Report on Problem 14: Circle of Light (GYPT 2015)
|
|
|
- Andra Fisher
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Report on Problem 14: Circle of Light (GYPT 2015) Tricia McMillan Team 42 : Arthur Dent, Tricia McMillan, Marvin Supervisors: Deep Thought, Zaphod Beeblebrox from: Institute of Magrathea December 6,
2 Contents 1 Introduction Basic explanation Background research Own research Theoretical model Experimental setup and data analysis Comparison of Experiment and Theory Discussion and outlook Interference observations Further geometrical description of the Circle Intensity Investigation Planned work until GYPT 7 References 8 2
3 1 Introduction In this report I will take a look at the following problem: When a laser beam is aimed at a wire, a circle of light can be observed on a screen perpendicular to the wire. Explain this phenomenon and investigate how it depends on the relevant parameters. One has to give a basic explanation why we can observe a circle of light, also a comprehensive research is required to determine how the outcome of the phenomenon changes depending on the exprimental setup, followed by a theoretical description. 1.1 Basic explanation The wire works as a cylindrical reflector. It is illuminated by the laser beam and reflects the light. Due to the cylindrical form of the wire the light is reflected on a circle if the screen is perpendicular to the wire. This pheomenon is demonstrated in figure 1a. To verify that the circle is caused only by reflection on cylinder the experiment was scaled up (see figure 1b). The fact that this phenomenon obviously also works with non monochromatic light (as in figure 1b) proofs that we don t need a laser to produce such a circle. (a) The phenomenon. Here the wire is mounted direclty on the screen with plasticine. (b) A pipe with small mirrors mounted on it illuminated by a flashlight to demonstrate how a cylindrical reflector works. The drawn green lines illustrate the path the light is going by reflection. (Picture by Simon Blumreisinger) 1.2 Background research The task includes monochromatic light and a thin object (the wire) which leads to the suggestion that diffraction might play a role for the phenomenon. Basic knowledge in this field can be found on common websites for students, like Leifi Physik [1]. According to the well known Babinett s Principle[babinet] one should observe diffraction pattern at thin objects if the light used consists of coherent monochromatic waves. Where these predicted diffraction pattern are visible in the presented phenomenon will also be investigated later in this report. Considering the phenomenon itself it might be interesting how the intensity of the light ring is distributed depending on the experiment parameters. For similar experiments there is already existing literature, for example the work of Sanches-Brea[2]. Before going on in this research all the theoretical assumptions which are made to provide a comprehensive theoretical description of the light ring have to be well studied. To summarize my work considering physical basics and specific theory for this phenomenon in literature I believe that the main part of this investigation can be done by applying basic geometry and optics knowledge taught in school. For 3
4 the more complex parts of the light ring, like the intensity distribution recent scientific work has to be taken into account. 2 Own research Here I will present my research process so far. I have designed a suitable experimental setup and developed a theory for the circle radius. I decided to focus on the geometrical parts of the phenomenon because they are easy to measure and seem to fully characterize this optical phenomenon. 2.1 Theoretical model My first step in this investigation was the prediction of the light ring size in dependency of the laser position and incidence angle of the beam. In figure 2 you can see a schematic sketch of the experimental setup to easily determine how these physical values depend on each other. Looking at the schematic laser beam screen radius r wire α β distance D Figure 2: If the wire is mounted as it is required in the task (perpendicular to a screen) the radius r of the light ring can be calculated by applying simple geometry. drawing gives this basic geometrical relation for the calculation of the light ring radius due to fact that the incidence angle equals the angle of excidence (α = β): 2.2 Experimental setup and data analysis r = D tan α (1) The experimental setup was realised as it is shown in figure 3 The radius r as well as D were obtained by using a tapeline or a ruler. The angle of incidence α can be controlled by a rotary socket and a adjusting plate as a setup base to keep the wire perpendicular to the screen. 2.3 Comparison of Experiment and Theory Because this setup can be controlled such easily the measurement error for the circle radius was really low, in fact the error of the radius measurements was between 1 and 4 centimenters. Expecially at large scales it was difficult to tell where the circle ended end where diffuse reflection started. The same measurement of the radius will be taken in dependency of α. These first results show that it is possible to predict the ring size if the basic setup parameters are known. It is also to determine α by simply fitting a linear regression curve through the data points in figure 4 which gives a value of α = 25 ±0.5 4
5 Figure 3: This is how the setup looks like. The incidence angle of the laser beam as well as the distance from the incidence point on the wire and the screen can be easily adjusted. (Setup and picture by Simon Blumreisinger) 4 3 r = D tan α experiment: α = 25 r/m Figure 4: The circle radius is dependend on the distance from the beam incidence point to the screen. This linear dependency regarding equation 1 fits the experimental data nearly perfectly. D/m 3 Discussion and outlook The experiment showed that we can easily predict the basic geometry of such a circle of light. My hypothesis that we can apply the theory of cylindrical reflector seems to be correct based on the shown basic experiment in section 1. The most important error source is the correct alignment and control of the single setup parts. For the basic geometry like the radius this does not influence the general outcome, but for all other investigations a more precise construction is needed. To demonstrate this, I made preliminary experiments on all the important phenomena I have found. In the following I will mention a few observed phenomena and their possible cause, as well as suitable investigation methods. 3.1 Interference observations As already told in the literature section interference and diffraction should play a role. It was possible for me to observe such an interference pattern in the ring, right at the point where the laser beam hits the screen directly (figure 5). This interference pattern can also be calculated. The average distance from the 0. maximum to the mth one y m,avg and the wire thickness d is resulting from my setup: y m,avg = λ m D d tan α (2) 5
6 D α typical setup setup given by task Figure 5: Interference pattern clearly visible when eigher very thin wires or large Ds are used. The close up image on the brightest illumination point shows also that the laser and the wire are not correctly aligned. 3.2 Further geometrical description of the Circle A rather interesting observation is that the complete ring is only visible if the the laser beam diameter is bigger than the wire diameter as it is illustrated in figure 6. To calculate the exact visible part of the Figure 6: Incomplete circles dependig on the ratio between beam and wire diameter and laser offset (incorrect alignement in figere 5). circle again basic geometry can be used. But for experimental comparison I have to find a better way to control the alignement of the laser with the wire, an idea would be a professional adjusting table from an optics lab. Another geometrical size is the circle circumference thickness which clearly varies as it can be seen in figure 1a and 6. This can be also done by applying simple geometry, but again the experimental verification is a huge problem because measuring the exact circumference thickness without a computerprogramm will result in huge measurement errors. And of course the experiment parameters have to be controlled way better. An intensity profile over the circumference should give at least improved 6
7 results for determining values out from pictures, but nevertheless professional lab equipment will be needed. 3.3 Intensity Investigation For the intensity distribution over the circle many factors have to be taken into account beside the geometrical ones. We reflectivity of the wire, the material of the screen (as I take the data for the distribution from a photo), the laser properties such as wavelength and power. In figure 7 such an example distribution is shown. The peak at θ = 0 is obvious because at this point the density of the reflected light is the highest. θ intensity/a.u angle/rad Figure 7: The intensity over the circle given in arbitrary units as the exact material properties of both, wire and screen are not known yet. 4 Planned work until GYPT 1. Determine all geometrical values from the experimental setup contact my school or institution for providing me with some more professional lab equipment 2. Study literature considering intensity distribution over the whole circle find proportionalities or even exact predictions for the intensity 3. More elaborated measurements and variying of all mentioned parameters: angle of beam incidence on wire, different lasers, different wires 7
8 References [1] Leifi Physik. url: (visited on 12/06/2016). [2] Luis Miguel Sanchez-Brea and Eusebio Bernabeu. Diffraction by cylinders illuminated in oblique, off-axis incidence. In: Optik-International Journal for Light and Electron Optics (2001),
Double-Slit Interference
 Double-Slit Interference 1. Objectives. The objective of this laboratory is to verify the double-slit interference relationship. 2. Theory. a. When monochromatic, coherent light is incident upon a double
Double-Slit Interference 1. Objectives. The objective of this laboratory is to verify the double-slit interference relationship. 2. Theory. a. When monochromatic, coherent light is incident upon a double
Michelson Interferometer
 Michelson Interferometer Objective Determination of the wave length of the light of the helium-neon laser by means of Michelson interferometer subsectionprinciple and Task Light is made to produce interference
Michelson Interferometer Objective Determination of the wave length of the light of the helium-neon laser by means of Michelson interferometer subsectionprinciple and Task Light is made to produce interference
Fig. 8.1 illustrates the three measurements. air medium A. ray 1. air medium A. ray 2. air medium A. ray 3. Fig For Examiner s Use
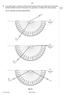 9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
9 9 9 14 8 In an optics lesson, a Physics student traces the paths of three s of light near the boundary between medium A and. The student uses a protractor to measure the various angles. Fig. 8.1 illustrates
REFLECTION AND REFRACTION
 S-108-2110 OPTICS 1/6 REFLECTION AND REFRACTION Student Labwork S-108-2110 OPTICS 2/6 Table of contents 1. Theory...3 2. Performing the measurements...4 2.1. Total internal reflection...4 2.2. Brewster
S-108-2110 OPTICS 1/6 REFLECTION AND REFRACTION Student Labwork S-108-2110 OPTICS 2/6 Table of contents 1. Theory...3 2. Performing the measurements...4 2.1. Total internal reflection...4 2.2. Brewster
Last Name: First Name Network-ID
 Last Name: First Name Network-ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Turn off your cell phone and put it out of sight. Keep your calculator on your own desk. Calculators cannot be shared. This is a
Last Name: First Name Network-ID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Turn off your cell phone and put it out of sight. Keep your calculator on your own desk. Calculators cannot be shared. This is a
PATENT FOR INVENTION
 PATENT FOR INVENTION 2308065 DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD TO A COHERENT FORM Patentee(s): Igor Nikolayevich Serov (RU) Inventor(s): Igor Nikolayevich Serov (RU) Application 2006127328 Priority
PATENT FOR INVENTION 2308065 DEVICE FOR CONVERTING ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELD TO A COHERENT FORM Patentee(s): Igor Nikolayevich Serov (RU) Inventor(s): Igor Nikolayevich Serov (RU) Application 2006127328 Priority
Name Final Exam May 1, 2017
 Name Final Exam May 1, 217 This test consists of five parts. Please note that in parts II through V, you can skip one question of those offered. Some possibly useful formulas appear below. Constants, etc.
Name Final Exam May 1, 217 This test consists of five parts. Please note that in parts II through V, you can skip one question of those offered. Some possibly useful formulas appear below. Constants, etc.
PHYSICS LABORATORY III
 T.C. MARMARA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ARTS AND SCIENCES PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHYSICS LABORATORY III DEPARTMENT: NAME: SURNAME: NUMBER: 2 T.C.MARMARA UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHYSICS LABORATORY III MANUAL
T.C. MARMARA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ARTS AND SCIENCES PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHYSICS LABORATORY III DEPARTMENT: NAME: SURNAME: NUMBER: 2 T.C.MARMARA UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHYSICS LABORATORY III MANUAL
Interference- Michelson Interferometer. Interference lecture by Dr. T.Vishwam
 Interference- Michelson Interferometer Interference lecture by Dr. T.Vishwam * Measurement of the coherence length of a spectral line * Measurement of thickness of thin transparent flakes * Measurement
Interference- Michelson Interferometer Interference lecture by Dr. T.Vishwam * Measurement of the coherence length of a spectral line * Measurement of thickness of thin transparent flakes * Measurement
Refracting prisms (Item No.: P )
 Teacher's/Lecturer's Sheet Refracting prisms (Item No.: P1065100) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physik Education Level: Klasse 7-10 Topic: Optik Subtopic: Reflexion und.rechung Experiment: Umlenkprisma
Teacher's/Lecturer's Sheet Refracting prisms (Item No.: P1065100) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physik Education Level: Klasse 7-10 Topic: Optik Subtopic: Reflexion und.rechung Experiment: Umlenkprisma
Atomic and Nuclear Physics
 Atomic and Nuclear Physics Introductory experiments ualism of wave and particle L Physics Leaflets P6.1.5.1 iffraction of electrons in a polycrystalline lattice (ebye-scherrer diffraction) Objects of the
Atomic and Nuclear Physics Introductory experiments ualism of wave and particle L Physics Leaflets P6.1.5.1 iffraction of electrons in a polycrystalline lattice (ebye-scherrer diffraction) Objects of the
Experiment 6: Interferometers
 Experiment 6: Interferometers Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30PM-6:30PM @ Pupin 1216 INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 NOTE: No labs and no lecture next week! Outline
Experiment 6: Interferometers Nate Saffold nas2173@columbia.edu Office Hour: Mondays, 5:30PM-6:30PM @ Pupin 1216 INTRO TO EXPERIMENTAL PHYS-LAB 1493/1494/2699 NOTE: No labs and no lecture next week! Outline
IO3. Modul Optics. Diffraction
 IO3 Modul Optics Diffraction The phenomenon of diffraction is an essential manifestation of the wave properties of light. As a part of geometrical optics, this phenomenon can not be understood because
IO3 Modul Optics Diffraction The phenomenon of diffraction is an essential manifestation of the wave properties of light. As a part of geometrical optics, this phenomenon can not be understood because
THE DIFFRACTION GRATING SPECTROMETER
 Purpose Theory THE DIFFRACTION GRATING SPECTROMETER a. To study diffraction of light using a diffraction grating spectrometer b. To measure the wavelengths of certain lines in the spectrum of the mercury
Purpose Theory THE DIFFRACTION GRATING SPECTROMETER a. To study diffraction of light using a diffraction grating spectrometer b. To measure the wavelengths of certain lines in the spectrum of the mercury
NEW ZEALAND SCHOLARSHIP 2004 ASSESSMENT SCHEDULE FOR PHYSICS
 NEW ZEALAND SCHOLARSHIP 2004 ASSESSMENT SCHEDULE FOR PHYSICS SECTION A: SHORT QUESTIONS 1(i) 2 210 4 206 84Po! 2He + 82Pb Initial mass m i = 209.983 amu Final mass m f = 209.977 amu Candidates do not successfully
NEW ZEALAND SCHOLARSHIP 2004 ASSESSMENT SCHEDULE FOR PHYSICS SECTION A: SHORT QUESTIONS 1(i) 2 210 4 206 84Po! 2He + 82Pb Initial mass m i = 209.983 amu Final mass m f = 209.977 amu Candidates do not successfully
CLASSROOM SCIENCE ACTIVITY TO SUPPORT STUDENT ENQUIRY-BASED LEARNING
 Red Moon CLASSROOM SCIENCE ACTIVITY TO SUPPORT STUDENT ENQUIRY-BASED LEARNING This classroom-tested teaching plan uses the four innovations of the TEMI project, as detailed in the Teaching the TEMI Way
Red Moon CLASSROOM SCIENCE ACTIVITY TO SUPPORT STUDENT ENQUIRY-BASED LEARNING This classroom-tested teaching plan uses the four innovations of the TEMI project, as detailed in the Teaching the TEMI Way
Chapter 10. Interference of Light
 Chapter 10. Interference of Light Last Lecture Wave equations Maxwell equations and EM waves Superposition of waves This Lecture Two-Beam Interference Young s Double Slit Experiment Virtual Sources Newton
Chapter 10. Interference of Light Last Lecture Wave equations Maxwell equations and EM waves Superposition of waves This Lecture Two-Beam Interference Young s Double Slit Experiment Virtual Sources Newton
Auto collimator. Introduction. Objectives: Apparatus: Theory:
 Auto collimator Introduction An autocollimator is an optical instrument that is used to measure small angles with very high sensitivity. As such, the autocollimator has a wide variety of applications including
Auto collimator Introduction An autocollimator is an optical instrument that is used to measure small angles with very high sensitivity. As such, the autocollimator has a wide variety of applications including
WAVE OPTICS GENERAL. Fig.1a The electromagnetic spectrum
 WAVE OPTICS GENERAL - The ray optics cannot explain the results of the two following experimental situations: a) When passing by small openings or illuminating small obstacles, the light bends around borders
WAVE OPTICS GENERAL - The ray optics cannot explain the results of the two following experimental situations: a) When passing by small openings or illuminating small obstacles, the light bends around borders
Waves & Oscillations
 Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 32 Electromagnetic Waves Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Electromagnetism Geometric optics overlooks the wave nature of light. Light inconsistent with longitudinal
Physics 42200 Waves & Oscillations Lecture 32 Electromagnetic Waves Spring 2016 Semester Matthew Jones Electromagnetism Geometric optics overlooks the wave nature of light. Light inconsistent with longitudinal
Week 7: Interference
 Week 7: Interference Superposition: Till now we have mostly discusssed single waves. While discussing group velocity we did talk briefly about superposing more than one wave. We will now focus on superposition
Week 7: Interference Superposition: Till now we have mostly discusssed single waves. While discussing group velocity we did talk briefly about superposing more than one wave. We will now focus on superposition
Electromagnetic Waves A.K.A. Light
 Electromagnetic Waves A.K.A. Light When Thomas Edison worked late into the night on the electric light, he had to do it by gas lamp or candle. I'm sure it made the work seem that much more urgent. George
Electromagnetic Waves A.K.A. Light When Thomas Edison worked late into the night on the electric light, he had to do it by gas lamp or candle. I'm sure it made the work seem that much more urgent. George
Electricity & Optics
 Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 26 Chapter 33 sec. 1-4 Fall 2017 Semester Professor Koltick Interference of Light Interference phenomena are a consequence of the wave-like nature of light Electric
Physics 24100 Electricity & Optics Lecture 26 Chapter 33 sec. 1-4 Fall 2017 Semester Professor Koltick Interference of Light Interference phenomena are a consequence of the wave-like nature of light Electric
SOLID STATE 18. Reciprocal Space
 SOLID STATE 8 Reciprocal Space Wave vectors and the concept of K-space can simplify the explanation of several properties of the solid state. They will be introduced to provide more information on diffraction
SOLID STATE 8 Reciprocal Space Wave vectors and the concept of K-space can simplify the explanation of several properties of the solid state. They will be introduced to provide more information on diffraction
TA/TI survey. Phy Phy
 TA/TI survey https://webapps.pas.rochester.edu/secure/phpq/ Phy121 7 60 73 Phy123 1 6 11 Chapter 34 The Wave Nature of Light; Interference Units of Chapter 34 34-5 Interference in Thin Films 34-6 Michelson
TA/TI survey https://webapps.pas.rochester.edu/secure/phpq/ Phy121 7 60 73 Phy123 1 6 11 Chapter 34 The Wave Nature of Light; Interference Units of Chapter 34 34-5 Interference in Thin Films 34-6 Michelson
Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 224. Your name Lab section
 Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 224 THE DIFFRACTION GRATING AND THE OPTICAL SPECTRUM Your name Lab section 1. What are the goals of this experiment? 2. If the period of a diffraction grating is d = 1,000 nm, where the
Pre-lab Quiz/PHYS 224 THE DIFFRACTION GRATING AND THE OPTICAL SPECTRUM Your name Lab section 1. What are the goals of this experiment? 2. If the period of a diffraction grating is d = 1,000 nm, where the
Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Varma Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee
 Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Varma Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee Module-03 Lecture-01 Interference of Light Part 01 Myself, Dr. JD Varma, Associate Professor in Department
Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Varma Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee Module-03 Lecture-01 Interference of Light Part 01 Myself, Dr. JD Varma, Associate Professor in Department
PHYSICS 122/124 Lab EXPERIMENT NO. 9 ATOMIC SPECTRA
 PHYSICS 1/14 Lab EXPERIMENT NO. 9 ATOMIC SPECTRA The purpose of this laboratory is to study energy levels of the Hydrogen atom by observing the spectrum of emitted light when Hydrogen atoms make transitions
PHYSICS 1/14 Lab EXPERIMENT NO. 9 ATOMIC SPECTRA The purpose of this laboratory is to study energy levels of the Hydrogen atom by observing the spectrum of emitted light when Hydrogen atoms make transitions
Physics 208 Final Exam
 Physics 208 Final Exam Name You are graded on your work, with partial credit. See the last pages of the exam for formula sheets. Please be clear and well-organized, so that we can easily follow each step
Physics 208 Final Exam Name You are graded on your work, with partial credit. See the last pages of the exam for formula sheets. Please be clear and well-organized, so that we can easily follow each step
Course: Technology II Training course topic: Metrology
 Department of machining, process planning and metrology ver.2017-01 Following problems and tasks will be solved during the first two weeks of the training courses of Technology II. Detailed information
Department of machining, process planning and metrology ver.2017-01 Following problems and tasks will be solved during the first two weeks of the training courses of Technology II. Detailed information
PHYSICS 253 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM. Student Number. The last two pages of the exam have some equations and some physical constants.
 PHYSICS 253 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM Name Student Number CHECK ONE: Instructor 1 10:00 Instructor 2 1:00 Note that problems 1-19 are worth 2 points each, while problem 20 is worth 15 points and problems 21 and
PHYSICS 253 SAMPLE FINAL EXAM Name Student Number CHECK ONE: Instructor 1 10:00 Instructor 2 1:00 Note that problems 1-19 are worth 2 points each, while problem 20 is worth 15 points and problems 21 and
Physics I : Oscillations and Waves Prof. S. Bharadwaj Department of Physics and Meteorology Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Physics I : Oscillations and Waves Prof. S. Bharadwaj Department of Physics and Meteorology Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 21 Diffraction-II Good morning. In the last class, we had
Physics I : Oscillations and Waves Prof. S. Bharadwaj Department of Physics and Meteorology Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 21 Diffraction-II Good morning. In the last class, we had
Experiment O-2. The Michelson Interferometer
 Experiment O-2 The Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the best known and historically important interferometers. It is a very accurate length-measuring device and has been
Experiment O-2 The Michelson Interferometer The Michelson interferometer is one of the best known and historically important interferometers. It is a very accurate length-measuring device and has been
Coherence and width of spectral lines with Michelson interferometer
 Coherence and width of spectral lines TEP Principle Fraunhofer and Fresnel diffraction, interference, spatial and time coherence, coherence conditions, coherence length for non punctual light sources,
Coherence and width of spectral lines TEP Principle Fraunhofer and Fresnel diffraction, interference, spatial and time coherence, coherence conditions, coherence length for non punctual light sources,
AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide
 AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The guide is marked based on effort, completeness, thoughtfulness, and neatness (not accuracy). Do your
AP Waves/Optics ~ Learning Guide Name: Instructions: Using a pencil, answer the following questions. The guide is marked based on effort, completeness, thoughtfulness, and neatness (not accuracy). Do your
Diffraction at a slit and Heisenberg's uncertainty principle (Item No.: P )
 Diffraction at a slit and Heisenberg's uncertainty principle (Item No.: P2230100) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: ILIAS Education Level: Physik Topic: Hochschule Subtopic: Licht und Optik Experiment:
Diffraction at a slit and Heisenberg's uncertainty principle (Item No.: P2230100) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: ILIAS Education Level: Physik Topic: Hochschule Subtopic: Licht und Optik Experiment:
Lab 4. Friction. Goals. Introduction
 Lab 4. Friction Goals To determine whether the simple model for the frictional force presented in the text, where friction is proportional to the product of a constant coefficient of friction, µ K, and
Lab 4. Friction Goals To determine whether the simple model for the frictional force presented in the text, where friction is proportional to the product of a constant coefficient of friction, µ K, and
Which of the following classes of electromagnetic waves will not ionise neutral atoms?
 1 In an experiment to demonstrate the photoelectric effect, a charged metal plate is illuminated with light from different sources. The plate loses its charge when an ultraviolet light source is used but
1 In an experiment to demonstrate the photoelectric effect, a charged metal plate is illuminated with light from different sources. The plate loses its charge when an ultraviolet light source is used but
EXPERIMENTAL COMPETITION
 Thursday, April 28 th, 2005 Before attempting to assemble your equipment, read the problem text completely! Please read this first: 1. The time available is 5 hours. 2. Use only the pen and equipments
Thursday, April 28 th, 2005 Before attempting to assemble your equipment, read the problem text completely! Please read this first: 1. The time available is 5 hours. 2. Use only the pen and equipments
Lab 5. Magnetic Fields
 Lab 5. Magnetic Fields Goals To visualize the magnetic fields produced by several different configurations of simple bar magnets using iron filings. To use small magnetic compasses to trace out the magnetic
Lab 5. Magnetic Fields Goals To visualize the magnetic fields produced by several different configurations of simple bar magnets using iron filings. To use small magnetic compasses to trace out the magnetic
Lab 11. Optical Instruments
 Lab 11. Optical Instruments Goals To construct a simple telescope with two positive lenses having known focal lengths, and to determine the angular magnification (analogous to the magnifying power of a
Lab 11. Optical Instruments Goals To construct a simple telescope with two positive lenses having known focal lengths, and to determine the angular magnification (analogous to the magnifying power of a
Physics H7C; Final. Monday, 5/12; 7-10 PM
 Physics H7C; Final Monday, 5/12; 7-10 PM Write your responses below, or on extra paper if needed. Show your work, and take care to explain what you are doing; partial credit will be given for incomplete
Physics H7C; Final Monday, 5/12; 7-10 PM Write your responses below, or on extra paper if needed. Show your work, and take care to explain what you are doing; partial credit will be given for incomplete
Lab 5. Magnetic Fields
 Lab 5. Magnetic Fields Goals To visualize the magnetic fields produced by several different configurations of simple bar magnets using iron filings. To use small magnetic compasses to trace out the magnetic
Lab 5. Magnetic Fields Goals To visualize the magnetic fields produced by several different configurations of simple bar magnets using iron filings. To use small magnetic compasses to trace out the magnetic
Telescopes: Portals of Discovery
 Telescopes: Portals of Discovery How do light and matter interact? Emission Absorption Transmission Transparent objects transmit light Opaque objects block (absorb) light Reflection or Scattering Reflection
Telescopes: Portals of Discovery How do light and matter interact? Emission Absorption Transmission Transparent objects transmit light Opaque objects block (absorb) light Reflection or Scattering Reflection
Page 2. Q1.Electrons and protons in two beams are travelling at the same speed. The beams are diffracted by objects of the same size.
 Q1.Electrons and protons in two beams are travelling at the same speed. The beams are diffracted by objects of the same size. Which correctly compares the de Broglie wavelength λ e of the electrons with
Q1.Electrons and protons in two beams are travelling at the same speed. The beams are diffracted by objects of the same size. Which correctly compares the de Broglie wavelength λ e of the electrons with
Conceptual Practice Problems for PHYS 1112 In-Class Exam #2A+2B
 Conceptual ractice roblems for HYS 1112 In-Class xam #2A+2B Thu. Mar. 19, 2009, 11:00am-12:15pm and 2:00pm-3:15pm C 2.01: In a two-source interference experiment two sources are oscillating in phase with
Conceptual ractice roblems for HYS 1112 In-Class xam #2A+2B Thu. Mar. 19, 2009, 11:00am-12:15pm and 2:00pm-3:15pm C 2.01: In a two-source interference experiment two sources are oscillating in phase with
Complete all the identification fields below or 10% of the lab value will be deduced from your final mark for this lab.
 Physical optics Identification page Instructions: Print this page and the following ones before your lab session to prepare your lab report. Staple them together with your graphs at the end. If you forgot
Physical optics Identification page Instructions: Print this page and the following ones before your lab session to prepare your lab report. Staple them together with your graphs at the end. If you forgot
LC circuit: Energy stored. This lecture reviews some but not all of the material that will be on the final exam that covers in Chapters
 Disclaimer: Chapter 29 Alternating-Current Circuits (1) This lecture reviews some but not all of the material that will be on the final exam that covers in Chapters 29-33. LC circuit: Energy stored LC
Disclaimer: Chapter 29 Alternating-Current Circuits (1) This lecture reviews some but not all of the material that will be on the final exam that covers in Chapters 29-33. LC circuit: Energy stored LC
Electric Fields. Goals. Introduction
 Lab 2. Electric Fields Goals To understand how contour lines of equal voltage, which are easily measured, relate to the electric field produced by electrically charged objects. To learn how to identify
Lab 2. Electric Fields Goals To understand how contour lines of equal voltage, which are easily measured, relate to the electric field produced by electrically charged objects. To learn how to identify
Chapter 7. Interference of Light
 Chapter 7. Interference of Light Last Lecture Superposition of waves Laser This Lecture Two-Beam Interference Young s Double Slit Experiment Virtual Sources Newton s Rings Film Thickness Measurement by
Chapter 7. Interference of Light Last Lecture Superposition of waves Laser This Lecture Two-Beam Interference Young s Double Slit Experiment Virtual Sources Newton s Rings Film Thickness Measurement by
Q1. The diagram below shows the paths of microwaves from two narrow slits, acting as coherent sources, through a vacuum to a detector.
 Q1. The diagram below shows the paths of microwaves from two narrow slits, acting as coherent sources, through a vacuum to a detector. (a) Explain what is meant by coherent sources. (b) (i) The frequency
Q1. The diagram below shows the paths of microwaves from two narrow slits, acting as coherent sources, through a vacuum to a detector. (a) Explain what is meant by coherent sources. (b) (i) The frequency
Lab 9. Rotational Dynamics
 Lab 9. Rotational Dynamics Goals To calculate the moment of inertia of two metal cylindrical masses from their measured dimensions and their distance from the axis of rotation. To use the principle of
Lab 9. Rotational Dynamics Goals To calculate the moment of inertia of two metal cylindrical masses from their measured dimensions and their distance from the axis of rotation. To use the principle of
Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Michelson Interferometer
 Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Michelson Interferometer Introduction An optical interferometer is an instrument which splits a beam of light into two beams, each beam follows a different path
Physics 476LW Advanced Physics Laboratory Michelson Interferometer Introduction An optical interferometer is an instrument which splits a beam of light into two beams, each beam follows a different path
Surface Plasmon Wave
 Surface Plasmon Wave In this experiment you will learn about a surface plasmon wave. Certain metals (Au, Ag, Co, etc) exhibit a negative dielectric constant at certain regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Surface Plasmon Wave In this experiment you will learn about a surface plasmon wave. Certain metals (Au, Ag, Co, etc) exhibit a negative dielectric constant at certain regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
INA I N. Practical training ellipsometry. Lab training nanosensorics Supervisor: Uh-Myong Ha. University of Kassel. Version: December 22, 2014
 INA I N nstitut für anostrukturtechnologie und Analytik Practical training ellipsometry Lab training nanosensorics Supervisor: Uh-Myong Ha Version: December 22, 2014 University of Kassel Contents 1 Introduction
INA I N nstitut für anostrukturtechnologie und Analytik Practical training ellipsometry Lab training nanosensorics Supervisor: Uh-Myong Ha Version: December 22, 2014 University of Kassel Contents 1 Introduction
Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1)
 EEL6935 Advanced MEMS (Spring 5) Instructor: Dr. Huikai Xie Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1) Agenda: Optics Review EEL6935 Advanced MEMS 5 H. Xie 3/8/5 1 Optics Review Nature of Light Reflection and Refraction
EEL6935 Advanced MEMS (Spring 5) Instructor: Dr. Huikai Xie Lecture 19 Optical MEMS (1) Agenda: Optics Review EEL6935 Advanced MEMS 5 H. Xie 3/8/5 1 Optics Review Nature of Light Reflection and Refraction
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Spring 2014 Final Exam Equation Sheet. B( r) = µ o 4π
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2014 Final Exam Equation Sheet Force Law: F q = q( E ext + v q B ext ) Poynting Vector: S = ( E B) / µ 0 Force on Current Carrying
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2014 Final Exam Equation Sheet Force Law: F q = q( E ext + v q B ext ) Poynting Vector: S = ( E B) / µ 0 Force on Current Carrying
Optics. n n. sin c. sin
 Optics Geometrical optics (model) Light-ray: extremely thin parallel light beam Using this model, the explanation of several optical phenomena can be given as the solution of simple geometric problems.
Optics Geometrical optics (model) Light-ray: extremely thin parallel light beam Using this model, the explanation of several optical phenomena can be given as the solution of simple geometric problems.
Physics 214 Midterm Exam Spring Last Name: First Name NetID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name:
 Physics 214 Midterm Exam Spring 215 Last Name: First Name NetID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. Keep your calculator on your own desk. Calculators
Physics 214 Midterm Exam Spring 215 Last Name: First Name NetID Discussion Section: Discussion TA Name: Instructions Turn off your cell phone and put it away. Keep your calculator on your own desk. Calculators
Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Vermaa Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee
 Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Vermaa Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee Module-04 Lecture-02 Diffraction Part - 02 In the previous lecture I discussed single slit and double
Engineering Physics 1 Prof. G.D. Vermaa Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology-Roorkee Module-04 Lecture-02 Diffraction Part - 02 In the previous lecture I discussed single slit and double
Experiment #5: Cauchy s Formula
 Experiment #5: Cauchy s Formula Carl Adams October 14, 2011 1 Purpose This experiment is a continuation of Experiment #4. It is assumed you have an aligned spectrometer. 2 Safety/Protocol 1. The gas discharge
Experiment #5: Cauchy s Formula Carl Adams October 14, 2011 1 Purpose This experiment is a continuation of Experiment #4. It is assumed you have an aligned spectrometer. 2 Safety/Protocol 1. The gas discharge
Physics 1252 Exam #2A
 Physics 1252 Exam #2A Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write on your
Physics 1252 Exam #2A Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write on your
Lesson Plan: Introduction to Quantum Mechanics via Wave Theory and the Photoelectric Effect
 Lesson Plan: Introduction to Quantum Mechanics via Wave Theory and the Photoelectric Effect Will Stoll, Norcross High School Problem: To understand the basic principles of Quantum Mechanics through an
Lesson Plan: Introduction to Quantum Mechanics via Wave Theory and the Photoelectric Effect Will Stoll, Norcross High School Problem: To understand the basic principles of Quantum Mechanics through an
Lab 2: Mach Zender Interferometer Overview
 Lab : Mach Zender Interferometer Overview Goals:. Study factors that govern the interference between two light waves with identical amplitudes and frequencies. Relative phase. Relative polarization. Learn
Lab : Mach Zender Interferometer Overview Goals:. Study factors that govern the interference between two light waves with identical amplitudes and frequencies. Relative phase. Relative polarization. Learn
Physics 1252 Exam #2A
 Physics 1252 Exam #2A Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write on your
Physics 1252 Exam #2A Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write on your
ACTIVITY 3. Light and Waves. Goal We will look at a property of light and learn how scientists conclude that light behaves as a wave.
 Name: WAVES of matter Class: Visual Quantum Mechanics ACTIVITY 3 Light and Waves Goal We will look at a property of light and learn how scientists conclude that light behaves as a wave. The light from
Name: WAVES of matter Class: Visual Quantum Mechanics ACTIVITY 3 Light and Waves Goal We will look at a property of light and learn how scientists conclude that light behaves as a wave. The light from
Home Lab 15 Diffraction Gratings
 Home Lab Lab 15 Diffraction Gratings Home Lab 15 Diffraction Gratings Activity 15 1: Diffraction from a Transmission Grating Objective: To accurately measure the wavelength of light from a laser pointer
Home Lab Lab 15 Diffraction Gratings Home Lab 15 Diffraction Gratings Activity 15 1: Diffraction from a Transmission Grating Objective: To accurately measure the wavelength of light from a laser pointer
Physics 1212 Exam #2B
 Physics 1212 Exam #2B Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write on your
Physics 1212 Exam #2B Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write on your
Solutions to Conceptual Practice Problems PHYS 1112 In-Class Exam #2A+2B
 Solutions to Conceptual ractice roblems HYS 1112 In-Class xam #2A+2B Thu. Mar. 19, 2009, 11:00am-12:15pm and 2:00pm-3:15pm C 2.01: In a two-source interference experiment two sources are oscillating in
Solutions to Conceptual ractice roblems HYS 1112 In-Class xam #2A+2B Thu. Mar. 19, 2009, 11:00am-12:15pm and 2:00pm-3:15pm C 2.01: In a two-source interference experiment two sources are oscillating in
Physics 1252 Exam #2C
 Physics 1252 Exam #2C Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write on your
Physics 1252 Exam #2C Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write on your
Physics Common Assessment Unit 5-8 3rd Nine Weeks
 1) What is the direction of the force(s) that maintain(s) circular motion? A) one force pulls the object inward toward the radial center while another force pushes the object at a right angle to the first
1) What is the direction of the force(s) that maintain(s) circular motion? A) one force pulls the object inward toward the radial center while another force pushes the object at a right angle to the first
Interference by Wavefront Division
 nterference by Wavefront Division One of the seminal experiments in physics was conducted in 1801 by Thomas Young, an English physicist who cut a small hole in an opaque screen, set a second screen in
nterference by Wavefront Division One of the seminal experiments in physics was conducted in 1801 by Thomas Young, an English physicist who cut a small hole in an opaque screen, set a second screen in
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics 8.03 Practice Final Exam 3
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics 8.03 Practice Final Exam 3 Instructions Please write your solutions in the white booklets. We will not grade anything written on the exam copy. This exam is
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics 8.03 Practice Final Exam 3 Instructions Please write your solutions in the white booklets. We will not grade anything written on the exam copy. This exam is
Tutorials. 1. Autocollimator. Angle Dekkor. General
 Tutorials 1. Autocollimator General An autocollimator is a Precise Optical Instrument for measurement of small angle deviations with very high sensitivity. Autocollimator is essentially an infinity telescope
Tutorials 1. Autocollimator General An autocollimator is a Precise Optical Instrument for measurement of small angle deviations with very high sensitivity. Autocollimator is essentially an infinity telescope
Physics 1252 Exam #2F
 Physics 1252 Exam #2F Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write on your
Physics 1252 Exam #2F Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write on your
4. Dispersion. The index of refraction of the prism at the input wavelength can be calculated using
 4. Dispersion In this lab we will explore how the index of refraction of a material depends on the of the incident light. We first study the phenomenon of minimum deviation of a prism. We then measure
4. Dispersion In this lab we will explore how the index of refraction of a material depends on the of the incident light. We first study the phenomenon of minimum deviation of a prism. We then measure
Lesson 11: Motion of a Falling Object
 Lesson 11: Motion of a Falling Object 11.1 Observe and find a pattern using your choice of one of the following: 1. The video at this web site: http://paer.rutgers.edu/pt3/experiment.php?topicid=2&exptid=38
Lesson 11: Motion of a Falling Object 11.1 Observe and find a pattern using your choice of one of the following: 1. The video at this web site: http://paer.rutgers.edu/pt3/experiment.php?topicid=2&exptid=38
A) n L < 1.0 B) n L > 1.1 C) n L > 1.3 D) n L < 1.1 E) n L < 1.3
 1. A beam of light passes from air into water. Which is necessarily true? A) The frequency is unchanged and the wavelength increases. B) The frequency is unchanged and the wavelength decreases. C) The
1. A beam of light passes from air into water. Which is necessarily true? A) The frequency is unchanged and the wavelength increases. B) The frequency is unchanged and the wavelength decreases. C) The
Physics 1212 Exam #4A (Final)
 Physics 1212 Exam #4A (Final) Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write
Physics 1212 Exam #4A (Final) Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write
LABORATORY WRITE-UP MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER LAB AUTHOR S NAME GOES HERE STUDENT NUMBER:
 LABORATORY WRITE-UP MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER LAB AUTHOR S NAME GOES HERE STUDENT NUMBER: 111-22-3333 MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER 1. PURPOSE The purpose of this experiment is to give some practice in using
LABORATORY WRITE-UP MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER LAB AUTHOR S NAME GOES HERE STUDENT NUMBER: 111-22-3333 MICHELSON INTERFEROMETER 1. PURPOSE The purpose of this experiment is to give some practice in using
Physics 1212 Exam #4B (Final)
 Physics 1212 Exam #4B (Final) Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write
Physics 1212 Exam #4B (Final) Instructions: This is a closed-book, closed-notes exam. You are allowed to use a clean print-out of your formula sheet, any scientific calculator, and a ruler. Do not write
General Physics II Summer Session 2013 Review Ch - 16, 17, 18
 95.104 General Physics II Summer Session 2013 Review Ch - 16, 17, 18 A metal ball hangs from the ceiling by an insulating thread. The ball is attracted to a positivecharged rod held near the ball. The
95.104 General Physics II Summer Session 2013 Review Ch - 16, 17, 18 A metal ball hangs from the ceiling by an insulating thread. The ball is attracted to a positivecharged rod held near the ball. The
Revisiting Fizeau s Observations: Spectral study of Na source using Newton s rings. Abstract
 Revisiting Fizeau s Observations: Spectral study of Na source using Newton s rings K S Umesh #, Denny Melkay, J Adithya, Sai Prem Shaji, N Ganesh, R Dharmaraj, Rajkumar Jain, S Nanjundan # Author for correspondence:
Revisiting Fizeau s Observations: Spectral study of Na source using Newton s rings K S Umesh #, Denny Melkay, J Adithya, Sai Prem Shaji, N Ganesh, R Dharmaraj, Rajkumar Jain, S Nanjundan # Author for correspondence:
4. What is the speed (in cm s - 1 ) of the tip of the minute hand?
 Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
Topic 4 Waves PROBLEM SET Formative Assessment NAME: TEAM: THIS IS A PRACTICE ASSESSMENT. Show formulas, substitutions, answers, and units! Topic 4.1 Oscillations A mass is attached to a horizontal spring.
4. Dispersion. The index of refraction of the prism at the input wavelength can be calculated using
 4. Dispersion In this lab we will explore how the index of refraction of a material depends on the of the incident light. We first study the phenomenon of minimum deviation of a prism. We then measure
4. Dispersion In this lab we will explore how the index of refraction of a material depends on the of the incident light. We first study the phenomenon of minimum deviation of a prism. We then measure
University of Maryland Department of Physics. Spring 2009 Final Exam 20. May (175 points) Post grades on web? (Initial, please) Yes No
 University of Maryland Department of Physics Physics 122 20. May 2009 (175 points) Post grades on web? (Initial, please) Yes No (If you agree, I will post your grades and your detailed scores for each
University of Maryland Department of Physics Physics 122 20. May 2009 (175 points) Post grades on web? (Initial, please) Yes No (If you agree, I will post your grades and your detailed scores for each
Protokoll. Grundpraktikum II - Optical Spectroscopy
 Protokoll Grundpraktikum II - Optical Spectroscopy 1 Elaboration 1.1 Optical Spectroscopy Student: Hauke Rasch, Martin Borchert Tutor: Madsen Date: 22.October2014 This experiment is about the fundamental
Protokoll Grundpraktikum II - Optical Spectroscopy 1 Elaboration 1.1 Optical Spectroscopy Student: Hauke Rasch, Martin Borchert Tutor: Madsen Date: 22.October2014 This experiment is about the fundamental
Double-slit Interference. Class 26: (ThT Q) Are both coherence and monochromaticity essential?
 Double-slit Interference Class 26: (ThT Q) Are both coherence and monochromaticity essential? Exam 2 Discussion #9. Consider an arbitrary engine whose work output is connected to a Carnot engine running
Double-slit Interference Class 26: (ThT Q) Are both coherence and monochromaticity essential? Exam 2 Discussion #9. Consider an arbitrary engine whose work output is connected to a Carnot engine running
LASER. Challenging MCQ questions by The Physics Cafe. Compiled and selected by The Physics Cafe
 LSER hallenging MQ questions by The Physics afe ompiled and selected by The Physics afe www.thephysicsafe.com www.pmc.sg 1 laser point creates a spot on a screen as it reflects 70% of the light striking
LSER hallenging MQ questions by The Physics afe ompiled and selected by The Physics afe www.thephysicsafe.com www.pmc.sg 1 laser point creates a spot on a screen as it reflects 70% of the light striking
Chapter 5. Past and Proposed Experiments Detecting Absolute Motion
 Chapter 5 Past and Proposed Experiments Detecting Absolute Motion In this Chapter I gave different interpretations for the results of some famous past experiments. My interpretations are based on the following
Chapter 5 Past and Proposed Experiments Detecting Absolute Motion In this Chapter I gave different interpretations for the results of some famous past experiments. My interpretations are based on the following
Optics in a Fish Tank Demonstrations for the Classroom
 Optics in a Fish Tank Demonstrations for the Classroom Introduction: This series of demonstrations will illustrate a number of optical phenomena. Using different light sources and a tank of water, you
Optics in a Fish Tank Demonstrations for the Classroom Introduction: This series of demonstrations will illustrate a number of optical phenomena. Using different light sources and a tank of water, you
Final examination. 3 hours (9am 12 noon) Total pages: 7 (seven) PLEASE DO NOT TURN OVER UNTIL EXAM STARTS PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET
 2.710 Final examination 3 hours (9am 12 noon) Total pages: 7 (seven) PLEASE DO NOT TURN OVER UNTIL EXAM STARTS Name: PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET WITH YOUR SOLUTION SHEET(S) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
2.710 Final examination 3 hours (9am 12 noon) Total pages: 7 (seven) PLEASE DO NOT TURN OVER UNTIL EXAM STARTS Name: PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET WITH YOUR SOLUTION SHEET(S) MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Diffraction of Electrons
 Diffraction of Electrons Object: Apparatus: Verify that electrons are waves; i.e., that they diffract just like light waves. This lab is then used to measure their wavelength or, alternatively, measure
Diffraction of Electrons Object: Apparatus: Verify that electrons are waves; i.e., that they diffract just like light waves. This lab is then used to measure their wavelength or, alternatively, measure
Name: Date: Room: No.
 Station 1 Projecting Visible Spectra (setting direction) Objective: To study the range of colors in the visible spectrum. Procedure: 1. Make a partition with a narrow slot in its center to block all but
Station 1 Projecting Visible Spectra (setting direction) Objective: To study the range of colors in the visible spectrum. Procedure: 1. Make a partition with a narrow slot in its center to block all but
Seat Number. Print and sign your name, and write your Student ID Number and seat number legibly in the spaces above.
 Physics 123A Final Spring 2001 Wednesday, June 6 Name last first initial Seat Number Signature Student Number Print and sign your name, and write your Student ID Number and seat number legibly in the spaces
Physics 123A Final Spring 2001 Wednesday, June 6 Name last first initial Seat Number Signature Student Number Print and sign your name, and write your Student ID Number and seat number legibly in the spaces
PH 222-3A Spring 2010
 PH -3A Spring 010 Interference Lecture 6-7 Chapter 35 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 35 Interference The concept of optical interference is critical to understanding
PH -3A Spring 010 Interference Lecture 6-7 Chapter 35 (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamentals of Physics 8 th edition) 1 Chapter 35 Interference The concept of optical interference is critical to understanding
Identifying the crystal orientation of the black phosphorus
 Identifying the crystal orientation of the black phosphorus Yu ZHANG I. Introduction Black phosphorus is a new member of 2D materials family. It has several noticeable properties, for instance, the direct
Identifying the crystal orientation of the black phosphorus Yu ZHANG I. Introduction Black phosphorus is a new member of 2D materials family. It has several noticeable properties, for instance, the direct
Science TEKS Verification
 Science EKS Verification (1) Scientific processes. he student conducts investigations, for at least 40% of instructional time, using safe, environmentally appropriate, and ethical practices. hese investigations
Science EKS Verification (1) Scientific processes. he student conducts investigations, for at least 40% of instructional time, using safe, environmentally appropriate, and ethical practices. hese investigations
Measurements in Optics for Civil Engineers
 Measurements in Optics for Civil Engineers I. FOCAL LENGTH OF LENSES The behavior of simplest optical devices can be described by the method of geometrical optics. For convex or converging and concave
Measurements in Optics for Civil Engineers I. FOCAL LENGTH OF LENSES The behavior of simplest optical devices can be described by the method of geometrical optics. For convex or converging and concave
