Making Cosmologyʼs Best Standard Candles Even Better
|
|
|
- Baldric Morris
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Making Cosmologyʼs Best Standard Candles Even Better The Nearby Supernova Factory and Spectrophotometric Observations of SNe Ia Stephen Bailey LPNHE, Paris for the Nearby Supernova Factory Deciphering the Universe through Spectroscopy Potsdam 22 September 2009 G. Aldering 2, P. Antilogus 1, C. Aragon 2, S.B. 1, C. Baltay 3, S. Bongard 1, C. Buton 4, M. Childress 2, N. Chotard 4, Y. Copin 4, D. Fouchez 6, E. Gangler 4, M. Kowalski 7, S. Loken 2, P. Nugent 2, K. Paesch 7, R. Pain 1, E. Pecontal 5, R. Pereira 4, S. Perlmutter 2, D. Rabinowitz 3, G. Rigaudier 5, P. Ripoche 1, K. Runge 2, R. Scalzo 3, G. Smadja 4, H. Swift 2, C. Tao 6, R.C. Thomas 2, C. Wu 1, J. Zylberberg 2 1 LPNHE (Paris), 2 LBL (Berkeley), 3 Yale (New Haven), 4 IPNL (Lyon), 5 CRAL (Lyon), 6 CPPM (Marsaille), 4 Universität Bonn
2 Overview SNe Ia were original method to discover dark energy Power comes from the ability to standardize their luminosities Better standardization = Better cosmology constraints This talk: new ways to standardize them with more accuracy Outline Background Cosmology measurements with SNe Ia The Nearby Supernova Factory Classic methods to standardize SNe Ia Spectral flux ratios Other spectral metrics Conclusions 2
3 Cosmology with Luminosity Distance dl(z) is a function of the cosmology Flux = L 4πd 2 L 5 log 10 dl + const MLCS2k2 fitted distance modulus (mag) nearby (JRK07) 103 SDSS-II (this paper) 56 ESSENCE (WV07) 62 SNLS (Astier06) 34 HST (Riess07) Kessler et al (SDSS) redshift (actually a fit to a different Hubble Diagram dataset, but a prettier plot) 3
4 Type Ia Supernovae What you need to measure luminosity distance dl: Very bright objects Uniformly bright objects Type Ia Supernova Thermonuclear runaway when white-dwarf accretes to Chandrasekhar mass Uniform starting conditions = (almost) uniform luminosity Can be as bright as host 4
5 Standardizable Candles Variations in peak magnitude correlate with other observables: Color c: bluer = brighter Shape x1: broader = brighter Correct observed peak mag using x1, c mb mb + αx1 - βc Color: E(B-V) color mb: Peak magnitude in restframe B-band Shape x1: Lightcurve shape/width parameter 5
6 Standardizable Candles Broader = Brighter Correct for stretch Peaks agree within ~15% S. Perlmutter, Physics Today, April 2003, p. 54 6
7 SN Cosmology Fitting Peak mag shape & color m B M + αx 1 βc 5 log 10 [d L (z; θ)] Normalization Standardization factors Luminosity distance depends on cosmology parameters θ: Ωm, ΩΛ, w,... Best fit with dark energy No dark energy Hicken et al
8 SN Cosmology Fitting Hicken et al 2009 Best fit with dark energy No dark energy 1 2 Cosmology constraints come from comparison of nearby and distant supernovae Why weʼre the Nearby Supernova Factory: currently low-z sample is limiting factor Better standardization = Better cosmology constraints The focus of this talk 8
9 Nearby Supernova Factory 1. Discover Palomar Nightly NERSC Search ended Sept 2008; >1000 SNe discovered in 28 months of searching 185 followed in detail, 0.02 < z < 0.09 Ref New New-Ref = ~10-7 of the area observed per night 3. Analyze 2. Observe SNIFS UH 2.2-m Every 2-3 nights Custom, unique spectrometer designed for nearby SN obs 9
10 SuperNova Integral Field Spectrometer (SNIFS) Photometric Channel Microlens array to two channel spectrograph 15x15 = 225 spectra R channel: Galaxy + Sky Extinction monitoring, calibration Acquisition, Guiding SN + Galaxy + Sky Pick-off Prism at SN loc Sky 9.4ʼ x 9.4ʼ FOV; 0.14 /pix Every obs: flux calibrated spectra, , nm coverage 6 x 6 FOV; 0.4 /spaxel On UH 2.2m on Mauna Kea; SNfactory uses every 2-3 nights for ~9 months/year Hard work... SN 10 12
11 Spectrophotometry From Spectra to Lightcurves synthetic photometry of SN2005el Slides: Rui Pereira 11
12 Spectrophotometry From Spectra to Lightcurves synthetic photometry of SN2005el Slides: Rui Pereira 11
13 Spectrophotometry From Spectra to Lightcurves synthetic photometry of SN2005el Slides: Rui Pereira 11
14 Spectrophotometry From Spectra to Lightcurves synthetic photometry of SN2005el Slides: Rui Pereira 11
15 Spectrophotometry From Spectra to Lightcurves synthetic photometry of SN2005el Slides: Rui Pereira 11
16 Spectrophotometry From Spectra to Lightcurves synthetic photometry of SN2005el Slides: Rui Pereira 11
17 Spectrophotometry From Spectra to Lightcurves synthetic photometry of SN2005el Slides: Rui Pereira 11
18 Spectrophotometry From Spectra to Lightcurves synthetic photometry of SN2005el One spectrum per point / night Synthesizable in any filter Lightcurves + spectral features Slides: Rui Pereira 11
19 Motivations for Spectrophotometry S-corrections K-corrections Relative Flux (F! ) Kowalski et al Wavelength (Å) Info for models etc. vs 12
20 Two Classic Corrections Classic corrections Δμorig ½= color Color: Bluer = Brighter Lightcurve shape: Broader = Brighter ~40% ~16 20% scatter Can we do better with spectral info? Search correlations of features with residuals ½= 0.68 Δμorig - βc 40% 16% x1 13
21 Previous Spectral Metrics Absorption Ratios e.g. RSi 1 4 Pseudo-Equivalent Widths / fractional absorption area e.g. EW(SiII 6355) Flux Ratios e.g. RSiS 2 Feature Velocities e.g. vsi 3 14
22 Generalized Flux Ratios Spectra sorted by SALT color Normalized flux + offset SNF SN2007bd SNF SNF SNF SNF SNF SNF SNF SNF SNF SNF SNF SN2005hc SNF SN2006dm SNF SNF SNF SN2007kk SNF SNF SNF SNF SNF SNF SNF SNF SNF Wavelength [A] Consider all flux ratio combos, not just ratios of known peaks Search for correlations with uncorrected Hubble residuals SNfactory spectra Flux calibrated to standard stars Smooth Hubble flow minimal peculiar velocity or cosmo uncertainties Within ±2.5 days of peak brightness Training and Validation Datasets Search with training set (28 SNe) Cross check w/ validation set (30 SNe) Minimizes bias and confirms results 15
23 Training Set ρ = 0.94 Flux Ratio Correlations Bailey et al 2009, A&A Letters, arxiv Lower diagonal: Decolor spectra before forming ratios Statistically Significant Develop method and pick ratios based upon training sample Then look at validation sample 16
24 Training Set ρ = 0.94 Flux Ratio Correlations Bailey et al 2009, A&A Letters, arxiv Validation Set ρ = 0.96 Lower diagonal: Decolor spectra before forming ratios Statistically Significant Correlations Develop method and pick ratios Stronger based upon than training color or sample stretch Selected only from training sample Then look at validation sample Confirmed by validation sample 16
25 Nearby Hubble Diagram Uncorrected σ = 0.40 mag 17
26 Nearby Hubble Diagram SALT2 corrects mag What if we fit with R643/442 instead? SALT2 µb = (mb M) Uncorrected + αx1 - βc σ = σ = 0.40 mag mag σcore = mag 17
27 Nearby Hubble Diagram SALT2 µb = (mb M) Uncorrected + αx1 - βc σ = σ = 0.40 mag mag σcore = mag SALT2 corrects mag What if we fit with R643/442 instead? Flux Ratios µb = (mb M) + γr σ = mag σcore = mag Flux Ratios standardize SNe Ia better than x1 and c combined Bailey et al 2009 Accepted by A&A Letters arxiv: Hubble Residuals Sample R642/443 x1, c Training Validation All
28 Hubble Residuals Bailey et al 2009, A&A Letters, arxiv Single parameter correction: Better at correcting red and peculiar SNe σ = 0.13 Combined with color: σ = 0.12 Traditional method (SALT2) σ = 0.16 σ = : statistically equivalent to having 1.8x as many SNe Better for oddballs: better systematics control 18
29 Literature SNe Comparison Bailey et al 2009, A&A Letters, arxiv Literature SNe from Matheson, with photometry from Jha and Hicken Overall, supports our results within the resolution of the data One outlier (99cl) known to be unusual: Very heavily reddened Time variable sodium absorption Very low RV value 19
30 Related Work: vsi and Color Bright Magnitude Dim Brighter = Bluer but what slope? Blue Color Red Slope of color correction related to Si velocity vsi Separating high/normal vsi significantly improves scatter ( mag) 99cl is in high vsi set X. Wang et al ApJ Letters, arxiv: Improved distances to Type Ia Supernovae with Two Spectroscopic Subclasses vsi 20
31 Traditional corrections applied to the luminosity are stretch and color, with # and $ tuned to minimize the residuals to the cosmological fit to the data.! Color cut Classic Metric Studies corr M = M α x1 β etc.) c b Complete study underway of classic metrics (RSib,+EW(4000), Ability to standardize SNe Ia! Spectral correction can be applied in a same way Here, example of EWSiII4000 to show the power o Covariance with each other and stretch and color the with indicators. Example: EW(SiII 4000) Hubble Residual se Color cut c& c& Correction None c & x1 EWSiII None c & x1 EWSiII EWSiII4000"s correlations with Color Cut Hubble residuals and x1 increase after the color cut (see table).! RMS nmad Standard deviation and normalized median absolute deviation. EWSiII4000 is independant of color and a good proxy for x1.! After EW(Si color IIcut, EWSiII ) + Color is an excellent candidate to estimate part of the SN competitive with intrinsic x1 + Color Ia variability and replace the x1 parameter. (cp Bronder EW alone) Nicolas=Chotard R642/443 F (642 nm)/f (443 nm) SNfactory Corrected Preliminary Hubble residuals EW(SiII 4000) Please do not reproduce without asking; we may have updated results... 21
32 K-correctionless Hubble Diagram Synthesize photometry on a redshift-dependent filter-set One filter integrates the same spectral range on all SNe Minimize systematic errors due to the light curve fitter spectral model (SALT2) Normalized flux z = 0.03 B SNf V SNf R SNf z=0.03 Normalized flux z = 0.08 B SNf V SNf R SNf z= Wavelength (Å) 10 4 (74 SNe) standard SALT2 no K-correction Δσ σcore (mag) SNe Ia σint (mag) SNfactory Preliminary Please do not reproduce without asking; we may have updated results... Rui Pereira 22
33 Deciphering the Universe through Spectroscopy Entering new era of understanding SNe Ia Driven by spectral measurements Standard methods: 8 10% accuracy on distance Flux Ratios can calibrate to ~6% using a single spectrum First spectral method with robust improvements over standard methods Bailey et al 2009, A&A Letters, arxiv vsi grouping improves standard corrections to similar level Better statistical power, better systematics control Need high-z programs to match Julien Guy (SuperNova Legacy Survey): We donʼt need more supernovae, we need better supernovae Spectral measurements are providing that 23
Results from the Nearby Supernova Factory
 Results from the Nearby Supernova Factory R. C. Thomas for the SNfactory KITP: 2007-03-23 A/K/A (it s okay) Rollins Thomas Tom Rollins Roland Thomas Collaboration LBL Yale LPNHE IPNL G. Aldering, PI C.
Results from the Nearby Supernova Factory R. C. Thomas for the SNfactory KITP: 2007-03-23 A/K/A (it s okay) Rollins Thomas Tom Rollins Roland Thomas Collaboration LBL Yale LPNHE IPNL G. Aldering, PI C.
Supernova Surveys. Julien GUY PPC2010, Torino, July LPNHE - IN2P3 - CNRS - Universités Paris 6 et Paris 7
 Supernova Surveys Julien GUY julien.guy@lpnhe.in2p3.fr LPNHE - IN2P3 - CNRS - Universités Paris 6 et Paris 7 PPC2010, Torino, July 2010 Outline 1 Cosmology wit Type Ia Supernovae 2 SN surveys SDSS Union2
Supernova Surveys Julien GUY julien.guy@lpnhe.in2p3.fr LPNHE - IN2P3 - CNRS - Universités Paris 6 et Paris 7 PPC2010, Torino, July 2010 Outline 1 Cosmology wit Type Ia Supernovae 2 SN surveys SDSS Union2
Precision cosmology with Type Ia Supernovae?
 Precision cosmology with Type Ia Supernovae? Reynald Pain LPNHE, CNRS/IN2P3 & Universités Paris 6 and Paris 7 Outline I will used the SNLS 1st year data and analysis to try answer the following questions
Precision cosmology with Type Ia Supernovae? Reynald Pain LPNHE, CNRS/IN2P3 & Universités Paris 6 and Paris 7 Outline I will used the SNLS 1st year data and analysis to try answer the following questions
Investigating anisotropies in the local universe with the Nearby Supernova Factory
 Investigating anisotropies in the local universe with the Nearby Supernova Factory TR33 - Summer Institute: Particles and the Universe Corfu, September 21, 2012 Ulrich Feindt Physikalisches Institut Universität
Investigating anisotropies in the local universe with the Nearby Supernova Factory TR33 - Summer Institute: Particles and the Universe Corfu, September 21, 2012 Ulrich Feindt Physikalisches Institut Universität
SN Ia analyses with the Nearby Supernova Factory spectrophotometric data
 SN Ia analyses with the Nearby Supernova Factory spectrophotometric data Nicolas Chotard THCA / IPNL 6th FCPPL Workshop March 28, 2013 LPNHE Laboratoire de physique nucléaire et des hautes énergies 1 CONTENTS
SN Ia analyses with the Nearby Supernova Factory spectrophotometric data Nicolas Chotard THCA / IPNL 6th FCPPL Workshop March 28, 2013 LPNHE Laboratoire de physique nucléaire et des hautes énergies 1 CONTENTS
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 17 May 2009
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 17 May 2009 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 17 May 2009](/thumbs/94/119855373.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. 1973 c ESO 2018 October 25, 2018 Letter to the Editor Using spectral flux ratios to standardize SN Ia luminosities The Nearby Supernova Factory: S. Bailey 1, G.
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. 1973 c ESO 2018 October 25, 2018 Letter to the Editor Using spectral flux ratios to standardize SN Ia luminosities The Nearby Supernova Factory: S. Bailey 1, G.
Cosmological constraints from the 3rd year SNLS dataset
 IAS Workshop on Dark Energy November 2008 Cosmological constraints from the 3rd year SNLS dataset preliminary results with focus on systematics Julien Guy LPNHE IN2P3/CNRS Univ. Paris VI & VII Systematic
IAS Workshop on Dark Energy November 2008 Cosmological constraints from the 3rd year SNLS dataset preliminary results with focus on systematics Julien Guy LPNHE IN2P3/CNRS Univ. Paris VI & VII Systematic
The Nearby Supernova Factory
 The Nearby Supernova Factory W. M. Wood-Vasey, G. Aldering, B. C. Lee, S. Loken, P. Nugent, S. Perlmutter, J. Siegrist, L. Wang Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, One Cyclotron Road, Mailstop 50R232,
The Nearby Supernova Factory W. M. Wood-Vasey, G. Aldering, B. C. Lee, S. Loken, P. Nugent, S. Perlmutter, J. Siegrist, L. Wang Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, One Cyclotron Road, Mailstop 50R232,
Improvements to Type Ia Supernova Models. Clare M. Saunders. A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the. requirements for the degree of
 Improvements to Type Ia Supernova Models by Clare M. Saunders A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Physics in the Graduate Division
Improvements to Type Ia Supernova Models by Clare M. Saunders A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Physics in the Graduate Division
The Nearby Supernova Factory
 The Nearby Supernova Factory Yannick Copin Institut de physique nucléaire de Lyon Université Lyon 1 Cosmology for dummies (or instrumentalists) 2 kc total = i =1 2 = 1 k components i H 0 M,,,,... Friedmann
The Nearby Supernova Factory Yannick Copin Institut de physique nucléaire de Lyon Université Lyon 1 Cosmology for dummies (or instrumentalists) 2 kc total = i =1 2 = 1 k components i H 0 M,,,,... Friedmann
Challenges of low and intermediate redshift supernova surveys
 Challenges of low and intermediate redshift supernova surveys Ribamar R. R. Reis Image credit: ESO / M. Kornmesser Introduction Type Ia supernovae (SNeIa) are thermonuclear explosions of CO white dwarfs
Challenges of low and intermediate redshift supernova surveys Ribamar R. R. Reis Image credit: ESO / M. Kornmesser Introduction Type Ia supernovae (SNeIa) are thermonuclear explosions of CO white dwarfs
Dependence of low redshift Type Ia Supernovae luminosities on host galaxies
 Research in Astron. Astrophys. 2013 Vol. 13 No. 9, 1087 1096 http://www.raa-journal.org http://www.iop.org/journals/raa Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics Dependence of low redshift Type Ia Supernovae
Research in Astron. Astrophys. 2013 Vol. 13 No. 9, 1087 1096 http://www.raa-journal.org http://www.iop.org/journals/raa Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics Dependence of low redshift Type Ia Supernovae
Cosmology of Photometrically- Classified Type Ia Supernovae
 Cosmology of Photometrically- Classified Type Ia Supernovae Campbell et al. 2013 arxiv:1211.4480 Heather Campbell Collaborators: Bob Nichol, Chris D'Andrea, Mat Smith, Masao Sako and all the SDSS-II SN
Cosmology of Photometrically- Classified Type Ia Supernovae Campbell et al. 2013 arxiv:1211.4480 Heather Campbell Collaborators: Bob Nichol, Chris D'Andrea, Mat Smith, Masao Sako and all the SDSS-II SN
Stages of a Big Project ***
 Stages of a Big Project *** The Five stages of SDSS: 1. Denial 2. Anger 3. Bargaining 4. Depression 5. Acceptance *** With apologies to Elizabeth Kubler Ross The Carnegie Supernovae Project Wendy Freedman
Stages of a Big Project *** The Five stages of SDSS: 1. Denial 2. Anger 3. Bargaining 4. Depression 5. Acceptance *** With apologies to Elizabeth Kubler Ross The Carnegie Supernovae Project Wendy Freedman
Constraining Dark Energy: First Results from the SDSS-II Supernova Survey
 Constraining Dark Energy: First Results from the SDSS-II Supernova Survey J. Craig Wheeler Department of Astronomy University of Texas at Austin (adapted from presentation by Josh Frieman) Texas Cosmology
Constraining Dark Energy: First Results from the SDSS-II Supernova Survey J. Craig Wheeler Department of Astronomy University of Texas at Austin (adapted from presentation by Josh Frieman) Texas Cosmology
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 22 Oct 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 22 Oct 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 22 Oct 2018](/thumbs/93/113751784.jpg) Draft version October 24, 218 Typeset using L A TEX manuscript style in AASTeX61 SNEMO: IMPROVED EMPIRICAL MODELS FOR TYPE IA SUPERNOVAE arxiv:181.9476v1 [astro-ph.co] 22 Oct 218 C. Saunders, 1, 2, 3 G.
Draft version October 24, 218 Typeset using L A TEX manuscript style in AASTeX61 SNEMO: IMPROVED EMPIRICAL MODELS FOR TYPE IA SUPERNOVAE arxiv:181.9476v1 [astro-ph.co] 22 Oct 218 C. Saunders, 1, 2, 3 G.
Type Ia Supernovae: Standardizable Candles and Crayons
 Type Ia Supernovae: Standardizable Candles and Crayons Ryan Foley Clay Fellow Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Collaborators: Stephane Blondin Dan Kasen Bob Kirshner Kaisey Mandel & Nathan Sanders
Type Ia Supernovae: Standardizable Candles and Crayons Ryan Foley Clay Fellow Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics Collaborators: Stephane Blondin Dan Kasen Bob Kirshner Kaisey Mandel & Nathan Sanders
Supernovae with Euclid
 Supernovae with Euclid Isobel Hook University of Oxford and INAF (Obs. Roma) Thanks to R. Nichol, M. Della Valle, F. Mannucci, A. Goobar, P. Astier, B. Leibundgut, A. Ealet Euclid Conference 17 18 Nov
Supernovae with Euclid Isobel Hook University of Oxford and INAF (Obs. Roma) Thanks to R. Nichol, M. Della Valle, F. Mannucci, A. Goobar, P. Astier, B. Leibundgut, A. Ealet Euclid Conference 17 18 Nov
Supernovae Observations of the Expanding Universe. Kevin Twedt PHYS798G April 17, 2007
 Supernovae Observations of the Expanding Universe Kevin Twedt PHYS798G April 17, 2007 Overview How do we measure expansion? Use of supernovae 1a as a good measuring stick Techniques for observing supernovae
Supernovae Observations of the Expanding Universe Kevin Twedt PHYS798G April 17, 2007 Overview How do we measure expansion? Use of supernovae 1a as a good measuring stick Techniques for observing supernovae
MEASURING TYPE IA SUPERNOVA POPULATIONS OF STRETCH AND COLOR AND PREDICTING DISTANCE BIASES
 May 11, 2016 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 MEASURING TYPE IA SUPERNOVA POPULATIONS OF STRETCH AND COLOR AND PREDICTING DISTANCE BIASES D. Scolnic 1 & R. Kessler 1 May 11, 2016
May 11, 2016 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 MEASURING TYPE IA SUPERNOVA POPULATIONS OF STRETCH AND COLOR AND PREDICTING DISTANCE BIASES D. Scolnic 1 & R. Kessler 1 May 11, 2016
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 17 Apr 2013
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 17 Apr 2013 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 17 Apr 2013](/thumbs/83/87289673.jpg) Draft version February 7, 2014 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 HOST GALAXY PROPERTIES AND HUBBLE RESIDUALS OF TYPE IA SUPERNOVAE FROM THE NEARBY SUPERNOVA FACTORY M. Childress,
Draft version February 7, 2014 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 5/2/11 HOST GALAXY PROPERTIES AND HUBBLE RESIDUALS OF TYPE IA SUPERNOVAE FROM THE NEARBY SUPERNOVA FACTORY M. Childress,
R. Pain CSP 07 June 17,
 http://www.cfht.hawaii.edu/snls R. Pain CSP 07 June 17, 2007 1 Outline SNLS : the SuperNova Legacy Survey Cosmological analysis & first results (+3yr update) Systematic uncertainties & expected precision
http://www.cfht.hawaii.edu/snls R. Pain CSP 07 June 17, 2007 1 Outline SNLS : the SuperNova Legacy Survey Cosmological analysis & first results (+3yr update) Systematic uncertainties & expected precision
SALT: a Spectral Adaptive Light curve Template for Type Ia Supernovae
 22nd Texas Symposium on Relativistic Astrophysics at Stanford University, Dec. 3, 2004 SALT: a Spectral Adaptive Light curve Template for Type Ia Supernovae J. Guy, P. Astier, S. Nobili, N. Regnault, and
22nd Texas Symposium on Relativistic Astrophysics at Stanford University, Dec. 3, 2004 SALT: a Spectral Adaptive Light curve Template for Type Ia Supernovae J. Guy, P. Astier, S. Nobili, N. Regnault, and
Cosmology with type Ia Supernovae
 Cosmology with type Ia Supernovae Pierre Astier LPNHE/IN2P3/CNRS Universités Paris VI&VII XII International Workshop on Neutrino Telescopes Supernovae: present classification scheme H / no H? Type II light
Cosmology with type Ia Supernovae Pierre Astier LPNHE/IN2P3/CNRS Universités Paris VI&VII XII International Workshop on Neutrino Telescopes Supernovae: present classification scheme H / no H? Type II light
Supernovae and the Accelerating Universe
 Supernovae and the Accelerating Universe Nicholas B. Suntzeff Mitchell Institute for Fundamental Physics Department of Physics & Astronomy Texas A&M University University of Texas/Austin Second Texas Cosmology
Supernovae and the Accelerating Universe Nicholas B. Suntzeff Mitchell Institute for Fundamental Physics Department of Physics & Astronomy Texas A&M University University of Texas/Austin Second Texas Cosmology
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 21 Aug 2007
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 21 Aug 2007 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph] 21 Aug 2007](/thumbs/93/113115929.jpg) Survey Requirements for Accurate and Precise Photometric Redshifts for Type Ia Supernovae Yun Wang 1, Gautham Narayan 2, and Michael Wood-Vasey 2 arxiv:0708.0033v2 [astro-ph] 21 Aug 2007 ABSTRACT In this
Survey Requirements for Accurate and Precise Photometric Redshifts for Type Ia Supernovae Yun Wang 1, Gautham Narayan 2, and Michael Wood-Vasey 2 arxiv:0708.0033v2 [astro-ph] 21 Aug 2007 ABSTRACT In this
SNLS supernovae photometric classification with machine learning
 SNLS supernovae photometric classification with machine learning Courtesy of D. Campbell-Wilson Anais Möller CAASTRO, Australian National University Statistical Challenges in Astronomy, Carnegie Mellon
SNLS supernovae photometric classification with machine learning Courtesy of D. Campbell-Wilson Anais Möller CAASTRO, Australian National University Statistical Challenges in Astronomy, Carnegie Mellon
The Observable Universe: Redshift, Distances and the Hubble-Law. Max Camenzind Sept 2010
 The Observable Universe: Redshift, Distances and the Hubble-Law Max Camenzind Bremen @ Sept 2010 Key Facts Universe 1. The Universe is expanding and presently even accelerating. Hubble Expansion: Space
The Observable Universe: Redshift, Distances and the Hubble-Law Max Camenzind Bremen @ Sept 2010 Key Facts Universe 1. The Universe is expanding and presently even accelerating. Hubble Expansion: Space
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 17 Dec 2010
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 17 Dec 2010 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 17 Dec 2010](/thumbs/72/67752322.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. specindic c ESO 2010 December 20, 2010 Do spectra improve distance measurements of Type Ia supernovae? S. Blondin 1, K. S. Mandel 2, and R. P. Kirshner 2 arxiv:1012.0005v2
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. specindic c ESO 2010 December 20, 2010 Do spectra improve distance measurements of Type Ia supernovae? S. Blondin 1, K. S. Mandel 2, and R. P. Kirshner 2 arxiv:1012.0005v2
Bayesian Modeling for Type Ia Supernova Data, Dust, and Distances
 Bayesian Modeling for Type Ia Supernova Data, Dust, and Distances Kaisey Mandel Supernova Group Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics ichasc Astrostatistics Seminar 17 Sept 213 1 Outline Brief Introduction
Bayesian Modeling for Type Ia Supernova Data, Dust, and Distances Kaisey Mandel Supernova Group Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics ichasc Astrostatistics Seminar 17 Sept 213 1 Outline Brief Introduction
SDSS-II Supernova Survey (continued) David Cinabro Wayne State University AIPW, Dubrovnik, Croatia 4-9 September 2006
 SDSS-II Supernova Survey (continued) David Cinabro Wayne State University AIPW, Dubrovnik, Croatia 4-9 September 2006 1 SDSS-II Supernova Survey Preliminary SNIa Volumetric Rate Core Collapse SN: Steps
SDSS-II Supernova Survey (continued) David Cinabro Wayne State University AIPW, Dubrovnik, Croatia 4-9 September 2006 1 SDSS-II Supernova Survey Preliminary SNIa Volumetric Rate Core Collapse SN: Steps
Supernovae Observations of the Accelerating Universe. K Twedt Department of Physics, University of Maryland, College Park, MD, 20740, USA
 Supernovae Observations of the Accelerating Universe K Twedt Department of Physics, University of Maryland, College Park, MD, 20740, USA Over the past three decades, supernovae observations have been the
Supernovae Observations of the Accelerating Universe K Twedt Department of Physics, University of Maryland, College Park, MD, 20740, USA Over the past three decades, supernovae observations have been the
Committee in charge: Professor Saul Perlmutter, Chair Professor Steve Boggs Professor Chung-Pei Ma
 Supernova Ia Spectra and Spectrophotometric Time Series: Recognizing Twins and the Consequences for Cosmological Distance Measurements by Hannah Kathleen Fakhouri A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction
Supernova Ia Spectra and Spectrophotometric Time Series: Recognizing Twins and the Consequences for Cosmological Distance Measurements by Hannah Kathleen Fakhouri A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction
Type Ia SNe standardization accounting for the environment. Lluís Galbany CENTRA-IST, UTL, Lisbon
 Type Ia SNe standardization accounting for the environment Lluís Galbany CENTRA-IST, UTL, Lisbon Benasc, 17 August 2012 Type Ia SNe as standard candles Used as a cosmological probes because of their bright
Type Ia SNe standardization accounting for the environment Lluís Galbany CENTRA-IST, UTL, Lisbon Benasc, 17 August 2012 Type Ia SNe as standard candles Used as a cosmological probes because of their bright
The Keck/SDSS SN Sample
 The Keck/SDSS SN Sample (#" "#' )*+,-./*!0! "#& "#% "#$ )*7.69,+7 " "#" "#$ "#( "#"!"#(!"#$ %" :" $" (" " $ 1;*?.@ AB*!C6D 1211 345!)*678.0- )*678.0-!( "(!$ "#"!"#(!"#$ "#:E "#:" "#$E "#$" "#(E :"""
The Keck/SDSS SN Sample (#" "#' )*+,-./*!0! "#& "#% "#$ )*7.69,+7 " "#" "#$ "#( "#"!"#(!"#$ %" :" $" (" " $ 1;*?.@ AB*!C6D 1211 345!)*678.0- )*678.0-!( "(!$ "#"!"#(!"#$ "#:E "#:" "#$E "#$" "#(E :"""
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 4 Jan 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 4 Jan 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 4 Jan 2018](/thumbs/78/78365628.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. ms c ESO 18 January 8, 18 Understanding Type Ia supernovae through their U-band spectra J. Nordin 1, G. Aldering, P. Antilogus 3, C. Aragon, S. Bailey, C. Baltay
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. ms c ESO 18 January 8, 18 Understanding Type Ia supernovae through their U-band spectra J. Nordin 1, G. Aldering, P. Antilogus 3, C. Aragon, S. Bailey, C. Baltay
Observational cosmology and Type Ia Supernovae, Part II
 Observational cosmology and Type Ia Supernovae, Part II Rahman Amanullah, The Oskar Klein Centre, Stockholm University rahman@fysik.su.se Cosmology fits SN Ia cosmology tutorial Spectrum Search Subtraction
Observational cosmology and Type Ia Supernovae, Part II Rahman Amanullah, The Oskar Klein Centre, Stockholm University rahman@fysik.su.se Cosmology fits SN Ia cosmology tutorial Spectrum Search Subtraction
Type II Supernovae as Standardized Candles
 Type II Supernovae as Standardized Candles Mario Hamuy 1 2 Steward Observatory, The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721 Philip A. Pinto Steward Observatory, The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721
Type II Supernovae as Standardized Candles Mario Hamuy 1 2 Steward Observatory, The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721 Philip A. Pinto Steward Observatory, The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721
arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.co] 24 Jan 2018
![arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.co] 24 Jan 2018 arxiv: v3 [astro-ph.co] 24 Jan 2018](/thumbs/87/97336127.jpg) Open Astron. 2017; 26:111 119 Research Article David F. Crawford* A problem with the analysis of type Ia supernovae arxiv:1711.11237v3 [astro-ph.co] 24 Jan 2018 Abstract: Type Ia supernovae have light
Open Astron. 2017; 26:111 119 Research Article David F. Crawford* A problem with the analysis of type Ia supernovae arxiv:1711.11237v3 [astro-ph.co] 24 Jan 2018 Abstract: Type Ia supernovae have light
Supernova Legacy Survey 3-years data sample Delphine HARDIN, on behalf of the Supernova Legacy Survey (SNLS)
 Supernova Legacy Survey 3-years data sample Delphine HARDIN, on behalf of the Supernova Legacy Survey (SNLS) LPNHE, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris, France E-mail: hardin@in2p3.fr We present the
Supernova Legacy Survey 3-years data sample Delphine HARDIN, on behalf of the Supernova Legacy Survey (SNLS) LPNHE, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris, France E-mail: hardin@in2p3.fr We present the
The universe is static
 The universe is static David F. Crawford 1 44 Market St, Naremburn, 2065, NSW, Australia Abstract It is shown that the light curve widths of type Ia supernovae do not have time dilation and that their
The universe is static David F. Crawford 1 44 Market St, Naremburn, 2065, NSW, Australia Abstract It is shown that the light curve widths of type Ia supernovae do not have time dilation and that their
Searching for the Progenitors of Subluminous Type Ia Supernovae with SN 2013bc
 Hubble Space Telescope Cycle 11 General Observer Proposal Searching for the Progenitors of Subluminous Type Ia Supernovae with SN 2013bc Principal Investigator: Institution: Electronic mail: Maximilian
Hubble Space Telescope Cycle 11 General Observer Proposal Searching for the Progenitors of Subluminous Type Ia Supernovae with SN 2013bc Principal Investigator: Institution: Electronic mail: Maximilian
Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc
 Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc (materials from http://www.sdss.org/) Shan Huang 17 February 2010 Survey type Status Imaging and Spectroscopy Basic Facts SDSS-II completed, SDSS-III
Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc (materials from http://www.sdss.org/) Shan Huang 17 February 2010 Survey type Status Imaging and Spectroscopy Basic Facts SDSS-II completed, SDSS-III
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 10 Sep 2013
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 10 Sep 2013 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 10 Sep 2013](/thumbs/92/108042976.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Halpha_environment c ESO 8 September, 8 Evidence of Environmental Dependencies of Type Ia Supernovae from the Nearby Supernova Factory indicated by Local Hα M. Rigault,
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. Halpha_environment c ESO 8 September, 8 Evidence of Environmental Dependencies of Type Ia Supernovae from the Nearby Supernova Factory indicated by Local Hα M. Rigault,
Infrared Light Curves of Type Ia Supernovae
 Infrared Light Curves of Type Ia Supernovae Andrew Friedman Harvard University Department of Astronomy www.cfa.harvard.edu/pairitel www.pairitel.org, afriedman@cfa.harvard.edu 1/5/10 AAS Thesis Talk 1
Infrared Light Curves of Type Ia Supernovae Andrew Friedman Harvard University Department of Astronomy www.cfa.harvard.edu/pairitel www.pairitel.org, afriedman@cfa.harvard.edu 1/5/10 AAS Thesis Talk 1
The Supernova Legacy Survey
 Astronomical Science The Supernova Legacy Survey Mark Sullivan Christophe Balland Department of Physics, University of Oxford, United Kingdom Laboratoire de Physique Nucléaire et des Hautes Énergies (LPNHE),
Astronomical Science The Supernova Legacy Survey Mark Sullivan Christophe Balland Department of Physics, University of Oxford, United Kingdom Laboratoire de Physique Nucléaire et des Hautes Énergies (LPNHE),
Type Ia Supernovae meet Maximum Likelihood Estimators
 Type Ia Supernovae meet Maximum Likelihood Estimators Alberto Guffanti Università degli Studi di Torino & INFN Torino J. Trøst Nielsen, AG and S. Sarkar, arxiv:1506.01354 J. Trøst Nielsen, arxiv:1508.07850
Type Ia Supernovae meet Maximum Likelihood Estimators Alberto Guffanti Università degli Studi di Torino & INFN Torino J. Trøst Nielsen, AG and S. Sarkar, arxiv:1506.01354 J. Trøst Nielsen, arxiv:1508.07850
Really, what universe do we live in? White dwarfs Supernova type Ia Accelerating universe Cosmic shear Lyman α forest
 Really, what universe do we live in? White dwarfs Supernova type Ia Accelerating universe Cosmic shear Lyman α forest White dwarf Core of solar mass star No energy from fusion or gravitational contraction
Really, what universe do we live in? White dwarfs Supernova type Ia Accelerating universe Cosmic shear Lyman α forest White dwarf Core of solar mass star No energy from fusion or gravitational contraction
A. KIM, M. KIM, J. LEE, R. PAIN 2, C. PENNYPACKER, S. PERLMUTTER AND B. BOYLE, P. BUNCLARK, D. CARTER, K. GLAZEBROOK 3 AND
 OBSERVATION OF COSMOLOGICAL TIME DILATION USING TYPE IA SUPERNOVAE AS CLOCKS The Supernova Cosmology Project : III G.GOLDHABER 1, S. DEUSTUA, S. GABI, D. GROOM, I. HOOK, A. KIM, M. KIM, J. LEE, R. PAIN
OBSERVATION OF COSMOLOGICAL TIME DILATION USING TYPE IA SUPERNOVAE AS CLOCKS The Supernova Cosmology Project : III G.GOLDHABER 1, S. DEUSTUA, S. GABI, D. GROOM, I. HOOK, A. KIM, M. KIM, J. LEE, R. PAIN
Data-driven approach to Type Ia supernovae: variable selection on the peak luminosity and clustering in visual analytics
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Data-driven approach to Type Ia supernovae: variable selection on the peak luminosity and clustering in visual analytics To cite this article: Makoto
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Data-driven approach to Type Ia supernovae: variable selection on the peak luminosity and clustering in visual analytics To cite this article: Makoto
Supplementary Information for SNLS-03D3bb a super- Chandrasekhar mass Type Ia supernova
 1 Supplementary Information for SNLS-03D3bb a super- Chandrasekhar mass Type Ia supernova SN Location SNLS-03D3bb is located at RA: 14:16:18.920 Dec: +52:14:53.66 (J2000) in the D3 (extended Groth Strip)
1 Supplementary Information for SNLS-03D3bb a super- Chandrasekhar mass Type Ia supernova SN Location SNLS-03D3bb is located at RA: 14:16:18.920 Dec: +52:14:53.66 (J2000) in the D3 (extended Groth Strip)
Set 5: Expansion of the Universe
 Set 5: Expansion of the Universe Cosmology Study of the origin, contents and evolution of the universe as a whole Expansion rate and history Space-time geometry Energy density composition Origin of structure
Set 5: Expansion of the Universe Cosmology Study of the origin, contents and evolution of the universe as a whole Expansion rate and history Space-time geometry Energy density composition Origin of structure
The PRIsm MUlti-object Survey (PRIMUS)
 The PRIsm MUlti-object Survey (PRIMUS) Alison Coil University of Arizona Steward Observatory March 2008 Overview: Galaxy evolution to z ~ 1 is still cosmic variance limited: DEEP2, VVDS, COMBO-17, COSMOS
The PRIsm MUlti-object Survey (PRIMUS) Alison Coil University of Arizona Steward Observatory March 2008 Overview: Galaxy evolution to z ~ 1 is still cosmic variance limited: DEEP2, VVDS, COMBO-17, COSMOS
The Supernova Legacy Survey (SNLS)
 The Supernova Legacy Survey (SNLS) Pierre Astier LPNHE IN2P3/CNRS Universités Paris VI&VII November 8, 2006 Supernovae and acceleration Distances to type Ia supernovae strongly favor a recent accelerated
The Supernova Legacy Survey (SNLS) Pierre Astier LPNHE IN2P3/CNRS Universités Paris VI&VII November 8, 2006 Supernovae and acceleration Distances to type Ia supernovae strongly favor a recent accelerated
Hubble s Law and the Cosmic Distance Scale
 Lab 7 Hubble s Law and the Cosmic Distance Scale 7.1 Overview Exercise seven is our first extragalactic exercise, highlighting the immense scale of the Universe. It addresses the challenge of determining
Lab 7 Hubble s Law and the Cosmic Distance Scale 7.1 Overview Exercise seven is our first extragalactic exercise, highlighting the immense scale of the Universe. It addresses the challenge of determining
Dec SNe. Mar SNe Jan SNe. N SN Ia. Mar SNe HST. Dec SNe. Preliminary Analysis 3. No Big Bang 90% 68% Ω Λ = Λ /(3H 0
 A REVIEW OF THE HIGH-REDSHIFT SUPERNOVA SEARCHES A.G. KIM PCC, College de France, 11, Place M. Berthelot, 7531 Paris, France Observations show that Type Ia Supernovae (SNe Ia) form a homogeneous class
A REVIEW OF THE HIGH-REDSHIFT SUPERNOVA SEARCHES A.G. KIM PCC, College de France, 11, Place M. Berthelot, 7531 Paris, France Observations show that Type Ia Supernovae (SNe Ia) form a homogeneous class
First results from the Stockholm VIMOS Supernova Survey
 First results from the Stockholm VIMOS Supernova Survey - Detection efficiencies and photometric accuracy in supernova surveys Outline The Stockholm VIMOS Supernova Survey, SVISS. First results from the
First results from the Stockholm VIMOS Supernova Survey - Detection efficiencies and photometric accuracy in supernova surveys Outline The Stockholm VIMOS Supernova Survey, SVISS. First results from the
First Results from the La Silla-QUEST Supernova Survey and the Carnegie Supernova Project
 First Results from the La Silla-QUEST Supernova Survey and the Carnegie Supernova Project E. S. Walker 1, C. Baltay 1, A. Campillay 2, C. Citrenbaum 1, C. Contreras 2,4, N. Ellman 1, U. Feindt 3, C. González
First Results from the La Silla-QUEST Supernova Survey and the Carnegie Supernova Project E. S. Walker 1, C. Baltay 1, A. Campillay 2, C. Citrenbaum 1, C. Contreras 2,4, N. Ellman 1, U. Feindt 3, C. González
The Old Stellar Population Studies with Subaru Young-Wook Lee Yonsei Univ., Seoul, Korea
 (Some humble suggestions for) The Old Stellar Population Studies with Subaru Young-Wook Lee Yonsei Univ., Seoul, Korea 1. Globular cluster Dwarf galaxy Connection (Some) Globular clusters show multiple
(Some humble suggestions for) The Old Stellar Population Studies with Subaru Young-Wook Lee Yonsei Univ., Seoul, Korea 1. Globular cluster Dwarf galaxy Connection (Some) Globular clusters show multiple
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 11 Jun 2018
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 11 Jun 2018 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 11 Jun 2018](/thumbs/88/114813656.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. main_arxiv c ESO 2018 June 12, 2018 arxiv:1806.03849v1 [astro-ph.co] 11 Jun 2018 Strong Dependence of Type Ia Supernova Standardization on the Local Specific Star
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. main_arxiv c ESO 2018 June 12, 2018 arxiv:1806.03849v1 [astro-ph.co] 11 Jun 2018 Strong Dependence of Type Ia Supernova Standardization on the Local Specific Star
PESSTO The Public ESO Spectroscopic Survey for Transient Objects
 PESSTO The Public ESO Spectroscopic Survey for Transient Objects Morgan Fraser Institute of Astronomy, University of Cambridge, UK Stefano Benetti INAF - Osservatorio Astronomico di Padova, Italy Cosimo
PESSTO The Public ESO Spectroscopic Survey for Transient Objects Morgan Fraser Institute of Astronomy, University of Cambridge, UK Stefano Benetti INAF - Osservatorio Astronomico di Padova, Italy Cosimo
ABSTRACT. 1. Introduction
 A&A 447, 31 48 (26) DOI: 1.151/4-6361:254185 c ESO 26 Astronomy & Astrophysics The Supernova Legacy Survey: measurement of Ω M, Ω Λ and w from the first year data set, P. Astier 1,J.Guy 1, N. Regnault
A&A 447, 31 48 (26) DOI: 1.151/4-6361:254185 c ESO 26 Astronomy & Astrophysics The Supernova Legacy Survey: measurement of Ω M, Ω Λ and w from the first year data set, P. Astier 1,J.Guy 1, N. Regnault
Supernovae explosions and the Accelerating Universe. Bodo Ziegler
 Nobel Prize for Physics 2011 Supernovae explosions and the Accelerating Universe Institute for Astronomy University of Vienna Since 09/2010: ouniprof University of Vienna 12/2008-08/10: Staff member European
Nobel Prize for Physics 2011 Supernovae explosions and the Accelerating Universe Institute for Astronomy University of Vienna Since 09/2010: ouniprof University of Vienna 12/2008-08/10: Staff member European
Photometric classification of SNe Ia in the SuperNova Legacy Survey with supervised learning
 Photometric classification of SNe Ia in the SuperNova Legacy Survey with supervised learning Courtesy of D. Campbell-Wilson CAASTRO Postdoc at the Australian National University (ANU) Photometric Classification
Photometric classification of SNe Ia in the SuperNova Legacy Survey with supervised learning Courtesy of D. Campbell-Wilson CAASTRO Postdoc at the Australian National University (ANU) Photometric Classification
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 25 Jan 1997
 Measurements of the Cosmological Parameters Ω and Λ from the First 7 Supernovae at z 0.35 arxiv:astro-ph/9608192v2 25 Jan 1997 S. Perlmutter, 1,2 S. Gabi, 1,3 G. Goldhaber, 1,2 A. Goobar, 1,2,4 D. E. Groom,
Measurements of the Cosmological Parameters Ω and Λ from the First 7 Supernovae at z 0.35 arxiv:astro-ph/9608192v2 25 Jan 1997 S. Perlmutter, 1,2 S. Gabi, 1,3 G. Goldhaber, 1,2 A. Goobar, 1,2,4 D. E. Groom,
The Extragalactic Distance Scale
 One of the important relations in Astronomy. It lets us Measure the distance to distance objects. Each rung on the ladder is calibrated using lower-rung calibrations. Distance Objects Technique 1-100 AU
One of the important relations in Astronomy. It lets us Measure the distance to distance objects. Each rung on the ladder is calibrated using lower-rung calibrations. Distance Objects Technique 1-100 AU
Constraints on Anisotropic Cosmic Expansion from Supernovae
 Constraints on Anisotropic Cosmic Expansion from Supernovae Based on BK, Schwarz, Seikel, Wiegand, arxiv:1212.3691 Benedict Kalus Bielefeld University 2 / 12 8. Kosmologietag 25 th April, 2013 IBZ, Bielefeld
Constraints on Anisotropic Cosmic Expansion from Supernovae Based on BK, Schwarz, Seikel, Wiegand, arxiv:1212.3691 Benedict Kalus Bielefeld University 2 / 12 8. Kosmologietag 25 th April, 2013 IBZ, Bielefeld
Novel Bayesian approaches to supernova type Ia cosmology
 Novel Bayesian approaches to supernova type Ia cosmology - MCMSki 2014 07/01/14 - www.robertotrotta.com The cosmological concordance model The ΛCDM cosmological concordance model is built on three pillars:
Novel Bayesian approaches to supernova type Ia cosmology - MCMSki 2014 07/01/14 - www.robertotrotta.com The cosmological concordance model The ΛCDM cosmological concordance model is built on three pillars:
The Extragalactic Distance Scale
 One of the important relations in Astronomy. It lets us Measure the distance to distance objects. Each rung on the ladder is calibrated using lower-rung calibrations. Distance Objects Technique 1-100 AU
One of the important relations in Astronomy. It lets us Measure the distance to distance objects. Each rung on the ladder is calibrated using lower-rung calibrations. Distance Objects Technique 1-100 AU
Set 1: Expansion of the Universe
 Set 1: Expansion of the Universe Syllabus Course text book: Ryden, Introduction to Cosmology, 2nd edition Olber s paradox, expansion of the universe: Ch 2 Cosmic geometry, expansion rate, acceleration:
Set 1: Expansion of the Universe Syllabus Course text book: Ryden, Introduction to Cosmology, 2nd edition Olber s paradox, expansion of the universe: Ch 2 Cosmic geometry, expansion rate, acceleration:
Determining distance. L 4π f. d = d = R θ. Standard candle. Standard ruler
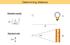 Determining distance Standard candle d = L 4π f 1 2 d L Standard ruler d = R θ θ R Determining distance: Parallax RULER tanπ = R d π R d π R = 1AU = 1.5 10 13 cm Define new distance unit: parsec (parallax-second)
Determining distance Standard candle d = L 4π f 1 2 d L Standard ruler d = R θ θ R Determining distance: Parallax RULER tanπ = R d π R d π R = 1AU = 1.5 10 13 cm Define new distance unit: parsec (parallax-second)
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 9 Oct 2012
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 9 Oct 2012 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 9 Oct 2012](/thumbs/95/124908872.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. SNFextinction c ESO 218 October 29, 218 arxiv:121.2619v1 [astro-ph.im] 9 Oct 212 Atmospheric extinction properties above Mauna Kea from the Nearby Supernova Factory
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. SNFextinction c ESO 218 October 29, 218 arxiv:121.2619v1 [astro-ph.im] 9 Oct 212 Atmospheric extinction properties above Mauna Kea from the Nearby Supernova Factory
Photometric Redshifts, DES, and DESpec
 Photometric Redshifts, DES, and DESpec Huan Lin, Photo-z s, DES, and DESpec, DESPec Workshop, KICP, Chicago, 30 May 2012 Outline DES photo-z calibrations: spectroscopic training set fields DES photo-z
Photometric Redshifts, DES, and DESpec Huan Lin, Photo-z s, DES, and DESpec, DESPec Workshop, KICP, Chicago, 30 May 2012 Outline DES photo-z calibrations: spectroscopic training set fields DES photo-z
Projet : SNSPEC PROGRAMME BLANC EDITION 2012 DOCUMENT SCIENTIFIQUE
 Important Ce document ne doit pas dépasser 30 pages, dans la mise en page et la typographie fournies par l ANR. Ce point constitue un critère de recevabilité de la proposition de projet. Les propositions
Important Ce document ne doit pas dépasser 30 pages, dans la mise en page et la typographie fournies par l ANR. Ce point constitue un critère de recevabilité de la proposition de projet. Les propositions
Lecture 7:Our Universe
 Lecture 7:Our Universe 1. Traditional Cosmological tests Theta-z Galaxy counts Tolman Surface Brightness test 2. Modern tests HST Key Project (H o ) Nucleosynthesis (Ω b ) BBN+Clusters (Ω M ) SN1a (Ω M
Lecture 7:Our Universe 1. Traditional Cosmological tests Theta-z Galaxy counts Tolman Surface Brightness test 2. Modern tests HST Key Project (H o ) Nucleosynthesis (Ω b ) BBN+Clusters (Ω M ) SN1a (Ω M
High Redshift Universe
 High Redshift Universe Finding high z galaxies Lyman break galaxies (LBGs) Photometric redshifts Deep fields Starburst galaxies Extremely red objects (EROs) Sub-mm galaxies Lyman α systems Finding high
High Redshift Universe Finding high z galaxies Lyman break galaxies (LBGs) Photometric redshifts Deep fields Starburst galaxies Extremely red objects (EROs) Sub-mm galaxies Lyman α systems Finding high
Strong gravitational lenses in the 2020s
 Strong gravitational lenses in the 2020s Masamune Oguri University of Tokyo 2014/7/18 TMT science forum @ Tucson Strong gravitational lenses are rare wide-field surveys find strong gravitational lenses
Strong gravitational lenses in the 2020s Masamune Oguri University of Tokyo 2014/7/18 TMT science forum @ Tucson Strong gravitational lenses are rare wide-field surveys find strong gravitational lenses
Allan Sandage and the Cosmic Expansion
 Allan Sandage and the Cosmic Expansion The Fundamental Cosmic Distance Scale Conference, Naples May 2 6, 2011 G. A. Tammann Allan Sandage a mentor, a collaborator, a friend for 47 years G. A. Tammann A.
Allan Sandage and the Cosmic Expansion The Fundamental Cosmic Distance Scale Conference, Naples May 2 6, 2011 G. A. Tammann Allan Sandage a mentor, a collaborator, a friend for 47 years G. A. Tammann A.
The Era of Synoptic Surveys. Peter Nugent (LBNL)
 The Era of Synoptic Surveys Peter Nugent (LBNL) Current Optical Surveys Photometric: Palomar Transient Factory La Silla Supernova Search SkyMapper PanSTARRS Spectroscopic: SDSS III All of these surveys
The Era of Synoptic Surveys Peter Nugent (LBNL) Current Optical Surveys Photometric: Palomar Transient Factory La Silla Supernova Search SkyMapper PanSTARRS Spectroscopic: SDSS III All of these surveys
EVOLUTION OF DUST EXTINCTION AND SUPERNOVA COSMOLOGY
 To Appear in ApJ Letters Preprint typeset using LATEX style emulateapj v. 04/03/99 EVOLUTION OF DUST EXTINCTION AND SUPERNOVA COSMOLOGY Tomonori Totani 1 and Chiaki Kobayashi 2 1 National Astronomical
To Appear in ApJ Letters Preprint typeset using LATEX style emulateapj v. 04/03/99 EVOLUTION OF DUST EXTINCTION AND SUPERNOVA COSMOLOGY Tomonori Totani 1 and Chiaki Kobayashi 2 1 National Astronomical
Cosmology with the Sloan Digital Sky Survey Supernova Search. David Cinabro
 Cosmology with the Sloan Digital Sky Survey Supernova Search David Cinabro Cosmology Background The study of the origin and evolution of the Universe. First real effort by Einstein in 1916 Gravity is all
Cosmology with the Sloan Digital Sky Survey Supernova Search David Cinabro Cosmology Background The study of the origin and evolution of the Universe. First real effort by Einstein in 1916 Gravity is all
IX. The Cosmological Constant. ASTR378 Cosmology : IX. The Cosmological Constant 96
 IX. The Cosmological Constant ASTR378 Cosmology : IX. The Cosmological Constant 96 Einstein s Greatest Blunder At the time (~1915), Universe believed static, supported by observational data Universe containing
IX. The Cosmological Constant ASTR378 Cosmology : IX. The Cosmological Constant 96 Einstein s Greatest Blunder At the time (~1915), Universe believed static, supported by observational data Universe containing
Chapter 7: From theory to observations
 Chapter 7: From theory to observations Given the stellar mass and chemical composition of a ZAMS, the stellar modeling can, in principle, predict the evolution of the stellar bolometric luminosity, effective
Chapter 7: From theory to observations Given the stellar mass and chemical composition of a ZAMS, the stellar modeling can, in principle, predict the evolution of the stellar bolometric luminosity, effective
The structure and evolution of stars. Learning Outcomes
 The structure and evolution of stars Lecture14: Type Ia Supernovae The Extravagant Universe By R. Kirshner 1 Learning Outcomes In these final two lectures the student will learn about the following issues:
The structure and evolution of stars Lecture14: Type Ia Supernovae The Extravagant Universe By R. Kirshner 1 Learning Outcomes In these final two lectures the student will learn about the following issues:
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 14 Oct 2005
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. cosmo February 5, 28 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) The Supernova Legacy Survey: Measurement ofω M,Ω Λ and w from the First Year Data Set arxiv:astro-ph/51447v1
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. cosmo February 5, 28 (DOI: will be inserted by hand later) The Supernova Legacy Survey: Measurement ofω M,Ω Λ and w from the First Year Data Set arxiv:astro-ph/51447v1
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 2 Oct 2014
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 2 Oct 2014 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 2 Oct 2014](/thumbs/88/115357854.jpg) Accepted by ApJ Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 COSMOLOGICAL PARAMETER UNCERTAINTIES FROM SALT-II TYPE IA SUPERNOVA LIGHT CURVE MODELS J. Mosher 1, J. Guy 2,3, R. Kessler 4,
Accepted by ApJ Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 12/16/11 COSMOLOGICAL PARAMETER UNCERTAINTIES FROM SALT-II TYPE IA SUPERNOVA LIGHT CURVE MODELS J. Mosher 1, J. Guy 2,3, R. Kessler 4,
The Next 2-3 Weeks. Important to read through Chapter 17 (Relativity) before I start lecturing on it.
 The Next 2-3 Weeks [27.1] The Extragalactic Distance Scale. [27.2] The Expansion of the Universe. [29.1] Newtonian Cosmology [29.2] The Cosmic Microwave Background [17] General Relativity & Black Holes
The Next 2-3 Weeks [27.1] The Extragalactic Distance Scale. [27.2] The Expansion of the Universe. [29.1] Newtonian Cosmology [29.2] The Cosmic Microwave Background [17] General Relativity & Black Holes
Embedding Supernova Cosmology into a Bayesian Hierarchical Model
 1 / 41 Embedding Supernova Cosmology into a Bayesian Hierarchical Model Xiyun Jiao Statistic Section Department of Mathematics Imperial College London Joint work with David van Dyk, Roberto Trotta & Hikmatali
1 / 41 Embedding Supernova Cosmology into a Bayesian Hierarchical Model Xiyun Jiao Statistic Section Department of Mathematics Imperial College London Joint work with David van Dyk, Roberto Trotta & Hikmatali
SDSS-II: DETERMINATION OF SHAPE AND COLOR PARAMETER COEFFICIENTS FOR SALT-II FIT MODEL
 SDSS-II: DETERMINATION OF SHAPE AND COLOR PARAMETER COEFFICIENTS FOR SALT-II FIT MODEL L. Dojcsak, 1 J. Marriner 2 August 14, 2010 ABSTRACT In this study we look at the SALT-II model of Type IA supernova
SDSS-II: DETERMINATION OF SHAPE AND COLOR PARAMETER COEFFICIENTS FOR SALT-II FIT MODEL L. Dojcsak, 1 J. Marriner 2 August 14, 2010 ABSTRACT In this study we look at the SALT-II model of Type IA supernova
Supernovae photometric classification of SNLS data with supervised learning
 Supernovae photometric classification of SNLS data with supervised learning Anais Möller CAASTRO & Australian National University A. Möller,V. Ruhlmann-Kleider, C. Leloup,J. Neveu, N. Palanque-Delabrouille,J.
Supernovae photometric classification of SNLS data with supervised learning Anais Möller CAASTRO & Australian National University A. Möller,V. Ruhlmann-Kleider, C. Leloup,J. Neveu, N. Palanque-Delabrouille,J.
SNLS spectroscopy: testing for evolution in type Ia supernovae ABSTRACT
 A&A 477, 717 734 (28) DOI: 1.151/4-6361:277655 c ESO 28 Astronomy & Astrophysics SNLS spectroscopy: testing for evolution in type Ia supernovae T. J. Bronder 1,,I.M.Hook 1, P. Astier 2,D.Balam 3,C.Balland
A&A 477, 717 734 (28) DOI: 1.151/4-6361:277655 c ESO 28 Astronomy & Astrophysics SNLS spectroscopy: testing for evolution in type Ia supernovae T. J. Bronder 1,,I.M.Hook 1, P. Astier 2,D.Balam 3,C.Balland
Type Ia Supernovae from Near-IR Photometry
 Type Ia Supernovae from Near-IR Photometry Kevin Krisciunas, Mark Phillips, Nick Suntzeff LasCampanasand Cerro Tololo Observatories References: Krisciunas et al. 2004 (astro-ph/0312626) Krisciunas et al.
Type Ia Supernovae from Near-IR Photometry Kevin Krisciunas, Mark Phillips, Nick Suntzeff LasCampanasand Cerro Tololo Observatories References: Krisciunas et al. 2004 (astro-ph/0312626) Krisciunas et al.
Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative.
 Chapter 6 Distances 6.1 Preliminaries Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative. Absolute distance measurements involve objects possibly unique
Chapter 6 Distances 6.1 Preliminaries Techniques for measuring astronomical distances generally come in two variates, absolute and relative. Absolute distance measurements involve objects possibly unique
HUBBLE RESIDUALS OF NEARBY SN IA ARE CORRELATED WITH HOST GALAXY MASSES
 Submitted to the Astrophysical Journal Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 03/07/07 SLAC-PUB-14050 HUBBLE RESIDUALS OF NEARBY SN IA ARE CORRELATED WITH HOST GALAXY MASSES Patrick L. Kelly
Submitted to the Astrophysical Journal Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 03/07/07 SLAC-PUB-14050 HUBBLE RESIDUALS OF NEARBY SN IA ARE CORRELATED WITH HOST GALAXY MASSES Patrick L. Kelly
2. Observations and data reduction
 Hamuy et al. (2001) Distances to core-collapse supernovae Elisabeth Gall (QUB/MPA), Rubina Kotak (QUB), Bruno Leibundgut (ESO), Stefan Taubenberger (ESO/MPA), Wolfgang Hillebrandt (MPA), Markus Kromer
Hamuy et al. (2001) Distances to core-collapse supernovae Elisabeth Gall (QUB/MPA), Rubina Kotak (QUB), Bruno Leibundgut (ESO), Stefan Taubenberger (ESO/MPA), Wolfgang Hillebrandt (MPA), Markus Kromer
What Supernovas Tell Us about Cosmology. Jon Thaler
 What Supernovas Tell Us about Cosmology Jon Thaler CU Astronomy Society Nov. 10, 2011 We know: What We Want to Learn The universe exploded about 14 billion years ago. The big bang. It is still expanding
What Supernovas Tell Us about Cosmology Jon Thaler CU Astronomy Society Nov. 10, 2011 We know: What We Want to Learn The universe exploded about 14 billion years ago. The big bang. It is still expanding
Present and Future Large Optical Transient Surveys. Supernovae Rates and Expectations
 Present and Future Large Optical Transient Surveys Supernovae Rates and Expectations Phil Marshall, Lars Bildsten, Mansi Kasliwal Transients Seminar Weds 12th December 2007 Many surveys designed to find
Present and Future Large Optical Transient Surveys Supernovae Rates and Expectations Phil Marshall, Lars Bildsten, Mansi Kasliwal Transients Seminar Weds 12th December 2007 Many surveys designed to find
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Apr 2019
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Apr 2019 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 3 Apr 2019](/thumbs/95/124870951.jpg) Forecasting Cosmological Bias due to Local Gravitational Redshift Haoting Xu, Zhiqi Huang, Na Zhang, and Yundong Jiang School of Physics and Astronomy, Sun Yat-sen University, 2 Daxue Road, Tangjia, Zhuhai,
Forecasting Cosmological Bias due to Local Gravitational Redshift Haoting Xu, Zhiqi Huang, Na Zhang, and Yundong Jiang School of Physics and Astronomy, Sun Yat-sen University, 2 Daxue Road, Tangjia, Zhuhai,
Outline. Cosmological parameters II. Deceleration parameter I. A few others. Covers chapter 6 in Ryden
 Outline Covers chapter 6 in Ryden Cosmological parameters I The most important ones in this course: M : Matter R : Radiation or DE : Cosmological constant or dark energy tot (or just ): Sum of the other
Outline Covers chapter 6 in Ryden Cosmological parameters I The most important ones in this course: M : Matter R : Radiation or DE : Cosmological constant or dark energy tot (or just ): Sum of the other
Outline. Go over AGN problem, again, should be rotating BH Go over problem 6.6 Olber's paradox Distances Parallax Distance ladder Direct checks
 Outline Go over AGN problem, again, should be rotating BH Go over problem 6.6 Olber's paradox Distances Parallax Distance ladder Direct checks Why is the night sky dark? (Olber s Paradox 1826) Or what
Outline Go over AGN problem, again, should be rotating BH Go over problem 6.6 Olber's paradox Distances Parallax Distance ladder Direct checks Why is the night sky dark? (Olber s Paradox 1826) Or what
