Connecting the small and large scales
|
|
|
- Silas Sharp
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cosmology at the Beach Playa del Carmen, Mexico January 12 th, 2010
2 Connecting the small and large scales Cosmology at the Beach Playa del Carmen, Mexico January 12 th, 2010
3 Connecting the small and large scales Rest of Conference Joe Wolf (UC Irvine) Cosmology at the Beach Playa del Carmen, Mexico January 12 th, 2010
4 Team Irvine: Greg Martinez James Bullock Manoj Kaplinghat Erik Tollerud Quinn Minor
5 Team Irvine: Greg Martinez James Bullock Manoj Kaplinghat Erik Tollerud Quinn Minor Haverford: Beth Willman KIPAC: Louie Strigari OCIW: Josh Simon Yale: Marla Geha Ricardo Munoz
6 1. An introduction to the local group 2. A new mass estimator: accurate without knowledge of anisotropy/beta 3. Utilizing new mass estimator to probe galaxy formation scenarios & to connect small and large scales
7 Roen Kelly / Astronomy (So, what s this redshift everyone keeps talking about?) M31: z =
8 The new dwarf galaxy pond after SDSS: Roen Kelly / Astronomy
9 Galaxy formation 1. Subhalos merge to form larger galaxies 2. Surviving dwarfs may be fossil relics of first galaxies
10 Galaxy formation 1. Subhalos merge to form larger galaxies 2. Surviving dwarfs may be fossil relics of first galaxies Large scale cosmology 1. Adjusting cosmological parameters affects small scale structure as well. Thus, new dark energy and gravity models must be able to reproduce small scale structure.
11 Subhalos are the building blocks of all larger galaxies.
12 Figure: James Bullock
13 Madau et al. 2008
14 Madau et al. 2008
15 Two significant problems with ΛCDM on small scales: 1. Cusp vs core 2. Missing satellite problem Strigari et al 2007
16 Two significant problems with ΛCDM on small scales: 1. Cusp vs core 2. Missing satellite problem Will not discuss these in detail now (feel free to ask me afterward). Just wanted to remind you all that ΛCDM may still need modification on the small scale!
17 Two significant problems with ΛCDM on small scales: 1. Cusp vs core 2. Missing satellite problem Will not discuss these in detail now (feel free to ask me afterward). Just wanted to remind you all that ΛCDM may still need modification on the small scale! Knowing accurate masses useful for testing galaxy formation theories, which includes demonstrating the connectedness of all galactic scales!
18 Many gas-poor dwarf galaxies, ellipticals, and clusters have a significant, usually dominant hot component. They are pressuresupported, not rotation supported. Consider a spherical, pressure-supported system whose stars are collisionless and are in equilibrium. Let us consider the Jeans Equation: We want mass Unknown: Anisotropy Free function Assume known: 3D deprojected stellar density Radial dispersion (depends on beta)
19 I will skip the details of the dynamical analysis in this talk (feel free to ask afterward).
20 I will skip the details of the dynamical analysis in this talk (feel free to ask afterward). Summary: MCMC algorithm is able to produce mass likelihoods from line-of-sight kinematics and photometry. Confidence Intervals: Cyan: 68% Purple: 95% Joe Wolf et al. arxiv:
21 Derived equation under several simplifications:
22 Derived equation under several simplifications: r 1/2 4/3 * R eff
23 Isn t this just the scalar virial theorem (SVT)? Nope! The SVT only gives you limits on the total mass of a system. This formula yields the mass within r 1/2, the 3D deprojected half-light radius, and is accurate independent of our ignorance of the stellar anisotropy.
24 Boom! Equation tested on systems spanning almost eight decades in luminosity after lifting simplifications. Joe Wolf et al.,
25 Classical MW dwarf spheroidals Dotted lines: 10% variation in factor of 3 in M Appx Joe Wolf et al.,
26 Error dominated by kinematics
27 Error dominated by kinematics Error dominated by anisotropy
28 Joe Wolf et al.,
29 Much information about feedback & galaxy formation can be summarized with this plot. Also note similar trend to number abundance matching. Joe Wolf et al.,
30 Much information about feedback & galaxy formation can be summarized with this plot. Also note similar trend to number abundance matching. Ultrafaint dsphs: most DM dominated systems known! Inefficient at galaxy formation Globulars: Offset from L* by factor of three (Hmm ) L * : Efficient at galaxy formation Joe Wolf et al.,
31 Last plot: Mass floor This plot: Luminosity ceiling Joe Wolf et al.,
32 The small and large are more connected that one may previously have thought.
33 Fundamental Plane: Independent Observables σ MLR: Intrinsic Properties M 1/2 R eff r 1/2 I eff L 1/2 Erik Tollerud, JW, et al. in prep.
34
35
36 Despite different feedback mechanisms, all systems sitting deeply embedded in DM halos lie on this one tube, which spans 10 orders of magnitude in luminosity! Globular clusters, which do not sit within DM halos, are offset from this tube. Erik Tollerud, JW, et al. in prep.
37 Joe Wolf et al. arxiv: Knowing M 1/2 accurately without knowledge of anisotropy gives new constraints for galaxy formation theories to match. - Future simulations must be able to reproduce the observed trends between M 1/2 and L for all pressuresupported systems, from dwarf spheroidals (L~10 2 ) to galaxy clusters (L~10 12 ). - Understanding the small scale is important for understanding the large scale and vice versa!
A tool to test galaxy formation theories. Joe Wolf (UC Irvine)
 A tool to test galaxy formation theories Joe Wolf (UC Irvine) SF09 Cosmology Summer Workshop July 7 2009 Team Irvine: Greg Martinez James Bullock Manoj Kaplinghat Frank Avedo KIPAC: Louie Strigari Haverford:
A tool to test galaxy formation theories Joe Wolf (UC Irvine) SF09 Cosmology Summer Workshop July 7 2009 Team Irvine: Greg Martinez James Bullock Manoj Kaplinghat Frank Avedo KIPAC: Louie Strigari Haverford:
Connecting observations to simulations arxiv: Joe Wolf (UC Irvine)
 Connecting observations to simulations arxiv: 0908.2995 Joe Wolf (UC Irvine) University of Maryland December 8 th, 2009 Team Irvine: Greg Martinez James Bullock Manoj Kaplinghat Erik Tollerud Quinn Minor
Connecting observations to simulations arxiv: 0908.2995 Joe Wolf (UC Irvine) University of Maryland December 8 th, 2009 Team Irvine: Greg Martinez James Bullock Manoj Kaplinghat Erik Tollerud Quinn Minor
A tool to test galaxy formation arxiv: Joe Wolf (UC Irvine)
 A tool to test galaxy formation arxiv: 0908.2995 Joe Wolf (UC Irvine) Hunting for the Dark: The Hidden Side of Galaxy Formation Malta October 22 nd, 2009 Team Irvine: Greg Martinez James Bullock Manoj
A tool to test galaxy formation arxiv: 0908.2995 Joe Wolf (UC Irvine) Hunting for the Dark: The Hidden Side of Galaxy Formation Malta October 22 nd, 2009 Team Irvine: Greg Martinez James Bullock Manoj
Connecting observations to simulations arxiv: Joe Wolf (UC Irvine)
 Connecting observations to simulations arxiv: 0908.2995 Joe Wolf (UC Irvine) September, 2009 Team Irvine: Greg Martinez James Bullock Manoj Kaplinghat Erik Tollerud Quinn Minor Team Irvine: Greg Martinez
Connecting observations to simulations arxiv: 0908.2995 Joe Wolf (UC Irvine) September, 2009 Team Irvine: Greg Martinez James Bullock Manoj Kaplinghat Erik Tollerud Quinn Minor Team Irvine: Greg Martinez
Dark Matter Halos of M31. Joe Wolf
 Dark Matter Halos of M31 Galaxies Joe Wolf TASC October 24 th, 2008 Dark Matter Halos of M31 Galaxies Joe Wolf Team Irvine: Louie Strigari, James Bullock, Manoj Kaplinghat TASC October 24 th, 2008 Dark
Dark Matter Halos of M31 Galaxies Joe Wolf TASC October 24 th, 2008 Dark Matter Halos of M31 Galaxies Joe Wolf Team Irvine: Louie Strigari, James Bullock, Manoj Kaplinghat TASC October 24 th, 2008 Dark
Masses of Dwarf Satellites of the Milky Way
 Masses of Dwarf Satellites of the Milky Way Manoj Kaplinghat Center for Cosmology UC Irvine Collaborators: Greg Martinez Quinn Minor Joe Wolf James Bullock Evan Kirby Marla Geha Josh Simon Louie Strigari
Masses of Dwarf Satellites of the Milky Way Manoj Kaplinghat Center for Cosmology UC Irvine Collaborators: Greg Martinez Quinn Minor Joe Wolf James Bullock Evan Kirby Marla Geha Josh Simon Louie Strigari
Dark Matter Distributions of the Milky Way Satellites and Implications for Indirect Detection
 Dark Matter Distributions of the Milky Way Satellites and Implications for Indirect Detection Kavli Institue for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, Physics Department, Stanford University, Stanford,
Dark Matter Distributions of the Milky Way Satellites and Implications for Indirect Detection Kavli Institue for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology, Physics Department, Stanford University, Stanford,
Dark Matter Dominated Objects. Louie Strigari Stanford
 Dark Matter Dominated Objects Louie Strigari Stanford Milky Way Circa 2009 Satellite Year Discovered LMC 1519 SMC 1519 Sculptor 1937 Fornax 1938 Leo II 1950 Leo I 1950 Ursa Minor 1954 Draco 1954 Carina
Dark Matter Dominated Objects Louie Strigari Stanford Milky Way Circa 2009 Satellite Year Discovered LMC 1519 SMC 1519 Sculptor 1937 Fornax 1938 Leo II 1950 Leo I 1950 Ursa Minor 1954 Draco 1954 Carina
Determining the Nature of Dark Matter with Astrometry
 Determining the Nature of Dark Matter with Astrometry Louie Strigari UC Irvine Center for Cosmology Fermilab, 4.16.2007 Collaborators: James Bullock, Juerg Diemand, Manoj Kaplinghat, Michael Kuhlen, Piero
Determining the Nature of Dark Matter with Astrometry Louie Strigari UC Irvine Center for Cosmology Fermilab, 4.16.2007 Collaborators: James Bullock, Juerg Diemand, Manoj Kaplinghat, Michael Kuhlen, Piero
The Structural Properties of Milky Way Dwarf Galaxies. Ricardo Muñoz (Universidad de Chile) Collaborators:
 The Structural Properties of Milky Way Dwarf Galaxies Ricardo Muñoz (Universidad de Chile) Milky Way inner 100 kpc Collaborators: Marla Geha (Yale) Patrick Côté (HIA/DAO) Peter Stetson (HIA/DAO) Josh Simon
The Structural Properties of Milky Way Dwarf Galaxies Ricardo Muñoz (Universidad de Chile) Milky Way inner 100 kpc Collaborators: Marla Geha (Yale) Patrick Côté (HIA/DAO) Peter Stetson (HIA/DAO) Josh Simon
Distinguishing Between Warm and Cold Dark Matter
 Distinguishing Between Warm and Cold Dark Matter Center for Cosmology Aspen Workshop Neutrinos in Physics & Astrophysics 2/2/2007 Collaborators: James Bullock, Manoj Kaplinghat astro-ph/0701581.. Motivations
Distinguishing Between Warm and Cold Dark Matter Center for Cosmology Aspen Workshop Neutrinos in Physics & Astrophysics 2/2/2007 Collaborators: James Bullock, Manoj Kaplinghat astro-ph/0701581.. Motivations
Mass modelling of dwarf spheroidals. Jorge Peñarrubia
 Mass modelling of dwarf spheroidals Jorge Peñarrubia Santiago de Chile 13 April 2015 Universe Composition Assumption: GR is correct WMAP7 DM particle models: Constraints 63 orders 51 orders DM particle
Mass modelling of dwarf spheroidals Jorge Peñarrubia Santiago de Chile 13 April 2015 Universe Composition Assumption: GR is correct WMAP7 DM particle models: Constraints 63 orders 51 orders DM particle
James Bullock UC Irvine
 Can Feedback Solve Too Big to Fail Problem? James Bullock UC Irvine Garrison-Kimmel, Oñorbe et al. Collaborators Shea Garrison-Kimmel Mike Boylan-Kolchin Jose Oñorbe Jaspreet Lally Manoj Kaplinghat dsphs
Can Feedback Solve Too Big to Fail Problem? James Bullock UC Irvine Garrison-Kimmel, Oñorbe et al. Collaborators Shea Garrison-Kimmel Mike Boylan-Kolchin Jose Oñorbe Jaspreet Lally Manoj Kaplinghat dsphs
Dark matter annihilation and decay factors in the Milky Way s dwarf spheroidal galaxies
 Dark matter annihilation and decay factors in the Milky Way s dwarf spheroidal galaxies Vincent Bonnivard bonnivard@lpsc.in2p3.fr TAUP 2015 07/09/15 Collaborators: D. Maurin, C. Combet, M. G. Walker, A.
Dark matter annihilation and decay factors in the Milky Way s dwarf spheroidal galaxies Vincent Bonnivard bonnivard@lpsc.in2p3.fr TAUP 2015 07/09/15 Collaborators: D. Maurin, C. Combet, M. G. Walker, A.
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 20 Feb 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 20 Feb 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 20 Feb 2009](/thumbs/93/111245659.jpg) 0 Dwarf Galaxies in 2010: Revealing Galaxy Formation s Threshold and Testing the Nature of Dark Matter James S. Bullock and Manoj Kaplinghat Physics & Astronomy Department, University of California, Irvine;
0 Dwarf Galaxies in 2010: Revealing Galaxy Formation s Threshold and Testing the Nature of Dark Matter James S. Bullock and Manoj Kaplinghat Physics & Astronomy Department, University of California, Irvine;
Insights into galaxy formation from dwarf galaxies
 Potsdam, August 2014 Insights into galaxy formation from dwarf galaxies Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Planck CMB map: the IC's for structure formation Planck CMB map: the IC's for structure
Potsdam, August 2014 Insights into galaxy formation from dwarf galaxies Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Planck CMB map: the IC's for structure formation Planck CMB map: the IC's for structure
Milky Way Satellite Galaxies with DES
 Milky Way Satellite Galaxies with DES Alex Drlica-Wagner kadrlica@fnal.gov! DES Milky Way Working Group Coordinator! January 11, 2015 Milky Way Satellite Galaxies Segue 1 The Milky Way is surrounded by
Milky Way Satellite Galaxies with DES Alex Drlica-Wagner kadrlica@fnal.gov! DES Milky Way Working Group Coordinator! January 11, 2015 Milky Way Satellite Galaxies Segue 1 The Milky Way is surrounded by
Galaxy population simulations
 Aspen, February 2014 Galaxy population simulations Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics semi-analytic simulations provide a tool... To explore the statistics and interactions of the many processes
Aspen, February 2014 Galaxy population simulations Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics semi-analytic simulations provide a tool... To explore the statistics and interactions of the many processes
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jan 2011
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jan 2011 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jan 2011](/thumbs/76/73863672.jpg) A Universe of Dwarf Galaxies, Lyon 2010 Editors : will be set by the publisher EAS Publications Series, Vol.?, 2017 arxiv:1101.2232v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jan 2011 HOW DOES FEEDBACK AFFECT MILKY WAY SATELLITE
A Universe of Dwarf Galaxies, Lyon 2010 Editors : will be set by the publisher EAS Publications Series, Vol.?, 2017 arxiv:1101.2232v1 [astro-ph.ga] 11 Jan 2011 HOW DOES FEEDBACK AFFECT MILKY WAY SATELLITE
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1
 Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
Gaia Revue des Exigences préliminaires 1 Global top questions 1. Which stars form and have been formed where? - Star formation history of the inner disk - Location and number of spiral arms - Extent of
The dark matter crisis
 The dark matter crisis Ben Moore Department of Physics, Durham University, UK. arxiv:astro-ph/0103100 v2 8 Mar 2001 Abstract I explore several possible solutions to the missing satellites problem that
The dark matter crisis Ben Moore Department of Physics, Durham University, UK. arxiv:astro-ph/0103100 v2 8 Mar 2001 Abstract I explore several possible solutions to the missing satellites problem that
Self-Interacting Dark Matter
 Self-Interacting Dark Matter James Bullock UC Irvine Garrison-Kimmel, Oñorbe et al. Act I Motivations Missing Satellites Problem (1999) Theory: N>>1000 Klypin et al. 1999; Moore et al. 1999; Kauffmann
Self-Interacting Dark Matter James Bullock UC Irvine Garrison-Kimmel, Oñorbe et al. Act I Motivations Missing Satellites Problem (1999) Theory: N>>1000 Klypin et al. 1999; Moore et al. 1999; Kauffmann
Beyond Collisionless DM
 Beyond Collisionless DM Sean Tulin University of Michigan Based on: ST, Haibo Yu, Kathryn Zurek (1210.0900 + 1302.3898) Manoj Kaplinghat, ST, Haibo Yu (1308.0618 + 13xx.xxxx) Exploring the dark sector
Beyond Collisionless DM Sean Tulin University of Michigan Based on: ST, Haibo Yu, Kathryn Zurek (1210.0900 + 1302.3898) Manoj Kaplinghat, ST, Haibo Yu (1308.0618 + 13xx.xxxx) Exploring the dark sector
Probing Dark Matter Halos with Satellite Kinematics & Weak Lensing
 Probing Dark Matter Halos with & Weak Lensing Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Surhud More, Marcello Cacciato UMass, August 2008 Probing Dark Matter Halos - p. 1/35 Galaxy Formation in a Nutshell
Probing Dark Matter Halos with & Weak Lensing Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Surhud More, Marcello Cacciato UMass, August 2008 Probing Dark Matter Halos - p. 1/35 Galaxy Formation in a Nutshell
Dark matter. Anne Green University of Nottingham
 Dark matter Anne Green University of Nottingham anne.green@nottingham.ac.uk 1. Observational evidence for DM and constraints on its properties Alternatives to dark matter (modified gravity) 2. The DM distribution
Dark matter Anne Green University of Nottingham anne.green@nottingham.ac.uk 1. Observational evidence for DM and constraints on its properties Alternatives to dark matter (modified gravity) 2. The DM distribution
Future DM indirect detection in dwarf spheroidal galaxies and Foreground effect on the J-factor estimation Koji Ichikawa
 Future DM indirect detection in dwarf spheroidal galaxies and Foreground effect on the J-factor estimation Koji Ichikawa In collaboration with Kohei Hayashi, Masahiro Ibe, Miho N. Ishigaki, Shigeki Matsumoto
Future DM indirect detection in dwarf spheroidal galaxies and Foreground effect on the J-factor estimation Koji Ichikawa In collaboration with Kohei Hayashi, Masahiro Ibe, Miho N. Ishigaki, Shigeki Matsumoto
The Self-Interacting Dark Matter (SIDM) model MANOJ KAPLINGHAT UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, IRVINE
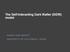 The Self-Interacting Dark Matter (SIDM) model MANOJ KAPLINGHAT UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, IRVINE The predictions of the ΛCDM model agree well with the observed large-scale structure of the Universe. Visible
The Self-Interacting Dark Matter (SIDM) model MANOJ KAPLINGHAT UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, IRVINE The predictions of the ΛCDM model agree well with the observed large-scale structure of the Universe. Visible
Where to Look for Dark Matter Weirdness
 Where to Look for Dark Matter Weirdness Dark Matter in Southern California (DaMaSC) - II James Bullock UC Irvine Garrison-Kimmel, Oñorbe et al. Collaborators Mike Boylan-Kolchin U. Maryland Miguel Rocha
Where to Look for Dark Matter Weirdness Dark Matter in Southern California (DaMaSC) - II James Bullock UC Irvine Garrison-Kimmel, Oñorbe et al. Collaborators Mike Boylan-Kolchin U. Maryland Miguel Rocha
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics. Fall 2014
 ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
ASTRON 449: Stellar (Galactic) Dynamics Fall 2014 In this course, we will cover the basic phenomenology of galaxies (including dark matter halos, stars clusters, nuclear black holes) theoretical tools
Dark Matter in Galaxies
 Dark Matter in Galaxies Garry W. Angus VUB FWO 3rd COSPA Meeting Université de Liège Ellipticals. Old stars. Gas poor. Low star formation rate. Spiral (disk) galaxies. Often gas rich => star formation.
Dark Matter in Galaxies Garry W. Angus VUB FWO 3rd COSPA Meeting Université de Liège Ellipticals. Old stars. Gas poor. Low star formation rate. Spiral (disk) galaxies. Often gas rich => star formation.
arxiv: v6 [astro-ph.co] 21 Sep 2010
![arxiv: v6 [astro-ph.co] 21 Sep 2010 arxiv: v6 [astro-ph.co] 21 Sep 2010](/thumbs/82/85453371.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 9 May 018 (MN LATEX style file v.) Accurate masses for dispersion-supported galaxies arxiv:0908.995v6 [astro-ph.co] 1 Sep 010 Joe Wolf 1, Gregory D.
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 9 May 018 (MN LATEX style file v.) Accurate masses for dispersion-supported galaxies arxiv:0908.995v6 [astro-ph.co] 1 Sep 010 Joe Wolf 1, Gregory D.
Dwarf Galaxy Dispersion Profile Calculations Using a Simplified MOND External Field Effect
 Dwarf Galaxy Dispersion Profile Calculations Using a Simplified MOND External Field Effect On the Shoulders of Giants Workshop Case Western Reserve University June 7, 2017 Stephen Alexander Physics Department
Dwarf Galaxy Dispersion Profile Calculations Using a Simplified MOND External Field Effect On the Shoulders of Giants Workshop Case Western Reserve University June 7, 2017 Stephen Alexander Physics Department
Small-scale problems of cosmology and how modified dynamics might address them
 Small-scale problems of cosmology and how modified dynamics might address them Marcel S. Pawlowski Email: marcel.pawlowski@case.edu Twitter: @8minutesold with support from the John Templeton Foundation
Small-scale problems of cosmology and how modified dynamics might address them Marcel S. Pawlowski Email: marcel.pawlowski@case.edu Twitter: @8minutesold with support from the John Templeton Foundation
What do we need to know about galaxy formation?
 What do we need to know about galaxy formation? rachel somerville University of Michigan Hubble Science Legacy Workshop April 2002 what s next? test the CDM paradigm constrain the nature of the dark matter
What do we need to know about galaxy formation? rachel somerville University of Michigan Hubble Science Legacy Workshop April 2002 what s next? test the CDM paradigm constrain the nature of the dark matter
The Current Status of Too Big To Fail problem! based on Warm Dark Matter cosmology
 The Current Status of Too Big To Fail problem! based on Warm Dark Matter cosmology 172th Astronomical Seminar Dec.3 2013 Chiba Lab.M2 Yusuke Komuro Key Word s Too Big To Fail TBTF Cold Dark Matter CDM
The Current Status of Too Big To Fail problem! based on Warm Dark Matter cosmology 172th Astronomical Seminar Dec.3 2013 Chiba Lab.M2 Yusuke Komuro Key Word s Too Big To Fail TBTF Cold Dark Matter CDM
Testing Cosmology with Phase-Space Correlations in Systems of Satellite Galaxies. Current Studies and Future Prospects
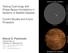 Observed MW satellites Testing Cosmology with Phase-Space Correlations in Systems of Satellite Galaxies Current Studies and Future Prospects http://marcelpawlowski.com/research/movies-astronomy/ Marcel
Observed MW satellites Testing Cosmology with Phase-Space Correlations in Systems of Satellite Galaxies Current Studies and Future Prospects http://marcelpawlowski.com/research/movies-astronomy/ Marcel
Dark Matter: Observational Constraints
 Dark Matter: Observational Constraints Properties of Dark Matter: What is it? And what isn t it? Leo Blitz UC Berkeley Stanford July 31, 2007 How much is there? WMAP results Rotation curves of Galaxies
Dark Matter: Observational Constraints Properties of Dark Matter: What is it? And what isn t it? Leo Blitz UC Berkeley Stanford July 31, 2007 How much is there? WMAP results Rotation curves of Galaxies
Structure and substructure in dark matter halos
 Satellites and Tidal Streams ING IAC joint Conference La Palma, May 2003 Structure and substructure in dark matter halos Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics 500 kpc A CDM Milky Way Does
Satellites and Tidal Streams ING IAC joint Conference La Palma, May 2003 Structure and substructure in dark matter halos Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics 500 kpc A CDM Milky Way Does
Robust estimate of the dark matter halo of the Milky-way's dwarf spheroidal galaxies
 Robust estimate of the dark matter halo of the Milky-way's dwarf spheroidal galaxies Koji Ichikawa arxiv:1701.xxxxx arxiv:1608.01749 (submitted in MNRAS) MNRAS, 461, 2914 (1603.08046 [astroph.ga]) In collaboration
Robust estimate of the dark matter halo of the Milky-way's dwarf spheroidal galaxies Koji Ichikawa arxiv:1701.xxxxx arxiv:1608.01749 (submitted in MNRAS) MNRAS, 461, 2914 (1603.08046 [astroph.ga]) In collaboration
Formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe: progress & challenges
 Obergurgl. April 2014 Formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe: progress & challenges Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Ly α forest spectra and small-scale initial structure
Obergurgl. April 2014 Formation and growth of galaxies in the young Universe: progress & challenges Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Ly α forest spectra and small-scale initial structure
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 12. The Problems with Satellite Galaxies
 Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 12 The Problems with Satellite Galaxies The Problems with Satellites (1) The Missing Satellites Problem (2) The Too Big to Fail Problem We ll examine potential solutions to each
Phys/Astro 689: Lecture 12 The Problems with Satellite Galaxies The Problems with Satellites (1) The Missing Satellites Problem (2) The Too Big to Fail Problem We ll examine potential solutions to each
Diverse Galactic Rotation Curves & Self-Interacting Dark Matter
 Diverse Galactic Rotation Curves & Self-Interacting Dark Matter Hai-Bo Yu University of California, Riverside TeVPA, August 7, 2017 See Anna Kwa s talk Review for Physics Reports: Sean Tulin, HBY arxiv:
Diverse Galactic Rotation Curves & Self-Interacting Dark Matter Hai-Bo Yu University of California, Riverside TeVPA, August 7, 2017 See Anna Kwa s talk Review for Physics Reports: Sean Tulin, HBY arxiv:
Reionization and the radial distribution of satellites
 Reionization and the radial distribution of satellites Andrew Graus (UC Irvine) Collaborators: James Bullock (UC Irvine) Tyler Kelley Oliver Elbert Claire Qi Michael Boylan-Kolchin (UT Austin) Alex Fitts
Reionization and the radial distribution of satellites Andrew Graus (UC Irvine) Collaborators: James Bullock (UC Irvine) Tyler Kelley Oliver Elbert Claire Qi Michael Boylan-Kolchin (UT Austin) Alex Fitts
Fossils of the First Galaxies in the Local Group: True Fossils and Ghost Halos
 Fossils of the First Galaxies in the Local Group: True Fossils and Ghost Halos Mia S. Bovill with Massimo Ricotti University of Maryland The Smallest Galaxies Minihalos DO NOT initiate gas condensation
Fossils of the First Galaxies in the Local Group: True Fossils and Ghost Halos Mia S. Bovill with Massimo Ricotti University of Maryland The Smallest Galaxies Minihalos DO NOT initiate gas condensation
Future prospects for finding Milky Way satellites. Amit and Carl 31 March 2010
 Future prospects for finding Milky Way satellites Amit and Carl 31 March 2010 Where have all the satellites gone? The missing satellite problem! DM simulations (like Via Lactea) predict that there should
Future prospects for finding Milky Way satellites Amit and Carl 31 March 2010 Where have all the satellites gone? The missing satellite problem! DM simulations (like Via Lactea) predict that there should
AS1001:Extra-Galactic Astronomy
 AS1001:Extra-Galactic Astronomy Lecture 5: Dark Matter Simon Driver Theatre B spd3@st-andrews.ac.uk http://www-star.st-and.ac.uk/~spd3 Stars and Gas in Galaxies Stars form from gas in galaxy In the high-density
AS1001:Extra-Galactic Astronomy Lecture 5: Dark Matter Simon Driver Theatre B spd3@st-andrews.ac.uk http://www-star.st-and.ac.uk/~spd3 Stars and Gas in Galaxies Stars form from gas in galaxy In the high-density
Current status of the ΛCDM structure formation model. Simon White Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik
 Current status of the ΛCDM structure formation model Simon White Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik The idea that DM might be a neutral, weakly interacting particle took off around 1980, following a measurement
Current status of the ΛCDM structure formation model Simon White Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik The idea that DM might be a neutral, weakly interacting particle took off around 1980, following a measurement
Firenze (JPO: 28/07/17) Small Scale Crisis for CDM: Fatal or a Baryon Physics Fix
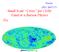 Firenze (JPO: 28/07/17) Small Scale Crisis for CDM: Fatal or a Baryon Physics Fix CBR Spectrum Planck and all-a Perfect Fit to the CDM Expectation Precise measurements of the CBR specify the cosmological
Firenze (JPO: 28/07/17) Small Scale Crisis for CDM: Fatal or a Baryon Physics Fix CBR Spectrum Planck and all-a Perfect Fit to the CDM Expectation Precise measurements of the CBR specify the cosmological
Dwarf galaxies vs. globular clusters: An observer s perspective
 Dwarf galaxies vs. globular clusters: An observer s perspective Jay Strader (Michigan St) with Beth Willman (Haverford) A globular cluster A galaxy Galaxy, Defined A galaxy is a gravitationally bound collection
Dwarf galaxies vs. globular clusters: An observer s perspective Jay Strader (Michigan St) with Beth Willman (Haverford) A globular cluster A galaxy Galaxy, Defined A galaxy is a gravitationally bound collection
What is an ultra-faint Galaxy?
 What is an ultra-faint Galaxy? UCSB KITP Feb 16 2012 Beth Willman (Haverford College) Large Magellanic Cloud, M V = -18 ~ 1/10 Milky Way luminosity image credit: Yuri Beletsky (ESO) and APOD NGC 205, M
What is an ultra-faint Galaxy? UCSB KITP Feb 16 2012 Beth Willman (Haverford College) Large Magellanic Cloud, M V = -18 ~ 1/10 Milky Way luminosity image credit: Yuri Beletsky (ESO) and APOD NGC 205, M
Galaxy Formation and Evolution
 Galaxy Formation and Evolution Houjun Mo Department of Astronomy, University of Massachusetts 710 North Pleasant Str., Amherst, MA 01003-9305, USA Frank van den Bosch Department of Physics & Astronomy,
Galaxy Formation and Evolution Houjun Mo Department of Astronomy, University of Massachusetts 710 North Pleasant Str., Amherst, MA 01003-9305, USA Frank van den Bosch Department of Physics & Astronomy,
Summary So Far! M87van der Maerl! NGC4342! van den Bosch! rotation velocity!
 Summary So Far Fundamental plane connects luminosity, scale length, surface brightness, stellar dynamics. age and chemical composition Elliptical galaxies are not randomly distributed within the 3D space
Summary So Far Fundamental plane connects luminosity, scale length, surface brightness, stellar dynamics. age and chemical composition Elliptical galaxies are not randomly distributed within the 3D space
Overview of Dynamical Modeling. Glenn van de Ven
 Overview of Dynamical Modeling Glenn van de Ven glenn@mpia.de 1 Why dynamical modeling? -- mass total mass stellar systems key is to their evolution compare luminous mass: constrain DM and/or IMF DM radial
Overview of Dynamical Modeling Glenn van de Ven glenn@mpia.de 1 Why dynamical modeling? -- mass total mass stellar systems key is to their evolution compare luminous mass: constrain DM and/or IMF DM radial
Zoccali et al. 2003, A&A, 399, 931. Overview of (old) Galactic components. bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo. metallicity & age distribution
 Chap.3 The nature of Galactic components Overview of (old) Galactic components bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo Globular clusters metallicity & age distribution Satellite galaxies spatial and metallicity
Chap.3 The nature of Galactic components Overview of (old) Galactic components bulge, thick disk, metal-weak halo Globular clusters metallicity & age distribution Satellite galaxies spatial and metallicity
Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes
 Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes Julio F. Navarro The Ursa Minor dwarf spheroidal First Light First Light The Planck Satellite The Cosmological Paradigm The Clustering of Dark Matter The Millennium
Dwarf Galaxies as Cosmological Probes Julio F. Navarro The Ursa Minor dwarf spheroidal First Light First Light The Planck Satellite The Cosmological Paradigm The Clustering of Dark Matter The Millennium
Dark matter from cosmological probes
 PLANCK 2014 Ferrara Dark matter from cosmological probes Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Dark matter was discovered in the Coma Cluster by Zwicky (1933) Fritz Zwicky Abell 2218 Corbelli
PLANCK 2014 Ferrara Dark matter from cosmological probes Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics Dark matter was discovered in the Coma Cluster by Zwicky (1933) Fritz Zwicky Abell 2218 Corbelli
Milky Way s Mass and Stellar Halo Velocity Dispersion Profiles
 Milky Way s Mass and Stellar Halo Velocity Dispersion Profiles Shanghai Astronomical Observatory In collaboration with Juntai Shen, Xiang Xiang Xue, Chao Liu, Chris Flynn, Ling Zhu, Jie Wang Contents 1
Milky Way s Mass and Stellar Halo Velocity Dispersion Profiles Shanghai Astronomical Observatory In collaboration with Juntai Shen, Xiang Xiang Xue, Chao Liu, Chris Flynn, Ling Zhu, Jie Wang Contents 1
The Radial Distribution of Galactic Satellites. Jacqueline Chen
 The Radial Distribution of Galactic Satellites Jacqueline Chen December 12, 2006 Introduction In the hierarchical assembly of dark matter (DM) halos, progenitor halos merge to form larger systems. Some
The Radial Distribution of Galactic Satellites Jacqueline Chen December 12, 2006 Introduction In the hierarchical assembly of dark matter (DM) halos, progenitor halos merge to form larger systems. Some
Galaxies: Structure, Dynamics, and Evolution. Dark Matter Halos and Large Scale Structure
 Galaxies: Structure, Dynamics, and Evolution Dark Matter Halos and Large Scale Structure Layout of the Course Feb 5: Review: Galaxies and Cosmology Feb 12: Review: Disk Galaxies and Galaxy Formation Basics
Galaxies: Structure, Dynamics, and Evolution Dark Matter Halos and Large Scale Structure Layout of the Course Feb 5: Review: Galaxies and Cosmology Feb 12: Review: Disk Galaxies and Galaxy Formation Basics
Modelling the galaxy population
 Modelling the galaxy population Simon White Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik IAU 277 Ouagadougou 1 The standard model reproduces -- the linear initial conditions -- IGM structure during galaxy formation
Modelling the galaxy population Simon White Max Planck Institut für Astrophysik IAU 277 Ouagadougou 1 The standard model reproduces -- the linear initial conditions -- IGM structure during galaxy formation
The tidal stirring model and its application to the Sagittarius dwarf
 The tidal stirring model and its application to the Sagittarius dwarf Ewa L. Łokas Copernicus Center, Warsaw Stelios Kazantzidis (Ohio State) Lucio Mayer (University of Zurich) Collaborators: Steven Majewski
The tidal stirring model and its application to the Sagittarius dwarf Ewa L. Łokas Copernicus Center, Warsaw Stelios Kazantzidis (Ohio State) Lucio Mayer (University of Zurich) Collaborators: Steven Majewski
Princeton December 2009 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos
 Princeton December 2009 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The dark matter structure of CDM halos A rich galaxy cluster halo Springel et al
Princeton December 2009 The fine-scale structure of dark matter halos Simon White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The dark matter structure of CDM halos A rich galaxy cluster halo Springel et al
CLUMPY: A public code for γ-ray and ν signals from dark matter structures.
 CLUMPY: A public code for γ-ray and ν signals from dark matter structures. Moritz Hütten, DESY Zeuthen for the CLUMPY developers: Vincent Bonnivard, Moritz Hütten, Emmanuel Nezri, Aldée Charbonnier, Céline
CLUMPY: A public code for γ-ray and ν signals from dark matter structures. Moritz Hütten, DESY Zeuthen for the CLUMPY developers: Vincent Bonnivard, Moritz Hütten, Emmanuel Nezri, Aldée Charbonnier, Céline
Splashback radius as a physical boundary of clusters
 Splashback radius as a physical boundary of clusters Andrey Kravtsov Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics The University of Chicago Abell 85 SDSS/ Chandra galaxy
Splashback radius as a physical boundary of clusters Andrey Kravtsov Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics Kavli Institute for Cosmological Physics The University of Chicago Abell 85 SDSS/ Chandra galaxy
Clusters: Observations
 Clusters: Observations Last time we talked about some of the context of clusters, and why observations of them have importance to cosmological issues. Some of the reasons why clusters are useful probes
Clusters: Observations Last time we talked about some of the context of clusters, and why observations of them have importance to cosmological issues. Some of the reasons why clusters are useful probes
Dark matter and galaxy formation
 Dark matter and galaxy formation Galaxy rotation The virial theorem Galaxy masses via K3 Mass-to-light ratios Rotation curves Milky Way Nearby galaxies Dark matter Baryonic or non-baryonic A problem with
Dark matter and galaxy formation Galaxy rotation The virial theorem Galaxy masses via K3 Mass-to-light ratios Rotation curves Milky Way Nearby galaxies Dark matter Baryonic or non-baryonic A problem with
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 21 Mar 2012
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 21 Mar 2012 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 21 Mar 2012](/thumbs/85/92397037.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 17 (2012) Printed 22 March 2012 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The Milky Way s bright satellites as an apparent failure of ΛCDM Michael Boylan-Kolchin, James S. Bullock and
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 17 (2012) Printed 22 March 2012 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) The Milky Way s bright satellites as an apparent failure of ΛCDM Michael Boylan-Kolchin, James S. Bullock and
ON THE CHEMICAL EVOLUTION OF THE MILKY WAY. The Metallicity distribution of the halo in the hierarchical merging paradigm
 ON THE CHEMICAL EVOLUTION OF THE MILKY WAY The Metallicity distribution of the halo in the hierarchical merging paradigm Halo abundance patterns and stellar yields Standard chemical evolution of solar
ON THE CHEMICAL EVOLUTION OF THE MILKY WAY The Metallicity distribution of the halo in the hierarchical merging paradigm Halo abundance patterns and stellar yields Standard chemical evolution of solar
Dynamical friction, galaxy merging, and radial-orbit instability in MOND
 Dynamical friction, galaxy merging, and radial-orbit instability in MOND Carlo Nipoti Dipartimento di Astronomia Università di Bologna Strasbourg, 29 June 2010 Outline MOND and Equivalent Newtonian Systems
Dynamical friction, galaxy merging, and radial-orbit instability in MOND Carlo Nipoti Dipartimento di Astronomia Università di Bologna Strasbourg, 29 June 2010 Outline MOND and Equivalent Newtonian Systems
The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters
 IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
IAU Joint Discussion # 10 Sydney, July, 2003 The Formation and Evolution of Galaxy Clusters Simon D.M. White Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics The WMAP of the whole CMB sky Bennett et al 2003 > 105
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 23 Sep 2010
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 23 Sep 2010 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 23 Sep 2010](/thumbs/92/108768147.jpg) 1 Notes on the Missing Satellites Problem James. S. Bullock (UC Irvine) arxiv:1009.4505v1 [astro-ph.co] 23 Sep 2010 Abstract The Missing Satellites Problem (MSP) broadly refers to the overabundance of
1 Notes on the Missing Satellites Problem James. S. Bullock (UC Irvine) arxiv:1009.4505v1 [astro-ph.co] 23 Sep 2010 Abstract The Missing Satellites Problem (MSP) broadly refers to the overabundance of
NMAGIC Made-to-Measure Modeling of Elliptical Galaxies NMAGIC - 2 M2M
 NMAGIC Made-to-Measure Modeling of Elliptical Galaxies Ortwin Gerhard, MPE, Garching gerhard@mpe.mpg.de I. Made-to-measure dynamical modeling with NMAGIC II Elliptical galaxy halo kinematics with planetary
NMAGIC Made-to-Measure Modeling of Elliptical Galaxies Ortwin Gerhard, MPE, Garching gerhard@mpe.mpg.de I. Made-to-measure dynamical modeling with NMAGIC II Elliptical galaxy halo kinematics with planetary
The Dark Matter - Galaxy Connection: HOD Estimation from Large Volume Hydrodynamical Simulations
 The Dark Matter - Galaxy Connection: HOD Estimation from Large Volume Hydrodynamical Simulations J. CASADO GÓMEZ (UAM) R. DOMÍNGUEZ-TENREIRO J. OÑORBE (UCA/Irvine) F. MARTINEZ - SERRANO (UMH) A. KNEBE
The Dark Matter - Galaxy Connection: HOD Estimation from Large Volume Hydrodynamical Simulations J. CASADO GÓMEZ (UAM) R. DOMÍNGUEZ-TENREIRO J. OÑORBE (UCA/Irvine) F. MARTINEZ - SERRANO (UMH) A. KNEBE
The impact of Sagittarius on the disk of the Milky Way
 The impact of Sagittarius on the disk of the Milky Way David Law James Bullock (UC Irvine) The impact of Sagittarius on the disk of the Milky Way Chris Purcell (Irvine U Pittsburgh) Erik Tollerud (Irvine)
The impact of Sagittarius on the disk of the Milky Way David Law James Bullock (UC Irvine) The impact of Sagittarius on the disk of the Milky Way Chris Purcell (Irvine U Pittsburgh) Erik Tollerud (Irvine)
Components of Galaxies: Dark Matter
 Components of Galaxies: Dark Matter Dark Matter: Any Form of matter whose existence is inferred solely through its gravitational effects. -B&T, pg 590 Nature of Major Component of Universe Galaxy Formation
Components of Galaxies: Dark Matter Dark Matter: Any Form of matter whose existence is inferred solely through its gravitational effects. -B&T, pg 590 Nature of Major Component of Universe Galaxy Formation
Fossil Galaxy Groups; Halo and all therein
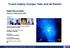 Fossil Galaxy Groups; Halo and all therein Habib Khosroshahi School of Astronomy, Thanks to Mojtaba Raouf, Amin Farhang, Halime Miraghaei School of Astronomy, Ghassem Gozali, Alexi Finoguenov University
Fossil Galaxy Groups; Halo and all therein Habib Khosroshahi School of Astronomy, Thanks to Mojtaba Raouf, Amin Farhang, Halime Miraghaei School of Astronomy, Ghassem Gozali, Alexi Finoguenov University
How Massive is the Milky Way?
 How Massive is the Milky Way? See also: Klypin et al. (2002) Simon s talk Matthias Steinmetz Astrophysical Institute Potsdam Overview Spectroscopic Surveys of the MW Geneva-Copenhagen, SDSS, RAVE Mass
How Massive is the Milky Way? See also: Klypin et al. (2002) Simon s talk Matthias Steinmetz Astrophysical Institute Potsdam Overview Spectroscopic Surveys of the MW Geneva-Copenhagen, SDSS, RAVE Mass
Dark matter halos as particle colliders. Sean Tulin
 Dark matter halos as particle colliders Sean Tulin Cold collisionless dark matter paradigm Dark matter (DM) is about 25% of the Universe WMAP Bullet cluster Cold collisionless dark matter (CDM) provides
Dark matter halos as particle colliders Sean Tulin Cold collisionless dark matter paradigm Dark matter (DM) is about 25% of the Universe WMAP Bullet cluster Cold collisionless dark matter (CDM) provides
THE DISCOVERY OF AN ULTRA-FAINT STAR CLUSTER IN THE CONSTELLATION OF URSA MINOR 1
 DRAFT VERSION APRIL 25, 2012 Preprint typeset using LATEX style emulateapj v. 8/13/10 THE DISCOVERY OF AN ULTRA-FAINT STAR CLUSTER IN THE CONSTELLATION OF URSA MINOR 1 R. R. MUÑOZ 2,3, M. GEHA 2, P. CÔTÉ
DRAFT VERSION APRIL 25, 2012 Preprint typeset using LATEX style emulateapj v. 8/13/10 THE DISCOVERY OF AN ULTRA-FAINT STAR CLUSTER IN THE CONSTELLATION OF URSA MINOR 1 R. R. MUÑOZ 2,3, M. GEHA 2, P. CÔTÉ
The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection
 The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection constraining cosmology & galaxy formation Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang (SHAO) Marcello Cacciato, Surhud More, Simone Weinmann
The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection constraining cosmology & galaxy formation Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang (SHAO) Marcello Cacciato, Surhud More, Simone Weinmann
Galaxies on FIRE: Burning up the small-scale crises of ΛCDM
 Galaxies on FIRE: Burning up the small-scale crises of ΛCDM Observed Starlight Molecular X-Rays Star Formation Cosmic evolution Shea Garrison-Kimmel (Einstein Fellow, Caltech) on behalf of Phil Hopkins
Galaxies on FIRE: Burning up the small-scale crises of ΛCDM Observed Starlight Molecular X-Rays Star Formation Cosmic evolution Shea Garrison-Kimmel (Einstein Fellow, Caltech) on behalf of Phil Hopkins
The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection
 The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection constraining cosmology & galaxy formation Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang (SHAO) Marcello Cacciato, Surhud More, Simone Weinmann
The Galaxy Dark Matter Connection constraining cosmology & galaxy formation Frank C. van den Bosch (MPIA) Collaborators: Houjun Mo (UMass), Xiaohu Yang (SHAO) Marcello Cacciato, Surhud More, Simone Weinmann
The Self-Interacting Dark Matter Paradigm
 The Self-Interacting Dark Matter Paradigm Hai-Bo Yu University of California, Riverside UCLA Dark Matter 2016, February 17-19, 2016 Small Scale Issues Core VS. Cusp problem Too-big-to-fail problem s r
The Self-Interacting Dark Matter Paradigm Hai-Bo Yu University of California, Riverside UCLA Dark Matter 2016, February 17-19, 2016 Small Scale Issues Core VS. Cusp problem Too-big-to-fail problem s r
Koji Ichikawa. (In preparation) TAUP, Torino, Sep. 7-11, 2015
 Koji Ichikawa (In preparation) In collaboration with Kohei Hayashi, Masahiro Ibe, Miho N. Ishigaki, Shigeki Matsumoto and Hajime Sugai. 1 TAUP, Torino, Sep. 7-11, 2015 Direct Detection Dark Matter Search
Koji Ichikawa (In preparation) In collaboration with Kohei Hayashi, Masahiro Ibe, Miho N. Ishigaki, Shigeki Matsumoto and Hajime Sugai. 1 TAUP, Torino, Sep. 7-11, 2015 Direct Detection Dark Matter Search
Precision kinematics Demonstration on Bootes dsph. Sergey Koposov Matt Walker, Vasily Belokurov, Gerry Gilmore, Jorge Pennarubia and others
 Precision kinematics Demonstration on Bootes dsph Sergey Koposov Matt Walker, Vasily Belokurov, Gerry Gilmore, Jorge Pennarubia and others Stellar kinematics in dwarfs Dwarfs most dark matter dominated
Precision kinematics Demonstration on Bootes dsph Sergey Koposov Matt Walker, Vasily Belokurov, Gerry Gilmore, Jorge Pennarubia and others Stellar kinematics in dwarfs Dwarfs most dark matter dominated
4. Structure of Dark Matter halos. Hence the halo mass, virial radius, and virial velocity are related by
 6-4-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c04-1 6-4-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c04-2 4. Structure of Dark Matter halos Obviously, we cannot
6-4-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c04-1 6-4-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c04-2 4. Structure of Dark Matter halos Obviously, we cannot
The First Galaxies. Erik Zackrisson. Department of Astronomy Stockholm University
 The First Galaxies Erik Zackrisson Department of Astronomy Stockholm University Outline The first galaxies what, when, why? What s so special about them? Why are they important for cosmology? How can we
The First Galaxies Erik Zackrisson Department of Astronomy Stockholm University Outline The first galaxies what, when, why? What s so special about them? Why are they important for cosmology? How can we
Milky Way S&G Ch 2. Milky Way in near 1 IR H-W Rixhttp://online.kitp.ucsb.edu/online/galarcheo-c15/rix/
 Why study the MW? its "easy" to study: big, bright, close Allows detailed studies of stellar kinematics, stellar evolution. star formation, direct detection of dark matter?? Milky Way S&G Ch 2 Problems
Why study the MW? its "easy" to study: big, bright, close Allows detailed studies of stellar kinematics, stellar evolution. star formation, direct detection of dark matter?? Milky Way S&G Ch 2 Problems
Probing growth of cosmic structure using galaxy dynamics: a converging picture of velocity bias. Hao-Yi Wu University of Michigan
 Probing growth of cosmic structure using galaxy dynamics: a converging picture of velocity bias Hao-Yi Wu University of Michigan Galaxies are not necessarily test particles Probing dark energy with growth
Probing growth of cosmic structure using galaxy dynamics: a converging picture of velocity bias Hao-Yi Wu University of Michigan Galaxies are not necessarily test particles Probing dark energy with growth
Illustris vs Real Universe: Satellite LF, ksz Effect,
 Illustris vs Real Universe: Satellite LF, ksz Effect, Hyunbae Park (KASI), + Many people SFR of High-z Galaxies 2017. 06. 02 (Uleung-Do) Simulation Setup Simulation code : AREPO (moving mesh code) Parameter
Illustris vs Real Universe: Satellite LF, ksz Effect, Hyunbae Park (KASI), + Many people SFR of High-z Galaxies 2017. 06. 02 (Uleung-Do) Simulation Setup Simulation code : AREPO (moving mesh code) Parameter
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 18 Nov 2016
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 18 Nov 2016 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 18 Nov 2016](/thumbs/92/110745437.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000,???? (2016) Printed 11 September 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Tidal features of classical Milky Way satellites in aλcdm universe arxiv:1611.00778v2 [astro-ph.ga] 18 Nov
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000,???? (2016) Printed 11 September 2018 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Tidal features of classical Milky Way satellites in aλcdm universe arxiv:1611.00778v2 [astro-ph.ga] 18 Nov
The Dark Matter Problem
 The Dark Matter Problem Dr. Yves Gaspar, Ph.D. ( University of Cambridge, UK) Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Brescia Department of Mathematics and Physics. Implications of astronomical data. James
The Dark Matter Problem Dr. Yves Gaspar, Ph.D. ( University of Cambridge, UK) Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Brescia Department of Mathematics and Physics. Implications of astronomical data. James
Lecture Three: Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd.! Hubble Sequence. Environment! Globular Clusters in Milky Way. kpc
 Hubble Sequence Lecture Three: Fundamental difference between Elliptical galaxies and galaxies with disks, and variations of disk type & importance of bulges Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd.! Monday
Hubble Sequence Lecture Three: Fundamental difference between Elliptical galaxies and galaxies with disks, and variations of disk type & importance of bulges Observed Properties of Galaxies, contd.! Monday
Lucio Mayer ETH Zwicky Prize Fellow
 The Local Group of galaxies in a cold dark matter Universe Collaborators: Lucio Mayer ETH Zwicky Prize Fellow Fabio Governato (U. of Washinhgton) Beth Willman (NYU) James Wadsley (McMaster) Greg Stinson
The Local Group of galaxies in a cold dark matter Universe Collaborators: Lucio Mayer ETH Zwicky Prize Fellow Fabio Governato (U. of Washinhgton) Beth Willman (NYU) James Wadsley (McMaster) Greg Stinson
Major Review: A very dense article" Dawes Review 4: Spiral Structures in Disc Galaxies; C. Dobbs and J Baba arxiv "
 The Components of a Spiral Galaxy-a Bit of a Review- See MBW chap 11! we have discussed this in the context of the Milky Way" Disks:" Rotationally supported, lots of gas, dust, star formation occurs in
The Components of a Spiral Galaxy-a Bit of a Review- See MBW chap 11! we have discussed this in the context of the Milky Way" Disks:" Rotationally supported, lots of gas, dust, star formation occurs in
Using Globular Clusters to. Study Elliptical Galaxies. The View Isn t Bad... Omega Centauri. Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office M13
 Using Globular Clusters to Omega Centauri Study Elliptical Galaxies Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office 10,000 1,000,000 stars up to 1000 stars/pc3 typical sizes ~10 parsec Mike Beasley (IAC, Tenerife)
Using Globular Clusters to Omega Centauri Study Elliptical Galaxies Terry Bridges Australian Gemini Office 10,000 1,000,000 stars up to 1000 stars/pc3 typical sizes ~10 parsec Mike Beasley (IAC, Tenerife)
Veilleux! see MBW ! 23! 24!
 Veilleux! see MBW 10.4.3! 23! 24! MBW pg 488-491! 25! But simple closed-box model works well for bulge of Milky Way! Outflow and/or accretion is needed to explain!!!metallicity distribution of stars in
Veilleux! see MBW 10.4.3! 23! 24! MBW pg 488-491! 25! But simple closed-box model works well for bulge of Milky Way! Outflow and/or accretion is needed to explain!!!metallicity distribution of stars in
The M31 Dwarf Galaxy Population
 The M31 Dwarf Galaxy Population Marla Geha (Yale) Google Sky IRAS map Raja Guhathakurta (UCSC) Jason Kalirai (STScI) Steve Majewski (UVa) Roeland van der Marel (STScI) Racheal Beaton (UVa) Kirsten Howley
The M31 Dwarf Galaxy Population Marla Geha (Yale) Google Sky IRAS map Raja Guhathakurta (UCSC) Jason Kalirai (STScI) Steve Majewski (UVa) Roeland van der Marel (STScI) Racheal Beaton (UVa) Kirsten Howley
Reionization. High-Redshift Galaxy UV Luminosity Function. Axion Dark Matter. Rosemary Wyse
 Reionization and the High-Redshift Galaxy UV Luminosity Function with Axion Dark Matter Rosemary Wyse Johns Hopkins University and University of Edinburgh Brandon Bozek, Doddy Marsh & Joe Silk Galaxy-scale
Reionization and the High-Redshift Galaxy UV Luminosity Function with Axion Dark Matter Rosemary Wyse Johns Hopkins University and University of Edinburgh Brandon Bozek, Doddy Marsh & Joe Silk Galaxy-scale
Evidence for/constraints on dark matter in galaxies and clusters
 Nov 11, 2015 Evidence for/constraints on dark matter in galaxies and clusters HW#9 is due; please hand in your summaries; then you get to talk (I have slides of the different facilities/telescopes. HW#10
Nov 11, 2015 Evidence for/constraints on dark matter in galaxies and clusters HW#9 is due; please hand in your summaries; then you get to talk (I have slides of the different facilities/telescopes. HW#10
