Recent developments of the NERSC version of MICOM
|
|
|
- Patricia Warren
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Recent developments of the NERSC version of MICOM Mats Bentsen Nansen Environmental and Remote Sensing Center Bjerknes Centre for Climate Research Nansen-Zhu International Research Centre
2 Outline New formulation of the pressure gradient force A suitable equation of state Modified mode splitting Results Two time-level time stepping
3 New formulation of the pressure gradient force (PGF) Classical approach in isopycnic ocean models: A more accurate approach was introduced by Sun et al. (1999): A different approach for layered ocean model was shown in the talk A proposed fix for HYCOM s thermobaricity problem by Rainer Bleck, Balu Nadiga, and Shan Sun:
4 Finite difference representation of
5 A suitable equation of state Functional form inspired by McDougall et al. (2003): Potential density is defined as Quadratic equations to solve Linear equation to solve
6 Analytic expression of specific enthalpy Can be used to accurately integrate geopotential over an isopycnic layer
7 Estimating coefficients by a weighted least square fit to the equation of state proposed by Feistel (2003). A funnel in (θ,s,p) space is used for the fit: In the pressure range [-750,2000] db, the potential temperature and salinity range used are [-5,37] C and [0,42] psu, respectively. For pressures above 2000 db, the potential temperature and salinity range are changing linearly towards [-3,10] C and [30,40] psu, respectively, at 6000 db. Density error [kg/m 3 ] at 2000 db RMS error in fitting range Black: McDougall et al. (2003) Blue: IES80 (UNESCO 1981) Magenta: Brydon et al. (1999), wide range Cyan: Brydon et al. (1999), narrow range Red: the proposed EOS
8 Modified mode splitting First order Taylor expansion of around Assume that on external gravity wave time scales On these time scales we arrive at an approximate sensitivity of vertical geopotential difference on bottom pressure changes:
9 Barotropic equation system solved: The bottom pressures in the barotropic and baroclinic systems are made consistent by correcting the baroclinic mass field with the mass flux difference between the two systems (Higdon, 2005).
10 Experience from initial testing Model layers that are statically stable in terms of potential density may be unstable in terms of in situ density. Currently we fix this by enhancing vertical diffusion in unstable regions. Local vertical density difference [kg/m 3 ]
11 Results Global model configuration with ~2.4 horizontal resolution and 35 isopycnic layers. We compare a model with reference pressure at 0 db and old PGF formulation with a model with reference pressure at 2000 db and the new PGF formulation. Initial conditions from Levitus (1994). NCEP daily forcing from is used. Strong surface relaxation with 30 days e-folding time scale. Results are averaged over the period and are from the second NCEP cycle.
12 Atlantic meridional overturning stream function [Sv] Old New
13 Sea surface height [m] Old New
14 Stream function of the vertically integrated mass transport [Sv] Old New
15 Two-level time-stepping schemes The scheme of Higdon (2002) applied to the linearized shallow water equations assuming wave solutions in space: u,v: non-dimensional velocities η: non-dimensional height γ: f t α k,l : ck k,l t Test various schemes with γ=0.25, α l =0, α k =α.
16 Higdon (2002): Hallberg (1997):
17 Generalized forward-backward method Schemes based on the work of Shchepetkin and McWilliams (2005). Expanded with optimized treatment of the Coriolis term. Explicit 2. order treatment of Coriolis term, possible with different odd/even updating of velocities
18 Non-time staggered version: Time staggered version:
19 Barotropic equation system solved: F k is a finite difference version of fk u k that in MICOM follow the formulation in Bleck and Smith (1990), based on the Sadourny (1975) potential enstrophy conserving scheme.
20 Time-stepping method for barotropic/baroclinic system Predictive barotropic integration Prediction of baroclinic variables Correction of baroclinic variables Corrective barotropic integration Correction of baroclinic bottom pressure
21 Bottom pressure at a grid point in the North Atlantic
22 Sea surface height [m] Old New
A Two-Level Time-Stepping Method for Layered Ocean Circulation Models: Further Development and Testing
 A Two-Level Time-Stepping Method for Layered Ocean Circulation Models: Further Development and Testing Robert L. Higdon Department of Mathematics Oregon State University Corvallis, Oregon 97331-4605 This
A Two-Level Time-Stepping Method for Layered Ocean Circulation Models: Further Development and Testing Robert L. Higdon Department of Mathematics Oregon State University Corvallis, Oregon 97331-4605 This
Overview of evolution of computational kernel of ROMS: How different things add up to make an ocean model.
 Overview of evolution of computational kernel of ROMS: How different things add up to make an ocean model. Alexander Shchepetkin, I.G.P.P. UCLA Venice, Italy, October 004 The purpose of this presentation
Overview of evolution of computational kernel of ROMS: How different things add up to make an ocean model. Alexander Shchepetkin, I.G.P.P. UCLA Venice, Italy, October 004 The purpose of this presentation
Quarter degree resolution ocean component of the Norwegian Earth System Model
 Quarter degree resolution ocean component of the Norwegian Earth System Model Mats Bentsen 1,2, Mehmet Ilicak 1,2, and Helge Drange 3,2 1 Uni, Uni Research Ltd 2 Bjerknes Centre for Research 3 Geophysical
Quarter degree resolution ocean component of the Norwegian Earth System Model Mats Bentsen 1,2, Mehmet Ilicak 1,2, and Helge Drange 3,2 1 Uni, Uni Research Ltd 2 Bjerknes Centre for Research 3 Geophysical
HYCOM Overview. By George Halliwell, 13 February 2002
 HYCOM Overview By George Halliwell, 13 February 2002 General Remarks The HYbrid Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM; (Halliwell et al., 1998; 2000; Bleck, 2001) is a primitive equation ocean general circulation
HYCOM Overview By George Halliwell, 13 February 2002 General Remarks The HYbrid Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM; (Halliwell et al., 1998; 2000; Bleck, 2001) is a primitive equation ocean general circulation
The Hybrid-Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM) Alex Megann, Southampton Oceanography Centre
 The Hybrid-Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM) Alex Megann, Southampton Oceanography Centre The Hybrid-Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM) Background: Level versus Isopycnic Coordinates The Miami Isopycnic Coordinate
The Hybrid-Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM) Alex Megann, Southampton Oceanography Centre The Hybrid-Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM) Background: Level versus Isopycnic Coordinates The Miami Isopycnic Coordinate
Lecture 1. Equations of motion - Newton s second law in three dimensions. Pressure gradient + force force
 Lecture 3 Lecture 1 Basic dynamics Equations of motion - Newton s second law in three dimensions Acceleration = Pressure Coriolis + gravity + friction gradient + force force This set of equations is the
Lecture 3 Lecture 1 Basic dynamics Equations of motion - Newton s second law in three dimensions Acceleration = Pressure Coriolis + gravity + friction gradient + force force This set of equations is the
A comparison of two formulations of barotropic-baroclinic splitting for layered models of ocean circulation
 A comparison of two formulations of barotropic-baroclinic splitting for layered models of ocean circulation Robert L. Higdon Department of Mathematics Oregon State University Corvallis, Oregon 97331-4605,
A comparison of two formulations of barotropic-baroclinic splitting for layered models of ocean circulation Robert L. Higdon Department of Mathematics Oregon State University Corvallis, Oregon 97331-4605,
Developing a nonhydrostatic isopycnalcoordinate
 Developing a nonhydrostatic isopycnalcoordinate ocean model Oliver Fringer Associate Professor The Bob and Norma Street Environmental Fluid Mechanics Laboratory Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering
Developing a nonhydrostatic isopycnalcoordinate ocean model Oliver Fringer Associate Professor The Bob and Norma Street Environmental Fluid Mechanics Laboratory Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering
Notes on the function gsw_internal_energy(sa,ct,p)
 Notes on gsw_internal_energy Notes on the function gsw_internal_energy(sa,ct,p) The function gsw_internal_energy(sa,ct,p) evaluates the specific internal energy of seawater as a function of Absolute Salinity,
Notes on gsw_internal_energy Notes on the function gsw_internal_energy(sa,ct,p) The function gsw_internal_energy(sa,ct,p) evaluates the specific internal energy of seawater as a function of Absolute Salinity,
Climate sensitivity of coupled models with differing ocean components
 Climate sensitivity of coupled models with differing ocean components Alex Megann, Adam Blaker and Adrian New National Oceanography Centre, Southampton, UK LOM Workshop, Miami, February 2011 Overview Introduction
Climate sensitivity of coupled models with differing ocean components Alex Megann, Adam Blaker and Adrian New National Oceanography Centre, Southampton, UK LOM Workshop, Miami, February 2011 Overview Introduction
Notes on the function gsw_sa_from_rho(rho,ct,p)
 Notes on gsw_sa_from_rho_ct Notes on the function gsw_sa_from_rho(rho,ct,p) The functions gsw_sa_from_rho(rho,ct,p) calculates (using the modified Newton Raphson iteration procedure of McDougall and Wotherspoon
Notes on gsw_sa_from_rho_ct Notes on the function gsw_sa_from_rho(rho,ct,p) The functions gsw_sa_from_rho(rho,ct,p) calculates (using the modified Newton Raphson iteration procedure of McDougall and Wotherspoon
OCEANIC SUBMESOSCALE SAMPLING WITH WIDE-SWATH ALTIMETRY. James C. McWilliams
 . OCEANIC SUBMESOSCALE SAMPLING WITH WIDE-SWATH ALTIMETRY James C. McWilliams Department of Atmospheric & Oceanic Sciences Institute of Geophysics & Planetary Physics U.C.L.A. Recall the long-standing
. OCEANIC SUBMESOSCALE SAMPLING WITH WIDE-SWATH ALTIMETRY James C. McWilliams Department of Atmospheric & Oceanic Sciences Institute of Geophysics & Planetary Physics U.C.L.A. Recall the long-standing
Comparison of of Assimilation Schemes for HYCOM
 Comparison of of Assimilation Schemes for HYCOM Ashwanth Srinivasan, C. Thacker, Z. Garraffo, E. P. Chassignet, O. M. Smedstad, J. Cummings, F. Counillon, L. Bertino, T. M. Chin, P. Brasseur and C. Lozano
Comparison of of Assimilation Schemes for HYCOM Ashwanth Srinivasan, C. Thacker, Z. Garraffo, E. P. Chassignet, O. M. Smedstad, J. Cummings, F. Counillon, L. Bertino, T. M. Chin, P. Brasseur and C. Lozano
Impact of stratification and climatic perturbations to stratification on barotropic tides
 Impact of stratification and climatic perturbations to stratification on barotropic tides Applied & Interdisciplinary Mathematics University of Michigan, Ann Arbor May 23, 213 Supported by funding from:
Impact of stratification and climatic perturbations to stratification on barotropic tides Applied & Interdisciplinary Mathematics University of Michigan, Ann Arbor May 23, 213 Supported by funding from:
Diagnostics for variability on HYCOM 1/12º Atlantic data assimilative simulations. Z.D.Garraffo, E.P.Chassignet, R.Baraille, O.M.Smedstad, M.
 Diagnostics for variability on HYCOM 1/12º Atlantic data assimilative simulations Z.D.Garraffo, E.P.Chassignet, R.Baraille, O.M.Smedstad, M.Gavart Motivation What is the Impact of data assimilation on
Diagnostics for variability on HYCOM 1/12º Atlantic data assimilative simulations Z.D.Garraffo, E.P.Chassignet, R.Baraille, O.M.Smedstad, M.Gavart Motivation What is the Impact of data assimilation on
OCEAN MODELING II. Parameterizations
 OCEAN MODELING II Parameterizations Gokhan Danabasoglu Oceanography Section Climate and Global Dynamics Division National Center for Atmospheric Research NCAR is sponsored by the National Science Foundation
OCEAN MODELING II Parameterizations Gokhan Danabasoglu Oceanography Section Climate and Global Dynamics Division National Center for Atmospheric Research NCAR is sponsored by the National Science Foundation
An Overview of Nested Regions Using HYCOM
 An Overview of Nested Regions Using HYCOM Patrick Hogan Alan Wallcraft Luis Zamudio Sergio DeRada Prasad Thoppil Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS 10 th HYCOM Consortium Meeting COAPS,
An Overview of Nested Regions Using HYCOM Patrick Hogan Alan Wallcraft Luis Zamudio Sergio DeRada Prasad Thoppil Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS 10 th HYCOM Consortium Meeting COAPS,
Progress in embedding global tides into HYCOM simulations. Brian K. Arbic Institute for Geophysics The University of Texas at Austin
 Progress in embedding global tides into HYCOM simulations Brian K. Arbic Institute for Geophysics The University of Texas at Austin Am working closely with Alan on global forward tide modeling with HYCOM.
Progress in embedding global tides into HYCOM simulations Brian K. Arbic Institute for Geophysics The University of Texas at Austin Am working closely with Alan on global forward tide modeling with HYCOM.
Fall Colloquium on the Physics of Weather and Climate: Regional Weather Predictability and Modelling. 29 September - 10 October, 2008
 1966-4 Fall Colloquium on the Physics of Weather and Climate: Regional Weather Predictability and Modelling 29 September - 10 October, 2008 Dynamics of the Eta model Part I Fedor Mesinger Environmental
1966-4 Fall Colloquium on the Physics of Weather and Climate: Regional Weather Predictability and Modelling 29 September - 10 October, 2008 Dynamics of the Eta model Part I Fedor Mesinger Environmental
Resolution-dependent Eddy Parameterizations for Large-scale Ocean Models
 Resolution-dependent Eddy Parameterizations for Large-scale Ocean Models Robert Hallberg with contributions from Alistair Adcroft NOAA / GFDL and Princeton University Mercator/Tripolar Resolution Required
Resolution-dependent Eddy Parameterizations for Large-scale Ocean Models Robert Hallberg with contributions from Alistair Adcroft NOAA / GFDL and Princeton University Mercator/Tripolar Resolution Required
Demonstration and Comparison of of Sequential Approaches for Altimeter Data Assimilation in in HYCOM
 Demonstration and Comparison of of Sequential Approaches for Altimeter Data Assimilation in in HYCOM A. Srinivasan, E. P. Chassignet, O. M. Smedstad, C. Thacker, L. Bertino, P. Brasseur, T. M. Chin,, F.
Demonstration and Comparison of of Sequential Approaches for Altimeter Data Assimilation in in HYCOM A. Srinivasan, E. P. Chassignet, O. M. Smedstad, C. Thacker, L. Bertino, P. Brasseur, T. M. Chin,, F.
Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate Dynamics Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.003 Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate Dynamics Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Problem
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 12.003 Atmosphere, Ocean and Climate Dynamics Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Problem
MERSEA IP WP 5 Integrated System Design and Assessment. Internal Metrics for the MERSEA Global Ocean: Specifications for Implementation
 MERSEA IP WP 5 Integrated System Design and Assessment Internal Metrics for the MERSEA Global Ocean: Specifications for Implementation Planning Workshop CSIRO Hobart, Australia 17-18 March 7 Participants
MERSEA IP WP 5 Integrated System Design and Assessment Internal Metrics for the MERSEA Global Ocean: Specifications for Implementation Planning Workshop CSIRO Hobart, Australia 17-18 March 7 Participants
Concurrent simulation of the eddying general circulation and tides in a global ocean model
 Concurrent simulation of the eddying general circulation and tides in a global ocean model Brian K. Arbic 1 E. Joseph Metzger 2 Alan J. Wallcraft 2 1 Department of Oceanography and Center for Ocean-Atmospheric
Concurrent simulation of the eddying general circulation and tides in a global ocean model Brian K. Arbic 1 E. Joseph Metzger 2 Alan J. Wallcraft 2 1 Department of Oceanography and Center for Ocean-Atmospheric
Climate Change Research Centre
 Lagrangian particles to study the ocean circulation All trajectories of buoys in the Global Drifter Program Erik van Sebille With input from Matthew England, Judith Helgers, Claire Paris, Bernadette Sloyan,
Lagrangian particles to study the ocean circulation All trajectories of buoys in the Global Drifter Program Erik van Sebille With input from Matthew England, Judith Helgers, Claire Paris, Bernadette Sloyan,
Modeling of the sea ice and the ocean in the Nares Strait
 Danish Meteorological Institute Modeling of the sea ice and the ocean in the Nares Strait Till Andreas Soya Rasmussen 1 Eigil Kaas 2 Nicolai Kliem 1 1/ Danish Meteorological Institute 2/ University of
Danish Meteorological Institute Modeling of the sea ice and the ocean in the Nares Strait Till Andreas Soya Rasmussen 1 Eigil Kaas 2 Nicolai Kliem 1 1/ Danish Meteorological Institute 2/ University of
GFDL, NCEP, & SODA Upper Ocean Assimilation Systems
 GFDL, NCEP, & SODA Upper Ocean Assimilation Systems Jim Carton (UMD) With help from Gennady Chepurin, Ben Giese (TAMU), David Behringer (NCEP), Matt Harrison & Tony Rosati (GFDL) Description Goals Products
GFDL, NCEP, & SODA Upper Ocean Assimilation Systems Jim Carton (UMD) With help from Gennady Chepurin, Ben Giese (TAMU), David Behringer (NCEP), Matt Harrison & Tony Rosati (GFDL) Description Goals Products
R. Hallberg, A. Adcroft, J. P. Dunne, J. P. Krasting and R. J. Stouffer NOAA/GFDL & Princeton University
 Sensitivity of 21st Century Steric Sea Level Rise to Ocean Model Formulation R. Hallberg, A. Adcroft, J. P. Dunne, J. P. Krasting and R. J. Stouffer NOAA/GFDL & Princeton University Hallberg, R., A. Adcroft,
Sensitivity of 21st Century Steric Sea Level Rise to Ocean Model Formulation R. Hallberg, A. Adcroft, J. P. Dunne, J. P. Krasting and R. J. Stouffer NOAA/GFDL & Princeton University Hallberg, R., A. Adcroft,
NCODA Implementation with re-layerization
 NCODA Implementation with re-layerization HeeSook Kang CIMAS/RSMAS/U. Miami with W. Carlisle Thacker NOAA/AOML HYCOM meeting December 6 2005 1 GULF OF MEXICO MODEL CONFIGURATION: Horizontal grid: 1/12
NCODA Implementation with re-layerization HeeSook Kang CIMAS/RSMAS/U. Miami with W. Carlisle Thacker NOAA/AOML HYCOM meeting December 6 2005 1 GULF OF MEXICO MODEL CONFIGURATION: Horizontal grid: 1/12
REQUEST FOR INFORMATION (RFI) HYCOM. Criteria #1: A strong partnership between the developers of the model and the CESM community
 REQUEST FOR INFORMATION (RFI) HYCOM Brief overview The HYbrid Coordinate Ocean Model (Bleck, 2002; Chassignet et al., 2003) is a global non- Boussinesq ocean circulation model that utilizes a generalized
REQUEST FOR INFORMATION (RFI) HYCOM Brief overview The HYbrid Coordinate Ocean Model (Bleck, 2002; Chassignet et al., 2003) is a global non- Boussinesq ocean circulation model that utilizes a generalized
Report Documentation Page
 MICOM-BASED NOWCAST/FORECAST SYSTEM FOR COASTAL/OPEN OCEAN REGIONS Eric P. Chassignet and Rainer Bleck Meteorology & Physical Oceanography University of Miami/RSMAS 4600 Rickenbacker Causeway, Miami, FL,
MICOM-BASED NOWCAST/FORECAST SYSTEM FOR COASTAL/OPEN OCEAN REGIONS Eric P. Chassignet and Rainer Bleck Meteorology & Physical Oceanography University of Miami/RSMAS 4600 Rickenbacker Causeway, Miami, FL,
Decay of Agulhas rings due to cross-frontal secondary circulations
 Decay of Agulhas rings due to cross-frontal secondary circulations S.S. Drijfhout Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute, De Bilt, The Netherlands L. de Steur, and P.J. van Leeuwen Institute for Marine
Decay of Agulhas rings due to cross-frontal secondary circulations S.S. Drijfhout Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute, De Bilt, The Netherlands L. de Steur, and P.J. van Leeuwen Institute for Marine
The Hybrid-Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM)
 The Hybrid-Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM) Alex Megann Southampton Oceanography Centre 1. Bacground: Level versus Isopycnic Coordinates Traditional ocean models, for example MOM, OPA or HadOM3, use constant
The Hybrid-Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM) Alex Megann Southampton Oceanography Centre 1. Bacground: Level versus Isopycnic Coordinates Traditional ocean models, for example MOM, OPA or HadOM3, use constant
Results from High Resolution North Atlantic HYCOM Simulations
 Results from High Resolution North Atlantic HYCOM Simulations Patrick Hogan, Alan Wallcraft, Harley Hurlburt, Tammy Townsend Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS Eric Chassignet RSMAS, University
Results from High Resolution North Atlantic HYCOM Simulations Patrick Hogan, Alan Wallcraft, Harley Hurlburt, Tammy Townsend Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS Eric Chassignet RSMAS, University
Chapter 3. Stability theory for zonal flows :formulation
 Chapter 3. Stability theory for zonal flows :formulation 3.1 Introduction Although flows in the atmosphere and ocean are never strictly zonal major currents are nearly so and the simplifications springing
Chapter 3. Stability theory for zonal flows :formulation 3.1 Introduction Although flows in the atmosphere and ocean are never strictly zonal major currents are nearly so and the simplifications springing
The World Ocean. Pacific Ocean 181 x 10 6 km 2. Indian Ocean 74 x 10 6 km 2. Atlantic Ocean 106 x 10 6 km 2
 The World Ocean The ocean and adjacent seas cover 70.8% of the surface of Earth, an area of 361,254,000 km 2 Pacific Ocean 181 x 10 6 km 2 Indian Ocean 74 x 10 6 km 2 Atlantic Ocean 106 x 10 6 km 2 Oceanic
The World Ocean The ocean and adjacent seas cover 70.8% of the surface of Earth, an area of 361,254,000 km 2 Pacific Ocean 181 x 10 6 km 2 Indian Ocean 74 x 10 6 km 2 Atlantic Ocean 106 x 10 6 km 2 Oceanic
(chose the sign to ensure that it is evaporative)
 SIO 210 (2-3:20 class) Problem Set 2 ANSWER KEY October 17, 2016 Due October 31, 2016 (10 points) 1. The salinity of the inflow to the Mediterranean Sea at the Strait of Gibraltar is about 36.1. The salinity
SIO 210 (2-3:20 class) Problem Set 2 ANSWER KEY October 17, 2016 Due October 31, 2016 (10 points) 1. The salinity of the inflow to the Mediterranean Sea at the Strait of Gibraltar is about 36.1. The salinity
The Regional Ocean Modeling System: A Split-Explicit, Free-Surface, Topography-Following-Coordinate Ocean Model
 The Regional Ocean Modeling System: A Split-Explicit, Free-Surface, Topography-Following-Coordinate Ocean Model Alexander F. Shchepetkin and James C. McWilliams Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics,
The Regional Ocean Modeling System: A Split-Explicit, Free-Surface, Topography-Following-Coordinate Ocean Model Alexander F. Shchepetkin and James C. McWilliams Institute of Geophysics and Planetary Physics,
Internal Tides in the Bab el Mandab Strait. Ewa Jarosz and Cheryl Ann Blain Naval Research Laboratory, Stennis Space Center, MS
 Internal Tides in the Bab el Mandab Strait Ewa Jarosz and Cheryl Ann Blain Naval Research Laboratory, Stennis Space Center, MS Project Objectives Numerical simulation of tides and exchange flow in the
Internal Tides in the Bab el Mandab Strait Ewa Jarosz and Cheryl Ann Blain Naval Research Laboratory, Stennis Space Center, MS Project Objectives Numerical simulation of tides and exchange flow in the
Ocean Temperatures. Atlantic Temp Section. Seasonal (Shallow) Thermocline. Better Atlantic Temp Section
 I. Fundamental Principles Physical Properties Conservation of Heat Why Does the Ocean Circulate? Waves & Tides Ocean Temperatures II. Ocean Circulation Conservation of Mass Forces & Balance of Forces Effects
I. Fundamental Principles Physical Properties Conservation of Heat Why Does the Ocean Circulate? Waves & Tides Ocean Temperatures II. Ocean Circulation Conservation of Mass Forces & Balance of Forces Effects
Implementation of the SEEK filter in HYCOM
 Implementation of the SEEK filter in HYCOM P. Brasseur, J. Verron, J.M. Brankart LEGI/CNRS, Grenoble, France HYCOM model SST, SSH, ocean colour Assimilation SEEK filter Y H x f In situ, XBT K x a Real-time
Implementation of the SEEK filter in HYCOM P. Brasseur, J. Verron, J.M. Brankart LEGI/CNRS, Grenoble, France HYCOM model SST, SSH, ocean colour Assimilation SEEK filter Y H x f In situ, XBT K x a Real-time
Formulation and performance of the Variable-Cubic Atmospheric Model
 Formulation and performance of the Variable-Cubic Atmospheric Model John McGregor CSIRO Marine and Atmospheric Research Aspendale, Melbourne Southern Hemisphere PDEs on the Sphere NCAR 11 April 2014 CSIRO
Formulation and performance of the Variable-Cubic Atmospheric Model John McGregor CSIRO Marine and Atmospheric Research Aspendale, Melbourne Southern Hemisphere PDEs on the Sphere NCAR 11 April 2014 CSIRO
Antarctic Circumpolar Current:
 Taking the Circumpolar out of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current: The ACC and the OC University of Washington, Program on Climate Change 2016 Summer Institute @ Friday Harbor Marine Lab Andrew Thompson,
Taking the Circumpolar out of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current: The ACC and the OC University of Washington, Program on Climate Change 2016 Summer Institute @ Friday Harbor Marine Lab Andrew Thompson,
The Shallow Water Equations
 If you have not already done so, you are strongly encouraged to read the companion file on the non-divergent barotropic vorticity equation, before proceeding to this shallow water case. We do not repeat
If you have not already done so, you are strongly encouraged to read the companion file on the non-divergent barotropic vorticity equation, before proceeding to this shallow water case. We do not repeat
The impacts of stochastic noise on climate models
 The impacts of stochastic noise on climate models Paul Williams Department of Meteorology, University of Reading, UK The impacts of στοχαστικός noise on climate models Paul Williams Department of Meteorology,
The impacts of stochastic noise on climate models Paul Williams Department of Meteorology, University of Reading, UK The impacts of στοχαστικός noise on climate models Paul Williams Department of Meteorology,
Jacob Schewe Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research. Ocean circulation under climate change: Examples of qualitative changes
 Jacob Schewe Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research Ocean circulation under climate change: Examples of qualitative changes Acknowledgments Anders Levermann Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact
Jacob Schewe Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research Ocean circulation under climate change: Examples of qualitative changes Acknowledgments Anders Levermann Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact
Stability of meridionally-flowing grounded abyssal currents in the ocean
 Advances in Fluid Mechanics VII 93 Stability of meridionally-flowing grounded abyssal currents in the ocean G. E. Swaters Applied Mathematics Institute, Department of Mathematical & Statistical Sciences
Advances in Fluid Mechanics VII 93 Stability of meridionally-flowing grounded abyssal currents in the ocean G. E. Swaters Applied Mathematics Institute, Department of Mathematical & Statistical Sciences
Argo data assimilation into HYCOM with an EnOI method in the Atlantic Ocean
 doi:10.5194/os-11-195-2015 Author(s) 2015. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Argo data assimilation into HYCOM with an EnOI method in the Atlantic Ocean D. Mignac 1,2, C. A. S. Tanajura 2,3,4, A. N. Santana
doi:10.5194/os-11-195-2015 Author(s) 2015. CC Attribution 3.0 License. Argo data assimilation into HYCOM with an EnOI method in the Atlantic Ocean D. Mignac 1,2, C. A. S. Tanajura 2,3,4, A. N. Santana
Feature resolution in OSTIA L4 analyses. Chongyuan Mao, Emma Fiedler, Simon Good, Jennie Waters, Matthew Martin
 Feature resolution in OSTIA L4 analyses Chongyuan Mao, Emma Fiedler, Simon Good, Jennie Waters, Matthew Martin GHRSST XVIII, Qingdao, China, 5-9 June 2017 Talk outline Introduction NEMOVAR in OSTIA Methods
Feature resolution in OSTIA L4 analyses Chongyuan Mao, Emma Fiedler, Simon Good, Jennie Waters, Matthew Martin GHRSST XVIII, Qingdao, China, 5-9 June 2017 Talk outline Introduction NEMOVAR in OSTIA Methods
LOM Layered Ocean Model Workshop, 2-4 June 2015, Copenhagen
 LOM Layered Ocean Model Workshop, 2-4 June 2015, Copenhagen 2 HYCOM Preliminary operational system Grid 1/3 (22 levels) Spin-up COADS 30 years (USP-UFBA) 2007/2008 NCEP atmospheric forcing HYCOM Grid nesting
LOM Layered Ocean Model Workshop, 2-4 June 2015, Copenhagen 2 HYCOM Preliminary operational system Grid 1/3 (22 levels) Spin-up COADS 30 years (USP-UFBA) 2007/2008 NCEP atmospheric forcing HYCOM Grid nesting
1.1 What do OGCMs cover?
 Chapter 1 OGCMs and MRI.COM This chapter outlines the ocean general circulation models (OGCM) and the status of MRI.COM. 1.1 What do OGCMs cover? OGCMs are supposed to simulate relatively large-scale phenomena
Chapter 1 OGCMs and MRI.COM This chapter outlines the ocean general circulation models (OGCM) and the status of MRI.COM. 1.1 What do OGCMs cover? OGCMs are supposed to simulate relatively large-scale phenomena
Jet Formation in the Equatorial Oceans Through Barotropic and Inertial Instabilities. Mark Fruman
 p. 1/24 Jet Formation in the Equatorial Oceans Through Barotropic and Inertial Instabilities Mark Fruman Bach Lien Hua, Richard Schopp, Marc d Orgeville, Claire Ménesguen LPO IFREMER, Brest, France IAU
p. 1/24 Jet Formation in the Equatorial Oceans Through Barotropic and Inertial Instabilities Mark Fruman Bach Lien Hua, Richard Schopp, Marc d Orgeville, Claire Ménesguen LPO IFREMER, Brest, France IAU
Tracer Based Ages, Transit Time Distributions, and Water Mass Composition: Observational and Computational Examples
 Tracer Based Ages, Transit Time Distributions, and Water Mass Composition: Observational and Computational Examples Frank Bryan Climate and Global Dynamics Division National Center for Atmospheric Research
Tracer Based Ages, Transit Time Distributions, and Water Mass Composition: Observational and Computational Examples Frank Bryan Climate and Global Dynamics Division National Center for Atmospheric Research
Multi-decadal simulation of Atlantic Ocean climate variability driven by realistic high-frequency atmospheric reanalysis
 Multi-decadal simulation of Atlantic Ocean climate variability driven by realistic high-frequency atmospheric reanalysis Z. Garraffo, G.Halliwell, L. Smith, G. Peng, E. Chassignet Discussions with B. Molinari,
Multi-decadal simulation of Atlantic Ocean climate variability driven by realistic high-frequency atmospheric reanalysis Z. Garraffo, G.Halliwell, L. Smith, G. Peng, E. Chassignet Discussions with B. Molinari,
LETTERS. Influence of the Thermohaline Circulation on Projected Sea Level Rise
 VOLUME 13 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE 15 JUNE 2000 LETTERS Influence of the Thermohaline Circulation on Projected Sea Level Rise RETO KNUTTI AND THOMAS F. STOCKER Climate and Environmental Physics, Physics Institute,
VOLUME 13 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE 15 JUNE 2000 LETTERS Influence of the Thermohaline Circulation on Projected Sea Level Rise RETO KNUTTI AND THOMAS F. STOCKER Climate and Environmental Physics, Physics Institute,
Baroclinic Rossby waves in the ocean: normal modes, phase speeds and instability
 Baroclinic Rossby waves in the ocean: normal modes, phase speeds and instability J. H. LaCasce, University of Oslo J. Pedlosky, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution P. E. Isachsen, Norwegian Meteorological
Baroclinic Rossby waves in the ocean: normal modes, phase speeds and instability J. H. LaCasce, University of Oslo J. Pedlosky, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution P. E. Isachsen, Norwegian Meteorological
Nested Gulf of Mexico Modeling with HYCOM
 Nested Gulf of Mexico Modeling with HYCOM Patrick J. Hogan Alan J. Wallcraft Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS HYCOM Meeting December 6-8, 2005 University of Miami, Miami, FL 1/25 (~4
Nested Gulf of Mexico Modeling with HYCOM Patrick J. Hogan Alan J. Wallcraft Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS HYCOM Meeting December 6-8, 2005 University of Miami, Miami, FL 1/25 (~4
Internal Wave Modeling in Oceanic General Circulation Models
 Internal Wave Modeling in Oceanic General Circulation Models Flavien Gouillon, Eric P. Chassignet Center for Ocean - Atmospheric Prediction Studies The Florida State University Introduction One of the
Internal Wave Modeling in Oceanic General Circulation Models Flavien Gouillon, Eric P. Chassignet Center for Ocean - Atmospheric Prediction Studies The Florida State University Introduction One of the
An Overview of Nested Regions Using HYCOM
 An Overview of Nested Regions Using HYCOM Patrick Hogan Alan Wallcraft Luis Zamudio Sergio DeRada Prasad Thoppil Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS 10 th HYCOM Consortium Meeting COAPS,
An Overview of Nested Regions Using HYCOM Patrick Hogan Alan Wallcraft Luis Zamudio Sergio DeRada Prasad Thoppil Naval Research Laboratory Stennis Space Center, MS 10 th HYCOM Consortium Meeting COAPS,
Fully-Coupled and Forced Ocean Sea-Ice Simulations Towards CESM2 (since mini-breck) Defining the Ocean Component of CESM2
 Fully-Coupled and Forced Ocean Sea-Ice Simulations Towards CESM2 (since mini-breck) Defining the Ocean Component of CESM2 OMWG PLAN FOR DEFINING THE CESM2 OCEAN COMPONENT Timeline 01 March 2016 22 April
Fully-Coupled and Forced Ocean Sea-Ice Simulations Towards CESM2 (since mini-breck) Defining the Ocean Component of CESM2 OMWG PLAN FOR DEFINING THE CESM2 OCEAN COMPONENT Timeline 01 March 2016 22 April
Ocean Circulation- PART- I: In Class. Must be done inclass, and turned in before you leave for credit.
 Name: Section/ TA: Ocean Circulation- PART- I: In Class. Must be done inclass, and turned in before you leave for credit. Activity 1: The Sverdrup In our homes, we are used to calculating water volumes
Name: Section/ TA: Ocean Circulation- PART- I: In Class. Must be done inclass, and turned in before you leave for credit. Activity 1: The Sverdrup In our homes, we are used to calculating water volumes
Heat Uptake and the Thermohaline Circulation in the Community Climate System Model, Version 2
 4058 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE VOLUME 17 Heat Uptake and the Thermohaline Circulation in the Community Climate System Model, Version 2 PETER R. GENT AND GOKHAN DANABASOGLU National Center for Atmospheric Research,*
4058 JOURNAL OF CLIMATE VOLUME 17 Heat Uptake and the Thermohaline Circulation in the Community Climate System Model, Version 2 PETER R. GENT AND GOKHAN DANABASOGLU National Center for Atmospheric Research,*
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation
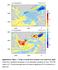 Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Supplementary Figure 1 Trends of annual mean maximum ocean mixed layer depth. Trends from uninitialized simulations (a) and assimilation simulation (b) from 1970-1995 (units: m yr -1 ). The dots show grids
Assimilating 20 years of Atlantic XBT data into HYCOM: a first look
 Ocean Modelling 7 (24) 183 21 www.elsevier.com/locate/ocemod Assimilating 2 years of Atlantic XBT data into HYCOM: a first look W.C. Thacker a, *, S.-K. Lee b, G.R. Halliwell Jr. c a Atlantic Oceanographic
Ocean Modelling 7 (24) 183 21 www.elsevier.com/locate/ocemod Assimilating 2 years of Atlantic XBT data into HYCOM: a first look W.C. Thacker a, *, S.-K. Lee b, G.R. Halliwell Jr. c a Atlantic Oceanographic
Assimilation of satellite altimetry referenced to the new GRACE geoid estimate
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L06601, doi:10.1029/2004gl021329, 2005 Assimilation of satellite altimetry referenced to the new GRACE geoid estimate F. Birol, 1 J. M. Brankart, 1 J. M. Lemoine,
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 32, L06601, doi:10.1029/2004gl021329, 2005 Assimilation of satellite altimetry referenced to the new GRACE geoid estimate F. Birol, 1 J. M. Brankart, 1 J. M. Lemoine,
Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics: the Ocean Circulation EESS 146B/246B
 Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics: the Ocean Circulation EESS 146B/246B Instructor: Leif Thomas TA: Gonçalo Zo Zo Gil http://pangea.stanford.edu/courses/eess146bweb/ Course Objectives Identify and characterize
Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics: the Ocean Circulation EESS 146B/246B Instructor: Leif Thomas TA: Gonçalo Zo Zo Gil http://pangea.stanford.edu/courses/eess146bweb/ Course Objectives Identify and characterize
How Sensitive Are Coarse General Circulation Models to Fundamental Approximations in the Equations of Motion?
 306 JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY VOLUME 34 How Sensitive Are Coarse General Circulation Models to Fundamental Approximations in the Equations of Motion? MARTIN LOSCH, ALISTAIR ADCROFT, AND JEAN-MICHEL
306 JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY VOLUME 34 How Sensitive Are Coarse General Circulation Models to Fundamental Approximations in the Equations of Motion? MARTIN LOSCH, ALISTAIR ADCROFT, AND JEAN-MICHEL
Physical Oceanography, MSCI 3001 Oceanographic Processes, MSCI Dr. Katrin Meissner Week 5.
 Physical Oceanography, MSCI 3001 Oceanographic Processes, MSCI 5004 Dr. Katrin Meissner k.meissner@unsw.e.au Week 5 Ocean Dynamics Transport of Volume, Heat & Salt Flux: Amount of heat, salt or volume
Physical Oceanography, MSCI 3001 Oceanographic Processes, MSCI 5004 Dr. Katrin Meissner k.meissner@unsw.e.au Week 5 Ocean Dynamics Transport of Volume, Heat & Salt Flux: Amount of heat, salt or volume
Multi-century climate integrations at NOC
 Multi-century climate integrations at NOC Alex Megann, Adam Blaker and Adrian New Marine Systems Modelling National Oceanography Centre, Southampton, UK LOM, Ann Arbor, May 2013 Multi-century climate integrations
Multi-century climate integrations at NOC Alex Megann, Adam Blaker and Adrian New Marine Systems Modelling National Oceanography Centre, Southampton, UK LOM, Ann Arbor, May 2013 Multi-century climate integrations
SENSITIVITY OF AN OCEAN GENERAL CIRCULATION MODEL TO A PARAMETERIZATION OF NEAR-SURFACE EDDY FLUXES. Gokhan Danabasoglu
 SENSITIVITY OF AN OCEAN GENERAL CIRCULATION MODEL TO A PARAMETERIZATION OF NEAR-SURFACE EDDY FLUXES Gokhan Danabasoglu National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO Raffaele Ferrari Massachusetts
SENSITIVITY OF AN OCEAN GENERAL CIRCULATION MODEL TO A PARAMETERIZATION OF NEAR-SURFACE EDDY FLUXES Gokhan Danabasoglu National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, CO Raffaele Ferrari Massachusetts
Performance of a 23 years TOPAZ reanalysis
 Performance of a 23 years TOPAZ reanalysis L. Bertino, F. Counillon, J. Xie,, NERSC LOM meeting, Copenhagen, 2 nd -4 th June 2015 Outline Presentation of the TOPAZ4 system Choice of modeling and assimilation
Performance of a 23 years TOPAZ reanalysis L. Bertino, F. Counillon, J. Xie,, NERSC LOM meeting, Copenhagen, 2 nd -4 th June 2015 Outline Presentation of the TOPAZ4 system Choice of modeling and assimilation
isopycnal outcrop w < 0 (downwelling), v < 0 L.I. V. P.
 Ocean 423 Vertical circulation 1 When we are thinking about how the density, temperature and salinity structure is set in the ocean, there are different processes at work depending on where in the water
Ocean 423 Vertical circulation 1 When we are thinking about how the density, temperature and salinity structure is set in the ocean, there are different processes at work depending on where in the water
An analysis of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (MOC) in an Atmosphere-Ocean General Circulation Model
 An analysis of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (MOC) in an Atmosphere-Ocean General Circulation Model Virginie Guemas, David Salas-Mélia Centre National de Recherches Météorologiques (CNRM)
An analysis of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (MOC) in an Atmosphere-Ocean General Circulation Model Virginie Guemas, David Salas-Mélia Centre National de Recherches Météorologiques (CNRM)
A hybrid coordinate ocean model for shelf sea simulation
 Ocean Modelling 13 (26) 221 237 www.elsevier.com/locate/ocemod A hybrid coordinate ocean model for shelf sea simulation Nina Gjerde Winther a, *, Geir Evensen a,b a Mohn-Sverdrup Center, Nansen Environmental
Ocean Modelling 13 (26) 221 237 www.elsevier.com/locate/ocemod A hybrid coordinate ocean model for shelf sea simulation Nina Gjerde Winther a, *, Geir Evensen a,b a Mohn-Sverdrup Center, Nansen Environmental
A possible mechanism for the strong weakening of the North Atlantic subpolar gyre in the mid-1990s
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L15602, doi:10.1029/2009gl039166, 2009 A possible mechanism for the strong weakening of the North Atlantic subpolar gyre in the mid-1990s Katja Lohmann, 1,2,3 Helge
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 36, L15602, doi:10.1029/2009gl039166, 2009 A possible mechanism for the strong weakening of the North Atlantic subpolar gyre in the mid-1990s Katja Lohmann, 1,2,3 Helge
O.M Smedstad 1, E.J. Metzger 2, R.A. Allard 2, R. Broome 1, D.S. Franklin 1 and A.J. Wallcraft 2. QinetiQ North America 2. Naval Research Laboratory
 An eddy-resolving ocean reanalysis using the 1/12 global HYbrid Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM) and the Navy Coupled Ocean Data Assimilation (NCODA) scheme O.M Smedstad 1, E.J. Metzger 2, R.A. Allard 2,
An eddy-resolving ocean reanalysis using the 1/12 global HYbrid Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM) and the Navy Coupled Ocean Data Assimilation (NCODA) scheme O.M Smedstad 1, E.J. Metzger 2, R.A. Allard 2,
Nonlinear baroclinic dynamics of surface cyclones crossing a zonal jet
 Nonlinear baroclinic dynamics of surface cyclones crossing a zonal jet Jean-Baptiste GILET, Matthieu Plu and Gwendal Rivière CNRM/GAME (Météo-France, CNRS) 3rd THORPEX International Science Symposium Monterey,
Nonlinear baroclinic dynamics of surface cyclones crossing a zonal jet Jean-Baptiste GILET, Matthieu Plu and Gwendal Rivière CNRM/GAME (Météo-France, CNRS) 3rd THORPEX International Science Symposium Monterey,
 This article was originally published in a journal published by Elsevier, and the attached copy is provided by Elsevier for the author s benefit and for the benefit of the author s institution, for non-commercial
This article was originally published in a journal published by Elsevier, and the attached copy is provided by Elsevier for the author s benefit and for the benefit of the author s institution, for non-commercial
Time-stepping of the CROCO hydrostatic code and its impact on code structure (and on advection schemes)
 Time-stepping of the CROCO hydrostatic code and its impact on code structure (and on advection schemes) Florian Lemarié Inria (EPI AIRSEA), Laboratoire Jean Kuntzmann, Grenoble, France General context
Time-stepping of the CROCO hydrostatic code and its impact on code structure (and on advection schemes) Florian Lemarié Inria (EPI AIRSEA), Laboratoire Jean Kuntzmann, Grenoble, France General context
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1189 Different magnitudes of projected subsurface ocean warming around Greenland and Antarctica Jianjun Yin 1*, Jonathan T. Overpeck 1, Stephen M. Griffies 2,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NGEO1189 Different magnitudes of projected subsurface ocean warming around Greenland and Antarctica Jianjun Yin 1*, Jonathan T. Overpeck 1, Stephen M. Griffies 2,
Overflow representation using K- profile and Turner parameterization in HYCOM
 Overflow representation using K- profile and Turner parameterization in HYCOM Xiaobiao Xu, Eric P. Chassignet, Tamay M. Özgömen, Yeon Chang, Hartmut Peters Thans to: Alan Wallcraft, George Halliwell, Zulema
Overflow representation using K- profile and Turner parameterization in HYCOM Xiaobiao Xu, Eric P. Chassignet, Tamay M. Özgömen, Yeon Chang, Hartmut Peters Thans to: Alan Wallcraft, George Halliwell, Zulema
Dynamical Evaluation of Gulf Stream Simulations in Models with High Vertical Resolution
 Dynamical Evaluation of Gulf Stream Simulations in Models with High Vertical Resolution Harley E. Hurlburt 1, Eric P. Chassignet 2, E. Joseph Metzger 1, James G. Richman 1, William J. Schmitz, Jr. 3, Jay
Dynamical Evaluation of Gulf Stream Simulations in Models with High Vertical Resolution Harley E. Hurlburt 1, Eric P. Chassignet 2, E. Joseph Metzger 1, James G. Richman 1, William J. Schmitz, Jr. 3, Jay
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (d) (e) Figure S1 Timeseries of the sea ice and overturning circulation response to a cessation of CO 2 emissions. Northern Hemisphere March sea ice cover (km 2 ), Northern Hemisphere
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION (d) (e) Figure S1 Timeseries of the sea ice and overturning circulation response to a cessation of CO 2 emissions. Northern Hemisphere March sea ice cover (km 2 ), Northern Hemisphere
Mean Stream-Coordinate Structure of the Kuroshio Extension First Meander Trough
 Mean Stream-Coordinate Structure of the Kuroshio Extension First Meander Trough 6 March, 2008 Penelope J. Howe, Kathleen A. Donohue, and D. Randolph Watts Graduate School of Oceanography University of
Mean Stream-Coordinate Structure of the Kuroshio Extension First Meander Trough 6 March, 2008 Penelope J. Howe, Kathleen A. Donohue, and D. Randolph Watts Graduate School of Oceanography University of
Assimilation of Satellite Sea-surface Salinity Fields: Validating Ocean Analyses and Identifying Errors in Surface Buoyancy Fluxes
 Assimilation of Satellite Sea-surface Salinity Fields: Validating Ocean Analyses and Identifying Errors in Surface Buoyancy Fluxes Eric Bayler Sudhir Nadiga Avichal Mehra David Behringer NOAA/NESDIS/STAR
Assimilation of Satellite Sea-surface Salinity Fields: Validating Ocean Analyses and Identifying Errors in Surface Buoyancy Fluxes Eric Bayler Sudhir Nadiga Avichal Mehra David Behringer NOAA/NESDIS/STAR
Instability of a coastal jet in a two-layer model ; application to the Ushant front
 Instability of a coastal jet in a two-layer model ; application to the Ushant front Marc Pavec (1,2), Xavier Carton (1), Steven Herbette (1), Guillaume Roullet (1), Vincent Mariette (2) (1) UBO/LPO, 6
Instability of a coastal jet in a two-layer model ; application to the Ushant front Marc Pavec (1,2), Xavier Carton (1), Steven Herbette (1), Guillaume Roullet (1), Vincent Mariette (2) (1) UBO/LPO, 6
An Assessment of Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) in Coordinated Ocean-ice Reference Experiments (CORE-II)
 An Assessment of Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) in Coordinated Ocean-ice Reference Experiments (CORE-II) G. Danabasoglu, S. G. Yeager, D. Bailey, E. Behrens, M. Bentsen, D. Bi, A. Biastoch,
An Assessment of Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) in Coordinated Ocean-ice Reference Experiments (CORE-II) G. Danabasoglu, S. G. Yeager, D. Bailey, E. Behrens, M. Bentsen, D. Bi, A. Biastoch,
North Atlantic circulation in three simulations of 1/12, 1/25, and 1/50
 North Atlantic circulation in three simulations of 1/12, 1/2, and 1/ Xiaobiao Xu and Eric Chassignet Center for ocean-atmospheric prediction studies Florida State University Motivation Numerical models
North Atlantic circulation in three simulations of 1/12, 1/2, and 1/ Xiaobiao Xu and Eric Chassignet Center for ocean-atmospheric prediction studies Florida State University Motivation Numerical models
Norwegian Climate Prediction Model (NorCPM) getting ready for CMIP6 DCPP
 Norwegian Climate Prediction Model (NorCPM) getting ready for CMIP6 DCPP Francois Counillon, Noel Keenlyside, Mats Bentsen, Ingo Bethke, Laurent Bertino, Teferi Demissie, Tor Eldevik, Shunya Koseki, Camille
Norwegian Climate Prediction Model (NorCPM) getting ready for CMIP6 DCPP Francois Counillon, Noel Keenlyside, Mats Bentsen, Ingo Bethke, Laurent Bertino, Teferi Demissie, Tor Eldevik, Shunya Koseki, Camille
SIO 210 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Mid-term examination November 3, 2014; 1 hour 20 minutes
 NAME: SIO 210 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Mid-term examination November 3, 2014; 1 hour 20 minutes Closed book; one sheet of your own notes is allowed. A calculator is allowed. (100 total points.)
NAME: SIO 210 Introduction to Physical Oceanography Mid-term examination November 3, 2014; 1 hour 20 minutes Closed book; one sheet of your own notes is allowed. A calculator is allowed. (100 total points.)
New Salinity Product in the Tropical Indian Ocean Estimated from OLR
 New Salinity Product in the Tropical Indian Ocean Estimated from OLR Aquarius Bulusu Subrahmanyam and James J. O Brien Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies, Florida State University V.S.N. Murty
New Salinity Product in the Tropical Indian Ocean Estimated from OLR Aquarius Bulusu Subrahmanyam and James J. O Brien Center for Ocean-Atmospheric Prediction Studies, Florida State University V.S.N. Murty
Ocean Model Uncertainty
 Ocean Model Uncertainty Chris Brierley University of Reading, UK Alan Thorpe Natural Environment Research Council, UK Mat Collins Hadley Centre, Met. Office, UK Malcolm MacVean European Centre for Medium-range
Ocean Model Uncertainty Chris Brierley University of Reading, UK Alan Thorpe Natural Environment Research Council, UK Mat Collins Hadley Centre, Met. Office, UK Malcolm MacVean European Centre for Medium-range
A modeling study of the North Pacific shallow overturning circulation. Takao Kawasaki, H. Hasumi, 2 M. Kurogi
 PICES 2011 Annual Meeting, Khabarovsk, Russia A modeling study of the North Pacific shallow overturning circulation 1 Takao Kawasaki, H. Hasumi, 2 M. Kurogi 1 Atmosphere and Ocean Research Institute, University
PICES 2011 Annual Meeting, Khabarovsk, Russia A modeling study of the North Pacific shallow overturning circulation 1 Takao Kawasaki, H. Hasumi, 2 M. Kurogi 1 Atmosphere and Ocean Research Institute, University
Lecture 4:the observed mean circulation. Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics EESS 146B/246B
 Lecture 4:the observed mean circulation Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics EESS 146B/246B The observed mean circulation Lateral structure of the surface circulation Vertical structure of the circulation
Lecture 4:the observed mean circulation Atmosphere, Ocean, Climate Dynamics EESS 146B/246B The observed mean circulation Lateral structure of the surface circulation Vertical structure of the circulation
A New Approach to the Spin-up Problem in Ocean Climate Models
 A New Approach to the Spin-up Problem in Ocean Climate Models ISBN 978-90-39354414 Copyright c 2010 Erik Bernsen, The Netherlands Institute for Marine and Atmospheric research Utrecht (IMAU) Faculty of
A New Approach to the Spin-up Problem in Ocean Climate Models ISBN 978-90-39354414 Copyright c 2010 Erik Bernsen, The Netherlands Institute for Marine and Atmospheric research Utrecht (IMAU) Faculty of
Simulated variability of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation
 Simulated variability of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation Mats Bentsen 1,2, Helge Drange 1,2,3,4, Tore Furevik 3,2, and Tianjun Zhou 5 1 Nansen Environmental and Remote Sensing Center, Bergen,
Simulated variability of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation Mats Bentsen 1,2, Helge Drange 1,2,3,4, Tore Furevik 3,2, and Tianjun Zhou 5 1 Nansen Environmental and Remote Sensing Center, Bergen,
MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY
 MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY Gokhan Danabasoglu National Center for Atmospheric Research OUTLINE: - Describe thermohaline and meridional overturning
MERIDIONAL OVERTURNING CIRCULATION: SOME BASICS AND ITS MULTI-DECADAL VARIABILITY Gokhan Danabasoglu National Center for Atmospheric Research OUTLINE: - Describe thermohaline and meridional overturning
The Fifth-Generation NCAR / Penn State Mesoscale Model (MM5) Mark Decker Feiqin Xie ATMO 595E November 23, 2004 Department of Atmospheric Science
 The Fifth-Generation NCAR / Penn State Mesoscale Model (MM5) Mark Decker Feiqin Xie ATMO 595E November 23, 2004 Department of Atmospheric Science Outline Basic Dynamical Equations Numerical Methods Initialization
The Fifth-Generation NCAR / Penn State Mesoscale Model (MM5) Mark Decker Feiqin Xie ATMO 595E November 23, 2004 Department of Atmospheric Science Outline Basic Dynamical Equations Numerical Methods Initialization
Overview of the Numerics of the ECMWF. Atmospheric Forecast Model
 Overview of the Numerics of the Atmospheric Forecast Model M. Hortal Seminar 6 Sept 2004 Slide 1 Characteristics of the model Hydrostatic shallow-atmosphere approimation Pressure-based hybrid vertical
Overview of the Numerics of the Atmospheric Forecast Model M. Hortal Seminar 6 Sept 2004 Slide 1 Characteristics of the model Hydrostatic shallow-atmosphere approimation Pressure-based hybrid vertical
MOX EXPONENTIAL INTEGRATORS FOR MULTIPLE TIME SCALE PROBLEMS OF ENVIRONMENTAL FLUID DYNAMICS. Innsbruck Workshop October
 Innsbruck Workshop October 29 21 EXPONENTIAL INTEGRATORS FOR MULTIPLE TIME SCALE PROBLEMS OF ENVIRONMENTAL FLUID DYNAMICS Luca Bonaventura - Modellistica e Calcolo Scientifico Dipartimento di Matematica
Innsbruck Workshop October 29 21 EXPONENTIAL INTEGRATORS FOR MULTIPLE TIME SCALE PROBLEMS OF ENVIRONMENTAL FLUID DYNAMICS Luca Bonaventura - Modellistica e Calcolo Scientifico Dipartimento di Matematica
