Partitioning of chlorine between H 2 O-bearing fluid and basaltic melt of Mt. Etna
|
|
|
- Bennett Garrett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Partitioning of chlorine between H 2 O-bearing fluid and basaltic melt of Mt. Etna Oliver Beermann Jan Stelling XXVII. (14.) Arbeitstagung DGK, Arbeitskreis Nichtkristalline und Partiellkristalline Strukturen Jena, km
2 Partitioning of chlorine between H 2 O-bearing fluid and basaltic melt of Mt. Etna Introduction the concentration and composition of volatile components in magmatic systems affect magma degassing significantly (magma: in general mixture of silicate melt, minerals and fluid) in contrast to water the concentration of sulfur and chlorine in basaltic magma is quite low (< ~ 5000 ppm). Formation of a fluid phase during magma ascent and pressure release causes an enrichment of these components in the hydrous fluid phase volcanic degassing of sulfur and chlorine has an eminent influence on our atmoshere and it has recently been suggested that supereruptions in Earth s history coupled with massive degassing changed the ecosystem on a global scale the interaction of complex volcanic H-C-O-S-Cl fluids with silicate melts is not well understood 1
3 Mt. Etna H 2 S HCl CO 2 H 2 O SO 2 COS CS2 HF HBr 30 km N 2
4 Partitioning of chlorine between H 2 O-bearing fluid and basaltic melt of Mt. Etna Chlorine and Sulfur solubility and partitioning data of chlorine and sulfur between melt and fluid phase of magmatic systems are important for a better understanding of eruption dynamics of volcanic systems Aiuppa et al. (2004) observed recently a correlation between the S/Cl ratio of the emitted gases and the eruption style of the 2002 eruption of Mt. Etna 1
5 S/Cl ratio vs. volcanic activity of Mt. Etna 2002/03 eruption total SO 2 emission: ~ t global SO 2 emission: ~ t/a modified after Aiuppa et al. (2004) 1
6 Partitioning of chlorine between H 2 O-bearing fluid and basaltic melt of Mt. Etna System Chlorine-H 2 O by now the partition behaviour of the volatile components sulfur and chlorine between hyrous fluids and basaltic melt is unknown even the physicochemical behaviour of simplifed chlorine-h 2 O and sulfur- H 2 O fluid in basaltic magma is not clarified so far thus, in a first step we performed partitioning experiments of the simplified system chlorine-h 2 O-bearing fluid and basaltic melt (fused natural rock sample from Etna volcano) 1
7 Experiments 35 experiments were carried out in one of our internally heated Ar/H 2 pressure vessels (IHPV) experimental conditions were: T = C, P = 200 MPa, 6 h run time, reducing conditions (log ƒo 2 = QFM+1, water saturated) 2
8 Sample preparation capsule material: Au 80 Pd 20 (iron presaturated) charged with rock powder (30-70 mg) + initial 10 wt % fluid phase rock powder: trachybasalt from Mt. Etna (errupt. 2001, Rifugio Sapienza) fluid phase: H 2 O-Cl different ratios Cl source: HCl solutions, PtCl 4, AgCl 2
9 Solubility of Water and Chlorine maximum solubility: Cl ~ 4 wt % H 2 O ~ 5.5 wt % H 2 O solubility increases with increasing Cl conc. in the melt with a maximum at ~ 2.5 wt % Cl within error no temperature dependence between C 3
10 Partitioning of Chlorine between Melt and Fluid increase of Cl conc. in the melt is more pronounced at low Cl# within error no temperature dependence between C Cl# = molar Cl/(Cl+H 2 O) ratio in the fluid coexisting with the silicate melt (calculated by mass balance) 3
11 Involved partitoning of Metal Oxides with increasing Cl#: loss of: Na 2 O, K 2 O, CaO and FeO from melt into the fluid 3
12 Reactions in and between Melt and Fluid up to ~ 2.5 wt % H 2 O in the melt without adding H 2 O chlorine source: MCl + ½ H 2 M + HCl (M = Pt, Ag) (1) reaction in the melt: (2) reaction in the fluid: HCl (Na, K) 2 O + 2 HCl melt HCl + O 2- OH - + Cl - fluid melt fluid (Na, K) 2 O melt 2 (Na, K)Cl + H 2 O fluid 4
13 Partitioning of chlorine between H 2 O-bearing fluid and basaltic melt of Mt. Etna Maximum Chlorine Capacity our experiments: ~ 4 wt % maximum capacity of chlorine in basaltic melt at 200 MPa, C previous studies: ~ 2.9 wt % maximum capacity of chlorine in basaltic melt at 200 MPa, C (Webster et al., 1999) ~ 2.7 wt % maximum capacity of chlorine calculated for our composition and P, T conditions using the model of Webster & De Vivo (2002) 4
14 Partitioning of chlorine between H 2 O-bearing fluid and basaltic melt of Mt. Etna Chlorine affects fluid/melt composition depletion of Na 2 O, K 2 O, CaO and FeO in the melt enrichment of Na 2 O, K 2 O, CaO and FeO in the fluid, forming (Na,K)Cl and (Ca, Fe)Cl 2 with HCl chlorine influences the melt/fluid composition chlorine affects crystallization path of silicate melt! 4
15 Partitioning of chlorine between H 2 O-bearing fluid and basaltic melt of Mt. Etna Conclusion complex behaviour of chlorine in hydreous magmatic systems chlorine has a noticeable influence on both, melt and fluid composition (depletion of Na 2 O, K 2 O, CaO and FeO in the melt, enrichment of Na 2 O, K 2 O, CaO and FeO in the fluid) chlorine has a positive effect on water solubility in basaltic melt water solubility increases from 4.5 to 5.5 wt % at 0.1 to 2.5 wt % chlorine in the melt, respectively (200 MPa, C ) consequently chlorine effects degassing processes significantly thus, compared to a CO 2 -containing magma, a chlorine-rich magma will start to degass at a shallower depth, wich may cause explosive eruption styles near the surface 5
16 Vielen Dank fürs Zuhören!
Heidy Mader, Michael Burton, Margherita Polacci. A combined physico-chemical model for passive degassing from Stromboli volcano.
 Heidy Mader, Michael Burton, Margherita Polacci A combined physico-chemical model for passive degassing from Stromboli volcano. 2 Degassing at Stromboli Degassing from basaltic volcanoes is the most common
Heidy Mader, Michael Burton, Margherita Polacci A combined physico-chemical model for passive degassing from Stromboli volcano. 2 Degassing at Stromboli Degassing from basaltic volcanoes is the most common
Volatile solubility models and their application to magma storage and transport in the mantle and he crust. Julie Roberge ESIA-Ticoman, IPN Mexico
 Volatile solubility models and their application to magma storage and transport in the mantle and he crust Julie Roberge ESIA-Ticoman, IPN Mexico Melt Inclusions What are they? How to use them volatiles
Volatile solubility models and their application to magma storage and transport in the mantle and he crust Julie Roberge ESIA-Ticoman, IPN Mexico Melt Inclusions What are they? How to use them volatiles
REVISION 1 JAMES D. WEBSTER 1, FRANCESCO VETERE 2, ROMAN E. BOTCHARNIKOV 2, BETH GOLDOFF 1, ALEXANDER MCBIRNEY 3, ANGELA L.
 REVISION 1 Experimental and Modeled Chlorine Solubilities in Aluminosilicate Melts at 1 to 7000 Bars and 700 to 1250 C: Applications to Magmas of Augustine Volcano, Alaska JAMES D. WEBSTER 1, FRANCESCO
REVISION 1 Experimental and Modeled Chlorine Solubilities in Aluminosilicate Melts at 1 to 7000 Bars and 700 to 1250 C: Applications to Magmas of Augustine Volcano, Alaska JAMES D. WEBSTER 1, FRANCESCO
Volatile rich Fe-oxide melts: base and precious metals enrichment trends. Is there an IOCG connection?
 Volatile rich Fe-oxide melts: base and precious metals enrichment trends. Is there an IOCG connection? Gregory W Lester M.A., MSc., PhD Curtin University Background Nelsonites and Low Ti, FeO deposits
Volatile rich Fe-oxide melts: base and precious metals enrichment trends. Is there an IOCG connection? Gregory W Lester M.A., MSc., PhD Curtin University Background Nelsonites and Low Ti, FeO deposits
Metal saturation in the upper mantle
 Vol 449 27 September 2007 Metal saturation in the upper mantle A. Rohrbach, C. Ballhaus, U. Golla Schindler, P. Ulmer,V.S. Kamenetsky, D.V. Kuzmin NS seminar 2007.10.25 The uppermost mantle is oxidized.
Vol 449 27 September 2007 Metal saturation in the upper mantle A. Rohrbach, C. Ballhaus, U. Golla Schindler, P. Ulmer,V.S. Kamenetsky, D.V. Kuzmin NS seminar 2007.10.25 The uppermost mantle is oxidized.
Lecture 36. Igneous geochemistry
 Lecture 36 Igneous geochemistry Reading - White Chapter 7 Today 1. Overview 2. solid-melt distribution coefficients Igneous geochemistry The chemistry of igneous systems provides clues to a number of important
Lecture 36 Igneous geochemistry Reading - White Chapter 7 Today 1. Overview 2. solid-melt distribution coefficients Igneous geochemistry The chemistry of igneous systems provides clues to a number of important
Chlorine Partitioning Between a Basaltic Melt and H2O-CO2 Fluids at Mount Etna
 Chlorine Partitioning Between a Basaltic Melt and H2O-CO2 Fluids at Mount Etna Marina Alletti, Don R. Baker, Bruno Scaillet, A. Aiuppa, R. Moretti, L. Ottolini To cite this version: Marina Alletti, Don
Chlorine Partitioning Between a Basaltic Melt and H2O-CO2 Fluids at Mount Etna Marina Alletti, Don R. Baker, Bruno Scaillet, A. Aiuppa, R. Moretti, L. Ottolini To cite this version: Marina Alletti, Don
predictive mineral discovery*cooperative Research Centre A legacy for mineral exploration science Mineral Systems Q3 Fluid reservoirs
 Mineral Systems Q3 Fluid reservoirs 1 Key Parameter Mineral System Exploration is reflected in scale-dependent translation A. Gradient in hydraulic potential B. Permeability C. Solubility sensitivity to
Mineral Systems Q3 Fluid reservoirs 1 Key Parameter Mineral System Exploration is reflected in scale-dependent translation A. Gradient in hydraulic potential B. Permeability C. Solubility sensitivity to
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes
 Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
Lecture 6 - Igneous Rocks and Volcanoes Learning objectives Understand and be able to predict where and why magma will be forming at different tectonic settings Understand the factors controlling magma
Supplementary Information. Analytics
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2013192 S. Kutterolf et al. Supplementary Information Analytics Table DR1: Summary of Nicaraguan tephra properties. Eruption ages and erupted magma masses from Kutterolf et al. (2007,
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2013192 S. Kutterolf et al. Supplementary Information Analytics Table DR1: Summary of Nicaraguan tephra properties. Eruption ages and erupted magma masses from Kutterolf et al. (2007,
Experimental Simulation of Closed-System Degassing in the System Basalt^H 2 O^CO 2^S^Cl
 JOURNAL OF PETROLOGY VOLUME 52 NUMBER 9 PAGES1737^1762 211 doi:1.193/petrology/egr27 Experimental Simulation of Closed-System Degassing in the System Basalt^ O^CO 2^S^Cl PRISCILLE LESNE 1 *, SIMON C. KOHN
JOURNAL OF PETROLOGY VOLUME 52 NUMBER 9 PAGES1737^1762 211 doi:1.193/petrology/egr27 Experimental Simulation of Closed-System Degassing in the System Basalt^ O^CO 2^S^Cl PRISCILLE LESNE 1 *, SIMON C. KOHN
ERTH 456 / GEOL 556 Volcanology. Lecture 06: Conduits
 1 / 28 ERTH 456 / GEOL 556 Volcanology Lecture 06: Conduits Ronni Grapenthin rg@nmt.edu MSEC 356, x5924 hours: TR 3-4PM or appt. September 12, 2016 2 / 28 How does magma get from source to surface? What
1 / 28 ERTH 456 / GEOL 556 Volcanology Lecture 06: Conduits Ronni Grapenthin rg@nmt.edu MSEC 356, x5924 hours: TR 3-4PM or appt. September 12, 2016 2 / 28 How does magma get from source to surface? What
The Nature of Igneous Rocks
 The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
The Nature of Igneous Rocks Form from Magma Hot, partially molten mixture of solid liquid and gas Mineral crystals form in the magma making a crystal slush Gases - H 2 O, CO 2, etc. - are dissolved in
c) Explain the observations in terms of the DYNAMIC NATURE of the equilibrium system.
 Chemical Equilibrium - Part A: 1. At 25 o C and 101.3 kpa one mole of hydrogen gas and one mol of chlorine gas are reacted in a stoppered reaction vessel. After a certain time, three gases are detected
Chemical Equilibrium - Part A: 1. At 25 o C and 101.3 kpa one mole of hydrogen gas and one mol of chlorine gas are reacted in a stoppered reaction vessel. After a certain time, three gases are detected
LECTURE #11: Volcanic Disasters: Lava Properties & Eruption Types
 GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #11: Volcanic Disasters: Lava Properties & Eruption Types Date: 13 February 2018 I. Exam I grades are posted on the class website (link at the bottom
GEOL 0820 Ramsey Natural Disasters Spring, 2018 LECTURE #11: Volcanic Disasters: Lava Properties & Eruption Types Date: 13 February 2018 I. Exam I grades are posted on the class website (link at the bottom
How does magma reach the surface?
 How does magma reach the surface? 2004-2008, effusive 1980, explosive Michael Manga Why do volcanoes (only sometimes) erupt explosively? 2004-2008, effusive 1980, explosive Michael Manga Gonnermann and
How does magma reach the surface? 2004-2008, effusive 1980, explosive Michael Manga Why do volcanoes (only sometimes) erupt explosively? 2004-2008, effusive 1980, explosive Michael Manga Gonnermann and
Magmatic Sulfur and Chlorine Abundances at Stromboli, Italy and their Role in the Formation of Vesicle-hosted Metal Alloys
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2008-08-07 Magmatic Sulfur and Chlorine Abundances at Stromboli, Italy and their Role in the Formation of Vesicle-hosted Metal
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Theses and Dissertations 2008-08-07 Magmatic Sulfur and Chlorine Abundances at Stromboli, Italy and their Role in the Formation of Vesicle-hosted Metal
Volatiles (H, C, N, F, S, Cl) in the lunar mantle, crust, and regolith: What questions remain and where to go next?
 Volatiles (H, C, N, F, S, Cl) in the lunar mantle, crust, and regolith: What questions remain and where to go next? Francis M. McCubbin & Charles K. Shearer Motivation behind this work 100, In Revision,
Volatiles (H, C, N, F, S, Cl) in the lunar mantle, crust, and regolith: What questions remain and where to go next? Francis M. McCubbin & Charles K. Shearer Motivation behind this work 100, In Revision,
1.1 Introduction to the Particulate Nature of Matter and Chemical Change MATTER. Homogeneous (SOLUTIONS)
 TOPIC 1: STOICHIOMETRIC RELATIONS 1.1 Introduction to the Particulate Nature of Matter and Chemical Change MATTER Mass Volume Particles Particles in constant motion MATTER Pure Matters Mixtures ELEMENTS
TOPIC 1: STOICHIOMETRIC RELATIONS 1.1 Introduction to the Particulate Nature of Matter and Chemical Change MATTER Mass Volume Particles Particles in constant motion MATTER Pure Matters Mixtures ELEMENTS
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115, B11202, doi: /2010jb007433, 2010
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2010jb007433, 2010 Magma plumbing system of the 2000 eruption of Miyakejima volcano, Japan, deduced from volatile and major component contents of
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2010jb007433, 2010 Magma plumbing system of the 2000 eruption of Miyakejima volcano, Japan, deduced from volatile and major component contents of
- low FeO*/MgO is controlled by the reaction relation oliv + liq! opx.
 Mantle melting trend to high-sio 2 - low FeO*/MgO is controlled by the reaction relation oliv + liq! opx. 4 3 2 1 Ol+Opx +Cpx+Sp +liq 79-35g 82-66 87S35 85-44 85-41c -ol +opx Mantle melting/reaction 0
Mantle melting trend to high-sio 2 - low FeO*/MgO is controlled by the reaction relation oliv + liq! opx. 4 3 2 1 Ol+Opx +Cpx+Sp +liq 79-35g 82-66 87S35 85-44 85-41c -ol +opx Mantle melting/reaction 0
Treatment of Data. Methods of determining analytical error -Counting statistics -Reproducibility of reference materials -Homogeneity of sample
 Treatment of Data Methods of determining analytical error -Counting statistics -Reproducibility of reference materials -Homogeneity of sample Detection Limits Assessment of analytical quality -Analytical
Treatment of Data Methods of determining analytical error -Counting statistics -Reproducibility of reference materials -Homogeneity of sample Detection Limits Assessment of analytical quality -Analytical
AP Study Questions
 Class: Date: AP 19.5-19.7 Study Questions Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 3. The value of G at 25 C for the formation of POCl 3 from its constituent
Class: Date: AP 19.5-19.7 Study Questions Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 3. The value of G at 25 C for the formation of POCl 3 from its constituent
Why do volcanoes (only sometimes) erupt explosively?
 Why do volcanoes (only sometimes) erupt explosively? 2004-2008, effusive 1980, explosive Michael Manga Gonnermann and Manga, Annual Reviews of Fluids Mechanics, 2007 Why do volcanoes erupt explosively?
Why do volcanoes (only sometimes) erupt explosively? 2004-2008, effusive 1980, explosive Michael Manga Gonnermann and Manga, Annual Reviews of Fluids Mechanics, 2007 Why do volcanoes erupt explosively?
Overview of the KAHT system. Ian E.M. Smith, School of Environment, University of Auckland
 Overview of the KAHT system Ian E.M. Smith, School of Environment, University of Auckland Tonga-Kermadec-New Zealand Arc Developed on the Pacific - Australian convergent margin Mainly intraoceanic except
Overview of the KAHT system Ian E.M. Smith, School of Environment, University of Auckland Tonga-Kermadec-New Zealand Arc Developed on the Pacific - Australian convergent margin Mainly intraoceanic except
TRU Chemistry Contest Chemistry 12 May 21, 2003 Time: 90 minutes
 TRU Chemistry Contest Chemistry 12 May 21, 2003 Time: 90 minutes Last Name First name School Teacher Please follow the instructions below. We will send your teacher a report on your performance. Top performers
TRU Chemistry Contest Chemistry 12 May 21, 2003 Time: 90 minutes Last Name First name School Teacher Please follow the instructions below. We will send your teacher a report on your performance. Top performers
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions
 Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions Reactions in which electrons are transferred from one reactant to another oxidation the loss of electrons reduction the gainof electrons LEO the lion says GER Oxidation
Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reactions Reactions in which electrons are transferred from one reactant to another oxidation the loss of electrons reduction the gainof electrons LEO the lion says GER Oxidation
Where are these melts generated in the mantle wedge?
 Melt generation processes in subduction zones T.L. Grove, C.B. Till, N. Chatterjee, E. Medard, S.W. Parman New experiments on H2O-saturated melting of mantle peridotite - The role of H2O in mantle wedge
Melt generation processes in subduction zones T.L. Grove, C.B. Till, N. Chatterjee, E. Medard, S.W. Parman New experiments on H2O-saturated melting of mantle peridotite - The role of H2O in mantle wedge
Zircon/fluid trace element partition coefficients measured by recrystallization of Mud Tank zircon at 1.5 GPa and C
 Zircon/fluid trace element partition coefficients measured by recrystallization of Mud Tank zircon at 1.5 GPa and 800-1000 C Tim Peters and John C. Ayers Vanderbilt University Funding by National Science
Zircon/fluid trace element partition coefficients measured by recrystallization of Mud Tank zircon at 1.5 GPa and 800-1000 C Tim Peters and John C. Ayers Vanderbilt University Funding by National Science
Fluorine and Chlorine in Alkaline Rocks and A-type Granites
 Fluorine and Chlorine in Alkaline Rocks and A-type Granites Using the fluorine and chlorine content of Amphibole, Apatite and Biotite to monitor magma halogen content Chilwa Province, Malawi, and Carboniferous
Fluorine and Chlorine in Alkaline Rocks and A-type Granites Using the fluorine and chlorine content of Amphibole, Apatite and Biotite to monitor magma halogen content Chilwa Province, Malawi, and Carboniferous
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Sample Description Rock 14053 is one of the most well-studied high-al basalts in the Apollo collection 2,3. This sample (14053,241) was chipped from a large (approx. 0.5 m long) boulder at station C2,
Sample Description Rock 14053 is one of the most well-studied high-al basalts in the Apollo collection 2,3. This sample (14053,241) was chipped from a large (approx. 0.5 m long) boulder at station C2,
High-temperature fracture of magma
 High-temperature fracture of magma Hugh Tuffen Peter Sammonds Rosanna Smith Harry Pinkerton Don Dingwell Jon Castro Cracks, Fractures and Faults in the Earth Thursday 19 th June 2008 Montserrat (Sparks
High-temperature fracture of magma Hugh Tuffen Peter Sammonds Rosanna Smith Harry Pinkerton Don Dingwell Jon Castro Cracks, Fractures and Faults in the Earth Thursday 19 th June 2008 Montserrat (Sparks
EASC100: EXAM1 (07) Lithosphere and Hydrosphere
 EASC100: EXAM1 (07) Lithosphere and Hydrosphere Name: 1. Why do Mercury and the Moon lack an atmosphere? A) They formed after all the gas had been used up. B) They are so cold that all their gases have
EASC100: EXAM1 (07) Lithosphere and Hydrosphere Name: 1. Why do Mercury and the Moon lack an atmosphere? A) They formed after all the gas had been used up. B) They are so cold that all their gases have
Worked Example of Batch Melting: Rb and Sr
 Worked Example of Batch Melting: Rb and Sr Basalt with the mode: Table 9.2. Conversion from mode to weight percent Mineral Mode Density Wt prop Wt% ol 15 3.6 54 0.18 cpx 33 3.4 112.2 0.37 plag 51 2.7 137.7
Worked Example of Batch Melting: Rb and Sr Basalt with the mode: Table 9.2. Conversion from mode to weight percent Mineral Mode Density Wt prop Wt% ol 15 3.6 54 0.18 cpx 33 3.4 112.2 0.37 plag 51 2.7 137.7
What is going on here?
 Major Digression! Atoms? Elements? Compounds? Minerals? Rocks? What is going on here? Source:SERC @ Carleton College http://www.brocku.ca/earthsciences/people/gfinn/petrology/periodic.gif http://www.meta-synthesis.com/webbook/35_pt/pt_database.php?pt_id=335
Major Digression! Atoms? Elements? Compounds? Minerals? Rocks? What is going on here? Source:SERC @ Carleton College http://www.brocku.ca/earthsciences/people/gfinn/petrology/periodic.gif http://www.meta-synthesis.com/webbook/35_pt/pt_database.php?pt_id=335
Bonding Mrs. Pugliese. Name March 02, 2011
 Bonding Mrs. Pugliese Name March 02, 2011 1. Atoms of which element have the greatest tendency to gain electrons? 1. bromine 3. fluorine 2. chlorine 4. iodine 2. Which polyatomic ion contains the greatest
Bonding Mrs. Pugliese Name March 02, 2011 1. Atoms of which element have the greatest tendency to gain electrons? 1. bromine 3. fluorine 2. chlorine 4. iodine 2. Which polyatomic ion contains the greatest
On the Chemical Composition of Europa s Icy Shell, Ocean and Unterlying Rocks
 On the Chemical Composition of Europa s Icy Shell, Ocean and Unterlying Rocks M. Yu. Zolotov (Arizona State University) J. S. Kargel (University of Arizona) By Isabella Kraus Overview Introduction Composition
On the Chemical Composition of Europa s Icy Shell, Ocean and Unterlying Rocks M. Yu. Zolotov (Arizona State University) J. S. Kargel (University of Arizona) By Isabella Kraus Overview Introduction Composition
Supplemental Information. I. Alternative version of Figure 1. II. Sample Preparation
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2012195 Watkins et al. Supplemental Information I. Alternative version of Figure 1 Figure DR1. CO 2 versus H 2 O for Mono Craters pyroclasts. Circles represent spot analyses on obsidian
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2012195 Watkins et al. Supplemental Information I. Alternative version of Figure 1 Figure DR1. CO 2 versus H 2 O for Mono Craters pyroclasts. Circles represent spot analyses on obsidian
The Martian Sedimentary Mass: Constraints on its Composition, Age and Size. Scott McLennan Department of Geosciences, SUNY Stony Brook
 The Martian Sedimentary Mass: Constraints on its Composition, Age and Size Scott McLennan Department of Geosciences, SUNY Stony Brook Exploring Mars Habitability Lisbon 14 June, 2011 Martian Crustal Chemistry
The Martian Sedimentary Mass: Constraints on its Composition, Age and Size Scott McLennan Department of Geosciences, SUNY Stony Brook Exploring Mars Habitability Lisbon 14 June, 2011 Martian Crustal Chemistry
Fall 2011 CHEM Test 4, Form A
 Fall 2011 CHEM 1110.40413 Test 4, Form A Part I. Multiple Choice: Clearly circle the best answer. (60 pts) Name: 1. The common constituent in all acid solutions is A) H 2 SO 4 B) H 2 C) H + D) OH 2. Which
Fall 2011 CHEM 1110.40413 Test 4, Form A Part I. Multiple Choice: Clearly circle the best answer. (60 pts) Name: 1. The common constituent in all acid solutions is A) H 2 SO 4 B) H 2 C) H + D) OH 2. Which
2011, Robert Ayton. All rights reserved.
 Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces Outline 1. Phase Diagrams and Triple Point Diagrams 2. Intermolecular Forces Review 1. Phase Diagrams and Triple Point Diagrams Phase Diagram of Water Triple
Liquids, Solids, and Intermolecular Forces Outline 1. Phase Diagrams and Triple Point Diagrams 2. Intermolecular Forces Review 1. Phase Diagrams and Triple Point Diagrams Phase Diagram of Water Triple
Anhydrite stability and the effect of Ca on the behavior of sulfur in felsic magmas
 Manuscript 4959 Revision 1 Anhydrite stability and the effect of Ca on the behavior of sulfur in felsic magmas RUIFANG HUANG 1,2 AND HANS KEPPLER 1* 1 Bayerisches Geoinstitut, 95440 Bayreuth, Germany 2
Manuscript 4959 Revision 1 Anhydrite stability and the effect of Ca on the behavior of sulfur in felsic magmas RUIFANG HUANG 1,2 AND HANS KEPPLER 1* 1 Bayerisches Geoinstitut, 95440 Bayreuth, Germany 2
GEOLOGY. Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02
 GEOLOGY Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02 Topic No. & Title : 37 Magma Bowen Series (Part 01) Academic Script What is Igneous Petrology? Igneous
GEOLOGY Subject : GEOLOGY (For under graduate student.) Paper No. : Paper 02 Introduction to Geology 02 Topic No. & Title : 37 Magma Bowen Series (Part 01) Academic Script What is Igneous Petrology? Igneous
A4 CAI COMPOSITION: DIVALENT ELEMENT PARTITIONING AND CATHODOLUMINESCENCE. A4.1 Anorthite and Melt compositions for Synthetic CAI Composition 224SAM
 147 A4 CAI COMPOSITION: DIVALENT ELEMENT PARTITIONING AND CATHODOLUMINESCENCE A4.1 Anorthite and Melt compositions for Synthetic CAI Composition 224SAM Anorthite-melt partitioning of divalent elements
147 A4 CAI COMPOSITION: DIVALENT ELEMENT PARTITIONING AND CATHODOLUMINESCENCE A4.1 Anorthite and Melt compositions for Synthetic CAI Composition 224SAM Anorthite-melt partitioning of divalent elements
V. B. NAUMOV 1, V. A. KOVALENKER 2 and V. L. RUSINOV 2
 CHEMICAL COMPOSITION, TRACE ELEMENTS, AND VOLATILE COMPONENTS OF MELTS: EVIDENCE FROM INCLUSIONS IN THE MINERALS OF NEOVOLCANITES FROM THE CENTRAL AND EASTERN SLOVAKIA V. B. NAUMOV 1, V. A. KOVALENKER
CHEMICAL COMPOSITION, TRACE ELEMENTS, AND VOLATILE COMPONENTS OF MELTS: EVIDENCE FROM INCLUSIONS IN THE MINERALS OF NEOVOLCANITES FROM THE CENTRAL AND EASTERN SLOVAKIA V. B. NAUMOV 1, V. A. KOVALENKER
Magma fertility: Concepts and JCU research at NQ
 Magma fertility: Concepts and JCU research at NQ Zhaoshan Chang*, Carl Spandler, Yanbo Cheng EGRU, JCU *Zhaoshan.chang@jcu.edu.au 27 May 2015 Townsville, Queensland, Australia Magma fertility Miners dream
Magma fertility: Concepts and JCU research at NQ Zhaoshan Chang*, Carl Spandler, Yanbo Cheng EGRU, JCU *Zhaoshan.chang@jcu.edu.au 27 May 2015 Townsville, Queensland, Australia Magma fertility Miners dream
Magma Formation and Behavior
 Magma Formation and Behavior Introduction: The study of body waves as they pass through Earth's interior provides strong evidence that the Earth's mantle is composed almost entirely of solid ultramafic
Magma Formation and Behavior Introduction: The study of body waves as they pass through Earth's interior provides strong evidence that the Earth's mantle is composed almost entirely of solid ultramafic
WHAT IS A MAGMA. Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth.
 UNIT - 8 VOLCANOES WHAT IS A MAGMA Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth. In some instances, it solidifies within the crust to form plutonic
UNIT - 8 VOLCANOES WHAT IS A MAGMA Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth. In some instances, it solidifies within the crust to form plutonic
Supplementary material to accompany the manuscript, Redox variations in HSDP2
 Supplementary material to accompany the manuscript, Redox variations in HSDP2 Mauna Kea lavas, the oxygen fugacity of the Hawaiian plume, and the role of volcanic gases in Earth s oxygenation by M. Brounce,
Supplementary material to accompany the manuscript, Redox variations in HSDP2 Mauna Kea lavas, the oxygen fugacity of the Hawaiian plume, and the role of volcanic gases in Earth s oxygenation by M. Brounce,
2. (12 pts) Write the reactions that correspond to the following enthalpy changes: a) H f o for solid aluminum oxide.
 1. (6 pts) Given the following data at 25 o C: 2 O 3 (g) > 3 O 2 (g) H o = 427 kj O 2 (g) > 2 O (g) H o = 495 kj NO (g) + O 3 (g) > NO 2 (g) + O 2 (g) H o = 199 kj Calculate H o for the following reaction
1. (6 pts) Given the following data at 25 o C: 2 O 3 (g) > 3 O 2 (g) H o = 427 kj O 2 (g) > 2 O (g) H o = 495 kj NO (g) + O 3 (g) > NO 2 (g) + O 2 (g) H o = 199 kj Calculate H o for the following reaction
Chemistry Section Review 7.3
 Chemistry Section Review 7.3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Put the LETTER of the correct answer in the blank. 1. The molar mass of an element
Chemistry Section Review 7.3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Put the LETTER of the correct answer in the blank. 1. The molar mass of an element
Solutions, Ions & Acids, Bases (Chapters 3-4) Example - Limiting Reagents. Percent Yield. Reaction Yields. Yield - example.
 Solutions, Ions & Acids, Bases (Chapters 3-4) Chem 107 T. Hughbanks Example - Limiting Reagents SiCl 4 is used in making computer chips. It is produced by the reaction: SiO 2 + 2 C + 2 Cl 2 SiCl 4 + 2
Solutions, Ions & Acids, Bases (Chapters 3-4) Chem 107 T. Hughbanks Example - Limiting Reagents SiCl 4 is used in making computer chips. It is produced by the reaction: SiO 2 + 2 C + 2 Cl 2 SiCl 4 + 2
Solutions, Ions & Acids, Bases (Chapters 3-4)
 Solutions, Ions & Acids, Bases (Chapters 3-4) Chem 107 T. Hughbanks Example - Limiting Reagents SiCl 4 is used in making computer chips. It is produced by the reaction: SiO 2 + 2 C + 2 Cl 2 SiCl 4 + 2
Solutions, Ions & Acids, Bases (Chapters 3-4) Chem 107 T. Hughbanks Example - Limiting Reagents SiCl 4 is used in making computer chips. It is produced by the reaction: SiO 2 + 2 C + 2 Cl 2 SiCl 4 + 2
GY 111: Physical Geology
 UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 9: Extrusive Igneous Rocks Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) The chemical composition of the crust 2) Crystallization of molten
UNIVERSITY OF SOUTH ALABAMA GY 111: Physical Geology Lecture 9: Extrusive Igneous Rocks Instructor: Dr. Douglas W. Haywick Last Time 1) The chemical composition of the crust 2) Crystallization of molten
Fluids, melts, and supercriticality in the MSH system and element transport in subduction zones
 cosmic rays Fluids, s, and supercriticality in the MSH system and element transport in subduction zones 10 Be volcanic front N, O 10 Be ocean water + CO 2 tracing petrologic and geotectonic processes (trace)
cosmic rays Fluids, s, and supercriticality in the MSH system and element transport in subduction zones 10 Be volcanic front N, O 10 Be ocean water + CO 2 tracing petrologic and geotectonic processes (trace)
Essentials of Geology, 11e
 Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Essentials of Geology, 11e Igneous Rocks and Intrusive Activity Chapter 3 Instructor Jennifer Barson Spokane Falls Community College Geology 101 Stanley Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Characteristics
Review. 8th grade science STAAR. Name Class. Underline your strong TEKS and circle your weak TEKS: 8.5A Atoms. 7.5C Energy Flow Through Ecosystems
 8th grade science STAAR Review Name Class Underline your strong TEKS and circle your weak TEKS: 8.5A Atoms 7.5C Energy Flow Through Ecosystems 8.5B Reactivity 8.5C Periodic Table 8.5D Chemical Formulas
8th grade science STAAR Review Name Class Underline your strong TEKS and circle your weak TEKS: 8.5A Atoms 7.5C Energy Flow Through Ecosystems 8.5B Reactivity 8.5C Periodic Table 8.5D Chemical Formulas
Sample collection was restricted to pumice from plinian fallout, from thin distal ignimbrite, and from
 DATA REPOSITORY APPENDIX 1. ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Sample collection was restricted to pumice from plinian fallout, from thin distal ignimbrite, and from proximal lithic breccias deposits (Fig. DR1 and
DATA REPOSITORY APPENDIX 1. ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Sample collection was restricted to pumice from plinian fallout, from thin distal ignimbrite, and from proximal lithic breccias deposits (Fig. DR1 and
Name: Date: M O L A R M A S S & P E R C E N T C O M P O S I T I O N
 Name: Date: M O L A R M A S S & P E R C E N T C O M P O S I T I O N I. Molar Masses Given a periodic table, you should be able to calculate the molecular mass (in amu s) or the molar mass (in grams) for
Name: Date: M O L A R M A S S & P E R C E N T C O M P O S I T I O N I. Molar Masses Given a periodic table, you should be able to calculate the molecular mass (in amu s) or the molar mass (in grams) for
Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark
 Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Effusive: lavas (e.g., Kilauea) Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Explosive: pyroclastic rocks (e.g., Krakatau) Factors Governing
Introduction to Earth s s Spheres The Benchmark Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Effusive: lavas (e.g., Kilauea) Volcanism Volcanic eruptions Explosive: pyroclastic rocks (e.g., Krakatau) Factors Governing
N = N 0 e -λt D* = N 0 -N D* = N 0 (1-e -λt ) or N(e λt -1) where N is number of parent atoms at time t, N 0
 N = N 0 e -λt D* = N 0 -N D* = N 0 (1-e -λt ) or N(e λt -1) where N is number of parent atoms at time t, N 0 is initial number of parents, D* is number of radiogenic daughter atoms, and λ is the decay
N = N 0 e -λt D* = N 0 -N D* = N 0 (1-e -λt ) or N(e λt -1) where N is number of parent atoms at time t, N 0 is initial number of parents, D* is number of radiogenic daughter atoms, and λ is the decay
STUDY OF GROWTH RATE OF ALKALI FELDSPAR IN PHLEGRAEAN FIELDS TRACHYTES
 STUDY OF GROWTH RATE OF ALKALI FELDSPAR IN PHLEGRAEAN FIELDS TRACHYTES MARTA CALZOLAIO Dipartimento di Scienze della Terra, Università di Camerino, Via Gentile III da Varano, 62032 Camerino (MC) INTRODUCTION
STUDY OF GROWTH RATE OF ALKALI FELDSPAR IN PHLEGRAEAN FIELDS TRACHYTES MARTA CALZOLAIO Dipartimento di Scienze della Terra, Università di Camerino, Via Gentile III da Varano, 62032 Camerino (MC) INTRODUCTION
Magmatic petrology and ore generating potential of the Zidarovo center, Eastern Srednogorie, Bulgaria.
 Magmatic petrology and ore generating potential of the Zidarovo center, Eastern Srednogorie, Bulgaria. Rossen Nedialkov, Robert Moritz, Denis Fontignie Main tectonic units of Bulgaria after Zh. Ivanov
Magmatic petrology and ore generating potential of the Zidarovo center, Eastern Srednogorie, Bulgaria. Rossen Nedialkov, Robert Moritz, Denis Fontignie Main tectonic units of Bulgaria after Zh. Ivanov
6 theoretical problems 2 practical problems
 4 th 6 theoretical problems 2 practical problems THE FOURTH INTERNATIONAL CHEMISTRY OLYMPIAD MOSCOW 1972 SOVIET UNION THEORETICAL PROBLEMS PROBLEM 1 A mixture of two solid elements with a mass of 1.52
4 th 6 theoretical problems 2 practical problems THE FOURTH INTERNATIONAL CHEMISTRY OLYMPIAD MOSCOW 1972 SOVIET UNION THEORETICAL PROBLEMS PROBLEM 1 A mixture of two solid elements with a mass of 1.52
Chapter 8 Chemical Reactions
 Chemistry/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 8 Chemical Reactions Chapter 8: 1 7, 9 18, 20, 21, 24 26, 29 31, 46, 55, 69 Practice Problems 1. Write a skeleton equation for each chemical reaction. Include the appropriate
Chemistry/ PEP Name: Date: Chapter 8 Chemical Reactions Chapter 8: 1 7, 9 18, 20, 21, 24 26, 29 31, 46, 55, 69 Practice Problems 1. Write a skeleton equation for each chemical reaction. Include the appropriate
4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table. GCSE Chemistry
 4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table GCSE Chemistry All substances are made of atoms this is cannot be chemically broken down it is the smallest part of an element. Elements are made of only one
4.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table GCSE Chemistry All substances are made of atoms this is cannot be chemically broken down it is the smallest part of an element. Elements are made of only one
CHAPTER 7: CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS. Chemistry 1-2 Enriched Mr. Chumbley
 CHAPTER 7: CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS Chemistry 1-2 Enriched Mr. Chumbley SECTION 1: CHEMICAL NAMES AND FORMULAS While the bulk of the content will come from the Naming Chemical Compounds
CHAPTER 7: CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND CHEMICAL COMPOUNDS Chemistry 1-2 Enriched Mr. Chumbley SECTION 1: CHEMICAL NAMES AND FORMULAS While the bulk of the content will come from the Naming Chemical Compounds
Imagine the first rock and the cycles that it has been through.
 A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
A rock is a naturally formed, consolidated material usually composed of grains of one or more minerals The rock cycle shows how one type of rocky material gets transformed into another The Rock Cycle Representation
9/4/2015. Feldspars White, pink, variable Clays White perfect Quartz Colourless, white, red, None
 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks Chapter 3.0: Weathering & soils Chapter 4.0: Geological
ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks Chapter 3.0: Weathering & soils Chapter 4.0: Geological
Our country, our future 525/1 S6 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 DURATION: 2 HOUR 45 MINUTES
 1 Our country, our future 525/1 S6 CHEMISTRY Exam 10 PAPER 1 DURATION: 2 HOUR 45 MINUTES For Marking guide contact and consultations: Dr. Bbosa Science 0776 802709, Instructions - This paper consists of
1 Our country, our future 525/1 S6 CHEMISTRY Exam 10 PAPER 1 DURATION: 2 HOUR 45 MINUTES For Marking guide contact and consultations: Dr. Bbosa Science 0776 802709, Instructions - This paper consists of
Cosmic Building Blocks: From What is Earth Made?
 Cosmic Building Blocks: From What is Earth Made? The Sun constitutes 99.87% of the mass of the Solar system. Earth is big and important, so its composition should be similar to that of the average Solar
Cosmic Building Blocks: From What is Earth Made? The Sun constitutes 99.87% of the mass of the Solar system. Earth is big and important, so its composition should be similar to that of the average Solar
Chemistry Spring Packet Study Guide for Benchmark Exam
 Chemistry Spring Packet-1 --- Study Guide for Benchmark Exam 1. Which action will result in a new product with new chemical properties? A. shredding a newspaper B. cutting wood C. breaking a mirror D.
Chemistry Spring Packet-1 --- Study Guide for Benchmark Exam 1. Which action will result in a new product with new chemical properties? A. shredding a newspaper B. cutting wood C. breaking a mirror D.
A Rock is a solid aggregate of minerals.
 Quartz A Rock is a solid aggregate of minerals. Orthoclase Feldspar Plagioclase Feldspar Biotite Four different minerals are obvious in this piece of Granite. The average automobile contains: Minerals
Quartz A Rock is a solid aggregate of minerals. Orthoclase Feldspar Plagioclase Feldspar Biotite Four different minerals are obvious in this piece of Granite. The average automobile contains: Minerals
PLATE TECTONICS, VOLCANISM AND IGNEOUS ROCKS
 PLATE TECTONICS, VOLCANISM AND IGNEOUS ROCKS PLATE TECTONICS TO IGNEOUS ROCKS Internal Heat Seafloor Spreading/Plate Tectonics Volcanism Plate Boundary Intra-plate (hot spot) Divergent Convergent Igneous
PLATE TECTONICS, VOLCANISM AND IGNEOUS ROCKS PLATE TECTONICS TO IGNEOUS ROCKS Internal Heat Seafloor Spreading/Plate Tectonics Volcanism Plate Boundary Intra-plate (hot spot) Divergent Convergent Igneous
What can noble gases really say about mantle. 2) Extent of mantle degassing
 What can noble gases really say about mantle convection and the deep Earth volatile cycles? 1) Constraints on mass flow 1) Constraints on mass flow 2) Extent of mantle degassing Outline: -Noble gas geochemistry
What can noble gases really say about mantle convection and the deep Earth volatile cycles? 1) Constraints on mass flow 1) Constraints on mass flow 2) Extent of mantle degassing Outline: -Noble gas geochemistry
Nitrogen speciation in upper mantle fluids and the origin of Earth s nitrogen-rich atmosphere
 Supporting Online Material for Nitrogen speciation in upper mantle fluids and the origin of Earth s nitrogen-rich atmosphere Sami Mikhail & Dimitri Sverjensky S1. Supplementary discussion S1.1 The selection
Supporting Online Material for Nitrogen speciation in upper mantle fluids and the origin of Earth s nitrogen-rich atmosphere Sami Mikhail & Dimitri Sverjensky S1. Supplementary discussion S1.1 The selection
Chemical Reactions and Equations
 Chemical Reactions and Equations 5-1 5.1 What is a Chemical Reaction? A chemical reaction is a chemical change. A chemical reaction occurs when one or more substances is converted into one or more new
Chemical Reactions and Equations 5-1 5.1 What is a Chemical Reaction? A chemical reaction is a chemical change. A chemical reaction occurs when one or more substances is converted into one or more new
Week 7 Submarine Pyroclastic Activity (there was no lecture for week 6)
 Week 7 Submarine Pyroclastic Activity (there was no lecture for week 6) Note: some of these slides were provided by Dave Clague, MBARI Two topics: fluidal clasts and bubble wall fragments internal water
Week 7 Submarine Pyroclastic Activity (there was no lecture for week 6) Note: some of these slides were provided by Dave Clague, MBARI Two topics: fluidal clasts and bubble wall fragments internal water
General Chemistry 1 CHM201 Unit 2 Practice Test
 General Chemistry 1 CHM201 Unit 2 Practice Test 1. Which statement about the combustion of propane (C 3H 8) is not correct? C 3H 8 5O 2 3CO 2 4H 2O a. For every propane molecule consumed, three molecules
General Chemistry 1 CHM201 Unit 2 Practice Test 1. Which statement about the combustion of propane (C 3H 8) is not correct? C 3H 8 5O 2 3CO 2 4H 2O a. For every propane molecule consumed, three molecules
GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Spring 2016 Score / 58. Midterm 1 Chapters 1-10
 GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Name KEY Spring 2016 Score / 58 Midterm 1 Chapters 1-10 1) Name two things that petrologists want to know about magmas (1 pt) Formation, source, composition,
GEOL 2312 Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology Name KEY Spring 2016 Score / 58 Midterm 1 Chapters 1-10 1) Name two things that petrologists want to know about magmas (1 pt) Formation, source, composition,
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204
 Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Engineering Geology ECIV 2204 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad 2017-2016 Chapter (3) Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth Igneous Rocks Chapter 3: Rocks: Materials of the Solid Earth
Name period AP Unit 8: equilibrium
 Name period AP Unit 8: equilibrium 1. What is equilibrium? Rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction 2. How can you tell when equilibrium has been reached? The concentrations
Name period AP Unit 8: equilibrium 1. What is equilibrium? Rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction 2. How can you tell when equilibrium has been reached? The concentrations
Practice Questions for Lecture 5 Geology 1200
 Practice Questions for Lecture 5 Geology 1200 Use these questions to test your knowledge of Lecture5. The exams will be similar in format, except that they will deal with more than one chapter, and will
Practice Questions for Lecture 5 Geology 1200 Use these questions to test your knowledge of Lecture5. The exams will be similar in format, except that they will deal with more than one chapter, and will
Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity. Aka Volcano Under the City
 Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity Aka Volcano Under the City 18.1 Magma Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Temperature and pressure increase
Chapter 18 - Volcanic Activity Aka Volcano Under the City 18.1 Magma Describe factors that affect the formation of magma. Compare and contrast the different types of magma. Temperature and pressure increase
Primary Topics in Equilibrium
 Primary Topics in Equilibrium Outline 1. Equilibrium Expression 2. Calculating Concentration Given K 3. Calculating K Given Concentration Review 1. Equilibrium Expression (only gas and aqueous do not include
Primary Topics in Equilibrium Outline 1. Equilibrium Expression 2. Calculating Concentration Given K 3. Calculating K Given Concentration Review 1. Equilibrium Expression (only gas and aqueous do not include
Balancing Equations Notes
 . Unit 9 Chemical Equations and Reactions What is a Chemical Equation? A is a written representation of the process that occurs in a chemical reaction. A chemical equation is written with the (starting
. Unit 9 Chemical Equations and Reactions What is a Chemical Equation? A is a written representation of the process that occurs in a chemical reaction. A chemical equation is written with the (starting
2 Igneous Rock. How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture of igneous rock? BEFORE YOU READ. Rocks: Mineral Mixtures
 CHAPTER 2 2 Igneous Rock SECTION Rocks: Mineral Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture
CHAPTER 2 2 Igneous Rock SECTION Rocks: Mineral Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do igneous rocks form? What factors affect the texture
Chlorine solubility in evolved alkaline magmas
 ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 48, N. 4/5, August/October 2005 Chlorine solubility in evolved alkaline magmas Michael R. Carroll Dipartimento di Scienze della Terra, Università degli Studi di Camerino, Italy
ANNALS OF GEOPHYSICS, VOL. 48, N. 4/5, August/October 2005 Chlorine solubility in evolved alkaline magmas Michael R. Carroll Dipartimento di Scienze della Terra, Università degli Studi di Camerino, Italy
What can isotopes tell us about mantle dynamics? Sujoy Mukhopadhyay. Harvard University
 What can isotopes tell us about mantle dynamics? Sujoy Mukhopadhyay Harvard University The mantle zoo Hofmann, 1997 187 Os/ 188 Os 0.168 0.156 0.144 0.132 EM1 Hawaii Pitcairn DMM peridotites Shield Basalts
What can isotopes tell us about mantle dynamics? Sujoy Mukhopadhyay Harvard University The mantle zoo Hofmann, 1997 187 Os/ 188 Os 0.168 0.156 0.144 0.132 EM1 Hawaii Pitcairn DMM peridotites Shield Basalts
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 12 Volcanoes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Plate tectonics explains the global pattern of volcanism. Key Figure 12.20 (page
1. How many protons, electrons, and neutrons are in one atom of the following isotopes (6 points)?
 Chemistry 11 Department of Physical Sciences Kingsborough Community College City University of New York NAME Exam 1: Chapters 1-3 50 points 1. How many protons, electrons, and neutrons are in one atom
Chemistry 11 Department of Physical Sciences Kingsborough Community College City University of New York NAME Exam 1: Chapters 1-3 50 points 1. How many protons, electrons, and neutrons are in one atom
E) Buffer capacity is the amount of acid that can be added until all of the base is used up.
 Chem 124 Spring 2016 Exam 3 VERSION 1 Name make sure you fill in your version number in the TN box on the side of your scantron sheet 1) Which of the following solutions is a good buffer system? A) a solution
Chem 124 Spring 2016 Exam 3 VERSION 1 Name make sure you fill in your version number in the TN box on the side of your scantron sheet 1) Which of the following solutions is a good buffer system? A) a solution
Atmospheric Chemistry During the Accretion of Earth-like Exoplanets
 Atmospheric Chemistry During the Accretion of Earth-like Exoplanets Bruce Fegley, Jr. Planetary Chemistry Laboratory McDonnell Center for the Space Sciences Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences Washington
Atmospheric Chemistry During the Accretion of Earth-like Exoplanets Bruce Fegley, Jr. Planetary Chemistry Laboratory McDonnell Center for the Space Sciences Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences Washington
Lab 3: Igneous Rocks
 Lab 3: Igneous Rocks The Geology in YOUR life initiative Mount Shinmoedake erupts in Japan (Jan 26, 2010) Volcanic smoke rises from Mount Shinmoedake on 1 February, 2011. Smoke rises from Mount Shinmoedake
Lab 3: Igneous Rocks The Geology in YOUR life initiative Mount Shinmoedake erupts in Japan (Jan 26, 2010) Volcanic smoke rises from Mount Shinmoedake on 1 February, 2011. Smoke rises from Mount Shinmoedake
Magmatic Processes at Subduction Zones
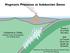 Magmatic Processes at Subduction Zones Katherine A. Kelley Graduate School of Oceanography Univ. of Rhode Island Thanks to Terry Plank Erik Hauri GVP: Liz Cottrell Simon Carn Jennifer Jay Ed Venzke Subduction
Magmatic Processes at Subduction Zones Katherine A. Kelley Graduate School of Oceanography Univ. of Rhode Island Thanks to Terry Plank Erik Hauri GVP: Liz Cottrell Simon Carn Jennifer Jay Ed Venzke Subduction
23/9/2013 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY. Chapter 2: Rock classification:
 ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 2: Rock classification: ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks
ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 2: Rock classification: ENGINEERING GEOLOGY Chapter 1.0: Introduction to engineering geology Chapter 2.0: Rock classification Igneous rocks Sedimentary rocks Metamorphic rocks
Unit 10: Solutions. soluble: will dissolve in miscible: refers to two liquids that mix evenly in all proportions -- e.g., food coloring and water
 Unit 10: Solutions Name: Solution Definitions solution: a homogeneous mixture -- -- e.g., alloy: a solid solution of metals -- e.g., solvent: the substance that dissolves the solute soluble: will dissolve
Unit 10: Solutions Name: Solution Definitions solution: a homogeneous mixture -- -- e.g., alloy: a solid solution of metals -- e.g., solvent: the substance that dissolves the solute soluble: will dissolve
Magma Formation and Behavior
 Magma Formation and Behavior Questions What causes mantle rock to melt, resulting in magma formation? Why is magma formation restricted to specific plate tectonic settings? Why are mafic (basaltic) magmas
Magma Formation and Behavior Questions What causes mantle rock to melt, resulting in magma formation? Why is magma formation restricted to specific plate tectonic settings? Why are mafic (basaltic) magmas
Igneous Rocks. Definition of Igneous Rocks. Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma
 Igneous Rocks Definition of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma Magma molten rock within the Earth Lava molten rock on the Earth s s surface Igneous
Igneous Rocks Definition of Igneous Rocks Igneous rocks form from cooling and crystallization of molten rock- magma Magma molten rock within the Earth Lava molten rock on the Earth s s surface Igneous
Chemistry Final Exam Sample Items
 Chemistry Final Exam Sample Items 1. Which best describes the current atomic theory? a. Atoms consist of electrons circling in definite orbits around a positive nucleus. b. Atoms are composed of electrons
Chemistry Final Exam Sample Items 1. Which best describes the current atomic theory? a. Atoms consist of electrons circling in definite orbits around a positive nucleus. b. Atoms are composed of electrons
