Heavy ion fusion energy program in Russia
|
|
|
- Merilyn Leslie Poole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 464 (2001) 1 5 Heavy ion fusion energy program in Russia B.Yu. Sharkov*, N.N. Alexeev, M.D. Churazov, A.A. Golubev, D.G. Koshkarev, P.R. Zenkevich Institute for Theoretical and Experimental Physics, Cheremushkinskaya 25, Moscow, Russia Abstract An overview of the activities in progress of the Russian Heavy-Ion Fusion Energy community is given for the period since the last Symposium in Heidelberg in The progress in up-grading of the ITEP accelerator complex (project ITEP-TWAC), target simulations and recent results on heavy ion beam plasma interaction physics are emphasized. # 2001 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved. PACS: Keywords: Inertial fusion; Heavy ions; Accelerator; Beam plasma interaction 1. Introduction There are numerous important changes in the development of Heavy-Ion Fusion energy (HIFE) program in Russia in the last two years. Scientific Council of Minatom of Russian Federation has approved the activities on HIFE and gave the green signal to the funding of the ITEP-TWAC project for period Structural stability for collaboration of the main participants ITEP- Moscow and VNIIEF-Sarovare given by two big projects: * Up-grading of ITEP accelerator complex (project ITEP-TWAC), funded by Minatom RF, and * Project # 1137 funded by ISTC. Scientific groups and individuals from about 10 institutions are involved in activities on HIFE. *Corresponding author. address: sharkov@vitep5.itep.ru (B.Yu. Sharkov). Overall funding of activities was doubled in 1999 compared to 1998 and was increased by a factor 1.5 in The list of key issues of the Russian HIFE program includes: * numerical simulations related to the HIFE target design, * heavy ion accelerator physics, * theoretical and experimental investigations of the state of matter under extreme conditions, * experimental and theoretical study on beam plasma interaction. 2. TeraWatt accumulator project A significant part of the activities of Russian HIFE community concentrates on the TeraWatt Accumulator project (ITEP-TWAC) in progress in ITEP-Moscow now. The goal of the project is to take advantage of existing accelerator facility based on two heavy ion synchrotron rings for /01/$ - see front matter # 2001 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved. PII: S (00)01319-X
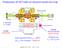
2 2 B.Yu. Sharkov et al. / Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 464 (2001) 1 5 high current HIFE related experiments. Non- Liouvillian stripping technique [1] is applied for stacking of many pulses accelerated in synchrotron UK into the storage ring U-10, see Fig. 1. Full stripping of He-like medium atomic mass ions is used to provide high efficiency of the non- Liouvillian stacking process. The whole acceleration-accumulation scenario looks as follows. A laser ion source produces about ions, which are accelerated in the pre-injector U-3 up to 1.6 MV/u, then injected into the 13 Tm booster ring UK (see Fig. 1). After acceleration up to 0.7 GeV/u, a 250 ns long bunch is injected in a single turn mode to the synchrotron ring U-10 using a non-liovillian stripping process. The charge state of the ions changes from He-like (two electrons of the inner atomic K-shell remain) to fully stripped by passing through a solid foil of about 5 mg/cm 2. The stripped beam is accepted by the synchrotron U-10, which serves as a storage ring, while no further acceleration is provided. To minimize the effect of the stripping foil, the accumulated beam circulating in the storage ring is directed on the stripper target only during the injection cycle of the next ion beam pulse coming from the UK booster. For this purpose a kickersystem for the beam, based on two fast coherent deflectors is foreseen. Since the cross-section of the accumulated beam is at least 25 times larger than the surface-area of the stripper target, the beam quality is expected not to deteriorate significantly by the scattering in the foil. Repeating this process several hundred times provides accumulation in the coasting beam until the Laslett space-charge limit ( 0.16) is reached in the synchrotron ring. A rapid switch on the RF in the synchrotron ring causes ballistic compression of the accumulated bunch from a length of 1000 ns down to 100 ns. Fig. 1. Lay-out of the ITEP TeraWatt Accumulator facility.
3 B.Yu. Sharkov et al. / Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 464 (2001) Fig. 2. Scheme of the RF rotational target illumination system. After compression, the bunch is extracted, transported and focused onto the target. The beam emittance of 5 cm mrad enables focusing down to a spot-size of 1 mm in diameter. The status of construction and commissioning of key elements of the accelerator facility at the beginning of March 2000 looks as follows: 1. Laser ion source, based on 5 J/0.5 Hz TEA CO 2 -laser, has been set in operation and installed in U3 pre-injector area. The 20 ma/ 20 ms Carbon ion beam was matched to the 2 MV/2.5 MHz U3preinjector. 2. The accelerated beam of 16 MeV C 4+ ions is guided by the beam transport line up to UK ring and injected. Intensity measured at injection point is /15 ms. Circulation of the C 4+ beam in UK ring at constant B field is obtained. 3. Magnetic components of the beam-transfer line connecting UK and U-10 rings, as well as of the multi-turn injection system have been manufactured and are in the process of installation and adjustment. 4. Powerful CO 2 -laser with output parameters 100 J/20 ns and rep-rate of 1 Hz is under construction now. 5. Beam transport line for the extracted beam to the beam-target interaction area is under design. 6. Up-grading of RF, vacuum and power supplies systems of both the synchrotron rings are in progress. 7. Pre-commissioning of the TWAC accelerator facility with demonstration of multi-turn stacking procedure for C 6+ ions is scheduled for December The expected output parameters of the ITEP- TWAC facility [1] give strong motivation for numerical simulations of forthcoming experiments on intense heavy ion beam plasma interaction related to the physics of HIF targets. The most promising appears to be the cylindrical geometry of the energy deposition region, inherent for TWAC beams. A multi-d, three temperature hydrodynamic Eulerian code has been developed for this purpose in ITEP [2]. It includes radiation transport and electron heat conductivity in diffusion approximation. Nuclear reactions and diffusion of charged particles are taken into account. This code is suitable for simulations of cylindrical conversion of multi-layers directly driven HIF targets with magnetized fuel. Capabilities of the code enable to follow the R T instability and mixing of the layers. A hollow beam combined with a hollow cylindrical target can provide extremely high densities and pressures on the axis of converging cylinder [3]. For performance of this kind of experiments a special RF system providing fast rotation of the TWAC beam is suggested in Fig. 2. Such a system can produce homogeneous irradiation of directly driven cylindrical layer. 3. Accelerator physics issues In the theoretical studies of accelerator physics emphasis is laid on the optimization of accumulation process in storage rings by using charge
4 4 B.Yu. Sharkov et al. / Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 464 (2001) 1 5 exchange injection and the electron cooling. Gaussian beam method and Monte-Carlo code have been employed for the beam evolution analysis in course of accumulation process. The Intra-Beam Scattering (IBS) has been found to be the main source for limitation of the phase space density of the accumulated beam. The IBS, leading to the energy transfer from the transverse plane to the longitudinal one, accompanied by random interaction of the beam with the stripping foil can result in considerable ion losses and in increase of the final momentum spread. Both mechanisms prevent the high final compression rate of the beam. Two ways to suppress the influence of these negative processes are suggested. One is to reduce the injection time by increasing the intensity and the rep-rate of the injected beam. The other is the implementation of the electron cooling which can give significant enhancement of the beam specific power and therefore of the plasma temperature of the irradiated target. Optimization of the accumulation scenario for 27 Al +13 shows the plasma temperature reaches saturation after ca.150 injection cycles for slow injection (10 10 ions per injection cycle) and cycles for fast injection (10 11 ions). Analysis of the coherent effects [4] has shown, that the most important is the transverse instability, induced due to the beam interaction with environment and with electrons, appearing by ionization of residual gas. For ion beam with small momentum spread required for beam compression, special broadband damping system suppressing the dipole instabilities is necessary. 4. Heavy ion beam plasma interaction physics Studies of the beam plasma interaction physics have been continued within the framework of wide international collaboration. Motivation for these activities is given by the necessity of precise matching of the geometric parameters of the low Z converter of an HIF target to the beam energy deposition profile. The effects governing the physical stopping length in matter have been studied in numerical simulations and in related experiments. Numerical simulations for nuclear fragmentation of different ion species in wide range of ion energies (from 100 MeV/u to 1 GeV/u) were carried out. The results show this effect can be neglected for ion energy less than 100 MeV/n. But for higher energies, up to several percent of the total beam energy can be deposited outside the fiducial converter layer. Influence of the energy straggling induced by finite Dp=p: of the 50 MeV/n ion beam in Be target as well as of the stochastic straggling of Coulomb collisions was investigated numerically by means of SRIM [5] and SIDEST codes [6]. In order to verify the results of numerical simulations a number of experiments have been performed by using the existing low intensity accelerators in combination with plasma targets. For this purpose carbon, krypton and lead ion beams from UNILAC in GSI are used for systematic study of charge dependent stopping of ions in capillary plasma target [7]. Explosively driven plasma target [8] has been tested with 3 MeV proton beam at ITEP experimental area with respect to the forthcoming experiments on ion stopping in non-ideal plasma. 5. Conclusions Russian HIFE program comprises theoretical and experimental activities on HIF targets design, study of accelerator-driver issues, beam plasma interaction and basics of high energy density in matter generated by intense heavy ion beams. * The essential part of the activity of Russian HIFE community is the TWAC project in progress in ITEP-Moscow now. Pre-commissioning of the key elements of the accelerator facility and demonstration of the beam gymnastics is scheduled for the end of * Significant results have been obtained in numerical simulations of the state of matter under extreme conditions generated by heavy ion beams with parameters corresponding to those expected from the ITEP-TWAC facility. Detectable level of the neutron yield is predicted in course of cylindrical compression.
5 B.Yu. Sharkov et al. / Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 464 (2001) * Important step forward has been achieved in numerical investigations of the beam dynamics, in particular, for ITEP-TWAC accumulator ring. * New experimental results on ion stopping in capillary plasma target and in explosively driven shock compressed plasma have been obtained. Acknowledgements This work was supported by Minatom of Russian Federation, by ISTC grant #1137, by RFBR grant # (17b). References [1] B.Yu. Sharkovet al., Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A 415 (1998) 20. [2] A. Aksenov, M. Churazov, 13 HIF symposium, San Diego, [3] M.D. Churazovet al., Fusion Eng. Design (1996) 615. [4] P. Zenkevich, AIP Conference Proceedings, Vol. 480, Woodbury, New York, 1998, p. 74. [5] SRIM-code, htm#srim. [6] M. Dornik, Ph.D. Dissertation, TH Darmstadt, Germany, [7] A. Golubevet al., Phys. Rev. E 27 (3) (1998) [8] V. Mintsevet al., Nucl. Instr. and Meth. A 415 (1998) 715.
Multi-Purpose Accelerator-Accumulator ITEP-TWAC for Nuclear Physics and Practical Applications
 Multi-Purpose Accelerator-Accumulator ITEP-TWAC for Nuclear Physics and Practical Applications N.N.Alexeev, D.G.Koshkarev and B.Yu.Sharkov Institute for Theoretical and Experimental Physics, B.Cheremushk.
Multi-Purpose Accelerator-Accumulator ITEP-TWAC for Nuclear Physics and Practical Applications N.N.Alexeev, D.G.Koshkarev and B.Yu.Sharkov Institute for Theoretical and Experimental Physics, B.Cheremushk.
SIMULATION STUDY FOR MEIC ELECTRON COOLING*
 SIMULATION STUDY FOR MEIC ELECTRON COOLING* He Zhang #, Yuhong Zhang, JLab, Newport News, VA 23606, USA Abstract Electron cooling of the ion beams is one critical R&D to achieve high luminosities in JLab
SIMULATION STUDY FOR MEIC ELECTRON COOLING* He Zhang #, Yuhong Zhang, JLab, Newport News, VA 23606, USA Abstract Electron cooling of the ion beams is one critical R&D to achieve high luminosities in JLab
Application of Proton Radiography to High Energy Density Research
 Application of Proton Radiography to High Energy Density Research S.A. Kolesnikov*, S.V. Dudin, V.B. Mintsev, A.V. Shutov, A.V. Utkin, V.E. Fortov IPCP RAS, Chernogolovka, Russia A.A. Golubev, V.S. Demidov,
Application of Proton Radiography to High Energy Density Research S.A. Kolesnikov*, S.V. Dudin, V.B. Mintsev, A.V. Shutov, A.V. Utkin, V.E. Fortov IPCP RAS, Chernogolovka, Russia A.A. Golubev, V.S. Demidov,
Statusreport. Status of the GSI accelerators for FRS operation. Jens Stadlmann (FAIR Synchrotrons)
 Statusreport Status of the GSI accelerators for FRS operation Jens Stadlmann (FAIR Synchrotrons) Overview Intensities reached and "candidates" for experiments. Uranium? Upgrade program New developments:
Statusreport Status of the GSI accelerators for FRS operation Jens Stadlmann (FAIR Synchrotrons) Overview Intensities reached and "candidates" for experiments. Uranium? Upgrade program New developments:
Optimization of the SIS100 Lattice and a Dedicated Collimation System for Ionisation Losses
 Optimization of the SIS100 Lattice and a Dedicated Collimation System for Ionisation Losses P. Spiller, K. Blasche, B. Franczak, J. Stadlmann, and C. Omet GSI Darmstadt, D-64291 Darmstadt, Germany Abstract:
Optimization of the SIS100 Lattice and a Dedicated Collimation System for Ionisation Losses P. Spiller, K. Blasche, B. Franczak, J. Stadlmann, and C. Omet GSI Darmstadt, D-64291 Darmstadt, Germany Abstract:
Proposal to convert TLS Booster for hadron accelerator
 Proposal to convert TLS Booster for hadron accelerator S.Y. Lee -- Department of Physics IU, Bloomington, IN -- NSRRC Basic design TLS is made of a 50 MeV electron linac, a booster from 50 MeV to 1.5 GeV,
Proposal to convert TLS Booster for hadron accelerator S.Y. Lee -- Department of Physics IU, Bloomington, IN -- NSRRC Basic design TLS is made of a 50 MeV electron linac, a booster from 50 MeV to 1.5 GeV,
STORAGE RINGS FOR RADIO-ISOTOPE BEAMS
 STORAGE RINGS FOR RADIO-ISOTOPE BEAMS Takeshi Katayama, Center for Nuclear Study, University of Tokyo, Wako, Japan INTRODUCTION In this decade, new era is opened in nuclear physics with use of radioactive
STORAGE RINGS FOR RADIO-ISOTOPE BEAMS Takeshi Katayama, Center for Nuclear Study, University of Tokyo, Wako, Japan INTRODUCTION In this decade, new era is opened in nuclear physics with use of radioactive
ELIC: A High Luminosity And Efficient Spin Manipulation Electron-Light Ion Collider Based At CEBAF
 ELIC: A High Luminosity And Efficient Spin Manipulation Electron-Light Ion Collider Based At CEBAF Lia Merminga and Yaroslav Derbenev Center for Advanced Studies of Accelerators, Jefferson Laboratory,
ELIC: A High Luminosity And Efficient Spin Manipulation Electron-Light Ion Collider Based At CEBAF Lia Merminga and Yaroslav Derbenev Center for Advanced Studies of Accelerators, Jefferson Laboratory,
THE GSI FUTURE PROJECT: AN INTERNATIONAL ACCELERATOR FACILITY FOR BEAMS OF IONS AND ANTIPROTONS
 THE GSI FUTURE PROJECT: AN INTERNATIONAL ACCELERATOR FACILITY FOR BEAMS OF IONS AND ANTIPROTONS Ina Pschorn Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung mbh, D-64291 Darmstadt, Germany 1. INTRODUCTION The GSI
THE GSI FUTURE PROJECT: AN INTERNATIONAL ACCELERATOR FACILITY FOR BEAMS OF IONS AND ANTIPROTONS Ina Pschorn Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung mbh, D-64291 Darmstadt, Germany 1. INTRODUCTION The GSI
OVERVIEW OF THE HEAVY ION FUSION PROGRAM *
 OVERVIEW OF THE HEAVY ION FUSION PROGRAM * C.M. Celata, Ernest Orlando Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA 94720, USA for the U.S. Virtual National Laboratory for Heavy Ion Fusion Abstract
OVERVIEW OF THE HEAVY ION FUSION PROGRAM * C.M. Celata, Ernest Orlando Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Berkeley, CA 94720, USA for the U.S. Virtual National Laboratory for Heavy Ion Fusion Abstract
BEAM COOLING AT NICA COLLIDER
 BEAM COOLING AT NICA COLLIDER T. Katayama, GSI, Darmstadt, Germany I. Meshkov, A. Sidorin and G. Trubnikov, JINR, Dubna, Russia. Abstract At the heavy ion collider NICA presently promoted at the JINR,
BEAM COOLING AT NICA COLLIDER T. Katayama, GSI, Darmstadt, Germany I. Meshkov, A. Sidorin and G. Trubnikov, JINR, Dubna, Russia. Abstract At the heavy ion collider NICA presently promoted at the JINR,
A Project to convert TLS Booster to hadron accelerator 1. Basic design. 2. The injection systems:
 A Project to convert TLS Booster to hadron accelerator 1. Basic design TLS is made of a 50 MeV electron linac, a booster from 50 MeV to 1.5 GeV, and a storage ring. The TLS storage ring is currently operating
A Project to convert TLS Booster to hadron accelerator 1. Basic design TLS is made of a 50 MeV electron linac, a booster from 50 MeV to 1.5 GeV, and a storage ring. The TLS storage ring is currently operating
THE SUPER-FRS PROJECT AT GSI
 THE SUPER-FRS PROJECT AT GSI M. Winkler 1,2, H. Geissel 2,1,, G. Münzenberg 2, V. Shiskine 2, H. Weick 2, H. Wollnik 1, M. Yavor 3 1 University of Giessen, Germany, 2 GSI, Germany, 3 Institute for Analytical
THE SUPER-FRS PROJECT AT GSI M. Winkler 1,2, H. Geissel 2,1,, G. Münzenberg 2, V. Shiskine 2, H. Weick 2, H. Wollnik 1, M. Yavor 3 1 University of Giessen, Germany, 2 GSI, Germany, 3 Institute for Analytical
FAIR AT GSI. P. Spiller, GSI, Darmstadt, Germany
 FAIR AT GSI P. Spiller, GSI, Darmstadt, Germany Abstract Based on the experience of the existing GSI facility and with the aim to apply new technical concepts in phase space cooling and fast ramping of
FAIR AT GSI P. Spiller, GSI, Darmstadt, Germany Abstract Based on the experience of the existing GSI facility and with the aim to apply new technical concepts in phase space cooling and fast ramping of
Theory of electron cooling
 Theory of electron cooling Daria Astapovych 03/12/2014 HSC Meeting Outline Motivation and idea of the particle beam cooling Cooler Low energy, high energy beam Electron beam Kinetics of electron cooling
Theory of electron cooling Daria Astapovych 03/12/2014 HSC Meeting Outline Motivation and idea of the particle beam cooling Cooler Low energy, high energy beam Electron beam Kinetics of electron cooling
Longitudinal stacking and electron cooling of ion beams in the ESR as a proof of principle for FAIR. C. Dimopoulou
 Longitudinal stacking and electron cooling of ion beams in the ESR as a proof of principle for FAIR C. Dimopoulou B. Franzke, T. Katayama, D. Möhl, G. Schreiber, M. Steck DESY Seminar, 20 November 2007
Longitudinal stacking and electron cooling of ion beams in the ESR as a proof of principle for FAIR C. Dimopoulou B. Franzke, T. Katayama, D. Möhl, G. Schreiber, M. Steck DESY Seminar, 20 November 2007
ELECTRON COOLING EXPERIMENTS AT S-LSR
 ELECTRON COOLING EXPERIMENTS AT S-LSR T. Shirai #, S. Fujimoto, M. Ikegami, H. Tongu, M. Tanabe, H. Souda, A. Noda ICR, Kyoto-U, Uji, Kyoto, Japan, K. Noda, NIRS, Anagawa, Inage, Chiba, Japan, T. Fujimoto,
ELECTRON COOLING EXPERIMENTS AT S-LSR T. Shirai #, S. Fujimoto, M. Ikegami, H. Tongu, M. Tanabe, H. Souda, A. Noda ICR, Kyoto-U, Uji, Kyoto, Japan, K. Noda, NIRS, Anagawa, Inage, Chiba, Japan, T. Fujimoto,
Beam Diagnostics and Instrumentation JUAS, Archamps Peter Forck Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschnung (GSI)
 Beam Diagnostics and Instrumentation JUAS, Archamps Peter Forck Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschnung (GSI), 2003, A dedicated proton accelerator for 1p-physics at the future GSI Demands facilities for
Beam Diagnostics and Instrumentation JUAS, Archamps Peter Forck Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschnung (GSI), 2003, A dedicated proton accelerator for 1p-physics at the future GSI Demands facilities for
Feasibility Studies for the EXL Project at FAIR *
 * a,b,, S. Bagchi c, S. Diebold d, C. Dimopoulou a, P. Egelhof a, V. Eremin e, S. Ilieva a, N. Kalantar-Nayestanaki c, O. Kiselev a,f, T. Kröll f, Y.A. Litvinov a,g, M. Mutterer a, M.A. Najafi c, N. Petridis
* a,b,, S. Bagchi c, S. Diebold d, C. Dimopoulou a, P. Egelhof a, V. Eremin e, S. Ilieva a, N. Kalantar-Nayestanaki c, O. Kiselev a,f, T. Kröll f, Y.A. Litvinov a,g, M. Mutterer a, M.A. Najafi c, N. Petridis
Run2 Problem List (Bold-faced items are those the BP Department can work on) October 4, 2002
 Run2 Problem List (Bold-faced items are those the BP Department can work on) October 4, 2002 Linac Booster o 4.5-4.8e12 ppp at 0.5 Hz o Space charge (30% loss in the first 5 ms) o Main magnet field quality
Run2 Problem List (Bold-faced items are those the BP Department can work on) October 4, 2002 Linac Booster o 4.5-4.8e12 ppp at 0.5 Hz o Space charge (30% loss in the first 5 ms) o Main magnet field quality
D-D FUSION NEUTRONS FROM A STRONG SPHERICAL SHOCK WAVE FOCUSED ON A DEUTERIUM BUBBLE IN WATER. Dr. Michel Laberge General Fusion Inc.
 D-D FUSION NEUTRONS FROM A STRONG SPHERICAL SHOCK WAVE FOCUSED ON A DEUTERIUM BUBBLE IN WATER Dr. Michel Laberge General Fusion Inc. SONOFUSION Sonofusion is making some noise A bit short in energy, ~mj
D-D FUSION NEUTRONS FROM A STRONG SPHERICAL SHOCK WAVE FOCUSED ON A DEUTERIUM BUBBLE IN WATER Dr. Michel Laberge General Fusion Inc. SONOFUSION Sonofusion is making some noise A bit short in energy, ~mj
ACCELERATION, DECELERATION AND BUNCHING OF STORED AND COOLED ION BEAMS AT THE TSR, HEIDELBERG
 ACCELERATION, DECELERATION AND BUNCHING OF STORED AND COOLED ION BEAMS AT THE TSR, HEIDELBERG M. Grieser, R. Bastert, K. Blaum, H. Buhr, R. von Hahn, M. B. Mendes, R. Repnow, A. Wolf Max-Planck-Institut
ACCELERATION, DECELERATION AND BUNCHING OF STORED AND COOLED ION BEAMS AT THE TSR, HEIDELBERG M. Grieser, R. Bastert, K. Blaum, H. Buhr, R. von Hahn, M. B. Mendes, R. Repnow, A. Wolf Max-Planck-Institut
HIGH-ENERGY HEAVY-ION ACCELERATORS
 HIGH-ENERGY HEAVY-ION ACCELERATORS D. DINEV Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Institute for Nuclear Research and Nuclear Energy Why heavy ions accelerated to high energies? QCD phase diagram (Artist s view)
HIGH-ENERGY HEAVY-ION ACCELERATORS D. DINEV Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Institute for Nuclear Research and Nuclear Energy Why heavy ions accelerated to high energies? QCD phase diagram (Artist s view)
High Energy Density Physics related to Inertial Fusion with Intense Ion and Laser Beams at GSI and FAIR in Darmstadt
 High Energy Density Physics related to Inertial Fusion with Intense Ion and Laser Beams at GSI and FAIR in Darmstadt Dieter H.H. Hoffmann Radiation- and Nuclear Physics Technical University Darmstadt HEDgeHOB
High Energy Density Physics related to Inertial Fusion with Intense Ion and Laser Beams at GSI and FAIR in Darmstadt Dieter H.H. Hoffmann Radiation- and Nuclear Physics Technical University Darmstadt HEDgeHOB
ACCELERATOR TECHNOLOGIES DEVELOPMENT AT ITEP
 ACCELERATOR TECHNOLOGIES DEVELOPMENT AT ITEP N.N.Alexeev, V.A.Andreev, A.A.Golubev, A.A.Kolomiets, A.M.Kozodaev, T.V.Kulevoy, V.I.Nikolaev, Ju.A.Satov, V.A.Schegolev, A.V.Shumshuruv, A.B.Zarubin, ITEP,
ACCELERATOR TECHNOLOGIES DEVELOPMENT AT ITEP N.N.Alexeev, V.A.Andreev, A.A.Golubev, A.A.Kolomiets, A.M.Kozodaev, T.V.Kulevoy, V.I.Nikolaev, Ju.A.Satov, V.A.Schegolev, A.V.Shumshuruv, A.B.Zarubin, ITEP,
PoS(EPS-HEP2017)533. First Physics Results of AWAKE, a Plasma Wakefield Acceleration Experiment at CERN. Patric Muggli, Allen Caldwell
 First Physics Results of AWAKE, a Plasma Wakefield Acceleration Experiment at CERN Patric Muggli, Max Planck Institute for Physics E-mail: muggli@mpp.mpg.de AWAKE is a plasma wakefield acceleration experiment
First Physics Results of AWAKE, a Plasma Wakefield Acceleration Experiment at CERN Patric Muggli, Max Planck Institute for Physics E-mail: muggli@mpp.mpg.de AWAKE is a plasma wakefield acceleration experiment
Advanced Design of the FAIR Storage Ring Complex
 Advanced Design of the FAIR Storage Ring Complex M. Steck for the FAIR Technical Division and the Accelerator Division of GSI The FAIR Accelerator Facility SIS300 existing GSI proton linac SIS18 UNILAC
Advanced Design of the FAIR Storage Ring Complex M. Steck for the FAIR Technical Division and the Accelerator Division of GSI The FAIR Accelerator Facility SIS300 existing GSI proton linac SIS18 UNILAC
Proton-driven plasma wakefield acceleration
 Proton-driven plasma wakefield acceleration Konstantin Lotov Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia Novosibirsk State University, Novosibirsk, Russia AWAKE Collaboration Motivation
Proton-driven plasma wakefield acceleration Konstantin Lotov Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia Novosibirsk State University, Novosibirsk, Russia AWAKE Collaboration Motivation
The Luminosity Upgrade at RHIC. G. Robert-Demolaize, Brookhaven National Laboratory
 The Luminosity Upgrade at RHIC G. Robert-Demolaize, Brookhaven National Laboratory RHIC accelerator complex: IPAC'15 - May 3-8, 2015 - Richmond, VA, USA 2 The Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) aims
The Luminosity Upgrade at RHIC G. Robert-Demolaize, Brookhaven National Laboratory RHIC accelerator complex: IPAC'15 - May 3-8, 2015 - Richmond, VA, USA 2 The Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) aims
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory FACET & TEST BEAM FACILITIES PROPOSAL
 SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory FACET & TEST BEAM FACILITIES PROPOSAL Date: 6/17/13 A. EXPERIMENT TITLE: Development of Electron Radiography for Material Science B. PROPOSERS & REQUESTED FACILITY:
SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory FACET & TEST BEAM FACILITIES PROPOSAL Date: 6/17/13 A. EXPERIMENT TITLE: Development of Electron Radiography for Material Science B. PROPOSERS & REQUESTED FACILITY:
Using an Electron Cooler for Space Charge Compensation in the GSI Synchrotron SIS18 William D. Stem Oliver Boine-Frankenheim
 Using an Electron Cooler for Space Charge Compensation in the GSI Synchrotron SIS18 William D. Stem Oliver Boine-Frankenheim April 2016 TU Darmstadt Schlossgartenstraße 8 Institut Theorie Elektromagnetischer
Using an Electron Cooler for Space Charge Compensation in the GSI Synchrotron SIS18 William D. Stem Oliver Boine-Frankenheim April 2016 TU Darmstadt Schlossgartenstraße 8 Institut Theorie Elektromagnetischer
Perspectives in High Intensity Heavy Ion Sources for Future Heavy Ion Accelerators. L. Sun
 IMP Perspectives in High Intensity Heavy Ion Sources for Future Heavy Ion Accelerators L. Sun Institute of Modern Physics, CAS, 730000, Lanzhou, China IPAC 18, April 29~May 4, 2018,Vancouver, CA Preface
IMP Perspectives in High Intensity Heavy Ion Sources for Future Heavy Ion Accelerators L. Sun Institute of Modern Physics, CAS, 730000, Lanzhou, China IPAC 18, April 29~May 4, 2018,Vancouver, CA Preface
HIRFL STATUS AND HIRFL-CSR PROJECT IN LANZHOU
 HIRFL STATUS AND HIRFL-CSR PROJECT IN LANZHOU J. W. Xia, Y. F. Wang, Y. N. Rao, Y. J. Yuan, M. T. Song, W. Z. Zhang, P. Yuan, W. Gu, X. T. Yang, X. D. Yang, S. L. Liu, H.W.Zhao, J.Y.Tang, W. L. Zhan, B.
HIRFL STATUS AND HIRFL-CSR PROJECT IN LANZHOU J. W. Xia, Y. F. Wang, Y. N. Rao, Y. J. Yuan, M. T. Song, W. Z. Zhang, P. Yuan, W. Gu, X. T. Yang, X. D. Yang, S. L. Liu, H.W.Zhao, J.Y.Tang, W. L. Zhan, B.
ELECTRON COOLING EXPERIMENTS IN CSR*
 ELECTRON COOLING EXPERIMENTS IN CSR* Xiaodong Yang #, Guohong Li, Jie Li, Xiaoming Ma, Lijun Mao, Ruishi Mao, Tailai Yan, Jiancheng Yang, Youjin Yuan, IMP, Lanzhou, 730000, China Vasily V. Parkhomchuk,
ELECTRON COOLING EXPERIMENTS IN CSR* Xiaodong Yang #, Guohong Li, Jie Li, Xiaoming Ma, Lijun Mao, Ruishi Mao, Tailai Yan, Jiancheng Yang, Youjin Yuan, IMP, Lanzhou, 730000, China Vasily V. Parkhomchuk,
Accelerator Complex U70 of IHEP-Protvino: Status and Prospects for Upgrade
 NRC Kurchatov Institute INSTITUTE FOR HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS () 1, Nauki Sq., Protvino, Moscow Region, 142281, Russia Accelerator Complex U70 of -Protvino: Status and Prospects for Upgrade Sergey IVANOV 16
NRC Kurchatov Institute INSTITUTE FOR HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS () 1, Nauki Sq., Protvino, Moscow Region, 142281, Russia Accelerator Complex U70 of -Protvino: Status and Prospects for Upgrade Sergey IVANOV 16
Beam halo formation in high-intensity beams
 Beam halo formation in high-intensity beams Alexei V. Fedotov,1,2 Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 11973, USA Abstract Studies of beam halo became an unavoidable feature of high-intensity machines
Beam halo formation in high-intensity beams Alexei V. Fedotov,1,2 Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 11973, USA Abstract Studies of beam halo became an unavoidable feature of high-intensity machines
A high intensity p-linac and the FAIR Project
 A high intensity p-linac and the FAIR Project Oliver Kester Institut für Angewandte Physik, Goethe-Universität Frankfurt and GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung Facility for Antiproton and Ion
A high intensity p-linac and the FAIR Project Oliver Kester Institut für Angewandte Physik, Goethe-Universität Frankfurt and GSI Helmholtzzentrum für Schwerionenforschung Facility for Antiproton and Ion
A Multi-beamlet Injector for Heavy Ion Fusion: Experiments and Modeling
 A Multi-beamlet Injector for Heavy Ion Fusion: Experiments and Modeling G.A. Westenskow, D.P. Grote; LLNL J.W. Kwan, F. Bieniosek; LBNL PAC07 - FRYAB01 Albuquerque, New Mexico June 29, 2007 This work has
A Multi-beamlet Injector for Heavy Ion Fusion: Experiments and Modeling G.A. Westenskow, D.P. Grote; LLNL J.W. Kwan, F. Bieniosek; LBNL PAC07 - FRYAB01 Albuquerque, New Mexico June 29, 2007 This work has
COHERENT DIPOLE SYNCHRO-BETATRON BEAM-BEAM MODES IN ASYMMETRIC RING COLLIDERS
 COHERENT DIPOLE SYNCHRO-BETATRON BEAM-BEAM MODES IN ASYMMETRIC RING COLLIDERS EA Perevedentsev and AA Valishev, Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics, 639, Novosibirsk, Russia Abstract Following the work
COHERENT DIPOLE SYNCHRO-BETATRON BEAM-BEAM MODES IN ASYMMETRIC RING COLLIDERS EA Perevedentsev and AA Valishev, Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics, 639, Novosibirsk, Russia Abstract Following the work
SPIN2010. I.Meshkov 1, Yu.Filatov 1,2. Forschungszentrum Juelich GmbH. 19th International Spin Physics Symposium September 27 October 2, 2010
 Forschungszentrum Juelich GmbH SPIN200 9th International Spin Physics Symposium September 27 October 2, 200 Jülich, Germany Polarized Hadron Beams in NICA Project I.Meshkov, Yu.Filatov,2 JINR, Dubna 2
Forschungszentrum Juelich GmbH SPIN200 9th International Spin Physics Symposium September 27 October 2, 200 Jülich, Germany Polarized Hadron Beams in NICA Project I.Meshkov, Yu.Filatov,2 JINR, Dubna 2
University of Alberta And. Edmonton, November 4, 2017
 Laser Fusion in Canada Robert Fedosejevs Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alberta And Alberta/Canada Fusion Technology Alliance Presented at the Fusion Forum Edmonton, November
Laser Fusion in Canada Robert Fedosejevs Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alberta And Alberta/Canada Fusion Technology Alliance Presented at the Fusion Forum Edmonton, November
Review of ISOL-type Radioactive Beam Facilities
 Review of ISOL-type Radioactive Beam Facilities, CERN Map of the nuclear landscape Outline The ISOL technique History and Geography Isotope Separation On-Line Existing facilities First generation facilities
Review of ISOL-type Radioactive Beam Facilities, CERN Map of the nuclear landscape Outline The ISOL technique History and Geography Isotope Separation On-Line Existing facilities First generation facilities
BEAM PARAMETERS FROM SIS18 AND SIS100 ON TARGETS
 BEAM PARAMETERS FROM SIS18 AND SIS100 ON TARGETS V. Kornilov Primary Beams, Beam Physics GSI Darmstadt, Germany Vladimir Kornilov, HIC4FAIR Workshop, 28-31 July 2015, Hamburg FAIR: BEAM PARAMETERS 2007:
BEAM PARAMETERS FROM SIS18 AND SIS100 ON TARGETS V. Kornilov Primary Beams, Beam Physics GSI Darmstadt, Germany Vladimir Kornilov, HIC4FAIR Workshop, 28-31 July 2015, Hamburg FAIR: BEAM PARAMETERS 2007:
ThomX Machine Advisory Committee. (LAL Orsay, March ) Ring Beam Dynamics
 ThomX Machine Advisory Committee (LAL Orsay, March 20-21 2017) Ring Beam Dynamics A. Loulergue, M. Biagini, C. Bruni, I. Chaikovska I. Debrot, N. Delerue, A. Gamelin, H. Guler, J. Zang Programme Investissements
ThomX Machine Advisory Committee (LAL Orsay, March 20-21 2017) Ring Beam Dynamics A. Loulergue, M. Biagini, C. Bruni, I. Chaikovska I. Debrot, N. Delerue, A. Gamelin, H. Guler, J. Zang Programme Investissements
ELIC Design. Center for Advanced Studies of Accelerators. Jefferson Lab. Second Electron-Ion Collider Workshop Jefferson Lab March 15-17, 2004
 ELIC Design Ya. Derbenev, K. Beard, S. Chattopadhyay, J. Delayen, J. Grames, A. Hutton, G. Krafft, R. Li, L. Merminga, M. Poelker, E. Pozdeyev, B. Yunn, Y. Zhang Center for Advanced Studies of Accelerators
ELIC Design Ya. Derbenev, K. Beard, S. Chattopadhyay, J. Delayen, J. Grames, A. Hutton, G. Krafft, R. Li, L. Merminga, M. Poelker, E. Pozdeyev, B. Yunn, Y. Zhang Center for Advanced Studies of Accelerators
The Superconducting SIS100 Synchrotron for High Intensity Proton and Heavy Ion Beams
 The Superconducting SIS100 Synchrotron for High Intensity Proton and Heavy Ion Beams Peter Spiller HB2008 26.8.2008 GSI/FAIR Accelerator Facility Primary Beam Intensity x 100-1000 Secondary Beam Intensity
The Superconducting SIS100 Synchrotron for High Intensity Proton and Heavy Ion Beams Peter Spiller HB2008 26.8.2008 GSI/FAIR Accelerator Facility Primary Beam Intensity x 100-1000 Secondary Beam Intensity
Beam Cooling. Beam Cooling. M. Steck, GSI, Darmstadt CERN Accelerator School Chios, Greece September 18 30, Introduction. 1.
 Beam Cooling, GSI, Darmstadt CERN Accelerator School, September 18 30, 2011 Beam Cooling Introduction 1.Electron Cooling 2.Ionization Cooling 3.Laser Cooling 4.Stochastic Cooling Beam Cooling Beam cooling
Beam Cooling, GSI, Darmstadt CERN Accelerator School, September 18 30, 2011 Beam Cooling Introduction 1.Electron Cooling 2.Ionization Cooling 3.Laser Cooling 4.Stochastic Cooling Beam Cooling Beam cooling
NICA Project at JINR Nuclotron-based Ion Collider facility I.Meshkov for NICA team
 Workshop on Beam Cooling and Related Topics COOL 11 NICA Project at JINR Nuclotron-based Ion Collider facility I.Meshkov for NICA team, Ukraine hosted by JINR, Dubna 1 Contents Introduction: The goal of
Workshop on Beam Cooling and Related Topics COOL 11 NICA Project at JINR Nuclotron-based Ion Collider facility I.Meshkov for NICA team, Ukraine hosted by JINR, Dubna 1 Contents Introduction: The goal of
Production of HCI with an electron beam ion trap
 Production of HCI with an electron beam ion trap I=450 ma E= 5 kev axially: electrodes radially: electron beam space charge total trap potential U trap 200 V (U trap ion charge) 10000 ev 15000 A/cm 2 n
Production of HCI with an electron beam ion trap I=450 ma E= 5 kev axially: electrodes radially: electron beam space charge total trap potential U trap 200 V (U trap ion charge) 10000 ev 15000 A/cm 2 n
Method of active correlations in the experiment 249 Cf+ 48 Ca n
 Method of active correlations in the experiment 249 Cf+ 48 Ca 297 118 +3n Yu.S.Tsyganov, A.M.Sukhov, A.N.Polyakov Abstract Two decay chains originated from the even-even isotope 294 118 produced in the
Method of active correlations in the experiment 249 Cf+ 48 Ca 297 118 +3n Yu.S.Tsyganov, A.M.Sukhov, A.N.Polyakov Abstract Two decay chains originated from the even-even isotope 294 118 produced in the
ERL FACILITY AT CERN FOR APPLICATIONS
 ERL FACILITY AT CERN FOR APPLICATIONS Erk Jensen (CERN) Big thanks to contributors: A. Bogacz (JLAB), O. Brüning, R. Calaga, V. Chetvertkova, E. Cormier (CELIA), R. Jones, M. Klein, A. Valloni, D. Pellegrini,
ERL FACILITY AT CERN FOR APPLICATIONS Erk Jensen (CERN) Big thanks to contributors: A. Bogacz (JLAB), O. Brüning, R. Calaga, V. Chetvertkova, E. Cormier (CELIA), R. Jones, M. Klein, A. Valloni, D. Pellegrini,
2. Acceleration Scheme
 2. Acceleration Scheme Accelerators in the RIBF consist of three existing accelerators and three ring cyclotrons under construction. The existing accelerators are the RIKEN Linear Accelerator (RILAC),
2. Acceleration Scheme Accelerators in the RIBF consist of three existing accelerators and three ring cyclotrons under construction. The existing accelerators are the RIKEN Linear Accelerator (RILAC),
FAIR. International Facility for Antiproton and Ion. Research
 FAIR International Facility for Antiproton and Ion Research FAIR One of the largest scientific project in the world with a broad spectrum of research programs: - Nuclear physics - Hadron physics - Atomic
FAIR International Facility for Antiproton and Ion Research FAIR One of the largest scientific project in the world with a broad spectrum of research programs: - Nuclear physics - Hadron physics - Atomic
SRF GUN CHARACTERIZATION - PHASE SPACE AND DARK CURRENT MEASUREMENTS AT ELBE*
 SRF GUN CHARACTERIZATION - PHASE SPACE AND DARK CURRENT MEASUREMENTS AT ELBE* E. Panofski #, A. Jankowiak, T. Kamps, Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin, Berlin, Germany P.N. Lu, J. Teichert, Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf,
SRF GUN CHARACTERIZATION - PHASE SPACE AND DARK CURRENT MEASUREMENTS AT ELBE* E. Panofski #, A. Jankowiak, T. Kamps, Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin, Berlin, Germany P.N. Lu, J. Teichert, Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf,
Development and application of the RFQs for FAIR and GSI Projects
 Development and application of the RFQs for FAIR and GSI Projects Stepan Yaramyshev GSI, Darmstadt Facility for Antiproton and Ion Research at Darmstadt The FAIR Accelerator Complex GSI Today SIS 100 SIS18
Development and application of the RFQs for FAIR and GSI Projects Stepan Yaramyshev GSI, Darmstadt Facility for Antiproton and Ion Research at Darmstadt The FAIR Accelerator Complex GSI Today SIS 100 SIS18
RECENT STATUS OF BEAM COOLING AT S-LSR*
 Proceedings of COOL 11, Alushta, Ukraine MOIO06 RECENT STATUS OF BEAM COOLING AT S-LSR* A. Noda, M. Nakao, H. Souda, H. Tongu, ICR, Kyoto U., Kyoto, Japan, K. Jimbo, IAE, Kyoto U., Kyoto, Japan, T. Fujimoto,
Proceedings of COOL 11, Alushta, Ukraine MOIO06 RECENT STATUS OF BEAM COOLING AT S-LSR* A. Noda, M. Nakao, H. Souda, H. Tongu, ICR, Kyoto U., Kyoto, Japan, K. Jimbo, IAE, Kyoto U., Kyoto, Japan, T. Fujimoto,
arxiv: v2 [nucl-ex] 11 Sep 2007
![arxiv: v2 [nucl-ex] 11 Sep 2007 arxiv: v2 [nucl-ex] 11 Sep 2007](/thumbs/96/127982036.jpg) arxiv:0709.1459v2 [nucl-ex] 11 Sep 2007 JINR, Dubna E-mail: toneev@theor.jinr.ru for the NICA/MPD working group A new project of Nuclotron-based Ion Collider facility (NICA) and Multi-Purpose Detector
arxiv:0709.1459v2 [nucl-ex] 11 Sep 2007 JINR, Dubna E-mail: toneev@theor.jinr.ru for the NICA/MPD working group A new project of Nuclotron-based Ion Collider facility (NICA) and Multi-Purpose Detector
The heavy-ion magnetic spectrometer PRISMA
 Nuclear Physics A 701 (2002) 217c 221c www.elsevier.com/locate/npe The heavy-ion magnetic spectrometer PRISMA A.M. Stefanini a,,l.corradi a,g.maron a,a.pisent a,m.trotta a, A.M. Vinodkumar a, S. Beghini
Nuclear Physics A 701 (2002) 217c 221c www.elsevier.com/locate/npe The heavy-ion magnetic spectrometer PRISMA A.M. Stefanini a,,l.corradi a,g.maron a,a.pisent a,m.trotta a, A.M. Vinodkumar a, S. Beghini
PAL LINAC UPGRADE FOR A 1-3 Å XFEL
 PAL LINAC UPGRADE FOR A 1-3 Å XFEL J. S. Oh, W. Namkung, Pohang Accelerator Laboratory, POSTECH, Pohang 790-784, Korea Y. Kim, Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron DESY, D-603 Hamburg, Germany Abstract With
PAL LINAC UPGRADE FOR A 1-3 Å XFEL J. S. Oh, W. Namkung, Pohang Accelerator Laboratory, POSTECH, Pohang 790-784, Korea Y. Kim, Deutsches Elektronen-Synchrotron DESY, D-603 Hamburg, Germany Abstract With
Beam Cooling. M. Steck, GSI, Darmstadt. JUAS, Archamps, France March 9, 2015
 Beam Cooling M. Steck, GSI, Darmstadt JUAS, Archamps, France March 9, 2015 time longitudinal (momentum) cooling Cooling injection into storage ring transverse cooling Xe 54+ 50 MeV/u p/p cooling off with
Beam Cooling M. Steck, GSI, Darmstadt JUAS, Archamps, France March 9, 2015 time longitudinal (momentum) cooling Cooling injection into storage ring transverse cooling Xe 54+ 50 MeV/u p/p cooling off with
Markus Roth TU Darmstadt
 Laser-driven Production of Particle Beams and their application to medical treatment Markus Roth TU Darmstadt The Case Laser-driven electrons Potential for Applications in Therapy Use of secondary Radiation
Laser-driven Production of Particle Beams and their application to medical treatment Markus Roth TU Darmstadt The Case Laser-driven electrons Potential for Applications in Therapy Use of secondary Radiation
Overview and Status of the Austrian Particle Therapy Facility MedAustron. Peter Urschütz
 Overview and Status of the Austrian Particle Therapy Facility MedAustron Peter Urschütz MedAustron Centre for ion beam therapy and non-clinical research Treatment of 1200 patients/year in full operation
Overview and Status of the Austrian Particle Therapy Facility MedAustron Peter Urschütz MedAustron Centre for ion beam therapy and non-clinical research Treatment of 1200 patients/year in full operation
ASTRA simulations of the slice longitudinal momentum spread along the beamline for PITZ
 ASTRA simulations of the slice longitudinal momentum spread along the beamline for PITZ Orlova Ksenia Lomonosov Moscow State University GSP-, Leninskie Gory, Moscow, 11999, Russian Federation Email: ks13orl@list.ru
ASTRA simulations of the slice longitudinal momentum spread along the beamline for PITZ Orlova Ksenia Lomonosov Moscow State University GSP-, Leninskie Gory, Moscow, 11999, Russian Federation Email: ks13orl@list.ru
STATUS OF HIRFL-CSR PROJECT *
 STATUS OF HIRFL-CSR PROJECT * Y.J. Yuan #, H.W. Zhao, J.W. Xia, X.D. Yang, H.S. Xu and CSR Group Institute of Modern Physics(IMP), CAS, Lanzhou, 730000, P.R. China. Abstract The HIRFL-CSR project is a
STATUS OF HIRFL-CSR PROJECT * Y.J. Yuan #, H.W. Zhao, J.W. Xia, X.D. Yang, H.S. Xu and CSR Group Institute of Modern Physics(IMP), CAS, Lanzhou, 730000, P.R. China. Abstract The HIRFL-CSR project is a
The Electron-Ion Collider
 The Electron-Ion Collider C. Tschalaer 1. Introduction In the past year, the idea of a polarized electron-proton (e-p) or electron-ion (e-a) collider of high luminosity (10 33 cm -2 s -1 or more) and c.m.
The Electron-Ion Collider C. Tschalaer 1. Introduction In the past year, the idea of a polarized electron-proton (e-p) or electron-ion (e-a) collider of high luminosity (10 33 cm -2 s -1 or more) and c.m.
Accelerator Physics. Tip World Scientific NEW JERSEY LONDON SINGAPORE BEIJING SHANGHAI HONG KONG TAIPEI BANGALORE. Second Edition. S. Y.
 Accelerator Physics Second Edition S. Y. Lee Department of Physics, Indiana University Tip World Scientific NEW JERSEY LONDON SINGAPORE BEIJING SHANGHAI HONG KONG TAIPEI BANGALORE Contents Preface Preface
Accelerator Physics Second Edition S. Y. Lee Department of Physics, Indiana University Tip World Scientific NEW JERSEY LONDON SINGAPORE BEIJING SHANGHAI HONG KONG TAIPEI BANGALORE Contents Preface Preface
Status of the ESR And Future Options
 Status of the ESR And Future Options M. Steck for the Storage Ring Division (C. Dimopoulou, A. Dolinskii, S. Litvinov, F. Nolden, P. Petri, U. Popp, I. Schurig) Outline 1) New Old ESR 2) Slow (Resonant)
Status of the ESR And Future Options M. Steck for the Storage Ring Division (C. Dimopoulou, A. Dolinskii, S. Litvinov, F. Nolden, P. Petri, U. Popp, I. Schurig) Outline 1) New Old ESR 2) Slow (Resonant)
First propositions of a lattice for the future upgrade of SOLEIL. A. Nadji On behalf of the Accelerators and Engineering Division
 First propositions of a lattice for the future upgrade of SOLEIL A. Nadji On behalf of the Accelerators and Engineering Division 1 SOLEIL : A 3 rd generation synchrotron light source 29 beamlines operational
First propositions of a lattice for the future upgrade of SOLEIL A. Nadji On behalf of the Accelerators and Engineering Division 1 SOLEIL : A 3 rd generation synchrotron light source 29 beamlines operational
The GSI Anomaly. M. Lindner. Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg. Sildes partially adopted from F. Bosch
 The GSI Anomaly M. Lindner Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg Sildes partially adopted from F. Bosch What is the GSI Anomaly? Periodically modualted exponential β-decay law of highly charged,
The GSI Anomaly M. Lindner Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik, Heidelberg Sildes partially adopted from F. Bosch What is the GSI Anomaly? Periodically modualted exponential β-decay law of highly charged,
Polarized ion source with nearly resonant chargeexchange plasma ionizer: parameters and possibilities for improvements
 Polarized ion source with nearly resonant chargeexchange plasma ionizer: parameters and possibilities for improvements Institute for Nuclear Research of Russian Academy of Sciences Moscow, 117312, Russia
Polarized ion source with nearly resonant chargeexchange plasma ionizer: parameters and possibilities for improvements Institute for Nuclear Research of Russian Academy of Sciences Moscow, 117312, Russia
External injection of electron bunches into plasma wakefields
 External injection of electron bunches into plasma wakefields Studies on emittance growth and bunch compression p x x Timon Mehrling, Julia Grebenyuk and Jens Osterhoff FLA, Plasma Acceleration Group (http://plasma.desy.de)
External injection of electron bunches into plasma wakefields Studies on emittance growth and bunch compression p x x Timon Mehrling, Julia Grebenyuk and Jens Osterhoff FLA, Plasma Acceleration Group (http://plasma.desy.de)
Physics with Exotic Nuclei
 Physics with Exotic Nuclei Hans-Jürgen Wollersheim NUclear STructure, Astrophysics and Reaction Outline Projectile Fragmentation A Route to Exotic Nuclei Fragmentation Cross Sections Nuclear Reaction Rates
Physics with Exotic Nuclei Hans-Jürgen Wollersheim NUclear STructure, Astrophysics and Reaction Outline Projectile Fragmentation A Route to Exotic Nuclei Fragmentation Cross Sections Nuclear Reaction Rates
AWAKE: The Proton Driven Plasma Wakefield Acceleration Experiment at CERN. Alexey Petrenko on behalf of the AWAKE Collaboration
 AWAKE: The Proton Driven Plasma Wakefield Acceleration Experiment at CERN Alexey Petrenko on behalf of the AWAKE Collaboration Outline Motivation AWAKE at CERN AWAKE Experimental Layout: 1 st Phase AWAKE
AWAKE: The Proton Driven Plasma Wakefield Acceleration Experiment at CERN Alexey Petrenko on behalf of the AWAKE Collaboration Outline Motivation AWAKE at CERN AWAKE Experimental Layout: 1 st Phase AWAKE
RHIC AND ITS UPGRADE PROGRAMS
 Proceedings of EPAC8, Genoa, Italy FRXAGM1 Abstract RHIC AND ITS UPGRADE PROGRAMS Thomas Roser Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, New York 11793-5, USA As the first hadron accelerator and collider
Proceedings of EPAC8, Genoa, Italy FRXAGM1 Abstract RHIC AND ITS UPGRADE PROGRAMS Thomas Roser Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, New York 11793-5, USA As the first hadron accelerator and collider
Conceptual design of an accumulator ring for the Diamond II upgrade
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Conceptual design of an accumulator ring for the Diamond II upgrade To cite this article: I P S Martin and R Bartolini 218 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 167
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Conceptual design of an accumulator ring for the Diamond II upgrade To cite this article: I P S Martin and R Bartolini 218 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 167
The FAIR Accelerator Facility
 The FAIR Accelerator Facility SIS300 existing GSI proton linac SIS18 UNILAC SIS100 HESR pbar target SuperFRS goals: higher intensity (low charge states) higher energy (high charge states) production of
The FAIR Accelerator Facility SIS300 existing GSI proton linac SIS18 UNILAC SIS100 HESR pbar target SuperFRS goals: higher intensity (low charge states) higher energy (high charge states) production of
Outline. Physics of Charge Particle Motion. Physics of Charge Particle Motion 7/31/2014. Proton Therapy I: Basic Proton Therapy
 Outline Proton Therapy I: Basic Proton Therapy Bijan Arjomandy, Ph.D. Narayan Sahoo, Ph.D. Mark Pankuch, Ph.D. Physics of charge particle motion Particle accelerators Proton interaction with matter Delivery
Outline Proton Therapy I: Basic Proton Therapy Bijan Arjomandy, Ph.D. Narayan Sahoo, Ph.D. Mark Pankuch, Ph.D. Physics of charge particle motion Particle accelerators Proton interaction with matter Delivery
Low energy electron storage ring with tunable compaction factor
 REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS 78, 075107 2007 Low energy electron storage ring with tunable compaction factor S. Y. Lee, J. Kolski, Z. Liu, X. Pang, C. Park, W. Tam, and F. Wang Department of Physics,
REVIEW OF SCIENTIFIC INSTRUMENTS 78, 075107 2007 Low energy electron storage ring with tunable compaction factor S. Y. Lee, J. Kolski, Z. Liu, X. Pang, C. Park, W. Tam, and F. Wang Department of Physics,
Influence of beam space charge on dynamical aperture of TWAC storage ring. V.V. Kapin, A.Ye. Bolshakov, P.R. Zenkevich ITEP, Moscow, Russia
 Influence of beam space charge on dynamical aperture of TWAC storage ring V.V. Kapin, A.Ye. Bolshakov, P.R. Zenkevich ITEP, Moscow, Russia Abstract High intensity ion beams are planned to store in Terra
Influence of beam space charge on dynamical aperture of TWAC storage ring V.V. Kapin, A.Ye. Bolshakov, P.R. Zenkevich ITEP, Moscow, Russia Abstract High intensity ion beams are planned to store in Terra
FY04 Luminosity Plan. SAG Meeting September 22, 2003 Dave McGinnis
 FY04 Luminosity Plan SAG Meeting September 22, 2003 Dave McGinnis FY03 Performance Accelerator Issues TEV Pbar Main Injector Reliability Operations Study Strategy Shot Strategy Outline FY04 Luminosity
FY04 Luminosity Plan SAG Meeting September 22, 2003 Dave McGinnis FY03 Performance Accelerator Issues TEV Pbar Main Injector Reliability Operations Study Strategy Shot Strategy Outline FY04 Luminosity
PULSE-TO-PULSE TRANSVERSE BEAM EMITTANCE CONTROLLING FOR MLF AND MR IN THE 3-GeV RCS OF J-PARC
 THO3AB3 Proceedings of HB, East-Lansing, MI, USA PULSE-TO-PULSE TRANSVERSE BEAM EMITTANCE CONTROLLING FOR MLF AND MR IN THE 3-GeV RCS OF J-PARC P.K. Saha, H. Harada, H. Hotchi and T. Takayanagi J-PARC
THO3AB3 Proceedings of HB, East-Lansing, MI, USA PULSE-TO-PULSE TRANSVERSE BEAM EMITTANCE CONTROLLING FOR MLF AND MR IN THE 3-GeV RCS OF J-PARC P.K. Saha, H. Harada, H. Hotchi and T. Takayanagi J-PARC
New developments in the theory of ICF targets, and fast ignition with heavy ions
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 45 (2003) A125 A132 PLASMA PHYSICS AND CONTROLLED FUSION PII: S0741-3335(03)68658-6 New developments in the theory of ICF targets, and fast
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 45 (2003) A125 A132 PLASMA PHYSICS AND CONTROLLED FUSION PII: S0741-3335(03)68658-6 New developments in the theory of ICF targets, and fast
BEAM TESTS OF THE LHC TRANSVERSE FEEDBACK SYSTEM
 JINR BEAM TESTS OF THE LHC TRANSVERSE FEEDBACK SYSTEM W.Höfle, G.Kotzian, E.Montesinos, M.Schokker, D.Valuch (CERN) V.M. Zhabitsky (JINR) XXII Russian Particle Accelerator Conference 27.9-1.1. 21, Protvino
JINR BEAM TESTS OF THE LHC TRANSVERSE FEEDBACK SYSTEM W.Höfle, G.Kotzian, E.Montesinos, M.Schokker, D.Valuch (CERN) V.M. Zhabitsky (JINR) XXII Russian Particle Accelerator Conference 27.9-1.1. 21, Protvino
What is. Inertial Confinement Fusion?
 What is Inertial Confinement Fusion? Inertial Confinement Fusion: dense & short-lived plasma Fusing D and T requires temperature to overcome Coulomb repulsion density & confinement time to maximize number
What is Inertial Confinement Fusion? Inertial Confinement Fusion: dense & short-lived plasma Fusing D and T requires temperature to overcome Coulomb repulsion density & confinement time to maximize number
EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH CERN - SL DIVISION. Multi-TeV CLIC Photon Collider Option. H. Burkhardt
 EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH CERN - SL DIVISION CERN-SL-2000-070 CLIC Note 463 AP Multi-TeV CLIC Photon Collider Option H. Burkhardt Considerations for an option of γγ collisions at multi-tev
EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH CERN - SL DIVISION CERN-SL-2000-070 CLIC Note 463 AP Multi-TeV CLIC Photon Collider Option H. Burkhardt Considerations for an option of γγ collisions at multi-tev
Comparison of simulated and observed beam profile broadening in the Proton Storage Ring and the role of space charge
 PHYSICAL REVIEW SPECIAL TOPICS - ACCELERATORS AND BEAMS, VOLUME 3, 3421 (2) Comparison of simulated and observed beam profile broadening in the Proton Storage Ring and the role of space charge J. D. Galambos,
PHYSICAL REVIEW SPECIAL TOPICS - ACCELERATORS AND BEAMS, VOLUME 3, 3421 (2) Comparison of simulated and observed beam profile broadening in the Proton Storage Ring and the role of space charge J. D. Galambos,
1.5-GeV FFAG Accelerator as Injector to the BNL-AGS
 1.5-GeV FFAG Accelerator as Injector to the BNL-AGS Alessandro G. Ruggiero M. Blaskiewicz,, T. Roser, D. Trbojevic,, N. Tsoupas,, W. Zhang Oral Contribution to EPAC 04. July 5-9, 5 2004 Present BNL - AGS
1.5-GeV FFAG Accelerator as Injector to the BNL-AGS Alessandro G. Ruggiero M. Blaskiewicz,, T. Roser, D. Trbojevic,, N. Tsoupas,, W. Zhang Oral Contribution to EPAC 04. July 5-9, 5 2004 Present BNL - AGS
Introduction to Collider Physics
 Introduction to Collider Physics William Barletta United States Particle Accelerator School Dept. of Physics, MIT The Very Big Picture Accelerators Figure of Merit 1: Accelerator energy ==> energy frontier
Introduction to Collider Physics William Barletta United States Particle Accelerator School Dept. of Physics, MIT The Very Big Picture Accelerators Figure of Merit 1: Accelerator energy ==> energy frontier
PoS(BORMIO2016)013. PANDA Forward Spectrometer Calorimeter. P.A. Semenov IHEP NRC KI S.I. Bukreeva IHEP NRC KI ITEP NRC KI
 PANDA Forward Spectrometer Calorimeter E-mail: psemenov@ihep.ru S.I. Bukreeva ITEP NRC KI S.K. Chernichenko A.V. Sukhih S. Diehl University of Giessen V. Dormenev University of Giessen R. Novotny University
PANDA Forward Spectrometer Calorimeter E-mail: psemenov@ihep.ru S.I. Bukreeva ITEP NRC KI S.K. Chernichenko A.V. Sukhih S. Diehl University of Giessen V. Dormenev University of Giessen R. Novotny University
Application of cooling methods at NICA project. G.Trubnikov JINR, Dubna
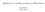 Application of cooling methods at NICA project G.Trubnikov JINR, Dubna Outline 1. NICA scheme, modes of operation, working cycles;. Booster scheme, parameters, beam requirements; 3. Status of the electron
Application of cooling methods at NICA project G.Trubnikov JINR, Dubna Outline 1. NICA scheme, modes of operation, working cycles;. Booster scheme, parameters, beam requirements; 3. Status of the electron
Proton induced spallation reaction and high power target station
 Proton induced spallation reaction and high power target station Hanjie Cai Institute of Modern Physics (IMP), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) High power spallation target station Accelerator-Driven
Proton induced spallation reaction and high power target station Hanjie Cai Institute of Modern Physics (IMP), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) High power spallation target station Accelerator-Driven
SLS at the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI), Villigen, Switzerland
 SLS at the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI), Villigen, Switzerland Michael Böge 1 SLS Team at PSI Michael Böge 2 Layout of the SLS Linac, Transferlines Booster Storage Ring (SR) Beamlines and Insertion Devices
SLS at the Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI), Villigen, Switzerland Michael Böge 1 SLS Team at PSI Michael Böge 2 Layout of the SLS Linac, Transferlines Booster Storage Ring (SR) Beamlines and Insertion Devices
Letter of Intent: Nuclear Fusion Reactions from laser-accelerated fissile ion beams
 Letter of Intent: Nuclear Fusion Reactions from laser-accelerated fissile ion beams Peter G. Thirolf, LMU Munich D. Habs, H. Ruhl, J. Schreiber, LMU Munich, MPQ Garching T. Dickel, H. Geissel, W. Plass,
Letter of Intent: Nuclear Fusion Reactions from laser-accelerated fissile ion beams Peter G. Thirolf, LMU Munich D. Habs, H. Ruhl, J. Schreiber, LMU Munich, MPQ Garching T. Dickel, H. Geissel, W. Plass,
CEPC Linac Injector. HEP Jan, Cai Meng, Guoxi Pei, Jingru Zhang, Xiaoping Li, Dou Wang, Shilun Pei, Jie Gao, Yunlong Chi
 HKUST Jockey Club Institute for Advanced Study CEPC Linac Injector HEP218 22 Jan, 218 Cai Meng, Guoxi Pei, Jingru Zhang, Xiaoping Li, Dou Wang, Shilun Pei, Jie Gao, Yunlong Chi Institute of High Energy
HKUST Jockey Club Institute for Advanced Study CEPC Linac Injector HEP218 22 Jan, 218 Cai Meng, Guoxi Pei, Jingru Zhang, Xiaoping Li, Dou Wang, Shilun Pei, Jie Gao, Yunlong Chi Institute of High Energy
ELECTRON COOLING OF PB54+ IONS IN LEIR
 ELECTRON COOLING OF PB+ IONS IN LEIR G. Tranquille, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Abstract Electron cooling is central in the preparation of dense bunches of lead beams for the LHC. Ion beam pulses from the
ELECTRON COOLING OF PB+ IONS IN LEIR G. Tranquille, CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Abstract Electron cooling is central in the preparation of dense bunches of lead beams for the LHC. Ion beam pulses from the
Simulations of the IR/THz Options at PITZ (High-gain FEL and CTR)
 Case Study of IR/THz source for Pump-Probe Experiment at the European XFEL Simulations of the IR/THz Options at PITZ (High-gain FEL and CTR) Introduction Outline Simulations of High-gain FEL (SASE) Simulation
Case Study of IR/THz source for Pump-Probe Experiment at the European XFEL Simulations of the IR/THz Options at PITZ (High-gain FEL and CTR) Introduction Outline Simulations of High-gain FEL (SASE) Simulation
Review of Heavy-Ion Inertial Fusion Physics
 Review of Heavy-Ion Inertial Fusion Physics S. Kawata 1, 2, *, T. Karino 1, and A. I. Ogoyski 3 1 Graduate School of Engineering, Utsunomiya University, Yohtoh 7-1-2, Utsunomiya 321-8585, Japan 2 CORE
Review of Heavy-Ion Inertial Fusion Physics S. Kawata 1, 2, *, T. Karino 1, and A. I. Ogoyski 3 1 Graduate School of Engineering, Utsunomiya University, Yohtoh 7-1-2, Utsunomiya 321-8585, Japan 2 CORE
S.Y. Lee Bloomington, Indiana, U.S.A. June 10, 2011
 Preface Accelerator science took off in the 20th century. Accelerator scientists invent many innovative technologies to produce and manipulate high energy and high quality beams that are instrumental to
Preface Accelerator science took off in the 20th century. Accelerator scientists invent many innovative technologies to produce and manipulate high energy and high quality beams that are instrumental to
WG2 on ERL light sources CHESS & LEPP
 Charge: WG2 on ERL light sources Address and try to answer a list of critical questions for ERL light sources. Session leaders can approach each question by means of (a) (Very) short presentations (b)
Charge: WG2 on ERL light sources Address and try to answer a list of critical questions for ERL light sources. Session leaders can approach each question by means of (a) (Very) short presentations (b)
High-Intensity Ion Beam Neutralization and Drift Compression Experiments
 1 / 37 High-Intensity Ion Beam Neutralization and Drift Compression Experiments Prabir K. Roy 1 1 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL) Berkeley, CA 94720 March 08, 2010 (with S. S. Yu, P.A. Seidl,
1 / 37 High-Intensity Ion Beam Neutralization and Drift Compression Experiments Prabir K. Roy 1 1 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL) Berkeley, CA 94720 March 08, 2010 (with S. S. Yu, P.A. Seidl,
