8B.3 THE RESPONSE OF THE EQUATORIAL PACIFIC OCEAN TO GLOBAL WARMING
|
|
|
- Sara Lester
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 8B.3 THE RESPONSE OF THE EQUATORIAL PACIFIC OCEAN TO GLOBAL WARMING Kristopher Karnauskas*, Richard Seager, Alexey Kaplan, Yochanan Kushnir, Mark Cane Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory, Columbia University, Palisades, NY 1. INTRODUCTION The basic pattern of sea surface temperature (SST) in the equatorial Pacific Ocean is characterized by a vast warm pool in the west (~29 C, annual mean), and a relatively narrow tongue of cold surface water extending westward from the coast of South America (~25 C, annual mean). The result is an approximately linear zonal gradient of SST where the west is ~4 C warmer than the east. A persistent change of the zonal SST gradient by a fraction of a degree centigrade was enough to cause the Dust Bowl drought of the 1930s and other major droughts (Schubert et al. 2004, Schubert 2004, Seager et al. 2005, Kumar et al. 1999). The zonal SST gradient exhibits strong seasonality that is dominated by the seasonality of the eastern equatorial Pacific (i.e., the cold tongue ) as SSTs in the west remain fairly constant. The cold tongue is weak during March (Fig. 1a) and strong during September (Fig. 1b), resulting in a strong seasonal cycle (Fig. 1c). Because of its importance in the global climate system, the past and future change of the equatorial Pacific zonal SST gradient, as well as the atmospheric circulation to which it is coupled, has been the subject of recent climate research. A weakening of the zonal SST gradient and atmospheric circulation has been termed El Niño like, and a strengthening thereof has been termed La Niña like. A theory has been proposed that global warming will result in an El Niño like response, including a weakened zonal atmospheric overturning circulation and SST gradient, based on the mass and energy balances of the atmosphere (Held and Soden 2006, Vecchi and Soden 2007). Recent analysis of observed trends in annual mean sea level pressure (SLP) in the Indo Pacific sector seem to support this theory (Vecchi et al. 2006). A more ocean centric theory has also been proposed, wherein global warming will result in a La Niña like response, because the strong upwelling in the cold tongue should dilute the warming in that region, hence resulting in a stronger contrast with the west (Clement et al. 1996, Seager and Murtugudde 1997). Observational evidence has been presented in support of this theory as well (Cane et al. 1997, Cane 2005). Although it appears that the zonal atmospheric overturning circulation of the equatorial Pacific has been weakening since the mid 1800s (Vecchi et al. 2006), no consensus has been achieved to date regarding the change in the zonal SST gradient. *Corresponding author address: Kristopher Karnauskas, LDEO of Columbia University, Palisades, NY; krisk@ldeo.columbia.edu. 2. DATA AND METHODOLOGY Here the most recent versions of three widely used observational data sets of historical monthly SST are analyzed to determine the change in the zonal SST gradient in the period of adequate, overlapping coverage ( ). Included in the present analysis are the U.K. Hadley Centre sea ice and temperature version 1 (HadISST1, Rayner et al. 2003), Kaplan Extended SST (Kaplan SST, Kaplan et al. 1998), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration Extended Reconstructed SST version 3 (NOAA ERSST v.3, Smith et al. 2008). The horizontal resolutions of HadISST1, Kaplan SST, and NOAA ERSST v.3 are 1, 5, and 2, respectively. Our metric of the zonal SST gradient is the difference between SST averaged over the rectangular boxes in the western and eastern equatorial Pacific shown in Fig. 1. Given the strong seasonality of the equatorial Pacific zonal SST gradient (Fig. 1), we analyze trends separately for each calendar month. Sea level pressure (SLP) is also analyzed in a similar fashion; here we use the U.K. Hadley Centre sea level pressure version 2 (HadSLP2, Allen and Ansell 2006), Kaplan sea level pressure (Kaplan SLP, Kaplan et al. 2000), and the NOAA Extended Reconstructed SLP (NOAA ERSLP, Smith and Reynolds 2004). Trends and statistical significance are estimated using the median slope approach (Sen s method; Sen 1968, Thiel 1950), and the Mann Kendall test (Mann 1945, Kendall 1975), both of which are nonparametric and resilient to outliers. Since we do not assume trends of a given sign a priori, we use the more stringent two tailed test for assessing levels of significance and determining if a trend is significantly different from zero. We also briefly comment on the agreement between the observed trends in the equatorial Pacific zonal SST and SLP gradients and those simulated by the coupled general circulation models included in the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fourth Assessment Report (IPCC AR4) and archived by the World Climate Research Program (WCRP) Coupled Model Intercomparison Project phase 3 (CMIP3) Multi Model Database. To compare with observations, we use the Climate of the 20 th Century experiment, which is initialized at a stable pre industrial state, and forced by the historical record of greenhouse gases, aerosols, volcanoes, and solar forcing. Included in our analysis are 24 models; one of the models included in the IPCC AR4 was not archived by the Database (BCC CM1), while two additional models have since been added to the Database (CSIRO MK3.5 [see pcmdi.llnl.gov/ipcc/model_documentation/csiro Mk3.5.htm] and INGV ECHAM4 [see 1
2 pcmdi.llnl.gov/ipcc/model_documentation/ingv SXG.htm]). Refer to Table 8.1 of the IPCC AR4 for complete references and basic model specifications. 3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION The seasonally stratified trends in the equatorial Pacific zonal SST gradient are in good agreement across the three data sets (Fig. 2a c) with a statistically significant strengthening of the equatorial Pacific zonal SST gradient from for several months throughout boreal fall and winter. The multi data set mean trend, averaged from June to January is 0.26 C per century, equivalent to 6.1% of the June January climatological mean gradient. During September, the multi data set mean trend is 0.36 C (7.7%) per century. Throughout boreal spring, trends are approximately or not significantly different from zero. Therefore, apart from the season when the zonal SST gradient is weakest, the equatorial Pacific zonal SST gradient has been strengthening since If the observed changes arose as a response to rising greenhouse gases, then this seasonal dependence of the forced change in SST gradient is consistent with a model prediction that emphasizes the ability of upwelling of cold water in the eastern equatorial Pacific, which maximizes in summer and fall, to offset warming forced by increased downward longwave radiation (Clement et al. 1996). Since the trend as a function of calendar month matches very closely the mean annual cycle (i.e., Fig. 1c), this implies a trend toward a stronger annual cycle of the zonal SST gradient. The observed strengthening of the zonal SST gradient has important consequences. The magnitude of the observed change in the zonal SST gradient over a period of 100 yr (e.g., 0.36 C for September) is comparable in magnitude to those associated with Pacific decadal variability (~0.24 C), which strongly influences global precipitation patterns and drought. According to well established theory (Bjerknes 1966), a stronger SST gradient should be coupled to a stronger SLP gradient and therefore the robust strengthening of the equatorial Pacific zonal SST gradient seems in conflict with the observed weakening of the zonal atmospheric overturning circulation (Vecchi et al. 2006). We turn to observational data sets of SLP from each of the three institutions that provide the SST data sets analyzed above. Based on the zonal SLP gradient, two out of the three data sets indeed suggest a significant weakening of the zonal atmospheric overturning circulation during boreal spring (Fig. 3a b). During boreal fall, however, each of the three data sets show trends in SLP gradient that are not significantly different from zero which is when the zonal SST gradient is a climatological maximum and has been strengthening. Since the mean annual cycle of the zonal SLP gradient is in phase with that of the zonal SST gradient, it is a valid interpretation of Fig. 3a c that, amidst a general weakening, the seasonality of the zonal atmospheric overturning circulation has also been strengthening, consistent with the observed change in the seasonality of the equatorial ocean surface. Of the 24 coupled general circulation models archived by the WCRP CMIP3 multi model database, 20 models faithfully reproduce the observed seasonal climatology of the equatorial Pacific zonal SST gradient, although few sustain the SST gradient into boreal winter (Fig. 4a). Using that subset of models, the multi model ensemble mean trend is positive (strengthening) all year long, but fails to reproduce the observed seasonality of the trends including an underestimation of the strengthening trend in boreal fall and winter (Fig. 4b). Also, the models do not reproduce the reduced strengthening trend in boreal spring, which may be attributable to a wide range of model deficiencies simulating tropical climatology. A smaller proportion of the models exhibit a reasonable climatological zonal SLP gradient (Fig. 4c). Using that subset of models, the multi model ensemble mean trend of the zonal SLP gradient is in good agreement with observations during boreal summer and fall, but fails to reproduce the observed weakening trend in boreal spring (Fig. 4d). Despite their obvious errors simulating the climatology and trends of tropical Pacific climate, the models do suggest that that it is possible, according to the physics within these models, for the zonal SST gradient to strengthen but for the SLP gradient to remain largely unchanged. Such a change contrasts with the coupled fluctuations of the strength of the SST and SLP gradients that occur during ENSO events, suggesting that the mechanisms of tropical Pacific climate change may be distinct from those of tropical Pacific climate variability. It has been shown that, even with fixed winds, the equatorial SST gradient can strengthen in response to positive radiative forcing because of an increase in the ocean's thermal stratification (Seager and Murtugudde 1997). Therefore, if this effect is sufficiently strong, it is possible that an increased SST gradient can result even if the SLP gradient and associated zonal winds weaken as a consequence of changes in the atmospheric energy and moisture budget (Vecchi et al. 2008). Future explanations of the response of the tropical Pacific climate system to radiative forcing will need to account for the full range of mechanisms that couple the tropical Pacific atmosphere and ocean, their relative strengths and their seasonal cycles. This understanding is required to determine how this key region of the global climate system will respond to anthropogenic climate forcing and how this will impact climate worldwide. 4. REFERENCES Allan, R. J. and Ansell, T. J., 2006: A new globally complete monthly historical mean sea level pressure Please note: This conference paper is based on a manuscript submitted to the Journal of Climate on 11/11/08 and currently under review. 2
3 data set (HadSLP2): , J. Climate, Bjerknes, J., 1966: The possible response of the atmospheric Hadley circulation to equatorial anomalies of ocean temperature. Tellus, 18, Cane, M.A., A. C. Clement, A. Kaplan, Y. Kushnir, D. Pozdnyakov, R. Seager, S. E. Zebiak and R. Murtugudde. 1997: Twentieth century sea surface temperature trends, Science, 275, Cane, M. A., 2005: The evolution of El Niño, past and future, Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 230, Clement A., R. Seager, M. A. Cane, and S. E. Zebiak, 1996: An ocean dynamical thermostat. J. Climate, 9, Held I. M., and B. J. Soden, 2006: Robust responses of the hydrological cycle to global warming. J. Climate, 19, IPCC. In Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (eds Solomon, S. D. et al.) (Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, UK, 2007). reports.htm Kaplan A., Y. Kushnir, and M. A. Cane, 2000: Reduced space optimal interpolation of historical marine sea level pressure, J. Climate, 13, Kaplan, A., M. Cane, Y. Kushnir, A. Clement, M. Blumenthal, and B. Rajagopalan, 1998: Analyses of global sea surface temperature , J. Geophys. Res., 103, 18,567 18,589. Kendall, M. G. (1975) Rank Correlation Methods. Griffin, London, UK. Kumar K. K., B. Rajagopalan, and M. A. Cane, 1999: On the weakening relationship between the Indian monsoon and ENSO. Science, 284, Mann, H. B., 1945: Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica, 13, Rayner N. A., D. E. Parker, E. B. Horton, C. K. Folland, L. V. Alexander, D. P. Rowell, E. C. Kent, and A. Kaplan, 2003: Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J. Geophys. Res., 108, 4407, doi: /2002jd Reynolds, R. W., N. A. Rayner, T. M. Smith, D. C. Stokes, and W. Wang, 2002: An improved in situ and satellite SST analysis for climate. J. Climate, 15, Schubert, S. D., M. J. Suarez, P. J. Pegion, R. D. Koster, and J. T. Bacmeister, 2004: Causes of long term drought in the US Great Plains. J. Climate, 17, Schubert, S. D., 2004: On the cause of the 1930s Dust Bowl. Science, 303, Seager, R., Y. Kushnir, C. Herweijer, N. Naik, and J. Velez, 2005: Modeling of tropical forcing of persistent droughts and pluvials over western North America: J. Climate, 18, Seager, R., and R. Murtugudde, 1997: Ocean dynamics, thermocline adjustment, and regulation of tropical SST. J. Climate, 10, Sen, P.K., 1968: Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall's tau. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 63, Smith, T. M., R. W. Reynolds, T. C. Peterson, and J. Lawrimore, 2008: Improvements to NOAA s historical merged land ocean surface temperature analysis ( ). J. Climate, 21, Smith, T. M., and R. W. Reynolds, 2004: Reconstruction of monthly mean oceanic sea level pressure based on COADS and station data ( ). J. Oceanic Atmos. Tech., 21, Thiel, H., 1950: A rank invariant method of linear and polynomial regression analysis, Part 3. Proceedings of Koninalijke Nederlandse Akademie van Weinenschatpen A, 53, Vecchi, G. A., A. Clement and B. J. Soden, 2008: Examining the tropical Pacific's response to global warming. EOS, Trans. Amer. Geophys. Union, 89(9), Vecchi, G. A., and B. J. Soden, 2007: Global warming and the weakening of the tropical circulation. J. Climate, 20, Vecchi, G. A., B. J. Soden, A. T. Wittenberg, I. M. Held, A. Leetmaa, and M. J. Harrison, 2006: Weakening of tropical Pacific atmospheric circulation due to anthropogenic forcing. Nature, 441(7089),
4 Figure 1. Observed tropical Pacific SST ( C) in March (a) and September (b) averaged over the modern satellite era ( ) from the NOAA OI v.2 SST data set (Reynolds et al. 2002). The white (black) rectangles represent the western (eastern) equatorial Pacific. Observed annual cycle of the equatorial Pacific zonal SST (black, C) and SLP (HadSLP2, red, hpa) gradients averaged over the same period (c). Open squares highlight March and September. Figure 2. Trends of observed zonal SST gradient (west east difference, C per century) from as a function of calendar month from HadISST1 (a), Kaplan SST (b), and NOAA ERSST v.3 (c). Gray regions denote 95% confidence intervals. Trends and confidence intervals calculated using the nonparametric Sen s median slope method. White circles (squares) represent trends significant at the 5% (10%) level based on the Mann Kendall test. Figure 3. As in Fig. 2, but for SLP from HadSLP2 (a), Kaplan SLP (b), and NOAA ERSLP (c). 4
5 Figure 4. Annual cycle of the equatorial Pacific zonal SST gradient (western minus eastern) computed over the Climate of the 20 th Century experiments (~ ) for 24 coupled GCMs (a). A subset of models is easily distinguishable as having an unrealistic SST gradient and/or annual cycle (red lines). The black line with open diamonds represents the multi model ensemble mean of the blue lines. The black line with closed squares represents the observations (multi data set mean, ). Multi model (blue lines) ensemble mean (open diamonds) and observed (multi data set mean, closed squares) linear trend in the west east SST difference as a function of calendar month (b). Trends calculated using the nonparametric Sen s median slope method. The gray shading represents ±2 standard errors of the multi model (blue lines) ensemble mean trends. Panels c and d as in a and b, but for SLP. 5
Observed Strengthening of the Zonal Sea Surface Temperature Gradient across the Equatorial Pacific Ocean*
 4316 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 22 Observed Strengthening of the Zonal Sea Surface Temperature Gradient across the Equatorial Pacific Ocean* KRISTOPHER B. KARNAUSKAS, RICHARD SEAGER, ALEXEY
4316 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 22 Observed Strengthening of the Zonal Sea Surface Temperature Gradient across the Equatorial Pacific Ocean* KRISTOPHER B. KARNAUSKAS, RICHARD SEAGER, ALEXEY
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Effect of remote sea surface temperature change on tropical cyclone potential intensity Gabriel A. Vecchi Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory NOAA Brian J. Soden Rosenstiel School for Marine and Atmospheric
Effect of remote sea surface temperature change on tropical cyclone potential intensity Gabriel A. Vecchi Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory NOAA Brian J. Soden Rosenstiel School for Marine and Atmospheric
Simulated Patterns of Unforced Centennial-Scale. Climate Variability in the Tropical Pacific
 Simulated Patterns of Unforced Centennial-Scale Climate Variability in the Tropical Pacific Kristopher B. Karnauskas Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Jason E. Smerdon and Richard Seager Lamont-Doherty
Simulated Patterns of Unforced Centennial-Scale Climate Variability in the Tropical Pacific Kristopher B. Karnauskas Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Jason E. Smerdon and Richard Seager Lamont-Doherty
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1840 RECENT MULTIDECADAL STRENGTHENING OF THE WALKER CIRCULATION ACROSS THE TROPICAL PACIFIC (1) Supplementary_Figures.pdf Adobe document 1.5MB SI Guide Supplementary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE1840 RECENT MULTIDECADAL STRENGTHENING OF THE WALKER CIRCULATION ACROSS THE TROPICAL PACIFIC (1) Supplementary_Figures.pdf Adobe document 1.5MB SI Guide Supplementary
The Formation of Precipitation Anomaly Patterns during the Developing and Decaying Phases of ENSO
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 1, 25 30 The Formation of Precipitation Anomaly Patterns during the Developing and Decaying Phases of ENSO HU Kai-Ming and HUANG Gang State Key
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2010, VOL. 3, NO. 1, 25 30 The Formation of Precipitation Anomaly Patterns during the Developing and Decaying Phases of ENSO HU Kai-Ming and HUANG Gang State Key
Inter-comparison of Historical Sea Surface Temperature Datasets
 Inter-comparison of Historical Sea Surface Temperature Datasets Sayaka Yasunaka 1, Kimio Hanawa 2 1 Center for Climate System Research, University of Tokyo, Japan 2 Graduate School of Science, Tohoku University,
Inter-comparison of Historical Sea Surface Temperature Datasets Sayaka Yasunaka 1, Kimio Hanawa 2 1 Center for Climate System Research, University of Tokyo, Japan 2 Graduate School of Science, Tohoku University,
Climate Change over the Equatorial Indo-Pacific in Global Warming*
 2678 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 22 Climate Change over the Equatorial Indo-Pacific in Global Warming* CHIE IHARA, YOCHANAN KUSHNIR, AND MARK A. CANE Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Columbia
2678 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 22 Climate Change over the Equatorial Indo-Pacific in Global Warming* CHIE IHARA, YOCHANAN KUSHNIR, AND MARK A. CANE Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Columbia
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11576 1. Trend patterns of SST and near-surface air temperature Bucket SST and NMAT have a similar trend pattern particularly in the equatorial Indo- Pacific (Fig. S1), featuring a reduced
doi:10.1038/nature11576 1. Trend patterns of SST and near-surface air temperature Bucket SST and NMAT have a similar trend pattern particularly in the equatorial Indo- Pacific (Fig. S1), featuring a reduced
Twentieth-Century Sea Surface Temperature Trends M.A. Cane, et al., Science 275, pp (1997) Jason P. Criscio GEOS Apr 2006
 Twentieth-Century Sea Surface Temperature Trends M.A. Cane, et al., Science 275, pp. 957-960 (1997) Jason P. Criscio GEOS 513 12 Apr 2006 Questions 1. What is the proposed mechanism by which a uniform
Twentieth-Century Sea Surface Temperature Trends M.A. Cane, et al., Science 275, pp. 957-960 (1997) Jason P. Criscio GEOS 513 12 Apr 2006 Questions 1. What is the proposed mechanism by which a uniform
DROUGHT IN AMERICA DURING THE PAST MILLENNIUM
 DROUGHT IN AMERICA DURING THE PAST MILLENNIUM Mark Cane Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University With Ed Cook, Richard Seager, Amy Clement and Michael Mann Photo: Rose Werner The New York
DROUGHT IN AMERICA DURING THE PAST MILLENNIUM Mark Cane Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University With Ed Cook, Richard Seager, Amy Clement and Michael Mann Photo: Rose Werner The New York
2. MULTIMODEL ASSESSMENT OF ANTHROPOGENIC INFLUENCE ON RECORD GLOBAL AND REGIONAL WARMTH DURING 2015
 2. MULTIMODEL ASSESSMENT OF ANTHROPOGENIC INFLUENCE ON RECORD GLOBAL AND REGIONAL WARMTH DURING 2015 Jonghun Kam, Thomas R. Knutson, Fanrong Zeng, and Andrew T. Wittenberg In 2015, record warm surface
2. MULTIMODEL ASSESSMENT OF ANTHROPOGENIC INFLUENCE ON RECORD GLOBAL AND REGIONAL WARMTH DURING 2015 Jonghun Kam, Thomas R. Knutson, Fanrong Zeng, and Andrew T. Wittenberg In 2015, record warm surface
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 25 February 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 25 February 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 25 February 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
Detectability of Changes in the Walker Circulation in Response to Global Warming*
 4038 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 26 Detectability of Changes in the Walker Circulation in Response to Global Warming* PEDRO N. DINEZIO International Pacific Research Center, School of Ocean
4038 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 26 Detectability of Changes in the Walker Circulation in Response to Global Warming* PEDRO N. DINEZIO International Pacific Research Center, School of Ocean
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 23 April 2012
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 23 April 2012 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 23 April 2012 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 5 August 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 5 August 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 5 August 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
the 2 past three decades
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2840 Atlantic-induced 1 pan-tropical climate change over the 2 past three decades 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 POP simulation forced by the Atlantic-induced atmospheric
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2840 Atlantic-induced 1 pan-tropical climate change over the 2 past three decades 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 POP simulation forced by the Atlantic-induced atmospheric
Will a warmer world change Queensland s rainfall?
 Will a warmer world change Queensland s rainfall? Nicholas P. Klingaman National Centre for Atmospheric Science-Climate Walker Institute for Climate System Research University of Reading The Walker-QCCCE
Will a warmer world change Queensland s rainfall? Nicholas P. Klingaman National Centre for Atmospheric Science-Climate Walker Institute for Climate System Research University of Reading The Walker-QCCCE
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 11 November 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 11 November 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 11 November 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 15 July 2013
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 15 July 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 15 July 2013 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index
Natural Centennial Tropical Pacific Variability in Coupled GCMs
 Natural Centennial Tropical Pacific Variability in Coupled GCMs Jason E. Smerdon 1 Kris Karnauskas 2 Richard Seager 1 J. Fidel Gonzalez-Rouco 3 1 LDEO, 2 WHOI and 3 UCM Millennial Climate Model Simulations
Natural Centennial Tropical Pacific Variability in Coupled GCMs Jason E. Smerdon 1 Kris Karnauskas 2 Richard Seager 1 J. Fidel Gonzalez-Rouco 3 1 LDEO, 2 WHOI and 3 UCM Millennial Climate Model Simulations
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 24 September 2012
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 24 September 2012 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 24 September 2012 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño
Moist static energy budget diagnostics for. monsoon research. H. Annamalai
 Moist static energy budget diagnostics for monsoon research H. Annamalai JJAS Precipitation and SST Climatology I III II Multiple regional heat sources - EIO and SPCZ still experience high precipitation
Moist static energy budget diagnostics for monsoon research H. Annamalai JJAS Precipitation and SST Climatology I III II Multiple regional heat sources - EIO and SPCZ still experience high precipitation
ENSO Amplitude Change in Observation and Coupled Models
 ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 25, NO. 3, 28, 361 366 ENSO Amplitude Change in Observation and Coupled Models ZHANG Qiong 1 (Ü ), GUAN Yue 1,3 (' ff), and YANG Haijun 2 (fl ) 1 State Key Laboratory
ADVANCES IN ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCES, VOL. 25, NO. 3, 28, 361 366 ENSO Amplitude Change in Observation and Coupled Models ZHANG Qiong 1 (Ü ), GUAN Yue 1,3 (' ff), and YANG Haijun 2 (fl ) 1 State Key Laboratory
lecture 11 El Niño/Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part II
 lecture 11 El Niño/Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part II SYSTEM MEMORY: OCEANIC WAVE PROPAGATION ASYMMETRY BETWEEN THE ATMOSPHERE AND OCEAN The atmosphere and ocean are not symmetrical in their responses
lecture 11 El Niño/Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part II SYSTEM MEMORY: OCEANIC WAVE PROPAGATION ASYMMETRY BETWEEN THE ATMOSPHERE AND OCEAN The atmosphere and ocean are not symmetrical in their responses
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP July 26, 2004
 ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP July 26, 2004 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic NiZo Index
ENSO Cycle: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by Climate Prediction Center / NCEP July 26, 2004 Outline Overview Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic NiZo Index
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System
 An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
The Impact of increasing greenhouse gases on El Nino/Southern Oscillation (ENSO)
 The Impact of increasing greenhouse gases on El Nino/Southern Oscillation (ENSO) David S. Battisti 1, Daniel J. Vimont 2, Julie Leloup 2 and William G.H. Roberts 3 1 Univ. of Washington, 2 Univ. of Wisconsin,
The Impact of increasing greenhouse gases on El Nino/Southern Oscillation (ENSO) David S. Battisti 1, Daniel J. Vimont 2, Julie Leloup 2 and William G.H. Roberts 3 1 Univ. of Washington, 2 Univ. of Wisconsin,
ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 9 November 2015
 ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 9 November 2015 Outline Summary Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index (ONI)
ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 9 November 2015 Outline Summary Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index (ONI)
SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences. Changes of the tropical Pacific Walker circulation simulated by two versions of FGOALS model
 SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences RESEARCH PAPER doi: 10.1007/s11430-014-4902-8 Changes of the tropical Pacific Walker circulation simulated by two versions of FGOALS model MA ShuangMei 1,2 & ZHOU TianJun 1,3*
SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences RESEARCH PAPER doi: 10.1007/s11430-014-4902-8 Changes of the tropical Pacific Walker circulation simulated by two versions of FGOALS model MA ShuangMei 1,2 & ZHOU TianJun 1,3*
Decadal variability of the IOD-ENSO relationship
 Chinese Science Bulletin 2008 SCIENCE IN CHINA PRESS ARTICLES Springer Decadal variability of the IOD-ENSO relationship YUAN Yuan 1,2 & LI ChongYin 1 1 State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling for Atmospheric
Chinese Science Bulletin 2008 SCIENCE IN CHINA PRESS ARTICLES Springer Decadal variability of the IOD-ENSO relationship YUAN Yuan 1,2 & LI ChongYin 1 1 State Key Laboratory of Numerical Modeling for Atmospheric
P2.18 Recent trend of Hadley and Walker circulation shown in water vapor transport potential
 P.8 Recent trend of Hadley and Walker circulation shown in water vapor transport potential Seong-Chan Park and *Byung-Ju Sohn School of Earth and Environmental Sciences Seoul National University, Seoul,
P.8 Recent trend of Hadley and Walker circulation shown in water vapor transport potential Seong-Chan Park and *Byung-Ju Sohn School of Earth and Environmental Sciences Seoul National University, Seoul,
Seasonal Climate Watch January to May 2016
 Seasonal Climate Watch January to May 2016 Date: Dec 17, 2015 1. Advisory Most models are showing the continuation of a strong El-Niño episode towards the latesummer season with the expectation to start
Seasonal Climate Watch January to May 2016 Date: Dec 17, 2015 1. Advisory Most models are showing the continuation of a strong El-Niño episode towards the latesummer season with the expectation to start
The Two Types of ENSO in CMIP5 Models
 1 2 3 The Two Types of ENSO in CMIP5 Models 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Seon Tae Kim and Jin-Yi Yu * Department of Earth System
1 2 3 The Two Types of ENSO in CMIP5 Models 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 Seon Tae Kim and Jin-Yi Yu * Department of Earth System
Rainfall variability over the Indochina peninsula during the Boreal Winter, Part I: Preliminary data analysis
 Rainfall variability over the Indochina peninsula during the Boreal Winter, Part I: Preliminary data analysis Sirapong Sooktawee*, sirapong@deqp.go.th; Atsamon Limsakul, atsamon@deqp.go.th, Environmental
Rainfall variability over the Indochina peninsula during the Boreal Winter, Part I: Preliminary data analysis Sirapong Sooktawee*, sirapong@deqp.go.th; Atsamon Limsakul, atsamon@deqp.go.th, Environmental
A Pacific Centennial Oscillation Predicted by Coupled GCMs*
 1SEPTEMBER 2012 K A R N A U S K A S E T A L. 5943 A Pacific Centennial Oscillation Predicted by Coupled GCMs* KRISTOPHER B. KARNAUSKAS Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, Massachusetts JASON
1SEPTEMBER 2012 K A R N A U S K A S E T A L. 5943 A Pacific Centennial Oscillation Predicted by Coupled GCMs* KRISTOPHER B. KARNAUSKAS Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, Massachusetts JASON
Different impacts of Northern, Tropical and Southern volcanic eruptions on the tropical Pacific SST in the last millennium
 Different impacts of Northern, Tropical and Southern volcanic eruptions on the tropical Pacific SST in the last millennium Meng Zuo, Wenmin Man, Tianjun Zhou Email: zuomeng@lasg.iap.ac.cn Sixth WMO International
Different impacts of Northern, Tropical and Southern volcanic eruptions on the tropical Pacific SST in the last millennium Meng Zuo, Wenmin Man, Tianjun Zhou Email: zuomeng@lasg.iap.ac.cn Sixth WMO International
Effect of anomalous warming in the central Pacific on the Australian monsoon
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L12704, doi:10.1029/2009gl038416, 2009 Effect of anomalous warming in the central Pacific on the Australian monsoon A. S. Taschetto, 1
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L12704, doi:10.1029/2009gl038416, 2009 Effect of anomalous warming in the central Pacific on the Australian monsoon A. S. Taschetto, 1
ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions. Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 30 October 2017
 ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 30 October 2017 Outline Summary Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index (ONI)
ENSO: Recent Evolution, Current Status and Predictions Update prepared by: Climate Prediction Center / NCEP 30 October 2017 Outline Summary Recent Evolution and Current Conditions Oceanic Niño Index (ONI)
How Will Low Clouds Respond to Global Warming?
 How Will Low Clouds Respond to Global Warming? By Axel Lauer & Kevin Hamilton CCSM3 UKMO HadCM3 UKMO HadGEM1 iram 2 ECHAM5/MPI OM 3 MIROC3.2(hires) 25 IPSL CM4 5 INM CM3. 4 FGOALS g1. 7 GISS ER 6 GISS
How Will Low Clouds Respond to Global Warming? By Axel Lauer & Kevin Hamilton CCSM3 UKMO HadCM3 UKMO HadGEM1 iram 2 ECHAM5/MPI OM 3 MIROC3.2(hires) 25 IPSL CM4 5 INM CM3. 4 FGOALS g1. 7 GISS ER 6 GISS
Seasonal Climate Outlook for South Asia (June to September) Issued in May 2014
 Ministry of Earth Sciences Earth System Science Organization India Meteorological Department WMO Regional Climate Centre (Demonstration Phase) Pune, India Seasonal Climate Outlook for South Asia (June
Ministry of Earth Sciences Earth System Science Organization India Meteorological Department WMO Regional Climate Centre (Demonstration Phase) Pune, India Seasonal Climate Outlook for South Asia (June
ANALYZING EL NIÑO- SOUTHERN OSCILLATION SENSITIVITY IN A LARGE ENSEMBLE OF OCEAN REANALYSES. A Thesis KELLEY BRADLEY
 ANALYZING EL NIÑO- SOUTHERN OSCILLATION SENSITIVITY IN A LARGE ENSEMBLE OF OCEAN REANALYSES A Thesis by KELLEY BRADLEY Submitted to the Office of Graduate and Professional Studies of Texas A&M University
ANALYZING EL NIÑO- SOUTHERN OSCILLATION SENSITIVITY IN A LARGE ENSEMBLE OF OCEAN REANALYSES A Thesis by KELLEY BRADLEY Submitted to the Office of Graduate and Professional Studies of Texas A&M University
Seasonal to decadal climate prediction: filling the gap between weather forecasts and climate projections
 Seasonal to decadal climate prediction: filling the gap between weather forecasts and climate projections Doug Smith Walter Orr Roberts memorial lecture, 9 th June 2015 Contents Motivation Practical issues
Seasonal to decadal climate prediction: filling the gap between weather forecasts and climate projections Doug Smith Walter Orr Roberts memorial lecture, 9 th June 2015 Contents Motivation Practical issues
Climate modeling: 1) Why? 2) How? 3) What?
 Climate modeling: 1) Why? 2) How? 3) What? Matthew Widlansky mwidlans@hawaii.edu 1) Why model the climate? Hawaii Fiji Sachs and Myhrvold: A Shifting Band of Rain 1 Evidence of Past Climate Change? Mean
Climate modeling: 1) Why? 2) How? 3) What? Matthew Widlansky mwidlans@hawaii.edu 1) Why model the climate? Hawaii Fiji Sachs and Myhrvold: A Shifting Band of Rain 1 Evidence of Past Climate Change? Mean
Alternating mutual influence of El Niño/Southern Oscillation and Indian monsoon
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2010gl045932, 2011 Alternating mutual influence of El Niño/Southern Oscillation and Indian monsoon I. I. Mokhov, 1 D. A. Smirnov, 2,3 P. I. Nakonechny,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2010gl045932, 2011 Alternating mutual influence of El Niño/Southern Oscillation and Indian monsoon I. I. Mokhov, 1 D. A. Smirnov, 2,3 P. I. Nakonechny,
Tropical Pacific response to 20th century Atlantic warming
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2010gl046248, 2011 Tropical Pacific response to 20th century Atlantic warming F. Kucharski, 1 I. S. Kang, 2 R. Farneti, 1 and L. Feudale 1 Received 16
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 38,, doi:10.1029/2010gl046248, 2011 Tropical Pacific response to 20th century Atlantic warming F. Kucharski, 1 I. S. Kang, 2 R. Farneti, 1 and L. Feudale 1 Received 16
lecture 10 El Niño and the Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part I sea surface height anomalies as measured by satellite altimetry
 lecture 10 El Niño and the Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part I sea surface height anomalies as measured by satellite altimetry SPATIAL STRUCTURE OF ENSO In 1899, the Indian monsoon failed, leading to drought
lecture 10 El Niño and the Southern Oscillation (ENSO) Part I sea surface height anomalies as measured by satellite altimetry SPATIAL STRUCTURE OF ENSO In 1899, the Indian monsoon failed, leading to drought
Extreme Weather Events and Climate Change
 Extreme Weather Events and Climate Change Robert M Rabin NOAA/National Severe Storms Lab Norman, Oklahoma Most material presented is from: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Intergovernmental
Extreme Weather Events and Climate Change Robert M Rabin NOAA/National Severe Storms Lab Norman, Oklahoma Most material presented is from: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Intergovernmental
Decadal changes of ENSO persistence barrier in SST and ocean heat content indices:
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jd007654, 2007 Decadal changes of ENSO persistence barrier in SST and ocean heat content indices: 1958 2001 Jin-Yi
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2006jd007654, 2007 Decadal changes of ENSO persistence barrier in SST and ocean heat content indices: 1958 2001 Jin-Yi
Potential of Equatorial Atlantic Variability to Enhance El Niño Prediction
 1 Supplementary Material Potential of Equatorial Atlantic Variability to Enhance El Niño Prediction N. S. Keenlyside 1, Hui Ding 2, and M. Latif 2,3 1 Geophysical Institute and Bjerknes Centre, University
1 Supplementary Material Potential of Equatorial Atlantic Variability to Enhance El Niño Prediction N. S. Keenlyside 1, Hui Ding 2, and M. Latif 2,3 1 Geophysical Institute and Bjerknes Centre, University
ENSO Outlook by JMA. Hiroyuki Sugimoto. El Niño Monitoring and Prediction Group Climate Prediction Division Japan Meteorological Agency
 ENSO Outlook by JMA Hiroyuki Sugimoto El Niño Monitoring and Prediction Group Climate Prediction Division Outline 1. ENSO impacts on the climate 2. Current Conditions 3. Prediction by JMA/MRI-CGCM 4. Summary
ENSO Outlook by JMA Hiroyuki Sugimoto El Niño Monitoring and Prediction Group Climate Prediction Division Outline 1. ENSO impacts on the climate 2. Current Conditions 3. Prediction by JMA/MRI-CGCM 4. Summary
Recent trends in sea level pressure in the Indian Ocean region
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L19712, doi:10.1029/2006gl027175, 2006 Recent trends in sea level pressure in the Indian Ocean region Dan Copsey, 1 Rowan Sutton, 1 and Jeff R. Knight 2 Received
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 33, L19712, doi:10.1029/2006gl027175, 2006 Recent trends in sea level pressure in the Indian Ocean region Dan Copsey, 1 Rowan Sutton, 1 and Jeff R. Knight 2 Received
JP1.7 A NEAR-ANNUAL COUPLED OCEAN-ATMOSPHERE MODE IN THE EQUATORIAL PACIFIC OCEAN
 JP1.7 A NEAR-ANNUAL COUPLED OCEAN-ATMOSPHERE MODE IN THE EQUATORIAL PACIFIC OCEAN Soon-Il An 1, Fei-Fei Jin 1, Jong-Seong Kug 2, In-Sik Kang 2 1 School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology, University
JP1.7 A NEAR-ANNUAL COUPLED OCEAN-ATMOSPHERE MODE IN THE EQUATORIAL PACIFIC OCEAN Soon-Il An 1, Fei-Fei Jin 1, Jong-Seong Kug 2, In-Sik Kang 2 1 School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology, University
Title. Author(s)Minobe, Shoshiro. Issue Date Doc URL. Type. Note. File Information. Updated Assessments of the 1998/99 Climate Change ov
 Title Updated Assessments of the 998/99 Climate Change ov Author(s)Minobe, Shoshiro Issue Date 24 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/25/3853 Type proceedings Note International Symposium on "Dawn of a New Natural
Title Updated Assessments of the 998/99 Climate Change ov Author(s)Minobe, Shoshiro Issue Date 24 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/25/3853 Type proceedings Note International Symposium on "Dawn of a New Natural
FUTURE PROJECTIONS OF PRECIPITATION CHARACTERISTICS IN ASIA
 FUTURE PROJECTIONS OF PRECIPITATION CHARACTERISTICS IN ASIA AKIO KITOH, MASAHIRO HOSAKA, YUKIMASA ADACHI, KENJI KAMIGUCHI Meteorological Research Institute Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0052, Japan It is anticipated
FUTURE PROJECTIONS OF PRECIPITATION CHARACTERISTICS IN ASIA AKIO KITOH, MASAHIRO HOSAKA, YUKIMASA ADACHI, KENJI KAMIGUCHI Meteorological Research Institute Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0052, Japan It is anticipated
High-Resolution MPAS Simulations for Analysis of Climate Change Effects on Weather Extremes
 High-Resolution MPAS Simulations for Analysis of Climate Change Effects on Weather Extremes ALLISON MICHAELIS, GARY LACKMANN, & WALT ROBINSON Department of Marine, Earth, and Atmospheric Sciences, North
High-Resolution MPAS Simulations for Analysis of Climate Change Effects on Weather Extremes ALLISON MICHAELIS, GARY LACKMANN, & WALT ROBINSON Department of Marine, Earth, and Atmospheric Sciences, North
Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L06704, doi:10.1029/2008gl036741, 2009 Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century Damianos F. Mantsis 1 and Amy C.
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L06704, doi:10.1029/2008gl036741, 2009 Simulated variability in the mean atmospheric meridional circulation over the 20th century Damianos F. Mantsis 1 and Amy C.
Interdecadal and Interannnual Variabilities of the Antarctic Oscillation Simulated by CAM3
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2014, VOL. 7, NO. 6, 515 520 Interdecadal and Interannnual Variabilities of the Antarctic Oscillation Simulated by CAM3 XUE Feng 1, SUN Dan 2,3, and ZHOU Tian-Jun
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2014, VOL. 7, NO. 6, 515 520 Interdecadal and Interannnual Variabilities of the Antarctic Oscillation Simulated by CAM3 XUE Feng 1, SUN Dan 2,3, and ZHOU Tian-Jun
Analysis of variability and trends of extreme rainfall events over India using 104 years of gridded daily rainfall data
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L18707, doi:10.1029/2008gl035143, 2008 Analysis of variability and trends of extreme rainfall events over India using 104 years of gridded
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L18707, doi:10.1029/2008gl035143, 2008 Analysis of variability and trends of extreme rainfall events over India using 104 years of gridded
An OLR perspective on El Niño and La Niña impacts on seasonal weather anomalies
 An OLR perspective on El Niño and La Niña impacts on seasonal weather anomalies Andy Chiodi & Ed Harrison Univ. of WA (JISAO) and NOAA/PMEL Seattle, USA An Outgoing-Longwave-Radiation (OLR) Perspective
An OLR perspective on El Niño and La Niña impacts on seasonal weather anomalies Andy Chiodi & Ed Harrison Univ. of WA (JISAO) and NOAA/PMEL Seattle, USA An Outgoing-Longwave-Radiation (OLR) Perspective
A coral-based picture of ENSO from the mid- Holocene tropical Pacific. Helen McGregor, University of Wollongong (LDEO Tharp Scholar)
 A coral-based picture of ENSO from the mid- Holocene tropical Pacific Helen McGregor, University of Wollongong (LDEO Tharp Scholar) Origins of interest in mid-holocene ENSO Laguna Pallcacocha (Ecuador)
A coral-based picture of ENSO from the mid- Holocene tropical Pacific Helen McGregor, University of Wollongong (LDEO Tharp Scholar) Origins of interest in mid-holocene ENSO Laguna Pallcacocha (Ecuador)
Is a global warming signature emerging in the tropical Pacific?
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2011gl050232, 2012 Is a global warming signature emerging in the tropical Pacific? K. Ashok, 1 T. P. Sabin, 1 P. Swapna, 1 and R. G. Murtugudde 2 Received
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2011gl050232, 2012 Is a global warming signature emerging in the tropical Pacific? K. Ashok, 1 T. P. Sabin, 1 P. Swapna, 1 and R. G. Murtugudde 2 Received
Lecture 28: Observed Climate Variability and Change
 Lecture 28: Observed Climate Variability and Change 1. Introduction This chapter focuses on 6 questions - Has the climate warmed? Has the climate become wetter? Are the atmosphere/ocean circulations changing?
Lecture 28: Observed Climate Variability and Change 1. Introduction This chapter focuses on 6 questions - Has the climate warmed? Has the climate become wetter? Are the atmosphere/ocean circulations changing?
Patterns and impacts of ocean warming and heat uptake
 Patterns and impacts of ocean warming and heat uptake Shang-Ping Xie Scripps Inst of Oceanography, UCSD Ocean warming & circulation change Ocean heat uptake & meridional overturning circulation Global
Patterns and impacts of ocean warming and heat uptake Shang-Ping Xie Scripps Inst of Oceanography, UCSD Ocean warming & circulation change Ocean heat uptake & meridional overturning circulation Global
Why Has the Land Memory Changed?
 3236 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE VOLUME 17 Why Has the Land Memory Changed? QI HU ANDSONG FENG Climate and Bio-Atmospheric Sciences Group, School of Natural Resource Sciences, University of Nebraska at Lincoln,
3236 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE VOLUME 17 Why Has the Land Memory Changed? QI HU ANDSONG FENG Climate and Bio-Atmospheric Sciences Group, School of Natural Resource Sciences, University of Nebraska at Lincoln,
Investigate the influence of the Amazon rainfall on westerly wind anomalies and the 2002 Atlantic Nino using QuikScat, Altimeter and TRMM data
 Investigate the influence of the Amazon rainfall on westerly wind anomalies and the 2002 Atlantic Nino using QuikScat, Altimeter and TRMM data Rong Fu 1, Mike Young 1, Hui Wang 2, Weiqing Han 3 1 School
Investigate the influence of the Amazon rainfall on westerly wind anomalies and the 2002 Atlantic Nino using QuikScat, Altimeter and TRMM data Rong Fu 1, Mike Young 1, Hui Wang 2, Weiqing Han 3 1 School
CLIVAR International Climate of the Twentieth Century (C20C) Project
 CLIVAR International Climate of the Twentieth Century (C20C) Project Chris Folland, UK Met office 6th Climate of the Twentieth Century Workshop, Melbourne, 5-8 Nov 2013 Purpose and basic methodology Initially
CLIVAR International Climate of the Twentieth Century (C20C) Project Chris Folland, UK Met office 6th Climate of the Twentieth Century Workshop, Melbourne, 5-8 Nov 2013 Purpose and basic methodology Initially
First-Order Draft Chapter 3 IPCC WG1 Fourth Assessment Report
 0 Figure... Estimates of linear trends in significant wave height (cm decade - ) for the regions along the major ship routes for the global ocean for the period 0 00. Trends are shown only for the locations
0 Figure... Estimates of linear trends in significant wave height (cm decade - ) for the regions along the major ship routes for the global ocean for the period 0 00. Trends are shown only for the locations
Mediterranean precipitation climatology, seasonal cycle,
 1 2 Mediterranean precipitation climatology, seasonal cycle, and trend as simulated by CMIP5 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Colin Kelley, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Columbia University, 61 Route 9W, Palisades,
1 2 Mediterranean precipitation climatology, seasonal cycle, and trend as simulated by CMIP5 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Colin Kelley, Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Columbia University, 61 Route 9W, Palisades,
Climate Feedbacks from ERBE Data
 Climate Feedbacks from ERBE Data Why Is Lindzen and Choi (2009) Criticized? Zhiyu Wang Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Utah March 9, 2010 / Earth Climate System Outline 1 Introduction
Climate Feedbacks from ERBE Data Why Is Lindzen and Choi (2009) Criticized? Zhiyu Wang Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Utah March 9, 2010 / Earth Climate System Outline 1 Introduction
The Role of Indian Ocean Sea Surface Temperature in Forcing East African Rainfall Anomalies during December January 1997/98
 DECEMBER 1999 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE 3497 The Role of Indian Ocean Sea Surface Temperature in Forcing East African Rainfall Anomalies during December January 1997/98 M. LATIF AND D. DOMMENGET Max-Planck-Institut
DECEMBER 1999 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE 3497 The Role of Indian Ocean Sea Surface Temperature in Forcing East African Rainfall Anomalies during December January 1997/98 M. LATIF AND D. DOMMENGET Max-Planck-Institut
Comparison of Global Mean Temperature Series
 ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH 2(4): 187 192, 2011 www.climatechange.cn DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1248.2011.00187 REVIEW Comparison of Global Mean Temperature Series Xinyu Wen 1,2, Guoli Tang 3, Shaowu Wang
ADVANCES IN CLIMATE CHANGE RESEARCH 2(4): 187 192, 2011 www.climatechange.cn DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1248.2011.00187 REVIEW Comparison of Global Mean Temperature Series Xinyu Wen 1,2, Guoli Tang 3, Shaowu Wang
Methods of assessing the performance of IPCC-AR4 models in simulating Australian rainfall teleconnections with Indo-Pacific climate drivers
 18 th World IMACS / MODSIM Congress, Cairns, Australia 13-17 July 2009 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim09 Methods of assessing the performance of IPCC-AR4 models in simulating Australian rainfall teleconnections
18 th World IMACS / MODSIM Congress, Cairns, Australia 13-17 July 2009 http://mssanz.org.au/modsim09 Methods of assessing the performance of IPCC-AR4 models in simulating Australian rainfall teleconnections
Influence of IOD on the following year s El Niño: robustness across the CMIP models?
 Influence of IOD on the following year s El Niño: robustness across the CMIP models? N.C. Jourdain Climate Change Research Center, University of New South Wales, Sydney M. Lengaigne, J. Vialard, T. Izumo
Influence of IOD on the following year s El Niño: robustness across the CMIP models? N.C. Jourdain Climate Change Research Center, University of New South Wales, Sydney M. Lengaigne, J. Vialard, T. Izumo
From El Nino to Atlantic Nino: pathways as seen in the QuikScat winds
 From El Nino to Atlantic Nino: pathways as seen in the QuikScat winds Rong Fu 1, Lei Huang 1, Hui Wang 2 Presented by Nicole Smith-Downey 1 1 Jackson School of Geosciences, The University of Texas at Austin
From El Nino to Atlantic Nino: pathways as seen in the QuikScat winds Rong Fu 1, Lei Huang 1, Hui Wang 2 Presented by Nicole Smith-Downey 1 1 Jackson School of Geosciences, The University of Texas at Austin
Christopher L. Castro Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Arizona
 Spatiotemporal Variability and Covariability of Temperature, Precipitation, Soil Moisture, and Vegetation in North America for Regional Climate Model Applications Christopher L. Castro Department of Atmospheric
Spatiotemporal Variability and Covariability of Temperature, Precipitation, Soil Moisture, and Vegetation in North America for Regional Climate Model Applications Christopher L. Castro Department of Atmospheric
3. Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 )
 3. Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Basic information on CO 2 with regard to environmental issues Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) is a significant greenhouse gas that has strong absorption bands in the infrared region and
3. Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Basic information on CO 2 with regard to environmental issues Carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) is a significant greenhouse gas that has strong absorption bands in the infrared region and
Conference on Teleconnections in the Atmosphere and Oceans November Fall-to-winter changes in the El Nino teleconnection
 1968-19 Conference on Teleconnections in the Atmosphere and Oceans 17-20 November 2008 Fall-to-winter changes in the El Nino teleconnection BLADE MENDOZA Ileana Universitat de Barcelona, Department D'Astronomia
1968-19 Conference on Teleconnections in the Atmosphere and Oceans 17-20 November 2008 Fall-to-winter changes in the El Nino teleconnection BLADE MENDOZA Ileana Universitat de Barcelona, Department D'Astronomia
The Coupled Model Predictability of the Western North Pacific Summer Monsoon with Different Leading Times
 ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2012, VOL. 5, NO. 3, 219 224 The Coupled Model Predictability of the Western North Pacific Summer Monsoon with Different Leading Times LU Ri-Yu 1, LI Chao-Fan 1,
ATMOSPHERIC AND OCEANIC SCIENCE LETTERS, 2012, VOL. 5, NO. 3, 219 224 The Coupled Model Predictability of the Western North Pacific Summer Monsoon with Different Leading Times LU Ri-Yu 1, LI Chao-Fan 1,
Improved Historical Reconstructions of SST and Marine Precipitation Variations
 Improved Historical Reconstructions of SST and Marine Precipitation Variations Thomas M. Smith 1 Richard W. Reynolds 2 Phillip A. Arkin 3 Viva Banzon 2 1. NOAA/NESDIS/STAR SCSB and CICS, College Park,
Improved Historical Reconstructions of SST and Marine Precipitation Variations Thomas M. Smith 1 Richard W. Reynolds 2 Phillip A. Arkin 3 Viva Banzon 2 1. NOAA/NESDIS/STAR SCSB and CICS, College Park,
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation
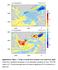 Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Oceanic origin of the interannual and interdecadal variability of the summertime western Pacific subtropical high
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L13701, doi:10.1029/2008gl034584, 2008 Oceanic origin of the interannual and interdecadal variability of the summertime western Pacific
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L13701, doi:10.1029/2008gl034584, 2008 Oceanic origin of the interannual and interdecadal variability of the summertime western Pacific
AMOC Impacts on Climate
 AMOC Impacts on Climate Rong Zhang GFDL/NOAA, Princeton, NJ, USA Paleo-AMOC Workshop, Boulder, CO, USA May 24, 2016 Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) Kuklbrodt et al. 2007 McManus et al.,
AMOC Impacts on Climate Rong Zhang GFDL/NOAA, Princeton, NJ, USA Paleo-AMOC Workshop, Boulder, CO, USA May 24, 2016 Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) Kuklbrodt et al. 2007 McManus et al.,
Understanding Global Environmental Trends and Projections. Ants Leetmaa Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Princeton, NJ 08542
 Understanding Global Environmental Trends and Projections Ants Leetmaa Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Princeton, NJ 08542 Climate Scenarios Used for Attribution Studies of Climate Variability and
Understanding Global Environmental Trends and Projections Ants Leetmaa Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory Princeton, NJ 08542 Climate Scenarios Used for Attribution Studies of Climate Variability and
2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK. June RMS Cat Response
 2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2013 - RMS Cat Response Season Outlook At the start of the 2013 Atlantic hurricane season, which officially runs from June 1 to November 30, seasonal forecasts
2013 ATLANTIC HURRICANE SEASON OUTLOOK June 2013 - RMS Cat Response Season Outlook At the start of the 2013 Atlantic hurricane season, which officially runs from June 1 to November 30, seasonal forecasts
The South Eastern Australian Climate Initiative
 The South Eastern Australian Climate Initiative Phase 2 of the South Eastern Australian Climate Initiative (SEACI) is a three-year (2009 2012), $9 million research program investigating the causes and
The South Eastern Australian Climate Initiative Phase 2 of the South Eastern Australian Climate Initiative (SEACI) is a three-year (2009 2012), $9 million research program investigating the causes and
Lecture 28. El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) part 5
 Lecture 28 El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) part 5 Understanding the phenomenon Until the 60s the data was so scant that it seemed reasonable to consider El Nino as an occasional departure from normal
Lecture 28 El Nino Southern Oscillation (ENSO) part 5 Understanding the phenomenon Until the 60s the data was so scant that it seemed reasonable to consider El Nino as an occasional departure from normal
MPACT OF EL-NINO ON SUMMER MONSOON RAINFALL OF PAKISTAN
 MPACT OF EL-NINO ON SUMMER MONSOON RAINFALL OF PAKISTAN Abdul Rashid 1 Abstract: El-Nino is the dominant mod of inter- annual climate variability on a planetary scale. Its impact is associated worldwide
MPACT OF EL-NINO ON SUMMER MONSOON RAINFALL OF PAKISTAN Abdul Rashid 1 Abstract: El-Nino is the dominant mod of inter- annual climate variability on a planetary scale. Its impact is associated worldwide
Supplemental Material for Evolution of the Atlantic Multidecadal. Variability in a model with an improved North Atlantic Current
 1 Supplemental Material for Evolution of the Atlantic Multidecadal 2 Variability in a model with an improved North Atlantic Current 3 Annika Drews 4 GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel, Kiel,
1 Supplemental Material for Evolution of the Atlantic Multidecadal 2 Variability in a model with an improved North Atlantic Current 3 Annika Drews 4 GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel, Kiel,
Climate Variability and Change Past, Present and Future An Overview
 Climate Variability and Change Past, Present and Future An Overview Dr Jim Salinger National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research Auckland, New Zealand INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON REDUCING VULNERABILITY
Climate Variability and Change Past, Present and Future An Overview Dr Jim Salinger National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research Auckland, New Zealand INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON REDUCING VULNERABILITY
Potential role of the ocean thermostat in determining regional differences in coral reef bleaching events
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L03613, doi:10.1029/2007gl032257, 2008 Potential role of the ocean thermostat in determining regional differences in coral reef bleaching events Joan A. Kleypas,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L03613, doi:10.1029/2007gl032257, 2008 Potential role of the ocean thermostat in determining regional differences in coral reef bleaching events Joan A. Kleypas,
EL NIÑO MODOKI IMPACTS ON AUSTRALIAN RAINFALL
 EL NIÑO MODOKI IMPACTS ON AUSTRALIAN RAINFALL Andréa S. Taschetto*, Alexander Sen Gupta, Caroline C. Ummenhofer and Matthew H. England Climate Change Research Centre (CCRC), University of New South Wales,
EL NIÑO MODOKI IMPACTS ON AUSTRALIAN RAINFALL Andréa S. Taschetto*, Alexander Sen Gupta, Caroline C. Ummenhofer and Matthew H. England Climate Change Research Centre (CCRC), University of New South Wales,
Increasing frequency of extremely severe cyclonic storms over the Arabian Sea
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-017-0008-6 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Increasing frequency of extremely severe cyclonic storms over the Arabian
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters https://doi.org/10.1038/s41558-017-0008-6 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Increasing frequency of extremely severe cyclonic storms over the Arabian
LETTERS. The cause of the fragile relationship between the Pacific El Niño and the Atlantic Niño
 Vol 443 21 September 2006 doi:10.1038/nature05053 The cause of the fragile relationship between the Pacific El Niño and the Atlantic Niño Ping Chang 1, Yue Fang 1, R. Saravanan 2, Link Ji 1 & Howard Seidel
Vol 443 21 September 2006 doi:10.1038/nature05053 The cause of the fragile relationship between the Pacific El Niño and the Atlantic Niño Ping Chang 1, Yue Fang 1, R. Saravanan 2, Link Ji 1 & Howard Seidel
Inter-comparison of Historical Sea Surface Temperature Datasets. Yasunaka, Sayaka (CCSR, Univ. of Tokyo, Japan) Kimio Hanawa (Tohoku Univ.
 Inter-comparison of Historical Sea Surface Temperature Datasets Yasunaka, Sayaka (CCSR, Univ. of Tokyo, Japan) Kimio Hanawa (Tohoku Univ., Japan) < Background > Sea surface temperature (SST) is the observational
Inter-comparison of Historical Sea Surface Temperature Datasets Yasunaka, Sayaka (CCSR, Univ. of Tokyo, Japan) Kimio Hanawa (Tohoku Univ., Japan) < Background > Sea surface temperature (SST) is the observational
Sensitivity of summer precipitation to tropical sea surface temperatures over East Asia in the GRIMs GMP
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 40, 1824 1831, doi:10.1002/grl.50389, 2013 Sensitivity of summer precipitation to tropical sea surface temperatures over East Asia in the GRIMs GMP Eun-Chul Chang, 1
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 40, 1824 1831, doi:10.1002/grl.50389, 2013 Sensitivity of summer precipitation to tropical sea surface temperatures over East Asia in the GRIMs GMP Eun-Chul Chang, 1
Operational event attribution
 Operational event attribution Peter Stott, NCAR, 26 January, 2009 August 2003 Events July 2007 January 2009 January 2009 Is global warming slowing down? Arctic Sea Ice Climatesafety.org climatesafety.org
Operational event attribution Peter Stott, NCAR, 26 January, 2009 August 2003 Events July 2007 January 2009 January 2009 Is global warming slowing down? Arctic Sea Ice Climatesafety.org climatesafety.org
Global Climate Change: Implications for South Florida
 Global Climate Change: Implications for South Florida Amy Clement Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science University of Miami IPCC 2007 + findings since the report + discussion of uncertainty
Global Climate Change: Implications for South Florida Amy Clement Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science University of Miami IPCC 2007 + findings since the report + discussion of uncertainty
AMO- and ENSO-Driven Summertime Circulation and Precipitation Variations in North America
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Papers in Natural Resources Natural Resources, School of 10-1-2012 AMO- and ENSO-Driven Summertime Circulation and Precipitation
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Papers in Natural Resources Natural Resources, School of 10-1-2012 AMO- and ENSO-Driven Summertime Circulation and Precipitation
ENSO and April SAT in MSA. This link is critical for our regression analysis where ENSO and
 Supplementary Discussion The Link between El Niño and MSA April SATs: Our study finds a robust relationship between ENSO and April SAT in MSA. This link is critical for our regression analysis where ENSO
Supplementary Discussion The Link between El Niño and MSA April SATs: Our study finds a robust relationship between ENSO and April SAT in MSA. This link is critical for our regression analysis where ENSO
Role of atmospheric adjustments in the tropical Indian Ocean warming during the 20th century in climate models
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L08712, doi:10.1029/2008gl033631, 2008 Role of atmospheric adjustments in the tropical Indian Ocean warming during the 20th century in
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L08712, doi:10.1029/2008gl033631, 2008 Role of atmospheric adjustments in the tropical Indian Ocean warming during the 20th century in
