Pennsylvania 1 Household Problem Preferences: max E X β t t=0 c 1 σ t 1 σ ψ l1+γ t 1+γ Budget constraint: c t + k t+1 = w t l t + r t
Macroeconomics Theory II
 Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco FEUNL February 2016 Francesco Franco (FEUNL) Macroeconomics Theory II February 2016 1 / 18 Road Map Research question: we want to understand businesses cycles.
Macroeconomics Theory II Francesco Franco FEUNL February 2016 Francesco Franco (FEUNL) Macroeconomics Theory II February 2016 1 / 18 Road Map Research question: we want to understand businesses cycles.
Getting to page 31 in Galí (2008)
 Getting to page 31 in Galí 2008) H J Department of Economics University of Copenhagen December 4 2012 Abstract This note shows in detail how to compute the solutions for output inflation and the nominal
Getting to page 31 in Galí 2008) H J Department of Economics University of Copenhagen December 4 2012 Abstract This note shows in detail how to compute the solutions for output inflation and the nominal
Simple New Keynesian Model without Capital
 Simple New Keynesian Model without Capital Lawrence J. Christiano January 5, 2018 Objective Review the foundations of the basic New Keynesian model without capital. Clarify the role of money supply/demand.
Simple New Keynesian Model without Capital Lawrence J. Christiano January 5, 2018 Objective Review the foundations of the basic New Keynesian model without capital. Clarify the role of money supply/demand.
Suggested Solutions to Homework #6 Econ 511b (Part I), Spring 2004
 Suggested Solutions to Homework #6 Econ 511b (Part I), Spring 2004 1. (a) Find the planner s optimal decision rule in the stochastic one-sector growth model without valued leisure by linearizing the Euler
Suggested Solutions to Homework #6 Econ 511b (Part I), Spring 2004 1. (a) Find the planner s optimal decision rule in the stochastic one-sector growth model without valued leisure by linearizing the Euler
Ramsey Cass Koopmans Model (1): Setup of the Model and Competitive Equilibrium Path
 Ramsey Cass Koopmans Model (1): Setup of the Model and Competitive Equilibrium Path Ryoji Ohdoi Dept. of Industrial Engineering and Economics, Tokyo Tech This lecture note is mainly based on Ch. 8 of Acemoglu
Ramsey Cass Koopmans Model (1): Setup of the Model and Competitive Equilibrium Path Ryoji Ohdoi Dept. of Industrial Engineering and Economics, Tokyo Tech This lecture note is mainly based on Ch. 8 of Acemoglu
Advanced Macroeconomics
 Advanced Macroeconomics The Ramsey Model Marcin Kolasa Warsaw School of Economics Marcin Kolasa (WSE) Ad. Macro - Ramsey model 1 / 30 Introduction Authors: Frank Ramsey (1928), David Cass (1965) and Tjalling
Advanced Macroeconomics The Ramsey Model Marcin Kolasa Warsaw School of Economics Marcin Kolasa (WSE) Ad. Macro - Ramsey model 1 / 30 Introduction Authors: Frank Ramsey (1928), David Cass (1965) and Tjalling
Comprehensive Exam. Macro Spring 2014 Retake. August 22, 2014
 Comprehensive Exam Macro Spring 2014 Retake August 22, 2014 You have a total of 180 minutes to complete the exam. If a question seems ambiguous, state why, sharpen it up and answer the sharpened-up question.
Comprehensive Exam Macro Spring 2014 Retake August 22, 2014 You have a total of 180 minutes to complete the exam. If a question seems ambiguous, state why, sharpen it up and answer the sharpened-up question.
PANEL DISCUSSION: THE ROLE OF POTENTIAL OUTPUT IN POLICYMAKING
 PANEL DISCUSSION: THE ROLE OF POTENTIAL OUTPUT IN POLICYMAKING James Bullard* Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis 33rd Annual Economic Policy Conference St. Louis, MO October 17, 2008 Views expressed are
PANEL DISCUSSION: THE ROLE OF POTENTIAL OUTPUT IN POLICYMAKING James Bullard* Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis 33rd Annual Economic Policy Conference St. Louis, MO October 17, 2008 Views expressed are
News Driven Business Cycles in Heterogenous Agents Economies
 News Driven Business Cycles in Heterogenous Agents Economies Paul Beaudry and Franck Portier DRAFT February 9 Abstract We present a new propagation mechanism for news shocks in dynamic general equilibrium
News Driven Business Cycles in Heterogenous Agents Economies Paul Beaudry and Franck Portier DRAFT February 9 Abstract We present a new propagation mechanism for news shocks in dynamic general equilibrium
Closed economy macro dynamics: AD-AS model and RBC model.
 Closed economy macro dynamics: AD-AS model and RBC model. Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics, UiO 22 September 2009 Lecture notes on closed economy macro dynamics AD-AS model Inflation targeting regime.
Closed economy macro dynamics: AD-AS model and RBC model. Ragnar Nymoen Department of Economics, UiO 22 September 2009 Lecture notes on closed economy macro dynamics AD-AS model Inflation targeting regime.
MA Advanced Macroeconomics: 7. The Real Business Cycle Model
 MA Advanced Macroeconomics: 7. The Real Business Cycle Model Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD Spring 2016 Karl Whelan (UCD) Real Business Cycles Spring 2016 1 / 38 Working Through A DSGE Model We have
MA Advanced Macroeconomics: 7. The Real Business Cycle Model Karl Whelan School of Economics, UCD Spring 2016 Karl Whelan (UCD) Real Business Cycles Spring 2016 1 / 38 Working Through A DSGE Model We have
Lecture 15 Real Business Cycle Model. Noah Williams
 Lecture 15 Real Business Cycle Model Noah Williams University of Wisconsin - Madison Economics 702/312 Real Business Cycle Model We will have a shock: change in technology. Then we will have a propagation
Lecture 15 Real Business Cycle Model Noah Williams University of Wisconsin - Madison Economics 702/312 Real Business Cycle Model We will have a shock: change in technology. Then we will have a propagation
Markov Perfect Equilibria in the Ramsey Model
 Markov Perfect Equilibria in the Ramsey Model Paul Pichler and Gerhard Sorger This Version: February 2006 Abstract We study the Ramsey (1928) model under the assumption that households act strategically.
Markov Perfect Equilibria in the Ramsey Model Paul Pichler and Gerhard Sorger This Version: February 2006 Abstract We study the Ramsey (1928) model under the assumption that households act strategically.
Monetary Economics: Solutions Problem Set 1
 Monetary Economics: Solutions Problem Set 1 December 14, 2006 Exercise 1 A Households Households maximise their intertemporal utility function by optimally choosing consumption, savings, and the mix of
Monetary Economics: Solutions Problem Set 1 December 14, 2006 Exercise 1 A Households Households maximise their intertemporal utility function by optimally choosing consumption, savings, and the mix of
RBC Model with Indivisible Labor. Advanced Macroeconomic Theory
 RBC Model with Indivisible Labor Advanced Macroeconomic Theory 1 Last Class What are business cycles? Using HP- lter to decompose data into trend and cyclical components Business cycle facts Standard RBC
RBC Model with Indivisible Labor Advanced Macroeconomic Theory 1 Last Class What are business cycles? Using HP- lter to decompose data into trend and cyclical components Business cycle facts Standard RBC
ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I
 Name: Students ID: ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I I. Short Questions (21/2 points each) Mark the following statements as True (T) or False (F) and give a brief explanation of your answer in each case. 1. 2.
Name: Students ID: ADVANCED MACROECONOMICS I I. Short Questions (21/2 points each) Mark the following statements as True (T) or False (F) and give a brief explanation of your answer in each case. 1. 2.
Business Cycles: The Classical Approach
 San Francisco State University ECON 302 Business Cycles: The Classical Approach Introduction Michael Bar Recall from the introduction that the output per capita in the U.S. is groing steady, but there
San Francisco State University ECON 302 Business Cycles: The Classical Approach Introduction Michael Bar Recall from the introduction that the output per capita in the U.S. is groing steady, but there
Indeterminacy with No-Income-Effect Preferences and Sector-Specific Externalities
 Indeterminacy with No-Income-Effect Preferences and Sector-Specific Externalities Jang-Ting Guo University of California, Riverside Sharon G. Harrison Barnard College, Columbia University July 9, 2008
Indeterminacy with No-Income-Effect Preferences and Sector-Specific Externalities Jang-Ting Guo University of California, Riverside Sharon G. Harrison Barnard College, Columbia University July 9, 2008
Problem 1 (30 points)
 Problem (30 points) Prof. Robert King Consider an economy in which there is one period and there are many, identical households. Each household derives utility from consumption (c), leisure (l) and a public
Problem (30 points) Prof. Robert King Consider an economy in which there is one period and there are many, identical households. Each household derives utility from consumption (c), leisure (l) and a public
Theoretical premises of the Keynesian approach
 origin of Keynesian approach to Growth can be traced back to an article written after the General Theory (1936) Roy Harrod, An Essay in Dynamic Theory, Economic Journal, 1939 Theoretical premises of the
origin of Keynesian approach to Growth can be traced back to an article written after the General Theory (1936) Roy Harrod, An Essay in Dynamic Theory, Economic Journal, 1939 Theoretical premises of the
Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3.
 Ph.D. Core Exam -- Macroeconomics 5 January 2015 -- 8:00 am to 3:00 pm Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3. A1 (required): Ending Quantitative Easing Now that the U.S.
Ph.D. Core Exam -- Macroeconomics 5 January 2015 -- 8:00 am to 3:00 pm Part A: Answer question A1 (required), plus either question A2 or A3. A1 (required): Ending Quantitative Easing Now that the U.S.
Economic Growth: Lecture 13, Stochastic Growth
 14.452 Economic Growth: Lecture 13, Stochastic Growth Daron Acemoglu MIT December 10, 2013. Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Economic Growth Lecture 13 December 10, 2013. 1 / 52 Stochastic Growth Models Stochastic
14.452 Economic Growth: Lecture 13, Stochastic Growth Daron Acemoglu MIT December 10, 2013. Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Economic Growth Lecture 13 December 10, 2013. 1 / 52 Stochastic Growth Models Stochastic
Income Effects and Indeterminacy in a Calibrated One-Sector Growth Model
 This work is distributed as a Discussion Paper by the STANFORD INSTITUTE FOR EONOMI POLIY RESEARH SIEPR Discussion Paper No. 07-12 Income Effects and Indeterminacy in a alibrated One-Sector Growth Model
This work is distributed as a Discussion Paper by the STANFORD INSTITUTE FOR EONOMI POLIY RESEARH SIEPR Discussion Paper No. 07-12 Income Effects and Indeterminacy in a alibrated One-Sector Growth Model
Lecture 2: Firms, Jobs and Policy
 Lecture 2: Firms, Jobs and Policy Economics 522 Esteban Rossi-Hansberg Princeton University Spring 2014 ERH (Princeton University ) Lecture 2: Firms, Jobs and Policy Spring 2014 1 / 34 Restuccia and Rogerson
Lecture 2: Firms, Jobs and Policy Economics 522 Esteban Rossi-Hansberg Princeton University Spring 2014 ERH (Princeton University ) Lecture 2: Firms, Jobs and Policy Spring 2014 1 / 34 Restuccia and Rogerson
ECOM 009 Macroeconomics B. Lecture 2
 ECOM 009 Macroeconomics B Lecture 2 Giulio Fella c Giulio Fella, 2014 ECOM 009 Macroeconomics B - Lecture 2 40/197 Aim of consumption theory Consumption theory aims at explaining consumption/saving decisions
ECOM 009 Macroeconomics B Lecture 2 Giulio Fella c Giulio Fella, 2014 ECOM 009 Macroeconomics B - Lecture 2 40/197 Aim of consumption theory Consumption theory aims at explaining consumption/saving decisions
Macroeconomics Qualifying Examination
 Macroeconomics Qualifying Examination August 2015 Department of Economics UNC Chapel Hill Instructions: This examination consists of 4 questions. Answer all questions. If you believe a question is ambiguously
Macroeconomics Qualifying Examination August 2015 Department of Economics UNC Chapel Hill Instructions: This examination consists of 4 questions. Answer all questions. If you believe a question is ambiguously
Macroeconomics II. Dynamic AD-AS model
 Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Dynamic AD-AS model vs. AD-AS model Notes. Dynamic AD-AS model in a few words Notes. Notation to incorporate time-dimension Notes
 Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Macroeconomics II Dynamic AD-AS model Vahagn Jerbashian Ch. 14 from Mankiw (2010) Spring 2018 Where we are heading to We will incorporate dynamics into the standard AD-AS model This will offer another
Economic Growth: Lecture 7, Overlapping Generations
 14.452 Economic Growth: Lecture 7, Overlapping Generations Daron Acemoglu MIT November 17, 2009. Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Economic Growth Lecture 7 November 17, 2009. 1 / 54 Growth with Overlapping Generations
14.452 Economic Growth: Lecture 7, Overlapping Generations Daron Acemoglu MIT November 17, 2009. Daron Acemoglu (MIT) Economic Growth Lecture 7 November 17, 2009. 1 / 54 Growth with Overlapping Generations
Economics 210B Due: September 16, Problem Set 10. s.t. k t+1 = R(k t c t ) for all t 0, and k 0 given, lim. and
 Economics 210B Due: September 16, 2010 Problem 1: Constant returns to saving Consider the following problem. c0,k1,c1,k2,... β t Problem Set 10 1 α c1 α t s.t. k t+1 = R(k t c t ) for all t 0, and k 0
Economics 210B Due: September 16, 2010 Problem 1: Constant returns to saving Consider the following problem. c0,k1,c1,k2,... β t Problem Set 10 1 α c1 α t s.t. k t+1 = R(k t c t ) for all t 0, and k 0
Uncertainty Per Krusell & D. Krueger Lecture Notes Chapter 6
 1 Uncertainty Per Krusell & D. Krueger Lecture Notes Chapter 6 1 A Two-Period Example Suppose the economy lasts only two periods, t =0, 1. The uncertainty arises in the income (wage) of period 1. Not that
1 Uncertainty Per Krusell & D. Krueger Lecture Notes Chapter 6 1 A Two-Period Example Suppose the economy lasts only two periods, t =0, 1. The uncertainty arises in the income (wage) of period 1. Not that
Chapter 4. Applications/Variations
 Chapter 4 Applications/Variations 149 4.1 Consumption Smoothing 4.1.1 The Intertemporal Budget Economic Growth: Lecture Notes For any given sequence of interest rates {R t } t=0, pick an arbitrary q 0
Chapter 4 Applications/Variations 149 4.1 Consumption Smoothing 4.1.1 The Intertemporal Budget Economic Growth: Lecture Notes For any given sequence of interest rates {R t } t=0, pick an arbitrary q 0
1 The social planner problem
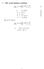 The social planner problem max C t;k t+ U t = E t X t C t () that can be written as: s.t.: Y t = A t K t (2) Y t = C t + I t (3) I t = K t+ (4) A t = A A t (5) et t i:i:d: 0; 2 max C t;k t+ U t = E t "
The social planner problem max C t;k t+ U t = E t X t C t () that can be written as: s.t.: Y t = A t K t (2) Y t = C t + I t (3) I t = K t+ (4) A t = A A t (5) et t i:i:d: 0; 2 max C t;k t+ U t = E t "
1 Bewley Economies with Aggregate Uncertainty
 1 Bewley Economies with Aggregate Uncertainty Sofarwehaveassumedawayaggregatefluctuations (i.e., business cycles) in our description of the incomplete-markets economies with uninsurable idiosyncratic risk
1 Bewley Economies with Aggregate Uncertainty Sofarwehaveassumedawayaggregatefluctuations (i.e., business cycles) in our description of the incomplete-markets economies with uninsurable idiosyncratic risk
Modelling Production
 Modelling Production David N. DeJong University of Pittsburgh Econ. 1540, Spring 2010 DND () Production Econ. 1540, Spring 2010 1 / 23 Introduction The production function is the foundation upon which
Modelling Production David N. DeJong University of Pittsburgh Econ. 1540, Spring 2010 DND () Production Econ. 1540, Spring 2010 1 / 23 Introduction The production function is the foundation upon which
Dynamic Macroeconomics: Problem Set 4
 Dynamic Macroeconomics: Problem Set 4 Universität Siegen Dynamic Macroeconomics 1 / 28 1 Computing growth rates 2 Golden rule saving rate 3 Simulation of the Solow Model 4 Growth accounting Dynamic Macroeconomics
Dynamic Macroeconomics: Problem Set 4 Universität Siegen Dynamic Macroeconomics 1 / 28 1 Computing growth rates 2 Golden rule saving rate 3 Simulation of the Solow Model 4 Growth accounting Dynamic Macroeconomics
A Note on the Ramsey Growth Model with the von Bertalanffy Population Law
 Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol 4, 2010, no 65, 3233-3238 A Note on the Ramsey Growth Model with the von Bertalanffy Population aw uca Guerrini Department of Mathematics for Economic and Social Sciences
Applied Mathematical Sciences, Vol 4, 2010, no 65, 3233-3238 A Note on the Ramsey Growth Model with the von Bertalanffy Population aw uca Guerrini Department of Mathematics for Economic and Social Sciences
Topic 8: Optimal Investment
 Topic 8: Optimal Investment Yulei Luo SEF of HKU November 22, 2013 Luo, Y. SEF of HKU) Macro Theory November 22, 2013 1 / 22 Demand for Investment The importance of investment. First, the combination of
Topic 8: Optimal Investment Yulei Luo SEF of HKU November 22, 2013 Luo, Y. SEF of HKU) Macro Theory November 22, 2013 1 / 22 Demand for Investment The importance of investment. First, the combination of
The TransPacific agreement A good thing for VietNam?
 The TransPacific agreement A good thing for VietNam? Jean Louis Brillet, France For presentation at the LINK 2014 Conference New York, 22nd 24th October, 2014 Advertisement!!! The model uses EViews The
The TransPacific agreement A good thing for VietNam? Jean Louis Brillet, France For presentation at the LINK 2014 Conference New York, 22nd 24th October, 2014 Advertisement!!! The model uses EViews The
Advanced Macroeconomics
 Advanced Macroeconomics The Ramsey Model Micha l Brzoza-Brzezina/Marcin Kolasa Warsaw School of Economics Micha l Brzoza-Brzezina/Marcin Kolasa (WSE) Ad. Macro - Ramsey model 1 / 47 Introduction Authors:
Advanced Macroeconomics The Ramsey Model Micha l Brzoza-Brzezina/Marcin Kolasa Warsaw School of Economics Micha l Brzoza-Brzezina/Marcin Kolasa (WSE) Ad. Macro - Ramsey model 1 / 47 Introduction Authors:
Volume 30, Issue 3. Ramsey Fiscal Policy and Endogenous Growth: A Comment. Jenn-hong Tang Department of Economics, National Tsing-Hua University
 Volume 30, Issue 3 Ramsey Fiscal Policy and Endogenous Growth: A Comment Jenn-hong Tang Department of Economics, National Tsing-Hua University Abstract Recently, Park (2009, Economic Theory 39, 377--398)
Volume 30, Issue 3 Ramsey Fiscal Policy and Endogenous Growth: A Comment Jenn-hong Tang Department of Economics, National Tsing-Hua University Abstract Recently, Park (2009, Economic Theory 39, 377--398)
Inthis article, I investigate the size of the returns to scale in aggregate
 Economic Quarterly Volume 102, Number 1 First Quarter 2016 Pages 79 10 3 How Large Are Returns to Scale in the U.S.? A View Across the Boundary Thomas A. Lubik Inthis article, I investigate the size of
Economic Quarterly Volume 102, Number 1 First Quarter 2016 Pages 79 10 3 How Large Are Returns to Scale in the U.S.? A View Across the Boundary Thomas A. Lubik Inthis article, I investigate the size of
OUTPUT DYNAMICS IN AN ENDOGENOUS GROWTH MODEL
 OUTPUT DYNAMICS IN AN ENDOGENOUS GROWTH MODEL by Ilaski Barañano and M. Paz Moral 2003 Working Paper Series: IL. 05/03 Departamento de Fundamentos del Análisis Económico I Ekonomi Analisiaren Oinarriak
OUTPUT DYNAMICS IN AN ENDOGENOUS GROWTH MODEL by Ilaski Barañano and M. Paz Moral 2003 Working Paper Series: IL. 05/03 Departamento de Fundamentos del Análisis Económico I Ekonomi Analisiaren Oinarriak
Assessing the Fed s Performance through the Effect of Technology Shocks: New Evidence
 through the Effect of Technology Shocks: New Evidence Carlo Coen Castellino September 2010 Abstract In this work I revisit the paper by Galí et al. (2003), which explains how the changes over time in the
through the Effect of Technology Shocks: New Evidence Carlo Coen Castellino September 2010 Abstract In this work I revisit the paper by Galí et al. (2003), which explains how the changes over time in the
Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle
 Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle David de la Croix 1,3 Gregory de Walque 2 Rafael Wouters 2,1 1 dept. of economics, Univ. cath. Louvain 2 National Bank of Belgium
Dynamics and Monetary Policy in a Fair Wage Model of the Business Cycle David de la Croix 1,3 Gregory de Walque 2 Rafael Wouters 2,1 1 dept. of economics, Univ. cath. Louvain 2 National Bank of Belgium
Habit Formation, Catching up with the Joneses, and Non-Scale Growth. Francisco Alvarez. Goncalo Monteiro. Stephen J. Turnovsky
 Habit Formation, Catching up with the Joneses, and Non-Scale Growth Francisco Alvarez Goncalo Monteiro Stephen J. Turnovsky Department of Economics University of Washington Box 353330, Seattle WA 98195
Habit Formation, Catching up with the Joneses, and Non-Scale Growth Francisco Alvarez Goncalo Monteiro Stephen J. Turnovsky Department of Economics University of Washington Box 353330, Seattle WA 98195
Deep Habits, Nominal Rigidities and Interest Rate Rules
 Deep Habits, Nominal Rigidities and Interest Rate Rules Sarah Zubairy August 18, 21 Abstract This paper explores how the introduction of deep habits in a standard new-keynesian model affects the properties
Deep Habits, Nominal Rigidities and Interest Rate Rules Sarah Zubairy August 18, 21 Abstract This paper explores how the introduction of deep habits in a standard new-keynesian model affects the properties
WORKING PAPER NO NON-STATIONARY HOURS IN A DSGE MODEL. Yongsung Chang Seoul National University. Taeyoung Doh University of Pennsylvania
 WORKING PAPER NO. 06-3 NON-STATIONARY HOURS IN A DSGE MODEL Yongsung Chang Seoul National University Taeyoung Doh University of Pennsylvania Frank Schorfheide University of Pennsylvania, CEPR, and Visiting
WORKING PAPER NO. 06-3 NON-STATIONARY HOURS IN A DSGE MODEL Yongsung Chang Seoul National University Taeyoung Doh University of Pennsylvania Frank Schorfheide University of Pennsylvania, CEPR, and Visiting
Growth Theory: Review
 Growth Theory: Review Lecture 1.1, Exogenous Growth Topics in Growth, Part 2 June 11, 2007 Lecture 1.1, Exogenous Growth 1/76 Topics in Growth, Part 2 Growth Accounting: Objective and Technical Framework
Growth Theory: Review Lecture 1.1, Exogenous Growth Topics in Growth, Part 2 June 11, 2007 Lecture 1.1, Exogenous Growth 1/76 Topics in Growth, Part 2 Growth Accounting: Objective and Technical Framework
A simple macro dynamic model with endogenous saving rate: the representative agent model
 A simple macro dynamic model with endogenous saving rate: the representative agent model Virginia Sánchez-Marcos Macroeconomics, MIE-UNICAN Macroeconomics (MIE-UNICAN) A simple macro dynamic model with
A simple macro dynamic model with endogenous saving rate: the representative agent model Virginia Sánchez-Marcos Macroeconomics, MIE-UNICAN Macroeconomics (MIE-UNICAN) A simple macro dynamic model with
Endogenous Growth Theory
 Endogenous Growth Theory Lecture Notes for the winter term 2010/2011 Ingrid Ott Tim Deeken October 21st, 2010 CHAIR IN ECONOMIC POLICY KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and National Laboratory
Endogenous Growth Theory Lecture Notes for the winter term 2010/2011 Ingrid Ott Tim Deeken October 21st, 2010 CHAIR IN ECONOMIC POLICY KIT University of the State of Baden-Wuerttemberg and National Laboratory
1. Money in the utility function (start)
 Monetary Economics: Macro Aspects, 1/3 2012 Henrik Jensen Department of Economics University of Copenhagen 1. Money in the utility function (start) a. The basic money-in-the-utility function model b. Optimal
Monetary Economics: Macro Aspects, 1/3 2012 Henrik Jensen Department of Economics University of Copenhagen 1. Money in the utility function (start) a. The basic money-in-the-utility function model b. Optimal
Optimal Simple And Implementable Monetary and Fiscal Rules
 Optimal Simple And Implementable Monetary and Fiscal Rules Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé Martín Uribe Duke University September 2007 1 Welfare-Based Policy Evaluation: Related Literature (ex: Rotemberg and Woodford,
Optimal Simple And Implementable Monetary and Fiscal Rules Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé Martín Uribe Duke University September 2007 1 Welfare-Based Policy Evaluation: Related Literature (ex: Rotemberg and Woodford,
Identifying the Monetary Policy Shock Christiano et al. (1999)
 Identifying the Monetary Policy Shock Christiano et al. (1999) The question we are asking is: What are the consequences of a monetary policy shock a shock which is purely related to monetary conditions
Identifying the Monetary Policy Shock Christiano et al. (1999) The question we are asking is: What are the consequences of a monetary policy shock a shock which is purely related to monetary conditions
Pricing To Habits and the Law of One Price
 Pricing To Habits and the Law of One Price Morten Ravn 1 Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé 2 Martin Uribe 2 1 European University Institute 2 Duke University Izmir, May 18, 27 Stylized facts we wish to address Pricing-to-Market:
Pricing To Habits and the Law of One Price Morten Ravn 1 Stephanie Schmitt-Grohé 2 Martin Uribe 2 1 European University Institute 2 Duke University Izmir, May 18, 27 Stylized facts we wish to address Pricing-to-Market:
The full RBC model. Empirical evaluation
 The full RBC model. Empirical evaluation Lecture 13 (updated version), ECON 4310 Tord Krogh October 24, 2012 Tord Krogh () ECON 4310 October 24, 2012 1 / 49 Today s lecture Add labor to the stochastic
The full RBC model. Empirical evaluation Lecture 13 (updated version), ECON 4310 Tord Krogh October 24, 2012 Tord Krogh () ECON 4310 October 24, 2012 1 / 49 Today s lecture Add labor to the stochastic
What are we going to do?
 RBC Model Analyzes to what extent growth and business cycles can be generated within the same framework Uses stochastic neoclassical growth model (Brock-Mirman model) as a workhorse, which is augmented
RBC Model Analyzes to what extent growth and business cycles can be generated within the same framework Uses stochastic neoclassical growth model (Brock-Mirman model) as a workhorse, which is augmented
