(10) Patent No.: US 7,557,694 B1
|
|
|
- Lorena Whitehead
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
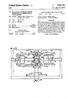
1 US B1 (12) United States Patent Graham (54) (76) (*) (21) (22) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) VEHICLE TRE TREAD DEPTH DETERMINING SYSTEM Inventor: Notice: Jeannell Graham, 3107 Federal House Ct., Waldorf, MD (US) Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this patent is extended or adjusted under 35 U.S.C. 154(b) by 387 days. Appl. No.: 11/ Filed: Jul. 31, 2006 Related U.S. Application Data Provisional application No. 60/704,153, filed on Aug. 1, Int. C. B60O I/00 ( ) U.S. Cl /438: 340/442 Field of Classification Search /438, 340/442: 362/500: 152/151,154.2, 209.1, 152/450, 523 See application file for complete search history. References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 4,226,274 A 10/1980 Awaya et al. (10) Patent No.: US 7,557,694 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 7, ,303,756 A 4, 1994 Hill 6,220,199 B1 * 4/2001 Williams ,208 6,298,889 B1 10/2001 Smith B2 * 6/2008 Dufournier /442 * cited by examiner Primary Examiner Toan N Pham Assistant Examiner Kerri L. McNally (57) ABSTRACT A vehicle tire tread depth determining system includes an annular member embedded beneath an outer Surface, and disposed beneath a tread layer, of a vehicle tire. The member has photo-chromatic properties that change color when exposed to ultraviolet light. The member also has a body extending inside an outer perimeter of a tire, and is spaced from the tread layer and formed therewith. A color determin ing mechanism is in visual communication with the member. A time period mechanism determines when the member has transgressed from a first color to a second color. A display screen is mounted on the dashboard, and includes a graphical user interface and a pictorial illustration of the member color. A controller is housed within a compartment of the vehicle and positioned on a dashboard. A tread depth determining mechanism is spaced from the tire and electrically coupled to a battery and an ignition controller. 9 Claims, 6 Drawing Sheets /
2
3 U.S. Patent Jul. 7, 2009 Sheet 2 of 6 US 7,557,694 B1
4 U.S. Patent Jul. 7, 2009 Sheet 3 of 6 US 7,557,694 B1 s r s p as no e s
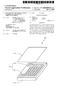
5 U.S. Patent Jul. 7, 2009 Sheet 4 of 6 US 7,557,694 B FIG. 4
6 U.S. Patent Jul. 7, 2009 Sheet 5 of 6 US 7,557,694 B1 FIG. 5
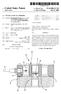
7 U.S. Patent Jul. 7, 2009 Sheet 6 of 6 US 7,557,694 B1 Annular Flourescent Strip (Photochromatic Properties) CONTROLLER - Digital Sensor Processor 44 Gre Display. Pane WEHICLE ENGINE Batte 19 Controller FIG. 6 47
8 1. VEHICLE TRE TREAD DEPTH DETERMINING SYSTEM CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS This application claims the benefit of U.S. Provisional Application No. 60/704,153, filed Aug. 1, STATEMENT REGARDING FEDERALLY SPONSORED RESEARCH ORDEVELOPMENT Not Applicable. REFERENCE TO AMICROFICHEAPPENDIX Not Applicable. BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION 1. Technical Field This invention relates to tire depth determining systems and, more particularly, to a vehicle tire tread depth determin ing system for warning a driveroflow tread depth on a vehicle tire. 2. Prior Art Pneumatic vehicle tires essentially consist of a tire carcass, which consists of plies of rubberized fabric, and tread rubber, which surrounds the exterior surface of the carcass. In belted tires, additional layers of fiber glass, steel, or aramid are placed between the plies and the tread rubber. During manu facture, the tire is Vulcanized to gain its final shape and strength characteristics. Besides equalizing the stresses within the tire body, the Vulcanization changes the rubber compound into a tough, highly elastic material and bonds the parts of the tire into one integral unit. During the Vulcanization process, the tread rubber is molded to form the tire treads which provide frictional engagement between the tire and the road Surface. The treads also protect the tire carcass from foreign obstacles on the road Surface which could damage the carcass. Since the effective ness of the tire tread as a cushioning and protective sheath is dependent upon the amount of tread rubber covering the carcass, this effectiveness is decreased as the treads are reduced by wear. If the tire is not routinely inspected, the tread may be worn down to a level where driving becomes danger OS. One prior art example shows a tire with a layer of a colored material embedded in the tread rubber to visually indicate the degree of tread wear. The tire includes positioning plies hav ing colored fibers at different tread depths to visually indicate when the tread has been worn to the point at which the tread should be recapped or the tire replaced. A second prior art example shows a tire having a Sub-Surface tread portion of a color contrasting to the outer portion of the tread to indicate when the tread is worn. Another prior art example shows a tire with a colored indicating means embedded within the tread portion of a tire. In this case, the indicating means is prefer ably made from rubber, metal, or plastic. Problems have arisen in connection with the above-de scribed colored tread wear indicators in that the coloring in the indicators degrades under the high temperature of Vulca nization. Moreover, in instances when the colored material is formed from plastic, the colored material may not sufficiently adhere to the tread rubber. Consequently, after the tire cools following Vulcanization, airpockets may remain between the US 7,557,694 B plastic tread wear indicators and the tread rubber, thereby reducing the integrity of the tire. Accordingly, a need remains for a vehicle tire tread depth determining system in order to overcome the above-noted shortcomings. The present invention satisfies such a need by providing a system that is convenient and easy to use, is lightweight yet durable in design, and provides an easy and effective means of notifying a driver that a tire is excessively worn and should be replaced. Such a system is advanta geously enclosed in a sturdy casing that is effectively embed ded in the tire tread. When exposed to the ground surface, the system conveniently shows a yellow strip on the worn tire, effectively indicating that a new tire is needed. The system includes an effective visual alert system conveniently mounted on the dashboard of the vehicle, thus advanta geously providing a lighted indicator of tire tread status that is visible while driving the car. The significantly and effectively decreases the risk of injuries or fatalities that result from motorists driving on worn or bald tires, thus advantageously helping to keep roadways safe while driving. BRIEF SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION In view of the foregoing background, it is therefore an object of the present invention to provide a vehicle tire tread depth determining system. These and other objects, features, and advantages of the invention are provided by a vehicle tire wear notification system for warning a driver of low tread depth on the vehicle tires. The depth measuring system conveniently includes an annular member advantageously embedded beneath an outer surface of the vehicle tire. Such an annular member is conve niently disposed beneath a tread layer of the vehicle tire such that the annular member is effectively prohibited from being exposed to ambient light when the tread layer has a predeter mined minimum thickness. The annular member may have photo-chromatic or thermo-chromatic properties such that the annular member advantageously changes color when exposed to ambient light, thus indicating when the tiretread is worn. The annular member has a single and continuous body extending inside an outer perimeter of the vehicle tire. The annular member is equidistantly spaced from the tread layer and monolithically formed with the vehicle tire. The system includes a mechanism for determining a color of the annular member. The color determining mechanism is in visual communication with the annular member. The sys tem also includes a mechanism for determining a time period after which the annular member has transgressed from a first color to a second color. The system further includes a display screen mounted on the dashboard. Such a display Screen includes a graphical user interface that graphically illustrates a location of the vehicle tire as well as a convenient pictorial illustration of the annular member color. The system has a controller advantageously housed within a compartment of the vehicle and conveniently positioned on a dashboard of the vehicle so that the driver can visually monitor the controller. Such a controller includes a mecha nism for determining a remaining tread depth on the vehicle tire based upon the first color of the annular member and the time period. The tread depth determining mechanism is effec tively spaced from the vehicle tire and electrically coupled to a battery of the vehicle and an ignition controller of the vehicle. The tread depth determining mechanism effectively interrupts power between the vehicle battery and ignition controller respectively, when the annular member has color properties exceeding at least one of a threshold color leveland a threshold time period respectively.
9 3 The system preferably includes a convenient color deter mining mechanism that includes an optical sensor visually and effectively cooperating with the annular member. Such an optical sensor is coupled directly to the vehicle tire and advantageously maintains a direct line of sight with the annu lar member. The optical sensor effectively generates and transmits an analog notification signal based upon a color change of the annular member. Such an analog notification signal advantageously has a first data stream that identifies a location of the vehicle tire and a second data stream that identifies the color of the annular member. The system may include a time period determining mecha nism that includes a timer circuit electrically coupled to the optical sensor. Such a timer circuit advantageously triggers an internal counter when the first color changes to the second color. The timer circuit effectively generates and transmits a timing data stream to the optical sensor. The system may further include a tread depth determining mechanism that conveniently includes an analog-to-digital converter that effectively receives and converts the analog notification signal to a digital notification signal. A digital signal processor is electrically coupled to such an analog-to digital converter and receives the digital notification signal. A convenient database contains a table of corresponding tread depths, annular member colors and time periods that corre spond to a predetermined model of the vehicletire. A memory electrically coupled to the digital signal processor conve niently includes software instructions that cause the tire wear notification system to effectively determine the tread depth of the vehicle tire based upon the color of the annular member and the time period associated therewith. Such software instructions include and calculate a logic algorithm including the steps of retrieving the first color of the annular member, retrieving the time period associated with the first color; if the time period is less than a predeter mined threshold time period, locating a tread depth value corresponding to the first color and the time period from the database; and if the time period is greater than the predeter mined threshold time period, locating a tread depth value corresponding with the second color and a new time period Set to Zero. The system may still further include a power interrupt switch advantageously seated between the vehicle battery and the ignition controller of the vehicle. Such a power interrupt Switch is electrically coupled to the digital signal processor and is toggled between open and closed positions when the tread depth falls below the minimum tread depth. There has thus been outlined, rather broadly, the more important features of the invention in order that the detailed description thereof that follows may be better understood, and in order that the present contribution to the art may be better appreciated. There are additional features of the inven tion that will be described hereinafter and which will form the Subject matter of the claims appended hereto. It is noted the purpose of the foregoing abstract is to enable the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and the public gener ally, especially the Scientists, engineers and practitioners in the art who are not familiar with patent or legal terms or phraseology, to determine quickly from a cursory inspection the nature and essence of the technical disclosure of the application. The abstract is neither intended to define the US 7,557,694 B invention of the application, which is measured by the claims, nor is it intended to be limiting as to the scope of the invention in any way. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE SEVERAL VIEWS OF THE DRAWING The novel features believed to be characteristic of this invention are set forth with particularity in the appended claims. The invention itself, however, both as to its organiza tion and method of operation, together with further objects and advantages thereof, may best be understood by reference to the following description taken in connection with the accompanying drawings in which: FIG. 1 is a perspective view showing a vehicle tire having an annular member embedded therebeneath, in accordance with the present invention; FIG. 2 is a side-elevational view of the system shown in FIG. 1: FIG.3 is a front-elevational view of the dashboard showing the display button, in accordance with the present invention; FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view of the vehicle tire and annular member shown in FIG. 1, taken along line 1-1; FIG.5 is a cross-sectional view of the vehicletire shown in FIG. 1 taken along line 2-2; and FIG. 6 is a schematic block diagram of the system, in accordance with the present invention. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION The present invention will now be described more fully hereinafter with reference to the accompanying drawings, in which a preferred embodiment of the invention is shown. This invention may, however, be embodied in many different forms and should not be construed as limited to the embodi ment set forth herein. Rather, this embodiment is provided so that this application will be thorough and complete, and will fully convey the true scope of the invention to those skilled in the art. Like numbers refer to like elements throughout the figures. The system of this invention is referred to generally in FIGS. 1-6 by the reference numeral 10 and is intended to provide a vehicle tire tread depth determining system. It should be understood that the system 10 may be used to determine the depth of tread of many different types of tires and should not be limited in use to determining the tread depth of only automobile tires. Referring initially to FIGS. 1, 2, 4, 5, and 6, the system 10 includes an annular member 30 advantageously embedded beneath an outer surface 11 of the vehicle tire 12. Such an annular member 30 is conveniently disposed beneath a tread layer 13 of the vehicletire 12 such that the annular member 30 is effectively prohibited from being exposed to ambient ultra violet light when the tread layer 13 has a predetermined minimum thickness. The annular member 30 has photo-chro matic properties such that the annular member 30 advanta geously changes color when exposed to ambient light, which is vital to effectively indicating when the tread layer 13 is worn. The annular member 30 has a single and continuous body 31 extending inside an outer perimeter 14 of the vehicle tire 12. The annular member 30 is equidistantly spaced from the tread layer 13 and monolithically formed with the vehicle tire 12. Referring to FIGS. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6, the system 10 includes a convenient mechanism 32 for determining a color of the annular member 30. As an example, the annular mem ber may employ DynaColorTM photochromic inks that are
10 5 invisible until they come into contact with UV light, like sunlight. When photochromic ink is exposed to UV light, it blooms into color. With photochromics, the present invention does not need a special technique to hide the annular member because the annular member may be colorless until you take it into the sun or expose it to UV light, i.e. when the tire tread has worn down beyond a minimum threshold. The color determining mechanism 32 is in visual communication with the annular member 30. Alternately, the annular member may employ thermochromatic properties such as DynaColorTM thermochromic inks that will change color as their tempera ture changes. These color-changing inks all work the same way: below the activation temperature they are colored and above the activation temperature they are clear or lightly colored. As the ink cools, the original color returns. The system 10 also conveniently includes a mechanism 33 for determining a time period after which the annular member 30 has transgressed from a first color to a second color. The system 10 further includes a display screen 34 conveniently mounted on the dashboard 15. Such a display screen 34 includes a graphical user interface 35 that graphically illus trates a location of the vehicle tire 12 as well as a convenient pictorial illustration of the annular member color. Of course, many different colors can be used for the annular member, as is obvious to a person of ordinary skill in the art. Referring to FIGS. 3 and 6, the system 10 includes a con troller36 advantageously housed within a compartment of the vehicle 16 and conveniently positioned on a dashboard 15 of the vehicle 16 so that the driver can visually monitor the controller 36. Such a controller 36 conveniently includes a mechanism 37 for determining a remaining tread depth on the vehicle tire 12 based upon the first color of the annular mem ber 30 and the time period. The tread depth determining mechanism 37 is effectively spaced from the vehicle tire 12 and electrically coupled to a battery 18 of the vehicle 16 and an ignition controller 19 of the vehicle 16. The tread depth determining mechanism 37 effectively interrupts power between the vehicle battery 18 and ignition controller 19 respectively, when the annular member 30 has color proper ties exceeding at least one of a threshold color level and a threshold time period respectively. Referring to FIGS. 2, 4, 5, and 6, the system includes a convenient color determining mechanism32 that includes an optical sensor 38 visually and effectively cooperating with the annular member 30. Such an optical sensor 38 is coupled directly to the vehicle tire 12, without the use of intervening elements, and advantageously maintains a direct line of sight with the annular member 30. The optical sensor 38 effectively generates and transmits an analog notification signal based upon a color change of the annular member 30. Such an analog notification signal advantageously has a first data stream that identifies a location of the vehicle tire 12 and a second data stream that identifies the color of the annular member 30. Again referring to FIGS. 2, 4, 5 and 6, the system also includes a time period determining mechanism 39 that con veniently includes a timer circuit 41 electrically coupled to the optical sensor 38. Such a timer circuit 41 advantageously triggers an internal counter 42 when the first color changes to the second color. The timer circuit 41 effectively generates and transmits a timing data stream to the optical sensor 38. US 7,557,694 B Referring to FIG. 6, the system still further includes a tread depth determining mechanism 37 that conveniently includes an analog-to-digital converter 43 that effectively receives and converts the analog notification signal to a digital notification signal. A digital signal processor 44 is electrically coupled to Such an analog-to-digital converter 43 and receives the digital notification signal. A convenient database 45 contains a table of corresponding tread depths, annular member colors and time periods that correspond to a predetermined model of the vehicle tire 12. A non-volatile memory 46 electrically coupled to the digital signal processor 44 includes Software instructions that cause the system 10 to effectively determine the tread depth of the vehicle tire 12 based upon the color of the annular member 30 and the time period associated there with. Such software instructions include and calculate a logic algorithm including the steps of retrieving the first color of the annular member 30; retrieving the time period associated with the first color; if the time period is less than a predeter mined threshold time period, locating a tread depth value corresponding to the first color and the time period from the database; and if the time period is greater than the predeter mined threshold time period, locating a tread depth value corresponding with the second color and a new time period Set to Zero. Again referring to FIG. 6, the system includes a power interrupt switch 47 advantageously seated between the vehicle battery 18 and the ignition controller 19 of the vehicle 16. Such a powerinterrupt switch 47 is electrically coupled to the digital signal processor 44 and is toggled between open and closed positions when the tread depth falls below the minimum tread depth. While the invention has been described with respect to a certain specific embodiment, it will be appreciated that many modifications and changes may be made by those skilled in the art without departing from the spirit of the invention. It is intended, therefore, by the appended claims to cover all such modifications and changes as fall within the true spirit and Scope of the invention. In particular, with respect to the above description, it is to be realized that the optimum dimensional relationships for the parts of the present invention may include variations in size, materials, shape, form, function and manner of opera tion. The assembly and use of the present invention are deemed readily apparent and obvious to one skilled in the art. What is claimed as new and what is desired to secure by Letters Patent of the United States is: 1. A vehicle tire wear notification system for warning a driver of low tread depth on the vehicle tires, said tire wear notification system comprising: an annular member embedded beneath an outer surface of the vehicle tire, said annular member being disposed beneath a tread layer of the vehicle tire such that said annular member is prohibited from being exposed to ambient light when the tread layer has a predetermined minimum thickness, said annular member having photo chromatic properties such that said annular member changes color when exposed to ambient light; means for determining a color of said annular member, said color determining means being in visual communication with said annular member,
11 7 means for determining a time period after which said annu lar member has transgressed from a first color to a sec ond color, and a controller housed within a compartment of the vehicle and positioned on a dashboard of the vehicle so that the driver can visually monitor said controller, said control ler comprising means for determining a remaining tread depth on the vehicle tire based upon said first color of said annular member and said time period, said tread depth determining means being spaced from the vehicle tire and electrically coupled to a battery of the vehicle and an ignition controller of the vehicle: wherein said tread depth determining means interrupts power between the vehicle battery and the ignition con troller respectively when the annular member has color properties exceeding at least one of a threshold color level and a threshold time period respectively. 2. The system of claim 1, wherein said color determining means comprises: an optical sensor visually cooperating with said annular member, said optical sensor being coupled directly to the vehicle tire and maintaining a direct line of sight with said annular member, said optical sensor generating and transmitting an analog notification signal based upon a color change of said annular member, said analog noti fication signal having a first data stream identifying a location of the vehicle tire and further having a second data stream identifying the color of said annular mem ber. 3. The system of claim 2, wherein said time period deter mining means comprises: a timer circuit electrically coupled to said optical sensor, said timer circuit triggering an internal counter when said first color changes to said second color, said timer circuit generating and transmitting a timing data stream to said optical sensor. 4. A vehicle tire wear notification system for warning a driver of low tread depth on the vehicle tires, said tire wear notification system comprising: an annular member embedded beneath an outer surface of the vehicle tire, said annular member being disposed beneath a tread layer of the vehicle tire such that said annular member is prohibited from being exposed to ambient light when the tread layer has a predetermined minimum thickness, said annular member having photo chromatic properties such that said annular member changes color when exposed to ambient light; wherein said annular member has a single and continuous body extending inside an outer perimeter of the vehicle tire, said annular member being equidistantly spaced from the tread layer and monolithically formed with the vehicle tire; means for determining a color of said annular member, said color determining means being in visual communication with said annular member; means for determining a time period after which said annu lar member has transgressed from a first color to a sec ond color, and a controller housed within a compartment of the vehicle and positioned on a dashboard of the vehicle so that the driver can visually monitor said controller, said control ler comprising means for determining a remaining tread depth on the vehicle tire based upon said first color of said annular member and said time period, said tread depth determining means being spaced from the vehicle tire and electrically coupled to a battery of the vehicle and an ignition controller of the vehicle: US 7,557,694 B wherein said tread depth determining means interrupts power between the vehicle battery and the ignition con troller respectively when the annular member has color properties exceeding at least one of a threshold color level and a threshold time period respectively. 5. The system of claim 4, wherein said color determining means comprises: an optical sensor visually cooperating with said annular member, said optical sensor being coupled directly to the vehicle tire and maintaining a direct line of sight with said annular member, said optical sensor generating and transmitting an analog notification signal based upon a color change of said annular member, said analog noti fication signal having a first data stream identifying a location of the vehicle tire and further having a second data stream identifying the color of said annular mem ber. 6. The system of claim 5, wherein said time period deter mining means comprises: a timer circuit electrically coupled to said optical sensor, said timer circuit triggering an internal counter when said first color changes to said second color, said timer circuit generating and transmitting a timing data stream to said optical sensor. 7. A vehicle tire wear notification system for warning a driver of low tread depth on the vehicle tires, said tire wear notification system comprising: an annular member embedded beneath an outer surface of the vehicle tire, said annular member being disposed beneath a tread layer of the vehicle tire such that said annular member is prohibited from being exposed to ambient light when the tread layer has a predetermined minimum thickness, said annular member having photo chromatic properties such that said annular member changes color when exposed to ambient light; wherein said annular member has a single and continuous body extending inside an outer perimeter of the vehicle tire, said annular member being equidistantly spaced from the tread layer and monolithically formed with the vehicle tire; means for determining a color of said annular member, said color determining means being in visual communication with said annular member, means for determining a time period after which said annu lar member has transgressed from a first color to a sec ond color, a display Screen mounted on the dashboard, said display Screen including a graphical user interface that graphi cally illustrates a location of the vehicle tire as well as a pictorial illustration of said annular member color; and a controller housed within a compartment of the vehicle and positioned on a dashboard of the vehicle so that the driver can visually monitor said controller, said control ler comprising means for determining a remaining tread depth on the vehicle tire based upon said first color of said annular member and said time period, said tread depth determining means being spaced from the vehicle tire and electrically coupled to a battery of the vehicle and an ignition controller of the vehicle: wherein said tread depth determining means interrupts power between the vehicle battery and the ignition con troller respectively when the annular member has color properties exceeding at least one of a threshold color level and a threshold time period respectively.
12 US 7,557,694 B The system of claim 7, wherein said color determining 9. The system of claim 8, wherein said time period deter means comprises: mining means comprises: an optical sensor visually cooperating with said annular member, said optical sensor being coupled directly to a timer circuit electrically coupled to said optical sensor, the vehicle tire and maintaining a direct line of sight with said timer circuit triggering an internal counter when said annular member, said optical sensor generating and said first color changes to said second color, said timer transmitting an analog notification signal based upon a circuit generating and transmitting a timing data stream color change of said annular member, said analog noti to said optical sensor. fication signal having a first data stream identifying a location of the vehicle tire and further having a second 10 data stream identifying the color of said annular mem ber. k....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
(19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
? Ns 54 F2 44. al-f2. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source.
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
Intelligent Hotspot Connection System
 (19) United States US 2010O246486A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0246486A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) INTELLIGENT HOTSPOT CONNECTION SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
(19) United States US 2010O246486A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0246486A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) INTELLIGENT HOTSPOT CONNECTION SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
/1977 schroeder. only a one step exposure process.
 US00569.5218A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,695.218 Nicosia 45 Date of Patent: Dec. 9, 1997 54 GLOW-N-THE-DARK BOOK 4,237,381 12/1980 Schroeder... 250/462 4.266,164 5/1981 Schroeder.. 315/169.1
US00569.5218A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,695.218 Nicosia 45 Date of Patent: Dec. 9, 1997 54 GLOW-N-THE-DARK BOOK 4,237,381 12/1980 Schroeder... 250/462 4.266,164 5/1981 Schroeder.. 315/169.1
(12) United States Patent
 US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0299603A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0299603 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FOG REMOVAL SYSTEM Publication Classification (75) Inventors:.
(19) United States US 2013 0299603A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0299603 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FOG REMOVAL SYSTEM Publication Classification (75) Inventors:.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0010407 A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0010407 A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 9,214,722 B2 Dec. 15, 2015
 I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 20040O83815A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0083815 A1 Lam et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 6, 2004 (54) PIPE FLAW DETECTOR (76) Inventors: Clive Chemo Lam,
(19) United States US 20040O83815A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0083815 A1 Lam et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 6, 2004 (54) PIPE FLAW DETECTOR (76) Inventors: Clive Chemo Lam,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO71481 B2 (12) United States Patent BaltZer () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 5, 2006 (54) HEADREST FOR ALLEVIATING WHIPLASH INURY AND THE USE OF SPECIFIC POLYURETHANE FOAMIS THEREN (76) Inventor:
USOO71481 B2 (12) United States Patent BaltZer () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 5, 2006 (54) HEADREST FOR ALLEVIATING WHIPLASH INURY AND THE USE OF SPECIFIC POLYURETHANE FOAMIS THEREN (76) Inventor:
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007191654B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,654 B2 Dwyer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR ADJUSTING (56) References Cited MAGNETIC RETURN PATH
(12) United States Patent US007191654B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,654 B2 Dwyer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR ADJUSTING (56) References Cited MAGNETIC RETURN PATH
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
(19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008
 US 2008.0017293A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0017293 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) AUTOMATICLEVEL ADJUSTMENT FOR Publication Classification
US 2008.0017293A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0017293 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) AUTOMATICLEVEL ADJUSTMENT FOR Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
(19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
I IIIII IIIII lll (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2. (45) Date of Patent:
 I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7777214B2 (12) United States Patent Shin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,777,214 B2 Aug. 17, 2010 (54) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE WITH A NOVEL ELECTRODE (75) Inventors: Jae-Min Shin,
USOO7777214B2 (12) United States Patent Shin et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,777,214 B2 Aug. 17, 2010 (54) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY DEVICE WITH A NOVEL ELECTRODE (75) Inventors: Jae-Min Shin,
(os) SSO. (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, (12) United States Patent (54) (75) (73)
 (12) United States Patent HOutSma USOO677929OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) SEMI PERMANENT BACKUP IRON SIGHT Inventor:
(12) United States Patent HOutSma USOO677929OB1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,779,290 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 24, 2004 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) SEMI PERMANENT BACKUP IRON SIGHT Inventor:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1
 US00782.5066B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1 Skaggs et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 2010 (54) RAPID FORMALDEHYDE (56) References Cited NEUTRALIZATION USING CHEMICALLY TREATED
US00782.5066B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1 Skaggs et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 2010 (54) RAPID FORMALDEHYDE (56) References Cited NEUTRALIZATION USING CHEMICALLY TREATED
III. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,143,451 (45. Date of Patent: Sep. 1, Millgard
 United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
United States Patent [19]
![United States Patent [19] United States Patent [19]](/thumbs/76/73521136.jpg) United States Patent [19] Murphy 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005479716A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE
United States Patent [19] Murphy 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005479716A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent KWOn USOO6943747B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2005 (54) SMALL AND OMNI-DIRECTIONAL BICONICAL ANTENNA FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS (75) Inventor: Do-Hoon Kwon,
(12) United States Patent KWOn USOO6943747B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2005 (54) SMALL AND OMNI-DIRECTIONAL BICONICAL ANTENNA FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS (75) Inventor: Do-Hoon Kwon,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140238873A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0238873 A1 Li et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 28, 2014 (54) MODIFIED BUBBLING TRANSFER METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. FOR
(19) United States US 20140238873A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0238873 A1 Li et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 28, 2014 (54) MODIFIED BUBBLING TRANSFER METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. FOR
(54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited
 USOO73442B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.3.442 B2 Aug. 7, 2007 (54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited CARBON NANOTUBES U.S. PATENT
USOO73442B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.3.442 B2 Aug. 7, 2007 (54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited CARBON NANOTUBES U.S. PATENT
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9633947B2 (12) United States Patent Jacob (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) FOLDED BALLISTC CONDUCTOR INTERCONNECT LINE Applicant:
USOO9633947B2 (12) United States Patent Jacob (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) FOLDED BALLISTC CONDUCTOR INTERCONNECT LINE Applicant:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2. Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007
 USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,412,650 B1
 USOO641265OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,412,650 B1 Warner (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) END CLOSURE MODULES FOR MULTI- 3,608,767 A * 9/1971 Elliot et al.... 220/4.12 CELL
USOO641265OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,412,650 B1 Warner (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2002 (54) END CLOSURE MODULES FOR MULTI- 3,608,767 A * 9/1971 Elliot et al.... 220/4.12 CELL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170139281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0139281 A1 Hou et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 18, 2017 (54) ALIGNMENT METHOD OF FFS TYPE GO2F I/335 (2006.01)
(19) United States US 20170139281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0139281 A1 Hou et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 18, 2017 (54) ALIGNMENT METHOD OF FFS TYPE GO2F I/335 (2006.01)
- o. ( 12 ) United States Patent. ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 10, 073, 092 B2. ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Sep. 11, Wang
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Wang TOMMUNI DI UNA US010073092B2 MULIAH DAN ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 10, 073, 092 B2 ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Sep. 11, 2018 ( 54 ) APPARATUS FOR ASSAY STRIP ( S ) WITH SPECIMEN
( 12 ) United States Patent Wang TOMMUNI DI UNA US010073092B2 MULIAH DAN ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 10, 073, 092 B2 ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Sep. 11, 2018 ( 54 ) APPARATUS FOR ASSAY STRIP ( S ) WITH SPECIMEN
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 2008.0035140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003514.0 A1 Placer et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SOLAR ROOF TILE (75) Inventors: Neil V. Placer, Frederick,
(19) United States US 2008.0035140A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/003514.0 A1 Placer et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) SOLAR ROOF TILE (75) Inventors: Neil V. Placer, Frederick,
: Y. ti- sk 22N. Sir S. United States Patent (19) Uhri 4,687,061. Aug. 18, Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4 g
 i, a 5 S R 4 g 68 7 6 United States Patent (19) Uhri 8 a g. A 87 OR 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1987 (54. STIMULATION OF EARTH FORMATIONS SURROUNDING A DEVIATED WELLBORE BYSEQUENTIAL
i, a 5 S R 4 g 68 7 6 United States Patent (19) Uhri 8 a g. A 87 OR 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: Aug. 18, 1987 (54. STIMULATION OF EARTH FORMATIONS SURROUNDING A DEVIATED WELLBORE BYSEQUENTIAL
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1
 USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7310217B2 (12) United States Patent Takashima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,310,217 B2 Dec. 18, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CAPACITOR AND MOUNTING STRUCTURE THEREOF (75) Inventors: Hirokazu
USOO7310217B2 (12) United States Patent Takashima et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,310,217 B2 Dec. 18, 2007 (54) MONOLITHIC CAPACITOR AND MOUNTING STRUCTURE THEREOF (75) Inventors: Hirokazu
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kramer et al. USOO661981 OB2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2003 (54) HALLOWEENTREAT CARRIER INCLUDING GLOW-IN-THE-DARK MATERIAL PUMPKIN DECORATING KIT, AND METHOD
(12) United States Patent Kramer et al. USOO661981 OB2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 16, 2003 (54) HALLOWEENTREAT CARRIER INCLUDING GLOW-IN-THE-DARK MATERIAL PUMPKIN DECORATING KIT, AND METHOD
United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al.
 United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al. (54) DEVICE FOR LOCATING AN OBJECT SITUATED CLOSE TO A DETECTION AREA AND A TRANSPARENT KEYBOARD USING SAID DEVICE 75 Inventors: Daniel Gruaz, Montigny le Bretonneux;
United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al. (54) DEVICE FOR LOCATING AN OBJECT SITUATED CLOSE TO A DETECTION AREA AND A TRANSPARENT KEYBOARD USING SAID DEVICE 75 Inventors: Daniel Gruaz, Montigny le Bretonneux;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 2004OOO7357A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0007357 A1 Gabler et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 15, 2004 (54) DRILLING MECHANICS LOAD CELL (22) Filed: Jul.
US 2004OOO7357A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0007357 A1 Gabler et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 15, 2004 (54) DRILLING MECHANICS LOAD CELL (22) Filed: Jul.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0289056A1 Bergman et al. US 20120289056A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) SELECTIVE SILICON NITRDEETCH
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0289056A1 Bergman et al. US 20120289056A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) SELECTIVE SILICON NITRDEETCH
AA. *alt24& DS. (12) United States Patent US 6,607,370 B2. Aug. 19, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: Fukamachi et al.
 (12) United States Patent Fukamachi et al. USOO660737OB2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,607,370 B2 Aug. 19, 2003 (54) MAGNETIC PUMP (75) Inventors: Masatoshi Fukamachi, Wako (JP); Osamu Sato,
(12) United States Patent Fukamachi et al. USOO660737OB2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,607,370 B2 Aug. 19, 2003 (54) MAGNETIC PUMP (75) Inventors: Masatoshi Fukamachi, Wako (JP); Osamu Sato,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O1483O8A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0148308A1 Rush (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 17, 2002 (54) GYROSCOPE BASED PROPULSION APPARATUS (76) Inventor: Alvaro
(19) United States US 2002O1483O8A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0148308A1 Rush (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 17, 2002 (54) GYROSCOPE BASED PROPULSION APPARATUS (76) Inventor: Alvaro
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9033892B2 (12) United States Patent Su et al. (54) PREDICTIVE DROWSINESSALARM METHOD (75) Inventors: Yu Jen Su, Kaohsiung (TW); Yen Hsien Lee, Taoyuan County (TW); Kuang I Chang, Taoyuan County (TW)
USOO9033892B2 (12) United States Patent Su et al. (54) PREDICTIVE DROWSINESSALARM METHOD (75) Inventors: Yu Jen Su, Kaohsiung (TW); Yen Hsien Lee, Taoyuan County (TW); Kuang I Chang, Taoyuan County (TW)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0295736A1 Wang US 20070295736A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2007 (54) WASTEBASKET OR BN HAVING ROCKING SPRINGS AT BOTTOM (75)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0295736A1 Wang US 20070295736A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2007 (54) WASTEBASKET OR BN HAVING ROCKING SPRINGS AT BOTTOM (75)
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Rajic et al. 54 FTIR SPECTROMETER WITH SOLID-STATE DRIVE SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Slobodan Rajic, Knoxville; Roland D. Seals; Charles M. Egert, both of Oak Ridge, all of Tenn. 73
United States Patent (19) Rajic et al. 54 FTIR SPECTROMETER WITH SOLID-STATE DRIVE SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Slobodan Rajic, Knoxville; Roland D. Seals; Charles M. Egert, both of Oak Ridge, all of Tenn. 73
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1
 USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
Si-iö, TH". ()SSS N I. 6-7 Zaf (54) United States Patent (19) Cuff (11 3,968,700. (45) July 13, (21) Appl. No.: 493,748
 United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
) USOO A. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994
 ) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
(ΐ2) United States Patent
 US009627440B2 US009627440B2 (ΐ2) United States Patent Russo et al. (ΐο) Patent No.: (4) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 17 (4) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY APPARATUSES (71) Applicant: Micron Technology, Inc., Boise, ID
US009627440B2 US009627440B2 (ΐ2) United States Patent Russo et al. (ΐο) Patent No.: (4) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 17 (4) PHASE CHANGE MEMORY APPARATUSES (71) Applicant: Micron Technology, Inc., Boise, ID
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1. Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003
 USOO6508132B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1 Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003 (54) DYNAMIC LOAD CELL APPARATUS 4,478,086 A * 10/1984 Gram... 73/781 5,739,411 A
USOO6508132B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1 Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003 (54) DYNAMIC LOAD CELL APPARATUS 4,478,086 A * 10/1984 Gram... 73/781 5,739,411 A
(12) United States Patent
 US007540229B2 (12) United States Patent Seo et al. (54) EXPLOSIVE REACTIVE ARMOR WITH MOMENTUMITRANSFER MECHANISM (75) Inventors: Yongseok Seo, Seongnam (KR): Jeong-Tae Kim, Daejeon (KR); Chang Choi, Daejeon
US007540229B2 (12) United States Patent Seo et al. (54) EXPLOSIVE REACTIVE ARMOR WITH MOMENTUMITRANSFER MECHANISM (75) Inventors: Yongseok Seo, Seongnam (KR): Jeong-Tae Kim, Daejeon (KR); Chang Choi, Daejeon
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O107994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0107994 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) BIOSENSOR Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 2015O107994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0107994 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) BIOSENSOR Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,604,442 B2
 USOO7604442B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,604,442 B2 Motta et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) MULTI-AXIS MACHINE TOOL (58) Field of Classification Search... 409/202, 409/212,
USOO7604442B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,604,442 B2 Motta et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 20, 2009 (54) MULTI-AXIS MACHINE TOOL (58) Field of Classification Search... 409/202, 409/212,
7" - seees / s (N 255 (N. Cases a1. C=s. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. es N? (19) United States.
 (19) United States US 20030085296A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0085296A1 Waxmanski (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2003 (54) HURRICANE AND TORNADO CONTROL DEVICE (76) Inventor: Andrew
(19) United States US 20030085296A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0085296A1 Waxmanski (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2003 (54) HURRICANE AND TORNADO CONTROL DEVICE (76) Inventor: Andrew
III M
 III1 11111111111111111111111111M 1 1 ))1111111 1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (lo) Pub. No.: US 2013/0343503 Al AGACE et al. ( 4 3 ) Pub. Date: D e c. 26, 2013 (54) SNAP-IN INSERT
III1 11111111111111111111111111M 1 1 ))1111111 1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (lo) Pub. No.: US 2013/0343503 Al AGACE et al. ( 4 3 ) Pub. Date: D e c. 26, 2013 (54) SNAP-IN INSERT
Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016
 (12) United States Patent USOO9453899B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.453,899 B2 Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016 (54) SYSTEM FOR EFFECTING THE (52) U.S. Cl. ROTATIONAL MOVEMENT OF A SOLAR CPC... G0IS
(12) United States Patent USOO9453899B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.453,899 B2 Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016 (54) SYSTEM FOR EFFECTING THE (52) U.S. Cl. ROTATIONAL MOVEMENT OF A SOLAR CPC... G0IS
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,882,745 B2
 USOO6882745B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Brankner et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS TRANSLATING DETECTED WAFER DEFECT COORDINATES
USOO6882745B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Brankner et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS TRANSLATING DETECTED WAFER DEFECT COORDINATES
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Fremery et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 1986 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR GAS PRESSURE MEASUREMENT BY THE GAS-FRCTION PRINCIPLE (75) Inventors: Johan
United States Patent (19) Fremery et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 1986 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR GAS PRESSURE MEASUREMENT BY THE GAS-FRCTION PRINCIPLE (75) Inventors: Johan
(54) (75) (73) (Us) (21) (22) (63) 1, 2007, provisional application No. 60/997,142,?led
 US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0106045 A1 Hata US 2002O106045A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2002 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR IDENTIFYING OBJECT BY USE OF DECAY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0106045 A1 Hata US 2002O106045A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2002 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR IDENTIFYING OBJECT BY USE OF DECAY
(12) United States Patent
 USOO868.4738B2 (12) United States Patent Wade (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 1, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) METHOD AND TOOL FOR FIREARM SIGHT TRAINING Inventor: Christian
USOO868.4738B2 (12) United States Patent Wade (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 1, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) METHOD AND TOOL FOR FIREARM SIGHT TRAINING Inventor: Christian
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,763,928 B2
 USOO7763928B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) MULTI-TIME PROGRAMMABLE MEMORY (58) Field of Classification Search... 257/314321, 257/E29.129,
USOO7763928B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lin et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 27, 2010 (54) MULTI-TIME PROGRAMMABLE MEMORY (58) Field of Classification Search... 257/314321, 257/E29.129,
100-N. (12) United States Patent N 2 Q US 7,234,334 B1. Jun. 26, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.: SZZ
 USOO7234,334B1 (12) United States Patent Pfabe (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,234,334 B1 Jun. 26, 2007 (54) SADDLE FOR BACKING ASSEMBLIES IN A ROLLING MILL (75) Inventor: Dennis P. Pfabe, Canton,
USOO7234,334B1 (12) United States Patent Pfabe (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,234,334 B1 Jun. 26, 2007 (54) SADDLE FOR BACKING ASSEMBLIES IN A ROLLING MILL (75) Inventor: Dennis P. Pfabe, Canton,
FIG.1. Form organic light emitting. Coat the encapsulation. encapsulation substrate. Prepare an. Prepare a substrate
 (19) United States US 2011 0057172A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0057172 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FILLER FOR SEALING ORGANIC LIGHT EMMITING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR
(19) United States US 2011 0057172A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0057172 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FILLER FOR SEALING ORGANIC LIGHT EMMITING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,167,752 B1. Raffer (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2001
 USOO6167752B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Raffer (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2001 (54) ROTARY VISCOMETER WITH AN AIR (56) References Cited BEARING N U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
USOO6167752B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Raffer (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2001 (54) ROTARY VISCOMETER WITH AN AIR (56) References Cited BEARING N U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
43&SS756) A. as S-AL.S /2. 7r A WINS Šs SC is U%.S. a 2 Y3 ( Aug. 1, 1967 J. C. VRANA 3,333,762 ATTORNEY JOHN C. WRANA O4.0.44,- INVEVTOR.
 Aug. 1, 1967 J. C. VRANA DIFFUSER FOR CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR Filed Nov. l6, l966 2. Sheets-Sheet li s A. as S-AL.S /2 7r A WINS Šs SC is U%.S. 43&SS76) - /27 Y a 2 Y3 ( C2CCCXCAVAXAS BY INVEVTOR. JOHN
Aug. 1, 1967 J. C. VRANA DIFFUSER FOR CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR Filed Nov. l6, l966 2. Sheets-Sheet li s A. as S-AL.S /2 7r A WINS Šs SC is U%.S. 43&SS76) - /27 Y a 2 Y3 ( C2CCCXCAVAXAS BY INVEVTOR. JOHN
Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions 7-6-2004 Lee Chow University of Central Florida Elvira Anoshkina University of Central
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Electrochemical Deposition of Carbon Nanotubes from Organic Solutions 7-6-2004 Lee Chow University of Central Florida Elvira Anoshkina University of Central
Writing Patent Specifications
 Writing Patent Specifications Japan Patent Office Asia-Pacific Industrial Property Center, JIPII 2013 Collaborator: Shoji HADATE, Patent Attorney, Intellectual Property Office NEXPAT CONTENTS Page 1. Patent
Writing Patent Specifications Japan Patent Office Asia-Pacific Industrial Property Center, JIPII 2013 Collaborator: Shoji HADATE, Patent Attorney, Intellectual Property Office NEXPAT CONTENTS Page 1. Patent
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O187665A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0187665 A1 Fu (43) Pub. Date: (54) AUTOMATIC YARD MOSTURE CONTROL Publication Classification SYSTEM (51) Int.
(19) United States US 2005O187665A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0187665 A1 Fu (43) Pub. Date: (54) AUTOMATIC YARD MOSTURE CONTROL Publication Classification SYSTEM (51) Int.
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,624,640 B2
 USOO662464OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lund et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2003 (54) CAPACITANCE MEASUREMENT 5,073,757 A * 12/1991 George... 324/677 (75) I nventors: t John Jonn
USOO662464OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lund et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2003 (54) CAPACITANCE MEASUREMENT 5,073,757 A * 12/1991 George... 324/677 (75) I nventors: t John Jonn
(19) Scott H. Stillinger, Los Gatos, Calif. Oddz0n Products, Campbell, Calif. 60,640 Jun. 11, 1987 Int. Cl'... A63B 37/14
 United States Patent Stillinger 54 (75) (73) 21 22 51 (52) (58 (56) (19) GENERALLY SPHERICAL OBJECT WITH FLOPPY FILAMENTS TO PROMOTE SURE CAPTURE Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed: Scott H. Stillinger,
United States Patent Stillinger 54 (75) (73) 21 22 51 (52) (58 (56) (19) GENERALLY SPHERICAL OBJECT WITH FLOPPY FILAMENTS TO PROMOTE SURE CAPTURE Inventor: Assignee: Appl. No.: Filed: Scott H. Stillinger,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O137474A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0137474 A1 Kontiola (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) METHOD FOR MEASURING INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE (76) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2005O137474A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0137474 A1 Kontiola (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) METHOD FOR MEASURING INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0164247 A1 Riehle et al. US 2004O164247A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 26, 2004 (54) (76) (21) (22) (30) PROCESS FOR MONITORING AND
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0164247 A1 Riehle et al. US 2004O164247A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 26, 2004 (54) (76) (21) (22) (30) PROCESS FOR MONITORING AND
in. ION SOURCE \, N. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1 (19) United States 1 N 4
 (19) United States US 20060219890A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0219890 A1 Yamaguchi (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 5, 2006 (54) TIME OF FLIGHT MASS SPECTROMETER (75) Inventor: Shinichi
(19) United States US 20060219890A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0219890 A1 Yamaguchi (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 5, 2006 (54) TIME OF FLIGHT MASS SPECTROMETER (75) Inventor: Shinichi
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016.0078974A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0078974A1 Jones (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2016 (54) XRF ANALYZER ROTATIONAL FILTER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G2IK
US 2016.0078974A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0078974A1 Jones (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 17, 2016 (54) XRF ANALYZER ROTATIONAL FILTER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... G2IK
TEPZZ A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H02M 7/483 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 7849 6A T (11) EP 2 784 926 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01..14 Bulletin 14/40 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 7/483 (07.01) (21) Application number: 14162389.2 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 7849 6A T (11) EP 2 784 926 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01..14 Bulletin 14/40 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 7/483 (07.01) (21) Application number: 14162389.2 (22) Date
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Ingles, JR. et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 OPTICAL FIBER (57) ABSTRACT
 (19) United States US 2004O150811A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150811 A1 Ingles, JR. et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 2004O150811A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150811 A1 Ingles, JR. et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.475,006 B2
 USOO8475006B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.475,006 B2 Ben-EZer (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2013 (54) DARK FIELD ILLUMINATOR AND A DARK (52) U.S. Cl. FIELD LLUMINATION METHOD USPC...
USOO8475006B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.475,006 B2 Ben-EZer (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 2, 2013 (54) DARK FIELD ILLUMINATOR AND A DARK (52) U.S. Cl. FIELD LLUMINATION METHOD USPC...
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,519 B1
 USOO6462519 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,519 B1 McDaniel et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) AUTOMATIC POWER FACTOR 4,771,225. A 9/1988 Nishikawa... 323/211 CORRECTION
USOO6462519 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,462,519 B1 McDaniel et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) AUTOMATIC POWER FACTOR 4,771,225. A 9/1988 Nishikawa... 323/211 CORRECTION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 200402369A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/023.6009 A1 Mafoti et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LW DENSITY ADHESIVES AND SEALANTS Publication Classification
US 200402369A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/023.6009 A1 Mafoti et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LW DENSITY ADHESIVES AND SEALANTS Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Young USOO6419519 B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 16, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) STRIN RELEF FOR ELECTRICL CONNECTORS Inventor: SSignee:
(12) United States Patent Young USOO6419519 B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 16, 2002 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (51) (52) (58) (56) STRIN RELEF FOR ELECTRICL CONNECTORS Inventor: SSignee:
s 1OO (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1 (19) United States WORKSTATION
 (19) United States US 20090267938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0267938A1 Nicol, II et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2009 (54) THREE-DIMENSIONAL (3D) VIRTUAL WORLD S (76)
(19) United States US 20090267938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0267938A1 Nicol, II et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2009 (54) THREE-DIMENSIONAL (3D) VIRTUAL WORLD S (76)
refore z 19, COMAU7AR f7 Sg 26 Sept. 2, 1969 H. SCHMOT 3,464,770 Horst Schmidt LASER TRANSM/TTER AT TORNEYS NVENTOR
 Sept. 2, 1969 H. SCHMOT COMBINED SIGHTING MECHANISM AND LASER RANGE FINDER Filed Oct. 21, 1965 2 Sheets-Sheet l LASER TRANSM/TTER 19, f7 Sg 26 COMAU7AR ------- V. 7 29 8 NVENTOR Horst Schmidt refore z
Sept. 2, 1969 H. SCHMOT COMBINED SIGHTING MECHANISM AND LASER RANGE FINDER Filed Oct. 21, 1965 2 Sheets-Sheet l LASER TRANSM/TTER 19, f7 Sg 26 COMAU7AR ------- V. 7 29 8 NVENTOR Horst Schmidt refore z
\ 108. (12) United States Patent US 9,502,356 B1. Nov. 22, (45) Date of Patent: NACSSZZNS 27 SCSS ASNZSZCN) 106. (10) Patent No.: 4.
 USOO9502356B1 (12) United States Patent Parvarandeh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 22, 2016 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD WITH PHYSICAL UNCLONABLE FUNCTION (71) Applicant: Maxim Integrated Products,
USOO9502356B1 (12) United States Patent Parvarandeh (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 22, 2016 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD WITH PHYSICAL UNCLONABLE FUNCTION (71) Applicant: Maxim Integrated Products,
(51) Int. Cl... D06F tank. The liquid level detector includes a first resistance
 US00605O112A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Walker (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2000 54). APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,798,698 8/1998 Politt et al.... 73/291 DETECTING ALIQUID LEVEL IN A SEALED
US00605O112A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Walker (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2000 54). APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,798,698 8/1998 Politt et al.... 73/291 DETECTING ALIQUID LEVEL IN A SEALED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0180261 A1 Beattie et al. US 2011 0180261A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (76) (21) (22) (86) (60) METHOD OF REMOVING CUTTERS Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0180261 A1 Beattie et al. US 2011 0180261A1 (43) Pub. Date: (54) (76) (21) (22) (86) (60) METHOD OF REMOVING CUTTERS Inventors:
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,517,600 B2. Wan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 27, 2013
 US008517600B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,517,600 B2 Wan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 27, 2013 (54) DEPOSITION SENSORBASED ON 4.595,297 A 6/1986 Liu et al. DIFFERENTAL, HEAT TRANSFER
US008517600B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,517,600 B2 Wan et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 27, 2013 (54) DEPOSITION SENSORBASED ON 4.595,297 A 6/1986 Liu et al. DIFFERENTAL, HEAT TRANSFER
Apparatus and Method for the Electrolysis of Water Employing a Sulfonated Solid Polymer Electrolyte
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Apparatus and Method for the Electrolysis of Water Employing a Sulfonated Solid Polymer Electrolyte 12-21-1993 Clovis Linkous University of Central Florida
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent Apparatus and Method for the Electrolysis of Water Employing a Sulfonated Solid Polymer Electrolyte 12-21-1993 Clovis Linkous University of Central Florida
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,473,187 B1. Manalis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2002
 USOO64731.87B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,473,187 B1 Manalis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2002 (54) HIGH-SENSITIVITY INTERFEROMETRIC Manalis, et al., Interdigital cantilevers for
USOO64731.87B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,473,187 B1 Manalis (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 29, 2002 (54) HIGH-SENSITIVITY INTERFEROMETRIC Manalis, et al., Interdigital cantilevers for
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0158290 A1 MARE-ROSE et al. US 2013 O158290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PRODUCTION OF OXYGENATED
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0158290 A1 MARE-ROSE et al. US 2013 O158290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PRODUCTION OF OXYGENATED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 2009.0160019A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0160019 A1 Yang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 25, 2009 (54) SEMICODUCTOR CAPACITOR Publication Classification (51)
(19) United States US 2009.0160019A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0160019 A1 Yang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 25, 2009 (54) SEMICODUCTOR CAPACITOR Publication Classification (51)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O223645A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0223645 A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2003 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR IMAGE (22) Filed: Mar. 31,
US 2003O223645A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0223645 A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2003 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR IMAGE (22) Filed: Mar. 31,
RIf i1p
 (19) United States 1111111111111111111111010111111RIf i1p01211111601111111111111111111111111111111111 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0255645 Al Zawodny (43) Pub. Date: Oct.
(19) United States 1111111111111111111111010111111RIf i1p01211111601111111111111111111111111111111111 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0255645 Al Zawodny (43) Pub. Date: Oct.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080249323A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0249323 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2008 (54) SORBITOL CONVERSION PROCESS Publication Classification
US 20080249323A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0249323 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2008 (54) SORBITOL CONVERSION PROCESS Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7487686B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7487,686 B2 Feb. 10, 2009 (54) HIGH-PRECISION VORTEX FLOW METER (75) Inventors: An-Bang Wang, Taipei (TW); Ming-Hsun
USOO7487686B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7487,686 B2 Feb. 10, 2009 (54) HIGH-PRECISION VORTEX FLOW METER (75) Inventors: An-Bang Wang, Taipei (TW); Ming-Hsun
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Rodov 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OF ZENER DODES (75 Inventor: Vladimir Rodov, Los Angeles, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) Rodov 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OF ZENER DODES (75 Inventor: Vladimir Rodov, Los Angeles, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. 21 Appl.
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO8680698B1 (10) Patent No.: Lai et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 25, 2014 (54) SELF-CONTAINED MECHANISM FOR THE (56) References Cited CONVERSION OF VERTICAL MOTION TO ROTATIONAL/TRANSLATIONAL
(12) United States Patent USOO8680698B1 (10) Patent No.: Lai et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 25, 2014 (54) SELF-CONTAINED MECHANISM FOR THE (56) References Cited CONVERSION OF VERTICAL MOTION TO ROTATIONAL/TRANSLATIONAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013
 US 2013 OOO1573A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0001573 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013 (54) THIN FILM TRANSISTOR AND METHOD OF Publication Classification
US 2013 OOO1573A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0001573 A1 LEE et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 3, 2013 (54) THIN FILM TRANSISTOR AND METHOD OF Publication Classification
III. United States Patent (19) Hyman, Jr. et al. 5,572,314 Nov. 5, Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Cambridge, Mass ; Cornelius S.
 United States Patent (19) Hyman, Jr. et al. 54 BREWSTER ANGLE REFRACTOMETER (76 Inventors: Mark Hyman, Jr., 1010 Memorial Dr., Cambridge, Mass. 02138; Cornelius S. Hurlbut, 1010 Waltham St., Lexington,
United States Patent (19) Hyman, Jr. et al. 54 BREWSTER ANGLE REFRACTOMETER (76 Inventors: Mark Hyman, Jr., 1010 Memorial Dr., Cambridge, Mass. 02138; Cornelius S. Hurlbut, 1010 Waltham St., Lexington,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,064,634 B2
 USOO9064634B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,064,634 B2 Nakamura (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 23, 2015 (54) CAPACITOR HOLDER (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Tatsuya Nakamura, Nagoya
USOO9064634B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,064,634 B2 Nakamura (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 23, 2015 (54) CAPACITOR HOLDER (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Tatsuya Nakamura, Nagoya
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015 0001700A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0001700 A1 Hartung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 1, 2015 (54) POWER MODULES WITH PARYLENE (52) U.S. Cl. COATING
(19) United States US 2015 0001700A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0001700 A1 Hartung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 1, 2015 (54) POWER MODULES WITH PARYLENE (52) U.S. Cl. COATING
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,692,397 B1
 USOO8692397 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lai et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2014 (54) MECHANISM FOR THE CONVERSION OF (58) Field of Classification Search VERTICAL MOTION TO TRANSLATIONAL
USOO8692397 B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lai et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 8, 2014 (54) MECHANISM FOR THE CONVERSION OF (58) Field of Classification Search VERTICAL MOTION TO TRANSLATIONAL
