UNIT-III-Dielectric and Magnetic properties of materials
|
|
|
- Christian Stone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 UNIT-III-Dilctric and Magntic prprtis f matrials Syllabus: Dilctric cnstant and plarizatin f dilctric matrials - Typs f plarizatin Equatin fr intrnal fild in liquids and slids ( n dimnsinal) Clausius Mstti quatin Frr and Piz lctricity (qualitativ) Frquncy dpndnc f dilctric cnstant- Imprtant applicatins f dilctric matrials. Classificatin f dia, para and frrmagntic matrials. Curi Tmpratur Hystrisis in frrmagntic matrials. Sft and Hard magntic matrials. Applicatins. Intrductin Dilctrics ar insulating r nn-cnducting cramic matrials and ar usd in many applicatins such as capacitrs, mmris, snsrs and actuatrs. Dilctrics ar insulating matrials that xhibit th prprty f lctrical plarizatin, thrby thy mdify th dilctric functin f th vacuum. A dilctric matrial is any matrial that supprts charg withut cnducting it t a significant dgr. In principl all insulatrs ar dilctric, althugh th capacity t supprt charg varis gratly btwn diffrnt insulatrs. Althugh ths matrials d nt cnduct lctrical currnt whn an lctric fild is applid, thy ar nt inrt t th lctric fild. Th fild may caus a slight shift in th balanc f charg within th matrial t frm an lctric dipl. Thus th matrials is calld dilctric matrial. Dilctric matrials ar usd in many applicatins, frm simpl lctrical insulatin t snsrs and circuit cmpnnts. Faraday was carrid ut th first numrical masurmnts n th prprtis f insulating matrials whn placd btwn th tw paralll plats (capacitr), ths matrials, h calld as dilctrics. H has fund that th capacity f a cndnsr was dpndnt n th natur f th matrial sparating th cnducting surfac. This discvry ncuragd furthr mpirical studis f insulating matrials aiming at maximizing th amunt f charg that can b strd by a capacitr. In sarch f suitabl dilctric matrials fr spcific applicatins, ths matrials hav bcm incrasingly cncrnd with th dtaild physical mchanism gvrning th bhavir f ths matrials. Th diffrnc btwn dilctric matrial and insulatr dpnds n its applicatin. Insulating matrials ar usd t rsist flw f currnt thrugh it, n th thr hand dilctric matrials ar usd t str lctrical nrgy. In cntrast t th insulatin aspct, th dilctric phnmna hav bcm mr gnral and fundamntal, as it has th rigin with th dilctric plarizatin.
2 Elctric dipls: Upn applicatin f a dc r static lctric fild, thr is a lng rang migratin f chargs. Hwvr, thr is a limitd mvmnt f chargs lading t th frmatin f charg dipls and th matrial, in this stat, is cnsidrd as plarizd. Ths dipls ar alignd in th dirctin f th applid fild. Th nt ffct is calld Plarizatin f th matrial. A dilctric supprts charg by acquiring a plarisatin in an lctric fild, whrby n surfac dvlps a nt psitiv charg whil th ppsit surfac dvlps a nt ngativ charg. This is mad pssibl by th prsnc f lctric dipls tw ppsit chargs sparatd by a crtain distanc n a micrscpic scal. 1. If tw discrt chargd particls f ppsit chargs ar sparatd by a crtain distanc, a dipl mmnt μ ariss.. If th cntr f psitiv charg within a givn rgin and th cntr f ngativ charg within th sam rgin ar nt in th sam psitin, a dipl mmnt μ ariss. Fr xampl, in th diagram blw th cntr f psitiv charg frm th 8 catins shwn is at X, whil th cntr f ngativ charg is lcatd sm distanc away n th anin. Th scnd viw f dipl mmnt is mr usful, sinc it can b applid vr a larg ara cntaining many chargs in rdr t find th nt dipl mmnt f th matrial. Th dipls can b alignd as wll as b inducd by th applid fild.
3 Nt that in th quatin fr dipl mmnt, r is a vctr (th sign cnvntin is that r pints frm ngativ t psitiv charg) thrfr th dipl mmnt μ is als a vctr Elctric fild intnsity r lctric fild strngth ( E ) Th frc xprincd by a unit tst charg is knwn as lctric fild strngth E Q E..(1) 4r whr is th prmittivity r dilctric cnstant f th mdium in which lctric charg is placd. Fr vacuum = = X1-1 Fm -1 Elctric flux dnsity r lctric displacmnt vctr ( D) Th lctric flux dnsity r lctric displacmnt vctr is th numbr f flux lins crssing nrmal t a unit surfac ara. Th lctric flux dnsity at a distanc frm th pint charg Q is Q D..() 4r thn frm (1) and () D = E.. () Dilctric cnstant ( r ) Th dilctric cnstant f a matrial is dfind as th rati f th prmittivity f th mdium () t th prmittivity f fr spac ( ). It can als dfind as th rati f th capacitanc with dilctric (C d ) and with air ( C A ) btwn th plats. Cd r..(4) C Capacitanc: Th prprty f a cnductr r systm f cnductr that dscribs its ability t str lctric charg. A C = q / V = A ε / d whr C is capacitanc f capacitr q is charg n th capacitr plat V is ptntial diffrnc btwn plats A is ara f capacitr plat ε is prmittivity f mdium d is distanc btwn capacitr plats Units: Farad. Plarizatin Whn an lctric fild is applid t a matrial with dilctrics, th psitiv chargs ar displacd ppsit t th dirctin f th fild and ngativ chargs displacd in th dirctin f th fild. Th displacmnt f ths tw chargs crat a lcal dipl, cratin f dipl by applying lctric fild is calld as plarizatin.
4 Plarizatin is dfind as inducd dipl mmnt pr unit vlum. P (5) Vlum Plarisability Th plarizatin P is dirctly prprtinal t th lctric fild strngth E P E (6) P E Whr prprtinality is cnstant calld as plarisability. Th plarisability is dfind as plarizatin pr unit applid lctric fild. If th matrial cntains N numbr f dipls pr unit vlum thn P NE.(7) Rlatin btwn plarizatin and dilctric cnstant Lt us apply Gauss thrm fr paralll plat cndnsr. q EdA Whr σ is th charg pr unit ara. q E A q E. (1) A Lt a dilctric slab placd btwn tw plats. Du t plarizatin, chargs appar n th tw facs f th slab, and stablish yt anthr fild within th dilctric mdia. Lt this fild b Eʹ. Th dirctin f Eʹ will b ppsit t that f E. Th rsultant fild E in th matrial can b writtn as, E = E - Eʹ.()
5 If σ p is th charg/unit ara n th insrtd dilctric slab surfacs, thn by fllwing quatin (1), w writ, ' ' q p E. () A Frm (1), () and (), p ` E. r E p (4) Sinc th magnitud f plarizatin P = dipl mmnt/ Unit Vlum But dipl mmnt = inducd charg X distanc Thrfr P = inducd charg/ Ara= p W knw that lctric displacmnt fildr lctric flux dnsity D is givn by charg /unit ara D = q/a= Thrfr Equatin 4 bcms E D P P D E..(5) in fr spac whr thr is n dilctric P= D E But in dilctric mdia th D changs. Frm lctrstatics D E Frm () r P E E r P E ( 1).(6) P E r 1 r Whr is lctric suscptibility f th dilctric mdium. It dsn t hav any units. Sinc P and E ar vctrs qn (6) can b writtn as
6 P E ( r 1) (7) This quatin rprsnts plarizatin vctr. Typs f plarizatin Dilctric plarizatin is th displacmnt f charg particls with th applid lctric fild. Th displacmnt f lctric chargs rsults in frmatin f lctric dipl mmnt in atms, ins r mlculs f th matrial. Thr ar fur diffrnt typs f plarizatin, thy ar listd blw. 1. Elctric plarizatin,. Inic plarizatin,. Orintatin plarizatin 4. Spac charg plarizatin Elctric plarizatin Th displacmnt f th psitivly chargd nuclus and th ngativly chargd lctrns f an atm in ppsit dirctins, n applicatin f an lctric fild, rsult in lctrnic plarizatin. On applying a fild, th lctrn clud arund th nuclus shifts twards th psitiv nd f th fild. As th nuclus and lctrn clud ar sparatd by a distanc, dipl mmnt is cratd within ach atm. Th xtnt f this shift is prprtinal t th fild strngth. Inducd dipl mmnt E E Whr is calld lctrnic plarizability. Th dipl mmnt pr unit vlum is calld lctrnic plarizatin. It incrass with incras f vlum f th atm. This kind f plarizatin is mstly xhibitd in mnatmic gass.(.g. H, N, Ar, Kr, X tc..)
7 It is indpndnt f tmpratur. It ccurs nly at ptical frquncis (1 15 Hz) Vast fast prcss: 1-15 ~1-16 s. Calculatin f lctrnic plarizability: Elctrnic plarizatin can b xplaind by classical mdl f an atm in gasss. In gass th atms ar assumd that th intractin amng th atms is ngligibl. Hr th nuclus f charg Z is surrundd by an lctrn clud f charg Z distributd in th sphr f radius R. Z Charg dnsity, (1) ( 4 / ) R Whn an lctric fild E is applid, th nuclus and lctrns xprinc Lrntz frc f magnitud ZE in ppsit dirctin. Thrfr th nuclus and lctrns ar pulld apart. As thy ar pulld apart a Culmb frc dvlps btwn thm. At quilibrium ths tw frcs ar qual and nuclus and lctrn clud ar sparatd by a small distanc x. Lrntz frc = ZE () Charg nclsd int hsphrfradiusx Culmb Frc = Z X 4 x Th charg nclsd = 4 x 4 Z Frm quatin (1) = x 4 R Zx R =
8 Z Hnc Culmb frc is = 4 x Zx Z x () X R 4 R At quilibrium Lrntz frc = Culmb frc (quatin () qual t ()) Z x ZE 4 R 4 R E x (4) Z Th displacmnt f th lctrn clud is prprtinal t applid lctric fild. Th lctric dipl mmnt Zx Z4 R E Z 4 R E E E (5) P Whr 4 R is calld lctrnic plarizability. N N E Whr N is th numbr f atms/m But plarizatin P E ( r 1) N E N ( r 1) r ( r 1) N Inic Plarizatin Inic plarizatin ccurs in inic slids such as NaCl, KBr, and LiBr. Whn an lctric fild is applid t an inic slid th psitiv and ngativ ins displac t thir rspctiv plaritis crating an lctric dipl this is calld as inic plarizatin. In th absnc f an lctric fild thr is n displacmnt f ins. Whn an lctric fild is applid an inducd dipl mmnt i is prducd. Lt x 1 and x b th displacmnt f psitiv and ngativ in rspctivly. Thn th inducd dipl mmnt.
9 x 1 x ) (6) i ( Lt F b rstring frc F x 1 x x 1 1 x Frm mchanics th spring cnstant f mass attachd t a spring is givn by =m At quilibrium th Lrntz frc = rstring frc E m x E E Thrfr x Thn x 1 m m E x M 1 1 E m M i E (7) 1 1 Whr i is calld as inic plarisability (8) m M Orintatin Plarizatin Orintatin plarizatin ccurs nly in plar mlculs (th mlculs which hav prmannt dipl mmnt g H O, Phnl, tc.). Whn an lctric fild is applid t a plar mlcul, th dipls xprinc a trqu and try t align paralll t th applid fild. Cnsidr a plar mlcul subjctd t an lctric fild E. Th alignmnt f lctric dipl with th lctric fild is similar t th alignmnt f magntic dipl with th applid magntic fild in paramagntic matrial. Th xprssin fr plarizatin can b btaind frm th thry f paramagntism. Th rintatin plarizatin is givn as N E P E KT (9) Whr is calld as rintatin plarisability KT (1) Spac charg plarizatin
10 Spac charg plarizatin ccurs du t th accumulatin f chargs at th lctrds r at intrfacs in a multiphas matrials. In th prsnc f an applid fild, th mbil psitiv ins and ngativ ins migrat tward th ngativ lctrd and psitiv lctrd rspctivly t an apprciabl distanc giving ris t rdistributin f chargs, but thy rmain rmains in th dilctric matrial (lctrd is blcking). Th spac charg plarizatin can b dfind as th rdistributin f chargs du t th applid lctric fild and th chargs accumulat n th surfac f th lctrds. It ccurs whn th rat f charg accumulatin is diffrnt frm rat f charg rmval. Spac charg plarizatin is nt significant in mst f th dilctric matrials. Intrnal fild in liquids and slids (n dimnsinal) In gass stat th atms ar sparatd by larg distancs and th intractin btwn th atms can b nglctd. Whn an xtrnal lctric fild E is applid, th intnsity f th lctric fild xprincd by an atm in gass stat will b qual t th applid lctric fild E. In slids and liquids, th atms ar cls t ach thr lading t strng intractin btwn thm. In slids and liquids th intnsity f th lctric fild at a givn pint f th matrial is nt qual t th applid lctric fild but qual t intrnal fild which is th sum f applid lctric fild and fild du t thr dipls prsnt in th matrial. Intrnal fild E i =E+E` (1) Th intrnal fild can b calculatd by Epstin mdl in th cas f n dimnsinal atmic array. Elctric fild alng th axis f an lctric dipl Cnsidr an lctric dipl f lngth d and charg Q, th fild alng th axis f th dipl at pint A is th sum f th lctric fild du t +Q and Q. Q Th lctric fild du t +Q at pint A is E 4 ( x d) Q Th lctric fild du t +Q at pint A is E 4 ( x d) Elctric fild f dipl at A is E A E E Q ( x d) ( x d) Q dx 4 ( x d) ( x d)
11 sinc x >> d (x-d) (x+d) x thn Q dx 4dQ 4 4 x 4 x i sinc dq = i E A () 4 x Cnsidr an array f n dimnsinal atms alng x- axis. Th all th atms ar similar, qually spacd and hav inducd lctric dipl mmnt i in an applid lctric fild E. Th lctric fild xprincd at th A is th sum f lctric filds f thr dipls and applid lctric fild E. Th fild at th inducd dipl B and L which ar at a distanc x is i E B EL 4 x Th lctric fild at A du t th inducd dipl C and M which ar at a distanc x is i E C EM 4 (x) Thrfr th fild du t thr dipls is lctric A du t E =E B + E L +E C +E M +E D +E N +. () i E 4 x 4i E 4 x i 4 x i 4 (x) i 4 (x) i 4 (x) i 4 (x) 4i 4 (x) 4i 4 (x) i E 1... x whr i E x 1.i Thrfr th intrnal fild Ei E (4) x
12 Th lcal fild in a thr dimnsinal slid is similar th abv quatin th numbr dnsity N f atms rplacs 1/a. Sinc Nμ i =P and 1./π is rplacd by γ. Thn th intrnal fild is E i 1.Ni 1.P E E P E γ dpnds n th intrnal structur Fr a cubic symmtry crystal γ valu is1/ E i P E (5) Th fild givn by th abv quatin is calld Lrntz fild. Clausius - Mstti quatin Lt us cnsidr lmntal slid dilctric which xhibits nly lctrnic plarizatin. If is th lctrnic plarisability pr atm, it is rlatd t th bulk plarizatin P thrugh th rlatin P N E i (6) P (7) NE i Whr N is th numbr f atms pr unit vlum and E i is th lcal fild using th rlatin (5) P (8) P N E By using th rlatin btwn th plarizatin and prmittivity w hav P E ( 1) (9) r P E ( r 1) (1) Substitut th valu f E frm (1) in (8) N ( P P 1) r P N ( 1) r 1 r ( 1) r
13 r 1 r N (11) Th abv quatin is knwn as Clausius Mstti quatin which is valid fr nnplar slids Dilctric lss: Dilctric lss is th dissipatin f nrgy thrugh th mvmnt f chargs in an altrnating lctrmagntic fild as plarisatin switchs dirctin. An fficint dilctric supprts a varying charg with minimal dissipatin f nrgy in th frm f hat is calld dilctric lss. Thr ar tw main frms f lss that may dissipat nrgy within a dilctric. In cnductin lss, a flw f charg thrugh th matrial causs nrgy dissipatin. Dilctric lss is spcially high arund th rlaxatin r rsnanc frquncis f th plarisatin mchanisms as th plarisatin lags bhind th applid fild, causing an intractin btwn th fild and th dilctric s plarisatin that rsults in hating. This is illustratd by th diagram blw (rcall that th dilctric cnstant drps as ach plarisatin mchanism bcms unabl t kp up with th switching lctric fild.) Dilctric lss quantifis a dilctric matrial's inhrnt dissipatin f lctrmagntic nrgy int,.g., hat. It can b rprsntd in trms lss tangnt tan δ and is dfind: Dilctric Brakdwn : Th dilctric brakdwn is th suddn chang in stat f a dilctric matrial subjctd t a vry high lctric fild, undr th influnc f which, th lctrns ar liftd int th cnductin band causing a surg f currnt, and th ability f th matrial t rsist th currnt flw suffrs a brakdwn. Or Whn a dilctric matrial lss its rsistivity and prmits vry larg currnt t flw thrugh it, thn th phnmnn is calld dilctric brakdwn Or At high lctric filds, a matrial that is nrmally an lctrical insulatr may bgin t cnduct lctricity i.. it cass t act as a dilctric. This phnmnn is knwn as dilctric brakdwn.
14 Frquncy dpndnc f plarizability: On applicatin f an lctric fild, plarizatin prcss ccurs as a functin f tim. Th plarizatin P(t) as a functin f tim. Th plarizatin P(t) as a functin f tim t is givn by P(t) = P[ 1- xp ( - t / t r )] Whr P max. Plarizatin attaind n prlngd applicatin f static fild. t r - rlaxatin tim fr particular plarizatin prcss Th rlaxatin tim t r is a masur f th tim scal f plarizatin prcss. It is th tim takn fr a plarizatin prcss t rach.6 f th max. valu. Elctrnic plarizatin is xtrmly rapid. Evn whn th frquncy f th applid vltag is vry high in th ptical rang ( 1 15 Hz), lctrnic plarizatin ccurs during vry cycl f th applid vltag. Inic plarizatin is du t displacmnt f ins vr a small distanc du t th applid fild. Sinc ins ar havir than lctrn clud, th tim takn fr displacmnt is largr. Th frquncy with which ins ar displacd is f th sam rdr as th lattic vibratin frquncy ( 11Hz). Hnc, at ptical frquncis, thr is n inic plarizatin. If th frquncy f th applid vltag is lss than 11 Hz, th ins rspnd. Orintatin plarizatin is vn slwr than inic plarizatin. Th rlaxatin tim fr rintatin plarizatin in a liquid is lss than that in a slid. Orintatin plarizatin ccurs, whn th frquncy f applid vltag is in audi rang (11 Hz). Spac charg plarizatin is th slwst prcss, as it invlvs th diffusin f ins vr svral intratmic distancs. Th rlaxatin tim fr this prcss is rlatd t frquncy f ins undr th influnc f applid fild. Spac charg plarizatin ccurs at pwr frquncis (5-6 Hz).
15 Frquncy Dpndnc f dilctric cnstant Whn a dilctric matrial is subjctd t an altrnating fild, th plarizatin cmpnnt rquird t fllw th fild in rdr t cntribut t th ttal plarizatin f th dilctrics. Th rlativ prmittivity which is a masur f th plarizatin als dpnds n th frquncy. Th dpndnc f r n frquncy f th lctric fild is shwn in th figur. At vry lw frquncy, th dipls will gt sufficint tim t rint thmslvs cmpltly with th fild and all typs f plarizatin xist. Sinc th dilctric is charactrizd by plarisability ( = + i + ) at lw frquncy i. at radifrquncy rgin th dilctric cnstant will b du t all plarisability. Th rintatin plarizatin, which is ffctiv at lw frquncis, is dampd ut fr highr frquncis. In th micrwav rgin th dipls fail t fllw th fild and th plarisability rducs t ( = + i ), as a rsult r dcrass t sm amunt. In th IR rgin th inic plarizatin fails t fllw th fild s th cntributin f inic plarizatin dis away. In this rgin nly lctrnic plarizatin cntributs t th ttal plarizatin. Thrfr ( = ) th r still dcrass and nly lctrnic plarizatin xist. W knw that P N E ( 1 E r ) Thn th rlativ prmittivity is r N 1 (1) In th ultravilt rgin vn th lctrn clud culd nt fllw th fild and lctrnic plarizability bcms almst zr and th prmittivity bcms n. 1 r X ray Fr xampl at lw frquncy th dilcric cnstant f watr at rm tmpratur is abut 8, but it fall t abut 1.8 in th ptical rgin.
16 Frquncy Dpndnc f dilctric lss: Dilctric lss tnds t b highr in matrials with highr dilctric cnstants. This is th dwnsid f using ths matrials in practical applicatins. Dilctric lss is utilisd t hat fd in a micrwav vn: th frquncy f th micrwavs usd is cls t th rlaxatin frquncy f th rintatinal plarisatin mchanism in watr, maning that any watr prsnt absrbs a lt f nrgy that is thn dissipatd as hat. Th xact frquncy usd is slightly away frm th frquncy at which maximum dilctric lss ccurs in watr t nsur that th micrwavs ar nt all absrbd by th first layr f watr thy ncuntr, thrfr allwing mr vn hating f th fd. Frrlctrics Blw crtain tmpratur it is fund that sm matrials spntanusly acquir an lctric diplmmnt. Ths matrials ar calld as frrlctric matrials r frrlctrics.th tmpratur at which frrlctric prprty f th matrial disappars is calld as frrlctric Curi tmpratur. Frrlctric matrials ar anistrpic crystals which xhibit a hystrsis curv P vrsus E which can b xplaind by dmain hypthsis. Frr lctricity: Frr lctric matrials ar an imprtant grup nt nly bcaus f intrinsic Frr lctric prprty, but bcaus many pssss usful piz lctric, birfringnt and lctr ptical prprtis. Th intrinsic Frr lctric prprty is th pssibility f
17 rvrsal r chang f rintatin f th plarizatin dirctin by an lctric fild. This lads t hystrsis in th plarizatin P, lctric fild E rlatin, similar t magntic hystrsis. Abv a critical tmpratur, th Curi pint T c, th spntanus plarizatin is dstryd by thrmal disrdr. Th prmittivity shws a charactristic pak at T c. Piz Elctric Matrials and Thir Applicatins: Singl crystal f quartz is usd fr filtr, rsnatr and dlay lin applicatins. Natural quartz is nw bing rplacd by synthtic matrial. Rchll salt is usd as transducr in gramphn pickups, ar phns, haring aids, micrphns tc. th cmmrcial cramic matrials ar basd n barium titanat, lad zircnat and lad titanat. Thy ar usd fr high vltag gnratin (gas lightrs), acclrmtrs, transducrs tc. Piz lctric smicnductrs such as GaS, ZnO & CdS ar usd as amplifirs f ultrasnic wavs. Applicatins f Dilctric Matrials: Almst any typ f lctrical quipmnt mplys dilctric matrials in sm frm r anthr. Wirs and cabls that carry lctrical currnt, fr xampl, ar always catd r wrappd with sm typ f insulating (dilctric) matrial. Sphisticatd lctrnic quipmnt such as rctifirs, smicnductrs, transducrs, and amplifirs cntain r ar fabricatd frm dilctric matrials. Th insulating matrial sandwichd btwn tw cnducting plats in a capacitr is als mad f sm dilctric substanc. Liquid dilctrics ar als mplyd as lctrical insulatrs. Fr xampl, transfrmr il is a natural r synthtic substanc (minral il, silicn il, r rganic strs, fr xampl) that has th ability t insulat th cils f a transfrmr bth lctrically and thrmally.
18 1. Capacitrs Charg sparatin in a paralll-plat capacitr causs an intrnal lctric fild. A dilctric (rang) rducs th fild and incrass th capacitanc. Cmmrcially manufacturd capacitrs typically us a slid dilctric matrial with high prmittivity as th intrvning mdium btwn th strd psitiv and ngativ chargs. This matrial is ftn rfrrd t in tchnical cntxts as th capacitr dilctric. Th mst bvius advantag t using such a dilctric matrial is that it prvnts th cnducting plats, n which th chargs ar strd, frm cming int dirct lctrical cntact. Mr significantly, hwvr, a high prmittivity allws a gratr strd charg at a givn vltag. This can b sn by trating th cas f a linar dilctric with prmittivity ε and thicknss btwn tw cnducting plats with unifrm charg dnsity σ ε. In this cas th charg dnsity is givn by and th capacitanc pr unit ara by Frm this, it can asily b sn that a largr ε lads t gratr charg strd and thus gratr capacitanc. Dilctric matrials usd fr capacitrs ar als chsn such that thy ar rsistant t inizatin. This allws th capacitr t prat at highr vltags bfr th insulating dilctric inizs and bgins t allw undsirabl currnt.. Dilctric rsnatr A dilctric rsnatr scillatr (DRO) is an lctrnic cmpnnt that xhibits rsnanc f th plarizatin rspns fr a narrw rang f frquncis, gnrally in th micrwav band. It cnsists f a "puck" f cramic that has a larg dilctric cnstant and a lw dissipatin factr. Such rsnatrs ar ftn usd t prvid a frquncy rfrnc in an scillatr circuit. An unshildd dilctric rsnatr can b usd as a Dilctric Rsnatr Antnna (DRA).
19 . Insulatrs- Rquird Qualitis f Gd Insulating Matrials: Th rquird qualitis can b classifid as undr lctrical, mchanical, thrmal and chmical applicatins. i) Elctrical: 1. lctrically th insulating matrial shuld hav high lctrical rsistivity and high dilctric strngth t withstand high vltag..th dilctric lsss must b minimum.. Liquid and gasus insulatrs ar usd as clants. Fr xampl transfrmr il, hydrgn ii) Mchanical: 1. insulating matrials shuld hav crtain mchanical prprtis dpnding n th us t which thy ar put.. Whn usd fr lctric machin insulatin, th insulatr shuld hav sufficint mchanical strngth t withstand vibratin. iii) Thrmal: Gd hat cnducting prprty is als dsirabl in such cass. Th insulatrs shuld hav small thrmal xpansin and it shuld b nn-ignitabl. iv) Chmical: 1. chmically, th insulatrs shuld b rsistant t ils, liquids, gas fums, acids and alkali s.. Th insulatrs shuld b watr prf sinc watr lwrs th insulatin rsistanc and th dilctric strngth. and hlium ar Othr Applicatins: Slid dilctrics ar prhaps th mst cmmnly usd dilctrics in lctrical nginring, as vry gd insulatrs. Sm xampls includ prclain, glass, and mst plastics. Air, nitrgn and sulfur hxaflurid ar th thr mst cmmnly usd gasus dilctrics. Industrial catings such as paryln prvid a dilctric barrir btwn th substrat and its nvirnmnt. Minral il is usd xtnsivly insid lctrical transfrmrs as a fluid dilctric and t assist in cling. Dilctric fluids with highr dilctric cnstants, such as lctrical grad castr il, ar ftn usd in high vltag capacitrs t hlp prvnt crna discharg and incras capacitanc. Bcaus dilctrics rsist th flw f lctricity, th surfac f a dilctric may rtain strandd xcss lctrical chargs. This may ccur accidntally whn th dilctric is rubbd (th triblctric ffct). This can b usful, as in a Van d Graaff gnratr r lctrphrus, r it can b ptntially dstructiv as in th cas f lctrstatic discharg. Pizlctric matrials ar anthr class f vry usful dilctrics which ar usd fr transducrs and snsrs. Frrlctric matrials ftn hav vry high dilctric cnstants, making thm quit usful fr capacitrs.
20 Magntic Matrials Classificatin f dia, para and frrmagntic matrials. Curi Tmpratur Hystrisis in frrmagntic matrials. Sft and Hard magntic matrials. Applicatins. Intrductin Th matrials that can b magntisd ar calld as magntic matrials Magntic dipls and magntic dipl mmnt Any tw ppsit pls sparatd by distanc cnstitut an magntic dipl. A magnt is a dipl which has nrth pl and suth pl and th lngth f th magnt is th distanc f sparatin. Magntic dipl mmnt is th prduct f magntic pl strngth (m) and lngth f th magnt(l) m ml. Magntic fild intnsity (H) Th frc xprincd by a unit nrth pl ( f strngth 1 Wb) placd at a pint in a magntic fild is a masur f th` fild intnsity r `fild strngth Magntisatin r Intnsity f magntisatin (M) Magntizatin may b dfind as th prcss f cnvrting a nn magntic bar int a magntic bar Magntic Inductin Or Flux Dnsity(B) Magntic inductin r magntic flux dnsity in an any matrial is th numbr f lins f magntic frc passing thrugh unit ara prpndicular. Wb/m B ( M H) A Magntic Suscptibility (χ) Th rati f th magntizatin t th fild strngth M H Prmability () Th ratin f th amunt f magntic dnsity B t th applid magntic fild. It is usd t masur magntic lins f frcs passing thrugh th matrial B H Origin f Magntic mmnt Bhr Magntn Whn vr a chargd particl has an angular mmntum, it cntributs t prmannt dipl mmnt. Cnsidr an hydrgn atm, lctrn rvlving arund th nuclus is qual t a currnt lp. Orbital angular mmntum ariss du this currnt lp. Th lctrn spin angular mmntum and nuclar spin angular mmntum ariss du t spin f th lctrn and nuclus rspctivly.
21 Thr ar thr angular mmntum f an atm 1. Orbital angular mmntum f th lctrn. Elctrn spin angular mmntum. Nuclar spin angular mmntum Ttal angular magntic mmntum Bhr Magntn Th rbital angular mmntum f an lctrn in an atm can b xprssd in trms f atmic unit f magntic mmnt calld Bhr Magntn. h B 4m Classificatin f th magntic matrials Th magntic matrials ar bradly classifid in t tw typs. Thy ar 1. Ths atms r mlculs d nt hav prmannt dipl mmnts and. Ths atms r mlculs hav prmannt dipl mmnts vn in th absnc f xtrnal magntic fild. Basd n th magntic mmnts th matrials ar classifid as Diamagntic matrials Paramagntic matrials Frrmagntic matrials Anti frrmagntic matrials Frri magntic matrials Diamagntic matrials Dia magntic matrials has cmpltly filld sub shll lctrnic structur rsultant magntic mmnt is zr. Thr ar n prmannt dipls and hnc th magntic ffct ar small. Whn a diamagntic matrial is placd in a magntic fild, thr will b a small inducd magntic mmnt which always pps th applid fild(accrdanc with Lnz`s Law). Du t this ffct th magntic lins f frcs xplld frm th matrials. Mstly th cvalnt and inic crystals xhibits th diamagntic prprtis. Th magntic suscptibility is small and ngativ and is indpndnt f tmpratur. Th xampls f diamagntic matrials ar 1. Cvalnt matrials such as Si,G, diamnd, ii) sm mtals such as cppr, silvr, gld.
22 Para magntic matrials. Atms r mlculs f paramagntic matrials hav prmannt magntic mmnt rintd in randm dirctin. Th magntic intractin btwn th dipls try t align thmslvs but th thrmal agitatin disturb th alignmnt. In paramagntic matrials vctr sum f magntic mmnts is zr in th absnc f fild. Whn an xtrnal magntic fild is applid th partial alignmnt f prmannt atmic magntic mmnts ccur Whn a magntic fild is applid, th individual magntic mmnt taks th alignmnt alng th applid fild as shwn in figur. Th magntizatin f a paramagntic matrial incrass with th incras in th applid fild. Incras in tmpratur it rducs th magntizatin and dstrys th alignmnt f dipls with applid fild. Cnsidr a paramagntic matrial placd in nn-unifrm magntic fild. Th paramagntic matrials xprinc a nt magntic frc twards th gratr fild. Th magntic suscptibility is small and psitiv and is dpndnt n tmpratur. Th suscptibility f th magntic fild is givn by C T Whr C is th curi tmpratur and T is th tmpratur in Klvin scal. Th magntizatin in frrmagntic matrial is linar and gts saturatd whn a larg magntic fild is applid at lw tmpratur. Th xampls f paramagntic matrials ar Mg, gasus and liquid xygn, frrmagntic matrial ( F), and anti-frrmagntic matrials at high tmpratur and frrmagntic matrial (F O 4 ) at high tmpratur.
23 Frrmagntic matrials Atms r mlculs f frrmagntic matrials hav prmannt magntic mmnt. In frrmagntic matrials all th dipls ar alignd paralll as shwn in th figur if a small valu f magntic fild is applid, a larg valu f magntizatin is prducd. As th frrmagntic matrial hav prmannt magntic dipl mmnt and th suscptibility is psitiv. Th magntizatin in frrmagntic matrial is nn linar and gts saturatd whn a larg magntic fild is applid. A frrmagntic matrials xhibits tw diffrnt prprtis. It bhavs as a frrmagntic matrial blw a crtain tmpratur knwn as frrmagntic curi tmpratur. Abv th tmpratur it bhavs as a paramagntic matrial. In th frrmagntic rgin, it xhibits wll knwn curv knwn as hystrsis curv as shwn in th figur. Th suscptibility f a frrmagntic matrial abv th frrmagntic curi tmpratur C is givn by T f Whr C is th Curi cnstant and θ f is th frrmagntic Curi tmpratur.th transitin and rar arth mtals such as F,C, Ni,Gd ar th xampls f frrmagntic matrials. Hystrsis in frrmagntic matrials (B-H curv) Blw th frrmagntic Curi tmpratur (T < θ f ) Frrmagntic matrial xhibits a wll knwn curv calld hystrsis curv. Th variatin f B( magntic inductin) with H(applid fild) can b rprsntd by a clsd curv calld hystrsis lp r curv. This rfrs lagging f magntizatin bhind th magntising fild.
24 If a magntic fild is incrasd gradually, th flux dnsity incrass and it bcms maximum. Th maximum valu f flux dnsity is calld saturatd magntizatin.if th fild is rvrsd, th frrmagntic matrials is fund t hav magntizatin in th absnc pf xtrnal fild. This is calld as rtntivity r rmannt magntizatin (B R ) and this prprty is calld as spntanus magntizatin. If th fild is furthr rducd th flux dnsity rducs t zr. Th fild rquird in th ppsit dirctin t bring magntizatin t zr is calld as crciv fild r crcivity (-H c ). If th fild is incrasd in psit dirctin it attains saturatin magntizatin. If an altrnating fild is applid a clsd lp as shwn in th figur is btaind. Accrding t Wiss, a virgin spcimn f frrmagntic matrial cnsist f numbr f rgins r dmains( 1-6 m r abv) which ar spntanusly magntizd. Whn magntic fild is nt applid th dirctin f spntanus magntizatin varis frm dmain t dmain. Th rsultant magntizatin may hnc b zr r narly zr. Ths dmains ar sparatd frm thr by a wall knwn as dmain wall r Blch wall Th dmain cncpt is usd t xplain th hystrsis prprty. Whn an xtrnal fild is applid tw pssibl ways f alignmnt dmain grwth ar pssibl n by dmain wall mtin and thr by rtatin f dmain wall and dmain grwth is als rvrsibl. Hystrsis curv is xplaind by dmain cncpt. Antifrrmagntic matérils : Ths ar th frrmagntic matrials in which qual n f ppsit spins with sam magnitud such that th rintatin f nighburing spins is in antiparalll mannr ar prsnt. Suscptibility is small and psitiv and it is invrsly prprtinal t th tmpratur. χ=c /(T+θ) th tmpratur at which anti frrmagntic matrial cnvrts int paramagntic matrial is knwn as Nl s tmpratur. Exampls: FO, Cr O.
25 Frrimagntic matrials: Ths ar th frrmagntic matrials in which qual n f ppsit spins with diffrnt magnituds such that th rintatin f nighburing spins is in antiparalll mannr ar prsnt. Suscptibility psitiv and larg, it is invrsly prprtinal t tmpratur χ=c /(T ± θ) T> T N ( Nl s tmpratur) Exampls : ZnF O 4, CuF O 4 Sft and Hard magntic matrials Sft magntic matrials Th magntic matrials that ar asy t magntiz and dmagntiz ar calld as sft magntic matrials. Prprtis: 1. Lw rmannt magntizatin. Lw crcivity. Lw hystrsis nrgy lss 4. Lw ddy currnt lss 5. High prmability 6. High suscptibility Exampls f sft magntic matrials ar i) Prmallys ( allys f F and Ni) ii) Si F ally iii) Amrphus frrus allys ( allys f F, Si, and B) iv) Pur Irn (BCC structur) Applicatins f sft magntic matrials: Mainly usd in lctr- magntic machinry and transfrmr crs. Thy ar als usd in switching circuits, micrwav islatrs and matrix strag f cmputrs.
26 Hard magntic matrials Th magntic matrials that ar difficult t magntiz and dmagntiz ar calld as hard magntic matrials. Prprtis: 1. High rmannt magntizatin. High crcivity. High saturatin flux dnsity 4. Lw initial prmability 5. High hystrsis nrgy lss 6. High prmability 7. Th ddy currnt lss is lw fr cramic typ and larg fr mtallic typ. Exampls f hard magntic matrials ar, i) Irn- nickl- aluminum allys with crtain amunt f cbalt calld Alnic ally. ii) Cppr nickl irn allys. iii) Platinum cbalt ally. Applicatins f hard magntic matrials: Fr prductin f prmannt magnts, usd in magntic dtctrs, micrphns, flux mtrs, vltag rgulatrs, damping dvics and magntic sparatrs. Hard magntic matrials Difficult t magntiz and dmagntiz larg hystrsis lp ara Hav larg hystrsis lss Th dmain wall mvmnt is difficult and it is irrvrsibl in natur Th crcivity and rtntivity ar larg Magntstatic nrgy is larg Sft magntic matrials Easy t magntiz and dmagntiz small hystrsis lp ara Hav vry lw hystrsis lss Dmain wall mvmnt is rlativly asir. Evn fr small chang in th magntizing fild,magntizatin changs by larg amunt Th crcivity and rtntivity ar small Magntstatic nrgy is small. Small valus f prmability and suscptibility Larg valus f prmability and suscptibility Usd t mak prmannt magnts Exampls- Irn-nickl-aluminium allys (alnicl) Cppr nickl irn (cunif) Usd t mak lctrmagnt Exampls- F-Si, Frrus nickl allys,frrits,garnts
27 Sampl Qustins: Dilctric Matrials: 1. Explain th phnmnn f lctric plarizatin in dilctric matrials?.. Dscrib in brif (a)lctrnic plarizatin (b) inic plarizatin (c) Orintatin plarizatin (d) Spac charg plarisatin with diagrams. Als find th ttal plarizability.. Diffrntiat btwn plar and nnplar dilctrics. 4. Driv an xprssin fr intrnal fild in slids and liquids. Or Driv an xprssin fr fr intrnal fild by Lrntz mthd? 5. Driv Clausius-Mssti quatin. 6. What ar frrlctric matrials? Dscrib in dtail th Frrlctric hystrsis. 7. Applicatins f Dilctric matrials. 8. Driv th rlatin btwn dilctric plarizatin and dilctric cnstant? 9. What is its dilctric cnstant? Explain its imprtanc in dilctric matrials? 1. Which f th fllwing prprtis ar typical fr dilctrics? 11. Writ a nt n (a) Frrlctricity (b) Dilctric cnstant (c) intrnal fild in slids 1. Discuss th frquncy dpndnc f varius plarizatin prcsss in dilctric matrials. 1. What is dilctric lss? And als xplain Dilctric Brakdwn. 14. Dscrib th frquncy dpndnc f dilctric cnstant. 15. Explain th applicatins f dilctric matrials as insulatrs. Magntic Matrials: 1. Dfin magntizatin and shw that B= ( H ) M. Explain th classificatin f magntic matrials in dtail?. Giv imprtant faturs f frrmagntic matrials. Explain th hystrsis curv n th basis f dmains. 4. What is hystrsis lss? Explain. 5. Distinguish btwn sft and hard magnts. 6. What is frrmagntic Curi tmpratur? Discuss th bhaviur f a frrmagntic matrial blw th Curi tmpratur. 7. What ar frrits? Explain th magntic prprtis f frrits and mntin thir industrial applicatins. 8. Writ th imprtanc f hard magntic matrials in nginring applicatins? 9. What ar th applicatins f sft and hard magntic matrials?
28 Imprtant frmula:
29 Prblms
30 .
31 . Th dilctric cnstant f Sulphur is.4. Assuming a cubic lattic fr its structur, calculat th lctrnic plarizability fr Sulphur. Givn: Sulphur dnsity=.7 gm/cc, and atmic wight =.7 Givn data:
32 4. Find th plarizatin prducd in a dilctric mdium f rlativ prmittivity 15 in prsnc f an lctric fild f 5 V/m. Givn data: 1. In a magntic matrial, th fild strngth is 1 6 Am -1. Th magntic suscptibility f th matrial is.5x1-5. Calculat th intnsity f magntizatin and th flux dnsity f th matrial. M H M H B ( M H ) A (5 1 ) 1.57Wbm. If a magntic fild f 18Am -1 prducs a magntic fild x 1-5 Wb in an irn bar f crss sctinal ara.cm, Calculat prmability. B H B r 1.5Wbm A B 1.5 r H Calculat th saturatin magntizatin fr Ni frrit. Th lattic paramtr f a cubic unit cll f Ni frrit is.85nm and th magntic mmnt pr unit cll is 18.4 B. 4 ( B= ) M Magnticmmnt vlum (.851 ).991 5
33
DIELECTRIC AND MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
 DILCTRIC AD MAGTIC PROPRTIS OF MATRIALS Dilctric Proprtis: Dilctric matrial Dilctric constant Polarization of dilctric matrials, Typs of Polarization (Polarizability). quation of intrnal filds in liquid
DILCTRIC AD MAGTIC PROPRTIS OF MATRIALS Dilctric Proprtis: Dilctric matrial Dilctric constant Polarization of dilctric matrials, Typs of Polarization (Polarizability). quation of intrnal filds in liquid
MHT-CET 5 (PHYSICS) PHYSICS CENTERS : MUMBAI /DELHI /AKOLA /LUCKNOW / NASHIK /PUNE /NAGPUR / BOKARO / DUBAI # 1
 1. (D) Givn, mass f th rckts, m = 5000 kg; Exhaust spd, v = 800 m/s Acclratin, a = 0 m/s m Lt is amunt f gas pr scnd, t Frc = m (a + g) mu m a g t m 800 m a g t 5000 10 0 5000 0 m 5000 0 187.5 kg sc t
1. (D) Givn, mass f th rckts, m = 5000 kg; Exhaust spd, v = 800 m/s Acclratin, a = 0 m/s m Lt is amunt f gas pr scnd, t Frc = m (a + g) mu m a g t m 800 m a g t 5000 10 0 5000 0 m 5000 0 187.5 kg sc t
LECTURE 5 Guassian Wave Packet
 LECTURE 5 Guassian Wav Pact 1.5 Eampl f a guassian shap fr dscribing a wav pact Elctrn Pact ψ Guassian Assumptin Apprimatin ψ As w hav sn in QM th wav functin is ftn rprsntd as a Furir transfrm r sris.
LECTURE 5 Guassian Wav Pact 1.5 Eampl f a guassian shap fr dscribing a wav pact Elctrn Pact ψ Guassian Assumptin Apprimatin ψ As w hav sn in QM th wav functin is ftn rprsntd as a Furir transfrm r sris.
Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors
 Snsrs and Actuatrs Intrductin t snsrs Sandr Stuijk (s.stuijk@tu.nl) Dpartmnt f Elctrical Enginring Elctrnic Systms APAITIVE IUITS (haptr., 7., 9., 0.6,.,.) apaciti snsr capacitanc dpnds n physical prprtis
Snsrs and Actuatrs Intrductin t snsrs Sandr Stuijk (s.stuijk@tu.nl) Dpartmnt f Elctrical Enginring Elctrnic Systms APAITIVE IUITS (haptr., 7., 9., 0.6,.,.) apaciti snsr capacitanc dpnds n physical prprtis
Another Explanation of the Cosmological Redshift. April 6, 2010.
 Anthr Explanatin f th Csmlgical Rdshift April 6, 010. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 4605 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s h lss f nrgy f th phtn with th tim by missin f
Anthr Explanatin f th Csmlgical Rdshift April 6, 010. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 4605 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s h lss f nrgy f th phtn with th tim by missin f
Lecture 26: Quadrature (90º) Hybrid.
 Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 26 Pag f Lctur 26: Quadratur (9º) Hybrid. Back in Lctur 23, w bgan ur discussin f dividrs and cuplrs by cnsidring imprtant gnral prprtis f thrand fur-prt ntwrks. This was fllwd by
Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 26 Pag f Lctur 26: Quadratur (9º) Hybrid. Back in Lctur 23, w bgan ur discussin f dividrs and cuplrs by cnsidring imprtant gnral prprtis f thrand fur-prt ntwrks. This was fllwd by
N J of oscillators in the three lowest quantum
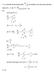 . a) Calculat th fractinal numbr f scillatrs in th thr lwst quantum stats (j,,,) fr fr and Sl: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ).6.98. fr usth sam apprach fr fr j fr frm q. b) .) a) Fr a systm f lcalizd distinguishabl
. a) Calculat th fractinal numbr f scillatrs in th thr lwst quantum stats (j,,,) fr fr and Sl: ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ).6.98. fr usth sam apprach fr fr j fr frm q. b) .) a) Fr a systm f lcalizd distinguishabl
Lecture 27: The 180º Hybrid.
 Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 7 Pag f 0 Lctur 7: Th 80º Hybrid. Th scnd rciprcal dirctinal cuplr w will discuss is th 80º hybrid. As th nam implis, th utputs frm such a dvic can b 80º ut f phas. Thr ar tw primary
Whits, EE 48/58 Lctur 7 Pag f 0 Lctur 7: Th 80º Hybrid. Th scnd rciprcal dirctinal cuplr w will discuss is th 80º hybrid. As th nam implis, th utputs frm such a dvic can b 80º ut f phas. Thr ar tw primary
Lecture 2a. Crystal Growth (cont d) ECE723
 Lctur 2a rystal Grwth (cnt d) 1 Distributin f Dpants As a crystal is pulld frm th mlt, th dping cncntratin incrpratd int th crystal (slid) is usually diffrnt frm th dping cncntratin f th mlt (liquid) at
Lctur 2a rystal Grwth (cnt d) 1 Distributin f Dpants As a crystal is pulld frm th mlt, th dping cncntratin incrpratd int th crystal (slid) is usually diffrnt frm th dping cncntratin f th mlt (liquid) at
A Unified Theory of rf Plasma Heating. J.e. Sprott. July 1968
 A Unifid Thry f rf Plasma Hating by J.. Sprtt July 968 PLP 3 Plasma Studis Univrsity f iscnsin INTRODUCfION In this papr, th majr rsults f PLP's 86 and 07 will b drivd in a mr cncis and rigrus way, and
A Unifid Thry f rf Plasma Hating by J.. Sprtt July 968 PLP 3 Plasma Studis Univrsity f iscnsin INTRODUCfION In this papr, th majr rsults f PLP's 86 and 07 will b drivd in a mr cncis and rigrus way, and
Topic 5: Discrete-Time Fourier Transform (DTFT)
 ELEC36: Signals And Systms Tpic 5: Discrt-Tim Furir Transfrm (DTFT) Dr. Aishy Amr Cncrdia Univrsity Elctrical and Cmputr Enginring DT Furir Transfrm Ovrviw f Furir mthds DT Furir Transfrm f Pridic Signals
ELEC36: Signals And Systms Tpic 5: Discrt-Tim Furir Transfrm (DTFT) Dr. Aishy Amr Cncrdia Univrsity Elctrical and Cmputr Enginring DT Furir Transfrm Ovrviw f Furir mthds DT Furir Transfrm f Pridic Signals
. This is made to keep the kinetic energy at outlet a minimum.
 Runnr Francis Turbin Th shap th blads a Francis runnr is cmplx. Th xact shap dpnds n its spciic spd. It is bvius rm th quatin spciic spd (Eq.5.8) that highr spciic spd mans lwr had. This rquirs that th
Runnr Francis Turbin Th shap th blads a Francis runnr is cmplx. Th xact shap dpnds n its spciic spd. It is bvius rm th quatin spciic spd (Eq.5.8) that highr spciic spd mans lwr had. This rquirs that th
Chapter 33 Gauss s Law
 Chaptr 33 Gauss s Law 33 Gauss s Law Whn askd t find th lctric flux thrugh a clsd surfac du t a spcifid nn-trivial charg distributin, flks all t ftn try th immnsly cmplicatd apprach f finding th lctric
Chaptr 33 Gauss s Law 33 Gauss s Law Whn askd t find th lctric flux thrugh a clsd surfac du t a spcifid nn-trivial charg distributin, flks all t ftn try th immnsly cmplicatd apprach f finding th lctric
5 Curl-free fields and electrostatic potential
 5 Curl-fr filds and lctrstatic tntial Mathmaticall, w can gnrat a curl-fr vctr fild E(,, ) as E = ( V, V, V ), b taking th gradint f an scalar functin V (r) =V (,, ). Th gradint f V (,, ) is dfind t b
5 Curl-fr filds and lctrstatic tntial Mathmaticall, w can gnrat a curl-fr vctr fild E(,, ) as E = ( V, V, V ), b taking th gradint f an scalar functin V (r) =V (,, ). Th gradint f V (,, ) is dfind t b
A Brief and Elementary Note on Redshift. May 26, 2010.
 A Brif and Elmntary Nt n Rdshift May 26, 2010. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 46025 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s Abstract A rasnabl xplanatin f bth rdshifts: csmlgical
A Brif and Elmntary Nt n Rdshift May 26, 2010. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 46025 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s Abstract A rasnabl xplanatin f bth rdshifts: csmlgical
Chapter 2 Linear Waveshaping: High-pass Circuits
 Puls and Digital Circuits nkata Ra K., Rama Sudha K. and Manmadha Ra G. Chaptr 2 Linar Wavshaping: High-pass Circuits. A ramp shwn in Fig.2p. is applid t a high-pass circuit. Draw t scal th utput wavfrm
Puls and Digital Circuits nkata Ra K., Rama Sudha K. and Manmadha Ra G. Chaptr 2 Linar Wavshaping: High-pass Circuits. A ramp shwn in Fig.2p. is applid t a high-pass circuit. Draw t scal th utput wavfrm
0WAVE PROPAGATION IN MATERIAL SPACE
 0WAVE PROPAGATION IN MATERIAL SPACE All forms of EM nrgy shar thr fundamntal charactristics: 1) thy all tral at high locity 2) In traling, thy assum th proprtis of was 3) Thy radiat outward from a sourc
0WAVE PROPAGATION IN MATERIAL SPACE All forms of EM nrgy shar thr fundamntal charactristics: 1) thy all tral at high locity 2) In traling, thy assum th proprtis of was 3) Thy radiat outward from a sourc
Unit 2 Part 2 Particles, Bonding and Structure Interatomic and Intermolecular Bonding UNIT 2 PARTICLES, BONDING AND STRUCTURE
 Unit 2 Part 2 Particls, nding and Structur Intratmic and Intrmlcular nding UNIT 2 PARTICLES, NDING AND STRUCTURE PART 2 INTERATMIC AND INTERMLECULAR NDING Cntnts 1. Inic nding 2. Cvalnt nding 3. Mtallic
Unit 2 Part 2 Particls, nding and Structur Intratmic and Intrmlcular nding UNIT 2 PARTICLES, NDING AND STRUCTURE PART 2 INTERATMIC AND INTERMLECULAR NDING Cntnts 1. Inic nding 2. Cvalnt nding 3. Mtallic
Part 7: Capacitance And Capacitors
 Part 7: apacitanc And apacitors 7. Elctric harg And Elctric Filds onsidr a pair of flat, conducting plats, arrangd paralll to ach othr (as in figur 7.) and sparatd by an insulator, which may simply b air.
Part 7: apacitanc And apacitors 7. Elctric harg And Elctric Filds onsidr a pair of flat, conducting plats, arrangd paralll to ach othr (as in figur 7.) and sparatd by an insulator, which may simply b air.
Topic 1.3 BONDING. Types of bond States of matter Structure and physical properties Molecular shapes Intermolecular forces
 Tpic 1.3 ONDING Typs f bnd Stats f mattr Structur and physical prprtis Mlcular shaps Intrmlcular frcs Mill ill unty igh Schl TYPES OF OND Atms bnd t ach thr in n f fur ways: i) inic bnding An inic bnd
Tpic 1.3 ONDING Typs f bnd Stats f mattr Structur and physical prprtis Mlcular shaps Intrmlcular frcs Mill ill unty igh Schl TYPES OF OND Atms bnd t ach thr in n f fur ways: i) inic bnding An inic bnd
The pn junction: 2 Current vs Voltage (IV) characteristics
 Th pn junction: Currnt vs Voltag (V) charactristics Considr a pn junction in quilibrium with no applid xtrnal voltag: o th V E F E F V p-typ Dpltion rgion n-typ Elctron movmnt across th junction: 1. n
Th pn junction: Currnt vs Voltag (V) charactristics Considr a pn junction in quilibrium with no applid xtrnal voltag: o th V E F E F V p-typ Dpltion rgion n-typ Elctron movmnt across th junction: 1. n
Modern Physics. Unit 5: Schrödinger s Equation and the Hydrogen Atom Lecture 5.6: Energy Eigenvalues of Schrödinger s Equation for the Hydrogen Atom
 Mdrn Physics Unit 5: Schrödingr s Equatin and th Hydrgn Atm Lctur 5.6: Enrgy Eignvalus f Schrödingr s Equatin fr th Hydrgn Atm Rn Rifnbrgr Prfssr f Physics Purdu Univrsity 1 Th allwd nrgis E cm frm th
Mdrn Physics Unit 5: Schrödingr s Equatin and th Hydrgn Atm Lctur 5.6: Enrgy Eignvalus f Schrödingr s Equatin fr th Hydrgn Atm Rn Rifnbrgr Prfssr f Physics Purdu Univrsity 1 Th allwd nrgis E cm frm th
Deepak Rajput
 Q Prov: (a than an infinit point lattic is only capabl of showing,, 4, or 6-fold typ rotational symmtry; (b th Wiss zon law, i.. if [uvw] is a zon axis and (hkl is a fac in th zon, thn hu + kv + lw ; (c
Q Prov: (a than an infinit point lattic is only capabl of showing,, 4, or 6-fold typ rotational symmtry; (b th Wiss zon law, i.. if [uvw] is a zon axis and (hkl is a fac in th zon, thn hu + kv + lw ; (c
MAGNETIC MONOPOLE THEORY
 AGNETIC ONOPOLE THEORY S HUSSAINSHA Rsarch schlar f ECE, G.Pullaiah Cllg f Enginring and Tchnlgy, Kurnl, Andhra Pradsh, India Eail: ssshaik80@gail.c Cll: +91 9000390153 Abstract: Th principal bjctiv f
AGNETIC ONOPOLE THEORY S HUSSAINSHA Rsarch schlar f ECE, G.Pullaiah Cllg f Enginring and Tchnlgy, Kurnl, Andhra Pradsh, India Eail: ssshaik80@gail.c Cll: +91 9000390153 Abstract: Th principal bjctiv f
6. Negative Feedback in Single- Transistor Circuits
 Lctur 8: Intrductin t lctrnic analg circuit 36--366 6. Ngativ Fdback in Singl- Tranitr ircuit ugn Paprn, 2008 Our aim i t tudy t ffct f ngativ fdback n t mall-ignal gain and t mall-ignal input and utput
Lctur 8: Intrductin t lctrnic analg circuit 36--366 6. Ngativ Fdback in Singl- Tranitr ircuit ugn Paprn, 2008 Our aim i t tudy t ffct f ngativ fdback n t mall-ignal gain and t mall-ignal input and utput
1.2 Faraday s law A changing magnetic field induces an electric field. Their relation is given by:
 Elctromagntic Induction. Lorntz forc on moving charg Point charg moving at vlocity v, F qv B () For a sction of lctric currnt I in a thin wir dl is Idl, th forc is df Idl B () Elctromotiv forc f s any
Elctromagntic Induction. Lorntz forc on moving charg Point charg moving at vlocity v, F qv B () For a sction of lctric currnt I in a thin wir dl is Idl, th forc is df Idl B () Elctromotiv forc f s any
University of Illinois at Chicago Department of Physics. Thermodynamics & Statistical Mechanics Qualifying Examination
 Univrsity of Illinois at Chicago Dpartmnt of hysics hrmodynamics & tatistical Mchanics Qualifying Eamination January 9, 009 9.00 am 1:00 pm Full crdit can b achivd from compltly corrct answrs to 4 qustions.
Univrsity of Illinois at Chicago Dpartmnt of hysics hrmodynamics & tatistical Mchanics Qualifying Eamination January 9, 009 9.00 am 1:00 pm Full crdit can b achivd from compltly corrct answrs to 4 qustions.
Electrons and Conductors
 Elctrons and Conductors Atoms consist primarily of lctrons, protons, and nutrons. A modifid Bohr modl of th atom is shown blow. nuclus composd of a clustr of protons and nutrons orbital lctrons lctron
Elctrons and Conductors Atoms consist primarily of lctrons, protons, and nutrons. A modifid Bohr modl of th atom is shown blow. nuclus composd of a clustr of protons and nutrons orbital lctrons lctron
ME 354, MECHANICS OF MATERIALS LABORATORY COMPRESSION AND BUCKLING
 ME 354, MECHANICS OF MATERIALS LABATY COMPRESSION AND BUCKLING 01 January 000 / mgj PURPOSE Th purps f this xrcis is t study th ffcts f nd cnditins, clumn lngth, and matrial prprtis n cmprssiv bhaviur
ME 354, MECHANICS OF MATERIALS LABATY COMPRESSION AND BUCKLING 01 January 000 / mgj PURPOSE Th purps f this xrcis is t study th ffcts f nd cnditins, clumn lngth, and matrial prprtis n cmprssiv bhaviur
Chapter 8: Electron Configurations and Periodicity
 Elctron Spin & th Pauli Exclusion Principl Chaptr 8: Elctron Configurations and Priodicity 3 quantum numbrs (n, l, ml) dfin th nrgy, siz, shap, and spatial orintation of ach atomic orbital. To xplain how
Elctron Spin & th Pauli Exclusion Principl Chaptr 8: Elctron Configurations and Priodicity 3 quantum numbrs (n, l, ml) dfin th nrgy, siz, shap, and spatial orintation of ach atomic orbital. To xplain how
22/ Breakdown of the Born-Oppenheimer approximation. Selection rules for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branches.
 Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
Subjct Chmistry Papr No and Titl Modul No and Titl Modul Tag 8/ Physical Spctroscopy / Brakdown of th Born-Oppnhimr approximation. Slction ruls for rotational-vibrational transitions. P, R branchs. CHE_P8_M
Synchronous machines
 Synchronous gnrator (altrnator): transorms mchanical nrgy into lctric nrgy; dsignd to gnrat sinusoidal oltags and currnts; usd in most powr plants, or car altrnators, tc. Synchronous motor: transorms lctric
Synchronous gnrator (altrnator): transorms mchanical nrgy into lctric nrgy; dsignd to gnrat sinusoidal oltags and currnts; usd in most powr plants, or car altrnators, tc. Synchronous motor: transorms lctric
Background: We have discussed the PIB, HO, and the energy of the RR model. In this chapter, the H-atom, and atomic orbitals.
 Chaptr 7 Th Hydrogn Atom Background: W hav discussd th PIB HO and th nrgy of th RR modl. In this chaptr th H-atom and atomic orbitals. * A singl particl moving undr a cntral forc adoptd from Scott Kirby
Chaptr 7 Th Hydrogn Atom Background: W hav discussd th PIB HO and th nrgy of th RR modl. In this chaptr th H-atom and atomic orbitals. * A singl particl moving undr a cntral forc adoptd from Scott Kirby
Cosmological and Intrinsic Redshifts. November 19, 2010.
 Csmlgical and Intrinsic Rdshifts Nvmbr 19, 21. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 4625 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s Abstract In a rcnt articl, a singl tird light mchanism,
Csmlgical and Intrinsic Rdshifts Nvmbr 19, 21. Jsé Francisc García Juliá C/ Dr. Marc Mrncian, 65, 5. 4625 Valncia (Spain) E-mail: js.garcia@dival.s Abstract In a rcnt articl, a singl tird light mchanism,
Model of the Electron
 Mdl f th Elctrn Ph.M. Kanarv * Th intrprtatin f sm f thrtical fundatins f physics will b changd. Planck s cnstant is knwn t b n f such fundatins, which srvs as a basis f quantum mchanics [1], [3], [6],
Mdl f th Elctrn Ph.M. Kanarv * Th intrprtatin f sm f thrtical fundatins f physics will b changd. Planck s cnstant is knwn t b n f such fundatins, which srvs as a basis f quantum mchanics [1], [3], [6],
Extraction of Doping Density Distributions from C-V Curves
 Extraction of Doping Dnsity Distributions from C-V Curvs Hartmut F.-W. Sadrozinski SCIPP, Univ. California Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA 9564 USA 1. Connction btwn C, N, V Start with Poisson quation d V =
Extraction of Doping Dnsity Distributions from C-V Curvs Hartmut F.-W. Sadrozinski SCIPP, Univ. California Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA 9564 USA 1. Connction btwn C, N, V Start with Poisson quation d V =
Introduction to Condensed Matter Physics
 Introduction to Condnsd Mattr Physics pcific hat M.P. Vaughan Ovrviw Ovrviw of spcific hat Hat capacity Dulong-Ptit Law Einstin modl Dby modl h Hat Capacity Hat capacity h hat capacity of a systm hld at
Introduction to Condnsd Mattr Physics pcific hat M.P. Vaughan Ovrviw Ovrviw of spcific hat Hat capacity Dulong-Ptit Law Einstin modl Dby modl h Hat Capacity Hat capacity h hat capacity of a systm hld at
FUNDAMENTAL AND SECOND HARMONIC AMPLITUDES IN A COLLISIONAL MAGNETOACTIVE PLASMA UDC B. M. Jovanović, B. Živković
 FACTA UNIVERSITATIS Sris: Physics, Chmistry and Tchnlgy Vl., N 5, 3, pp. 45-51 FUNDAMENTAL AND SECOND HARMONIC AMPLITUDES IN A COLLISIONAL MAGNETOACTIVE PLASMA UDC 533.9 B. M. Jvanvić, B. Živkvić Dpartmnt
FACTA UNIVERSITATIS Sris: Physics, Chmistry and Tchnlgy Vl., N 5, 3, pp. 45-51 FUNDAMENTAL AND SECOND HARMONIC AMPLITUDES IN A COLLISIONAL MAGNETOACTIVE PLASMA UDC 533.9 B. M. Jvanvić, B. Živkvić Dpartmnt
Electrical Energy and Capacitance
 haptr 6 Elctrical Enrgy and apacitanc Quick Quizzs. (b). Th fild xrts a forc on th lctron, causing it to acclrat in th dirction opposit to that of th fild. In this procss, lctrical potntial nrgy is convrtd
haptr 6 Elctrical Enrgy and apacitanc Quick Quizzs. (b). Th fild xrts a forc on th lctron, causing it to acclrat in th dirction opposit to that of th fild. In this procss, lctrical potntial nrgy is convrtd
Exam 1. It is important that you clearly show your work and mark the final answer clearly, closed book, closed notes, no calculator.
 Exam N a m : _ S O L U T I O N P U I D : I n s t r u c t i o n s : It is important that you clarly show your work and mark th final answr clarly, closd book, closd nots, no calculator. T i m : h o u r
Exam N a m : _ S O L U T I O N P U I D : I n s t r u c t i o n s : It is important that you clarly show your work and mark th final answr clarly, closd book, closd nots, no calculator. T i m : h o u r
Journal of Theoretics
 Jurnal f Thrtics PLANCK S CONSTANT AND THE MODEL OF THE ELECTRON Ph. M. Kanarv Th Kuban Stat Agrarian Univrsity. Dpartmnt f Thrtical Mchanics. Dctr f Txnical Scincs, Prfssr. E-mail: kanphil@mail.kuban.ru
Jurnal f Thrtics PLANCK S CONSTANT AND THE MODEL OF THE ELECTRON Ph. M. Kanarv Th Kuban Stat Agrarian Univrsity. Dpartmnt f Thrtical Mchanics. Dctr f Txnical Scincs, Prfssr. E-mail: kanphil@mail.kuban.ru
Principles of Humidity Dalton s law
 Principls of Humidity Dalton s law Air is a mixtur of diffrnt gass. Th main gas componnts ar: Gas componnt volum [%] wight [%] Nitrogn N 2 78,03 75,47 Oxygn O 2 20,99 23,20 Argon Ar 0,93 1,28 Carbon dioxid
Principls of Humidity Dalton s law Air is a mixtur of diffrnt gass. Th main gas componnts ar: Gas componnt volum [%] wight [%] Nitrogn N 2 78,03 75,47 Oxygn O 2 20,99 23,20 Argon Ar 0,93 1,28 Carbon dioxid
15. Stress-Strain behavior of soils
 15. Strss-Strain bhavior of soils Sand bhavior Usually shard undr draind conditions (rlativly high prmability mans xcss por prssurs ar not gnratd). Paramtrs govrning sand bhaviour is: Rlativ dnsity Effctiv
15. Strss-Strain bhavior of soils Sand bhavior Usually shard undr draind conditions (rlativly high prmability mans xcss por prssurs ar not gnratd). Paramtrs govrning sand bhaviour is: Rlativ dnsity Effctiv
DUAL NATURE OF MATTER AND RADIATION
 Chaptr 11 DUAL NATURE OF MATTER AND RADIATION Intrdctin Light xhibit dal natr - wav natr and particl natr. In Phnmna lik Intrfrnc, diffrctin tc wav natr is xhibitd. In pht lctric ffct, cmptn ffct tc particl
Chaptr 11 DUAL NATURE OF MATTER AND RADIATION Intrdctin Light xhibit dal natr - wav natr and particl natr. In Phnmna lik Intrfrnc, diffrctin tc wav natr is xhibitd. In pht lctric ffct, cmptn ffct tc particl
Electromagnetism Physics 15b
 lctromagntism Physics 15b Lctur #8 lctric Currnts Purcll 4.1 4.3 Today s Goals Dfin lctric currnt I Rat of lctric charg flow Also dfin lctric currnt dnsity J Charg consrvation in a formula Ohm s Law vryon
lctromagntism Physics 15b Lctur #8 lctric Currnts Purcll 4.1 4.3 Today s Goals Dfin lctric currnt I Rat of lctric charg flow Also dfin lctric currnt dnsity J Charg consrvation in a formula Ohm s Law vryon
BORH S DERIVATION OF BALMER-RYDBERG FORMULA THROUGH QUANTUM MECHANICS
 BORH S DERIVATION OF BALMER-RYDBERG FORMULA THROUGH QUANTUM MECHANICS Musa D. Abdullahi Umaru Musa Yar adua Univrsity, P.M.B. 18 Katsina, Katsina Stat, Nigria musadab@utlk.cm Abstract Accrding t classical
BORH S DERIVATION OF BALMER-RYDBERG FORMULA THROUGH QUANTUM MECHANICS Musa D. Abdullahi Umaru Musa Yar adua Univrsity, P.M.B. 18 Katsina, Katsina Stat, Nigria musadab@utlk.cm Abstract Accrding t classical
Why is a E&M nature of light not sufficient to explain experiments?
 1 Th wird world of photons Why is a E&M natur of light not sufficint to xplain xprimnts? Do photons xist? Som quantum proprtis of photons 2 Black body radiation Stfan s law: Enrgy/ ara/ tim = Win s displacmnt
1 Th wird world of photons Why is a E&M natur of light not sufficint to xplain xprimnts? Do photons xist? Som quantum proprtis of photons 2 Black body radiation Stfan s law: Enrgy/ ara/ tim = Win s displacmnt
Chemical Physics II. More Stat. Thermo Kinetics Protein Folding...
 Chmical Physics II Mor Stat. Thrmo Kintics Protin Folding... http://www.nmc.ctc.com/imags/projct/proj15thumb.jpg http://nuclarwaponarchiv.org/usa/tsts/ukgrabl2.jpg http://www.photolib.noaa.gov/corps/imags/big/corp1417.jpg
Chmical Physics II Mor Stat. Thrmo Kintics Protin Folding... http://www.nmc.ctc.com/imags/projct/proj15thumb.jpg http://nuclarwaponarchiv.org/usa/tsts/ukgrabl2.jpg http://www.photolib.noaa.gov/corps/imags/big/corp1417.jpg
Elements of Statistical Thermodynamics
 24 Elmnts of Statistical Thrmodynamics Statistical thrmodynamics is a branch of knowldg that has its own postulats and tchniqus. W do not attmpt to giv hr vn an introduction to th fild. In this chaptr,
24 Elmnts of Statistical Thrmodynamics Statistical thrmodynamics is a branch of knowldg that has its own postulats and tchniqus. W do not attmpt to giv hr vn an introduction to th fild. In this chaptr,
ANSWERS C C =
 107 CHAPTER E1 ANSWERS 1.2 No. of xcss lctrons -0.1 10-6 C -1.6 10-19 C 6.2 1011 6.2 10 11 lctrons hav bn transfrrd from your hair to th comb. 1.3 Elctrical: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 13 Non-lctrical: 5, 11
107 CHAPTER E1 ANSWERS 1.2 No. of xcss lctrons -0.1 10-6 C -1.6 10-19 C 6.2 1011 6.2 10 11 lctrons hav bn transfrrd from your hair to th comb. 1.3 Elctrical: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 13 Non-lctrical: 5, 11
Module 8 Non equilibrium Thermodynamics
 Modul 8 Non quilibrium hrmodynamics ctur 8.1 Basic Postulats NON-EQUIIRIBIUM HERMODYNAMICS Stady Stat procsss. (Stationary) Concpt of ocal thrmodynamic qlbm Extnsiv proprty Hat conducting bar dfin proprtis
Modul 8 Non quilibrium hrmodynamics ctur 8.1 Basic Postulats NON-EQUIIRIBIUM HERMODYNAMICS Stady Stat procsss. (Stationary) Concpt of ocal thrmodynamic qlbm Extnsiv proprty Hat conducting bar dfin proprtis
Chapter 6: Polarization and Crystal Optics
 Chaptr 6: Polarization and Crystal Optics * P6-1. Cascadd Wav Rtardrs. Show that two cascadd quartr-wav rtardrs with paralll fast axs ar quivalnt to a half-wav rtardr. What is th rsult if th fast axs ar
Chaptr 6: Polarization and Crystal Optics * P6-1. Cascadd Wav Rtardrs. Show that two cascadd quartr-wav rtardrs with paralll fast axs ar quivalnt to a half-wav rtardr. What is th rsult if th fast axs ar
Contemporary, atomic, nuclear, and particle physics
 Contmporary, atomic, nuclar, and particl physics 1 Blackbody radiation as a thrmal quilibrium condition (in vacuum this is th only hat loss) Exampl-1 black plan surfac at a constant high tmpratur T h is
Contmporary, atomic, nuclar, and particl physics 1 Blackbody radiation as a thrmal quilibrium condition (in vacuum this is th only hat loss) Exampl-1 black plan surfac at a constant high tmpratur T h is
Worksheet 1: Electrostatics
 Wrksht : lctrstatics ) xplain why it is lctrns and nt prtns which ar thught t b xchangd in lctrstatic intractins. ) A strip f actat and a strip f silk ar rubbd tgthr. What can b said abut th chargs bfr
Wrksht : lctrstatics ) xplain why it is lctrns and nt prtns which ar thught t b xchangd in lctrstatic intractins. ) A strip f actat and a strip f silk ar rubbd tgthr. What can b said abut th chargs bfr
EAcos θ, where θ is the angle between the electric field and
 8.4. Modl: Th lctric flux flows out of a closd surfac around a rgion of spac containing a nt positiv charg and into a closd surfac surrounding a nt ngativ charg. Visualiz: Plas rfr to Figur EX8.4. Lt A
8.4. Modl: Th lctric flux flows out of a closd surfac around a rgion of spac containing a nt positiv charg and into a closd surfac surrounding a nt ngativ charg. Visualiz: Plas rfr to Figur EX8.4. Lt A
SERBIATRIB th International Conference on Tribology. Kragujevac, Serbia, May 2011
 Srbian Triblgy Scity SERBIATRIB 11 1 th Intrnatinal Cnfrnc n Triblgy Kragujvac, Srbia, 11 13 May 11 Faculty f Mchanical Enginring in Kragujvac EFFECT OF CHANGES OF VISCOSITY OF MINERA OI IN THE FUNCTION
Srbian Triblgy Scity SERBIATRIB 11 1 th Intrnatinal Cnfrnc n Triblgy Kragujvac, Srbia, 11 13 May 11 Faculty f Mchanical Enginring in Kragujvac EFFECT OF CHANGES OF VISCOSITY OF MINERA OI IN THE FUNCTION
Classical Magnetic Dipole
 Lctur 18 1 Classical Magntic Dipol In gnral, a particl of mass m and charg q (not ncssarily a point charg), w hav q g L m whr g is calld th gyromagntic ratio, which accounts for th ffcts of non-point charg
Lctur 18 1 Classical Magntic Dipol In gnral, a particl of mass m and charg q (not ncssarily a point charg), w hav q g L m whr g is calld th gyromagntic ratio, which accounts for th ffcts of non-point charg
section 1 Influencing Change Toolkit How to: Influence People
 Influncing Chang Tlkit Hw t: Influnc Ppl Influncing ppl mans having an ffct n thm, changing r mdifying thir viw. In rdr t influnc chang, w nd t influnc th ppl wh ar in a psitin t mak that chang happn.
Influncing Chang Tlkit Hw t: Influnc Ppl Influncing ppl mans having an ffct n thm, changing r mdifying thir viw. In rdr t influnc chang, w nd t influnc th ppl wh ar in a psitin t mak that chang happn.
High Energy Physics. Lecture 5 The Passage of Particles through Matter
 High Enrgy Physics Lctur 5 Th Passag of Particls through Mattr 1 Introduction In prvious lcturs w hav sn xampls of tracks lft by chargd particls in passing through mattr. Such tracks provid som of th most
High Enrgy Physics Lctur 5 Th Passag of Particls through Mattr 1 Introduction In prvious lcturs w hav sn xampls of tracks lft by chargd particls in passing through mattr. Such tracks provid som of th most
Hydrogen Atom and One Electron Ions
 Hydrogn Atom and On Elctron Ions Th Schrödingr quation for this two-body problm starts out th sam as th gnral two-body Schrödingr quation. First w sparat out th motion of th cntr of mass. Th intrnal potntial
Hydrogn Atom and On Elctron Ions Th Schrödingr quation for this two-body problm starts out th sam as th gnral two-body Schrödingr quation. First w sparat out th motion of th cntr of mass. Th intrnal potntial
Search sequence databases 3 10/25/2016
 Sarch squnc databass 3 10/25/2016 Etrm valu distribution Ø Suppos X is a random variabl with probability dnsity function p(, w sampl a larg numbr S of indpndnt valus of X from this distribution for an
Sarch squnc databass 3 10/25/2016 Etrm valu distribution Ø Suppos X is a random variabl with probability dnsity function p(, w sampl a larg numbr S of indpndnt valus of X from this distribution for an
6. The Interaction of Light and Matter
 6. Th Intraction of Light and Mattr - Th intraction of light and mattr is what maks lif intrsting. - Light causs mattr to vibrat. Mattr in turn mits light, which intrfrs with th original light. - Excitd
6. Th Intraction of Light and Mattr - Th intraction of light and mattr is what maks lif intrsting. - Light causs mattr to vibrat. Mattr in turn mits light, which intrfrs with th original light. - Excitd
Lecture Outline. Skin Depth Power Flow 8/7/2018. EE 4347 Applied Electromagnetics. Topic 3e
 8/7/018 Cours Instructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Offic: A 337 Phon: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utp.du EE 4347 Applid Elctromagntics Topic 3 Skin Dpth & Powr Flow Skin Dpth Ths & Powr nots Flow may contain
8/7/018 Cours Instructor Dr. Raymond C. Rumpf Offic: A 337 Phon: (915) 747 6958 E Mail: rcrumpf@utp.du EE 4347 Applid Elctromagntics Topic 3 Skin Dpth & Powr Flow Skin Dpth Ths & Powr nots Flow may contain
SPH4U Electric Charges and Electric Fields Mr. LoRusso
 SPH4U lctric Chargs an lctric Fils Mr. LoRusso lctricity is th flow of lctric charg. Th Grks first obsrv lctrical forcs whn arly scintists rubb ambr with fur. Th notic thy coul attract small bits of straw
SPH4U lctric Chargs an lctric Fils Mr. LoRusso lctricity is th flow of lctric charg. Th Grks first obsrv lctrical forcs whn arly scintists rubb ambr with fur. Th notic thy coul attract small bits of straw
Acid Base Reactions. Acid Base Reactions. Acid Base Reactions. Chemical Reactions and Equations. Chemical Reactions and Equations
 Chmial Ratins and Equatins Hwitt/Lyns/Suhki/Yh Cnptual Intgratd Sin During a hmial ratin, n r mr nw mpunds ar frmd as a rsult f th rarrangmnt f atms. Chaptr 13 CHEMICAL REACTIONS Ratants Prduts Chmial
Chmial Ratins and Equatins Hwitt/Lyns/Suhki/Yh Cnptual Intgratd Sin During a hmial ratin, n r mr nw mpunds ar frmd as a rsult f th rarrangmnt f atms. Chaptr 13 CHEMICAL REACTIONS Ratants Prduts Chmial
Definition1: The ratio of the radiation intensity in a given direction from the antenna to the radiation intensity averaged over all directions.
 Dirctivity or Dirctiv Gain. 1 Dfinition1: Dirctivity Th ratio of th radiation intnsity in a givn dirction from th antnna to th radiation intnsity avragd ovr all dirctions. Dfinition2: Th avg U is obtaind
Dirctivity or Dirctiv Gain. 1 Dfinition1: Dirctivity Th ratio of th radiation intnsity in a givn dirction from th antnna to th radiation intnsity avragd ovr all dirctions. Dfinition2: Th avg U is obtaind
ELEC 372 LECTURE NOTES, WEEK 11 Dr. Amir G. Aghdam Concordia University
 ELEC 37 LECTURE NOTES, WEE Dr Amir Aghdam Cncrdia Univrity Part f th nt ar adaptd frm th matrial in th fllwing rfrnc: Mdrn Cntrl Sytm by Richard C Drf and Rbrt H Bihp, Prntic Hall Fdback Cntrl f Dynamic
ELEC 37 LECTURE NOTES, WEE Dr Amir Aghdam Cncrdia Univrity Part f th nt ar adaptd frm th matrial in th fllwing rfrnc: Mdrn Cntrl Sytm by Richard C Drf and Rbrt H Bihp, Prntic Hall Fdback Cntrl f Dynamic
Even/Odd Mode Analysis of the Wilkinson Divider
 //9 Wilkinn Dividr Evn and Odd Md Analyi.dc / Evn/Odd Md Analyi f th Wilkinn Dividr Cnidr a matchd Wilkinn pwr dividr, with a urc at prt : Prt Prt Prt T implify thi chmatic, w rmv th grund plan, which
//9 Wilkinn Dividr Evn and Odd Md Analyi.dc / Evn/Odd Md Analyi f th Wilkinn Dividr Cnidr a matchd Wilkinn pwr dividr, with a urc at prt : Prt Prt Prt T implify thi chmatic, w rmv th grund plan, which
REFRACTIVE INDICES, ORDER PARAMETER AND DENSITY STUDY OF BKS/B07 NEMATIC LIQUID CRYSTAL
 Dpartmnt f Physical Chmistry 4-1 Rgina Elisabta Blvd, District, Bucharst phn: +40-1-14508; fax: +40-1-15949 pissn: 10-871X ISSN: 1844-0401 ARS DOCENDI PUBLISHING HOUSE Ss. Panduri 90, District 5 Bucharst
Dpartmnt f Physical Chmistry 4-1 Rgina Elisabta Blvd, District, Bucharst phn: +40-1-14508; fax: +40-1-15949 pissn: 10-871X ISSN: 1844-0401 ARS DOCENDI PUBLISHING HOUSE Ss. Panduri 90, District 5 Bucharst
2. Background Material
 S. Blair Sptmbr 3, 003 4. Background Matrial Th rst of this cours dals with th gnration, modulation, propagation, and ction of optical radiation. As such, bic background in lctromagntics and optics nds
S. Blair Sptmbr 3, 003 4. Background Matrial Th rst of this cours dals with th gnration, modulation, propagation, and ction of optical radiation. As such, bic background in lctromagntics and optics nds
SAFE HANDS & IIT-ian's PACE EDT-15 (JEE) SOLUTIONS
 It is not possibl to find flu through biggr loop dirctly So w will find cofficint of mutual inductanc btwn two loops and thn find th flu through biggr loop Also rmmbr M = M ( ) ( ) EDT- (JEE) SOLUTIONS
It is not possibl to find flu through biggr loop dirctly So w will find cofficint of mutual inductanc btwn two loops and thn find th flu through biggr loop Also rmmbr M = M ( ) ( ) EDT- (JEE) SOLUTIONS
Title: Vibrational structure of electronic transition
 Titl: Vibrational structur of lctronic transition Pag- Th band spctrum sn in th Ultra-Violt (UV) and visibl (VIS) rgions of th lctromagntic spctrum can not intrprtd as vibrational and rotational spctrum
Titl: Vibrational structur of lctronic transition Pag- Th band spctrum sn in th Ultra-Violt (UV) and visibl (VIS) rgions of th lctromagntic spctrum can not intrprtd as vibrational and rotational spctrum
ELECTROSTATIC FIELDS IN MATERIAL MEDIA
 MF LCTROSTATIC FILDS IN MATRIAL MDIA 3/4/07 LCTURS Materials media may be classified in terms f their cnductivity σ (S/m) as: Cnductrs The cnductivity usually depends n temperature and frequency A material
MF LCTROSTATIC FILDS IN MATRIAL MDIA 3/4/07 LCTURS Materials media may be classified in terms f their cnductivity σ (S/m) as: Cnductrs The cnductivity usually depends n temperature and frequency A material
:2;$-$(01*%<*=,-./-*=0;"%/;"-*
 !"#$%'()%"*#%*+,-./-*+01.2(.*3+456789*!"#$%"'()'*+,-."/0.%+1'23"45'46'7.89:89'/' ;8-,"$4351415,8:+#9' Dr. Ptr T. Gallaghr Astrphyscs Rsarch Grup Trnty Cllg Dubln :2;$-$(01*%
!"#$%'()%"*#%*+,-./-*+01.2(.*3+456789*!"#$%"'()'*+,-."/0.%+1'23"45'46'7.89:89'/' ;8-,"$4351415,8:+#9' Dr. Ptr T. Gallaghr Astrphyscs Rsarch Grup Trnty Cllg Dubln :2;$-$(01*%
Voltage, Current, Power, Series Resistance, Parallel Resistance, and Diodes
 Lctur 1. oltag, Currnt, Powr, Sris sistanc, Paralll sistanc, and Diods Whn you start to dal with lctronics thr ar thr main concpts to start with: Nam Symbol Unit oltag volt Currnt ampr Powr W watt oltag
Lctur 1. oltag, Currnt, Powr, Sris sistanc, Paralll sistanc, and Diods Whn you start to dal with lctronics thr ar thr main concpts to start with: Nam Symbol Unit oltag volt Currnt ampr Powr W watt oltag
OPTICAL OSCILLATOR STRENGTHS FOR THE ELECTRON QUANTUM TRANSITIONS IN ELLIPTIC NANOTUBES
 OPTICAL OSCILLATOR STRENGTHS FOR THE ELECTRON QUANTUM TRANSITIONS IN ELLIPTIC NANOTUBES V. A. HOLOVATSKY, O. M. VOITSEKHIVSKA, V. I. GUTSUL Chrnivtsi Natinal Univrsity, Chrnivtsi, 58012, Ukrain, thrphys@chnu.cv.ua
OPTICAL OSCILLATOR STRENGTHS FOR THE ELECTRON QUANTUM TRANSITIONS IN ELLIPTIC NANOTUBES V. A. HOLOVATSKY, O. M. VOITSEKHIVSKA, V. I. GUTSUL Chrnivtsi Natinal Univrsity, Chrnivtsi, 58012, Ukrain, thrphys@chnu.cv.ua
PHYS ,Fall 05, Term Exam #1, Oct., 12, 2005
 PHYS1444-,Fall 5, Trm Exam #1, Oct., 1, 5 Nam: Kys 1. circular ring of charg of raius an a total charg Q lis in th x-y plan with its cntr at th origin. small positiv tst charg q is plac at th origin. What
PHYS1444-,Fall 5, Trm Exam #1, Oct., 1, 5 Nam: Kys 1. circular ring of charg of raius an a total charg Q lis in th x-y plan with its cntr at th origin. small positiv tst charg q is plac at th origin. What
MCB137: Physical Biology of the Cell Spring 2017 Homework 6: Ligand binding and the MWC model of allostery (Due 3/23/17)
 MCB37: Physical Biology of th Cll Spring 207 Homwork 6: Ligand binding and th MWC modl of allostry (Du 3/23/7) Hrnan G. Garcia March 2, 207 Simpl rprssion In class, w drivd a mathmatical modl of how simpl
MCB37: Physical Biology of th Cll Spring 207 Homwork 6: Ligand binding and th MWC modl of allostry (Du 3/23/7) Hrnan G. Garcia March 2, 207 Simpl rprssion In class, w drivd a mathmatical modl of how simpl
A central nucleus. Protons have a positive charge Electrons have a negative charge
 Atomic Structur Lss than ninty yars ago scintists blivd that atoms wr tiny solid sphrs lik minut snookr balls. Sinc thn it has bn discovrd that atoms ar not compltly solid but hav innr and outr parts.
Atomic Structur Lss than ninty yars ago scintists blivd that atoms wr tiny solid sphrs lik minut snookr balls. Sinc thn it has bn discovrd that atoms ar not compltly solid but hav innr and outr parts.
2. Laser physics - basics
 . Lasr physics - basics Spontanous and stimulatd procsss Einstin A and B cofficints Rat quation analysis Gain saturation What is a lasr? LASER: Light Amplification by Stimulatd Emission of Radiation "light"
. Lasr physics - basics Spontanous and stimulatd procsss Einstin A and B cofficints Rat quation analysis Gain saturation What is a lasr? LASER: Light Amplification by Stimulatd Emission of Radiation "light"
120~~60 o D 12~0 1500~30O, 15~30 150~30. ..,u 270,,,, ~"~"-4-~qno 240 2~o 300 v 240 ~70O 300
 1 Find th plar crdinats that d nt dscrib th pint in th givn graph. (-2, 30 ) C (2,30 ) B (-2,210 ) D (-2,-150 ) Find th quatin rprsntd in th givn graph. F 0=3 H 0=2~ G r=3 J r=2 0 :.1 2 3 ~ 300 2"~ 2,
1 Find th plar crdinats that d nt dscrib th pint in th givn graph. (-2, 30 ) C (2,30 ) B (-2,210 ) D (-2,-150 ) Find th quatin rprsntd in th givn graph. F 0=3 H 0=2~ G r=3 J r=2 0 :.1 2 3 ~ 300 2"~ 2,
Einstein Equations for Tetrad Fields
 Apiron, Vol 13, No, Octobr 006 6 Einstin Equations for Ttrad Filds Ali Rıza ŞAHİN, R T L Istanbul (Turky) Evry mtric tnsor can b xprssd by th innr product of ttrad filds W prov that Einstin quations for
Apiron, Vol 13, No, Octobr 006 6 Einstin Equations for Ttrad Filds Ali Rıza ŞAHİN, R T L Istanbul (Turky) Evry mtric tnsor can b xprssd by th innr product of ttrad filds W prov that Einstin quations for
Effect of Warm Ionized Plasma Medium on Radiation Properties of Mismatched Microstrip Termination
 J. Elctrmagntic Analysis & Alicatins, 9, 3: 181-186 di:1.436/jmaa.9.137 Publishd Onlin Stmbr 9 (www.scip.rg/jurnal/jmaa) 181 Effct f Warm Inizd Plasma Mdium n adiatin Prrtis f Mismatchd Micrstri Trminatin
J. Elctrmagntic Analysis & Alicatins, 9, 3: 181-186 di:1.436/jmaa.9.137 Publishd Onlin Stmbr 9 (www.scip.rg/jurnal/jmaa) 181 Effct f Warm Inizd Plasma Mdium n adiatin Prrtis f Mismatchd Micrstri Trminatin
Ch. 24 Molecular Reaction Dynamics 1. Collision Theory
 Ch. 4 Molcular Raction Dynamics 1. Collision Thory Lctur 16. Diffusion-Controlld Raction 3. Th Matrial Balanc Equation 4. Transition Stat Thory: Th Eyring Equation 5. Transition Stat Thory: Thrmodynamic
Ch. 4 Molcular Raction Dynamics 1. Collision Thory Lctur 16. Diffusion-Controlld Raction 3. Th Matrial Balanc Equation 4. Transition Stat Thory: Th Eyring Equation 5. Transition Stat Thory: Thrmodynamic
Electrochemical Energy Systems Spring 2014 MIT, M. Z. Bazant. Midterm Exam
 10.66 Elctrochmical Enrgy Systms Spring 014 MIT, M. Z. Bazant Midtrm Exam Instructions. This is a tak-hom, opn-book xam du in Lctur. Lat xams will not b accptd. You may consult any books, handouts, or
10.66 Elctrochmical Enrgy Systms Spring 014 MIT, M. Z. Bazant Midtrm Exam Instructions. This is a tak-hom, opn-book xam du in Lctur. Lat xams will not b accptd. You may consult any books, handouts, or
7.4 Potential Difference and Electric Potential
 7.4 Potntial Diffrnc and Elctric Potntial In th prvious sction, you larnd how two paralll chargd surfacs produc a uniform lctric fild. From th dfinition of an lctric fild as a forc acting on a charg, it
7.4 Potntial Diffrnc and Elctric Potntial In th prvious sction, you larnd how two paralll chargd surfacs produc a uniform lctric fild. From th dfinition of an lctric fild as a forc acting on a charg, it
Sundials and Linear Algebra
 Sundials and Linar Algbra M. Scot Swan July 2, 25 Most txts on crating sundials ar dirctd towards thos who ar solly intrstd in making and using sundials and usually assums minimal mathmatical background.
Sundials and Linar Algbra M. Scot Swan July 2, 25 Most txts on crating sundials ar dirctd towards thos who ar solly intrstd in making and using sundials and usually assums minimal mathmatical background.
ph People Grade Level: basic Duration: minutes Setting: classroom or field site
 ph Popl Adaptd from: Whr Ar th Frogs? in Projct WET: Curriculum & Activity Guid. Bozman: Th Watrcours and th Council for Environmntal Education, 1995. ph Grad Lvl: basic Duration: 10 15 minuts Stting:
ph Popl Adaptd from: Whr Ar th Frogs? in Projct WET: Curriculum & Activity Guid. Bozman: Th Watrcours and th Council for Environmntal Education, 1995. ph Grad Lvl: basic Duration: 10 15 minuts Stting:
MAGENTIC PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
 MAGENTIC PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS Dia, Para and Frro magntism, Qualitativ planation basd on lctron structur, Curi and Curi-Wiss law (qualitativ). all Effct, prssion for carrir concntration. Basd on th bhavior
MAGENTIC PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS Dia, Para and Frro magntism, Qualitativ planation basd on lctron structur, Curi and Curi-Wiss law (qualitativ). all Effct, prssion for carrir concntration. Basd on th bhavior
90 Th He γ
 Nam Hnrs Chmistry / / Nuclar Chmistry Th prprtis f th nuclus ar nt f primary imprtanc t chmists. Fr th mst part, th nuclus can b rgardd as a cllctin f nuclns (nutrns and prtns). Th numbr f prtns in a particular
Nam Hnrs Chmistry / / Nuclar Chmistry Th prprtis f th nuclus ar nt f primary imprtanc t chmists. Fr th mst part, th nuclus can b rgardd as a cllctin f nuclns (nutrns and prtns). Th numbr f prtns in a particular
Preliminary Fundamentals
 1.0 Introduction Prliminary Fundamntals In all of our prvious work, w assumd a vry simpl modl of th lctromagntic torqu T (or powr) that is rquird in th swing quation to obtain th acclrating torqu. This
1.0 Introduction Prliminary Fundamntals In all of our prvious work, w assumd a vry simpl modl of th lctromagntic torqu T (or powr) that is rquird in th swing quation to obtain th acclrating torqu. This
Direct Approach for Discrete Systems One-Dimensional Elements
 CONTINUUM & FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Dirct Approach or Discrt Systms On-Dimnsional Elmnts Pro. Song Jin Par Mchanical Enginring, POSTECH Dirct Approach or Discrt Systms Dirct approach has th ollowing aturs:
CONTINUUM & FINITE ELEMENT METHOD Dirct Approach or Discrt Systms On-Dimnsional Elmnts Pro. Song Jin Par Mchanical Enginring, POSTECH Dirct Approach or Discrt Systms Dirct approach has th ollowing aturs:
PHYS-333: Problem set #2 Solutions
 PHYS-333: Problm st #2 Solutions Vrsion of March 5, 2016. 1. Visual binary 15 points): Ovr a priod of 10 yars, two stars sparatd by an angl of 1 arcsc ar obsrvd to mov through a full circl about a point
PHYS-333: Problm st #2 Solutions Vrsion of March 5, 2016. 1. Visual binary 15 points): Ovr a priod of 10 yars, two stars sparatd by an angl of 1 arcsc ar obsrvd to mov through a full circl about a point
UIUC Physics 436 EM Fields & Sources II Fall Semester, 2015 Lect. Notes 8.5 Prof. Steven Errede LECTURE NOTES 8.5
 UIUC Physics 436 EM Filds & Surcs II Fall Smstr, 05 Lct. Nts 8.5 Prf. Stvn Errd LECTURE NOTES 8.5 Rflctin and Rfractin f EM Wavs at th Bundary f a Disprsiv/Absrbing/Cnducting Mdium Cnsidr a situatin whr
UIUC Physics 436 EM Filds & Surcs II Fall Smstr, 05 Lct. Nts 8.5 Prf. Stvn Errd LECTURE NOTES 8.5 Rflctin and Rfractin f EM Wavs at th Bundary f a Disprsiv/Absrbing/Cnducting Mdium Cnsidr a situatin whr
Superheterodyne Amplification for Increase the Working Frequency
 Jurnal f Elctrmagntic Analysis and Applicatins, 7, 9, 43-5 http://www.scirp.rg/jurnal/jmaa ISSN Onlin: 94-749 ISSN Print: 94-73 Suprhtrdyn Amplificatin fr Incras th Wrking Frquncy Svtlana Kshvaya, Vladimir
Jurnal f Elctrmagntic Analysis and Applicatins, 7, 9, 43-5 http://www.scirp.rg/jurnal/jmaa ISSN Onlin: 94-749 ISSN Print: 94-73 Suprhtrdyn Amplificatin fr Incras th Wrking Frquncy Svtlana Kshvaya, Vladimir
SCALING OF SYNCHROTRON RADIATION WITH MULTIPOLE ORDER. J. C. Sprott
 SCALING OF SYNCHROTRON RADIATION WITH MULTIPOLE ORDER J. C. Sprott PLP 821 Novmbr 1979 Plasma Studis Univrsity of Wisconsin Ths PLP Rports ar informal and prliminary and as such may contain rrors not yt
SCALING OF SYNCHROTRON RADIATION WITH MULTIPOLE ORDER J. C. Sprott PLP 821 Novmbr 1979 Plasma Studis Univrsity of Wisconsin Ths PLP Rports ar informal and prliminary and as such may contain rrors not yt
The failure of the classical mechanics
 h failur of th classical mchanics W rviw som xprimntal vidncs showing that svral concpts of classical mchanics cannot b applid. - h blac-body radiation. - Atomic and molcular spctra. - h particl-li charactr
h failur of th classical mchanics W rviw som xprimntal vidncs showing that svral concpts of classical mchanics cannot b applid. - h blac-body radiation. - Atomic and molcular spctra. - h particl-li charactr
de/dx Effectively all charged particles except electrons
 de/dx Lt s nxt turn our attntion to how chargd particls los nrgy in mattr To start with w ll considr only havy chargd particls lik muons, pions, protons, alphas, havy ions, Effctivly all chargd particls
de/dx Lt s nxt turn our attntion to how chargd particls los nrgy in mattr To start with w ll considr only havy chargd particls lik muons, pions, protons, alphas, havy ions, Effctivly all chargd particls
The Electromagnetic Mass of a Charged Particle
 In mmry f M.I. Kuligina (1914 1994) Th Elctrmagntic Mass f a Chargd Particl V.A. Kuligin, G.A. Kuligina, M.V. Krnva Dpartmnt f Physics, Stat Univrsity Univrsittskaya Sq. 1, Vrnh 394693, Russia A slutin
In mmry f M.I. Kuligina (1914 1994) Th Elctrmagntic Mass f a Chargd Particl V.A. Kuligin, G.A. Kuligina, M.V. Krnva Dpartmnt f Physics, Stat Univrsity Univrsittskaya Sq. 1, Vrnh 394693, Russia A slutin
The van der Waals interaction 1 D. E. Soper 2 University of Oregon 20 April 2012
 Th van dr Waals intraction D. E. Sopr 2 Univrsity of Orgon 20 pril 202 Th van dr Waals intraction is discussd in Chaptr 5 of J. J. Sakurai, Modrn Quantum Mchanics. Hr I tak a look at it in a littl mor
Th van dr Waals intraction D. E. Sopr 2 Univrsity of Orgon 20 pril 202 Th van dr Waals intraction is discussd in Chaptr 5 of J. J. Sakurai, Modrn Quantum Mchanics. Hr I tak a look at it in a littl mor
