Review: Learning Bimodal Structures in Audio-Visual Data
|
|
|
- Bethanie Wilkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review: Learning Bimodal Structures in Audio-Visual Data CSE 704 : Readings in Joint Visual, Lingual and Physical Models and Inference Algorithms Suren Kumar Vision and Perceptual Machines Lab 106 Davis Hall UB North Campus surenkum@buffalo.edu January 28, 2014 Suren Kumar January 28, /19
2 Summary What? Learn bimodally informative structures from audio-visual signals Why? Understand complex relationship between the inputs to different sensory modalities How? Represent audio-video signals as sparse sum of kernels consisting of audio-waveform and a spatio-temporal visual basis. Motivation: Biological Evidence, Evolution Suren Kumar January 28, 2014 Introduction 2/19
3 Literature Detect synchronous co-occurrences of transient structures in different modalities. 1. Extract fixed and predefined unimodal features in audio and video stream separately 2. Analyze correlation between the resulting feature representation What is the problem with it? Suren Kumar January 28, 2014 Introduction 3/19
4 Literature Detect synchronous co-occurrences of transient structures in different modalities. 1. Extract fixed and predefined unimodal features in audio and video stream separately 2. Analyze correlation between the resulting feature representation What is the problem with it? Suren Kumar January 28, 2014 Introduction 3/19
5 Basic Steps Capture bimodal signal structure by shift-invariance sparse generative model. Unsupervised learning for forming an overcomplete dictionary Suren Kumar January 28, 2014 Introduction 4/19
6 p th norm of a vector x in Euclidean space is defined as x p = ( n i=1 x i p ) 1 p Suren Kumar January 28, 2014 Background 5/19
7 Matching Pursuit Consider a dictionary D = (g) g D in a Hilbert space H. The dictionary is countable, normalized ( g = 1), complete, but not orthogonal and possibly redundant. Sparse Approximation Problem: Given N > 0 and f H, construct an N-term combination f N = k=1,2,..n c kg k with g k D which approximates f at best, and study how fast f N converges to f. Sparse Recovery Problem: if f has an unknown representation f = g c g g with (c g ) g D a (possibly) sparse sequence, recover this sequence exactly or approximately from the data of f. Building an optimal sparse representation of arbitrary signals is NP-hard problem. Suren Kumar January 28, 2014 Background:Matching Pursuit 6/19
8 Matching Pursuit Matching pursuit is a greedy approximation to the problem. Initialization f 0 = 0 Projection Step: At step k 1, projection step is the approximation of f f k 1 = Span{g 1,..., g k 1 } Selection Step: Choice of next element based on residual r k 1 = f f k 1 g k = arg max g D < r k 1, g > Suren Kumar January 28, 2014 Background:Matching Pursuit 7/19
9 Convolutional Generative Model Audio visual data s = (a, v), a(t), v(x, y, t) Dictionary {φ k }, φ k = (φ (a) k (t), φ(v) k (x, y, t)) Each atom can be translated to any point in space and time using operator T (p,q,r) T (p,q,r) = (φ (a) k (t r), φ(v) k (x p, y q, t r)) Thus an audio-visual signal can be represented as s K nk k=1 i=1 c k i T (p,q,r)ki φ k, c ki = (c (a), c (v) k i ) Coding Find the coefficients (sparse) Learning Learning the dictionary k i Suren Kumar January 28, 2014 Audio-Visual Representation 8/19
10 Audio-Visual Matching Pursuit Transient substructures that co-occur simultaneously are indicative of common underlying physical cause. Discrete audio-visual translation τ Signal Approximation. Start with R 0 s = s Suren Kumar January 28, 2014 Audio-Visual Representation 9/19
11 Audio-Visual Matching Pursuit The function φ 0 and its spatio-temporal translation are chosen maximizing similarity measures C(R 0 s, φ) When to Stop? Suren Kumar January 28, 2014 Audio-Visual Representation 10/19
12 Audio-Visual Matching Pursuit The function φ 0 and its spatio-temporal translation are chosen maximizing similarity measures C(R 0 s, φ) When to Stop? Number of iterations N or the maximum value of C between residual and dictionary elements falls below a threshold. Similarity measure should reflect properties of human perception Unaffected by small relative time-shifts Suren Kumar January 28, 2014 Audio-Visual Representation 10/19
13 Choosing the norm Suren Kumar January 28, 2014 Audio-Visual Representation 11/19
14 Learning Find the kernel functions from a given set of audio-visual data. Assuming the noise to be gaussian Suren Kumar January 28, 2014 Learning:Gradient Ascent Learning 12/19
15 Learning Find the kernel functions from a given set of audio-visual data. Assuming the noise to be gaussian Suren Kumar January 28, 2014 Learning:Gradient Ascent Learning 12/19
16 Learning Update: φ k [j] = φ k [j 1] + ηδφ k Suren Kumar January 28, 2014 Learning:Gradient Ascent Learning 13/19
17 Learning Key Idea : Update only one atom φ k Update each function with principal component of the residual errors. In general has faster convergence compared to GA. Suren Kumar January 28, 2014 Learning:K-SVD algorithm 14/19
18 Synthetic Data Audio - 3 sine waves and video has four black shapes Suren Kumar January 28, 2014 Experiments 15/19
19 Audio-Visual Speech Speaker uttering the digits from zero to nine in english Study convergence for 1 and 2 norm with GA and K-SVD C 1 encodes joint audio-visual structures better. K-SVD is faster compared to GA. Suren Kumar January 28, 2014 Experiments 16/19
20 Suren Kumar January 28, 2014 Experiments 17/19
21 Sound Source Localization CUAVE - Visual Distractor and Acoustin Distractor Filter Audio Corresponding audio filter audio function and store the maximum projection Filter with corresponding video function and store maximum projection. Cluster video position Suren Kumar January 28, 2014 Experiments 18/19
22 Summary Audio - Visual Matching Pursuit Similarity measures and learning algorithms Testing for speaker localization with distractors. Suren Kumar January 28, 2014 Experiments 19/19
23 Reference popov/learning/cohen.pdf Suren Kumar January 28, 2014 Experiments 20/19
Sparse linear models
 Sparse linear models Optimization-Based Data Analysis http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/obda_spring16 Carlos Fernandez-Granda 2/22/2016 Introduction Linear transforms Frequency representation Short-time
Sparse linear models Optimization-Based Data Analysis http://www.cims.nyu.edu/~cfgranda/pages/obda_spring16 Carlos Fernandez-Granda 2/22/2016 Introduction Linear transforms Frequency representation Short-time
EUSIPCO
 EUSIPCO 013 1569746769 SUBSET PURSUIT FOR ANALYSIS DICTIONARY LEARNING Ye Zhang 1,, Haolong Wang 1, Tenglong Yu 1, Wenwu Wang 1 Department of Electronic and Information Engineering, Nanchang University,
EUSIPCO 013 1569746769 SUBSET PURSUIT FOR ANALYSIS DICTIONARY LEARNING Ye Zhang 1,, Haolong Wang 1, Tenglong Yu 1, Wenwu Wang 1 Department of Electronic and Information Engineering, Nanchang University,
Greedy Signal Recovery and Uniform Uncertainty Principles
 Greedy Signal Recovery and Uniform Uncertainty Principles SPIE - IE 2008 Deanna Needell Joint work with Roman Vershynin UC Davis, January 2008 Greedy Signal Recovery and Uniform Uncertainty Principles
Greedy Signal Recovery and Uniform Uncertainty Principles SPIE - IE 2008 Deanna Needell Joint work with Roman Vershynin UC Davis, January 2008 Greedy Signal Recovery and Uniform Uncertainty Principles
Applied Machine Learning for Biomedical Engineering. Enrico Grisan
 Applied Machine Learning for Biomedical Engineering Enrico Grisan enrico.grisan@dei.unipd.it Data representation To find a representation that approximates elements of a signal class with a linear combination
Applied Machine Learning for Biomedical Engineering Enrico Grisan enrico.grisan@dei.unipd.it Data representation To find a representation that approximates elements of a signal class with a linear combination
Recent developments on sparse representation
 Recent developments on sparse representation Zeng Tieyong Department of Mathematics, Hong Kong Baptist University Email: zeng@hkbu.edu.hk Hong Kong Baptist University Dec. 8, 2008 First Previous Next Last
Recent developments on sparse representation Zeng Tieyong Department of Mathematics, Hong Kong Baptist University Email: zeng@hkbu.edu.hk Hong Kong Baptist University Dec. 8, 2008 First Previous Next Last
An Introduction to Sparse Approximation
 An Introduction to Sparse Approximation Anna C. Gilbert Department of Mathematics University of Michigan Basic image/signal/data compression: transform coding Approximate signals sparsely Compress images,
An Introduction to Sparse Approximation Anna C. Gilbert Department of Mathematics University of Michigan Basic image/signal/data compression: transform coding Approximate signals sparsely Compress images,
Machine Learning for Signal Processing Sparse and Overcomplete Representations
 Machine Learning for Signal Processing Sparse and Overcomplete Representations Abelino Jimenez (slides from Bhiksha Raj and Sourish Chaudhuri) Oct 1, 217 1 So far Weights Data Basis Data Independent ICA
Machine Learning for Signal Processing Sparse and Overcomplete Representations Abelino Jimenez (slides from Bhiksha Raj and Sourish Chaudhuri) Oct 1, 217 1 So far Weights Data Basis Data Independent ICA
Machine Learning: Basis and Wavelet 김화평 (CSE ) Medical Image computing lab 서진근교수연구실 Haar DWT in 2 levels
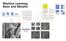 Machine Learning: Basis and Wavelet 32 157 146 204 + + + + + - + - 김화평 (CSE ) Medical Image computing lab 서진근교수연구실 7 22 38 191 17 83 188 211 71 167 194 207 135 46 40-17 18 42 20 44 31 7 13-32 + + - - +
Machine Learning: Basis and Wavelet 32 157 146 204 + + + + + - + - 김화평 (CSE ) Medical Image computing lab 서진근교수연구실 7 22 38 191 17 83 188 211 71 167 194 207 135 46 40-17 18 42 20 44 31 7 13-32 + + - - +
Sparse analysis Lecture III: Dictionary geometry and greedy algorithms
 Sparse analysis Lecture III: Dictionary geometry and greedy algorithms Anna C. Gilbert Department of Mathematics University of Michigan Intuition from ONB Key step in algorithm: r, ϕ j = x c i ϕ i, ϕ j
Sparse analysis Lecture III: Dictionary geometry and greedy algorithms Anna C. Gilbert Department of Mathematics University of Michigan Intuition from ONB Key step in algorithm: r, ϕ j = x c i ϕ i, ϕ j
Machine Learning for Signal Processing Sparse and Overcomplete Representations. Bhiksha Raj (slides from Sourish Chaudhuri) Oct 22, 2013
 Machine Learning for Signal Processing Sparse and Overcomplete Representations Bhiksha Raj (slides from Sourish Chaudhuri) Oct 22, 2013 1 Key Topics in this Lecture Basics Component-based representations
Machine Learning for Signal Processing Sparse and Overcomplete Representations Bhiksha Raj (slides from Sourish Chaudhuri) Oct 22, 2013 1 Key Topics in this Lecture Basics Component-based representations
MLCC 2018 Variable Selection and Sparsity. Lorenzo Rosasco UNIGE-MIT-IIT
 MLCC 2018 Variable Selection and Sparsity Lorenzo Rosasco UNIGE-MIT-IIT Outline Variable Selection Subset Selection Greedy Methods: (Orthogonal) Matching Pursuit Convex Relaxation: LASSO & Elastic Net
MLCC 2018 Variable Selection and Sparsity Lorenzo Rosasco UNIGE-MIT-IIT Outline Variable Selection Subset Selection Greedy Methods: (Orthogonal) Matching Pursuit Convex Relaxation: LASSO & Elastic Net
Statistical approach for dictionary learning
 Statistical approach for dictionary learning Tieyong ZENG Joint work with Alain Trouvé Page 1 Introduction Redundant dictionary Coding, denoising, compression. Existing algorithms to generate dictionary
Statistical approach for dictionary learning Tieyong ZENG Joint work with Alain Trouvé Page 1 Introduction Redundant dictionary Coding, denoising, compression. Existing algorithms to generate dictionary
Compressed Sensing and Neural Networks
 and Jan Vybíral (Charles University & Czech Technical University Prague, Czech Republic) NOMAD Summer Berlin, September 25-29, 2017 1 / 31 Outline Lasso & Introduction Notation Training the network Applications
and Jan Vybíral (Charles University & Czech Technical University Prague, Czech Republic) NOMAD Summer Berlin, September 25-29, 2017 1 / 31 Outline Lasso & Introduction Notation Training the network Applications
SHIFT-INVARIANT DICTIONARY LEARNING FOR SPARSE REPRESENTATIONS: EXTENDING K-SVD
 SHIFT-INVARIANT DICTIONARY LEARNING FOR SPARSE REPRESENTATIONS: EXTENDING K-SVD Boris Mailhé, Sylvain Lesage,Rémi Gribonval and Frédéric Bimbot Projet METISS Centre de Recherche INRIA Rennes - Bretagne
SHIFT-INVARIANT DICTIONARY LEARNING FOR SPARSE REPRESENTATIONS: EXTENDING K-SVD Boris Mailhé, Sylvain Lesage,Rémi Gribonval and Frédéric Bimbot Projet METISS Centre de Recherche INRIA Rennes - Bretagne
Detecting Sparse Structures in Data in Sub-Linear Time: A group testing approach
 Detecting Sparse Structures in Data in Sub-Linear Time: A group testing approach Boaz Nadler The Weizmann Institute of Science Israel Joint works with Inbal Horev, Ronen Basri, Meirav Galun and Ery Arias-Castro
Detecting Sparse Structures in Data in Sub-Linear Time: A group testing approach Boaz Nadler The Weizmann Institute of Science Israel Joint works with Inbal Horev, Ronen Basri, Meirav Galun and Ery Arias-Castro
Introduction to Machine Learning. PCA and Spectral Clustering. Introduction to Machine Learning, Slides: Eran Halperin
 1 Introduction to Machine Learning PCA and Spectral Clustering Introduction to Machine Learning, 2013-14 Slides: Eran Halperin Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) The singular value decomposition (SVD)
1 Introduction to Machine Learning PCA and Spectral Clustering Introduction to Machine Learning, 2013-14 Slides: Eran Halperin Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) The singular value decomposition (SVD)
EE 381V: Large Scale Optimization Fall Lecture 24 April 11
 EE 381V: Large Scale Optimization Fall 2012 Lecture 24 April 11 Lecturer: Caramanis & Sanghavi Scribe: Tao Huang 24.1 Review In past classes, we studied the problem of sparsity. Sparsity problem is that
EE 381V: Large Scale Optimization Fall 2012 Lecture 24 April 11 Lecturer: Caramanis & Sanghavi Scribe: Tao Huang 24.1 Review In past classes, we studied the problem of sparsity. Sparsity problem is that
Introduction to Machine Learning
 10-701 Introduction to Machine Learning PCA Slides based on 18-661 Fall 2018 PCA Raw data can be Complex, High-dimensional To understand a phenomenon we measure various related quantities If we knew what
10-701 Introduction to Machine Learning PCA Slides based on 18-661 Fall 2018 PCA Raw data can be Complex, High-dimensional To understand a phenomenon we measure various related quantities If we knew what
When Dictionary Learning Meets Classification
 When Dictionary Learning Meets Classification Bufford, Teresa 1 Chen, Yuxin 2 Horning, Mitchell 3 Shee, Liberty 1 Mentor: Professor Yohann Tendero 1 UCLA 2 Dalhousie University 3 Harvey Mudd College August
When Dictionary Learning Meets Classification Bufford, Teresa 1 Chen, Yuxin 2 Horning, Mitchell 3 Shee, Liberty 1 Mentor: Professor Yohann Tendero 1 UCLA 2 Dalhousie University 3 Harvey Mudd College August
Unsupervised Learning
 2018 EE448, Big Data Mining, Lecture 7 Unsupervised Learning Weinan Zhang Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://wnzhang.net http://wnzhang.net/teaching/ee448/index.html ML Problem Setting First build and
2018 EE448, Big Data Mining, Lecture 7 Unsupervised Learning Weinan Zhang Shanghai Jiao Tong University http://wnzhang.net http://wnzhang.net/teaching/ee448/index.html ML Problem Setting First build and
PCA & ICA. CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Spring Soleymani
 PCA & ICA CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Spring 2015 Soleymani Dimensionality Reduction: Feature Selection vs. Feature Extraction Feature selection Select a subset of a given
PCA & ICA CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Spring 2015 Soleymani Dimensionality Reduction: Feature Selection vs. Feature Extraction Feature selection Select a subset of a given
Shankar Shivappa University of California, San Diego April 26, CSE 254 Seminar in learning algorithms
 Recognition of Visual Speech Elements Using Adaptively Boosted Hidden Markov Models. Say Wei Foo, Yong Lian, Liang Dong. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, May 2004. Shankar
Recognition of Visual Speech Elements Using Adaptively Boosted Hidden Markov Models. Say Wei Foo, Yong Lian, Liang Dong. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, May 2004. Shankar
Sparse Approximation of Signals with Highly Coherent Dictionaries
 Sparse Approximation of Signals with Highly Coherent Dictionaries Bishnu P. Lamichhane and Laura Rebollo-Neira b.p.lamichhane@aston.ac.uk, rebollol@aston.ac.uk Support from EPSRC (EP/D062632/1) is acknowledged
Sparse Approximation of Signals with Highly Coherent Dictionaries Bishnu P. Lamichhane and Laura Rebollo-Neira b.p.lamichhane@aston.ac.uk, rebollol@aston.ac.uk Support from EPSRC (EP/D062632/1) is acknowledged
SINGLE CHANNEL SPEECH MUSIC SEPARATION USING NONNEGATIVE MATRIX FACTORIZATION AND SPECTRAL MASKS. Emad M. Grais and Hakan Erdogan
 SINGLE CHANNEL SPEECH MUSIC SEPARATION USING NONNEGATIVE MATRIX FACTORIZATION AND SPECTRAL MASKS Emad M. Grais and Hakan Erdogan Faculty of Engineering and Natural Sciences, Sabanci University, Orhanli
SINGLE CHANNEL SPEECH MUSIC SEPARATION USING NONNEGATIVE MATRIX FACTORIZATION AND SPECTRAL MASKS Emad M. Grais and Hakan Erdogan Faculty of Engineering and Natural Sciences, Sabanci University, Orhanli
Adapting Wavenet for Speech Enhancement DARIO RETHAGE JULY 12, 2017
 Adapting Wavenet for Speech Enhancement DARIO RETHAGE JULY 12, 2017 I am v Master Student v 6 months @ Music Technology Group, Universitat Pompeu Fabra v Deep learning for acoustic source separation v
Adapting Wavenet for Speech Enhancement DARIO RETHAGE JULY 12, 2017 I am v Master Student v 6 months @ Music Technology Group, Universitat Pompeu Fabra v Deep learning for acoustic source separation v
MATCHING PURSUIT WITH STOCHASTIC SELECTION
 2th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 22) Bucharest, Romania, August 27-3, 22 MATCHING PURSUIT WITH STOCHASTIC SELECTION Thomas Peel, Valentin Emiya, Liva Ralaivola Aix-Marseille Université
2th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 22) Bucharest, Romania, August 27-3, 22 MATCHING PURSUIT WITH STOCHASTIC SELECTION Thomas Peel, Valentin Emiya, Liva Ralaivola Aix-Marseille Université
Sparse Time-Frequency Transforms and Applications.
 Sparse Time-Frequency Transforms and Applications. Bruno Torrésani http://www.cmi.univ-mrs.fr/~torresan LATP, Université de Provence, Marseille DAFx, Montreal, September 2006 B. Torrésani (LATP Marseille)
Sparse Time-Frequency Transforms and Applications. Bruno Torrésani http://www.cmi.univ-mrs.fr/~torresan LATP, Université de Provence, Marseille DAFx, Montreal, September 2006 B. Torrésani (LATP Marseille)
Learning Eigenfunctions: Links with Spectral Clustering and Kernel PCA
 Learning Eigenfunctions: Links with Spectral Clustering and Kernel PCA Yoshua Bengio Pascal Vincent Jean-François Paiement University of Montreal April 2, Snowbird Learning 2003 Learning Modal Structures
Learning Eigenfunctions: Links with Spectral Clustering and Kernel PCA Yoshua Bengio Pascal Vincent Jean-François Paiement University of Montreal April 2, Snowbird Learning 2003 Learning Modal Structures
Model-Based Compressive Sensing for Signal Ensembles. Marco F. Duarte Volkan Cevher Richard G. Baraniuk
 Model-Based Compressive Sensing for Signal Ensembles Marco F. Duarte Volkan Cevher Richard G. Baraniuk Concise Signal Structure Sparse signal: only K out of N coordinates nonzero model: union of K-dimensional
Model-Based Compressive Sensing for Signal Ensembles Marco F. Duarte Volkan Cevher Richard G. Baraniuk Concise Signal Structure Sparse signal: only K out of N coordinates nonzero model: union of K-dimensional
Scalable color image coding with Matching Pursuit
 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING - STI SIGNAL PROCESSING INSTITUTE Rosa M. Figueras i Ventura CH-115 LAUSANNE Telephone: +4121 6935646 Telefax: +4121 69376 e-mail: rosa.figueras@epfl.ch ÉCOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FÉDÉRALE
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING - STI SIGNAL PROCESSING INSTITUTE Rosa M. Figueras i Ventura CH-115 LAUSANNE Telephone: +4121 6935646 Telefax: +4121 69376 e-mail: rosa.figueras@epfl.ch ÉCOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FÉDÉRALE
Over-enhancement Reduction in Local Histogram Equalization using its Degrees of Freedom. Alireza Avanaki
 Over-enhancement Reduction in Local Histogram Equalization using its Degrees of Freedom Alireza Avanaki ABSTRACT A well-known issue of local (adaptive) histogram equalization (LHE) is over-enhancement
Over-enhancement Reduction in Local Histogram Equalization using its Degrees of Freedom Alireza Avanaki ABSTRACT A well-known issue of local (adaptive) histogram equalization (LHE) is over-enhancement
Multi-scale Geometric Summaries for Similarity-based Upstream S
 Multi-scale Geometric Summaries for Similarity-based Upstream Sensor Fusion Duke University, ECE / Math 3/6/2019 Overall Goals / Design Choices Leverage multiple, heterogeneous modalities in identification
Multi-scale Geometric Summaries for Similarity-based Upstream Sensor Fusion Duke University, ECE / Math 3/6/2019 Overall Goals / Design Choices Leverage multiple, heterogeneous modalities in identification
Gaussian Processes for Audio Feature Extraction
 Gaussian Processes for Audio Feature Extraction Dr. Richard E. Turner (ret26@cam.ac.uk) Computational and Biological Learning Lab Department of Engineering University of Cambridge Machine hearing pipeline
Gaussian Processes for Audio Feature Extraction Dr. Richard E. Turner (ret26@cam.ac.uk) Computational and Biological Learning Lab Department of Engineering University of Cambridge Machine hearing pipeline
Structured matrix factorizations. Example: Eigenfaces
 Structured matrix factorizations Example: Eigenfaces An extremely large variety of interesting and important problems in machine learning can be formulated as: Given a matrix, find a matrix and a matrix
Structured matrix factorizations Example: Eigenfaces An extremely large variety of interesting and important problems in machine learning can be formulated as: Given a matrix, find a matrix and a matrix
Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers. 6. Mixture Models and Expectation-Maximization
 Prof. Daniel Cremers 6. Mixture Models and Expectation-Maximization Motivation Often the introduction of latent (unobserved) random variables into a model can help to express complex (marginal) distributions
Prof. Daniel Cremers 6. Mixture Models and Expectation-Maximization Motivation Often the introduction of latent (unobserved) random variables into a model can help to express complex (marginal) distributions
17 Random Projections and Orthogonal Matching Pursuit
 17 Random Projections and Orthogonal Matching Pursuit Again we will consider high-dimensional data P. Now we will consider the uses and effects of randomness. We will use it to simplify P (put it in a
17 Random Projections and Orthogonal Matching Pursuit Again we will consider high-dimensional data P. Now we will consider the uses and effects of randomness. We will use it to simplify P (put it in a
Nonparametric Bayesian Dictionary Learning for Machine Listening
 Nonparametric Bayesian Dictionary Learning for Machine Listening Dawen Liang Electrical Engineering dl2771@columbia.edu 1 Introduction Machine listening, i.e., giving machines the ability to extract useful
Nonparametric Bayesian Dictionary Learning for Machine Listening Dawen Liang Electrical Engineering dl2771@columbia.edu 1 Introduction Machine listening, i.e., giving machines the ability to extract useful
TUTORIAL PART 1 Unsupervised Learning
 TUTORIAL PART 1 Unsupervised Learning Marc'Aurelio Ranzato Department of Computer Science Univ. of Toronto ranzato@cs.toronto.edu Co-organizers: Honglak Lee, Yoshua Bengio, Geoff Hinton, Yann LeCun, Andrew
TUTORIAL PART 1 Unsupervised Learning Marc'Aurelio Ranzato Department of Computer Science Univ. of Toronto ranzato@cs.toronto.edu Co-organizers: Honglak Lee, Yoshua Bengio, Geoff Hinton, Yann LeCun, Andrew
Package sgpca. R topics documented: July 6, Type Package. Title Sparse Generalized Principal Component Analysis. Version 1.0.
 Package sgpca July 6, 2013 Type Package Title Sparse Generalized Principal Component Analysis Version 1.0 Date 2012-07-05 Author Frederick Campbell Maintainer Frederick Campbell
Package sgpca July 6, 2013 Type Package Title Sparse Generalized Principal Component Analysis Version 1.0 Date 2012-07-05 Author Frederick Campbell Maintainer Frederick Campbell
Wavelet Footprints: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications
 1306 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 51, NO. 5, MAY 2003 Wavelet Footprints: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications Pier Luigi Dragotti, Member, IEEE, and Martin Vetterli, Fellow, IEEE Abstract
1306 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON SIGNAL PROCESSING, VOL. 51, NO. 5, MAY 2003 Wavelet Footprints: Theory, Algorithms, and Applications Pier Luigi Dragotti, Member, IEEE, and Martin Vetterli, Fellow, IEEE Abstract
Deep Learning Basics Lecture 7: Factor Analysis. Princeton University COS 495 Instructor: Yingyu Liang
 Deep Learning Basics Lecture 7: Factor Analysis Princeton University COS 495 Instructor: Yingyu Liang Supervised v.s. Unsupervised Math formulation for supervised learning Given training data x i, y i
Deep Learning Basics Lecture 7: Factor Analysis Princeton University COS 495 Instructor: Yingyu Liang Supervised v.s. Unsupervised Math formulation for supervised learning Given training data x i, y i
Audiovisual Gestalts. Gianluca Monaci, Pierre Vandergheynst Signal Processing Institute, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Switzerland
 Audiovisual Gestalts Gianluca Monaci, Pierre Vandergheynst Signal Processing Institute, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Switzerland {gianluca.monaci,pierre.vandergheynst}@epfl.ch - http://lts2www.epfl.ch
Audiovisual Gestalts Gianluca Monaci, Pierre Vandergheynst Signal Processing Institute, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Switzerland {gianluca.monaci,pierre.vandergheynst}@epfl.ch - http://lts2www.epfl.ch
Deep Learning: Approximation of Functions by Composition
 Deep Learning: Approximation of Functions by Composition Zuowei Shen Department of Mathematics National University of Singapore Outline 1 A brief introduction of approximation theory 2 Deep learning: approximation
Deep Learning: Approximation of Functions by Composition Zuowei Shen Department of Mathematics National University of Singapore Outline 1 A brief introduction of approximation theory 2 Deep learning: approximation
Signal Processing COS 323
 Signal Processing COS 323 Digital Signals D: functions of space or time e.g., sound 2D: often functions of 2 spatial dimensions e.g. images 3D: functions of 3 spatial dimensions CAT, MRI scans or 2 space,
Signal Processing COS 323 Digital Signals D: functions of space or time e.g., sound 2D: often functions of 2 spatial dimensions e.g. images 3D: functions of 3 spatial dimensions CAT, MRI scans or 2 space,
Lecture Notes 5: Multiresolution Analysis
 Optimization-based data analysis Fall 2017 Lecture Notes 5: Multiresolution Analysis 1 Frames A frame is a generalization of an orthonormal basis. The inner products between the vectors in a frame and
Optimization-based data analysis Fall 2017 Lecture Notes 5: Multiresolution Analysis 1 Frames A frame is a generalization of an orthonormal basis. The inner products between the vectors in a frame and
Independent Component Analysis and Unsupervised Learning
 Independent Component Analysis and Unsupervised Learning Jen-Tzung Chien National Cheng Kung University TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Independent Component Analysis 2. Case Study I: Speech Recognition Independent
Independent Component Analysis and Unsupervised Learning Jen-Tzung Chien National Cheng Kung University TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Independent Component Analysis 2. Case Study I: Speech Recognition Independent
Sparse linear models and denoising
 Lecture notes 4 February 22, 2016 Sparse linear models and denoising 1 Introduction 1.1 Definition and motivation Finding representations of signals that allow to process them more effectively is a central
Lecture notes 4 February 22, 2016 Sparse linear models and denoising 1 Introduction 1.1 Definition and motivation Finding representations of signals that allow to process them more effectively is a central
Source Separation of Convolutive and Noisy Mixtures using Audio-Visual Dictionary Learning and Probabilistic Time-Frequency Masking
 1 Source Separation of Convolutive and Noisy Mixtures using Audio-isual Dictionary Learning and Probabilistic Time-Frequency Masking Qingju Liu, Wenwu Wang, Philip JB Jackson, Mark Barnard, Josef Kittler,
1 Source Separation of Convolutive and Noisy Mixtures using Audio-isual Dictionary Learning and Probabilistic Time-Frequency Masking Qingju Liu, Wenwu Wang, Philip JB Jackson, Mark Barnard, Josef Kittler,
Estimation Error Bounds for Frame Denoising
 Estimation Error Bounds for Frame Denoising Alyson K. Fletcher and Kannan Ramchandran {alyson,kannanr}@eecs.berkeley.edu Berkeley Audio-Visual Signal Processing and Communication Systems group Department
Estimation Error Bounds for Frame Denoising Alyson K. Fletcher and Kannan Ramchandran {alyson,kannanr}@eecs.berkeley.edu Berkeley Audio-Visual Signal Processing and Communication Systems group Department
Analysis of audio intercepts: Can we identify and locate the speaker?
 Motivation Analysis of audio intercepts: Can we identify and locate the speaker? K V Vijay Girish, PhD Student Research Advisor: Prof A G Ramakrishnan Research Collaborator: Dr T V Ananthapadmanabha Medical
Motivation Analysis of audio intercepts: Can we identify and locate the speaker? K V Vijay Girish, PhD Student Research Advisor: Prof A G Ramakrishnan Research Collaborator: Dr T V Ananthapadmanabha Medical
Neuroscience Introduction
 Neuroscience Introduction The brain As humans, we can identify galaxies light years away, we can study particles smaller than an atom. But we still haven t unlocked the mystery of the three pounds of matter
Neuroscience Introduction The brain As humans, we can identify galaxies light years away, we can study particles smaller than an atom. But we still haven t unlocked the mystery of the three pounds of matter
Digital Audio Resampling Detection Based on Sparse Representation Classifier and Periodicity of Second Derivative
 Digital Audio Resampling Detection Based on Sparse Representation Classifier and Periodicity of Second Derivative Jing XU 1, Jeffrey XIA 2 1 College of Computer Science & Technology, Guizhou University
Digital Audio Resampling Detection Based on Sparse Representation Classifier and Periodicity of Second Derivative Jing XU 1, Jeffrey XIA 2 1 College of Computer Science & Technology, Guizhou University
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining. More PCA Fall 2016
 CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining More PCA Fall 2016 A2/Midterm: Admin Grades/solutions posted. Midterms can be viewed during office hours. Assignment 4: Due Monday. Extra office hours: Thursdays
CPSC 340: Machine Learning and Data Mining More PCA Fall 2016 A2/Midterm: Admin Grades/solutions posted. Midterms can be viewed during office hours. Assignment 4: Due Monday. Extra office hours: Thursdays
Sparse Approximation and Variable Selection
 Sparse Approximation and Variable Selection Lorenzo Rosasco 9.520 Class 07 February 26, 2007 About this class Goal To introduce the problem of variable selection, discuss its connection to sparse approximation
Sparse Approximation and Variable Selection Lorenzo Rosasco 9.520 Class 07 February 26, 2007 About this class Goal To introduce the problem of variable selection, discuss its connection to sparse approximation
Motivation Sparse Signal Recovery is an interesting area with many potential applications. Methods developed for solving sparse signal recovery proble
 Bayesian Methods for Sparse Signal Recovery Bhaskar D Rao 1 University of California, San Diego 1 Thanks to David Wipf, Zhilin Zhang and Ritwik Giri Motivation Sparse Signal Recovery is an interesting
Bayesian Methods for Sparse Signal Recovery Bhaskar D Rao 1 University of California, San Diego 1 Thanks to David Wipf, Zhilin Zhang and Ritwik Giri Motivation Sparse Signal Recovery is an interesting
POLYNOMIAL SINGULAR VALUES FOR NUMBER OF WIDEBAND SOURCES ESTIMATION AND PRINCIPAL COMPONENT ANALYSIS
 POLYNOMIAL SINGULAR VALUES FOR NUMBER OF WIDEBAND SOURCES ESTIMATION AND PRINCIPAL COMPONENT ANALYSIS Russell H. Lambert RF and Advanced Mixed Signal Unit Broadcom Pasadena, CA USA russ@broadcom.com Marcel
POLYNOMIAL SINGULAR VALUES FOR NUMBER OF WIDEBAND SOURCES ESTIMATION AND PRINCIPAL COMPONENT ANALYSIS Russell H. Lambert RF and Advanced Mixed Signal Unit Broadcom Pasadena, CA USA russ@broadcom.com Marcel
Info-Greedy Sequential Adaptive Compressed Sensing
 Info-Greedy Sequential Adaptive Compressed Sensing Yao Xie Joint work with Gabor Braun and Sebastian Pokutta Georgia Institute of Technology Presented at Allerton Conference 2014 Information sensing for
Info-Greedy Sequential Adaptive Compressed Sensing Yao Xie Joint work with Gabor Braun and Sebastian Pokutta Georgia Institute of Technology Presented at Allerton Conference 2014 Information sensing for
Single Channel Signal Separation Using MAP-based Subspace Decomposition
 Single Channel Signal Separation Using MAP-based Subspace Decomposition Gil-Jin Jang, Te-Won Lee, and Yung-Hwan Oh 1 Spoken Language Laboratory, Department of Computer Science, KAIST 373-1 Gusong-dong,
Single Channel Signal Separation Using MAP-based Subspace Decomposition Gil-Jin Jang, Te-Won Lee, and Yung-Hwan Oh 1 Spoken Language Laboratory, Department of Computer Science, KAIST 373-1 Gusong-dong,
CONVOLUTIVE NON-NEGATIVE MATRIX FACTORISATION WITH SPARSENESS CONSTRAINT
 CONOLUTIE NON-NEGATIE MATRIX FACTORISATION WITH SPARSENESS CONSTRAINT Paul D. O Grady Barak A. Pearlmutter Hamilton Institute National University of Ireland, Maynooth Co. Kildare, Ireland. ABSTRACT Discovering
CONOLUTIE NON-NEGATIE MATRIX FACTORISATION WITH SPARSENESS CONSTRAINT Paul D. O Grady Barak A. Pearlmutter Hamilton Institute National University of Ireland, Maynooth Co. Kildare, Ireland. ABSTRACT Discovering
Generalized Orthogonal Matching Pursuit- A Review and Some
 Generalized Orthogonal Matching Pursuit- A Review and Some New Results Department of Electronics and Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur, INDIA Table of Contents
Generalized Orthogonal Matching Pursuit- A Review and Some New Results Department of Electronics and Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur, INDIA Table of Contents
New Coherence and RIP Analysis for Weak. Orthogonal Matching Pursuit
 New Coherence and RIP Analysis for Wea 1 Orthogonal Matching Pursuit Mingrui Yang, Member, IEEE, and Fran de Hoog arxiv:1405.3354v1 [cs.it] 14 May 2014 Abstract In this paper we define a new coherence
New Coherence and RIP Analysis for Wea 1 Orthogonal Matching Pursuit Mingrui Yang, Member, IEEE, and Fran de Hoog arxiv:1405.3354v1 [cs.it] 14 May 2014 Abstract In this paper we define a new coherence
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning
 STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 11 Project
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 11 Project
Overview of Statistical Tools. Statistical Inference. Bayesian Framework. Modeling. Very simple case. Things are usually more complicated
 Fall 3 Computer Vision Overview of Statistical Tools Statistical Inference Haibin Ling Observation inference Decision Prior knowledge http://www.dabi.temple.edu/~hbling/teaching/3f_5543/index.html Bayesian
Fall 3 Computer Vision Overview of Statistical Tools Statistical Inference Haibin Ling Observation inference Decision Prior knowledge http://www.dabi.temple.edu/~hbling/teaching/3f_5543/index.html Bayesian
Unsupervised Machine Learning and Data Mining. DS 5230 / DS Fall Lecture 7. Jan-Willem van de Meent
 Unsupervised Machine Learning and Data Mining DS 5230 / DS 4420 - Fall 2018 Lecture 7 Jan-Willem van de Meent DIMENSIONALITY REDUCTION Borrowing from: Percy Liang (Stanford) Dimensionality Reduction Goal:
Unsupervised Machine Learning and Data Mining DS 5230 / DS 4420 - Fall 2018 Lecture 7 Jan-Willem van de Meent DIMENSIONALITY REDUCTION Borrowing from: Percy Liang (Stanford) Dimensionality Reduction Goal:
CSC 576: Variants of Sparse Learning
 CSC 576: Variants of Sparse Learning Ji Liu Department of Computer Science, University of Rochester October 27, 205 Introduction Our previous note basically suggests using l norm to enforce sparsity in
CSC 576: Variants of Sparse Learning Ji Liu Department of Computer Science, University of Rochester October 27, 205 Introduction Our previous note basically suggests using l norm to enforce sparsity in
The Iteration-Tuned Dictionary for Sparse Representations
 The Iteration-Tuned Dictionary for Sparse Representations Joaquin Zepeda #1, Christine Guillemot #2, Ewa Kijak 3 # INRIA Centre Rennes - Bretagne Atlantique Campus de Beaulieu, 35042 Rennes Cedex, FRANCE
The Iteration-Tuned Dictionary for Sparse Representations Joaquin Zepeda #1, Christine Guillemot #2, Ewa Kijak 3 # INRIA Centre Rennes - Bretagne Atlantique Campus de Beaulieu, 35042 Rennes Cedex, FRANCE
Dimension Reduction Techniques. Presented by Jie (Jerry) Yu
 Dimension Reduction Techniques Presented by Jie (Jerry) Yu Outline Problem Modeling Review of PCA and MDS Isomap Local Linear Embedding (LLE) Charting Background Advances in data collection and storage
Dimension Reduction Techniques Presented by Jie (Jerry) Yu Outline Problem Modeling Review of PCA and MDS Isomap Local Linear Embedding (LLE) Charting Background Advances in data collection and storage
Clustering with k-means and Gaussian mixture distributions
 Clustering with k-means and Gaussian mixture distributions Machine Learning and Object Recognition 2017-2018 Jakob Verbeek Clustering Finding a group structure in the data Data in one cluster similar to
Clustering with k-means and Gaussian mixture distributions Machine Learning and Object Recognition 2017-2018 Jakob Verbeek Clustering Finding a group structure in the data Data in one cluster similar to
ON SCALABLE CODING OF HIDDEN MARKOV SOURCES. Mehdi Salehifar, Tejaswi Nanjundaswamy, and Kenneth Rose
 ON SCALABLE CODING OF HIDDEN MARKOV SOURCES Mehdi Salehifar, Tejaswi Nanjundaswamy, and Kenneth Rose Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Santa Barbara, CA, 93106
ON SCALABLE CODING OF HIDDEN MARKOV SOURCES Mehdi Salehifar, Tejaswi Nanjundaswamy, and Kenneth Rose Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Santa Barbara, CA, 93106
Independent Component Analysis and Unsupervised Learning. Jen-Tzung Chien
 Independent Component Analysis and Unsupervised Learning Jen-Tzung Chien TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Independent Component Analysis 2. Case Study I: Speech Recognition Independent voices Nonparametric likelihood
Independent Component Analysis and Unsupervised Learning Jen-Tzung Chien TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Independent Component Analysis 2. Case Study I: Speech Recognition Independent voices Nonparametric likelihood
Multimedia communications
 Multimedia communications Comunicazione multimediale G. Menegaz gloria.menegaz@univr.it Prologue Context Context Scale Scale Scale Course overview Goal The course is about wavelets and multiresolution
Multimedia communications Comunicazione multimediale G. Menegaz gloria.menegaz@univr.it Prologue Context Context Scale Scale Scale Course overview Goal The course is about wavelets and multiresolution
Oslo Class 6 Sparsity based regularization
 RegML2017@SIMULA Oslo Class 6 Sparsity based regularization Lorenzo Rosasco UNIGE-MIT-IIT May 4, 2017 Learning from data Possible only under assumptions regularization min Ê(w) + λr(w) w Smoothness Sparsity
RegML2017@SIMULA Oslo Class 6 Sparsity based regularization Lorenzo Rosasco UNIGE-MIT-IIT May 4, 2017 Learning from data Possible only under assumptions regularization min Ê(w) + λr(w) w Smoothness Sparsity
Clustering by Mixture Models. General background on clustering Example method: k-means Mixture model based clustering Model estimation
 Clustering by Mixture Models General bacground on clustering Example method: -means Mixture model based clustering Model estimation 1 Clustering A basic tool in data mining/pattern recognition: Divide
Clustering by Mixture Models General bacground on clustering Example method: -means Mixture model based clustering Model estimation 1 Clustering A basic tool in data mining/pattern recognition: Divide
2.3. Clustering or vector quantization 57
 Multivariate Statistics non-negative matrix factorisation and sparse dictionary learning The PCA decomposition is by construction optimal solution to argmin A R n q,h R q p X AH 2 2 under constraint :
Multivariate Statistics non-negative matrix factorisation and sparse dictionary learning The PCA decomposition is by construction optimal solution to argmin A R n q,h R q p X AH 2 2 under constraint :
Generalized Power Method for Sparse Principal Component Analysis
 Generalized Power Method for Sparse Principal Component Analysis Peter Richtárik CORE/INMA Catholic University of Louvain Belgium VOCAL 2008, Veszprém, Hungary CORE Discussion Paper #2008/70 joint work
Generalized Power Method for Sparse Principal Component Analysis Peter Richtárik CORE/INMA Catholic University of Louvain Belgium VOCAL 2008, Veszprém, Hungary CORE Discussion Paper #2008/70 joint work
Why Sparse Coding Works
 Why Sparse Coding Works Mathematical Challenges in Deep Learning Shaowei Lin (UC Berkeley) shaowei@math.berkeley.edu 10 Aug 2011 Deep Learning Kickoff Meeting What is Sparse Coding? There are many formulations
Why Sparse Coding Works Mathematical Challenges in Deep Learning Shaowei Lin (UC Berkeley) shaowei@math.berkeley.edu 10 Aug 2011 Deep Learning Kickoff Meeting What is Sparse Coding? There are many formulations
Gatsby Theoretical Neuroscience Lectures: Non-Gaussian statistics and natural images Parts I-II
 Gatsby Theoretical Neuroscience Lectures: Non-Gaussian statistics and natural images Parts I-II Gatsby Unit University College London 27 Feb 2017 Outline Part I: Theory of ICA Definition and difference
Gatsby Theoretical Neuroscience Lectures: Non-Gaussian statistics and natural images Parts I-II Gatsby Unit University College London 27 Feb 2017 Outline Part I: Theory of ICA Definition and difference
Finite Frame Quantization
 Finite Frame Quantization Liam Fowl University of Maryland August 21, 2018 1 / 38 Overview 1 Motivation 2 Background 3 PCM 4 First order Σ quantization 5 Higher order Σ quantization 6 Alternative Dual
Finite Frame Quantization Liam Fowl University of Maryland August 21, 2018 1 / 38 Overview 1 Motivation 2 Background 3 PCM 4 First order Σ quantization 5 Higher order Σ quantization 6 Alternative Dual
Deep learning / Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville. - Cambridge, MA ; London, Spis treści
 Deep learning / Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville. - Cambridge, MA ; London, 2017 Spis treści Website Acknowledgments Notation xiii xv xix 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Who Should Read This Book?
Deep learning / Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville. - Cambridge, MA ; London, 2017 Spis treści Website Acknowledgments Notation xiii xv xix 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Who Should Read This Book?
Multiple Kernel Learning
 CS 678A Course Project Vivek Gupta, 1 Anurendra Kumar 2 Sup: Prof. Harish Karnick 1 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering 2 Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology,
CS 678A Course Project Vivek Gupta, 1 Anurendra Kumar 2 Sup: Prof. Harish Karnick 1 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering 2 Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology,
Dictionary Learning for photo-z estimation
 Dictionary Learning for photo-z estimation Joana Frontera-Pons, Florent Sureau, Jérôme Bobin 5th September 2017 - Workshop Dictionary Learning on Manifolds MOTIVATION! Goal : Measure the radial positions
Dictionary Learning for photo-z estimation Joana Frontera-Pons, Florent Sureau, Jérôme Bobin 5th September 2017 - Workshop Dictionary Learning on Manifolds MOTIVATION! Goal : Measure the radial positions
STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing
 STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing Numerical Linear Algebra Background Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis May 15, 2018 Linear Algebra Background Vectors A vector has a direction and a magnitude
STA141C: Big Data & High Performance Statistical Computing Numerical Linear Algebra Background Cho-Jui Hsieh UC Davis May 15, 2018 Linear Algebra Background Vectors A vector has a direction and a magnitude
Sparse molecular image representation
 Sparse molecular image representation Sofia Karygianni a, Pascal Frossard a a Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Signal Processing Laboratory (LTS4), CH-115, Lausanne, Switzerland Abstract
Sparse molecular image representation Sofia Karygianni a, Pascal Frossard a a Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Signal Processing Laboratory (LTS4), CH-115, Lausanne, Switzerland Abstract
Expectation Maximization (EM)
 Expectation Maximization (EM) The Expectation Maximization (EM) algorithm is one approach to unsupervised, semi-supervised, or lightly supervised learning. In this kind of learning either no labels are
Expectation Maximization (EM) The Expectation Maximization (EM) algorithm is one approach to unsupervised, semi-supervised, or lightly supervised learning. In this kind of learning either no labels are
Random Processes. By: Nick Kingsbury
 Random Processes By: Nick Kingsbury Random Processes By: Nick Kingsbury Online: < http://cnx.org/content/col10204/1.3/ > C O N N E X I O N S Rice University, Houston, Texas This selection and arrangement
Random Processes By: Nick Kingsbury Random Processes By: Nick Kingsbury Online: < http://cnx.org/content/col10204/1.3/ > C O N N E X I O N S Rice University, Houston, Texas This selection and arrangement
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder. Canberra February June 2018
 Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 218 Outlines Overview Introduction Linear Algebra Probability Linear Regression 1
Cheng Soon Ong & Christian Walder Research Group and College of Engineering and Computer Science Canberra February June 218 Outlines Overview Introduction Linear Algebra Probability Linear Regression 1
L26: Advanced dimensionality reduction
 L26: Advanced dimensionality reduction The snapshot CA approach Oriented rincipal Components Analysis Non-linear dimensionality reduction (manifold learning) ISOMA Locally Linear Embedding CSCE 666 attern
L26: Advanced dimensionality reduction The snapshot CA approach Oriented rincipal Components Analysis Non-linear dimensionality reduction (manifold learning) ISOMA Locally Linear Embedding CSCE 666 attern
Some Recent Advances. in Non-convex Optimization. Purushottam Kar IIT KANPUR
 Some Recent Advances in Non-convex Optimization Purushottam Kar IIT KANPUR Outline of the Talk Recap of Convex Optimization Why Non-convex Optimization? Non-convex Optimization: A Brief Introduction Robust
Some Recent Advances in Non-convex Optimization Purushottam Kar IIT KANPUR Outline of the Talk Recap of Convex Optimization Why Non-convex Optimization? Non-convex Optimization: A Brief Introduction Robust
Sketching for Large-Scale Learning of Mixture Models
 Sketching for Large-Scale Learning of Mixture Models Nicolas Keriven Université Rennes 1, Inria Rennes Bretagne-atlantique Adv. Rémi Gribonval Outline Introduction Practical Approach Results Theoretical
Sketching for Large-Scale Learning of Mixture Models Nicolas Keriven Université Rennes 1, Inria Rennes Bretagne-atlantique Adv. Rémi Gribonval Outline Introduction Practical Approach Results Theoretical
Mathematical Formulation of Our Example
 Mathematical Formulation of Our Example We define two binary random variables: open and, where is light on or light off. Our question is: What is? Computer Vision 1 Combining Evidence Suppose our robot
Mathematical Formulation of Our Example We define two binary random variables: open and, where is light on or light off. Our question is: What is? Computer Vision 1 Combining Evidence Suppose our robot
Clustering with k-means and Gaussian mixture distributions
 Clustering with k-means and Gaussian mixture distributions Machine Learning and Category Representation 2012-2013 Jakob Verbeek, ovember 23, 2012 Course website: http://lear.inrialpes.fr/~verbeek/mlcr.12.13
Clustering with k-means and Gaussian mixture distributions Machine Learning and Category Representation 2012-2013 Jakob Verbeek, ovember 23, 2012 Course website: http://lear.inrialpes.fr/~verbeek/mlcr.12.13
Rice University. Endogenous Sparse Recovery. Eva L. Dyer. A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
 Rice University Endogenous Sparse Recovery by Eva L. Dyer A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Masters of Science Approved, Thesis Committee: Dr. Richard G. Baraniuk,
Rice University Endogenous Sparse Recovery by Eva L. Dyer A Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Masters of Science Approved, Thesis Committee: Dr. Richard G. Baraniuk,
Designing Information Devices and Systems I Discussion 13B
 EECS 6A Fall 7 Designing Information Devices and Systems I Discussion 3B. Orthogonal Matching Pursuit Lecture Orthogonal Matching Pursuit (OMP) algorithm: Inputs: A set of m songs, each of length n: S
EECS 6A Fall 7 Designing Information Devices and Systems I Discussion 3B. Orthogonal Matching Pursuit Lecture Orthogonal Matching Pursuit (OMP) algorithm: Inputs: A set of m songs, each of length n: S
Bayesian Methods for Sparse Signal Recovery
 Bayesian Methods for Sparse Signal Recovery Bhaskar D Rao 1 University of California, San Diego 1 Thanks to David Wipf, Jason Palmer, Zhilin Zhang and Ritwik Giri Motivation Motivation Sparse Signal Recovery
Bayesian Methods for Sparse Signal Recovery Bhaskar D Rao 1 University of California, San Diego 1 Thanks to David Wipf, Jason Palmer, Zhilin Zhang and Ritwik Giri Motivation Motivation Sparse Signal Recovery
A tutorial on sparse modeling. Outline:
 A tutorial on sparse modeling. Outline: 1. Why? 2. What? 3. How. 4. no really, why? Sparse modeling is a component in many state of the art signal processing and machine learning tasks. image processing
A tutorial on sparse modeling. Outline: 1. Why? 2. What? 3. How. 4. no really, why? Sparse modeling is a component in many state of the art signal processing and machine learning tasks. image processing
LECTURE :ICA. Rita Osadchy. Based on Lecture Notes by A. Ng
 LECURE :ICA Rita Osadchy Based on Lecture Notes by A. Ng Cocktail Party Person 1 2 s 1 Mike 2 s 3 Person 3 1 Mike 1 s 2 Person 2 3 Mike 3 microphone signals are mied speech signals 1 2 3 ( t) ( t) ( t)
LECURE :ICA Rita Osadchy Based on Lecture Notes by A. Ng Cocktail Party Person 1 2 s 1 Mike 2 s 3 Person 3 1 Mike 1 s 2 Person 2 3 Mike 3 microphone signals are mied speech signals 1 2 3 ( t) ( t) ( t)
Sparse analysis Lecture V: From Sparse Approximation to Sparse Signal Recovery
 Sparse analysis Lecture V: From Sparse Approximation to Sparse Signal Recovery Anna C. Gilbert Department of Mathematics University of Michigan Connection between... Sparse Approximation and Compressed
Sparse analysis Lecture V: From Sparse Approximation to Sparse Signal Recovery Anna C. Gilbert Department of Mathematics University of Michigan Connection between... Sparse Approximation and Compressed
Lecture 7: Con3nuous Latent Variable Models
 CSC2515 Fall 2015 Introduc3on to Machine Learning Lecture 7: Con3nuous Latent Variable Models All lecture slides will be available as.pdf on the course website: http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~urtasun/courses/csc2515/
CSC2515 Fall 2015 Introduc3on to Machine Learning Lecture 7: Con3nuous Latent Variable Models All lecture slides will be available as.pdf on the course website: http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~urtasun/courses/csc2515/
Machine Learning Techniques for Computer Vision
 Machine Learning Techniques for Computer Vision Part 2: Unsupervised Learning Microsoft Research Cambridge x 3 1 0.5 0.2 0 0.5 0.3 0 0.5 1 ECCV 2004, Prague x 2 x 1 Overview of Part 2 Mixture models EM
Machine Learning Techniques for Computer Vision Part 2: Unsupervised Learning Microsoft Research Cambridge x 3 1 0.5 0.2 0 0.5 0.3 0 0.5 1 ECCV 2004, Prague x 2 x 1 Overview of Part 2 Mixture models EM
STRUCTURE-AWARE DICTIONARY LEARNING WITH HARMONIC ATOMS
 19th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 2011) Barcelona, Spain, August 29 - September 2, 2011 STRUCTURE-AWARE DICTIONARY LEARNING WITH HARMONIC ATOMS Ken O Hanlon and Mark D.Plumbley Queen
19th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO 2011) Barcelona, Spain, August 29 - September 2, 2011 STRUCTURE-AWARE DICTIONARY LEARNING WITH HARMONIC ATOMS Ken O Hanlon and Mark D.Plumbley Queen
