Welcome back to Physics 215
|
|
|
- Beryl Flynn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Welcome back to Physics 215 Lecture
2 Last time: Displacement, velocity, graphs Today: Constant acceleration, free fall
3 2-2.1: An object moves with constant acceleration, starting from rest at t = 0 s. In the first four seconds, it travels 10 cm. What will be the displacement of the object in the following four seconds (i.e. between t = 4 s and t = 8 s)? A. 10 cm B. 20 cm C. 30 cm D. 40 cm
4 Motion with constant acceleration: v = v i + at v av = ( 1 / 2 ) (v i + v) x = x i + v i t + ( 1 / 2 ) a t 2 v 2 = v 2 i + 2a (x - x i ) *where x i, v i refer to time = 0 s ; x, v to time t
5 Sample problem A brick is dropped (zero initial speed) from the roof of a building. The brick strikes the ground in 2.50 s. Ignore air resistance, so the brick is in free fall. How tall, in meters, is the building? What is the magnitude of the brick s velocity just before it reaches the ground? Sketch a(t), v(t), and y(t) for the motion of the brick
6 Sample problem A student standing on the ground throws a ball straight up. The ball leaves the student s hand with a speed of 15 m/s when the hand is 2.0 m above the ground. How long is the ball in the air before it hits the ground? Assume that the student moves her hand out of the way
7 Sample problem A cheetah spots a Thomson s gazelle, its preferred prey, and leaps into action, quickly accelerating to its top speed of 30 m/s, the highest of any land animal. However, a cheetah can maintain this extreme speed for only 15 s before having to let up. The cheetah is 170 m from the gazelle as it reaches top speed, and the gazelle sees the cheetah at just this instant. With negligible reaction time, the gazelle heads directly away from the cheetah, accelerating at 4.6 m/s 2 for 5.0 s, then running at constant speed. Does the gazelle escape? If so, by what distance is the gazelle in front when the cheetah gives up?
8 Sample problem A sprinter can accelerate with constant acceleration for 4.0 s before reaching top speed. He can run the 100 meter dash in 10.0 s. What is his speed as he crosses the finish line?
9 Motion in more than 1 dimension Have seen that 1D kinematics is written in terms of quantities with a magnitude and a sign Examples of 1D vectors To extend to d > 1, we need a more general definition of vector
10 Vectors: basic properties are used to denote quantities that have magnitude and direction can be added and subtracted can be multiplied or divided by a number can be manipulated graphically (i.e., by drawing them out) or algebraically (by considering components)
11 Vectors: examples and properties Some vectors we will encounter: position, velocity, force Vectors commonly denoted by boldface letters, or sometimes arrow on top Magnitude of A is written A, or no boldface and no absolute value signs Some quantities which are not vectors: temperature, pressure, volume
12 Drawing a vector A vector is represented graphically by a line with an arrow on one end. Length of line gives the magnitude of the vector. Orientation of line and sense of arrow give the direction of the vector. Location of vector in space does not matter -- two vectors with the same magnitude and direction are equivalent, independent of their location
13 Adding vectors To add vector B to vector A Draw vector A Draw vector B with its tail starting from the tip of A The sum vector A+B is the vector drawn from the tail of vector A to the tip of vector B
14 Multiplying vectors by a number Direction of vector not affected (care with negative numbers see below) Magnitude (length) scaled, e.g. 1*A=A 2*A is given by arrow of twice length, but same direction 0*A = 0 null vector A A 1 x = A 2 x = A 0 x = -A = -1*A is arrow of same length, but reversed in direction A -1 x =
15
16 2-2.2: Which of the vectors in the second row shows?
17 QuickCheck 2-2.2: 3.1 Which of the vectors in the second row shows?
18 QuickCheck 2-2.3: 3.2 Which of the vectors in the second row shows 2 -?
19 QuickCheck Clicker 2-2.3: 3.2 Which of the vectors in the second row shows 2 -?
20 Projection of a vector How much a vector acts along some arbitrary direction Component of a vector Projection onto one of the coordinate axes (x, y, z)
21 Components y A = A x + A y j i A x A = a x i + a y j i = unit vector in x direction j = unit vector in y direction Projection of A along coordinate axes a x, a y = components of vector A
22 More on vector components Relate components to direction (2D): or a x = A cosθ, a y = A sinθ j y i θ A A x A y x Direction: tanθ = a y /a x Magnitude: A 2 = a x 2 + a y
23 2-2.4: A bird is flying along a straight line in a direction somewhere East of North. After the bird has flown a distance of 2.5 miles, it is 2 miles North of where it started. How far to the East is it from its starting point? A. 0 miles B. 0.5 miles C. 1.0 mile D. 1.5 miles
24 Why are components useful? Addition: just add components e.g. if C = A + B c x = a x + b x ; c y = a y + b y y Subtraction similar Multiplying a vector by a number just multiply components: if D = n*a j i A B x d x = n*a x ; d y = n*a y Even more useful in 3 (or higher) dimensions
25 Sample problem Sam leaves his house and follows the following three step path: He heads 50.0 m due east. Then he travels 20.0m at 48 0 north of east. He then travels 70.0m 62 0 north of west. Sketch the graph of Sam s path in two-dimensions. What is Sam s net displacement? What is the total distance that Sam travels? If Sam moves at constant speed and the trip takes 100s, what is Sam s speed? What is the magnitude of Sam s average velocity?
26 2D Motion in components y y Q Note: component of position vector along x-direction is the x-coordinate! Q j i s vector position x Q s = x Q i + y Q j x
27 Displacement in 2D Motion y Δs s I s F s vector position Displacement Δs = s F - s I, also a vector! O x
Welcome back to Physics 211
 Welcome back to Physics 211 Lecture 2-2 02-2 1 Last time: Displacement, velocity, graphs Today: Constant acceleration, free fall 02-2 2 Simplest case with non-zero acceleration Constant acceleration: a
Welcome back to Physics 211 Lecture 2-2 02-2 1 Last time: Displacement, velocity, graphs Today: Constant acceleration, free fall 02-2 2 Simplest case with non-zero acceleration Constant acceleration: a
Welcome back to Physics 211
 Welcome back to Physics 211 Lecture 2-1 02-1 1 Last time: Displacement, velocity, graphs Today: Using graphs to solve problems Constant acceleration, free fall 02-1 2 1-2.6-8: Acceleration from graph of
Welcome back to Physics 211 Lecture 2-1 02-1 1 Last time: Displacement, velocity, graphs Today: Using graphs to solve problems Constant acceleration, free fall 02-1 2 1-2.6-8: Acceleration from graph of
PSI AP Physics 1 Kinematics. Free Response Problems
 PSI AP Physics 1 Kinematics Free Response Problems 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will
PSI AP Physics 1 Kinematics Free Response Problems 1. A car whose speed is 20 m/s passes a stationary motorcycle which immediately gives chase with a constant acceleration of 2.4 m/s 2. a. How far will
Adding Vectors in Two Dimensions
 Slide 37 / 125 Adding Vectors in Two Dimensions Return to Table of Contents Last year, we learned how to add vectors along a single axis. The example we used was for adding two displacements. Slide 38
Slide 37 / 125 Adding Vectors in Two Dimensions Return to Table of Contents Last year, we learned how to add vectors along a single axis. The example we used was for adding two displacements. Slide 38
Kinematics Multiple- Choice Questions (answers on page 16)
 Kinematics Multiple- Choice Questions (answers on page 16) 1. An object moves around a circular path of radius R. The object starts from point A, goes to point B and describes an arc of half of the circle.
Kinematics Multiple- Choice Questions (answers on page 16) 1. An object moves around a circular path of radius R. The object starts from point A, goes to point B and describes an arc of half of the circle.
Vector and Relative motion discussion/ in class notes. Projectile Motion discussion and launch angle problem. Finish 2 d motion and review for test
 AP Physics 1 Unit 2: 2 Dimensional Kinematics Name: Date In Class Homework to completed that evening (before coming to next class period) 9/6 Tue (B) 9/7 Wed (C) 1D Kinematics Test Unit 2 Video 1: Vectors
AP Physics 1 Unit 2: 2 Dimensional Kinematics Name: Date In Class Homework to completed that evening (before coming to next class period) 9/6 Tue (B) 9/7 Wed (C) 1D Kinematics Test Unit 2 Video 1: Vectors
New concepts: scalars, vectors, unit vectors, vector components, vector equations, scalar product. reading assignment read chap 3
 New concepts: scalars, vectors, unit vectors, vector components, vector equations, scalar product reading assignment read chap 3 Most physical quantities are described by a single number or variable examples:
New concepts: scalars, vectors, unit vectors, vector components, vector equations, scalar product reading assignment read chap 3 Most physical quantities are described by a single number or variable examples:
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio
 AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio demaiod@middletownk12.org Welcome to AP Physics 1 for the 2018-2019 school year. AP Physics 1 is an algebra based, introductory college-level physics course.
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment 2018 Mrs. DeMaio demaiod@middletownk12.org Welcome to AP Physics 1 for the 2018-2019 school year. AP Physics 1 is an algebra based, introductory college-level physics course.
Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors
 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors & Scalars!! Scalars They are specified only by a number and units and have no direction associated with them, such as time, mass, and temperature.!! Vectors
Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors & Scalars!! Scalars They are specified only by a number and units and have no direction associated with them, such as time, mass, and temperature.!! Vectors
(a) On the diagram above, draw an arrow showing the direction of velocity of the projectile at point A.
 QUESTION 1 The path of a projectile in a uniform gravitational field is shown in the diagram below. When the projectile reaches its maximum height, at point A, its speed v is 8.0 m s -1. Assume g = 10
QUESTION 1 The path of a projectile in a uniform gravitational field is shown in the diagram below. When the projectile reaches its maximum height, at point A, its speed v is 8.0 m s -1. Assume g = 10
Progressive Science Initiative. Click to go to website:
 Slide 1 / 246 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and
Slide 1 / 246 New Jersey Center for Teaching and Learning Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and
CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS
 CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: represent the magnitude and direction of a vector using a protractor
CHAPTER 3 KINEMATICS IN TWO DIMENSIONS; VECTORS OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: represent the magnitude and direction of a vector using a protractor
Motion in Two Dimensions Reading Notes
 Motion in Two Dimensions Reading Notes Name: Section 3-1: Vectors and Scalars What typeface do we use to indicate a vector? Test Your Understanding: Circle the quantities that are vectors. Acceleration
Motion in Two Dimensions Reading Notes Name: Section 3-1: Vectors and Scalars What typeface do we use to indicate a vector? Test Your Understanding: Circle the quantities that are vectors. Acceleration
Welcome Back to Physics 211!
 Welcome Back to Physics 211! (General Physics I) Thurs. Aug 30 th, 2012 Physics 211 -Fall 2014 Lecture01-2 1 Last time: Syllabus, mechanics survey Unit conversions Today: Using your clicker 1D displacement,
Welcome Back to Physics 211! (General Physics I) Thurs. Aug 30 th, 2012 Physics 211 -Fall 2014 Lecture01-2 1 Last time: Syllabus, mechanics survey Unit conversions Today: Using your clicker 1D displacement,
Each dot represents an object moving, between constant intervals of time. Describe the motion that you see. equation symbol: units: Velocity
 What is displacement, velocity and acceleration? what units do they have? vector vs scalar? One dimensional motion, and graphing Moving man worksheet moving man doc - todo Introduction to simple graphing
What is displacement, velocity and acceleration? what units do they have? vector vs scalar? One dimensional motion, and graphing Moving man worksheet moving man doc - todo Introduction to simple graphing
PHY 2053 announcements: January 7, 2010
 PHY 2053 announcements: January 7, 2010 Textbook: College Physics I by Serway/Vuille soft cover with white background Optional course packet/solutions (blue book): available at Target copy on Univ. Ave.
PHY 2053 announcements: January 7, 2010 Textbook: College Physics I by Serway/Vuille soft cover with white background Optional course packet/solutions (blue book): available at Target copy on Univ. Ave.
Example problem: Free Fall
 Example problem: Free Fall A ball is thrown from the top of a building with an initial velocity of 20.0 m/s straight upward, at an initial height of 50.0 m above the ground. The ball just misses the edge
Example problem: Free Fall A ball is thrown from the top of a building with an initial velocity of 20.0 m/s straight upward, at an initial height of 50.0 m above the ground. The ball just misses the edge
Kinematics in Two Dimensions; 2D- Vectors
 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; 2D- Vectors Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods Below are two example vector additions of 1-D displacement vectors. For vectors in one dimension, simple addition and subtraction
Kinematics in Two Dimensions; 2D- Vectors Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods Below are two example vector additions of 1-D displacement vectors. For vectors in one dimension, simple addition and subtraction
Definitions In physics we have two types of measurable quantities: vectors and scalars.
 1 Definitions In physics we have two types of measurable quantities: vectors and scalars. Scalars: have magnitude (magnitude means size) only Examples of scalar quantities include time, mass, volume, area,
1 Definitions In physics we have two types of measurable quantities: vectors and scalars. Scalars: have magnitude (magnitude means size) only Examples of scalar quantities include time, mass, volume, area,
Announcements 9 Sep 2014
 Announcements 9 Sep 2014 1. Prayer 2. Course homepage via: physics.byu.edu Class web pages Physics 105 (Colton J) Colton - Lecture 3 - pg 1 Which of the problems from last night's HW assignment would you
Announcements 9 Sep 2014 1. Prayer 2. Course homepage via: physics.byu.edu Class web pages Physics 105 (Colton J) Colton - Lecture 3 - pg 1 Which of the problems from last night's HW assignment would you
Demo: x-t, v-t and a-t of a falling basket ball.
 Demo: x-t, v-t and a-t of a falling basket ball. I-clicker question 3-1: A particle moves with the position-versus-time graph shown. Which graph best illustrates the velocity of the particle as a function
Demo: x-t, v-t and a-t of a falling basket ball. I-clicker question 3-1: A particle moves with the position-versus-time graph shown. Which graph best illustrates the velocity of the particle as a function
Physics 1A. Lecture 1B
 Physics 1A Lecture 1B Angles: a Tricky Unit θ Angles are formally defined as a ratio of lengths; e.g. θ = Arclength/Radius [θ] = L/L = 1 This makes the angle unitless! The fundamental unit of angle is
Physics 1A Lecture 1B Angles: a Tricky Unit θ Angles are formally defined as a ratio of lengths; e.g. θ = Arclength/Radius [θ] = L/L = 1 This makes the angle unitless! The fundamental unit of angle is
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors
 Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors and Scalars Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods (One and Two- Dimension) Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar Subtraction of Vectors Graphical
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions; Vectors Vectors and Scalars Addition of Vectors Graphical Methods (One and Two- Dimension) Multiplication of a Vector by a Scalar Subtraction of Vectors Graphical
Vector Quantities A quantity such as force, that has both magnitude and direction. Examples: Velocity, Acceleration
 Projectile Motion Vector Quantities A quantity such as force, that has both magnitude and direction. Examples: Velocity, Acceleration Scalar Quantities A quantity such as mass, volume, and time, which
Projectile Motion Vector Quantities A quantity such as force, that has both magnitude and direction. Examples: Velocity, Acceleration Scalar Quantities A quantity such as mass, volume, and time, which
UNIT-05 VECTORS. 3. Utilize the characteristics of two or more vectors that are concurrent, or collinear, or coplanar.
 UNIT-05 VECTORS Introduction: physical quantity that can be specified by just a number the magnitude is known as a scalar. In everyday life you deal mostly with scalars such as time, temperature, length
UNIT-05 VECTORS Introduction: physical quantity that can be specified by just a number the magnitude is known as a scalar. In everyday life you deal mostly with scalars such as time, temperature, length
1. Joseph runs along a long straight track. The variation of his speed v with time t is shown below.
 Kinematics 1. Joseph runs along a long straight track. The variation of his speed v with time t is shown below. After 25 seconds Joseph has run 200 m. Which of the following is correct at 25 seconds? Instantaneous
Kinematics 1. Joseph runs along a long straight track. The variation of his speed v with time t is shown below. After 25 seconds Joseph has run 200 m. Which of the following is correct at 25 seconds? Instantaneous
Name: Total Points: Physics 201. Midterm 1
 Physics 201 Midterm 1 QUESTION 1 [25 points] An object moves in 1 dimension It starts at rest and uniformly accelerates at 5m/s 2 for 2s It then moves with constant velocity for 4s It then uniformly accelerates
Physics 201 Midterm 1 QUESTION 1 [25 points] An object moves in 1 dimension It starts at rest and uniformly accelerates at 5m/s 2 for 2s It then moves with constant velocity for 4s It then uniformly accelerates
acceleration versus time. LO Determine a particle s change in position by graphical integration on a graph of velocity versus time.
 Chapter: Chapter 2 Learning Objectives LO 2.1.0 Solve problems related to position, displacement, and average velocity to solve problems. LO 2.1.1 Identify that if all parts of an object move in the same
Chapter: Chapter 2 Learning Objectives LO 2.1.0 Solve problems related to position, displacement, and average velocity to solve problems. LO 2.1.1 Identify that if all parts of an object move in the same
QuickCheck. A cart slows down while moving away from the origin. What do the position and velocity graphs look like? Slide 2-65
 QuickCheck A cart slows down while moving away from the origin. What do the position and velocity graphs look like? Slide 2-65 QuickCheck A cart speeds up toward the origin. What do the position and velocity
QuickCheck A cart slows down while moving away from the origin. What do the position and velocity graphs look like? Slide 2-65 QuickCheck A cart speeds up toward the origin. What do the position and velocity
Vector Addition and Subtraction: Graphical Methods
 Vector Addition and Subtraction: Graphical Methods Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Displacement can be determined graphically using a scale map, such as this one of the Hawaiian Islands. A journey from Hawai i to
Vector Addition and Subtraction: Graphical Methods Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Displacement can be determined graphically using a scale map, such as this one of the Hawaiian Islands. A journey from Hawai i to
Vectors and Kinematics Notes 1 Review
 Velocity is defined as the change in displacement with respect to time. Vectors and Kinematics Notes 1 Review Note that this formula is only valid for finding constant velocity or average velocity. Also,
Velocity is defined as the change in displacement with respect to time. Vectors and Kinematics Notes 1 Review Note that this formula is only valid for finding constant velocity or average velocity. Also,
Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension
 Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension The Cheetah: A cat that is built for speed. Its strength and agility allow it to sustain a top speed of over 100 km/h. Such speeds can only be maintained for about
Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension The Cheetah: A cat that is built for speed. Its strength and agility allow it to sustain a top speed of over 100 km/h. Such speeds can only be maintained for about
Kinematics 2. What equation relates the known quantities to what is being asked?
 Physics R Date: 1. A cheetah goes from rest to 60 miles per hour (26.8 m/s) in 3 seconds. Calculate the acceleration of the cheetah. Kinematics Equations Kinematics 2 How to solve a Physics problem: List
Physics R Date: 1. A cheetah goes from rest to 60 miles per hour (26.8 m/s) in 3 seconds. Calculate the acceleration of the cheetah. Kinematics Equations Kinematics 2 How to solve a Physics problem: List
10.1 Vectors. c Kun Wang. Math 150, Fall 2017
 10.1 Vectors Definition. A vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. A vector is often represented graphically as an arrow where the direction is the direction of the arrow, and the magnitude
10.1 Vectors Definition. A vector is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction. A vector is often represented graphically as an arrow where the direction is the direction of the arrow, and the magnitude
Lecture PowerPoints. Chapter 3 Physics for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli
 Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 3 Physics for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided
Lecture PowerPoints Chapter 3 Physics for Scientists & Engineers, with Modern Physics, 4 th edition Giancoli 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided
r y The angle theta defines a vector that points from the boat to the top of the cliff where rock breaks off. That angle is given as 30 0
 From a boat in the English Channel, you slowly approach the White Cliffs of Dover. You want to know how far you are from the base of the cliff. Then suddenly you see a rock break off from the top and hit
From a boat in the English Channel, you slowly approach the White Cliffs of Dover. You want to know how far you are from the base of the cliff. Then suddenly you see a rock break off from the top and hit
Section 1.4: Adding and Subtracting Linear and Perpendicular Vectors
 Section 1.4: Adding and Subtracting Linear and Perpendicular Vectors Motion in two dimensions must use vectors and vector diagrams. Vector Representation: tail head magnitude (size): given by the length
Section 1.4: Adding and Subtracting Linear and Perpendicular Vectors Motion in two dimensions must use vectors and vector diagrams. Vector Representation: tail head magnitude (size): given by the length
Introduction to 1-D Motion Distance versus Displacement
 Introduction to 1-D Motion Distance versus Displacement Kinematics! Kinematics is the branch of mechanics that describes the motion of objects without necessarily discussing what causes the motion.! 1-Dimensional
Introduction to 1-D Motion Distance versus Displacement Kinematics! Kinematics is the branch of mechanics that describes the motion of objects without necessarily discussing what causes the motion.! 1-Dimensional
Interactive Engagement via Thumbs Up. Today s class. Next class. Chapter 2: Motion in 1D Example 2.10 and 2.11 Any Question.
 PHYS 01 Interactive Engagement via Thumbs Up 1 Chap.1 Sumamry Today s class SI units Dimensional analysis Scientific notation Errors Vectors Next class Chapter : Motion in 1D Example.10 and.11 Any Question
PHYS 01 Interactive Engagement via Thumbs Up 1 Chap.1 Sumamry Today s class SI units Dimensional analysis Scientific notation Errors Vectors Next class Chapter : Motion in 1D Example.10 and.11 Any Question
Physics 12 Unit 1: Kinematics Notes. Name: What you will be able to do by the end of this unit:
 Physics 12 Unit 1: Kinematics Notes. Name: What you will be able to do by the end of this unit: B1. Perform vector analysis in one or two dimensions identify scalars and vectors resolve a vector into two
Physics 12 Unit 1: Kinematics Notes. Name: What you will be able to do by the end of this unit: B1. Perform vector analysis in one or two dimensions identify scalars and vectors resolve a vector into two
Unit 1, Lessons 2-5: Vectors in Two Dimensions
 Unit 1, Lessons 2-5: Vectors in Two Dimensions Textbook Sign-Out Put your name in it and let s go! Check-In Any questions from last day s homework? Vector Addition 1. Find the resultant displacement
Unit 1, Lessons 2-5: Vectors in Two Dimensions Textbook Sign-Out Put your name in it and let s go! Check-In Any questions from last day s homework? Vector Addition 1. Find the resultant displacement
INTRODUCTION AND KINEMATICS. Physics Unit 1 Chapters 1-3
 INTRODUCTION AND KINEMATICS Physics Unit 1 Chapters 1-3 This Slideshow was developed to accompany the textbook OpenStax Physics Available for free at https://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
INTRODUCTION AND KINEMATICS Physics Unit 1 Chapters 1-3 This Slideshow was developed to accompany the textbook OpenStax Physics Available for free at https://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/college-physics
AP Physics First Nine Weeks Review
 AP Physics First Nine Weeks Review 1. If F1 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the Earth on a satellite in orbit about the Earth and F2 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the satellite on the
AP Physics First Nine Weeks Review 1. If F1 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the Earth on a satellite in orbit about the Earth and F2 is the magnitude of the force exerted by the satellite on the
10.2 Introduction to Vectors
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 2934: Calculus III Dr. Marcel B Finan 10.2 Introduction to Vectors In the previous calculus classes we have seen that the study of motion involved the introduction of a variety
Arkansas Tech University MATH 2934: Calculus III Dr. Marcel B Finan 10.2 Introduction to Vectors In the previous calculus classes we have seen that the study of motion involved the introduction of a variety
Understanding. 28. Given:! d inital. = 1750 m [W];! d final Required:!! d T Analysis:!! d T. Solution:!! d T
![Understanding. 28. Given:! d inital. = 1750 m [W];! d final Required:!! d T Analysis:!! d T. Solution:!! d T Understanding. 28. Given:! d inital. = 1750 m [W];! d final Required:!! d T Analysis:!! d T. Solution:!! d T](/thumbs/88/115127324.jpg) Unit 1 Review, pages 100 107 Knowledge 1. (c). (c) 3. (b) 4. (d) 5. (b) 6. (c) 7. (d) 8. (b) 9. (d) 10. (b) 11. (b) 1. True 13. True 14. False. The average velocity of an object is the change in displacement
Unit 1 Review, pages 100 107 Knowledge 1. (c). (c) 3. (b) 4. (d) 5. (b) 6. (c) 7. (d) 8. (b) 9. (d) 10. (b) 11. (b) 1. True 13. True 14. False. The average velocity of an object is the change in displacement
Chapter 3. Table of Contents. Section 1 Introduction to Vectors. Section 2 Vector Operations. Section 3 Projectile Motion. Section 4 Relative Motion
 Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Vectors Section 2 Vector Operations Section 3 Projectile Motion Section 4 Relative Motion Section 1 Introduction to Vectors
Two-Dimensional Motion and Vectors Table of Contents Section 1 Introduction to Vectors Section 2 Vector Operations Section 3 Projectile Motion Section 4 Relative Motion Section 1 Introduction to Vectors
Chapter 3 Acceleration
 Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 Chapter 3: Acceleration Chapter Goal: To extend the description of motion in one dimension to include changes in velocity. This type of motion is called acceleration. Slide
Chapter 3 Acceleration Slide 3-1 Chapter 3: Acceleration Chapter Goal: To extend the description of motion in one dimension to include changes in velocity. This type of motion is called acceleration. Slide
Chapter 3. Vectors and Two-Dimensional Motion
 Chapter 3 Vectors and Two-Dimensional Motion 1 Vector vs. Scalar Review All physical quantities encountered in this text will be either a scalar or a vector A vector quantity has both magnitude (size)
Chapter 3 Vectors and Two-Dimensional Motion 1 Vector vs. Scalar Review All physical quantities encountered in this text will be either a scalar or a vector A vector quantity has both magnitude (size)
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION
 CHAPTER 2 DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: state from memory the meaning of the key terms and phrases
CHAPTER 2 DESCRIBING MOTION: KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this chapter, the student should be able to: state from memory the meaning of the key terms and phrases
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 PHYS 101 Fall 2013 (Purcell), Fake Midterm #1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The figure shows the graph of the position x as a
PHYS 101 Fall 2013 (Purcell), Fake Midterm #1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The figure shows the graph of the position x as a
1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False Answer: B Var: 1
 University Physics, 13e (Young/Freedman) Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line 2.1 Conceptual Questions 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
University Physics, 13e (Young/Freedman) Chapter 2 Motion Along a Straight Line 2.1 Conceptual Questions 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) If the acceleration of an object is negative, the object must be slowing down. A) True B) False
1-D Motion: Free Falling Objects
 v (m/s) a (m/s^2) 1-D Motion: Free Falling Objects So far, we have only looked at objects moving in a horizontal dimension. Today, we ll look at objects moving in the vertical. Then, we ll look at both
v (m/s) a (m/s^2) 1-D Motion: Free Falling Objects So far, we have only looked at objects moving in a horizontal dimension. Today, we ll look at objects moving in the vertical. Then, we ll look at both
UNIT I: MECHANICS Chapter 5: Projectile Motion
 IMPORTANT TERMS: Component Projectile Resolution Resultant Satellite Scalar quantity Vector Vector quantity UNIT I: MECHANICS Chapter 5: Projectile Motion I. Vector and Scalar Quantities (5-1) A. Vector
IMPORTANT TERMS: Component Projectile Resolution Resultant Satellite Scalar quantity Vector Vector quantity UNIT I: MECHANICS Chapter 5: Projectile Motion I. Vector and Scalar Quantities (5-1) A. Vector
Physics 151 Homework Assignment #3 Due June 20
 Physics 151 Homework Assignment #3 Due June 20 #1 Ships A and B leave port together. For the next two hours, ship A travels at 20mph in a direction 30 west of north, while ship B travels 20 east of north
Physics 151 Homework Assignment #3 Due June 20 #1 Ships A and B leave port together. For the next two hours, ship A travels at 20mph in a direction 30 west of north, while ship B travels 20 east of north
Problem: Projectile (CM-1998) Justify your answer: Problem: Projectile (CM-1998) 5 10 m/s 3. Show your work: 3 m/s 2
 Physics C -D Kinematics Name: AP Review Packet Vectors have both magnitude and direction displacement, velocity, acceleration Scalars have magnitude only distance, speed, time, mass Unit vectors Specify
Physics C -D Kinematics Name: AP Review Packet Vectors have both magnitude and direction displacement, velocity, acceleration Scalars have magnitude only distance, speed, time, mass Unit vectors Specify
Unit 1 Test Review Physics Basics, Movement, and Vectors Chapters 2-3
 A.P. Physics B Unit 1 Test Review Physics Basics, Movement, and Vectors Chapters - 3 * In studying for your test, make sure to study this review sheet along with your quizzes and homework assignments.
A.P. Physics B Unit 1 Test Review Physics Basics, Movement, and Vectors Chapters - 3 * In studying for your test, make sure to study this review sheet along with your quizzes and homework assignments.
Review! Kinematics: Free Fall, A Special Case. Review! A Few Facts About! Physics 101 Lecture 3 Kinematics: Vectors and Motion in 1 Dimension
 Phsics 101 Lecture 3 Kinematics: Vectors and Motion in 1 Dimension What concepts did ou find most difficult, or what would ou like to be sure we discuss in lecture? Acceleration vectors. Will ou go over
Phsics 101 Lecture 3 Kinematics: Vectors and Motion in 1 Dimension What concepts did ou find most difficult, or what would ou like to be sure we discuss in lecture? Acceleration vectors. Will ou go over
Do not fill out the information below until instructed to do so! Name: Signature: Student ID: Section Number:
 Do not fill out the information below until instructed to do so! Name: Signature: Student ID: E-mail: Section Number: Formulae are provided on the last page. You may NOT use any other formula sheet. You
Do not fill out the information below until instructed to do so! Name: Signature: Student ID: E-mail: Section Number: Formulae are provided on the last page. You may NOT use any other formula sheet. You
Chapter 2. Kinematics in One Dimension. continued
 Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension continued 2.6 Freely Falling Bodies Example 10 A Falling Stone A stone is dropped from the top of a tall building. After 3.00s of free fall, what is the displacement
Chapter 2 Kinematics in One Dimension continued 2.6 Freely Falling Bodies Example 10 A Falling Stone A stone is dropped from the top of a tall building. After 3.00s of free fall, what is the displacement
Assignment 6 solutions
 Assignment 6 solutions 1) You are traveling on a hilly road. At a particular spot, when your car is perfectly horizontal, the road follows a circular arc of some unknown radius. Your speedometer reads
Assignment 6 solutions 1) You are traveling on a hilly road. At a particular spot, when your car is perfectly horizontal, the road follows a circular arc of some unknown radius. Your speedometer reads
2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics. f i i
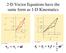 2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = v + at f i 1 r = r + v t+ at f i i 2 2 2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = viˆ+ v ˆj f x y = ( v + ati ) ˆ+ ( v +
2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = v + at f i 1 r = r + v t+ at f i i 2 2 2-D Vector Equations have the same form as 1-D Kinematics v = viˆ+ v ˆj f x y = ( v + ati ) ˆ+ ( v +
Chapter 3 Homework Packet. Conceptual Questions
 Chapter 3 Homework Packet Conceptual Questions 1) Which one of the following is an example of a vector quantity? A) mass B) area C) distance D) velocity A vector quantity has both magnitude and direction.
Chapter 3 Homework Packet Conceptual Questions 1) Which one of the following is an example of a vector quantity? A) mass B) area C) distance D) velocity A vector quantity has both magnitude and direction.
Lecture Notes (Vectors)
 Lecture Notes (Vectors) Intro: - up to this point we have learned that physical quantities can be categorized as either scalars or vectors - a vector is a physical quantity that requires the specification
Lecture Notes (Vectors) Intro: - up to this point we have learned that physical quantities can be categorized as either scalars or vectors - a vector is a physical quantity that requires the specification
4.1 Motion Is Relative. An object is moving if its position relative to a fixed point is changing. You can describe the motion of an object by its
 4.1 Motion Is Relative You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, and acceleration. An object is moving if its position relative to a fixed point is changing. 4.1 Motion
4.1 Motion Is Relative You can describe the motion of an object by its position, speed, direction, and acceleration. An object is moving if its position relative to a fixed point is changing. 4.1 Motion
AP Physics C Mechanics Vectors
 1 AP Physics C Mechanics Vectors 2015 12 03 www.njctl.org 2 Scalar Versus Vector A scalar has only a physical quantity such as mass, speed, and time. A vector has both a magnitude and a direction associated
1 AP Physics C Mechanics Vectors 2015 12 03 www.njctl.org 2 Scalar Versus Vector A scalar has only a physical quantity such as mass, speed, and time. A vector has both a magnitude and a direction associated
Vectors v Scalars. Physics 1 st Six Weeks
 Vectors v Scalars Physics 1 st Six Weeks An Appetizer to Start... Vectors vs. Scalars In Physics all quantities are in two categories: scalars & vectors. Scalar quantities are described by magnitude (i.e.
Vectors v Scalars Physics 1 st Six Weeks An Appetizer to Start... Vectors vs. Scalars In Physics all quantities are in two categories: scalars & vectors. Scalar quantities are described by magnitude (i.e.
Topic 1: 2D Motion PHYSICS 231
 Topic 1: 2D Motion PHYSICS 231 Current Assignments Homework Set 1 due this Thursday, Jan 20, 11 pm Homework Set 2 due Thursday, Jan 27, 11pm Reading: Chapter 4,5 for next week 2/1/11 Physics 231 Spring
Topic 1: 2D Motion PHYSICS 231 Current Assignments Homework Set 1 due this Thursday, Jan 20, 11 pm Homework Set 2 due Thursday, Jan 27, 11pm Reading: Chapter 4,5 for next week 2/1/11 Physics 231 Spring
Classical Physics - pre Kinematics & Mechanics Energy & Light & Heat Electricity & Magnetism Wave Motion. Modern Physics - post 1900
 Scientific Method Observation or question Hypothesis - belief thru reason Procedure thru experiment Data, Calculations Analysis - conclusion to theory or law Prediction - check on theory for repeatability
Scientific Method Observation or question Hypothesis - belief thru reason Procedure thru experiment Data, Calculations Analysis - conclusion to theory or law Prediction - check on theory for repeatability
Graphing Motion Part 2
 Kinematics 2: Motion Graphs & Free Fall Sep 5 10:34 AM Sep 5 1:25 PM Graphing Motion Part 2 How do you calculate the slope of a line? What would the slope of a distance vs time graph represent? What would
Kinematics 2: Motion Graphs & Free Fall Sep 5 10:34 AM Sep 5 1:25 PM Graphing Motion Part 2 How do you calculate the slope of a line? What would the slope of a distance vs time graph represent? What would
CHAPTER 3 MOTION IN TWO AND THREE DIMENSIONS
 CHAPTER 3 MOTION IN TWO AND THREE DIMENSIONS General properties of vectors displacement vector position and velocity vectors acceleration vector equations of motion in 2- and 3-dimensions Projectile motion
CHAPTER 3 MOTION IN TWO AND THREE DIMENSIONS General properties of vectors displacement vector position and velocity vectors acceleration vector equations of motion in 2- and 3-dimensions Projectile motion
Planar Motion with Constant Acceleration
 Planar Motion with Constant Acceleration 1. If the acceleration vector of an object is perpendicular to its velocity vector, which of the following must be true? (a) The speed is changing. (b) The direction
Planar Motion with Constant Acceleration 1. If the acceleration vector of an object is perpendicular to its velocity vector, which of the following must be true? (a) The speed is changing. (b) The direction
3 Vectors and Two- Dimensional Motion
 May 25, 1998 3 Vectors and Two- Dimensional Motion Kinematics of a Particle Moving in a Plane Motion in two dimensions is easily comprehended if one thinks of the motion as being made up of two independent
May 25, 1998 3 Vectors and Two- Dimensional Motion Kinematics of a Particle Moving in a Plane Motion in two dimensions is easily comprehended if one thinks of the motion as being made up of two independent
a. Determine the sprinter's constant acceleration during the first 2 seconds.
 AP Physics 1 FR Practice Kinematics 1d 1 The first meters of a 100-meter dash are covered in 2 seconds by a sprinter who starts from rest and accelerates with a constant acceleration. The remaining 90
AP Physics 1 FR Practice Kinematics 1d 1 The first meters of a 100-meter dash are covered in 2 seconds by a sprinter who starts from rest and accelerates with a constant acceleration. The remaining 90
VERTICAL PROJECTILE MOTION (LIVE) 08 APRIL 2015 Section A: Summary Notes and Examples
 VERTICAL PROJECTILE MOTION (LIVE) 08 APRIL 2015 Section A: Summary Notes and Examples Equations of Motion When an object is thrown, projected or shot upwards or downwards, it is said to be a projectile.
VERTICAL PROJECTILE MOTION (LIVE) 08 APRIL 2015 Section A: Summary Notes and Examples Equations of Motion When an object is thrown, projected or shot upwards or downwards, it is said to be a projectile.
Quiz No. 1: Tuesday Jan. 31. Assignment No. 2, due Thursday Feb 2: Problems 8.4, 8.13, 3.10, 3.28 Conceptual questions: 8.1, 3.6, 3.12, 3.
 Quiz No. 1: Tuesday Jan. 31 Assignment No. 2, due Thursday Feb 2: Problems 8.4, 8.13, 3.10, 3.28 Conceptual questions: 8.1, 3.6, 3.12, 3.20 Chapter 3 Vectors and Two-Dimensional Kinematics Properties of
Quiz No. 1: Tuesday Jan. 31 Assignment No. 2, due Thursday Feb 2: Problems 8.4, 8.13, 3.10, 3.28 Conceptual questions: 8.1, 3.6, 3.12, 3.20 Chapter 3 Vectors and Two-Dimensional Kinematics Properties of
Day 1: Introduction to Vectors + Vector Arithmetic
 Day 1: Introduction to Vectors + Vector Arithmetic A is a quantity that has magnitude but no direction. You can have signed scalar quantities as well. A is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
Day 1: Introduction to Vectors + Vector Arithmetic A is a quantity that has magnitude but no direction. You can have signed scalar quantities as well. A is a quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
Lecture Presentation Chapter 1 Representing Motion
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 1 Representing Motion Suggested Videos for Chapter 1 Prelecture Videos Introduction Putting Numbers on Nature Video Tutor Solutions Representing Motion Class Videos Series
Lecture Presentation Chapter 1 Representing Motion Suggested Videos for Chapter 1 Prelecture Videos Introduction Putting Numbers on Nature Video Tutor Solutions Representing Motion Class Videos Series
Linear Motion. By Jack, Cole, Kate and Linus
 Linear Motion By Jack, Cole, Kate and Linus What is it? -Linear Motion is the study of motion, Kinematics, and Dynamics Motion Motion is dependent on the reference frame in which you are observing. If
Linear Motion By Jack, Cole, Kate and Linus What is it? -Linear Motion is the study of motion, Kinematics, and Dynamics Motion Motion is dependent on the reference frame in which you are observing. If
Review Session 1. Page 1
 Review Session 1 1. Which combination of fundamental units can be used to express the amount of work done on an object? 2. The height of a typical kitchen table is approximately A) 10-2 m B) 10 0 m C)
Review Session 1 1. Which combination of fundamental units can be used to express the amount of work done on an object? 2. The height of a typical kitchen table is approximately A) 10-2 m B) 10 0 m C)
Welcome Back to Physics 211!
 Welcome Back to Physics 211! (General Physics I) Thurs. Aug 30 th, 2012 Physics 211 -Fall 2012 Lecture01-2 1 Last time: Syllabus, mechanics survey Particle model Today: Using your clicker 1D displacement,
Welcome Back to Physics 211! (General Physics I) Thurs. Aug 30 th, 2012 Physics 211 -Fall 2012 Lecture01-2 1 Last time: Syllabus, mechanics survey Particle model Today: Using your clicker 1D displacement,
Four Basic Types of Motion Pearson Education, Inc.
 Four Basic Types of Motion Making a Motion Diagram An easy way to study motion is to make a video of a moving object. A video camera takes images at a fixed rate, typically 30 every second. Each separate
Four Basic Types of Motion Making a Motion Diagram An easy way to study motion is to make a video of a moving object. A video camera takes images at a fixed rate, typically 30 every second. Each separate
Vectors. In kinematics, the simplest concept is position, so let s begin with a position vector shown below:
 Vectors Extending the concepts of kinematics into two and three dimensions, the idea of a vector becomes very useful. By definition, a vector is a quantity with both a magnitude and a spatial direction.
Vectors Extending the concepts of kinematics into two and three dimensions, the idea of a vector becomes very useful. By definition, a vector is a quantity with both a magnitude and a spatial direction.
Chapter 3. Kinematics in Two Dimensions
 Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions 3.1 Trigonometry 3.1 Trigonometry sin! = h o h cos! = h a h tan! = h o h a 3.1 Trigonometry tan! = h o h a tan50! = h o 67.2m h o = tan50! ( 67.2m) = 80.0m 3.1 Trigonometry!
Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two Dimensions 3.1 Trigonometry 3.1 Trigonometry sin! = h o h cos! = h a h tan! = h o h a 3.1 Trigonometry tan! = h o h a tan50! = h o 67.2m h o = tan50! ( 67.2m) = 80.0m 3.1 Trigonometry!
A SCALAR is ANY quantity in physics that has MAGNITUDE, but NOT a direction associated with it. Magnitude A numerical value with units.
 Vectors and Scalars A SCALAR is ANY quantity in physics that has MAGNITUDE, but NOT a direction associated with it. Magnitude A numerical value with units. Scalar Example Speed Distance Age Heat Number
Vectors and Scalars A SCALAR is ANY quantity in physics that has MAGNITUDE, but NOT a direction associated with it. Magnitude A numerical value with units. Scalar Example Speed Distance Age Heat Number
3.1 Using Vectors 3.3 Coordinate Systems and Vector Components.notebook September 19, 2017
 Using Vectors A vector is a quantity with both a size (magnitude) and a direction. Figure 3.1 shows how to represent a particle s velocity as a vector. Section 3.1 Using Vectors The particle s speed at
Using Vectors A vector is a quantity with both a size (magnitude) and a direction. Figure 3.1 shows how to represent a particle s velocity as a vector. Section 3.1 Using Vectors The particle s speed at
2018 AP PHYSICS 1 FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS. PHYSICS 1 Section II 1 Questions Time 25 minutes
 2018 AP FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS Time 25 minutes Directions: Question 1 is a long free-response question that requires about 25 minutes to answer and is worth 12 points. Show your work for each part in
2018 AP FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS Time 25 minutes Directions: Question 1 is a long free-response question that requires about 25 minutes to answer and is worth 12 points. Show your work for each part in
Welcome Back to Physics 215!
 Welcome Back to Physics 215! (General Physics I) Thurs. Jan 18 th, 2018 Lecture01-2 1 Last time: Syllabus Units and dimensional analysis Today: Displacement, velocity, acceleration graphs Next time: More
Welcome Back to Physics 215! (General Physics I) Thurs. Jan 18 th, 2018 Lecture01-2 1 Last time: Syllabus Units and dimensional analysis Today: Displacement, velocity, acceleration graphs Next time: More
What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction
 What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction We frequently use vectors when solving problems in Physics Example: Change in position (displacement) Velocity
What is a Vector? A vector is a mathematical object which describes magnitude and direction We frequently use vectors when solving problems in Physics Example: Change in position (displacement) Velocity
Chapter 1 Problem 28: Agenda. Quantities in Motion. Displacement Isn t Distance. Velocity. Speed 1/23/14
 Agenda We need a note-taker! If you re interested, see me after class. Today: HW Quiz #1, 1D Motion Lecture for this week: Chapter 2 (finish reading Chapter 2 by Thursday) Homework #2: continue to check
Agenda We need a note-taker! If you re interested, see me after class. Today: HW Quiz #1, 1D Motion Lecture for this week: Chapter 2 (finish reading Chapter 2 by Thursday) Homework #2: continue to check
Chapter 3. Vectors and. Two-Dimensional Motion Vector vs. Scalar Review
 Chapter 3 Vectors and Two-Dimensional Motion Vector vs. Scalar Review All physical quantities encountered in this text will be either a scalar or a vector A vector quantity has both magnitude (size) and
Chapter 3 Vectors and Two-Dimensional Motion Vector vs. Scalar Review All physical quantities encountered in this text will be either a scalar or a vector A vector quantity has both magnitude (size) and
Vectors in Physics. Topics to review:
 Vectors in Physics Topics to review: Scalars Versus Vectors The Components of a Vector Adding and Subtracting Vectors Unit Vectors Position, Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration Vectors Relative Motion
Vectors in Physics Topics to review: Scalars Versus Vectors The Components of a Vector Adding and Subtracting Vectors Unit Vectors Position, Displacement, Velocity, and Acceleration Vectors Relative Motion
GENERAL PHYSICS (101 PHYS)
 INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) PHYS 101- LECTURE 1 GENERAL PHYSICS (101 PHYS) DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM LECTURES & CLASS ACTIVITIES https://inayacollegedrmohammedemam.wordpress.com/ Password: drmohammedemam
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) PHYS 101- LECTURE 1 GENERAL PHYSICS (101 PHYS) DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM LECTURES & CLASS ACTIVITIES https://inayacollegedrmohammedemam.wordpress.com/ Password: drmohammedemam
Coordinate Systems. Chapter 3. Cartesian Coordinate System. Polar Coordinate System
 Chapter 3 Vectors Coordinate Systems Used to describe the position of a point in space Coordinate system consists of a fixed reference point called the origin specific axes with scales and labels instructions
Chapter 3 Vectors Coordinate Systems Used to describe the position of a point in space Coordinate system consists of a fixed reference point called the origin specific axes with scales and labels instructions
Notes: Vectors and Scalars
 A particle moving along a straight line can move in only two directions and we can specify which directions with a plus or negative sign. For a particle moving in three dimensions; however, a plus sign
A particle moving along a straight line can move in only two directions and we can specify which directions with a plus or negative sign. For a particle moving in three dimensions; however, a plus sign
Multiple-Choice Questions
 Multiple-Choice Questions 1. A rock is thrown straight up from the edge of a cliff. The rock reaches the maximum height of 15 m above the edge and then falls down to the bottom of the cliff 35 m below
Multiple-Choice Questions 1. A rock is thrown straight up from the edge of a cliff. The rock reaches the maximum height of 15 m above the edge and then falls down to the bottom of the cliff 35 m below
STRAIGHT LINE MOTION TEST
 STRAIGHT LINE MOTION TEST Name: 1. The number of significant figures in the number 0.030 is a) b) 3 c) d) 5. The number 35.5 rounded to significant figures is a) 35.0 b) 35 c) 35.5 d) 0 3. Five different
STRAIGHT LINE MOTION TEST Name: 1. The number of significant figures in the number 0.030 is a) b) 3 c) d) 5. The number 35.5 rounded to significant figures is a) 35.0 b) 35 c) 35.5 d) 0 3. Five different
*************************************************************************
 Your Name: TEST #1 Print clearly. On the Scantron, fill out your student ID, leaving the first column empty and starting in the second column. Also write your name, class time (11:30 or 12:30), and Test
Your Name: TEST #1 Print clearly. On the Scantron, fill out your student ID, leaving the first column empty and starting in the second column. Also write your name, class time (11:30 or 12:30), and Test
Motion Along a Straight Line
 PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER Motion Along a Straight Line Position & displacement Average & instantaneous velocity Average & instantaneous acceleration Constant acceleration Free fall Graphical
PHYS 101 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER Motion Along a Straight Line Position & displacement Average & instantaneous velocity Average & instantaneous acceleration Constant acceleration Free fall Graphical
Introduction to Vectors
 Introduction to Vectors Why Vectors? Say you wanted to tell your friend that you re running late and will be there in five minutes. That s precisely enough information for your friend to know when you
Introduction to Vectors Why Vectors? Say you wanted to tell your friend that you re running late and will be there in five minutes. That s precisely enough information for your friend to know when you
