Fractional quantum Hall effect and duality. Dam T. Son (University of Chicago) Canterbury Tales of hot QFTs, Oxford July 11, 2017
|
|
|
- Brent Miles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fractional quantum Hall effect and duality Dam T. Son (University of Chicago) Canterbury Tales of hot QFTs, Oxford July 11, 2017
2 Plan
3 Plan General prologue: Fractional Quantum Hall Effect (FQHE)
4 Plan General prologue: Fractional Quantum Hall Effect (FQHE) Composite fermions
5 Plan General prologue: Fractional Quantum Hall Effect (FQHE) Composite fermions The puzzle of particle-hole symmetry
6 Plan General prologue: Fractional Quantum Hall Effect (FQHE) Composite fermions The puzzle of particle-hole symmetry Dirac composite fermions
7 General Prologue QCD is a prime example of a strongly coupled theory The particle excitations of the vacuum are very different from the microscopic degree of freedom A very similar situation in FQHE
8 The setup H = X a (p a + ea a ) 2 2m + X ha,bi e 2 x a x b
9 Integer quantum Hall effect Ignore Coulomb interactions When electrons moving in 2D in a magnetic field, energy is quantized: Landau level IQHE: electrons filling n Landau levels n=3 n=2 = B m n=1 degeneracy BA 2
10 Plateaux require energy gap
11 Fractional QHE Assume we have less particles than states on LLL n=3 n=2 n=1 In the approximation of noninteracting electrons: exponential degeneracy of states
12 Fractional QHE Assume we have less particles than states on LLL n=3 n=2 n=1 In the approximation of noninteracting electrons: exponential degeneracy of states
13 Why the FQH problem is hard degenerate perturbation theory Starting point: exponentially large number of degenerate states Any small perturbation lifts the degeneracy no small parameter
14 Lowest Landau level limit H = X a (p a + ea a ) 2 2m + X ha,bi e 2 x a x b B m n=1 n=0
15 Lowest Landau level limit H = X a (p a + ea a ) 2 2m + X ha,bi e 2 x a x b m! 0 B m!1 n=1 n=0
16 Lowest Landau level limit H = X a (p a + ea a ) 2 2m + X ha,bi e 2 x a x b m! 0 n=1 H = P LLL X a,b e 2 x a x b B m!1 Projection to n=0 lowest Landau level
17 Experimental hints
18 Jain s sequences of QH plateaux = n +1 2n +1 = n 2n +1
19 Systematics of Jain s sequences Gapped states Energy gap goes down ~ 1/n for n n= : gapless, likely Fermi liquid state
20 A powerful theory with a flaw
21 Flux attachment (Wilczek 1982, Jain 1989) Flux attachment: statistics does not change by attaching an even number of flux quanta
22 Flux attachment (Wilczek 1982, Jain 1989) Flux attachment: statistics does not change by attaching an even number of flux quanta
23 Flux attachment (Wilczek 1982, Jain 1989) Flux attachment: statistics does not change by attaching an even number of flux quanta ( 1)
24 Flux attachment (Wilczek 1982, Jain 1989) Flux attachment: statistics does not change by attaching an even number of flux quanta ( 1)
25 Flux attachment (Wilczek 1982, Jain 1989) Flux attachment: statistics does not change by attaching an even number of flux quanta ( 1) exp(i ) = (+1)
26 Flux attachment (Wilczek 1982, Jain 1989) Flux attachment: statistics does not change by attaching an even number of flux quanta ( 1)
27 Flux attachment (Wilczek 1982, Jain 1989) Flux attachment: statistics does not change by attaching an even number of flux quanta ( 1)
28 Flux attachment (Wilczek 1982, Jain 1989) Flux attachment: statistics does not change by attaching an even number of flux quanta ( 1) exp(2i ) =( 1)
29 Flux attachment (Wilczek 1982, Jain 1989) Flux attachment: statistics does not change by attaching an even number of flux quanta ( 1) exp(2i ) =( 1) e = CF
30 Composite fermion =1/3 FQH e e e per e
31 Composite fermion =1/3 FQH cf cf cf per e
32 Composite fermion =1/3 FQH cf cf cf per e average per cf
33 Composite fermion =1/3 FQH cf cf cf per e average per cf IQHE of CFs with ν=1
34 Composite fermion =2/3 FQH F F F F per F F average per F F FQHE for original fermions = IQHE for composite fermions (n=2)
35 HLR field theory L = i (@ 0 ia 0 + ia 0 ) 1 2m (@ i ia i + ia i ) µ a a b = r a =2 2 flux attachment mean field: B e = B b = B 4 n = 1 2 B e =0
36 Jain s sequence of plateaux Using the composite fermion most observed fractions can be explained Electrons Composite fermions = n 2n +1 CF = n = n +1 2n +1 CF = n +1
37 Prediction for nu=1/2 state Halperin Lee Read 1993 e e e per e
38 Prediction for nu=1/2 state Halperin Lee Read 1993 cf cf cf per e
39 Prediction for nu=1/2 state Halperin Lee Read 1993 cf cf cf per e Zero B field for cf
40 Prediction for nu=1/2 state Halperin Lee Read 1993 cf cf cf per e Zero B field for cf CFs form a Fermi liquid; HLR theory
41
42 ν=1/2
43 Is the composite fermion real? Composite fermion can be detected as a quasiparticle near half-filling large semiclassical orbit when magnetic fields do not exactly cancel
44 R (k ) 3 2 (a) W = 40 nm a = 200 nm n = 1.74 x cm -2 T = 0.3 K ν = ν = 1/2 i = B (T) (Kamburov et al, 2014)
45 For a long time it was thought that the HLR theory (zoomed in the near Fermi surface region) gives the correct low-energy effective theory There is one crucial problem
46
47 The problem of particle-hole symmetry
48 Particle-hole symmetry emptyi = fulli PH symmetry c k 1 = c k i 1 = i! 1 exact symmetry the Hamiltonian on the LLL, when mixing of higher LLs negligible
49 PH symmetry in the CF theory PH conjugate pairs of FQH states = n 2n +1 = n +1 2n +1 ν=1/3 ν=2/3
50 PH symmetry in the CF theory PH conjugate pairs of FQH states = n 2n +1 = n +1 2n +1 ν=2/5 ν=3/5
51 PH symmetry in the CF theory PH conjugate pairs of FQH states = n 2n +1 = n +1 2n +1 ν=3/7 ν=4/7
52 PH symmetry in the CF theory PH conjugate pairs of FQH states = n 2n +1 = n +1 2n +1 ν=3/7 ν=4/7 CF picture does not respect PH symmetry
53 PH symmetry of a Fermi liquid?
54 PH symmetry of a Fermi liquid? PH
55 PH symmetry of a Fermi liquid? PH
56 PH symmetry of a Fermi liquid? =?
57 PH symmetry in HLR HLR Lagrangian does not have any symmetry that can be identified with PH symmetry ~1997 The problem was considered hard as it requires projection to lowest Landau level PH conjugation acts nonlocally
58 Sharpening the problem Consider a 2-component massless Dirac fermion Can realize fractional quantum Hall effect Natural particle-hole symmetry at zero density E 0
59 The puzzle of QHE for Dirac fermion Half filled Landau level arises naturally at zero chemical potential Turn on a magnetic field: ground state is a Fermi liquid Volume of Fermi sphere ~ magnetic field Which conserved charge in Luttinger s theorem???
60 Solution to the problem of particlehole symmetry
61 Prelude to solution: particle-vortex duality Peskin; Dasgupta, Halperin L 1 µ 2 m L 2 = (@ µ a µ ) 2 m Goldstone boson particle photon vortex
62 Coupling to external gauge field L 1 = (@ µ A µ ) 2 m L 2 = (@ µ a µ ) 2 m µ A a j µ = 1 2 a
63 Hypothetical duality DTS 2015 Metlitski, Vishwanath 2015 Wang, Senthil 2015 electron theory L = i e µ (@ µ ia µ ) e CF theory L = i µ (@ µ ia µ ) 1 4 µ A a
64 Particle-vortex duality S = Z d 3 x apple i µ (@ µ ia µ ) 1 4 µ A a = S A 0 = b 4 S a 0 =0! h 0 i = B 4 Turn on magnetic field lead to a finite density Landau s reasoning: Fermi surface original fermion ψ magnetic field density composite fermion ψe density magnetic field
65 Dirac composite fermion Low energy dynamics of a half-filled Landau level is described by a low-energy effective theory of a new fermion ( composite fermion ) coupled to a dynamical gauge field The composite fermion is electrically neutral Density of composite fermion = physical magnetic field
66 Particle-hole symmetry as CT symmetry Magnetic field breaks C, P, T preserves PT, CT, CP Particle-hole symmetry of the n=0 Landau level can be identified with CT Effective theory of the composite fermion has CT symmetry
67 Action of CT A 0 (t, x)! A 0 ( t, x) A i (t, x)! A i ( t, x) a 0 (t, x)! a 0 ( t, x) a i (t, x)! a i ( t, x) (t, x)! i 2 ( t, x)
68 CT on composite fermion
69 CT on composite fermion PH
70 CT on composite fermion PH
71 CT on composite fermion PH
72 CT on composite fermion PH Particle-hole symmetry maps particle to particle k! k! i 2
73 CT on composite fermion PH Particle-hole symmetry maps particle to particle k! k! i 2 DTS 2015
74 Away from half filling S = Z d 3 x apple i µ (@ µ ia µ ) 1 4 µ A a = S A 0 = b 4 S a 0 =0! h 0 i = B 4 =0 Now the CFs move in large circular orbits
75 R (k ) 3 2 (a) W = 40 nm a = 200 nm n = 1.74 x cm -2 T = 0.3 K ν = ν = 1/2 i = B (T) (Kamburov et al, 2014)
76 Mapping Jain s sequences = n 2n +1 CF = n = n +1 2n +1 CF = n +1
77 Mapping Jain s sequences = n 2n +1 = n +1 2n +1 CF = n + 1 2?
78 Mapping Jain s sequences = n 2n +1 CF = n + 1 2? = n +1 2n +1 CFs form an IQH state at half-integer filling factor: must be a Dirac fermion
79 IQHE in graphene xy = n + 1 e ~ Figure 4 QHE for massless Dirac fermions. Hall conductivity j xy and longitudinal resistivity r xx of graphene as a function of their concentration at B ¼ 14 T and T ¼ 4 K. j xy ; (4e 2 /h)n is calculated from the measured dependences of (V ) and (V ) as ¼ /( 2 þ 2 ). The Novoselov et al 2005
80 (Particle-hole) 2 Θ 2 = ±1 Θ
81 On a single Landau level M
82 On a single Landau level 2 =( 1) M(M 1)/ M
83 On a single Landau level 2 =( 1) M(M 1)/ M M =2N CF 2 =( 1) N CF
84 On a single Landau level 2 =( 1) M(M 1)/ M M =2N CF 2 =( 1) N CF Dirac CF:! ( i 2 ) 2 = Geraedts, Zaletel, Mong, Metlitski, Vishwanath, Motrunich; Levin, Son
85 Consequences of PH symmetry j = xx E + xy E ẑ + xx rt + xy rt ẑ conductivities thermoelectric coefficients At exact half filling, in the presence of particle-hole symmetric disorders HLR xy = e2 2h xy = 2h e 2 xx =0 Potter, Serbyn, Vishwanath 2015
86 A new gapped state The composite fermions can form Cooper pairs Simplest pairing does not break particle-hole symmetry h i6=0 A new gapped state: PH-Pfaffian state
87 Consequences of Dirac CF Suppression of Friedel oscillations in correlations of particle-hole symmetric observables Ô =( 0 )r 2 k k k k Geraedts, Zaletel, Mong, Metlitsky, Vishwanath, Montrunich, 2015 Direct proof of Berry phase π of the composite fermion
88 A window to duality Fermionic particle-vortex duality can be derived of a more elementary fermion-boson duality Karch, Tong; Seiberg, Senthil, Wang, Witten small N version of duality between CS theories, tested at large N New dualities can be obtained Example: Nf=2 QED3 is self-dual Cenke Xu
89 The elementary duality L = L[,A] AdA L = L[,a]+ 1 4 ada Ada
90 Comments on duality One side of duality is a theory of a single 2- component Dirac fermion coupled to U(1) gauge field It is usually thought QED3 with Nf fermions is unstable with respect to SSB for Nf<Nf*. Nf* ~ 6 in Schwinger-Dyson One lattice simulation (Karthik, Narayanan 2015) indicates Nf* < 2. The stability of theory with Nf=1 is not required for fractional quantum Hall effect (finite density)
91 Conclusion The low-energy quasiparticle of half-filled Landau level is completely different from the electron Symmetries allowed to guess the form of the lowenergy effective theory Hints on new field-theoretic dualities in 2+1 D
92 References
93 References DTS, PRX 5, (2015) Wang, Senthil Metlitski, Vishwanath Geraedts et al., Mross, Alicea, Motrunich,
Fractional quantum Hall effect and duality. Dam Thanh Son (University of Chicago) Strings 2017, Tel Aviv, Israel June 26, 2017
 Fractional quantum Hall effect and duality Dam Thanh Son (University of Chicago) Strings 2017, Tel Aviv, Israel June 26, 2017 Plan Fractional quantum Hall effect Halperin-Lee-Read (HLR) theory Problem
Fractional quantum Hall effect and duality Dam Thanh Son (University of Chicago) Strings 2017, Tel Aviv, Israel June 26, 2017 Plan Fractional quantum Hall effect Halperin-Lee-Read (HLR) theory Problem
The Dirac composite fermions in fractional quantum Hall effect. Dam Thanh Son (University of Chicago) Nambu Memorial Symposium March 12, 2016
 The Dirac composite fermions in fractional quantum Hall effect Dam Thanh Son (University of Chicago) Nambu Memorial Symposium March 12, 2016 A story of a symmetry lost and recovered Dam Thanh Son (University
The Dirac composite fermions in fractional quantum Hall effect Dam Thanh Son (University of Chicago) Nambu Memorial Symposium March 12, 2016 A story of a symmetry lost and recovered Dam Thanh Son (University
Is the composite fermion a Dirac particle?
 Is the composite fermion a Dirac particle? Dam T. Son GGI conference Gauge/gravity duality 2015 Ref.: 1502.03446 Plan Plan Fractional quantum Hall effect Plan Fractional quantum Hall effect Composite fermion
Is the composite fermion a Dirac particle? Dam T. Son GGI conference Gauge/gravity duality 2015 Ref.: 1502.03446 Plan Plan Fractional quantum Hall effect Plan Fractional quantum Hall effect Composite fermion
Is the composite fermion a Dirac particle?
 Is the composite fermion a Dirac particle? Dam T. Son (University of Chicago) Cold atoms meet QFT, 2015 Ref.: 1502.03446 Plan Plan Composite fermion: quasiparticle of Fractional Quantum Hall Effect (FQHE)
Is the composite fermion a Dirac particle? Dam T. Son (University of Chicago) Cold atoms meet QFT, 2015 Ref.: 1502.03446 Plan Plan Composite fermion: quasiparticle of Fractional Quantum Hall Effect (FQHE)
The Half-Filled Landau Level
 Nigel Cooper Department of Physics, University of Cambridge Celebration for Bert Halperin s 75th January 31, 2017 Chong Wang, Bert Halperin & Ady Stern. [C. Wang, NRC, B. I. Halperin & A. Stern, arxiv:1701.00007].
Nigel Cooper Department of Physics, University of Cambridge Celebration for Bert Halperin s 75th January 31, 2017 Chong Wang, Bert Halperin & Ady Stern. [C. Wang, NRC, B. I. Halperin & A. Stern, arxiv:1701.00007].
Supersymmetric Mirror Duality and Half-filled Landau level S. Kachru, M Mulligan, G Torroba and H. Wang Phys.Rev.
 Supersymmetric Mirror Duality and Half-filled Landau level S. Kachru, M Mulligan, G Torroba and H. Wang Phys.Rev. B92 (2015) 235105 Huajia Wang University of Illinois Urbana Champaign Introduction/Motivation
Supersymmetric Mirror Duality and Half-filled Landau level S. Kachru, M Mulligan, G Torroba and H. Wang Phys.Rev. B92 (2015) 235105 Huajia Wang University of Illinois Urbana Champaign Introduction/Motivation
Integer quantum Hall effect for bosons: A physical realization
 Integer quantum Hall effect for bosons: A physical realization T. Senthil (MIT) and Michael Levin (UMCP). (arxiv:1206.1604) Thanks: Xie Chen, Zhengchen Liu, Zhengcheng Gu, Xiao-gang Wen, and Ashvin Vishwanath.
Integer quantum Hall effect for bosons: A physical realization T. Senthil (MIT) and Michael Levin (UMCP). (arxiv:1206.1604) Thanks: Xie Chen, Zhengchen Liu, Zhengcheng Gu, Xiao-gang Wen, and Ashvin Vishwanath.
Dualities, Old and New. David Tong: MIT Pappalardo Fellow,
 Dualities, Old and New David Tong: MIT Pappalardo Fellow, 2001-2004 Quantum Field Theory Quantum Field Theory... is hard 1. Numerics: How to Proceed? How to Proceed? 1. Numerics: 2. Toy Models (e.g. supersymmetry)
Dualities, Old and New David Tong: MIT Pappalardo Fellow, 2001-2004 Quantum Field Theory Quantum Field Theory... is hard 1. Numerics: How to Proceed? How to Proceed? 1. Numerics: 2. Toy Models (e.g. supersymmetry)
(Effective) Field Theory and Emergence in Condensed Matter
 (Effective) Field Theory and Emergence in Condensed Matter T. Senthil (MIT) Effective field theory in condensed matter physics Microscopic models (e.g, Hubbard/t-J, lattice spin Hamiltonians, etc) `Low
(Effective) Field Theory and Emergence in Condensed Matter T. Senthil (MIT) Effective field theory in condensed matter physics Microscopic models (e.g, Hubbard/t-J, lattice spin Hamiltonians, etc) `Low
Topological Insulators in 3D and Bosonization
 Topological Insulators in 3D and Bosonization Andrea Cappelli, INFN Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Outline Topological states of matter: bulk and edge Fermions and bosons on the (1+1)-dimensional
Topological Insulators in 3D and Bosonization Andrea Cappelli, INFN Florence (w. E. Randellini, J. Sisti) Outline Topological states of matter: bulk and edge Fermions and bosons on the (1+1)-dimensional
Many faces of Mirror Symmetries
 Many faces of Mirror Symmetries Huajia Wang University of llinois at Urbana Champaign S. Kachru, M. Mulligan, G.Torroba, H. Wang, arxiv: 1608.05077 S. Kachru, M. Mulligan, G.Torroba, H. Wang, arxiv: 1609.02149
Many faces of Mirror Symmetries Huajia Wang University of llinois at Urbana Champaign S. Kachru, M. Mulligan, G.Torroba, H. Wang, arxiv: 1608.05077 S. Kachru, M. Mulligan, G.Torroba, H. Wang, arxiv: 1609.02149
Beyond the Quantum Hall Effect
 Beyond the Quantum Hall Effect Jim Eisenstein California Institute of Technology School on Low Dimensional Nanoscopic Systems Harish-chandra Research Institute January February 2008 Outline of the Lectures
Beyond the Quantum Hall Effect Jim Eisenstein California Institute of Technology School on Low Dimensional Nanoscopic Systems Harish-chandra Research Institute January February 2008 Outline of the Lectures
The Quantum Hall Effects
 The Quantum Hall Effects Integer and Fractional Michael Adler July 1, 2010 1 / 20 Outline 1 Introduction Experiment Prerequisites 2 Integer Quantum Hall Effect Quantization of Conductance Edge States 3
The Quantum Hall Effects Integer and Fractional Michael Adler July 1, 2010 1 / 20 Outline 1 Introduction Experiment Prerequisites 2 Integer Quantum Hall Effect Quantization of Conductance Edge States 3
Braid Group, Gauge Invariance and Topological Order
 Braid Group, Gauge Invariance and Topological Order Yong-Shi Wu Department of Physics University of Utah Topological Quantum Computing IPAM, UCLA; March 2, 2007 Outline Motivation: Topological Matter (Phases)
Braid Group, Gauge Invariance and Topological Order Yong-Shi Wu Department of Physics University of Utah Topological Quantum Computing IPAM, UCLA; March 2, 2007 Outline Motivation: Topological Matter (Phases)
Superinsulator: a new topological state of matter
 Superinsulator: a new topological state of matter M. Cristina Diamantini Nips laboratory, INFN and Department of Physics and Geology University of Perugia Coll: Igor Lukyanchuk, University of Picardie
Superinsulator: a new topological state of matter M. Cristina Diamantini Nips laboratory, INFN and Department of Physics and Geology University of Perugia Coll: Igor Lukyanchuk, University of Picardie
Holographic Anyonic Superfluids
 Holographic Anyonic Superfluids Matt Lippert (Amsterdam) with Niko Jokela (USC) and Gilad Lifschytz (Haifa) Plan Anyons, SL(2,Z), and Quantum Hall Effect Superfluids and Anyon Superfliuds A Holographic
Holographic Anyonic Superfluids Matt Lippert (Amsterdam) with Niko Jokela (USC) and Gilad Lifschytz (Haifa) Plan Anyons, SL(2,Z), and Quantum Hall Effect Superfluids and Anyon Superfliuds A Holographic
Symmetry Protected Topological Phases of Matter
 Symmetry Protected Topological Phases of Matter T. Senthil (MIT) Review: T. Senthil, Annual Reviews of Condensed Matter Physics, 2015 Topological insulators 1.0 Free electron band theory: distinct insulating
Symmetry Protected Topological Phases of Matter T. Senthil (MIT) Review: T. Senthil, Annual Reviews of Condensed Matter Physics, 2015 Topological insulators 1.0 Free electron band theory: distinct insulating
Berry Phase and Anomalous Transport of the Composite Fermions at the Half-Filled Landau Level
 Berry Phase and Anomalous Transport of the Composite Fermions at the Half-Filled Landau Level W. Pan 1,*, W. Kang 2,*, K.W. Baldwin 3, K.W. West 3, L.N. Pfeiffer 3, and D.C. Tsui 3 1 Sandia National Laboratories,
Berry Phase and Anomalous Transport of the Composite Fermions at the Half-Filled Landau Level W. Pan 1,*, W. Kang 2,*, K.W. Baldwin 3, K.W. West 3, L.N. Pfeiffer 3, and D.C. Tsui 3 1 Sandia National Laboratories,
Emergence and Mechanism in the Fractional Quantum Hall Effect
 Emergence and Mechanism in the Fractional Quantum Hall Effect Jonathan Bain Department of Technology, Culture and Society Tandon School of Engineering, New York University Brooklyn, New York 1. Two Versions
Emergence and Mechanism in the Fractional Quantum Hall Effect Jonathan Bain Department of Technology, Culture and Society Tandon School of Engineering, New York University Brooklyn, New York 1. Two Versions
Composite Dirac liquids
 Composite Dirac liquids Composite Fermi liquid non-interacting 3D TI surface Interactions Composite Dirac liquid ~ Jason Alicea, Caltech David Mross, Andrew Essin, & JA, Physical Review X 5, 011011 (2015)
Composite Dirac liquids Composite Fermi liquid non-interacting 3D TI surface Interactions Composite Dirac liquid ~ Jason Alicea, Caltech David Mross, Andrew Essin, & JA, Physical Review X 5, 011011 (2015)
Confinement-deconfinement transitions in Z 2 gauge theories, and deconfined criticality
 HARVARD Confinement-deconfinement transitions in Z 2 gauge theories, and deconfined criticality Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Pune Subir Sachdev November 15, 2017 Talk online: sachdev.physics.harvard.edu
HARVARD Confinement-deconfinement transitions in Z 2 gauge theories, and deconfined criticality Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Pune Subir Sachdev November 15, 2017 Talk online: sachdev.physics.harvard.edu
Zooming in on the Quantum Hall Effect
 Zooming in on the Quantum Hall Effect Cristiane MORAIS SMITH Institute for Theoretical Physics, Utrecht University, The Netherlands Capri Spring School p.1/31 Experimental Motivation Historical Summary:
Zooming in on the Quantum Hall Effect Cristiane MORAIS SMITH Institute for Theoretical Physics, Utrecht University, The Netherlands Capri Spring School p.1/31 Experimental Motivation Historical Summary:
The Geometry of the Quantum Hall Effect
 The Geometry of the Quantum Hall Effect Dam Thanh Son (University of Chicago) Refs: Carlos Hoyos, DTS arxiv:1109.2651 DTS, M.Wingate cond-mat/0509786 Plan Review of quantum Hall physics Summary of results
The Geometry of the Quantum Hall Effect Dam Thanh Son (University of Chicago) Refs: Carlos Hoyos, DTS arxiv:1109.2651 DTS, M.Wingate cond-mat/0509786 Plan Review of quantum Hall physics Summary of results
SPT: a window into highly entangled phases
 SPT: a window into highly entangled phases T. Senthil (MIT) Collaborators: Chong Wang, A. Potter Why study SPT? 1. Because it may be there... Focus on electronic systems with realistic symmetries in d
SPT: a window into highly entangled phases T. Senthil (MIT) Collaborators: Chong Wang, A. Potter Why study SPT? 1. Because it may be there... Focus on electronic systems with realistic symmetries in d
Conformal Field Theory of Composite Fermions in the QHE
 Conformal Field Theory of Composite Fermions in the QHE Andrea Cappelli (INFN and Physics Dept., Florence) Outline Introduction: wave functions, edge excitations and CFT CFT for Jain wfs: Hansson et al.
Conformal Field Theory of Composite Fermions in the QHE Andrea Cappelli (INFN and Physics Dept., Florence) Outline Introduction: wave functions, edge excitations and CFT CFT for Jain wfs: Hansson et al.
Quantum Hall effect. Quantization of Hall resistance is incredibly precise: good to 1 part in I believe. WHY?? G xy = N e2 h.
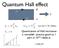 Quantum Hall effect V1 V2 R L I I x = N e2 h V y V x =0 G xy = N e2 h n.b. h/e 2 = 25 kohms Quantization of Hall resistance is incredibly precise: good to 1 part in 10 10 I believe. WHY?? Robustness Why
Quantum Hall effect V1 V2 R L I I x = N e2 h V y V x =0 G xy = N e2 h n.b. h/e 2 = 25 kohms Quantization of Hall resistance is incredibly precise: good to 1 part in 10 10 I believe. WHY?? Robustness Why
Effective Field Theories of Topological Insulators
 Effective Field Theories of Topological Insulators Eduardo Fradkin University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Workshop on Field Theoretic Computer Simulations for Particle Physics and Condensed Matter
Effective Field Theories of Topological Insulators Eduardo Fradkin University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Workshop on Field Theoretic Computer Simulations for Particle Physics and Condensed Matter
Laughlin quasiparticle interferometer: Observation of Aharonov-Bohm superperiod and fractional statistics
 Laughlin quasiparticle interferometer: Observation of Aharonov-Bohm superperiod and fractional statistics F.E. Camino, W. Zhou and V.J. Goldman Stony Brook University Outline Exchange statistics in 2D,
Laughlin quasiparticle interferometer: Observation of Aharonov-Bohm superperiod and fractional statistics F.E. Camino, W. Zhou and V.J. Goldman Stony Brook University Outline Exchange statistics in 2D,
Condensed Matter Physics and the Nature of Spacetime
 Condensed Matter Physics and the Nature of Spacetime Jonathan Bain Polytechnic University Prospects for modeling spacetime as a phenomenon that emerges in the low-energy limit of a quantum liquid. 1. EFTs
Condensed Matter Physics and the Nature of Spacetime Jonathan Bain Polytechnic University Prospects for modeling spacetime as a phenomenon that emerges in the low-energy limit of a quantum liquid. 1. EFTs
Correlated 2D Electron Aspects of the Quantum Hall Effect
 Correlated 2D Electron Aspects of the Quantum Hall Effect Magnetic field spectrum of the correlated 2D electron system: Electron interactions lead to a range of manifestations 10? = 4? = 2 Resistance (arb.
Correlated 2D Electron Aspects of the Quantum Hall Effect Magnetic field spectrum of the correlated 2D electron system: Electron interactions lead to a range of manifestations 10? = 4? = 2 Resistance (arb.
Luttinger Liquid at the Edge of a Graphene Vacuum
 Luttinger Liquid at the Edge of a Graphene Vacuum H.A. Fertig, Indiana University Luis Brey, CSIC, Madrid I. Introduction: Graphene Edge States (Non-Interacting) II. III. Quantum Hall Ferromagnetism and
Luttinger Liquid at the Edge of a Graphene Vacuum H.A. Fertig, Indiana University Luis Brey, CSIC, Madrid I. Introduction: Graphene Edge States (Non-Interacting) II. III. Quantum Hall Ferromagnetism and
Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field
 Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field by B. I. Halperin Nano-QT 2016 Kyiv October 11, 2016 Based on work with So Takei (CUNY), Yaroslav Tserkovnyak (UCLA), and Amir Yacoby (Harvard)
Spin Superfluidity and Graphene in a Strong Magnetic Field by B. I. Halperin Nano-QT 2016 Kyiv October 11, 2016 Based on work with So Takei (CUNY), Yaroslav Tserkovnyak (UCLA), and Amir Yacoby (Harvard)
Symmetry protected topological phases in quantum spin systems
 10sor network workshop @Kashiwanoha Future Center May 14 (Thu.), 2015 Symmetry protected topological phases in quantum spin systems NIMS U. Tokyo Shintaro Takayoshi Collaboration with A. Tanaka (NIMS)
10sor network workshop @Kashiwanoha Future Center May 14 (Thu.), 2015 Symmetry protected topological phases in quantum spin systems NIMS U. Tokyo Shintaro Takayoshi Collaboration with A. Tanaka (NIMS)
Entanglement, holography, and strange metals
 Entanglement, holography, and strange metals PCTS, Princeton, October 26, 2012 Subir Sachdev Talk online at sachdev.physics.harvard.edu HARVARD Liza Huijse Max Metlitski Brian Swingle Complex entangled
Entanglement, holography, and strange metals PCTS, Princeton, October 26, 2012 Subir Sachdev Talk online at sachdev.physics.harvard.edu HARVARD Liza Huijse Max Metlitski Brian Swingle Complex entangled
Quantum numbers and collective phases of composite fermions
 Quantum numbers and collective phases of composite fermions Quantum numbers Effective magnetic field Mass Magnetic moment Charge Statistics Fermi wave vector Vorticity (vortex charge) Effective magnetic
Quantum numbers and collective phases of composite fermions Quantum numbers Effective magnetic field Mass Magnetic moment Charge Statistics Fermi wave vector Vorticity (vortex charge) Effective magnetic
Universal phase transitions in Topological lattice models
 Universal phase transitions in Topological lattice models F. J. Burnell Collaborators: J. Slingerland S. H. Simon September 2, 2010 Overview Matter: classified by orders Symmetry Breaking (Ferromagnet)
Universal phase transitions in Topological lattice models F. J. Burnell Collaborators: J. Slingerland S. H. Simon September 2, 2010 Overview Matter: classified by orders Symmetry Breaking (Ferromagnet)
Defects in topologically ordered states. Xiao-Liang Qi Stanford University Mag Lab, Tallahassee, 01/09/2014
 Defects in topologically ordered states Xiao-Liang Qi Stanford University Mag Lab, Tallahassee, 01/09/2014 References Maissam Barkeshli & XLQ, PRX, 2, 031013 (2012) Maissam Barkeshli, Chaoming Jian, XLQ,
Defects in topologically ordered states Xiao-Liang Qi Stanford University Mag Lab, Tallahassee, 01/09/2014 References Maissam Barkeshli & XLQ, PRX, 2, 031013 (2012) Maissam Barkeshli, Chaoming Jian, XLQ,
Lecture 2: Deconfined quantum criticality
 Lecture 2: Deconfined quantum criticality T. Senthil (MIT) General theoretical questions Fate of Landau-Ginzburg-Wilson ideas at quantum phase transitions? (More precise) Could Landau order parameters
Lecture 2: Deconfined quantum criticality T. Senthil (MIT) General theoretical questions Fate of Landau-Ginzburg-Wilson ideas at quantum phase transitions? (More precise) Could Landau order parameters
Lecture 2 2D Electrons in Excited Landau Levels
 Lecture 2 2D Electrons in Excited Landau Levels What is the Ground State of an Electron Gas? lower density Wigner Two Dimensional Electrons at High Magnetic Fields E Landau levels N=2 N=1 N= Hartree-Fock
Lecture 2 2D Electrons in Excited Landau Levels What is the Ground State of an Electron Gas? lower density Wigner Two Dimensional Electrons at High Magnetic Fields E Landau levels N=2 N=1 N= Hartree-Fock
Properties of monopole operators in 3d gauge theories
 Properties of monopole operators in 3d gauge theories Silviu S. Pufu Princeton University Based on: arxiv:1303.6125 arxiv:1309.1160 (with Ethan Dyer and Mark Mezei) work in progress with Ethan Dyer, Mark
Properties of monopole operators in 3d gauge theories Silviu S. Pufu Princeton University Based on: arxiv:1303.6125 arxiv:1309.1160 (with Ethan Dyer and Mark Mezei) work in progress with Ethan Dyer, Mark
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 10 Jan 2018
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 10 Jan 2018 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.str-el] 10 Jan 2018](/thumbs/77/74797497.jpg) Dirac Composite Fermion - A Particle-Hole Spinor Jian Yang, arxiv:7.85v [cond-mat.str-el] Jan 8 Te particle-ole PH symmetry at alf-filled Landau level requires te relationsip between te flux number N φ
Dirac Composite Fermion - A Particle-Hole Spinor Jian Yang, arxiv:7.85v [cond-mat.str-el] Jan 8 Te particle-ole PH symmetry at alf-filled Landau level requires te relationsip between te flux number N φ
Critical Spin-liquid Phases in Spin-1/2 Triangular Antiferromagnets. In collaboration with: Olexei Motrunich & Jason Alicea
 Critical Spin-liquid Phases in Spin-1/2 Triangular Antiferromagnets In collaboration with: Olexei Motrunich & Jason Alicea I. Background Outline Avoiding conventional symmetry-breaking in s=1/2 AF Topological
Critical Spin-liquid Phases in Spin-1/2 Triangular Antiferromagnets In collaboration with: Olexei Motrunich & Jason Alicea I. Background Outline Avoiding conventional symmetry-breaking in s=1/2 AF Topological
THE CASES OF ν = 5/2 AND ν = 12/5. Reminder re QHE:
 LECTURE 6 THE FRACTIONAL QUANTUM HALL EFFECT : THE CASES OF ν = 5/2 AND ν = 12/5 Reminder re QHE: Occurs in (effectively) 2D electron system ( 2DES ) (e.g. inversion layer in GaAs - GaAlAs heterostructure)
LECTURE 6 THE FRACTIONAL QUANTUM HALL EFFECT : THE CASES OF ν = 5/2 AND ν = 12/5 Reminder re QHE: Occurs in (effectively) 2D electron system ( 2DES ) (e.g. inversion layer in GaAs - GaAlAs heterostructure)
Nonabelian hierarchies
 Nonabelian hierarchies collaborators: Yoran Tournois, UzK Maria Hermanns, UzK Hans Hansson, SU Steve H. Simon, Oxford Susanne Viefers, UiO Quantum Hall hierarchies, arxiv:1601.01697 Outline Haldane-Halperin
Nonabelian hierarchies collaborators: Yoran Tournois, UzK Maria Hermanns, UzK Hans Hansson, SU Steve H. Simon, Oxford Susanne Viefers, UiO Quantum Hall hierarchies, arxiv:1601.01697 Outline Haldane-Halperin
Dual vortex theory of doped antiferromagnets
 Dual vortex theory of doped antiferromagnets Physical Review B 71, 144508 and 144509 (2005), cond-mat/0502002, cond-mat/0511298 Leon Balents (UCSB) Lorenz Bartosch (Harvard) Anton Burkov (Harvard) Predrag
Dual vortex theory of doped antiferromagnets Physical Review B 71, 144508 and 144509 (2005), cond-mat/0502002, cond-mat/0511298 Leon Balents (UCSB) Lorenz Bartosch (Harvard) Anton Burkov (Harvard) Predrag
Superuniversality and non-abelian bosonization in 2+1 dimensions
 Superuniversality and non-abelian bosonization in + dimensions Burgess & Dolan (000) Micael Mulligan UC Riverside Institute for CM Teory UIUC in collusion wit: Aaron Hui and Eun-A Kim pase transitions
Superuniversality and non-abelian bosonization in + dimensions Burgess & Dolan (000) Micael Mulligan UC Riverside Institute for CM Teory UIUC in collusion wit: Aaron Hui and Eun-A Kim pase transitions
Non-Abelian Statistics. in the Fractional Quantum Hall States * X. G. Wen. School of Natural Sciences. Institute of Advanced Study
 IASSNS-HEP-90/70 Sep. 1990 Non-Abelian Statistics in the Fractional Quantum Hall States * X. G. Wen School of Natural Sciences Institute of Advanced Study Princeton, NJ 08540 ABSTRACT: The Fractional Quantum
IASSNS-HEP-90/70 Sep. 1990 Non-Abelian Statistics in the Fractional Quantum Hall States * X. G. Wen School of Natural Sciences Institute of Advanced Study Princeton, NJ 08540 ABSTRACT: The Fractional Quantum
A Brief Introduction to Duality Web
 A Brief Introduction to Duality Web WeiHan Hsiao a a Department of Physics, The University of Chicago E-mail: weihanhsiao@uchicago.edu Abstract: This note is prepared for the journal club talk given on
A Brief Introduction to Duality Web WeiHan Hsiao a a Department of Physics, The University of Chicago E-mail: weihanhsiao@uchicago.edu Abstract: This note is prepared for the journal club talk given on
Preface Introduction to the electron liquid
 Table of Preface page xvii 1 Introduction to the electron liquid 1 1.1 A tale of many electrons 1 1.2 Where the electrons roam: physical realizations of the electron liquid 5 1.2.1 Three dimensions 5 1.2.2
Table of Preface page xvii 1 Introduction to the electron liquid 1 1.1 A tale of many electrons 1 1.2 Where the electrons roam: physical realizations of the electron liquid 5 1.2.1 Three dimensions 5 1.2.2
Topological Properties of Quantum States of Condensed Matter: some recent surprises.
 Topological Properties of Quantum States of Condensed Matter: some recent surprises. F. D. M. Haldane Princeton University and Instituut Lorentz 1. Berry phases, zero-field Hall effect, and one-way light
Topological Properties of Quantum States of Condensed Matter: some recent surprises. F. D. M. Haldane Princeton University and Instituut Lorentz 1. Berry phases, zero-field Hall effect, and one-way light
team Hans Peter Büchler Nicolai Lang Mikhail Lukin Norman Yao Sebastian Huber
 title 1 team 2 Hans Peter Büchler Nicolai Lang Mikhail Lukin Norman Yao Sebastian Huber motivation: topological states of matter 3 fermions non-interacting, filled band (single particle physics) topological
title 1 team 2 Hans Peter Büchler Nicolai Lang Mikhail Lukin Norman Yao Sebastian Huber motivation: topological states of matter 3 fermions non-interacting, filled band (single particle physics) topological
Topological Phases under Strong Magnetic Fields
 Topological Phases under Strong Magnetic Fields Mark O. Goerbig ITAP, Turunç, July 2013 Historical Introduction What is the common point between graphene, quantum Hall effects and topological insulators?...
Topological Phases under Strong Magnetic Fields Mark O. Goerbig ITAP, Turunç, July 2013 Historical Introduction What is the common point between graphene, quantum Hall effects and topological insulators?...
Quantum Choreography: Exotica inside Crystals
 Quantum Choreography: Exotica inside Crystals U. Toronto - Colloquia 3/9/2006 J. Alicea, O. Motrunich, T. Senthil and MPAF Electrons inside crystals: Quantum Mechanics at room temperature Quantum Theory
Quantum Choreography: Exotica inside Crystals U. Toronto - Colloquia 3/9/2006 J. Alicea, O. Motrunich, T. Senthil and MPAF Electrons inside crystals: Quantum Mechanics at room temperature Quantum Theory
Matrix product states for the fractional quantum Hall effect
 Matrix product states for the fractional quantum Hall effect Roger Mong (California Institute of Technology) University of Virginia Feb 24, 2014 Collaborators Michael Zaletel UC Berkeley (Stanford/Station
Matrix product states for the fractional quantum Hall effect Roger Mong (California Institute of Technology) University of Virginia Feb 24, 2014 Collaborators Michael Zaletel UC Berkeley (Stanford/Station
Quantum oscillations in insulators with neutral Fermi surfaces
 Quantum oscillations in insulators with neutral Fermi surfaces ITF-Seminar IFW Institute - Dresden October 4, 2017 Inti Sodemann MPI-PKS Dresden Contents Theory of quantum oscillations of insulators with
Quantum oscillations in insulators with neutral Fermi surfaces ITF-Seminar IFW Institute - Dresden October 4, 2017 Inti Sodemann MPI-PKS Dresden Contents Theory of quantum oscillations of insulators with
Kai Sun. University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. Collaborators: Krishna Kumar and Eduardo Fradkin (UIUC)
 Kai Sun University of Michigan, Ann Arbor Collaborators: Krishna Kumar and Eduardo Fradkin (UIUC) Outline How to construct a discretized Chern-Simons gauge theory A necessary and sufficient condition for
Kai Sun University of Michigan, Ann Arbor Collaborators: Krishna Kumar and Eduardo Fradkin (UIUC) Outline How to construct a discretized Chern-Simons gauge theory A necessary and sufficient condition for
9 Quantum Field Theory for Children
 101 9 Quantum Field Theory for Children The theories (known and hypothetical) needed to describe the (very) early universe are quantum field theories (QFT). The fundamental entities of these theories are
101 9 Quantum Field Theory for Children The theories (known and hypothetical) needed to describe the (very) early universe are quantum field theories (QFT). The fundamental entities of these theories are
Graphite, graphene and relativistic electrons
 Graphite, graphene and relativistic electrons Introduction Physics of E. graphene Y. Andrei Experiments Rutgers University Transport electric field effect Quantum Hall Effect chiral fermions STM Dirac
Graphite, graphene and relativistic electrons Introduction Physics of E. graphene Y. Andrei Experiments Rutgers University Transport electric field effect Quantum Hall Effect chiral fermions STM Dirac
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 1 Jun 2017
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 1 Jun 2017 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 1 Jun 2017](/thumbs/94/121725176.jpg) Symmetric-Gapped Surface States of Fractional Topological Insulators arxiv:1706.0049v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 1 Jun 017 Gil Young Cho, 1, Jeffrey C. Y. Teo, 3 and Eduardo Fradkin 4 1 School of Physics, Korea
Symmetric-Gapped Surface States of Fractional Topological Insulators arxiv:1706.0049v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 1 Jun 017 Gil Young Cho, 1, Jeffrey C. Y. Teo, 3 and Eduardo Fradkin 4 1 School of Physics, Korea
Cenke Xu. Quantum Phase Transitions between Bosonic Symmetry Protected Topological States without sign problem 许岑珂
 Quantum Phase Transitions between Bosonic Symmetry Protected Topological States without sign problem Cenke Xu 许岑珂 University of California, Santa Barbara Quantum Phase Transitions between bosonic Symmetry
Quantum Phase Transitions between Bosonic Symmetry Protected Topological States without sign problem Cenke Xu 许岑珂 University of California, Santa Barbara Quantum Phase Transitions between bosonic Symmetry
Quantum Hall Effect in Graphene p-n Junctions
 Quantum Hall Effect in Graphene p-n Junctions Dima Abanin (MIT) Collaboration: Leonid Levitov, Patrick Lee, Harvard and Columbia groups UIUC January 14, 2008 Electron transport in graphene monolayer New
Quantum Hall Effect in Graphene p-n Junctions Dima Abanin (MIT) Collaboration: Leonid Levitov, Patrick Lee, Harvard and Columbia groups UIUC January 14, 2008 Electron transport in graphene monolayer New
Strongly correlated Cooper pair insulators and superfluids
 Strongly correlated Cooper pair insulators and superfluids Predrag Nikolić George Mason University Acknowledgments Collaborators Subir Sachdev Eun-Gook Moon Anton Burkov Arun Paramekanti Affiliations and
Strongly correlated Cooper pair insulators and superfluids Predrag Nikolić George Mason University Acknowledgments Collaborators Subir Sachdev Eun-Gook Moon Anton Burkov Arun Paramekanti Affiliations and
Fermi liquids and fractional statistics in one dimension
 UiO, 26. april 2017 Fermi liquids and fractional statistics in one dimension Jon Magne Leinaas Department of Physics University of Oslo JML Phys. Rev. B (April, 2017) Related publications: M Horsdal, M
UiO, 26. april 2017 Fermi liquids and fractional statistics in one dimension Jon Magne Leinaas Department of Physics University of Oslo JML Phys. Rev. B (April, 2017) Related publications: M Horsdal, M
Symmetries in Quantum Transport : From Random Matrix Theory to Topological Insulators. Philippe Jacquod. U of Arizona
 Symmetries in Quantum Transport : From Random Matrix Theory to Topological Insulators Philippe Jacquod U of Arizona UA Phys colloquium - feb 1, 2013 Continuous symmetries and conservation laws Noether
Symmetries in Quantum Transport : From Random Matrix Theory to Topological Insulators Philippe Jacquod U of Arizona UA Phys colloquium - feb 1, 2013 Continuous symmetries and conservation laws Noether
Symmetric Surfaces of Topological Superconductor
 Symmetric Surfaces of Topological Superconductor Sharmistha Sahoo Zhao Zhang Jeffrey Teo Outline Introduction Brief description of time reversal symmetric topological superconductor. Coupled wire model
Symmetric Surfaces of Topological Superconductor Sharmistha Sahoo Zhao Zhang Jeffrey Teo Outline Introduction Brief description of time reversal symmetric topological superconductor. Coupled wire model
Geometric responses of Quantum Hall systems
 Geometric responses of Quantum Hall systems Alexander Abanov December 14, 2015 Cologne Geometric Aspects of the Quantum Hall Effect Fractional Quantum Hall state exotic fluid Two-dimensional electron gas
Geometric responses of Quantum Hall systems Alexander Abanov December 14, 2015 Cologne Geometric Aspects of the Quantum Hall Effect Fractional Quantum Hall state exotic fluid Two-dimensional electron gas
Boson Vortex duality. Abstract
 Boson Vortex duality Subir Sachdev Department of Physics, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 0238, USA and Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics, Waterloo, Ontario N2L 2Y5, Canada (Dated:
Boson Vortex duality Subir Sachdev Department of Physics, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts, 0238, USA and Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics, Waterloo, Ontario N2L 2Y5, Canada (Dated:
Fractional Quantum Hall States with Conformal Field Theories
 Fractional Quantum Hall States with Conformal Field Theories Lei Su Department of Physics, University of Chicago Abstract: Fractional quantum Hall (FQH states are topological phases with anyonic excitations
Fractional Quantum Hall States with Conformal Field Theories Lei Su Department of Physics, University of Chicago Abstract: Fractional quantum Hall (FQH states are topological phases with anyonic excitations
Non-Abelian Anyons in the Quantum Hall Effect
 Non-Abelian Anyons in the Quantum Hall Effect Andrea Cappelli (INFN and Physics Dept., Florence) with L. Georgiev (Sofia), G. Zemba (Buenos Aires), G. Viola (Florence) Outline Incompressible Hall fluids:
Non-Abelian Anyons in the Quantum Hall Effect Andrea Cappelli (INFN and Physics Dept., Florence) with L. Georgiev (Sofia), G. Zemba (Buenos Aires), G. Viola (Florence) Outline Incompressible Hall fluids:
5 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry
 Phys62.nb 63 5 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry It is impossible to have quantum Hall effect without breaking the time-reversal symmetry. xy xy. If we want xy to be invariant under, xy
Phys62.nb 63 5 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry It is impossible to have quantum Hall effect without breaking the time-reversal symmetry. xy xy. If we want xy to be invariant under, xy
Part 1. March 5, 2014 Quantum Hadron Physics Laboratory, RIKEN, Wako, Japan 2
 MAR 5, 2014 Part 1 March 5, 2014 Quantum Hadron Physics Laboratory, RIKEN, Wako, Japan 2 ! Examples of relativistic matter Electrons, protons, quarks inside compact stars (white dwarfs, neutron, hybrid
MAR 5, 2014 Part 1 March 5, 2014 Quantum Hadron Physics Laboratory, RIKEN, Wako, Japan 2 ! Examples of relativistic matter Electrons, protons, quarks inside compact stars (white dwarfs, neutron, hybrid
The Superfluid-Insulator transition
 The Superfluid-Insulator transition Boson Hubbard model M.P. A. Fisher, P.B. Weichmann, G. Grinstein, and D.S. Fisher, Phys. Rev. B 40, 546 (1989). Superfluid-insulator transition Ultracold 87 Rb atoms
The Superfluid-Insulator transition Boson Hubbard model M.P. A. Fisher, P.B. Weichmann, G. Grinstein, and D.S. Fisher, Phys. Rev. B 40, 546 (1989). Superfluid-insulator transition Ultracold 87 Rb atoms
Topological Quantum Computation A very basic introduction
 Topological Quantum Computation A very basic introduction Alessandra Di Pierro alessandra.dipierro@univr.it Dipartimento di Informatica Università di Verona PhD Course on Quantum Computing Part I 1 Introduction
Topological Quantum Computation A very basic introduction Alessandra Di Pierro alessandra.dipierro@univr.it Dipartimento di Informatica Università di Verona PhD Course on Quantum Computing Part I 1 Introduction
Topological insulator part I: Phenomena
 Phys60.nb 5 Topological insulator part I: Phenomena (Part II and Part III discusses how to understand a topological insluator based band-structure theory and gauge theory) (Part IV discusses more complicated
Phys60.nb 5 Topological insulator part I: Phenomena (Part II and Part III discusses how to understand a topological insluator based band-structure theory and gauge theory) (Part IV discusses more complicated
Bosonic Symmetry Protected Topological States: Theory, Numerics, And Experimental Platform. Zhen Bi University of California, Santa Barbara
 Bosonic Symmetry Protected Topological States: Theory, Numerics, And Experimental Platform Zhen Bi University of California, Santa Barbara Acknowledgements Collaborators from UCSB: Cenke Xu, Leon Balents,
Bosonic Symmetry Protected Topological States: Theory, Numerics, And Experimental Platform Zhen Bi University of California, Santa Barbara Acknowledgements Collaborators from UCSB: Cenke Xu, Leon Balents,
Deconfined Quantum Critical Points
 Deconfined Quantum Critical Points Leon Balents T. Senthil, MIT A. Vishwanath, UCB S. Sachdev, Yale M.P.A. Fisher, UCSB Outline Introduction: what is a DQCP Disordered and VBS ground states and gauge theory
Deconfined Quantum Critical Points Leon Balents T. Senthil, MIT A. Vishwanath, UCB S. Sachdev, Yale M.P.A. Fisher, UCSB Outline Introduction: what is a DQCP Disordered and VBS ground states and gauge theory
Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry
 Phys620.nb 101 7 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry Q: Can we get a topological insulator that preserves the time-reversal symmetry? A: Yes, with the help of the spin degree of freedom.
Phys620.nb 101 7 Topological insulator with time-reversal symmetry Q: Can we get a topological insulator that preserves the time-reversal symmetry? A: Yes, with the help of the spin degree of freedom.
Introduction to particle physics Lecture 6
 Introduction to particle physics Lecture 6 Frank Krauss IPPP Durham U Durham, Epiphany term 2009 Outline 1 Fermi s theory, once more 2 From effective to full theory: Weak gauge bosons 3 Massive gauge bosons:
Introduction to particle physics Lecture 6 Frank Krauss IPPP Durham U Durham, Epiphany term 2009 Outline 1 Fermi s theory, once more 2 From effective to full theory: Weak gauge bosons 3 Massive gauge bosons:
Topological insulators. Pavel Buividovich (Regensburg)
 Topological insulators Pavel Buividovich (Regensburg) Hall effect Classical treatment Dissipative motion for point-like particles (Drude theory) Steady motion Classical Hall effect Cyclotron frequency
Topological insulators Pavel Buividovich (Regensburg) Hall effect Classical treatment Dissipative motion for point-like particles (Drude theory) Steady motion Classical Hall effect Cyclotron frequency
J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2)
 Part I - Mechanics J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2) J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2) s α l θ g z x A uniform rod of length l and mass m moves in the x-z plane. One end of the rod is suspended from a straight
Part I - Mechanics J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2) J10M.1 - Rod on a Rail (M93M.2) s α l θ g z x A uniform rod of length l and mass m moves in the x-z plane. One end of the rod is suspended from a straight
Topological insulator part II: Berry Phase and Topological index
 Phys60.nb 11 3 Topological insulator part II: Berry Phase and Topological index 3.1. Last chapter Topological insulator: an insulator in the bulk and a metal near the boundary (surface or edge) Quantum
Phys60.nb 11 3 Topological insulator part II: Berry Phase and Topological index 3.1. Last chapter Topological insulator: an insulator in the bulk and a metal near the boundary (surface or edge) Quantum
Fermi liquid & Non- Fermi liquids. Sung- Sik Lee McMaster University Perimeter Ins>tute
 Fermi liquid & Non- Fermi liquids Sung- Sik Lee McMaster University Perimeter Ins>tute Goal of many- body physics : to extract a small set of useful informa>on out of a large number of degrees of freedom
Fermi liquid & Non- Fermi liquids Sung- Sik Lee McMaster University Perimeter Ins>tute Goal of many- body physics : to extract a small set of useful informa>on out of a large number of degrees of freedom
Classification of Symmetry Protected Topological Phases in Interacting Systems
 Classification of Symmetry Protected Topological Phases in Interacting Systems Zhengcheng Gu (PI) Collaborators: Prof. Xiao-Gang ang Wen (PI/ PI/MIT) Prof. M. Levin (U. of Chicago) Dr. Xie Chen(UC Berkeley)
Classification of Symmetry Protected Topological Phases in Interacting Systems Zhengcheng Gu (PI) Collaborators: Prof. Xiao-Gang ang Wen (PI/ PI/MIT) Prof. M. Levin (U. of Chicago) Dr. Xie Chen(UC Berkeley)
Building Frac-onal Topological Insulators. Collaborators: Michael Levin Maciej Kosh- Janusz Ady Stern
 Building Frac-onal Topological Insulators Collaborators: Michael Levin Maciej Kosh- Janusz Ady Stern The program Background: Topological insulators Frac-onaliza-on Exactly solvable Hamiltonians for frac-onal
Building Frac-onal Topological Insulators Collaborators: Michael Levin Maciej Kosh- Janusz Ady Stern The program Background: Topological insulators Frac-onaliza-on Exactly solvable Hamiltonians for frac-onal
Quantum Oscillations in Graphene in the Presence of Disorder
 WDS'9 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 97, 9. ISBN 978-8-778-- MATFYZPRESS Quantum Oscillations in Graphene in the Presence of Disorder D. Iablonskyi Taras Shevchenko National University of
WDS'9 Proceedings of Contributed Papers, Part III, 97, 9. ISBN 978-8-778-- MATFYZPRESS Quantum Oscillations in Graphene in the Presence of Disorder D. Iablonskyi Taras Shevchenko National University of
2D Electron Systems: Magneto-Transport Quantum Hall Effects
 Hauptseminar: Advanced Physics of Nanosystems 2D Electron Systems: Magneto-Transport Quantum Hall Effects Steffen Sedlak The Hall Effect P.Y. Yu,, M.Cardona, Fundamentals of Semiconductors, Springer Verlag,
Hauptseminar: Advanced Physics of Nanosystems 2D Electron Systems: Magneto-Transport Quantum Hall Effects Steffen Sedlak The Hall Effect P.Y. Yu,, M.Cardona, Fundamentals of Semiconductors, Springer Verlag,
Detecting collective excitations of quantum spin liquids. Talk online: sachdev.physics.harvard.edu
 Detecting collective excitations of quantum spin liquids Talk online: sachdev.physics.harvard.edu arxiv:0809.0694 Yang Qi Harvard Cenke Xu Harvard Max Metlitski Harvard Ribhu Kaul Microsoft Roger Melko
Detecting collective excitations of quantum spin liquids Talk online: sachdev.physics.harvard.edu arxiv:0809.0694 Yang Qi Harvard Cenke Xu Harvard Max Metlitski Harvard Ribhu Kaul Microsoft Roger Melko
Topological Kondo Insulator SmB 6. Tetsuya Takimoto
 Topological Kondo Insulator SmB 6 J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 80 123720, (2011). Tetsuya Takimoto Department of Physics, Hanyang University Collaborator: Ki-Hoon Lee (POSTECH) Content 1. Introduction of SmB 6 in-gap
Topological Kondo Insulator SmB 6 J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 80 123720, (2011). Tetsuya Takimoto Department of Physics, Hanyang University Collaborator: Ki-Hoon Lee (POSTECH) Content 1. Introduction of SmB 6 in-gap
Topology and Fractionalization in 2D Electron Systems
 Lectures on Mesoscopic Physics and Quantum Transport, June 1, 018 Topology and Fractionalization in D Electron Systems Xin Wan Zhejiang University xinwan@zju.edu.cn Outline Two-dimensional Electron Systems
Lectures on Mesoscopic Physics and Quantum Transport, June 1, 018 Topology and Fractionalization in D Electron Systems Xin Wan Zhejiang University xinwan@zju.edu.cn Outline Two-dimensional Electron Systems
Ψ({z i }) = i<j(z i z j ) m e P i z i 2 /4, q = ± e m.
 Fractionalization of charge and statistics in graphene and related structures M. Franz University of British Columbia franz@physics.ubc.ca January 5, 2008 In collaboration with: C. Weeks, G. Rosenberg,
Fractionalization of charge and statistics in graphene and related structures M. Franz University of British Columbia franz@physics.ubc.ca January 5, 2008 In collaboration with: C. Weeks, G. Rosenberg,
Strange metal from local quantum chaos
 Strange metal from local quantum chaos John McGreevy (UCSD) hello based on work with Daniel Ben-Zion (UCSD) 2017-08-26 Compressible states of fermions at finite density The metallic states that we understand
Strange metal from local quantum chaos John McGreevy (UCSD) hello based on work with Daniel Ben-Zion (UCSD) 2017-08-26 Compressible states of fermions at finite density The metallic states that we understand
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 May 2010
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 May 2010 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 May 2010](/thumbs/81/83686509.jpg) MIT-CTP/4147 Correlated Topological Insulators and the Fractional Magnetoelectric Effect B. Swingle, M. Barkeshli, J. McGreevy, and T. Senthil Department of Physics, Massachusetts Institute of Technology,
MIT-CTP/4147 Correlated Topological Insulators and the Fractional Magnetoelectric Effect B. Swingle, M. Barkeshli, J. McGreevy, and T. Senthil Department of Physics, Massachusetts Institute of Technology,
Deconfined Quantum Critical Points
 Deconfined Quantum Critical Points Outline: with T. Senthil, Bangalore A. Vishwanath, UCB S. Sachdev, Yale L. Balents, UCSB conventional quantum critical points Landau paradigm Seeking a new paradigm -
Deconfined Quantum Critical Points Outline: with T. Senthil, Bangalore A. Vishwanath, UCB S. Sachdev, Yale L. Balents, UCSB conventional quantum critical points Landau paradigm Seeking a new paradigm -
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 Jul 2011
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 Jul 2011 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 Jul 2011](/thumbs/71/65754027.jpg) Phase Diagram of the Kane-Mele-Hubbard model arxiv:1107.145v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 Jul 011 Christian Griset 1 and Cenke Xu 1 1 Department of Physics, University of California, Santa Barbara, CA 93106 (Dated:
Phase Diagram of the Kane-Mele-Hubbard model arxiv:1107.145v1 [cond-mat.str-el] 6 Jul 011 Christian Griset 1 and Cenke Xu 1 1 Department of Physics, University of California, Santa Barbara, CA 93106 (Dated:
Fractional Charge. Particles with charge e/3 and e/5 have been observed experimentally......and they re not quarks.
 Fractional Charge Particles with charge e/3 and e/5 have been observed experimentally......and they re not quarks. 1 Outline: 1. What is fractional charge? 2. Observing fractional charge in the fractional
Fractional Charge Particles with charge e/3 and e/5 have been observed experimentally......and they re not quarks. 1 Outline: 1. What is fractional charge? 2. Observing fractional charge in the fractional
Generalized Global Symmetries
 Generalized Global Symmetries Anton Kapustin Simons Center for Geometry and Physics, Stony Brook April 9, 2015 Anton Kapustin (Simons Center for Geometry and Physics, Generalized StonyGlobal Brook) Symmetries
Generalized Global Symmetries Anton Kapustin Simons Center for Geometry and Physics, Stony Brook April 9, 2015 Anton Kapustin (Simons Center for Geometry and Physics, Generalized StonyGlobal Brook) Symmetries
The underdoped cuprates as fractionalized Fermi liquids (FL*)
 The underdoped cuprates as fractionalized Fermi liquids (FL*) R. K. Kaul, A. Kolezhuk, M. Levin, S. Sachdev, and T. Senthil, Physical Review B 75, 235122 (2007) R. K. Kaul, Y. B. Kim, S. Sachdev, and T.
The underdoped cuprates as fractionalized Fermi liquids (FL*) R. K. Kaul, A. Kolezhuk, M. Levin, S. Sachdev, and T. Senthil, Physical Review B 75, 235122 (2007) R. K. Kaul, Y. B. Kim, S. Sachdev, and T.
Topological Insulators
 Topological Insulators Aira Furusai (Condensed Matter Theory Lab.) = topological insulators (3d and 2d) Outline Introduction: band theory Example of topological insulators: integer quantum Hall effect
Topological Insulators Aira Furusai (Condensed Matter Theory Lab.) = topological insulators (3d and 2d) Outline Introduction: band theory Example of topological insulators: integer quantum Hall effect
Entanglement Chern numbers for random systems
 POSTECH, Korea, July 31 (2015) Ψ = 1 D D Entanglement Chern numbers for random systems j Ψ j Ψj Yasuhiro Hatsugai Institute of Physics, Univ. of Tsukuba Ref: T. Fukui & Y. Hatsugai, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.
POSTECH, Korea, July 31 (2015) Ψ = 1 D D Entanglement Chern numbers for random systems j Ψ j Ψj Yasuhiro Hatsugai Institute of Physics, Univ. of Tsukuba Ref: T. Fukui & Y. Hatsugai, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.
2. Spin liquids and valence bond solids
 Outline 1. Coupled dimer antiferromagnets Landau-Ginzburg quantum criticality 2. Spin liquids and valence bond solids (a) Schwinger-boson mean-field theory - square lattice (b) Gauge theories of perturbative
Outline 1. Coupled dimer antiferromagnets Landau-Ginzburg quantum criticality 2. Spin liquids and valence bond solids (a) Schwinger-boson mean-field theory - square lattice (b) Gauge theories of perturbative
