Long-Term Climate Projections : Perspectives on a Scientific Assessment
|
|
|
- Clinton Walton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Long-Term Climate Projections : Perspectives on a Scientific Assessment Sandrine Bony LMD/IPSL, CNRS, Paris (France) Co-Chair of the WCRP Working Group on Coupled Models (WGCM) With the Writing Team of our Position Paper : (available on the WCRP Open Science Conference website) Jean-Louis Dufresne, Kerry Emanuel, Pierre Friedlingstein, Stephen Griffies, Isaac Held, John Mitchell, Cath Senior and Bjorn Stevens WCRP Open Science Conference, Denver, Oct
2 Climate Modelling Challenge Climate change projections are increasingly used to support climate-related decision making and planning. The need to provide reliable assessments of future climate changes has never been so high : How to improve scientific assessments? By developing more realistic models but this is not sufficient...
3 Modelling Long-Term Climate Change The WCRP Working Group on Coupled Models (WGCM) promotes and coordinates global climate simulations to : evaluate climate models on recent and longer past (incl. paleo) provide projections of future climate change assess and understand uncertainties associated with projections Currently, these efforts are deployed within the so-called CMIP5 project, - designed in collaboration with many scientific commnunities - within WCRP and beyond (e.g. IGBP). CMIP5 simulations will be assessed by the 5th Assessment Report of the IPCC. CLIVAR Exchanges CMIP5 Special Issue May 2011
4 CMIP5 results becoming available on the Earth System Grid Multi-model analyses starting... CMIP5 participating modelling groups 50+ models from 23 groups (15 countries) As of 17 Oct 2011: about half is already available Early results presented in Parallel and Poster sessions of the OSC Courtesy Karl Taylor (PCMDI)
5 CMIP5 results becoming available on the Earth System Grid Multi-model analyses starting... Workshop Announcements : PMIP Using paleo-climate model-data comparisons to constrain future CMIP5 Model Analysis Workshop March 5-9, 2012 IPRC, University of Hawaii, Honolulu climate projections March 1-3, 2012 Bishop Museum, Honolulu Contact: G. Schmidt & V Masson-Delmotte Check WGCM website for upcoming announcement: CFMIP Assessing Cloud-Climate Feedbacks in CMIP5 models May 28 June 1, 2012 Paris, France Check CFMIP website for upcoming annoucement
6 How to Assess our Confidence in Model Projections? Long-standing characteristics of long-term projections from climate models : - Some aspects robust amongst models - Others associated with large inter-model differences CMIP3 Global warming projections CMIP3 Precipitation projections DJF Hawkins and Sutton (2009) IPCC AR4 (2007) How to assess our confidence in climate projections? - Are consensual results reliable? - Reasons for inter-model differences? Are some results more credible than others? Key questions for long-term climate change assessments
7 An Early Assessment of Long-Term Climate Change : The Charney Report (1979) Jule Charney ( )
8 An Early Assessment of Long-Term Climate Change : The Charney Report (1979) Available material : - simple climate models (EBM, 1D..) - a few early general circulation models - very few global observations Amazingly prescient in its assessment :... of the effects of increased CO2 on climate : - timing of doubling of CO2 concentration - 2 x CO2 radiative forcing : ~ 4 W/m 2 - pattern of surface warming (land/ocean, polar) - water vapor and sea-ice feedback estimates - climate sensitivity estimates : range : K ; likely value : 3 K - etc... of key uncertainties : - cloud feedbacks - role of the ocean in carbon and heat uptake - regional precipitation changes - etc
9 An Early Assessment of Long-Term Climate Change : The Charney Report (1979) - What explains the prescience of the Charney report (1979)? - What progress have we made in assessing the effects of increased CO2 on climate? - What lessons do we draw from 30 years of climate modelling and climate change research? - Recommendations for future progress
10 The insights of the Charney Report were not an accident They reflect the power of the scientific approach underlying the assessment : In order to assess the climatic effects of increased CO2, we consider first the primary physical processes that influence the climate system as a whole. These processes are best studied in simple models whose physical characteristics may readily be comprehended. The understanding derived from these studies enables one better to assess the performance of the 3D circulation models. Our confidence in our conclusion that a doubling of CO2 will eventually result in significant temperature increases and other climate changes is based on the fact that the results of the radiative-convective and heat-balance model studies can be understood in purely physical terms and are verified by the more complex GCMs. Likely to remain a productive approach in the future
11 Model predictive capabilities for long-term climate change Unlike in weather prediction, the reliability of model predictive capabilities for long-term climate change can not be established in a straightforward way... but only through indirect routes. Few observational tests are fully discriminating of long-term projections. Strength of the observational constraint [availability and / or quality of observations] Do we apply relevant observational tests? Confidence in climate projections thus remains disproportionately dependent on the development of understanding Relevance for constraining long-term climate projections
12 Our physical understanding of the climate system relies on a spectrum of models and theories Model simplicity (relative to system) System complexity Our confidence in modelling results depends on our ability : to connect robust behavior across a spectrum of relevant models to connect this behavior both to basic physical principles and to observations
13 CMIP5 is part of our current descriptive horizon Long-Term Set of Climate Experiments : CMIP5 compared to previous CMIPs : Wider spectrum of models, configurations and experiments (e.g. ESM, AOGCM, AGCM Aqua-planet AGCM..) More (idealized) experiments aiming at better understanding the model results More comprehensive set of model output Originally independent MIPs into a single MIP Synergistic opportunities for greater scientific understanding
14 Climate Sensitivity Subset of CMIP5 models : Courtesy Tim Andrews, Karl Taylor et al. (cf Session B12) Preliminary analyses suggest that inter-model differences in cloud feedback, once again, remain a primary contributor to this uncertainty
15 What Progress in our Understanding of Climate Change Cloud Feebdacks? Charney Report (1979) : Clouds response recognized as a key source of uncertainty But only a vague idea as to why clouds should change... + no evaluation of model clouds
16 What Progress in our Understanding of Climate Change Cloud Feebdacks? Charney Report (1979) : Clouds response recognized as a key source of uncertainty But only a vague idea as to why clouds should change... + no evaluation of model clouds Since then : GCM analysis through a spectrum of models Process studies (in-situ obs, LES/CRMs) Understanding Satellite observations & simulators (COSP) Evaluation Assessment of cloud-climate feedbacks CFMIP (Cloud Feedback Model Intercomparison Project)
17 What Progress in our Understanding of Climate Change Cloud Feebdacks? Charney Report (1979) : Clouds response recognized as a key source of uncertainty But only a vague idea as to why clouds should change... + no evaluation of model clouds Since then : CMIP5 A variety of physical mechanisms have been proposed, such as : - upward shift of cloud layers - poleward migration of extratropical storm tracks satellite simulator + process diagnostics - thermodynamical controls on CWP - fast response to CO2 radiative forcing idealized experiments - changing PBL stability, depth and structure - changing profiles of moist static energy Opportunities to better assess cloud feedbacks in CMIP5 models
18 First evaluations of the 3D distribution of clouds simulated by climate models CALIPSO lidar Other satellite observations considered : ISCCP, CloudSat, Parasol, MODIS, MISR..
19 Understanding the response of low-level clouds through a spectrum of models In a CMIP5 General Circulation Model (IPSL-CM5A) Positive low-cloud feedback analyzed through a range of CMIP5 experiments and configurations (OAGCM, AGCM, aqua-planet, 1D) MSE deficit Primary physical mechanisms controlling the feedback identified (e.g. vertical gradient of MSE at the top of the PBL) (Talk by Florent Brient in B12 session) MSE deficit (Brient & Bony, Clim. Dyn, submitted)
20 Understanding the response of low-level clouds through a spectrum of models In multiple Large-Eddy Simulation (5 LES) models and Single-Column Model versions of CMIP5 GCMs (16 SCM) [ CFMIP-GCSS CGILS project ] What are the primary physical processes controling the formation and response of low-level clouds to (idealized) climate change? Talk in B6 session by Chris Bretherton, Peter Blossey, Minghua Zhang et al.
21 Observational opportunities to test processes critical for CMIP5 model cloud feebdacks High-frequency (half-hourly) detailed model outputs from CMIP5 models over 120 sites where cloud feedbacks are particularly uncertain, or for which observations facilities (ARM, CloudNet..), field experiments and/or satellite observations are available CFMIP sites with detailed CMIP5 outputs
22 What Progress in our Understanding of Climate Change Cloud Feebdacks? Charney Report (1979) : Clouds response recognized as a key source of uncertainty But only a vague idea as to why clouds should change... + no evaluation of model clouds Since then : CMIP5 A wide variety of physical mechanisms have been proposed, such as : - upward shift of cloud layers - poleward migration of extratropical storm tracks satellite simulator + process diagnostics - thermodynamical controls on CWP - fast response to CO2 radiative forcing idealized experiments - changing PBL stability, depth and structure - changing profiles of moist static energy Opportunities to better assess cloud feedbacks in CMIP5 models
23 Conclusions Our ability to anticipate long-term climate changes primarily relies on our physical understanding of how the climate system works Therefore, to better assess predictive capabilities of models and improve our assessment of future climate changes : - Developing more realistic climate models (more comprehensive, complex, higher-resolution) and better quantifying uncertainty in projections : NECESSARY...BUT NOT SUFFICIENT - Of equal importance : Need to physically interpret model results in terms of processes or basic principles, and to connect them to simpler models, concepts, theories and observations. We should strive do as well as the Charney Report did for global to zonal scales, but for global to regional scales A key for : Assessing our relative confidence in different aspects of the projections Determining how available observations might help to assess projections Communicating with the public and society Actionable Science is needed, i. e. sufficiently predictive, accepted and understandable to support decision-making (David Behar)
24 Recommendations to WCRP Recognize that progress in climate change assessments does not only rely on the growth in complexity of the models upon which they are based, but primarily relies on our ability to better understand how the climate system works. The science of climate and climate change is not done! Be pro-active in encouraging the community to tackle long-standing, difficult problems in addition to new uncharted problems (e.g. model errors, influence of cloud and moist processes on large-scale circulation, ocean mixing, land hydrology) Promote the physical understanding of CMIP5 results and projections by facilitating connections between communities dealing with theory, simple/complex modelling, processes & observations. A strategy may include Climate Process Teams (or Climate Projection Understanding Teams) and organizing Workshops on Understanding climate change through a hierarchy of models. Consider organizing a series of bottom-up community assessments about specific aspects of climate projections (cf SPARC) to complement and facilitate IPCC assessments.
25 Thank You Your feedback on our position paper will be welcome : Carbon Dioxide and Climate : Perspectives on a Scientific Assessment
26 Evolution of Atmospheric CO2 Predicted for Different Emission Scenarios RCP 8.5 Emissions : + 2%/year : Charney report (1979) vs Coupled carbon-climate model RCP 6 RCP 4.5 RCP 2.6 Emissions : constant Charney report (1979) vs Coupled carbon-climate model
27 Understanding the response of shallow cumulus clouds through a spectrum of models In a Large-Eddy Simulation (LES) model Idealized experiment assuming a nearly unchanged relative humidity atmosphere (Rieck, Nuijens and Stevens, submitted)
How to tackle long-standing uncertainties?
 How to tackle long-standing uncertainties? Sandrine Bony LMD/IPSL, CNRS, Paris Thanks to all members of the ClimaConf project Bjorn Stevens (MPI) & the WCRP Grand Challenge team Colloque ClimaConf; 20-21
How to tackle long-standing uncertainties? Sandrine Bony LMD/IPSL, CNRS, Paris Thanks to all members of the ClimaConf project Bjorn Stevens (MPI) & the WCRP Grand Challenge team Colloque ClimaConf; 20-21
Clouds, Circulation and Climate Sensitivity
 Clouds, Circulation and Climate Sensitivity A WCRP Grand Challenge coordinated by WGCM in close collaboration with GEWEX, SPARC and WGNE Lead coordinators : Sandrine Bony (LMD/IPSL) & Bjorn Stevens (MPI)
Clouds, Circulation and Climate Sensitivity A WCRP Grand Challenge coordinated by WGCM in close collaboration with GEWEX, SPARC and WGNE Lead coordinators : Sandrine Bony (LMD/IPSL) & Bjorn Stevens (MPI)
The JSC/CLIVAR Working Group on Coupled Models (WGCM) Report to CLIVAR SSG-18
 The JSC/CLIVAR Working Group on Coupled Models (WGCM) Report to CLIVAR SSG-18 Sandrine Bony & Jerry Meehl WGCM co-chairs Paris, May 2011 Contribution of WGCM to CLIVAR Imperatives : CLIVAR Imperatives
The JSC/CLIVAR Working Group on Coupled Models (WGCM) Report to CLIVAR SSG-18 Sandrine Bony & Jerry Meehl WGCM co-chairs Paris, May 2011 Contribution of WGCM to CLIVAR Imperatives : CLIVAR Imperatives
Cloud Feedbacks: their Role in Climate Sensitivity and How to Assess them
 Cloud Feedbacks: their Role in Climate Sensitivity and How to Assess them Sandrine Bony, Jean Louis Dufresne Hélène Chepfer, Marjolaine Chiriaco, Ionela Musat, Geneviève Sèze LMD/IPSL et SA/IPSL, Paris,
Cloud Feedbacks: their Role in Climate Sensitivity and How to Assess them Sandrine Bony, Jean Louis Dufresne Hélène Chepfer, Marjolaine Chiriaco, Ionela Musat, Geneviève Sèze LMD/IPSL et SA/IPSL, Paris,
Using Satellite Simulators to Diagnose Cloud-Processes in CMIP5 Models
 Using Satellite Simulators to Diagnose Cloud-Processes in CMIP5 Models Stephen A. Klein Program for Climate Model Diagnosis and Intercomparison / LLNL Alejandro Bodas-Salcedo & Mark Webb United Kingdom
Using Satellite Simulators to Diagnose Cloud-Processes in CMIP5 Models Stephen A. Klein Program for Climate Model Diagnosis and Intercomparison / LLNL Alejandro Bodas-Salcedo & Mark Webb United Kingdom
Transpose-AMIP. Steering committee: Keith Williams (chair), David Williamson, Steve Klein, Christian Jakob, Catherine Senior
 Transpose-AMIP Steering committee: Keith Williams (chair), David Williamson, Steve Klein, Christian Jakob, Catherine Senior WGNE - THORPEX-PDP workshop, Zurich, 08/07/10 What is Transpose-AMIP? Basically,
Transpose-AMIP Steering committee: Keith Williams (chair), David Williamson, Steve Klein, Christian Jakob, Catherine Senior WGNE - THORPEX-PDP workshop, Zurich, 08/07/10 What is Transpose-AMIP? Basically,
CFMIP-CMIP6 Experiments
 CFMIP-CMIP6 Experiments Mark Webb, Timothy Andrews, Alejandro Bodas-Salcedo, Sandrine Bony, Chris Bretherton, Robin Chadwick, Hélène Chepfer, Hervé Douville, Peter Good, Jennifer Kay, Stephen Klein, Roger
CFMIP-CMIP6 Experiments Mark Webb, Timothy Andrews, Alejandro Bodas-Salcedo, Sandrine Bony, Chris Bretherton, Robin Chadwick, Hélène Chepfer, Hervé Douville, Peter Good, Jennifer Kay, Stephen Klein, Roger
Do climate models over-estimate cloud feedbacks?
 Do climate models over-estimate cloud feedbacks? Sandrine Bony CNRS, LMD/IPSL, Paris with contributions from Jessica Vial (LMD), David Coppin (LMD) Florent Brient (ETH), Tobias Becker (MPI), Kevin Reed
Do climate models over-estimate cloud feedbacks? Sandrine Bony CNRS, LMD/IPSL, Paris with contributions from Jessica Vial (LMD), David Coppin (LMD) Florent Brient (ETH), Tobias Becker (MPI), Kevin Reed
How may low-cloud radiative properties simulated in the current climate influence low-cloud feedbacks under global warming?
 How may low-cloud radiative properties simulated in the current climate influence low-cloud feedbacks under global warming? F. Brient, S. Bony To cite this version: F. Brient, S. Bony. How may low-cloud
How may low-cloud radiative properties simulated in the current climate influence low-cloud feedbacks under global warming? F. Brient, S. Bony To cite this version: F. Brient, S. Bony. How may low-cloud
A hierarchical approach to climate sensitivity Bjorn Stevens
 A hierarchical approach to climate sensitivity Bjorn Stevens Based on joint work with: T. Becker, S. Bony, D. Coppin, C Hohenegger, B. Medeiros, D. Fläschner, K. Reed as part of the WCRP Grand Science
A hierarchical approach to climate sensitivity Bjorn Stevens Based on joint work with: T. Becker, S. Bony, D. Coppin, C Hohenegger, B. Medeiros, D. Fläschner, K. Reed as part of the WCRP Grand Science
Cloud - Radiation Interactions
 Cloud - Radiation Interactions Sandrine Bony LMD/IPSL, CNRS, Paris Outline : Why are these interactions so critical for climate modelling? Impact on the global energy balance Interactions with atmospheric
Cloud - Radiation Interactions Sandrine Bony LMD/IPSL, CNRS, Paris Outline : Why are these interactions so critical for climate modelling? Impact on the global energy balance Interactions with atmospheric
Obs4MIPs(and(the(WGNE/WGCM(Metrics(&(Diagnos<cs(Panel(
 Obs4MIPsandtheWGNE/WGCMMetrics&Diagnos
Obs4MIPsandtheWGNE/WGCMMetrics&Diagnos
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NGEO1799 Robust direct effect of carbon dioxide on tropical circulation and regional precipitation Sandrine Bony 1,, Gilles Bellon 2, Daniel Klocke 3, Steven Sherwood
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.138/NGEO1799 Robust direct effect of carbon dioxide on tropical circulation and regional precipitation Sandrine Bony 1,, Gilles Bellon 2, Daniel Klocke 3, Steven Sherwood
The linear additivity of the forcings' responses in the energy and water cycles. Nathalie Schaller, Jan Cermak, Reto Knutti and Martin Wild
 The linear additivity of the forcings' responses in the energy and water cycles Nathalie Schaller, Jan Cermak, Reto Knutti and Martin Wild WCRP OSP, Denver, 27th October 2011 1 Motivation How will precipitation
The linear additivity of the forcings' responses in the energy and water cycles Nathalie Schaller, Jan Cermak, Reto Knutti and Martin Wild WCRP OSP, Denver, 27th October 2011 1 Motivation How will precipitation
Modeling multiscale interactions in the climate system
 Modeling multiscale interactions in the climate system Christopher S. Bretherton Atmospheric Sciences and Applied Mathematics University of Washington 08.09.2017 Aqua Worldview Motivation Weather and climate
Modeling multiscale interactions in the climate system Christopher S. Bretherton Atmospheric Sciences and Applied Mathematics University of Washington 08.09.2017 Aqua Worldview Motivation Weather and climate
Hurricanes: Their physics and relationship to climate. Kerry Emanuel Massachusetts Institute of Technology
 Hurricanes: Their physics and relationship to climate Kerry Emanuel Massachusetts Institute of Technology Topics Overview of Tropical Cyclones Tropical Cyclone Physics What have TCs been like in the past,
Hurricanes: Their physics and relationship to climate Kerry Emanuel Massachusetts Institute of Technology Topics Overview of Tropical Cyclones Tropical Cyclone Physics What have TCs been like in the past,
Overview of proposed CFMIP3/CMIP6 GCM Experiments
 Overview of proposed CFMIP3/CMIP6 GCM Experiments CFMIP Committee: Mark Webb, Chris Bretherton, Sandrine Bony, Hervé Douville, Jen Kay, Steve Klein, Pier Siebesma, Bjorn Stevens, George Tselioudis, Masahiro
Overview of proposed CFMIP3/CMIP6 GCM Experiments CFMIP Committee: Mark Webb, Chris Bretherton, Sandrine Bony, Hervé Douville, Jen Kay, Steve Klein, Pier Siebesma, Bjorn Stevens, George Tselioudis, Masahiro
What you need to know in Ch. 12. Lecture Ch. 12. Atmospheric Heat Engine
 Lecture Ch. 12 Review of simplified climate model Revisiting: Kiehl and Trenberth Overview of atmospheric heat engine Current research on clouds-climate Curry and Webster, Ch. 12 For Wednesday: Read Ch.
Lecture Ch. 12 Review of simplified climate model Revisiting: Kiehl and Trenberth Overview of atmospheric heat engine Current research on clouds-climate Curry and Webster, Ch. 12 For Wednesday: Read Ch.
Report to WGNE: Selected GFDL Research Activities
 Report to WGNE: Selected GFDL Research Activities GFDL s Atmospheric Model-4 (AM4) Excerpted from a presentation by Chris Golaz at the 2014 American Meteorological Society Annual Meeting, Climate Processes
Report to WGNE: Selected GFDL Research Activities GFDL s Atmospheric Model-4 (AM4) Excerpted from a presentation by Chris Golaz at the 2014 American Meteorological Society Annual Meeting, Climate Processes
Which Climate Model is Best?
 Which Climate Model is Best? Ben Santer Program for Climate Model Diagnosis and Intercomparison Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA 94550 Adapting for an Uncertain Climate: Preparing
Which Climate Model is Best? Ben Santer Program for Climate Model Diagnosis and Intercomparison Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, Livermore, CA 94550 Adapting for an Uncertain Climate: Preparing
Global Observations for Climate Model Evaluation
 Global Observations for Climate Evaluation João Teixeira with R. Ferraro, J. Jiang, F. Li, H. Su, D. Waliser, USA Outline: Observations for CMIP Satellite Simulators Conditional sampling methods Copyright
Global Observations for Climate Evaluation João Teixeira with R. Ferraro, J. Jiang, F. Li, H. Su, D. Waliser, USA Outline: Observations for CMIP Satellite Simulators Conditional sampling methods Copyright
WCRP Grand Challenge Workshop: Clouds, Circulation and Climate Sensitivity
 WCRP Grand Challenge Workshop: Clouds, Circulation and Climate Sensitivity Schloss Ringberg, 3700 Rottach-Egern, Germany March 24-28, 2014 This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department
WCRP Grand Challenge Workshop: Clouds, Circulation and Climate Sensitivity Schloss Ringberg, 3700 Rottach-Egern, Germany March 24-28, 2014 This work was performed under the auspices of the U.S. Department
An update on CMIP(6), obs4mips and the WGCM/WGNE Diagnostics and Metrics Panel
 An update on CMIP(6), obs4mips and the WGCM/WGNE Diagnostics and Metrics Panel Peter J. Gleckler WGNE 31, Pretoria, South Africa, April 27, 2016 REMOTE PRESENTATION Talk outline 2 CMIP6 status obs4mips
An update on CMIP(6), obs4mips and the WGCM/WGNE Diagnostics and Metrics Panel Peter J. Gleckler WGNE 31, Pretoria, South Africa, April 27, 2016 REMOTE PRESENTATION Talk outline 2 CMIP6 status obs4mips
BJORN STEVENS, SANDRINE BONY, MARK WEBB
 CLOUDS ON-OFF KLIMATE INTERCOMPARISON EXPERIMENT (COOKIE) BJORN STEVENS, SANDRINE BONY, MARK WEBB 1. Synopsis Cloud-radiative effects are expected to control many aspects of the current and future climates,
CLOUDS ON-OFF KLIMATE INTERCOMPARISON EXPERIMENT (COOKIE) BJORN STEVENS, SANDRINE BONY, MARK WEBB 1. Synopsis Cloud-radiative effects are expected to control many aspects of the current and future climates,
Photo courtesy National Geographic
 Welcome to the Polar Climate WG! Quick update: 1. CSL proposal (~85% allocation awarded, 16 month POP starts October 1) 2. All NCAR CMIP5 data on ESG within next month 3. Observational needs/uses living
Welcome to the Polar Climate WG! Quick update: 1. CSL proposal (~85% allocation awarded, 16 month POP starts October 1) 2. All NCAR CMIP5 data on ESG within next month 3. Observational needs/uses living
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System
 An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
What you need to know in Ch. 12. Lecture Ch. 12. Atmospheric Heat Engine. The Atmospheric Heat Engine. Atmospheric Heat Engine
 Lecture Ch. 1 Review of simplified climate model Revisiting: Kiehl and Trenberth Overview of atmospheric heat engine Current research on clouds-climate Curry and Webster, Ch. 1 For Wednesday: Read Ch.
Lecture Ch. 1 Review of simplified climate model Revisiting: Kiehl and Trenberth Overview of atmospheric heat engine Current research on clouds-climate Curry and Webster, Ch. 1 For Wednesday: Read Ch.
Physical systematic biases
 Physical systematic biases Aspen Model Evaluation Workshop Greg Flato Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis August, 2017 Issues Many large-scale errors/biases persist from one generation of
Physical systematic biases Aspen Model Evaluation Workshop Greg Flato Canadian Centre for Climate Modelling and Analysis August, 2017 Issues Many large-scale errors/biases persist from one generation of
Transformational Climate Science. The future of climate change research following the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report
 Transformational Climate Science The future of climate change research following the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report www.exeter.ac.uk/climate2014 Working Group I The challenge of climate change #climate2014
Transformational Climate Science The future of climate change research following the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report www.exeter.ac.uk/climate2014 Working Group I The challenge of climate change #climate2014
Obs4MIPs - Satellite Observations Rehosted for GCM Model Evaluation
 Obs4MIPs - Satellite Observations Rehosted for GCM Model Evaluation Obs4MIPs Robert Ferraro Jet Propulsion Laboratory This project is collaboration between NASA and DOE, and is overseen by an International
Obs4MIPs - Satellite Observations Rehosted for GCM Model Evaluation Obs4MIPs Robert Ferraro Jet Propulsion Laboratory This project is collaboration between NASA and DOE, and is overseen by an International
Evaluation of CMIP5 Simulated Clouds and TOA Radiation Budgets in the SMLs Using NASA Satellite Observations
 Evaluation of CMIP5 Simulated Clouds and TOA Radiation Budgets in the SMLs Using NASA Satellite Observations Erica K. Dolinar Xiquan Dong and Baike Xi University of North Dakota This talk is based on Dolinar
Evaluation of CMIP5 Simulated Clouds and TOA Radiation Budgets in the SMLs Using NASA Satellite Observations Erica K. Dolinar Xiquan Dong and Baike Xi University of North Dakota This talk is based on Dolinar
SPARC Dynamics and Variability Project and its Connection to C20C. Paul J. Kushner (Project Coordinator) University of Toronto
 SPARC Dynamics and Variability Project and its Connection to C20C Paul J. Kushner (Project Coordinator) University of Toronto Mark Baldwin, Neil Butchart, Norm McFarlane, Alan O Neill, Judith Perlwitz,
SPARC Dynamics and Variability Project and its Connection to C20C Paul J. Kushner (Project Coordinator) University of Toronto Mark Baldwin, Neil Butchart, Norm McFarlane, Alan O Neill, Judith Perlwitz,
CMIP3/CMIP5 differences: Scenario (SRESA1B vs RCP4.5) Ensemble mean Tas responses: CMIP3 = 2.8 K CMIP5 = 1.9 K CMIP5 higher average resolution
 CMIP3/CMIP5 differences: Scenario (SRESA1B vs RCP4.5) Ensemble mean Tas responses: CMIP3 = 2.8 K CMIP5 = 1.9 K CMIP5 higher average resolution Several `high-top models in CMIP5 Key question What are
CMIP3/CMIP5 differences: Scenario (SRESA1B vs RCP4.5) Ensemble mean Tas responses: CMIP3 = 2.8 K CMIP5 = 1.9 K CMIP5 higher average resolution Several `high-top models in CMIP5 Key question What are
Moving from Global to Regional Projections of Climate Change
 Moving from Global to Regional Projections of Climate Change Mat Collins College of Engineering, Mathematics and Physical Sciences, University of Exeter, UK Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Joint Met Office
Moving from Global to Regional Projections of Climate Change Mat Collins College of Engineering, Mathematics and Physical Sciences, University of Exeter, UK Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Joint Met Office
Link between land-ocean warming contrast and surface relative humidities in simulations with coupled climate models
 Link between land-ocean warming contrast and surface relative humidities in simulations with coupled climate models The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access
Link between land-ocean warming contrast and surface relative humidities in simulations with coupled climate models The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access
FIRST DRAFT. Science underpinning the prediction and attribution of extreme events
 FIRST WCRP Grand Challenges Science underpinning the prediction and attribution of extreme events David Karoly, with input from CLIVAR, ETCCDI, GEWEX, WGSIP, WGCM Needs consultation and feedback Introduction
FIRST WCRP Grand Challenges Science underpinning the prediction and attribution of extreme events David Karoly, with input from CLIVAR, ETCCDI, GEWEX, WGSIP, WGCM Needs consultation and feedback Introduction
An Interconnected Planet
 An Interconnected Planet How Clouds, Aerosols, and the Ocean Cause Distant Rainfall Anomalies Dargan M. W. Frierson University of Washington CESM Workshop, 6-15-15 New Connections Recent research has uncovered
An Interconnected Planet How Clouds, Aerosols, and the Ocean Cause Distant Rainfall Anomalies Dargan M. W. Frierson University of Washington CESM Workshop, 6-15-15 New Connections Recent research has uncovered
EUREC 4 A. A proposal for a HALO deployment out of Barbados to measure the winter North Atlantic Trades in February 2020
 EUREC 4 A A proposal for a HALO deployment out of Barbados to measure the winter North Atlantic Trades in February 2020 Felix Ament, Sandrine Bony, Susanne Crewell, Bernhard Mayer, Markus Rapp, Bjorn Stevens,
EUREC 4 A A proposal for a HALO deployment out of Barbados to measure the winter North Atlantic Trades in February 2020 Felix Ament, Sandrine Bony, Susanne Crewell, Bernhard Mayer, Markus Rapp, Bjorn Stevens,
Energetic and precipitation responses in the Sahel to sea surface temperature perturbations
 Energetic and precipitation responses in the Sahel to sea surface temperature perturbations Spencer A. Hill Yi Ming, Isaac Held, Leo Donner, Ming Zhao Motivations Severe uncertainty in rainfall response
Energetic and precipitation responses in the Sahel to sea surface temperature perturbations Spencer A. Hill Yi Ming, Isaac Held, Leo Donner, Ming Zhao Motivations Severe uncertainty in rainfall response
Schematic from Vallis: Rossby waves and the jet
 Schematic from Vallis: Rossby waves and the jet Schematic from Vallis: Rossby waves and the jet A Barotropic Model Stochastic stirring + linear damping Force barotropic vort. eqn. with white noise in storm
Schematic from Vallis: Rossby waves and the jet Schematic from Vallis: Rossby waves and the jet A Barotropic Model Stochastic stirring + linear damping Force barotropic vort. eqn. with white noise in storm
Consequences for Climate Feedback Interpretations
 CO 2 Forcing Induces Semi-direct Effects with Consequences for Climate Feedback Interpretations Timothy Andrews and Piers M. Forster School of Earth and Environment, University of Leeds, Leeds, LS2 9JT,
CO 2 Forcing Induces Semi-direct Effects with Consequences for Climate Feedback Interpretations Timothy Andrews and Piers M. Forster School of Earth and Environment, University of Leeds, Leeds, LS2 9JT,
IPCC Chapter 12: Long- term climate change: projections, commitments and irreversibility
 GEF4400 The Earth System Autumn 2015 23.11.2015 IPCC Chapter 12: Long- term climate change: projections, commitments and irreversibility Introduction and Background (from Chapter 10 and 11) Climate Model
GEF4400 The Earth System Autumn 2015 23.11.2015 IPCC Chapter 12: Long- term climate change: projections, commitments and irreversibility Introduction and Background (from Chapter 10 and 11) Climate Model
An Introduction to Climate Modeling
 An Introduction to Climate Modeling A. Gettelman & J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline What is Climate & why do we care Hierarchy of atmospheric modeling strategies
An Introduction to Climate Modeling A. Gettelman & J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline What is Climate & why do we care Hierarchy of atmospheric modeling strategies
climateprediction.net Predicting 21 st Century Climate
 climateprediction.net Predicting 21 st Century Climate Sylvia Knight, Myles Allen, Charlotte Calnan, Peter Campbell, Jonathan Gray, June Haighton, John Harris, Jules Hoult, Andrew Hunt, Robert Lang, Angela
climateprediction.net Predicting 21 st Century Climate Sylvia Knight, Myles Allen, Charlotte Calnan, Peter Campbell, Jonathan Gray, June Haighton, John Harris, Jules Hoult, Andrew Hunt, Robert Lang, Angela
Forecasts for the Future: Understanding Climate Models and Climate Projections for the 21 st Century
 Forecasts for the Future: Understanding Climate Models and Climate Projections for the 21 st Century Linda E. Sohl NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies and the Center for Climate Systems Reseearch
Forecasts for the Future: Understanding Climate Models and Climate Projections for the 21 st Century Linda E. Sohl NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies and the Center for Climate Systems Reseearch
GEWEX Cloud System Study (GCSS)
 GEWEX Cloud System Study (GCSS) The goal of GCSS is to improve the parameterization of cloud systems in GCMs (global climate models) and NWP (numerical weather prediction) models through improved physical
GEWEX Cloud System Study (GCSS) The goal of GCSS is to improve the parameterization of cloud systems in GCMs (global climate models) and NWP (numerical weather prediction) models through improved physical
Feedbacks: their inconstancy & dependence on SST pa6erns
 Feedbacks: their inconstancy & dependence on SST pa6erns Timothy Andrews, Mark Webb & Jonathan Gregory Ringberg 2015 Thinking fast & slow: SST pa3erns & feedbacks The surface warming pa6ern is not constant,
Feedbacks: their inconstancy & dependence on SST pa6erns Timothy Andrews, Mark Webb & Jonathan Gregory Ringberg 2015 Thinking fast & slow: SST pa3erns & feedbacks The surface warming pa6ern is not constant,
Evaluation of the IPSL climate model in a weather-forecast mode
 Evaluation of the IPSL climate model in a weather-forecast mode CFMIP/GCSS/EUCLIPSE Meeting, The Met Office, Exeter 2011 Solange Fermepin, Sandrine Bony and Laurent Fairhead Introduction Transpose AMIP
Evaluation of the IPSL climate model in a weather-forecast mode CFMIP/GCSS/EUCLIPSE Meeting, The Met Office, Exeter 2011 Solange Fermepin, Sandrine Bony and Laurent Fairhead Introduction Transpose AMIP
Clouds and Climate Group in CMMAP. and more
 Clouds and Climate Group in CMMAP and more Clouds and Climate Group in CMMAP Many names: - Low Cloud Feedbacks - Cloud-Climate Interactions - Clouds and Climate - Clouds & Climate Modeling (after our merger
Clouds and Climate Group in CMMAP and more Clouds and Climate Group in CMMAP Many names: - Low Cloud Feedbacks - Cloud-Climate Interactions - Clouds and Climate - Clouds & Climate Modeling (after our merger
An Introduction to Physical Parameterization Techniques Used in Atmospheric Models
 An Introduction to Physical Parameterization Techniques Used in Atmospheric Models J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline Frame broader scientific problem Hierarchy
An Introduction to Physical Parameterization Techniques Used in Atmospheric Models J. J. Hack National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado USA Outline Frame broader scientific problem Hierarchy
BJORN STEVENS MAX PLANCK INSTITUTE FOR METEOROLOGY, HAMBURG GERMANY
 PROPOSAL FOR AN ISSI (BERN) INTERNATIONAL TEAM BJORN STEVENS MAX PLANCK INSTITUTE FOR METEOROLOGY, HAMBURG GERMANY Abstract The aim of the International Team will be to advance understanding of what controls
PROPOSAL FOR AN ISSI (BERN) INTERNATIONAL TEAM BJORN STEVENS MAX PLANCK INSTITUTE FOR METEOROLOGY, HAMBURG GERMANY Abstract The aim of the International Team will be to advance understanding of what controls
Development of a high-resolution Earth System model and its application in CMIP6
 Development of a high-resolution Earth System model and its application in CMIP6 Complex Earth system models, such as the model of the Max Planck Institute for Meteorology (MPI- ESM), have a reduced resolution
Development of a high-resolution Earth System model and its application in CMIP6 Complex Earth system models, such as the model of the Max Planck Institute for Meteorology (MPI- ESM), have a reduced resolution
FOLLOW THE ENERGY! EARTH S DYNAMIC CLIMATE SYSTEM
 Investigation 1B FOLLOW THE ENERGY! EARTH S DYNAMIC CLIMATE SYSTEM Driving Question How does energy enter, flow through, and exit Earth s climate system? Educational Outcomes To consider Earth s climate
Investigation 1B FOLLOW THE ENERGY! EARTH S DYNAMIC CLIMATE SYSTEM Driving Question How does energy enter, flow through, and exit Earth s climate system? Educational Outcomes To consider Earth s climate
Using volcanic eruptions to unlock the secrets of aerosol-cloud interactions. Jim Haywood
 Using volcanic eruptions to unlock the secrets of aerosol-cloud interactions Jim Haywood Malavelle, F., et al., Strong constraints on aerosol-cloud interactions from volcanic eruptions, Nature, June 22
Using volcanic eruptions to unlock the secrets of aerosol-cloud interactions Jim Haywood Malavelle, F., et al., Strong constraints on aerosol-cloud interactions from volcanic eruptions, Nature, June 22
Projected future increase of tropical cyclones near Hawaii. Hiroyuki Murakami, Bin Wang, Tim Li, and Akio Kitoh University of Hawaii at Manoa, IPRC
 Projected future increase of tropical cyclones near Hawaii Hiroyuki Murakami, Bin Wang, Tim Li, and Akio Kitoh University of Hawaii at Manoa, IPRC Review of effect of global warming on TC activity Knutson
Projected future increase of tropical cyclones near Hawaii Hiroyuki Murakami, Bin Wang, Tim Li, and Akio Kitoh University of Hawaii at Manoa, IPRC Review of effect of global warming on TC activity Knutson
Importance of clouds and aerosols in assessing climate change
 Importance of clouds and aerosols in assessing climate change Olivier Boucher, Dave Randall Chapter 7 lead authors Chapter 8 coordinating lead authors Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Climate-relevant aerosol
Importance of clouds and aerosols in assessing climate change Olivier Boucher, Dave Randall Chapter 7 lead authors Chapter 8 coordinating lead authors Yann Arthus-Bertrand / Altitude Climate-relevant aerosol
Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System
 Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System -So far in this class, we ve mostly discussed conceptual models models that qualitatively describe the system example: Daisyworld examined stable and unstable
Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System -So far in this class, we ve mostly discussed conceptual models models that qualitatively describe the system example: Daisyworld examined stable and unstable
How might extratropical storms change in the future? Len Shaffrey National Centre for Atmospheric Science University of Reading
 How might extratropical storms change in the future? Len Shaffrey National Centre for Atmospheric Science University of Reading Extratropical storms Extratropical storms Strong winds, extreme waves, storm
How might extratropical storms change in the future? Len Shaffrey National Centre for Atmospheric Science University of Reading Extratropical storms Extratropical storms Strong winds, extreme waves, storm
Carbon dioxide s direct weakening of the tropical circulation: from comprehensive climate models to axisymmetric Hadley cell theory
 Carbon dioxide s direct weakening of the tropical circulation: from comprehensive climate models to axisymmetric Hadley cell theory Timothy M. Merlis McGill University Key point The spatial structure of
Carbon dioxide s direct weakening of the tropical circulation: from comprehensive climate models to axisymmetric Hadley cell theory Timothy M. Merlis McGill University Key point The spatial structure of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1854 Anthropogenic aerosol forcing of Atlantic tropical storms N. J. Dunstone 1, D. S. Smith 1, B. B. B. Booth 1, L. Hermanson 1, R. Eade 1 Supplementary information
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1854 Anthropogenic aerosol forcing of Atlantic tropical storms N. J. Dunstone 1, D. S. Smith 1, B. B. B. Booth 1, L. Hermanson 1, R. Eade 1 Supplementary information
Interhemispheric climate connections: What can the atmosphere do?
 Interhemispheric climate connections: What can the atmosphere do? Raymond T. Pierrehumbert The University of Chicago 1 Uncertain feedbacks plague estimates of climate sensitivity 2 Water Vapor Models agree
Interhemispheric climate connections: What can the atmosphere do? Raymond T. Pierrehumbert The University of Chicago 1 Uncertain feedbacks plague estimates of climate sensitivity 2 Water Vapor Models agree
WCRP/CLIVAR efforts to understand El Niño in a changing climate
 WCRP/CLIVAR efforts to understand El Niño in a changing climate Eric Guilyardi IPSL/LOCEAN, Paris & NCAS-Climate, U. Reading Thanks to Andrew Wittenberg, Mike McPhaden, Matthieu Lengaigne 2015 El Niño
WCRP/CLIVAR efforts to understand El Niño in a changing climate Eric Guilyardi IPSL/LOCEAN, Paris & NCAS-Climate, U. Reading Thanks to Andrew Wittenberg, Mike McPhaden, Matthieu Lengaigne 2015 El Niño
NSF Expeditions in Computing. Understanding Climate Change: A Data Driven Approach. Vipin Kumar University of Minnesota
 NSF Expeditions in Computing Understanding Climate Change: A Data Driven Approach Vipin Kumar University of Minnesota kumar@cs.umn.edu www.cs.umn.edu/~kumar Vipin Kumar UCC Aug 15, 2011 Climate Change:
NSF Expeditions in Computing Understanding Climate Change: A Data Driven Approach Vipin Kumar University of Minnesota kumar@cs.umn.edu www.cs.umn.edu/~kumar Vipin Kumar UCC Aug 15, 2011 Climate Change:
Challenges for Climate Science in the Arctic. Ralf Döscher Rossby Centre, SMHI, Sweden
 Challenges for Climate Science in the Arctic Ralf Döscher Rossby Centre, SMHI, Sweden The Arctic is changing 1) Why is Arctic sea ice disappearing so rapidly? 2) What are the local and remote consequences?
Challenges for Climate Science in the Arctic Ralf Döscher Rossby Centre, SMHI, Sweden The Arctic is changing 1) Why is Arctic sea ice disappearing so rapidly? 2) What are the local and remote consequences?
Decreasing trend of tropical cyclone frequency in 228-year high-resolution AGCM simulations
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053360, 2012 Decreasing trend of tropical cyclone frequency in 228-year high-resolution AGCM simulations Masato Sugi 1,2 and Jun Yoshimura 2 Received
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053360, 2012 Decreasing trend of tropical cyclone frequency in 228-year high-resolution AGCM simulations Masato Sugi 1,2 and Jun Yoshimura 2 Received
How closely do changes in surface and column water vapor follow Clausius-Clapeyron scaling in climate change simulations?
 How closely do changes in surface and column water vapor follow Clausius-Clapeyron scaling in climate change simulations? The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access
How closely do changes in surface and column water vapor follow Clausius-Clapeyron scaling in climate change simulations? The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access
UK plans and recommendations for CMIP6
 UK plans and recommendations for CMIP6 Catherine Senior Presentation to WGCM17, Victoria, October 1st, 2013 UK Model Development for CMIP6 2013/4: HadGEM3-GC2 (physical coupled N216(~60km), O(1/4)º) NEMO+CICE
UK plans and recommendations for CMIP6 Catherine Senior Presentation to WGCM17, Victoria, October 1st, 2013 UK Model Development for CMIP6 2013/4: HadGEM3-GC2 (physical coupled N216(~60km), O(1/4)º) NEMO+CICE
Short Term forecasts along the GCSS Pacific Cross-section: Evaluating new Parameterizations in the Community Atmospheric Model
 Short Term forecasts along the GCSS Pacific Cross-section: Evaluating new Parameterizations in the Community Atmospheric Model Cécile Hannay, Dave Williamson, Jerry Olson, Rich Neale, Andrew Gettelman,
Short Term forecasts along the GCSS Pacific Cross-section: Evaluating new Parameterizations in the Community Atmospheric Model Cécile Hannay, Dave Williamson, Jerry Olson, Rich Neale, Andrew Gettelman,
REQUEST FOR A SPECIAL PROJECT
 REQUEST FOR A SPECIAL PROJECT 2017 2019 MEMBER STATE: Sweden.... 1 Principal InvestigatorP0F P: Wilhelm May... Affiliation: Address: Centre for Environmental and Climate Research, Lund University Sölvegatan
REQUEST FOR A SPECIAL PROJECT 2017 2019 MEMBER STATE: Sweden.... 1 Principal InvestigatorP0F P: Wilhelm May... Affiliation: Address: Centre for Environmental and Climate Research, Lund University Sölvegatan
Climate Modeling Dr. Jehangir Ashraf Awan Pakistan Meteorological Department
 Climate Modeling Dr. Jehangir Ashraf Awan Pakistan Meteorological Department Source: Slides partially taken from A. Pier Siebesma, KNMI & TU Delft Key Questions What is a climate model? What types of climate
Climate Modeling Dr. Jehangir Ashraf Awan Pakistan Meteorological Department Source: Slides partially taken from A. Pier Siebesma, KNMI & TU Delft Key Questions What is a climate model? What types of climate
An Experimental Design to Investigate Low Cloud Feedbacks in General Circulation. Models for CGILS by Using Single-Column and Large-Eddy Models
 An Experimental Design to Investigate Low Cloud Feedbacks in General Circulation Models for CGILS by Using Single-Column and Large-Eddy Models Minghua Zhang 1, Christopher Bretherton 2, Peter Blossey 2,
An Experimental Design to Investigate Low Cloud Feedbacks in General Circulation Models for CGILS by Using Single-Column and Large-Eddy Models Minghua Zhang 1, Christopher Bretherton 2, Peter Blossey 2,
Clouds in the Climate System: Why is this such a difficult problem, and where do we go from here?
 Clouds in the Climate System: Why is this such a difficult problem, and where do we go from here? Joel Norris Scripps Institution of Oceanography CERES Science Team Meeting April 29, 2009 Collaborators
Clouds in the Climate System: Why is this such a difficult problem, and where do we go from here? Joel Norris Scripps Institution of Oceanography CERES Science Team Meeting April 29, 2009 Collaborators
Extratropical and Polar Cloud Systems
 Extratropical and Polar Cloud Systems Gunilla Svensson Department of Meteorology & Bolin Centre for Climate Research George Tselioudis Extratropical and Polar Cloud Systems Lecture 1 Extratropical cyclones
Extratropical and Polar Cloud Systems Gunilla Svensson Department of Meteorology & Bolin Centre for Climate Research George Tselioudis Extratropical and Polar Cloud Systems Lecture 1 Extratropical cyclones
Changing Width of Tropical Belt WG Update. Qiang Fu Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington
 Changing Width of Tropical Belt WG Update Qiang Fu Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington v Motivation v Implication v WG Plan v Motivation Tropical width Tropical boundaries are defined
Changing Width of Tropical Belt WG Update Qiang Fu Department of Atmospheric Sciences University of Washington v Motivation v Implication v WG Plan v Motivation Tropical width Tropical boundaries are defined
Why build a climate model
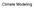 Climate Modeling Why build a climate model Atmosphere H2O vapor and Clouds Absorbing gases CO2 Aerosol Land/Biota Surface vegetation Ice Sea ice Ice sheets (glaciers) Ocean Box Model (0 D) E IN = E OUT
Climate Modeling Why build a climate model Atmosphere H2O vapor and Clouds Absorbing gases CO2 Aerosol Land/Biota Surface vegetation Ice Sea ice Ice sheets (glaciers) Ocean Box Model (0 D) E IN = E OUT
Boundary layer parameterization and climate. Chris Bretherton. University of Washington
 Boundary layer parameterization and climate Chris Bretherton University of Washington Some PBL-related climate modeling issues PBL cloud feedbacks on tropical circulations, climate sensitivity and aerosol
Boundary layer parameterization and climate Chris Bretherton University of Washington Some PBL-related climate modeling issues PBL cloud feedbacks on tropical circulations, climate sensitivity and aerosol
Correspondence between short and long timescale systematic errors in CAM4/CAM5 explored by YOTC data
 Correspondence between short and long timescale systematic errors in CAM4/CAM5 explored by YOTC data Hsi-Yen Ma In collaboration with Shaocheng Xie, James Boyle, Stephen Klein, and Yuying Zhang Program
Correspondence between short and long timescale systematic errors in CAM4/CAM5 explored by YOTC data Hsi-Yen Ma In collaboration with Shaocheng Xie, James Boyle, Stephen Klein, and Yuying Zhang Program
Modeling the Atmosphere and Ocean
 M E E T I N G S Modeling the Atmosphere and Ocean Fine-resolution modeling of the atmosphere and ocean is a major focus for collaboration between IPRC scientists and their JAMSTEC colleagues. With the
M E E T I N G S Modeling the Atmosphere and Ocean Fine-resolution modeling of the atmosphere and ocean is a major focus for collaboration between IPRC scientists and their JAMSTEC colleagues. With the
Radiative-Convective Instability
 Radiative-Convective Instability Kerry Emanuel, Allison Wing, and Emmanuel Vincent Massachusetts Institute of Technology Self-Aggregation of Deep Moist Convection Cloud Clusters Tropical Cyclone Genesis
Radiative-Convective Instability Kerry Emanuel, Allison Wing, and Emmanuel Vincent Massachusetts Institute of Technology Self-Aggregation of Deep Moist Convection Cloud Clusters Tropical Cyclone Genesis
Article Title: Cloud feedback mechanisms and their representation in global climate models. Article Type: Advanced Review
 Article Title: Cloud feedback mechanisms and their representation in global climate models Article Type: Advanced Review Authors: Paulo Ceppi Department of Meteorology, University of Reading, Reading,
Article Title: Cloud feedback mechanisms and their representation in global climate models Article Type: Advanced Review Authors: Paulo Ceppi Department of Meteorology, University of Reading, Reading,
Coupling between clouds and their environment: using observations to constrain models
 Coupling between clouds and their environment: using observations to constrain models Louise Nuijens ECMWF Annual Seminar 2015 Brian Medeiros, Irina Sandu and Maike Alhgrimm Photograph: Frederic Batier
Coupling between clouds and their environment: using observations to constrain models Louise Nuijens ECMWF Annual Seminar 2015 Brian Medeiros, Irina Sandu and Maike Alhgrimm Photograph: Frederic Batier
WDAC report to JSC37. Geneva, April 26, 2015
 WDAC report to JSC37 Geneva, April 26, 2015 Mission WCRP Data Advisory Council (WDAC) act as a single entry point for all WCRP data, information, and observation activities with its sister programmes,
WDAC report to JSC37 Geneva, April 26, 2015 Mission WCRP Data Advisory Council (WDAC) act as a single entry point for all WCRP data, information, and observation activities with its sister programmes,
Importance of minor treatments in parameterizations in GCMs for the cloud representations and the cloud feedbacks
 The WCRP Grand Challenge Workshop, 25 March. 2014 Importance of minor treatments in parameterizations in GCMs for the cloud representations and the cloud feedbacks Hideaki Kawai Meteorological Research
The WCRP Grand Challenge Workshop, 25 March. 2014 Importance of minor treatments in parameterizations in GCMs for the cloud representations and the cloud feedbacks Hideaki Kawai Meteorological Research
Future directions for parametrization of cloud and precipitation microphysics
 Future directions for parametrization of cloud and precipitation microphysics Richard Forbes (ECMWF) ECMWF-JCSDA Workshop, 15-17 June 2010 Cloud and Precipitation Microphysics A Complex System! Ice Nucleation
Future directions for parametrization of cloud and precipitation microphysics Richard Forbes (ECMWF) ECMWF-JCSDA Workshop, 15-17 June 2010 Cloud and Precipitation Microphysics A Complex System! Ice Nucleation
High-Resolution MPAS Simulations for Analysis of Climate Change Effects on Weather Extremes
 High-Resolution MPAS Simulations for Analysis of Climate Change Effects on Weather Extremes ALLISON MICHAELIS, GARY LACKMANN, & WALT ROBINSON Department of Marine, Earth, and Atmospheric Sciences, North
High-Resolution MPAS Simulations for Analysis of Climate Change Effects on Weather Extremes ALLISON MICHAELIS, GARY LACKMANN, & WALT ROBINSON Department of Marine, Earth, and Atmospheric Sciences, North
Ocean Model Intercomparison Project (OMIP)
 Ocean Model Intercomparison Project (OMIP) Co Chairs Gokhan Danabasoglu (NCAR, USA) Stephen Griffies (NOAA/GFDL, USA) James Orr (IPSL, France) Scientific Steering Committee Physical Processes (CLIVAR Ocean
Ocean Model Intercomparison Project (OMIP) Co Chairs Gokhan Danabasoglu (NCAR, USA) Stephen Griffies (NOAA/GFDL, USA) James Orr (IPSL, France) Scientific Steering Committee Physical Processes (CLIVAR Ocean
Climate change and variability -
 Climate change and variability - Current capabilities - a synthesis of IPCC AR4 (WG1) Pete Falloon, Manager Impacts Model Development, Met Office Hadley Centre WMO CaGM/SECC Workshop, Orlando, 18 November
Climate change and variability - Current capabilities - a synthesis of IPCC AR4 (WG1) Pete Falloon, Manager Impacts Model Development, Met Office Hadley Centre WMO CaGM/SECC Workshop, Orlando, 18 November
Scale-aware and definition-aware evaluation of CESM1 near-surface precipitation frequency using CloudSat observations
 Scale-aware and definition-aware evaluation of CESM1 near-surface precipitation frequency using CloudSat observations Jen Kay, University of Colorado (CU) Tristan L Ecuyer (UW-Madison), Angie Pendergrass
Scale-aware and definition-aware evaluation of CESM1 near-surface precipitation frequency using CloudSat observations Jen Kay, University of Colorado (CU) Tristan L Ecuyer (UW-Madison), Angie Pendergrass
Presentation A simple model of multiple climate regimes
 A simple model of multiple climate regimes Kerry Emanuel March 21, 2012 Overview 1. Introduction 2. Essential Climate Feedback Processes Ocean s Thermohaline Circulation, Large-Scale Circulation of the
A simple model of multiple climate regimes Kerry Emanuel March 21, 2012 Overview 1. Introduction 2. Essential Climate Feedback Processes Ocean s Thermohaline Circulation, Large-Scale Circulation of the
Climate change with an iris-effect. Thorsten Mauritsen and Bjorn Stevens Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg
 Climate change with an iris-effect! Thorsten Mauritsen and Bjorn Stevens Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg AR4 Temperature anomaly ( C) w.r.t. 1961 1990 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 } AR4 CMIP3 } Observations
Climate change with an iris-effect! Thorsten Mauritsen and Bjorn Stevens Max Planck Institute for Meteorology, Hamburg AR4 Temperature anomaly ( C) w.r.t. 1961 1990 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 } AR4 CMIP3 } Observations
Climate Change Scenario, Climate Model and Future Climate Projection
 Training on Concept of Climate Change: Impacts, Vulnerability, Adaptation and Mitigation 6 th December 2016, CEGIS, Dhaka Climate Change Scenario, Climate Model and Future Climate Projection A.K.M. Saiful
Training on Concept of Climate Change: Impacts, Vulnerability, Adaptation and Mitigation 6 th December 2016, CEGIS, Dhaka Climate Change Scenario, Climate Model and Future Climate Projection A.K.M. Saiful
Climate Modelling: Basics
 Climate Modelling: Basics Lecture at APN-TERI Student Seminar Teri University, 16 th Feb 2015 Saurabh Bhardwaj Associate Fellow Earth Science & Climate Change Division TERI saurabh.bhardwaj@teri.res.in
Climate Modelling: Basics Lecture at APN-TERI Student Seminar Teri University, 16 th Feb 2015 Saurabh Bhardwaj Associate Fellow Earth Science & Climate Change Division TERI saurabh.bhardwaj@teri.res.in
Extremes of Weather and the Latest Climate Change Science. Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading
 Extremes of Weather and the Latest Climate Change Science Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Extreme weather climate change Recent extreme weather focusses debate on climate
Extremes of Weather and the Latest Climate Change Science Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Extreme weather climate change Recent extreme weather focusses debate on climate
CALIPSO and the clouds. Hélène Chepfer LMD/IPSL, University Pierre and Marie Curie
 CALIPSO and the clouds Hélène Chepfer LMD/IPSL, University Pierre and Marie Curie Outline On the use of Calipso to evaluate climate models (GOCCP and COSP/lidar) Low level tropical clouds Deep convecgve
CALIPSO and the clouds Hélène Chepfer LMD/IPSL, University Pierre and Marie Curie Outline On the use of Calipso to evaluate climate models (GOCCP and COSP/lidar) Low level tropical clouds Deep convecgve
NSF 2005 CPT Report. Jeffrey T. Kiehl & Cecile Hannay
 NSF 2005 CPT Report Jeffrey T. Kiehl & Cecile Hannay Introduction: The focus of our research is on the role of low tropical clouds in affecting climate sensitivity. Comparison of climate simulations between
NSF 2005 CPT Report Jeffrey T. Kiehl & Cecile Hannay Introduction: The focus of our research is on the role of low tropical clouds in affecting climate sensitivity. Comparison of climate simulations between
Remote sensing of ice clouds
 Remote sensing of ice clouds Carlos Jimenez LERMA, Observatoire de Paris, France GDR microondes, Paris, 09/09/2008 Outline : ice clouds and the climate system : VIS-NIR, IR, mm/sub-mm, active 3. Observing
Remote sensing of ice clouds Carlos Jimenez LERMA, Observatoire de Paris, France GDR microondes, Paris, 09/09/2008 Outline : ice clouds and the climate system : VIS-NIR, IR, mm/sub-mm, active 3. Observing
Global warming and Extremes of Weather. Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading
 Global warming and Extremes of Weather Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Extreme weather climate change Recent extreme weather focusses debate on climate change Can we
Global warming and Extremes of Weather Prof. Richard Allan, Department of Meteorology University of Reading Extreme weather climate change Recent extreme weather focusses debate on climate change Can we
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY. Climate Models: An Assessment of Strengths and Limitations
 Climate Models: An Assessment of Strengths and Limitations EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Scientists extensively use mathematical models of Earth s climate, executed on the most powerful computers available, to examine
Climate Models: An Assessment of Strengths and Limitations EXECUTIVE SUMMARY Scientists extensively use mathematical models of Earth s climate, executed on the most powerful computers available, to examine
Global Cloud Climatologies from satellite-based InfraRed Sounders (TOVS, AIRS, IASI) +
 Global Cloud Climatologies from satellite-based InfraRed Sounders (TOVS, AIRS, IASI) + AIRS-CALIPSO-CloudSat Synergy Claudia Stubenrauch * until 2010 S. Cros*, A. Guignard, N. Lamquin*, R. Armante, A.
Global Cloud Climatologies from satellite-based InfraRed Sounders (TOVS, AIRS, IASI) + AIRS-CALIPSO-CloudSat Synergy Claudia Stubenrauch * until 2010 S. Cros*, A. Guignard, N. Lamquin*, R. Armante, A.
Climate model evaluation using GPS-RO data
 Climate model evaluation using GPS-RO data Mark Ringer, Met Office Hadley Centre ROM-SAF workshop, ECMWF, 16-18 June 2014 Outline Intro using satellite data for model evaluation Evaluation of the new Hadley
Climate model evaluation using GPS-RO data Mark Ringer, Met Office Hadley Centre ROM-SAF workshop, ECMWF, 16-18 June 2014 Outline Intro using satellite data for model evaluation Evaluation of the new Hadley
