Towards More Precise Photometric Redshifts: Calibration Via. CCD Photometry
|
|
|
- Adam Foster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Towards More Precise Photometric Redshifts: Calibration Via CCD Photometry Robert J. Brunner 1,2, Andrew J. Connolly 1, and Alexander S. Szalay 1 rbrunner@pha.jhu.edu, ajc@pha.jhu.edu, szalay@pha.jhu.edu Department of Physics & Astronomy, The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD and Matthew A. Bershady 1 mab@astro.psu.edu Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics, Penn State University, University Park, PA Received ; accepted 1 Visiting Astronomer, Kitt Peak National Observatory, National Optical Astronomy Observatories, which is operated by the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc. (AURA) under cooperative agreement with the National Science Foundation. 2 NASA GSRP Fellow
2 2 ABSTRACT We present the initial results from a deep, multi-band photometric survey of selected high Galactic latitude redshift fields. Previous work using the photographic data of Koo and Kron demonstrated that the distribution of galaxies in the multi-dimensional flux space U, B, R, & I is nearly planar. The position of a galaxy within this plane is determined by its redshift, luminosity and spectral type (Connolly et al. 1995). Using recently acquired deep CCD photometry in existing, published redshift fields, we have redetermined the distribution of galaxies in this four-dimensional magnitude space. Furthermore, from our CCD photometry and the published redshifts, we have quantified the photometric-redshift relation within the standard AB magnitude system. This empirical relation has a measured dispersion of σ z 0.02 for z<0.4. With this work we are reaching the asymptotic intrinsic dispersions (σ z for z<0.4) that were predicted from simulated distributions of galaxy colors. This result will prove useful in providing estimated redshifts for large photometric surveys, as well as improve the sampling of specific redshift regions for spectroscopic surveys through the use of an estimated redshift selection criteria. Subject headings: cosmology: observations - galaxies: evolution - galaxies: photometry
3 3 1. Introduction The utility of deriving galaxy redshifts from photometric data has long been known (Baum 1962, Koo 1985, Loh & Spillar 1986). Recently, Connolly et al developed an empirical approach as opposed to the previous model fitting methods. Utilizing photographic data, they were able to estimate a redshift out to z 0.5 withameasured dispersion of δz < The uncertainties in that result were dominated by the photometric errors. Simulations indicated that with improved photometry the dispersion within the relationship could be significantly reduced. As a result, we have embarked on an observational program designed to obtain deep CCD multi-band photometry in existing redshift fields. In this paper we present the first results of this survey by extending the previous approach using CCD photometry. Section two outlines the basic reduction steps taken in the preparation of the sample for this work. Section three discusses the actual fitting techniques and investigates the intrinsic dispersion. We conclude this letter with a discussion of the ramifications of this work and possible future directions. 2. Data The photometric data used in this analysis were taken using the PFCCD camera with the standard U, B, R, & I filters on the Mayall 4m at Kitt Peak National Observatory on the nights of March 31 April 3, 1995, March 18 20, 1996, and May 14 16, This camera uses a CCD (T2KB) witha0.47 /pixel scale and a read noise of 4e /pixel. The gain used for these observations was 5.4 e /ADU, a value which resulted from a tradeoff between maximizing the available dynamic range and minimizing the effects of the charge depletion problem with the CCD electronics. These observations were chosen to
4 4 coincide with the published 14 hour redshift field of the Canada-France Redshift Survey (CFRS). A complete discussion of the observational program including an analysis of the custom reduction software are beyond the scope of this letter and will be published elsewhere (Brunner 1997). All three runs were reduced separately using the standard IRAF routines. The images were initially debiased and flat fielded using dome flats. Illumination corrections were created by stacking the image frames in each filter, with high and low rejection to remove objects, and then boxcar smoothing the stacked image. The individual fields were registered to a common position in each filter, and then stacked using a weighted average. The weights were determined by measuring the signal to noise for several randomly chosen stars on each frame. The stacked images for each filter were then registered to a common image to simplify the photometric measurement in matched apertures. The final images for each of the three runs were then registered and stacked again using the weighted average. Object detection and photometry were performed using a custom pipeline. The object detection was done separately in each filter using the SExtractor package (Bertin & Arnouts 1996). The separate detections in each filter were then matched using a growing annulus technique in the order of B, U, R, theniand a master detection list was produced. Using this list, photometry was determined in both SExtractor s modified Kron (Kron 1980) aperture and a 10 diameter aperture matched in each band. The actual photometry algorithm used involved a modification to SExtractor in both the background calculation and pixel assignment within the aperture of interest. The detections were photometrically calibrated using published standards (Landolt 1992) which were measured at similar airmasses to the object frames. The photometric zeropoint was then adjusted to the AB system (Oke & Gunn, 1983) using published transformations (Fukugita et al. 1995): U AB = U +0.69, B AB = B 0.14, R AB = R +0.17, and I AB = I
5 5 Astrometric transformations were determined from the HST Guide Star Catalog II (Lasker 1996), after which the redshifts in the Canada France Redshift Survey (CFRS) 14 hour field were matched to our photometric sample. The measured dispersion between the CFRS I AB isophotal magnitudes and our I AB automatic magnitudes was σ 0.13 to I 23 with no evident systematic deviations from a linear relationship. 3. Analysis In an effort to minimize the dispersion in our relationship, we imposed two conditions on the data used in this analysis. First, we restricted the photometric sample such that all object magnitudes were below the appropriate magnitude limit at which a typical galaxy had a measured 1σ rms magnitude error of approximately 0.1 magnitudes. Second, we required that only the most reliable spectroscopic identifications be incorporated into the fitting procedure. This involved pruning the CFRS catalog such that only non-stellar objects with redshifts having a confidence greater than 95% were retained. This was accomplished by restricting the redshifts used to the following quality classes: 3,4,8,93,94,98 (cf. Le Fevre et al. 1995). The final sample contained 89 redshifts with the following distribution: 40 redshifts in the range (0.0, 0.4] and 49 redshifts in the range (0.4, 0.8]. For these two subsets, we fit a second order polynomial in UBRI,UBR,andBRIto the measured photometry and published redshifts. In each region, the degrees of freedom remained a substantial fraction of the original data (a second order fit in four variables requires 15 parameters). This technique is a simple approach designed to quantify the accuracy of our method for estimating redshifts and is not the optimal parameterization of the topology of the galaxy distribution, which is the subject of ongoing work.
6 6 EDITOR: PLACE TABLE 1 HERE. The redshift intervals were not chosen randomly. This technique has been previously shown to be more sensitive to broad spectroscopic continuum features (primarily the break in the continuum spectra at around 4000 Å, which moves between the B and R bands at z 0.4, and the R and I bands at z 0.8) rather than specific absorption/emission features (Connolly et al. 1995). This is clearly demonstrated in Table 1 where the standard deviation in the redshift range (0.0,0.4] is only slightly higher when the I band is not included in the fit. On the other hand, when the U band is excluded from the fit, the standard deviation more than doubles. This reflects the fact that the I band is sampling the same flat region of the spectrum as the R band within this redshift range, and is thereby providing predominantly redundant information to the fit. In the second redshift range, the continuum break is moving from the B band into the R band, which is reflected in the lower significance of the U band information. We also show the expected intrinsic dispersion in this relationship from simulations using all four bands (cf. Connolly et al. 1995), which clearly shows that our measured dispersion is completely dominated by the intrinsic scatter within the relationship. EDITOR: PLACE FIGURE 1 HERE. The relative importance of the different bands in the individual redshift intervals reflects the curvature inherent within the distribution of galaxies in the multi-dimensional magnitude space. In a given redshift range, the curvature is accurately parameterized by a second order polynomial. Between redshift intervals, however, the distribution displays a higher order curvature term (cf. the previous discussion concerning the continuum break), which requires the use of a piecewise second-order parameterization. As a result, the application of these results requires an iterative approach. First, a third order global
7 7 photometric redshift relation is used to determine an approximate redshift. From this initial redshift estimate, the appropriate second-order relationship can then be used. If the initial estimate is on the border between two subsets (z [0.35, 0.45]), both relationships should be applied and the mean of the two results used. With the introduction of the four-vector C = (U, B, R, I), the second-order photometric-redshift relationships can be summarized in the following manner: z = Z α + C V α + C M α C T where the scalar Z α, vector V α, and matrix M α components are listed in Table 2 for the two different redshift regimes. The parameters for the third order fit are listed in Table Discussion We have shown that using a simple iterative process, redshifts can be reliably estimated for objects from broadband photometry out to z 0.8. A comparison of our measured dispersion with the published intrinsic dispersion from simulations (Connolly et al. 1995) indicates that we have approached the inherent scatter within the photometric-redshift relationship. These simulations provide an absolute lower limit to the intrinsic scatter, as they only assumed an evolved (15 Gigayear) SED. As the additional effects of metallicity, dust, and stellar histories can only increase the scatter within the relationship, we do not include them in our estimation of the minimal intrinsic scatter within the photometric-redshift relation. Thus it is quite remarkable that we measure such a small scatter as compared to the simple, single age, solar metallicity, and dust free galaxies produced in the simulations. Actual galaxies are clearly more complex, spanning a wide range of star formation histories, ages, metallicities, and dust content, all of which would be expected to significantly increase
8 8 the measured dispersion. We see that this is not the case, which leads us to two related conclusions. First, this technique is extremely dependent on the 4000 Å break which is present in nearly all galaxies. Second, metallicity, dust, and age variations have similar effects in this multidimensional space, albeit almost orthogonal to the redshift vector (Koo 1986). We plan on improving our understanding of the multidimensional nature of the observed galaxy population through the use of SED modeling. This will allow us to quantify the importance of the metallicity, dust, and different stellar histories and explore any possible degeneracies. The photometric-redshift estimation technique can be considered to be the equivalent of a low resolution (4 element) spectrograph. By using more filters that are increasingly narrow, we increase the spectral resolution of this technique. Taken to the extreme, however, this approach will emulate a spectrograph, losing the observing efficiency that is the primary advantage of this technique. From a comparison between the dispersion from the three band and the four band quadratic fits, it is clear that a marginal gain is achieved by adding a fourth band within a given redshift regime. As a result, we believe that the benefits achieved by adding more bands to this approach is more than offset in the loss of observational efficiency. The simulations used the standard U, B, R, & I filters in order to be reliably compared to our observations. We are working to extend this analysis in two principal areas. First, we are now focusing on improving our understanding of the distribution of galaxies in this multi-dimensional flux space. This requires the use of a stratified sampling strategy to obtain redshifts throughout the photometric sample. These additional redshifts are primarily being obtained using the Keck telescope within the DEEP collaboration. In addition, we are incorporating additional physical parameters (eg. surface brightness and shape parameters) via HST WFPC2 imaging to quantify the different morphological tracts within the cumulative
9 9 galaxy distribution. Second, we are extending this work to higher redshifts. For redshifts below z 1.2, we are working to increase the size and stratification of our redshift sample. This involves increasing our photometry-redshift catalog through the addition of published redshifts and our participation in several spectroscopic surveys. In the redshift region 1.2 z 2.8, we are adding near-infrared photometry to our catalog in order to sample the continuum features our technique requires. Until a large quantity of reliable spectra can be obtained within this region (the arrival of the blue camera on LRIS will help alleviate this quandary), we will use our understanding of the z<1.2regime and the published high z work of others (Steidel et al. 1996) as boundary conditions. We can then use SED models to extrapolate into this region, while maintaining the boundary condition requirements at both redshift ends. As spectra in this area become available, we will add them into the fitting procedure. Eventually this work will allow for the estimation of not only the redshift, but also the spectral type of an object solely from broadband photometry. First we wish to acknowledge Gyula Szokoly for assistance in obtaining the data. We also would like to thank the referee for useful comments, and Barry Lasker, Gretchen Greene, and Brian McLean for allowing us access to an early version of the GSC II. We also wish to acknowledge useful discussions with Mark Dickinson, Mark Subbarao, and David Koo. RJB would like to acknowledge support from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration Graduate Student Researchers Program. AJC acknowledges partial support from NASA grant AR A. ASZ has been supported by the NASA LTSA program.
10 10 REFERENCES Baum, W.A. 1962, Problems of Extragalactic Research, IAU Symposium No. 15., 390. Bertin, E., & Arnout, S., 1996, A&AS, 117, 393. Brunner, R.J, PhD. Thesis, The Johns Hopkins University, Connolly, A.J., Csabai, I., Szalay, A.S., Koo, D.C., Kron, R.G., and Munn, J.A., 1995, AJ, 110, 6. Fukugita, M., Shimasaku, K., Ichikawa, T., 1995, PASP, 107, 945. Koo, D.C., 1985, AJ, 90, 418. Koo, D.C., 1986, ApJ, 311, 651. Kron, R.G., 1980, ApJS, 43, 305. Landolt, A.U. 1992, AJ, 104, 340. Lasker, B., 1996, Private Communication. Le Fevre, O., Crampton, D., Lilly, S.J., Hammer, F., and Tresse, L., 1995, ApJ, 455, 60. Loh, E.D., & Spillar, E.J., 1986, ApJ, 303, 154. Oke, J.B., & Gunn, J.E., 1983, ApJ, 266, 713. Steidel, C.C., Giavalisco, M., Pettini, M., Dickinson, M., & Adelberger, K.L., 1996, ApJ, 462, L17. This manuscript was prepared with the AAS L A TEX macros v4.0.
11 11 Table 1. The standard deviation between measured and estimated redshifts. Redshift Range σ Z (UBRI ) σ Z (UBR ) σ Z (BRI ) σ Z (Simulation) (0.0,0.4] (0.4,0.8]
12 12 Table 2. The 2 nd order polynomial terms. Redshift Range Scalar Vector Matrix U B R I (0.0,0.4] U B R I (0.4,0.8] U B R I
13 13 Table 3. The 3 rd order polynomial terms. Scalar Vector Matrix U B R I U B R I Third Order Terms U B R I UBR U UBI B URI R BRI I 2
14 14 Fig. 1. The correlation between estimated and measured redshifts are shown in (a) for the second order fit in the redshift interval (0.0,0.4], (b) for the second order fit in the redshift interval (0.4,0.8], and (c) for the third order fit in the redshift interval (0.0,0.8]. Indicated in each figure are the number of redshifts (N Z ), dispersion (σ Z ), skewness (S Z ), and a straight line of unit slope, which is not a fit to the data. A histogram of the residuals for the third order fit are displayed in (d).
15 (a) (b) (c) (d)
A Calibration Method for Wide Field Multicolor. Photometric System 1
 A Calibration Method for Wide Field Multicolor Photometric System 1 Xu Zhou,Jiansheng Chen, Wen Xu, Mei Zhang... Beijing Astronomical Observatory,Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100080, China Beijing
A Calibration Method for Wide Field Multicolor Photometric System 1 Xu Zhou,Jiansheng Chen, Wen Xu, Mei Zhang... Beijing Astronomical Observatory,Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100080, China Beijing
APLUS: A Data Reduction Pipeline for HST/ACS and WFC3 Images
 APLUS: A Data Reduction Pipeline for HST/ACS and WFC3 Images Wei Zheng 1,AmitSaraff 2,3,LarryBradley 4,DanCoe 4,AlexViana 4 and Sara Ogaz 4 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Johns Hopkins University,
APLUS: A Data Reduction Pipeline for HST/ACS and WFC3 Images Wei Zheng 1,AmitSaraff 2,3,LarryBradley 4,DanCoe 4,AlexViana 4 and Sara Ogaz 4 1 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Johns Hopkins University,
Improving the Absolute Astrometry of HST Data with GSC-II
 The 2005 HST Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 2005 A. M. Koekemoer, P. Goudfrooij, and L. L. Dressel, eds. Improving the Absolute Astrometry of HST Data with GSC-II A. M. Koekemoer,
The 2005 HST Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 2005 A. M. Koekemoer, P. Goudfrooij, and L. L. Dressel, eds. Improving the Absolute Astrometry of HST Data with GSC-II A. M. Koekemoer,
Stellar Mass Estimates of Galaxies in Superclusters at z~1
 Stellar Mass Estimates of Galaxies in Superclusters at z~1 Catherine Whiting The University of Iowa Advisor: Dr. Roy Gal Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawai i at Manoa Abstract. A simple method
Stellar Mass Estimates of Galaxies in Superclusters at z~1 Catherine Whiting The University of Iowa Advisor: Dr. Roy Gal Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawai i at Manoa Abstract. A simple method
Dust properties of galaxies at redshift z 5-6
 Dust properties of galaxies at redshift z 5-6 Ivana Barisic 1, Supervisor: Dr. Peter L. Capak 2, and Co-supervisor: Dr. Andreas Faisst 2 1 Physics Department, University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia 2 Infrared
Dust properties of galaxies at redshift z 5-6 Ivana Barisic 1, Supervisor: Dr. Peter L. Capak 2, and Co-supervisor: Dr. Andreas Faisst 2 1 Physics Department, University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia 2 Infrared
Measuring the Redshift of M104 The Sombrero Galaxy
 Measuring the Redshift of M104 The Sombrero Galaxy Robert R. MacGregor 1 Rice University Written for Astronomy Laboratory 230 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Rice University May 3, 2004 2 Abstract
Measuring the Redshift of M104 The Sombrero Galaxy Robert R. MacGregor 1 Rice University Written for Astronomy Laboratory 230 Department of Physics and Astronomy, Rice University May 3, 2004 2 Abstract
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 2 Nov 2017
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 2 Nov 2017 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.ep] 2 Nov 2017](/thumbs/79/78819041.jpg) Palomar Optical Spectrum of Hyperbolic Near-Earth Object A/2017 U1 Joseph R. Masiero 1 ABSTRACT arxiv:1710.09977v2 [astro-ph.ep] 2 Nov 2017 We present optical spectroscopy of the recently discovered hyperbolic
Palomar Optical Spectrum of Hyperbolic Near-Earth Object A/2017 U1 Joseph R. Masiero 1 ABSTRACT arxiv:1710.09977v2 [astro-ph.ep] 2 Nov 2017 We present optical spectroscopy of the recently discovered hyperbolic
The HST Set of Absolute Standards for the 0.12 µm to 2.5 µm Spectral Range
 Instrument Science Report CAL/SCS-010 The HST Set of Absolute Standards for the 0.12 µm to 2.5 µm Spectral Range L. Colina, R. Bohlin, D. Calzetti, C. Skinner, S. Casertano October 3, 1996 ABSTRACT A proposal
Instrument Science Report CAL/SCS-010 The HST Set of Absolute Standards for the 0.12 µm to 2.5 µm Spectral Range L. Colina, R. Bohlin, D. Calzetti, C. Skinner, S. Casertano October 3, 1996 ABSTRACT A proposal
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 29 Aug 2000
 Accepted to AJ A Probabilistic Quantification of Galaxy Cluster Membership R.J. Brunner and L.M. Lubin 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0008462v1 29 Aug 2000 Department of Astronomy, California Institute of Technology,
Accepted to AJ A Probabilistic Quantification of Galaxy Cluster Membership R.J. Brunner and L.M. Lubin 1 arxiv:astro-ph/0008462v1 29 Aug 2000 Department of Astronomy, California Institute of Technology,
Modern Image Processing Techniques in Astronomical Sky Surveys
 Modern Image Processing Techniques in Astronomical Sky Surveys Items of the PhD thesis József Varga Astronomy MSc Eötvös Loránd University, Faculty of Science PhD School of Physics, Programme of Particle
Modern Image Processing Techniques in Astronomical Sky Surveys Items of the PhD thesis József Varga Astronomy MSc Eötvös Loránd University, Faculty of Science PhD School of Physics, Programme of Particle
CHEMICAL ABUNDANCE ANALYSIS OF RC CANDIDATE STAR HD (46 LMi) : PRELIMINARY RESULTS
 Dig Sites of Stellar Archeology: Giant Stars in the Milky Way Ege Uni. J. of Faculty of Sci., Special Issue, 2014, 145-150 CHEMICAL ABUNDANCE ANALYSIS OF RC CANDIDATE STAR HD 94264 (46 LMi) : PRELIMINARY
Dig Sites of Stellar Archeology: Giant Stars in the Milky Way Ege Uni. J. of Faculty of Sci., Special Issue, 2014, 145-150 CHEMICAL ABUNDANCE ANALYSIS OF RC CANDIDATE STAR HD 94264 (46 LMi) : PRELIMINARY
First results from the Stockholm VIMOS Supernova Survey
 First results from the Stockholm VIMOS Supernova Survey - Detection efficiencies and photometric accuracy in supernova surveys Outline The Stockholm VIMOS Supernova Survey, SVISS. First results from the
First results from the Stockholm VIMOS Supernova Survey - Detection efficiencies and photometric accuracy in supernova surveys Outline The Stockholm VIMOS Supernova Survey, SVISS. First results from the
Automated Search for Lyman Alpha Emitters in the DEEP3 Galaxy Redshift Survey
 Automated Search for Lyman Alpha Emitters in the DEEP3 Galaxy Redshift Survey Victoria Dean Castilleja School Automated Search for Lyman-alpha Emitters in the DEEP3 Galaxy Redshift Survey Abstract This
Automated Search for Lyman Alpha Emitters in the DEEP3 Galaxy Redshift Survey Victoria Dean Castilleja School Automated Search for Lyman-alpha Emitters in the DEEP3 Galaxy Redshift Survey Abstract This
Type II Supernovae as Standardized Candles
 Type II Supernovae as Standardized Candles Mario Hamuy 1 2 Steward Observatory, The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721 Philip A. Pinto Steward Observatory, The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721
Type II Supernovae as Standardized Candles Mario Hamuy 1 2 Steward Observatory, The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721 Philip A. Pinto Steward Observatory, The University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 17 Oct 2002
 The K correction David W. Hogg 1,2, Ivan K. Baldry 3, Michael R. Blanton 1, and Daniel J. Eisenstein 4 ABSTRACT arxiv:astro-ph/0210394 v1 17 Oct 2002 The K correction corrects for the fact that sources
The K correction David W. Hogg 1,2, Ivan K. Baldry 3, Michael R. Blanton 1, and Daniel J. Eisenstein 4 ABSTRACT arxiv:astro-ph/0210394 v1 17 Oct 2002 The K correction corrects for the fact that sources
The SKYGRID Project A Calibration Star Catalog for New Sensors. Stephen A. Gregory Boeing LTS. Tamara E. Payne Boeing LTS. John L. Africano Boeing LTS
 The SKYGRID Project A Calibration Star Catalog for New Sensors Stephen A. Gregory Boeing LTS Tamara E. Payne Boeing LTS John L. Africano Boeing LTS Paul Kervin Air Force Research Laboratory POSTER SESSION
The SKYGRID Project A Calibration Star Catalog for New Sensors Stephen A. Gregory Boeing LTS Tamara E. Payne Boeing LTS John L. Africano Boeing LTS Paul Kervin Air Force Research Laboratory POSTER SESSION
STUDIES OF SELECTED VOIDS. SURFACE PHOTOMETRY OF FAINT GALAXIES IN THE DIRECTION OF IN HERCULES VOID
 STUDIES OF SELECTED VOIDS. SURFACE PHOTOMETRY OF FAINT GALAXIES IN THE DIRECTION OF 1600+18 IN HERCULES VOID G.Petrov [1], A.Y.Kniazev [2], and J.W. Fried [2] 1 Institute of Astronomy, Bulgarian Academy
STUDIES OF SELECTED VOIDS. SURFACE PHOTOMETRY OF FAINT GALAXIES IN THE DIRECTION OF 1600+18 IN HERCULES VOID G.Petrov [1], A.Y.Kniazev [2], and J.W. Fried [2] 1 Institute of Astronomy, Bulgarian Academy
The HII Regions of Sextans A
 Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific 6: 765-769, 1994 July The HII Regions of Sextans A Paul Hodge 1 Astronomy Department, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington 98195 Electronic
Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific 6: 765-769, 1994 July The HII Regions of Sextans A Paul Hodge 1 Astronomy Department, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington 98195 Electronic
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 24 Sep 2009
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 24 Sep 2009 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.co] 24 Sep 2009](/thumbs/83/87517307.jpg) Draft version September 24, 29 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 8/22/9 BROADBAND IMAGING SEGREGATION OF z 3 Lyα EMITTING AND Lyα ABSORBING GALAXIES arxiv:99.4536v1 [astro-ph.co] 24 Sep
Draft version September 24, 29 Preprint typeset using L A TEX style emulateapj v. 8/22/9 BROADBAND IMAGING SEGREGATION OF z 3 Lyα EMITTING AND Lyα ABSORBING GALAXIES arxiv:99.4536v1 [astro-ph.co] 24 Sep
The Long Faint Tail of the High-Redshift Galaxy Population
 At the Edge of the Universe, October 2006, Sintra, Portugal ASP Conference Series, Vol. *, 2007 Eds. J. Afonso, H. Ferguson and R. Norris The Long Faint Tail of the High-Redshift Galaxy Population M. Sawicki
At the Edge of the Universe, October 2006, Sintra, Portugal ASP Conference Series, Vol. *, 2007 Eds. J. Afonso, H. Ferguson and R. Norris The Long Faint Tail of the High-Redshift Galaxy Population M. Sawicki
Lab 4 Radial Velocity Determination of Membership in Open Clusters
 Lab 4 Radial Velocity Determination of Membership in Open Clusters Sean Lockwood 1, Dipesh Bhattarai 2, Neil Lender 3 December 2, 2007 Abstract We used the Doppler velocity of 29 stars in the open clusters
Lab 4 Radial Velocity Determination of Membership in Open Clusters Sean Lockwood 1, Dipesh Bhattarai 2, Neil Lender 3 December 2, 2007 Abstract We used the Doppler velocity of 29 stars in the open clusters
Absolute Flux Calibration for STIS First-Order, Low-Resolution Modes
 Instrument Science Report STIS 97-14 Absolute Flux Calibration for STIS First-Order, Low-Resolution Modes Ralph Bohlin, Space Telescope Science Institute Nicholas Collins, Hughes STX/LASP/GSFC Anne Gonnella,
Instrument Science Report STIS 97-14 Absolute Flux Calibration for STIS First-Order, Low-Resolution Modes Ralph Bohlin, Space Telescope Science Institute Nicholas Collins, Hughes STX/LASP/GSFC Anne Gonnella,
The Accuracy of WFPC2 Photometric Zeropoints
 The Accuracy of WFPC2 Photometric Zeropoints Inge Heyer, Marin Richardson, Brad Whitmore, Lori Lubin July 23, 2004 ABSTRACT The accuracy of WFPC2 photometric zeropoints is examined using two methods. The
The Accuracy of WFPC2 Photometric Zeropoints Inge Heyer, Marin Richardson, Brad Whitmore, Lori Lubin July 23, 2004 ABSTRACT The accuracy of WFPC2 photometric zeropoints is examined using two methods. The
FLAT FIELDS FROM THE MOONLIT EARTH
 Instrument Science Report WFPC2 2008-01 FLAT FIELDS FROM THE MOONLIT EARTH R. C. Bohlin, J. Mack, and J. Biretta 2008 February 4 ABSTRACT The Earth illuminated by light from the full Moon was observed
Instrument Science Report WFPC2 2008-01 FLAT FIELDS FROM THE MOONLIT EARTH R. C. Bohlin, J. Mack, and J. Biretta 2008 February 4 ABSTRACT The Earth illuminated by light from the full Moon was observed
The x Factor: Determining the Strength of Activity in Low-Mass Dwarfs
 Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 116:1105 1110, 2004 November 2004. The Astronomical Society of the Pacific. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. The x Factor: Determining the
Publications of the Astronomical Society of the Pacific, 116:1105 1110, 2004 November 2004. The Astronomical Society of the Pacific. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. The x Factor: Determining the
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 26 Nov 2004
 13 Color Photometry of Open Cluster M48 Zhen-Yu Wu, Xu Zhou, Jun Ma, Zhao-Ji Jiang, Jian-Sheng Chen National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 20A Datun Road, arxiv:astro-ph/0411711v1
13 Color Photometry of Open Cluster M48 Zhen-Yu Wu, Xu Zhou, Jun Ma, Zhao-Ji Jiang, Jian-Sheng Chen National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 20A Datun Road, arxiv:astro-ph/0411711v1
THE GAS MASS AND STAR FORMATION RATE
 THE GAS MASS AND STAR FORMATION RATE OF STAR-FORMING GALAXIES AT z ~ 1.3 Nissim Kanekar National Centre for Radio Astrophysics, Pune Apurba Bera Shiv Sethi Ben Weiner K. Dwarakanath Image: B. Premkumar
THE GAS MASS AND STAR FORMATION RATE OF STAR-FORMING GALAXIES AT z ~ 1.3 Nissim Kanekar National Centre for Radio Astrophysics, Pune Apurba Bera Shiv Sethi Ben Weiner K. Dwarakanath Image: B. Premkumar
Distant galaxies: a future 25-m submm telescope
 Distant galaxies: a future 25-m submm telescope Andrew Blain Caltech 11 th October 2003 Cornell-Caltech Workshop Contents Galaxy populations being probed Modes of investigation Continuum surveys Line surveys
Distant galaxies: a future 25-m submm telescope Andrew Blain Caltech 11 th October 2003 Cornell-Caltech Workshop Contents Galaxy populations being probed Modes of investigation Continuum surveys Line surveys
Setting UBVRI Photometric Zero-Points Using Sloan Digital Sky Survey ugriz Magnitudes
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Martin Gaskell Publications Research Papers in Physics and Astronomy 10-1-2007 Setting UBVRI Photometric Zero-Points Using
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Martin Gaskell Publications Research Papers in Physics and Astronomy 10-1-2007 Setting UBVRI Photometric Zero-Points Using
COS FUV Focus Determination for the G140L Grating
 Instrument Science Report COS 2012-01 COS FUV Focus Determination for the G140L Grating Parviz Ghavamian 1 Space Telescope Science Institute, Baltimore, MD October 03, 2012 ABSTRACT The procedures for
Instrument Science Report COS 2012-01 COS FUV Focus Determination for the G140L Grating Parviz Ghavamian 1 Space Telescope Science Institute, Baltimore, MD October 03, 2012 ABSTRACT The procedures for
Relative Astrometry Within ACS Visits
 Instrument Science Report ACS 2006-005 Relative Astrometry Within ACS Visits Richard L. White August 07, 2006 ABSTRACT The log files from APSIS, the ACS science team s image processing pipeline, have been
Instrument Science Report ACS 2006-005 Relative Astrometry Within ACS Visits Richard L. White August 07, 2006 ABSTRACT The log files from APSIS, the ACS science team s image processing pipeline, have been
Exploring the substellar IMF in the Taurus cloud
 Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 76, 253 c SAIt 2005 Memorie della Exploring the substellar IMF in the Taurus cloud New brown dwarfs in the Taurus star forming region S. Guieu 1, C. Dougados 1, J.-L. Monin 1,4, E. Magnier
Mem. S.A.It. Vol. 76, 253 c SAIt 2005 Memorie della Exploring the substellar IMF in the Taurus cloud New brown dwarfs in the Taurus star forming region S. Guieu 1, C. Dougados 1, J.-L. Monin 1,4, E. Magnier
Calibration of ACS Prism Slitless Spectroscopy Modes
 The 2005 HST Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 2005 A. M. Koekemoer, P. Goudfrooij, and L. L. Dressel, eds. Calibration of ACS Prism Slitless Spectroscopy Modes S. S. Larsen, M. Kümmel
The 2005 HST Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 2005 A. M. Koekemoer, P. Goudfrooij, and L. L. Dressel, eds. Calibration of ACS Prism Slitless Spectroscopy Modes S. S. Larsen, M. Kümmel
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey
 The Sloan Digital Sky Survey Robert Lupton Xiaohui Fan Jim Gunn Željko Ivezić Jill Knapp Michael Strauss University of Chicago, Fermilab, Institute for Advanced Study, Japanese Participation Group, Johns
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey Robert Lupton Xiaohui Fan Jim Gunn Željko Ivezić Jill Knapp Michael Strauss University of Chicago, Fermilab, Institute for Advanced Study, Japanese Participation Group, Johns
Photometric redshifts of galaxies from SDSS and 2MASS
 Research in Astron. Astrophys. 2009 Vol. 9 No. 4, 390 400 http://www.raa-journal.org http://www.iop.org/journals/raa Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics Photometric redshifts of galaxies from SDSS and
Research in Astron. Astrophys. 2009 Vol. 9 No. 4, 390 400 http://www.raa-journal.org http://www.iop.org/journals/raa Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics Photometric redshifts of galaxies from SDSS and
EVOLUTION OF CLUSTER ELLIPTICALS AT 0.2 <z<1.2 FROM HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPE IMAGING 1,2
 EVOLUTION OF CLUSTER ELLIPTICALS AT 0.2
EVOLUTION OF CLUSTER ELLIPTICALS AT 0.2
The Giant Branches of Open and Globular Clusters in the Infrared as Metallicity Indicators: A Comparison with Theory
 Accepted for publicaton in The Astronomical Journal The Giant Branches of Open and Globular Clusters in the Infrared as Metallicity Indicators: A Comparison with Theory GlennP.Tiede,PaulMartini,&JayA.Frogel
Accepted for publicaton in The Astronomical Journal The Giant Branches of Open and Globular Clusters in the Infrared as Metallicity Indicators: A Comparison with Theory GlennP.Tiede,PaulMartini,&JayA.Frogel
WHAT DO RADIAL VELOCITY MEASUREMENTS TELL ABOUT RV TAURI STARS?
 Dig Sites of Stellar Archeology: Giant Stars in the Milky Way Ege Uni. J. of Faculty of Sci., Special Issue, 2014, 113-120 WHAT DO RADIAL VELOCITY MEASUREMENTS TELL ABOUT RV TAURI STARS? Timur Şahin 1*,
Dig Sites of Stellar Archeology: Giant Stars in the Milky Way Ege Uni. J. of Faculty of Sci., Special Issue, 2014, 113-120 WHAT DO RADIAL VELOCITY MEASUREMENTS TELL ABOUT RV TAURI STARS? Timur Şahin 1*,
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 23 Sep 2003
 Bright Lyman Break Galaxies in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey First Data Release Misty C. Bentz, Patrick S. Osmer, and David H. Weinberg Department of Astronomy, The Ohio State University arxiv:astro-ph/0309641v1
Bright Lyman Break Galaxies in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey First Data Release Misty C. Bentz, Patrick S. Osmer, and David H. Weinberg Department of Astronomy, The Ohio State University arxiv:astro-ph/0309641v1
The SDSS is Two Surveys
 The SDSS is Two Surveys The Fuzzy Blob Survey The Squiggly Line Survey The Site The telescope 2.5 m mirror Digital Cameras 1.3 MegaPixels $150 4.3 Megapixels $850 100 GigaPixels $10,000,000 CCDs CCDs:
The SDSS is Two Surveys The Fuzzy Blob Survey The Squiggly Line Survey The Site The telescope 2.5 m mirror Digital Cameras 1.3 MegaPixels $150 4.3 Megapixels $850 100 GigaPixels $10,000,000 CCDs CCDs:
Detection of Exoplanets Using the Transit Method
 Detection of Exoplanets Using the Transit Method De nnis A fanase v, T h e Geo rg e W a s h i n g t o n Un i vers i t y, Washington, DC 20052 dennisafa@gwu.edu Abstract I conducted differential photometry
Detection of Exoplanets Using the Transit Method De nnis A fanase v, T h e Geo rg e W a s h i n g t o n Un i vers i t y, Washington, DC 20052 dennisafa@gwu.edu Abstract I conducted differential photometry
C. Watson, E. Churchwell, R. Indebetouw, M. Meade, B. Babler, B. Whitney
 Reliability and Completeness for the GLIMPSE Survey C. Watson, E. Churchwell, R. Indebetouw, M. Meade, B. Babler, B. Whitney Abstract This document examines the GLIMPSE observing strategy and criteria
Reliability and Completeness for the GLIMPSE Survey C. Watson, E. Churchwell, R. Indebetouw, M. Meade, B. Babler, B. Whitney Abstract This document examines the GLIMPSE observing strategy and criteria
Exploring Data. Keck LRIS spectra. Handbook of CCD Astronomy by Steve Howell Chap. 4, parts of 6
 Exploring Data Keck LRIS spectra Handbook of CCD Astronomy by Steve Howell Chap. 4, parts of 6 FITS: Flexible Image Transport System Digital file format used to store astronomical images, data, and catalogs.
Exploring Data Keck LRIS spectra Handbook of CCD Astronomy by Steve Howell Chap. 4, parts of 6 FITS: Flexible Image Transport System Digital file format used to store astronomical images, data, and catalogs.
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 13 Apr 2006
 **FULL TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Clusters of Galaxies at 1 < z < 2 : The Spitzer Adaptation of the Red-Sequence Cluster Survey arxiv:astro-ph/0604289
**FULL TITLE** ASP Conference Series, Vol. **VOLUME**, **YEAR OF PUBLICATION** **NAMES OF EDITORS** Clusters of Galaxies at 1 < z < 2 : The Spitzer Adaptation of the Red-Sequence Cluster Survey arxiv:astro-ph/0604289
COS FUV Dispersion Solution Verification at the New Lifetime Position
 SPACE TELESCOPE SCIENCE INSTITUTE Operated for NASA by AURA Instrument Science Report COS 2013-06(v1) COS FUV Dispersion Solution Verification at the New Lifetime Position Paule Sonnentrucker 1, Julia
SPACE TELESCOPE SCIENCE INSTITUTE Operated for NASA by AURA Instrument Science Report COS 2013-06(v1) COS FUV Dispersion Solution Verification at the New Lifetime Position Paule Sonnentrucker 1, Julia
Quantifying correlations between galaxy emission lines and stellar continua
 Quantifying correlations between galaxy emission lines and stellar continua R. Beck, L. Dobos, C.W. Yip, A.S. Szalay and I. Csabai 2016 astro-ph: 1601.0241 1 Introduction / Technique Data Emission line
Quantifying correlations between galaxy emission lines and stellar continua R. Beck, L. Dobos, C.W. Yip, A.S. Szalay and I. Csabai 2016 astro-ph: 1601.0241 1 Introduction / Technique Data Emission line
Near-Infrared Imaging Observations of the Orion A-W Star Forming Region
 Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. Vol. 2 (2002), No. 3, 260 265 ( http: /www.chjaa.org or http: /chjaa.bao.ac.cn ) Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics Near-Infrared Imaging Observations of the Orion
Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. Vol. 2 (2002), No. 3, 260 265 ( http: /www.chjaa.org or http: /chjaa.bao.ac.cn ) Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics Near-Infrared Imaging Observations of the Orion
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 14 Mar 1996
 HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPE IMAGING OF STAR-FORMING GALAXIES AT REDSHIFTS Z > 3 1 arxiv:astro-ph/9603062v1 14 Mar 1996 Mauro Giavalisco 2 Observatories of the Carnegie Institution of Washington, 813 Santa Barbara
HUBBLE SPACE TELESCOPE IMAGING OF STAR-FORMING GALAXIES AT REDSHIFTS Z > 3 1 arxiv:astro-ph/9603062v1 14 Mar 1996 Mauro Giavalisco 2 Observatories of the Carnegie Institution of Washington, 813 Santa Barbara
TECHNICAL REPORT. Doc #: Date: Rev: JWST-STScI , SM-12 August 31, Authors: Karl Gordon, Ralph Bohlin. Phone:
 When there is a discrepancy between the information in this technical report and information in JDox, assume JDox is correct. TECHNICAL REPORT Title: Title: JWST Absolute Flux Calibration II: Expanded
When there is a discrepancy between the information in this technical report and information in JDox, assume JDox is correct. TECHNICAL REPORT Title: Title: JWST Absolute Flux Calibration II: Expanded
Extraction of Point Source Spectra from STIS Long Slit Data
 1997 HST Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 1997 S. Casertano, et al., eds. Extraction of Point Source Spectra from STIS Long Slit Data J. R. Walsh Spect Telescope European Coordinating
1997 HST Calibration Workshop Space Telescope Science Institute, 1997 S. Casertano, et al., eds. Extraction of Point Source Spectra from STIS Long Slit Data J. R. Walsh Spect Telescope European Coordinating
Fourteen-color Photometry of M13 and Ruprecht 8 using the Dichroic-Mirror Camera (DMC)
 Fourteen-color Photometry of M13 and Ruprecht 8 using the Dichroic-Mirror Camera (DMC) MASTER S THESIS A manuscript written as one requirement to obtain Master s degree from Institut Teknologi Bandung
Fourteen-color Photometry of M13 and Ruprecht 8 using the Dichroic-Mirror Camera (DMC) MASTER S THESIS A manuscript written as one requirement to obtain Master s degree from Institut Teknologi Bandung
Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc
 Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc (materials from http://www.sdss.org/) Shan Huang 17 February 2010 Survey type Status Imaging and Spectroscopy Basic Facts SDSS-II completed, SDSS-III
Introduction to SDSS -instruments, survey strategy, etc (materials from http://www.sdss.org/) Shan Huang 17 February 2010 Survey type Status Imaging and Spectroscopy Basic Facts SDSS-II completed, SDSS-III
Reduction procedure of long-slit optical spectra. Astrophysical observatory of Asiago
 Reduction procedure of long-slit optical spectra Astrophysical observatory of Asiago Spectrograph: slit + dispersion grating + detector (CCD) It produces two-dimension data: Spatial direction (x) along
Reduction procedure of long-slit optical spectra Astrophysical observatory of Asiago Spectrograph: slit + dispersion grating + detector (CCD) It produces two-dimension data: Spatial direction (x) along
BV R photometry of comparison stars in selected blazar fields
 ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS JUNE I 1998, PAGE 305 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 130, 305 310 (1998) BV R photometry of comparison stars in selected blazar fields I. Photometric sequences
ASTRONOMY & ASTROPHYSICS JUNE I 1998, PAGE 305 SUPPLEMENT SERIES Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 130, 305 310 (1998) BV R photometry of comparison stars in selected blazar fields I. Photometric sequences
OPTICAL PHOTOMETRY. Observational Astronomy (2011) 1
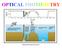 OPTICAL PHOTOMETRY Observational Astronomy (2011) 1 The optical photons coming from an astronomical object (star, galaxy, quasar, etc) can be registered in the pixels of a frame (or image). Using a ground-based
OPTICAL PHOTOMETRY Observational Astronomy (2011) 1 The optical photons coming from an astronomical object (star, galaxy, quasar, etc) can be registered in the pixels of a frame (or image). Using a ground-based
Infra-red imaging of perpendicular nested bars in spiral galaxies with the Infra-red Camera at the Carlos Sanchez Telescope
 Infra-red imaging of perpendicular nested bars in spiral galaxies with the Infra-red Camera at the Carlos Sanchez Telescope S.N. Kemp (skemp@ll.iac.es) Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, E-38200 La
Infra-red imaging of perpendicular nested bars in spiral galaxies with the Infra-red Camera at the Carlos Sanchez Telescope S.N. Kemp (skemp@ll.iac.es) Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias, E-38200 La
9. Evolution with redshift - z > 1.5. Selection in the rest-frame UV
 11-5-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c09-1 11-5-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c09-2 9. Evolution with redshift - z > 1.5 Selection in
11-5-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c09-1 11-5-10see http://www.strw.leidenuniv.nl/ franx/college/galaxies10 10-c09-2 9. Evolution with redshift - z > 1.5 Selection in
Precision Tracking of Decimeter Targets at GEO Distances using the Magdalena Ridge Observatory 2.4-meter Telescope
 Precision Tracking of Decimeter Targets at GEO Distances using the Magdalena Ridge Observatory 2.4-meter Telescope William H. Ryan and Eileen V. Ryan Magdalena Ridge Observatory, New Mexico Institute of
Precision Tracking of Decimeter Targets at GEO Distances using the Magdalena Ridge Observatory 2.4-meter Telescope William H. Ryan and Eileen V. Ryan Magdalena Ridge Observatory, New Mexico Institute of
THE ABSOLUTE DIMENSIONS OF THE OVERCONTACT BINARY FI BOOTIS
 The Astronomical Journal, 132:1153Y1157, 2006 September # 2006. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A THE ABSOLUTE DIMENSIONS OF THE OVERCONTACT BINARY FI BOOTIS Dirk
The Astronomical Journal, 132:1153Y1157, 2006 September # 2006. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A THE ABSOLUTE DIMENSIONS OF THE OVERCONTACT BINARY FI BOOTIS Dirk
The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope
 The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope Philip A. Pinto Steward Observatory University of Arizona for the LSST Collaboration 17 May, 2006 NRAO, Socorro Large Synoptic Survey Telescope The need for a facility
The Large Synoptic Survey Telescope Philip A. Pinto Steward Observatory University of Arizona for the LSST Collaboration 17 May, 2006 NRAO, Socorro Large Synoptic Survey Telescope The need for a facility
FIVE FUNDED* RESEARCH POSITIONS
 OBSERVATION Sub-GROUP: 1. Masters (MSc, 1 year): Exploring extreme star-forming galaxies for SALT in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey 2. Masters (MSc,1 year): HI masses of extreme star-forming galaxies in
OBSERVATION Sub-GROUP: 1. Masters (MSc, 1 year): Exploring extreme star-forming galaxies for SALT in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey 2. Masters (MSc,1 year): HI masses of extreme star-forming galaxies in
The Two Micron All-Sky Survey: Removing the Infrared Foreground
 University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Astronomy Department Faculty Publication Series Astronomy 2000 The Two Micron All-Sky Survey: Removing the Infrared Foreground John E. Gizis
University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Astronomy Department Faculty Publication Series Astronomy 2000 The Two Micron All-Sky Survey: Removing the Infrared Foreground John E. Gizis
UVOT Measurements of Dust and Star Formation in the SMC and M33
 UVOT Measurements of Dust and Star Formation in the SMC and M33 Lea M. Z. Hagen E-mail: lea.zernow.hagen@gmail.com Michael Siegel E-mail: siegel@swift.psu.edu Caryl Gronwall E-mail: caryl@astro.psu.edu
UVOT Measurements of Dust and Star Formation in the SMC and M33 Lea M. Z. Hagen E-mail: lea.zernow.hagen@gmail.com Michael Siegel E-mail: siegel@swift.psu.edu Caryl Gronwall E-mail: caryl@astro.psu.edu
BUILDING GALAXIES. Question 1: When and where did the stars form?
 BUILDING GALAXIES The unprecedented accuracy of recent observations of the power spectrum of the cosmic microwave background leaves little doubt that the universe formed in a hot big bang, later cooling
BUILDING GALAXIES The unprecedented accuracy of recent observations of the power spectrum of the cosmic microwave background leaves little doubt that the universe formed in a hot big bang, later cooling
High-dispersion Spectroscopic Observations of the T Tauri-type Stars with Weak Emission Lines
 ELSEVIER Chinese Astronomy and Astrophysics 37 (2013) 418 427 CHINESE ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS High-dispersion Spectroscopic Observations of the T Tauri-type Stars with Weak Emission Lines XING Li-feng
ELSEVIER Chinese Astronomy and Astrophysics 37 (2013) 418 427 CHINESE ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS High-dispersion Spectroscopic Observations of the T Tauri-type Stars with Weak Emission Lines XING Li-feng
1 A photometric probe for Pan-STARRS
 The Pan-STARRS Imaging Sky Probe B.R. Granett, K.C. Chambers, E.A. Magnier, K. Fletcher and the Pan-STARRS Project Team University of Hawai i Institute for Astronomy Abstract Photometric performance is
The Pan-STARRS Imaging Sky Probe B.R. Granett, K.C. Chambers, E.A. Magnier, K. Fletcher and the Pan-STARRS Project Team University of Hawai i Institute for Astronomy Abstract Photometric performance is
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 9 May 2013
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 9 May 2013 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.im] 9 May 2013](/thumbs/94/121058460.jpg) Astron. Nachr. / AN Volume, No. Issue, 1 4 (212) / DOI DOI Photo-Met: a non-parametric method for estimating stellar metallicity from photometric observations Gyöngyi Kerekes 1, István Csabai 1, László
Astron. Nachr. / AN Volume, No. Issue, 1 4 (212) / DOI DOI Photo-Met: a non-parametric method for estimating stellar metallicity from photometric observations Gyöngyi Kerekes 1, István Csabai 1, László
The Pulsation Properties of the Double-Mode RR Lyrae Variable V79 in Messier 3
 336 The Pulsation Properties of the Double-Mode RR Lyrae Variable V79 in Messier 3 Christine M. Clement Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, M5S 3H8, Canada Mike
336 The Pulsation Properties of the Double-Mode RR Lyrae Variable V79 in Messier 3 Christine M. Clement Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, M5S 3H8, Canada Mike
Table of Contents and Executive Summary Final Report, ReSTAR Committee Renewing Small Telescopes for Astronomical Research (ReSTAR)
 For the complete report, see http://www.noao.edu/system/restar 1 TableofContentsandExecutiveSummary FinalReport,ReSTARCommittee RenewingSmallTelescopesforAstronomical Research(ReSTAR) ForthecompletereportandmoreinformationabouttheReSTARcommittee,
For the complete report, see http://www.noao.edu/system/restar 1 TableofContentsandExecutiveSummary FinalReport,ReSTARCommittee RenewingSmallTelescopesforAstronomical Research(ReSTAR) ForthecompletereportandmoreinformationabouttheReSTARcommittee,
Photometric Studies of GEO Debris
 Photometric Studies of GEO Debris Patrick Seitzer Department of Astronomy, University of Michigan 500 Church St. 818 Dennison Bldg, Ann Arbor, MI 48109 pseitzer@umich.edu Heather M. Cowardin ESCG/Jacobs
Photometric Studies of GEO Debris Patrick Seitzer Department of Astronomy, University of Michigan 500 Church St. 818 Dennison Bldg, Ann Arbor, MI 48109 pseitzer@umich.edu Heather M. Cowardin ESCG/Jacobs
WHAT PHOTOMETRIC PRECISION CAN I ACHIEVE? DAVID BOYD
 WHAT PHOTOMETRIC PRECISION CAN I ACHIEVE? DAVID BOYD If you start using a CCD camera to carry out photometry on variable stars, this is a question that sooner or later you will ask yourself. Prompted by
WHAT PHOTOMETRIC PRECISION CAN I ACHIEVE? DAVID BOYD If you start using a CCD camera to carry out photometry on variable stars, this is a question that sooner or later you will ask yourself. Prompted by
Scattered Light from the Earth Limb Measured with the STIS CCD
 Instrument Science Report STIS 98 21 Scattered Light from the Earth Limb Measured with the STIS CCD Dick Shaw, Merle Reinhart, and Jennifer Wilson 17 June 1998 ABSTRACT We describe a recent program to
Instrument Science Report STIS 98 21 Scattered Light from the Earth Limb Measured with the STIS CCD Dick Shaw, Merle Reinhart, and Jennifer Wilson 17 June 1998 ABSTRACT We describe a recent program to
arxiv:astro-ph/ v1 15 Dec 2000
 Virtual Observatories of the Future ASP Conference Series, Vol. 225, 2001 R.J. Brunner, S.G. Djorgovski, and A.S. Szalay, eds. The New Paradigm: Novel, Virtual Observatory Enabled Science arxiv:astro-ph/0012361v1
Virtual Observatories of the Future ASP Conference Series, Vol. 225, 2001 R.J. Brunner, S.G. Djorgovski, and A.S. Szalay, eds. The New Paradigm: Novel, Virtual Observatory Enabled Science arxiv:astro-ph/0012361v1
IRS Spectroscopy of z~2 Galaxies
 IRS Spectroscopy of z~2 Galaxies Houck et al., ApJ, 2005 Weedman et al., ApJ, 2005 Lutz et al., ApJ, 2005 Astronomy 671 Jason Marshall Opening the IR Wavelength Regime for Discovery One of the primary
IRS Spectroscopy of z~2 Galaxies Houck et al., ApJ, 2005 Weedman et al., ApJ, 2005 Lutz et al., ApJ, 2005 Astronomy 671 Jason Marshall Opening the IR Wavelength Regime for Discovery One of the primary
Ay Fall 2012 Imaging and Photometry Part I
 Ay 122 - Fall 2012 Imaging and Photometry Part I (Many slides today c/o Mike Bolte, UCSC) Imaging and Photometry Now essentially always done with imaging arrays (e.g., CCDs); it used to be with single-channel
Ay 122 - Fall 2012 Imaging and Photometry Part I (Many slides today c/o Mike Bolte, UCSC) Imaging and Photometry Now essentially always done with imaging arrays (e.g., CCDs); it used to be with single-channel
Studies of diffuse UV radiation
 Bull. Astr. Soc. India (2007) 35, 295 300 Studies of diffuse UV radiation N. V. Sujatha and Jayant Murthy Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Bangalore 560 034, India Abstract. The upcoming TAUVEX mission
Bull. Astr. Soc. India (2007) 35, 295 300 Studies of diffuse UV radiation N. V. Sujatha and Jayant Murthy Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Bangalore 560 034, India Abstract. The upcoming TAUVEX mission
Note on OSIRIS Wavelength Calibrations D. Le Mignant, Oct. 5, 2007
 Note on OSIRIS Wavelength Calibrations D. Le Mignant, Oct. 5, 2007 1. Observations and data reduction In this short note, we report on some on-going analysis of OSIRIS data in an effort to document our
Note on OSIRIS Wavelength Calibrations D. Le Mignant, Oct. 5, 2007 1. Observations and data reduction In this short note, we report on some on-going analysis of OSIRIS data in an effort to document our
Study of the evolution of the ACS/WFC sensitivity loss
 Instrument Science Report ACS 2013 01 Study of the evolution of the ACS/WFC sensitivity loss Leonardo Úbeda and Jay Anderson Space Telescope Science Institute January 28, 2013 ABSTRACT We present a study
Instrument Science Report ACS 2013 01 Study of the evolution of the ACS/WFC sensitivity loss Leonardo Úbeda and Jay Anderson Space Telescope Science Institute January 28, 2013 ABSTRACT We present a study
Optical and Near- Infrared Photometric Study of NGC 6724
 Research in Astron. Astrophys. Vol.0 (201x) No.0, 000 000 http://www.raa-journal.org http://www.iop.org/journals/raa Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics Optical and Near- Infrared Photometric Study
Research in Astron. Astrophys. Vol.0 (201x) No.0, 000 000 http://www.raa-journal.org http://www.iop.org/journals/raa Research in Astronomy and Astrophysics Optical and Near- Infrared Photometric Study
Here Be Dragons: Characterization of ACS/WFC Scattered Light Anomalies
 Instrument Science Report ACS 2016-06 Here Be Dragons: Characterization of ACS/WFC Scattered Light Anomalies Blair Porterfield, Dan Coe, Shireen Gonzaga, Jay Anderson, Norman Grogin November 1, 2016 Abstract
Instrument Science Report ACS 2016-06 Here Be Dragons: Characterization of ACS/WFC Scattered Light Anomalies Blair Porterfield, Dan Coe, Shireen Gonzaga, Jay Anderson, Norman Grogin November 1, 2016 Abstract
Sparse Composite Models of Galaxy Spectra (or Anything) using L1 Norm Regularization. Benjamin Weiner Steward Observatory University of Arizona
 Sparse Composite Models of Galaxy Spectra (or Anything) using L1 Norm Regularization Benjamin Weiner Steward Observatory University of Arizona Inference of mass, redshift, etc. from physical models Many
Sparse Composite Models of Galaxy Spectra (or Anything) using L1 Norm Regularization Benjamin Weiner Steward Observatory University of Arizona Inference of mass, redshift, etc. from physical models Many
Searching primeval galaxies through gravitational telescopes
 Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 19, 258 c SAIt 2012 Memorie della Supplementi Searching primeval galaxies through gravitational telescopes A. Monna 1 and G. Covone 1,2,3 1 Dipartimento di Scienze Fisiche, Università
Mem. S.A.It. Suppl. Vol. 19, 258 c SAIt 2012 Memorie della Supplementi Searching primeval galaxies through gravitational telescopes A. Monna 1 and G. Covone 1,2,3 1 Dipartimento di Scienze Fisiche, Università
Cross-Talk in the ACS WFC Detectors. I: Description of the Effect
 Cross-Talk in the ACS WFC Detectors. I: Description of the Effect Mauro Giavalisco August 10, 2004 ABSTRACT Images acquired with the Wide Field Channel (WFC) of the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) are
Cross-Talk in the ACS WFC Detectors. I: Description of the Effect Mauro Giavalisco August 10, 2004 ABSTRACT Images acquired with the Wide Field Channel (WFC) of the Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) are
A DIRECT MEASUREMENT OF MAJOR GALAXY MERGERS AT z d 3 Christopher J. Conselice, 1,2 Matthew A. Bershady, 3 Mark Dickinson, 4 and Casey Papovich 5
 The Astronomical Journal, 126:1183 1207, 2003 September # 2003. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A DIRECT MEASUREMENT OF MAJOR GALAXY MERGERS AT z d 3 Christopher
The Astronomical Journal, 126:1183 1207, 2003 September # 2003. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. A DIRECT MEASUREMENT OF MAJOR GALAXY MERGERS AT z d 3 Christopher
On the Effects of Extended-Source Morphology on Emission-Line Redshift Accuracy
 WFIRST Technical Report Rev: A Date: October 27, 2016 On the Effects of Extended-Source Morphology on Emission-Line Redshift Accuracy R. E. Ryan Jr., S. Casertano, & N. Pirzkal Abstract We discuss the
WFIRST Technical Report Rev: A Date: October 27, 2016 On the Effects of Extended-Source Morphology on Emission-Line Redshift Accuracy R. E. Ryan Jr., S. Casertano, & N. Pirzkal Abstract We discuss the
K-band Galaxy Counts 1. Steward Observatory, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ and. E. V. Tollestrup, G. G. Fazio
 K-band Galaxy Counts 1 B. A. McLeod, G. M. Bernstein 2, M. J. Rieke Steward Observatory, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721 and E. V. Tollestrup, G. G. Fazio Harvard{Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics,
K-band Galaxy Counts 1 B. A. McLeod, G. M. Bernstein 2, M. J. Rieke Steward Observatory, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721 and E. V. Tollestrup, G. G. Fazio Harvard{Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics,
Hubble s Law and the Cosmic Distance Scale
 Lab 7 Hubble s Law and the Cosmic Distance Scale 7.1 Overview Exercise seven is our first extragalactic exercise, highlighting the immense scale of the Universe. It addresses the challenge of determining
Lab 7 Hubble s Law and the Cosmic Distance Scale 7.1 Overview Exercise seven is our first extragalactic exercise, highlighting the immense scale of the Universe. It addresses the challenge of determining
Chapter 10: Unresolved Stellar Populations
 Chapter 10: Unresolved Stellar Populations We now consider the case when individual stars are not resolved. So we need to use photometric and spectroscopic observations of integrated magnitudes, colors
Chapter 10: Unresolved Stellar Populations We now consider the case when individual stars are not resolved. So we need to use photometric and spectroscopic observations of integrated magnitudes, colors
Photometric Systems. Neil Phillips 08 April Introduction 1. 2 Magnitudes and Colours 2
 Photometric Systems Neil Phillips 8 April 28 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Magnitudes and Colours 2 3 Performing photometry 2 3.1 The System Response R λ....................................
Photometric Systems Neil Phillips 8 April 28 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Magnitudes and Colours 2 3 Performing photometry 2 3.1 The System Response R λ....................................
GOODS/FORS2 Final Data Release: Version 3.0
 ESO Phase 3 Data Release Description Data Collection GOODS_FORS2 Release Number 1 Data Provider C. Cesarsky Date 30.10.2007 update 11.07.2014 GOODS/FORS2 Final Data Release: Version 3.0 As part of the
ESO Phase 3 Data Release Description Data Collection GOODS_FORS2 Release Number 1 Data Provider C. Cesarsky Date 30.10.2007 update 11.07.2014 GOODS/FORS2 Final Data Release: Version 3.0 As part of the
Mass Estimates of Shear Selected Galaxy Clusters
 Mass Estimates of Shear Selected Galaxy Clusters Aaron Nowack UC Davis September 14, 2009 Abstract The detection of galaxy clusters has traditionally been done through optical selection methods by detecting
Mass Estimates of Shear Selected Galaxy Clusters Aaron Nowack UC Davis September 14, 2009 Abstract The detection of galaxy clusters has traditionally been done through optical selection methods by detecting
Addendum: GLIMPSE Validation Report
 August 18, 2004 Addendum: GLIMPSE Validation Report The GLIMPSE Team 1. Motivation In our Validation Report of Jan. 30, 2004, we produced reliability calculations and discussed photometric accuracy estimates
August 18, 2004 Addendum: GLIMPSE Validation Report The GLIMPSE Team 1. Motivation In our Validation Report of Jan. 30, 2004, we produced reliability calculations and discussed photometric accuracy estimates
Astronomical image reduction using the Tractor
 the Tractor DECaLS Fin Astronomical image reduction using the Tractor Dustin Lang McWilliams Postdoc Fellow Carnegie Mellon University visiting University of Waterloo UW / 2015-03-31 1 Astronomical image
the Tractor DECaLS Fin Astronomical image reduction using the Tractor Dustin Lang McWilliams Postdoc Fellow Carnegie Mellon University visiting University of Waterloo UW / 2015-03-31 1 Astronomical image
Water Ice on the Satellite of Kuiper Belt Object 2003 EL61
 Water Ice on the Satellite of Kuiper Belt Object 2003 EL61 K.M Barkume, M.E. Brown, and E.L. Schaller Division of Geological and Planetary Sciences, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125
Water Ice on the Satellite of Kuiper Belt Object 2003 EL61 K.M Barkume, M.E. Brown, and E.L. Schaller Division of Geological and Planetary Sciences, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125
LSST, Euclid, and WFIRST
 LSST, Euclid, and WFIRST Steven M. Kahn Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory Stanford University SMK Perspective I believe I bring three potentially
LSST, Euclid, and WFIRST Steven M. Kahn Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory Stanford University SMK Perspective I believe I bring three potentially
Testing the COBE/IRAS All-Sky Reddening Map Using the Galactic Globular Clusters
 Testing the COBE/IRAS All-Sky Reddening Map Using the Galactic Globular Clusters K. Z. Stanek 1 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden St., MS20, Cambridge, MA 02138 e-mail: kstanek@cfa.harvard.edu
Testing the COBE/IRAS All-Sky Reddening Map Using the Galactic Globular Clusters K. Z. Stanek 1 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden St., MS20, Cambridge, MA 02138 e-mail: kstanek@cfa.harvard.edu
Wavelength Calibration Accuracy for the STIS CCD and MAMA Modes
 SPACE TELESCOPE SCIENCE INSTITUTE Operated for NASA by AURA Instrument Science Report STIS 11-1(v1) Wavelength Calibration Accuracy for the STIS CCD and MAMA Modes Ilaria Pascucci 1, Phil Hodge 1, Charles
SPACE TELESCOPE SCIENCE INSTITUTE Operated for NASA by AURA Instrument Science Report STIS 11-1(v1) Wavelength Calibration Accuracy for the STIS CCD and MAMA Modes Ilaria Pascucci 1, Phil Hodge 1, Charles
How to calibrate interferometric data
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology How to calibrate interferometric data Rachel Akeson 28 July 2006 Outline Calibration basics System
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology How to calibrate interferometric data Rachel Akeson 28 July 2006 Outline Calibration basics System
The Canada-France Redshift Survey XIII: The luminosity density and star-formation history of the Universe to z 1. S. J. Lilly 1
 The Canada-France Redshift Survey XIII: The luminosity density and star-formation history of the Universe to z 1 S. J. Lilly 1 Department of Astronomy, University of Toronto, 60 St George Street, Toronto,
The Canada-France Redshift Survey XIII: The luminosity density and star-formation history of the Universe to z 1 S. J. Lilly 1 Department of Astronomy, University of Toronto, 60 St George Street, Toronto,
Analyzing Spiral Galaxies Observed in Near-Infrared
 Analyzing Spiral Galaxies Observed in Near-Infrared Preben Grosbøl European Southern Observatory Karl-Schwarzschild-Str. 2, D-85748 Garching, Germany Abstract A sample of 54 spiral galaxies was observed
Analyzing Spiral Galaxies Observed in Near-Infrared Preben Grosbøl European Southern Observatory Karl-Schwarzschild-Str. 2, D-85748 Garching, Germany Abstract A sample of 54 spiral galaxies was observed
