The role of magnetic fields during massive star formation
|
|
|
- Della Lawson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The role of magnetic fields during massive star formation Wouter Vlemmings Chalmers University of Technology / Onsala Space Observatory / Nordic ALMA Regional Center with: Gabriele Surcis, Kalle Torstensson, Richard Dodson, Ramiro Franco, Rosy Torres, Huib Jan van Langevelde, Sharmila Goedhart, Chema Torrelles and others.
2 Star formation magnetic fields Strongly magnetized ISM Weakly magnetized stars Strong increase in mass-to-flux ratio a classic problem in star formation (e.g. Mestel & Spitzer 1956) Magnetic fields essential in many current theories of jet launching angular momentum transfer Regulating molecular cloud core collapse Observations are few! 2 /21
3 State of the Art: Massive Star Formation Massive stars Inject significant amounts of energy into the ISM Produce all the heavy elements Low-mass star formation strongly influenced by massive stars Radiation pressure constraint General spherical considerations rule out M > 11M sun non-spherical accretion (disks?) Formation scenario yet unknown Competing formation scenarios: Core collapse and Competitive accretion Key Question: How does the magnetic field affect MSF? 3 /21
4 Competing Massive Star Formation Scenarios Modified low-mass star formation (core accretion): - Increased accretion rates - Disk geometry helps accretion processes - Radiation pressure escapes through outflow cavities Coalescence and competitive accretion: - Massive stars form only in clusters. - Fragmentation and accretion toward objects in the cluster center - At high densities protostars entities merge Bate, Bonnell et al. Pudritz & Banerjee 5 4 /21
5 Competing Massive Star Formation Scenarios Modified low-mass star formation (core accretion): - Increased accretion rates - Disk geometry helps accretion processes - Radiation pressure escapes through outflow cavities Coalescence and competitive accretion: - Massive stars form only in clusters. - Fragmentation and accretion toward objects in the cluster center - At high densities protostars entities merge How to differentiate between both scenarios? - Molecular outflows and accretion disks. - Fragmentation and global collapse. Bate, Bonnell et al. Pudritz & Banerjee 5 5 /21
6 Magnetic fields during massive SF Turbulence, feedback & magnetic fields? Outflows ubiquitous MHD launching? B-fields suppress fragmentation? Field (de)stabilize accretion disks? Most effects close to protostars Need high-density, small scale B-field tracer masers! Less fragmentation for increasing B- field (Bate et al. 7) 6 /21
7 Recent models D. Seifried et al. log(n [cm-2]) 26. t = yr log(n [cm-2]) 26. t = yr x / AU log(bz [G]) 25. y / AU y / AU t = yr y / AU x / AU 1 km/s x / AU 1 km/s 6 log(n [cm-2]) log(n [cm-2]) t = yr -4 - t = yr 1 km/s t = yr log(bz [G]) y / AU y / AU y / AU x / AU 6 1 km/s - - x / AU 6 1 km/s x / AU 6 1 km/s Only weakly magnetized cores form Keplerian disks if turbulence is not present Figure 5. Column density of the disc after yr (left) and yr (middle) for run 26-4 (top) and run (bottom). White dots mark the projected positions of the sink particles, black vectors the velocity field in the midplane. In run 26-4 the disc is well defined with its inner region being subject to fragmentation. In contrast, in run a disc with sub-keplerian motions forms. The bubble like structures in this run are caused by the high magnetic pressure in the midplane driving material outwards (see also Section 4.1). Right: z-component of the magnetic field in the midplane for run 26-4 (top) and run (bottom) at the end of the simulation, i.e. after yr. The tight correlation between field strength and matter is due to the condition of ideal MHD. Note the di erent spatial scales in the upper and lower panel. More strongly magnetized cores form sub-keplerian disks (unless turbulent motions relieve magnetic braking), less collimated outflows but with high accretion and little fragmentation Seifried et al. 211,213 7 /21
8 Polarized SF Masers Maser polarization observed from: OH (1.6 and 6 GHz) Faraday rotation H2O (22 GHz) Shocks SiO (43 and 86 GHz) rare, polarization interpretation CH3OH (methanol, 6.7, 12.2, 36 GHz) Common MSF maser, strong 8 /21
9 Methanol maser magnetic field observations 9 /21
10 The Zeeman splitting of 6.7 GHz methanol R-L splitting observed in 8 ~.1-.5% circular attributed to Zeeman splitting with a coefficient of 49 m/s Gauss -1 B-fields of ~13 mg But: Zeeman coefficient 5 m/s Gauss -1 B-fields order of magnitude higher unrealistic? non-zeeman or wrong coefficient? no indication of non-zeeman! [Anisotropic scattering??] ~1 mg on co-located 6 GHz OH masers Vlemmings et al. 8, 211 A&A New lab data needed to settle the issue! 1/21
11 Sample Results Significant detection in 33/44 SF regions <VZ>=.6 m/s ~13 mg? Field variation across maser spectrum typically within factor 3 Field reversal in 2 sources 11/21
12 Field mapping: Cepheus A HW 2 Cepheus A HW2 ~2 7 pc (Jiménez-Serra et al. 7; Moscadelli et al. 9) Thermal radio jet, ionized gas at ~5 km/s (Curiel et al. 6) Rotating dust (R~33 AU) and molecular gas (R~58 AU) disk structure to outflow (Patel et al. 5, Jiménez-Serra et al. 7, Torrelles et al. 7) made up of at least 3 YSOs (e.g. Comito et al. 7) Flattened 6.7 GHz methanol maser structure near disk plane (R~65 AU, h~3 AU) infall at ~1.7 km/s (Torstensson et al.) SO 2 12 /21
13 Field mapping: Cepheus A HW 2 MERLIN image of the polarization of methanol masers around the outflow Cepheus A HW2 75 AU 13/21
14 Field mapping: Cepheus A HW 2 MERLIN image of the polarization of methanol masers around the outflow Cepheus A HW2 75 AU 14/21
15 Field mapping: Cepheus A HW 2 MERLIN image of the polarization of methanol masers around the outflow Cepheus A HW2 75 AU Submm dust polarization (Curran & Chrysostomou 7) 15/21
16 3D view of the Cepheus A disc Cepheus A HW2 (Vlemmings et al. MNRAS 21) 16/21
17 Infall motions consistent with current models of magnetic accretion Model comparison T=1 K T= K Banerjee & Pudritz 7 17/21
18 DECLINATION (J) Methanol vs. large scale dust W51 IRS2 d W51 e2 DECLINATION (J) RIGHT ASCENSION (J) RIGHT ASCENSION (J) Remarkable agreement between methanol linear polarization EVPAs and those measured from dust polarization (Surcis et al. 212, overlay on Tang et al. ) 18/21
19 Overview of sources al.: EVN group:magneticfield IRAS In Table 4, named as I I , we report all the identified 6.7-GHz CH 3 OH maser features. In particular, they are associated with the source G N and they can be divided in two groups (A and B). Group A is composed of 2 ed around H maser xdensity color. A larization ionp l,are 19/21
20 Magnetic field and outflows Apparent preferred orientation of the outflow along the magnetic field Misalignment <32 degrees <1% chance of random alignment (Surcis et al. 213) 2/21
21 Conclusions Significant Zeeman splitting detected in 33/ GHz methanol maser sources associated with high-mass star formation Corresponds to B =23 ± 5 mg in the methanol region (n H2 ~ cm -3 ) Larger than B crit ~12 mg dynamically important Average field ~6 times higher than average 1.6 GHz OH maser field Interferometric methanol maser observations probe large scale (and possibly 3D) magnetic field structure close to massive protostars Magnetic field regulated infall on Cepheus A HW2 disk Preferentially aligned with outflow direction 21/21
Massive Star Formation with RT-MHD Simulations
 Massive Star Formation with RT-MHD Simulations Robi Banerjee Hamburg University Collaborators: Thomas Peters (Zurich), Daniel Seifried (Hamburg), Philipp Girichidis (MPA), Roberto Galvan-Madrid (UNAM,
Massive Star Formation with RT-MHD Simulations Robi Banerjee Hamburg University Collaborators: Thomas Peters (Zurich), Daniel Seifried (Hamburg), Philipp Girichidis (MPA), Roberto Galvan-Madrid (UNAM,
Magnetic fields in the early phase of massive star formation
 Magnetic fields in the early phase of massive star formation FLASH workshop in Hamburg 16.2.2012 Daniel Seifried Hamburger Sternwarte, University of Hamburg (Robi Banerjee, Ralf Klessen, Ralph Pudritz,
Magnetic fields in the early phase of massive star formation FLASH workshop in Hamburg 16.2.2012 Daniel Seifried Hamburger Sternwarte, University of Hamburg (Robi Banerjee, Ralf Klessen, Ralph Pudritz,
Ionization Feedback in Massive Star Formation
 Ionization Feedback in Massive Star Formation Thomas Peters Institut für Theoretische Astrophysik Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Ralf Klessen, Robi Banerjee (ITA, Heidelberg) Mordecai-Mark
Ionization Feedback in Massive Star Formation Thomas Peters Institut für Theoretische Astrophysik Zentrum für Astronomie der Universität Heidelberg Ralf Klessen, Robi Banerjee (ITA, Heidelberg) Mordecai-Mark
Outflows from young stellar objects and their impact on star formation
 Outflows from young stellar objects and their impact on star formation Robi Banerjee 1, @ 1 : Hamburg Sternewarte, University of Hamburg Gojenbergsweg 112 21209 Hamburg - Germany Jets and outflows are
Outflows from young stellar objects and their impact on star formation Robi Banerjee 1, @ 1 : Hamburg Sternewarte, University of Hamburg Gojenbergsweg 112 21209 Hamburg - Germany Jets and outflows are
Theory of star formation
 Theory of star formation Monday 8th 17.15 18.00 Molecular clouds and star formation: Introduction Tuesday 9th 13.15 14.00 Molecular clouds: structure, physics, and chemistry 16.00 16.45 Cloud cores: statistics
Theory of star formation Monday 8th 17.15 18.00 Molecular clouds and star formation: Introduction Tuesday 9th 13.15 14.00 Molecular clouds: structure, physics, and chemistry 16.00 16.45 Cloud cores: statistics
Protostellar Jets in the ngvla Era
 Protostellar Jets in the ngvla Era Luis F. Rodríguez (IRyA- UNAM, Mexico) In collabora@on with G. Anglada, C. Carrasco- González, L. Zapata, A. Palau, R. Galván- Madrid, C. Rodríguez- Kamenetzky, A. Araudo,
Protostellar Jets in the ngvla Era Luis F. Rodríguez (IRyA- UNAM, Mexico) In collabora@on with G. Anglada, C. Carrasco- González, L. Zapata, A. Palau, R. Galván- Madrid, C. Rodríguez- Kamenetzky, A. Araudo,
First detection of a THz water maser in NGC7538-IRS1
 First detection of a THz water maser in NGC7538-IRS1 Fabrice Herpin Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Bordeaux - France A. Baudry, A.M.S Richards, M.D. Gray, N. Schneider, K.M. Menten, F. Wyrowski, S. Bontemps,
First detection of a THz water maser in NGC7538-IRS1 Fabrice Herpin Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Bordeaux - France A. Baudry, A.M.S Richards, M.D. Gray, N. Schneider, K.M. Menten, F. Wyrowski, S. Bontemps,
SMA observations of Magnetic fields in Star Forming Regions. Josep Miquel Girart Institut de Ciències de l Espai (CSIC-IEEC)
 SMA observations of Magnetic fields in Star Forming Regions Josep Miquel Girart Institut de Ciències de l Espai (CSIC-IEEC) SMA Community Day, July 11, 2011 Simultaneous process of infall and outflow"
SMA observations of Magnetic fields in Star Forming Regions Josep Miquel Girart Institut de Ciències de l Espai (CSIC-IEEC) SMA Community Day, July 11, 2011 Simultaneous process of infall and outflow"
Payne-Scott workshop on Hyper Compact HII regions Sydney, September 8, 2010
 Payne-Scott workshop on Hyper Compact HII regions Sydney, September 8, 2010 Aim Review the characteristics of regions of ionized gas within young massive star forming regions. Will focus the discussion
Payne-Scott workshop on Hyper Compact HII regions Sydney, September 8, 2010 Aim Review the characteristics of regions of ionized gas within young massive star forming regions. Will focus the discussion
Formation of massive stars: a review
 Formation of massive stars: a review Patrick Hennebelle Thanks to: Benoît Commerçon, Marc Joos, Andrea Ciardi Gilles Chabrier, Romain Teyssier How massive stars form? -Can we form massive stars in spite
Formation of massive stars: a review Patrick Hennebelle Thanks to: Benoît Commerçon, Marc Joos, Andrea Ciardi Gilles Chabrier, Romain Teyssier How massive stars form? -Can we form massive stars in spite
PoS(11th EVN Symposium)031
 Detailed structures of accretion and outflow probed by molecular masers in high-mass protostars Joint Institute for VLBI in Europe, Postbus 2, NL-7990 AA Dwingeloo, the Netherlands E-mail: goddi@jive.nl
Detailed structures of accretion and outflow probed by molecular masers in high-mass protostars Joint Institute for VLBI in Europe, Postbus 2, NL-7990 AA Dwingeloo, the Netherlands E-mail: goddi@jive.nl
Probing the embedded phase of star formation with JWST spectroscopy
 Probing the embedded phase of star formation with JWST spectroscopy NIRSPEC Spitzer NGC 1333 Low mass Herschel Cygnus X High mass Jorgensen et al. Gutermuth et al. 10 10 Motte, Henneman et al. E.F. van
Probing the embedded phase of star formation with JWST spectroscopy NIRSPEC Spitzer NGC 1333 Low mass Herschel Cygnus X High mass Jorgensen et al. Gutermuth et al. 10 10 Motte, Henneman et al. E.F. van
Brown Dwarf Formation and Jet Propagation in Core Collapse Simulations
 Brown Dwarf Formation and Jet Propagation in Core Collapse Simulations Knot Knot Cavity (proto-b.d) Observation Riaz et al. (2017) Masahiro N Machida (Kyushu Univ.) Clumps B.D mass object Simulation Collaborators:
Brown Dwarf Formation and Jet Propagation in Core Collapse Simulations Knot Knot Cavity (proto-b.d) Observation Riaz et al. (2017) Masahiro N Machida (Kyushu Univ.) Clumps B.D mass object Simulation Collaborators:
Interferometric Observations of S140-IRS1
 Interferometric Observations of S140-IRS1 e-merlin early science workshop April 2014 Luke T. Maud University of Leeds, UK Melvin G. Hoare University of Leeds Star formation scenario Collapse of a core
Interferometric Observations of S140-IRS1 e-merlin early science workshop April 2014 Luke T. Maud University of Leeds, UK Melvin G. Hoare University of Leeds Star formation scenario Collapse of a core
Collapse of Massive Cloud Cores
 Collapse of Massive Cloud Cores Robi Banerjee ITA, University of Heidelberg Based on 3D MHD, AMR* Simulations * Adaptive Mesh Refinement Collapse of Hydrostatic Cores Cloud formation by TI Slowly rotating
Collapse of Massive Cloud Cores Robi Banerjee ITA, University of Heidelberg Based on 3D MHD, AMR* Simulations * Adaptive Mesh Refinement Collapse of Hydrostatic Cores Cloud formation by TI Slowly rotating
Disk Formation and Jet Driving in Collapsing Cloud Cores
 Disk Formation and Jet Driving in Collapsing Cloud Cores Masahiro Machida (Kyushu University) Star Formation Process Observations have shown that Low-velocity outflows and high-velocity jets are ubiquitous
Disk Formation and Jet Driving in Collapsing Cloud Cores Masahiro Machida (Kyushu University) Star Formation Process Observations have shown that Low-velocity outflows and high-velocity jets are ubiquitous
Formation of massive stars : a review
 Formation of massive stars : a review Patrick Hennebelle (a former «star formation ignorant» Ant s postdoc) Benoit Commerçon, Marc Joos, Andrea Ciardi, Gilles Chabrier One of the Constellation network
Formation of massive stars : a review Patrick Hennebelle (a former «star formation ignorant» Ant s postdoc) Benoit Commerçon, Marc Joos, Andrea Ciardi, Gilles Chabrier One of the Constellation network
An overview of star formation
 An overview of star formation Paul Clark ITA: Ralf Klessen Robi Banerjee Simon Glover Ian Bonnell Clare Dobbs Jim Dale Why study star formation? Stars chemically the enrich the Universe, so star formation
An overview of star formation Paul Clark ITA: Ralf Klessen Robi Banerjee Simon Glover Ian Bonnell Clare Dobbs Jim Dale Why study star formation? Stars chemically the enrich the Universe, so star formation
Zooming into high-mass star-forming regions
 Zooming into high-mass star-forming regions Henrik Beuther SMA ATCA PdBI VLA Important questions - What are the characteristics of accretion disks/large toroid in high-mass star formation? - Can we constrain
Zooming into high-mass star-forming regions Henrik Beuther SMA ATCA PdBI VLA Important questions - What are the characteristics of accretion disks/large toroid in high-mass star formation? - Can we constrain
! what determines the initial mass function of stars (IMF)? dn /dm
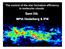 ! what determines the initial mass function of stars (IMF)? dn /dm M ! what determines the initial mass function of stars (IMF)?! What determines the total mass of stars that can form in the cloud? dn
! what determines the initial mass function of stars (IMF)? dn /dm M ! what determines the initial mass function of stars (IMF)?! What determines the total mass of stars that can form in the cloud? dn
Frédérique Motte (AIM Paris-Saclay)
 Clusters of high-mass protostars: From extreme clouds to minibursts of star formation Frédérique Motte (AIM Paris-Saclay) Special thanks to S. Bontemps, T. Csengeri, P. Didelon, M. Hennemann, T. Hill,
Clusters of high-mass protostars: From extreme clouds to minibursts of star formation Frédérique Motte (AIM Paris-Saclay) Special thanks to S. Bontemps, T. Csengeri, P. Didelon, M. Hennemann, T. Hill,
Disk+outflow system in G
 EAVW 2018 @ PyeongChang Disk+outflow system in G25.82-0.17 Jungha Kim (D2/SOKENDAI/NAOJ) Tomoya Hirota, Kee-Tae Kim, KaVA SWG for star formation CONTENTS Introduction Observations Results - KaVA imaging
EAVW 2018 @ PyeongChang Disk+outflow system in G25.82-0.17 Jungha Kim (D2/SOKENDAI/NAOJ) Tomoya Hirota, Kee-Tae Kim, KaVA SWG for star formation CONTENTS Introduction Observations Results - KaVA imaging
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 20 Mar 2012
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 20 Mar 2012 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 20 Mar 2012](/thumbs/74/70387496.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. 18658 c ESO 2012 March 22, 2012 EVN observations of 6.7 GHz methanol maser polarization in massive star-forming regions. G. Surcis,1,2, W.H.T. Vlemmings 1,3, H.J.
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. 18658 c ESO 2012 March 22, 2012 EVN observations of 6.7 GHz methanol maser polarization in massive star-forming regions. G. Surcis,1,2, W.H.T. Vlemmings 1,3, H.J.
Lecture 26 Clouds, Clumps and Cores. Review of Molecular Clouds
 Lecture 26 Clouds, Clumps and Cores 1. Review of Dense Gas Observations 2. Atomic Hydrogen and GMCs 3. Formation of Molecular Clouds 4. Internal Structure 5. Observing Cores 6. Preliminary Comments on
Lecture 26 Clouds, Clumps and Cores 1. Review of Dense Gas Observations 2. Atomic Hydrogen and GMCs 3. Formation of Molecular Clouds 4. Internal Structure 5. Observing Cores 6. Preliminary Comments on
The large-scale magnetic field in protoplanetary disks
 The large-scale magnetic field in protoplanetary disks Jérôme Guilet MPA, Garching Max-Planck-Princeton center for plasma physics In collaboration with Gordon Ogilvie (Cambridge) 1/24 Talk outline 1) Impacts
The large-scale magnetic field in protoplanetary disks Jérôme Guilet MPA, Garching Max-Planck-Princeton center for plasma physics In collaboration with Gordon Ogilvie (Cambridge) 1/24 Talk outline 1) Impacts
Dead zones in protoplanetary discs
 Dead zones in protoplanetary discs Mark Wardle Macquarie University Raquel Salmeron (ANU) BP Pandey (Macquarie) Protoplanetary discs Magnetic fields Dead zones MRI and diffusion Modification to dead zones
Dead zones in protoplanetary discs Mark Wardle Macquarie University Raquel Salmeron (ANU) BP Pandey (Macquarie) Protoplanetary discs Magnetic fields Dead zones MRI and diffusion Modification to dead zones
The Early Phases of Disc Formation and Disc Evolution
 The Early Phases of Disc Formation and Disc Evolution modelling prospective Robi Banerjee Hamburger Sternwarte Topics Angular momentum Fragmentation Disc-envelope evolution Initial angular momentum of
The Early Phases of Disc Formation and Disc Evolution modelling prospective Robi Banerjee Hamburger Sternwarte Topics Angular momentum Fragmentation Disc-envelope evolution Initial angular momentum of
Water released in a protostellar accretion burst
 CENTRE FOR STAR AND PLANET FORMATION Water released in a protostellar accretion burst Per Bjerkeli J. K. Jørgensen, E. A. Bergin, S. Frimann, D. Harsono, S. K. Jacobsen, M. Persson, J. Lindberg, N. Sakai,
CENTRE FOR STAR AND PLANET FORMATION Water released in a protostellar accretion burst Per Bjerkeli J. K. Jørgensen, E. A. Bergin, S. Frimann, D. Harsono, S. K. Jacobsen, M. Persson, J. Lindberg, N. Sakai,
Deflection of a Protostellar Outflow: The Bent Story of NGC 1333 IRAS 4A. NGC 1333 Cluster Forming Region. Driving Source. IRAS 4A Protobinary System
 Deflection of a Protostellar Outflow: The Bent Story of NGC 1333 IRAS 4A SNU Colloquium 2006. 3. 22. Minho Choi Evolutionary Scenario of Low-Mass Young Stellar Objects Classification Spectral Energy Distribution
Deflection of a Protostellar Outflow: The Bent Story of NGC 1333 IRAS 4A SNU Colloquium 2006. 3. 22. Minho Choi Evolutionary Scenario of Low-Mass Young Stellar Objects Classification Spectral Energy Distribution
Formation Mechanisms of Brown Dwarfs: Observations & Theories. Dan Li April 2009
 Formation Mechanisms of Brown Dwarfs: Observations & Theories Dan Li April 2009 What is brown dwarf (BD)? BD Mass : upper-limit ~ 0.075 M lower-limit ~ 0.013 M (?) Differences between BD and giant planet:
Formation Mechanisms of Brown Dwarfs: Observations & Theories Dan Li April 2009 What is brown dwarf (BD)? BD Mass : upper-limit ~ 0.075 M lower-limit ~ 0.013 M (?) Differences between BD and giant planet:
From Massive Cores to Massive Stars
 From Massive Cores to Massive Stars Mark Krumholz Princeton University / UC Santa Cruz Collaborators: Richard Klein, Christopher McKee (UC Berkeley) Kaitlin Kratter, Christopher Matzner (U. Toronto) Jonathan
From Massive Cores to Massive Stars Mark Krumholz Princeton University / UC Santa Cruz Collaborators: Richard Klein, Christopher McKee (UC Berkeley) Kaitlin Kratter, Christopher Matzner (U. Toronto) Jonathan
Formation of Rotationally Supported Protostellar Disks: Some Theoretical Difficulties. Ruben Krasnopolsky Zhi-Yun Li Hsien Shang
 Formation of Rotationally Supported Protostellar Disks: Some Theoretical Difficulties Ruben Krasnopolsky Zhi-Yun Li Hsien Shang Protostars and disks Jet Envelope Jet Inside a protostellar core, a star
Formation of Rotationally Supported Protostellar Disks: Some Theoretical Difficulties Ruben Krasnopolsky Zhi-Yun Li Hsien Shang Protostars and disks Jet Envelope Jet Inside a protostellar core, a star
High resolution magnetic field measurements in high-mass star-forming regions
 High resolution magnetic field measurements in high-mass star-forming regions Dissertation zur Erlangung des Doktorgrades (Dr. rer. nat.) der Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Fakultät der Rheinischen
High resolution magnetic field measurements in high-mass star-forming regions Dissertation zur Erlangung des Doktorgrades (Dr. rer. nat.) der Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftlichen Fakultät der Rheinischen
!"#$%&'(#)*'+*,+ %#--./&+0&'-&+1*"&-+ 0*2'+(*+! #"#1(&".9.'$+:"*(*1;<(&"-+
 !"#$%&'(#)*'+*,+ %#--./&+0&'-&+1*"&-+ 0*2'+(*+!3444+567+ 18#"#1(&".9.'$+:"*(*1;
!"#$%&'(#)*'+*,+ %#--./&+0&'-&+1*"&-+ 0*2'+(*+!3444+567+ 18#"#1(&".9.'$+:"*(*1;
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 7 Feb 2019
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 7 Feb 2019 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ga] 7 Feb 2019](/thumbs/88/116483529.jpg) Draft version February 8, 2019 Typeset using LATEX twocolumn style in AASTeX62 An Ordered Envelope-disk Transition in the Massive Protostellar Source G339.88-1.26 Yichen Zhang, 1 Jonathan C. Tan, 2, 3
Draft version February 8, 2019 Typeset using LATEX twocolumn style in AASTeX62 An Ordered Envelope-disk Transition in the Massive Protostellar Source G339.88-1.26 Yichen Zhang, 1 Jonathan C. Tan, 2, 3
Chapter 16 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition. Star Birth Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 16 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Birth 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Star Birth The dust and gas between the star in our galaxy is referred to as the Interstellar medium (ISM).
Chapter 16 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Star Birth 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Star Birth The dust and gas between the star in our galaxy is referred to as the Interstellar medium (ISM).
Radiative MHD. in Massive Star Formation and Accretion Disks. Rolf Kuiper, Hubert Klahr, Mario Flock, Henrik Beuther, Thomas Henning
 Radiative MHD in Massive Star Formation and Accretion Disks, Hubert Klahr, Mario Flock, Henrik Beuther, Thomas Henning, Radiative MHD with Makemake and Pluto : We developed a fast 3D frequency-dependent
Radiative MHD in Massive Star Formation and Accretion Disks, Hubert Klahr, Mario Flock, Henrik Beuther, Thomas Henning, Radiative MHD with Makemake and Pluto : We developed a fast 3D frequency-dependent
Polarimetry with the SMA
 Polarimetry with the SMA Ramprasad Rao Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Academia Sinica (ASIAA) Collaborators: J. M. Girart (IEEC-CSIC), D. P. Marrone (NRAO/U. Chicago), Y. Tang (ASIAA), and a
Polarimetry with the SMA Ramprasad Rao Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Academia Sinica (ASIAA) Collaborators: J. M. Girart (IEEC-CSIC), D. P. Marrone (NRAO/U. Chicago), Y. Tang (ASIAA), and a
Origin of high-mass protostars in Cygnus-X
 T. Csengeri Service d Astrophysique, CEA-Saclay Supervisor: Co-advisor: Collaborators: S. Bontemps N. Schneider F. Motte F. Gueth P. Hennebelle S. Dib Ph. André 7. April 2010 - From stars to Galaxies,
T. Csengeri Service d Astrophysique, CEA-Saclay Supervisor: Co-advisor: Collaborators: S. Bontemps N. Schneider F. Motte F. Gueth P. Hennebelle S. Dib Ph. André 7. April 2010 - From stars to Galaxies,
Observational signatures of proto brown dwarf formation in protostellar disks
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 84, 88 c SAIt 213 Memorie della Observational signatures of proto brown dwarf formation in protostellar disks O. V. Zakhozhay 1, E. I. Vorobyov 2,3, and M. M. Dunham 4 1 Main Astronomical
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 84, 88 c SAIt 213 Memorie della Observational signatures of proto brown dwarf formation in protostellar disks O. V. Zakhozhay 1, E. I. Vorobyov 2,3, and M. M. Dunham 4 1 Main Astronomical
Near-Infrared Imaging Observations of the Orion A-W Star Forming Region
 Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. Vol. 2 (2002), No. 3, 260 265 ( http: /www.chjaa.org or http: /chjaa.bao.ac.cn ) Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics Near-Infrared Imaging Observations of the Orion
Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. Vol. 2 (2002), No. 3, 260 265 ( http: /www.chjaa.org or http: /chjaa.bao.ac.cn ) Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics Near-Infrared Imaging Observations of the Orion
Lecture 23 Internal Structure of Molecular Clouds
 Lecture 23 Internal Structure of Molecular Clouds 1. Location of the Molecular Gas 2. The Atomic Hydrogen Content 3. Formation of Clouds 4. Clouds, Clumps and Cores 5. Observing Molecular Cloud Cores References
Lecture 23 Internal Structure of Molecular Clouds 1. Location of the Molecular Gas 2. The Atomic Hydrogen Content 3. Formation of Clouds 4. Clouds, Clumps and Cores 5. Observing Molecular Cloud Cores References
Does magnetic-field-angular-momentum misalignment strengthens or weakens magnetic braking? (Is magnetic braking dynamically important?
 Does magnetic-field-angular-momentum misalignment strengthens or weakens magnetic braking? (Is magnetic braking dynamically important?) Yusuke Tsukamoto Kagoshima University S. Okuzumi, K. Iwasaki, M.
Does magnetic-field-angular-momentum misalignment strengthens or weakens magnetic braking? (Is magnetic braking dynamically important?) Yusuke Tsukamoto Kagoshima University S. Okuzumi, K. Iwasaki, M.
GMC as a site of high-mass star formation
 ALMA Image: N159W GMC as a site of high-mass star formation From galaxy evolution to individual star formation kpc 1-100pc GMCs: 10 4-10 6 Mo n(h 2 ) ~ 1000cm -3 Clumps, Cores 10 2-10 3 Mo n(h 2 ) ~ >10
ALMA Image: N159W GMC as a site of high-mass star formation From galaxy evolution to individual star formation kpc 1-100pc GMCs: 10 4-10 6 Mo n(h 2 ) ~ 1000cm -3 Clumps, Cores 10 2-10 3 Mo n(h 2 ) ~ >10
Unraveling the Envelope and Disk: The ALMA Perspective
 Unraveling the Envelope and Disk: The ALMA Perspective Leslie Looney (UIUC) Lee Mundy (UMd), Hsin-Fang Chiang (UIUC), Kostas Tassis (UChicago), Woojin Kwon (UIUC) The Early Disk Disks are probable generic
Unraveling the Envelope and Disk: The ALMA Perspective Leslie Looney (UIUC) Lee Mundy (UMd), Hsin-Fang Chiang (UIUC), Kostas Tassis (UChicago), Woojin Kwon (UIUC) The Early Disk Disks are probable generic
Anatomy of the S255-S257 complex - Triggered high-mass star formation
 Proceedings Title IAU Symposium Proceedings IAU Symposium No. IAUS237, 2006 A.C. Editor, B.D. Editor & C.E. Editor, eds. c 2006 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X Anatomy of
Proceedings Title IAU Symposium Proceedings IAU Symposium No. IAUS237, 2006 A.C. Editor, B.D. Editor & C.E. Editor, eds. c 2006 International Astronomical Union DOI: 00.0000/X000000000000000X Anatomy of
Collapse of magnetized dense cores. Is there a fragmentation crisis?
 Collapse of magnetized dense cores Is there a fragmentation crisis? Patrick Hennebelle (ENS-Observatoire de Paris) Collaborators: Benoît Commerçon, Andréa Ciardi, Sébastien Fromang, Romain Teyssier, Philippe
Collapse of magnetized dense cores Is there a fragmentation crisis? Patrick Hennebelle (ENS-Observatoire de Paris) Collaborators: Benoît Commerçon, Andréa Ciardi, Sébastien Fromang, Romain Teyssier, Philippe
Masers and Star Formation
 Masers and Star Formation A Review Vincent L. Fish 12 March 2007 IAU Symposium 242: Astrophysical Masers and Their Environments Alice Springs, NT, Australia Introduction Review of literature regarding
Masers and Star Formation A Review Vincent L. Fish 12 March 2007 IAU Symposium 242: Astrophysical Masers and Their Environments Alice Springs, NT, Australia Introduction Review of literature regarding
Cosmic Evolution, Part II. Heavy Elements to Molecules
 Cosmic Evolution, Part II Heavy Elements to Molecules First a review of terminology: Element Atom Electro- magnetic Electrons Nucleus Electromagnetic Strong Nuclear Compound Molecule Protons Neutrons Neutral
Cosmic Evolution, Part II Heavy Elements to Molecules First a review of terminology: Element Atom Electro- magnetic Electrons Nucleus Electromagnetic Strong Nuclear Compound Molecule Protons Neutrons Neutral
Star Formation. Stellar Birth
 Star Formation Lecture 12 Stellar Birth Since stars don t live forever, then they must be born somewhere and at some time in the past. How does this happen? And when stars are born, so are planets! 1 Molecular
Star Formation Lecture 12 Stellar Birth Since stars don t live forever, then they must be born somewhere and at some time in the past. How does this happen? And when stars are born, so are planets! 1 Molecular
(Numerical) study of the collapse and of the fragmentation of prestellar dense core
 (Numerical) study of the collapse and of the fragmentation of prestellar dense core Benoît Commerçon Supervisors: E. Audit, G. Chabrier and P. Hennebelle Collaborator: R. Teyssier (3D - AMR) CEA/DSM/IRFU/SAp
(Numerical) study of the collapse and of the fragmentation of prestellar dense core Benoît Commerçon Supervisors: E. Audit, G. Chabrier and P. Hennebelle Collaborator: R. Teyssier (3D - AMR) CEA/DSM/IRFU/SAp
Characterization of methanol as a magnetic field tracer in star-forming regions
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters https://doi.org/10.1038/s41550-017-0341-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Characterization of methanol as a magnetic field tracer in star-forming regions
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters https://doi.org/10.1038/s41550-017-0341-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Characterization of methanol as a magnetic field tracer in star-forming regions
PoS(AASKA14)121. Radio Jets in Young Stellar Objects with the SKA. Guillem Anglada. Luis F. Rodríguez
 Radio Jets in Young Stellar Objects with the SKA Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía, CSIC, Spain E-mail: guillem@iaa.es Luis F. Rodríguez Centro de Radioastronomía y Astrofísica, UNAM, México E-mail:
Radio Jets in Young Stellar Objects with the SKA Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía, CSIC, Spain E-mail: guillem@iaa.es Luis F. Rodríguez Centro de Radioastronomía y Astrofísica, UNAM, México E-mail:
The methanol maser ring G after 9 years
 The methanol maser ring G23.657.127 after 9 years Torun Centre for Astronomy, Faculty of Physics, Astronomy and Informatics, Nicolaus Copernicus University, Poland E-mail: annan@astro.umk.pl Alberto Sanna
The methanol maser ring G23.657.127 after 9 years Torun Centre for Astronomy, Faculty of Physics, Astronomy and Informatics, Nicolaus Copernicus University, Poland E-mail: annan@astro.umk.pl Alberto Sanna
Stellar evolution Part I of III Star formation
 Stellar evolution Part I of III Star formation The interstellar medium (ISM) The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful
Stellar evolution Part I of III Star formation The interstellar medium (ISM) The space between the stars is not completely empty, but filled with very dilute gas and dust, producing some of the most beautiful
The Competitive Accretion Debate
 The Competitive Accretion Debate 1,2 Paul C. Clark 2 Ralf S. Klessen 3 Ian A. Bonnell 3 Rowan J. Smith 1 KITP 2 University of Heidelberg 3 University of St Andrews What is CA and how does it work? Theory
The Competitive Accretion Debate 1,2 Paul C. Clark 2 Ralf S. Klessen 3 Ian A. Bonnell 3 Rowan J. Smith 1 KITP 2 University of Heidelberg 3 University of St Andrews What is CA and how does it work? Theory
Challenges for the Study of Hot Cores with ALMA: NGC 6334I
 Challenges for the Study of Hot Cores with ALMA: NGC 6334I Crystal Brogan (NRAO/North American ALMA Science Center) Collaborators: Todd Hunter (NRAO) Remy Indebetouw (UVa/NRAO), Ken (Taco) Young (CfA),
Challenges for the Study of Hot Cores with ALMA: NGC 6334I Crystal Brogan (NRAO/North American ALMA Science Center) Collaborators: Todd Hunter (NRAO) Remy Indebetouw (UVa/NRAO), Ken (Taco) Young (CfA),
Continuum and Line ALMA band 5: the supergiant VY CMa
 Continuum and Line Polarisation @ ALMA band 5: the supergiant VY CMa Wouter Vlemmings, Chalmers Univ. of Technology w. Theo Khouri, Daniel Tafoya, Ivan Marti-Vidal, Liz Humphreys, Anita Richards, Eamon
Continuum and Line Polarisation @ ALMA band 5: the supergiant VY CMa Wouter Vlemmings, Chalmers Univ. of Technology w. Theo Khouri, Daniel Tafoya, Ivan Marti-Vidal, Liz Humphreys, Anita Richards, Eamon
Feedback in Galaxy Clusters
 Feedback in Galaxy Clusters Brian Morsony University of Maryland 1 Not talking about Galaxy-scale feedback Local accretion disk feedback 2 Outline Galaxy cluster properties Cooling flows the need for feedback
Feedback in Galaxy Clusters Brian Morsony University of Maryland 1 Not talking about Galaxy-scale feedback Local accretion disk feedback 2 Outline Galaxy cluster properties Cooling flows the need for feedback
Chapter 11 The Formation and Structure of Stars
 Chapter 11 The Formation and Structure of Stars Guidepost The last chapter introduced you to the gas and dust between the stars that are raw material for new stars. Here you will begin putting together
Chapter 11 The Formation and Structure of Stars Guidepost The last chapter introduced you to the gas and dust between the stars that are raw material for new stars. Here you will begin putting together
The Birth Of Stars. How do stars form from the interstellar medium Where does star formation take place How do we induce star formation
 Goals: The Birth Of Stars How do stars form from the interstellar medium Where does star formation take place How do we induce star formation Interstellar Medium Gas and dust between stars is the interstellar
Goals: The Birth Of Stars How do stars form from the interstellar medium Where does star formation take place How do we induce star formation Interstellar Medium Gas and dust between stars is the interstellar
FLASH Code Tutorial. part III sink particles & feedback. Robi Banerjee Hamburger Sternwarte
 FLASH Code Tutorial part III sink particles & feedback Robi Banerjee Hamburger Sternwarte banerjee@hs.uni-hamburg.de Motivation: modelling of dense regions in collapse simulations, e.g. star formation
FLASH Code Tutorial part III sink particles & feedback Robi Banerjee Hamburger Sternwarte banerjee@hs.uni-hamburg.de Motivation: modelling of dense regions in collapse simulations, e.g. star formation
Cosmic Evolution, Part II. Heavy Elements to Molecules
 Cosmic Evolution, Part II Heavy Elements to Molecules Heavy elements molecules First a review of terminology: Electromagnetic Electrons Element Atom Nucleus Compound Molecule Electromagnetic Strong Nuclear
Cosmic Evolution, Part II Heavy Elements to Molecules Heavy elements molecules First a review of terminology: Electromagnetic Electrons Element Atom Nucleus Compound Molecule Electromagnetic Strong Nuclear
The Most Detailed Picture Yet of a Massive Star in Formation
 The Most Detailed Picture Yet of a Massive Star in Formation L. Greenhill (CfA/Kavli Inst./Berkeley) How do high-mass stars (M *»1 M ) form? What lies < 200 AU from high-mass YSOs? Do magnetic fields drive
The Most Detailed Picture Yet of a Massive Star in Formation L. Greenhill (CfA/Kavli Inst./Berkeley) How do high-mass stars (M *»1 M ) form? What lies < 200 AU from high-mass YSOs? Do magnetic fields drive
The dynamics of photon-dominated regions (PDRs)
 The dynamics of photon-dominated regions (PDRs) V. Ossenkopf, M. Röllig, N. Schneider, B. Mookerjea, Z. Makai, O. Ricken, P. Pilleri, Y. Okada, M. Gerin Page 1 Main question: What happens here? Impact
The dynamics of photon-dominated regions (PDRs) V. Ossenkopf, M. Röllig, N. Schneider, B. Mookerjea, Z. Makai, O. Ricken, P. Pilleri, Y. Okada, M. Gerin Page 1 Main question: What happens here? Impact
Astr 2310 Thurs. March 23, 2017 Today s Topics
 Astr 2310 Thurs. March 23, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 16: The Interstellar Medium and Star Formation Interstellar Dust and Dark Nebulae Interstellar Dust Dark Nebulae Interstellar Reddening Interstellar
Astr 2310 Thurs. March 23, 2017 Today s Topics Chapter 16: The Interstellar Medium and Star Formation Interstellar Dust and Dark Nebulae Interstellar Dust Dark Nebulae Interstellar Reddening Interstellar
Three Major Components
 The Milky Way Three Major Components Bulge young and old stars Disk young stars located in spiral arms Halo oldest stars and globular clusters Components are chemically, kinematically, and spatially distinct
The Milky Way Three Major Components Bulge young and old stars Disk young stars located in spiral arms Halo oldest stars and globular clusters Components are chemically, kinematically, and spatially distinct
STUDYING COMPACT RADIO SOURCES ASSOCIATED WITH UCHII REGIONS
 STUDYING COMPACT RADIO SOURCES ASSOCIATED WITH UCHII REGIONS Josep Maria Masqué Saumell Departamento de Astronomía Universidad de Guanajuato Collaborators: Universidad de Guanajuato: Miguel Angel Trinidad,
STUDYING COMPACT RADIO SOURCES ASSOCIATED WITH UCHII REGIONS Josep Maria Masqué Saumell Departamento de Astronomía Universidad de Guanajuato Collaborators: Universidad de Guanajuato: Miguel Angel Trinidad,
The Superbubble Power Problem: Overview and Recent Developments. S. Oey
 The Superbubble Power Problem: Overview and Recent Developments S. Oey It has been known for decades that superbubbles generated by massive star winds and supernovae are smaller than expected based on
The Superbubble Power Problem: Overview and Recent Developments S. Oey It has been known for decades that superbubbles generated by massive star winds and supernovae are smaller than expected based on
Astronomy. Astrophysics. EVN observations of 6.7 GHz methanol maser polarization in massive star-forming regions. II. First statistical results
 A&A 556, A73 (2013) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201321501 c ESO 2013 Astronomy & Astrophysics EVN observations of 6.7 GHz methanol maser polarization in massive star-forming regions II. First statistical results
A&A 556, A73 (2013) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201321501 c ESO 2013 Astronomy & Astrophysics EVN observations of 6.7 GHz methanol maser polarization in massive star-forming regions II. First statistical results
Kengo TOMIDA Kohji Tomisaka, Masahiro N. Machida, Tomoaki Matsumoto, Satoshi Okuzumi, Yasunori Hori
 09/19/2014 Department of Astrophysical Sciences, Princeton University Department of Physics, University of Tokyo JSPS Research Fellow Kengo TOMIDA Kohji Tomisaka, Masahiro N. Machida, Tomoaki Matsumoto,
09/19/2014 Department of Astrophysical Sciences, Princeton University Department of Physics, University of Tokyo JSPS Research Fellow Kengo TOMIDA Kohji Tomisaka, Masahiro N. Machida, Tomoaki Matsumoto,
Magnetic fields and massive star formation. Qizhou Zhang Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics
 Magnetic fields and massive star formation Qizhou Zhang Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Role of Magnetic Field in Star Formation Cloud scale: formation/support magnetic or turbulent? Clump
Magnetic fields and massive star formation Qizhou Zhang Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Role of Magnetic Field in Star Formation Cloud scale: formation/support magnetic or turbulent? Clump
MASSIVE STAR FORMATION
 MASSIVE STAR FORMATION PP VI Heidelberg July 16, 2013 Hubble Heritage image of S 106 Jonathan Tan Maria Beltran Paola Caselli Francesco Fontani Asuncion Fuente Mark Krumholz Christopher McKee Andrea Stolte
MASSIVE STAR FORMATION PP VI Heidelberg July 16, 2013 Hubble Heritage image of S 106 Jonathan Tan Maria Beltran Paola Caselli Francesco Fontani Asuncion Fuente Mark Krumholz Christopher McKee Andrea Stolte
Philamentary Structure and Velocity Gradients in the Orion A Cloud
 Red: CO from Mini survey Orion B Philamentary Structure and Velocity Gradients in the Orion A Cloud Spitzer Orion Cloud Survey: 10 sq. degrees in Orion A and Orion B mapped between 2004-2009 Orion A Green
Red: CO from Mini survey Orion B Philamentary Structure and Velocity Gradients in the Orion A Cloud Spitzer Orion Cloud Survey: 10 sq. degrees in Orion A and Orion B mapped between 2004-2009 Orion A Green
Outflows in regions of massive star formation. Suzanne Ramsay (ESO), Watson Varricatt (UKIRT), Chris Davis (NSF)
 Outflows in regions of massive star formation Suzanne Ramsay (ESO), Watson Varricatt (UKIRT), Chris Davis (NSF) How do massive stars form? Do high mass stars (>8Msolar) form in the same way as low mass
Outflows in regions of massive star formation Suzanne Ramsay (ESO), Watson Varricatt (UKIRT), Chris Davis (NSF) How do massive stars form? Do high mass stars (>8Msolar) form in the same way as low mass
Star formation. Protostellar accretion disks
 Star formation Protostellar accretion disks Summary of previous lectures and goal for today Collapse Protostars - main accretion phase - not visible in optical (dust envelope) Pre-main-sequence phase -
Star formation Protostellar accretion disks Summary of previous lectures and goal for today Collapse Protostars - main accretion phase - not visible in optical (dust envelope) Pre-main-sequence phase -
3/1/18 LETTER. Instructors: Jim Cordes & Shami Chatterjee. Reading: as indicated in Syllabus on web
 Astro 2299 The Search for Life in the Universe Lecture 9 Last time: Star formation Formation of protostars and planetary systems This time A few things about the epoch of reionization and free fall times
Astro 2299 The Search for Life in the Universe Lecture 9 Last time: Star formation Formation of protostars and planetary systems This time A few things about the epoch of reionization and free fall times
Multi-Physics of Feedback in Massive Star Formation
 Multi-Physics of Feedback in Massive Star Formation Rolf Kuiper1,2 H. W. Yorke3, N. J. Turner3, T. Hosokawa4 1 - Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, University of Tübingen, Germany 2 - Emmy Noether
Multi-Physics of Feedback in Massive Star Formation Rolf Kuiper1,2 H. W. Yorke3, N. J. Turner3, T. Hosokawa4 1 - Institute of Astronomy and Astrophysics, University of Tübingen, Germany 2 - Emmy Noether
The FIR-Radio Correlation & Implications for GLAST Observations of Starburst Galaxies Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley)
 The FIR-Radio Correlation & Implications for GLAST Observations of Starburst Galaxies Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) w/ Todd Thompson & Eli Waxman Thompson, Quataert, & Waxman 2007, ApJ, 654, 219 Thompson,
The FIR-Radio Correlation & Implications for GLAST Observations of Starburst Galaxies Eliot Quataert (UC Berkeley) w/ Todd Thompson & Eli Waxman Thompson, Quataert, & Waxman 2007, ApJ, 654, 219 Thompson,
Number of Stars: 100 billion (10 11 ) Mass : 5 x Solar masses. Size of Disk: 100,000 Light Years (30 kpc)
 THE MILKY WAY GALAXY Type: Spiral galaxy composed of a highly flattened disk and a central elliptical bulge. The disk is about 100,000 light years (30kpc) in diameter. The term spiral arises from the external
THE MILKY WAY GALAXY Type: Spiral galaxy composed of a highly flattened disk and a central elliptical bulge. The disk is about 100,000 light years (30kpc) in diameter. The term spiral arises from the external
Protostars and pre-main sequence evolution. Definitions. Timescales
 Protostars and pre-main sequence evolution 1. Timescales 2. Early growth and collapse 3. Dust envelope 4. Stellar structure I. Mass-radius relation II. Deuterium burning III. Lithium destruction IV. Hydrogen
Protostars and pre-main sequence evolution 1. Timescales 2. Early growth and collapse 3. Dust envelope 4. Stellar structure I. Mass-radius relation II. Deuterium burning III. Lithium destruction IV. Hydrogen
The chemo-dynamical simulations of molecular cloud collapse: why dust properties define the size of circustellar disks.
 The chemo-dynamical simulations of molecular cloud collapse: why dust properties define the size of circustellar disks. Natalia Dzyurkevich (CSUN, ENS Paris) B. Commerçon (ENS Lyon) P. Lesaffre (ENS Paris)
The chemo-dynamical simulations of molecular cloud collapse: why dust properties define the size of circustellar disks. Natalia Dzyurkevich (CSUN, ENS Paris) B. Commerçon (ENS Lyon) P. Lesaffre (ENS Paris)
Stellar Birth. Stellar Formation. A. Interstellar Clouds. 1b. What is the stuff. Astrophysics: Stellar Evolution. A. Interstellar Clouds (Nebulae)
 Astrophysics: Stellar Evolution 1 Stellar Birth Stellar Formation A. Interstellar Clouds (Nebulae) B. Protostellar Clouds 2 C. Protostars Dr. Bill Pezzaglia Updated: 10/02/2006 A. Interstellar Clouds 1.
Astrophysics: Stellar Evolution 1 Stellar Birth Stellar Formation A. Interstellar Clouds (Nebulae) B. Protostellar Clouds 2 C. Protostars Dr. Bill Pezzaglia Updated: 10/02/2006 A. Interstellar Clouds 1.
Accretion-Disk-outflow System in High Mass Star Formation. Yuefang Wu Astronomy Department Peking University, China
 Accretion-Disk-outflow System in High Mass Star Formation Yuefang Wu Astronomy Department Peking University, China Outline 1. A debate two models of high mass star formation 2. Our related work- observational
Accretion-Disk-outflow System in High Mass Star Formation Yuefang Wu Astronomy Department Peking University, China Outline 1. A debate two models of high mass star formation 2. Our related work- observational
Theory of Protostellar Disk Formation Zhi-Yun Li (University of Virginia)
 Theory of Protostellar Disk Formation Zhi-Yun Li (University of Virginia) Collaborators: Ruben Krasnopolsky (ASIAA) Sienny Shang (ASIAA) 1 Focus on magnetic effects on disk formation Investigated by many
Theory of Protostellar Disk Formation Zhi-Yun Li (University of Virginia) Collaborators: Ruben Krasnopolsky (ASIAA) Sienny Shang (ASIAA) 1 Focus on magnetic effects on disk formation Investigated by many
Disks, Envelopes and Magne2c Field. Infall, Ou9lows and Magne2c Braking
 Disks, Envelopes and Magne2c Field Infall, Ou9lows and Magne2c Braking Envelopes and Infall Signatures What is the evidence of infall in the envelope? How can ALMA strengthen the evidence? What is the
Disks, Envelopes and Magne2c Field Infall, Ou9lows and Magne2c Braking Envelopes and Infall Signatures What is the evidence of infall in the envelope? How can ALMA strengthen the evidence? What is the
Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Ṁ M gas / dyn. Log SFR. Kennicutt Log. gas / dyn
 Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Ṁ 0.017 M gas / dyn Log SFR Kennicutt 1998 Log gas / dyn Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Moster 2009 No Feedback 10% of baryons Log(
Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Ṁ 0.017 M gas / dyn Log SFR Kennicutt 1998 Log gas / dyn Motivation Q: WHY IS STAR FORMATION SO INEFFICIENT? Moster 2009 No Feedback 10% of baryons Log(
A Radio Jet Drives a Molecular & Atomic Gas Outflow in Multiple Regions within 1 kpc 2 of the Nucleus of IC5063
 A Radio Jet Drives a Molecular & Atomic Gas Outflow in Multiple Regions within 1 kpc 2 of the Nucleus of IC5063 K. M. Dasyra (University of Athens) F. Combes (College de France; Observatoire de Paris)
A Radio Jet Drives a Molecular & Atomic Gas Outflow in Multiple Regions within 1 kpc 2 of the Nucleus of IC5063 K. M. Dasyra (University of Athens) F. Combes (College de France; Observatoire de Paris)
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 2 Nov 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 2 Nov 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 2 Nov 2018](/thumbs/89/100156673.jpg) Draft version November 5, 218 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/12/14 DISK WIND FEEDBACK FROM HIGH-MASS PROTOSTARS Jan E. Staff College of Science and Math, University of the Virgin
Draft version November 5, 218 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/12/14 DISK WIND FEEDBACK FROM HIGH-MASS PROTOSTARS Jan E. Staff College of Science and Math, University of the Virgin
Components of Galaxies Stars What Properties of Stars are Important for Understanding Galaxies?
 Components of Galaxies Stars What Properties of Stars are Important for Understanding Galaxies? Temperature Determines the λ range over which the radiation is emitted Chemical Composition metallicities
Components of Galaxies Stars What Properties of Stars are Important for Understanding Galaxies? Temperature Determines the λ range over which the radiation is emitted Chemical Composition metallicities
Interstellar Medium and Star Birth
 Interstellar Medium and Star Birth Interstellar dust Lagoon nebula: dust + gas Interstellar Dust Extinction and scattering responsible for localized patches of darkness (dark clouds), as well as widespread
Interstellar Medium and Star Birth Interstellar dust Lagoon nebula: dust + gas Interstellar Dust Extinction and scattering responsible for localized patches of darkness (dark clouds), as well as widespread
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 15 Apr 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 15 Apr 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.sr] 15 Apr 2014](/thumbs/93/114019092.jpg) Astronomy& Astrophysics manuscript no. rev_main c ESO 2018 August 25, 2018 A multiple system of high-mass YSOs surrounded by disks in NGC7538 IRS1 Gas Dynamics on Scales 10 700 AU from CH 3 OH Maser and
Astronomy& Astrophysics manuscript no. rev_main c ESO 2018 August 25, 2018 A multiple system of high-mass YSOs surrounded by disks in NGC7538 IRS1 Gas Dynamics on Scales 10 700 AU from CH 3 OH Maser and
Growing and merging massive black holes
 Growing and merging massive black holes Marta Volonteri Institut d Astrophysique de Paris S. Cielo (IAP) R. Bieri (MPA) Y. Dubois (IAP) M. Habouzit (Flatiron Institute) T. Hartwig (IAP) H. Pfister (IAP)
Growing and merging massive black holes Marta Volonteri Institut d Astrophysique de Paris S. Cielo (IAP) R. Bieri (MPA) Y. Dubois (IAP) M. Habouzit (Flatiron Institute) T. Hartwig (IAP) H. Pfister (IAP)
Masers in Regions of High-Masss Star Formation. Karl M. Menten
 Masers in Regions of High-Masss Star Formation Karl M. Menten Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Bonn Massive Star Formation: Observations Confront Theory Heidelberg, September 2007 IRDC HCHIIR UCHIIR
Masers in Regions of High-Masss Star Formation Karl M. Menten Max-Planck-Institut für Radioastronomie, Bonn Massive Star Formation: Observations Confront Theory Heidelberg, September 2007 IRDC HCHIIR UCHIIR
Upper mass limit? Dominant feedback? Now & Then?
 Metallicity Dependence of Multiple Feedback in Massive Star Formation Kei E. I. Tanaka (Osaka Univ. / NAOJ) J. C. Tan (Chalmers/Virginia), Y. Zhang (RIKEN), T. Hosokawa (Kyoto), V. Rosero (Virginia), J.
Metallicity Dependence of Multiple Feedback in Massive Star Formation Kei E. I. Tanaka (Osaka Univ. / NAOJ) J. C. Tan (Chalmers/Virginia), Y. Zhang (RIKEN), T. Hosokawa (Kyoto), V. Rosero (Virginia), J.
Theory of star formation
 Theory of star formation Monday 8th 17.15 18.00 Molecular clouds and star formation: Introduction Tuesday 9th 13.15 14.00 Molecular clouds: structure, physics, and chemistry 16.00 16.45 Cloud cores: statistics
Theory of star formation Monday 8th 17.15 18.00 Molecular clouds and star formation: Introduction Tuesday 9th 13.15 14.00 Molecular clouds: structure, physics, and chemistry 16.00 16.45 Cloud cores: statistics
Observational Programme in Kent
 Observational Programme in Kent ASTRO-F, WFCAM, SCUBA-2, SALT UKIRT: individual protostellar outflows SAO/MMT/LBT: individual high- mass protostars NTT/Calar Alto + SEST: rho Ophiuchus 2MASS/NTT: Rosette
Observational Programme in Kent ASTRO-F, WFCAM, SCUBA-2, SALT UKIRT: individual protostellar outflows SAO/MMT/LBT: individual high- mass protostars NTT/Calar Alto + SEST: rho Ophiuchus 2MASS/NTT: Rosette
Masers around evolved stars from kinematics to physics
 Masers around evolved stars from kinematics to physics Anita Richards UK ARC, JBCA, Manchester with thanks to Al-Muntafki, Bains, Bartkiewicz, Diamond, Elitzur, Etoka, Gray, Humphreys, Murakawa, Rosa-Gonzalez,
Masers around evolved stars from kinematics to physics Anita Richards UK ARC, JBCA, Manchester with thanks to Al-Muntafki, Bains, Bartkiewicz, Diamond, Elitzur, Etoka, Gray, Humphreys, Murakawa, Rosa-Gonzalez,
Maria Cunningham, UNSW. CO, CS or other molecules?
 Maria Cunningham, UNSW CO, CS or other molecules? Wide field Surveys at mm wavelengths: pu8ng the whole picture together Follow chemical abundances through the whole ISM. Follow energy transfer through
Maria Cunningham, UNSW CO, CS or other molecules? Wide field Surveys at mm wavelengths: pu8ng the whole picture together Follow chemical abundances through the whole ISM. Follow energy transfer through
Topics for Today s Class
 Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Chapter 11 Formation of Stars and Structure of Stars Topics for Today s Class 1. Making Stars from the Interstellar Medium 2. Evidence of Star Formation: The Orion Nebula
Foundations of Astronomy 13e Seeds Chapter 11 Formation of Stars and Structure of Stars Topics for Today s Class 1. Making Stars from the Interstellar Medium 2. Evidence of Star Formation: The Orion Nebula
