NON-EQUILIBRIUM MOLECULAR DYNAMICS CALCULATION OF THE
|
|
|
- Amie Burns
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FluidPhaseEquilibria, 53 (1989) Elsevier Science Publishers B.V., Amsterdam - Printed in The Netherlands 191 NON-EQUILIBRIUM MOLECULAR DYNAMICS CALCULATION OF THE TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF CARBON DIOXIDE B. Y. WANG and P. T. CUMMINGS Department of Chemical Engineering Thornton Hall, University of Virginia Charlottesville, VA ABSTRACT We compute the thermal conductivity and diffusion coefficient of supercritical carbon dioxide along the 313 K isotherm using non-equilibrium molecular dynamics. Comparisons are made with experiment at four densities corresponding to pressures of 30, 70, 200 and 500 bar. Two intermolecular potential models for carbon dioxide are compared. INTRODUCTION In a previous paper (Wang and Cummings, 1988), we reported calculations of the shear viscosity of supercritical carbon dioxide along the 313 K isotherm using non-equilibrium molecular dynamics (NEMD). This paper continues this study of the transport properties of supercritical fluids and focuses on the thermal conductivity and the self-diffusion coefficient of carbon dioxide along the 313 K supercritical isotherm. These papers are part of our continuing research program aimed at studying the transport properties of supercritical fluids using NEMD. The NEMD algorithms for computing thermal conductivity and self-diffusion coefficient are similar to the one used for the calculation of shear viscosity. All three algorithms involve /89/$ Elsevier Science Publishers B.V.
2 192 simulating a system at steady state away from equilibrium, where the steady state is attained through the application of an external field. Th e ratio of the field-induced current to the field itself gives the transport coefficient of interest. It has been found that shear viscosity exhibits a strong dependence on the external field (which in the case of the shear viscosity is the strain field) leading to non-newtonian behavior (i.e. strain rate dependent shear viscosity) (Evans, 1983). However, little is known about the effects of the external fields employed in the NEMD algorithms for thermal conductivity and the self-diffusion coefficient. It is one of our objectives to examine these effects. One difference between the NEMD algorithm for shear viscosity and the NEMD algorithms for thermal conductivity and diffusivity is that in the former case, the strain field is physical and produces an experimentally realizable planar Couette flow. In the latter case, the applied fields are synthetic: they yield the correct hydrodynamic transport coefficients in the linear response regime, but outside the linear response regime the results obtained from simulation are not experimentally realizable (Evans and Morriss, 1984). In the simulation of the shear viscosity, we used three different intermolecular potential models: a simple spherically symmetric Lennard-Jones potential with parameters determined by fitting to the gas phase viscosity (Bird etal, 1960); a two-site Lennard-Jones model in which the oxygen centers are explicitly modeled (Gibbons and Klein, 1974); and a threesite model (in which the centers of the oxygen and carbon atoms are explicitly represented) with a quadrupole-quadrupole interaction to represent the electrostatic interaction due to the permanent quadrupole moment of CO2 (Murthy and Singer, 1981). The simulated shear viscosity using the three-site model yielded the best agreement with the experimental data. In this study, we choose the three-site intermolecular potential model. We also use the simple spherically symmetric potential model for the sake of comparison. In the next section, the NEMD algorithms are briefly described. In the section following, our results are described and compared with experimental data where available. We conclude with a summary of our findings. NEMD ALGORITHMS FOR THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY AND DIFFUSIVITY The NEMD algorithms for thermal conductivity and diffusivity for simple fluids are described by Evans (1986). For molecular fluids, one simply needs to augment these equations with the rotational equations of motion. The equations of motion for a simulated system of N molecules with a fictitious external field $, which essentially plays the same role as the temperature gradient VT in experiment, are 1 (1) where E, is the instantaneous configurational energy of molecule i, E is the average total
3 193 energy, E = CiEi/N. The rotational equations of motion are the same singularity-free equations (Evans and Murad, 1977) used in our previous paper (Wang and Cummings, 1988). The parameter (Y, the thermostating multiplier, is used to constrain the translational motion so that the translational kinetic energy is fixed at the required temperature. The functional form of the equation containing LY is obtained from application of Gauss s principle of least constraint (Evans et al., 1983). Th e isokinetic requirement yields The boundary conditions imposed on the simulated system are the usual periodic boundary conditions employed in equilibrium molecular dynamics simulations which are described adequated elsewhere (Allen and Tildesley, 1987). The constitutive relation between the heat current JQ and the thermal conductivity X is given by Evans (1986) + A=& (3) e In this equation, T is the temperature of the simulated system, and & is the microscopic heat current given by (4) The NEMD algorithm for computing the diffusion coefficient is based on applying a synthetic color field to the simulated system. This color field acts in the same way as a chemical potential gradient which drives diffusion. The translational equations of motion are given by Evans and Morriss (1984) dc/dt = p7 Jm (5) dpzi/dt = Fzi - XdCi dpgildt = Fyi - Aspy; (6) dpzi Jdt = Fzi - Xspzi I where c, is the color charge of molecule i, c; = (-l)i, The parameter Xd is the driving constraint of the color field. The function form of Xd follows from the application of Gauss s principle of least constraint where the constraint of color field is T,E-Jc=O (7) In the equation, J, is the color current applied to the simulated system. The thermostating constraint parameter, X,, is obtained in similar fashion to the thermostating constraint a in the NEMD algorithm for thermal conductivit,y. Thus, we have the following equations for Xd snd X,: Xd = k Ci CjF,; As = C;(pigFig + PizFiz)/ Ci(PTy + Pfz) (8)
4 194 Table 1: NEMD results of thermal conductivity for the one-site model of CO2 along the 313 K isotherm. F, Timesteps u f/(nk*t) x x lo3 (ky?m3) i,b/ (W/m I<) x lo x 10s x 10s x lo x x Table 2: NEMD results of self-diffusion coefficient for the one-site model of CO* along the 313 K isotherm. (ky/4n3) J,* Timesteps u /(NkBT) D, x 10 (cm2/s) The work, Pd, generated by color constraint Ad, is given by: pd = Ad c &hi (9) I The self-diffusion coefficient, D,, is then obtained from D =_(N-l) J, k T.9 7-B < Pd > (10) where kg is Boltzmann s constant and < Pd > is the ensemble average of Pd. RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS In Tables 1 and 3, we report the pressure, configurational internal energy and thermal conductivity for the one-site and two-site model of COs; in Tables 2 and 4, we report the configurational internal energy and self-diffusion coefficient. The simulations of the one-site model were performed on systems of 108 molecules with time step 1.32 x lo-l4 set; the threesite model simulations were performed on systems of 125 molecules with time step lo-l5 sec.
5 195 rable 3: NEMD results of thermal conductivity for the three-site model of CO2 along the 313 K isotherm. (ky;m ) F, Timesteps p ucon /(NkgT) x x lo3 (atm) (W/m. K) Table 4: NEMD results of self-diffusion coefficient for the three-site model of CO2 along the 313 K isotherm. (ks/4n3) J, Timesteps u f/(nk,t) D, x lo4 (cm /s) The spherical cutoff of the intermolecular potential is 12Afor the one-site simulations and loafor the three-site model. The diffusion coefficient simulations for the three-site model were computed on a CSPI bit word array processor (attached to a VAX 11/750 located in the Center for Computer-Aided Engineering at the University of Virginia) and the rest of the simulations were carried out on a IBM 3090/100 (located in the Academic Computing Center at the University of Virginia). At the state conditions studied, the onesite model is apparently more supercritical than the three-site model as is evidenced by the much higher pressures for the one-site model. From Table 5, the diffusion coefficient of the three-site model yields the best agreement with experimental data (which was not available at the highest pressure). The thermal con- ductivity of the three-site model given in Table 5 agrees well with experiment at low pressure
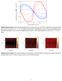
6 196 A : p=840.8 kg VI-~ I: p=992.1 kg ni UW~~) a n-- a o,o~~ ~---.._*.._~ I OO I I I I Fe Figure 1: The thermal conductivity X for the one-site model (dashed lines) and the three-site model (solid line) of CO2 as a function of F,*. The symbols are simulation results (to which the straight lines are least squared fits) and the arrows indicate the experimental data. I p= k.g mm _ = --- _& p=199.8 kg me 0 0 D,x104 (cm2/s) Figure 2: The self-diffusion coefficient D, for the one-site model (on the left) and three-site model (on the right) of COs as a function of Jz. The symbols, lines, and arrows have the same significance as in Figure 1.
7 197 Table 5: Comparison between thermal conductivity and diffusivity calculated via NEMD and experimental data (Vargaftik, 1983; McHugh and Krukonis, 1986). (JVk3) Model ANEMD x lo3 &,, X lo3 DJNEMD X lo4 Dsezp x lo4 (at4 (at4 (W/m I<) (Wlm. K) One-site Three-site 9.4 One-site Three-site One-site unavailable Three-site but overestimates the experimental value at the higher pressure. The simulation results and experimental values are also shown in Figures 1 and 2. In our previous study of the shear viscosity of COs, the shear viscosity exhibits the same behavior (slight underestimate at low density, overestimate at high density). The similarity in results is likely due to the similarity in collisional mechanisms for momentum and kinetic energy transfer. At the lowest density state point, which is nearest of those considered to the experimental critical point of CO2 where the critical temperature T = K and critical pressure P = 72.8 atm, the thermal conductivities obtained from NEMD for the three-site model are negative, while for the one-site model they are very large (see Tables 1 and 3). Evans (1986) noted this behavior in simple fluid systems and proposed that it is due to long-time tail effects in the conductivity with respect to the external field. In order to verify that this behavior only occurs near the critical point, we performed a simulation for which the pressure (30 atm) is much lower than the critical pressure. As shown in Table 3, at this state point the NEMD thermal conductivity is positive and agrees well with experiment. One final note is that all properties appear to behave nearly linearly as a function of applied synthetic field. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of this research by the National Science Foundation through grant CBT and through equipment grant CPE which provided matching fundings for the purchase of the CSPI 6420 array processor used in this research. We are grateful to Professor Sohail Murad for helpful discussions. LIST OF SYMBOLS color charge in NEMD algorithm for diffusivity >, self-diffusion coefficient E average configurational energy & instantaneous configurational energy of molecule i Fc fictitious field in NEMD algorithm for thermal conductivity
8 198 pi 43 JC JQ k.b In N p pd q(t) ; VT t V * x Ad x, P force on the center of mass of molecule i force on molecule i due to molecule j color field in NEMD algorithm for diffusivity heat current in NEMD algorithm for thermal conductivity Boltzmann s constant mass of a molecule number of molecule linear momentum vector work generated by color constraint in NEMD algorithm for diffusivity spatial coordinates position vector temperature temperature gradient time volume thermostatting constraint in NEMD algorithm for thermal conductivity thermal conductivity driving constraint of the color field thermostatting constraint in NEMD algorithm for diffusivity density REFERENCES Allen, M. P. and Tildesley, D. J., Computer Simulation of Liquids, First Edition, Clarendon Press, Oxford, p. 24. Bird, R. B., Stewart, W. E. and Lightfoot, E. N., Transport Phenomena, Wiley and Sons, New York, Appendix B. Evans, D. J., Computer experiment for nonlinear thermodynamics of Couette flow. J. Chem. Phys., 78: Evans, D. J., Thermal conductivity of the Lennard-Jones fluids. Phys. Rev. A, 34: Evans, D. J., Hoover, W. G., Failor, B. H., Moran B. and Ladd, A. J. C., Nonequilib- rium molecular dynamics via Gauss s principle of least constraint. Phys. Rev. A, 28: Evans, D. J. and Morriss, G. P., Non-Newtonian molecular dynamics. Comp. Phys. Rep., 1: Evans, D. J. and Murad, S., Singularity-free algorithm for molecular dynamics simulation of rigid polyatomics. Mol. Phys., 34: Gibbons, T. G. and Klein, M. L., J. Chem. Phys., 60: 112. McHugh, M. A. and Krukonis, V. J., Supercritical Fluid Extraction, Principles and Practice. Butterworths, Boston. Murthy, C. S. and Singer, K., Interaction site models for Carbon Dioxide. Mol. Phys.. 44, 1: Vargaftik, N. B., Handbook of Physical Properties of Liquids and Gases. Second Edition, Hemisphere, New York. Wang, B. Y. and Cummings, P. T., Non-equilibrium Molecular Dynamics CalcuIa- tion of the Shear Viscosity of Carbon Dioxide. Int. J. Thermophysics, accepted for publication.
Shear viscosity of liquid rubidium at the triple point
 J. Phys. F: Met. Phys. 18 (1988) 1439-1447. Printed in the UK Shear viscosity of liquid rubidium at the triple point P T Cummingsi- and G P Morriss-l: i Department of Chemical Engineering, Thornton Hall,
J. Phys. F: Met. Phys. 18 (1988) 1439-1447. Printed in the UK Shear viscosity of liquid rubidium at the triple point P T Cummingsi- and G P Morriss-l: i Department of Chemical Engineering, Thornton Hall,
Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study of Transport Properties of Diatomic Gases
 MD Simulation of Diatomic Gases Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 14, Vol. 35, No. 1 357 http://dx.doi.org/1.51/bkcs.14.35.1.357 Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study of Transport Properties of Diatomic Gases Song
MD Simulation of Diatomic Gases Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 14, Vol. 35, No. 1 357 http://dx.doi.org/1.51/bkcs.14.35.1.357 Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study of Transport Properties of Diatomic Gases Song
Non-equilibrium molecular dynamics calculation of the shear viscosity of liquid rubidium
 J. Phys. F: Met. Phys. 17 (1987) 593-604. Printed in the UK Non-equilibrium molecular dynamics calculation of the shear viscosity of liquid rubidium P T Cummingsf and G P Morrisst + Department of Chemical
J. Phys. F: Met. Phys. 17 (1987) 593-604. Printed in the UK Non-equilibrium molecular dynamics calculation of the shear viscosity of liquid rubidium P T Cummingsf and G P Morrisst + Department of Chemical
Shear viscosity of model mixtures by nonequilibrium molecular dynamics. I. Argon-krypton mixtures
 Shear viscosity of model mixtures by nonequilibrium molecular dynamics. I. Argon-krypton mixtures Song Hi Leea) and Peter T. Cummingsb) Department of ChemicaI Engineering, Thornton Hall, University of
Shear viscosity of model mixtures by nonequilibrium molecular dynamics. I. Argon-krypton mixtures Song Hi Leea) and Peter T. Cummingsb) Department of ChemicaI Engineering, Thornton Hall, University of
Statistical Mechanics of Nonequilibrium Liquids
 1. Introduction Mechanics provides a complete microscopic description of the state of a system. When the equations of motion are combined with initial conditions and boundary conditions, the subsequent
1. Introduction Mechanics provides a complete microscopic description of the state of a system. When the equations of motion are combined with initial conditions and boundary conditions, the subsequent
Nonequilibrium Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Shear Viscosity: Isoamyl Alcohol, n-butyl Acetate and Their Mixtures
 Draft Date: October 5, 1999 Nonequilibrium Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Shear Viscosity: Isoamyl Alcohol, n-butyl Acetate and Their Mixtures Y. Yang 1, T. A. Pakkanen, 2 and R. L. Rowley 1,3 Draft
Draft Date: October 5, 1999 Nonequilibrium Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Shear Viscosity: Isoamyl Alcohol, n-butyl Acetate and Their Mixtures Y. Yang 1, T. A. Pakkanen, 2 and R. L. Rowley 1,3 Draft
4. The Green Kubo Relations
 4. The Green Kubo Relations 4.1 The Langevin Equation In 1828 the botanist Robert Brown observed the motion of pollen grains suspended in a fluid. Although the system was allowed to come to equilibrium,
4. The Green Kubo Relations 4.1 The Langevin Equation In 1828 the botanist Robert Brown observed the motion of pollen grains suspended in a fluid. Although the system was allowed to come to equilibrium,
The Effect of Model Internal Flexibility Upon NEMD Simulations of Viscosity
 Draft: September 29, 1999 The Effect of Model Internal Flexibility Upon NEMD Simulations of Viscosity N. G. Fuller 1 and R. L. Rowley 1,2 Abstract The influence of model flexibility upon simulated viscosity
Draft: September 29, 1999 The Effect of Model Internal Flexibility Upon NEMD Simulations of Viscosity N. G. Fuller 1 and R. L. Rowley 1,2 Abstract The influence of model flexibility upon simulated viscosity
Molecular dynamics simulation of limiting conductances for LiCl, NaBr, and CsBr in supercritical water
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 112, NUMBER 2 8 JANUARY 2000 Molecular dynamics simulation of limiting conductances for LiCl, NaBr, and CsBr in supercritical water S. H. Lee Department of Chemistry,
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 112, NUMBER 2 8 JANUARY 2000 Molecular dynamics simulation of limiting conductances for LiCl, NaBr, and CsBr in supercritical water S. H. Lee Department of Chemistry,
Introduction to Simulation - Lectures 17, 18. Molecular Dynamics. Nicolas Hadjiconstantinou
 Introduction to Simulation - Lectures 17, 18 Molecular Dynamics Nicolas Hadjiconstantinou Molecular Dynamics Molecular dynamics is a technique for computing the equilibrium and non-equilibrium properties
Introduction to Simulation - Lectures 17, 18 Molecular Dynamics Nicolas Hadjiconstantinou Molecular Dynamics Molecular dynamics is a technique for computing the equilibrium and non-equilibrium properties
Oleg A. Mazyar, Guoai Pan and Clare McCabe*
 Molecular Physics Vol. 107, No. 14, 20 July 2009, 1423 1429 RESEARCH ARTICLE Transient time correlation function calculation of the viscosity of a molecular fluid at low shear rates: a comparison of stress
Molecular Physics Vol. 107, No. 14, 20 July 2009, 1423 1429 RESEARCH ARTICLE Transient time correlation function calculation of the viscosity of a molecular fluid at low shear rates: a comparison of stress
Gibbs ensemble simulation of phase equilibrium in the hard core two-yukawa fluid model for the Lennard-Jones fluid
 MOLECULAR PHYSICS, 1989, VOL. 68, No. 3, 629-635 Gibbs ensemble simulation of phase equilibrium in the hard core two-yukawa fluid model for the Lennard-Jones fluid by E. N. RUDISILL and P. T. CUMMINGS
MOLECULAR PHYSICS, 1989, VOL. 68, No. 3, 629-635 Gibbs ensemble simulation of phase equilibrium in the hard core two-yukawa fluid model for the Lennard-Jones fluid by E. N. RUDISILL and P. T. CUMMINGS
Non-Equilibrium Molecular Dynamics Approach to the Rheology of Model Polymer Fluids
 Fluid Phase Equilibria, 88 (1993) 99-113 Elsevier Science Publishers B.V., msterdam 99 Non-Equilibrium Molecular Dynamics pproach to the Rheology of Model Polymer Fluids J. W. Rudisill and P. T. Cummings
Fluid Phase Equilibria, 88 (1993) 99-113 Elsevier Science Publishers B.V., msterdam 99 Non-Equilibrium Molecular Dynamics pproach to the Rheology of Model Polymer Fluids J. W. Rudisill and P. T. Cummings
Structural transition and solid-like behavior of alkane films confined in nano-spacing
 Fluid Phase Equilibria 183 184 (2001) 381 387 Structural transition and solid-like behavior of alkane films confined in nano-spacing S.T. Cui a,b,, P.T. Cummings b,c, H.D. Cochran a,b a Department of Chemical
Fluid Phase Equilibria 183 184 (2001) 381 387 Structural transition and solid-like behavior of alkane films confined in nano-spacing S.T. Cui a,b,, P.T. Cummings b,c, H.D. Cochran a,b a Department of Chemical
Shear viscosity of molten sodium chloride
 Shear viscosity of molten sodium chloride Jerome Delhommelle and Janka Petravic Citation: The Journal of Chemical Physics 118, 2783 (2003); doi: 10.1063/1.1535213 View online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1535213
Shear viscosity of molten sodium chloride Jerome Delhommelle and Janka Petravic Citation: The Journal of Chemical Physics 118, 2783 (2003); doi: 10.1063/1.1535213 View online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.1535213
 Title Super- and subcritical hydration of Thermodynamics of hydration Author(s) Matubayasi, N; Nakahara, M Citation JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS (2000), 8109 Issue Date 2000-05-08 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/50350
Title Super- and subcritical hydration of Thermodynamics of hydration Author(s) Matubayasi, N; Nakahara, M Citation JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS (2000), 8109 Issue Date 2000-05-08 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/50350
1.3 Molecular Level Presentation
 1.3.1 Introduction A molecule is the smallest chemical unit of a substance that is capable of stable, independent existence. Not all substances are composed of molecules. Some substances are composed of
1.3.1 Introduction A molecule is the smallest chemical unit of a substance that is capable of stable, independent existence. Not all substances are composed of molecules. Some substances are composed of
The viscosity-radius relationship from scaling arguments
 The viscosity-radius relationship from scaling arguments D. E. Dunstan Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, University of Melbourne, VIC 3010, Australia. davided@unimelb.edu.au Abstract
The viscosity-radius relationship from scaling arguments D. E. Dunstan Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, University of Melbourne, VIC 3010, Australia. davided@unimelb.edu.au Abstract
CHE 611 Advanced Chemical Reaction Engineering
 CHE 611 Advanced Chemical Reaction Engineering Dr. Muhammad Rashid Usman Institute of Chemical Engineering and Technology University of the Punjab, Lahore 54590 mrusman.icet@pu.edu.pk 1 Diffusion and reaction
CHE 611 Advanced Chemical Reaction Engineering Dr. Muhammad Rashid Usman Institute of Chemical Engineering and Technology University of the Punjab, Lahore 54590 mrusman.icet@pu.edu.pk 1 Diffusion and reaction
A Nonequilibrium Molecular Dynamics Study of. the Rheology of Alkanes. S.A. Gupta, S. T. Cui, P. T. Cummings and H. D. Cochran
 A Nonequilibrium Molecular Dynamics Study of the Rheology of Alkanes S.A. Gupta, S. T. Cui, P. T. Cummings and H. D. Cochran Department of Chemical Engineering University of Tennessee Knoxville, TN 37996-2200
A Nonequilibrium Molecular Dynamics Study of the Rheology of Alkanes S.A. Gupta, S. T. Cui, P. T. Cummings and H. D. Cochran Department of Chemical Engineering University of Tennessee Knoxville, TN 37996-2200
Multiscale Materials Modeling
 Multiscale Materials Modeling Lecture 02 Capabilities of Classical Molecular Simulation These notes created by David Keffer, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, 2009. Outline Capabilities of Classical
Multiscale Materials Modeling Lecture 02 Capabilities of Classical Molecular Simulation These notes created by David Keffer, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, 2009. Outline Capabilities of Classical
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Poiseuille flow to measure the viscosity of particle model fluids. Backer, J.A.; Lowe, C.P.; Hoefsloot, H.C.J.; Iedema, P.D. Published in: Journal of Chemical Physics
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Poiseuille flow to measure the viscosity of particle model fluids. Backer, J.A.; Lowe, C.P.; Hoefsloot, H.C.J.; Iedema, P.D. Published in: Journal of Chemical Physics
Efficient viscosity estimation from molecular dynamics simulation via momentum impulse relaxation
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 113, NUMBER 6 8 AUGUST 2000 Efficient viscosity estimation from molecular dynamics simulation via momentum impulse relaxation Gaurav Arya, Edward J. Maginn, a) and Hsueh-Chia
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 113, NUMBER 6 8 AUGUST 2000 Efficient viscosity estimation from molecular dynamics simulation via momentum impulse relaxation Gaurav Arya, Edward J. Maginn, a) and Hsueh-Chia
A MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION OF A BUBBLE NUCLEATION ON SOLID SURFACE
 A MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION OF A BUBBLE NUCLEATION ON SOLID SURFACE Shigeo Maruyama and Tatsuto Kimura Department of Mechanical Engineering The University of Tokyo 7-- Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo -866,
A MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION OF A BUBBLE NUCLEATION ON SOLID SURFACE Shigeo Maruyama and Tatsuto Kimura Department of Mechanical Engineering The University of Tokyo 7-- Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo -866,
Studies on flow through and around a porous permeable sphere: II. Heat Transfer
 Studies on flow through and around a porous permeable sphere: II. Heat Transfer A. K. Jain and S. Basu 1 Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Delhi New Delhi 110016, India
Studies on flow through and around a porous permeable sphere: II. Heat Transfer A. K. Jain and S. Basu 1 Department of Chemical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Delhi New Delhi 110016, India
MOLECULAR DYNAMICS STUDY OF THE NUCLEATION OF BUBBLE
 CAV2:sessionA.5 MOLECULAR DYNAMICS STUDY OF THE NUCLEATION OF BUBBLE Takashi Tokumasu, Kenjiro Kamijo, Mamoru Oike and Yoichiro Matsumoto 2 Tohoku University, Sendai, Miyagi, 98-8577, Japan 2 The University
CAV2:sessionA.5 MOLECULAR DYNAMICS STUDY OF THE NUCLEATION OF BUBBLE Takashi Tokumasu, Kenjiro Kamijo, Mamoru Oike and Yoichiro Matsumoto 2 Tohoku University, Sendai, Miyagi, 98-8577, Japan 2 The University
Navier-Stokes Equation: Principle of Conservation of Momentum
 Navier-tokes Equation: Principle of Conservation of Momentum R. hankar ubramanian Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Clarkson University Newton formulated the principle of conservation
Navier-tokes Equation: Principle of Conservation of Momentum R. hankar ubramanian Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Clarkson University Newton formulated the principle of conservation
Chapter 1 Fluid Characteristics
 Chapter 1 Fluid Characteristics 1.1 Introduction 1.1.1 Phases Solid increasing increasing spacing and intermolecular liquid latitude of cohesive Fluid gas (vapor) molecular force plasma motion 1.1.2 Fluidity
Chapter 1 Fluid Characteristics 1.1 Introduction 1.1.1 Phases Solid increasing increasing spacing and intermolecular liquid latitude of cohesive Fluid gas (vapor) molecular force plasma motion 1.1.2 Fluidity
Comparison of the DSMC Method with an Exact Solution of the Boltzmann Equation
 Comparison of the DSMC Method with an Exact Solution of the Boltzmann Equation J M Montanero and A Santos Departamento de Fisica, Universidad de Extremadura, Spain Abstract Results obtained from the Direct
Comparison of the DSMC Method with an Exact Solution of the Boltzmann Equation J M Montanero and A Santos Departamento de Fisica, Universidad de Extremadura, Spain Abstract Results obtained from the Direct
Non-equilibrium phenomena and fluctuation relations
 Non-equilibrium phenomena and fluctuation relations Lamberto Rondoni Politecnico di Torino Beijing 16 March 2012 http://www.rarenoise.lnl.infn.it/ Outline 1 Background: Local Thermodyamic Equilibrium 2
Non-equilibrium phenomena and fluctuation relations Lamberto Rondoni Politecnico di Torino Beijing 16 March 2012 http://www.rarenoise.lnl.infn.it/ Outline 1 Background: Local Thermodyamic Equilibrium 2
DIRECT EVALUATION OF VAPOUR-LIQUID EQUILIBRIA BY MOLECULAR DYNAMICS USING GIBBS-DUHEM INTEGRATION
 Molecular Simulation, 1996, Vol. 17, pp. 21-39 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only 0 1996 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) Amsterdam B.V. Published
Molecular Simulation, 1996, Vol. 17, pp. 21-39 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only 0 1996 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) Amsterdam B.V. Published
Predicting the viscosity of alkanes using nonequilibrium molecular dynamics: Evaluation of intermolecular potential models
 Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Faculty Publications 1997-06-22 Predicting the viscosity of alkanes using nonequilibrium molecular dynamics: Evaluation of intermolecular potential models
Brigham Young University BYU ScholarsArchive All Faculty Publications 1997-06-22 Predicting the viscosity of alkanes using nonequilibrium molecular dynamics: Evaluation of intermolecular potential models
Chemical Physics Letters
 Chemical Physics Letters 542 (2012) 37 41 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Chemical Physics Letters journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/cplett Thermal conductivity, shear viscosity
Chemical Physics Letters 542 (2012) 37 41 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Chemical Physics Letters journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/cplett Thermal conductivity, shear viscosity
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Thermodynamics of Three-phase Equilibrium in Lennard Jones System with a Simplified Equation of State
 23 Bulletin of Research Center for Computing and Multimedia Studies, Hosei University, 28 (2014) Thermodynamics of Three-phase Equilibrium in Lennard Jones System with a Simplified Equation of State Yosuke
23 Bulletin of Research Center for Computing and Multimedia Studies, Hosei University, 28 (2014) Thermodynamics of Three-phase Equilibrium in Lennard Jones System with a Simplified Equation of State Yosuke
Effect of oscillatory shear on the fluid solid phase transition of supercooled water
 Ž. Fluid Phase Equilibria 150 151 1998 Effect of oscillatory shear on the fluid solid phase transition of supercooled water Istvan Borzsak a,b,), Peter T. Cummings a,b a Department of Chemical Engineering,
Ž. Fluid Phase Equilibria 150 151 1998 Effect of oscillatory shear on the fluid solid phase transition of supercooled water Istvan Borzsak a,b,), Peter T. Cummings a,b a Department of Chemical Engineering,
Universities of Leeds, Sheffield and York
 promoting access to White Rose research papers Universities of Leeds, Sheffield and York http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/ This is an author produced version of a paper published in The Journal of Chemical
promoting access to White Rose research papers Universities of Leeds, Sheffield and York http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/ This is an author produced version of a paper published in The Journal of Chemical
 1 Points to Remember Subject: Chemistry Class: XI Chapter: States of matter Top concepts 1. Intermolecular forces are the forces of attraction and repulsion between interacting particles (atoms and molecules).
1 Points to Remember Subject: Chemistry Class: XI Chapter: States of matter Top concepts 1. Intermolecular forces are the forces of attraction and repulsion between interacting particles (atoms and molecules).
Nosé-Hoover chain method for nonequilibrium molecular dynamics simulation
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 61, NUMBER 5 MAY 000 Nosé-Hoover chain method for nonequilibrium molecular dynamics simulation A. C. Brańka Institute of Molecular Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences, Smoluchowskiego
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 61, NUMBER 5 MAY 000 Nosé-Hoover chain method for nonequilibrium molecular dynamics simulation A. C. Brańka Institute of Molecular Physics, Polish Academy of Sciences, Smoluchowskiego
Stress Overshoot of Polymer Solutions at High Rates of Shear
 Stress Overshoot of Polymer Solutions at High Rates of Shear K. OSAKI, T. INOUE, T. ISOMURA Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University, Uji, Kyoto 611-0011, Japan Received 3 April 2000; revised
Stress Overshoot of Polymer Solutions at High Rates of Shear K. OSAKI, T. INOUE, T. ISOMURA Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University, Uji, Kyoto 611-0011, Japan Received 3 April 2000; revised
2 Lyapunov Exponent exponent number. Lyapunov spectrum for colour conductivity of 8 WCA disks.
 3 2 Lyapunov Exponent 1-1 -2-3 5 1 15 exponent number Lyapunov spectrum for colour conductivity of 8 WCA disks. 2 3 Lyapunov exponent 2 1-1 -2-3 5 1 15 exponent number Lyapunov spectrum for shear flow
3 2 Lyapunov Exponent 1-1 -2-3 5 1 15 exponent number Lyapunov spectrum for colour conductivity of 8 WCA disks. 2 3 Lyapunov exponent 2 1-1 -2-3 5 1 15 exponent number Lyapunov spectrum for shear flow
Molecular Dynamics Study on the Binary Collision of Nanometer-Sized Droplets of Liquid Argon
 Molecular Dynamics Study on the Binary Collision Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, Vol. 32, No. 6 2027 DOI 10.5012/bkcs.2011.32.6.2027 Molecular Dynamics Study on the Binary Collision of Nanometer-Sized Droplets
Molecular Dynamics Study on the Binary Collision Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, Vol. 32, No. 6 2027 DOI 10.5012/bkcs.2011.32.6.2027 Molecular Dynamics Study on the Binary Collision of Nanometer-Sized Droplets
6. Transport phenomena. Basel, 2008
 6. Transport phenomena Basel, 2008 6. Transport phenomena 1. Introduction 2. Phenomenological equations for transport properties 3. Transport properties of a perfect gas 4. Diffusion in a fluid 5. Measurement
6. Transport phenomena Basel, 2008 6. Transport phenomena 1. Introduction 2. Phenomenological equations for transport properties 3. Transport properties of a perfect gas 4. Diffusion in a fluid 5. Measurement
Introduction to Nonequilibrium Molecular Dynamics
 Introduction to Nonequilibrium Molecular Dynamics Dr Billy D. Todd Centre for Molecular Simulation Swinburne University of Technology PO Box 218, Hawthorn Victoria 3122, Australia Email: btodd@swin.edu.au
Introduction to Nonequilibrium Molecular Dynamics Dr Billy D. Todd Centre for Molecular Simulation Swinburne University of Technology PO Box 218, Hawthorn Victoria 3122, Australia Email: btodd@swin.edu.au
Direct Simulation Monte Carlo Calculation: Strategies for Using Complex Initial Conditions
 Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 731 2002 Materials Research Society Direct Simulation Monte Carlo Calculation: Strategies for Using Complex Initial Conditions Michael I. Zeifman 1, Barbara J. Garrison
Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. Vol. 731 2002 Materials Research Society Direct Simulation Monte Carlo Calculation: Strategies for Using Complex Initial Conditions Michael I. Zeifman 1, Barbara J. Garrison
arxiv:nlin/ v1 [nlin.cd] 8 May 2001
![arxiv:nlin/ v1 [nlin.cd] 8 May 2001 arxiv:nlin/ v1 [nlin.cd] 8 May 2001](/thumbs/74/70351420.jpg) Field dependent collision frequency of the two-dimensional driven random Lorentz gas arxiv:nlin/0105017v1 [nlin.cd] 8 May 2001 Christoph Dellago Department of Chemistry, University of Rochester, Rochester,
Field dependent collision frequency of the two-dimensional driven random Lorentz gas arxiv:nlin/0105017v1 [nlin.cd] 8 May 2001 Christoph Dellago Department of Chemistry, University of Rochester, Rochester,
Unusual Entropy of Adsorbed Methane on Zeolite Templated Carbon. Supporting Information. Part 2: Statistical Mechanical Model
 Unusual Entropy of Adsorbed Methane on Zeolite Templated Carbon Supporting Information Part 2: Statistical Mechanical Model Nicholas P. Stadie*, Maxwell Murialdo, Channing C. Ahn, and Brent Fultz W. M.
Unusual Entropy of Adsorbed Methane on Zeolite Templated Carbon Supporting Information Part 2: Statistical Mechanical Model Nicholas P. Stadie*, Maxwell Murialdo, Channing C. Ahn, and Brent Fultz W. M.
Non-equilibrium molecular dynamics simulation study of the behavior of hydrocarbon-isomers in silicalite
 Fluid Phase Equilibria 194 197 (2002) 309 317 Non-equilibrium molecular dynamics simulation study of the behavior of hydrocarbon-isomers in silicalite S. Furukawa a,b,, C. McCabe a,c, T. Nitta b, P.T.
Fluid Phase Equilibria 194 197 (2002) 309 317 Non-equilibrium molecular dynamics simulation study of the behavior of hydrocarbon-isomers in silicalite S. Furukawa a,b,, C. McCabe a,c, T. Nitta b, P.T.
Viscosity of confined inhomogeneous nonequilibrium fluids
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 121, NUMBER 21 1 DECEMBER 2004 Viscosity of confined inhomogeneous nonequilibrium fluids Junfang Zhang and B. D. Todd a) Centre for Molecular Simulation, Swinburne University
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 121, NUMBER 21 1 DECEMBER 2004 Viscosity of confined inhomogeneous nonequilibrium fluids Junfang Zhang and B. D. Todd a) Centre for Molecular Simulation, Swinburne University
PROPERTIES OF POLYMERS
 PROPERTIES OF POLYMERS THEIR CORRELATION WITH CHEMICAL STRUCTURE; THEIR NUMERICAL ESTIMATION AND PREDICTION FROM ADDITIVE GROUP CONTRIBUTIONS Third, completely revised edition By D.W. VÄN KREVELEN Professor-Emeritus,
PROPERTIES OF POLYMERS THEIR CORRELATION WITH CHEMICAL STRUCTURE; THEIR NUMERICAL ESTIMATION AND PREDICTION FROM ADDITIVE GROUP CONTRIBUTIONS Third, completely revised edition By D.W. VÄN KREVELEN Professor-Emeritus,
FUNDAMENTALS OF CHEMISTRY Vol. II - Irreversible Processes: Phenomenological and Statistical Approach - Carlo Cercignani
 IRREVERSIBLE PROCESSES: PHENOMENOLOGICAL AND STATISTICAL APPROACH Carlo Dipartimento di Matematica, Politecnico di Milano, Milano, Italy Keywords: Kinetic theory, thermodynamics, Boltzmann equation, Macroscopic
IRREVERSIBLE PROCESSES: PHENOMENOLOGICAL AND STATISTICAL APPROACH Carlo Dipartimento di Matematica, Politecnico di Milano, Milano, Italy Keywords: Kinetic theory, thermodynamics, Boltzmann equation, Macroscopic
Thermodynamic behaviour of mixtures containing CO 2. A molecular simulation study
 Thermodynamic behaviour of mixtures containing. A molecular simulation study V. Lachet, C. Nieto-Draghi, B. Creton (IFPEN) Å. Ervik, G. Skaugen, Ø. Wilhelmsen, M. Hammer (SINTEF) Introduction quality issues
Thermodynamic behaviour of mixtures containing. A molecular simulation study V. Lachet, C. Nieto-Draghi, B. Creton (IFPEN) Å. Ervik, G. Skaugen, Ø. Wilhelmsen, M. Hammer (SINTEF) Introduction quality issues
Fluid Mechanics Theory I
 Fluid Mechanics Theory I Last Class: 1. Introduction 2. MicroTAS or Lab on a Chip 3. Microfluidics Length Scale 4. Fundamentals 5. Different Aspects of Microfluidcs Today s Contents: 1. Introduction to
Fluid Mechanics Theory I Last Class: 1. Introduction 2. MicroTAS or Lab on a Chip 3. Microfluidics Length Scale 4. Fundamentals 5. Different Aspects of Microfluidcs Today s Contents: 1. Introduction to
Phase transitions of quadrupolar fluids
 Phase transitions of quadrupolar fluids Seamus F. O Shea Department of Chemistry, University of Lethbridge, Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada, T1K 3M4 Girija S. Dubey Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, New
Phase transitions of quadrupolar fluids Seamus F. O Shea Department of Chemistry, University of Lethbridge, Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada, T1K 3M4 Girija S. Dubey Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, New
CE 530 Molecular Simulation
 1 CE 530 Molecular Simulation Lecture 1 David A. Kofke Department of Chemical Engineering SUNY Buffalo kofke@eng.buffalo.edu 2 Time/s Multi-Scale Modeling Based on SDSC Blue Horizon (SP3) 1.728 Tflops
1 CE 530 Molecular Simulation Lecture 1 David A. Kofke Department of Chemical Engineering SUNY Buffalo kofke@eng.buffalo.edu 2 Time/s Multi-Scale Modeling Based on SDSC Blue Horizon (SP3) 1.728 Tflops
On the Asymptotic Convergence. of the Transient and Steady State Fluctuation Theorems. Gary Ayton and Denis J. Evans. Research School Of Chemistry
 1 On the Asymptotic Convergence of the Transient and Steady State Fluctuation Theorems. Gary Ayton and Denis J. Evans Research School Of Chemistry Australian National University Canberra, ACT 0200 Australia
1 On the Asymptotic Convergence of the Transient and Steady State Fluctuation Theorems. Gary Ayton and Denis J. Evans Research School Of Chemistry Australian National University Canberra, ACT 0200 Australia
CHEM 1211K Test IV. 3) The phase diagram of a substance is given above. This substance is a at 25 o C and 1.0 atm.
 CEM 1211K Test IV A MULTIPLE COICE. ( points) 1) A sample of a gas (5.0 mol) at 1.0 atm is expanded at constant temperature from 10 L to 15 L. The final pressure is atm. A). B) 1.5 C) 15 D) 7.5 E) 0.67
CEM 1211K Test IV A MULTIPLE COICE. ( points) 1) A sample of a gas (5.0 mol) at 1.0 atm is expanded at constant temperature from 10 L to 15 L. The final pressure is atm. A). B) 1.5 C) 15 D) 7.5 E) 0.67
INTERMOLECULAR FORCES
 INTERMOLECULAR FORCES Their Origin and Determination By GEOFFREY C. MAITLAND Senior Research Scientist Schlumberger Cambridge Research, Cambridge MAURICE RIGBY Lecturer in the Department of Chemistry King's
INTERMOLECULAR FORCES Their Origin and Determination By GEOFFREY C. MAITLAND Senior Research Scientist Schlumberger Cambridge Research, Cambridge MAURICE RIGBY Lecturer in the Department of Chemistry King's
= = 10.1 mol. Molar Enthalpies of Vaporization (at Boiling Point) Molar Enthalpy of Vaporization (kj/mol)
 Ch 11 (Sections 11.1 11.5) Liquid Phase Volume and Density - Liquid and solid are condensed phases and their volumes are not simple to calculate. - This is different from gases, which have volumes that
Ch 11 (Sections 11.1 11.5) Liquid Phase Volume and Density - Liquid and solid are condensed phases and their volumes are not simple to calculate. - This is different from gases, which have volumes that
Translational and rotational dynamics in supercritical methanol from molecular dynamics simulation*
 Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 76, No. 1, pp. 203 213, 2004. 2004 IUPAC Translational and rotational dynamics in supercritical methanol from molecular dynamics simulation* Michalis Chalaris and Jannis Samios Physical
Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 76, No. 1, pp. 203 213, 2004. 2004 IUPAC Translational and rotational dynamics in supercritical methanol from molecular dynamics simulation* Michalis Chalaris and Jannis Samios Physical
Entropy production fluctuation theorem and the nonequilibrium work relation for free energy differences
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 60, NUMBER 3 SEPTEMBER 1999 Entropy production fluctuation theorem and the nonequilibrium work relation for free energy differences Gavin E. Crooks* Department of Chemistry, University
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 60, NUMBER 3 SEPTEMBER 1999 Entropy production fluctuation theorem and the nonequilibrium work relation for free energy differences Gavin E. Crooks* Department of Chemistry, University
Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering 150A Transport Processes Spring Semester 2017
 Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering 150A Transport Processes Spring Semester 2017 Objective: Text: To introduce the basic concepts of fluid mechanics and heat transfer necessary for solution of engineering
Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering 150A Transport Processes Spring Semester 2017 Objective: Text: To introduce the basic concepts of fluid mechanics and heat transfer necessary for solution of engineering
Initial position, x p (0)/L
 .4 ) xp().2 ) ( 2L 2 xp Dc ( Displacement, /L.2.4.5.5 Initial position, x p ()/L Supplementary Figure Computed displacements of (red) positively- and (blue) negatively-charged particles at several CO 2
.4 ) xp().2 ) ( 2L 2 xp Dc ( Displacement, /L.2.4.5.5 Initial position, x p ()/L Supplementary Figure Computed displacements of (red) positively- and (blue) negatively-charged particles at several CO 2
Lecture 6: Irreversible Processes
 Materials Science & Metallurgy Master of Philosophy, Materials Modelling, Course MP4, Thermodynamics and Phase Diagrams, H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia Lecture 6: Irreversible Processes Thermodynamics generally
Materials Science & Metallurgy Master of Philosophy, Materials Modelling, Course MP4, Thermodynamics and Phase Diagrams, H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia Lecture 6: Irreversible Processes Thermodynamics generally
Dynamics of sheared gases
 Computer Physics Communications 121 122 (1999) 225 230 www.elsevier.nl/locate/cpc Dynamics of sheared gases Patricio Cordero a,1, Dino Risso b a Departamento de Física, Facultad de Ciencias Físicas y Matemáticas,
Computer Physics Communications 121 122 (1999) 225 230 www.elsevier.nl/locate/cpc Dynamics of sheared gases Patricio Cordero a,1, Dino Risso b a Departamento de Física, Facultad de Ciencias Físicas y Matemáticas,
A Corresponding State Theory for the Viscosity of Liquids Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2008, Vol. 29, No Articles
 A Corresponding State Theory for the Viscosity of Liquids Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2008, Vol. 29, No. 1 33 Articles A Corresponding State Theory for the Viscosity of Liquids Wonsoo Kim * and Sukbae Lee
A Corresponding State Theory for the Viscosity of Liquids Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2008, Vol. 29, No. 1 33 Articles A Corresponding State Theory for the Viscosity of Liquids Wonsoo Kim * and Sukbae Lee
Simulation of Nematic-Isotropic Phase Coexistence in Liquid Crystals under Shear
 Simulation of Nematic-Isotropic Phase Coexistence in Liquid Crystals under Shear Guido Germano 1,2 and Friederike Schmid 2 1 Physical Chemistry Philipps-University 3532 Marburg, Germany E-mail: germano@staff.uni-marburg.de
Simulation of Nematic-Isotropic Phase Coexistence in Liquid Crystals under Shear Guido Germano 1,2 and Friederike Schmid 2 1 Physical Chemistry Philipps-University 3532 Marburg, Germany E-mail: germano@staff.uni-marburg.de
Thermodynamic and transport properties of carbon dioxide from molecular simulation
 Thermodynamic and transport properties of carbon dioxide from molecular simulation Carlos Nieto-Draghi, Theodorus de Bruin, Javier Pérez-Pellitero, Josep Bonet Avalos, and Allan D. Mackie Citation: The
Thermodynamic and transport properties of carbon dioxide from molecular simulation Carlos Nieto-Draghi, Theodorus de Bruin, Javier Pérez-Pellitero, Josep Bonet Avalos, and Allan D. Mackie Citation: The
Molecular dynamics simulation of nanofluidics and nanomachining
 Molecular dynamics simulation of nanofluidics and nanomachining M. T. Horsch,1, 4 S. Stephan,1 S. Becker,1 M. Heier,1 M. P. Lautenschläger,1 F. Diewald,2 R. Müller,2 H. M. Urbassek,3 and H. Hasse1 1 Engineering
Molecular dynamics simulation of nanofluidics and nanomachining M. T. Horsch,1, 4 S. Stephan,1 S. Becker,1 M. Heier,1 M. P. Lautenschläger,1 F. Diewald,2 R. Müller,2 H. M. Urbassek,3 and H. Hasse1 1 Engineering
MD Thermodynamics. Lecture 12 3/26/18. Harvard SEAS AP 275 Atomistic Modeling of Materials Boris Kozinsky
 MD Thermodynamics Lecture 1 3/6/18 1 Molecular dynamics The force depends on positions only (not velocities) Total energy is conserved (micro canonical evolution) Newton s equations of motion (second order
MD Thermodynamics Lecture 1 3/6/18 1 Molecular dynamics The force depends on positions only (not velocities) Total energy is conserved (micro canonical evolution) Newton s equations of motion (second order
A comparative study between dissipative particle dynamics and molecular dynamics for simple- and complex-geometry flows
 THE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS 123, 104107 2005 A comparative study between dissipative particle dynamics and molecular dynamics for simple- and complex-geometry flows Eric E. Keaveny, Igor V. Pivkin,
THE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS 123, 104107 2005 A comparative study between dissipative particle dynamics and molecular dynamics for simple- and complex-geometry flows Eric E. Keaveny, Igor V. Pivkin,
Speed Distribution at CONSTANT Temperature is given by the Maxwell Boltzmann Speed Distribution
 Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
Temperature ~ Average KE of each particle Particles have different speeds Gas Particles are in constant RANDOM motion Average KE of each particle is: 3/2 kt Pressure is due to momentum transfer Speed Distribution
Suspension Stability; Why Particle Size, Zeta Potential and Rheology are Important
 ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 20, 2012 Suspension Stability; Why Particle Size, Zeta Potential and Rheology are Important Mats Larsson 1, Adrian Hill 2, and John Duffy 2 1 Malvern
ANNUAL TRANSACTIONS OF THE NORDIC RHEOLOGY SOCIETY, VOL. 20, 2012 Suspension Stability; Why Particle Size, Zeta Potential and Rheology are Important Mats Larsson 1, Adrian Hill 2, and John Duffy 2 1 Malvern
Gas flow around a longitudinally oscillating plate at arbitrary ratio of collision frequency to oscillation frequency
 Gas flow around a longitudinally oscillating plate at arbitrary ratio of collision frequency to oscillation frequency Feli Sharipov and Denize Kalempa Departamento de Física, Universidade Federal do Paraná
Gas flow around a longitudinally oscillating plate at arbitrary ratio of collision frequency to oscillation frequency Feli Sharipov and Denize Kalempa Departamento de Física, Universidade Federal do Paraná
Comparative study on methodology in molecular dynamics simulation of nucleation
 THE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS 126, 224517 2007 Comparative study on methodology in molecular dynamics simulation of nucleation Jan Julin, Ismo Napari, and Hanna Vehkamäki Department of Physical Sciences,
THE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS 126, 224517 2007 Comparative study on methodology in molecular dynamics simulation of nucleation Jan Julin, Ismo Napari, and Hanna Vehkamäki Department of Physical Sciences,
Towards a computational chemical potential for nonequilibrium steady-state systems
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 60, NUMBER 5 NOVEMBER 1999 Towards a computational chemical potential for nonequilibrium steady-state systems András Baranyai Department of Theoretical Chemistry, Eötvös University,
PHYSICAL REVIEW E VOLUME 60, NUMBER 5 NOVEMBER 1999 Towards a computational chemical potential for nonequilibrium steady-state systems András Baranyai Department of Theoretical Chemistry, Eötvös University,
Structural order in glassy water
 Structural order in glassy water Nicolas Giovambattista, 1 Pablo G. Debenedetti, 1 Francesco Sciortino, 2 and H. Eugene Stanley 3 1 Department of Chemical Engineering, Princeton University, Princeton,
Structural order in glassy water Nicolas Giovambattista, 1 Pablo G. Debenedetti, 1 Francesco Sciortino, 2 and H. Eugene Stanley 3 1 Department of Chemical Engineering, Princeton University, Princeton,
Supporting Information
 Projection of atomistic simulation data for the dynamics of entangled polymers onto the tube theory: Calculation of the segment survival probability function and comparison with modern tube models Pavlos
Projection of atomistic simulation data for the dynamics of entangled polymers onto the tube theory: Calculation of the segment survival probability function and comparison with modern tube models Pavlos
MODELING OF PHASE EQUILIBRIA FOR BINARY AND TERNARY MIXTURES OF CARBON DIOXIDE, HYDROGEN AND METHANOL
 MODELING OF PHASE EQUILIBRIA FOR BINARY AND TERNARY MIXTURES OF CARBON DIOXIDE, HYDROGEN AND METHANOL Neil R. Foster *, Keivan Bezanehtak, Fariba Dehghani School of Chemical Engineering and Industrial
MODELING OF PHASE EQUILIBRIA FOR BINARY AND TERNARY MIXTURES OF CARBON DIOXIDE, HYDROGEN AND METHANOL Neil R. Foster *, Keivan Bezanehtak, Fariba Dehghani School of Chemical Engineering and Industrial
MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION ON TOTAL THERMAL RESISTANCE OF NANO TRIANGULAR PIPE
 ISTP-16, 2005, PRAGUE 16 TH INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON TRANSPORT PHENOMENA MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION ON TOTAL THERMAL RESISTANCE OF NANO TRIANGULAR PIPE C.S. Wang* J.S. Chen* and S. Maruyama** * Department
ISTP-16, 2005, PRAGUE 16 TH INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM ON TRANSPORT PHENOMENA MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION ON TOTAL THERMAL RESISTANCE OF NANO TRIANGULAR PIPE C.S. Wang* J.S. Chen* and S. Maruyama** * Department
MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION OF HETEROGENEOUS NUCLEATION OF LIQUID DROPLET ON SOLID SURFACE
 MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION OF HETEROGENEOUS NUCLEATION OF LIQUID DROPLET ON SOLID SURFACE Tatsuto Kimura* and Shigeo Maruyama** *Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Tokyo 7-- Hongo,
MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION OF HETEROGENEOUS NUCLEATION OF LIQUID DROPLET ON SOLID SURFACE Tatsuto Kimura* and Shigeo Maruyama** *Department of Mechanical Engineering, The University of Tokyo 7-- Hongo,
The Analysis of the Equilibrium Cluster Structure in Supercritical Carbon Dioxide
 American Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 3, 899-904 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajac.2012.312a119 Published Online December 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajac) The Analysis of the Equilibrium
American Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 3, 899-904 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajac.2012.312a119 Published Online December 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajac) The Analysis of the Equilibrium
Multiple time step Monte Carlo
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 117, NUMBER 18 8 NOVEMBER 2002 Multiple time step Monte Carlo Balázs Hetényi a) Department of Chemistry, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 and Department of Chemistry
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 117, NUMBER 18 8 NOVEMBER 2002 Multiple time step Monte Carlo Balázs Hetényi a) Department of Chemistry, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544 and Department of Chemistry
Prediction of Fluid Mixture Transport Properties by Molecular Dynamics 1
 International Journal of Thermophysics, Vol. 19, No. 2, 1998 Prediction of Fluid Mixture Transport Properties by Molecular Dynamics 1 D. K. Dysthe, 2 A. H. Fuchs, 2 and B. Rousseau 2, 3 Equilibrium molecular
International Journal of Thermophysics, Vol. 19, No. 2, 1998 Prediction of Fluid Mixture Transport Properties by Molecular Dynamics 1 D. K. Dysthe, 2 A. H. Fuchs, 2 and B. Rousseau 2, 3 Equilibrium molecular
RESEARCH NOTE. DOUGLAS HENDERSON? Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Brigham Young University, Provo, Utah USA
 MOLECULAR PHYSICS, 1999, VOL. 96, No. 7, 1145-1149 RESEARCH NOTE A simple theory for the partial molar volumes of a binary mixture DOUGLAS HENDERSON? Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Brigham Young
MOLECULAR PHYSICS, 1999, VOL. 96, No. 7, 1145-1149 RESEARCH NOTE A simple theory for the partial molar volumes of a binary mixture DOUGLAS HENDERSON? Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Brigham Young
KINETICE THEROY OF GASES
 INTRODUCTION: Kinetic theory of gases relates the macroscopic properties of gases (like pressure, temperature, volume... etc) to the microscopic properties of the gas molecules (like speed, momentum, kinetic
INTRODUCTION: Kinetic theory of gases relates the macroscopic properties of gases (like pressure, temperature, volume... etc) to the microscopic properties of the gas molecules (like speed, momentum, kinetic
Monte Carlo Calculations of Effective Surface Tension for Small Clusters
 Monte Carlo Calculations of Effective Surface Tension for Small Clusters Barbara N. Hale Physics Department and Cloud and Aerosol Science Laboratory, University of Missouri- Rolla, Rolla, MO 65401, USA
Monte Carlo Calculations of Effective Surface Tension for Small Clusters Barbara N. Hale Physics Department and Cloud and Aerosol Science Laboratory, University of Missouri- Rolla, Rolla, MO 65401, USA
Michael W. Mahoney Department of Physics, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut 06520
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 115, NUMBER 23 15 DECEMBER 2001 Quantum, intramolecular flexibility, and polarizability effects on the reproduction of the density anomaly of liquid water by simple potential
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 115, NUMBER 23 15 DECEMBER 2001 Quantum, intramolecular flexibility, and polarizability effects on the reproduction of the density anomaly of liquid water by simple potential
Derivation of Van der Waal s equation of state in microcanonical ensemble formulation
 arxiv:180.01963v1 [physics.gen-ph] 9 Nov 017 Derivation of an der Waal s equation of state in microcanonical ensemble formulation Aravind P. Babu, Kiran S. Kumar and M. Ponmurugan* Department of Physics,
arxiv:180.01963v1 [physics.gen-ph] 9 Nov 017 Derivation of an der Waal s equation of state in microcanonical ensemble formulation Aravind P. Babu, Kiran S. Kumar and M. Ponmurugan* Department of Physics,
Viscoelastic Flows in Abrupt Contraction-Expansions
 Viscoelastic Flows in Abrupt Contraction-Expansions I. Fluid Rheology extension. In this note (I of IV) we summarize the rheological properties of the test fluid in shear and The viscoelastic fluid consists
Viscoelastic Flows in Abrupt Contraction-Expansions I. Fluid Rheology extension. In this note (I of IV) we summarize the rheological properties of the test fluid in shear and The viscoelastic fluid consists
DETERMINATION OF THE POTENTIAL ENERGY SURFACES OF REFRIGERANT MIXTURES AND THEIR GAS TRANSPORT COEFFICIENTS
 THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 07, Vo., No. 6B, pp. 85-858 85 DETERMINATION OF THE POTENTIAL ENERGY SURFACES OF REFRIGERANT MIXTURES AND THEIR GAS TRANSPORT COEFFICIENTS Introduction by Bo SONG, Xiaopo WANG *,
THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 07, Vo., No. 6B, pp. 85-858 85 DETERMINATION OF THE POTENTIAL ENERGY SURFACES OF REFRIGERANT MIXTURES AND THEIR GAS TRANSPORT COEFFICIENTS Introduction by Bo SONG, Xiaopo WANG *,
Nonequilibrium temperature measurement in a thermal conduction process
 PHYSICAL REVIEW E 95, 33 (7) Nonequilibrium temperature measurement in a thermal conduction process Puneet Kumar Patra * and Romesh C. Batra Department of Biomedical Engineering and Mechanics, M/C 9, Virginia
PHYSICAL REVIEW E 95, 33 (7) Nonequilibrium temperature measurement in a thermal conduction process Puneet Kumar Patra * and Romesh C. Batra Department of Biomedical Engineering and Mechanics, M/C 9, Virginia
Application of the Dissipative Particle Dynamics Method to Ferromagnetic Colloidal Dispersions
 Application of the Dissipative Particle Dynamics Method to Ferromagnetic Colloidal Dispersions AKIRA SATOH Professor, Akita Prefectural University, Japan Roy W. Chantrell Professor, York University, U.
Application of the Dissipative Particle Dynamics Method to Ferromagnetic Colloidal Dispersions AKIRA SATOH Professor, Akita Prefectural University, Japan Roy W. Chantrell Professor, York University, U.
CFD SIMULATIONS OF FLOW, HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER IN THIN-FILM EVAPORATOR
 Distillation Absorption 2010 A.B. de Haan, H. Kooijman and A. Górak (Editors) All rights reserved by authors as per DA2010 copyright notice CFD SIMULATIONS OF FLOW, HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER IN THIN-FILM
Distillation Absorption 2010 A.B. de Haan, H. Kooijman and A. Górak (Editors) All rights reserved by authors as per DA2010 copyright notice CFD SIMULATIONS OF FLOW, HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER IN THIN-FILM
Chem 4501 Introduction to Thermodynamics, 3 Credits Kinetics, and Statistical Mechanics
 Chem 4501 Introduction to hermodynamics, 3 Credits Kinetics, and Statistical Mechanics Module Number 2 Active Learning Answers and Optional Problems/Solutions 1. McQuarrie and Simon, 2-6. Paraphrase: How
Chem 4501 Introduction to hermodynamics, 3 Credits Kinetics, and Statistical Mechanics Module Number 2 Active Learning Answers and Optional Problems/Solutions 1. McQuarrie and Simon, 2-6. Paraphrase: How
Poiseuille flow of Lennard-Jones fluids in narrow slit pores
 JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 112, NUMBER 4 22 JANUARY 2000 Poiseuille flow of Lennard-Jones fluids in narrow slit pores Karl P. Travis a) and Keith E. Gubbins Department of Chemical Engineering,
JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS VOLUME 112, NUMBER 4 22 JANUARY 2000 Poiseuille flow of Lennard-Jones fluids in narrow slit pores Karl P. Travis a) and Keith E. Gubbins Department of Chemical Engineering,
Effect of Adsorption in Flow of Gases in Organic Nanopores: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Mohammad Kazemi Ali Takbiri-Borujeni West Virginia University
 Effect of Adsorption in Flow of Gases in Organic Nanopores: A Molecular Dynamics Study Mohammad Kazemi Ali Takbiri-Borujeni West Virginia University Multiscale Nature of Gas production Slide 2 Slide 3
Effect of Adsorption in Flow of Gases in Organic Nanopores: A Molecular Dynamics Study Mohammad Kazemi Ali Takbiri-Borujeni West Virginia University Multiscale Nature of Gas production Slide 2 Slide 3
The influence of axial orientation of spheroidal particles on the adsorption
 The influence of axial orientation of spheroidal particles on the adsorption rate in a granular porous medium F. A. Coutelieris National Center for Scientific Research Demokritos, 1510 Aghia Paraskevi
The influence of axial orientation of spheroidal particles on the adsorption rate in a granular porous medium F. A. Coutelieris National Center for Scientific Research Demokritos, 1510 Aghia Paraskevi
CHAPTER 4. Basics of Fluid Dynamics
 CHAPTER 4 Basics of Fluid Dynamics What is a fluid? A fluid is a substance that can flow, has no fixed shape, and offers little resistance to an external stress In a fluid the constituent particles (atoms,
CHAPTER 4 Basics of Fluid Dynamics What is a fluid? A fluid is a substance that can flow, has no fixed shape, and offers little resistance to an external stress In a fluid the constituent particles (atoms,
