Recent NIR-optical-UV Observations. of Rotation-powered
|
|
|
- Rafe Scott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Recent NIR-optical-UV Observations Pulsars of Rotation-powered George Pavlov (Penn State; Polytech.Univ SPb) Martin Durant (Univ. of Florida) Oleg Kargaltsev (Univ. of Florida) Collaborators: Roberto Mignani (Univ. College London) Bettina Posselt (Penn State) Piotr Kowalski (Helmholtz Center Potsdam) Marten van Kerkwijk (Univ. of Toronto) David Kaplan (Univ. of Wisconsin, Milwaukee)
2 Rotation-Powered Pulsars (RPPs): Neutron stars (NSs) whose radiation is powered by NS rotation (via creation-acceleration of e+e- pairs in strong magn. field) Luminosity L proportional to spin-down power Edot L = η Edot η radiative efficiency Detected RPPs: Why so few in the optical? ~2000 in radio ~10 in optical (+NIR+UV) ~100 in X-rays ~100 in -rays (1) Intrinsically faint (most of them require HST) (2) Hostile attitude of classical optical astronomers
3 9 (+4?) RPPs detected in NIR-opt-UV (in 40+ years!) Name log Edot log age mag d(kpc) log L opt - log η opt Crab (V) B ? ~26(R) B (V) Vela (V) B ? ~25 (V) 2.5 ~31 ~6 B (V) Geminga (V) B (U) 0.35? J ~26 (U) ~27 ~6.6 B (U) B (V) B ? ~28 (B) 0.35 ~27 ~5 J ? (U) 0.24 ~27 ~4
4 Radio-to- -rays spectrum of an RPP η ν = F 4 d 2 / Edot -- spectral efficiency Three main components: coherent magnetospheric (radio), incoherent magnetospheric (NIR through gamma-rays), thermal from NS surface (FUV soft X-rays)
5 Recent results from our group ( ) PSR B (Mignani, GP, Kargaltsev 2010) Edot = 3e34 erg/s; age = 535 kyr; B = 1e12 G; d ~ 700 pc (from DM), The oldest of the Three Musketeers (J. Trümper); thermal soft X-rays, bright in Gev range Many attempts to detect with ground-based telescopes, unsuccessful because of a bright star (V=14) 4 from the pulsar Possible detection with HST FOC: U = 24.8 (Mignani et al 1997) Ten (!) unsuccessful attempts to get another HST observation HST proposal accepted in Cycle 16, when STIS and ACS/WFC were dead Pulsar detected with ACS/SBC (F140LP) and WFC2 (F555W, F702W)
6 PSR B : HST Images Star A PSR ACS/SBC F140LP image ( A) WFC2 F702W image ( A) The pulsar candidate has moved ~0.5 wrt Star A in 11 years. Proper motion 42+/-5 mas/yr, P.A. =94+/-7 deg; V = 70 d 350 km/s first measurement of proper motion, confirmed by radio timing
7 PSR B : Spectra Optical-UV spectrum: likely magnetospheric (optical, PL O ) and thermal (UV; Rayleigh-Jeans) components. Spectral slope in the optical O = =1.05+/-0.34; brightness temperature T O = (0.66+/- +/-0.10) d R O,13-2 MK. Optical UV - X-ray spectrum: some mismatch of the components: e.g., a factor of 4 excess of the RJ spectrum over extrapolation of the X-ray thermal component (X-rays from a smaller area?); Optical UV X-ray -ray spectrum: possibly the same spectral slope from optical (ev) to GeV? (should be measured more accurately)
8 PSR B : Summary Optical-UV counterpart confirmed Proper motion measured Likely, two components magnetospheric and thermal Likely, the distance is about twice lower than that determined from DM New HST observations needed to measure phase-dependent spectrum and separate thermal and magnetospheric components, measure T, etc A proposal was submitted, and Strengths:. The need for HST is well documented. Weaknesses: This was a good proposal, but to some degree the projected results seemed incremental. More discussion about the larger role neutron star evolution plays in astrophysics would also be helpful. The panel also felt that the imaging
9 PSR J (Durant et al. 2011, subm.) The only millisecond (recycled) RPP detected in the optical (UV) P = 5.8 ms, Edot = 2.3*10 33 erg/s, age = 6.7 Gyr, d = /- 1.3 pc (from parallax; Deller et al. 2009) Binary: P bin = 5.5 d, cold WD with T~4000 K, dominates in NIR-optical; M WD = M sol, M NS = 1.76 M sol First optical-uv observation of the pulsar: HST/STIS FUV-MAMA ( A), Rayleigh-Jeans spectrum, brightness temperature ~ 10 5 K (re)heating? (Kargaltsev et al 2004) HST proposal accepted for Cycle 14 with STIS/FUV-MAMA; STIS died a few days before the scheduled observation date. New HST proposal accepted for Cycle 15 to observe with ACS/SBC (FUV) and ACS/HRC (NUV) Independently observed with Spitzer (IRAC and MIPS), Magellan (PANIC), VLT/FORS1 We collected and analyzed all the observations.
10 PSR J : UV and UV-optical-IR spectra (F λ vs λ) NS WD λ = A (4 instruments); F λ ~ λ -4 at shorter λ (Rayleigh-Jeans), rise at longer λ λ = m (8 instruments); Neutron star + white dwarf spectrum
11 J : Spectral fits for UV-opt-IR NS WD NS WD NS: WD: Power-law + blackbody (poor fit) = /- 0.4 T BB = /- 40 K R BB = (20 +/- 1)*10 3 km Power-law + hydrogen WD atmosphere (good fit) = /- 0.2, T eff = /- 150 K (age 6.0+/-0.5 Gyr) log g = / (He core WD) M WD = M sol R WD = (19 +/- 2)*10 3 km
12 PSR J : Thermal fits to FUV spectrum (F vs 0.7 < (T /10 5 K) < 3.5 ; 8 < (R/1 km) < 24 (formal limits) T = 1.25*10 5 K for R = 15 km (T and R for distant observer)
13 J : X-ray spectrum (Chandra + XMM-Newton) NSA(tmosphere) + PL fit: kt = 138 +/- 2 ev (T = 1.5*10 6 K), R = / km hot, small; photon index = /- 0.03; N H = 7*10 19 cm -2 Better fit is given by NSA+NSA+PL model: kt 1 = 140 ev, R 1 = 0.4 km; kt 2 = 30 ev, R 2 = 7 km; = 1.9 nonuniform T + magnetosphere
14 PSR J : Multiwavelength spectrum (F vs ) Multiwavelength fit: WD atm + BB1 + BB2 +BB3 + cut-off PL = 1.56(1), E cut = 1.1(2) GeV, L PL =8*10 31 erg/s = 0.03 Edot T = 3.3(3), 16.9(6), 33.9(8) *10 5 K R = 5.3(5), 0.162(7), 0.038(3) km
15 PSR J : Summary IR-optical observations most detailed investigation of a very old, very cold WD (Helium core, Hydrogen envelope) UV surface of the very old NS is hot, T ~ 1.5*10 5 K for R = 13 km (re)heating, possibly rotochemical heating (Reisenegger 1995) Temperature distribution is strongly nonuniform: 0.12 < T < 3.5 MK; high temperatures in polar caps (Harding & Muslimov 2001) A single PL component ( = 1.6, η = 0.03) may be responsible for magnetospheric emission from UV to GeV -rays synchrotron radiation of electrons with a wide PL spectrum (p = 2.1; 10 2 < <10 7, if B = B LC = 3*10 4 G)?
16 PSR B (Durant et al. 2011, subm.) The youngest Musketeer, one of the best studied RPPs P=385 ms, Edot = 3.8*10 34 erg/s, age = 110 kyr, d=288+/-30 pc (Brisken et al 2003) Detailed X-ray observations with Chandra and XMM-Newton (Pavlov et al 2002; de Luca et al. 2005) Optical emission discovered with NTT (Caraveo et al 1994), studied in many HST observations, from NIR to FUV (Pavlov et al 1996,1997; Mignani et al 200; Koptsevich et al 2001; Shibanov et al. 2005; Zharikov et al. 2007; Kargaltsev & Pavlov 2007) Pulsations were discovered in optical, NUV and FUV (Kern et al 2003, Shibanov et al 2005; Kargaltsev & Pavlov 2007), polarization in the optical (Kern et al 2003 ) Broad-band optical-uv spectrum was interpreted as the sum of two components: power-law (magnetospheric) and Rayleigh-Jeans (thermal emission from the NS surface) Pavlov et al (1997), Kargaltsev & Pavlov (2007). Spectral observation with VLT/FORS1 has shown hints of spectral features (Zharikov et al 2007)
17 We observed B with HST ACS/WFC (10 ramp filters), STIS/FUV-MAMA/G140L and COS/FUV to better understand the spectrum, reanalyzed NICMOS and STIS/NUV-MAMA data, and added all the observations. Composite NIR FUV spectrum (F vs. )
18 PSR B : Spectral features Two continuum components do not fit. Fit with power-law ( = /- 0.06) + Rayleigh-Jeans + cold BB (500 K) marginally acceptable Power-law ( = /- 0.05) + two absorption lines (0.37 +/- 0.4 m and 1.0 +/- 0.1 m) acceptable Power-law ( = 0.4) + cold BB (1200+/- 400 K) + emission feature (0.77 +/- 0.1 m) - acceptable
19 PSR B : Interpretation of spectral features Electron cyclotron absorption/emission requires magnetic fields B ~ a few 10 8 G could only occur in the magnetosphere, at R ~ 300 R NS. Absorbing/emitting electrons should be in a relatively narrow layer(s) to be consistent with the feature width(s). Looks somewhat artificial but not ruled out. Proton (ion) cyclotron absorption/emission requires B ~ a few G (vs B NS = 5*10 12 G for the dipole component). Looks rather improbable. Transitions between highly excited ( H-like ) atomic levels in the NS atmosphere requires calculations, but does not look very probable The absorption at 1 m (the rise to longer in the NIR) could be indicative of a fall-back disk (T ~ K); unfortunately, observations in IR are complicated by the presence of a red galaxy projected near the pulsar (at ~1 2 ).
20 B : Multiwavelength spectrum (F vs. ) NIR -ray (1 ev 1 GeV) spectrum can be described by BBcold + BBhot + PL ( = 1.5 +/- 0.05) synchrotron emission from a very wide electron spectrum (10 3 < < 10 7 in B = B LC = 800 G)? Observation in hard X-rays soft -rays would be particularly useful
21 Multiwavelength spectra of other RPPs with optical detections Each pulsar s nonthermal spectrum can be described by a single PL with a break or cut-off at GeV energies? (not so for Crab and B ) 1.20 < < 1.65, 0.7 < E cut < 4.5 GeV
22 Spectral efficiencies of the same 6 pulsars η = 4 d 2 F /Edot
23 PSR B065+14: Pulsations Pulsations in FUV weaker than in NUV NUV and optical pulse profiles are is very similar Two peaks in FUV, NUV and optical but only one in hard X-rays. pf=60% 1. FUV emission is dominated by thermal radiation from NS surface, with 2 nonthermal peaks seating on top of the shallow thermal pulse. 2. NUV dominated by non-thermal emission. pf=80% 3. Single peak in hard X-rays implies different geometry of emitting regions for the nonthermal emission in UV and X-rays.
24 Some other highlights of recent work We detected the Vela pulsar with Spitzer IRAC, found a mir excess; another spectral component? fall-back disk? ultra-compact PWN? (Danilenko et al 2011) -- see poster by Andrey Danilenko (session 9). Young pulsars embedded in pulsar wind nebulae have likely been detected in optical/nir: PSR J in 3C58 (Shibanov et al 2008), PSR in G (Zharikov et al 2008; Zyuzin et al 2009) talk by Yurii Shibanov and poster by Dmitry Zyuzin. A candidate optical counterpart of the young PSR J has been detected - see poster by Ada Kirichenko (session 9).
25 RPPs: Overview of current status Nine RPPs are firmly detected in NIR-opt-UV, 4 (7?) require confirmation; much more RPPs could be detected with HST RPP spectra show at least two components: magnetospheric (optical) and thermal (UV), perhaps a third component in IR-NIR (a disk?) Strange spectral features are seen in at least one RPP (B ); origin uncertain Magnetospheric spectra of not too young/powerful pulsars show about the same slope from NIR-optical (ev) to -rays (GeV) a very broad power-law energy spectrum of radiating particles + the same emission mechanism? Mismatch of Rayleigh-Jeans (UV) tails of thermal components with Wien (X-ray) tails are smaller than in INSs (MFDPP? talks by Kaplan and Kamble) ; can be explained by nonuniformity of surface temperature The only recycled RPP detected in optical (UV) shows a high surface temperature (re)heating is important at least in recycled pulsars
X-ray Properties of Rotation Powered Pulsars and Thermally Emitting Neutron Stars
 X-ray Properties of Rotation Powered Pulsars and Thermally Emitting Neutron Stars George Pavlov (Penn State; Polytech.Univ SPb) Collaborators: Oleg Kargaltsev (George Washington Univ.) Bettina Posselt
X-ray Properties of Rotation Powered Pulsars and Thermally Emitting Neutron Stars George Pavlov (Penn State; Polytech.Univ SPb) Collaborators: Oleg Kargaltsev (George Washington Univ.) Bettina Posselt
X-ray Observations of Rotation Powered Pulsars
 X-ray Observations of Rotation Powered Pulsars George Pavlov (Penn State) Oleg Kargaltsev (George Washington Univ.) Martin Durant (Univ. of Toronto) Bettina Posselt (Penn State) Isolated neutron stars
X-ray Observations of Rotation Powered Pulsars George Pavlov (Penn State) Oleg Kargaltsev (George Washington Univ.) Martin Durant (Univ. of Toronto) Bettina Posselt (Penn State) Isolated neutron stars
Thermal Radiation from Isolated Neutron Stars
 Thermal Radiation from Isolated Neutron Stars George Pavlov Penn State Slava Zavlin MSFC (Huntsville) Divas Sanwal Penn State Oleg Kargaltsev Penn State Roger Romani Stanford Thermal emission: Why important?
Thermal Radiation from Isolated Neutron Stars George Pavlov Penn State Slava Zavlin MSFC (Huntsville) Divas Sanwal Penn State Oleg Kargaltsev Penn State Roger Romani Stanford Thermal emission: Why important?
New optical/uv counterparts and SEDs of Isolated NS ATISH KAMBLE, D. KAPLAN (UW-MILWAUKEE), M. VAN KERKWIJK (TORONTO) AND W.
 New optical/uv counterparts and SEDs of Isolated NS ATISH KAMBLE, D. KAPLAN (UW-MILWAUKEE), M. VAN KERKWIJK (TORONTO) AND W. HO (SOUTHAMPTON) RX J1856...a puzzle! Featureless BB spectrum instead of harder
New optical/uv counterparts and SEDs of Isolated NS ATISH KAMBLE, D. KAPLAN (UW-MILWAUKEE), M. VAN KERKWIJK (TORONTO) AND W. HO (SOUTHAMPTON) RX J1856...a puzzle! Featureless BB spectrum instead of harder
Emission from Isolated Neutron Stars. Observations and model applications
 Thermal Emission from Isolated Neutron Stars Theoretical aspects Observations and model applications Slava Zavlin (MPE, Garching) A Short History Chi & Salpeter (1964) and Tsuruta (1964): thermal radiation
Thermal Emission from Isolated Neutron Stars Theoretical aspects Observations and model applications Slava Zavlin (MPE, Garching) A Short History Chi & Salpeter (1964) and Tsuruta (1964): thermal radiation
XMM observations of three middle-aged pulsars
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 75, 458 c SAIt 2004 Memorie della MM observations of three middle-aged pulsars V. E. Zavlin 1 and G. G. Pavlov 2 1 Max-Planck Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, 85748 Garching, Germany
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 75, 458 c SAIt 2004 Memorie della MM observations of three middle-aged pulsars V. E. Zavlin 1 and G. G. Pavlov 2 1 Max-Planck Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, 85748 Garching, Germany
Cooling Limits for the
 Cooling Limits for the Page et al. 2004 Youngest Neutron Stars Cooling from the Youngest NSs SNR Zone NSs younger than ~50 kyr offer strong constraints on rapid cooling - the associated physical processes
Cooling Limits for the Page et al. 2004 Youngest Neutron Stars Cooling from the Youngest NSs SNR Zone NSs younger than ~50 kyr offer strong constraints on rapid cooling - the associated physical processes
Pulsars and Pulsar-Wind Nebulae: TeV to X-Ray Connection. Oleg Kargaltsev (University of Florida) George Pavlov (Penn State University)
 Pulsars and Pulsar-Wind Nebulae: TeV to X-Ray Connection Oleg Kargaltsev (University of Florida) George Pavlov (Penn State University) Pulsar Wind Nebulae. All active pulsars emit relativistic winds c
Pulsars and Pulsar-Wind Nebulae: TeV to X-Ray Connection Oleg Kargaltsev (University of Florida) George Pavlov (Penn State University) Pulsar Wind Nebulae. All active pulsars emit relativistic winds c
Extended X- ray emission from PSR B /LS 2883 and other gamma- ray binaries
 Extended X- ray emission from PSR B1259-63/LS 2883 and other gamma- ray binaries George Pavlov (Pennsylvania State University) Oleg Kargaltsev (George Washington University) Martin Durant (University of
Extended X- ray emission from PSR B1259-63/LS 2883 and other gamma- ray binaries George Pavlov (Pennsylvania State University) Oleg Kargaltsev (George Washington University) Martin Durant (University of
X-ray and multiwavelength observations of pulsarwind
 X-ray and multiwavelength observations of pulsarwind nebulae. Oleg Kargaltsev (George Washington University) Collaborators: Martin Durant ( University of Toronto) George Pavlov (Penn State University)
X-ray and multiwavelength observations of pulsarwind nebulae. Oleg Kargaltsev (George Washington University) Collaborators: Martin Durant ( University of Toronto) George Pavlov (Penn State University)
Progress in Pulsar detection
 Progress in Pulsar detection With EINSTEIN & EXOSAT: 7 radio pulsars detected in X-rays With ROSAT, ASCA & BSAX: 33 radio pulsars detected in X-rays After ~8 yrs with XMM & Chandra: 81 radio pulsars detected
Progress in Pulsar detection With EINSTEIN & EXOSAT: 7 radio pulsars detected in X-rays With ROSAT, ASCA & BSAX: 33 radio pulsars detected in X-rays After ~8 yrs with XMM & Chandra: 81 radio pulsars detected
X-ray emission properties vary with spin-down age. Crab-like pulsars (< 10 4 yrs)
 X-ray emission properties vary with spin-down age Crab-like pulsars (< 10 4 yrs) X-ray emission properties vary with spin-down age Crab-like pulsars (< 10 4 yrs) Cooling neutron stars ( ~10 5-10 6 yrs)
X-ray emission properties vary with spin-down age Crab-like pulsars (< 10 4 yrs) X-ray emission properties vary with spin-down age Crab-like pulsars (< 10 4 yrs) Cooling neutron stars ( ~10 5-10 6 yrs)
The Magnificent Seven Similarities and Differences
 The Magnificent Seven Similarities and Differences Frank Haberl Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik (MPE), Garching The discovery of thermal, radio quiet isolated neutron stars New XMM-Newton
The Magnificent Seven Similarities and Differences Frank Haberl Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik (MPE), Garching The discovery of thermal, radio quiet isolated neutron stars New XMM-Newton
Surface emission of neutron stars
 Surface emission of neutron stars NS Radii A NS with homogeneous surface temperature and local blackbody emission L 4 R 2 T 4 From dispersion measure F 4 L D 2 2 R / D T 4 From X-ray spectroscopy NS Radii
Surface emission of neutron stars NS Radii A NS with homogeneous surface temperature and local blackbody emission L 4 R 2 T 4 From dispersion measure F 4 L D 2 2 R / D T 4 From X-ray spectroscopy NS Radii
Particle acceleration and pulsars
 Meudon, nov. 2013 p. 1/17 Particle acceleration and pulsars Fabrice Mottez LUTH - Obs. Paris-Meudon - CNRS - Univ. Paris Diderot Meudon, nov. 2013 p. 2/17 Pulsars (PSR) and pulsar wind nebulae (PWNe) Mostly
Meudon, nov. 2013 p. 1/17 Particle acceleration and pulsars Fabrice Mottez LUTH - Obs. Paris-Meudon - CNRS - Univ. Paris Diderot Meudon, nov. 2013 p. 2/17 Pulsars (PSR) and pulsar wind nebulae (PWNe) Mostly
Extended X-ray object ejected from the PSR B /LS 2883 binary
 Extended X-ray object ejected from the PSR B1259-63/LS 2883 binary Oleg Kargaltsev (George Washington University) George Pavlov (Pennsylvania State University) Jeremy Hare (George Washington University)
Extended X-ray object ejected from the PSR B1259-63/LS 2883 binary Oleg Kargaltsev (George Washington University) George Pavlov (Pennsylvania State University) Jeremy Hare (George Washington University)
Pulsar Wind Nebulae. Pennsylvania State University. General outlook Chandra results Polarization in radio and optical X-ray polarization
 Pulsar Wind Nebulae George Pavlov & Oleg Kargaltsev Pennsylvania State University General outlook Chandra results Polarization in radio and optical X-ray polarization Pulsar Wind Nebulae: extended objects
Pulsar Wind Nebulae George Pavlov & Oleg Kargaltsev Pennsylvania State University General outlook Chandra results Polarization in radio and optical X-ray polarization Pulsar Wind Nebulae: extended objects
Pulsar Winds in High Energy Astrophysics
 Pulsar Winds in High Energy Astrophysics Dmitry Khangulyan Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS/JAXA) The extreme Universe viewed in very high energy gamma-rays, Kashiwa 09/25/2012 OUTLINE
Pulsar Winds in High Energy Astrophysics Dmitry Khangulyan Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS/JAXA) The extreme Universe viewed in very high energy gamma-rays, Kashiwa 09/25/2012 OUTLINE
Radio Observations of TeV and GeV emitting Supernova Remnants
 Radio Observations of TeV and GeV emitting Supernova Remnants Denis Leahy University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta, Canada (collaborator Wenwu Tian, National Astronomical Observatories of China) outline
Radio Observations of TeV and GeV emitting Supernova Remnants Denis Leahy University of Calgary, Calgary, Alberta, Canada (collaborator Wenwu Tian, National Astronomical Observatories of China) outline
Pulsar Wind Nebulae: A Multiwavelength Perspective
 Pulsar Wind Nebulae: Collaborators: J. D. Gelfand T. Temim D. Castro S. M. LaMassa B. M. Gaensler J. P. Hughes S. Park D. J. Helfand O. C. de Jager A. Lemiere S. P. Reynolds S. Funk Y. Uchiyama A Multiwavelength
Pulsar Wind Nebulae: Collaborators: J. D. Gelfand T. Temim D. Castro S. M. LaMassa B. M. Gaensler J. P. Hughes S. Park D. J. Helfand O. C. de Jager A. Lemiere S. P. Reynolds S. Funk Y. Uchiyama A Multiwavelength
Victoria Kaspi (McGill University, Montreal, Canada)
 Victoria Kaspi (McGill University, Montreal, Canada) C. Espinoza M. Gonzalez M. Kramer M. Livingstone A. Lyne M. McLaughlin S. Olausen C.Y. Ng G. Pavlov W. Zhu Victoria Kaspi (McGill University, Montreal,
Victoria Kaspi (McGill University, Montreal, Canada) C. Espinoza M. Gonzalez M. Kramer M. Livingstone A. Lyne M. McLaughlin S. Olausen C.Y. Ng G. Pavlov W. Zhu Victoria Kaspi (McGill University, Montreal,
X-ray Isolated Neutron Stars: The Challenge of Simplicity
 X-ray Isolated Neutron Stars: The Challenge of Simplicity The Magnificent Seven R Turolla Department of Physics University of Padova, Italy M Cropper, CP De Vries, JJ Drake, F Haberl, A Treves J Vink,
X-ray Isolated Neutron Stars: The Challenge of Simplicity The Magnificent Seven R Turolla Department of Physics University of Padova, Italy M Cropper, CP De Vries, JJ Drake, F Haberl, A Treves J Vink,
Subaru optical observations of the two middle-aged pulsars PSR B and Geminga ABSTRACT
 A&A 448, 313 326 (2006) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20054178 c ESO 2006 Astronomy & Astrophysics Subaru optical observations of the two middle-aged pulsars PSR B0656+14 and Geminga Y. A. Shibanov 1,S.V.Zharikov
A&A 448, 313 326 (2006) DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361:20054178 c ESO 2006 Astronomy & Astrophysics Subaru optical observations of the two middle-aged pulsars PSR B0656+14 and Geminga Y. A. Shibanov 1,S.V.Zharikov
The Magnificent Seven: Nearby, Thermally Emitting, Isolated Neutron Stars
 The Magnificent Seven: Nearby, Thermally Emitting, Isolated Neutron Stars Frank Haberl Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik (MPE), Garching A legacy of ROSAT Proper motions and distances Observations
The Magnificent Seven: Nearby, Thermally Emitting, Isolated Neutron Stars Frank Haberl Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik (MPE), Garching A legacy of ROSAT Proper motions and distances Observations
Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines!
 Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines Idealized 21cm spectra Example observed 21cm spectra HI densities
Some HI is in reasonably well defined clouds. Motions inside the cloud, and motion of the cloud will broaden and shift the observed lines Idealized 21cm spectra Example observed 21cm spectra HI densities
A Detailed Study of. the Pulsar Wind Nebula 3C 58
 A Detailed Study of Collaborators: D. J. Helfand S. S. Murray S. Ransom F. D. Seward B. M. Gaensler E. V. Gotthelf E. van der Swaluw the Pulsar Wind Nebula 3C 58 Pulsar Wind Nebulae Young NS powers a particle/magnetic
A Detailed Study of Collaborators: D. J. Helfand S. S. Murray S. Ransom F. D. Seward B. M. Gaensler E. V. Gotthelf E. van der Swaluw the Pulsar Wind Nebula 3C 58 Pulsar Wind Nebulae Young NS powers a particle/magnetic
Subaru optical observations of the two middle-aged pulsars PSR B and Geminga
 Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. 4178 c ESO 2005 October 21, 2005 Subaru optical observations of the two middle-aged pulsars PSR B0656+14 and Geminga Yuri A. Shibanov 1, Sergei V. Zharikov 2, Viktoria
Astronomy & Astrophysics manuscript no. 4178 c ESO 2005 October 21, 2005 Subaru optical observations of the two middle-aged pulsars PSR B0656+14 and Geminga Yuri A. Shibanov 1, Sergei V. Zharikov 2, Viktoria
The Neutron Star Zoo. Stephen C.-Y. Ng ( 吳志勇 ) HKU
 The Neutron Star Zoo Stephen C.-Y. Ng ( 吳志勇 ) HKU Overview Introduction to neutron stars Different classes of neutron stars: Radio Pulsars MSPs Magnetars DINS CCOs Unification 6/12/2017 NAOC Stephen Ng
The Neutron Star Zoo Stephen C.-Y. Ng ( 吳志勇 ) HKU Overview Introduction to neutron stars Different classes of neutron stars: Radio Pulsars MSPs Magnetars DINS CCOs Unification 6/12/2017 NAOC Stephen Ng
(Anomalous) X-Ray Pulsars. Vicky Kaspi. Montreal, Canada. Stanford December 16, 2004
 (Anomalous) X-Ray Pulsars Vicky Kaspi Montreal, Canada Texas @ Stanford December 16, 2004 Summary Introduction to AXPs Evidence that AXPs are magnetars Open Issues and Recent Results: IR emission Transient
(Anomalous) X-Ray Pulsars Vicky Kaspi Montreal, Canada Texas @ Stanford December 16, 2004 Summary Introduction to AXPs Evidence that AXPs are magnetars Open Issues and Recent Results: IR emission Transient
Infrared-Optical observations of magnetars
 Infrared-Optical observations of magnetars Mikio Morii Tokyo Institute of Technology 2012.09.01 @ Rikkyo Univ. Contents Search for Near-Infrared Pulsation of the AXP 4U 0142+61 M. M., N. Kobayashi, N.
Infrared-Optical observations of magnetars Mikio Morii Tokyo Institute of Technology 2012.09.01 @ Rikkyo Univ. Contents Search for Near-Infrared Pulsation of the AXP 4U 0142+61 M. M., N. Kobayashi, N.
Lecture 3 Pulsars and pulsar wind nebulae
 Lecture 3 Pulsars and pulsar wind nebulae Pulsars Characteristic parameters Pulsar wind nebulae Properties Evolution Exotic central compact objects - Magnetars The Crab Pulsar http://www.jb.man.ac.uk/~pulsar/education/sounds/sounds.html
Lecture 3 Pulsars and pulsar wind nebulae Pulsars Characteristic parameters Pulsar wind nebulae Properties Evolution Exotic central compact objects - Magnetars The Crab Pulsar http://www.jb.man.ac.uk/~pulsar/education/sounds/sounds.html
X-ray and Gamma-ray. Emission Pulsars and Pulsar Wind Nebulae. K.S. Cheng Department of Physics University of Hong Kong Hong Kong, China
 X-ray and Gamma-ray Emission Pulsars and Pulsar Wind Nebulae K.S. Cheng Department of Physics University of Hong Kong Hong Kong, China X-ray luminosity (L x ) vs spin-down power (L sd ) Becker and Trumper
X-ray and Gamma-ray Emission Pulsars and Pulsar Wind Nebulae K.S. Cheng Department of Physics University of Hong Kong Hong Kong, China X-ray luminosity (L x ) vs spin-down power (L sd ) Becker and Trumper
Fermi-Large Area Telescope Observations of Pulsar Wind Nebulae and their associated pulsars
 Fermi-Large Area Telescope Observations of Pulsar Wind Nebulae and their associated pulsars Marie-Hélène Grondin CENBG, Bordeaux (France) on behalf of the Fermi-LAT Collaboration and the Pulsar Timing
Fermi-Large Area Telescope Observations of Pulsar Wind Nebulae and their associated pulsars Marie-Hélène Grondin CENBG, Bordeaux (France) on behalf of the Fermi-LAT Collaboration and the Pulsar Timing
XMM-Observations of Pulsars: A study of thermal- vs. non-thermal emission W. Becker & J. Tríumper Max-Planck-Institut fíur extraterr. Physik, Giessenb
 XMM-Observations of Pulsars: A study of thermal- vs. non-thermal emission W. Becker & J. Tríumper Max-Planck-Institut fíur extraterr. Physik, Giessenbachstrasse 1, D-85740 Garching ABSTRACT Recent X-ray
XMM-Observations of Pulsars: A study of thermal- vs. non-thermal emission W. Becker & J. Tríumper Max-Planck-Institut fíur extraterr. Physik, Giessenbachstrasse 1, D-85740 Garching ABSTRACT Recent X-ray
Pulsars. The maximum angular frequency of a spinning star can be found by equating the centripetal and gravitational acceleration M R 2 R 3 G M
 Pulsars Pulsating stars were discovered in 1967 via radio dipole antennae by Jocelyn Bell and Anthony Hewish Pulse period of PSR 1919+21 is 1.337 s Most pulsars have periods between 0.25 s and 2 s The
Pulsars Pulsating stars were discovered in 1967 via radio dipole antennae by Jocelyn Bell and Anthony Hewish Pulse period of PSR 1919+21 is 1.337 s Most pulsars have periods between 0.25 s and 2 s The
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 16 Oct 2003
 Young Neutron Stars and Their Environments IAU Symposium, Vol. 218, 2004 F. Camilo and B. M. Gaensler, eds. Observational manifestations of young neutron stars: Spin-powered pulsars arxiv:astro-ph/0310451v1
Young Neutron Stars and Their Environments IAU Symposium, Vol. 218, 2004 F. Camilo and B. M. Gaensler, eds. Observational manifestations of young neutron stars: Spin-powered pulsars arxiv:astro-ph/0310451v1
H.E.S.S. Unidentified Gamma-ray Sources in a Pulsar Wind Nebula Scenario And HESS J
 H.E.S.S. Unidentified Gamma-ray Sources in a Pulsar Wind Nebula Scenario And HESS J1303-631 Matthew Dalton Humboldt University at Berlin For the H.E.S.S. Collaboration TeV Particle Astrophysics, Paris.
H.E.S.S. Unidentified Gamma-ray Sources in a Pulsar Wind Nebula Scenario And HESS J1303-631 Matthew Dalton Humboldt University at Berlin For the H.E.S.S. Collaboration TeV Particle Astrophysics, Paris.
Rotating RAdio Transients (RRATs) ApJ, 2006, 646, L139 Nature, 2006, 439, 817 Astro-ph/
 Rotating RAdio Transients (RRATs) ApJ, 2006, 646, L139 Nature, 2006, 439, 817 Astro-ph/0608311 Introduction 11 Rotating RAdio Transients (RRATs) (Mclaughlin et al 2006) Repeated, irregular radio bursts
Rotating RAdio Transients (RRATs) ApJ, 2006, 646, L139 Nature, 2006, 439, 817 Astro-ph/0608311 Introduction 11 Rotating RAdio Transients (RRATs) (Mclaughlin et al 2006) Repeated, irregular radio bursts
Fermi Large Area Telescope:
 Fermi Large Area Telescope: Early Results on Pulsars Kent Wood Naval Research Lab kent.wood@nrl.navy.mil for the Fermi LAT Collaboration Tokyo Institute of Technology 7 March 2009 K. Wood (NRL) 1/30 Fermi
Fermi Large Area Telescope: Early Results on Pulsars Kent Wood Naval Research Lab kent.wood@nrl.navy.mil for the Fermi LAT Collaboration Tokyo Institute of Technology 7 March 2009 K. Wood (NRL) 1/30 Fermi
Observations of. Pulsar Wind Nebulae
 Observations of Pulsar Wind Nebulae I. Injection Spectrum I. Late-Phase Evolution II. PWNe and Magnetars PWNe and Their SNRs PWN Shock Reverse Shock Forward Shock Pulsar Wind Pulsar Termination Shock PWN
Observations of Pulsar Wind Nebulae I. Injection Spectrum I. Late-Phase Evolution II. PWNe and Magnetars PWNe and Their SNRs PWN Shock Reverse Shock Forward Shock Pulsar Wind Pulsar Termination Shock PWN
The distance and radius of the neutron star PSR B
 The distance and radius of the neutron star PSR B0656+14 Walter F. Brisken, 1 S. E. Thorsett, 2 A. Golden, 3 &W.M.Goss 1 ABSTRACT We present the result of astrometric observations of the radio pulsar PSR
The distance and radius of the neutron star PSR B0656+14 Walter F. Brisken, 1 S. E. Thorsett, 2 A. Golden, 3 &W.M.Goss 1 ABSTRACT We present the result of astrometric observations of the radio pulsar PSR
Mass loss from stars
 Mass loss from stars Can significantly affect a star s evolution, since the mass is such a critical parameter (e.g., L ~ M 4 ) Material ejected into interstellar medium (ISM) may be nuclear-processed:
Mass loss from stars Can significantly affect a star s evolution, since the mass is such a critical parameter (e.g., L ~ M 4 ) Material ejected into interstellar medium (ISM) may be nuclear-processed:
Sources of GeV Photons and the Fermi Results
 Sources of GeV Photons and the Fermi Results 1. GeV instrumentation and the GeV sky with the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope 2. First Fermi Catalog of Gamma Ray Sources and the Fermi Pulsar Catalog 3.
Sources of GeV Photons and the Fermi Results 1. GeV instrumentation and the GeV sky with the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope 2. First Fermi Catalog of Gamma Ray Sources and the Fermi Pulsar Catalog 3.
Spectral Analysis of the Double Pulsar PSR J with XMM-Newton
 Spectral Analysis of the Double Pulsar PSR J0737-3039 with XMM-Newton * E. Egron, A. Pellizzoni, M.N. Iacolina, A. Pollock, et al. INAF - Osservatorio Astronomico di Cagliari, Italy * ESAC, Madrid, Spain
Spectral Analysis of the Double Pulsar PSR J0737-3039 with XMM-Newton * E. Egron, A. Pellizzoni, M.N. Iacolina, A. Pollock, et al. INAF - Osservatorio Astronomico di Cagliari, Italy * ESAC, Madrid, Spain
arxiv:astro-ph/ v2 11 Jun 2002
 Thermal Radiation from Neutron Stars: Chandra Results G.G. Pavlov 1, V.E. Zavlin 2 and D. Sanwal 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0206024v2 11 Jun 2002 1 The Pennsylvania State University, 525 Davey Lab., University Park,
Thermal Radiation from Neutron Stars: Chandra Results G.G. Pavlov 1, V.E. Zavlin 2 and D. Sanwal 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0206024v2 11 Jun 2002 1 The Pennsylvania State University, 525 Davey Lab., University Park,
Pulsar Wind and pulsar wind nebulae
 Pulsar Wind and pulsar wind nebulae Takata Jumpei 1 Outline S1, Pulsar Wind (PW) and Pulsar Wind Nebula(PWN) around isolate pulsars. -PWN nebula around the Crab pulsar -Formation of PW and PWNe -Kennel
Pulsar Wind and pulsar wind nebulae Takata Jumpei 1 Outline S1, Pulsar Wind (PW) and Pulsar Wind Nebula(PWN) around isolate pulsars. -PWN nebula around the Crab pulsar -Formation of PW and PWNe -Kennel
Gamma-ray observations of millisecond pulsars with the Fermi LAT. Lucas Guillemot, MPIfR Bonn. NS2012 in Bonn 27/02/12.
 Gamma-ray observations of millisecond pulsars with the Fermi LAT Lucas Guillemot, MPIfR Bonn guillemo@mpifr-bonn.mpg.de NS2012 in Bonn 27/02/12 The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Fermi = Large Area Telescope
Gamma-ray observations of millisecond pulsars with the Fermi LAT Lucas Guillemot, MPIfR Bonn guillemo@mpifr-bonn.mpg.de NS2012 in Bonn 27/02/12 The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Fermi = Large Area Telescope
Pulsars ASTR2110 Sarazin. Crab Pulsar in X-rays
 Pulsars ASTR2110 Sarazin Crab Pulsar in X-rays Test #2 Monday, November 13, 11-11:50 am Ruffner G006 (classroom) Bring pencils, paper, calculator You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other
Pulsars ASTR2110 Sarazin Crab Pulsar in X-rays Test #2 Monday, November 13, 11-11:50 am Ruffner G006 (classroom) Bring pencils, paper, calculator You may not consult the text, your notes, or any other
What We Can Learn from High-Resolution Observations of Pulsar Wind Nebulae
 What We Can Learn from High-Resolution Observations of Pulsar Wind Nebulae Noel Klingler The George Washington University Oleg Kargaltsev The George Washington University George Pavlov Pennsylvania State
What We Can Learn from High-Resolution Observations of Pulsar Wind Nebulae Noel Klingler The George Washington University Oleg Kargaltsev The George Washington University George Pavlov Pennsylvania State
Particle acceleration during the gamma-ray flares of the Crab Nebular
 Particle acceleration during the gamma-ray flares of the Crab Nebular SLAC Accelerator seminar SLAC 15 June 2011 R. Buehler for the LAT collaboration and A. Tennant, E. Costa, D. Horns, C. Ferrigno, A.
Particle acceleration during the gamma-ray flares of the Crab Nebular SLAC Accelerator seminar SLAC 15 June 2011 R. Buehler for the LAT collaboration and A. Tennant, E. Costa, D. Horns, C. Ferrigno, A.
Pulsar Wind Nebulae as seen by Fermi-Large Area Telescope
 Pulsar Wind Nebulae as seen by Fermi-Large Area Telescope Marie-Hélène Grondin Centre d'etudes Nucléaires de Bordeaux- Gradignan SNR/PWN Workshop Montpellier, 2010 June 1 th M.-H. Grondin, SNR/PWN Wokshop,
Pulsar Wind Nebulae as seen by Fermi-Large Area Telescope Marie-Hélène Grondin Centre d'etudes Nucléaires de Bordeaux- Gradignan SNR/PWN Workshop Montpellier, 2010 June 1 th M.-H. Grondin, SNR/PWN Wokshop,
Pulsars & Double Pulsars:! A Multiwavelength Approach!
 Pulsars & Double Pulsars:! A Multiwavelength Approach! Marta Burgay INAF, Cagliari Observatory! X-Ray Astronomy 2009 Bologna 08/09/2009! Spin-Powered Pulsars! Radio! High Energy! RRATs! Magnetars! XDINS!
Pulsars & Double Pulsars:! A Multiwavelength Approach! Marta Burgay INAF, Cagliari Observatory! X-Ray Astronomy 2009 Bologna 08/09/2009! Spin-Powered Pulsars! Radio! High Energy! RRATs! Magnetars! XDINS!
Polarized (Surface) X-Rays from Highly Magnetized Neutron Stars
 Polarized (Surface) X-Rays from Highly Magnetized Neutron Stars Dong Lai Cornell University The Coming Age of X-Ray Polarimetry, April 29, 2009, Rome, Italy Thermal (Surface) Radiation from Neutron Stars
Polarized (Surface) X-Rays from Highly Magnetized Neutron Stars Dong Lai Cornell University The Coming Age of X-Ray Polarimetry, April 29, 2009, Rome, Italy Thermal (Surface) Radiation from Neutron Stars
Pulsar Observations with the Fermi Large Area Telescope
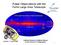 Pulsar Observations with the Fermi Large Area Telescope First Light sky survey (4 days of exposure)) Launch: 11 June 2008 Gottfried Kanbach & Matthew Baring for the Fermi-LAT Collaboration 1 The high-energy
Pulsar Observations with the Fermi Large Area Telescope First Light sky survey (4 days of exposure)) Launch: 11 June 2008 Gottfried Kanbach & Matthew Baring for the Fermi-LAT Collaboration 1 The high-energy
Thermal Emission from Isolated Neutron Stars
 Thermal Emission from Isolated Neutron Stars R. Turolla Dept. of Physics, University of Padova, Italy IWARA09 - Maresias, October 4-8 2009 1 Outline Are INSs thermal emitters? Observations of INSs Importance
Thermal Emission from Isolated Neutron Stars R. Turolla Dept. of Physics, University of Padova, Italy IWARA09 - Maresias, October 4-8 2009 1 Outline Are INSs thermal emitters? Observations of INSs Importance
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 23 Nov 2003
 Young Neutron Stars and Their Environments IAU Symposium, Vol. 218, 2004 F. Camilo and B. M. Gaensler, eds. Central Compact Objects in Supernova Remnants arxiv:astro-ph/0311526v1 23 Nov 2003 George G.
Young Neutron Stars and Their Environments IAU Symposium, Vol. 218, 2004 F. Camilo and B. M. Gaensler, eds. Central Compact Objects in Supernova Remnants arxiv:astro-ph/0311526v1 23 Nov 2003 George G.
The Stellar Graveyard
 Life and Death of High Mass Stars (M > 8 M sun ) AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Last stage: Iron core surrounded by shells of increasingly lighter elements. Announcements MIDTERM #2
Life and Death of High Mass Stars (M > 8 M sun ) AST 101 Introduction to Astronomy: Stars & Galaxies Last stage: Iron core surrounded by shells of increasingly lighter elements. Announcements MIDTERM #2
Accretion Disks. 1. Accretion Efficiency. 2. Eddington Luminosity. 3. Bondi-Hoyle Accretion. 4. Temperature profile and spectrum of accretion disk
 Accretion Disks Accretion Disks 1. Accretion Efficiency 2. Eddington Luminosity 3. Bondi-Hoyle Accretion 4. Temperature profile and spectrum of accretion disk 5. Spectra of AGN 5.1 Continuum 5.2 Line Emission
Accretion Disks Accretion Disks 1. Accretion Efficiency 2. Eddington Luminosity 3. Bondi-Hoyle Accretion 4. Temperature profile and spectrum of accretion disk 5. Spectra of AGN 5.1 Continuum 5.2 Line Emission
Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy
 Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy Dave Thompson NASA GSFC On behalf of the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Large Area Telescope Collaboration Neutrino Oscillation Workshop Otranto, Lecce, Italy
Fermi: Highlights of GeV Gamma-ray Astronomy Dave Thompson NASA GSFC On behalf of the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope Large Area Telescope Collaboration Neutrino Oscillation Workshop Otranto, Lecce, Italy
Astronomy. Chapter 15 Stellar Remnants: White Dwarfs, Neutron Stars, and Black Holes
 Astronomy Chapter 15 Stellar Remnants: White Dwarfs, Neutron Stars, and Black Holes are hot, compact stars whose mass is comparable to the Sun's and size to the Earth's. A. White dwarfs B. Neutron stars
Astronomy Chapter 15 Stellar Remnants: White Dwarfs, Neutron Stars, and Black Holes are hot, compact stars whose mass is comparable to the Sun's and size to the Earth's. A. White dwarfs B. Neutron stars
Broadband Emission of Magnetar Wind Nebulae
 Broadband Emission of Magnetar Wind Nebulae Shuta Tanaka ICRR, The Univ. of Tokyo 29, Oct., 2015, TeVPA 2015 @ Kashiwa 1 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Spectral Evolution of young PWNe 3. A Spectral Model
Broadband Emission of Magnetar Wind Nebulae Shuta Tanaka ICRR, The Univ. of Tokyo 29, Oct., 2015, TeVPA 2015 @ Kashiwa 1 Contents 1. Introduction 2. Spectral Evolution of young PWNe 3. A Spectral Model
FERMI. YOUNG PULSAR SPECTRA WITH THE LAT FERMI TELESCOPE Ateliers pulsars. 25 novembre 2008 Damien Parent. Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope
 FERMI Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope YOUNG PULSAR SPECTRA WITH THE LAT FERMI TELESCOPE Ateliers pulsars 25 novembre 2008 1 Topics 1. Young pulsars, our best candidates 2 examples : J0205+6449 and
FERMI Gamma-ray Large Area Space Telescope YOUNG PULSAR SPECTRA WITH THE LAT FERMI TELESCOPE Ateliers pulsars 25 novembre 2008 1 Topics 1. Young pulsars, our best candidates 2 examples : J0205+6449 and
Future Gamma-Ray Observations of Pulsars and their Environments
 Future Gamma-Ray Observations of Pulsars and their Environments David J. Thompson NASA Goddard Space Flight Center GLAST Large Area Telescope Collaboration djt@egret.gsfc.nasa.gov D. Thompson 363 rd Heraeus
Future Gamma-Ray Observations of Pulsars and their Environments David J. Thompson NASA Goddard Space Flight Center GLAST Large Area Telescope Collaboration djt@egret.gsfc.nasa.gov D. Thompson 363 rd Heraeus
Discovery of a transitional Redback millisecond pulsar J !
 Discovery of a transitional Redback millisecond pulsar J1227-4853! By Jayanta Roy!! JBCA, University of Manchester!! and!! National Centre for Radio Astrophysics (NCRA-TIFR) Neutron stars at the crossroads,
Discovery of a transitional Redback millisecond pulsar J1227-4853! By Jayanta Roy!! JBCA, University of Manchester!! and!! National Centre for Radio Astrophysics (NCRA-TIFR) Neutron stars at the crossroads,
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 15 Dec 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 15 Dec 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.he] 15 Dec 2009](/thumbs/80/81120594.jpg) Optical, ultraviolet, and infrared observations of isolated neutron stars arxiv:0912.2931v1 [astro-ph.he] 15 Dec 2009 Abstract Roberto P. Mignani MSSL-UCL, Holmbury St. Mary, Dorking, Surrey, RH5 6NT,
Optical, ultraviolet, and infrared observations of isolated neutron stars arxiv:0912.2931v1 [astro-ph.he] 15 Dec 2009 Abstract Roberto P. Mignani MSSL-UCL, Holmbury St. Mary, Dorking, Surrey, RH5 6NT,
The X-ray Spectrum of the Vela Pulsar Resolved with Chandra
 The X-ray Spectrum of the Vela Pulsar Resolved with Chandra G. G. Pavlov 1, V. E. Zavlin 2, D. Sanwal 1, V. Burwitz 2, and G. P. Garmire 1 Received ; accepted 1 The Pennsylvania State University, 525 Davey
The X-ray Spectrum of the Vela Pulsar Resolved with Chandra G. G. Pavlov 1, V. E. Zavlin 2, D. Sanwal 1, V. Burwitz 2, and G. P. Garmire 1 Received ; accepted 1 The Pennsylvania State University, 525 Davey
Physics Homework Set I Su2015
 1) The particles which enter into chemical reactions are the atom's: 1) _ A) protons. B) positrons. C) mesons. D) electrons. E) neutrons. 2) Which of the following type of electromagnetic radiation has
1) The particles which enter into chemical reactions are the atom's: 1) _ A) protons. B) positrons. C) mesons. D) electrons. E) neutrons. 2) Which of the following type of electromagnetic radiation has
Composite Supernova Remnants: Multiwavelength Observations and Theoretical Modelling
 Composite Supernova Remnants: Multiwavelength Observations and Theoretical Modelling Okkie de Jager & Stefan Ferreira (NWU, South Africa) Regis Terrier & Arache Djannati-Ataï (Univ. of Paris VII, France)
Composite Supernova Remnants: Multiwavelength Observations and Theoretical Modelling Okkie de Jager & Stefan Ferreira (NWU, South Africa) Regis Terrier & Arache Djannati-Ataï (Univ. of Paris VII, France)
Gas 1: Molecular clouds
 Gas 1: Molecular clouds > 4000 known with masses ~ 10 3 to 10 5 M T ~ 10 to 25 K (cold!); number density n > 10 9 gas particles m 3 Emission bands in IR, mm, radio regions from molecules comprising H,
Gas 1: Molecular clouds > 4000 known with masses ~ 10 3 to 10 5 M T ~ 10 to 25 K (cold!); number density n > 10 9 gas particles m 3 Emission bands in IR, mm, radio regions from molecules comprising H,
Pulsar Polarimetry. Roberto P. Mignani. INAF-Istituto di Astrofisica Spaziale, Milan (Italy) Kepler Institute of Astronomy, Zielona Gora (Poland)
 Pulsar Polarimetry Roberto P. Mignani INAF-Istituto di Astrofisica Spaziale, Milan (Italy) Kepler Institute of Astronomy, Zielona Gora (Poland) With: P. Moran, A. Sherarer, (NUIG), A. Slowikowska (UZG),
Pulsar Polarimetry Roberto P. Mignani INAF-Istituto di Astrofisica Spaziale, Milan (Italy) Kepler Institute of Astronomy, Zielona Gora (Poland) With: P. Moran, A. Sherarer, (NUIG), A. Slowikowska (UZG),
Stellar Binary Systems and CTA. Guillaume Dubus Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Grenoble
 Stellar Binary Systems and CTA Guillaume Dubus Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Grenoble Barcelona Cherenkov Telescope Array Meeting, 24-25 January 2008 X-ray binaries picture by H. Spruit relativistic outflow
Stellar Binary Systems and CTA Guillaume Dubus Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Grenoble Barcelona Cherenkov Telescope Array Meeting, 24-25 January 2008 X-ray binaries picture by H. Spruit relativistic outflow
Dark Matter ASTR 2120 Sarazin. Bullet Cluster of Galaxies - Dark Matter Lab
 Dark Matter ASTR 2120 Sarazin Bullet Cluster of Galaxies - Dark Matter Lab Mergers: Test of Dark Matter vs. Modified Gravity Gas behind DM Galaxies DM = location of gravity Gas = location of most baryons
Dark Matter ASTR 2120 Sarazin Bullet Cluster of Galaxies - Dark Matter Lab Mergers: Test of Dark Matter vs. Modified Gravity Gas behind DM Galaxies DM = location of gravity Gas = location of most baryons
Neutron Stars. We now know that SN 1054 was a Type II supernova that ended the life of a massive star and left behind a neutron star.
 Neutron Stars Neutron Stars The emission from the supernova that produced the crab nebula was observed in 1054 AD by Chinese, Japanese, Native Americans, and Persian/Arab astronomers as being bright enough
Neutron Stars Neutron Stars The emission from the supernova that produced the crab nebula was observed in 1054 AD by Chinese, Japanese, Native Americans, and Persian/Arab astronomers as being bright enough
Spatial Profile of the Emission from Pulsar Wind Nebulae with steady-state 1D Modeling
 Spatial Profile of the Emission from Pulsar Wind Nebulae with steady-state 1D Modeling Wataru Ishizaki ( Department of Physics, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo ) Abstract The pulsar
Spatial Profile of the Emission from Pulsar Wind Nebulae with steady-state 1D Modeling Wataru Ishizaki ( Department of Physics, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo ) Abstract The pulsar
Components of Galaxies Stars What Properties of Stars are Important for Understanding Galaxies?
 Components of Galaxies Stars What Properties of Stars are Important for Understanding Galaxies? Temperature Determines the λ range over which the radiation is emitted Chemical Composition metallicities
Components of Galaxies Stars What Properties of Stars are Important for Understanding Galaxies? Temperature Determines the λ range over which the radiation is emitted Chemical Composition metallicities
The Time Evolution of Pulsar Wind Nebulae
 The Time Evolution of Pulsar Wind Nebulae Okkie de Jager, S. Ferreira (NWU, South Africa) Science with the New Generation of High Energy Gamma-Ray Experiments (6th Workshop), Padova 8 10 October 2008 Contents
The Time Evolution of Pulsar Wind Nebulae Okkie de Jager, S. Ferreira (NWU, South Africa) Science with the New Generation of High Energy Gamma-Ray Experiments (6th Workshop), Padova 8 10 October 2008 Contents
Search for Pulsed Emission in Archival VERITAS Data
 Search for Pulsed Emission in Archival VERITAS Data Avery Archer * for The VERITAS Collaboration Washington University in St. Louis E-mail: a.archer@wustl.edu Since the 2011 VERITAS discovery of very high
Search for Pulsed Emission in Archival VERITAS Data Avery Archer * for The VERITAS Collaboration Washington University in St. Louis E-mail: a.archer@wustl.edu Since the 2011 VERITAS discovery of very high
Probing Pulsar Winds With X-rays!
 Probing Pulsar Winds With X-rays! Collaborators:! Bryan Gaensler! Steve Reynolds! David Helfand! Stephen Ng! Anne Lemiere! Okkie de Jager! Stephanie LaMassa! Jack Hughes! PWNe and Their SNRs! PWN Shock
Probing Pulsar Winds With X-rays! Collaborators:! Bryan Gaensler! Steve Reynolds! David Helfand! Stephen Ng! Anne Lemiere! Okkie de Jager! Stephanie LaMassa! Jack Hughes! PWNe and Their SNRs! PWN Shock
Measuring the Neutron Star Mass-Radius Relationship with X-ray Spectroscopy
 Measuring the Neutron Star Mass-Radius Relationship with X-ray Spectroscopy Bob Rutledge McGill University Collaborators: Lars Bildsten (ITP/UCSB) Ed Brown (MSU) George Pavlov (PSU) Slava Zavlin (MSFC)
Measuring the Neutron Star Mass-Radius Relationship with X-ray Spectroscopy Bob Rutledge McGill University Collaborators: Lars Bildsten (ITP/UCSB) Ed Brown (MSU) George Pavlov (PSU) Slava Zavlin (MSFC)
Today. Logistics. Visible vs. X-ray X. Synchrotron Radiation. Pulsars and Neutron Stars. ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies
 ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Today Binary mass transfer Joys of nearest supernova: SN 1987A How mass transfer from binary companion can spin-up pulsar White dwarf supernovae from mass transfer
ASTR 1040 Accel Astro: Stars & Galaxies Today Binary mass transfer Joys of nearest supernova: SN 1987A How mass transfer from binary companion can spin-up pulsar White dwarf supernovae from mass transfer
AG Draconis. A high density plasma laboratory. Dr Peter Young Collaborators A.K. Dupree S.J. Kenyon B. Espey T.B.
 AG Draconis A high density plasma laboratory Collaborators A.K. Dupree S.J. Kenyon B. Espey T.B. Ake p.r.young@rl.ac.uk Overview CHIANTI database Symbiotic Stars AG Draconis FUSE FUSE observations of AG
AG Draconis A high density plasma laboratory Collaborators A.K. Dupree S.J. Kenyon B. Espey T.B. Ake p.r.young@rl.ac.uk Overview CHIANTI database Symbiotic Stars AG Draconis FUSE FUSE observations of AG
A Supermassive Black Hole in the Dwarf Starburst Galaxy Henize Amy Reines Einstein Fellow National Radio Astronomy Observatory
 A Supermassive Black Hole in the Dwarf Starburst Galaxy Henize 2-10 Amy Reines Einstein Fellow National Radio Astronomy Observatory Supermassive black holes and galaxy evolution Supermassive black holes
A Supermassive Black Hole in the Dwarf Starburst Galaxy Henize 2-10 Amy Reines Einstein Fellow National Radio Astronomy Observatory Supermassive black holes and galaxy evolution Supermassive black holes
The Crab Nebula in the infrared: a review
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 83, 92 c SAIt 2012 Memorie della The Crab Nebula in the infrared: a review P. Persi IASF-ROMA/INAF, Via Fosso del Cavaliere 100, 00133 Roma, Italy e-mail: paolo.persi@iasf-roma.inaf.it
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 83, 92 c SAIt 2012 Memorie della The Crab Nebula in the infrared: a review P. Persi IASF-ROMA/INAF, Via Fosso del Cavaliere 100, 00133 Roma, Italy e-mail: paolo.persi@iasf-roma.inaf.it
PULSE PHASE VARIATIONS OF THE X-RAY SPECTRAL FEATURES IN THE RADIO-QUIET NEUTRON STAR 1E S. Mereghetti, A. De Luca, and P. A.
 The Astrophysical Journal, 581:1280 1285, 2002 December 20 # 2002. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. PULSE PHASE VARIATIONS OF THE X-RAY SPECTRAL FEATURES IN THE
The Astrophysical Journal, 581:1280 1285, 2002 December 20 # 2002. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. PULSE PHASE VARIATIONS OF THE X-RAY SPECTRAL FEATURES IN THE
- Synchrotron emission: A brief history. - Examples. - Cyclotron radiation. - Synchrotron radiation. - Synchrotron power from a single electron
 - Synchrotron emission: A brief history - Examples - Cyclotron radiation - Synchrotron radiation - Synchrotron power from a single electron - Relativistic beaming - Relativistic Doppler effect - Spectrum
- Synchrotron emission: A brief history - Examples - Cyclotron radiation - Synchrotron radiation - Synchrotron power from a single electron - Relativistic beaming - Relativistic Doppler effect - Spectrum
Radio counterparts of gamma-ray pulsars
 Radio counterparts of gamma-ray pulsars Lucas Guillemot, MPIfR Bonn guillemo@mpifr-bonn.mpg.de on behalf of the Fermi LAT Collaboration IAU Symposium 2012, Beijing 20/08/12 117 gamma-ray pulsars! 41 young
Radio counterparts of gamma-ray pulsars Lucas Guillemot, MPIfR Bonn guillemo@mpifr-bonn.mpg.de on behalf of the Fermi LAT Collaboration IAU Symposium 2012, Beijing 20/08/12 117 gamma-ray pulsars! 41 young
RX J and RX J : recent results and status
 RX J0806+15 and RX J1914+24: recent results and status Gavin Ramsay (Armagh Observatory) Overview of talk Remind you what they are! Recent observational work since Nijmegen Meeting. Modelling and theoretical
RX J0806+15 and RX J1914+24: recent results and status Gavin Ramsay (Armagh Observatory) Overview of talk Remind you what they are! Recent observational work since Nijmegen Meeting. Modelling and theoretical
XMM-Newton Observations of the Isolated Neutron Star 1RXS J / RBS 1774
 XMM-Newton Observations of the Isolated Neutron Star 1RXS J214303.7+065419 / RBS 1774 Mark Cropper, Silvia Zane Roberto Turolla Luca Zampieri Matteo Chieregato Jeremy Drake Aldo Treves MSSL/UCL Univ Padova
XMM-Newton Observations of the Isolated Neutron Star 1RXS J214303.7+065419 / RBS 1774 Mark Cropper, Silvia Zane Roberto Turolla Luca Zampieri Matteo Chieregato Jeremy Drake Aldo Treves MSSL/UCL Univ Padova
3/13/18. Things to do. Synchrotron Radiation. Today on Stellar Explosions
 ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Peri Johnson, Ryan Horton Lecture 17 Tues 13 Mar 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Ring Nebula Today on Stellar Explosions Revisit Pulsars spinning
ASTR 1040: Stars & Galaxies Prof. Juri Toomre TAs: Peri Johnson, Ryan Horton Lecture 17 Tues 13 Mar 2018 zeus.colorado.edu/astr1040-toomre Ring Nebula Today on Stellar Explosions Revisit Pulsars spinning
Distribution of X-ray binary stars in the Galaxy (RXTE) High-Energy Astrophysics Lecture 8: Accretion and jets in binary stars
 High-Energy Astrophysics Lecture 8: Accretion and jets in binary stars Distribution of X-ray binary stars in the Galaxy (RXTE) Robert Laing Primary Compact accreting binary systems Compact star WD NS BH
High-Energy Astrophysics Lecture 8: Accretion and jets in binary stars Distribution of X-ray binary stars in the Galaxy (RXTE) Robert Laing Primary Compact accreting binary systems Compact star WD NS BH
Gamma-ray binaries as pulsars spectral & variability behaviour Guillaume Dubus. Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Grenoble UMR 5571 UJF / CNRS
 Gamma-ray binaries as pulsars spectral & variability behaviour Guillaume Dubus Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Grenoble UMR 5571 UJF / CNRS Image: Mirabel 2006 1 Pulsars & massive stars Young pulsars, magnetic
Gamma-ray binaries as pulsars spectral & variability behaviour Guillaume Dubus Laboratoire d Astrophysique de Grenoble UMR 5571 UJF / CNRS Image: Mirabel 2006 1 Pulsars & massive stars Young pulsars, magnetic
The Nature of Pulsars! Agenda for Ast 309N, Nov. 1. To See or Not to See (a Pulsar) The Slowing & Fading of Pulsars!
 Agenda for Ast 309N, Nov. 1 Quiz 7 Card 10/30 feedback More on pulsars and other neutron stars Begin: the saga of interacting binary systems Card: questions for review Reading: - Kaler, ch. 7 Wheeler,
Agenda for Ast 309N, Nov. 1 Quiz 7 Card 10/30 feedback More on pulsars and other neutron stars Begin: the saga of interacting binary systems Card: questions for review Reading: - Kaler, ch. 7 Wheeler,
TeV Emission from Millisecond Pulsars in Compact Binaries? Mallory Roberts Eureka Scientific/NRL
 TeV Emission from Millisecond Pulsars in Compact Binaries? Mallory Roberts Eureka Scientific/NRL Binary Period in Days Millisecond Pulsars Spun up by a low mass companion such that their spin period P
TeV Emission from Millisecond Pulsars in Compact Binaries? Mallory Roberts Eureka Scientific/NRL Binary Period in Days Millisecond Pulsars Spun up by a low mass companion such that their spin period P
Isolated And Accreting Magnetars Viewed In Hard X-rays
 The XXVII Texas Symposium on Relativistic Astrophysics Isolated And Accreting Magnetars Viewed In Hard X-rays Wei Wang National Astronomical Observatories, Beijing China Dec 8 13 2013, Dallas TX, USA Contents
The XXVII Texas Symposium on Relativistic Astrophysics Isolated And Accreting Magnetars Viewed In Hard X-rays Wei Wang National Astronomical Observatories, Beijing China Dec 8 13 2013, Dallas TX, USA Contents
Remnants and Pulsar Wind
 High Energy Supernova Remnants and Pulsar Wind Nebulae F. Giordano Dipartimento Interateneo di Fisica and INFN Sez. Bari For the Fermi-LAT Collaboration Scineghe 2010 The Afterlife of a star IC443 Crab
High Energy Supernova Remnants and Pulsar Wind Nebulae F. Giordano Dipartimento Interateneo di Fisica and INFN Sez. Bari For the Fermi-LAT Collaboration Scineghe 2010 The Afterlife of a star IC443 Crab
Neutron Stars. Melissa Louie
 Neutron Stars Melissa Louie 11-08-10 Outline History, Formation, Properties Detection Pulsars Crab Nebula Pulsar Pulsar Timing Pulsars in Binary Systems Isolated Neutron Stars J185635-3754 Summary 2 The
Neutron Stars Melissa Louie 11-08-10 Outline History, Formation, Properties Detection Pulsars Crab Nebula Pulsar Pulsar Timing Pulsars in Binary Systems Isolated Neutron Stars J185635-3754 Summary 2 The
The Fermi Large Area Telescope View of Gamma-ray Pulsars
 The Fermi Large Area Telescope View of Gamma-ray Pulsars 1 Tyrel J. Johnson, D.A. Smith2, M. Kerr3, & P. R. den Hartog4 on behalf of the Fermi Large Area Telescope Collaboration and the Pulsar Timing and
The Fermi Large Area Telescope View of Gamma-ray Pulsars 1 Tyrel J. Johnson, D.A. Smith2, M. Kerr3, & P. R. den Hartog4 on behalf of the Fermi Large Area Telescope Collaboration and the Pulsar Timing and
Millisecond Pulsar Populations in Globular Clusters
 Millisecond Pulsar Populations in Globular Clusters David C. Y. Hui Department of Astronomy & Space Science Chungnam National University 1. Introduction 2. Dynamical formation of millisecond pulsars (MSPs)
Millisecond Pulsar Populations in Globular Clusters David C. Y. Hui Department of Astronomy & Space Science Chungnam National University 1. Introduction 2. Dynamical formation of millisecond pulsars (MSPs)
Gamma-ray Astrophysics with VERITAS: Exploring the violent Universe
 Gamma-ray Astrophysics with VERITAS: Exploring the violent Universe K. Ragan McGill University Soup & Science 11-Jan-2008 Soup & Science Jan. '08 1 How do we know about the Universe? Historically, all
Gamma-ray Astrophysics with VERITAS: Exploring the violent Universe K. Ragan McGill University Soup & Science 11-Jan-2008 Soup & Science Jan. '08 1 How do we know about the Universe? Historically, all

 Synchrotron Radiation II Cyclotron v
Synchrotron Radiation II Cyclotron v