Online Path Computation & Function Placement in SDNs
|
|
|
- Diana Warren
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Online Path Computation & Function Placement in SDNs Guy Even Tel Aviv University Moti Medina MPI for Informatics Boaz Patt-Shamir Tel Aviv University
2 Today s Focus: Online Virtual Circuit Routing Network: G = V, E, c V is the set of nodes E is the set of links c: E N + edge capacities Requests: paths r j = s j, t j, b j, d j, α j, β j s j source node t j destination node b j benefit (per time step) d j BW requirement α j, β j arrival/depart times β j is either known or unknown upfront. r 1 = r 2 = load(e) flow(e)/c(e)
3 Performance Measure - Competitive Ratio [Sleator, Tarajan 85] ALG : Online alg σ : sequence of path requests ALG σ : total benefit due to σ OPT σ : Max benefit from σ by a feasible allocation ρ ALG inf σ ALG(σ) OPT(σ)
4 unknown Duration known Online Versions ACC/REJECT Model ACC/STDBY Benefits: ACC/REJECT = accepted b j ACC/STDBY= t accepted(t) b j? [AAP93] C. R. = log V b max Tight Unbounded C. R. time Same as? ACC/REJECT New: C. R. = log V b max Known duration only arrivals (persistent requests)
5 Proposal: ACC/STDBY model r j arrives Unknown duration Active ACCEPT Route? STDBY Active? No preemption (!) No rerouting (!) Request pays b j per served time unit. end end Question: what about online competitive analysis?
6 unknown Duration known Online Versions ACC/REJECT Model ACC/STDBY Benefits: ACC/REJECT = accepted b j ACC/STDBY= t accepted(t) b j [AAP93] C. R. = log V b max Tight Unbounded C. R. time Same as ACC/REJECT New: C. R. = log V b max Tight Known duration only arrivals (persistent requests)
7 Online Persistent Routing Algorithm [AAP93] (known duration, ACC/REJ) State: accepted requests r j, path j acc. r j arrives: r j arrives Path Oracle REJECT Oracle(r j ) w e = exp(load(e)) Search for a path s j t j s.t. e pathj w(e) < b j Success: return(path j ) Fail: REJECT ACCEPT Allocate path j to r j load(e) flow(e)/c(e)
8 Our Algorithm (unknown duration, ACC/STDBY) State: accepted requests r j, path j, acc. STDBY list. r j arrives: r j arrives Path Oracle STDBY Active? Oracle(r j ) w e = exp(load(e)) Search for a path s j t j s.t. e pathj w(e) < b j Success: return(path j ) Fail: STDBY active ACCEPT Allocate path j to r j end end load(e) flow(e)/c(e)
9 Main Result (virtual circuit routing version) Thm. Small demands in each time step t, benefit t ALG benefit t OPT log V b max. Remarks: 1. Small demands: d max c min log V b max. 2. If served, request is served continuously until it ends. 3. Even when OPT is fractional, may preempt, may reroute, i.e., MCF in every time step. 4. Proof idea: repeating the game of persistent routing. 5. Asymptotically optimal! 6. Extends to the SDN modeling (next slide).
10 Modeling SDN Single source packets arrive from here Req served by any s t path. Needs mapping to N Network N = V, E V set of servers E set of links c: V E N + i.e, Processing, BW Online requests r j = G j, d j, b j, U j G j = (X j, Y j ) PR-graph d j : X j Y j N demand b j N + : benefit per served time step U j : X j Y j 2 V 2 E mapping Can be implemented by U x 1 = {v 17, v 23, v 97, } e can be implemented by v 0 p v k if i v i 1, v i U(e) PR-graph Action vertices enc/dec, comp/decomp s j x 1 x 2 x 3 e x 4 t j Single sink packets are destined to here
11 Examples Simple Routing I want to route a connection of 100 mbps from v to v PR-graph s e t U s = {v}, U t = {v }, U e = E, d e = 120 mbps Serial Processing Stream, Pass k transformations a 1,, a k in series. PR-graph s a 1 a k t U a i V implements a i Can model BW changes E.g., a j is COMPRESS. How? Set diff demands to diff PRedges.
12 Summary Need to allocate network resources in online fashion. Each request specifies sequence(s) of functions. Map desired functions to real network devices. Route the request between these devices. Security: want to avoid some nodes. Flexibility: customer does not want to commit to the duration upfront the duration is unknown. Maximum benefit: maximizing the benefit rate.
13
Shrinking Maxima, Decreasing Costs: New Online Packing and Covering Problems
 Shrinking Maxima, Decreasing Costs: New Online Packing and Covering Problems Pierre Fraigniaud Magnús M. Halldórsson Boaz Patt-Shamir CNRS, U. Paris Diderot Dror Rawitz Tel Aviv U. Reykjavik U. Adi Rosén
Shrinking Maxima, Decreasing Costs: New Online Packing and Covering Problems Pierre Fraigniaud Magnús M. Halldórsson Boaz Patt-Shamir CNRS, U. Paris Diderot Dror Rawitz Tel Aviv U. Reykjavik U. Adi Rosén
CMSC 451: Max-Flow Extensions
 CMSC 51: Max-Flow Extensions Slides By: Carl Kingsford Department of Computer Science University of Maryland, College Park Based on Section 7.7 of Algorithm Design by Kleinberg & Tardos. Circulations with
CMSC 51: Max-Flow Extensions Slides By: Carl Kingsford Department of Computer Science University of Maryland, College Park Based on Section 7.7 of Algorithm Design by Kleinberg & Tardos. Circulations with
Competitive Management of Non-Preemptive Queues with Multiple Values
 Competitive Management of Non-Preemptive Queues with Multiple Values Nir Andelman and Yishay Mansour School of Computer Science, Tel-Aviv University, Tel-Aviv, Israel Abstract. We consider the online problem
Competitive Management of Non-Preemptive Queues with Multiple Values Nir Andelman and Yishay Mansour School of Computer Science, Tel-Aviv University, Tel-Aviv, Israel Abstract. We consider the online problem
arxiv: v1 [cs.ds] 25 Jan 2015
![arxiv: v1 [cs.ds] 25 Jan 2015 arxiv: v1 [cs.ds] 25 Jan 2015](/thumbs/83/88797326.jpg) TSP with Time Windows and Service Time Yossi Azar Adi Vardi August 20, 2018 arxiv:1501.06158v1 [cs.ds] 25 Jan 2015 Abstract We consider TSP with time windows and service time. In this problem we receive
TSP with Time Windows and Service Time Yossi Azar Adi Vardi August 20, 2018 arxiv:1501.06158v1 [cs.ds] 25 Jan 2015 Abstract We consider TSP with time windows and service time. In this problem we receive
CHAPTER 4. Networks of queues. 1. Open networks Suppose that we have a network of queues as given in Figure 4.1. Arrivals
 CHAPTER 4 Networks of queues. Open networks Suppose that we have a network of queues as given in Figure 4.. Arrivals Figure 4.. An open network can occur from outside of the network to any subset of nodes.
CHAPTER 4 Networks of queues. Open networks Suppose that we have a network of queues as given in Figure 4.. Arrivals Figure 4.. An open network can occur from outside of the network to any subset of nodes.
7600 Series Routers Adjacency Allocation Method
 7600 Series Routers Adjacency Allocation Method Document ID: 118393 Contributed by Amit Goyal and Ruchir Jain, Cisco TAC Engineers. Nov 06, 2014 Contents Introduction Background Information Adjacency Entry
7600 Series Routers Adjacency Allocation Method Document ID: 118393 Contributed by Amit Goyal and Ruchir Jain, Cisco TAC Engineers. Nov 06, 2014 Contents Introduction Background Information Adjacency Entry
Online Packet Buffering
 Online Packet Buffering Dissertation zur Erlangung des Doktorgrades der Fakultät für Angewandte Wissenschaften der Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg im Breisgau Markus Schmidt Freiburg im Breisgau Februar
Online Packet Buffering Dissertation zur Erlangung des Doktorgrades der Fakultät für Angewandte Wissenschaften der Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg im Breisgau Markus Schmidt Freiburg im Breisgau Februar
Linear Programming Applications. Transportation Problem
 Linear Programming Applications Transportation Problem 1 Introduction Transportation problem is a special problem of its own structure. Planning model that allocates resources, machines, materials, capital
Linear Programming Applications Transportation Problem 1 Introduction Transportation problem is a special problem of its own structure. Planning model that allocates resources, machines, materials, capital
Two Applications of Maximum Flow
 Two Applications of Maximum Flow The Bipartite Matching Problem a bipartite graph as a flow network maximum flow and maximum matching alternating paths perfect matchings 2 Circulation with Demands flows
Two Applications of Maximum Flow The Bipartite Matching Problem a bipartite graph as a flow network maximum flow and maximum matching alternating paths perfect matchings 2 Circulation with Demands flows
COMP9334: Capacity Planning of Computer Systems and Networks
 COMP9334: Capacity Planning of Computer Systems and Networks Week 2: Operational analysis Lecturer: Prof. Sanjay Jha NETWORKS RESEARCH GROUP, CSE, UNSW Operational analysis Operational: Collect performance
COMP9334: Capacity Planning of Computer Systems and Networks Week 2: Operational analysis Lecturer: Prof. Sanjay Jha NETWORKS RESEARCH GROUP, CSE, UNSW Operational analysis Operational: Collect performance
A Virtual Queue Approach to Loss Estimation
 A Virtual Queue Approach to Loss Estimation Guoqiang Hu, Yuming Jiang, Anne Nevin Centre for Quantifiable Quality of Service in Communication Systems Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Norway
A Virtual Queue Approach to Loss Estimation Guoqiang Hu, Yuming Jiang, Anne Nevin Centre for Quantifiable Quality of Service in Communication Systems Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Norway
New Online Algorithms for Story Scheduling in Web Advertising
 New Online Algorithms for Story Scheduling in Web Advertising Susanne Albers TU Munich Achim Paßen HU Berlin Online advertising Worldwide online ad spending 2012/13: $ 100 billion Expected to surpass print
New Online Algorithms for Story Scheduling in Web Advertising Susanne Albers TU Munich Achim Paßen HU Berlin Online advertising Worldwide online ad spending 2012/13: $ 100 billion Expected to surpass print
Dynamic Traveling Repair Problem with an Arbitrary Time Window
 Dynamic Traveling Repair Problem with an Arbitrary Time Window Yossi Azar (B) and Adi Vardi (B) School of Computer Science, Tel-Aviv University, 69978 Tel-Aviv, Israel azar@tau.ac.il, adi.vardi@gmail.com
Dynamic Traveling Repair Problem with an Arbitrary Time Window Yossi Azar (B) and Adi Vardi (B) School of Computer Science, Tel-Aviv University, 69978 Tel-Aviv, Israel azar@tau.ac.il, adi.vardi@gmail.com
Online Interval Coloring and Variants
 Online Interval Coloring and Variants Leah Epstein 1, and Meital Levy 1 Department of Mathematics, University of Haifa, 31905 Haifa, Israel. Email: lea@math.haifa.ac.il School of Computer Science, Tel-Aviv
Online Interval Coloring and Variants Leah Epstein 1, and Meital Levy 1 Department of Mathematics, University of Haifa, 31905 Haifa, Israel. Email: lea@math.haifa.ac.il School of Computer Science, Tel-Aviv
Dynamic Service Placement in Geographically Distributed Clouds
 Dynamic Service Placement in Geographically Distributed Clouds Qi Zhang 1 Quanyan Zhu 2 M. Faten Zhani 1 Raouf Boutaba 1 1 School of Computer Science University of Waterloo 2 Department of Electrical and
Dynamic Service Placement in Geographically Distributed Clouds Qi Zhang 1 Quanyan Zhu 2 M. Faten Zhani 1 Raouf Boutaba 1 1 School of Computer Science University of Waterloo 2 Department of Electrical and
6 Solving Queueing Models
 6 Solving Queueing Models 6.1 Introduction In this note we look at the solution of systems of queues, starting with simple isolated queues. The benefits of using predefined, easily classified queues will
6 Solving Queueing Models 6.1 Introduction In this note we look at the solution of systems of queues, starting with simple isolated queues. The benefits of using predefined, easily classified queues will
Online bin packing 24.Januar 2008
 Rob van Stee: Approximations- und Online-Algorithmen 1 Online bin packing 24.Januar 2008 Problem definition First Fit and other algorithms The asymptotic performance ratio Weighting functions Lower bounds
Rob van Stee: Approximations- und Online-Algorithmen 1 Online bin packing 24.Januar 2008 Problem definition First Fit and other algorithms The asymptotic performance ratio Weighting functions Lower bounds
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems
 Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Performance Evaluation of Queuing Systems Introduction to Queuing Systems System Performance Measures & Little s Law Equilibrium Solution of Birth-Death Processes Analysis of Single-Station Queuing Systems
Dynamic Power Allocation and Routing for Time Varying Wireless Networks
 Dynamic Power Allocation and Routing for Time Varying Wireless Networks X 14 (t) X 12 (t) 1 3 4 k a P ak () t P a tot X 21 (t) 2 N X 2N (t) X N4 (t) µ ab () rate µ ab µ ab (p, S 3 ) µ ab µ ac () µ ab (p,
Dynamic Power Allocation and Routing for Time Varying Wireless Networks X 14 (t) X 12 (t) 1 3 4 k a P ak () t P a tot X 21 (t) 2 N X 2N (t) X N4 (t) µ ab () rate µ ab µ ab (p, S 3 ) µ ab µ ac () µ ab (p,
Efficient Network-wide Available Bandwidth Estimation through Active Learning and Belief Propagation
 Efficient Network-wide Available Bandwidth Estimation through Active Learning and Belief Propagation mark.coates@mcgill.ca McGill University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Montreal,
Efficient Network-wide Available Bandwidth Estimation through Active Learning and Belief Propagation mark.coates@mcgill.ca McGill University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Montreal,
Flow-level performance of wireless data networks
 Flow-level performance of wireless data networks Aleksi Penttinen Department of Communications and Networking, TKK Helsinki University of Technology CLOWN seminar 28.8.08 1/31 Outline 1. Flow-level model
Flow-level performance of wireless data networks Aleksi Penttinen Department of Communications and Networking, TKK Helsinki University of Technology CLOWN seminar 28.8.08 1/31 Outline 1. Flow-level model
SOFA: Strategyproof Online Frequency Allocation for Multihop Wireless Networks
 SOFA: Strategyproof Online Frequency Allocation for Multihop Wireless Networks Ping Xu and Xiang-Yang Li Department of Computer Science, Illinois Institute of Technology, Chicago, IL, 60616. pxu3@iit.edu,
SOFA: Strategyproof Online Frequency Allocation for Multihop Wireless Networks Ping Xu and Xiang-Yang Li Department of Computer Science, Illinois Institute of Technology, Chicago, IL, 60616. pxu3@iit.edu,
Welfare Maximization with Production Costs: A Primal Dual Approach
 Welfare Maximization with Production Costs: A Primal Dual Approach Zhiyi Huang Anthony Kim The University of Hong Kong Stanford University January 4, 2015 Zhiyi Huang, Anthony Kim Welfare Maximization
Welfare Maximization with Production Costs: A Primal Dual Approach Zhiyi Huang Anthony Kim The University of Hong Kong Stanford University January 4, 2015 Zhiyi Huang, Anthony Kim Welfare Maximization
Clock-driven scheduling
 Clock-driven scheduling Also known as static or off-line scheduling Michal Sojka Czech Technical University in Prague, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Department of Control Engineering November 8, 2017
Clock-driven scheduling Also known as static or off-line scheduling Michal Sojka Czech Technical University in Prague, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Department of Control Engineering November 8, 2017
On-line Bin-Stretching. Yossi Azar y Oded Regev z. Abstract. We are given a sequence of items that can be packed into m unit size bins.
 On-line Bin-Stretching Yossi Azar y Oded Regev z Abstract We are given a sequence of items that can be packed into m unit size bins. In the classical bin packing problem we x the size of the bins and try
On-line Bin-Stretching Yossi Azar y Oded Regev z Abstract We are given a sequence of items that can be packed into m unit size bins. In the classical bin packing problem we x the size of the bins and try
Online Optimization Competitive Analysis and Beyond
 Konrad-Zuse-Zentrum für Informationstechnik Berlin Takustraße 7 D-14195 Berlin-Dahlem Germany SVEN O. KRUMKE Online Optimization Competitive Analysis and Beyond ZIB-Report 02-25 (June 2002) Online Optimization
Konrad-Zuse-Zentrum für Informationstechnik Berlin Takustraße 7 D-14195 Berlin-Dahlem Germany SVEN O. KRUMKE Online Optimization Competitive Analysis and Beyond ZIB-Report 02-25 (June 2002) Online Optimization
Online Scheduling with Interval Conflicts
 Online Scheduling with Interval Conflicts Magnús M. Halldórsson 1, Boaz Patt-Shamir 2, and Dror Rawitz 2 1 School of Computer Science, Reykjavik University, Menntavegur 1, 101 Reykjavik, Iceland. mmh@ru.is
Online Scheduling with Interval Conflicts Magnús M. Halldórsson 1, Boaz Patt-Shamir 2, and Dror Rawitz 2 1 School of Computer Science, Reykjavik University, Menntavegur 1, 101 Reykjavik, Iceland. mmh@ru.is
Network Games with Friends and Foes
 Network Games with Friends and Foes Stefan Schmid T-Labs / TU Berlin Who are the participants in the Internet? Stefan Schmid @ Tel Aviv Uni, 200 2 How to Model the Internet? Normal participants : - e.g.,
Network Games with Friends and Foes Stefan Schmid T-Labs / TU Berlin Who are the participants in the Internet? Stefan Schmid @ Tel Aviv Uni, 200 2 How to Model the Internet? Normal participants : - e.g.,
Lecture 8 Network Optimization Algorithms
 Advanced Algorithms Floriano Zini Free University of Bozen-Bolzano Faculty of Computer Science Academic Year 2013-2014 Lecture 8 Network Optimization Algorithms 1 21/01/14 Introduction Network models have
Advanced Algorithms Floriano Zini Free University of Bozen-Bolzano Faculty of Computer Science Academic Year 2013-2014 Lecture 8 Network Optimization Algorithms 1 21/01/14 Introduction Network models have
Online Dial-a-Ride Problems: Minimizing the Completion Time
 Online Dial-a-Ride Problems: Minimizing the Completion Time Norbert Ascheuer, Sven O. Krumke, and Jörg Rambau Konrad-Zuse-Zentrum für Informationstechnik Berlin, Department Optimization, Takustr. 7, D-14195
Online Dial-a-Ride Problems: Minimizing the Completion Time Norbert Ascheuer, Sven O. Krumke, and Jörg Rambau Konrad-Zuse-Zentrum für Informationstechnik Berlin, Department Optimization, Takustr. 7, D-14195
IS 709/809: Computational Methods in IS Research Fall Exam Review
 IS 709/809: Computational Methods in IS Research Fall 2017 Exam Review Nirmalya Roy Department of Information Systems University of Maryland Baltimore County www.umbc.edu Exam When: Tuesday (11/28) 7:10pm
IS 709/809: Computational Methods in IS Research Fall 2017 Exam Review Nirmalya Roy Department of Information Systems University of Maryland Baltimore County www.umbc.edu Exam When: Tuesday (11/28) 7:10pm
A Mechanism for Pricing Service Guarantees
 A Mechanism for Pricing Service Guarantees Bruce Hajek Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering and the Coordinated Science Laboratory University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Sichao Yang Qualcomm
A Mechanism for Pricing Service Guarantees Bruce Hajek Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering and the Coordinated Science Laboratory University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Sichao Yang Qualcomm
On the Price of Anarchy in Unbounded Delay Networks
 On the Price of Anarchy in Unbounded Delay Networks Tao Wu Nokia Research Center Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA tao.a.wu@nokia.com David Starobinski Boston University Boston, Massachusetts, USA staro@bu.edu
On the Price of Anarchy in Unbounded Delay Networks Tao Wu Nokia Research Center Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA tao.a.wu@nokia.com David Starobinski Boston University Boston, Massachusetts, USA staro@bu.edu
Comparison-based FIFO Buffer Management in QoS Switches
 Comparison-based FIFO Buffer Management in QoS Switches Kamal Al-Bawani 1, Matthias Englert 2, and Matthias Westermann 3 1 Department of Computer Science, RWTH Aachen University, Germany kbawani@cs.rwth-aachen.de
Comparison-based FIFO Buffer Management in QoS Switches Kamal Al-Bawani 1, Matthias Englert 2, and Matthias Westermann 3 1 Department of Computer Science, RWTH Aachen University, Germany kbawani@cs.rwth-aachen.de
Network Design Problems Notation and Illustrations
 B CHAPTER 2 Network Design Problems Notation and Illustrations In Chapter 1, we have presented basic ideas about communication and computer network design problems that a network provider is likely to
B CHAPTER 2 Network Design Problems Notation and Illustrations In Chapter 1, we have presented basic ideas about communication and computer network design problems that a network provider is likely to
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS DECISION SCIENCE
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS DECISION SCIENCE 1. Decision Science approach is a. Multi-disciplinary b. Scientific c. Intuitive 2. For analyzing a problem, decision-makers should study a. Its qualitative aspects
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS DECISION SCIENCE 1. Decision Science approach is a. Multi-disciplinary b. Scientific c. Intuitive 2. For analyzing a problem, decision-makers should study a. Its qualitative aspects
Network coding for online and dynamic networking problems. Tracey Ho Center for the Mathematics of Information California Institute of Technology
 Network coding for online and dynamic networking problems Tracey Ho Center for the Mathematics of Information California Institute of Technology 1 Work done in collaboration with: Harish Viswanathan: Bell
Network coding for online and dynamic networking problems Tracey Ho Center for the Mathematics of Information California Institute of Technology 1 Work done in collaboration with: Harish Viswanathan: Bell
Allocating Resources, in the Future
 Allocating Resources, in the Future Sid Banerjee School of ORIE May 3, 2018 Simons Workshop on Mathematical and Computational Challenges in Real-Time Decision Making online resource allocation: basic model......
Allocating Resources, in the Future Sid Banerjee School of ORIE May 3, 2018 Simons Workshop on Mathematical and Computational Challenges in Real-Time Decision Making online resource allocation: basic model......
CS 798: Homework Assignment 3 (Queueing Theory)
 1.0 Little s law Assigned: October 6, 009 Patients arriving to the emergency room at the Grand River Hospital have a mean waiting time of three hours. It has been found that, averaged over the period of
1.0 Little s law Assigned: October 6, 009 Patients arriving to the emergency room at the Grand River Hospital have a mean waiting time of three hours. It has been found that, averaged over the period of
Notes on Alvarez and Jermann, "Efficiency, Equilibrium, and Asset Pricing with Risk of Default," Econometrica 2000
 Notes on Alvarez Jermann, "Efficiency, Equilibrium, Asset Pricing with Risk of Default," Econometrica 2000 Jonathan Heathcote November 1st 2005 1 Model Consider a pure exchange economy with I agents one
Notes on Alvarez Jermann, "Efficiency, Equilibrium, Asset Pricing with Risk of Default," Econometrica 2000 Jonathan Heathcote November 1st 2005 1 Model Consider a pure exchange economy with I agents one
Delay bounds (Simon S. Lam) 1
 1 Pacet Scheduling: End-to-End E d Delay Bounds Delay bounds (Simon S. Lam) 1 2 Reerences Delay Guarantee o Virtual Cloc server Georey G. Xie and Simon S. Lam, Delay Guarantee o Virtual Cloc Server, IEEE/ACM
1 Pacet Scheduling: End-to-End E d Delay Bounds Delay bounds (Simon S. Lam) 1 2 Reerences Delay Guarantee o Virtual Cloc server Georey G. Xie and Simon S. Lam, Delay Guarantee o Virtual Cloc Server, IEEE/ACM
Strategic Network Formation through Peering and Service Agreements
 Strategic Network Formation through Peering and Service Agreements Elliot Anshelevich Bruce Shepherd Gordon Wilfong April 2006 Abstract We introduce a game theoretic model of network formation in an effort
Strategic Network Formation through Peering and Service Agreements Elliot Anshelevich Bruce Shepherd Gordon Wilfong April 2006 Abstract We introduce a game theoretic model of network formation in an effort
The Parking Permit Problem
 The Parking Permit Problem Adam Meyerson November 3, 2004 Abstract We consider online problems where purchases have time durations which expire regardless of whether the purchase is used or not. The Parking
The Parking Permit Problem Adam Meyerson November 3, 2004 Abstract We consider online problems where purchases have time durations which expire regardless of whether the purchase is used or not. The Parking
Competitive Algorithms for Fine-Grain Real-Time Scheduling
 Competitive Algorithms for Fine-Grain Real-Time Scheduling Michael A. Palis Department of Computer Science Rutgers University NJ 08102 palis@crab.rutgers.edu Abstract Thispaper investigates the task scheduling
Competitive Algorithms for Fine-Grain Real-Time Scheduling Michael A. Palis Department of Computer Science Rutgers University NJ 08102 palis@crab.rutgers.edu Abstract Thispaper investigates the task scheduling
Jitter-Approximation Tradeoff for Periodic Scheduling
 Jitter-Approximation Tradeoff for Periodic Scheduling Zvika Brakerski Dept. of Electrical Engineering Tel Aviv University Tel Aviv 69978 Israel zvika@eng.tau.ac.il Boaz Patt-Shamir HP Cambridge Research
Jitter-Approximation Tradeoff for Periodic Scheduling Zvika Brakerski Dept. of Electrical Engineering Tel Aviv University Tel Aviv 69978 Israel zvika@eng.tau.ac.il Boaz Patt-Shamir HP Cambridge Research
Secretary Problems. Petropanagiotaki Maria. January MPLA, Algorithms & Complexity 2
 January 15 2015 MPLA, Algorithms & Complexity 2 Simplest form of the problem 1 The candidates are totally ordered from best to worst with no ties. 2 The candidates arrive sequentially in random order.
January 15 2015 MPLA, Algorithms & Complexity 2 Simplest form of the problem 1 The candidates are totally ordered from best to worst with no ties. 2 The candidates arrive sequentially in random order.
SPLITTING AND MERGING OF PACKET TRAFFIC: MEASUREMENT AND MODELLING
 SPLITTING AND MERGING OF PACKET TRAFFIC: MEASUREMENT AND MODELLING Nicolas Hohn 1 Darryl Veitch 1 Tao Ye 2 1 CUBIN, Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering University of Melbourne, Vic 3010 Australia
SPLITTING AND MERGING OF PACKET TRAFFIC: MEASUREMENT AND MODELLING Nicolas Hohn 1 Darryl Veitch 1 Tao Ye 2 1 CUBIN, Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering University of Melbourne, Vic 3010 Australia
Bayesian Ignorance. May 9, Abstract
 Bayesian Ignorance Noga Alon Yuval Emek Michal Feldman Moshe Tennenholtz May 9, 2010 Abstract We quantify the effect of Bayesian ignorance by comparing the social cost obtained in a Bayesian game by agents
Bayesian Ignorance Noga Alon Yuval Emek Michal Feldman Moshe Tennenholtz May 9, 2010 Abstract We quantify the effect of Bayesian ignorance by comparing the social cost obtained in a Bayesian game by agents
Robust Network Codes for Unicast Connections: A Case Study
 Robust Network Codes for Unicast Connections: A Case Study Salim Y. El Rouayheb, Alex Sprintson, and Costas Georghiades Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University College Station,
Robust Network Codes for Unicast Connections: A Case Study Salim Y. El Rouayheb, Alex Sprintson, and Costas Georghiades Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Texas A&M University College Station,
CSC501 Operating Systems Principles. Deadlock
 CSC501 Operating Systems Principles Deadlock 1 Last Lecture q Priority Inversion Q Priority Inheritance Protocol q Today Q Deadlock 2 The Deadlock Problem q Definition Q A set of blocked processes each
CSC501 Operating Systems Principles Deadlock 1 Last Lecture q Priority Inversion Q Priority Inheritance Protocol q Today Q Deadlock 2 The Deadlock Problem q Definition Q A set of blocked processes each
UNIVERSITY OF YORK. MSc Examinations 2004 MATHEMATICS Networks. Time Allowed: 3 hours.
 UNIVERSITY OF YORK MSc Examinations 2004 MATHEMATICS Networks Time Allowed: 3 hours. Answer 4 questions. Standard calculators will be provided but should be unnecessary. 1 Turn over 2 continued on next
UNIVERSITY OF YORK MSc Examinations 2004 MATHEMATICS Networks Time Allowed: 3 hours. Answer 4 questions. Standard calculators will be provided but should be unnecessary. 1 Turn over 2 continued on next
The canadian traveller problem and its competitive analysis
 J Comb Optim (2009) 18: 195 205 DOI 10.1007/s10878-008-9156-y The canadian traveller problem and its competitive analysis Yinfeng Xu Maolin Hu Bing Su Binhai Zhu Zhijun Zhu Published online: 9 April 2008
J Comb Optim (2009) 18: 195 205 DOI 10.1007/s10878-008-9156-y The canadian traveller problem and its competitive analysis Yinfeng Xu Maolin Hu Bing Su Binhai Zhu Zhijun Zhu Published online: 9 April 2008
arxiv: v2 [cs.ds] 5 Aug 2015
![arxiv: v2 [cs.ds] 5 Aug 2015 arxiv: v2 [cs.ds] 5 Aug 2015](/thumbs/95/126042574.jpg) Online Algorithms with Advice for Bin Packing and Scheduling Problems Marc P. Renault a,,2, Adi Rosén a,2, Rob van Stee b arxiv:3.7589v2 [cs.ds] 5 Aug 205 a CNRS and Université Paris Diderot, France b
Online Algorithms with Advice for Bin Packing and Scheduling Problems Marc P. Renault a,,2, Adi Rosén a,2, Rob van Stee b arxiv:3.7589v2 [cs.ds] 5 Aug 205 a CNRS and Université Paris Diderot, France b
Contents college 5 and 6 Branch and Bound; Beam Search (Chapter , book)! general introduction
 Contents college 5 and 6 Branch and Bound; Beam Search (Chapter 3.4-3.5, book)! general introduction Job Shop Scheduling (Chapter 5.1-5.3, book) ffl branch and bound (5.2) ffl shifting bottleneck heuristic
Contents college 5 and 6 Branch and Bound; Beam Search (Chapter 3.4-3.5, book)! general introduction Job Shop Scheduling (Chapter 5.1-5.3, book) ffl branch and bound (5.2) ffl shifting bottleneck heuristic
Overflow Management with Multipart Packets
 Overflow Management with Multipart Packets Yishay Mansour School of Computer Science Tel Aviv University Tel Aviv 69978, Israel mansour@cstauacil Boaz Patt-Shamir Dror Rawitz School of Electrical Engineering
Overflow Management with Multipart Packets Yishay Mansour School of Computer Science Tel Aviv University Tel Aviv 69978, Israel mansour@cstauacil Boaz Patt-Shamir Dror Rawitz School of Electrical Engineering
Greedy Online Algorithms for Routing Permanent Virtual Circuits
 Greedy Online Algorithms for Routing Permanent Virtual Circuits Jessen T. Havill, 1 Weizhen Mao 2 1 Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, Denison University, Granville, Ohio 43023 2 Department
Greedy Online Algorithms for Routing Permanent Virtual Circuits Jessen T. Havill, 1 Weizhen Mao 2 1 Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, Denison University, Granville, Ohio 43023 2 Department
Aggregating Multicast Demands on Virtual Path Trees
 Telecommunication Systems 16:3,4, 483 501, 2001 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Aggregating Multicast Demands on Virtual Path Trees MICHAEL MONTGOMERY and GUSTAVO DE VECIANA
Telecommunication Systems 16:3,4, 483 501, 2001 2001 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Manufactured in The Netherlands. Aggregating Multicast Demands on Virtual Path Trees MICHAEL MONTGOMERY and GUSTAVO DE VECIANA
An Ins t Ins an t t an Primer
 An Instant Primer Links from Course Web Page Network Coding: An Instant Primer Fragouli, Boudec, and Widmer. Network Coding an Introduction Koetter and Medard On Randomized Network Coding Ho, Medard, Shi,
An Instant Primer Links from Course Web Page Network Coding: An Instant Primer Fragouli, Boudec, and Widmer. Network Coding an Introduction Koetter and Medard On Randomized Network Coding Ho, Medard, Shi,
Online algorithms December 13, 2007
 Sanders/van Stee: Approximations- und Online-Algorithmen 1 Online algorithms December 13, 2007 Information is revealed to the algorithm in parts Algorithm needs to process each part before receiving the
Sanders/van Stee: Approximations- und Online-Algorithmen 1 Online algorithms December 13, 2007 Information is revealed to the algorithm in parts Algorithm needs to process each part before receiving the
NEAR-OPTIMALITY OF DISTRIBUTED NETWORK MANAGEMENT WITH A MACHINE LEARNING APPROACH
 NEAR-OPTIMALITY OF DISTRIBUTED NETWORK MANAGEMENT WITH A MACHINE LEARNING APPROACH A Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty by Sung-eok Jeon In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
NEAR-OPTIMALITY OF DISTRIBUTED NETWORK MANAGEMENT WITH A MACHINE LEARNING APPROACH A Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty by Sung-eok Jeon In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
Energy Optimal Control for Time Varying Wireless Networks. Michael J. Neely University of Southern California
 Energy Optimal Control for Time Varying Wireless Networks Michael J. Neely University of Southern California http://www-rcf.usc.edu/~mjneely Part 1: A single wireless downlink (L links) L 2 1 S={Totally
Energy Optimal Control for Time Varying Wireless Networks Michael J. Neely University of Southern California http://www-rcf.usc.edu/~mjneely Part 1: A single wireless downlink (L links) L 2 1 S={Totally
Linear Model Predictive Control for Queueing Networks in Manufacturing and Road Traffic
 Linear Model Predictive Control for ueueing Networks in Manufacturing and Road Traffic Yoni Nazarathy Swinburne University of Technology, Melbourne. Joint work with: Erjen Lefeber (manufacturing), Hai
Linear Model Predictive Control for ueueing Networks in Manufacturing and Road Traffic Yoni Nazarathy Swinburne University of Technology, Melbourne. Joint work with: Erjen Lefeber (manufacturing), Hai
4888 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 15, NO. 7, JULY 2016
 4888 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 15, NO. 7, JULY 2016 Online Power Control Optimization for Wireless Transmission With Energy Harvesting and Storage Fatemeh Amirnavaei, Student Member,
4888 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 15, NO. 7, JULY 2016 Online Power Control Optimization for Wireless Transmission With Energy Harvesting and Storage Fatemeh Amirnavaei, Student Member,
CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs224w.stanford.edu Find most influential set S of size k: largest expected cascade size f(s) if set S is activated
CS224W: Social and Information Network Analysis Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs224w.stanford.edu Find most influential set S of size k: largest expected cascade size f(s) if set S is activated
arxiv: v1 [cs.ni] 18 Apr 2017
![arxiv: v1 [cs.ni] 18 Apr 2017 arxiv: v1 [cs.ni] 18 Apr 2017](/thumbs/95/123668315.jpg) Zijun Zhang Dept. of Computer Science University of Calgary zijun.zhang@ucalgary.ca Zongpeng Li Dept. of Computer Science University of Calgary zongpeng@ucalgary.ca Chuan Wu Dept. of Computer Science The
Zijun Zhang Dept. of Computer Science University of Calgary zijun.zhang@ucalgary.ca Zongpeng Li Dept. of Computer Science University of Calgary zongpeng@ucalgary.ca Chuan Wu Dept. of Computer Science The
Fleet Management for Autonomous Vehicles Using Multicommodity Coupled Flows in Time-Expanded Networks
 Fleet Management for Autonomous Vehicles Using Multicommodity Coupled Flows in Time-Expanded Networks Sahar Bsaybes Université Grenoble Alpes Institute of Engineering (Grenoble INP), G-SCOP F-38000 Grenoble,
Fleet Management for Autonomous Vehicles Using Multicommodity Coupled Flows in Time-Expanded Networks Sahar Bsaybes Université Grenoble Alpes Institute of Engineering (Grenoble INP), G-SCOP F-38000 Grenoble,
Network Analysis with ArcGIS Online. Deelesh Mandloi Dmitry Kudinov
 Deelesh Mandloi Dmitry Kudinov Introductions Who are we? - Network Analyst Product Engineers Who are you? - Network Analyst users? - ArcGIS Online users? - Trying to figure out what is ArcGIS Online? Slides
Deelesh Mandloi Dmitry Kudinov Introductions Who are we? - Network Analyst Product Engineers Who are you? - Network Analyst users? - ArcGIS Online users? - Trying to figure out what is ArcGIS Online? Slides
Queueing Networks G. Rubino INRIA / IRISA, Rennes, France
 Queueing Networks G. Rubino INRIA / IRISA, Rennes, France February 2006 Index 1. Open nets: Basic Jackson result 2 2. Open nets: Internet performance evaluation 18 3. Closed nets: Basic Gordon-Newell result
Queueing Networks G. Rubino INRIA / IRISA, Rennes, France February 2006 Index 1. Open nets: Basic Jackson result 2 2. Open nets: Internet performance evaluation 18 3. Closed nets: Basic Gordon-Newell result
Minimum cost transportation problem
 Minimum cost transportation problem Complements of Operations Research Giovanni Righini Università degli Studi di Milano Definitions The minimum cost transportation problem is a special case of the minimum
Minimum cost transportation problem Complements of Operations Research Giovanni Righini Università degli Studi di Milano Definitions The minimum cost transportation problem is a special case of the minimum
CS599: Convex and Combinatorial Optimization Fall 2013 Lecture 17: Combinatorial Problems as Linear Programs III. Instructor: Shaddin Dughmi
 CS599: Convex and Combinatorial Optimization Fall 2013 Lecture 17: Combinatorial Problems as Linear Programs III Instructor: Shaddin Dughmi Announcements Today: Spanning Trees and Flows Flexibility awarded
CS599: Convex and Combinatorial Optimization Fall 2013 Lecture 17: Combinatorial Problems as Linear Programs III Instructor: Shaddin Dughmi Announcements Today: Spanning Trees and Flows Flexibility awarded
Resource Sharing, Routing, Chip Design. Jens Vygen
 Resource Sharing, Routing, Chip Design Jens Vygen University of Bonn joint work with Markus Ahrens, Michael Gester, Stephan Held, Niko Klewinghaus, Dirk Müller, Tim Nieberg, Christian Panten, Sven Peyer,
Resource Sharing, Routing, Chip Design Jens Vygen University of Bonn joint work with Markus Ahrens, Michael Gester, Stephan Held, Niko Klewinghaus, Dirk Müller, Tim Nieberg, Christian Panten, Sven Peyer,
Theoretical Computer Science
 Theoretical Computer Science 452 (2012) 1 11 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Theoretical Computer Science journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/tcs Bayesian ignorance Noga Alon a,b,
Theoretical Computer Science 452 (2012) 1 11 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Theoretical Computer Science journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/tcs Bayesian ignorance Noga Alon a,b,
QUESTION ONE Let 7C = Total Cost MC = Marginal Cost AC = Average Cost
 ANSWER QUESTION ONE Let 7C = Total Cost MC = Marginal Cost AC = Average Cost Q = Number of units AC = 7C MC = Q d7c d7c 7C Q Derivation of average cost with respect to quantity is different from marginal
ANSWER QUESTION ONE Let 7C = Total Cost MC = Marginal Cost AC = Average Cost Q = Number of units AC = 7C MC = Q d7c d7c 7C Q Derivation of average cost with respect to quantity is different from marginal
Revenue Maximization in a Cloud Federation
 Revenue Maximization in a Cloud Federation Makhlouf Hadji and Djamal Zeghlache September 14th, 2015 IRT SystemX/ Telecom SudParis Makhlouf Hadji Outline of the presentation 01 Introduction 02 03 04 05
Revenue Maximization in a Cloud Federation Makhlouf Hadji and Djamal Zeghlache September 14th, 2015 IRT SystemX/ Telecom SudParis Makhlouf Hadji Outline of the presentation 01 Introduction 02 03 04 05
The Competition Complexity of Auctions: Bulow-Klemperer Results for Multidimensional Bidders
 The : Bulow-Klemperer Results for Multidimensional Bidders Oxford, Spring 2017 Alon Eden, Michal Feldman, Ophir Friedler @ Tel-Aviv University Inbal Talgam-Cohen, Marie Curie Postdoc @ Hebrew University
The : Bulow-Klemperer Results for Multidimensional Bidders Oxford, Spring 2017 Alon Eden, Michal Feldman, Ophir Friedler @ Tel-Aviv University Inbal Talgam-Cohen, Marie Curie Postdoc @ Hebrew University
Chapter 3: Technology Related Modelling Examples
 Chapter 3: Technology Related Modelling Examples Deep Medhi University of Missouri Kansas City dmedhi@umkc.edu DRAFT Version August 2005 Note: These slides are based on material from the book: M. Pióro
Chapter 3: Technology Related Modelling Examples Deep Medhi University of Missouri Kansas City dmedhi@umkc.edu DRAFT Version August 2005 Note: These slides are based on material from the book: M. Pióro
Minimizing the Maximum Flow Time in the Online-TSP on the Real Line
 Minimizing the Maximum Flow Time in the Online-TSP on the Real Line Sven O. Krumke a,1 Luigi Laura b Maarten Lipmann c,3 Alberto Marchetti-Spaccamela b Willem E. de Paepe d,3 Diana Poensgen a,3 Leen Stougie
Minimizing the Maximum Flow Time in the Online-TSP on the Real Line Sven O. Krumke a,1 Luigi Laura b Maarten Lipmann c,3 Alberto Marchetti-Spaccamela b Willem E. de Paepe d,3 Diana Poensgen a,3 Leen Stougie
Jitter-approximation tradeoff for periodic scheduling
 Wireless Netw (2006) 12:723 731 DOI 10.1007/s11276-006-6531-4 Jitter-approximation tradeoff for periodic scheduling Zvika Brakerski Boaz Patt-Shamir Published online: 19 May 2006 C Science + Business Media,
Wireless Netw (2006) 12:723 731 DOI 10.1007/s11276-006-6531-4 Jitter-approximation tradeoff for periodic scheduling Zvika Brakerski Boaz Patt-Shamir Published online: 19 May 2006 C Science + Business Media,
arxiv: v1 [cs.ds] 12 Oct 2015
![arxiv: v1 [cs.ds] 12 Oct 2015 arxiv: v1 [cs.ds] 12 Oct 2015](/thumbs/92/110992449.jpg) On the Smoothness of Paging Algorithms Jan Reineke and Alejandro Salinger 2 Department of Computer Science, Saarland University, Saarbrücken, Germany reineke@cs.uni-saarland.de 2 SAP SE, Walldorf, Germany
On the Smoothness of Paging Algorithms Jan Reineke and Alejandro Salinger 2 Department of Computer Science, Saarland University, Saarbrücken, Germany reineke@cs.uni-saarland.de 2 SAP SE, Walldorf, Germany
An Improved Bound for Minimizing the Total Weighted Completion Time of Coflows in Datacenters
 An Improved Bound for Minimizing the Total Weighted Completion Time of Coflows in Datacenters Mehrnoosh Shafiee, and Javad Ghaderi Electrical Engineering Department Columbia University arxiv:704.0857v
An Improved Bound for Minimizing the Total Weighted Completion Time of Coflows in Datacenters Mehrnoosh Shafiee, and Javad Ghaderi Electrical Engineering Department Columbia University arxiv:704.0857v
M.SC. MATHEMATICS - II YEAR
 MANONMANIAM SUNDARANAR UNIVERSITY DIRECTORATE OF DISTANCE & CONTINUING EDUCATION TIRUNELVELI 627012, TAMIL NADU M.SC. MATHEMATICS - II YEAR DKM24 - OPERATIONS RESEARCH (From the academic year 2016-17)
MANONMANIAM SUNDARANAR UNIVERSITY DIRECTORATE OF DISTANCE & CONTINUING EDUCATION TIRUNELVELI 627012, TAMIL NADU M.SC. MATHEMATICS - II YEAR DKM24 - OPERATIONS RESEARCH (From the academic year 2016-17)
Homework 1 - SOLUTION
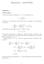 Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
Homework - SOLUTION Problem M/M/ Queue ) Use the fact above to express π k, k > 0, as a function of π 0. π k = ( ) k λ π 0 µ 2) Using λ < µ and the fact that all π k s sum to, compute π 0 (as a function
ISyE 2030 Practice Test 1
 1 NAME ISyE 2030 Practice Test 1 Summer 2005 This test is open notes, open books. You have exactly 90 minutes. 1. Some Short-Answer Flow Questions (a) TRUE or FALSE? One of the primary reasons why theoretical
1 NAME ISyE 2030 Practice Test 1 Summer 2005 This test is open notes, open books. You have exactly 90 minutes. 1. Some Short-Answer Flow Questions (a) TRUE or FALSE? One of the primary reasons why theoretical
Networked Embedded Systems WS 2016/17
 Networked Embedded Systems WS 2016/17 Lecture 2: Real-time Scheduling Marco Zimmerling Goal of Today s Lecture Introduction to scheduling of compute tasks on a single processor Tasks need to finish before
Networked Embedded Systems WS 2016/17 Lecture 2: Real-time Scheduling Marco Zimmerling Goal of Today s Lecture Introduction to scheduling of compute tasks on a single processor Tasks need to finish before
Classic Network Measurements meets Software Defined Networking
 Classic Network s meets Software Defined Networking Ran Ben Basat, Technion, Israel Joint work with Gil Einziger and Erez Waisbard (Nokia Bell Labs) Roy Friedman (Technion) and Marcello Luzieli (UFGRS)
Classic Network s meets Software Defined Networking Ran Ben Basat, Technion, Israel Joint work with Gil Einziger and Erez Waisbard (Nokia Bell Labs) Roy Friedman (Technion) and Marcello Luzieli (UFGRS)
Reconnect 04 Introduction to Integer Programming
 Sandia is a multiprogram laboratory operated by Sandia Corporation, a Lockheed Martin Company, Reconnect 04 Introduction to Integer Programming Cynthia Phillips, Sandia National Laboratories Integer programming
Sandia is a multiprogram laboratory operated by Sandia Corporation, a Lockheed Martin Company, Reconnect 04 Introduction to Integer Programming Cynthia Phillips, Sandia National Laboratories Integer programming
A Demand Response Calculus with Perfect Batteries
 A Demand Response Calculus with Perfect Batteries Dan-Cristian Tomozei Joint work with Jean-Yves Le Boudec CCW, Sedona AZ, 07/11/2012 Demand Response by Quantity = distribution network operator may interrupt
A Demand Response Calculus with Perfect Batteries Dan-Cristian Tomozei Joint work with Jean-Yves Le Boudec CCW, Sedona AZ, 07/11/2012 Demand Response by Quantity = distribution network operator may interrupt
CSM: Operational Analysis
 CSM: Operational Analysis 2016-17 Computer Science Tripos Part II Computer Systems Modelling: Operational Analysis by Ian Leslie Richard Gibbens, Ian Leslie Operational Analysis Based on the idea of observation
CSM: Operational Analysis 2016-17 Computer Science Tripos Part II Computer Systems Modelling: Operational Analysis by Ian Leslie Richard Gibbens, Ian Leslie Operational Analysis Based on the idea of observation
Utility Maximizing Routing to Data Centers
 0-0 Utility Maximizing Routing to Data Centers M. Sarwat, J. Shin and S. Kapoor (Presented by J. Shin) Sep 26, 2011 Sep 26, 2011 1 Outline 1. Problem Definition - Data Center Allocation 2. How to construct
0-0 Utility Maximizing Routing to Data Centers M. Sarwat, J. Shin and S. Kapoor (Presented by J. Shin) Sep 26, 2011 Sep 26, 2011 1 Outline 1. Problem Definition - Data Center Allocation 2. How to construct
Inventory optimization of distribution networks with discrete-event processes by vendor-managed policies
 Inventory optimization of distribution networks with discrete-event processes by vendor-managed policies Simona Sacone and Silvia Siri Department of Communications, Computer and Systems Science University
Inventory optimization of distribution networks with discrete-event processes by vendor-managed policies Simona Sacone and Silvia Siri Department of Communications, Computer and Systems Science University
CS 598RM: Algorithmic Game Theory, Spring Practice Exam Solutions
 CS 598RM: Algorithmic Game Theory, Spring 2017 1. Answer the following. Practice Exam Solutions Agents 1 and 2 are bargaining over how to split a dollar. Each agent simultaneously demands share he would
CS 598RM: Algorithmic Game Theory, Spring 2017 1. Answer the following. Practice Exam Solutions Agents 1 and 2 are bargaining over how to split a dollar. Each agent simultaneously demands share he would
Efficiency and Braess Paradox under Pricing
 Efficiency and Braess Paradox under Pricing Asuman Ozdaglar Joint work with Xin Huang, [EECS, MIT], Daron Acemoglu [Economics, MIT] October, 2004 Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Dept. Massachusetts
Efficiency and Braess Paradox under Pricing Asuman Ozdaglar Joint work with Xin Huang, [EECS, MIT], Daron Acemoglu [Economics, MIT] October, 2004 Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Dept. Massachusetts
Tachun Lin 1 Zhili Zhou 2 Krishnaiyan Thulasiraman 1. Oklahoma, USA 2 IBM T. J. Watson Research Center. New York, USA
 Logical Topology Survivability in IP-over-WDM Networks: Survivable Lightpath Routing for Maximum Logical Topology Capacity and Minimum Spare Capacity Requirements Tachun Lin 1 Zhili Zhou 2 Krishnaiyan
Logical Topology Survivability in IP-over-WDM Networks: Survivable Lightpath Routing for Maximum Logical Topology Capacity and Minimum Spare Capacity Requirements Tachun Lin 1 Zhili Zhou 2 Krishnaiyan
Scheduling I. Today. Next Time. ! Introduction to scheduling! Classical algorithms. ! Advanced topics on scheduling
 Scheduling I Today! Introduction to scheduling! Classical algorithms Next Time! Advanced topics on scheduling Scheduling out there! You are the manager of a supermarket (ok, things don t always turn out
Scheduling I Today! Introduction to scheduling! Classical algorithms Next Time! Advanced topics on scheduling Scheduling out there! You are the manager of a supermarket (ok, things don t always turn out
Graphs and Network Flows IE411. Lecture 12. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Graphs and Network Flows IE411 Lecture 12 Dr. Ted Ralphs IE411 Lecture 12 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 21.1 21.2 References AMO Chapter 6 CLRS Sections 26.1 26.2 IE411 Lecture
Graphs and Network Flows IE411 Lecture 12 Dr. Ted Ralphs IE411 Lecture 12 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 21.1 21.2 References AMO Chapter 6 CLRS Sections 26.1 26.2 IE411 Lecture
Routing. Topics: 6.976/ESD.937 1
 Routing Topics: Definition Architecture for routing data plane algorithm Current routing algorithm control plane algorithm Optimal routing algorithm known algorithms and implementation issues new solution
Routing Topics: Definition Architecture for routing data plane algorithm Current routing algorithm control plane algorithm Optimal routing algorithm known algorithms and implementation issues new solution
Fairness and Optimal Stochastic Control for Heterogeneous Networks
 λ 91 λ 93 Fairness and Optimal Stochastic Control for Heterogeneous Networks sensor network wired network wireless 9 8 7 6 5 λ 48 λ 42 4 3 0 1 2 λ n R n U n Michael J. Neely (USC) Eytan Modiano (MIT) Chih-Ping
λ 91 λ 93 Fairness and Optimal Stochastic Control for Heterogeneous Networks sensor network wired network wireless 9 8 7 6 5 λ 48 λ 42 4 3 0 1 2 λ n R n U n Michael J. Neely (USC) Eytan Modiano (MIT) Chih-Ping
A Framework for Automated Competitive Analysis of On-line Scheduling of Firm-Deadline Tasks
 A Framework for Automated Competitive Analysis of On-line Scheduling of Firm-Deadline Tasks Krishnendu Chatterjee 1, Andreas Pavlogiannis 1, Alexander Kößler 2, Ulrich Schmid 2 1 IST Austria, 2 TU Wien
A Framework for Automated Competitive Analysis of On-line Scheduling of Firm-Deadline Tasks Krishnendu Chatterjee 1, Andreas Pavlogiannis 1, Alexander Kößler 2, Ulrich Schmid 2 1 IST Austria, 2 TU Wien
Online Tree Caching. CCS Concepts
 Online Tree Caching Marcin Bienkowski Institute of Computer Science, University of Wrocław, Poland Stefan Schmid Department of Computer Science, Aalborg University, Denmark Jan Marcinkowski Institute of
Online Tree Caching Marcin Bienkowski Institute of Computer Science, University of Wrocław, Poland Stefan Schmid Department of Computer Science, Aalborg University, Denmark Jan Marcinkowski Institute of
CO759: Algorithmic Game Theory Spring 2015
 CO759: Algorithmic Game Theory Spring 2015 Instructor: Chaitanya Swamy Assignment 1 Due: By Jun 25, 2015 You may use anything proved in class directly. I will maintain a FAQ about the assignment on the
CO759: Algorithmic Game Theory Spring 2015 Instructor: Chaitanya Swamy Assignment 1 Due: By Jun 25, 2015 You may use anything proved in class directly. I will maintain a FAQ about the assignment on the
