Based on the original slides of Hung-yi Lee
|
|
|
- Natalie Charles
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Based on the original slides of Hung-yi Lee
2 Google Trends Deep learning obtains many exciting results. Can contribute to new Smart Services in the Context of the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT Services need to learn from raw data. Classification and Prediction
3 Part I: Introduction of Deep Learning Part II: Why Deep? Part III: Tips for Training Deep Neural Network Part IV: Neural Network with Memory
4 What people already knew in 980s
5 Handwriting Digit Recognition Machine 2
6 INPUT OUTPUT x y 0. is 6 x 6 = 256 Ink No ink 0 x 2 x 256 y y is 2 is 0 The image is 2 Each dimension represents the confidence of a digit.
7 Handwriting Digit Recognition x y x 2 y 2 Machine 2 x 256 f: R 256 R 0 y 0 In deep learning, the function f is represented by neural network
8 Neuron f: R K R a w z a w a 2 w 2 a K w K b a 2 w 2 w K z z a a K weights b bias Activation function
9 neuron Input x Layer Layer 2 Layer L Output y x 2 y 2 x N y M Input Layer Hidden Layers Output Layer Deep means many hidden layers
10 Sigmoid Function z e z z z
11
12 f: R 2 R 2 f = f 0 0 = Different parameters define different function
13 y y 2 σ =
14 x y x 2 x N W W 2 W L b b 2 x a a 2 y b L y 2 y M σ W x + b σ W 2 a + b 2 σ W L a L- + b L
15 x y x 2 x N W W 2 W L b b 2 b L x a a 2 y y 2 y M y = f x Using parallel computing techniques to speed up matrix operation = σ W L σ W 2 σ W x + b + b 2 + b L
16 Softmax layer as the output layer Ordinary Layer z z 2 y y z 2 z 2 In general, the output of network can be any value. z 3 y 3 z 3 May not be easy to interpret
17 Softmax layer as the output layer Softmax Layer Probability: > y i > 0 y i = i z z 2 z 3 3 e e e e z 20 e z 2 e z 3 3 j 0.05 z j e 0.88 y 0.2 y 0 y 2 3 e e e z z z j 3 j 3 j e e e z z z j j j
18 x θ = W, b, W 2, b 2, W L, b L y 0. is 6 x 6 = 256 Ink No ink 0 x 2 x 256 y y 0 Set the network parameters θ such that Input: Input: Softmax How to let the neural network achieve this is 2 is 0 y has the maximum value y 2 has the maximum value
19 Preparing training data: images and their labels Using the training data to find the network parameters.
20 Given a set of network parameters θ, each example has a cost value. x y 0.2 x 2 x 256 y y Cost L(θ) 0 0 Cost can be Euclidean distance or cross entropy of the network output and target target
21 For all training data x x 2 x R NN NN NN y y 2 L θ L 2 θ y y 2 x 3 NN y 3 y 3 L 3 θ y R y R L R θ Total Cost: R C θ = L r θ r= How bad the network parameters θ is on this task Find the network parameters θ that minimize this value
22 Error Surface The colors represent the value of C. Assume there are only two parameters w and w 2 in a network. θ = w, w 2 Randomly pick a starting point θ 0 w 2 η C θ 0 θ 0 C θ 0 θ C θ 0 = C θ0 / w C θ 0 / w 2 Compute the negative gradient at θ 0 C θ 0 Times the learning rate η η C θ 0 w
23 w 2 η C θ θ 2 θ 0 Eventually, we would reach a minima.. η C θ 2 θ C C θ θ 2 Randomly pick a starting point θ 0 Compute the negative gradient at θ 0 C θ 0 Times the learning rate η η C θ 0 w
24 Gradient descent never guarantee global minima Different initial point θ 0 C w w 2 Reach different minima, so different results Who is Afraid of Non-Convex Loss Functions? _lecun_wia/
25 cost Very slow at the plateau Stuck at saddle point Stuck at local minima C θ 0 C θ = 0 parameter space C θ = 0
26 Momentum How about put this phenomenon in gradient descent?
27 cost Still not guarantee reaching global minima, but give some hope Movement = Negative of Gradient + Momentum Negative of Gradient Momentum Real Movement Gradient = 0
28 Mini-batch Mini-batch x NN y y L x 3 NN y 3 y 3 x 2 NN L 3 y 2 y 2 L 2 x 6 NN y 6 y 6 L 6 Randomly initialize θ 0 Pick the st batch C = L + L 3 + θ θ 0 η C θ 0 Pick the 2 nd batch C = L 2 + L 6 + θ 2 θ η C θ C is different each time when we update parameters!
29 Original Gradient Descent With Mini-batch unstable The colors represent the total C on all training data.
30 Mini-batch Mini-batch Faster Better! x NN y y C x 3 NN y 3 y 3 x 2 NN C 3 y 2 y 2 C 2 x 6 NN y 6 y 6 C 6 Randomly initialize θ 0 Pick the st batch C = C + C 3 + θ θ 0 η C θ 0 Pick the 2 nd batch C = C 2 + C 6 + θ 2 θ η C θ Until all mini-batches have been picked one epoch Repeat the above process
31 A network can have millions of parameters. Backpropagation is the way to compute the gradients efficiently Ref: 2/Lecture/DNN%20backprop.ecm.mp4/index.html Many toolkits can compute the gradients automatically Ref: ture/theano%20dnn.ecm.mp4/index.html
32
33 Layer X Size Word Error Rate (%) X 2k X 2k X 2k X 2k 7.8 Layer X Size Word Error Rate (%) Not surprised, more parameters, better performance 5 X 2k 7.2 X X 2k 7. X X 6k 22. Seide, Frank, Gang Li, and Dong Yu. "Conversational Speech Transcription Using Context-Dependent Deep Neural Networks." Interspeech. 20.
34 Any continuous function f f : R N R M Can be realized by a network with one hidden layer (given enough hidden neurons) Reference for the reason: eplearning.com/chap4.html Why Deep neural network not Fat neural network?
35 The same number of parameters Which one is better? x x 2 xn Shallow x x 2 xn Deep
36 Layer X Size Word Error Rate (%) X 2k X 2k X 2k X 2k 7.8 Layer X Size Word Error Rate (%) 5 X 2k 7.2 X X 2k 7. X X 6k 22. Seide, Frank, Gang Li, and Dong Yu. "Conversational Speech Transcription Using Context-Dependent Deep Neural Networks." Interspeech. 20.
37 can be trained by little data Deep Modularization Classifier Girls with long hair Image Boy or Girl? Basic Classifie Long r or short? Sharing by the following classifiers as module Classifier 2 fine Classifier 3 Classifier 4 Boys with long Little hair data Girls with short hair Boys with short hair
38 Deep Modularization x Deep Learning also works on small data set like TIMIT. Less training data? x 2 x N The modularization is automatically learned from data. The most basic classifiers Use st layer as module to build classifiers Use 2 nd layer as module
39 Hand-crafted kernel function SVM Deep Learning x Apply simple classifier Source of image: Learnable kernel φ x simple classifier y x x 2 y 2 x N y M
40 A two levels of basic logic gates can represent any Boolean function. However, no one uses two levels of logic gates to build computers Using multiple layers of logic gates to build some functions are much simpler (less gates needed).
41 Boosting Deep Learning x x 2 Input x Weak classifier Weak classifier Weak classifier Weak classifier Boosted weak classifier Combine Boosted Boosted weak classifier x N
42 Before 2006, deeper usually does not imply better.
43
44
45 Don t forget! Modify the Network Better optimization Strategy overfittin g Preventing Overfitting
46 Modify the Network New activation functions, for example, ReLU or Maxout Better optimization Strategy Adaptive learning rates Prevent Overfitting Dropout Only use this approach when you already obtained good results on the training data.
47 Neural Networks and Deep Learning written by Michael Nielsen Deep Learning (not finished yet) Written by Yoshua Bengio, Ian J. Goodfellow and Aaron Courville
Deep Learning Tutorial. 李宏毅 Hung-yi Lee
 Deep Learning Tutorial 李宏毅 Hung-yi Lee Outline Part I: Introduction of Deep Learning Part II: Why Deep? Part III: Tips for Training Deep Neural Network Part IV: Neural Network with Memory Part I: Introduction
Deep Learning Tutorial 李宏毅 Hung-yi Lee Outline Part I: Introduction of Deep Learning Part II: Why Deep? Part III: Tips for Training Deep Neural Network Part IV: Neural Network with Memory Part I: Introduction
Deep learning attracts lots of attention.
 Deep Learning Deep learning attracts lots of attention. I believe you have seen lots of exciting results before. Deep learning trends at Google. Source: SIGMOD/Jeff Dean Ups and downs of Deep Learning
Deep Learning Deep learning attracts lots of attention. I believe you have seen lots of exciting results before. Deep learning trends at Google. Source: SIGMOD/Jeff Dean Ups and downs of Deep Learning
Tips for Deep Learning
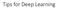 Tips for Deep Learning Recipe of Deep Learning Step : define a set of function Step : goodness of function Step 3: pick the best function NO Overfitting! NO YES Good Results on Testing Data? YES Good Results
Tips for Deep Learning Recipe of Deep Learning Step : define a set of function Step : goodness of function Step 3: pick the best function NO Overfitting! NO YES Good Results on Testing Data? YES Good Results
Tips for Deep Learning
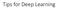 Tips for Deep Learning Recipe of Deep Learning Step : define a set of function Step : goodness of function Step 3: pick the best function NO Overfitting! NO YES Good Results on Testing Data? YES Good Results
Tips for Deep Learning Recipe of Deep Learning Step : define a set of function Step : goodness of function Step 3: pick the best function NO Overfitting! NO YES Good Results on Testing Data? YES Good Results
Deep Learning Tutorial. 李宏毅 Hung-yi Lee
 Deep Learning Tutorial 李宏毅 Hung-yi Lee Deep learning attracts lots of attention. Google Trends Deep learning obtains many exciting results. The talks in this afternoon This talk will focus on the technical
Deep Learning Tutorial 李宏毅 Hung-yi Lee Deep learning attracts lots of attention. Google Trends Deep learning obtains many exciting results. The talks in this afternoon This talk will focus on the technical
Based on the original slides of Hung-yi Lee
 Based on the original slides of Hung-yi Lee New Activation Function Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) σ z a a = z Reason: 1. Fast to compute 2. Biological reason a = 0 [Xavier Glorot, AISTATS 11] [Andrew L.
Based on the original slides of Hung-yi Lee New Activation Function Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) σ z a a = z Reason: 1. Fast to compute 2. Biological reason a = 0 [Xavier Glorot, AISTATS 11] [Andrew L.
Need for Deep Networks Perceptron. Can only model linear functions. Kernel Machines. Non-linearity provided by kernels
 Need for Deep Networks Perceptron Can only model linear functions Kernel Machines Non-linearity provided by kernels Need to design appropriate kernels (possibly selecting from a set, i.e. kernel learning)
Need for Deep Networks Perceptron Can only model linear functions Kernel Machines Non-linearity provided by kernels Need to design appropriate kernels (possibly selecting from a set, i.e. kernel learning)
Need for Deep Networks Perceptron. Can only model linear functions. Kernel Machines. Non-linearity provided by kernels
 Need for Deep Networks Perceptron Can only model linear functions Kernel Machines Non-linearity provided by kernels Need to design appropriate kernels (possibly selecting from a set, i.e. kernel learning)
Need for Deep Networks Perceptron Can only model linear functions Kernel Machines Non-linearity provided by kernels Need to design appropriate kernels (possibly selecting from a set, i.e. kernel learning)
Deep Learning, Data Irregularities and Beyond
 Deep Learning, Data Irregularities and Beyond Dr. Swagatam Das Electronics and Communication Sciences Unit, Indian Statistical Institute, Kolkata 700 108, India. E-mail: swagatam.das@isical.ac.in Road
Deep Learning, Data Irregularities and Beyond Dr. Swagatam Das Electronics and Communication Sciences Unit, Indian Statistical Institute, Kolkata 700 108, India. E-mail: swagatam.das@isical.ac.in Road
Classification goals: Make 1 guess about the label (Top-1 error) Make 5 guesses about the label (Top-5 error) No Bounding Box
 ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever, Geoffrey E. Hinton Motivation Classification goals: Make 1 guess about the label (Top-1 error) Make 5 guesses
ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever, Geoffrey E. Hinton Motivation Classification goals: Make 1 guess about the label (Top-1 error) Make 5 guesses
Deep Learning. Hung-yi Lee 李宏毅
 Deep Learning Hung-yi Lee 李宏毅 Deep learning attracts lots of attention. I believe you have seen lots of exciting results before. Deep learning trends at Google. Source: SIGMOD 206/Jeff Dean 958: Perceptron
Deep Learning Hung-yi Lee 李宏毅 Deep learning attracts lots of attention. I believe you have seen lots of exciting results before. Deep learning trends at Google. Source: SIGMOD 206/Jeff Dean 958: Perceptron
Introduction to Neural Networks
 CUONG TUAN NGUYEN SEIJI HOTTA MASAKI NAKAGAWA Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Copyright by Nguyen, Hotta and Nakagawa 1 Pattern classification Which category of an input? Example: Character
CUONG TUAN NGUYEN SEIJI HOTTA MASAKI NAKAGAWA Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology Copyright by Nguyen, Hotta and Nakagawa 1 Pattern classification Which category of an input? Example: Character
Neural Networks. Nicholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas
 Neural Networks Nicholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas Handwritten Digit Recognition Given a collection of handwritten digits and their corresponding labels, we d like to be able to correctly classify
Neural Networks Nicholas Ruozzi University of Texas at Dallas Handwritten Digit Recognition Given a collection of handwritten digits and their corresponding labels, we d like to be able to correctly classify
ECE521 Lectures 9 Fully Connected Neural Networks
 ECE521 Lectures 9 Fully Connected Neural Networks Outline Multi-class classification Learning multi-layer neural networks 2 Measuring distance in probability space We learnt that the squared L2 distance
ECE521 Lectures 9 Fully Connected Neural Networks Outline Multi-class classification Learning multi-layer neural networks 2 Measuring distance in probability space We learnt that the squared L2 distance
Grundlagen der Künstlichen Intelligenz
 Grundlagen der Künstlichen Intelligenz Neural networks Daniel Hennes 21.01.2018 (WS 2017/18) University Stuttgart - IPVS - Machine Learning & Robotics 1 Today Logistic regression Neural networks Perceptron
Grundlagen der Künstlichen Intelligenz Neural networks Daniel Hennes 21.01.2018 (WS 2017/18) University Stuttgart - IPVS - Machine Learning & Robotics 1 Today Logistic regression Neural networks Perceptron
More Tips for Training Neural Network. Hung-yi Lee
 More Tips for Training Neural Network Hung-yi ee Outline Activation Function Cost Function Data Preprocessing Training Generalization Review: Training Neural Network Neural network: f ; θ : input (vector)
More Tips for Training Neural Network Hung-yi ee Outline Activation Function Cost Function Data Preprocessing Training Generalization Review: Training Neural Network Neural network: f ; θ : input (vector)
Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
 Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) nojunk@snu.ac.kr http://mipal.snu.ac.kr Department of Transdisciplinary Studies Seoul National University, Korea Jan. 2016 Many slides are from Fei-Fei
Introduction to Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) nojunk@snu.ac.kr http://mipal.snu.ac.kr Department of Transdisciplinary Studies Seoul National University, Korea Jan. 2016 Many slides are from Fei-Fei
What Do Neural Networks Do? MLP Lecture 3 Multi-layer networks 1
 What Do Neural Networks Do? MLP Lecture 3 Multi-layer networks 1 Multi-layer networks Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 3 7 October 2015 MLP Lecture 3 Multi-layer networks 2 What Do Single
What Do Neural Networks Do? MLP Lecture 3 Multi-layer networks 1 Multi-layer networks Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 3 7 October 2015 MLP Lecture 3 Multi-layer networks 2 What Do Single
CSE446: Neural Networks Spring Many slides are adapted from Carlos Guestrin and Luke Zettlemoyer
 CSE446: Neural Networks Spring 2017 Many slides are adapted from Carlos Guestrin and Luke Zettlemoyer Human Neurons Switching time ~ 0.001 second Number of neurons 10 10 Connections per neuron 10 4-5 Scene
CSE446: Neural Networks Spring 2017 Many slides are adapted from Carlos Guestrin and Luke Zettlemoyer Human Neurons Switching time ~ 0.001 second Number of neurons 10 10 Connections per neuron 10 4-5 Scene
Neural Networks. Single-layer neural network. CSE 446: Machine Learning Emily Fox University of Washington March 10, /9/17
 3/9/7 Neural Networks Emily Fox University of Washington March 0, 207 Slides adapted from Ali Farhadi (via Carlos Guestrin and Luke Zettlemoyer) Single-layer neural network 3/9/7 Perceptron as a neural
3/9/7 Neural Networks Emily Fox University of Washington March 0, 207 Slides adapted from Ali Farhadi (via Carlos Guestrin and Luke Zettlemoyer) Single-layer neural network 3/9/7 Perceptron as a neural
Neural networks and optimization
 Neural networks and optimization Nicolas Le Roux INRIA 8 Nov 2011 Nicolas Le Roux (INRIA) Neural networks and optimization 8 Nov 2011 1 / 80 1 Introduction 2 Linear classifier 3 Convolutional neural networks
Neural networks and optimization Nicolas Le Roux INRIA 8 Nov 2011 Nicolas Le Roux (INRIA) Neural networks and optimization 8 Nov 2011 1 / 80 1 Introduction 2 Linear classifier 3 Convolutional neural networks
Introduction to Neural Networks
 Introduction to Neural Networks Philipp Koehn 3 October 207 Linear Models We used before weighted linear combination of feature values h j and weights λ j score(λ, d i ) = j λ j h j (d i ) Such models
Introduction to Neural Networks Philipp Koehn 3 October 207 Linear Models We used before weighted linear combination of feature values h j and weights λ j score(λ, d i ) = j λ j h j (d i ) Such models
Neural Networks: Optimization & Regularization
 Neural Networks: Optimization & Regularization Shan-Hung Wu shwu@cs.nthu.edu.tw Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan Machine Learning Shan-Hung Wu (CS, NTHU) NN Opt & Reg
Neural Networks: Optimization & Regularization Shan-Hung Wu shwu@cs.nthu.edu.tw Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan Machine Learning Shan-Hung Wu (CS, NTHU) NN Opt & Reg
Lecture 35: Optimization and Neural Nets
 Lecture 35: Optimization and Neural Nets CS 4670/5670 Sean Bell DeepDream [Google, Inceptionism: Going Deeper into Neural Networks, blog 2015] Aside: CNN vs ConvNet Note: There are many papers that use
Lecture 35: Optimization and Neural Nets CS 4670/5670 Sean Bell DeepDream [Google, Inceptionism: Going Deeper into Neural Networks, blog 2015] Aside: CNN vs ConvNet Note: There are many papers that use
Feedforward Neural Networks. Michael Collins, Columbia University
 Feedforward Neural Networks Michael Collins, Columbia University Recap: Log-linear Models A log-linear model takes the following form: p(y x; v) = exp (v f(x, y)) y Y exp (v f(x, y )) f(x, y) is the representation
Feedforward Neural Networks Michael Collins, Columbia University Recap: Log-linear Models A log-linear model takes the following form: p(y x; v) = exp (v f(x, y)) y Y exp (v f(x, y )) f(x, y) is the representation
Machine Learning. Neural Networks. (slides from Domingos, Pardo, others)
 Machine Learning Neural Networks (slides from Domingos, Pardo, others) For this week, Reading Chapter 4: Neural Networks (Mitchell, 1997) See Canvas For subsequent weeks: Scaling Learning Algorithms toward
Machine Learning Neural Networks (slides from Domingos, Pardo, others) For this week, Reading Chapter 4: Neural Networks (Mitchell, 1997) See Canvas For subsequent weeks: Scaling Learning Algorithms toward
Machine Learning for Computer Vision 8. Neural Networks and Deep Learning. Vladimir Golkov Technical University of Munich Computer Vision Group
 Machine Learning for Computer Vision 8. Neural Networks and Deep Learning Vladimir Golkov Technical University of Munich Computer Vision Group INTRODUCTION Nonlinear Coordinate Transformation http://cs.stanford.edu/people/karpathy/convnetjs/
Machine Learning for Computer Vision 8. Neural Networks and Deep Learning Vladimir Golkov Technical University of Munich Computer Vision Group INTRODUCTION Nonlinear Coordinate Transformation http://cs.stanford.edu/people/karpathy/convnetjs/
Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function.
 Bayesian learning: Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function. Let y be the true label and y be the predicted
Bayesian learning: Machine learning comes from Bayesian decision theory in statistics. There we want to minimize the expected value of the loss function. Let y be the true label and y be the predicted
Machine Learning
 Machine Learning 10-315 Maria Florina Balcan Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University 03/29/2019 Today: Artificial neural networks Backpropagation Reading: Mitchell: Chapter 4 Bishop: Chapter
Machine Learning 10-315 Maria Florina Balcan Machine Learning Department Carnegie Mellon University 03/29/2019 Today: Artificial neural networks Backpropagation Reading: Mitchell: Chapter 4 Bishop: Chapter
CSC 578 Neural Networks and Deep Learning
 CSC 578 Neural Networks and Deep Learning Fall 2018/19 3. Improving Neural Networks (Some figures adapted from NNDL book) 1 Various Approaches to Improve Neural Networks 1. Cost functions Quadratic Cross
CSC 578 Neural Networks and Deep Learning Fall 2018/19 3. Improving Neural Networks (Some figures adapted from NNDL book) 1 Various Approaches to Improve Neural Networks 1. Cost functions Quadratic Cross
Jakub Hajic Artificial Intelligence Seminar I
 Jakub Hajic Artificial Intelligence Seminar I. 11. 11. 2014 Outline Key concepts Deep Belief Networks Convolutional Neural Networks A couple of questions Convolution Perceptron Feedforward Neural Network
Jakub Hajic Artificial Intelligence Seminar I. 11. 11. 2014 Outline Key concepts Deep Belief Networks Convolutional Neural Networks A couple of questions Convolution Perceptron Feedforward Neural Network
Lecture 17: Neural Networks and Deep Learning
 UVA CS 6316 / CS 4501-004 Machine Learning Fall 2016 Lecture 17: Neural Networks and Deep Learning Jack Lanchantin Dr. Yanjun Qi 1 Neurons 1-Layer Neural Network Multi-layer Neural Network Loss Functions
UVA CS 6316 / CS 4501-004 Machine Learning Fall 2016 Lecture 17: Neural Networks and Deep Learning Jack Lanchantin Dr. Yanjun Qi 1 Neurons 1-Layer Neural Network Multi-layer Neural Network Loss Functions
Course 395: Machine Learning - Lectures
 Course 395: Machine Learning - Lectures Lecture 1-2: Concept Learning (M. Pantic) Lecture 3-4: Decision Trees & CBC Intro (M. Pantic & S. Petridis) Lecture 5-6: Evaluating Hypotheses (S. Petridis) Lecture
Course 395: Machine Learning - Lectures Lecture 1-2: Concept Learning (M. Pantic) Lecture 3-4: Decision Trees & CBC Intro (M. Pantic & S. Petridis) Lecture 5-6: Evaluating Hypotheses (S. Petridis) Lecture
Neural Networks. Yan Shao Department of Linguistics and Philology, Uppsala University 7 December 2016
 Neural Networks Yan Shao Department of Linguistics and Philology, Uppsala University 7 December 2016 Outline Part 1 Introduction Feedforward Neural Networks Stochastic Gradient Descent Computational Graph
Neural Networks Yan Shao Department of Linguistics and Philology, Uppsala University 7 December 2016 Outline Part 1 Introduction Feedforward Neural Networks Stochastic Gradient Descent Computational Graph
Machine Learning for Large-Scale Data Analysis and Decision Making A. Neural Networks Week #6
 Machine Learning for Large-Scale Data Analysis and Decision Making 80-629-17A Neural Networks Week #6 Today Neural Networks A. Modeling B. Fitting C. Deep neural networks Today s material is (adapted)
Machine Learning for Large-Scale Data Analysis and Decision Making 80-629-17A Neural Networks Week #6 Today Neural Networks A. Modeling B. Fitting C. Deep neural networks Today s material is (adapted)
DEEP LEARNING AND NEURAL NETWORKS: BACKGROUND AND HISTORY
 DEEP LEARNING AND NEURAL NETWORKS: BACKGROUND AND HISTORY 1 On-line Resources http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/index.html Online book by Michael Nielsen http://matlabtricks.com/post-5/3x3-convolution-kernelswith-online-demo
DEEP LEARNING AND NEURAL NETWORKS: BACKGROUND AND HISTORY 1 On-line Resources http://neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com/index.html Online book by Michael Nielsen http://matlabtricks.com/post-5/3x3-convolution-kernelswith-online-demo
Neural networks and optimization
 Neural networks and optimization Nicolas Le Roux Criteo 18/05/15 Nicolas Le Roux (Criteo) Neural networks and optimization 18/05/15 1 / 85 1 Introduction 2 Deep networks 3 Optimization 4 Convolutional
Neural networks and optimization Nicolas Le Roux Criteo 18/05/15 Nicolas Le Roux (Criteo) Neural networks and optimization 18/05/15 1 / 85 1 Introduction 2 Deep networks 3 Optimization 4 Convolutional
OPTIMIZATION METHODS IN DEEP LEARNING
 Tutorial outline OPTIMIZATION METHODS IN DEEP LEARNING Based on Deep Learning, chapter 8 by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville Presented By Nadav Bhonker Optimization vs Learning Surrogate
Tutorial outline OPTIMIZATION METHODS IN DEEP LEARNING Based on Deep Learning, chapter 8 by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville Presented By Nadav Bhonker Optimization vs Learning Surrogate
Convolutional Neural Networks. Srikumar Ramalingam
 Convolutional Neural Networks Srikumar Ramalingam Reference Many of the slides are prepared using the following resources: neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com (mainly Chapter 6) http://cs231n.github.io/convolutional-networks/
Convolutional Neural Networks Srikumar Ramalingam Reference Many of the slides are prepared using the following resources: neuralnetworksanddeeplearning.com (mainly Chapter 6) http://cs231n.github.io/convolutional-networks/
Neural Networks and Deep Learning
 Neural Networks and Deep Learning Professor Ameet Talwalkar November 12, 2015 Professor Ameet Talwalkar Neural Networks and Deep Learning November 12, 2015 1 / 16 Outline 1 Review of last lecture AdaBoost
Neural Networks and Deep Learning Professor Ameet Talwalkar November 12, 2015 Professor Ameet Talwalkar Neural Networks and Deep Learning November 12, 2015 1 / 16 Outline 1 Review of last lecture AdaBoost
Deep Learning for NLP
 Deep Learning for NLP CS224N Christopher Manning (Many slides borrowed from ACL 2012/NAACL 2013 Tutorials by me, Richard Socher and Yoshua Bengio) Machine Learning and NLP NER WordNet Usually machine learning
Deep Learning for NLP CS224N Christopher Manning (Many slides borrowed from ACL 2012/NAACL 2013 Tutorials by me, Richard Socher and Yoshua Bengio) Machine Learning and NLP NER WordNet Usually machine learning
Neural Networks: Backpropagation
 Neural Networks: Backpropagation Machine Learning Fall 2017 Based on slides and material from Geoffrey Hinton, Richard Socher, Dan Roth, Yoav Goldberg, Shai Shalev-Shwartz and Shai Ben-David, and others
Neural Networks: Backpropagation Machine Learning Fall 2017 Based on slides and material from Geoffrey Hinton, Richard Socher, Dan Roth, Yoav Goldberg, Shai Shalev-Shwartz and Shai Ben-David, and others
Lecture 5: Logistic Regression. Neural Networks
 Lecture 5: Logistic Regression. Neural Networks Logistic regression Comparison with generative models Feed-forward neural networks Backpropagation Tricks for training neural networks COMP-652, Lecture
Lecture 5: Logistic Regression. Neural Networks Logistic regression Comparison with generative models Feed-forward neural networks Backpropagation Tricks for training neural networks COMP-652, Lecture
Artificial Neural Networks D B M G. Data Base and Data Mining Group of Politecnico di Torino. Elena Baralis. Politecnico di Torino
 Artificial Neural Networks Data Base and Data Mining Group of Politecnico di Torino Elena Baralis Politecnico di Torino Artificial Neural Networks Inspired to the structure of the human brain Neurons as
Artificial Neural Networks Data Base and Data Mining Group of Politecnico di Torino Elena Baralis Politecnico di Torino Artificial Neural Networks Inspired to the structure of the human brain Neurons as
epochs epochs
 Neural Network Experiments To illustrate practical techniques, I chose to use the glass dataset. This dataset has 214 examples and 6 classes. Here are 4 examples from the original dataset. The last values
Neural Network Experiments To illustrate practical techniques, I chose to use the glass dataset. This dataset has 214 examples and 6 classes. Here are 4 examples from the original dataset. The last values
SGD and Deep Learning
 SGD and Deep Learning Subgradients Lets make the gradient cheating more formal. Recall that the gradient is the slope of the tangent. f(w 1 )+rf(w 1 ) (w w 1 ) Non differentiable case? w 1 Subgradients
SGD and Deep Learning Subgradients Lets make the gradient cheating more formal. Recall that the gradient is the slope of the tangent. f(w 1 )+rf(w 1 ) (w w 1 ) Non differentiable case? w 1 Subgradients
11/3/15. Deep Learning for NLP. Deep Learning and its Architectures. What is Deep Learning? Advantages of Deep Learning (Part 1)
 11/3/15 Machine Learning and NLP Deep Learning for NLP Usually machine learning works well because of human-designed representations and input features CS224N WordNet SRL Parser Machine learning becomes
11/3/15 Machine Learning and NLP Deep Learning for NLP Usually machine learning works well because of human-designed representations and input features CS224N WordNet SRL Parser Machine learning becomes
Importance Reweighting Using Adversarial-Collaborative Training
 Importance Reweighting Using Adversarial-Collaborative Training Yifan Wu yw4@andrew.cmu.edu Tianshu Ren tren@andrew.cmu.edu Lidan Mu lmu@andrew.cmu.edu Abstract We consider the problem of reweighting a
Importance Reweighting Using Adversarial-Collaborative Training Yifan Wu yw4@andrew.cmu.edu Tianshu Ren tren@andrew.cmu.edu Lidan Mu lmu@andrew.cmu.edu Abstract We consider the problem of reweighting a
Apprentissage, réseaux de neurones et modèles graphiques (RCP209) Neural Networks and Deep Learning
 Apprentissage, réseaux de neurones et modèles graphiques (RCP209) Neural Networks and Deep Learning Nicolas Thome Prenom.Nom@cnam.fr http://cedric.cnam.fr/vertigo/cours/ml2/ Département Informatique Conservatoire
Apprentissage, réseaux de neurones et modèles graphiques (RCP209) Neural Networks and Deep Learning Nicolas Thome Prenom.Nom@cnam.fr http://cedric.cnam.fr/vertigo/cours/ml2/ Département Informatique Conservatoire
Backpropagation Introduction to Machine Learning. Matt Gormley Lecture 12 Feb 23, 2018
 10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Backpropagation Matt Gormley Lecture 12 Feb 23, 2018 1 Neural Networks Outline
10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University Backpropagation Matt Gormley Lecture 12 Feb 23, 2018 1 Neural Networks Outline
Supervised Learning. George Konidaris
 Supervised Learning George Konidaris gdk@cs.brown.edu Fall 2017 Machine Learning Subfield of AI concerned with learning from data. Broadly, using: Experience To Improve Performance On Some Task (Tom Mitchell,
Supervised Learning George Konidaris gdk@cs.brown.edu Fall 2017 Machine Learning Subfield of AI concerned with learning from data. Broadly, using: Experience To Improve Performance On Some Task (Tom Mitchell,
Deep Neural Networks (1) Hidden layers; Back-propagation
 Deep Neural Networs (1) Hidden layers; Bac-propagation Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 3 4 October 2017 / 9 October 2017 MLP Lecture 3 Deep Neural Networs (1) 1 Recap: Softmax single
Deep Neural Networs (1) Hidden layers; Bac-propagation Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 3 4 October 2017 / 9 October 2017 MLP Lecture 3 Deep Neural Networs (1) 1 Recap: Softmax single
Deep Feedforward Networks. Seung-Hoon Na Chonbuk National University
 Deep Feedforward Networks Seung-Hoon Na Chonbuk National University Neural Network: Types Feedforward neural networks (FNN) = Deep feedforward networks = multilayer perceptrons (MLP) No feedback connections
Deep Feedforward Networks Seung-Hoon Na Chonbuk National University Neural Network: Types Feedforward neural networks (FNN) = Deep feedforward networks = multilayer perceptrons (MLP) No feedback connections
Large-Scale Feature Learning with Spike-and-Slab Sparse Coding
 Large-Scale Feature Learning with Spike-and-Slab Sparse Coding Ian J. Goodfellow, Aaron Courville, Yoshua Bengio ICML 2012 Presented by Xin Yuan January 17, 2013 1 Outline Contributions Spike-and-Slab
Large-Scale Feature Learning with Spike-and-Slab Sparse Coding Ian J. Goodfellow, Aaron Courville, Yoshua Bengio ICML 2012 Presented by Xin Yuan January 17, 2013 1 Outline Contributions Spike-and-Slab
Deep Learning book, by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville
 Deep Learning book, by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville Chapter 6 :Deep Feedforward Networks Benoit Massé Dionyssos Kounades-Bastian Benoit Massé, Dionyssos Kounades-Bastian Deep Feedforward
Deep Learning book, by Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio and Aaron Courville Chapter 6 :Deep Feedforward Networks Benoit Massé Dionyssos Kounades-Bastian Benoit Massé, Dionyssos Kounades-Bastian Deep Feedforward
Machine Learning. Neural Networks. (slides from Domingos, Pardo, others)
 Machine Learning Neural Networks (slides from Domingos, Pardo, others) For this week, Reading Chapter 4: Neural Networks (Mitchell, 1997) See Canvas For subsequent weeks: Scaling Learning Algorithms toward
Machine Learning Neural Networks (slides from Domingos, Pardo, others) For this week, Reading Chapter 4: Neural Networks (Mitchell, 1997) See Canvas For subsequent weeks: Scaling Learning Algorithms toward
ECE G: Special Topics in Signal Processing: Sparsity, Structure, and Inference
 ECE 18-898G: Special Topics in Signal Processing: Sparsity, Structure, and Inference Neural Networks: A brief touch Yuejie Chi Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring 2018 1/41 Outline
ECE 18-898G: Special Topics in Signal Processing: Sparsity, Structure, and Inference Neural Networks: A brief touch Yuejie Chi Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring 2018 1/41 Outline
Day 3 Lecture 3. Optimizing deep networks
 Day 3 Lecture 3 Optimizing deep networks Convex optimization A function is convex if for all α [0,1]: f(x) Tangent line Examples Quadratics 2-norms Properties Local minimum is global minimum x Gradient
Day 3 Lecture 3 Optimizing deep networks Convex optimization A function is convex if for all α [0,1]: f(x) Tangent line Examples Quadratics 2-norms Properties Local minimum is global minimum x Gradient
Machine Learning. Neural Networks. (slides from Domingos, Pardo, others)
 Machine Learning Neural Networks (slides from Domingos, Pardo, others) Human Brain Neurons Input-Output Transformation Input Spikes Output Spike Spike (= a brief pulse) (Excitatory Post-Synaptic Potential)
Machine Learning Neural Networks (slides from Domingos, Pardo, others) Human Brain Neurons Input-Output Transformation Input Spikes Output Spike Spike (= a brief pulse) (Excitatory Post-Synaptic Potential)
CS 4700: Foundations of Artificial Intelligence
 CS 4700: Foundations of Artificial Intelligence Prof. Bart Selman selman@cs.cornell.edu Machine Learning: Neural Networks R&N 18.7 Intro & perceptron learning 1 2 Neuron: How the brain works # neurons
CS 4700: Foundations of Artificial Intelligence Prof. Bart Selman selman@cs.cornell.edu Machine Learning: Neural Networks R&N 18.7 Intro & perceptron learning 1 2 Neuron: How the brain works # neurons
Statistical Machine Learning (BE4M33SSU) Lecture 5: Artificial Neural Networks
 Statistical Machine Learning (BE4M33SSU) Lecture 5: Artificial Neural Networks Jan Drchal Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering Department of Computer Science Topics covered
Statistical Machine Learning (BE4M33SSU) Lecture 5: Artificial Neural Networks Jan Drchal Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering Department of Computer Science Topics covered
Lecture 2: Learning with neural networks
 Lecture 2: Learning with neural networks Deep Learning @ UvA LEARNING WITH NEURAL NETWORKS - PAGE 1 Lecture Overview o Machine Learning Paradigm for Neural Networks o The Backpropagation algorithm for
Lecture 2: Learning with neural networks Deep Learning @ UvA LEARNING WITH NEURAL NETWORKS - PAGE 1 Lecture Overview o Machine Learning Paradigm for Neural Networks o The Backpropagation algorithm for
CS60010: Deep Learning
 CS60010: Deep Learning Sudeshna Sarkar Spring 2018 16 Jan 2018 FFN Goal: Approximate some unknown ideal function f : X! Y Ideal classifier: y = f*(x) with x and category y Feedforward Network: Define parametric
CS60010: Deep Learning Sudeshna Sarkar Spring 2018 16 Jan 2018 FFN Goal: Approximate some unknown ideal function f : X! Y Ideal classifier: y = f*(x) with x and category y Feedforward Network: Define parametric
Neural Networks (Part 1) Goals for the lecture
 Neural Networks (Part ) Mark Craven and David Page Computer Sciences 760 Spring 208 www.biostat.wisc.edu/~craven/cs760/ Some of the slides in these lectures have been adapted/borrowed from materials developed
Neural Networks (Part ) Mark Craven and David Page Computer Sciences 760 Spring 208 www.biostat.wisc.edu/~craven/cs760/ Some of the slides in these lectures have been adapted/borrowed from materials developed
Lecture 4: Perceptrons and Multilayer Perceptrons
 Lecture 4: Perceptrons and Multilayer Perceptrons Cognitive Systems II - Machine Learning SS 2005 Part I: Basic Approaches of Concept Learning Perceptrons, Artificial Neuronal Networks Lecture 4: Perceptrons
Lecture 4: Perceptrons and Multilayer Perceptrons Cognitive Systems II - Machine Learning SS 2005 Part I: Basic Approaches of Concept Learning Perceptrons, Artificial Neuronal Networks Lecture 4: Perceptrons
Serious limitations of (single-layer) perceptrons: Cannot learn non-linearly separable tasks. Cannot approximate (learn) non-linear functions
 BACK-PROPAGATION NETWORKS Serious limitations of (single-layer) perceptrons: Cannot learn non-linearly separable tasks Cannot approximate (learn) non-linear functions Difficult (if not impossible) to design
BACK-PROPAGATION NETWORKS Serious limitations of (single-layer) perceptrons: Cannot learn non-linearly separable tasks Cannot approximate (learn) non-linear functions Difficult (if not impossible) to design
Deep Feedforward Networks
 Deep Feedforward Networks Liu Yang March 30, 2017 Liu Yang Short title March 30, 2017 1 / 24 Overview 1 Background A general introduction Example 2 Gradient based learning Cost functions Output Units 3
Deep Feedforward Networks Liu Yang March 30, 2017 Liu Yang Short title March 30, 2017 1 / 24 Overview 1 Background A general introduction Example 2 Gradient based learning Cost functions Output Units 3
Neural networks and support vector machines
 Neural netorks and support vector machines Perceptron Input x 1 Weights 1 x 2 x 3... x D 2 3 D Output: sgn( x + b) Can incorporate bias as component of the eight vector by alays including a feature ith
Neural netorks and support vector machines Perceptron Input x 1 Weights 1 x 2 x 3... x D 2 3 D Output: sgn( x + b) Can incorporate bias as component of the eight vector by alays including a feature ith
Linear discriminant functions
 Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Discriminative learning Discriminative vs generative Generative learning assumes knowledge of the distribution governing the data Discriminative
Andrea Passerini passerini@disi.unitn.it Machine Learning Discriminative learning Discriminative vs generative Generative learning assumes knowledge of the distribution governing the data Discriminative
Multilayer Neural Networks. (sometimes called Multilayer Perceptrons or MLPs)
 Multilayer Neural Networks (sometimes called Multilayer Perceptrons or MLPs) Linear separability Hyperplane In 2D: w x + w 2 x 2 + w 0 = 0 Feature x 2 = w w 2 x w 0 w 2 Feature 2 A perceptron can separate
Multilayer Neural Networks (sometimes called Multilayer Perceptrons or MLPs) Linear separability Hyperplane In 2D: w x + w 2 x 2 + w 0 = 0 Feature x 2 = w w 2 x w 0 w 2 Feature 2 A perceptron can separate
Introduction to Deep Neural Networks
 Introduction to Deep Neural Networks Presenter: Chunyuan Li Pattern Classification and Recognition (ECE 681.01) Duke University April, 2016 Outline 1 Background and Preliminaries Why DNNs? Model: Logistic
Introduction to Deep Neural Networks Presenter: Chunyuan Li Pattern Classification and Recognition (ECE 681.01) Duke University April, 2016 Outline 1 Background and Preliminaries Why DNNs? Model: Logistic
Deep Neural Networks (1) Hidden layers; Back-propagation
 Deep Neural Networs (1) Hidden layers; Bac-propagation Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 3 2 October 2018 http://www.inf.ed.ac.u/teaching/courses/mlp/ MLP Lecture 3 / 2 October 2018 Deep
Deep Neural Networs (1) Hidden layers; Bac-propagation Steve Renals Machine Learning Practical MLP Lecture 3 2 October 2018 http://www.inf.ed.ac.u/teaching/courses/mlp/ MLP Lecture 3 / 2 October 2018 Deep
CS 4700: Foundations of Artificial Intelligence
 CS 4700: Foundations of Artificial Intelligence Prof. Bart Selman selman@cs.cornell.edu Machine Learning: Neural Networks R&N 18.7 Intro & perceptron learning 1 2 Neuron: How the brain works # neurons
CS 4700: Foundations of Artificial Intelligence Prof. Bart Selman selman@cs.cornell.edu Machine Learning: Neural Networks R&N 18.7 Intro & perceptron learning 1 2 Neuron: How the brain works # neurons
COGS Q250 Fall Homework 7: Learning in Neural Networks Due: 9:00am, Friday 2nd November.
 COGS Q250 Fall 2012 Homework 7: Learning in Neural Networks Due: 9:00am, Friday 2nd November. For the first two questions of the homework you will need to understand the learning algorithm using the delta
COGS Q250 Fall 2012 Homework 7: Learning in Neural Networks Due: 9:00am, Friday 2nd November. For the first two questions of the homework you will need to understand the learning algorithm using the delta
Neural Networks Learning the network: Backprop , Fall 2018 Lecture 4
 Neural Networks Learning the network: Backprop 11-785, Fall 2018 Lecture 4 1 Recap: The MLP can represent any function The MLP can be constructed to represent anything But how do we construct it? 2 Recap:
Neural Networks Learning the network: Backprop 11-785, Fall 2018 Lecture 4 1 Recap: The MLP can represent any function The MLP can be constructed to represent anything But how do we construct it? 2 Recap:
Deep Feedforward Networks. Han Shao, Hou Pong Chan, and Hongyi Zhang
 Deep Feedforward Networks Han Shao, Hou Pong Chan, and Hongyi Zhang Deep Feedforward Networks Goal: approximate some function f e.g., a classifier, maps input to a class y = f (x) x y Defines a mapping
Deep Feedforward Networks Han Shao, Hou Pong Chan, and Hongyi Zhang Deep Feedforward Networks Goal: approximate some function f e.g., a classifier, maps input to a class y = f (x) x y Defines a mapping
ECE521 Lecture7. Logistic Regression
 ECE521 Lecture7 Logistic Regression Outline Review of decision theory Logistic regression A single neuron Multi-class classification 2 Outline Decision theory is conceptually easy and computationally hard
ECE521 Lecture7 Logistic Regression Outline Review of decision theory Logistic regression A single neuron Multi-class classification 2 Outline Decision theory is conceptually easy and computationally hard
Course 10. Kernel methods. Classical and deep neural networks.
 Course 10 Kernel methods. Classical and deep neural networks. Kernel methods in similarity-based learning Following (Ionescu, 2018) The Vector Space Model ò The representation of a set of objects as vectors
Course 10 Kernel methods. Classical and deep neural networks. Kernel methods in similarity-based learning Following (Ionescu, 2018) The Vector Space Model ò The representation of a set of objects as vectors
Deep Feedforward Networks
 Deep Feedforward Networks Liu Yang March 30, 2017 Liu Yang Short title March 30, 2017 1 / 24 Overview 1 Background A general introduction Example 2 Gradient based learning Cost functions Output Units 3
Deep Feedforward Networks Liu Yang March 30, 2017 Liu Yang Short title March 30, 2017 1 / 24 Overview 1 Background A general introduction Example 2 Gradient based learning Cost functions Output Units 3
22c145-Fall 01: Neural Networks. Neural Networks. Readings: Chapter 19 of Russell & Norvig. Cesare Tinelli 1
 Neural Networks Readings: Chapter 19 of Russell & Norvig. Cesare Tinelli 1 Brains as Computational Devices Brains advantages with respect to digital computers: Massively parallel Fault-tolerant Reliable
Neural Networks Readings: Chapter 19 of Russell & Norvig. Cesare Tinelli 1 Brains as Computational Devices Brains advantages with respect to digital computers: Massively parallel Fault-tolerant Reliable
Machine Learning Lecture 14
 Machine Learning Lecture 14 Tricks of the Trade 07.12.2017 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Course Outline Fundamentals Bayes Decision Theory Probability
Machine Learning Lecture 14 Tricks of the Trade 07.12.2017 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Course Outline Fundamentals Bayes Decision Theory Probability
From perceptrons to word embeddings. Simon Šuster University of Groningen
 From perceptrons to word embeddings Simon Šuster University of Groningen Outline A basic computational unit Weighting some input to produce an output: classification Perceptron Classify tweets Written
From perceptrons to word embeddings Simon Šuster University of Groningen Outline A basic computational unit Weighting some input to produce an output: classification Perceptron Classify tweets Written
Neural Networks biological neuron artificial neuron 1
 Neural Networks biological neuron artificial neuron 1 A two-layer neural network Output layer (activation represents classification) Weighted connections Hidden layer ( internal representation ) Input
Neural Networks biological neuron artificial neuron 1 A two-layer neural network Output layer (activation represents classification) Weighted connections Hidden layer ( internal representation ) Input
CSE 190 Fall 2015 Midterm DO NOT TURN THIS PAGE UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO START!!!!
 CSE 190 Fall 2015 Midterm DO NOT TURN THIS PAGE UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO START!!!! November 18, 2015 THE EXAM IS CLOSED BOOK. Once the exam has started, SORRY, NO TALKING!!! No, you can t even say see ya
CSE 190 Fall 2015 Midterm DO NOT TURN THIS PAGE UNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO START!!!! November 18, 2015 THE EXAM IS CLOSED BOOK. Once the exam has started, SORRY, NO TALKING!!! No, you can t even say see ya
Neural Network Training
 Neural Network Training Sargur Srihari Topics in Network Training 0. Neural network parameters Probabilistic problem formulation Specifying the activation and error functions for Regression Binary classification
Neural Network Training Sargur Srihari Topics in Network Training 0. Neural network parameters Probabilistic problem formulation Specifying the activation and error functions for Regression Binary classification
Computational statistics
 Computational statistics Lecture 3: Neural networks Thierry Denœux 5 March, 2016 Neural networks A class of learning methods that was developed separately in different fields statistics and artificial
Computational statistics Lecture 3: Neural networks Thierry Denœux 5 March, 2016 Neural networks A class of learning methods that was developed separately in different fields statistics and artificial
Introduction to Machine Learning (67577)
 Introduction to Machine Learning (67577) Shai Shalev-Shwartz School of CS and Engineering, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Deep Learning Shai Shalev-Shwartz (Hebrew U) IML Deep Learning Neural Networks
Introduction to Machine Learning (67577) Shai Shalev-Shwartz School of CS and Engineering, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem Deep Learning Shai Shalev-Shwartz (Hebrew U) IML Deep Learning Neural Networks
Neural networks. Chapter 19, Sections 1 5 1
 Neural networks Chapter 19, Sections 1 5 Chapter 19, Sections 1 5 1 Outline Brains Neural networks Perceptrons Multilayer perceptrons Applications of neural networks Chapter 19, Sections 1 5 2 Brains 10
Neural networks Chapter 19, Sections 1 5 Chapter 19, Sections 1 5 1 Outline Brains Neural networks Perceptrons Multilayer perceptrons Applications of neural networks Chapter 19, Sections 1 5 2 Brains 10
Understanding Neural Networks : Part I
 TensorFlow Workshop 2018 Understanding Neural Networks Part I : Artificial Neurons and Network Optimization Nick Winovich Department of Mathematics Purdue University July 2018 Outline 1 Neural Networks
TensorFlow Workshop 2018 Understanding Neural Networks Part I : Artificial Neurons and Network Optimization Nick Winovich Department of Mathematics Purdue University July 2018 Outline 1 Neural Networks
Neural Networks. Chapter 18, Section 7. TB Artificial Intelligence. Slides from AIMA 1/ 21
 Neural Networks Chapter 8, Section 7 TB Artificial Intelligence Slides from AIMA http://aima.cs.berkeley.edu / 2 Outline Brains Neural networks Perceptrons Multilayer perceptrons Applications of neural
Neural Networks Chapter 8, Section 7 TB Artificial Intelligence Slides from AIMA http://aima.cs.berkeley.edu / 2 Outline Brains Neural networks Perceptrons Multilayer perceptrons Applications of neural
Machine Learning. Neural Networks
 Machine Learning Neural Networks Bryan Pardo, Northwestern University, Machine Learning EECS 349 Fall 2007 Biological Analogy Bryan Pardo, Northwestern University, Machine Learning EECS 349 Fall 2007 THE
Machine Learning Neural Networks Bryan Pardo, Northwestern University, Machine Learning EECS 349 Fall 2007 Biological Analogy Bryan Pardo, Northwestern University, Machine Learning EECS 349 Fall 2007 THE
CSC321 Lecture 7: Optimization
 CSC321 Lecture 7: Optimization Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 7: Optimization 1 / 25 Overview We ve talked a lot about how to compute gradients. What do we actually do with them? Today s lecture:
CSC321 Lecture 7: Optimization Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 7: Optimization 1 / 25 Overview We ve talked a lot about how to compute gradients. What do we actually do with them? Today s lecture:
Neural Network Tutorial & Application in Nuclear Physics. Weiguang Jiang ( 蒋炜光 ) UTK / ORNL
 Neural Network Tutorial & Application in Nuclear Physics Weiguang Jiang ( 蒋炜光 ) UTK / ORNL Machine Learning Logistic Regression Gaussian Processes Neural Network Support vector machine Random Forest Genetic
Neural Network Tutorial & Application in Nuclear Physics Weiguang Jiang ( 蒋炜光 ) UTK / ORNL Machine Learning Logistic Regression Gaussian Processes Neural Network Support vector machine Random Forest Genetic
CSC321 Lecture 8: Optimization
 CSC321 Lecture 8: Optimization Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 8: Optimization 1 / 26 Overview We ve talked a lot about how to compute gradients. What do we actually do with them? Today s lecture:
CSC321 Lecture 8: Optimization Roger Grosse Roger Grosse CSC321 Lecture 8: Optimization 1 / 26 Overview We ve talked a lot about how to compute gradients. What do we actually do with them? Today s lecture:
Welcome to the Machine Learning Practical Deep Neural Networks. MLP Lecture 1 / 18 September 2018 Single Layer Networks (1) 1
 Welcome to the Machine Learning Practical Deep Neural Networks MLP Lecture 1 / 18 September 2018 Single Layer Networks (1) 1 Introduction to MLP; Single Layer Networks (1) Steve Renals Machine Learning
Welcome to the Machine Learning Practical Deep Neural Networks MLP Lecture 1 / 18 September 2018 Single Layer Networks (1) 1 Introduction to MLP; Single Layer Networks (1) Steve Renals Machine Learning
CMSC 421: Neural Computation. Applications of Neural Networks
 CMSC 42: Neural Computation definition synonyms neural networks artificial neural networks neural modeling connectionist models parallel distributed processing AI perspective Applications of Neural Networks
CMSC 42: Neural Computation definition synonyms neural networks artificial neural networks neural modeling connectionist models parallel distributed processing AI perspective Applications of Neural Networks
Understanding How ConvNets See
 Understanding How ConvNets See Slides from Andrej Karpathy Springerberg et al, Striving for Simplicity: The All Convolutional Net (ICLR 2015 workshops) CSC321: Intro to Machine Learning and Neural Networks,
Understanding How ConvNets See Slides from Andrej Karpathy Springerberg et al, Striving for Simplicity: The All Convolutional Net (ICLR 2015 workshops) CSC321: Intro to Machine Learning and Neural Networks,
Artifical Neural Networks
 Neural Networks Artifical Neural Networks Neural Networks Biological Neural Networks.................................. Artificial Neural Networks................................... 3 ANN Structure...........................................
Neural Networks Artifical Neural Networks Neural Networks Biological Neural Networks.................................. Artificial Neural Networks................................... 3 ANN Structure...........................................
Deep Learning for Speech Recognition. Hung-yi Lee
 Deep Learning for Speech Recognition Hung-yi Lee Outline Conventional Speech Recognition How to use Deep Learning in acoustic modeling? Why Deep Learning? Speaker Adaptation Multi-task Deep Learning New
Deep Learning for Speech Recognition Hung-yi Lee Outline Conventional Speech Recognition How to use Deep Learning in acoustic modeling? Why Deep Learning? Speaker Adaptation Multi-task Deep Learning New
CSCI 1951-G Optimization Methods in Finance Part 12: Variants of Gradient Descent
 CSCI 1951-G Optimization Methods in Finance Part 12: Variants of Gradient Descent April 27, 2018 1 / 32 Outline 1) Moment and Nesterov s accelerated gradient descent 2) AdaGrad and RMSProp 4) Adam 5) Stochastic
CSCI 1951-G Optimization Methods in Finance Part 12: Variants of Gradient Descent April 27, 2018 1 / 32 Outline 1) Moment and Nesterov s accelerated gradient descent 2) AdaGrad and RMSProp 4) Adam 5) Stochastic
