There are only two important things in chemistry, kinetics and thermodynamics. And, exp(-δg/rt) = k 1 /k -1, so there s really only one thing.
|
|
|
- Dayna Montgomery
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-1 There are only two important things in chemistry, kinetics and thermodynamics. And, exp(-δg/rt) = k 1 /k -1, so there s really only one thing. Kinetics provides information about the transition state of a reaction. We ll use a simple example to learn the basic tools, then look at more applications to catalysis. 1 st step: measure change in concentration over time under known conditions. Common techniques: GC UV/Vis NMR IR HPLC Note: data for EtCN are hypothetical
2 An aside on reaction deceleration Crude Data [EtI] = [NaCN] Concentration [EtCN] Time
3 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-2 Data can be plotted to determine reaction s overall order: 0 th : -d[a]/dt = k [A] = kt 1 st : -d[a]/dt = k[a] [A] = exp(kt) ln[a] = kt 2 nd : -d[a]/dt = k[a] 2 1/[A] = kt (also for k[a][b] if [A] = [B]
4 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-3 2 common methods to determine order in individual components. Pseudo 1 st -order: one component in huge excess (its concentration ~ constant) Collect data at various excessive concentrations Note [EtI] =1 0, but [NaCN] = 10 9 up to Rate = k[nacn][eti] ~ k[nacn] 0 [EtI] = k obs [EtI]
5 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-4 Replot data in 1 st order coordinates Slope of line = k obs Plot slope v [NaCN] Rxn is 1 st order in NaCN!! But is equiv NaCN really representative??
6 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-5 An alternative is the method of initial rates Keep one component constant (EtI) and vary the other (NaCN), but keep close to synthetic conditions Look at the first 10% of the reaction. Assume concentrations don t change much at low conversion. i.e. v = k[eti][nacn] ~ k[eti] 0 [NaCN] 0(c = 0 10%)
7 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-6 Notes Need more data points/time for initial rate Data looks pretty linear for first 10% Slope of best-fit line is kobs Kobs = k[nacn][eti] and [EtI] was constant Again, the rxn is first order in [NaCN] But we ignored 90% of the reaction.
8 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-7 Case Study 1: Bergman, JACS, 1981, 7028
9 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-8 Case Study 1: Bergman, JACS, 1981, 7028 Actual data Rxn in THF and 3-MeTHF look like superposition of concerted attack and premigration Rxn in 2,5 Me 2 THF only shows concerted attack. How to explain? Solvent assistance.
10 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-9 Case Study 1: Bergman, JACS, 1981, 7028 Mechanism predicts 1 st order dependence on THF. Do expt in 2,5-Me 2 THF, add THF (note only minor change in dipole
11 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-10 Case Study 2: Corey, JACS, 1996, 319 Previous work (JACS 1993, 12226) had shown 1 st order in OsO4-L, zero order in Fe(III)
12 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-11 Case Study 2: Corey, JACS, 1996, 319 Proposed structure of L*OsO 4 (olefin) for allyl benzoate These are saturation kinetics!!. Same as many enzymes and Lewis-Acid cat Rxns
13 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics Case Study 2: Corey, JACS, 1996, 319 Binding appears correlated to selectivity in asymmetric dihydroxylation Poor correlation between rate and selectivity
14 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-12 Case Study 3: Jacobsen, JACS, 1996, The reaction The data:
15 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-13 Case Study 3: Jacobsen, JACS, 1996, Rate = k[(salen)cr] 2 [epoxide] -1 [Azide] 0 2 Cr s involved in RDS Epoxide inhibits rxn!! Azide either (a) involved after RDS or (b) present in ground state
16 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-14 Case Study 4: Jacobsen, JACS 1999, 6086 and unpublished work The rxn: Data: Rate = k obs [Co] 2 V = k[a] n log(v) = log(k[a] n ) = n*log(k[a])
17 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-15 Case Study 4: Jacobsen, JACS 1999, 6086 and unpublished work Saturation kinetics with epoxide Inhibition by PhOH
18 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-16 Case Study 4: Jacobsen, JACS 1999, 6086 and unpublished work
19 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-17 Case Study 5: Stahl, JACS 2002, 766 The rxn The data: DMSO critical, but is not reduced (O2 required) or oxidized (no dimethyl sulfone is formed) 2 formed:o 2 consumed = 2 (O 2 is a 4 e- oxidant here) Under the rxn conditions, disproportionation observed (sometimes referred to as catalase activity ) Pd black (precipitated Pd metal) observed during course of reaction
20 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-18 Case Study 5: Stahl, JACS 2002, 766 Also: Pd black correlates with rate decrease Rate independent of [ROH] Conclude oxidation of Pd is rate limiting Predicts rate = k[o2][pd] (i.e. linear increase in rate with [Pd]) Propose catalyst decomposition is time-dependent. Decomposition is bimolecular; more pronounced at higher [Pd] Described by k dec competitive with k cat Eq 7 models data in trace B
21 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-19 Case Study 5: Stahl, JACS 2002, 766 Integrated form models experimental data Proposed mechanism fast
22 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-20 Case Study 6: Foa et al., J. Chem Soc. Dalton, 1975, The data
23 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-21 Case Study 6: Foa et al., J. Chem Soc. Dalton, 1975, For p-cl 2 Ph: k 1 = 1 x 10-4 Kk 2 = 1.1 x 10-5 k 2 ~ 10 So Ni[PPh 3 ] x more reactive than Ni [PPh 3 ] 3, but much less prevalent
24 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-case study 7 Coates, JACS, 2007, 4948 High yields for terminal and internal epoxides; stereospecific:
25 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-case study 7 Coates, JACS, 2007, 4948 Unusual kinetics observed: Anhydride formation displays induction period; no anhydride formed until epoxide consumed. Independent rxns similar in rate; show first order dependence on catalyst.
26 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-case study 7 Rate (lactone) = k[epox] 0 [CO] 0 [catalyst] 1 [Solvent] 1 Rate (anhydride) = k[lactone] 1 [CO] 0 [catalyst] 1 [Solvent] -1 Epoxide (and solvent) inhibit lactone anhydride Coates, JACS, 2007, 4948
27 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-case study 7 Resting state in presence of epoxide (no open LA sites) Resting state, no epoxide Coates, JACS, 2007, 4948
28 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-Van t Hoff Recall: ΔG = -RT*ln(K) and ΔG = ΔH TΔS Merging and rearranging gives the Van t Hoff Equation: ln(k) = (-ΔH/R)(1/T) + (ΔS/R) Ln(K) vs. 1/T gives ΔH and ΔS n.b. increasing temperature decreases contribution of ΔH Hartwig, JACS, 2006, 9306
29 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-Erying Equation The Eyring equation: determination of ΔH and ΔS. Supports associative mechanism (usually associative approx -30eu Dissociative eu) Stahl, JACS, 2004, 14832
30 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-Erying Equation Potential mechanisms: Small entropy of activation inconsistent with mechanism a. (Labeling studies ruled out mechanism b). Bergman, 1995, 6382
31 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics-Erying Equation Use in asymmetric catalysis ln(e.r) = (ΔΔH /R)(1/T) ΔΔS /R ΔΔH = ΔH minor - ΔH major ΔΔS = ΔS minor - ΔH major Biggest change in selectivity with temperature when ΔΔH dominates. Note with 2e, ee decrease with decreasing T Jacobsen, JACS, 1998, 948.
32 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics Practice problem: oxidative addition of ArX to Pd(0). Hartwig, JACS, 2005, 6944 Kinetics studied for ArCl, ArBr and ArI Your job: derive rate laws for each path; determine which one(s) is(are) consistent with data. w/ PhBr: rate = [ArBr] 0 [L] 0 Small ΔS ; same rate with sub. ArBr s Lineweaver-Burk Plot w/ PhI w/arcl
33 Ready; Catalysis Kinetics Hartwig, Science, 307, 2005, 1082 Determine the mechanism for oxidative addition of ammonia to Ir(I) olefin complex Data: Rxn with ND 3 showed no D incorporation into ligand
34
CHEM 251 (4 credits): Description
 CHEM 251 (4 credits): Intermediate Reactions of Nucleophiles and Electrophiles (Reactivity 2) Description: An understanding of chemical reactivity, initiated in Reactivity 1, is further developed based
CHEM 251 (4 credits): Intermediate Reactions of Nucleophiles and Electrophiles (Reactivity 2) Description: An understanding of chemical reactivity, initiated in Reactivity 1, is further developed based
Recapping where we are so far
 Recapping where we are so far Valence bond constructions, valence, valence electron counting, formal charges, etc Equivalent neutral classification and MLX plots Basic concepts for mechanism and kinetics
Recapping where we are so far Valence bond constructions, valence, valence electron counting, formal charges, etc Equivalent neutral classification and MLX plots Basic concepts for mechanism and kinetics
( ) Thermodynamic selectivity (reversible reactions)
 II. Reactivity A) General Principles Fundamental Equations G o Ea / RT = "RT ln K eq k = Ae 1) Kinetics vs Thermodynamics Kinetic selectivity (irreversible reactions) [ P 1 ] [ ] = ln k 1 P 2 ( ) = " #G
II. Reactivity A) General Principles Fundamental Equations G o Ea / RT = "RT ln K eq k = Ae 1) Kinetics vs Thermodynamics Kinetic selectivity (irreversible reactions) [ P 1 ] [ ] = ln k 1 P 2 ( ) = " #G
A. One-Substrate Reactions (1) Kinetic concepts
 A. One-Substrate Reactions (1) Kinetic concepts (2) Kinetic analysis (a) Briggs-Haldane steady-state treatment (b) Michaelis constant (K m ) (c) Specificity constant (3) Graphical analysis (4) Practical
A. One-Substrate Reactions (1) Kinetic concepts (2) Kinetic analysis (a) Briggs-Haldane steady-state treatment (b) Michaelis constant (K m ) (c) Specificity constant (3) Graphical analysis (4) Practical
Rate laws, Reaction Orders. Reaction Order Molecularity. Determining Reaction Order
 Rate laws, Reaction Orders The rate or velocity of a chemical reaction is loss of reactant or appearance of product in concentration units, per unit time d[p] = d[s] The rate law for a reaction is of the
Rate laws, Reaction Orders The rate or velocity of a chemical reaction is loss of reactant or appearance of product in concentration units, per unit time d[p] = d[s] The rate law for a reaction is of the
Enzyme Reactions. Lecture 13: Kinetics II Michaelis-Menten Kinetics. Margaret A. Daugherty Fall v = k 1 [A] E + S ES ES* EP E + P
![Enzyme Reactions. Lecture 13: Kinetics II Michaelis-Menten Kinetics. Margaret A. Daugherty Fall v = k 1 [A] E + S ES ES* EP E + P Enzyme Reactions. Lecture 13: Kinetics II Michaelis-Menten Kinetics. Margaret A. Daugherty Fall v = k 1 [A] E + S ES ES* EP E + P](/thumbs/76/74341799.jpg) Lecture 13: Kinetics II Michaelis-Menten Kinetics Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 Enzyme Reactions E + S ES ES* EP E + P E = enzyme ES = enzyme-substrate complex ES* = enzyme/transition state complex EP
Lecture 13: Kinetics II Michaelis-Menten Kinetics Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 Enzyme Reactions E + S ES ES* EP E + P E = enzyme ES = enzyme-substrate complex ES* = enzyme/transition state complex EP
Michaelis-Menten Kinetics. Lecture 13: Kinetics II. Enzyme Reactions. Margaret A. Daugherty. Fall Substrates bind to the enzyme s active site
 Lecture 13: Kinetics II Michaelis-Menten Kinetics Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 Enzyme Reactions E + S ES ES* EP E + P E = enzyme ES = enzyme-substrate complex ES* = enzyme/transition state complex EP
Lecture 13: Kinetics II Michaelis-Menten Kinetics Margaret A. Daugherty Fall 2003 Enzyme Reactions E + S ES ES* EP E + P E = enzyme ES = enzyme-substrate complex ES* = enzyme/transition state complex EP
Determining Rate Order
 Determining Rate Order As mentioned earlier, the rate order of a reaction can only be determined experimentally. A number of methods can be used to determine both the reaction order and the rate constant.
Determining Rate Order As mentioned earlier, the rate order of a reaction can only be determined experimentally. A number of methods can be used to determine both the reaction order and the rate constant.
Basics of Catalysis and Kinetics
 Basics of Catalysis and Kinetics Nobel laureates in catalysis: Haber (1918) Ziegler and Natta (1963) Wilkinson, Fischer (1973) Knowles, Noyori, Sharpless (2001) Grubbs, Schrock, Chauvin (2006) Ertl (2007)
Basics of Catalysis and Kinetics Nobel laureates in catalysis: Haber (1918) Ziegler and Natta (1963) Wilkinson, Fischer (1973) Knowles, Noyori, Sharpless (2001) Grubbs, Schrock, Chauvin (2006) Ertl (2007)
TOPIC 6: Chemical kinetics
 TOPIC 6: Chemical kinetics Reaction rates Reaction rate laws Integrated reaction rate laws Reaction mechanism Kinetic theories Arrhenius law Catalysis Enzimatic catalysis Fuente: Cedre http://loincognito.-iles.wordpress.com/202/04/titanic-
TOPIC 6: Chemical kinetics Reaction rates Reaction rate laws Integrated reaction rate laws Reaction mechanism Kinetic theories Arrhenius law Catalysis Enzimatic catalysis Fuente: Cedre http://loincognito.-iles.wordpress.com/202/04/titanic-
Chapter 14 Chemical Kinetics
 7/10/003 Chapter 14 Chemical Kinetics 14-1 Rates of Chemical Reactions 14- Reaction Rates and Concentrations 14-3 The Dependence of Concentrations on Time 14-4 Reaction Mechanisms 14-5 Reaction Mechanism
7/10/003 Chapter 14 Chemical Kinetics 14-1 Rates of Chemical Reactions 14- Reaction Rates and Concentrations 14-3 The Dependence of Concentrations on Time 14-4 Reaction Mechanisms 14-5 Reaction Mechanism
Macromolecular Interactions the equilibrium element
 Macromolecular Interactions the equilibrium element Physical Reality Quantitative P + L PL K d,overall K d,overall = [P][L] [PL] Driving force is difference in ground state free energies ΔG f o ΔG f o
Macromolecular Interactions the equilibrium element Physical Reality Quantitative P + L PL K d,overall K d,overall = [P][L] [PL] Driving force is difference in ground state free energies ΔG f o ΔG f o
1. Introduction to Chemical Kinetics
 1. Introduction to Chemical Kinetics objectives of chemical kinetics 1) Determine empirical rate laws H 2 + I 2 2HI How does the concentration of H 2, I 2, and HI change with time? 2) Determine the mechanism
1. Introduction to Chemical Kinetics objectives of chemical kinetics 1) Determine empirical rate laws H 2 + I 2 2HI How does the concentration of H 2, I 2, and HI change with time? 2) Determine the mechanism
!n[a] =!n[a] o. " kt. Half lives. Half Life of a First Order Reaction! Pressure of methyl isonitrile as a function of time!
![!n[a] =!n[a] o. kt. Half lives. Half Life of a First Order Reaction! Pressure of methyl isonitrile as a function of time! !n[a] =!n[a] o. kt. Half lives. Half Life of a First Order Reaction! Pressure of methyl isonitrile as a function of time!](/thumbs/77/76481346.jpg) Half lives Half life: t 1/2 t 1/2 is the time it takes for the concentration of a reactant to drop to half of its initial value. For the reaction A! products Half Life of a First Order Reaction! Pressure
Half lives Half life: t 1/2 t 1/2 is the time it takes for the concentration of a reactant to drop to half of its initial value. For the reaction A! products Half Life of a First Order Reaction! Pressure
Michaelis-Menton kinetics
 Michaelis-Menton kinetics The rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction in which substrate S is converted into products P depends on the concentration of the enzyme E even though the enzyme does not undergo
Michaelis-Menton kinetics The rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction in which substrate S is converted into products P depends on the concentration of the enzyme E even though the enzyme does not undergo
Chapter 14 Chemical Kinetics
 4//004 Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics 4- Rates of Chemical Reactions 4- Reaction Rates and Concentrations 4-3 The Dependence of Concentrations on Time 4-4 Reaction Mechanisms 4-5 Reaction Mechanism and Rate
4//004 Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics 4- Rates of Chemical Reactions 4- Reaction Rates and Concentrations 4-3 The Dependence of Concentrations on Time 4-4 Reaction Mechanisms 4-5 Reaction Mechanism and Rate
k 3 ) and Κ3 /Κ 2 at 37 C? (d) (4) What will be the ratio of [D]/[C] after 25 min of reaction at 37 C? 1.0E E+07 k 1 /T 1.
![k 3 ) and Κ3 /Κ 2 at 37 C? (d) (4) What will be the ratio of [D]/[C] after 25 min of reaction at 37 C? 1.0E E+07 k 1 /T 1. k 3 ) and Κ3 /Κ 2 at 37 C? (d) (4) What will be the ratio of [D]/[C] after 25 min of reaction at 37 C? 1.0E E+07 k 1 /T 1.](/thumbs/75/72064759.jpg) 1. (35 points) Compound A reacts to form compounds B, C and D via parallel unimolecular pathways, as shown immediately below. A k 1 B (1) A k 2 C (2) A k 3 The plot on the graph shown below displays the
1. (35 points) Compound A reacts to form compounds B, C and D via parallel unimolecular pathways, as shown immediately below. A k 1 B (1) A k 2 C (2) A k 3 The plot on the graph shown below displays the
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company. 6 Enzymes
 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 6 Enzymes CHAPTER 6 Enzymes Key topics about enzyme function: Physiological significance of enzymes Origin of catalytic power of enzymes Chemical mechanisms of catalysis
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 6 Enzymes CHAPTER 6 Enzymes Key topics about enzyme function: Physiological significance of enzymes Origin of catalytic power of enzymes Chemical mechanisms of catalysis
Enzyme Kinetics. Michaelis-Menten Theory Dehaloperoxidase: Multi-functional Enzyme. NC State University
 Enzyme Kinetics Michaelis-Menten Theory Dehaloperoxidase: Multi-functional Enzyme NC State University Michaelis-Menton kinetics The rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction in which substrate S is converted
Enzyme Kinetics Michaelis-Menten Theory Dehaloperoxidase: Multi-functional Enzyme NC State University Michaelis-Menton kinetics The rate of an enzyme catalyzed reaction in which substrate S is converted
Chemical Equilibria & the Application of Le Châtelier s Principle to General Equilibria
 Chemical Equilibria & the Application of Le Châtelier s Principle to General Equilibria CHEM 102! T. Hughbanks! Example of Equilibrium N 2 (g) + 3H 2 (g) 2 NH 3 (g) Reactions can occur, in principle, in
Chemical Equilibria & the Application of Le Châtelier s Principle to General Equilibria CHEM 102! T. Hughbanks! Example of Equilibrium N 2 (g) + 3H 2 (g) 2 NH 3 (g) Reactions can occur, in principle, in
A proposed mechanism for the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide by iodide ion is: slow fast (D) H 2 O
 Chemistry 112, Spring 2007 Prof. Metz Exam 2 Practice Use the following information to answer questions 1 through 3 A proposed mechanism for the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide by iodide ion is: H 2
Chemistry 112, Spring 2007 Prof. Metz Exam 2 Practice Use the following information to answer questions 1 through 3 A proposed mechanism for the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide by iodide ion is: H 2
Part II => PROTEINS and ENZYMES. 2.7 Enzyme Kinetics 2.7a Chemical Kinetics 2.7b Enzyme Inhibition
 Part II => PROTEINS and ENZYMES 2.7 Enzyme Kinetics 2.7a Chemical Kinetics 2.7b Enzyme Inhibition Section 2.7a: Chemical Kinetics Synopsis 2.7a - Chemical kinetics (or reaction kinetics) is the study of
Part II => PROTEINS and ENZYMES 2.7 Enzyme Kinetics 2.7a Chemical Kinetics 2.7b Enzyme Inhibition Section 2.7a: Chemical Kinetics Synopsis 2.7a - Chemical kinetics (or reaction kinetics) is the study of
Shi Asymmetric Epoxidation
 Shi Asymmetric Epoxidation Chiral dioxirane strategy: R 3 + 1 xone, ph 10.5, K 2 C 3, H 2, C R 3 formed in situ catalyst (10-20 mol%) is prepared from D-fructose, and its enantiomer from L-sorbose oxone,
Shi Asymmetric Epoxidation Chiral dioxirane strategy: R 3 + 1 xone, ph 10.5, K 2 C 3, H 2, C R 3 formed in situ catalyst (10-20 mol%) is prepared from D-fructose, and its enantiomer from L-sorbose oxone,
Elementary Organometallic Reactions
 Elementary eactions CE 966 (Tunge) Elementary rganometallic eactions All mechanisms are simply a combination of elementary reactions. 1) Coordination -- issociation 2) xidative Addition -- eductive Elimination
Elementary eactions CE 966 (Tunge) Elementary rganometallic eactions All mechanisms are simply a combination of elementary reactions. 1) Coordination -- issociation 2) xidative Addition -- eductive Elimination
Chemical Kinetics. What Influences Kinetics?
 Chemical Kinetics Predictions of likelihood for a reaction to occur have been based on difference in energy between products and reactants: Thermodynamics only compares reactants to products, says nothing
Chemical Kinetics Predictions of likelihood for a reaction to occur have been based on difference in energy between products and reactants: Thermodynamics only compares reactants to products, says nothing
Kinetic Resolutions. Some definitions and examples Resolution: A process leading to the separation of enantiomers, or derivatives thereof.
 Material outline: For the Scientist in you: Definitions Theoretical treatment Kinetic esolutions General eferences: Vedejs, ACIEE, 2005, 3974 Jacobsen, Adv. Syn. Cat. 2001, 5 Kagan, Topics in Stereochemistry,
Material outline: For the Scientist in you: Definitions Theoretical treatment Kinetic esolutions General eferences: Vedejs, ACIEE, 2005, 3974 Jacobsen, Adv. Syn. Cat. 2001, 5 Kagan, Topics in Stereochemistry,
( ) Reac%on Rates and Temperature N A. = exp ΔE /k N B. Boltzmann law: At higher temperatures, more molecules have enough energy to react.
 eac%on ates and Temperature Boltzmann law: B A ( ) = exp ΔE /k B T! B E A At higher temperatures, more molecules have enough energy to react. Thus, reac;on rates increase with temperature: Arrhenius Equa%on
eac%on ates and Temperature Boltzmann law: B A ( ) = exp ΔE /k B T! B E A At higher temperatures, more molecules have enough energy to react. Thus, reac;on rates increase with temperature: Arrhenius Equa%on
Chapter 14. Chemical Kinetics
 Chapter 14. Chemical Kinetics 14.1 Factors that Affect Reaction Rates The speed at which a chemical reaction occurs is the reaction rate. Chemical kinetics is the study of how fast chemical reactions occur.
Chapter 14. Chemical Kinetics 14.1 Factors that Affect Reaction Rates The speed at which a chemical reaction occurs is the reaction rate. Chemical kinetics is the study of how fast chemical reactions occur.
or more general example: aa + bb cc + dd r = -1/a da/dt = -1/b db/dt = 1/c dc/dt = 1/d dd/dt
 Chem 344--Physical Chemistry for Biochemists II --F'12 I. Introduction see syllabus II. Experimental Chemical kinetics (Atkins, Ch.6) How fast is reaction? Rate of formation of product or loss of reactant
Chem 344--Physical Chemistry for Biochemists II --F'12 I. Introduction see syllabus II. Experimental Chemical kinetics (Atkins, Ch.6) How fast is reaction? Rate of formation of product or loss of reactant
AP Chemistry - Notes - Chapter 12 - Kinetics Page 1 of 7 Chapter 12 outline : Chemical kinetics
 AP Chemistry - Notes - Chapter 12 - Kinetics Page 1 of 7 Chapter 12 outline : Chemical kinetics A. Chemical Kinetics - chemistry of reaction rates 1. Reaction Rates a. Reaction rate- the change in concentration
AP Chemistry - Notes - Chapter 12 - Kinetics Page 1 of 7 Chapter 12 outline : Chemical kinetics A. Chemical Kinetics - chemistry of reaction rates 1. Reaction Rates a. Reaction rate- the change in concentration
Full file at https://fratstock.eu
 Chapter 03 1. a. DG=DH-TDS Δ G = 80 kj ( 98 K) 0.790 kj = 44.6 kj K b. ΔG = 0 @ T m. Unfolding will be favorable at temperatures above the T m. Δ G =Δ H TΔ S 0 kj kj 80 ( xk) 0.790 K 0 Δ G = = 354.4 K
Chapter 03 1. a. DG=DH-TDS Δ G = 80 kj ( 98 K) 0.790 kj = 44.6 kj K b. ΔG = 0 @ T m. Unfolding will be favorable at temperatures above the T m. Δ G =Δ H TΔ S 0 kj kj 80 ( xk) 0.790 K 0 Δ G = = 354.4 K
Computer Modeling (Physical Chemistry) of Enzyme Catalysis, Metalloenzymes
 Computer Modeling (Physical Chemistry) of Enzyme Catalysis, Metalloenzymes Lubomír Rulíšek, Martin Srnec Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry AS CR J. Heyrovský Institute of Physical Chemistry
Computer Modeling (Physical Chemistry) of Enzyme Catalysis, Metalloenzymes Lubomír Rulíšek, Martin Srnec Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry AS CR J. Heyrovský Institute of Physical Chemistry
Chemical kinetics and catalysis
 Chemical kinetics and catalysis Outline Classification of chemical reactions Definition of chemical kinetics Rate of chemical reaction The law of chemical raction rate Collision theory of reactions, transition
Chemical kinetics and catalysis Outline Classification of chemical reactions Definition of chemical kinetics Rate of chemical reaction The law of chemical raction rate Collision theory of reactions, transition
CHAPTER 13 (MOORE) CHEMICAL KINETICS: RATES AND MECHANISMS OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS
 CHAPTER 13 (MOORE) CHEMICAL KINETICS: RATES AND MECHANISMS OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS This chapter deals with reaction rates, or how fast chemical reactions occur. Reaction rates vary greatly some are very
CHAPTER 13 (MOORE) CHEMICAL KINETICS: RATES AND MECHANISMS OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS This chapter deals with reaction rates, or how fast chemical reactions occur. Reaction rates vary greatly some are very
Chapter 14. Principles of Catalysis
 Organometallics Study Meeting 2011/08/28 Kimura Chapter 14. Principles of Catalysis 14. 1. General Principles 14.1.1. Definition of a Catalyst 14.1.2. Energetics of Catalysis 14.1.3. Reaction Coordinate
Organometallics Study Meeting 2011/08/28 Kimura Chapter 14. Principles of Catalysis 14. 1. General Principles 14.1.1. Definition of a Catalyst 14.1.2. Energetics of Catalysis 14.1.3. Reaction Coordinate
CH361/361H Week 7 Lecture Gas Chromatography and Thermodynamics
 CH36/36H Week 7 Lecture Gas Chromatography and Thermodynamics Experiment II Overview: Preparation & Equilibration of Isomeric 2,3-Dimethylbutenes 2 3 4 H + cat. 2 3 4 K eq =? ΔG =? ΔH =? ΔS =? 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene
CH36/36H Week 7 Lecture Gas Chromatography and Thermodynamics Experiment II Overview: Preparation & Equilibration of Isomeric 2,3-Dimethylbutenes 2 3 4 H + cat. 2 3 4 K eq =? ΔG =? ΔH =? ΔS =? 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene
Week 14/Th: Lecture Units 34 & 35
 Week 14/Th: Lecture Units 34 & 35 Unit 33: Colligative Properties Unit 34: Introduction to Equilibria -- Rate of reaction -- Reaction pathway -- Forward / Reverse Rxns. Unit 35: Equilibrium Constants --
Week 14/Th: Lecture Units 34 & 35 Unit 33: Colligative Properties Unit 34: Introduction to Equilibria -- Rate of reaction -- Reaction pathway -- Forward / Reverse Rxns. Unit 35: Equilibrium Constants --
An Overview of Organic Reactions. Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants:
 An Overview of Organic Reactions Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants: 1. Addition (forward) Gain of atoms across a bond Example:
An Overview of Organic Reactions Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants: 1. Addition (forward) Gain of atoms across a bond Example:
Chapter 11: CHEMICAL KINETICS
 Chapter : CHEMICAL KINETICS Study of the rate of a chemical reaction. Reaction Rate (fast or slow?) Igniting gasoline? Making of oil? Iron rusting? We know about speed (miles/hr). Speed Rate = changes
Chapter : CHEMICAL KINETICS Study of the rate of a chemical reaction. Reaction Rate (fast or slow?) Igniting gasoline? Making of oil? Iron rusting? We know about speed (miles/hr). Speed Rate = changes
Key for Unit Exam: Kinetics
 Key for Unit Exam: Kinetics On the following pages are problems covering material in kinetics. Read each question carefully and consider how you will approach it before you put pen or pencil to paper.
Key for Unit Exam: Kinetics On the following pages are problems covering material in kinetics. Read each question carefully and consider how you will approach it before you put pen or pencil to paper.
Chemical Kinetics Ch t ap 1 er
 Chemical Kinetics Chapter 13 1 Chemical Kinetics Thermodynamics does a reaction take place? Kinetics how fast does a reaction proceed? Reaction rate is the change in the concentration of a reactant or
Chemical Kinetics Chapter 13 1 Chemical Kinetics Thermodynamics does a reaction take place? Kinetics how fast does a reaction proceed? Reaction rate is the change in the concentration of a reactant or
Rate Law Summary. Rate Laws vary as a function of time
 Rate Law Summary Measure the instantaneous rate of a reaction: this is a number with units of M/s! Measure the rate of loss of a reactant r... the rate of appearance of a product Repeat the experiment
Rate Law Summary Measure the instantaneous rate of a reaction: this is a number with units of M/s! Measure the rate of loss of a reactant r... the rate of appearance of a product Repeat the experiment
Biochemistry. Lecture 8 Enzyme Kinetics
 Biochemistry Lecture 8 Enzyme Kinetics Why Enzymes? igher reaction rates Greater reaction specificity Milder reaction conditions Capacity for regulation C - - C N 2 - C N 2 - C - C Chorismate mutase -
Biochemistry Lecture 8 Enzyme Kinetics Why Enzymes? igher reaction rates Greater reaction specificity Milder reaction conditions Capacity for regulation C - - C N 2 - C N 2 - C - C Chorismate mutase -
Chem 116 POGIL Worksheet - Week 6 Kinetics - Concluded
 Chem 116 POGIL Worksheet - Week 6 Kinetics - Concluded Why? The half-life idea is most useful in conjunction with first-order kinetics, which include many chemical reactions and all nuclear decay processes.
Chem 116 POGIL Worksheet - Week 6 Kinetics - Concluded Why? The half-life idea is most useful in conjunction with first-order kinetics, which include many chemical reactions and all nuclear decay processes.
Chemical Kinetics. Rate = [B] t. Rate = [A] t. Chapter 12. Reaction Rates 01. Reaction Rates 02. Reaction Rates 03
![Chemical Kinetics. Rate = [B] t. Rate = [A] t. Chapter 12. Reaction Rates 01. Reaction Rates 02. Reaction Rates 03 Chemical Kinetics. Rate = [B] t. Rate = [A] t. Chapter 12. Reaction Rates 01. Reaction Rates 02. Reaction Rates 03](/thumbs/76/74051389.jpg) Chapter Chemical Kinetics Reaction Rates 0 Reaction Rate: The change in the concentration of a reactant or a product with time (M/s). Reactant Products aa bb Rate = [A] t Rate = [B] t Reaction Rates 0
Chapter Chemical Kinetics Reaction Rates 0 Reaction Rate: The change in the concentration of a reactant or a product with time (M/s). Reactant Products aa bb Rate = [A] t Rate = [B] t Reaction Rates 0
Streamlining Reaction Discovery and Development Through Kinetic Analysis
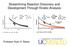 Streamlining Reaction Discovery and Development Through Kinetic Analysis R 3 Si X Ni(0) Ligand R 3 Si X [Substrate] 0 0 Time J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 5728 Professor Ryan D. Baxter utline: Direct Comparison
Streamlining Reaction Discovery and Development Through Kinetic Analysis R 3 Si X Ni(0) Ligand R 3 Si X [Substrate] 0 0 Time J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 5728 Professor Ryan D. Baxter utline: Direct Comparison
Chapter 12. Chemical Kinetics
 Chapter 12 Chemical Kinetics Chapter 12 Table of Contents 12.1 Reaction Rates 12.2 Rate Laws: An Introduction 12.3 Determining the Form of the Rate Law 12.4 The Integrated Rate Law 12.5 Reaction Mechanisms
Chapter 12 Chemical Kinetics Chapter 12 Table of Contents 12.1 Reaction Rates 12.2 Rate Laws: An Introduction 12.3 Determining the Form of the Rate Law 12.4 The Integrated Rate Law 12.5 Reaction Mechanisms
Chemistry 112, Spring 2007 Prof. Metz Exam 2 Solutions April 5, 2007 Each question is worth 5 points, unless otherwise indicated
 Chemistry 11, Spring 007 Prof. Metz Exam Solutions April 5, 007 Each question is worth 5 points, unless otherwise indicated 1. A proposed mechanism for the reaction of NO with Br to give BrNO is NO + NO
Chemistry 11, Spring 007 Prof. Metz Exam Solutions April 5, 007 Each question is worth 5 points, unless otherwise indicated 1. A proposed mechanism for the reaction of NO with Br to give BrNO is NO + NO
AP CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 12 KINETICS
 AP CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 12 KINETICS Thermodynamics tells us if a reaction can occur. Kinetics tells us how quickly the reaction occurs. Some reactions that are thermodynamically feasible are kinetically so
AP CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 12 KINETICS Thermodynamics tells us if a reaction can occur. Kinetics tells us how quickly the reaction occurs. Some reactions that are thermodynamically feasible are kinetically so
REACTION KINETICS. Catalysts substances that increase the rates of chemical reactions without being used up. e.g. enzymes.
 REACTION KINETICS Study of reaction rates Why? Rates of chemical reactions are primarily controlled by 5 factors: the chemical nature of the reactants 2 the ability of the reactants to come in contact
REACTION KINETICS Study of reaction rates Why? Rates of chemical reactions are primarily controlled by 5 factors: the chemical nature of the reactants 2 the ability of the reactants to come in contact
Bifunctional Asymmetric Catalysts: Design and Applications. Junqi Li CHEM Sep 2010
 Bifunctional Asymmetric Catalysts: Design and Applications Junqi Li CHEM 535 27 Sep 2010 Enzyme Catalysis vs Small-Molecule Catalysis Bronsted acid Lewis acid Lewis acid Bronsted base Activation of both
Bifunctional Asymmetric Catalysts: Design and Applications Junqi Li CHEM 535 27 Sep 2010 Enzyme Catalysis vs Small-Molecule Catalysis Bronsted acid Lewis acid Lewis acid Bronsted base Activation of both
Chapter 14. Chemical Kinetics
 Chapter 14. Chemical Kinetics Common Student Misconceptions It is possible for mathematics to get in the way of some students understanding of the chemistry of this chapter. Students often assume that
Chapter 14. Chemical Kinetics Common Student Misconceptions It is possible for mathematics to get in the way of some students understanding of the chemistry of this chapter. Students often assume that
Catalysis Lectures W.H. Green 5.68J/10.652J Spring Handouts: Norskov et al., J. Catalysis Imbihl and Ertl, Chem. Rev. (partial) Homework
 Catalysis Lectures W.H. Green 5.68J/10.652J Spring 2003 Handouts: Norskov et al., J. Catalysis Imbihl and Ertl, Chem. Rev. (partial) Homework Major points: 1) Why reactions have barriers, and how catalysts
Catalysis Lectures W.H. Green 5.68J/10.652J Spring 2003 Handouts: Norskov et al., J. Catalysis Imbihl and Ertl, Chem. Rev. (partial) Homework Major points: 1) Why reactions have barriers, and how catalysts
Non-Enzymatic Enantioselective Polyene Cyclizations. Adam Hill Chem 535 May, 2 nd 2013
 Non-Enzymatic Enantioselective Polyene Cyclizations Adam Hill Chem 535 May, 2 nd 2013 Enantioselective Polyene Cyclization (?) General Method to Rapidly Build Molecular Complexity (+) Exquisite Stereo-
Non-Enzymatic Enantioselective Polyene Cyclizations Adam Hill Chem 535 May, 2 nd 2013 Enantioselective Polyene Cyclization (?) General Method to Rapidly Build Molecular Complexity (+) Exquisite Stereo-
Lecture # 3, 4 Selecting a Catalyst (Non-Kinetic Parameters), Review of Enzyme Kinetics, Selectivity, ph and Temperature Effects
 1.492 - Integrated Chemical Engineering (ICE Topics: Biocatalysis MIT Chemical Engineering Department Instructor: Professor Kristala Prather Fall 24 Lecture # 3, 4 Selecting a Catalyst (Non-Kinetic Parameters,
1.492 - Integrated Chemical Engineering (ICE Topics: Biocatalysis MIT Chemical Engineering Department Instructor: Professor Kristala Prather Fall 24 Lecture # 3, 4 Selecting a Catalyst (Non-Kinetic Parameters,
Understanding Organic Reactions
 Understanding Organic Reactions Energy Diagrams For the general reaction: The energy diagram would be shown as: Understanding Organic Reactions Energy Diagrams Energy Diagrams Understanding Organic Reactions
Understanding Organic Reactions Energy Diagrams For the general reaction: The energy diagram would be shown as: Understanding Organic Reactions Energy Diagrams Energy Diagrams Understanding Organic Reactions
Exp.3 Determination of the Thermodynamic functions for the Borax Solution
 Exp.3 Determination of the Thermodynamic functions for the Borax Solution Theory: The relationship between Gibb s energy (ΔG), Enthalpy (ΔH), Entropy (ΔS) and the equilibrium constant (K) for a chemical
Exp.3 Determination of the Thermodynamic functions for the Borax Solution Theory: The relationship between Gibb s energy (ΔG), Enthalpy (ΔH), Entropy (ΔS) and the equilibrium constant (K) for a chemical
Reaction rate. reaction rate describes change in concentration of reactants and products with time -> r = dc j
 Reaction rate ChE 400 - Reactive Process Engineering reaction rate describes change in concentration of reactants and products with time -> r = dc j /dt r is proportional to the reactant concentrations
Reaction rate ChE 400 - Reactive Process Engineering reaction rate describes change in concentration of reactants and products with time -> r = dc j /dt r is proportional to the reactant concentrations
Enantioselective 1,1-Arylborylation of. Transfer with Pd Catalysis
 Enantioselective 1,1-Arylborylation of Alkenes: Merging Chiral Anion Phase Transfer with Pd Catalysis Reporter: Lian-Jin Liu Checker: Wen-Xue Huang Date: 12/05/2015 F. Dean Toste University of California,
Enantioselective 1,1-Arylborylation of Alkenes: Merging Chiral Anion Phase Transfer with Pd Catalysis Reporter: Lian-Jin Liu Checker: Wen-Xue Huang Date: 12/05/2015 F. Dean Toste University of California,
Chemical Kinetics. What quantities do we study regarding chemical reactions? 15 Chemical Kinetics
 Chemical Kinetics Chemical kinetics: the study of reaction rate, a quantity conditions affecting it, the molecular events during a chemical reaction (mechanism), and presence of other components (catalysis).
Chemical Kinetics Chemical kinetics: the study of reaction rate, a quantity conditions affecting it, the molecular events during a chemical reaction (mechanism), and presence of other components (catalysis).
Chapter 12 - Chemical Kinetics
 Chapter 1 - Chemical Kinetics 1.1 Reaction Rates A. Chemical kinetics 1. Study of the speed with which reactants are converted to products B. Reaction Rate 1. The change in concentration of a reactant
Chapter 1 - Chemical Kinetics 1.1 Reaction Rates A. Chemical kinetics 1. Study of the speed with which reactants are converted to products B. Reaction Rate 1. The change in concentration of a reactant
Chapter 6 Chemical Reactivity and Mechanisms
 Chapter 6 Chemical Reactivity and Mechanisms 6.1 Enthalpy Enthalpy (ΔH or q) is the heat energy exchange between the reaction and its surroundings at constant pressure Breaking a bond requires the system
Chapter 6 Chemical Reactivity and Mechanisms 6.1 Enthalpy Enthalpy (ΔH or q) is the heat energy exchange between the reaction and its surroundings at constant pressure Breaking a bond requires the system
Lecture 22: The Arrhenius Equation and reaction mechanisms. As we wrap up kinetics we will:
 As we wrap up kinetics we will: Lecture 22: The Arrhenius Equation and reaction mechanisms. Briefly summarize the differential and integrated rate law equations for 0, 1 and 2 order reaction Learn how
As we wrap up kinetics we will: Lecture 22: The Arrhenius Equation and reaction mechanisms. Briefly summarize the differential and integrated rate law equations for 0, 1 and 2 order reaction Learn how
Chemistry 335 Supplemental Slides: Interlude 1. Reduction: addition of hydrogen to the substrate. Oxidation: addition of oxygen to the substrate
 Interlude 1: Oxidations, Reductions & Other Functional Group Interconversions (FGI) 1. Definition of Oxidation and Reduction For practical purposes in organic chemistry, oxidation and reduction are defined
Interlude 1: Oxidations, Reductions & Other Functional Group Interconversions (FGI) 1. Definition of Oxidation and Reduction For practical purposes in organic chemistry, oxidation and reduction are defined
ENZYME SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING PROF. SUBHASH CHAND DEPARTMENT OF BIOCHEMICAL ENGINEERING AND BIOTECHNOLOGY IIT DELHI LECTURE 3
 ENZYME SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING PROF. SUBHASH CHAND DEPARTMENT OF BIOCHEMICAL ENGINEERING AND BIOTECHNOLOGY IIT DELHI LECTURE 3 ENZYMES AS BIOCATALYSTS * CATALYTIC EFFICIENCY *SPECIFICITY Having discussed
ENZYME SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING PROF. SUBHASH CHAND DEPARTMENT OF BIOCHEMICAL ENGINEERING AND BIOTECHNOLOGY IIT DELHI LECTURE 3 ENZYMES AS BIOCATALYSTS * CATALYTIC EFFICIENCY *SPECIFICITY Having discussed
Chapter 12. Chemical Kinetics
 Chapter 12 Chemical Kinetics Section 12.1 Reaction Rates Section 12.1 Reaction Rates Section 12.1 Reaction Rates Section 12.1 Reaction Rates Section 12.1 Reaction Rates Section 12.1 Reaction Rates Section
Chapter 12 Chemical Kinetics Section 12.1 Reaction Rates Section 12.1 Reaction Rates Section 12.1 Reaction Rates Section 12.1 Reaction Rates Section 12.1 Reaction Rates Section 12.1 Reaction Rates Section
Chem 6 sample exam 1 (100 points total)
 Chem 6 sample exam 1 (100 points total) @ This is a closed book exam to which the Honor Principle applies. @ The last page contains several equations which may be useful; you can detach it for easy reference.
Chem 6 sample exam 1 (100 points total) @ This is a closed book exam to which the Honor Principle applies. @ The last page contains several equations which may be useful; you can detach it for easy reference.
is the Michaelis constant. It represents the apparent dissociation constant of ES to E and S.
 Lecture 35 Chapt 28, Sections 1-4 Bimolecular reactions in the gas phase Anouncements: Exam tomorrow 2:00 is the primary time. vdw 237 I have gotten several suggestions for lecture ideas, thanks and keep
Lecture 35 Chapt 28, Sections 1-4 Bimolecular reactions in the gas phase Anouncements: Exam tomorrow 2:00 is the primary time. vdw 237 I have gotten several suggestions for lecture ideas, thanks and keep
Chapter 11 Rate of Reaction
 William L Masterton Cecile N. Hurley http://academic.cengage.com/chemistry/masterton Chapter 11 Rate of Reaction Edward J. Neth University of Connecticut Outline 1. Meaning of reaction rate 2. Reaction
William L Masterton Cecile N. Hurley http://academic.cengage.com/chemistry/masterton Chapter 11 Rate of Reaction Edward J. Neth University of Connecticut Outline 1. Meaning of reaction rate 2. Reaction
CHEMISTRY 5309 Test Number 2 Fall, 2003 ANSWER KEY
 EMISTRY 5309 Test Number 2 Fall, 2003 ANSWER KEY 1. Explain briefly why the dipole moment of 2,3-dichloro-2,3-dimethylbutane changes with temperature, as shown in the table below. (The solvent is heptane.)
EMISTRY 5309 Test Number 2 Fall, 2003 ANSWER KEY 1. Explain briefly why the dipole moment of 2,3-dichloro-2,3-dimethylbutane changes with temperature, as shown in the table below. (The solvent is heptane.)
Chapter 14 Chemical Kinetics
 How fast do chemical processes occur? There is an enormous range of time scales. Chapter 14 Chemical Kinetics Kinetics also sheds light on the reaction mechanism (exactly how the reaction occurs). Why
How fast do chemical processes occur? There is an enormous range of time scales. Chapter 14 Chemical Kinetics Kinetics also sheds light on the reaction mechanism (exactly how the reaction occurs). Why
Branched-Regioselective Hydroformylation with Catalytic Amounts of a Reversibly Bound Directing Group
 1/12 Branched-egioselective ydroformylation with Catalytic Amounts of a eversibly Bound Directing Group h(i)/me C/ 2 MS 4A branched major by Christian U. Grünanger and Bernhard Breit Angew. Chem. Int.
1/12 Branched-egioselective ydroformylation with Catalytic Amounts of a eversibly Bound Directing Group h(i)/me C/ 2 MS 4A branched major by Christian U. Grünanger and Bernhard Breit Angew. Chem. Int.
Reactivity within Confined Nano-spaces
 Reactivity within Confined Nano-spaces Larry Wolf Group Meeting 11-17-09 Encapsulating Cyclobutadiene hemicarcerand Anslyn, E. V; Dougherty, D. A. Modern Physical Organic Chemistry Cram. D. J. et. al.
Reactivity within Confined Nano-spaces Larry Wolf Group Meeting 11-17-09 Encapsulating Cyclobutadiene hemicarcerand Anslyn, E. V; Dougherty, D. A. Modern Physical Organic Chemistry Cram. D. J. et. al.
Chemistry 123: Physical and Organic Chemistry Topic 2: Thermochemistry S H 2 = S H 2 R ln P H2 P NH
 N (g) + 3 H (g) NH 3 (g) S N = S H = S NH 3 = S N R ln P N S H R ln P H S NH 3 R ln P NH3 ΔS rxn = (S Rln P NH 3 NH3 ) (S N Rln P N ) 3 (S H Rln P H ) ΔS rxn = S S NH 3 N 3S H + Rln P P 3 N H ΔS rxn =
N (g) + 3 H (g) NH 3 (g) S N = S H = S NH 3 = S N R ln P N S H R ln P H S NH 3 R ln P NH3 ΔS rxn = (S Rln P NH 3 NH3 ) (S N Rln P N ) 3 (S H Rln P H ) ΔS rxn = S S NH 3 N 3S H + Rln P P 3 N H ΔS rxn =
THE THERMODYNAMICS OF POTASSIUM NITRATE DISSOLVING IN WATER 1
 THE THERMODYNAMICS OF POTASSIUM NITRATE DISSOLVING IN WATER 1 OBJECTIVE In this experiment, the changes in free energy (ΔG), enthalpy (ΔH), and entropy (ΔS) of the potassium nitrate (KNO 3 ) dissolving
THE THERMODYNAMICS OF POTASSIUM NITRATE DISSOLVING IN WATER 1 OBJECTIVE In this experiment, the changes in free energy (ΔG), enthalpy (ΔH), and entropy (ΔS) of the potassium nitrate (KNO 3 ) dissolving
Part One: Reaction Rates. 1. Even though a reaction is thermodynamically favorable it may not occur at all if it is kinetically very slow.
 CHAPTER 13: RATES OF REACTION Part One: Reaction Rates A. Chemical Kinetics deals with: 1. 2. B. Importance: 1. Even though a reaction is thermodynamically favorable it may not occur at all if it is kinetically
CHAPTER 13: RATES OF REACTION Part One: Reaction Rates A. Chemical Kinetics deals with: 1. 2. B. Importance: 1. Even though a reaction is thermodynamically favorable it may not occur at all if it is kinetically
2/23/2018. Familiar Kinetics. ...and the not so familiar. Chemical kinetics is the study of how fast reactions take place.
 CHEMICAL KINETICS & REACTION MECHANISMS Readings, Examples & Problems Petrucci, et al., th ed. Chapter 20 Petrucci, et al., 0 th ed. Chapter 4 Familiar Kinetics...and the not so familiar Reaction Rates
CHEMICAL KINETICS & REACTION MECHANISMS Readings, Examples & Problems Petrucci, et al., th ed. Chapter 20 Petrucci, et al., 0 th ed. Chapter 4 Familiar Kinetics...and the not so familiar Reaction Rates
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Entropy and free energy
 Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Entropy and free energy Learning goals and key skills: Explain and apply the terms spontaneous process, reversible process, irreversible process, and isothermal process.
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics Entropy and free energy Learning goals and key skills: Explain and apply the terms spontaneous process, reversible process, irreversible process, and isothermal process.
Chapter 12. Chemical Kinetics
 Chapter 12 Chemical Kinetics Section 12.1 Reaction Rates Reaction Rate Change in concentration of a reactant or product per unit time. Rate = concentration of A at time t t 2 1 2 1 concentration of A at
Chapter 12 Chemical Kinetics Section 12.1 Reaction Rates Reaction Rate Change in concentration of a reactant or product per unit time. Rate = concentration of A at time t t 2 1 2 1 concentration of A at
Chemical Kinetics. Kinetics is the study of how fast chemical reactions occur. There are 4 important factors which affect rates of reactions:
 Chemical Kinetics Kinetics is the study of how fast chemical reactions occur. There are 4 important factors which affect rates of reactions: reactant concentration temperature action of catalysts surface
Chemical Kinetics Kinetics is the study of how fast chemical reactions occur. There are 4 important factors which affect rates of reactions: reactant concentration temperature action of catalysts surface
ASSIGNMENT SHEET #11 APQ ANSWERS
 ASSIGNMENT SHEET #11 APQ ANSWERS #1 a. The unit for q must be an energy unit, typically Joules or calories. The unit for mass is the gram. The unit for specific heat is J per gram-degree or calorie per
ASSIGNMENT SHEET #11 APQ ANSWERS #1 a. The unit for q must be an energy unit, typically Joules or calories. The unit for mass is the gram. The unit for specific heat is J per gram-degree or calorie per
Elimination reactions
 Chapter 9 Elimination reactions E2 and E1 reactions Competition between S N and E Elimination reactions Ch 9 #2 elimination and/or substitution 2 mechanisms ~ E2 and E1 E2: bimolecular elimination rxn
Chapter 9 Elimination reactions E2 and E1 reactions Competition between S N and E Elimination reactions Ch 9 #2 elimination and/or substitution 2 mechanisms ~ E2 and E1 E2: bimolecular elimination rxn
Stereodivergent Catalysis. Aragorn Laverny SED Group Meeting July
 Stereodivergent Catalysis Aragorn Laverny SED Group Meeting July 31 2018 1 Stereodivergent Catalysis In the context of asymmetric synthesis, a stereodivergent process is one that allows access to any given
Stereodivergent Catalysis Aragorn Laverny SED Group Meeting July 31 2018 1 Stereodivergent Catalysis In the context of asymmetric synthesis, a stereodivergent process is one that allows access to any given
Part One: Reaction Rates. 1. Rates of chemical reactions. (how fast products are formed and/or reactants are used up)
 A. Chemical Kinetics deals with: CHAPTER 13: RATES OF REACTION Part One: Reaction Rates 1. Rates of chemical reactions. (how fast products are formed and/or reactants are used up) 2. Mechanisms of chemical
A. Chemical Kinetics deals with: CHAPTER 13: RATES OF REACTION Part One: Reaction Rates 1. Rates of chemical reactions. (how fast products are formed and/or reactants are used up) 2. Mechanisms of chemical
Molybdenum-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation
 Molybdenum-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation X MoL n u u * Tommy Bui 9/14/04 Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation from a Synthetic Viewpoint X X M u u * and/or u form a C-C bond with the creation of a new
Molybdenum-Catalyzed Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation X MoL n u u * Tommy Bui 9/14/04 Asymmetric Allylic Alkylation from a Synthetic Viewpoint X X M u u * and/or u form a C-C bond with the creation of a new
Lecture 13: Data Analysis for the V versus [S] Experiment and Interpretation of the Michaelis-Menten Parameters
![Lecture 13: Data Analysis for the V versus [S] Experiment and Interpretation of the Michaelis-Menten Parameters Lecture 13: Data Analysis for the V versus [S] Experiment and Interpretation of the Michaelis-Menten Parameters](/thumbs/89/100978514.jpg) Biological Chemistry Laboratory Biology 3515/Chemistry 3515 Spring 2018 Lecture 13: Data Analysis for the V versus [S] Experiment and Interpretation of the Michaelis-Menten Parameters 20 February 2018
Biological Chemistry Laboratory Biology 3515/Chemistry 3515 Spring 2018 Lecture 13: Data Analysis for the V versus [S] Experiment and Interpretation of the Michaelis-Menten Parameters 20 February 2018
special interest were means of increasing the availability of the five-coordinate
 136 Chapter 6 137 Introduction The chromium(iii)/chromium(v) couple is attractive for use as a catalyst in oxo atom transfer chemistry. 1-3 The challenge is to render the chromium(v) corrole more reactive
136 Chapter 6 137 Introduction The chromium(iii)/chromium(v) couple is attractive for use as a catalyst in oxo atom transfer chemistry. 1-3 The challenge is to render the chromium(v) corrole more reactive
FST 123 Problem Set 3 Spring, V o at [S] 0 = 10 mm (mm/min)
![FST 123 Problem Set 3 Spring, V o at [S] 0 = 10 mm (mm/min) FST 123 Problem Set 3 Spring, V o at [S] 0 = 10 mm (mm/min)](/thumbs/86/93227301.jpg) FST 23 Problem Set 3 Spring, 2009 Name. A student needed to know the activity versus ph profile for an enzyme that he was going to use in a later application. He collected the appropriate data and determined
FST 23 Problem Set 3 Spring, 2009 Name. A student needed to know the activity versus ph profile for an enzyme that he was going to use in a later application. He collected the appropriate data and determined
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Boehr et al. 10.1073/pnas.0914163107 SI Text Materials and Methods. R 2 relaxation dispersion experiments. 15 NR 2 relaxation dispersion data measured at 1 H Larmor frequencies of
Supporting Information Boehr et al. 10.1073/pnas.0914163107 SI Text Materials and Methods. R 2 relaxation dispersion experiments. 15 NR 2 relaxation dispersion data measured at 1 H Larmor frequencies of
Kinetics. Chapter 14. Chemical Kinetics
 Lecture Presentation Chapter 14 Yonsei University In kinetics we study the rate at which a chemical process occurs. Besides information about the speed at which reactions occur, kinetics also sheds light
Lecture Presentation Chapter 14 Yonsei University In kinetics we study the rate at which a chemical process occurs. Besides information about the speed at which reactions occur, kinetics also sheds light
Bio-inspired C-H functionalization by metal-oxo complexes
 1 Literature Seminar Bio-inspired C-H functionalization by metal-oxo complexes 2016. 7. 23. Nagashima Nozomu 2 C-H functionalization by enzymes Enzymes enable aliphatic C-H functionalization 3 P450 oxidation
1 Literature Seminar Bio-inspired C-H functionalization by metal-oxo complexes 2016. 7. 23. Nagashima Nozomu 2 C-H functionalization by enzymes Enzymes enable aliphatic C-H functionalization 3 P450 oxidation
We will briefly go over Answer Key
 Chem 310 Test 1 12-15 % of Grade (I ll decide later) Tests will be returned no later than 1 week after taken Reminder on regrades We will briefly go over Answer Key Oops forgot to do this!! So answer
Chem 310 Test 1 12-15 % of Grade (I ll decide later) Tests will be returned no later than 1 week after taken Reminder on regrades We will briefly go over Answer Key Oops forgot to do this!! So answer
Acid-Base Strength. Chapter 6. Monday, November 2, 2015
 Acid-Base Strength Chapter 6 Monday, November 2, 2015 Acid-Base Strength We ve seen that the reactivity of acids and bases can be viewed through the HSAB Model or the EC Model. Both of these models try
Acid-Base Strength Chapter 6 Monday, November 2, 2015 Acid-Base Strength We ve seen that the reactivity of acids and bases can be viewed through the HSAB Model or the EC Model. Both of these models try
CHEM Chapter 14. Chemical Kinetics (Homework) Ky40
 CHEM 1412. Chapter 14. Chemical Kinetics (Homework) Ky40 1. Chlorine dioxide reacts in basic water to form chlorite and chlorate according to the following chemical equation: 2ClO 2 (aq) + 2OH (aq) ClO
CHEM 1412. Chapter 14. Chemical Kinetics (Homework) Ky40 1. Chlorine dioxide reacts in basic water to form chlorite and chlorate according to the following chemical equation: 2ClO 2 (aq) + 2OH (aq) ClO
CHAPTER 21: Reaction Dynamics
 CHAPTER 21: Reaction Dynamics I. Microscopic Theories of the Rate Constant. A. The Reaction Profile (Potential Energy diagram): Highly schematic and generalized. A---B-C B. Collision Theory of Bimolecular
CHAPTER 21: Reaction Dynamics I. Microscopic Theories of the Rate Constant. A. The Reaction Profile (Potential Energy diagram): Highly schematic and generalized. A---B-C B. Collision Theory of Bimolecular
Enzyme reaction example of Catalysis, simplest form: E + P at end of reaction No consumption of E (ES): enzyme-substrate complex Intermediate
 V 41 Enzyme Kinetics Enzyme reaction example of Catalysis, simplest form: k 1 E + S k -1 ES E at beginning and ES k 2 k -2 E + P at end of reaction No consumption of E (ES): enzyme-substrate complex Intermediate
V 41 Enzyme Kinetics Enzyme reaction example of Catalysis, simplest form: k 1 E + S k -1 ES E at beginning and ES k 2 k -2 E + P at end of reaction No consumption of E (ES): enzyme-substrate complex Intermediate
O CH 3. Mn CH 3 OC C. 16eelimination
 igratory Insertion igratory Insertion/Elimination 1 A migratory insertion reaction is when a cisoidal anionic and neutral ligand on a metal complex couple together to generate a new coordinated anionic
igratory Insertion igratory Insertion/Elimination 1 A migratory insertion reaction is when a cisoidal anionic and neutral ligand on a metal complex couple together to generate a new coordinated anionic
Chapter 14. Chemical Kinetics
 Chapter 14. Chemical Kinetics Common Student Misconceptions It is possible for mathematics to get in the way of some students understanding of the chemistry of this chapter. Students often assume that
Chapter 14. Chemical Kinetics Common Student Misconceptions It is possible for mathematics to get in the way of some students understanding of the chemistry of this chapter. Students often assume that
a) Write the reaction that occurs (pay attention to and label ends correctly) 5 AGCTG CAGCT > 5 AGCTG 3 3 TCGAC 5
 Chem 315 Applications Practice Problem Set 1.As you learned in Chem 315, DNA higher order structure formation is a two step process. The first step, nucleation, is entropically the least favorable. The
Chem 315 Applications Practice Problem Set 1.As you learned in Chem 315, DNA higher order structure formation is a two step process. The first step, nucleation, is entropically the least favorable. The
Ch 13 Rates of Reaction (Chemical Kinetics)
 Ch 13 Rates of Reaction (Chemical Kinetics) Reaction Rates and Kinetics - The reaction rate is how fast reactants are converted to products. - Chemical kinetics is the study of reaction rates. Kinetics
Ch 13 Rates of Reaction (Chemical Kinetics) Reaction Rates and Kinetics - The reaction rate is how fast reactants are converted to products. - Chemical kinetics is the study of reaction rates. Kinetics
