APPENDIX 1: EXTENDED SAMPLE INFORMATION.
|
|
|
- Francine O’Brien’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 APPENDIX 1: EXTENDED SAMPLE INFORMATION. Location map of the giant bar between Inya and Little Jaloman (topographic map 1:50,000). The circle marks the sampling location. Giant bar boulders (location 1 see Fig. 1) Photograph Information Height above ground [m] Basal plane area [m²] IN m 23.2 m²
2 2 Photograph Information Height above ground [m] Basal plane area [m²] IN m 3.6 m³ IN m 2.8 m² IN m 5.4 m²
3 3 Photograph Information Height above ground [m] Basal plane area [m²] Boulders in the former lake basin (locations 2, 3, 4 see Fig. 1) KO m 15 m² KU m 12 m² CHU m 7.5 m²
4 4 APPENDIX 2: Analytical techniques and calculation scheme s were taken from the center of the boulder surfaces. The samples were crushed and ground and the quartz fraction was separated following the procedures described by Kohl & Nishiizumi (1992) and Ivy-Ochs (1996). BeO was extracted using a combination of column chemistry separation and selective hydroxide precipitation (Ochs & Ivy-Ochs, 1997). Apparent exposure ages were calculated from the measured 10Be nuclide concentration, the sampling depth and the site-specific production rate (Lal, 1991; Stone, 2000). The ages were corrected for topographic shielding (Dunne et al., 1999), variations in the geomagnetic field (Laj et al., 2004), erosion, snow cover and uplift, considering the following aspects: (i) The erosion rate for granitic rock in the study area was calculated from the measured nuclide concentration in a bedrock sample west of the Chuya gorge (CH-03-02). The sample was taken from glacially abraded bedrock behind a prominent moraine ridge. The moraine was deposited after the flood event and dated to 13.8±1.4 ka (Reuther, 2005). Quartz crystals on the glacially abraded granitic bedrock protruded about 2.5 cm above the surrounding rock. This grain-to-grain relief (2.5 cm) and the apparent exposure age of the surface (13 ka) were used to calculate the local erosion rate in a first order approximation (1.9 mm/ka-1). Only the sample KO was not corrected for erosion because here a quartz vein in a fine-grained schist matrix was sampled which did not protrude above the rock matrix, indicating negligible surface erosion. information: Lat / Long Altitude thickness fcorr (topo, slope)* 10 Be atom AMS error Production rate Apparent age # [ ] [m asl] [cm] [g -1 SiO 2-1 *10 5 ] [%] [atm g -1 yr -1 ] [ 10 Be kyr ] 50.2 N, CH , E * correction factor for the effect of topographic shielding and surface geometry (exponential depth profile, nucleonic attenuation length 155 g cm -2, muonic attenuation length 1510 g cm -2, coefficient m=2.3). blank-corrected. local production rate corrected for geometry, topography, sample thickness, erosion, snow cover, uplift and geomagnetic variations. # corrected only for topographic shielding, geometry and sample thickness.
5 5 (ii) The Altai mountain region is currently subject to uplift (Larroque et al., 2001). Uplift rates from the neighboring Gobi Altai are reported to be around 1 mm a-1 (Owen et al., 1997). This value is used in the age calculation. (iii) Snow cover corrections were only applied to the boulders on the giant bar in accordance with field observations. The three high-standing boulders in the basins are assumed to have not been covered by snow because it is likely they were windswept. For the other samples, a conservative value of 15 cm snow cover for 4 months per year was assumed (Onuchin & Burenina, 1996; Krenke, 1998). References: Dunne, J., Elmore, D. and Muzikar, P., 1999, Scaling factors for the rates of production of cosmogenic nuclides for geometric shielding and attenuation at depth of sloped surfaces: Geomorphology, v. 27, p Ivy-Ochs, S., 1996, The dating of rock surfaces in situ produced 10 Be, 26 Al and 36 Cl with examples from Antarctica and the Swiss Alps. PhD Thesis No 11763, ETH Zürich, 196 p. Kohl, C.P. and Nishiizumi, K., 1992, Chemical isolation of quartz for measurement of in-situ produced cosmogenic nuclides: Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, v. 56, p Krenke, A., 1998, updated 2004, Former Soviet Union Hydrological Snow Surveys: edited by NSIDC. Boulder, CO: National Snow and Ice Data Center/World Data Center for Glaciology. Digital media. Laj, C., Kissel, C. and Beer, J., 2004, High resolution global paleointensity stack since 75 kyr (GLOPIS-75) calibrated to absolute values: Geophysical Monograph Series 145, p Lal, D., 1991, Cosmic ray labeling of erosion surfaces: in situ nuclide production rates and erosion models: Earth and Planetary Science Letters, v. 104, p Larroque, C. Ritz, J.-F., Stéphan, J.-F., Sankov, V., Arjannikova, A., Calais, E., Dévercherre, J., and Loncke, L., 2001, Interaction compression extension à la limite Monglie-Sibérie: Comptes Rendue de l Academie de Sciences Paris, v. 332, p Ochs, M. and Ivy-Ochs, S., 1997, The chemical behavior of Be, Al, Fe, Ca, and Mg, during AMS target preparation from terrestrial silicates modeled with chemical speciation calculations: Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B, v. B123, p Onuchin, A. A. and Burenina, T. A., 1996, Climatic and geographic patterns in snow density dynamics, Northern Eurasia: Arctic Alpine Research, v. 28, p
6 6 Owen, L.A., Windley, B.F., Cunningham, W.D., Badamgarav, J. and Dorjnamjaa, D., 1997, Quaternary alluvial fans in the Gobi of southern Mongolia: evidence for neotectonics and climate change: Journal of Quaternary Science, v. 12, p Reuther, A.U., 2005, Surface exposure dating of glacial deposits from the last glacial cycle. Evidence from the Eastern Alps, the Bavarian Forest, the Southern Carpathians and the Altai Mountains: PhD thesis, University of Regensburg, Germany (accepted for publication in the series: Relief, Klima, Paläoboden, publisher: Schweizerbart, Stuttgart/Germany). Stone, J. O., 2000, Air pressure and cosmogenic isotope production: Journal of Geophysical Research, v. 105 B10, p
radionuclide laboratory using procedures according to Kohl and Nishiizumi (1992), Ivy-Ochs
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2010117 APPENDIX DR1 Methodology: Cosmogenic 10 Be exposure dating The cosmogenic 10 Be samples were processed at the University of Colorado cosmogenic radionuclide laboratory using
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2010117 APPENDIX DR1 Methodology: Cosmogenic 10 Be exposure dating The cosmogenic 10 Be samples were processed at the University of Colorado cosmogenic radionuclide laboratory using
Cosmogenic sample collection, preparation and analysis. Alluvium was collected from active channel beds and sieved in the field to yield a
 Data Repository Item - 1 - Cosmogenic sample collection, preparation and analysis. Alluvium was collected from active channel beds and sieved in the field to yield a sample with size fraction of 125-250
Data Repository Item - 1 - Cosmogenic sample collection, preparation and analysis. Alluvium was collected from active channel beds and sieved in the field to yield a sample with size fraction of 125-250
Sutherland et al: Glacial chronology, NZ
 Orbital forcing of mid-latitude southern hemisphere glaciation since 100 ka, inferred from cosmogenic nuclide ages of moraine boulders from the Cascade Plateau, southwest New Zealand Rupert Sutherland
Orbital forcing of mid-latitude southern hemisphere glaciation since 100 ka, inferred from cosmogenic nuclide ages of moraine boulders from the Cascade Plateau, southwest New Zealand Rupert Sutherland
Supplementary Fig. 1. Locations of thinning transects and photos of example samples. Mt Suess/Gondola Ridge transects extended metres above
 Supplementary Fig. 1. Locations of thinning transects and photos of example samples. Mt Suess/Gondola Ridge transects extended 260 24 metres above the modern surface of Mackay Glacier, and included 16
Supplementary Fig. 1. Locations of thinning transects and photos of example samples. Mt Suess/Gondola Ridge transects extended 260 24 metres above the modern surface of Mackay Glacier, and included 16
STRUCTURE AND HOLOCENE SLIP OF THE JID FAULT, MONGOLIA ALTAI
 STRUCTURE AND HOLOCENE SLIP OF THE JID FAULT, MONGOLIA ALTAI LAURA K.O. SMITH AND SARAHTSETSEG PUREDORG Princeton University, Mongolian University of Science and Technology Sponsors: Ramon Gonzalez-Mieres
STRUCTURE AND HOLOCENE SLIP OF THE JID FAULT, MONGOLIA ALTAI LAURA K.O. SMITH AND SARAHTSETSEG PUREDORG Princeton University, Mongolian University of Science and Technology Sponsors: Ramon Gonzalez-Mieres
Stock 1 GSA DATA REPOSITORY ITEM DR APPENDIX 1: SAMPLE PREPARATION AND ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES
 Stock 1 GSA DATA REPOSITORY ITEM DR2006152 APPENDIX 1: SAMPLE PREPARATION AND ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Apatite (U-Th)/He thermochronometry We collected modern fluvial sediment from Inyo Creek and Lone Pine
Stock 1 GSA DATA REPOSITORY ITEM DR2006152 APPENDIX 1: SAMPLE PREPARATION AND ANALYTICAL TECHNIQUES Apatite (U-Th)/He thermochronometry We collected modern fluvial sediment from Inyo Creek and Lone Pine
GSA Data Repository item for Munroe et al., Geology, Latest Pleistocene advance of alpine
 Munroe et al., p. DR1 GSA Data Repository item for Munroe et al., Geology, Latest Pleistocene advance of alpine glaciers in the southwestern Uinta Mountains, Utah, USA: Evidence for the influence of local
Munroe et al., p. DR1 GSA Data Repository item for Munroe et al., Geology, Latest Pleistocene advance of alpine glaciers in the southwestern Uinta Mountains, Utah, USA: Evidence for the influence of local
Amazing Ice: Glaciers and Ice Ages
 Amazing Ice: Glaciers and Ice Ages Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts Based on slides prepared by: Ronald L. Parker, Senior
Amazing Ice: Glaciers and Ice Ages Updated by: Rick Oches, Professor of Geology & Environmental Sciences Bentley University Waltham, Massachusetts Based on slides prepared by: Ronald L. Parker, Senior
Glacial landscape reconstructions in the eastern Dolomites since the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM)
 UNIMORE PhD Course in Models and Methods for Materials and Environmental Sciences XXXII cycle Glacial landscape reconstructions in the eastern Dolomites since the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) PhD student:
UNIMORE PhD Course in Models and Methods for Materials and Environmental Sciences XXXII cycle Glacial landscape reconstructions in the eastern Dolomites since the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) PhD student:
Supplementary File to Effects of physical erosion on chemical denudation rates: a numerical modeling study of soil-mantled hillslopes
 Supplementary File to Effects of physical erosion on chemical denudation rates: a numerical modeling study of soil-mantled hillslopes Ken L. Ferrier Department of Earth and Planetary Science, University
Supplementary File to Effects of physical erosion on chemical denudation rates: a numerical modeling study of soil-mantled hillslopes Ken L. Ferrier Department of Earth and Planetary Science, University
Low rates of bedrock outcrop erosion in the central Appalachian Mountains inferred from in situ 10 Be
 DR2013023 Low rates of bedrock outcrop erosion in the central Appalachian Mountains inferred from in situ 10 Be Eric W. Portenga Department of Geology University of Vermont Burlington, VT 05405 Paul R.
DR2013023 Low rates of bedrock outcrop erosion in the central Appalachian Mountains inferred from in situ 10 Be Eric W. Portenga Department of Geology University of Vermont Burlington, VT 05405 Paul R.
How do glaciers form?
 Glaciers What is a Glacier? A large mass of moving ice that exists year round is called a glacier. Glaciers are formed when snowfall exceeds snow melt year after year Snow and ice remain on the ground
Glaciers What is a Glacier? A large mass of moving ice that exists year round is called a glacier. Glaciers are formed when snowfall exceeds snow melt year after year Snow and ice remain on the ground
DETAILS OF CATCHMENTS STUDIED
 GSA Data Data Repository itemitem 2006048 DETAILS OF CATCHMENTS STUDIED 0 10 20 km Jacksons Bay Cascade River A Martyr R. Jerry R. B Cascade River Hokuri Creek, North Hokuri Creek, South Lake McKerrow
GSA Data Data Repository itemitem 2006048 DETAILS OF CATCHMENTS STUDIED 0 10 20 km Jacksons Bay Cascade River A Martyr R. Jerry R. B Cascade River Hokuri Creek, North Hokuri Creek, South Lake McKerrow
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint. Chapter 6 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens
 Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 6 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 6 Earth Science 11e Tarbuck/Lutgens 2006 Pearson Prentice Hall This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors
University of Washington, Mail Stop , Seattle, WA USA
 A simple, internally consistent, and easily accessible means of calculating surface exposure ages or erosion rates from 10 Be and 26 Al measurements DRAFT Greg Balco a, John O. H. Stone a a Quaternary
A simple, internally consistent, and easily accessible means of calculating surface exposure ages or erosion rates from 10 Be and 26 Al measurements DRAFT Greg Balco a, John O. H. Stone a a Quaternary
(Denton et al., 1991 ; Ing lfsson et al., 1998 ; Anderson, 1999 ;Denton et al.,1984), (Dowsett et al.,1996)
 16 1 Vol. 16, No. 1 2004 3 CHIN ESE JOURNAL OF POLAR RESEARCH March 2004 (, 100029) (, 100085) (, 100029) 10 Be 26 Al, 2Ma, (L GM), 200m,, (L GM), 10 Be 26 Al 1 2600 km 3, 83 %, 60 (Denton,2002),,, (Denton
16 1 Vol. 16, No. 1 2004 3 CHIN ESE JOURNAL OF POLAR RESEARCH March 2004 (, 100029) (, 100085) (, 100029) 10 Be 26 Al, 2Ma, (L GM), 200m,, (L GM), 10 Be 26 Al 1 2600 km 3, 83 %, 60 (Denton,2002),,, (Denton
Glacial Modification of Terrain
 Glacial Modification Part I Stupendous glaciers and crystal snowflakes -- every form of animate or inanimate existence leaves its impress upon the soul of man. 1 -Orison Swett Marden Glacial Modification
Glacial Modification Part I Stupendous glaciers and crystal snowflakes -- every form of animate or inanimate existence leaves its impress upon the soul of man. 1 -Orison Swett Marden Glacial Modification
Supplemental Online Material. Lifton et al. - Constraints on late Quaternary glacial history, E. Kyrgyz Tian Shan
 Supplemental Online Material Lifton et al. - Constraints on late Quaternary glacial history, E. Kyrgyz Tian Shan Lifton et al. Constraints on late Quaternary glacial history, E. Kyrgyz Tian Shan Page 2
Supplemental Online Material Lifton et al. - Constraints on late Quaternary glacial history, E. Kyrgyz Tian Shan Lifton et al. Constraints on late Quaternary glacial history, E. Kyrgyz Tian Shan Page 2
Supplementary material
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY2014088 Supplementary material Dominance of tectonics over climate in Himalayan denudation Vincent Godard, Didier L. Bourlès, Françoise Spinabella, Douglas W. Burbank, Bodo Bookhagen,
GSA DATA REPOSITORY2014088 Supplementary material Dominance of tectonics over climate in Himalayan denudation Vincent Godard, Didier L. Bourlès, Françoise Spinabella, Douglas W. Burbank, Bodo Bookhagen,
OBSERVING AND MAPPING THE ROCK STREAMS AND QUARRIES IN SOME MASSIFS FROM THE ROMANIAN CARPATHIANS BY MEANS OF SATELLITE IMAGES
 VASILE LOGHIN 371 OBSERVING AND MAPPING THE ROCK STREAMS AND QUARRIES IN SOME MASSIFS FROM THE ROMANIAN CARPATHIANS BY MEANS OF SATELLITE IMAGES Key words: rock streams, quarries, satellite images, Carpathians
VASILE LOGHIN 371 OBSERVING AND MAPPING THE ROCK STREAMS AND QUARRIES IN SOME MASSIFS FROM THE ROMANIAN CARPATHIANS BY MEANS OF SATELLITE IMAGES Key words: rock streams, quarries, satellite images, Carpathians
Vendredi 27 août : les glaciers rocheux de la Valpisella, les plus spectaculaires de la vallée.
 Vendredi 27 août : les glaciers rocheux de la Valpisella, les plus spectaculaires de la vallée. groupe A : Refuge des Forni, Valpisella, glaciers rocheux, arête du Cima dei Forni (3233 m, passages faciles
Vendredi 27 août : les glaciers rocheux de la Valpisella, les plus spectaculaires de la vallée. groupe A : Refuge des Forni, Valpisella, glaciers rocheux, arête du Cima dei Forni (3233 m, passages faciles
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output
 mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
mountain rivers fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) high transport capacity low storage input output strong interaction between streams & hillslopes Sediment Budgets for Mountain Rivers Little
Science EOG Review: Landforms
 Mathematician Science EOG Review: Landforms Vocabulary Definition Term canyon deep, large, V- shaped valley formed by a river over millions of years of erosion; sometimes called gorges (example: Linville
Mathematician Science EOG Review: Landforms Vocabulary Definition Term canyon deep, large, V- shaped valley formed by a river over millions of years of erosion; sometimes called gorges (example: Linville
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa
 Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Glacial and Arid Landscapes Foundations, 6e - Chapter 4 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Glaciers Glaciers are parts of two basic cycles
Foundations of Earth Science, 6e Lutgens, Tarbuck, & Tasa Glacial and Arid Landscapes Foundations, 6e - Chapter 4 Stan Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Glaciers Glaciers are parts of two basic cycles
Geologic Mapping Regional Tournament Trial Event
 Geologic Mapping Regional Tournament Trial Event A TEAM OF UP TO: 2 Team Name AVAILABLE TIME: 50 min Required Materials: Each team MUST have a protractor, ruler, non-programmable calculator, colored pencils,
Geologic Mapping Regional Tournament Trial Event A TEAM OF UP TO: 2 Team Name AVAILABLE TIME: 50 min Required Materials: Each team MUST have a protractor, ruler, non-programmable calculator, colored pencils,
Ecoregions Glossary. 7.8B: Changes To Texas Land Earth and Space
 Ecoregions Glossary Ecoregions The term ecoregions was developed by combining the terms ecology and region. Ecology is the study of the interrelationship of organisms and their environments. The term,
Ecoregions Glossary Ecoregions The term ecoregions was developed by combining the terms ecology and region. Ecology is the study of the interrelationship of organisms and their environments. The term,
JOB VAN ROIJEN, KI,AAS VAN DER BORG, ARIE DE JONG
 A CORRECTION FOR IN-SITU 14C IN ANTARCTIC ICE WITH 14C0 JOB VAN ROIJEN, KI,AAS VAN DER BORG, ARIE DE JONG Department of Subatomic Physics, Universiteit Utrecht, P.O. Box 80,000, NL-3508 TA Utrecht The
A CORRECTION FOR IN-SITU 14C IN ANTARCTIC ICE WITH 14C0 JOB VAN ROIJEN, KI,AAS VAN DER BORG, ARIE DE JONG Department of Subatomic Physics, Universiteit Utrecht, P.O. Box 80,000, NL-3508 TA Utrecht The
Chapter 3 Erosion and Deposition. The Big Question:
 Chapter 3 Erosion and Deposition The Big Question: 1 Design a way to represent and describe the 4 types of mass movement. You may use pictures, diagrams, list, web, chart, etc 2 Chapter 3: Erosion and
Chapter 3 Erosion and Deposition The Big Question: 1 Design a way to represent and describe the 4 types of mass movement. You may use pictures, diagrams, list, web, chart, etc 2 Chapter 3: Erosion and
Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1)
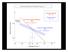 Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1) Detachment Limited S d >> S t Transport Limited Channel Gradient (m/m) 10-1 Stochastic Variation { Detachment Limited Equilibrium Slope S d = k sd A -θ d S
Down-stream process transition (f (q s ) = 1) Detachment Limited S d >> S t Transport Limited Channel Gradient (m/m) 10-1 Stochastic Variation { Detachment Limited Equilibrium Slope S d = k sd A -θ d S
Wind River Glaciers. High altitude Reservoirs. WWDC Green River Basin Advisory Group May 9, 2011
 Wind River Glaciers Wyoming s No cost, Zeromaintenance, Fully automatic, High altitude Reservoirs WWDC Green River Basin Advisory Group May 9, 2011 Wind River Range, Sublette Co. Thompson/Love Wind River
Wind River Glaciers Wyoming s No cost, Zeromaintenance, Fully automatic, High altitude Reservoirs WWDC Green River Basin Advisory Group May 9, 2011 Wind River Range, Sublette Co. Thompson/Love Wind River
Relief History and Coupling of Erosional Processes in the Teton Range, Wyoming
 University of Wyoming National Park Service Research Center Annual Report Volume 30 30th Annual Report, 2006-2007 Article 27 1-1-2006 Relief History and Coupling of Erosional Processes in the Teton Range,
University of Wyoming National Park Service Research Center Annual Report Volume 30 30th Annual Report, 2006-2007 Article 27 1-1-2006 Relief History and Coupling of Erosional Processes in the Teton Range,
A Geological Tour of Tumbledown Mountain, Maine
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities April, 1998 A Geological Tour of Tumbledown Mountain, Maine 44 45 3.21 N, 70 32 50.24 W Text by Robert G. Marvinney, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities April, 1998 A Geological Tour of Tumbledown Mountain, Maine 44 45 3.21 N, 70 32 50.24 W Text by Robert G. Marvinney, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry
Extra Credit Assignment (Chapters 4, 5, 6, and 10)
 GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Extra Credit Assignment (Chapters 4, 5, 6, and 10) For this assignment you will require: a calculator and metric ruler. Chapter 4 Objectives:
GEOLOGY 306 Laboratory Instructor: TERRY J. BOROUGHS NAME: Extra Credit Assignment (Chapters 4, 5, 6, and 10) For this assignment you will require: a calculator and metric ruler. Chapter 4 Objectives:
What is a Glacier? Types of Glaciers
 Alpine & Continental Glaciers Glacial Mass Balance Glacial Ice Formation Glacial Movement & Erosion Erosional and Depositional Landforms The Pleistocene Epoch Geomorphology of SW Manitoba Chapter 17 1
Alpine & Continental Glaciers Glacial Mass Balance Glacial Ice Formation Glacial Movement & Erosion Erosional and Depositional Landforms The Pleistocene Epoch Geomorphology of SW Manitoba Chapter 17 1
Paleoceanography Spring 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.740 Paleoceanography Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. PALEOCEANOGRAPHY 12.740 SPRING
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.740 Paleoceanography Spring 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. PALEOCEANOGRAPHY 12.740 SPRING
4. The map below shows a meandering stream. Points A, B, C, and D represent locations along the stream bottom.
 1. Sediment is deposited as a river enters a lake because the A) velocity of the river decreases B) force of gravity decreases C) volume of water increases D) slope of the river increases 2. Which diagram
1. Sediment is deposited as a river enters a lake because the A) velocity of the river decreases B) force of gravity decreases C) volume of water increases D) slope of the river increases 2. Which diagram
Ages of Prehistoric Earthquakes Revealed by Cosmogenic Chlorine- 36 in a Bedrock Fault Scarp at Hebgen Lake
 Ages of Prehistoric Earthquakes Revealed by Cosmogenic Chlorine- 6 in a Bedrock Fault Scarp at Hebgen Lake Marek Zreda and Jay S. Noller Marek Zreda, Department of Hydrology and Water Resources, University
Ages of Prehistoric Earthquakes Revealed by Cosmogenic Chlorine- 6 in a Bedrock Fault Scarp at Hebgen Lake Marek Zreda and Jay S. Noller Marek Zreda, Department of Hydrology and Water Resources, University
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 1) Which property would best distinguish sediment deposited by a river from sediment deposited by a glacier? thickness of sediment layers age of fossils found in the sediment mineral composition
Name: 1) Which property would best distinguish sediment deposited by a river from sediment deposited by a glacier? thickness of sediment layers age of fossils found in the sediment mineral composition
2/23/2009. Visualizing Earth Science. Chapter Overview. Deserts and Drylands. Glaciers and Ice Sheets
 Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 6 Deserts, Glaciers and Ice Sheets Chapter Overview Deserts and Drylands Glaciers and Ice Sheets Deserts Geography Categorization of deserts
Visualizing Earth Science By Z. Merali and B. F. Skinner Chapter 6 Deserts, Glaciers and Ice Sheets Chapter Overview Deserts and Drylands Glaciers and Ice Sheets Deserts Geography Categorization of deserts
SAMPLE PAGE. pulses. The Ice Age By: Sue Peterson
 Page 61 Objective sight words (pulses, intermittent, isotopes, chronicle, methane, tectonic plates, volcanism, configurations, land-locked, erratic); concepts (geological evidence and specific terminology
Page 61 Objective sight words (pulses, intermittent, isotopes, chronicle, methane, tectonic plates, volcanism, configurations, land-locked, erratic); concepts (geological evidence and specific terminology
EROSION AND DEPOSITION
 CHAPTER 8 EROSION AND DEPOSITION SECTION 8 1 Changing Earth s Surface (pages 252-255) This section explains how sediment is carried away and deposited elsewhere to wear down and build up Earth s surface.
CHAPTER 8 EROSION AND DEPOSITION SECTION 8 1 Changing Earth s Surface (pages 252-255) This section explains how sediment is carried away and deposited elsewhere to wear down and build up Earth s surface.
GEOSPATIAL ANALYSIS OF GLACIAL DYNAMICS OF SHIGAR AND SHAYOK BASINS. Syed Naseem Abbas Gilany 1
 GEOSPATIAL ANALYSIS OF GLACIAL DYNAMICS OF SHIGAR AND SHAYOK BASINS 1 OUTLINE Introduction Problem Statement / Rationale Objectives Material and Methods Study Area Datasets Required Data Analysis / Assessment
GEOSPATIAL ANALYSIS OF GLACIAL DYNAMICS OF SHIGAR AND SHAYOK BASINS 1 OUTLINE Introduction Problem Statement / Rationale Objectives Material and Methods Study Area Datasets Required Data Analysis / Assessment
1. What define planetary surfaces geologically? 2. What controls the evolution of planetary surfaces?
 Planetary Surfaces: 1. What define planetary surfaces geologically? 2. What controls the evolution of planetary surfaces? 3. How do surface-shaping processes scale across planetary bodies of different
Planetary Surfaces: 1. What define planetary surfaces geologically? 2. What controls the evolution of planetary surfaces? 3. How do surface-shaping processes scale across planetary bodies of different
For submission to California Geology. February 13, Revisiting the age of the Blackhawk: Landslide dating using 10 Be and 26 Al
 For submission to California Geology February 13, 2002 Revisiting the age of the Blackhawk: Landslide dating using 10 Be and 26 Al *Kyle K. Nichols Paul R. Bierman School of Natural Resources and Department
For submission to California Geology February 13, 2002 Revisiting the age of the Blackhawk: Landslide dating using 10 Be and 26 Al *Kyle K. Nichols Paul R. Bierman School of Natural Resources and Department
common time scale developed for Greenland and Antarctic ice core records. Central to this
 1 Supplemental Material Age scale: For the dating of the EDML and EDC ice cores (Figure S1) we used for the first time a new common time scale developed for Greenland and Antarctic ice core records. Central
1 Supplemental Material Age scale: For the dating of the EDML and EDC ice cores (Figure S1) we used for the first time a new common time scale developed for Greenland and Antarctic ice core records. Central
Natural and anthropogenic climate change Lessons from ice cores
 Natural and anthropogenic climate change Lessons from ice cores Eric Wolff British Antarctic Survey, Cambridge ewwo@bas.ac.uk ASE Annual Conference 2011; ESTA/ESEU lecture Outline What is British Antarctic
Natural and anthropogenic climate change Lessons from ice cores Eric Wolff British Antarctic Survey, Cambridge ewwo@bas.ac.uk ASE Annual Conference 2011; ESTA/ESEU lecture Outline What is British Antarctic
Lecture 10 Glaciers and glaciation
 Lecture 10 Glaciers and glaciation Outline Importance of ice to people! Basics of glaciers formation, classification, mechanisms of movement Glacial landscapes erosion and deposition by glaciers and the
Lecture 10 Glaciers and glaciation Outline Importance of ice to people! Basics of glaciers formation, classification, mechanisms of movement Glacial landscapes erosion and deposition by glaciers and the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION A
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION A tuff cone erupted under frozen-bed ice (northern Victoria Land, Antarctica): linking glaciovolcanic and cosmogenic nuclide data for ice sheet reconstructions Smellie, J.L. 1*,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION A tuff cone erupted under frozen-bed ice (northern Victoria Land, Antarctica): linking glaciovolcanic and cosmogenic nuclide data for ice sheet reconstructions Smellie, J.L. 1*,
Lecture 21: Glaciers and Paleoclimate Read: Chapter 15 Homework due Thursday Nov. 12. What we ll learn today:! Learning Objectives (LO)
 Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 21: Glaciers and Paleoclimate Read: Chapter 15 Homework due Thursday Nov. 12 What we ll learn today:! 1. 1. Glaciers and where they occur! 2. 2. Compare depositional and
Learning Objectives (LO) Lecture 21: Glaciers and Paleoclimate Read: Chapter 15 Homework due Thursday Nov. 12 What we ll learn today:! 1. 1. Glaciers and where they occur! 2. 2. Compare depositional and
Sediment dynamics and sub-recent sediment budget of the braided sandur system at Sandane, Erdalen (Nordfjord, western Norway)
 Sediment dynamics and sub-recent sediment budget of the braided sandur system at Sandane, Erdalen (Nordfjord, western Norway) A.A. Beylich (1,2), L. Hansen (1), S. Liermann (3), D. Gintz (3), K. Laute
Sediment dynamics and sub-recent sediment budget of the braided sandur system at Sandane, Erdalen (Nordfjord, western Norway) A.A. Beylich (1,2), L. Hansen (1), S. Liermann (3), D. Gintz (3), K. Laute
Post-depositional impacts on Findlinge (erratic boulders) and their implications for surface-exposure dating
 Swiss J Geosci (2011) 104:445 453 DOI 10.1007/s00015-011-0088-7 Post-depositional impacts on Findlinge (erratic boulders) and their implications for surface-exposure dating Naki Akçar Susan Ivy-Ochs Peter
Swiss J Geosci (2011) 104:445 453 DOI 10.1007/s00015-011-0088-7 Post-depositional impacts on Findlinge (erratic boulders) and their implications for surface-exposure dating Naki Akçar Susan Ivy-Ochs Peter
GEOCHEMISTRY UNIFORM SYLLABUS
 GEOCHEMISTRY UNIFORM SYLLABUS The Association of Professional Engineers and Geoscientists of the Province of British Columbia Note: 1. This Syllabus May Be Subject To Change 2. These Courses Are Required
GEOCHEMISTRY UNIFORM SYLLABUS The Association of Professional Engineers and Geoscientists of the Province of British Columbia Note: 1. This Syllabus May Be Subject To Change 2. These Courses Are Required
Sediments and bedrock erosion
 Eroding landscapes: fluvial processes Sediments and bedrock erosion Mikaël ATTAL Marsyandi valley, Himalayas, Nepal Acknowledgements: Jérôme Lavé, Peter van der Beek and other scientists from LGCA (Grenoble)
Eroding landscapes: fluvial processes Sediments and bedrock erosion Mikaël ATTAL Marsyandi valley, Himalayas, Nepal Acknowledgements: Jérôme Lavé, Peter van der Beek and other scientists from LGCA (Grenoble)
Which landscape best represents the shape of the valleys occupied by glaciers? A) B) C) D)
 1. Glaciers often form parallel scratches and grooves in bedrock because glaciers A) deposit sediment in unsorted piles B) deposit rounded sand in V-shaped valleys C) continually melt and refreeze D) drag
1. Glaciers often form parallel scratches and grooves in bedrock because glaciers A) deposit sediment in unsorted piles B) deposit rounded sand in V-shaped valleys C) continually melt and refreeze D) drag
Chapter 1 Section 2. Land, Water, and Climate
 Chapter 1 Section 2 Land, Water, and Climate Vocabulary 1. Landforms- natural features of the Earth s land surface 2. Elevation- height above sea level 3. Relief- changes in height 4. Core- most inner
Chapter 1 Section 2 Land, Water, and Climate Vocabulary 1. Landforms- natural features of the Earth s land surface 2. Elevation- height above sea level 3. Relief- changes in height 4. Core- most inner
Objectives: Define Relative Age, Absolute Age
 S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. g. Describe how fossils show evidence of the changing surface
S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth s surface is formed. c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. g. Describe how fossils show evidence of the changing surface
Uplift and Denudation of the Teton Range, Wyoming
 University of Wyoming National Park Service Research Center Annual Report Volume 31 31st Annual Report, 2008 Article 24 1-1-2008 Uplift and Denudation of the Teton Range, Wyoming Lisa Tranel Virginia Polytechnic
University of Wyoming National Park Service Research Center Annual Report Volume 31 31st Annual Report, 2008 Article 24 1-1-2008 Uplift and Denudation of the Teton Range, Wyoming Lisa Tranel Virginia Polytechnic
Physiographic Provinces (West, Ch. 13)
 Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 13 Physiographic Provinces (West, Ch. 13) The definition of the term Physiography Physiography (n.) The science which treats of the earth's exterior physical features,
Geology 229 Engineering Geology Lecture 13 Physiographic Provinces (West, Ch. 13) The definition of the term Physiography Physiography (n.) The science which treats of the earth's exterior physical features,
ENVIRONMENTAL GEOSCIENCE UNIFORM SYLLABUS
 ENVIRONMENTAL GEOSCIENCE UNIFORM SYLLABUS The Association of Professional Engineers and Geoscientists of the Province of British Columbia Note: 1. This Syllabus May Be Subject To Change 2. These Courses
ENVIRONMENTAL GEOSCIENCE UNIFORM SYLLABUS The Association of Professional Engineers and Geoscientists of the Province of British Columbia Note: 1. This Syllabus May Be Subject To Change 2. These Courses
Quantifying sediment supply at the end of the last glaciation: dynamic reconstruction of an alpine debris flow fan
 Data Repository 2014086 Savi et al., GSA Bullettin Quantifying sediment supply at the end of the last glaciation: dynamic reconstruction of an alpine debris flow fan APPENDIX 1 STRATIGRAPHIC DATA The 8
Data Repository 2014086 Savi et al., GSA Bullettin Quantifying sediment supply at the end of the last glaciation: dynamic reconstruction of an alpine debris flow fan APPENDIX 1 STRATIGRAPHIC DATA The 8
Guided Notes Surface Processes. Erosion & Deposition By: Glaciers
 Guided Notes Surface Processes Erosion & Deposition By: Glaciers K. Coder 2015 26) How does moving ice erode and deposit sediments? Glaciers (Movement of Ice): a naturally formed mass of ice and snow that
Guided Notes Surface Processes Erosion & Deposition By: Glaciers K. Coder 2015 26) How does moving ice erode and deposit sediments? Glaciers (Movement of Ice): a naturally formed mass of ice and snow that
Supplementary Figure 1. Normalized glacier terminus elevation changes versus normalized glacier length changes.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normalized glacier terminus elevation changes versus normalized glacier length changes. Supplementary Figure 2. Normalized glacier lengths through time, as shown in Fig. 2 in the
Supplementary Figure 1. Normalized glacier terminus elevation changes versus normalized glacier length changes. Supplementary Figure 2. Normalized glacier lengths through time, as shown in Fig. 2 in the
The Agents of Erosion
 The Agents of Erosion 1. Erosion & Deposition 2. Water 3. Wind 4. Ice California Science Project 1 1. Erosion and Deposition Erosion is the physical removal and transport of material by mobile agents such
The Agents of Erosion 1. Erosion & Deposition 2. Water 3. Wind 4. Ice California Science Project 1 1. Erosion and Deposition Erosion is the physical removal and transport of material by mobile agents such
Chapter 2. Wearing Down Landforms: Rivers and Ice. Physical Weathering
 Chapter 2 Wearing Down Landforms: Rivers and Ice Physical Weathering Weathering vs. Erosion Weathering is the breakdown of rock and minerals. Erosion is a two fold process that starts with 1) breakdown
Chapter 2 Wearing Down Landforms: Rivers and Ice Physical Weathering Weathering vs. Erosion Weathering is the breakdown of rock and minerals. Erosion is a two fold process that starts with 1) breakdown
Ch 10 Deposition Practice Questions
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the data table below. Six identical cylinders, A through F, were filled with equal volumes of sorted spherical particles. The data table shows the particle
1. Base your answer to the following question on the data table below. Six identical cylinders, A through F, were filled with equal volumes of sorted spherical particles. The data table shows the particle
Practice Test Rocks and Minerals. Name. Page 1
 Name Practice Test Rocks and Minerals 1. Which rock would be the best source of the mineral garnet? A) basalt B) limestone C) schist D) slate 2. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite
Name Practice Test Rocks and Minerals 1. Which rock would be the best source of the mineral garnet? A) basalt B) limestone C) schist D) slate 2. Which mineral is mined for its iron content? A) hematite
NAME: GEL 109 Final Study Guide - Winter 2008 Questions 6-24 WILL be on the final exactly as written here; this is 60% of the test.
 GEL 109 Final Study Guide - Winter 2008 Questions 6-24 WILL be on the final exactly as written here; this is 60% of the test. 1. Sketch a map view of three types of deltas showing the differences in river,
GEL 109 Final Study Guide - Winter 2008 Questions 6-24 WILL be on the final exactly as written here; this is 60% of the test. 1. Sketch a map view of three types of deltas showing the differences in river,
Deducing Erosion Rates of the Mt. Langley Summit Flat using 21 Ne in Quartz. Curtis Baden 1. David L. Shuster 1,2, Advisor. Greg Balco 2, Collaborator
 Deducing Erosion Rates of the Mt. Langley Summit Flat using 21 Ne in Quartz Curtis Baden 1 David L. Shuster 1,2, Advisor Greg Balco 2, Collaborator 1: Earth and Planetary Science; University of California,
Deducing Erosion Rates of the Mt. Langley Summit Flat using 21 Ne in Quartz Curtis Baden 1 David L. Shuster 1,2, Advisor Greg Balco 2, Collaborator 1: Earth and Planetary Science; University of California,
within the dendro-calibration curve, the landslide of Köfels, Ötz Valley, Austria
 ELSEVIER Earth and Planetary Science Letters 161 (1998) 231 241 10 Be and 26 Al production rates deduced from an instantaneous event within the dendro-calibration curve, the landslide of Köfels, Ötz Valley,
ELSEVIER Earth and Planetary Science Letters 161 (1998) 231 241 10 Be and 26 Al production rates deduced from an instantaneous event within the dendro-calibration curve, the landslide of Köfels, Ötz Valley,
CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS ON ICE REGIME OF THE RIVERS IN MONGOLIA
 Ice in the Environment: Proceedings of the 16th IAHR International Symposium on Ice Dunedin, New Zealand, 2nd 6th December 2002 International Association of Hydraulic Engineering and Research CLIMATE CHANGE
Ice in the Environment: Proceedings of the 16th IAHR International Symposium on Ice Dunedin, New Zealand, 2nd 6th December 2002 International Association of Hydraulic Engineering and Research CLIMATE CHANGE
Glacial Erosion: Processes, Rates & Landforms. Bernard Hallet ESS
 Glacial Erosion: Processes, Rates & Landforms Bernard Hallet ESS 685-2409 hallet@u.washington.edu Over the last decade the Earth Science community interested in glacial erosion has expanded and diversified
Glacial Erosion: Processes, Rates & Landforms Bernard Hallet ESS 685-2409 hallet@u.washington.edu Over the last decade the Earth Science community interested in glacial erosion has expanded and diversified
B) color B) Sediment must be compacted and cemented before it can change to sedimentary rock. D) igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks
 1. Which characteristic of nonsedimentary rocks would provide the least evidence about the environment in which the rocks were formed? A) structure B) color C) crystal size D) mineral composition 2. Which
1. Which characteristic of nonsedimentary rocks would provide the least evidence about the environment in which the rocks were formed? A) structure B) color C) crystal size D) mineral composition 2. Which
GEL 109 Midterm W05, Page points total (1 point per minute is a good pace, but it is good to have time to recheck your answers!
 GEL 109 Midterm W05, Page 1 50 points total (1 point per minute is a good pace, but it is good to have time to recheck your answers!) 1. Are the following flow types typically laminar or turbulent and
GEL 109 Midterm W05, Page 1 50 points total (1 point per minute is a good pace, but it is good to have time to recheck your answers!) 1. Are the following flow types typically laminar or turbulent and
The elevations on the interior plateau generally vary between 300 and 650 meters with
 11 2. HYDROLOGICAL SETTING 2.1 Physical Features and Relief Labrador is bounded in the east by the Labrador Sea (Atlantic Ocean), in the west by the watershed divide, and in the south, for the most part,
11 2. HYDROLOGICAL SETTING 2.1 Physical Features and Relief Labrador is bounded in the east by the Labrador Sea (Atlantic Ocean), in the west by the watershed divide, and in the south, for the most part,
Chapter 16 Weathering, Erosion, Mass Wasting. Chapter 16 Weathering, Erosion, Mass Wasting. Mechanical Weathering
 Weathering, Erosion and Mass Wasting Weathering is the the breakdown of solid rock at or near the Earth's surface. Chapter 16 Weathering, Erosion, Mass Wasting Does weathering of rock remove or add CO
Weathering, Erosion and Mass Wasting Weathering is the the breakdown of solid rock at or near the Earth's surface. Chapter 16 Weathering, Erosion, Mass Wasting Does weathering of rock remove or add CO
Lab Final Review 4/16/18
 Lab Final Review 4/16/18 Overall goals from lab Think about geology on recent timescales, predict the direction change Be able to identify how different landforms or patterns (e.g. drainage patterns, dune
Lab Final Review 4/16/18 Overall goals from lab Think about geology on recent timescales, predict the direction change Be able to identify how different landforms or patterns (e.g. drainage patterns, dune
FROM CRYOSPHERE TO ANTHROPOGENIC IMPACTS
 FROM CRYOSPHERE Balázs Nagy Department of Physical Geography Eötvös Loránd University, Budapest TO ANTHROPOGENIC IMPACTS primary data and environmental applications: - summary of the Hungarian high altitude
FROM CRYOSPHERE Balázs Nagy Department of Physical Geography Eötvös Loránd University, Budapest TO ANTHROPOGENIC IMPACTS primary data and environmental applications: - summary of the Hungarian high altitude
CHAPTER 4: PRINCIPLES OF EXPOSURE AGE DETERMINATION USING
 CHAPTER 4: PRINCIPLES OF EXPOSURE AGE DETERMINATION USING TERRESTRIAL IN SITU PRODUCED COSMOGENIC NUCLIDES (TCN) After the discovery of the cosmic radiation in the 1910 s, Grosse (1934) was the first who
CHAPTER 4: PRINCIPLES OF EXPOSURE AGE DETERMINATION USING TERRESTRIAL IN SITU PRODUCED COSMOGENIC NUCLIDES (TCN) After the discovery of the cosmic radiation in the 1910 s, Grosse (1934) was the first who
T. Perron Glaciers 1. Glaciers
 T. Perron 12.001 Glaciers 1 Glaciers I. Why study glaciers? [PPT: Perito Moreno glacier, Argentina] Role in freshwater budget o Fraction of earth s water that is fresh (non-saline): 3% o Fraction of earth
T. Perron 12.001 Glaciers 1 Glaciers I. Why study glaciers? [PPT: Perito Moreno glacier, Argentina] Role in freshwater budget o Fraction of earth s water that is fresh (non-saline): 3% o Fraction of earth
Chapter 5: Glaciers and Deserts
 I. Glaciers and Glaciation Chapter 5: Glaciers and Deserts A. A thick mass of ice that forms over land from the compaction and recrystallization of snow and shows evidence of past or present flow B. Types
I. Glaciers and Glaciation Chapter 5: Glaciers and Deserts A. A thick mass of ice that forms over land from the compaction and recrystallization of snow and shows evidence of past or present flow B. Types
3.13Glaciers past and present
 3.13Glaciers past and present We start with a headline from The Scotsman newspaper that rocked Britain s scientific establishment on the morning of 7 October 1840: 3 Discovery of the Former Existence of
3.13Glaciers past and present We start with a headline from The Scotsman newspaper that rocked Britain s scientific establishment on the morning of 7 October 1840: 3 Discovery of the Former Existence of
THE ACTION OF GLACIERS
 Surface processes THE ACTION OF GLACIERS Glaciers are enormous masses of ice which are formed due to accumulation, compaction and re-crystallisation of the snow deposited in very cold regions (the majority
Surface processes THE ACTION OF GLACIERS Glaciers are enormous masses of ice which are formed due to accumulation, compaction and re-crystallisation of the snow deposited in very cold regions (the majority
RAYMOND SIEVER Harvard University
 E A R T H FOURTH EDITION FRANK PRESS National Academy of Sciences RAYMOND SIEVER Harvard University W. H. Freeman and Company New York Preface xiii Acknowledgments xviii PART I PROLOGUE CHAPTER 1 HISTORY
E A R T H FOURTH EDITION FRANK PRESS National Academy of Sciences RAYMOND SIEVER Harvard University W. H. Freeman and Company New York Preface xiii Acknowledgments xviii PART I PROLOGUE CHAPTER 1 HISTORY
Unit 7.2 W.E.D. & Topography Test
 Name: Score: Unit 7.2 W.E.D. & Topography Test 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 1. The formation of mountains is due mainly to while the destruction
Name: Score: Unit 7.2 W.E.D. & Topography Test 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 1. The formation of mountains is due mainly to while the destruction
DATA REPOSITORY TABLES
 GSA Data Repository Item 2016354 Portenga, E.W., Bierman P.R., Trodick, C.D., Jr., Greene, S.E., DeJong, B.D., Rood, D.H., and Pavich, M.J., 2016, Background rates of erosion and sediment generation in
GSA Data Repository Item 2016354 Portenga, E.W., Bierman P.R., Trodick, C.D., Jr., Greene, S.E., DeJong, B.D., Rood, D.H., and Pavich, M.J., 2016, Background rates of erosion and sediment generation in
Electrical imaging techniques for hydrological and risk assessment studies
 Séminaire IPG le 9 mars 2006 Strasbourg Institute of Geophysics ETH Hoenggerberg CH-8093 Zurich Electrical imaging techniques for hydrological and risk assessment studies Laurent Marescot laurent@aug.ig.erdw.ethz.ch
Séminaire IPG le 9 mars 2006 Strasbourg Institute of Geophysics ETH Hoenggerberg CH-8093 Zurich Electrical imaging techniques for hydrological and risk assessment studies Laurent Marescot laurent@aug.ig.erdw.ethz.ch
Laboratory Exercise #3 The Hydrologic Cycle and Running Water Processes
 Laboratory Exercise #3 The Hydrologic Cycle and Running Water Processes page - 1 Section A - The Hydrologic Cycle Figure 1 illustrates the hydrologic cycle which quantifies how water is cycled throughout
Laboratory Exercise #3 The Hydrologic Cycle and Running Water Processes page - 1 Section A - The Hydrologic Cycle Figure 1 illustrates the hydrologic cycle which quantifies how water is cycled throughout
Accelerator mass spectrometry in geologic research
 Accelerator mass spectrometry in geologic research Paul Muzikar David Elmore Department of Physics, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana 47907, USA Darryl E. Granger Department of Earth and Atmospheric
Accelerator mass spectrometry in geologic research Paul Muzikar David Elmore Department of Physics, Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana 47907, USA Darryl E. Granger Department of Earth and Atmospheric
Landscape evolution. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities and life
 Landforms Landscape evolution A Natural landscape is the original landscape that exists before it is acted upon by human culture. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities
Landforms Landscape evolution A Natural landscape is the original landscape that exists before it is acted upon by human culture. An Anthropic landscape is the landscape modified by humans for their activities
Basin-scale analysis of long-term sediment-generation rates derived from 10 Be in river sediment:
 Basin-scale analysis of long-term sediment-generation rates derived from 10 Be in river sediment: The Susquehanna River basin and beyond Joanna M. Reuter M.S. Proposal April 30, 2003 Paul Bierman, advisor
Basin-scale analysis of long-term sediment-generation rates derived from 10 Be in river sediment: The Susquehanna River basin and beyond Joanna M. Reuter M.S. Proposal April 30, 2003 Paul Bierman, advisor
Lecture Outline Lecture Outline Monday April 9-16, 2018 Questions? Announcements:
 Lecture Outline Lecture Outline Monday April 9-16, 2018 Questions? Announcements: Geology 101 Night Video: The Day After Tomorrow Hollywood disaster movie about the onset of a glacial period When: Monday
Lecture Outline Lecture Outline Monday April 9-16, 2018 Questions? Announcements: Geology 101 Night Video: The Day After Tomorrow Hollywood disaster movie about the onset of a glacial period When: Monday
The Geology of Sebago Lake State Park
 Maine Geologic Facts and Localities September, 2002 43 55 17.46 N, 70 34 13.07 W Text by Robert Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by Robert Johnston Introduction Sebago
Maine Geologic Facts and Localities September, 2002 43 55 17.46 N, 70 34 13.07 W Text by Robert Johnston, Department of Agriculture, Conservation & Forestry 1 Map by Robert Johnston Introduction Sebago
Mountain Rivers. Gutta cavat lapidem. (Dripping water hollows out a stone) -Ovid, Epistulae Ex Ponto, Book 3, no. 10, 1. 5
 Mountain Rivers Gutta cavat lapidem (Dripping water hollows out a stone) -Ovid, Epistulae Ex Ponto, Book 3, no. 10, 1. 5 Mountain Rivers Fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) High transport
Mountain Rivers Gutta cavat lapidem (Dripping water hollows out a stone) -Ovid, Epistulae Ex Ponto, Book 3, no. 10, 1. 5 Mountain Rivers Fixed channel boundaries (bedrock banks and bed) High transport
Spring break reading. Glacial formation. Surface processes: Glaciers and deserts. The Control of Nature
 suggested Spring break reading The Control of Nature by John McPhee Surface processes: Glaciers and deserts describes our efforts to control three natural hazards: 1. The Mississippi Floods 2. The Heimaey
suggested Spring break reading The Control of Nature by John McPhee Surface processes: Glaciers and deserts describes our efforts to control three natural hazards: 1. The Mississippi Floods 2. The Heimaey
Veronica Sosa-Gonzalez Defense Presentation
 Veronica Sosa-Gonzalez Defense Presentation Background Introduction Methods Results and Interpretations Conclusion Final remarks Photo credits: K. Nichols Determine long-term erosion rates in Panama, using
Veronica Sosa-Gonzalez Defense Presentation Background Introduction Methods Results and Interpretations Conclusion Final remarks Photo credits: K. Nichols Determine long-term erosion rates in Panama, using
A Thesis Proposal Presented. Lucas Jonathan Reusser. The Faculty of the Geology Department. The University of Vermont.
 USING COSMOGENIC NUCLIDES TO DETERMINE THE TIMING, SPATIAL PATTERN, AND RATE OF FLUVIAL INCISION WITHIN BEDROCK CHANNELS OF THE SUSQUEHANNA RIVER, PENNSYLVANIA A Thesis Proposal Presented by Lucas Jonathan
USING COSMOGENIC NUCLIDES TO DETERMINE THE TIMING, SPATIAL PATTERN, AND RATE OF FLUVIAL INCISION WITHIN BEDROCK CHANNELS OF THE SUSQUEHANNA RIVER, PENNSYLVANIA A Thesis Proposal Presented by Lucas Jonathan
GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 5
 UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 5 Sedimentation Rocks Formed by Surface Processes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Mineralogy of sandstones Key Figure 5.12
UNDERSTANDING EARTH, SIXTH EDITION GROTZINGER JORDAN GEOLOGY MEDIA SUITE Chapter 5 Sedimentation Rocks Formed by Surface Processes 2010 W.H. Freeman and Company Mineralogy of sandstones Key Figure 5.12
Rapid Communication. Constraining Holocene 10 Be production rates in Greenland. Introduction. Jakobshavn Isfjord, west Greenland. Radiocarbon dating
 JOURNAL OF QUATERNARY SCIENCE (2012) 27(1) 2 6 ISSN 0267-8179. DOI: 10.1002/jqs.1562 Rapid Communication Constraining Holocene 10 Be production rates in Greenland JASON P. BRINER, 1 * NICOLÁS E. YOUNG,
JOURNAL OF QUATERNARY SCIENCE (2012) 27(1) 2 6 ISSN 0267-8179. DOI: 10.1002/jqs.1562 Rapid Communication Constraining Holocene 10 Be production rates in Greenland JASON P. BRINER, 1 * NICOLÁS E. YOUNG,
Erosion and Deposition
 Erosion and Deposition Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Water erosion begins when runoff from rainfall flows in a thin layer over the land
Erosion and Deposition Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Water erosion begins when runoff from rainfall flows in a thin layer over the land
THE FLUVIAL ACTION OF THE KARLA BASIN STREAMS IN A NATURAL AND MAN MADE ENVIRONMENT
 Δελτίο της Ελληνικής Γεωλογικής Εταιρίας, 2010 Bulletin of the Geological Society of Greece, 2010 Πρακτικά 12ου Διεθνούς Συνεδρίου Proceedings of the 12th International Congress Πάτρα, Μάιος 2010 Patras,
Δελτίο της Ελληνικής Γεωλογικής Εταιρίας, 2010 Bulletin of the Geological Society of Greece, 2010 Πρακτικά 12ου Διεθνούς Συνεδρίου Proceedings of the 12th International Congress Πάτρα, Μάιος 2010 Patras,
