XMM-Newton. XMM-Newton Science Analysis System 15.0 scientific validation. XMM-SOC-USR-TN-0026 Issue 1.0
|
|
|
- Carol Higgins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 XMM-Newton XMM-Newton Science Analysis System 15.0 scientific validation XMM-SOC-USR-TN-0026 Issue 1.0 C.Gabriel, I. de la Calle, A.Ibarra, R.González-Riestra, E.Ojero, J.V.Perea, P.Rodríguez, R.Saxton, M. Smith, M.Stuhlinger, A.Talavera XMM-Newton Science Operations Centre July 15, 2016 Revision history Revision number Date Revision author Comments 0.9 June 15, 2016 C. Gabriel first issue 1.0 July 15, 2016 C. Gabriel after revision i
2 Page: ii Contents 1 Introduction Methodology Calibration data to be used New and updated in SAS Updated in SAS 15.0: attcalc and a number of related tasks affected by the wrong sign of the Euler ψ angle New in SAS 15.0: ebkgreg, a task for determining optimal background position for a source in the FOV Updated in SAS 15.0: eimagecombine, a script introduced in SAS 14 for producing (combined) EPIC background subtracted, exposure corrected smoothed images New in SAS 15.0: Extraction of separated redistribution matrix (RMF) and ancillary response function (ARF) for RGS New in SAS 15 - use of embadpixfind for RGS bad pixel / column finding New in SAS 15.0: RGS filtering without flagging FIFO buffer full periods New in SAS 15.0: Only one 32bits Linux version released Validation results Validation schedule Processing of standard datasets RGS data - standard dataset SAS OM data processing Dedicated analysis EPIC data - G EPIC data - PKS Standard tests of esas OM Fast Mode processing Interactive tasks:omsource and omgsource Repeatability of OM filter photometry New and updated in SAS15 - Validation Updated in SAS 15: attcalc and all the tasks affected by the wrong sign of the Euler ψ angle Updated in SAS15: eimagecombine New in SAS 15: ebkgreg - determining the optimal background position for a source in the FOV New in SAS 15: Extraction of separated redistribution matrix (RMF) and ancillary response function (ARF) for RGS New in SASv15.0: - use of adapted embadpixfind for RGS bad pixel / column finding New in SASv15.0: RGS filtering without flagging FIFO buffer full periods Validation Conclusion 16
3 Page: 1 1 Introduction The SAS scientific validation is performed on a standard set of XMM-Newton observations, which cover all commissioned observational modes, and a number of observations, specially chosen for testing new / special aspects of the data reduction corresponding to the version to be validated. Table 1 lists all the datasets used for the validation of SAS version Some of these observations are particularly suitable to test calibration-related items, as specified in the rightmost column of Tab. 1. These datasets are partly intended as a standard reference, which has been and will be used to verify the performances of all SAS versions. However, additional datasets may occasionally be used to test version-specific SAS items. This is the case, for instance, for the datasets discussed in Sect. 2 of this report. Datasets discussed in a given report and not listed in Tab. 1 do not belong to the reference datasets, and are therefore not intended to be discussed in later SAS versions validation reports. 1.1 Methodology The SV for SAS v15.0 consisted of the following steps: 1. all the datasets listed in Tab. 1 were processed through the SAS 15.0 based testing Pipeline System (PPS) running at the SOC, and 2. the same datasets were also processed through the SAS reduction meta-tasks: e[mp]proc, om[ifg]chain, rgsproc 3. all the SAS threads were ran as documented, for checking the integrity of the software and the validity of the threads 4. products generated by the above steps were used as basis for the interactive SV analysis. Standard scientific products (images, light curves, spectra, source lists) were generated and analysed. This allowed us to: test the SAS interactive tasks. verify the calibration accuracy obtained with SAS v15.0, and compare it with the expected accuracy on the basis of the calibration status at the time the SV is performed. 5. in addition the whole cross-calibration database has been reduced by standard analysis scripts based on SAS but including also model fitting through Xspec.
4 Page: 2 Table 1: SV datasets Instrument Mode Object Revolution ID Calibration item Obs. ID EPIC MOS Full Frame Lockman Hole Astrometry + source detection G Effective area Small Window (W2) Mkn Large Window (W3) PKS Effective area Timing Uncompressed Her X Timing EPIC-pn Full Frame Lockman Hole Astrometry Full Frame/Small Window PKS Effective area Large Window AB Dor Small Window PKS Effective area Fast Timing Her X Timing Crab Fast Burst Crab Timing Crab Timing Extended Full Frame G Effective area Slew Data Slew data processing Slew Data Slew data processing RGS SPEC+Q PKS Mkn Effective area AB Dor Wavelength scale AB Dor Wavelength scale AB Dor Wavelength scale AB Dor Wavelength scale OM Image Mode BPM Photometry Fast Mode X FF Low Resolution BPM Astrometry Optical grism Hz Wavelength scale & flux calibration UV Grism HD13499 (offset) Wavelength scale & flux calibration
5 Page: Calibration data to be used The calibration data to be used for this version was derived from the full public calibration constituents as of 21 December 2015, plus the following components which at this date were not yet public: XMM BORESIGHT 0026.CCF (made public with the SAS 15 release, since it is related to a new ALGOID for the upgraded astrometry), RGS1 ADUCONV 0026.CCF, RGS2 ADUCONV 0033.CCF, RGS1 CTI 0014.CCF and RGS2 CTI 0015.CCF (all of them were already approved at mid December, but were waiting for editorial work of the corresponding release note to be made public), and XRT3 XPSF 0017.CCF (it was waiting for the release note to be written, affecting only source detection by slew data). 2 New and updated in SAS 15.0 V is a main yearly release of the SAS, containing some new capabilities of the package. The main item of the upgrade, though, was the correction of a problem related to the conversion between image (POS, X/Y) and camera (DET or RAW) coordinates, manifested in several conversions in the SAS infrastructure. The error introduced very early in the SAS history increased with off-axis angle and could go up to 7-8 arc-seconds. It originated in a wrong sign of the Euler ψ angle, contained within the boresight matrix and also in the task attcalc, in which the wrong sign of ψ was introduced. Since the boresight misalignments angles have been calculated using that matrix, whenever this is used by attcalc the error cancels out. This is the reason why the source positions in eg. the XMM-Newton source catalogues are not affected. However, the usage of fundamental routines for coordinates transformation using the boresight misalignment angles was affected. SAS 15 contains also a new task (ebkgreg) for optimal background position determination for any source in the FOV. Especially designed for optimising the pipeline processing of specific source products, it can also help the interactive SAS user for obtaining net spectra and light curves of multiple sources after source detection. Further important upgrades have been performed in the RGS data analysis area. Now it is possible to obtain separated ARF and RMF matrices for RGS. Also a new non-default bad column / pixel determination for RGS has been developed, based on the algorithm used for the same purpose with the MOS data. In addition, filtering out so called FIFO full events can be disabled. 2.1 Updated in SAS 15.0: attcalc and a number of related tasks affected by the wrong sign of the Euler ψ angle A full campaign has taken place for validating all the changes introduced to get the conversion between image and camera coordinates right. The results are shown in a separate technical note ( but also summarised in this validation document.
6 Page: New in SAS 15.0: ebkgreg, a task for determining optimal background position for a source in the FOV This task has so far been implemented only for PN. Interactive use has been tested, including its behaviour by crowded images. A number of observations with many sources in the FoV (i.e. deep observations of the Lockman Hole area) as well as with extended sources (eg. clusters) were used for the validation. 2.3 Updated in SAS 15.0: eimagecombine, a script introduced in SAS 14 for producing (combined) EPIC background subtracted, exposure corrected smoothed images The basic work is performed by another introduced task with SAS 14, eimageget, which creates a set of images from one EPIC exposure, which make possible the derivation of combined background-subtracted exposure corrected images. (eimagecombine is a perl script around that task for the combination of the images derived from one or several observations). The script was not running on Mac platforms under certain circumstances and has been upgraded and made more robust. Validation of the task has been done processing different observations covering certain regions of the sky and creating the corresponding mosaic. In addition the products should be compared to interactive sophisticated background estimation and mosaic creation with esas. 2.4 New in SAS 15.0: Extraction of separated redistribution matrix (RMF) and ancillary response function (ARF) for RGS The task rgsrmfgen is capable now of producing RMF and ARF in separate files. This can ease the analysis in many cases, making it much more efficient. Validation has been performed by comparing spectral results with the (default) combined matrix and with the individual ARF and RMF for the same observations. 2.5 New in SAS 15 - use of embadpixfind for RGS bad pixel / column finding The task embadpixfind has been adapted for its use on the RGS data reduction chain. The corresponding (default) task rgsbadpix used for flagging bad pixels and columns has been reported to discard in certain circumstances columns belonging to bright emission lines, when actually these columns should be perfectly valid. A thorough validation has to show the advantages in those cases, but also the results of applying this new bad pixel recognition to data of continuum sources, i.e. in the absence of emission or absorption lines. Validation has been therefore done comparing the results of tens of observations showing emission lines at different wavelengths (ie. AB Dor, HR1099) using both methods for flagging bad columns, as well as of continuum observations at different signal levels (ie. different observations of Markarian 421). 2.6 New in SAS 15.0: RGS filtering without flagging FIFO buffer full periods FIFO buffer full periods are those reported in the HK data when the number of events getting into the RGS on-board processor reaches a certain limit, which eventually can be followed by not accepting events anymore. The data in those frames going through the processor, however, get processed correctly. So far, the data during those periods, due to bright sources or to
7 Page: 5 high radiation, with FIFO Buffer full, were discarded. It has been shown that the data can be perfectly valid in those periods, and that a counter NLOSTEVT in the science data is actually more reliable. If a frame shows NLOSTEVT=0 then the frame is perfectly acceptable. Validation was performed processing a large number of observations comparing them with and without this flag been used for filtering. Especially data from bright sources showing periods discarded due to the FIFO Buffer Full flag has been processed in both ways and compared as well as the spectra obtained in the different periods (with and without FIFO Buffer Full). 2.7 New in SAS 15.0: Only one 32bits Linux version released This SAS version has been released in diverse Linux OS 64 bits versions as well as two MacOs versions, to cover a broad band of kernels. And for the last time probably one 32 bits Linux version has been included. The number of 32bit users of the latest SAS version (in three different Linux flavors) is around 18%, according to the collected download statistics. Releasing just the most downloaded 32 bit version, we would be affecting less than 10% of the SAS users. A validation cross check has been performed testing this version under other 32bit operating systems, by running the testing sequences.
8 Page: 6 3 Validation results 3.1 Validation schedule The schedule for the validation had foreseen a total of 6 weeks for performing the different tasks (for the period from going into release track mode to final release). This was the projected schedule with the different milestones: SAS into release track mode - 14 December 2015 SAS builds on different platforms - 18 December SAS 15 binaries (at least 1 platform) - 18 December Processing of all the standard datasets - finished - 22 December Installation of SAS 15 binary in XCal grid - 18 December Communication to validators about success and data location - 22 December Preparation of a SAS 15 based PPS test version - 8 January Processing of standard datasets by testing pipeline - 15 January Processing of standard datasets by all binaries - 22 January Processing of XCal archive - 15 January Processing with single 32bit SAS binary on diverse OS - 15 January First I/A analysis of standard data - to be ready by 22 January Integrity checks running all the existing SAS threads - to be ready by 29 January Evaluation of XCal - to be ready by 29 January Screening of PPS processed standard datasets - 29 January Dedicated analysis - to be ready by 29 January: 1. ebkgreg tests 2. eimageget and eimagecombine 3. RGS data processed with separate ARF / RMF 4. RGS new bad pixel finding method 5. RGS new filtering (no FIFO buffer full) Summary reports due on 29 January Release notes + SAS 15 web pages contents ready + XMM Newsletter text - 3 February SAS 15 distribution tar files ready - 3 February Final SV individual reports - 4 March SAS 15 release - 4 February Final SV Report compilation
9 Page: 7 With small variations in the order of days, the plan was followed. The release date was respected, so that SAS 15 has been released punctually on February Processing of standard datasets All the data listed in Tab. 1 have been processed with the full data reduction scripts used for validation without any failure, on the 11 building platforms (9 Linux and 2 MacOs). In addition, the 32 bit SAS 15 binaries produced for Ubuntu 14, has been used by the other three 32bit platforms (Fedora 20, RHEL 5.8 and SuSe 13.1) for cross-checking. The processing was fully satisfactory. A test pipeline version, built on the basis of SAS 15, has also been used for the data reduction of the standard sets. No errors were found, and the output was correctly derived. Screening of the PPS processed data has taken place with fully satisfactory results. The test pipeline version has evolved into the final released PPS based on SAS 15, operational since end of April. The XCal archive was also populated with all the products from processing with SAS15 all the data in the calibration database. Again, no failures found, the analysis of the data and the comparisons with products from former validation campaigns form the basis for further calibration activities and reports RGS data - standard dataset Output products of the whole processing by rgsproc have been compared with the results of processing with previous versions of SAS. No significative differences have been found. Detailed studies are referred further below SAS OM data processing There are no major changes in the OM tasks in this version of SAS. The changes in the use of the XMM-Newton Boresight CCF in the attitude reconstruction tasks of EPIC do not affect OM. Only an update of the variable component of the boresight has been implemented via the corresponding CCF. A bug has been corrected: it affected the deadfraction correction of the rates of sources detected in mosaiced or stacked images. In previous versions of SAS, running ommosaic assigned to the final image the maximum frametime and deadfraction of the component images. This is contradictory because both parameters are inversely proportional, thus once the frametime is assigned (the maximum one) the corresponding deadfraction is deduced from that frametime. The error of the wrong assignement in the final count rates was very small, less than 2 %. Now this inconsistency has been solved. In addition to checking the mentioned new implementations, as in previous deliveries, this Science validation has been devoted to check and confirm that the main functionalities already present in previous versions are maintained, in other words, we confirm the overall stability of the system. The reader is thus referred to previous Science Validation Reports for more detailed comments or descriptions. 3.3 Dedicated analysis EPIC data - G The non-thermal SNR G has been used as one of the standard targets for the validation of the EPIC effective area calibration. Additionally, this source has proven useful in multi-
10 Page: 8 mission cross-calibration studies (Tsujimoto et al. 2011). Its spectrum can be well modelled by a simple power-law combined with a photoelectric absorption. In observation , G was observed with MOS in Full Frame mode and PN in Extended Full Frame Mode (all using Medium Filter) for 30 ks. MOS and PN source spectra were extracted from a circular region ( 2.5 arcmin radius) around the SNR, and spatially filtered through their common exposure mask. MOS background spectra were obtained from annular regions around the source, whereas PN background was obtained from neighbouring source free regions. EPIC data were reduced with SAS 15.0 and spectra were extracted with standard event pattern selection. The results of the comparison of PN and MOS are summarised in Fig. 1, and are essentially in agreement with the previous SAS science validation study. This is as expected, as no significant changes in energy scale calibration have been introduced in the meantime. Figure 1: Comparison of PN versus MOS spectral fits of G Spectra based on data reduced with SAS 15.0, using standard pattern selection. Left panel: the 2-20 kev flux confidence contours for PN versus MOS1 (red) and MOS2 (green). Right panel: column density versus photon index confidence contours for PN (black), MOS1 (red), MOS2 (green). Levels shown are at 68%, 90% and 99% confidence EPIC data - PKS PKS is a well studied radio loud Narrow Line Seyfert 1 galaxy (e.g. Siebert et al. 1999), and has been observed by XMM-Newton as calibration target. Its 2-10 kev spectrum is characterised by a spectral slope Γ 2.2, and the kev emission is dominated by a large and featureless soft excess. EPIC spectra of ObsId are compared as part of this science validation. PN was operated in Small Window Mode, and both MOS instruments in Large Window Mode. Data were reduced with SAS 15.0 (using the respective latest calibration files), and resulting spectra were fit in the kev band with a model consisting of a power-law and bremsstrahlung component with an ISM absorption model (Papadakis et al. 2010). As the MOS data are subject to pile-up the spectra were extracted from annular regions. The best fit results are summarised in Table 2. The main differences between instruments are due to the imperfect relative effective area calibration, resulting in fluxes which are formally not consistent across all three instruments.
11 Page: 9 Table 2: Comparison of MOS and PN spectral fits to PKS (ObsId ) with a power-law plus bremsstrahlung model. Instrument kt Γ Flux χ 2 /d.o.f. kev erg cm 2 s 1 ( kev) ( kev) MOS MOS PN / / / Standard tests of esas Due to the special characteristics of esas, the package for analysis of extended sources observed with the EPIC cameras, particular validation tests are run with every new SAS version, to ensure its integrity and the validity of their separate calibration files. With this purpose the full thread for esas images extraction ( has been run on the odf (Abel 1795 cluster), with both PN and MOS data, and the comparison to earlier results showed no discrepancies OM Fast Mode processing The inconsistency reported in the validation of SAS 14 in relation to the contents of the BACK- GROUND column in time series files (*TIMESR*) is still present: the values of the BACK- GROUND have different scaling depending on the type of measurement. If it is obtained from the fast mode data, the background is given for the extraction area, while if from image data it is scaled to a 12 pixels aperture radius Interactive tasks:omsource and omgsource Here, again the caveats reported in the validation of SAS 14 are still valid: omsource After performing the interactive photometry of a given source, the results can be written to a FITS file. The photometric values for the source (rate, magnitude, flux) are correct, while other file columns giving the applied corrections are wrong. omgsource During the interactive extraction of grism spectra (in 64 bits installations), a temporary plot is produced. This plot may be wrong. However, the final extracted spectra are correct Repeatability of OM filter photometry Several spectrophotometric standard stars are observed repeatedly with OM in order to establish and monitor the photometric and flux calibrations. These are the white dwarfs GD 153, HZ 2 and BPM As we have done in the past all existing data of these stars have been reprocessed using SAS 15. The results are presented in Tab. 3 and in Tab. 4.
12 Page: 10 The quoted errors are the standard deviation of the mean values given as percentage. We see that after all corrections are applied, the count rates of these stars obtained from all observations taken during the life of OM vary within 3 %. Table 3: Standard stars processed with SAS 10.0: average count rates of several observations star N obs UVW2 UVM2 UVW1 U B V GD error (%) HZ error (%) BPM error (%) Table 4: Standard stars processed with SAS 15.0: average count rates of several observations star N obs UVW2 UVM2 UVW1 U B V GD error (%) HZ error (%) BPM error (%) New and updated in SAS15 - Validation 4.1 Updated in SAS 15: attcalc and all the tasks affected by the wrong sign of the Euler ψ angle The CCF release note XMM-CCF-REL-332, related to calibration file XMM BORESIGHT 0026 ( derived after correcting the sign of the Euler ψ angle in the attcalc task, reports on all the tests performed for validating both the calibration file and the several tasks affected by the error introduced with ψ. They include not only checks that the celestial positions of sources detected by SAS 15 are not significantly altered by all the changes introduced (see Fig. 2 taken from that release note) but also that the RGS and OM data are not affected.
13 Page: 11 Figure 2: Differences between the celestial positions of EPIC-pn sources returned by SAS v14 with XMM BORESIGHT 0024.CCF and SAS v15 with XMM BORESIGHT 0026.CCF from a sample of 28 observations spread evenly in time from 2000 to Upper: Differences in RA and DEC of sources in the full sample; Middle: Difference in the declination of source positions as a function of the off-axis angle; Bottom: Difference in the right ascension of source positions as a function of the off-axis angle.
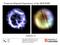
14 Page: Updated in SAS15: eimagecombine The upgrade of the task with the aim of increasing its robustness, and particularly to solve the problems for running it on Mac platforms, has been tested with positive results. The functionality is fully OK, the combination of different images as produced by eimageget for producing a background-subtracted, vignetting-corrected and smoothed mosaic has been confirmed. While a report comparing its level of reliability against interactive sophisticated background estimation and mosaic creation as performed with esas is still missing, eimageget and eimagecombine offer a fast and easy background corrected mosaic production method. Fig. 3 shows an RGB image obtained with a mosaic production combining three observations with all three EPIC cameras in three spectral bands (red=[200,1000]ev, green=[1000,2000]ev and blue=[2000,4500]ev) e e e e e e e e e-05 Figure 3: RGB image using three spectral bands (red=[200,1000]ev, green=[1000,2000]ev and blue=[2000,4500]ev) from a mosaic obtained combining the data from three observations with the three EPIC cameras. 4.3 New in SAS 15: ebkgreg - determining the optimal background position for a source in the FOV The new task has been tested extensively within the pipeline, and it is showing the expected behaviour. In SAS 15 it works only with PN data, but it is planned to be extended to MOS in the next SAS version. Fig. 4 shows the source positions and corresponding background regions obtained with the Lockman Hole data, for those detected sources showing more than 150 counts.
15 Page: 13 Figure 4: Detected sources, including background positions as derived by ebkgreg in a Lockman Hole observation. Background extraction positions are only shown for sources with more than 100 counts (sources in red circles with extraction radius and identification numbers in red, background derived regions in black circles with corresponding numbers in black, as calculated by the task). 4.4 New in SAS 15: Extraction of separated redistribution matrix (RMF) and ancillary response function (ARF) for RGS The task rgsrmfgen can now produce separate RMF and ARF files. Validation has be performed by comparing the result of spectral fits obtained with the default combined matrix and with the individual ARF and RMF for the same observations. We show in Table 5 the results of the XSPEC spectral fit of the RGS spectra of PKS in revolution 1543 (ObsId ) using combined and separate ARF and RMF. The assumed spectral model is an absorbed power-law. The table lists the best fit parameters and the 90% confidence intervals. Same results are obtained with both sets of response matrices. 4.5 New in SASv15.0: - use of adapted embadpixfind for RGS bad pixel / column finding The use of this adaptation of the MOS task for bad pixel and column finding looked very promising to solve the problem, reported time ago, that the rgsbadpixfind task is filtering out many emission lines of bright sources, misidentifying them as bad columns. Fig. 5 shows a comparison between fluxed spectra processed using the default and the new method. With rgsbadpixfind several columns are missed, especially the Fe XVII triplet emission lines at 15-
16 Page: 14 Table 5: Fits using combined and separate ARF and RMF files RGS 1 order1 combined separate H Column Density (10 22 cm 2 ) ( ) ( ) Photon Index 2.61 ( ) 2.61 ( ) Normalisation ( ) ( ) RGS 2 order 1 combined separate H Column Density (10 22 cm 2 ) ( ) ( ) Photon Index 2.57 ( ) 2.57 ( ) Normalisation ( ) ( ) RGS 1 order 2 combined separate H Column Density (10 22 cm 2 ) ( ) ( ) Photon Index 3.00 ( ) 3.00 ( ) Normalisation ( ) ( ) RGS 2 order 2 combined separate H Column Density (10 22 cm 2 ) ( ) ( ) Photon Index 2.86 ( ) 2.85 ( ) Normalisation ( ) ( ) 15.5 Angstrom and the OVII emission line at 17 Angstrom are highly disturbed, while most of them are recovered using the new algorithm. Figure 5: Capella fluxed spectra processed using rgsbadpixfind (above) and rgsembadpixfind (below). In order to validate the new task, several tests have been conducted with two aims, to see its efficiency a) in the absence of emission lines, and b) with more or less bright lines of different strengths. To the first purpose, 64 observations of the BL Lac Mrk421 have been processed, showing basically a line-free continuum in this spectral range at different brightness levels, with the one and the other task for bad pixel/column recognition. The results were undistinguishable. For analysing the main cases of emission rich sources, we have chosen three sources, the stars Capella (27 observations), AB Dor (35 observations) and HR1099 (33 observations). All of them have undergone full data reduction using alternatively rgsbadpixfind and the modified!
17 Page: 15 embadpixfind. The procedure foresaw simultaneous fitting of the 1st and 2nd order spectra of both RGS1 and RGS2, with a model, capable of catching most emission lines present. After that, a comparison of number of columns discarded and the goodness of fitting in the one and the other case was performed. We started with the AB Dor observations, using the ISIS spectral fitting package, with an APED model with three temperatures and free abundances, provided to us by the authors of Sanz-Forcada et al., similar to the one used in that publication. We were not interested in the physics, but needed just an approximation fitting most lines, and all prominent ones without exception. This was reached just by adjusting the abundances. The results were very promising favouring the new algorithm, with many few hot columns (actually false positives in the rgsbadpixfind case), typically 100 less hot columns found per observation with the new algorithm (counting the four spectra together), and in almost all cases, smaller Cash values per degree of freedom, ie. fitting perfectly those non-discarded columns. The problem was the non-detection of eminent hot columns in three observations out of the 35 analysed (see Fig. 6). This deficiency points to the necessity of assessment of the full parameter space of the new task rgsembadpixfind, something which goes beyond the scope of this validation exercise, and expected to be performed before the next SAS version release. The task rgsembadpixfind has been, therefore, withdrawn from SAS 15. Figure 6: Results comparing rgsbadpixfind and rgsembadpixfind: left the number of valid columns in the four spectra per observation is plotted, right the Cash value per degree of freedom obtained per observation. The three high values are due to non-recognised isolated hot columns. 4.6 New in SASv15.0: RGS filtering without flagging FIFO buffer full periods FIFO Buffer Full periods are those reported in the housekeeping data when the number of events going into the RGS on-board processor reaches a certain limit, which eventually can be followed by not accepting events anymore. So far, the data during periods with FIFO Buffer Full were discarded during the generation of GTIs. Nevertheless, it has been shown that events in those frames going through the processor get processed correctly and, if the NLOSTEVT counter counter is zero, data in those periods are
18 Page: 16 valid. SASv15.0 implements in rgsproc a new parameter (includeinputfifofull) allowing to enable/disable the inclusion of the periods with FIFO buffer full in the housekeeping GTIs. For the time being, the default value of this parameter is no, i.e., these periods are discarded Validation The test has been done processing 40 observations of bright targets for which a large loss of exposure time (and events) during the standard processing with rgsproc has been previously detected. These observations have been processed with SASv15.0 with default value includeinputfifofull=no and with the new option includeinputfifofull=yes, and the results have been compared. Table 6 shows the exposure time (ONTIME keyword) obtained with both options, ONTa for the default processing, ONTb for the new option. In some cases the gain in time is as large as 5 ks. The other columns show the difference in total GTI duration for individual CCDs. In all the studied observations there is a net gain in exposure time; for clarity, we show in the table only the cases in which the difference is larger than 1000s. The same test has been made in 40 randomly chosen observations: no difference in exposure time has been found for those cases. Three of the observations in Table 6 have been studied in more detail (see Table 7). ObsId (Crab) is the case for which the largest difference in exposure time has been found: 5.5 ks for RGS1 and 6.5 ks for RGS2. ObsId (RS Oph) is a peculiar case, since there is a large difference for RGS1 (4.2 ks), but almost no difference for RGS2. Finally, ObsId (GX339-4) has a similar countrate than , but in this case the gain in exposure time for both RGS is of the same order. Figures 7, 8 and 9 show, for these three cases, the spectra and the light curves obtained with the two filtering options. 5 Conclusion The SAS scientific validation process concluded that SAS 15 was validated and should be released, as it happened on February 4, The only caveat with respect to the originally planned contents of this release was the necessity of withdrawing the task rgsembadpixfind from it, leaving it for a future release after determination of optimal task parameters.
19 Page: 17 Table 6: Comparison of the processing of observations of bright sources with includeinputfifofull=no/yes RGS1 ObsId Target ONTa ONTb S004 Crab S005 Cyg X S004 RS Oph S005 Cyg X S004 Cyg X S004 GX S004 Crab S004 Crab S004 Cyg X S004 Crab RGS2 ObsId Target ONTa ONTb S005 Crab S005 XTE J S013 Cyg X S013 Cyg X S007 Crab S005 Cyg X S005 Cyg X S005 GX S006 Crab S005 Crab S003 GRO J S006 Crab S006 Crab U002 Crab S005 Crab S005 Crab S006 Crab S006 Crab S006 Crab S005 Crab S005 Crab S047 Crab S007 Crab S005 Crab S005 Crab S007 Crab S007 Sco X U003 Crab ONTa: ONTIME (s) for includeinputfifofull=no ONTb: ONTIME (s) for includeinputfifofull=yes The rest of the columns list the difference (in s) of the GTIs for individual CCDs: GTI(include...=yes) - GTI(include..=no)
20 Page: 18 Figure 7: Example of processing with/without FIFO full periods for Crab ObsId , top: spectra, bottom: lightcurves
21 Page: 19 Figure 8: Example of processing with/without FIFO full periods for RS Oph ObsId , top: spectra, bottom: lightcurves
22 Page: 20 Figure 9: Example of processing with/without FIFO full periods for GX339-4 ObsId , top: spectra, bottom: lightcurves
23 Page: 21 Table 7: Details of selected observations RGS1 RGS2 includeinputfifofull texp counts rate texp counts rate s cts/s s cts/s Crab no ± ±3 yes ± ±3 RS Oph no ± ±2 yes ± ±2 GX no ± ±2 yes ± ±1 counts: counts in total first order extracted spectrum (source+background) rate: average countrate in first order light curve created with rgslccorr, with 100 s bin for and , and 30 s bin for References Papadakis, I.E. et al. 2010, A&A 510, A65 Sanz-Forcada, J., Micela, G., & Maggio, A. 2007, in XMM-Newton: The Next Decade, p3 Siebert, J. et al. 1999, A&A 348, 678 Tsujimoto, M. et al. 2011, A&A 525, A25
XMM-Newton Calibration
 XMM-Newton Calibration Michael Smith, on behalf of XMM-SOC and Instrument Teams 18 th XMM-Newton Users Group Meeting, ESAC, 11 May 2017 ESA UNCLASSIFIED - For Official Use Outline 1. Status of calibration
XMM-Newton Calibration Michael Smith, on behalf of XMM-SOC and Instrument Teams 18 th XMM-Newton Users Group Meeting, ESAC, 11 May 2017 ESA UNCLASSIFIED - For Official Use Outline 1. Status of calibration
XMM-Newton. XMM-Newton Science Analysis System 17.0 scientific validation. XMM-SOC-USR-TN-0029 Issue 1.1
 XMM-Newton XMM-Newton Science Analysis System 17.0 scientific validation XMM-SOC-USR-TN-0029 Issue 1.1 R. Saxton, C.Gabriel, I. de la Calle, A.Ibarra, R.González-Riestra, E.Ojero, J.V.Perea, P.Rodríguez,
XMM-Newton XMM-Newton Science Analysis System 17.0 scientific validation XMM-SOC-USR-TN-0029 Issue 1.1 R. Saxton, C.Gabriel, I. de la Calle, A.Ibarra, R.González-Riestra, E.Ojero, J.V.Perea, P.Rodríguez,
XMM-Newton. XMM-Newton Science Analysis System 12.0 scientific validation. XMM-SOC-USR-TN-0019 Issue 1.1
 XMM-Newton XMM-Newton Science Analysis System 12.0 scientific validation XMM-SOC-USR-TN-0019 Issue 1.1 C.Gabriel, I. de la Calle, A.Ibarra, E. Chapin, R.González-Riestra, M.Guainazzi, A.Pollock, R.Saxton,
XMM-Newton XMM-Newton Science Analysis System 12.0 scientific validation XMM-SOC-USR-TN-0019 Issue 1.1 C.Gabriel, I. de la Calle, A.Ibarra, E. Chapin, R.González-Riestra, M.Guainazzi, A.Pollock, R.Saxton,
XMM-Newton SOC Technical Note
 XMM-Newton SOC Technical Note XMM-SOC-CAL-TN-0082 Accuracy of energy reconstruction in EPIC-MOS Timing Mode M. Guainazzi April 6, 2009 History Version Date Editor Note 1.0 April 6, 2009 M.Guainazzi SASv8.0
XMM-Newton SOC Technical Note XMM-SOC-CAL-TN-0082 Accuracy of energy reconstruction in EPIC-MOS Timing Mode M. Guainazzi April 6, 2009 History Version Date Editor Note 1.0 April 6, 2009 M.Guainazzi SASv8.0
Status of the EPIC calibration
 Status of the calibration 16 October 2003 Marcus G. F. Kirsch Marcus G. F. Kirsch with the input of the whole consortium Page 1 progress in calibration general absolute timing problem seems to be solved
Status of the calibration 16 October 2003 Marcus G. F. Kirsch Marcus G. F. Kirsch with the input of the whole consortium Page 1 progress in calibration general absolute timing problem seems to be solved
Analysis of extended sources with the EPIC cameras
 Analysis of extended sources with the EPIC cameras 7 th ESAC SAS Workshop June 19 22, 2007 Science Operations Centre 1 Status Analysis of extended sources is complex, challenging and time-consuming There
Analysis of extended sources with the EPIC cameras 7 th ESAC SAS Workshop June 19 22, 2007 Science Operations Centre 1 Status Analysis of extended sources is complex, challenging and time-consuming There
XMM-Newton Optical-UV Monitor: introduction and calibration status OM instrument and calibration
 XMM-Newton Optical-UV Monitor: introduction and calibration status OM instrument and calibration Antonio Talavera XMM-Newton Science Operation Centre, ESAC, ESA OM: Instrument Description 30 cm Ritchey-Chretien
XMM-Newton Optical-UV Monitor: introduction and calibration status OM instrument and calibration Antonio Talavera XMM-Newton Science Operation Centre, ESAC, ESA OM: Instrument Description 30 cm Ritchey-Chretien
The Behaviour of the XMM-Newton Background: From the beginning of the mission until May XMM-SOC-GEN-TN-0014 issue 3.10
 The Behaviour of the XMM-Newton Background: From the beginning of the mission until May 2017 XMM-SOC-GEN-TN-0014 issue 3.10 R. González-Riestra and P.M. Rodríguez-Pascual XMM-SOC User Support Group June
The Behaviour of the XMM-Newton Background: From the beginning of the mission until May 2017 XMM-SOC-GEN-TN-0014 issue 3.10 R. González-Riestra and P.M. Rodríguez-Pascual XMM-SOC User Support Group June
XMM-Newton Calibration Technical Note
 XMM-Newton Calibration Technical Note XMM-SOC-USR-TN-0020 EPIC calibration+science exposures: how to deal with them? Matteo Guainazzi 1, Konrad Dennerl 2, Michael Freyberg 2, Fabio Gastaldello 3, Nora
XMM-Newton Calibration Technical Note XMM-SOC-USR-TN-0020 EPIC calibration+science exposures: how to deal with them? Matteo Guainazzi 1, Konrad Dennerl 2, Michael Freyberg 2, Fabio Gastaldello 3, Nora
ENERGY SCALE IN EPIC-PN TIMING MODE
 ENERGY SCALE IN EPIC-PN TIMING MODE Matteo Guainazzi1, Frank Haberl2, Michael Freyberg2, Michael Smith1 1 ESAC-ESA; 2MPE Outline What is the Timing Mode in EPIC-pn? Count rate dependence of the energy
ENERGY SCALE IN EPIC-PN TIMING MODE Matteo Guainazzi1, Frank Haberl2, Michael Freyberg2, Michael Smith1 1 ESAC-ESA; 2MPE Outline What is the Timing Mode in EPIC-pn? Count rate dependence of the energy
Evaluation of the capabilities of the XMM-Newton SciSim from the EPIC calibration point-of-view. André Burzlaff, FH Aachen
 Evaluation of the capabilities of the XMM-Newton SciSim from the EPIC calibration point-of-view André Burzlaff, FH Aachen Menu XMM-Newton and EPIC SciSim Test Results Conclusion Outlook XMM Newton Launched
Evaluation of the capabilities of the XMM-Newton SciSim from the EPIC calibration point-of-view André Burzlaff, FH Aachen Menu XMM-Newton and EPIC SciSim Test Results Conclusion Outlook XMM Newton Launched
RGS CALIBRATION STATUS
 RGS CALIBRATION STATUS ROSARIO GONZÁLEZ-RIESTRA XMM-NEWTON SCIENCE OPERATIONS CENTRE ON BEHALF OF THE SRON AND ESAC RGS TEAMS ESA UNCLASSIFIED - For Official Use Rosario Gonzalez-Riestra 17/05/2018 Slide
RGS CALIBRATION STATUS ROSARIO GONZÁLEZ-RIESTRA XMM-NEWTON SCIENCE OPERATIONS CENTRE ON BEHALF OF THE SRON AND ESAC RGS TEAMS ESA UNCLASSIFIED - For Official Use Rosario Gonzalez-Riestra 17/05/2018 Slide
A Library of the X-ray Universe: Generating the XMM-Newton Source Catalogues
 A Library of the X-ray Universe: Generating the XMM-Newton Source Catalogues Iris Traulsen Axel Schwope, Georg Lamer Leibniz-Institut für Astrophysik Potsdam (AIP) on behalf of the XMM-Newton Survey Science
A Library of the X-ray Universe: Generating the XMM-Newton Source Catalogues Iris Traulsen Axel Schwope, Georg Lamer Leibniz-Institut für Astrophysik Potsdam (AIP) on behalf of the XMM-Newton Survey Science
High Resolution X-Ray Spectra A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL OF THE HOT UNIVERSE
 High Resolution X-Ray Spectra A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL OF THE HOT UNIVERSE Katarzyna Bensch Rosario González-Riestra María Santos-Lleó XMM-NEWTON / ESAC The RGS Instruments THE REFLECTION GRATING SPECTROMETER
High Resolution X-Ray Spectra A DIAGNOSTIC TOOL OF THE HOT UNIVERSE Katarzyna Bensch Rosario González-Riestra María Santos-Lleó XMM-NEWTON / ESAC The RGS Instruments THE REFLECTION GRATING SPECTROMETER
Serendipitous UV source catalogues for 10 years of XMM and 5 years of Swift
 Astrophys Space Sci (2014) 354:97 101 DOI 10.1007/s10509-014-1944-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Serendipitous UV source catalogues for 10 years of XMM and 5 years of Swift V.N. Yershov Received: 15 January 2014 /
Astrophys Space Sci (2014) 354:97 101 DOI 10.1007/s10509-014-1944-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Serendipitous UV source catalogues for 10 years of XMM and 5 years of Swift V.N. Yershov Received: 15 January 2014 /
A Cluster of Galaxies, Abell 496
 A Cluster of Galaxies, Abell 496 F. Nobels and W. Mulder MSc Astronomy & Kapteyn Astronomical Institute, University of Groningen (Dated: November 11, 2015) As part of the course High-Energy Astrophysics,
A Cluster of Galaxies, Abell 496 F. Nobels and W. Mulder MSc Astronomy & Kapteyn Astronomical Institute, University of Groningen (Dated: November 11, 2015) As part of the course High-Energy Astrophysics,
XMM-Newton. Routine Calibration Plan. Version Edited by: M. J. S. Smith. September 6, Revision history
 XMM-Newton Routine Calibration Plan Version 2.26 Edited by: M. J. S. Smith September 6, 2017 Revision history Revision number Date Revision author Comments Version 2.26 06/09/2017 M. J. S. Smith 3C 273
XMM-Newton Routine Calibration Plan Version 2.26 Edited by: M. J. S. Smith September 6, 2017 Revision history Revision number Date Revision author Comments Version 2.26 06/09/2017 M. J. S. Smith 3C 273
NuSTAR observation of the Arches cluster: X-ray spectrum extraction from a 2D image
 NuSTAR observation of the Arches cluster: X-ray spectrum extraction from a 2D image Space Research Institute (IKI), Moscow, Russia E-mail: krivonos@iki.rssi.ru The NuSTAR mission performed a long (200
NuSTAR observation of the Arches cluster: X-ray spectrum extraction from a 2D image Space Research Institute (IKI), Moscow, Russia E-mail: krivonos@iki.rssi.ru The NuSTAR mission performed a long (200
XMM-Newton Chandra Blazar Flux Comparison. M.J.S. Smith (ESAC) & H. Marshall (MIT) 7 th IACHEC, Napa, March 2012
 XMM-Newton Chandra Blazar Flux Comparison M.J.S. Smith (ESAC) & H. Marshall (MIT) 7 th IACHEC, Napa, March 2012 Blazar Sample Objective: Comparison of XMM-Newton Chandra fluxes in various bands. Using
XMM-Newton Chandra Blazar Flux Comparison M.J.S. Smith (ESAC) & H. Marshall (MIT) 7 th IACHEC, Napa, March 2012 Blazar Sample Objective: Comparison of XMM-Newton Chandra fluxes in various bands. Using
e e-03. which is distributed with standard chandra processing. visual inspection are included.
 1 SUMMARY 1 SNR 0505-67.9 1 Summary Common Name: DEM L71 Distance: 50 kpc (distance to LMC, Westerlund(1990) ) Center of X-ray emission (J2000): ( 05 05 42.0, -67 52 39.8 ) X-ray size: 86 x 74 Description:
1 SUMMARY 1 SNR 0505-67.9 1 Summary Common Name: DEM L71 Distance: 50 kpc (distance to LMC, Westerlund(1990) ) Center of X-ray emission (J2000): ( 05 05 42.0, -67 52 39.8 ) X-ray size: 86 x 74 Description:
XMM-Newton Calibration Technical Note
 XMM-Newton Calibration Technical Note XMM-SOC-CAL-TN-0018 EPIC Status of Calibration and Data Analysis Edited by M.J.S. Smith (ESAC) on behalf of the EPIC Consortium December 12, 2016 History Version Date
XMM-Newton Calibration Technical Note XMM-SOC-CAL-TN-0018 EPIC Status of Calibration and Data Analysis Edited by M.J.S. Smith (ESAC) on behalf of the EPIC Consortium December 12, 2016 History Version Date
EPIC-BG Meeting June/July`05 - Introduction
 -BG Meeting June/July`05 - Introduction At the end of the last UG meeting, and in line with the conclusions from Previous UG meetings, it was highlighted that there is a need for to progress in the description
-BG Meeting June/July`05 - Introduction At the end of the last UG meeting, and in line with the conclusions from Previous UG meetings, it was highlighted that there is a need for to progress in the description
Study of the evolution of the ACS/WFC sensitivity loss
 Instrument Science Report ACS 2013 01 Study of the evolution of the ACS/WFC sensitivity loss Leonardo Úbeda and Jay Anderson Space Telescope Science Institute January 28, 2013 ABSTRACT We present a study
Instrument Science Report ACS 2013 01 Study of the evolution of the ACS/WFC sensitivity loss Leonardo Úbeda and Jay Anderson Space Telescope Science Institute January 28, 2013 ABSTRACT We present a study
Analysis of Off-Nuclear X-Ray Sources in Galaxy NGC Sarah M. Harrison
 SLAC-TN-6-19 August 26 Analysis of Off-Nuclear X-Ray Sources in Galaxy NGC 4945 Sarah M. Harrison Office of Science, Science Undergraduate Laboratory Internship (SULI) Massachusetts Institute of Technology
SLAC-TN-6-19 August 26 Analysis of Off-Nuclear X-Ray Sources in Galaxy NGC 4945 Sarah M. Harrison Office of Science, Science Undergraduate Laboratory Internship (SULI) Massachusetts Institute of Technology
NICMOS Status and Plans
 1997 HST Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 1997 S. Casertano, et al., eds. NICMOS Status and Plans Rodger I. Thompson Steward Observatory, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721
1997 HST Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 1997 S. Casertano, et al., eds. NICMOS Status and Plans Rodger I. Thompson Steward Observatory, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721
The 3XMM catalogue. Natalie Webb. Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planétologie Toulouse, France
 The 3XMM catalogue Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planétologie Toulouse, France and for the XMM Newton Survey Science Centre (SSC) 1 XMM Newton Survey Science Centre (SSC) The XMM Newton Survey
The 3XMM catalogue Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planétologie Toulouse, France and for the XMM Newton Survey Science Centre (SSC) 1 XMM Newton Survey Science Centre (SSC) The XMM Newton Survey
Legacy IACHEC Working Group: the first steps
 Legacy IACHEC Working Group: the first steps Matteo Guainazzi 1 & Andy Pollock 2 1 Astro-H & MM-Newton ESA-SOC, ESAC, Spain 2 GAIA and multi-mission Archive Scientist, ESA-SOC, ESA, Spain Scope Provide
Legacy IACHEC Working Group: the first steps Matteo Guainazzi 1 & Andy Pollock 2 1 Astro-H & MM-Newton ESA-SOC, ESAC, Spain 2 GAIA and multi-mission Archive Scientist, ESA-SOC, ESA, Spain Scope Provide
Spectral Analysis of High Resolution X-ray Binary Data
 Spectral Analysis of High Resolution X-ray Binary Data Michael Nowak, mnowak@space.mit.edu X-ray Astronomy School; Aug. 1-5, 2011 Introduction This exercise takes a look at X-ray binary observations using
Spectral Analysis of High Resolution X-ray Binary Data Michael Nowak, mnowak@space.mit.edu X-ray Astronomy School; Aug. 1-5, 2011 Introduction This exercise takes a look at X-ray binary observations using
Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 86 (2009), TURKISH NATIONAL OBSERVATORY (TUG) VIEW OF CLUSTERS OF GALAXIES
 Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 86 (2009), 125-130 Contributed paper TURKISH NATIONAL OBSERVATORY (TUG) VIEW OF CLUSTERS OF GALAXIES M. HUDAVERDI 1,2, E. N. ERCAN 2, M. BOZKURT 2, F. GÖK3 and E. AKTEKIN
Publ. Astron. Obs. Belgrade No. 86 (2009), 125-130 Contributed paper TURKISH NATIONAL OBSERVATORY (TUG) VIEW OF CLUSTERS OF GALAXIES M. HUDAVERDI 1,2, E. N. ERCAN 2, M. BOZKURT 2, F. GÖK3 and E. AKTEKIN
Sequence Obs ID Instrument Exposure uf Exposure f Date Observed Aimpoint (J2000) (ks) (ks) (α, δ)
 1 SUMMARY 1 G120.1+01.4 1 Summary Common Name: Tycho s Distance: 2.4 kpc ( Chevalier et al., 1980 ) Center of X-ray emission (J2000): ( 00 25 19.9, 64 08 18.2 ) X-ray size: 8.7 x8.6 Description: 1.1 Summary
1 SUMMARY 1 G120.1+01.4 1 Summary Common Name: Tycho s Distance: 2.4 kpc ( Chevalier et al., 1980 ) Center of X-ray emission (J2000): ( 00 25 19.9, 64 08 18.2 ) X-ray size: 8.7 x8.6 Description: 1.1 Summary
XMM-Newton Observations of the Isolated Neutron Star 1RXS J / RBS 1774
 XMM-Newton Observations of the Isolated Neutron Star 1RXS J214303.7+065419 / RBS 1774 Mark Cropper, Silvia Zane Roberto Turolla Luca Zampieri Matteo Chieregato Jeremy Drake Aldo Treves MSSL/UCL Univ Padova
XMM-Newton Observations of the Isolated Neutron Star 1RXS J214303.7+065419 / RBS 1774 Mark Cropper, Silvia Zane Roberto Turolla Luca Zampieri Matteo Chieregato Jeremy Drake Aldo Treves MSSL/UCL Univ Padova
NAOYUKI TAMURA Subaru Instrument Astronomer Subaru Telescope, NAOJ
 FMOS status tt report Science workshop 2011.02.2802 28-03.0202 NAOYUKI TAMURA Subaru Instrument Astronomer Subaru Telescope, NAOJ * Overview * Recent history & current status t * Schedule & future plan
FMOS status tt report Science workshop 2011.02.2802 28-03.0202 NAOYUKI TAMURA Subaru Instrument Astronomer Subaru Telescope, NAOJ * Overview * Recent history & current status t * Schedule & future plan
Major Releases: BG analysis web page with recommended information, papers, summary tables etc:
 BGWG -Newton BackGround Working Group founded (~1.5 years ago). Steering and supervising committee to provide the user with clear information on the Background and (SAS)-Tools to treat the Background correctly
BGWG -Newton BackGround Working Group founded (~1.5 years ago). Steering and supervising committee to provide the user with clear information on the Background and (SAS)-Tools to treat the Background correctly
XMM. XMM-Newton Optical and UV Monitor (OM) Calibration Status. XMM-SOC-CAL-TN-0019 Issue 6.0
 XMM XMM-Newton Optical and UV Monitor (OM) Calibration Status XMM-SOC-CAL-TN-0019 Issue 6.0 Antonio Talavera, OMCal Team XMM-Newton Science Operations Center OMCal Team MSSL-UCL 20 January 2011 Revision
XMM XMM-Newton Optical and UV Monitor (OM) Calibration Status XMM-SOC-CAL-TN-0019 Issue 6.0 Antonio Talavera, OMCal Team XMM-Newton Science Operations Center OMCal Team MSSL-UCL 20 January 2011 Revision
GOODS/VIMOS Spectroscopy: Data Release Version 2.0.1
 ESO Phase 3 Data Release Description Data Collection GOODS_VIMOS_SPEC Release Number 1 Data Provider C. Cesarsky Date 10.03.2010 Migrated to Phase 3 infrastructure 08.12.2014 GOODS/VIMOS Spectroscopy:
ESO Phase 3 Data Release Description Data Collection GOODS_VIMOS_SPEC Release Number 1 Data Provider C. Cesarsky Date 10.03.2010 Migrated to Phase 3 infrastructure 08.12.2014 GOODS/VIMOS Spectroscopy:
IBIS/ISGRI STATUS. Philippe Laurent, Volodymyr Savchenko, François Lebrun, Christian Gouiffès, Aleksandra Gros, Andréa Goldwurm, Aymeric Sauvageon
 IBIS/ISGRI STATUS Philippe Laurent, Volodymyr Savchenko, François Lebrun, Christian Gouiffès, Aleksandra Gros, Andréa Goldwurm, Aymeric Sauvageon CEA/DRF/IRFU/Sap & APC IUG 09/03/2016 ISGRI ENERGY CALIBRATION
IBIS/ISGRI STATUS Philippe Laurent, Volodymyr Savchenko, François Lebrun, Christian Gouiffès, Aleksandra Gros, Andréa Goldwurm, Aymeric Sauvageon CEA/DRF/IRFU/Sap & APC IUG 09/03/2016 ISGRI ENERGY CALIBRATION
NuStar has similar area kev, Astro-H better at E> 80 Kev
 NuStar has similar area 20-80 kev, Astro-H better at E> 80 Kev 10 3 1 HXI Effective Area [cm 2 ] 10 2 10 1 5 10 30 80 Energy [kev] NuStar and Astro-H HXI should have similar FOV HXI becomes background
NuStar has similar area 20-80 kev, Astro-H better at E> 80 Kev 10 3 1 HXI Effective Area [cm 2 ] 10 2 10 1 5 10 30 80 Energy [kev] NuStar and Astro-H HXI should have similar FOV HXI becomes background
Temporal &Spatial Dependency of the MOS RMF
 Temporal &Spatial Dependency of the RMF 1ES0102-72 1 Thin filter 0447 2 Thin filter 0447 0433 1ES0102 0.1-0.35 kev images Good spectra clean images Bad spectra bright patch - Able to do spectral analysis
Temporal &Spatial Dependency of the RMF 1ES0102-72 1 Thin filter 0447 2 Thin filter 0447 0433 1ES0102 0.1-0.35 kev images Good spectra clean images Bad spectra bright patch - Able to do spectral analysis
The XMM-Newton EPIC background and the production of background blank sky event files. J. A. Carter and A. M. Read ABSTRACT
 A&A 464, 1155 1166 (2007) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20065882 c ESO 2007 Astronomy & Astrophysics The XMM-Newton EPIC background and the production of background blank sky event files J. A. Carter and A. M.
A&A 464, 1155 1166 (2007) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20065882 c ESO 2007 Astronomy & Astrophysics The XMM-Newton EPIC background and the production of background blank sky event files J. A. Carter and A. M.
Laura Barragán. Universidad Complutense de Madrid
 . Universidad Complutense de Madrid Tutors: Erik Kuulkers & Peter Kretschmar INTEGRAL: International Gamma-Ray Astrophysics Laboratory The payload The mission The project IBIS (Imager on-board the Integral
. Universidad Complutense de Madrid Tutors: Erik Kuulkers & Peter Kretschmar INTEGRAL: International Gamma-Ray Astrophysics Laboratory The payload The mission The project IBIS (Imager on-board the Integral
ACIS ( , ) Total e e e e-10 4.
 1 SUMMARY 1 G21.5-0.9 1 Summary Distance: 5 kpc ( Safi-Harb et al., 2001 ) Position of Central Source (J2000): ( 18 33 34.0, -10 34 15.3 ) X-ray size: 4.7 x4.6 Description: 1.1 Summary of Chandra Observations
1 SUMMARY 1 G21.5-0.9 1 Summary Distance: 5 kpc ( Safi-Harb et al., 2001 ) Position of Central Source (J2000): ( 18 33 34.0, -10 34 15.3 ) X-ray size: 4.7 x4.6 Description: 1.1 Summary of Chandra Observations
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 6 May 2004
 XMM-NEWTON OBSERVATIONS OF THREE HIGH REDSHIFT RADIO GALAXIES arxiv:astro-ph/0405116 v1 6 May 2004 Abstract E. Belsole, D.M. Worrall, M. J. Hardcastle Department of Physics - University of Bristol Tyndall
XMM-NEWTON OBSERVATIONS OF THREE HIGH REDSHIFT RADIO GALAXIES arxiv:astro-ph/0405116 v1 6 May 2004 Abstract E. Belsole, D.M. Worrall, M. J. Hardcastle Department of Physics - University of Bristol Tyndall
The Galaxy Viewed at Very Short Time-Scales with the Berkeley Visible Image Tube (BVIT)
 The Galaxy Viewed at Very Short Time-Scales with the Berkeley Visible Image Tube (BVIT) Barry Y. Welsh, O.H.W. Siegmund, J. McPhate, D. Rogers & J.V. Vallerga Space Sciences Laboratory University of California,
The Galaxy Viewed at Very Short Time-Scales with the Berkeley Visible Image Tube (BVIT) Barry Y. Welsh, O.H.W. Siegmund, J. McPhate, D. Rogers & J.V. Vallerga Space Sciences Laboratory University of California,
Report on the new EFOSC2 VPH grisms
 Report on the new EFOSC2 VPH grisms Ivo Saviane Lorenzo Monaco v 1.0 March 01, 2008 1 Introduction In January 2008 the ULTRASPEC project delivered two volume-phased holographic grisms (VPHG) to be used
Report on the new EFOSC2 VPH grisms Ivo Saviane Lorenzo Monaco v 1.0 March 01, 2008 1 Introduction In January 2008 the ULTRASPEC project delivered two volume-phased holographic grisms (VPHG) to be used
Hughes et al., 1998 ApJ, 505, 732 : ASCA. Westerlund, 1990 A&ARv, 2, 29 : Distance to LMC 1 ) ) (ergs s F X L X. 2 s 1. ) (ergs cm
 1 SUMMARY 1 SNR 0525-66.1 1 Summary Common Name: N 49 Distance: 50 kpc (distance to LMC, Westerlund(1990) ) Position of Central Source (J2000): ( 05 25 59.9, -66 04 50.8 ) X-ray size: 85 x 65 Description:??
1 SUMMARY 1 SNR 0525-66.1 1 Summary Common Name: N 49 Distance: 50 kpc (distance to LMC, Westerlund(1990) ) Position of Central Source (J2000): ( 05 25 59.9, -66 04 50.8 ) X-ray size: 85 x 65 Description:??
IBIS - IN FLIGHT CALIBRATION ACTIVITIES
 IBIS - IN FLIGHT CALIBRATION ACTIVITIES Natalucci on behalf of the IBIS Team INTEGRAL/IBIS Calibration Update THE IBIS INSTRUMENT coded mask, placed 3.2m above detector (1m2) Collection area ~ 3000 cm2
IBIS - IN FLIGHT CALIBRATION ACTIVITIES Natalucci on behalf of the IBIS Team INTEGRAL/IBIS Calibration Update THE IBIS INSTRUMENT coded mask, placed 3.2m above detector (1m2) Collection area ~ 3000 cm2
X-ray Observations of Nearby Galaxies
 X-ray Observations of Nearby Galaxies Wolfgang Pietsch Max Planck Institut für extraterrestrische Physik XMM-Newton EPIC view of the starburst galaxy NGC 253 Wolfgang Pietsch Max Planck Institut für extraterrestrische
X-ray Observations of Nearby Galaxies Wolfgang Pietsch Max Planck Institut für extraterrestrische Physik XMM-Newton EPIC view of the starburst galaxy NGC 253 Wolfgang Pietsch Max Planck Institut für extraterrestrische
Science and source catalogs with JEM-X. Niels Jørgen Westergaard National Space Institute, Technical University of Denmark
 Science and source catalogs with JEM-X Niels Jørgen Westergaard National Space Institute, Technical University of Denmark Outline 1. Presentation of JEM-X 2. Search for X-ray bursts (Søren Brandt, Jérôme
Science and source catalogs with JEM-X Niels Jørgen Westergaard National Space Institute, Technical University of Denmark Outline 1. Presentation of JEM-X 2. Search for X-ray bursts (Søren Brandt, Jérôme
Open Cluster Research Project
 Open Cluster Research Project I. Introduction The observational data indicate that all stars form in clusters. In a cloud of hydrogen gas, laced with helium and a trace of other elements, something triggers
Open Cluster Research Project I. Introduction The observational data indicate that all stars form in clusters. In a cloud of hydrogen gas, laced with helium and a trace of other elements, something triggers
XMM-Newton Observations of Unidentified Gamma-Ray Objects
 XMM-Newton Observations of Unidentified Gamma-Ray Objects - New Results in X-ray Astronomy, MSSL, 11th July 2006 - R. Mignani (UCL-MSSL) N. La Palombara, P.A. Caraveo (IASF) E. Hatziminaouglou, M. Schirmer
XMM-Newton Observations of Unidentified Gamma-Ray Objects - New Results in X-ray Astronomy, MSSL, 11th July 2006 - R. Mignani (UCL-MSSL) N. La Palombara, P.A. Caraveo (IASF) E. Hatziminaouglou, M. Schirmer
AstroBITS: Open Cluster Project
 AstroBITS: Open Cluster Project I. Introduction The observational data that astronomers have gathered over many years indicate that all stars form in clusters. In a cloud of hydrogen gas, laced with helium
AstroBITS: Open Cluster Project I. Introduction The observational data that astronomers have gathered over many years indicate that all stars form in clusters. In a cloud of hydrogen gas, laced with helium
EPIC Straylight. telescopes/sieves/rga revisited. David Lumb, Athena Study Scientist
 EPIC Straylight telescopes/sieves/rga revisited David Lumb, Athena Study Scientist Leicester BOC 7 Mar 2012 Topics Covered 1. The X-ray sieves 2. Initial in flight calibration (Crab ~Rev 54-56) 3. Sco
EPIC Straylight telescopes/sieves/rga revisited David Lumb, Athena Study Scientist Leicester BOC 7 Mar 2012 Topics Covered 1. The X-ray sieves 2. Initial in flight calibration (Crab ~Rev 54-56) 3. Sco
Mapping the non thermal emission in Coma cluster of galaxies using the FeXXV/FeXXVI line ratio
 Mapping the non thermal emission in Coma cluster of galaxies using the FeXXV/FeXXVI line ratio J. Nevalainen 1 & D. Eckert 2 1 Helsinki University Observatory, Finland 2 ISDC, Geneva, Switzerland Evidence
Mapping the non thermal emission in Coma cluster of galaxies using the FeXXV/FeXXVI line ratio J. Nevalainen 1 & D. Eckert 2 1 Helsinki University Observatory, Finland 2 ISDC, Geneva, Switzerland Evidence
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 14 Mar 2014
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 14 Mar 2014 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 14 Mar 2014](/thumbs/92/110392049.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper c ESO 2018 September 10, 2018 arxiv:1403.3555v1 [astro-ph.im] 14 Mar 2014 Cross-Calibration of the XMM-Newton EPIC pn & MOS On-Axis Effective Areas Using 2XMM
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. paper c ESO 2018 September 10, 2018 arxiv:1403.3555v1 [astro-ph.im] 14 Mar 2014 Cross-Calibration of the XMM-Newton EPIC pn & MOS On-Axis Effective Areas Using 2XMM
CLEA/VIREO PHOTOMETRY OF THE PLEIADES
 CLEA/VIREO PHOTOMETRY OF THE PLEIADES Starting up the program The computer program you will use is a realistic simulation of a UBV photometer attached to a small (diameter=0.4 meters) research telescope.
CLEA/VIREO PHOTOMETRY OF THE PLEIADES Starting up the program The computer program you will use is a realistic simulation of a UBV photometer attached to a small (diameter=0.4 meters) research telescope.
X-ray spectral Analysis
 X-ray spectral Analysis xamples Problems Algorithm Model types Statistic Fitting procedure Practical problems with Chandra CCD data Disk N(N) Disk N(S) Nucleus Plume Based partly on the lecture given by
X-ray spectral Analysis xamples Problems Algorithm Model types Statistic Fitting procedure Practical problems with Chandra CCD data Disk N(N) Disk N(S) Nucleus Plume Based partly on the lecture given by
Soft X-ray Emission Lines in Active Galactic Nuclei. Mat Page
 Soft X-ray Emission Lines in Active Galactic Nuclei Mat Page MSSL-UCL Observations of soft X-ray line emission allow us to investigate highly ionized plasmas in galaxies and AGN. I ll start with the most
Soft X-ray Emission Lines in Active Galactic Nuclei Mat Page MSSL-UCL Observations of soft X-ray line emission allow us to investigate highly ionized plasmas in galaxies and AGN. I ll start with the most
Gaia Photometric Data Analysis Overview
 Gaia Photometric Data Analysis Overview Gaia photometric system Paola Marrese Sterrewacht Leiden marrese@strw.leidenuniv.nl Role of photometry in overall Gaia data analysis Photometric data analysis goals
Gaia Photometric Data Analysis Overview Gaia photometric system Paola Marrese Sterrewacht Leiden marrese@strw.leidenuniv.nl Role of photometry in overall Gaia data analysis Photometric data analysis goals
The in-orbit wavelength calibration of the WFC G800L grism
 The in-orbit wavelength calibration of the WFC G800L grism A. Pasquali, N. Pirzkal, J.R. Walsh March 5, 2003 ABSTRACT We present the G800L grism spectra of the Wolf-Rayet stars WR45 and WR96 acquired with
The in-orbit wavelength calibration of the WFC G800L grism A. Pasquali, N. Pirzkal, J.R. Walsh March 5, 2003 ABSTRACT We present the G800L grism spectra of the Wolf-Rayet stars WR45 and WR96 acquired with
PoS(INTEGRAL 2012)090
 XMM-Newton observations of five INTEGRAL sources located towards the Scutum Arm UC Berkeley - Space Sciences Laboratory E-mail: bodaghee@ssl.berkeley.edu John A. Tomsick UC Berkeley - Space Sciences Laboratory
XMM-Newton observations of five INTEGRAL sources located towards the Scutum Arm UC Berkeley - Space Sciences Laboratory E-mail: bodaghee@ssl.berkeley.edu John A. Tomsick UC Berkeley - Space Sciences Laboratory
XMM-Newton - Chandra Synergy: Maximizing their Future Science Impact over the Next Decade
 XMM-Newton - Chandra Synergy: Maximizing their Future Science Impact over the Next Decade Norbert Schartel XMM-Newton Project Scientist, ESA, ESAC, Spain 17.8.2016 Instruments Draft N. Schartel XMM-NEWTON
XMM-Newton - Chandra Synergy: Maximizing their Future Science Impact over the Next Decade Norbert Schartel XMM-Newton Project Scientist, ESA, ESAC, Spain 17.8.2016 Instruments Draft N. Schartel XMM-NEWTON
AGILE AGN Working Group S.Mereghetti - on behalf of the AGILE Team
 AGILE Scientific Program and S. Mereghetti on behalf of the AGILE team Data Rights AGILE Science Management Plan High level document issued in February 2004 Defines: Scientific Management of the mission
AGILE Scientific Program and S. Mereghetti on behalf of the AGILE team Data Rights AGILE Science Management Plan High level document issued in February 2004 Defines: Scientific Management of the mission
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades
 Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Document SM 2: Version 0.96lab Department of Physics Gettysburg College
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Document SM 2: Version 0.96lab Department of Physics Gettysburg College
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual
 Name: Lab Partner: Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Edited by Lucy Kulbago, John Carroll University 11/24/2008
Name: Lab Partner: Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Edited by Lucy Kulbago, John Carroll University 11/24/2008
Transiting Exoplanet in the Near Infra-red for the XO-3 System
 Transiting Exoplanet in the Near Infra-red for the XO-3 System Nathaniel Rodriguez August 26, 2009 Abstract Our research this summer focused on determining if sufficient precision could be gained from
Transiting Exoplanet in the Near Infra-red for the XO-3 System Nathaniel Rodriguez August 26, 2009 Abstract Our research this summer focused on determining if sufficient precision could be gained from
The origin of UV / Optical Variability of AGN: Relationship to X-ray Variability. Ian M c Hardy. University of Southampton 1
 The origin of UV / Optical Variability of AGN: Relationship to X-ray Variability Ian M c Hardy University of 1 Main Questions What drives UV/optical variability in AGN? How is the X-ray band related to
The origin of UV / Optical Variability of AGN: Relationship to X-ray Variability Ian M c Hardy University of 1 Main Questions What drives UV/optical variability in AGN? How is the X-ray band related to
INTEGRAL. Science Operations Centre. Announcement of Opportunity for Observing Proposals (AO-11) INT/OAG/ /Dc Issue 1.
 Science Operations Centre Announcement of Opportunity for Observing Proposals (AO-11) INT/OAG/13-0383/Dc Issue 1.0 25 February 2013 Prepared by Miguel Arregui, Emilio Salazar Date: 25 February 2013 Page:
Science Operations Centre Announcement of Opportunity for Observing Proposals (AO-11) INT/OAG/13-0383/Dc Issue 1.0 25 February 2013 Prepared by Miguel Arregui, Emilio Salazar Date: 25 February 2013 Page:
The Survey Science Centre report to the XMM Newton Users Group
 The Survey Science Centre report to the XMM Newton Users Group Natalie Webb XMM-Newton Users Group 1 Topics SSC status/activities The 3XMM catalogue Development : 4XMM and the stacked catalogue SSC outreach
The Survey Science Centre report to the XMM Newton Users Group Natalie Webb XMM-Newton Users Group 1 Topics SSC status/activities The 3XMM catalogue Development : 4XMM and the stacked catalogue SSC outreach
EPIC OBSERVATIONS OF BRIGHT BL LAC OBJECTS: WHAT CAN WE LEARN FROM THE X-RAY SPECTRA ABOUT THE ISM
 1 EPIC OBSERVATIONS OF BRIGHT BL LAC OBJECTS: WHAT CAN WE LEARN FROM THE X-RAY SPECTRA ABOUT THE ISM F. Haberl 1, S. Sembay 2, B. Altieri 3, and W. Brinkmann 1 1 Max-Planck-Institut fu r extraterrestrische
1 EPIC OBSERVATIONS OF BRIGHT BL LAC OBJECTS: WHAT CAN WE LEARN FROM THE X-RAY SPECTRA ABOUT THE ISM F. Haberl 1, S. Sembay 2, B. Altieri 3, and W. Brinkmann 1 1 Max-Planck-Institut fu r extraterrestrische
V5116 Sgr (Nova Sgr 2005b): an eclipsing supersoft postoutburst nova?
 V5116 Sgr (Nova Sgr 2005b): an eclipsing supersoft postoutburst nova? (UPC-IEEC, Barcelona) Margarita Hernanz, Carlo Ferri (CSIC-IEEC, Barcelona) Jochen Greiner (MPE, Garching) X-ray emission from Classical
V5116 Sgr (Nova Sgr 2005b): an eclipsing supersoft postoutburst nova? (UPC-IEEC, Barcelona) Margarita Hernanz, Carlo Ferri (CSIC-IEEC, Barcelona) Jochen Greiner (MPE, Garching) X-ray emission from Classical
Polar alignment in 5 steps based on the Sánchez Valente method
 1 Polar alignment in 5 steps based on the Sánchez Valente method Compared to the drift alignment method, this one, allows you to easily achieve a perfect polar alignment in just one step. By "perfect polar
1 Polar alignment in 5 steps based on the Sánchez Valente method Compared to the drift alignment method, this one, allows you to easily achieve a perfect polar alignment in just one step. By "perfect polar
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual
 Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Document SM 2: Version 1.1.1 lab Department of Physics Gettysburg College
Photoelectric Photometry of the Pleiades Student Manual A Manual to Accompany Software for the Introductory Astronomy Lab Exercise Document SM 2: Version 1.1.1 lab Department of Physics Gettysburg College
MANUAL for GLORIA light curve demonstrator experiment test interface implementation
 GLORIA is funded by the European Union 7th Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under grant agreement n 283783 MANUAL for GLORIA light curve demonstrator experiment test interface implementation Version:
GLORIA is funded by the European Union 7th Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under grant agreement n 283783 MANUAL for GLORIA light curve demonstrator experiment test interface implementation Version:
PoS(extremesky2009)018
 Swift/XRT follow-up observations of unidentified INTEGRAL/IBIS sources E-mail: landi@iasfbo.inaf.it L. Bassani E-mail: bassani@iasfbo.inaf.it A. Malizia E-mail: malizia@iasfbo.inaf.it J. B. Stephen E-mail:
Swift/XRT follow-up observations of unidentified INTEGRAL/IBIS sources E-mail: landi@iasfbo.inaf.it L. Bassani E-mail: bassani@iasfbo.inaf.it A. Malizia E-mail: malizia@iasfbo.inaf.it J. B. Stephen E-mail:
Spitzer Space Telescope Calibration Strategy: The Use of Asteroids
 Spitzer Space Telescope Calibration Strategy: The Use of Asteroids 1, J. Stansberry 2, C. Engelbracht 2, M. Blaylock 2, A. Noriega-Crespo 1 2004 December 3 Herschel Calibration Workshop, Leiden, The Netherlands
Spitzer Space Telescope Calibration Strategy: The Use of Asteroids 1, J. Stansberry 2, C. Engelbracht 2, M. Blaylock 2, A. Noriega-Crespo 1 2004 December 3 Herschel Calibration Workshop, Leiden, The Netherlands
Multi-wavelength behaviour of III Zw2
 Multi-wavelength behaviour of III Zw2 Nikita Salvi, Mat J. Page, Jason A. Stevens, Keith O. Mason and Kinwah Wu arxiv:astro-ph/0201545v1 31 Jan 2002 Mullard Space Science Laboratory, University College
Multi-wavelength behaviour of III Zw2 Nikita Salvi, Mat J. Page, Jason A. Stevens, Keith O. Mason and Kinwah Wu arxiv:astro-ph/0201545v1 31 Jan 2002 Mullard Space Science Laboratory, University College
Chapter 6: Transforming your data
 Why is transformation necessary? Chapter 6: Transforming your data The AAVSO International Database is composed of data collected from many different observers, at different times, from around the globe.
Why is transformation necessary? Chapter 6: Transforming your data The AAVSO International Database is composed of data collected from many different observers, at different times, from around the globe.
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 28 Nov 2008
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 28 Nov 2008 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph] 28 Nov 2008](/thumbs/95/124866649.jpg) Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. ms c ESO 2008 November 28, 2008 Swift follow-up observations of 17 INTEGRAL sources of uncertain or unknown nature J. Rodriguez 1, J.A. Tomsick 2, and S. Chaty 1
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. ms c ESO 2008 November 28, 2008 Swift follow-up observations of 17 INTEGRAL sources of uncertain or unknown nature J. Rodriguez 1, J.A. Tomsick 2, and S. Chaty 1
Rotation of the Hot Gas around the Milky Way. Edmund Hodges-Kluck Matthew Miller and Joel Bregman University of Michigan
 Rotation of the Hot Gas around the Milky Way Edmund Hodges-Kluck Matthew Miller and Joel Bregman University of Michigan Agenda Galaxy Halos OVII Absorption Lines in the RGS Archive Halo Model Halo Rotation?
Rotation of the Hot Gas around the Milky Way Edmund Hodges-Kluck Matthew Miller and Joel Bregman University of Michigan Agenda Galaxy Halos OVII Absorption Lines in the RGS Archive Halo Model Halo Rotation?
Analysis of wavelength shifts reported for X-shooter spectra
 Analysis of wavelength shifts reported for X-shooter spectra S. Moehler (SDP) June 15, 2015 Executive Summary I investigated the causes for wavelength offsets seen in telluric lines and sky lines of extracted
Analysis of wavelength shifts reported for X-shooter spectra S. Moehler (SDP) June 15, 2015 Executive Summary I investigated the causes for wavelength offsets seen in telluric lines and sky lines of extracted
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 28 Jun 2002
 arxiv:astro-ph/0206506v1 28 Jun 2002 The INTEGRAL Science Data Centre V. Beckmann on behalf of the ISDC team INTEGRAL Science Data Centre, Chemin d Ecogia 16, CH-1290 Versoix, Switzerland The INTEGRAL
arxiv:astro-ph/0206506v1 28 Jun 2002 The INTEGRAL Science Data Centre V. Beckmann on behalf of the ISDC team INTEGRAL Science Data Centre, Chemin d Ecogia 16, CH-1290 Versoix, Switzerland The INTEGRAL
Simultaneous XMM-Newton Radio Observations of the Mode-switching Radio Pulsar PSR B Wim Hermsen 1,2
 Simultaneous XMM-Newton Radio Observations of the Mode-switching Radio Pulsar PSR B1822-09 Wim Hermsen 1,2 Collaborators: J.W.T. Hessels 3,2, L. Kuiper 1, J. van Leeuwen 3,2, D. Mitra 4, J.M. Rankin 2,5,
Simultaneous XMM-Newton Radio Observations of the Mode-switching Radio Pulsar PSR B1822-09 Wim Hermsen 1,2 Collaborators: J.W.T. Hessels 3,2, L. Kuiper 1, J. van Leeuwen 3,2, D. Mitra 4, J.M. Rankin 2,5,
Reduced data products in the ESO Phase 3 archive (Status: 02 August 2017)
 Reduced data products in the ESO Phase 3 archive (Status: 02 August 2017) The ESO Phase 3 archive provides access to reduced and calibrated data products. All these data are stored in standard formats
Reduced data products in the ESO Phase 3 archive (Status: 02 August 2017) The ESO Phase 3 archive provides access to reduced and calibrated data products. All these data are stored in standard formats
Multi-frequency. Observations Using REM at la Silla. Filippo Maria Zerbi INAF Osservatorio di Brera On behalf of the REM/ROSS team
 Multi-frequency Observations Using REM at la Silla Filippo Maria Zerbi INAF Osservatorio di Brera On behalf of the REM/ROSS team A fast moving telescope Alt-az 60 cm f/8 RC silver-coated 2 Nasmyth foci
Multi-frequency Observations Using REM at la Silla Filippo Maria Zerbi INAF Osservatorio di Brera On behalf of the REM/ROSS team A fast moving telescope Alt-az 60 cm f/8 RC silver-coated 2 Nasmyth foci
Calculating K corrections using S Lang and Sherpa
 Calculating K corrections using S Lang and Sherpa Sherpa Threads (CIAO 3.4) Calculating K corrections using S Lang and Sherpa 1 Table of Contents Getting Started Setting up the spectral model Evaluate
Calculating K corrections using S Lang and Sherpa Sherpa Threads (CIAO 3.4) Calculating K corrections using S Lang and Sherpa 1 Table of Contents Getting Started Setting up the spectral model Evaluate
The SKYGRID Project A Calibration Star Catalog for New Sensors. Stephen A. Gregory Boeing LTS. Tamara E. Payne Boeing LTS. John L. Africano Boeing LTS
 The SKYGRID Project A Calibration Star Catalog for New Sensors Stephen A. Gregory Boeing LTS Tamara E. Payne Boeing LTS John L. Africano Boeing LTS Paul Kervin Air Force Research Laboratory POSTER SESSION
The SKYGRID Project A Calibration Star Catalog for New Sensors Stephen A. Gregory Boeing LTS Tamara E. Payne Boeing LTS John L. Africano Boeing LTS Paul Kervin Air Force Research Laboratory POSTER SESSION
Absolute Flux Calibration for STIS First-Order, Low-Resolution Modes
 Instrument Science Report STIS 97-14 Absolute Flux Calibration for STIS First-Order, Low-Resolution Modes Ralph Bohlin, Space Telescope Science Institute Nicholas Collins, Hughes STX/LASP/GSFC Anne Gonnella,
Instrument Science Report STIS 97-14 Absolute Flux Calibration for STIS First-Order, Low-Resolution Modes Ralph Bohlin, Space Telescope Science Institute Nicholas Collins, Hughes STX/LASP/GSFC Anne Gonnella,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11096 Spectroscopic redshifts of CDF-N X-ray sources We have taken a recent compilation 13 as our main source of spectroscopic redshifts. These redshifts are given to two decimal places,
doi:10.1038/nature11096 Spectroscopic redshifts of CDF-N X-ray sources We have taken a recent compilation 13 as our main source of spectroscopic redshifts. These redshifts are given to two decimal places,
Chandra Analysis of a Possible Cooling Core Galaxy Cluster at z = 1.03
 Chandra Analysis of a Possible Cooling Core Galaxy Cluster at z = 1.03 Kyle Dolan Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawaii at Manoa (Dated: 12 August 2005) We present an analysis of Chandra observations
Chandra Analysis of a Possible Cooling Core Galaxy Cluster at z = 1.03 Kyle Dolan Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawaii at Manoa (Dated: 12 August 2005) We present an analysis of Chandra observations
INTEGRAL. Science Operations Centre. Announcement of Opportunity for Observing Proposals (AO-7) Integral AO Tools Software User Manual
 Science Operations Centre Announcement of Opportunity for Observing Proposals (AO-7) Software User Manual INT/OAG/08-0309/Dc Issue 1.0 12 January 2009 Prepared by S. de Castro Authorised by A.N. Parmar
Science Operations Centre Announcement of Opportunity for Observing Proposals (AO-7) Software User Manual INT/OAG/08-0309/Dc Issue 1.0 12 January 2009 Prepared by S. de Castro Authorised by A.N. Parmar
Improving the Relative Accuracy of the HETGS Effective Area
 October 14, 2005 Improving the Relative Accuracy of the HETGS Effective Area Herman L. Marshall (MIT Kavli Institute) hermanm@space.mit.edu ABSTRACT I present updates to the HETGS grating efficiencies.
October 14, 2005 Improving the Relative Accuracy of the HETGS Effective Area Herman L. Marshall (MIT Kavli Institute) hermanm@space.mit.edu ABSTRACT I present updates to the HETGS grating efficiencies.
Color-Magnitude Diagram Lab Manual
 Color-Magnitude Diagram Lab Manual Due Oct. 21, 2011 1 Pre-Lab 1.1 Photometry and the Magnitude Scale The brightness of stars is represented by its value on the magnitude scale. The ancient Greek astronomer
Color-Magnitude Diagram Lab Manual Due Oct. 21, 2011 1 Pre-Lab 1.1 Photometry and the Magnitude Scale The brightness of stars is represented by its value on the magnitude scale. The ancient Greek astronomer
Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets
 Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets Stellar Classification Program Plan NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA. 94035 Warning! This printed copy may not be the latest released version. It is
Kepler: A Search for Terrestrial Planets Stellar Classification Program Plan NASA Ames Research Center Moffett Field, CA. 94035 Warning! This printed copy may not be the latest released version. It is
9.1 Years of All-Sky Hard X-ray Monitoring with BATSE
 9.1 Years of All-Sky Hard X-ray Monitoring with CGRO BATSE Large Area Detector (LAD) BATSE 1 of 8 BATSE Colleen A. Wilson (NASA/MSFC), for the BATSE teams at MSFC and Southampton Abstract The hard X-ray
9.1 Years of All-Sky Hard X-ray Monitoring with CGRO BATSE Large Area Detector (LAD) BATSE 1 of 8 BATSE Colleen A. Wilson (NASA/MSFC), for the BATSE teams at MSFC and Southampton Abstract The hard X-ray
The HST Set of Absolute Standards for the 0.12 µm to 2.5 µm Spectral Range
 Instrument Science Report CAL/SCS-010 The HST Set of Absolute Standards for the 0.12 µm to 2.5 µm Spectral Range L. Colina, R. Bohlin, D. Calzetti, C. Skinner, S. Casertano October 3, 1996 ABSTRACT A proposal
Instrument Science Report CAL/SCS-010 The HST Set of Absolute Standards for the 0.12 µm to 2.5 µm Spectral Range L. Colina, R. Bohlin, D. Calzetti, C. Skinner, S. Casertano October 3, 1996 ABSTRACT A proposal
PoS(extremesky2009)013
 Correlating the WFC and the IBIS hard X-ray surveys IASF-Roma INAF. Via Fosso del Cavaliere, 100 00133 Rome Italy E-mail: fiamma.capitanio@iasf-roma.inaf.it A. J. Bird School of Physics and Astronomy,
Correlating the WFC and the IBIS hard X-ray surveys IASF-Roma INAF. Via Fosso del Cavaliere, 100 00133 Rome Italy E-mail: fiamma.capitanio@iasf-roma.inaf.it A. J. Bird School of Physics and Astronomy,
Reduction procedure of long-slit optical spectra. Astrophysical observatory of Asiago
 Reduction procedure of long-slit optical spectra Astrophysical observatory of Asiago Spectrograph: slit + dispersion grating + detector (CCD) It produces two-dimension data: Spatial direction (x) along
Reduction procedure of long-slit optical spectra Astrophysical observatory of Asiago Spectrograph: slit + dispersion grating + detector (CCD) It produces two-dimension data: Spatial direction (x) along
Measuring the distances, masses and radii of neutron stars
 Measuring the distances, masses and radii of neutron stars Tolga Güver, Feryal Özel, Antonio Cabrera-Lavers, Patricia Wroblewski, Larry Camarota, Dimitrios Psaltis University of Arizona 1 Distances, Masses,
Measuring the distances, masses and radii of neutron stars Tolga Güver, Feryal Özel, Antonio Cabrera-Lavers, Patricia Wroblewski, Larry Camarota, Dimitrios Psaltis University of Arizona 1 Distances, Masses,
X- ray surface brightness fluctuations and turbulence in galaxy clusters. Jeremy Sanders. Andy Fabian. Sanders & Fabian 2011, MNRAS, submitted
 X- ray surface brightness fluctuations and turbulence in galaxy clusters Jeremy Sanders Andy Fabian Sanders & Fabian 2011, MNRAS, submitted Simulations predict that in galaxy clusters turbulent energy
X- ray surface brightness fluctuations and turbulence in galaxy clusters Jeremy Sanders Andy Fabian Sanders & Fabian 2011, MNRAS, submitted Simulations predict that in galaxy clusters turbulent energy
STAR CATALOGUE FACILITY
 STAR CATALOGUE FACILITY Alan Batten Science Systems (Space) Ltd., 23 Clothier Road, Bristol BS4 5SS Phone: +44 117 9717251. Fax: +44 117 9711125 E-mail: Alan.Batten@scisys.co.uk ABSTRACT The provision
STAR CATALOGUE FACILITY Alan Batten Science Systems (Space) Ltd., 23 Clothier Road, Bristol BS4 5SS Phone: +44 117 9717251. Fax: +44 117 9711125 E-mail: Alan.Batten@scisys.co.uk ABSTRACT The provision
