(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
|
|
|
- Louise Bryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1 Riehle et al. US 2004O164247A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 26, 2004 (54) (76) (21) (22) (30) PROCESS FOR MONITORING AND CONTROLLING NITRATING PROCESSES WITH THE AD OF AN ONLINE SPECTROMETER Inventors: Claus Riehle, Odenthal (DE); Marcus Brand, Dormagen (DE); Frank Hilgers, Dormagen (DE); Klaus Jager, Leverkusen (DE); Rainer Giesen, Krefeld (DE); Heinz-Josef Hamacher, Bedburg (DE); Udo Wolf, Kempen (DE) Correspondence Address: BAYER POLYMERS LLC 100 BAYER ROAD PITTSBURGH, PA (US) Appl. No.: 10/769,997 Filed: Feb. 2, 2004 Foreign Application Priority Data Feb. 5, 2003 (DE) Publication Classification (51) Int. Cl."... G01N 21/35 (52) U.S. Cl / (57) ABSTRACT A process for monitoring and/or controlling a nitrating process, having the following Steps: measuring inline infrared spectra of nitric acid content in a reaction mixture Stream downstream of the nitration reaction, preferably near-infrared Spectra, evaluating the measured spectra by means of a com puter-assisted, matrix-specific calibration model for the purpose of determining the content of nitric acid, transmitting the results of Spectrometric examination to a process control System, inputting the results of spectrometric examination for the purpose of Specifying the content of nitric acid in the acid phase into a regulator (224) for control of the metering (207, 217) of nitric acid into a nitrating reactor
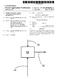
2 Patent Application Publication Aug. 26, 2004 Sheet 1 of 5 US 2004/ A1 Fig
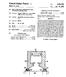
3 Patent Application Publication Aug. 26, 2004 Sheet 2 of 5 US 2004/ A1 s s s S. s S. CN L s s S
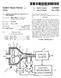
4 Patent Application Publication Aug. 26, 2004 Sheet 3 of 5 US 2004/ A1 (1-u10) CONH+ (%1) GL G OOGG OOOG
5 Patent Application Publication Aug. 26, 2004 Sheet 4 of 5 US 2004/ A1 Fig
6 Patent Application Publication Aug. 26, 2004 Sheet 5 of 5 Fig. 5 US 2004/ A1 500
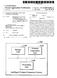
7 US 2004/ A1 Aug. 26, 2004 PROCESS FOR MONITORING AND CONTROLLING NITRATING PROCESSES WITH THE AD OF AN ONLINE SPECTROMETER BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION The present invention relates to a process for monitoring and for controlling a nitrating process, in par ticular for the nitration of toluene, with the aid of a com puter-assisted, matrix-specific calibration model and a pro cess model Various nitration processes are known in the prior art. For example, toluene is nitrated with nitric acid to yield nitrotoluidines by way of intermediate dye products. It is also known to nitrate toluene with mixed acids to yield nitrotoluene and dinitrotoluene. Dinitrotoluene is, for example, processed further to yield diamines, diisocyanates, trinitrotoluene or phloroglucinol For economic reasons, the aim in the course of nitration is to conduct the nitration with as Small an excess of acid as possible. To this end, it is known from the state of the art to take Samples from the process manually and to examine them analytically in the laboratory. The process is then readjusted manually when required One disadvantage of such manual sampling and adjustment is the high cost of labor for the Sampling and for the laboratory analysis. Another disadvantage is that the effort increases linearly with the number of measuring points. Furthermore, manual Sampling is problematic from the point of View of industrial Safety, Since, particularly in the case of 2-nitrotoluene, it is a question of working with a Substance that is detrimental to health. Therefore in the course of handling 2-nitrotoluene, the wearing of respiratory protection at all times as a precaution is prescribed Another disadvantage of manual sampling with Subsequent laboratory analysis is the fact that readjustment of the process can only be effected irregularly and after relatively long time-intervals. This may result in use of a relatively large excess of acid; the plant cannot then be operated in optimal manner, either technically or economi cally. SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION 0006 An object of the present invention is therefore to create an improved process for monitoring and controlling nitrating processes that enables a diminution of the excess of acid. Further objects underlying the invention are to create an online method of measurement with a computer-assisted process model and to create an appropriate production process for the nitration The objects of the present invention are achieved by online spectrometric measurement of the acid phase from the reaction mixture and transmission of that data to a process control System. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS 0008 FIG. 1 is a flow chart for the process of the present invention for improved monitoring and control of nitrating processes by virtue of the online measurement of the acid phase and the improved metering of nitric acid FIG. 2 is a block diagram of a two-stage nitration process according to the invention FIG. 3 shows various NIR spectra for various concentrations of nitric acid FIG. 4 is a flow chart for the process of creating the matrix-specific calibration model, the validation and enhancement thereof FIG. 5 is a schematic representation of a bypass with a measuring cell. DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION 0013 In accordance with the present invention, the acid phase recovered from the nitration reaction mixture is spec trometrically examined online. This is preferably done by infrared spectrometry. Such measurements are also desig nated as infrared spectroscopy. Appropriate IR spectrom eters, in particular for the near-infrared range (NIR) are commercially available, for example from Polytec GmbH and other manufacturers In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the content of nitric acid in the acid phase is determined online after nitration by means of an NIR spectrometer and a Suitable computer-assisted calibration model. Data for quan tifying the content of nitric acid are then transmitted from the NIR spectrometer to the process control system, for example via a field bus. On the basis of the nitric-acid content in the acid phase that is determined after nitration, regulation by the process control System for the Supply of nitric acid is possible. The online control of a production plant for the purpose of regulating various polymerization parameters is disclosed in U.S. Pat. No. 5,121,337 and EP B1 (sic). In these disclosed processes, a predictive model created on the basis of measured spectra is used In a particularly preferred embodiment of the invention, the measured NIR spectrum is evaluated with the aid of a matrix-specific calibration model. The physical matrix is predetermined by the nitrating process and is dependent on the parameters of the process. With the aid of chemometric methods, the measured spectra are referenced against results obtained from laboratory examinations This is effected in Such a way that the same sample for which an NIR spectrum was determined online is also analyzed in the laboratory with the aid of titration measure ments. By virtue of the examination and the comparison of a Suitable number of varying Samples, it is possible to create a matrix-specific calibration model with the aid of chemom etry. This matrix-specific calibration model is Stored on a computer that is programmed to control the recording of the Spectrum and to evaluate the measured spectrum online with the aid of the calibration model, so that the nitric acid content is available to the process control System online The nitration of toluene to yield dinitrotoluene (DNT) is generally conducted in two stages. The spectro metric examination of the acid phase is undertaken at least after the Second nitrating Stage, in order to readjust the Supply of nitric acid to the first and/or the Second nitrating Stage In another preferred embodiment of the invention, the NIR spectrometer is connected to Several measuring
8 US 2004/ A1 Aug. 26, 2004 points. The NIR spectrometer is multiplexed, in order to carry out spectrometric measurements in Succession at the various measuring-points. By reason of this multiplex opera tion of the NIR spectrometer, the measurement effort increases degressively with the number of measuring-points The invention is particularly advantageous because it enables distinctly improved process control. In particular, the invention enables the production plant to be operated continuously, close to the technical and economic optimum. Another advantage is the improvement in industrial Safety Preferred embodiments of the invention will be elucidated in greater detail below with reference to the drawings FIG. 1 is a flow chart for a process according to the invention for monitoring and controlling nitrating processes. In step 100, nitric acid (HNO) is supplied continuously to a nitrating Stage. The product of the nitrating Stage is a two-phase System composed of nitrated organic phase and acid phase. An NIR spectrum of the acid phase is recorded by means of a Suitable measuring cell and an NIR spec trometer. This is undertaken in step 102. In step 104, the HNO, content in the acid phase is determined by evaluation of the NIR spectrum by means of a matrix-specific calibra tion model. This measurement is preferably undertaken inline or online, i.e. in the current product Stream In step 106, the HNO content that has been ascer tained is transmitted to a process control System. In Step 108, the quantity of continuously Supplied HNO is readjusted manually or by the process control System, in order to reduce the HNO content in the acid phase if necessary FIG. 2 is a block diagram of an embodiment of an appropriate plant. The plant has a reactor 200 for the purpose of realizing a first nitrating stage (mononitration MNT). The feed materials are toluene 201, Sulfuric acid 202 and nitric acid 203. The product of the first nitrating stage is a two-phase System which is Separated, in the Separator 208 connected downstream, into the organic phase 211 and the acid phase A measuring-point 205 for recording an NIR spec trum of the acid phase may be provided downstream of the reactor 200. To this end, an NIR spectrometer 220 may be connected to the measuring-point 205 via an optical waveguide The separator 208 is followed by a further reactor 210 for the purpose of realizing the Second nitrating Stage (dinitration DNT). The feed materials are MNT 211, sulfuric acid 212 and nitric acid 213. The product of the second nitrating Stage is a two-phase System which is Separated, in the Separator 218 connected downstream, into the organic phase 230 and the acid phase A measuring-point 215 is preferably arranged downstream of the output of the reactor 210. The NIR Spectrometer 220 is connected to the measuring-point 215 via an optical waveguide 216. As a result, NIR spectra for the acid phase can be recorded The measuring-points 205 and 215 may each be operated with their own spectrometer; however, they are preferably operated with a single spectrometer 220 which Switches between the measuring-points 205 and The NIR spectrometer 220 passes on the measured NR spectra for evaluation by means of the matrix-specific computer-assisted calibration model 222. The computer with the matrix-specific calibration model 222 passes on its results for the content of nitric acid to the process control System 224. The Subsequent regulation (manual or auto mated) of the metering 207 or 217 of the first 200 and/or the Second 210 nitrating Stage, respectively, permits improved monitoring of the process and improved process control for the content of HNO in the acid phase within the range 0-5%, in particular close to 0%, preferably within the range from 0% to 0.3% In a preferred embodiment of the invention, the HNO, content is determined only at measuring-point 215 and not at measuring-point 205. The measurement of the HNO, content at measuring-point 215 after the second nitrat ing Stage is generally Sufficient for regulation of the pro duction of dinitrotoluene In the case where production of dinitrotoluene is undertaken in multiple lines, Several parallel measuring points 215 may be provided. All the measuring-points 215 are then preferably connected to the same NIR spectrometer 220, which operates in multiplex mode. The NIR spectrom eter 220 accordingly measures the Spectra at the measuring points 215 in Succession, in cyclic Sequence. By virtue of the multiplexing of the NIR spectrometer 220, it is possible for the instrumentation effort for implementation of the HNO measurements to be optimized FIG. 3 shows the spectra 300,302 and 304. Spec trum 300 has been recorded for 75% sulfuric acid without nitric-acid content. Spectrum 302 has been recorded for 75% sulfuric acid with 1% nitric-acid content. Spectrum 304 has been recorded for 75% sulfuric acid with 5% nitric-acid COntent. 0032) The measured NIR spectra 300, 302 and 304 accordingly differ distinctly, depending on the percentage content of nitric acid in the acid phase. In corresponding manner it is possible for the nitric-acid content in the acid phase to be determined by measurement of the NIR spec trum. To this end, a matrix-specific calibration model based on comparative titration measurements is preferably used FIG. 4 illustrates the procedure for obtaining a database for the generation of a matrix-specific calibration model. Step 400 illustrates the creation of such a calibration model; step 420 illustrates the validation of this model Step 402 represents the physical matrix, which is process-specific and dependent on the process parameters with regard to its Special composition The nitric-acid content, which is ascertained by means of manual Sampling 406 with Subsequent titration 408, is used for creation of the calibration model. Sampling and titration may also be undertaken in automated manner and online, or manually and offline. In parallel, a measuring cell, with which the NIR spectra pertaining to the Samples can be recorded, is installed in the process flow. This is undertaken in step ). In step 410, the results from the titration determi nations are compared and are correlated with the respective NIR spectra with the aid of chemometric methods.
9 US 2004/ A1 Aug. 26, In step 412, all of the comparisons between all of the NIR spectra and all of the titration results are combined and are correlated in a model. The parameters of the model are adapted and adjusted in Such a way that the content of nitric acid for the existing Substance System and the existing process parameters are reproduced optimally. Once the model has been adapted and optimized, the matrix-specific calibration model is available at the end of step Subsequently, in step 420, validation of the model is undertaken in respect of the current process. Whenever titration results are available in a manner temporally appro priate to the Spectra arising from the process, Said results can be integrated in accordance with step 400 for the purpose of Successive enhancement of the model (Step 422) FIG. 5 shows an embodiment of the invention with a measuring-point (for example, measuring-point 215 of FIG. 2). The product stream of the current production flows through the line 500. Abypass 502 is located on the line 500. The bypass 502 has a measuring cell 504. Located upstream and downstream of the measuring cell 504 in the direction of flow is a shut-off device 506 and 508, respectively. The shut-off devices enable access to the measuring cell while the product Stream is running List of Reference Symbols 0041 reactor toluene sulfuric acid ) nitric acid measuring-point ) optical waveguide regulation of metering separator acid phase reactor mononitrotoluene (MNT) sulfuric acid ) nitric acid measuring-point optical waveguide regulation of metering separator acid phase ) 0060) ) 0063) ) NIR spectrometer 220 calibration model 222 process control System 224 organic phase 230 spectrum 300 spectrum 302 spectrum 304 line bypass measuring cell shut-off device shut-off device Although the invention has been described in detail in the foregoing for the purpose of illustration, it is to be understood that Such detail is Solely for that purpose and that variations can be made therein by those skilled in the art without departing from the Spirit and Scope of the invention except as it may be limited by the claims. What is claimed is: 1. A process for monitoring and/or controlling at least one nitrating process comprising: a) measuring spectrometrically and online composition of an acid phase of a nitration reaction mixture, b) relaying data from a) to a process control System in order to monitor and to control the production process. 2. The process of claim 1 in which an infrared spectrom eter is used in a). 3. The process of claim 1 in which a near infrared spectrometer is used in a). 4. The process of claim 1 in which a measuring cell for spectrometric measurement in a) is located in a by-pass. 5. The process of claim 1 in which the data are based on the spectrometric online measurement and evaluation with a matrix-specific calibration model. 6. The process of claim 5 in which a spectrum obtained by online measurement is evaluated with a matrix-specific calibration model based on comparative titration measure ments. 7. The process of claims 1 to 6 in which a first supply of nitric acid for mononitration and a Second Supply of nitric acid for dinitration is monitored and/or controlled after Spectrometric examination after mononitration and/or after dinitration. 8. The process of claims 1 to 6 in which an infrared Spectrometer is connected to Several measuring-points and is operated in multiplex mode in a) one or Several nitration units. 9. The process of claim 8 in which the infrared spectrom eter is a near infrared spectrometer. 10. A product capable of automatically implementing the Steps of a) evaluating data obtained by a spectrometric examina tion of an acid phase after a nitration to determine the content of nitric acid in the acid phase, and b) relaying the nitric-acid content data from a) to a regulator to control metering of nitric acid to a nitration reaction mixture. 11. The product of claim 8 having a matrix-specific calibration model for evaluating the nitric acid content data from a). 12. The product of claim 10 which is designed for automated regulation of the nitrating process. 13. A facility for monitoring and/or controlling a nitrating process comprising: a) means for spectrometric examination of an acid phase after a nitration, and
10 US 2004/ A1 Aug. 26, 2004 b) regulating means for metering nitric acid into at least one nitrating reactor, the regulating means being designed to regulate metering of nitric acid on the basis of the Spectrometric examination. 14. The facility of claim 13 in which the means for Spectrometric examination comprises an infrared spectrom eter. 15. The facility of claim 13 in which the means for Spectrometric examination comprises a near infrared Spec trometer. 16. The facility of claims 13 to 15 having a bypass downstream from at least one nitrating reactor with a measuring cell for the Spectrometric examination located in the bypass. 17. The facility of claims 13 to 16 having means for measuring a spectrum and means for evaluating the mea Surement with a matrix-specific calibration model based on comparative titration measurements. 18. The facility of claims 13 to 17 in which the means for Spectrometric measurement comprises an infrared spectrom eter with electronic evaluating unit, and the infrared Spec trometer is connected to Several measuring-points for Spec trometric examination of the acid phase after a nitration, and the infrared spectrometer is designed for multiplex opera tion. 19. The facility of claims 13 to 18 having a process control System for the regulating means and a connection of the means for spectrometric examination to the process control System.
in. ION SOURCE \, N. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/ A1 (19) United States 1 N 4
 (19) United States US 20060219890A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0219890 A1 Yamaguchi (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 5, 2006 (54) TIME OF FLIGHT MASS SPECTROMETER (75) Inventor: Shinichi
(19) United States US 20060219890A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0219890 A1 Yamaguchi (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 5, 2006 (54) TIME OF FLIGHT MASS SPECTROMETER (75) Inventor: Shinichi
ZZZZZZZZZZYZZZZZZZZZZZZZz6
 USOO5898752A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Van Der Wal (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 1999 54) X-RAY ANALYSIS APPARATUS PROVIDED Primary Examiner-Craig E. Church WITH A DOUBLE COLLIMATOR MASK
USOO5898752A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Van Der Wal (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 27, 1999 54) X-RAY ANALYSIS APPARATUS PROVIDED Primary Examiner-Craig E. Church WITH A DOUBLE COLLIMATOR MASK
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/ A1
 US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0010407 A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2001 OO10407A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2001/0010407 A1 Ker et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LOW-CAPACITANCE BONDING PAD FOR (30) Foreign Application Priority
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 20170139281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0139281 A1 Hou et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 18, 2017 (54) ALIGNMENT METHOD OF FFS TYPE GO2F I/335 (2006.01)
(19) United States US 20170139281A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0139281 A1 Hou et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 18, 2017 (54) ALIGNMENT METHOD OF FFS TYPE GO2F I/335 (2006.01)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 2005.0068.047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0068047 A1 Claus (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR Publication Classification DISTINGUISHING
US 2005.0068.047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0068047 A1 Claus (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 31, 2005 (54) METHOD AND DEVICE FOR Publication Classification DISTINGUISHING
Intelligent Hotspot Connection System
 (19) United States US 2010O246486A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0246486A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) INTELLIGENT HOTSPOT CONNECTION SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
(19) United States US 2010O246486A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0246486A1 Lin et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 30, 2010 (54) INTELLIGENT HOTSPOT CONNECTION SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 US 20080249323A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0249323 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2008 (54) SORBITOL CONVERSION PROCESS Publication Classification
US 20080249323A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0249323 A1 Liu et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 9, 2008 (54) SORBITOL CONVERSION PROCESS Publication Classification
? Ns 54 F2 44. al-f2. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0199986 A1 Miller US 2013 0199986A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) ON EXCHANGE EXOSKELETON
(12) United States Patent
 US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
US00928.1819B2 (12) United States Patent Chou et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2016 (54) SOURCE DRIVING CIRCUIT AND RESISTOR RENORMALIZATION METHOD (71) Applicant: Raydium Semiconductor
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,167,752 B1. Raffer (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2001
 USOO6167752B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Raffer (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2001 (54) ROTARY VISCOMETER WITH AN AIR (56) References Cited BEARING N U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
USOO6167752B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Raffer (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 2001 (54) ROTARY VISCOMETER WITH AN AIR (56) References Cited BEARING N U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS (75) Inventor:
- X. (bka III IIII. United States Patent (19) Sobata et al e (2. o
 United States Patent (19) Sobata et al. 54 ACTIVITY CONTROL APPARATUS FOR ZINC PHOSPHATE TREATMENT SOLUTION 75) Inventors: Tamotsu Sobata, Ibaraki; Katsuhiro Takeshita, Hirakata, both of Japan 73) Assignee:
United States Patent (19) Sobata et al. 54 ACTIVITY CONTROL APPARATUS FOR ZINC PHOSPHATE TREATMENT SOLUTION 75) Inventors: Tamotsu Sobata, Ibaraki; Katsuhiro Takeshita, Hirakata, both of Japan 73) Assignee:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 (19) United States US 20040O83815A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0083815 A1 Lam et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 6, 2004 (54) PIPE FLAW DETECTOR (76) Inventors: Clive Chemo Lam,
(19) United States US 20040O83815A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0083815 A1 Lam et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 6, 2004 (54) PIPE FLAW DETECTOR (76) Inventors: Clive Chemo Lam,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO7487686B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7487,686 B2 Feb. 10, 2009 (54) HIGH-PRECISION VORTEX FLOW METER (75) Inventors: An-Bang Wang, Taipei (TW); Ming-Hsun
USOO7487686B2 (12) United States Patent Wang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7487,686 B2 Feb. 10, 2009 (54) HIGH-PRECISION VORTEX FLOW METER (75) Inventors: An-Bang Wang, Taipei (TW); Ming-Hsun
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
(19) United States US 20110248723A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0248723 A1 YEH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 13, 2011 (54) CAPACITIVE SENSOR HAVING CALIBRATION MECHANISMAND
7" - seees / s (N 255 (N. Cases a1. C=s. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. es N? (19) United States.
 (19) United States US 20030085296A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0085296A1 Waxmanski (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2003 (54) HURRICANE AND TORNADO CONTROL DEVICE (76) Inventor: Andrew
(19) United States US 20030085296A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0085296A1 Waxmanski (43) Pub. Date: May 8, 2003 (54) HURRICANE AND TORNADO CONTROL DEVICE (76) Inventor: Andrew
Sep. 2, 1993 (JP) Japan (51 int. Cl... GOR 33/02
 United States Patent (19) Tomita et al. 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MEASURING AMAGNETIC FELD USNGA MAGNETIC FORCE MCROSCOPE BY MAGNETZNG A PROBE AND CORRECTING A DETECTED MAGNETIC FIELD 75) Inventors:
United States Patent (19) Tomita et al. 54 METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR MEASURING AMAGNETIC FELD USNGA MAGNETIC FORCE MCROSCOPE BY MAGNETZNG A PROBE AND CORRECTING A DETECTED MAGNETIC FIELD 75) Inventors:
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Rajic et al. 54 FTIR SPECTROMETER WITH SOLID-STATE DRIVE SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Slobodan Rajic, Knoxville; Roland D. Seals; Charles M. Egert, both of Oak Ridge, all of Tenn. 73
United States Patent (19) Rajic et al. 54 FTIR SPECTROMETER WITH SOLID-STATE DRIVE SYSTEM 75 Inventors: Slobodan Rajic, Knoxville; Roland D. Seals; Charles M. Egert, both of Oak Ridge, all of Tenn. 73
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent US007191654B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,654 B2 Dwyer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR ADJUSTING (56) References Cited MAGNETIC RETURN PATH
(12) United States Patent US007191654B2 (10) Patent No.: US 7,191,654 B2 Dwyer et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 20, 2007 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR ADJUSTING (56) References Cited MAGNETIC RETURN PATH
United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al.
 United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al. (54) DEVICE FOR LOCATING AN OBJECT SITUATED CLOSE TO A DETECTION AREA AND A TRANSPARENT KEYBOARD USING SAID DEVICE 75 Inventors: Daniel Gruaz, Montigny le Bretonneux;
United States Patent (19) Gruaz et al. (54) DEVICE FOR LOCATING AN OBJECT SITUATED CLOSE TO A DETECTION AREA AND A TRANSPARENT KEYBOARD USING SAID DEVICE 75 Inventors: Daniel Gruaz, Montigny le Bretonneux;
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2016O247659A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0247659 A1 OH et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 25, 2016 (54) ELECTROSTATIC QUADRUPOLE Publication Classification
Process Analytical Technology Diagnosis, Optimization and Monitoring of Chemical Processes
 FRAUNHOFER INSTITUTe FoR Chemical Technology ICT Process Analytical Technology Diagnosis, Optimization and Monitoring of Chemical Processes Process Analytical Technology Diagnosis, Optimization and Monitoring
FRAUNHOFER INSTITUTe FoR Chemical Technology ICT Process Analytical Technology Diagnosis, Optimization and Monitoring of Chemical Processes Process Analytical Technology Diagnosis, Optimization and Monitoring
Si-iö, TH". ()SSS N I. 6-7 Zaf (54) United States Patent (19) Cuff (11 3,968,700. (45) July 13, (21) Appl. No.: 493,748
 United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
United States Patent (19) Cuff (54) DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ROTARY MOTION INTO A UNIDIRECTIONAL LINEAR MOTION 76) Inventor: Calvin I. Cuff, 135 Ocean Ave., Brooklyn, N.Y. 11225 22 Filed: Aug. 1, 1974 (21)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140238873A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0238873 A1 Li et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 28, 2014 (54) MODIFIED BUBBLING TRANSFER METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. FOR
(19) United States US 20140238873A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0238873 A1 Li et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 28, 2014 (54) MODIFIED BUBBLING TRANSFER METHOD (52) U.S. Cl. FOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
(19) United States US 20140216484A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0216484 A1 Liu (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 7, 2014 (54) ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A24F 47/008 (2013.01)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O137474A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0137474 A1 Kontiola (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) METHOD FOR MEASURING INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE (76) Inventor:
(19) United States US 2005O137474A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0137474 A1 Kontiola (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 23, 2005 (54) METHOD FOR MEASURING INTRAOCULAR PRESSURE (76) Inventor:
High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source.
 University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
University of Central Florida UCF Patents Patent High Efficiency Collector for Laser Plasma EUV Source. 7-11-2006 Jonathan Arenberg Northrop Grumman Corporation Find similar works at: http://stars.library.ucf.edu/patents
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1. Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003
 USOO6508132B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1 Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003 (54) DYNAMIC LOAD CELL APPARATUS 4,478,086 A * 10/1984 Gram... 73/781 5,739,411 A
USOO6508132B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,508,132 B1 Lohr et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 21, 2003 (54) DYNAMIC LOAD CELL APPARATUS 4,478,086 A * 10/1984 Gram... 73/781 5,739,411 A
(54) (75) (73) (Us) (21) (22) (63) 1, 2007, provisional application No. 60/997,142,?led
 US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
US 20120120398A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0120398 A1 Armani et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 17, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) MICRO-CAVITY GAS AND VAPOR
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0106045 A1 Hata US 2002O106045A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2002 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR IDENTIFYING OBJECT BY USE OF DECAY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0106045 A1 Hata US 2002O106045A1 (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 8, 2002 (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR IDENTIFYING OBJECT BY USE OF DECAY
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
(19) United States US 20090009193A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0009193 A1 Hsiung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 8, 2009 (54) MOISTURE-SENSITIVE ELEMENT WITH AN INTERDIGITAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0158290 A1 MARE-ROSE et al. US 2013 O158290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PRODUCTION OF OXYGENATED
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0158290 A1 MARE-ROSE et al. US 2013 O158290A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 20, 2013 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PRODUCTION OF OXYGENATED
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 20050O25974A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0025974 A1 Lennhoff (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 3, 2005 (54) CARBON AND ELECTROSPUN Publication Classification NANOSTRUCTURES
(19) United States US 20050O25974A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0025974 A1 Lennhoff (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 3, 2005 (54) CARBON AND ELECTROSPUN Publication Classification NANOSTRUCTURES
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Jongema 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF SODUM CHILORIDE 75) Inventor: Pieter Jongema, Brummen, Netherlands (73) Assignee: Akzo N.V., Netherlands (21) Appl. No.: 815,090 (22)
United States Patent (19) Jongema 54 PROCESS FOR THE PREPARATION OF SODUM CHILORIDE 75) Inventor: Pieter Jongema, Brummen, Netherlands (73) Assignee: Akzo N.V., Netherlands (21) Appl. No.: 815,090 (22)
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Fremery et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 1986 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR GAS PRESSURE MEASUREMENT BY THE GAS-FRCTION PRINCIPLE (75) Inventors: Johan
United States Patent (19) Fremery et al. 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 28, 1986 54 METHOD OF AND APPARATUS FOR GAS PRESSURE MEASUREMENT BY THE GAS-FRCTION PRINCIPLE (75) Inventors: Johan
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1
 US00782.5066B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1 Skaggs et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 2010 (54) RAPID FORMALDEHYDE (56) References Cited NEUTRALIZATION USING CHEMICALLY TREATED
US00782.5066B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7825,066 B1 Skaggs et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 2, 2010 (54) RAPID FORMALDEHYDE (56) References Cited NEUTRALIZATION USING CHEMICALLY TREATED
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.:
 (19) TEPZZ 6 6697A_T (11) EP 2 626 697 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.08.2013 Bulletin 2013/33 (1) Int Cl.: G01N 30/32 (2006.01) G01N 30/20 (2006.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 6 6697A_T (11) EP 2 626 697 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 14.08.2013 Bulletin 2013/33 (1) Int Cl.: G01N 30/32 (2006.01) G01N 30/20 (2006.01) (21) Application
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 2015O107994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0107994 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) BIOSENSOR Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
(19) United States US 2015O107994A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0107994 A1 CHO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 23, 2015 (54) BIOSENSOR Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
US 9,214,722 B2 Dec. 15, 2015
 I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US009214 722B2 c12) United States Patent Georgakopoulos et al. (IO) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,214,722 B2
United States Patent (19) Foosnaes et al.
 United States Patent (19) Foosnaes et al. USOO5606419A 11 Patent Number: 5,606,419 45 Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 1997 54 SPECTROSCOPIC MEASURING DEVICE HAVING FILTER CONSISTING OF INTERFERENCE FILTER, ONE
United States Patent (19) Foosnaes et al. USOO5606419A 11 Patent Number: 5,606,419 45 Date of Patent: Feb. 25, 1997 54 SPECTROSCOPIC MEASURING DEVICE HAVING FILTER CONSISTING OF INTERFERENCE FILTER, ONE
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1
 USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
USOO731.5677B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,315,677 B1 Li et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2008 (54) DUAL DOPANT DUAL ALPHA MULTIMODE 2006/0285809 A1* 12/2006 Bickham et al.... 385,123
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0087941A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0087941 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 11, 2013 (54) METHOD OF PRODUCING CARBON NANOTUBE SPONGES (75)
(19) United States US 2013 0087941A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0087941 A1 Chang et al. (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 11, 2013 (54) METHOD OF PRODUCING CARBON NANOTUBE SPONGES (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1. Ingles, JR. et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 OPTICAL FIBER (57) ABSTRACT
 (19) United States US 2004O150811A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150811 A1 Ingles, JR. et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (52) U.S. Cl....
(19) United States US 2004O150811A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0150811 A1 Ingles, JR. et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 5, 2004 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR (52) U.S. Cl....
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/ A1
 US 200402369A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/023.6009 A1 Mafoti et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LW DENSITY ADHESIVES AND SEALANTS Publication Classification
US 200402369A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/023.6009 A1 Mafoti et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) LW DENSITY ADHESIVES AND SEALANTS Publication Classification
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0286850 A1 Peterson et al. US 20140286850A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) METHOD OF MAKING SODIUM
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0286850 A1 Peterson et al. US 20140286850A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) METHOD OF MAKING SODIUM
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,624,640 B2
 USOO662464OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lund et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2003 (54) CAPACITANCE MEASUREMENT 5,073,757 A * 12/1991 George... 324/677 (75) I nventors: t John Jonn
USOO662464OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Lund et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 23, 2003 (54) CAPACITANCE MEASUREMENT 5,073,757 A * 12/1991 George... 324/677 (75) I nventors: t John Jonn
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent KWOn USOO6943747B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2005 (54) SMALL AND OMNI-DIRECTIONAL BICONICAL ANTENNA FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS (75) Inventor: Do-Hoon Kwon,
(12) United States Patent KWOn USOO6943747B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 13, 2005 (54) SMALL AND OMNI-DIRECTIONAL BICONICAL ANTENNA FOR WIRELESS COMMUNICATIONS (75) Inventor: Do-Hoon Kwon,
I IIIII IIIII lll (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2. (45) Date of Patent:
 I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
I 1111111111111111 11111 1111111111 111111111111111 IIIII IIIII lll111111111111111 US007165566B2 c12) United States Patent Beebe (IO) Patent No.: US 7,165,566 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Jan.23,2007 (54) METHOD
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1. (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art.
 (19) TEPZZ 988 79A_T (11) EP 2 988 279 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 24.02.16 Bulletin 16/08 (21) Application number: 1478028.3
(19) TEPZZ 988 79A_T (11) EP 2 988 279 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION published in accordance with Art. 13(4) EPC (43) Date of publication: 24.02.16 Bulletin 16/08 (21) Application number: 1478028.3
United States Patent [19]
![United States Patent [19] United States Patent [19]](/thumbs/76/73521136.jpg) United States Patent [19] Murphy 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005479716A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE
United States Patent [19] Murphy 111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US005479716A [11] Patent Number: 5,479,716 [4S] Date of Patent: Jan. 2, 1996 [S4] CAPACITIVE
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: G01J 5/62 ( ) G01J 3/28 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 9474 A_T (11) EP 2 947 43 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 2.11.1 Bulletin 1/48 (1) Int Cl.: G01J /62 (06.01) G01J 3/28 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1164674.2
(19) TEPZZ 9474 A_T (11) EP 2 947 43 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 2.11.1 Bulletin 1/48 (1) Int Cl.: G01J /62 (06.01) G01J 3/28 (06.01) (21) Application number: 1164674.2
Stratospheric Welsbach seeding for reduction of global warming
 ( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 5,003,186 Chang, et al. March 26, 1991 Stratospheric Welsbach seeding for reduction of global warming Abstract A method is described for reducing atmospheric or global warming
( 1 of 1 ) United States Patent 5,003,186 Chang, et al. March 26, 1991 Stratospheric Welsbach seeding for reduction of global warming Abstract A method is described for reducing atmospheric or global warming
United States Patent (19) Kawana et al.
 - United States Patent (19) Kawana et al. (54) METHANOL FUEL CELL 75) Inventors: Hidejiro Kawana; Tatsuo Horiba; Kazuo Iwamoto, all of Hitachi; Kazunori Fujita, Tohkai; Kohki Tamura, Hitachi, all of Japan
- United States Patent (19) Kawana et al. (54) METHANOL FUEL CELL 75) Inventors: Hidejiro Kawana; Tatsuo Horiba; Kazuo Iwamoto, all of Hitachi; Kazunori Fujita, Tohkai; Kohki Tamura, Hitachi, all of Japan
% 2 S2 NSS 43 2 % 25%SS. (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Jul.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0160792 A1 B00ker US 2005O160792A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 28, 2005 (54) PARTICULATE MATTER ANALYZER AND METHOD OF ANALYSIS (76)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0160792 A1 B00ker US 2005O160792A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 28, 2005 (54) PARTICULATE MATTER ANALYZER AND METHOD OF ANALYSIS (76)
) USOO A. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994
 ) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
) USOO5363458A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,363,458 Pan et al. 45 Date of Patent: Nov. 8, 1994 54 FIBER OPTIC LIGHT DIFFUSER 5,119,461 6/1992 Beyer et al.... 385/147 5,168,538 12/1992
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/ A1
 (19) United States US 2011 0164795A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0164795 A1 YAMANO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2011 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING SPECIFIC (30) Foreign Application
(19) United States US 2011 0164795A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0164795 A1 YAMANO et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 7, 2011 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING SPECIFIC (30) Foreign Application
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1
 USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
USOO6249200B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,249,200 B1 Stelter et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Jun. 19, 2001 (54) COMBINATION OF MAGNETS FOR 4.673,482 * 6/1987 Setoyama et al.... 204/298
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States US 2009.0160019A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0160019 A1 Yang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 25, 2009 (54) SEMICODUCTOR CAPACITOR Publication Classification (51)
(19) United States US 2009.0160019A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. o.: US 2009/0160019 A1 Yang (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 25, 2009 (54) SEMICODUCTOR CAPACITOR Publication Classification (51)
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Leonard 54 PREPARATION OF FORMIC ACID BY HYDROLYSIS OF METHYL FORMATE (76) Inventor: Jackson D. Leonard, 7002 Blvd. East, Guttenberg, N.J. 07093 (21) Appl. No. 912,189 22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Leonard 54 PREPARATION OF FORMIC ACID BY HYDROLYSIS OF METHYL FORMATE (76) Inventor: Jackson D. Leonard, 7002 Blvd. East, Guttenberg, N.J. 07093 (21) Appl. No. 912,189 22 Filed:
TEPZZ A T EP A2 (19) (11) EP A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: H02M 7/483 ( )
 (19) TEPZZ 7849 6A T (11) EP 2 784 926 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01..14 Bulletin 14/40 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 7/483 (07.01) (21) Application number: 14162389.2 (22) Date
(19) TEPZZ 7849 6A T (11) EP 2 784 926 A2 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 01..14 Bulletin 14/40 (1) Int Cl.: H02M 7/483 (07.01) (21) Application number: 14162389.2 (22) Date
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O223645A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0223645 A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2003 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR IMAGE (22) Filed: Mar. 31,
US 2003O223645A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0223645 A1 Sun et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 4, 2003 (54) METHODS AND SYSTEMS FOR IMAGE (22) Filed: Mar. 31,
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2. Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007
 USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
USOO7303925B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,303,925 B2 Sidewell et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 4, 2007 (54) METHOD OF DETECTING AN ANALYTE (56) References Cited FOR LATERAL FLOW IMMUNOASSAY
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,933,792 Andersen et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Aug. 3, 1999
 USOO5933792A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Andersen et al. () Date of Patent: *Aug. 3, 1999 54 METHOD OF STANDARDIZING A 5,272,3 12/1993 Durham et al.... 0/373 SPECTROMETER 5,5,895 8/1996
USOO5933792A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Andersen et al. () Date of Patent: *Aug. 3, 1999 54 METHOD OF STANDARDIZING A 5,272,3 12/1993 Durham et al.... 0/373 SPECTROMETER 5,5,895 8/1996
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,882,745 B2
 USOO6882745B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Brankner et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS TRANSLATING DETECTED WAFER DEFECT COORDINATES
USOO6882745B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Brankner et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 19, 2005 (54) METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS TRANSLATING DETECTED WAFER DEFECT COORDINATES
United States Patent (19) Tanaka
 United States Patent (19) Tanaka 4 CAPACTANCE-VOLTAGE CONVERTER 7 inventor: Katsuaki Tanaka, Sagamihara, Japan 73 Assignee: Iwasaki Tsushinki Kabushiki Kaisha, Japan 22 Filed: May 16, 1973 (21) Appl. No.:
United States Patent (19) Tanaka 4 CAPACTANCE-VOLTAGE CONVERTER 7 inventor: Katsuaki Tanaka, Sagamihara, Japan 73 Assignee: Iwasaki Tsushinki Kabushiki Kaisha, Japan 22 Filed: May 16, 1973 (21) Appl. No.:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1. Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008
 US 2008.0017293A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0017293 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) AUTOMATICLEVEL ADJUSTMENT FOR Publication Classification
US 2008.0017293A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0017293 A1 Chung et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 24, 2008 (54) AUTOMATICLEVEL ADJUSTMENT FOR Publication Classification
Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016
 (12) United States Patent USOO9453899B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.453,899 B2 Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016 (54) SYSTEM FOR EFFECTING THE (52) U.S. Cl. ROTATIONAL MOVEMENT OF A SOLAR CPC... G0IS
(12) United States Patent USOO9453899B2 (10) Patent No.: US 9.453,899 B2 Paponneau (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 27, 2016 (54) SYSTEM FOR EFFECTING THE (52) U.S. Cl. ROTATIONAL MOVEMENT OF A SOLAR CPC... G0IS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/ A1
 (19) United States US 2002O115373A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: LaZerman (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 22, 2002 (54) MODULAR STRUCTURE (76) Inventor: Leon Lazerman, Woodbrige (CA) Correspondence
(19) United States US 2002O115373A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: LaZerman (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 22, 2002 (54) MODULAR STRUCTURE (76) Inventor: Leon Lazerman, Woodbrige (CA) Correspondence
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Harrigan 54 LEVITATION DEVICE 76 Inventor: Roy M. Harrigan, Bromley Mountain Rd., Manchester, Vt. O54 21 22 63 51 (52) 58 Appl. No.: 105,239 Fed: Dec. 19, 1979 Related U.S. Application
United States Patent (19) Harrigan 54 LEVITATION DEVICE 76 Inventor: Roy M. Harrigan, Bromley Mountain Rd., Manchester, Vt. O54 21 22 63 51 (52) 58 Appl. No.: 105,239 Fed: Dec. 19, 1979 Related U.S. Application
FIG.1. Form organic light emitting. Coat the encapsulation. encapsulation substrate. Prepare an. Prepare a substrate
 (19) United States US 2011 0057172A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0057172 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FILLER FOR SEALING ORGANIC LIGHT EMMITING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR
(19) United States US 2011 0057172A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0057172 A1 Song et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FILLER FOR SEALING ORGANIC LIGHT EMMITING DEVICE AND METHOD FOR
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Black, Jr. et al. (54 75 73 21 22) 51 52) 58 (56) SELFACTIVATING FERROFLUD SEAL APPARATUS AND METHOD Inventors: Thomas J. Black, Jr., Lowell; Philip Stahl, Holliston, both of
United States Patent (19) Black, Jr. et al. (54 75 73 21 22) 51 52) 58 (56) SELFACTIVATING FERROFLUD SEAL APPARATUS AND METHOD Inventors: Thomas J. Black, Jr., Lowell; Philip Stahl, Holliston, both of
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,949,001 Willeke (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 7, 1999
 USOO5949001A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,949,001 Willeke (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 7, 1999 54 METHOD FOR AERODYNAMIC PARTICLE Primary Examiner Robert Raevis SIZE ANALYSIS Attorney, Agent,
USOO5949001A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,949,001 Willeke (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 7, 1999 54 METHOD FOR AERODYNAMIC PARTICLE Primary Examiner Robert Raevis SIZE ANALYSIS Attorney, Agent,
Method of modifying weather
 Page 1 of 8 Method of modifying weather Abstract ( 6 of 42 ) United States Patent 6,315,213 Cordani November 13, 2001 A method for artificially modifying the weather by seeding rain clouds of a storm with
Page 1 of 8 Method of modifying weather Abstract ( 6 of 42 ) United States Patent 6,315,213 Cordani November 13, 2001 A method for artificially modifying the weather by seeding rain clouds of a storm with
- o. ( 12 ) United States Patent. ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 10, 073, 092 B2. ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Sep. 11, Wang
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Wang TOMMUNI DI UNA US010073092B2 MULIAH DAN ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 10, 073, 092 B2 ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Sep. 11, 2018 ( 54 ) APPARATUS FOR ASSAY STRIP ( S ) WITH SPECIMEN
( 12 ) United States Patent Wang TOMMUNI DI UNA US010073092B2 MULIAH DAN ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 10, 073, 092 B2 ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Sep. 11, 2018 ( 54 ) APPARATUS FOR ASSAY STRIP ( S ) WITH SPECIMEN
Combustion knock detection and control through statistical characterization of knock levels
 Michigan Technological University Digital Commons @ Michigan Tech Michigan Tech Patents Vice President for Research Office 8-19-2008 Combustion knock detection and control through statistical characterization
Michigan Technological University Digital Commons @ Michigan Tech Michigan Tech Patents Vice President for Research Office 8-19-2008 Combustion knock detection and control through statistical characterization
United States Patent (19) Schrader
 United States Patent (19) Schrader US005534997A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 1996 54 RAMAN SPECTROMETER USING A REMOTE PROBE WITHENHANCED EFFICIENCY 75 Inventor: Bernhard Schrader, Essen-Heisingen,
United States Patent (19) Schrader US005534997A 11 Patent Number: (45) Date of Patent: Jul. 9, 1996 54 RAMAN SPECTROMETER USING A REMOTE PROBE WITHENHANCED EFFICIENCY 75 Inventor: Bernhard Schrader, Essen-Heisingen,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO71481 B2 (12) United States Patent BaltZer () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 5, 2006 (54) HEADREST FOR ALLEVIATING WHIPLASH INURY AND THE USE OF SPECIFIC POLYURETHANE FOAMIS THEREN (76) Inventor:
USOO71481 B2 (12) United States Patent BaltZer () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 5, 2006 (54) HEADREST FOR ALLEVIATING WHIPLASH INURY AND THE USE OF SPECIFIC POLYURETHANE FOAMIS THEREN (76) Inventor:
s 1OO (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1 (19) United States WORKSTATION
 (19) United States US 20090267938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0267938A1 Nicol, II et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2009 (54) THREE-DIMENSIONAL (3D) VIRTUAL WORLD S (76)
(19) United States US 20090267938A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0267938A1 Nicol, II et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 29, 2009 (54) THREE-DIMENSIONAL (3D) VIRTUAL WORLD S (76)
(54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited
 USOO73442B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.3.442 B2 Aug. 7, 2007 (54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited CARBON NANOTUBES U.S. PATENT
USOO73442B2 (12) United States Patent Huang et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.3.442 B2 Aug. 7, 2007 (54) THERMAL INTERFACE MATERIAL WITH (56) References Cited CARBON NANOTUBES U.S. PATENT
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1
 US 2003O237058A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0237058A1 Burghaus et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR THE (30) Foreign Application Priority
US 2003O237058A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0237058A1 Burghaus et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) METHOD AND SYSTEM FOR THE (30) Foreign Application Priority
USOO610427OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,104,270 Elias (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 15, 2000
 USOO610427OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Elias (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 15, 2000 54) LIFTER WITH ELECTROPERMANENT 4.956,625 9/1990 Cardone et al.... 335/290 MAGNETS PROVIDED WITH A SAFETY
USOO610427OA United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Elias (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 15, 2000 54) LIFTER WITH ELECTROPERMANENT 4.956,625 9/1990 Cardone et al.... 335/290 MAGNETS PROVIDED WITH A SAFETY
/1977 schroeder. only a one step exposure process.
 US00569.5218A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,695.218 Nicosia 45 Date of Patent: Dec. 9, 1997 54 GLOW-N-THE-DARK BOOK 4,237,381 12/1980 Schroeder... 250/462 4.266,164 5/1981 Schroeder.. 315/169.1
US00569.5218A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,695.218 Nicosia 45 Date of Patent: Dec. 9, 1997 54 GLOW-N-THE-DARK BOOK 4,237,381 12/1980 Schroeder... 250/462 4.266,164 5/1981 Schroeder.. 315/169.1
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
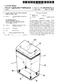 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0295736A1 Wang US 20070295736A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2007 (54) WASTEBASKET OR BN HAVING ROCKING SPRINGS AT BOTTOM (75)
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0295736A1 Wang US 20070295736A1 (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 27, 2007 (54) WASTEBASKET OR BN HAVING ROCKING SPRINGS AT BOTTOM (75)
Writing Patent Specifications
 Writing Patent Specifications Japan Patent Office Asia-Pacific Industrial Property Center, JIPII 2013 Collaborator: Shoji HADATE, Patent Attorney, Intellectual Property Office NEXPAT CONTENTS Page 1. Patent
Writing Patent Specifications Japan Patent Office Asia-Pacific Industrial Property Center, JIPII 2013 Collaborator: Shoji HADATE, Patent Attorney, Intellectual Property Office NEXPAT CONTENTS Page 1. Patent
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 20130269420A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0269420 A1 VALENZA, II et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 17, 2013 (54) METHODS OF MEASURING POROSITY ON Publication
(19) United States US 20130269420A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0269420 A1 VALENZA, II et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 17, 2013 (54) METHODS OF MEASURING POROSITY ON Publication
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0289056A1 Bergman et al. US 20120289056A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) SELECTIVE SILICON NITRDEETCH
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0289056A1 Bergman et al. US 20120289056A1 (43) Pub. Date: Nov. 15, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (60) SELECTIVE SILICON NITRDEETCH
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8681329B2 (12) United States Patent Becker-Ro?B et al. (54) ECHELLE SPECTROMETER ARRANGEMENT USING INTERNAL PREDIS PERSION (75) Inventors: Helmut Becker-Ro?B, Berlin (DE): Stefan Florek, Berlin (DE);
USOO8681329B2 (12) United States Patent Becker-Ro?B et al. (54) ECHELLE SPECTROMETER ARRANGEMENT USING INTERNAL PREDIS PERSION (75) Inventors: Helmut Becker-Ro?B, Berlin (DE): Stefan Florek, Berlin (DE);
III. United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,143,451 (45. Date of Patent: Sep. 1, Millgard
 United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
United States Patent (19) Millgard 54 METHOD TO MEASURE A TEMPERATURE WITH A PELTER ELEMENT 75 Inventor: 73) Assignee: 21) 22 Appl. No.: Filed: Lars O. A. Millgard, Ostersund, Sweden Affairsverket FFV,
UV3000. Accurate, precise, and portable ambient gas point analyzer
 UV3000 Accurate, precise, and portable ambient gas point analyzer The Cerex UV3000 is a multifunction analyzer designed to detect part per billion (ppb) to percent level concentrations of multiple gases
UV3000 Accurate, precise, and portable ambient gas point analyzer The Cerex UV3000 is a multifunction analyzer designed to detect part per billion (ppb) to percent level concentrations of multiple gases
(12) United States Patent
 USOO743665OB2 (12) United States Patent Oguni et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.436,650 B2 Oct. 14, 2008 (54) LAMINATED CERAMIC CAPACITOR (75) Inventors: Toshimi Oguni, Izumo (JP); Hiroyuki
USOO743665OB2 (12) United States Patent Oguni et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7.436,650 B2 Oct. 14, 2008 (54) LAMINATED CERAMIC CAPACITOR (75) Inventors: Toshimi Oguni, Izumo (JP); Hiroyuki
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0103105 A1 Nakama et al. US 201601031 05A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0103105 A1 Nakama et al. US 201601031 05A1 (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY
BY ye; v P. April 29, 1969 C. S. KELLEY 3,441,626. TEMPERATURE CONTROL of EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS Filed March 6, 1967 INVENTOR. PRODUCT C. S.
 April 29, 1969 C. S. KELLEY TEMPERATURE CONTROL of EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS Filed March 6, 1967 PRODUCT INVENTOR. C. S. KELLEY BY ye; v P. A 77OAPAWAYS United States Patent Office Patented Apr. 29, 1969 1.
April 29, 1969 C. S. KELLEY TEMPERATURE CONTROL of EXOTHERMIC REACTIONS Filed March 6, 1967 PRODUCT INVENTOR. C. S. KELLEY BY ye; v P. A 77OAPAWAYS United States Patent Office Patented Apr. 29, 1969 1.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/ A1
 (19) United States US 2013 0299603A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0299603 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FOG REMOVAL SYSTEM Publication Classification (75) Inventors:.
(19) United States US 2013 0299603A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0299603 A1 Choi et al. (43) Pub. Date: (54) FOG REMOVAL SYSTEM Publication Classification (75) Inventors:.
''. United States Patent (19) Tsikos. 11 4,353,056 45) Oct. 5, the finger under investigation. The sensing member. 21 Appl. No.
 United States Patent (19) Tsikos 54 CAPACITIVE FINGERPRINT SENSOR 75 Inventor: Constantine Tsikos, Pennsauken, N.J 73 Assignee: Siemens Corporation, Iselin, N.J. 21 Appl. No.: 156,571 22 Filed: Jun. 5,
United States Patent (19) Tsikos 54 CAPACITIVE FINGERPRINT SENSOR 75 Inventor: Constantine Tsikos, Pennsauken, N.J 73 Assignee: Siemens Corporation, Iselin, N.J. 21 Appl. No.: 156,571 22 Filed: Jun. 5,
United States Patent (19) Kato et al.
 United States Patent (19) Kato et al. 54) DISPERSIN-SHIFTED FIBER 75 Inventors: Takatoshi Kato; Yoshiyuki Suetsugu, Masayuki Nishimura, all of Yokohama, Japan 73 Assignee: Sumitomo Electric Industries,
United States Patent (19) Kato et al. 54) DISPERSIN-SHIFTED FIBER 75 Inventors: Takatoshi Kato; Yoshiyuki Suetsugu, Masayuki Nishimura, all of Yokohama, Japan 73 Assignee: Sumitomo Electric Industries,
(51) Int. Cl... D06F tank. The liquid level detector includes a first resistance
 US00605O112A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Walker (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2000 54). APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,798,698 8/1998 Politt et al.... 73/291 DETECTING ALIQUID LEVEL IN A SEALED
US00605O112A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Walker (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 18, 2000 54). APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR 5,798,698 8/1998 Politt et al.... 73/291 DETECTING ALIQUID LEVEL IN A SEALED
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Rodov 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OF ZENER DODES (75 Inventor: Vladimir Rodov, Los Angeles, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. 21 Appl.
United States Patent (19) Rodov 54 METHOD OF MANUFACTURE OF ZENER DODES (75 Inventor: Vladimir Rodov, Los Angeles, Calif. 73) Assignee: International Rectifier Corporation, Los Angeles, Calif. 21 Appl.
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9033892B2 (12) United States Patent Su et al. (54) PREDICTIVE DROWSINESSALARM METHOD (75) Inventors: Yu Jen Su, Kaohsiung (TW); Yen Hsien Lee, Taoyuan County (TW); Kuang I Chang, Taoyuan County (TW)
USOO9033892B2 (12) United States Patent Su et al. (54) PREDICTIVE DROWSINESSALARM METHOD (75) Inventors: Yu Jen Su, Kaohsiung (TW); Yen Hsien Lee, Taoyuan County (TW); Kuang I Chang, Taoyuan County (TW)
Industrial In-line and Multi Component Monitor Using Absorption Spectroscopy and Its Application
 FFeature Article Article Industrial In-line and Multi Component Monitor Using Absorption Spectroscopy and Its Application Yoko NAKAI HORIBA s CS-Series chemical concentration monitors that use ultraviolet
FFeature Article Article Industrial In-line and Multi Component Monitor Using Absorption Spectroscopy and Its Application Yoko NAKAI HORIBA s CS-Series chemical concentration monitors that use ultraviolet
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,173,272 B2
 US007 73272B2 (2) United States Patent (0) Patent No.: US 7,73,272 B2 Ralph (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 6, 2007 (54) QUANTUM OPTICAL CNOT GATE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Tuptly Cameron Ralph, Queensland
US007 73272B2 (2) United States Patent (0) Patent No.: US 7,73,272 B2 Ralph (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 6, 2007 (54) QUANTUM OPTICAL CNOT GATE (56) References Cited (75) Inventor: Tuptly Cameron Ralph, Queensland
RIf i1p
 (19) United States 1111111111111111111111010111111RIf i1p01211111601111111111111111111111111111111111 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0255645 Al Zawodny (43) Pub. Date: Oct.
(19) United States 1111111111111111111111010111111RIf i1p01211111601111111111111111111111111111111111 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0255645 Al Zawodny (43) Pub. Date: Oct.
