Errors in Airglow & Auroral Emission Measurements
|
|
|
- Augustus Perry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Errors in Airglow & Auroral Emission Measurements D. Pallamraju Center for Space Physics Boston University CEDAR Tutorial: June 17, 2003
2 Acknowledgments Jeffrey Baumgardner Boston University Timothy Cook Supriya Chakrabarti
3 Outline Introduction Errors related to airglow/auroal brightness measurements: Systematic (Determinate) errors Limitations Random (Indeterminate) errors SNR for different scenarios Summary
4 Scope of the tutorial Know the limitations and errors in airglow/auroral brightness measurements. With this information, take proper account of the sources in the data analysis. Guide one to estimate the SNR to expect for a given system.
5 What is airglow/aurora? Airglow/Aurora is the luminosity of an atmosphere. Airglow: Initial excitation source is solar photons. Aurora: Initial excitation source is energetic particles. e - H + / hν / + X /XY /XY + X /XY* /XY* + e - /H collisions + + X* /XY* /XY* + X /XY /XY + + hν (FUV-IR) (AIRGLOW) We will use Emissions to refer to both Airglow & Aurora
6 Why measure Airglow/Aurora? Airglow/Auroral measurements are effective and fairly inexpensive method of remote sensing the behavior of the upper atmosphere. Physical Parameter(s) that can be derived Concentrations & Compositions: Neutral temperatures and winds: Altitude coupling, (vertical propagation of waves): Latitude & Longitude coupling: Plasma drifts, TEC: Requirements Reaction rates, tomography. High spectral-resolution measurements (Doppler & Rotational). Twilight emissions. Emission rates at multiple wavelengths. Large field-of-view; measurements from multiple sites. Redline & 7774 Å emissions. Energy inputs into earth: Electron & proton induced aurora.
7 Different emissions originate at different altitudes Emission altitudes are a function of the concentration of reactants, life times of the excited species and collision frequencies. Some Commonly measured emissions: OI 630.0nm (250km) 777.4nm (F-peak) 557.7nm (100km) N nm (150km) 427.8nm (150km) 470.9nm (150km) H β 486.1nm ( km) H α 656.3nm ( km) Na 589.3nm (92km) OH 731.6nm (85km) Observational Means Ground Rocket Space We will only discuss ground-based observations of visible emissions
8 How bright are nighttime atmospheric emissions? Stars, Zodiacal light, Diffuse galactic light, Airglow (Direct + Scattered) Airglow = (Observed light calculated due to astrophysical sources) (Derived) Airglow as fraction of total (%) Band U B V R λ Range (nm) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Reference λ % 38 % 53 % 56 % Priedhorsky, 1996 (Appl. Opt)
9 Historical development of Detectors for emission measurements: 5X? CCD, ICCD,IPD 1-D 2-D 100X Photomultiplier Tube (PMT) Intensified TV Photographic Films
10 Large scale aspects of many atmospheric phenomena have been discovered by all-sky optical measurements OI 557.7nm Arecibo OI 557.7nm McDonald Obs. OI 630.0nm Arecibo Taylor and Garcia, 1995 Smith et al., 2003 Kelley et al., 2000 OI 630.0nm Tucuman OI 135.6nm IMAGE OI 135.6nm POLAR * Martinis et al., 2003 Sagawa et al., 2003 POLAR VIS Earth Camera. Courtesy: F. Sigwarth & L. Frank
11 There is enormous beauty to the phenomena that occur in nature. Optical emission measurements are a very effective tool to unravel some of the nature s beauty! But, before appreciating the beauty we need to remember what Sir Eddington said And so we see that the poetry fades out of the problem, and by the time the serious applications of exact science begins we are left with only pointer readings. -- Sir Eddington
12 Systematic errors: (Determinate) Random errors: (Indeterminate) Dynamic errors: (Miscellaneous) Illegitimate errors: (Miscellaneous) Different types of errors Often called accuracy; (measured value the truth ). Often called precision. Errors related to dynamic properties of the instrumentation; ex., setting time, time constants, etc. Blunders, different units, computational glitches (rounding off, insufficient algorithms, double precision, etc.) Uncertainty = Systematic + Random + Miscellaneous errors. Uncertainty gives a measure of overall confidence of a measurement (σ).
13 Schematic of a typical optical system Aperture Collimator Band pass, interference filter, etc. Filter Dispersing element Fabry Perot, Grating, Grism, etc. Reimaging Lens PMT, IPD, CCD, ICCD, etc. Detector Not all systems may need all these components
14 Origin of Systematic/Determinate errors (same size and sign) for emission measurements Note: In the following, the relevant issues are in red color and their solutions are shown in blue.
15 Detector Quantum efficiency Systematic (i) Variation of QE with time. (ii) Moisture condensation on the chip while cooling: (a) in places of high humidity, or (b) due to loss in vacuum. Periodic calibrations with known source (ground standards or stars).
16 Filter Transmission (i) For small bandwidth reduction in transmission from low angles. Systematic (ii) For large bandwidth contribution from other wavelengths not avoidable. AT 20 o INCIDENCE 61% AT 0 o INCIDENCE 10% (a) Be careful with all-sky measurements with narrow bandwidth filters.
17 Filter Transmission (Contd.) Systematic (iii) Temperature tuning discrepancy between actual and displayed temperature. (Typical values: Å o C -1 ) (iv) Tilting of filter for background. (v) Variation of filter characteristics with time. (vi) Spatial variation in the transmission. (b) Periodic calibration. (c) Flat-fielding with monochromator.
18 Angular/Geometric Calibration Systematic The relation between the view angles/sky position and pixels on the detector. Observations of stars when possible. Laboratory calibration. Sky H tanθ H θ CCD
19 van Rhijn effect: Systematic Column int. emissions vary with zenith angle (uniform slab). Can be corrected with the assumption of uniform emission layer I I ( z ) ( zenith ) = 1 R R + 1 h 2 sin 2 z Where, z is the zenith angle, R is Radius of earth, h is the height of the emission and I(z) is the Intensity at a zenith angle z. Roach and Gordon, 1973.
20 Flat field correction: Systematic (i) Vignetting: The decrease in illumination away from the optical axis in an optical system. (ii) Structures or dust within the instrument, hot pixels on the detector, etc. I ( x, y ) I dark ( x, y ) I corrected Correcting the image with a structure-less white light image. Before After Before After ( x, y ) = I flat ( x, y ) I dark ( x, y ) K Imaging techniques need to correct every image by a flat-field
21 Limitations of optical emission measurements: Issues on which we do not have any control
22 Sky Transmission: (i) Thin sub-visual clouds. (ii) Haze, fog, mist, dust. (iii) Varies for different angles. (iv) Ground lights magnify the effect. (a) Measurements from high altitudes. (b) Measurements from dry/desert locations. (c) Observing stars of known intensities. Limitations C A B
23 Emission height variation: Limitations (i) The F-layer movement (down or up) will produce more or less emissions. (ii) This will affect the doppler width (= T n ) of the observed emission profile. N e W 1 Emission layer N e W 2 (a) Data from other instruments, such as a digisondes will effectively complement the emission measurements to derive accurate physical parameters.
24 Structures in Emission height? Limitations The obtained emissions are column integrated. So the information on vertical structures, if any, is integrated out.
25 Origin of Random/Indeterminate errors (different size and sign) for emission measurements
26 Photon noise: Random (i) Dependent on signal strength. (ii) Not additive. (a) Large signal or large time integration. (b) Detectors of high sensitivity.
27 Thermal noise or Dark current: Random (i) Cannot be distinguished from photoelectrons due to signal. (ii) Production rate of thermal electrons exponentially increases with temperature. (iii)thermal electrons reduce the dynamic range of a detector. (a) Reduces by a factor of 2 for every 6 C reduction in temperature for CCDs. (b)take several dark images and subtract with the image containing data.
28 Read Noise: Random (i) Readout noise is additive. (ii) Independent of signal. (iii) Dependent on the readout rates. (iv) It has a Gaussian deviation and is therefore expressed as its standard deviation (rms value). Use small number of co-adds during data acquisition. Quantization Noise: Rounding off caused by the Analog-to-digital converter in converting the amplitude of electronic signal into a binary representation. Insignificant and usually ignored.
29 Indeterminate Vs Determinate errors Determinate errors can be more serious than indeterminate errors. Because: There is no method of discovering and identifying them just by looking at the data. One can not reduce its adverse effects by repeating the experiment as it has the same sign and magnitude.
30 Photon statistics is governed by Poisson Distribution Poisson statistics describes the result of experiments where one counts events that occur at random, but at a definite average rate. Distribution for different µ µ P ( x, µ ) x µ = e x! Mean <x> = µ ; Standard deviation, σ = µ The final count is = µ ± µ Fractional uncertainty is = µ 1 = µ µ
31 Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) Assuming that systematic error is taken care of, the SNR is SNR = ( S + B S ) + D + R Here the contributions to noise in addition to signal are the Background B, dark noise or thermal noise of the detector, D and the read noise of the detector, R. Relation between Uncertainty and SNR Measurement uncertainty = 1/SNR SNR = 10 a 10% error in a single measurement and SNR = 20 a 5% error in a single measurement and so on..
32 SNR = where, qe s ft t bg fa d ro be af no k se qe s ft t be af no k se ] [ qe ( s ft + bg fa ) t be af no k se + d t be af no + no af ( ro ) 2 detector quantum efficiency, signal strength, R filter transmission, exposure time, sec background continuum, RÅ -1 S SNR = ( S + B ) + D + R filter area (or bandwidth where background is considered), Å Dark noise, e - pix -1 s -1 read out noise, e (RMS) number of pixels binned before readout, number of pixels binned after readout, number of co-adds, photons s 1 R -1 incident on a pixel for a given f/#. system efficiency. Adapted from: Roesler, Baumgardner et al., 1993.
33 Atmospheric emissions can be: (i) Photon statistics limited or (ii) Read noise limited. Let us consider different scenarios: 1. Small signal on small background (ex. Geocorona or proton aurora) 2. Large signal on small background (ex. Airglow/ aurora during night time) 3. Large signal on large background (ex. Airglow/ auroral emissions during Daytime or twilight time).
34 For investigating the SNR for different observational scenarios, following values have been used in the SNR relation: qe s ft t bg fa d ro be af no se k 0.8 for CCD and 0.2 for ICCD R 0.75, 1-20 s 3 RÅ -1 5 MRÅ -1 8 Å for nighttime and 0.18 Å for daytime emissions 0.1 e - pix -1 s -1 6.e (RMS) for CCD For f/3= 4 x 10-2 ; f/11 = 2.9 x 10-3 photons s 1 R -1 pixel -1 (for 24µ pixel)
35 1. Small signal on small background (ex. Geocorona or proton aurora) s= 4-20R; bg=3r/å Galand et al., 2003 Read out noise & dark signal affect the SNR. ICCD a better option than bare CCD for dynamically varying phenomena. SNR = ( S + B S ) + D + R
36 2. Large signal on small background (ex. Nighttime emissions) s= 300R; bg=3r/å Both read out noise & dark signal affect the SNR. Bare CCD to be used with large integrations. ICCD still useful for observing dynamically varying phenomena. S SNR = ( S + B ) + D + R
37 3. Large signal on large background (ex. Daytime or twilighttime emissions) s= 3 kr; bg=1-5 MR/Å S SNR = ( S + B ) + D + R SNR is limited by photon statistics. Read out noise & Dark noise DONOT affect the SNR. Ring effect: Filling-in of Solar Fraunhofer lines due to scattering by earths atmospheric gases: Needs to be accounted for.
38 Example: HIRISE data Application of SNR Relation se=0.16 Pallamraju et al., 2001; JGR Ring effect: Pallamraju et al., 2000; GRL
39 Future Requirements CCDs with: Zero read noise! Small pixel sizes Better filters 5X? CCD, ICCD,IPD 200? 1-D 2-D 100X Photomultiplier Tube (PMT) Intensified TV Photographic Films
40 Summary Airglow & Auroral measurements provide unique perspective of the atmospheric behavior. Atmospheric transparency is the major unknown for the nighttime emissions. Statistical fluctuation of photon noise is the major factor for daytime measurements. Periodic calibrations help correct systematic errors. Random errors can be reduced by: large time integrations, binning more pixels and more co-adds, and more sensitive detectors.
Brightness Calibration of Optical Spectrographs
 Brightness Calibration of Optical Spectrographs D. Pallamraju 1, J. Baumgardner 1, and R. Doe 2 1 Center for Space Physics, Boston University, MA 2 SRI International, Menlo Park, CA CEDAR, Santa Fe NM.
Brightness Calibration of Optical Spectrographs D. Pallamraju 1, J. Baumgardner 1, and R. Doe 2 1 Center for Space Physics, Boston University, MA 2 SRI International, Menlo Park, CA CEDAR, Santa Fe NM.
EXPOSURE TIME ESTIMATION
 ASTR 511/O Connell Lec 12 1 EXPOSURE TIME ESTIMATION An essential part of planning any observation is to estimate the total exposure time needed to satisfy your scientific goal. General considerations
ASTR 511/O Connell Lec 12 1 EXPOSURE TIME ESTIMATION An essential part of planning any observation is to estimate the total exposure time needed to satisfy your scientific goal. General considerations
Astro 500 A500/L-15 1
 Astro 500 A500/L-15 1 Lecture Outline Spectroscopy from a 3D Perspective ü Basics of spectroscopy and spectrographs ü Fundamental challenges of sampling the data cube Approaches and example of available
Astro 500 A500/L-15 1 Lecture Outline Spectroscopy from a 3D Perspective ü Basics of spectroscopy and spectrographs ü Fundamental challenges of sampling the data cube Approaches and example of available
AS 101: Day Lab #2 Summer Spectroscopy
 Spectroscopy Goals To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are related To see spectral lines from different elements in emission and
Spectroscopy Goals To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are related To see spectral lines from different elements in emission and
AS750 Observational Astronomy
 Lecture 9 0) Poisson! (quantum limitation) 1) Diffraction limit 2) Detection (aperture) limit a)simple case b)more realistic case 3) Atmosphere 2) Aperture limit (More realistic case) Aperture has m pixels
Lecture 9 0) Poisson! (quantum limitation) 1) Diffraction limit 2) Detection (aperture) limit a)simple case b)more realistic case 3) Atmosphere 2) Aperture limit (More realistic case) Aperture has m pixels
You, too, can make useful and beautiful astronomical images at Mees: Lesson 3
 You, too, can make useful and beautiful astronomical images at Mees: Lesson 3 Calibration and data reduction Useful references, besides Lessons 1 and 2: The AST 142 Projects manual: http://www.pas.rochester.edu/~dmw/ast142/projects/project.pdf
You, too, can make useful and beautiful astronomical images at Mees: Lesson 3 Calibration and data reduction Useful references, besides Lessons 1 and 2: The AST 142 Projects manual: http://www.pas.rochester.edu/~dmw/ast142/projects/project.pdf
Fabry-Perot Measurement of Aeronomic Winds and Temperatures
 FPI T 2014 Introduction section Page: 1 Fabry-Perot Measurement of Aeronomic Winds and Temperatures Mark Conde University of Alaska Fairbanks This talk is a tutorial on the technique of using Fabry-Perot
FPI T 2014 Introduction section Page: 1 Fabry-Perot Measurement of Aeronomic Winds and Temperatures Mark Conde University of Alaska Fairbanks This talk is a tutorial on the technique of using Fabry-Perot
Lecture 32. Lidar Error and Sensitivity Analysis
 Lecture 3. Lidar Error and Sensitivity Analysis Introduction Accuracy in lidar measurements Precision in lidar measurements Error analysis for Na Doppler lidar Sensitivity analysis Summary 1 Errors vs.
Lecture 3. Lidar Error and Sensitivity Analysis Introduction Accuracy in lidar measurements Precision in lidar measurements Error analysis for Na Doppler lidar Sensitivity analysis Summary 1 Errors vs.
DAY LABORATORY EXERCISE: SPECTROSCOPY
 AS101 - Day Laboratory: Spectroscopy Page 1 DAY LABORATORY EXERCISE: SPECTROSCOPY Goals: To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are
AS101 - Day Laboratory: Spectroscopy Page 1 DAY LABORATORY EXERCISE: SPECTROSCOPY Goals: To see light dispersed into its constituent colors To study how temperature, light intensity, and light color are
UVOIR FLUX MEASUREMENTS AND SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIOS
 ASTR 511/O Connell Lec 7 1 UVOIR FLUX MEASUREMENTS AND SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIOS Comparison of photographic and CCD exposures of same field with 4-m; Left: 45 min photographic plate; Right: 2 hr CCD (stacked)
ASTR 511/O Connell Lec 7 1 UVOIR FLUX MEASUREMENTS AND SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIOS Comparison of photographic and CCD exposures of same field with 4-m; Left: 45 min photographic plate; Right: 2 hr CCD (stacked)
Astr 2310 Thurs. March 3, 2016 Today s Topics
 Astr 2310 Thurs. March 3, 2016 Today s Topics Chapter 6: Telescopes and Detectors Optical Telescopes Simple Optics and Image Formation Resolution and Magnification Invisible Astronomy Ground-based Radio
Astr 2310 Thurs. March 3, 2016 Today s Topics Chapter 6: Telescopes and Detectors Optical Telescopes Simple Optics and Image Formation Resolution and Magnification Invisible Astronomy Ground-based Radio
Taking Fingerprints of Stars, Galaxies, and Other Stuff. The Bohr Atom. The Bohr Atom Model of Hydrogen atom. Bohr Atom. Bohr Atom
 Periodic Table of Elements Taking Fingerprints of Stars, Galaxies, and Other Stuff Absorption and Emission from Atoms, Ions, and Molecules Universe is mostly (97%) Hydrogen and Helium (H and He) The ONLY
Periodic Table of Elements Taking Fingerprints of Stars, Galaxies, and Other Stuff Absorption and Emission from Atoms, Ions, and Molecules Universe is mostly (97%) Hydrogen and Helium (H and He) The ONLY
THE OBSERVATION AND ANALYSIS OF STELLAR PHOTOSPHERES
 THE OBSERVATION AND ANALYSIS OF STELLAR PHOTOSPHERES DAVID F. GRAY University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface to the first edition Preface to the
THE OBSERVATION AND ANALYSIS OF STELLAR PHOTOSPHERES DAVID F. GRAY University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface to the first edition Preface to the
Reduction procedure of long-slit optical spectra. Astrophysical observatory of Asiago
 Reduction procedure of long-slit optical spectra Astrophysical observatory of Asiago Spectrograph: slit + dispersion grating + detector (CCD) It produces two-dimension data: Spatial direction (x) along
Reduction procedure of long-slit optical spectra Astrophysical observatory of Asiago Spectrograph: slit + dispersion grating + detector (CCD) It produces two-dimension data: Spatial direction (x) along
NEON Archive School 2006
 NEON Archive School 2006 Introduction to Spectroscopic Techniques (low dispersion) M. Dennefeld (IAP-Paris) Outline Basic optics of gratings and spectrographs (with emphasis on long-slit spectroscopy)
NEON Archive School 2006 Introduction to Spectroscopic Techniques (low dispersion) M. Dennefeld (IAP-Paris) Outline Basic optics of gratings and spectrographs (with emphasis on long-slit spectroscopy)
Chapter 8. Spectroscopy. 8.1 Purpose. 8.2 Introduction
 Chapter 8 Spectroscopy 8.1 Purpose In the experiment atomic spectra will be investigated. The spectra of three know materials will be observed. The composition of an unknown material will be determined.
Chapter 8 Spectroscopy 8.1 Purpose In the experiment atomic spectra will be investigated. The spectra of three know materials will be observed. The composition of an unknown material will be determined.
Problem Solving. radians. 180 radians Stars & Elementary Astrophysics: Introduction Press F1 for Help 41. f s. picture. equation.
 Problem Solving picture θ f = 10 m s =1 cm equation rearrange numbers with units θ factors to change units s θ = = f sinθ fθ = s / cm 10 m f 1 m 100 cm check dimensions 1 3 π 180 radians = 10 60 arcmin
Problem Solving picture θ f = 10 m s =1 cm equation rearrange numbers with units θ factors to change units s θ = = f sinθ fθ = s / cm 10 m f 1 m 100 cm check dimensions 1 3 π 180 radians = 10 60 arcmin
Taking fingerprints of stars, galaxies, and interstellar gas clouds
 - - Taking fingerprints of stars, galaxies, and interstellar gas clouds Absorption and emission from atoms, ions, and molecules Periodic Table of Elements The universe is mostly hydrogen H and helium He
- - Taking fingerprints of stars, galaxies, and interstellar gas clouds Absorption and emission from atoms, ions, and molecules Periodic Table of Elements The universe is mostly hydrogen H and helium He
Overview: Astronomical Spectroscopy
 Overview: Astronomical Spectroscopy or How to Start Thinking Creatively about Measuring the Universe Basic Spectrograph Optics Objective Prism Spectrometers - AESoP Slit Spectrometers Spectrometers for
Overview: Astronomical Spectroscopy or How to Start Thinking Creatively about Measuring the Universe Basic Spectrograph Optics Objective Prism Spectrometers - AESoP Slit Spectrometers Spectrometers for
Spectroscopy for planetary upper atmospheres きょくたん
 Spectroscopy for planetary upper atmospheres きょくたん Spectrum of Venus atmosphere Spectrum of Jupiter and Io Figure 1. An EUV spectrum measured by Hisaki spacecraft. The spectrograph mixes spatial and spectral
Spectroscopy for planetary upper atmospheres きょくたん Spectrum of Venus atmosphere Spectrum of Jupiter and Io Figure 1. An EUV spectrum measured by Hisaki spacecraft. The spectrograph mixes spatial and spectral
Astronomy 203 practice final examination
 Astronomy 203 practice final examination Fall 1999 If this were a real, in-class examination, you would be reminded here of the exam rules, which are as follows: You may consult only one page of formulas
Astronomy 203 practice final examination Fall 1999 If this were a real, in-class examination, you would be reminded here of the exam rules, which are as follows: You may consult only one page of formulas
Taking fingerprints of stars, galaxies, and interstellar gas clouds. Absorption and emission from atoms, ions, and molecules
 Taking fingerprints of stars, galaxies, and interstellar gas clouds Absorption and emission from atoms, ions, and molecules 1 Periodic Table of Elements The universe is mostly hydrogen H and helium He
Taking fingerprints of stars, galaxies, and interstellar gas clouds Absorption and emission from atoms, ions, and molecules 1 Periodic Table of Elements The universe is mostly hydrogen H and helium He
APPLICATION NOTE. Filter Set Prescription Alan Holmes
 APPLICATION NOTE Filter Set Prescription Alan Holmes August 1st, 22 SBIG has a color filter set prescription specifically designed to achieve correctly balanced color images for galaxies and nebulae. Our
APPLICATION NOTE Filter Set Prescription Alan Holmes August 1st, 22 SBIG has a color filter set prescription specifically designed to achieve correctly balanced color images for galaxies and nebulae. Our
Continuous ground based multiwavelength airglow measurements
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011ja016901, 2011 Continuous ground based multiwavelength airglow measurements R. A. Marshall, 1,2 S. Smith, 2 J. Baumgardner, 2 and S. Chakrabarti
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 116,, doi:10.1029/2011ja016901, 2011 Continuous ground based multiwavelength airglow measurements R. A. Marshall, 1,2 S. Smith, 2 J. Baumgardner, 2 and S. Chakrabarti
Transiting Exoplanet in the Near Infra-red for the XO-3 System
 Transiting Exoplanet in the Near Infra-red for the XO-3 System Nathaniel Rodriguez August 26, 2009 Abstract Our research this summer focused on determining if sufficient precision could be gained from
Transiting Exoplanet in the Near Infra-red for the XO-3 System Nathaniel Rodriguez August 26, 2009 Abstract Our research this summer focused on determining if sufficient precision could be gained from
Detectors for IR astronomy
 Detectors for IR astronomy Where does infrared begin? Wavelength sensi?vity of the human eye vs. wavelength Note: the eye has some (limited) sensi?vity to IR light at ~1000nm (=0.5x energy of photons the
Detectors for IR astronomy Where does infrared begin? Wavelength sensi?vity of the human eye vs. wavelength Note: the eye has some (limited) sensi?vity to IR light at ~1000nm (=0.5x energy of photons the
ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section IV
 ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section IV Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser Department of Physics and Astronomy East Tennessee State University Edition 2.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use
ASTR-1010: Astronomy I Course Notes Section IV Dr. Donald G. Luttermoser Department of Physics and Astronomy East Tennessee State University Edition 2.0 Abstract These class notes are designed for use
Visualization of Xe and Sn Atoms Generated from Laser-Produced Plasma for EUV Light Source
 3rd International EUVL Symposium NOVEMBER 1-4, 2004 Miyazaki, Japan Visualization of Xe and Sn Atoms Generated from Laser-Produced Plasma for EUV Light Source H. Tanaka, A. Matsumoto, K. Akinaga, A. Takahashi
3rd International EUVL Symposium NOVEMBER 1-4, 2004 Miyazaki, Japan Visualization of Xe and Sn Atoms Generated from Laser-Produced Plasma for EUV Light Source H. Tanaka, A. Matsumoto, K. Akinaga, A. Takahashi
Astronomy. Optics and Telescopes
 Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Optics and Telescopes - Refraction, lenses and refracting telescopes - Mirrors and reflecting telescopes - Diffraction limit,
Astronomy A. Dayle Hancock adhancock@wm.edu Small 239 Office hours: MTWR 10-11am Optics and Telescopes - Refraction, lenses and refracting telescopes - Mirrors and reflecting telescopes - Diffraction limit,
Detection of Exoplanets Using the Transit Method
 Detection of Exoplanets Using the Transit Method De nnis A fanase v, T h e Geo rg e W a s h i n g t o n Un i vers i t y, Washington, DC 20052 dennisafa@gwu.edu Abstract I conducted differential photometry
Detection of Exoplanets Using the Transit Method De nnis A fanase v, T h e Geo rg e W a s h i n g t o n Un i vers i t y, Washington, DC 20052 dennisafa@gwu.edu Abstract I conducted differential photometry
Simulations for H.E.S.S.
 Simulations for H.E.S.S. by K. Bernlöhr MPIK Heidelberg & HU Berlin Air shower measurement methods Imaging atmospheric Cherenkov telescopes In the imaging atmospheric Cherenkov telescope (IACT) technique,
Simulations for H.E.S.S. by K. Bernlöhr MPIK Heidelberg & HU Berlin Air shower measurement methods Imaging atmospheric Cherenkov telescopes In the imaging atmospheric Cherenkov telescope (IACT) technique,
Neutral Winds in the Upper Atmosphere. Qian Wu National Center for Atmospheric Research
 Neutral Winds in the Upper Atmosphere Qian Wu National Center for Atmospheric Research Outline Overview of the upper atmosphere. Ozone heating. Neutral wind tides (the strongest dynamic feature). Why do
Neutral Winds in the Upper Atmosphere Qian Wu National Center for Atmospheric Research Outline Overview of the upper atmosphere. Ozone heating. Neutral wind tides (the strongest dynamic feature). Why do
Astronomical Techniques I
 Astronomical Techniques I Lecture 8 Yogesh Wadadekar Jan-Feb 2015 IUCAA-NCRA Grad School 1 / 28 Assignment 1 will be posted on the website by tonight or tomorrow morning. Kaustubh Vaghmare (kaustubh@iucaa.ernet.in)
Astronomical Techniques I Lecture 8 Yogesh Wadadekar Jan-Feb 2015 IUCAA-NCRA Grad School 1 / 28 Assignment 1 will be posted on the website by tonight or tomorrow morning. Kaustubh Vaghmare (kaustubh@iucaa.ernet.in)
Optical/NIR Spectroscopy A3130. John Wilson Univ of Virginia
 Optical/NIR Spectroscopy A3130 John Wilson Univ of Virginia Topics: Photometry is low resolution spectroscopy Uses of spectroscopy in astronomy Data cubes and dimensionality challenge Spectrograph design
Optical/NIR Spectroscopy A3130 John Wilson Univ of Virginia Topics: Photometry is low resolution spectroscopy Uses of spectroscopy in astronomy Data cubes and dimensionality challenge Spectrograph design
Observing Habitable Environments Light & Radiation
 Homework 1 Due Thurs 1/14 Observing Habitable Environments Light & Radiation Given what we know about the origin of life on Earth, how would you recognize life on another world? Would this require a physical
Homework 1 Due Thurs 1/14 Observing Habitable Environments Light & Radiation Given what we know about the origin of life on Earth, how would you recognize life on another world? Would this require a physical
Detection of X-Rays. Solid state detectors Proportional counters Microcalorimeters Detector characteristics
 Detection of X-Rays Solid state detectors Proportional counters Microcalorimeters Detector characteristics Solid State X-ray Detectors X-ray interacts in material to produce photoelectrons which are collected
Detection of X-Rays Solid state detectors Proportional counters Microcalorimeters Detector characteristics Solid State X-ray Detectors X-ray interacts in material to produce photoelectrons which are collected
Lab 4 Radial Velocity Determination of Membership in Open Clusters
 Lab 4 Radial Velocity Determination of Membership in Open Clusters Sean Lockwood 1, Dipesh Bhattarai 2, Neil Lender 3 December 2, 2007 Abstract We used the Doppler velocity of 29 stars in the open clusters
Lab 4 Radial Velocity Determination of Membership in Open Clusters Sean Lockwood 1, Dipesh Bhattarai 2, Neil Lender 3 December 2, 2007 Abstract We used the Doppler velocity of 29 stars in the open clusters
Today. Kirchoff s Laws. Emission and Absorption. Stellar Spectra & Composition. Doppler Effect & Motion. Extrasolar Planets
 Today Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Stellar Spectra & Composition Doppler Effect & Motion Extrasolar Planets Three basic types of spectra Continuous Spectrum Intensity Emission Line Spectrum
Today Kirchoff s Laws Emission and Absorption Stellar Spectra & Composition Doppler Effect & Motion Extrasolar Planets Three basic types of spectra Continuous Spectrum Intensity Emission Line Spectrum
Ionospheric studies using a network of all-sky imagers from equatorial to sub-auroral latitudes
 Ionospheric studies using a network of all-sky imagers from equatorial to sub-auroral latitudes C. Martinis, J. Baumgardner, J. Wroten, M. Mendillo, D. Hickey, B. Alford, R. Finnan Center for Space Physics
Ionospheric studies using a network of all-sky imagers from equatorial to sub-auroral latitudes C. Martinis, J. Baumgardner, J. Wroten, M. Mendillo, D. Hickey, B. Alford, R. Finnan Center for Space Physics
Lecture 6 - spectroscopy
 Lecture 6 - spectroscopy 1 Light Electromagnetic radiation can be thought of as either a wave or as a particle (particle/wave duality). For scattering of light by particles, air, and surfaces, wave theory
Lecture 6 - spectroscopy 1 Light Electromagnetic radiation can be thought of as either a wave or as a particle (particle/wave duality). For scattering of light by particles, air, and surfaces, wave theory
LECTURE 1: Introduction to Galaxies. The Milky Way on a clear night
 LECTURE 1: Introduction to Galaxies The Milky Way on a clear night VISIBLE COMPONENTS OF THE MILKY WAY Our Sun is located 28,000 light years (8.58 kiloparsecs from the center of our Galaxy) in the Orion
LECTURE 1: Introduction to Galaxies The Milky Way on a clear night VISIBLE COMPONENTS OF THE MILKY WAY Our Sun is located 28,000 light years (8.58 kiloparsecs from the center of our Galaxy) in the Orion
Atmospheric Extinction
 Atmospheric Extinction Calibrating stellar photometry requires correction for loss of light passing through the atmosphere. Atmospheric Rayleigh and aerosol scattering preferentially redirects blue light
Atmospheric Extinction Calibrating stellar photometry requires correction for loss of light passing through the atmosphere. Atmospheric Rayleigh and aerosol scattering preferentially redirects blue light
Course Details. Analytical Techniques Based on Optical Spectroscopy. Course Details. Textbook. SCCH 211: Analytical Chemistry I
 SCCH 211: Analytical Chemistry I Analytical Techniques Based on Optical Spectroscopy Course Details September 22 October 10 September 22 November 7 November 17 December 1 Topic Period Introduction to Spectrometric
SCCH 211: Analytical Chemistry I Analytical Techniques Based on Optical Spectroscopy Course Details September 22 October 10 September 22 November 7 November 17 December 1 Topic Period Introduction to Spectrometric
PHSC 3033: Meteorology Atmospheric Optics
 PHSC 3033: Meteorology Atmospheric Optics Hot Radiating Objects Imagine a piece of metal placed in a hot furnace. At first, the metal becomes warm, although its visual appearance doesn't change. As it
PHSC 3033: Meteorology Atmospheric Optics Hot Radiating Objects Imagine a piece of metal placed in a hot furnace. At first, the metal becomes warm, although its visual appearance doesn't change. As it
Studies of diffuse UV radiation
 Bull. Astr. Soc. India (2007) 35, 295 300 Studies of diffuse UV radiation N. V. Sujatha and Jayant Murthy Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Bangalore 560 034, India Abstract. The upcoming TAUVEX mission
Bull. Astr. Soc. India (2007) 35, 295 300 Studies of diffuse UV radiation N. V. Sujatha and Jayant Murthy Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Bangalore 560 034, India Abstract. The upcoming TAUVEX mission
The Emission Spectra of Light
 The Emission Spectra of Light Objectives: Theory: 1.... measured the wavelength limits of the color bands in the visible spectrum, 2.... measured the wavelengths of the emission lines of the hydrogen Balmer
The Emission Spectra of Light Objectives: Theory: 1.... measured the wavelength limits of the color bands in the visible spectrum, 2.... measured the wavelengths of the emission lines of the hydrogen Balmer
Passive Optics activities in Japan
 Passive Optics Workshop, NCAR, April 8, 2004 Passive Optics activities in Japan Mamoru Ishii 1, Minoru Kubota 1, Kazuyo Sakanoi 1, Kazuo Shiokawa 2, Makoto Taguchi 3, Takeshi Sakanoi 4, Yukihiro Takahashi
Passive Optics Workshop, NCAR, April 8, 2004 Passive Optics activities in Japan Mamoru Ishii 1, Minoru Kubota 1, Kazuyo Sakanoi 1, Kazuo Shiokawa 2, Makoto Taguchi 3, Takeshi Sakanoi 4, Yukihiro Takahashi
Some Topics in Optics
 Some Topics in Optics The HeNe LASER The index of refraction and dispersion Interference The Michelson Interferometer Diffraction Wavemeter Fabry-Pérot Etalon and Interferometer The Helium Neon LASER A
Some Topics in Optics The HeNe LASER The index of refraction and dispersion Interference The Michelson Interferometer Diffraction Wavemeter Fabry-Pérot Etalon and Interferometer The Helium Neon LASER A
OPTICAL PHOTOMETRY. Observational Astronomy (2011) 1
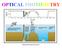 OPTICAL PHOTOMETRY Observational Astronomy (2011) 1 The optical photons coming from an astronomical object (star, galaxy, quasar, etc) can be registered in the pixels of a frame (or image). Using a ground-based
OPTICAL PHOTOMETRY Observational Astronomy (2011) 1 The optical photons coming from an astronomical object (star, galaxy, quasar, etc) can be registered in the pixels of a frame (or image). Using a ground-based
The Performance of the EUV Spectroscope (EXCEED) Onboard the SPRINT-A Mission
 The Performance of the EUV Spectroscope (EXCEED) Onboard the SPRINT-A Mission K. Yoshioka, G. Murakami, A. Yamazaki, K. Uemizu, T. Kimura (ISAS/JAXA), I. Yoshikawa, K. Uji (Univ. Tokyo) F. Tsuchiya, and
The Performance of the EUV Spectroscope (EXCEED) Onboard the SPRINT-A Mission K. Yoshioka, G. Murakami, A. Yamazaki, K. Uemizu, T. Kimura (ISAS/JAXA), I. Yoshikawa, K. Uji (Univ. Tokyo) F. Tsuchiya, and
Narrowband Imaging, or How to Image in Downtown Portland. Duncan Kitchin OMSI Astro Imaging Conference 2010
 Narrowband Imaging, or How to Image in Downtown Portland Duncan Kitchin OMSI Astro Imaging Conference 2010 Agenda Sources of noise in astro images Selectively removing light pollution Narrowband filters
Narrowband Imaging, or How to Image in Downtown Portland Duncan Kitchin OMSI Astro Imaging Conference 2010 Agenda Sources of noise in astro images Selectively removing light pollution Narrowband filters
HICO Science Mission Overview
 HICO Science Mission Overview Michael R. Corson* and Curtiss O. Davis** * Naval Research Laboratory Washington, DC corson@nrl.navy.mil ** College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Oregon State University
HICO Science Mission Overview Michael R. Corson* and Curtiss O. Davis** * Naval Research Laboratory Washington, DC corson@nrl.navy.mil ** College of Oceanic and Atmospheric Sciences Oregon State University
Counting Photons to Calibrate a Photometer for Stellar Intensity Interferometry
 Counting Photons to Calibrate a Photometer for Stellar Intensity Interferometry A Senior Project Presented to the Department of Physics California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo In Partial
Counting Photons to Calibrate a Photometer for Stellar Intensity Interferometry A Senior Project Presented to the Department of Physics California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo In Partial
VRI Photometry of M67 for CCD Standardization at 2.3m VBT
 J. Astrophys. Astr. (1992) 13, 293 305 VRI Photometry of M67 for CCD Standardization at 2.3m VBT P. N. Bhat & K. P. Singh Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Bombay 400 005 T. P. Prabhu Indian Institute
J. Astrophys. Astr. (1992) 13, 293 305 VRI Photometry of M67 for CCD Standardization at 2.3m VBT P. N. Bhat & K. P. Singh Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Bombay 400 005 T. P. Prabhu Indian Institute
First observations of the second solar spectrum with spatial resolution at the Lunette Jean Rösch
 First observations of the second solar spectrum with spatial resolution at the Lunette Jean Rösch Malherbe, J.-M., Moity, J., Arnaud, J., Roudier, Th., July 2006 The experiment setup in spectroscopic mode
First observations of the second solar spectrum with spatial resolution at the Lunette Jean Rösch Malherbe, J.-M., Moity, J., Arnaud, J., Roudier, Th., July 2006 The experiment setup in spectroscopic mode
5. 3P PIV Measurements
 Micro PIV Last Class: 1. Data Validation 2. Vector Field Operator (Differentials & Integrals) 3. Standard Differential Scheme 4. Implementation of Differential & Integral quantities with PIV data 5. 3P
Micro PIV Last Class: 1. Data Validation 2. Vector Field Operator (Differentials & Integrals) 3. Standard Differential Scheme 4. Implementation of Differential & Integral quantities with PIV data 5. 3P
25 Instruments for Optical Spectrometry
 25 Instruments for Optical Spectrometry 25A INSTRUMENT COMPONENTS (1) source of radiant energy (2) wavelength selector (3) sample container (4) detector (5) signal processor and readout (a) (b) (c) Fig.
25 Instruments for Optical Spectrometry 25A INSTRUMENT COMPONENTS (1) source of radiant energy (2) wavelength selector (3) sample container (4) detector (5) signal processor and readout (a) (b) (c) Fig.
Design and Development of a Smartphone Based Visible Spectrophotometer for Analytical Applications
 Design and Development of a Smartphone Based Visible Spectrophotometer for Analytical Applications Bedanta Kr. Deka, D. Thakuria, H. Bora and S. Banerjee # Department of Physicis, B. Borooah College, Ulubari,
Design and Development of a Smartphone Based Visible Spectrophotometer for Analytical Applications Bedanta Kr. Deka, D. Thakuria, H. Bora and S. Banerjee # Department of Physicis, B. Borooah College, Ulubari,
Optical/IR Observational Astronomy Spectroscopy. David Buckley, SALT
 David Buckley, SALT 1 Background is really just monochromatic photometry History 1637 Descartes explained the origin of the rainbow. 1666 Newton s classic experiments on the nature of colour. 1752 Melvil
David Buckley, SALT 1 Background is really just monochromatic photometry History 1637 Descartes explained the origin of the rainbow. 1666 Newton s classic experiments on the nature of colour. 1752 Melvil
SALT s Venture into Near Infrared Astronomy with RSS NIR
 SALT s Venture into Near Infrared Astronomy with RSS NIR Marsha Wolf University of Wisconsin Madison IUCAA RSS VIS future RSS NIR 5 June 2015 SALT Science Conference 2015 2 Robert Stobie Spectrograph 5
SALT s Venture into Near Infrared Astronomy with RSS NIR Marsha Wolf University of Wisconsin Madison IUCAA RSS VIS future RSS NIR 5 June 2015 SALT Science Conference 2015 2 Robert Stobie Spectrograph 5
Fundamentals of Exoplanet Observing
 Fundamentals of Exoplanet Observing Dennis M. Conti Chair, AAVSO Exoplanet Section Copyright Dennis M. Conti 2017 1 The Strange World of Exoplanets Most exoplanets we have discovered are close-in, large
Fundamentals of Exoplanet Observing Dennis M. Conti Chair, AAVSO Exoplanet Section Copyright Dennis M. Conti 2017 1 The Strange World of Exoplanets Most exoplanets we have discovered are close-in, large
Fundamentals of Exoplanet Observing
 Fundamentals of Exoplanet Observing Dennis M. Conti Chair, AAVSO Exoplanet Section Copyright Dennis M. Conti 2017 1 The Strange World of Exoplanets Most exoplanets we have discovered are close-in, large
Fundamentals of Exoplanet Observing Dennis M. Conti Chair, AAVSO Exoplanet Section Copyright Dennis M. Conti 2017 1 The Strange World of Exoplanets Most exoplanets we have discovered are close-in, large
Spectroscopy in Astronomy
 Spectroscopy in Astronomy History 1814 German optician Joseph von Fraunhofer sun with 600+ spectral lines; now we know more than 3000 lines 1860 German chemists Gustav Kirchhoff and Robert W. Bunsen Chemical
Spectroscopy in Astronomy History 1814 German optician Joseph von Fraunhofer sun with 600+ spectral lines; now we know more than 3000 lines 1860 German chemists Gustav Kirchhoff and Robert W. Bunsen Chemical
Chapter 4. Spectroscopy. Dr. Tariq Al-Abdullah
 Chapter 4 Spectroscopy Dr. Tariq Al-Abdullah Learning Goals: 4.1 Spectral Lines 4.2 Atoms and Radiation 4.3 Formation of the Spectral Lines 4.4 Molecules 4.5 Spectral Line Analysis 2 DR. T. AL-ABDULLAH
Chapter 4 Spectroscopy Dr. Tariq Al-Abdullah Learning Goals: 4.1 Spectral Lines 4.2 Atoms and Radiation 4.3 Formation of the Spectral Lines 4.4 Molecules 4.5 Spectral Line Analysis 2 DR. T. AL-ABDULLAH
Measurements of Hot Air in Alaska
 Measurements of Hot Air in Alaska John Meriwether, Professor of Physics, Clemson University Research focus: Which way does the wind blow, how fast, and how hot? The answer to this question is needed for
Measurements of Hot Air in Alaska John Meriwether, Professor of Physics, Clemson University Research focus: Which way does the wind blow, how fast, and how hot? The answer to this question is needed for
1 A photometric probe for Pan-STARRS
 The Pan-STARRS Imaging Sky Probe B.R. Granett, K.C. Chambers, E.A. Magnier, K. Fletcher and the Pan-STARRS Project Team University of Hawai i Institute for Astronomy Abstract Photometric performance is
The Pan-STARRS Imaging Sky Probe B.R. Granett, K.C. Chambers, E.A. Magnier, K. Fletcher and the Pan-STARRS Project Team University of Hawai i Institute for Astronomy Abstract Photometric performance is
The Quantum Model of the Hydrogen Atom
 Physics 109 Science 1 Experiment 1 1 The Quantum Model of the Hydrogen Atom In this experiment you will use a spectrometer to determine the wavelengths of the visible lines of atomic hydrogen. The goal
Physics 109 Science 1 Experiment 1 1 The Quantum Model of the Hydrogen Atom In this experiment you will use a spectrometer to determine the wavelengths of the visible lines of atomic hydrogen. The goal
Lecture 30. Lidar Error and Sensitivity Analysis
 Lecture 30. Lidar Error and Sensitivity Analysis q Introduction q Accuracy versus Precision q Accuracy in lidar measurements q Precision in lidar measurements q Propagation of errors vs. differential method
Lecture 30. Lidar Error and Sensitivity Analysis q Introduction q Accuracy versus Precision q Accuracy in lidar measurements q Precision in lidar measurements q Propagation of errors vs. differential method
1. Give short answers to the following questions. a. What limits the size of a corrected field of view in AO?
 Astronomy 418/518 final practice exam 1. Give short answers to the following questions. a. What limits the size of a corrected field of view in AO? b. Describe the visibility vs. baseline for a two element,
Astronomy 418/518 final practice exam 1. Give short answers to the following questions. a. What limits the size of a corrected field of view in AO? b. Describe the visibility vs. baseline for a two element,
Sky Glow from Cities : The Army Illumination Model v2
 Sky Glow from Cities : The Army Illumination Model v2 Richard Shirkey Army Research Laboratory Computational & Information Sciences Directorate Battlefield Environment Division WSMR, NM richard.shirkey@us.army.mil
Sky Glow from Cities : The Army Illumination Model v2 Richard Shirkey Army Research Laboratory Computational & Information Sciences Directorate Battlefield Environment Division WSMR, NM richard.shirkey@us.army.mil
OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE DIRC FUSED SILICA CHERENKOV RADIATOR
 OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE DIRC FUSED SILICA CHERENKOV RADIATOR J. Cohen-Tanugi, M. Convery, B. Ratcliff, X. Sarazin, J. Schwiening, and J. Va'vra * Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford University,
OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF THE DIRC FUSED SILICA CHERENKOV RADIATOR J. Cohen-Tanugi, M. Convery, B. Ratcliff, X. Sarazin, J. Schwiening, and J. Va'vra * Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, Stanford University,
SMTN-002: Calculating LSST limiting magnitudes and SNR
 SMTN-002: Calculating LSST limiting magnitudes and SNR Release Lynne Jones 2017-12-05 Contents 1 Source Counts 3 2 Instrumental Zeropoints 5 3 Sky Counts 7 4 Instrumental Noise 9 5 Source footprint (n
SMTN-002: Calculating LSST limiting magnitudes and SNR Release Lynne Jones 2017-12-05 Contents 1 Source Counts 3 2 Instrumental Zeropoints 5 3 Sky Counts 7 4 Instrumental Noise 9 5 Source footprint (n
Advanced Spectroscopy Laboratory
 Advanced Spectroscopy Laboratory - Raman Spectroscopy - Emission Spectroscopy - Absorption Spectroscopy - Raman Microscopy - Hyperspectral Imaging Spectroscopy FERGIELAB TM Raman Spectroscopy Absorption
Advanced Spectroscopy Laboratory - Raman Spectroscopy - Emission Spectroscopy - Absorption Spectroscopy - Raman Microscopy - Hyperspectral Imaging Spectroscopy FERGIELAB TM Raman Spectroscopy Absorption
Optical aurora detectors: using natural optics to motivate education and outreach
 Optical aurora detectors: using natural optics to motivate education and outreach Joseph A. Shaw,* Jesse M. Way, Nathan J. Pust, Paul W. Nugent, Hans Coate, Daniel Balster Montana State University, Bozeman,
Optical aurora detectors: using natural optics to motivate education and outreach Joseph A. Shaw,* Jesse M. Way, Nathan J. Pust, Paul W. Nugent, Hans Coate, Daniel Balster Montana State University, Bozeman,
Estimating the peak auroral emission altitude from all-sky images
 ÓPTICA PURA Y APLICADA. www.sedoptica.es Sección Especial: 37 th AMASOM / Special Section: 37 th AMASOM Aurora Estimating the peak auroral emission altitude from all-sky images L. Sangalli (1,*), B. Gustavsson
ÓPTICA PURA Y APLICADA. www.sedoptica.es Sección Especial: 37 th AMASOM / Special Section: 37 th AMASOM Aurora Estimating the peak auroral emission altitude from all-sky images L. Sangalli (1,*), B. Gustavsson
The Doppler Method, or Radial Velocity Detection of Planets: I. Technique
 ASTs309L The Doppler Method, or Radial Velocity Detection of Planets: I. Technique 1. Keplerian Orbits 2. Spectrographs/Doppler shifts 3. Precise Radial Velocity measurements ASTs309L The Doppler Effect:
ASTs309L The Doppler Method, or Radial Velocity Detection of Planets: I. Technique 1. Keplerian Orbits 2. Spectrographs/Doppler shifts 3. Precise Radial Velocity measurements ASTs309L The Doppler Effect:
MERIS US Workshop. Instrument Characterization Overview. Steven Delwart
 MERIS US Workshop Instrument Characterization Overview Steven Delwart Presentation Overview On-Ground Characterisation 1. Diffuser characterisation 2. Polarization sensitivity 3. Optical Transmission 4.
MERIS US Workshop Instrument Characterization Overview Steven Delwart Presentation Overview On-Ground Characterisation 1. Diffuser characterisation 2. Polarization sensitivity 3. Optical Transmission 4.
Title of Report: INVESTIGATION OF ESF TRIGGERS USING BALLOON-BASED AND GROUND-BASED DIAGNOSTICS
 Title of Report: INVESTIGATION OF ESF TRIGGERS USING BALLOON-BASED AND GROUND-BASED DIAGNOSTICS Author: Dr. Duggirala Pallamraju Co-PI Principal Investigator (AOARD Grant): Prof. K. Niranjan Contracting
Title of Report: INVESTIGATION OF ESF TRIGGERS USING BALLOON-BASED AND GROUND-BASED DIAGNOSTICS Author: Dr. Duggirala Pallamraju Co-PI Principal Investigator (AOARD Grant): Prof. K. Niranjan Contracting
Electronic Imaging in Astronomy
 Ian S, McLean Electronic Imaging in Astronomy Detectors and Instrumentation (Second Edition) j""v Published f udiisnea in association with witn fyj Springer Praxis PubUshing Publisl PR Chichester, UK Contents
Ian S, McLean Electronic Imaging in Astronomy Detectors and Instrumentation (Second Edition) j""v Published f udiisnea in association with witn fyj Springer Praxis PubUshing Publisl PR Chichester, UK Contents
Near-IR Background Fluctuation Results from the Cosmic Infrared Background Experiment
 Near-IR Background Fluctuation Results from the Cosmic Infrared Background Experiment Michael Zemcov The Near- IR Background II: From Reionization to the Present Epoch Max- Planck- Gesellschaft, June 2,
Near-IR Background Fluctuation Results from the Cosmic Infrared Background Experiment Michael Zemcov The Near- IR Background II: From Reionization to the Present Epoch Max- Planck- Gesellschaft, June 2,
HMI Filter Calibration
 HMI Filter Calibration Purpose: to make sure we can characterize the transmission profile (transmittance) of the HMI filter system through accurate enough measurements Data needed: maps of the relative
HMI Filter Calibration Purpose: to make sure we can characterize the transmission profile (transmittance) of the HMI filter system through accurate enough measurements Data needed: maps of the relative
Note on OSIRIS Wavelength Calibrations D. Le Mignant, Oct. 5, 2007
 Note on OSIRIS Wavelength Calibrations D. Le Mignant, Oct. 5, 2007 1. Observations and data reduction In this short note, we report on some on-going analysis of OSIRIS data in an effort to document our
Note on OSIRIS Wavelength Calibrations D. Le Mignant, Oct. 5, 2007 1. Observations and data reduction In this short note, we report on some on-going analysis of OSIRIS data in an effort to document our
7. Telescopes: Portals of Discovery Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison Wesley
 7. Telescopes: Portals of Discovery Parts of the Human Eye pupil allows light to enter the eye lens focuses light to create an image retina detects the light and generates signals which are sent to the
7. Telescopes: Portals of Discovery Parts of the Human Eye pupil allows light to enter the eye lens focuses light to create an image retina detects the light and generates signals which are sent to the
Earth Flats. 1. Introduction. Instrument Science Report ACS R. C. Bohlin, J. Mack, G. Hartig, & M. Sirianni October 25, 2005
 Instrument Science Report ACS 2005-12 Earth Flats R. C. Bohlin, J. Mack, G. Hartig, & M. Sirianni October 25, 2005 ABSTRACT Since the last ISR 2003-02 on the use of Earth observations for a source of flat
Instrument Science Report ACS 2005-12 Earth Flats R. C. Bohlin, J. Mack, G. Hartig, & M. Sirianni October 25, 2005 ABSTRACT Since the last ISR 2003-02 on the use of Earth observations for a source of flat
Small Aperture Amateur Observational Capabilities/Tools (Imaging/Photometry/Spectroscopy)
 Small Aperture Amateur Observational Capabilities/Tools (Imaging/Photometry/Spectroscopy) Over several thousand years, astronomy continues to be popular subject among amateurs. Day by day, advancements
Small Aperture Amateur Observational Capabilities/Tools (Imaging/Photometry/Spectroscopy) Over several thousand years, astronomy continues to be popular subject among amateurs. Day by day, advancements
Lecture 7: Optical Spectroscopy. Astrophysical Spectroscopy. Broadband Filters. Fabry-Perot Filters. Interference Filters. Prism Spectrograph
 Lecture 7: Optical Spectroscopy Outline 1 Astrophysical Spectroscopy 2 Broadband Filters 3 Fabry-Perot Filters 4 Interference Filters 5 Prism Spectrograph 6 Grating Spectrograph 7 Fourier Transform Spectrometer
Lecture 7: Optical Spectroscopy Outline 1 Astrophysical Spectroscopy 2 Broadband Filters 3 Fabry-Perot Filters 4 Interference Filters 5 Prism Spectrograph 6 Grating Spectrograph 7 Fourier Transform Spectrometer
Extragalactic Background Light Rebecca A Bernstein. Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics P. Murdin
 eaa.iop.org DOI: 10.1888/0333750888/2639 Extragalactic Background Light Rebecca A Bernstein From Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics P. Murdin IOP Publishing Ltd 2006 ISBN: 0333750888 Institute of
eaa.iop.org DOI: 10.1888/0333750888/2639 Extragalactic Background Light Rebecca A Bernstein From Encyclopedia of Astronomy & Astrophysics P. Murdin IOP Publishing Ltd 2006 ISBN: 0333750888 Institute of
Review: Properties of a wave
 Radiation travels as waves. Waves carry information and energy. Review: Properties of a wave wavelength (λ) crest amplitude (A) trough velocity (v) λ is a distance, so its units are m, cm, or mm, etc.
Radiation travels as waves. Waves carry information and energy. Review: Properties of a wave wavelength (λ) crest amplitude (A) trough velocity (v) λ is a distance, so its units are m, cm, or mm, etc.
LIGHT. Question. Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light.
 LIGHT Question Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light. What kind of information can we get from light? 1 Light
LIGHT Question Until very recently, the study of ALL astronomical objects, outside of the Solar System, has been with telescopes observing light. What kind of information can we get from light? 1 Light
Nonlinear regression method for estimating neutral wind and temperature from Fabry Perot interferometer data
 Nonlinear regression method for estimating neutral wind and temperature from Fabry Perot interferometer data Brian J. Harding,* Thomas W. Gehrels, and Jonathan J. Makela Department of Electrical and Computer
Nonlinear regression method for estimating neutral wind and temperature from Fabry Perot interferometer data Brian J. Harding,* Thomas W. Gehrels, and Jonathan J. Makela Department of Electrical and Computer
Jim Hagerman 4/12/99
 This is an electro-optical analysis of the UCMS (underwater camera mapping system) designed for TerraSystems. Jim Hagerman 4/1/99 For simplicity the SNR of only one 5nm wide channel near 5nm is determined.
This is an electro-optical analysis of the UCMS (underwater camera mapping system) designed for TerraSystems. Jim Hagerman 4/1/99 For simplicity the SNR of only one 5nm wide channel near 5nm is determined.
Because light behaves like a wave, we can describe it in one of two ways by its wavelength or by its frequency.
 Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
Light We can use different terms to describe light: Color Wavelength Frequency Light is composed of electromagnetic waves that travel through some medium. The properties of the medium determine how light
Chapter 23. Light, Astronomical Observations, and the Sun
 Chapter 23 Light, Astronomical Observations, and the Sun The study of light Electromagnetic radiation Visible light is only one small part of an array of energy Electromagnetic radiation includes Gamma
Chapter 23 Light, Astronomical Observations, and the Sun The study of light Electromagnetic radiation Visible light is only one small part of an array of energy Electromagnetic radiation includes Gamma
Southern African Large Telescope. Prime Focus Imaging Spectrograph. Instrument Acceptance Testing Plan
 Southern African Large Telescope Prime Focus Imaging Spectrograph Instrument Acceptance Testing Plan Eric B. Burgh University of Wisconsin Document Number: SALT-3160AP0003 Revision 1.0 18 February 2003
Southern African Large Telescope Prime Focus Imaging Spectrograph Instrument Acceptance Testing Plan Eric B. Burgh University of Wisconsin Document Number: SALT-3160AP0003 Revision 1.0 18 February 2003
Single Emitter Detection with Fluorescence and Extinction Spectroscopy
 Single Emitter Detection with Fluorescence and Extinction Spectroscopy Michael Krall Elements of Nanophotonics Associated Seminar Recent Progress in Nanooptics & Photonics May 07, 2009 Outline Single molecule
Single Emitter Detection with Fluorescence and Extinction Spectroscopy Michael Krall Elements of Nanophotonics Associated Seminar Recent Progress in Nanooptics & Photonics May 07, 2009 Outline Single molecule
Analysis of extended sources with the EPIC cameras
 Analysis of extended sources with the EPIC cameras 7 th ESAC SAS Workshop June 19 22, 2007 Science Operations Centre 1 Status Analysis of extended sources is complex, challenging and time-consuming There
Analysis of extended sources with the EPIC cameras 7 th ESAC SAS Workshop June 19 22, 2007 Science Operations Centre 1 Status Analysis of extended sources is complex, challenging and time-consuming There
Digital Holographic Measurement of Nanometric Optical Excitation on Soft Matter by Optical Pressure and Photothermal Interactions
 Ph.D. Dissertation Defense September 5, 2012 Digital Holographic Measurement of Nanometric Optical Excitation on Soft Matter by Optical Pressure and Photothermal Interactions David C. Clark Digital Holography
Ph.D. Dissertation Defense September 5, 2012 Digital Holographic Measurement of Nanometric Optical Excitation on Soft Matter by Optical Pressure and Photothermal Interactions David C. Clark Digital Holography
The TV3 ground calibrations of the WFC3 NIR grisms
 The TV3 ground calibrations of the WFC3 NIR grisms H. Kuntschner, H. Bushouse, J. R. Walsh, M. Kümmel July 10, 2008 ABSTRACT Based on thermal vacuum tests (TV3; March/April 2008), the performance of the
The TV3 ground calibrations of the WFC3 NIR grisms H. Kuntschner, H. Bushouse, J. R. Walsh, M. Kümmel July 10, 2008 ABSTRACT Based on thermal vacuum tests (TV3; March/April 2008), the performance of the
Introduction to Spectroscopic Techniques (low dispersion) M. Dennefeld (IAP-Paris) NEON school June 2008 La Palma
 NEON Observing School 2008 Introduction to Spectroscopic Techniques (low dispersion) (IAP-Paris) Outline Basic optics of gratings and spectrographs (with emphasis on long-slit spectroscopy) Observing steps,
NEON Observing School 2008 Introduction to Spectroscopic Techniques (low dispersion) (IAP-Paris) Outline Basic optics of gratings and spectrographs (with emphasis on long-slit spectroscopy) Observing steps,
aka Light Properties of Light are simultaneously
 Today Interaction of Light with Matter Thermal Radiation Kirchhoff s Laws aka Light Properties of Light are simultaneously wave-like AND particle-like Sometimes it behaves like ripples on a pond (waves).
Today Interaction of Light with Matter Thermal Radiation Kirchhoff s Laws aka Light Properties of Light are simultaneously wave-like AND particle-like Sometimes it behaves like ripples on a pond (waves).
